⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-03 更新
AdaHuman: Animatable Detailed 3D Human Generation with Compositional Multiview Diffusion
Authors:Yangyi Huang, Ye Yuan, Xueting Li, Jan Kautz, Umar Iqbal
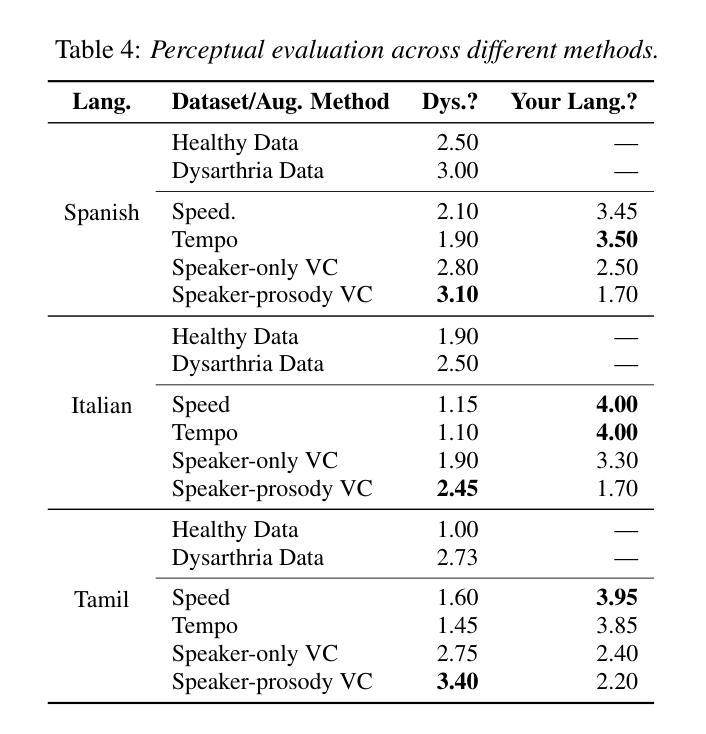
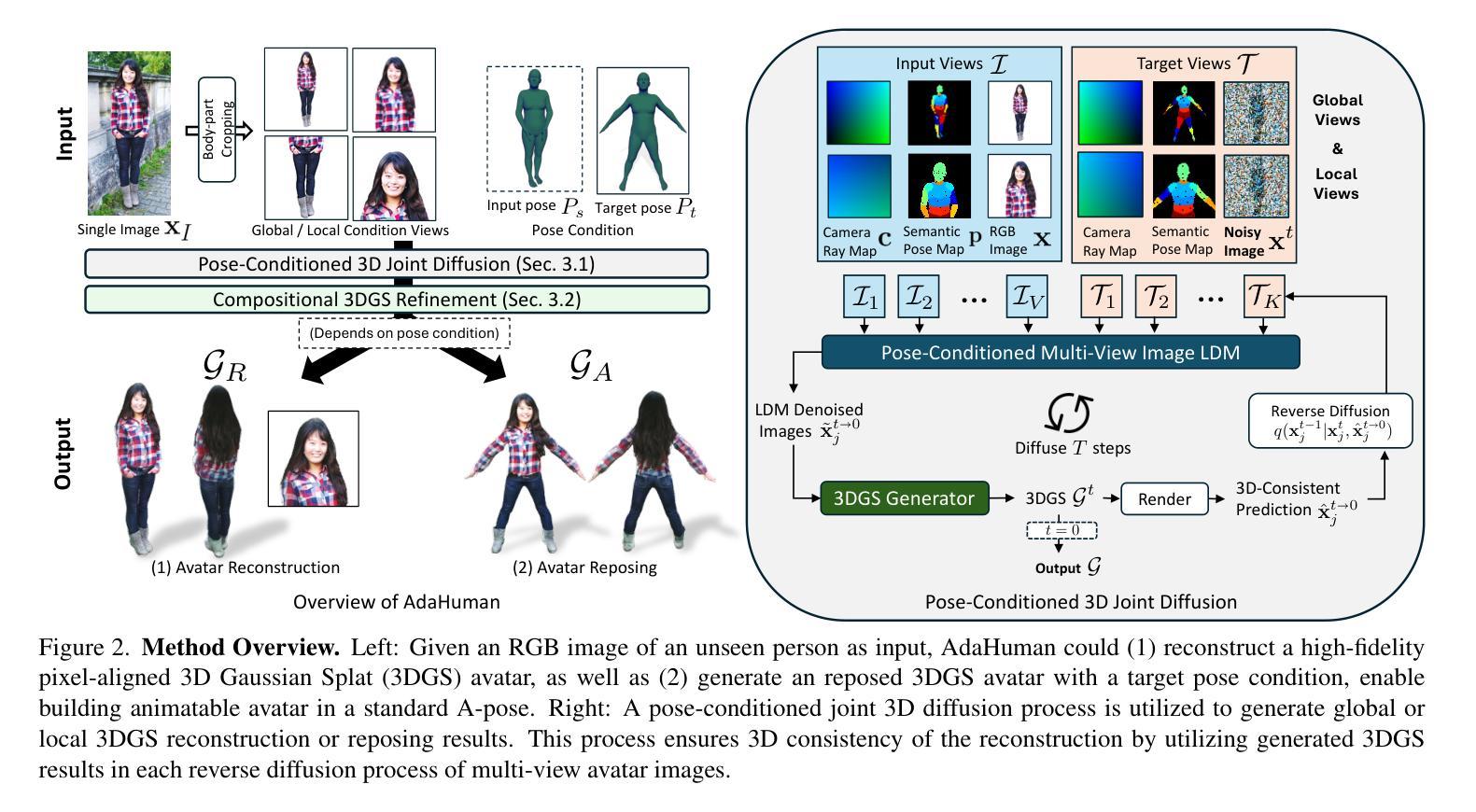
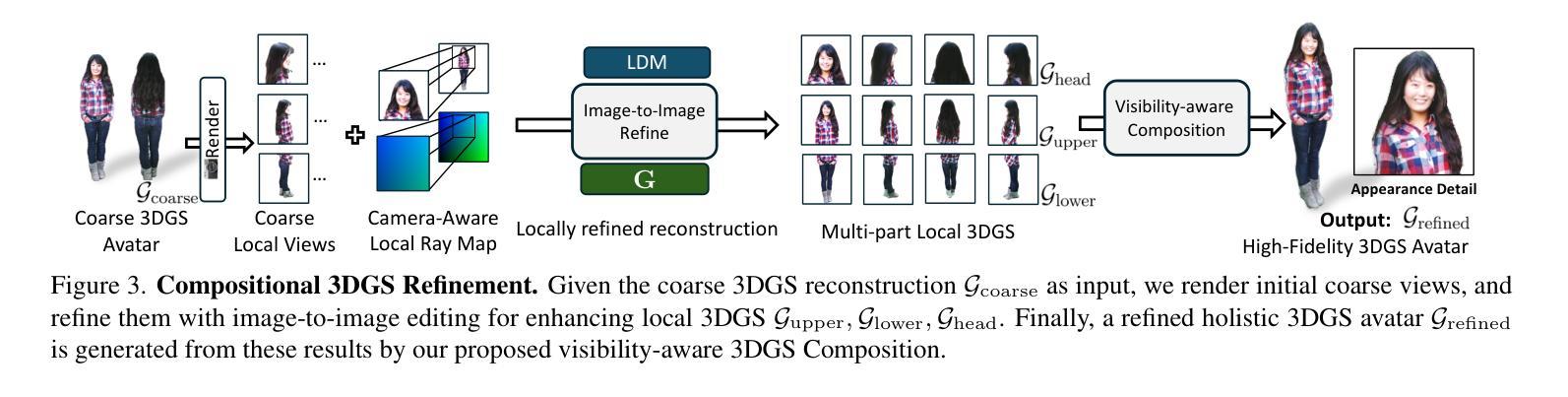
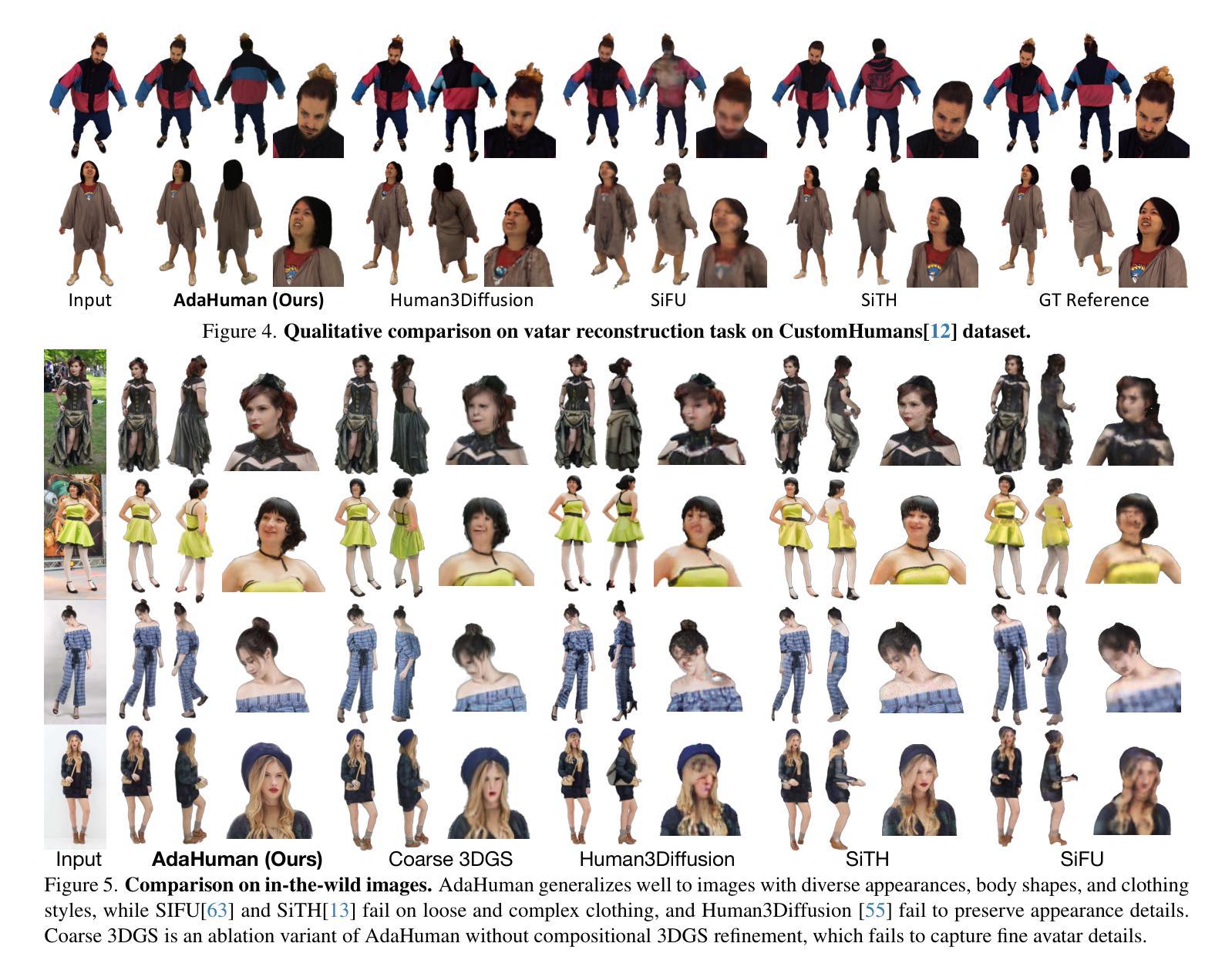
Existing methods for image-to-3D avatar generation struggle to produce highly detailed, animation-ready avatars suitable for real-world applications. We introduce AdaHuman, a novel framework that generates high-fidelity animatable 3D avatars from a single in-the-wild image. AdaHuman incorporates two key innovations: (1) A pose-conditioned 3D joint diffusion model that synthesizes consistent multi-view images in arbitrary poses alongside corresponding 3D Gaussian Splats (3DGS) reconstruction at each diffusion step; (2) A compositional 3DGS refinement module that enhances the details of local body parts through image-to-image refinement and seamlessly integrates them using a novel crop-aware camera ray map, producing a cohesive detailed 3D avatar. These components allow AdaHuman to generate highly realistic standardized A-pose avatars with minimal self-occlusion, enabling rigging and animation with any input motion. Extensive evaluation on public benchmarks and in-the-wild images demonstrates that AdaHuman significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both avatar reconstruction and reposing. Code and models will be publicly available for research purposes.
现有方法在进行图像到3D角色的生成过程中,难以产生适用于真实世界应用的高度详细且适合动画的角色。我们引入了AdaHuman,这是一个新型框架,可以从一张野外图像生成高度逼真的动画3D角色。AdaHuman融合了两项关键创新:首先是姿态感知的3D关节扩散模型,它能够在任意的姿态下合成一致的多视角图像,并在每一步扩散时都进行对应的3D高斯splat(3DGS)重建;其次是组合式3DGS优化模块,它通过图像到图像的细化来提升局部身体部位的细节,并使用新型裁剪感知相机射线图无缝集成它们,从而生成连贯的详细3D角色。这些组件使得AdaHuman能够生成高度逼真的标准化A姿态角色,具有最小的自我遮挡,并能够使用任何输入动作进行骨骼绑定和动画。在公共基准测试和野外图像上的广泛评估表明,AdaHuman在角色重建和姿态重塑方面都显著优于当前最先进的方法。为了研究目的,我们将公开提供代码和模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Website: https://nvlabs.github.io/AdaHuman
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为AdaHuman的新型框架,该框架可从单张图像生成高保真度动画3D阿凡达。其两大创新点包括:姿势控制的3D关节扩散模型,可以在任意姿势下合成一致的多视角图像,并在每个扩散步骤中重建相应的3D高斯斯通(3DGS);以及组合式3DGS优化模块,通过图像到图像的细节优化,并通过全新的作物感知相机射线图无缝集成,产生连贯的详细3D阿凡达。AdaHuman能生成高度逼真的标准化A姿势阿凡达,自我遮挡最少,并能与任何输入动作进行骨骼绑定和动画。在公共基准测试和真实图像上的广泛评估表明,AdaHuman在阿凡达重建和重新定位方面显著优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- AdaHuman是一个新型框架,能够从单一图像生成高保真动画3D阿凡达。
- AdaHuman采用姿势控制的3D关节扩散模型,在任意姿势下合成一致的多视角图像。
- AdaHuman在每个扩散步骤中进行对应的3D高斯斯通(3DGS)重建。
- AdaHuman采用组合式3DGS优化模块,提升局部身体部分的细节。
- AdaHuman通过图像到图像的细化以及作物感知相机射线图无缝集成局部细节,产生连贯的详细3D阿凡达。
- AdaHuman生成的阿凡达具有高度逼真、标准化A姿势、最小自我遮挡的特点。
- AdaHuman在公共基准测试和真实图像上的表现优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

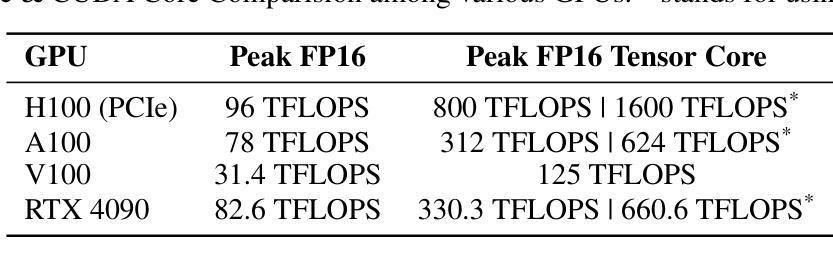
TC-GS: A Faster Gaussian Splatting Module Utilizing Tensor Cores
Authors:Zimu Liao, Jifeng Ding, Rong Fu, Siwei Cui, Ruixuan Gong, Li Wang, Boni Hu, Yi Wang, Hengjie Li, XIngcheng Zhang, Hui Wang
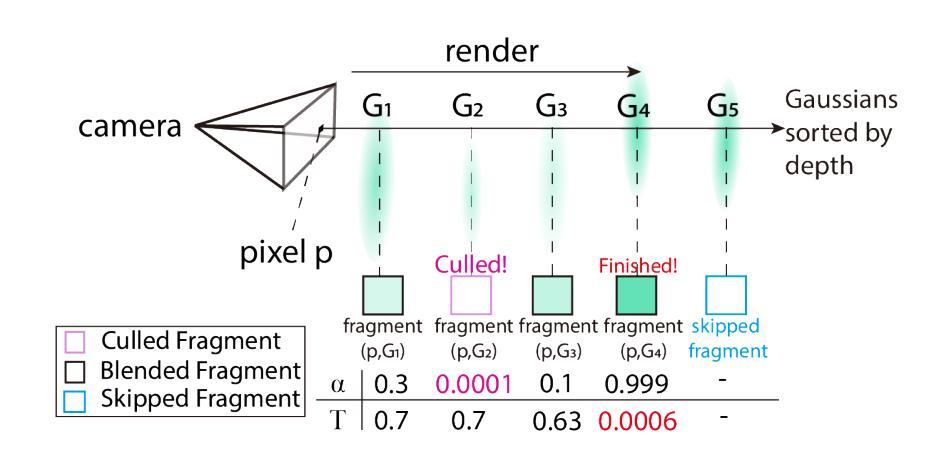
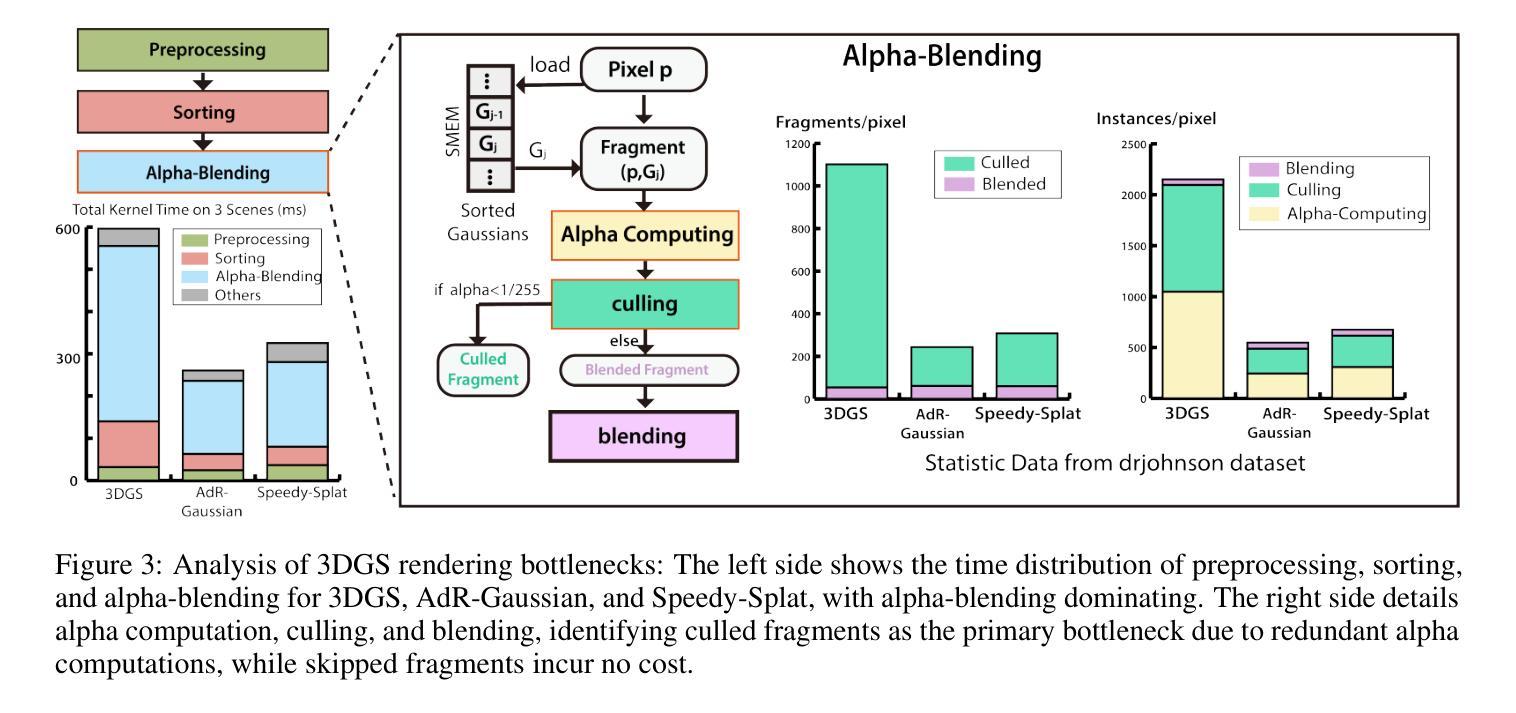
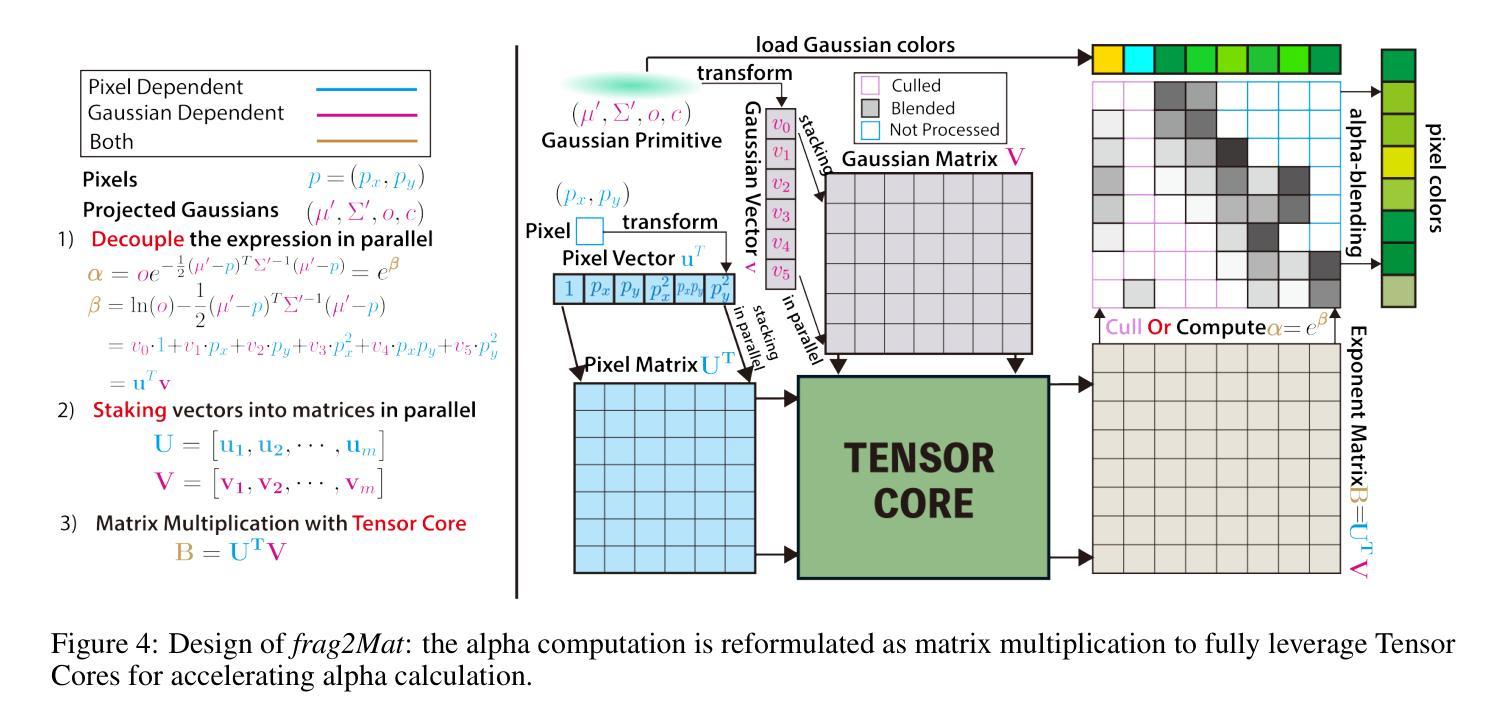
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) renders pixels by rasterizing Gaussian primitives, where conditional alpha-blending dominates the time cost in the rendering pipeline. This paper proposes TC-GS, an algorithm-independent universal module that expands Tensor Core (TCU) applicability for 3DGS, leading to substantial speedups and seamless integration into existing 3DGS optimization frameworks. The key innovation lies in mapping alpha computation to matrix multiplication, fully utilizing otherwise idle TCUs in existing 3DGS implementations. TC-GS provides plug-and-play acceleration for existing top-tier acceleration algorithms tightly coupled with rendering pipeline designs, like Gaussian compression and redundancy elimination algorithms. Additionally, we introduce a global-to-local coordinate transformation to mitigate rounding errors from quadratic terms of pixel coordinates caused by Tensor Core half-precision computation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method maintains rendering quality while providing an additional 2.18x speedup over existing Gaussian acceleration algorithms, thus reaching up to a total 5.6x acceleration. The code is currently available at anonymous \href{https://github.com/TensorCore3DGS/3DGSTensorCore}
三维高斯模糊(3DGS)通过光栅化高斯基本形状来渲染像素,其中条件alpha混合主导了渲染流水线的时间成本。本文提出了TC-GS,这是一个独立于算法的通用模块,扩展了Tensor Core(TCU)在3DGS中的应用,从而实现显著的速度提升并无缝集成到现有的3DGS优化框架中。关键创新在于将alpha计算映射到矩阵乘法,充分利用现有3DGS实现中通常空闲的TCU。TC-GS为现有顶级加速算法提供与渲染流水线设计紧密耦合的即插即用加速,例如高斯压缩和冗余消除算法。此外,我们引入全局到局部坐标变换,以缓解由于Tensor Core半精度计算导致的像素坐标二次项引起的舍入误差。大量实验表明,我们的方法在保持渲染质量的同时,对现有高斯加速算法提供了额外的2.18倍加速,从而达到了总计5.6倍的加速。代码目前可在匿名网址https://github.com/TensorCore3DGS/3DGSTensorCore上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 6 figures
Summary
本文介绍了针对三维高斯渲染技术(3DGS)的优化模块TC-GS。它通过利用Tensor Core(TCU)进行alpha计算,映射到矩阵乘法中,提高了渲染速度,同时实现了与现有顶级加速算法的无缝集成。通过全球到局部的坐标变换,解决了由于Tensor Core半精度计算导致的二次项像素坐标舍入误差问题。实验证明,该方法在保证渲染质量的同时,较现有的高斯加速算法实现了额外的2.18倍加速,总加速达到5.6倍。
Key Takeaways
- TC-GS是一种针对3DGS的算法优化模块,旨在利用Tensor Core(TCU)进行加速。
- 通过将alpha计算映射到矩阵乘法中,TC-GS实现了高速渲染。
- TC-GS可以无缝集成到现有的顶级加速算法中,如高斯压缩和冗余消除算法。
- 采用全球到局部的坐标变换解决了因Tensor Core半精度计算而产生的像素坐标舍入误差问题。
- 实验显示,TC-GS在保证渲染质量的同时,较现有方法实现了显著的速度提升。
- TC-GS代码已公开,可访问特定链接获取。
点此查看论文截图

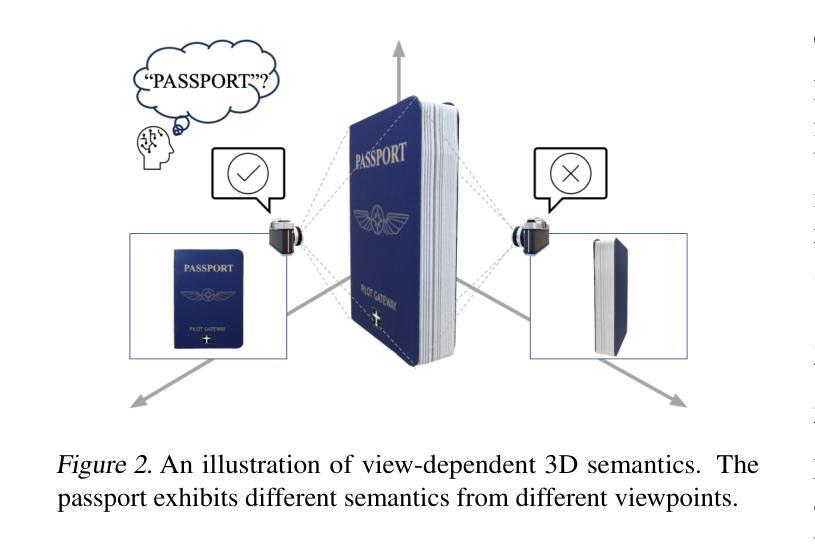
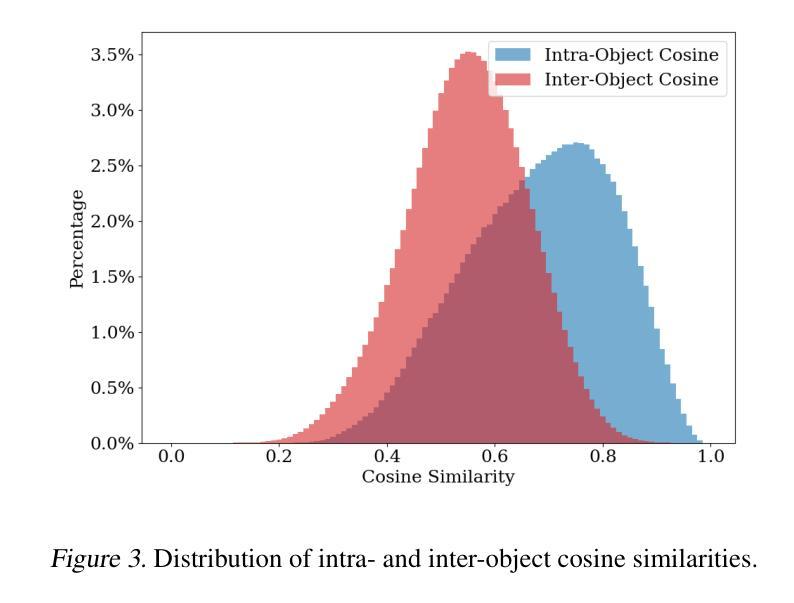
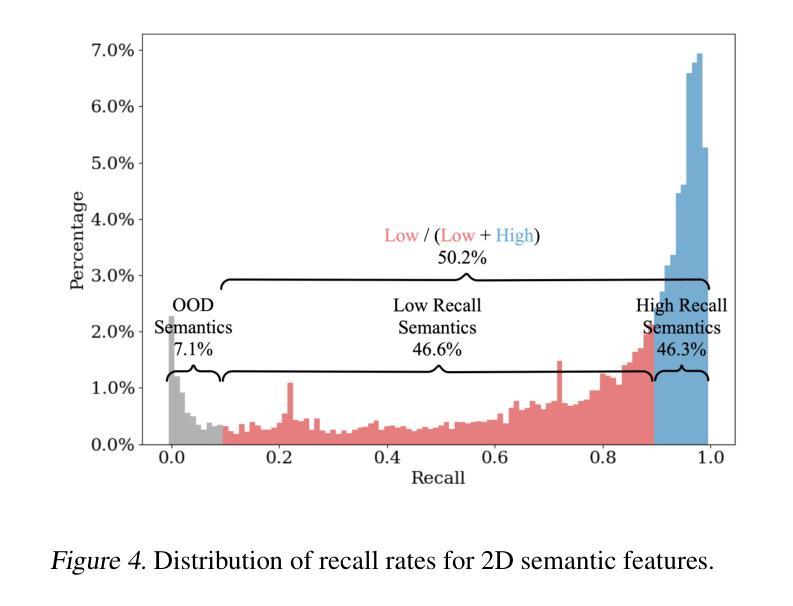
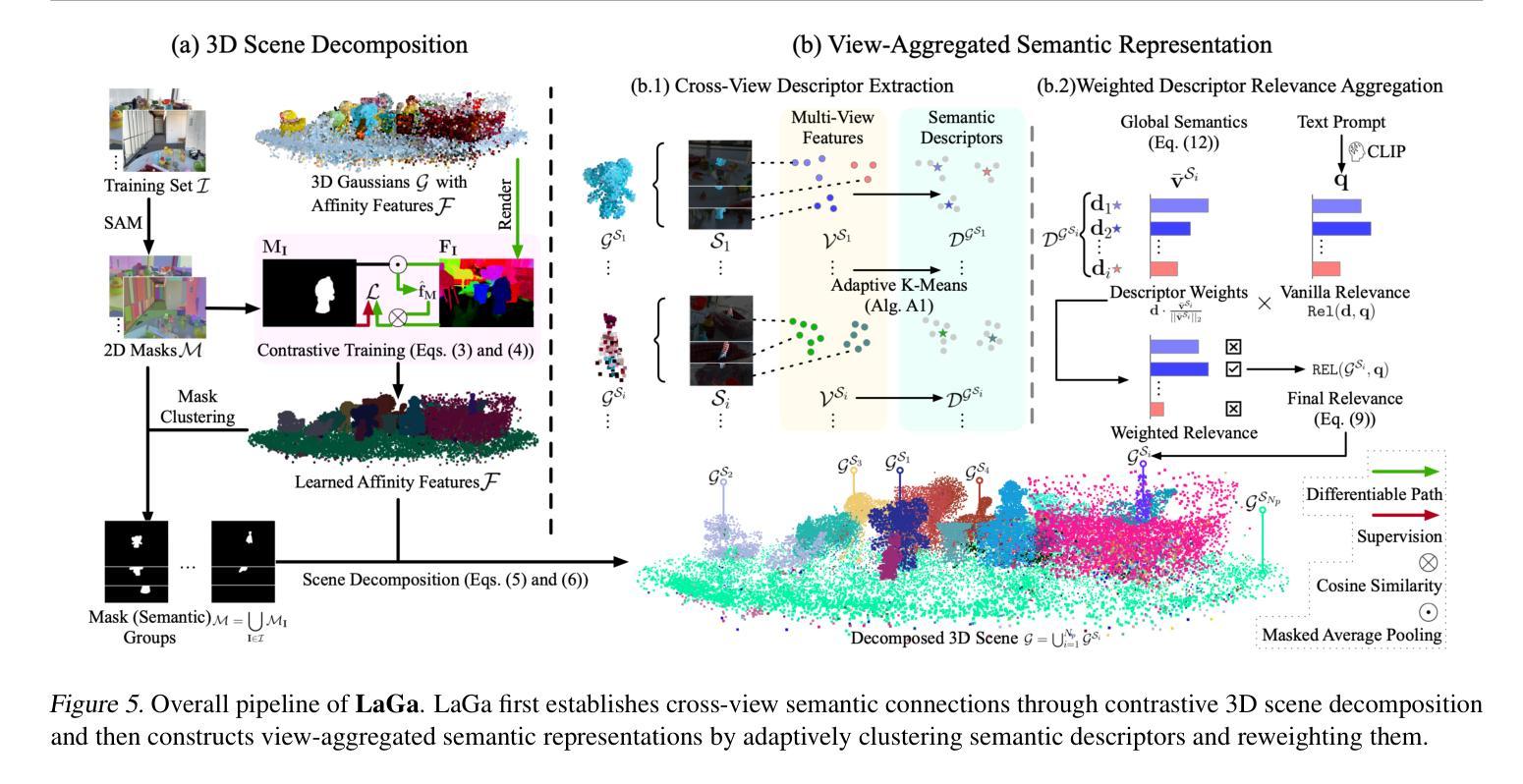
Tackling View-Dependent Semantics in 3D Language Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jiazhong Cen, Xudong Zhou, Jiemin Fang, Changsong Wen, Lingxi Xie, Xiaopeng Zhang, Wei Shen, Qi Tian
Recent advancements in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) enable high-quality 3D scene reconstruction from RGB images. Many studies extend this paradigm for language-driven open-vocabulary scene understanding. However, most of them simply project 2D semantic features onto 3D Gaussians and overlook a fundamental gap between 2D and 3D understanding: a 3D object may exhibit various semantics from different viewpoints–a phenomenon we term view-dependent semantics. To address this challenge, we propose LaGa (Language Gaussians), which establishes cross-view semantic connections by decomposing the 3D scene into objects. Then, it constructs view-aggregated semantic representations by clustering semantic descriptors and reweighting them based on multi-view semantics. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LaGa effectively captures key information from view-dependent semantics, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of 3D scenes. Notably, under the same settings, LaGa achieves a significant improvement of +18.7% mIoU over the previous SOTA on the LERF-OVS dataset. Our code is available at: https://github.com/SJTU-DeepVisionLab/LaGa.
近期,三维高斯贴图(3D-GS)的进展使得从RGB图像进行高质量的三维场景重建成为可能。许多研究将此范式扩展应用于语言驱动的开放词汇场景理解。然而,大多数研究仅将二维语义特征投影到三维高斯上,忽视了二维和三维理解之间的基本差距:一个三维物体从不同的视角可能会表现出不同的语义——我们将这种现象称为视角相关语义。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了LaGa(语言高斯),它通过分解三维场景中的物体来建立跨视角的语义连接。然后,它通过聚类语义描述符并根据多视角语义重新加权它们,构建视角聚合的语义表示。大量实验表明,LaGa有效地捕捉了视角相关语义的关键信息,实现了对三维场景的更全面理解。值得注意的是,在同一设置下,LaGa在LERF-OVS数据集上较之前的最优方法提高了+18.7%的mIoU。我们的代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/SJTU-DeepVisionLab/LaGa。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025 camera ready. Project Page: https://jumpat.github.io/laga-page/
Summary
基于RGB图像的高质量三维场景重建,最新的三维高斯延展技术(3D-GS)取得进展。现有研究多将这种技术应用于语言驱动的开词汇场景理解。然而,大多数研究仅将二维语义特征映射到三维高斯上,忽视了二维和三维理解之间的基本差距:同一物体从不同视角观察可能呈现不同的语义特征,我们称之为视角依赖语义。为解决这一挑战,我们提出LaGa(语言高斯)技术,它通过分解三维场景物体来建立跨视角的语义连接,然后通过聚类语义描述符并结合多视角语义来构建视角聚合语义表示。实验表明,LaGa能有效捕捉视角依赖语义的关键信息,实现对三维场景的更全面理解。在相同设置下,LaGa在LERF-OVS数据集上的mIoU较之前的最优方法提高了18.7%。我们的代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/SJTU-DeepVisionLab/LaGa。
Key Takeaways:
一、研究使用三维高斯延展技术(3D-GS)实现高质量的RGB图像三维场景重建;
二、目前多数相关研究仅仅关注将二维语义特征映射到三维空间中,忽视了不同视角带来的视角依赖语义问题;
三、LaGa技术通过分解三维场景物体建立跨视角的语义连接;
四、LaGa通过聚类语义描述符并结合多视角语义构建视角聚合语义表示;
五、实验证明LaGa能有效捕捉视角依赖语义的关键信息;
六、相较于现有方法,LaGa在LERF-OVS数据集上的mIoU提升显著;
点此查看论文截图

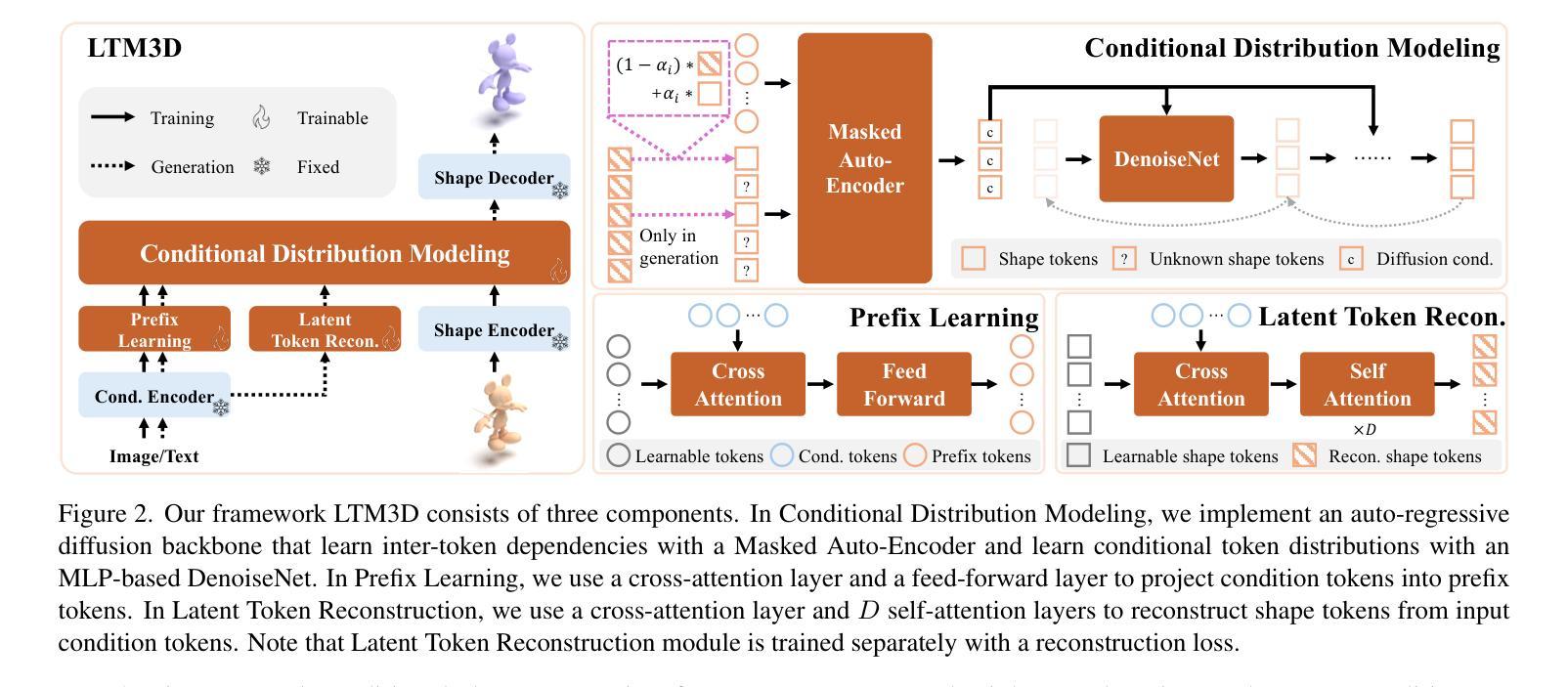
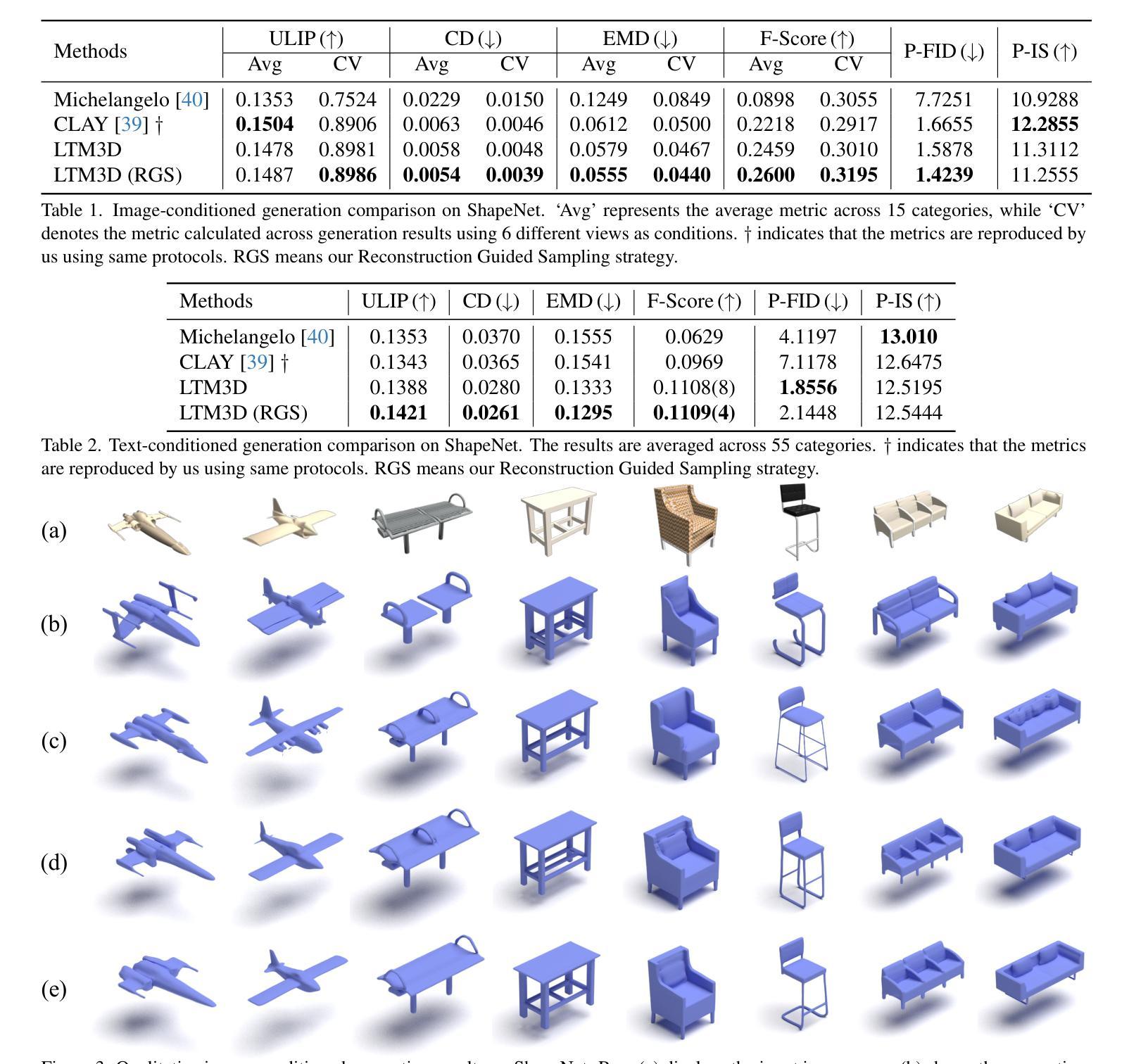
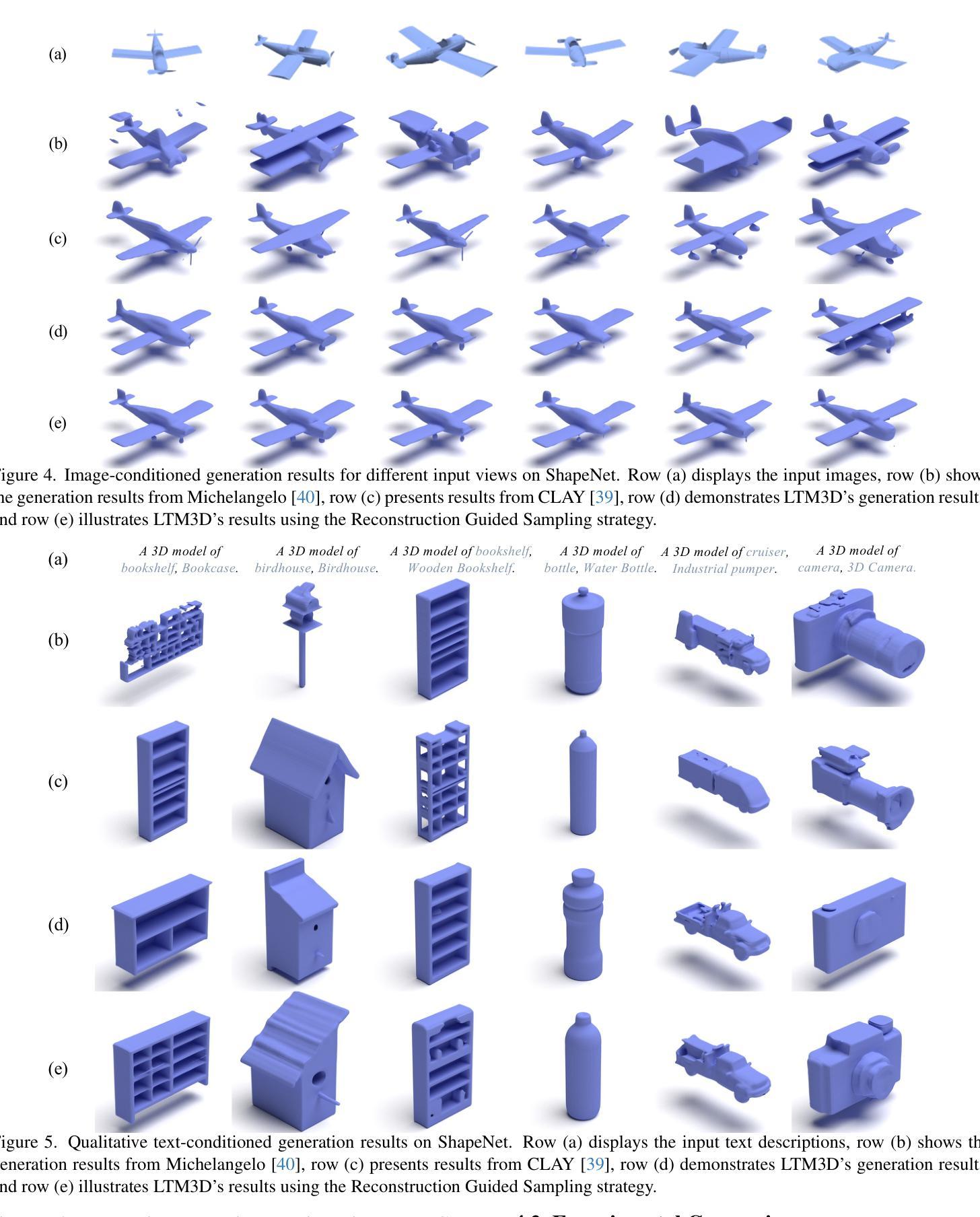
LTM3D: Bridging Token Spaces for Conditional 3D Generation with Auto-Regressive Diffusion Framework
Authors:Xin Kang, Zihan Zheng, Lei Chu, Yue Gao, Jiahao Li, Hao Pan, Xuejin Chen, Yan Lu
We present LTM3D, a Latent Token space Modeling framework for conditional 3D shape generation that integrates the strengths of diffusion and auto-regressive (AR) models. While diffusion-based methods effectively model continuous latent spaces and AR models excel at capturing inter-token dependencies, combining these paradigms for 3D shape generation remains a challenge. To address this, LTM3D features a Conditional Distribution Modeling backbone, leveraging a masked autoencoder and a diffusion model to enhance token dependency learning. Additionally, we introduce Prefix Learning, which aligns condition tokens with shape latent tokens during generation, improving flexibility across modalities. We further propose a Latent Token Reconstruction module with Reconstruction-Guided Sampling to reduce uncertainty and enhance structural fidelity in generated shapes. Our approach operates in token space, enabling support for multiple 3D representations, including signed distance fields, point clouds, meshes, and 3D Gaussian Splatting. Extensive experiments on image- and text-conditioned shape generation tasks demonstrate that LTM3D outperforms existing methods in prompt fidelity and structural accuracy while offering a generalizable framework for multi-modal, multi-representation 3D generation.
我们介绍了LTM3D,这是一种用于条件三维形状生成的潜在令牌空间建模框架,它结合了扩散和自回归(AR)模型的优势。虽然基于扩散的方法有效地对连续潜在空间进行建模,而AR模型在捕获令牌间依赖性方面表现出色,但将这些范式相结合用于三维形状生成仍是一个挑战。为了解决这一问题,LTM3D采用条件分布建模主干,利用掩码自动编码器和扩散模型增强令牌依赖性学习。此外,我们引入了前缀学习,在生成过程中将条件令牌与形状潜在令牌对齐,提高跨模态的灵活性。我们进一步提出了带有重建引导采样的潜在令牌重建模块,以减少不确定性并增强生成形状的结构保真度。我们的方法运行在令牌空间,支持多种三维表示,包括符号距离场、点云、网格和三维高斯贴图。在图像和文本条件形状生成任务的广泛实验表明,LTM3D在提示保真度和结构准确性方面优于现有方法,同时提供了一个用于多模态、多表示的三维生成的可推广框架。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LTM3D是一个基于潜在符号空间的建模框架,结合了扩散模型和自回归模型的优势,用于条件性三维形状生成。它通过条件分布建模、前缀学习和潜在符号重建等方法,提高了形状生成的灵活性、不确定性的降低以及结构保真度。该框架支持多种三维表示,包括符号距离场、点云、网格和三维高斯喷溅等。实验表明,LTM3D在图像和文本条件下的形状生成任务中表现出优异性能。
Key Takeaways
- LTM3D是一个用于条件性三维形状生成的框架,结合了扩散模型和自回归模型的优势。
- 它通过条件分布建模来增强形状生成的能力。
- LTM3D引入了前缀学习,以提高形状生成过程中的条件符号与形状潜在符号的对齐。
- 潜在符号重建模块与重建引导采样用于减少生成形状的不确定性,提高其结构保真度。
- LTM3D操作于符号空间,支持多种三维表示,包括符号距离场、点云、网格等。
- 实验证明,LTM3D在形状生成的提示保真度和结构准确性方面优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

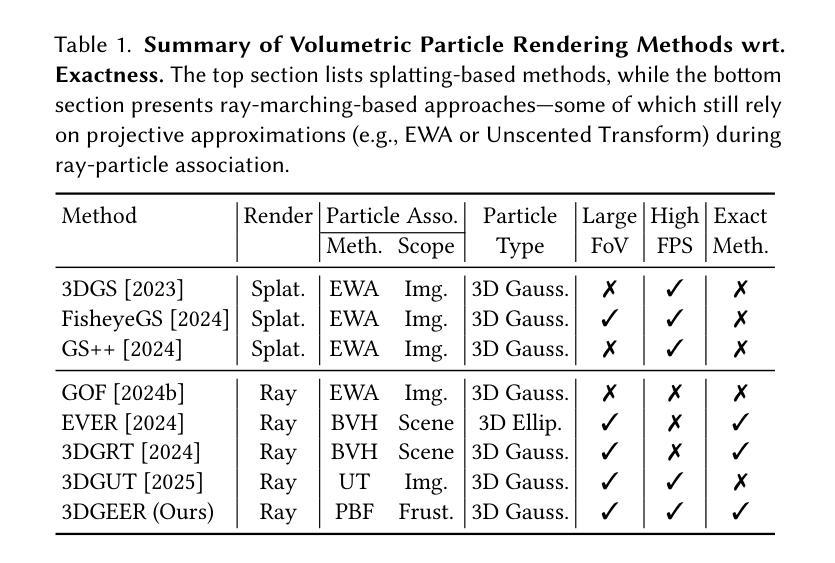
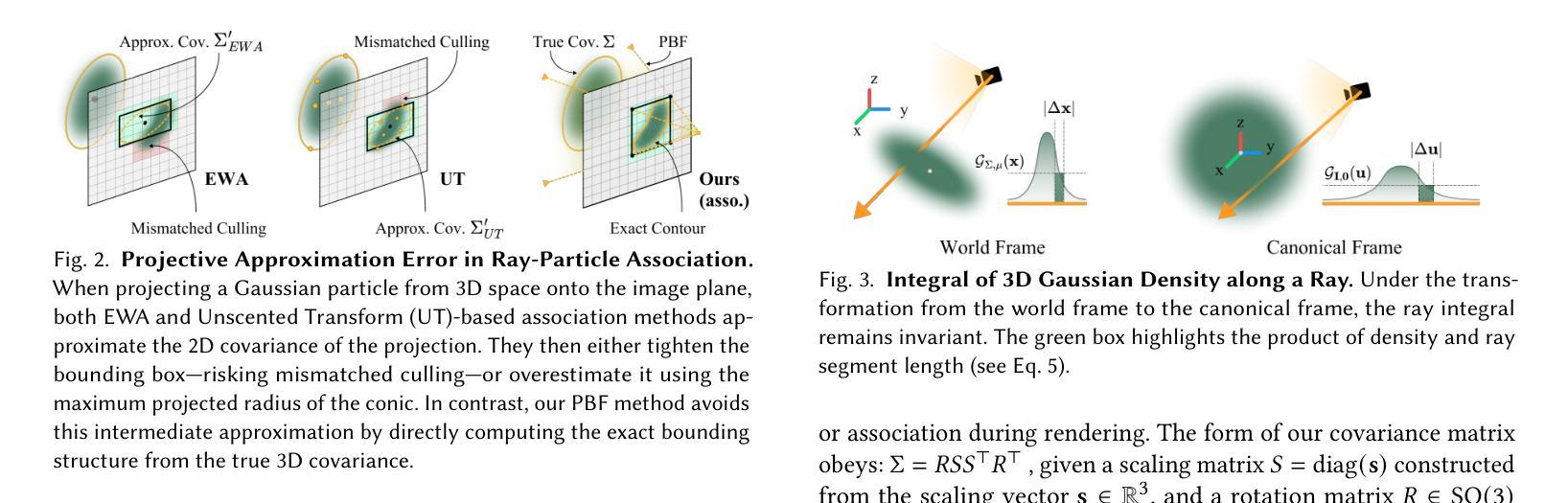
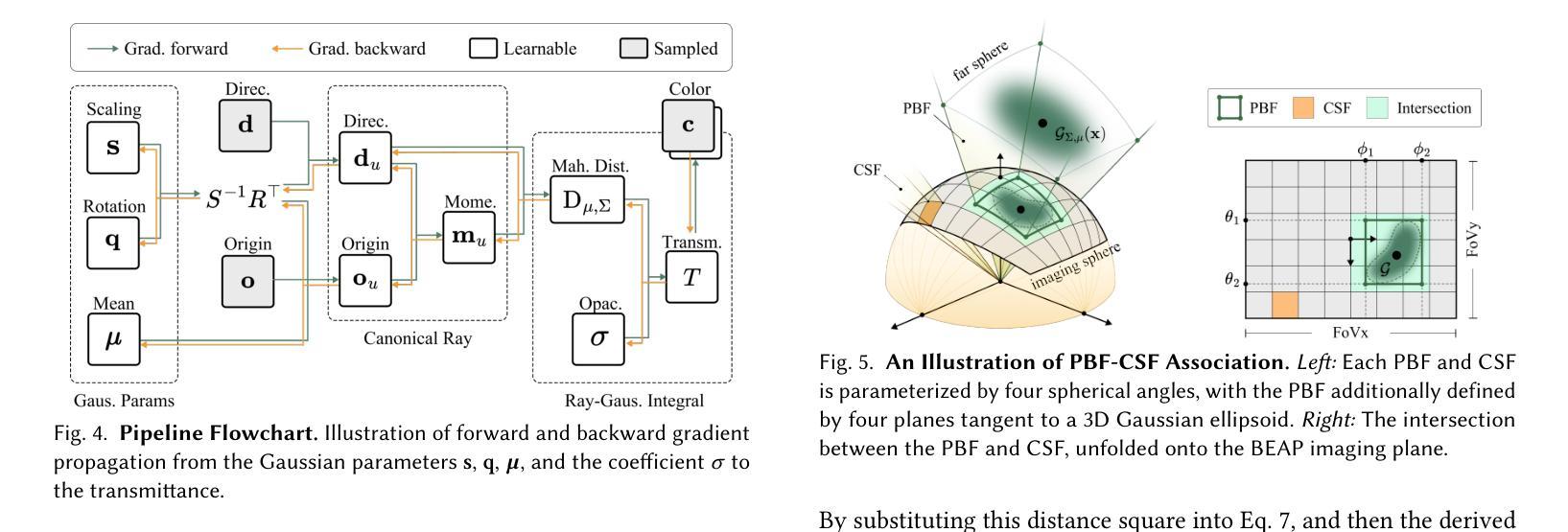
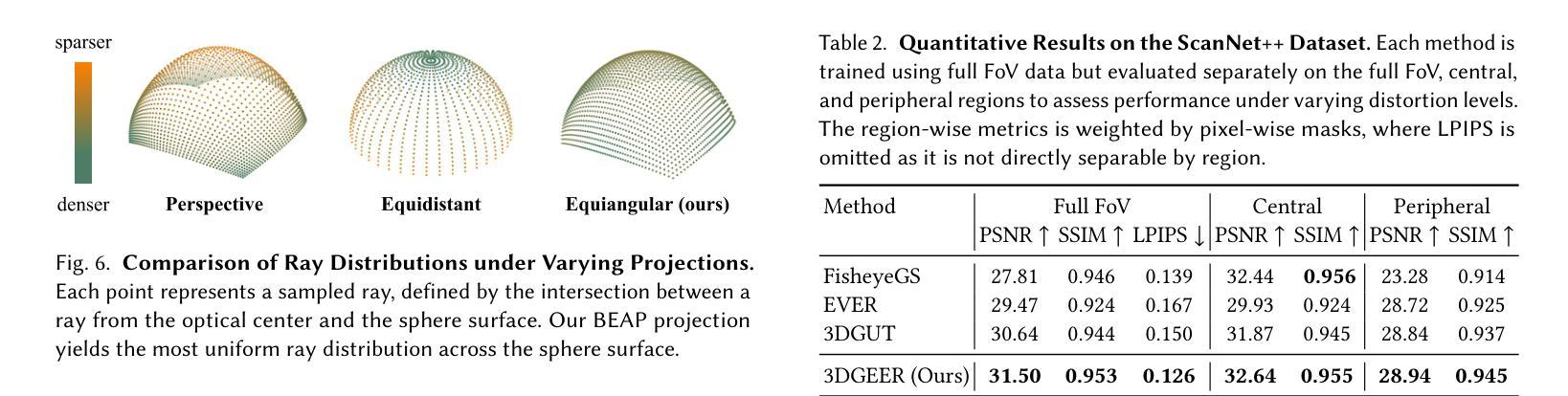
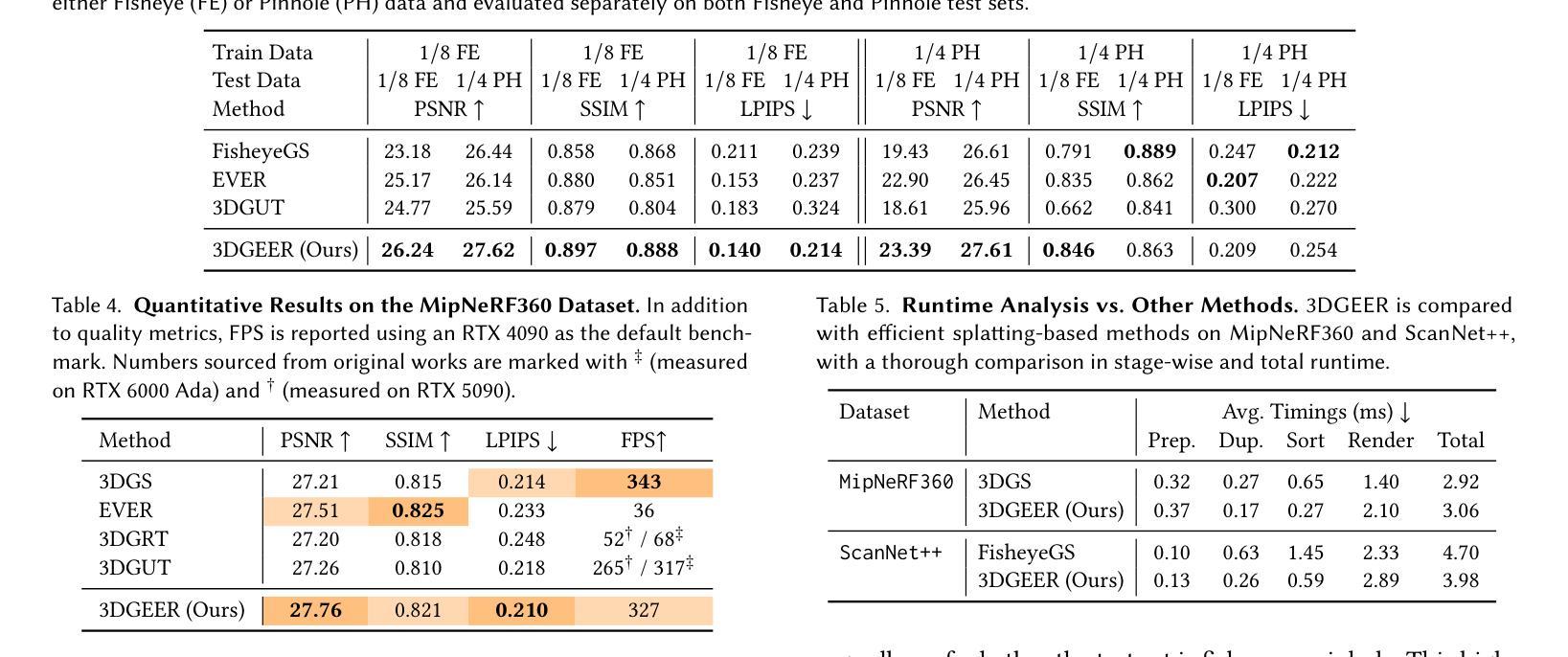
3DGEER: Exact and Efficient Volumetric Rendering with 3D Gaussians
Authors:Zixun Huang, Cho-Ying Wu, Yuliang Guo, Xinyu Huang, Liu Ren
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) marks a significant milestone in balancing the quality and efficiency of differentiable rendering. However, its high efficiency stems from an approximation of projecting 3D Gaussians onto the image plane as 2D Gaussians, which inherently limits rendering quality–particularly under large Field-of-View (FoV) camera inputs. While several recent works have extended 3DGS to mitigate these approximation errors, none have successfully achieved both exactness and high efficiency simultaneously. In this work, we introduce 3DGEER, an Exact and Efficient Volumetric Gaussian Rendering method. Starting from first principles, we derive a closed-form expression for the density integral along a ray traversing a 3D Gaussian distribution. This formulation enables precise forward rendering with arbitrary camera models and supports gradient-based optimization of 3D Gaussian parameters. To ensure both exactness and real-time performance, we propose an efficient method for computing a tight Particle Bounding Frustum (PBF) for each 3D Gaussian, enabling accurate and efficient ray-Gaussian association. We also introduce a novel Bipolar Equiangular Projection (BEAP) representation to accelerate ray association under generic camera models. BEAP further provides a more uniform ray sampling strategy to apply supervision, which empirically improves reconstruction quality. Experiments on multiple pinhole and fisheye datasets show that our method consistently outperforms prior methods, establishing a new state-of-the-art in real-time neural rendering.
3D 高斯拼接(3DGS)在平衡可微分渲染的质量和效率方面取得了重要里程碑式的进展。然而,其高效率来源于将3D高斯投影到图像平面上近似为2D高斯,这固有地限制了渲染质量,特别是在大视野(FoV)相机输入下。虽然最近有几项工作对3DGS进行了扩展,以减轻这些近似误差,但没有任何工作能够同时实现精确性和高效率。在这项工作中,我们引入了3DGEER,一种精确高效的体积高斯渲染方法。我们从基本原理出发,推导出了沿穿过3D高斯分布的射线密度积分的封闭形式表达式。这一公式化使得使用任意相机模型进行精确正向渲染成为可能,并支持基于梯度的3D高斯参数优化。为了确保准确性和实时性能,我们提出了一种有效的方法来为每个3D高斯计算紧密的粒子边界框(PBF),从而实现精确高效的射线-高斯关联。我们还引入了一种新的双向等角投影(BEAP)表示,以加速通用相机模型下的射线关联。BEAP进一步提供了更均匀的射线采样策略来应用监督,这经验性地提高了重建质量。在多孔和鱼眼数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法始终优于以前的方法,在实时神经渲染领域树立了新的最新技术标杆。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了三维高斯渲染(3DGS)的局限性,并因此提出了一种精确高效的体积高斯渲染方法——3DGEER。该方法通过推导三维高斯分布在射线遍历时的密度积分公式,实现了精确的前向渲染和基于梯度的三维高斯参数优化。同时,为了提高效率,提出了粒子边界框(PBF)技术和双向等角投影(BEAP)表示方法,实现了准确高效的射线-高斯关联。实验证明,该方法在多孔和鱼眼数据集上的表现均优于先前的方法,为实时神经渲染树立了新的标杆。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS在高效率的同时牺牲了渲染质量,特别是在大视野相机输入下。
- 提出的3DGEER方法实现了精确的前向渲染和基于梯度的三维高斯参数优化。
- 通过推导三维高斯分布的密度积分公式,支持任意相机模型的精确渲染。
- 通过粒子边界框(PBF)技术,实现了准确高效的射线-高斯关联。
- 双向等角投影(BEAP)表示方法加速了射线关联过程,提供了更均匀的射线采样策略,可提高重建质量。
点此查看论文截图

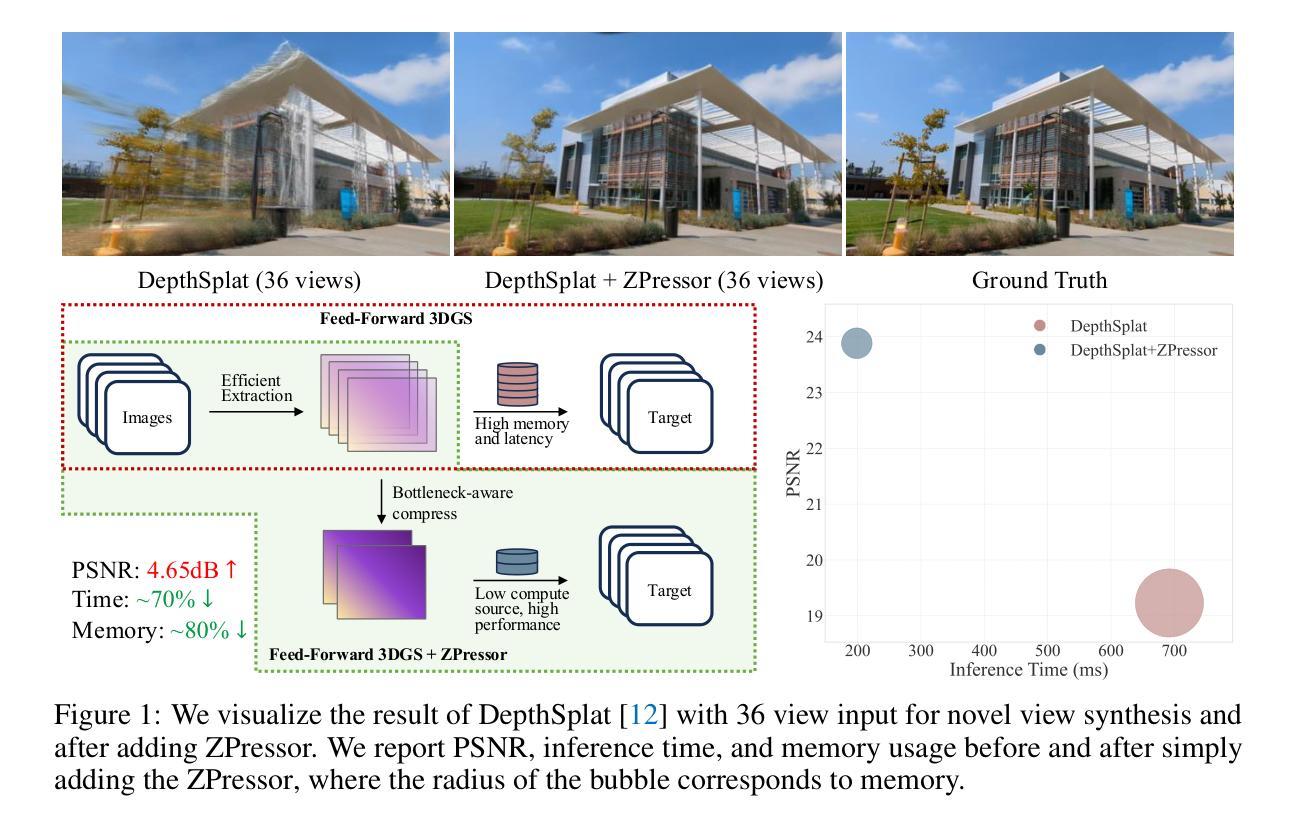
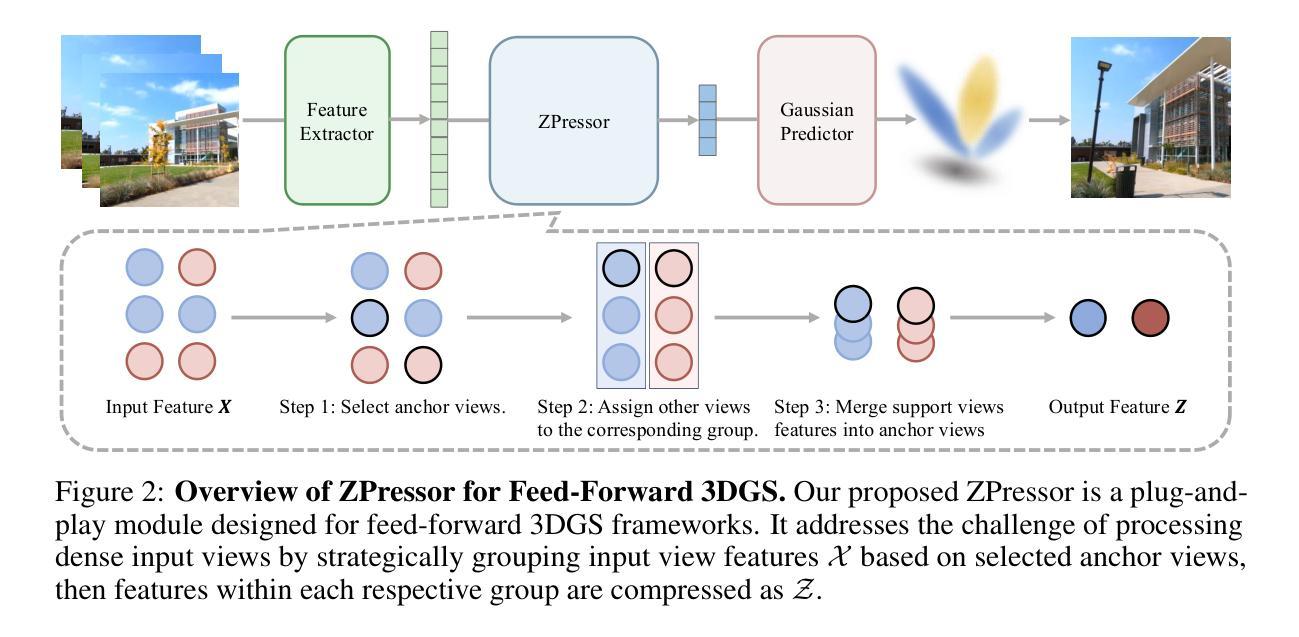
ZPressor: Bottleneck-Aware Compression for Scalable Feed-Forward 3DGS
Authors:Weijie Wang, Donny Y. Chen, Zeyu Zhang, Duochao Shi, Akide Liu, Bohan Zhuang
Feed-forward 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) models have recently emerged as a promising solution for novel view synthesis, enabling one-pass inference without the need for per-scene 3DGS optimization. However, their scalability is fundamentally constrained by the limited capacity of their encoders, leading to degraded performance or excessive memory consumption as the number of input views increases. In this work, we analyze feed-forward 3DGS frameworks through the lens of the Information Bottleneck principle and introduce ZPressor, a lightweight architecture-agnostic module that enables efficient compression of multi-view inputs into a compact latent state $Z$ that retains essential scene information while discarding redundancy. Concretely, ZPressor enables existing feed-forward 3DGS models to scale to over 100 input views at 480P resolution on an 80GB GPU, by partitioning the views into anchor and support sets and using cross attention to compress the information from the support views into anchor views, forming the compressed latent state $Z$. We show that integrating ZPressor into several state-of-the-art feed-forward 3DGS models consistently improves performance under moderate input views and enhances robustness under dense view settings on two large-scale benchmarks DL3DV-10K and RealEstate10K. The video results, code and trained models are available on our project page: https://lhmd.top/zpressor.
前馈三维高斯贴图(3DGS)模型最近作为合成新视角的一种有前途的解决方案而出现,它能够实现一次推断,无需针对每个场景的3DGS进行优化。然而,其可扩展性从根本上受到编码器容量的限制,随着输入视角数量的增加,性能会下降或内存消耗过大。在这项工作中,我们通过信息瓶颈原理分析前馈3DGS框架,并引入ZPressor,这是一个轻量级的、与架构无关的模块,它能够将多视角输入有效地压缩成紧凑的潜在状态Z,同时保留关键场景信息并丢弃冗余信息。具体来说,ZPressor能够将现有的前馈3DGS模型在80GB GPU上以480P分辨率扩展到超过100个输入视角,通过将视角划分为锚点和支撑集并使用交叉注意力将支撑视角的信息压缩到锚点视角中,形成压缩的潜在状态Z。我们表明,将ZPressor集成到几种最新前馈3DGS模型中,在DL3DV-10K和RealEstate1 0K两个大规模基准测试上,适度输入视角下的性能持续提高,密集视角设置下的稳健性增强。视频结果、代码和训练模型可在我们的项目页面查看:https://lhmd.top/zpressor。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://lhmd.top/zpressor, Code: https://github.com/ziplab/ZPressor
Summary
本文研究了基于前馈的3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)模型在处理多视角输入时的可扩展性问题。通过引入信息瓶颈原理,提出了一种轻量级的架构无关模块——ZPressor。它能有效地将多视角输入压缩成一个紧凑的潜在状态Z,保留场景的关键信息,同时去除冗余。ZPressor能将现有前馈3DGS模型扩展至处理超过100个视角的输入,且在性能上有所提升。整合到最新前馈3DGS模型的ZPressor在两个大规模数据集DL3DV-10K和RealEstate10K上的表现均表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 前馈3DGS模型在处理多视角输入时面临可扩展性问题。
- ZPressor模块基于信息瓶颈原理,能有效压缩多视角输入到一个紧凑的潜在状态Z。
- ZPressor通过分区视角和使用交叉注意力机制将辅助视角的信息压缩到主视角中,形成压缩潜在状态Z。
- ZPressor能使得现有前馈3DGS模型在超过100个视角的输入时依然保持良好的性能。
- 在两个大规模数据集上,整合了ZPressor的前馈3DGS模型表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

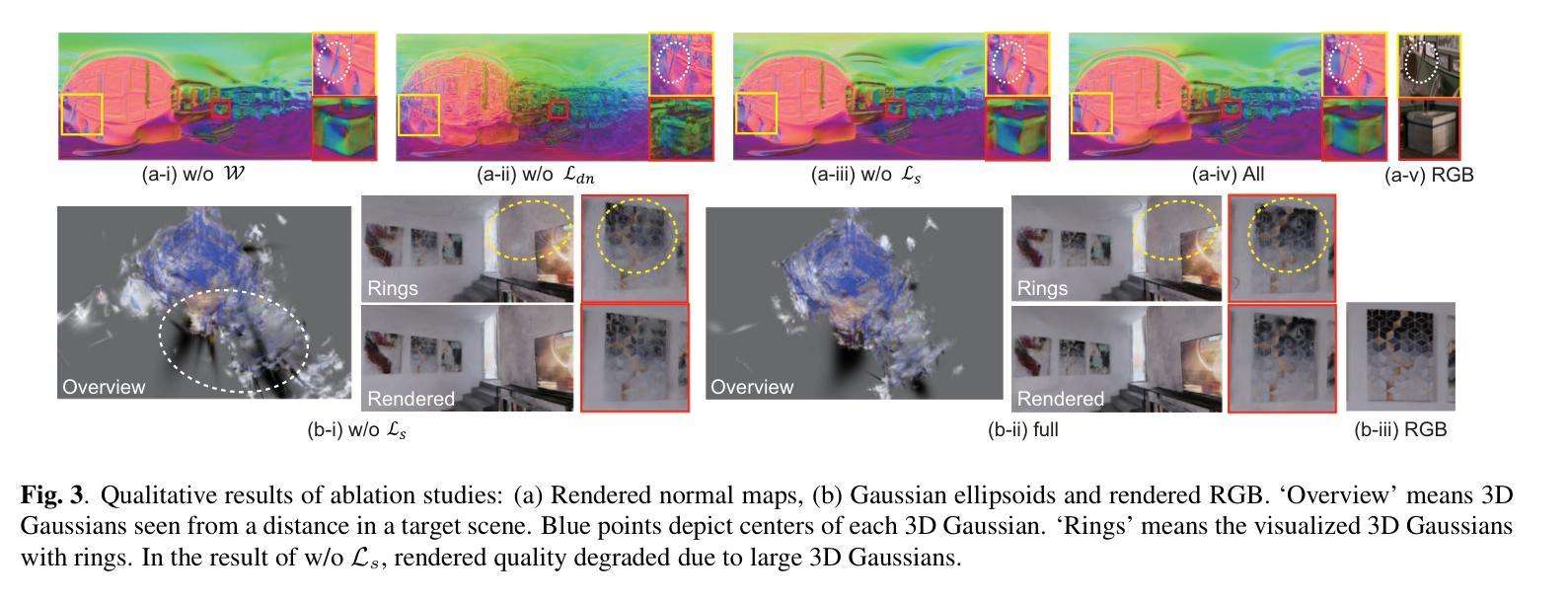
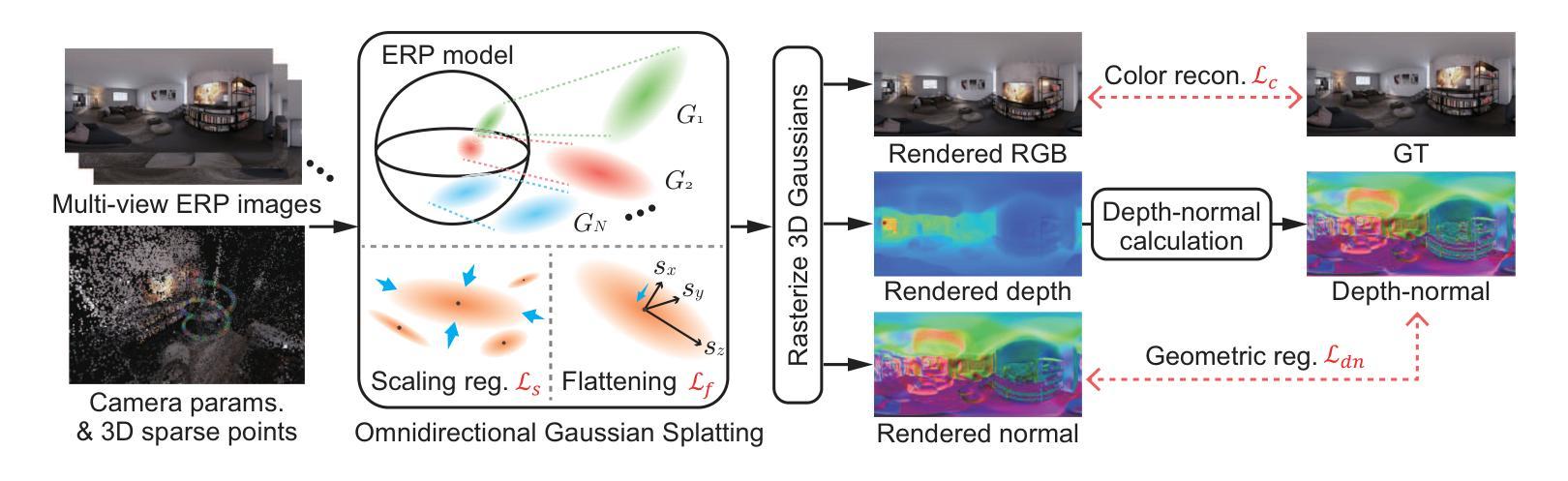
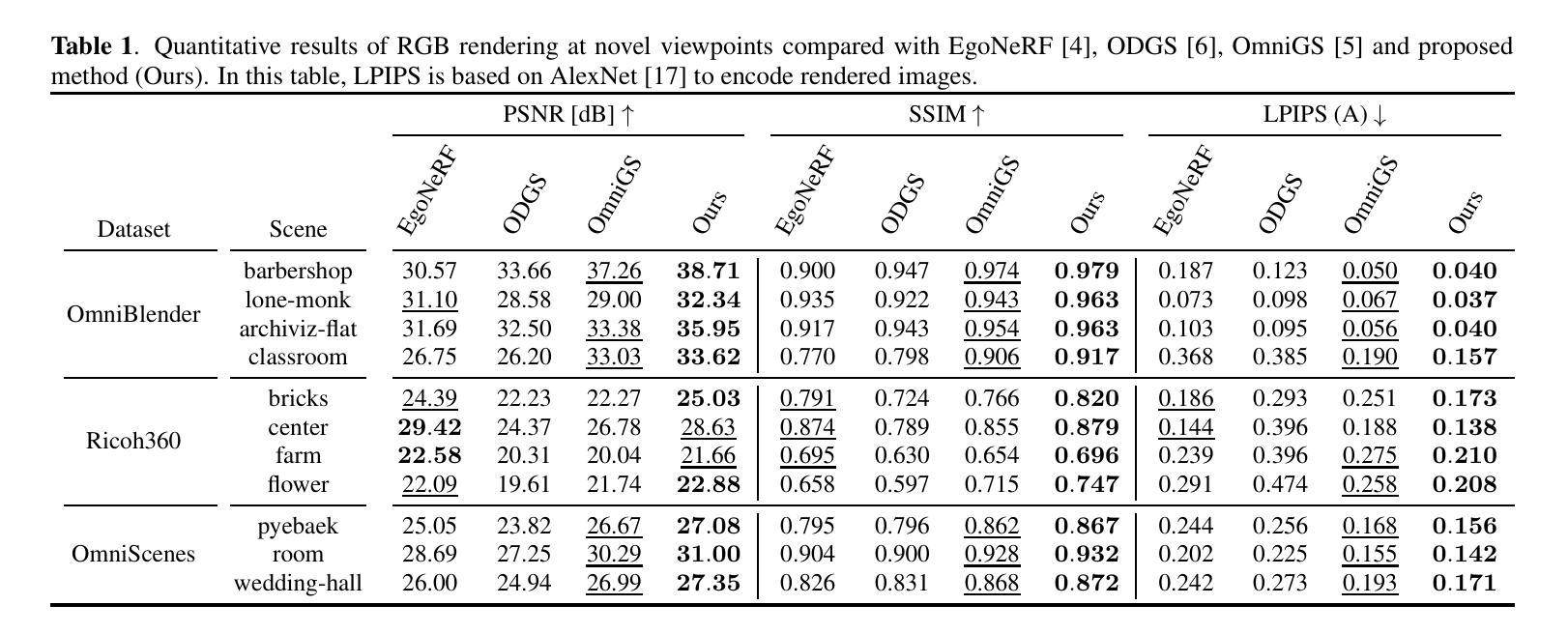
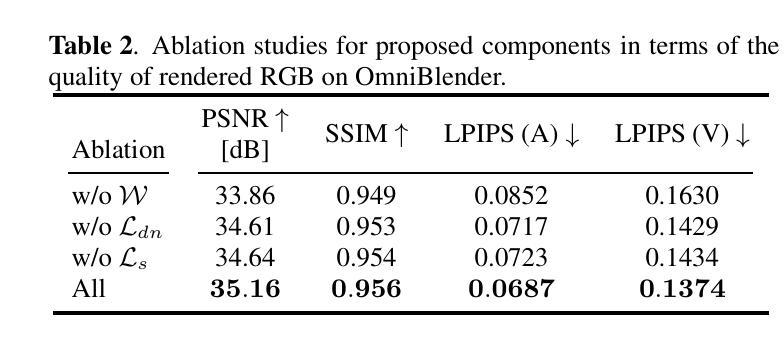
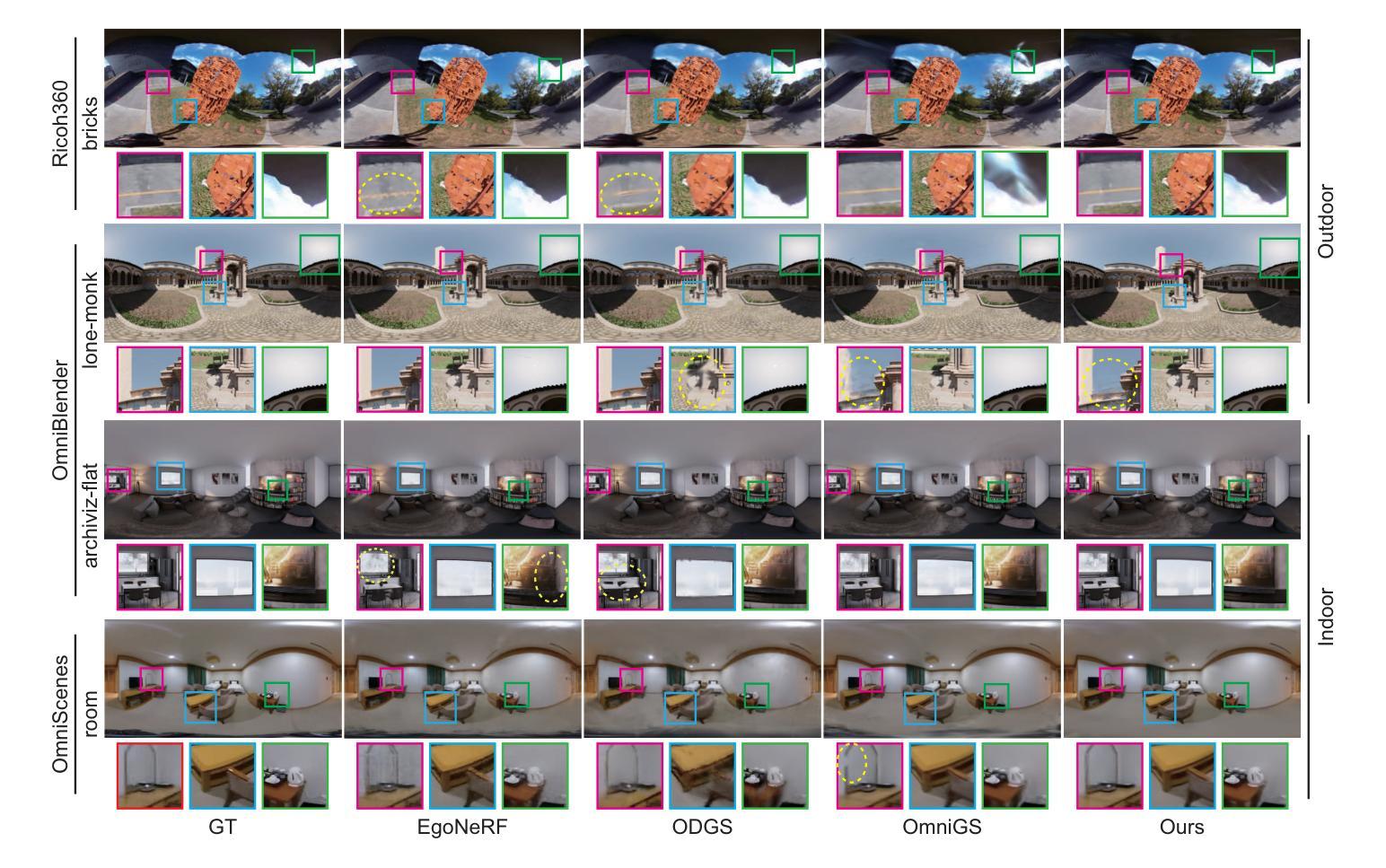
ErpGS: Equirectangular Image Rendering enhanced with 3D Gaussian Regularization
Authors:Shintaro Ito, Natsuki Takama, Koichi Ito, Hwann-Tzong Chen, Takafumi Aoki
The use of multi-view images acquired by a 360-degree camera can reconstruct a 3D space with a wide area. There are 3D reconstruction methods from equirectangular images based on NeRF and 3DGS, as well as Novel View Synthesis (NVS) methods. On the other hand, it is necessary to overcome the large distortion caused by the projection model of a 360-degree camera when equirectangular images are used. In 3DGS-based methods, the large distortion of the 360-degree camera model generates extremely large 3D Gaussians, resulting in poor rendering accuracy. We propose ErpGS, which is Omnidirectional GS based on 3DGS to realize NVS addressing the problems. ErpGS introduce some rendering accuracy improvement techniques: geometric regularization, scale regularization, and distortion-aware weights and a mask to suppress the effects of obstacles in equirectangular images. Through experiments on public datasets, we demonstrate that ErpGS can render novel view images more accurately than conventional methods.
使用360度相机拍摄的多视角图像可以重建一个广阔区域的3D空间。存在基于NeRF和3DGS的等距图像3D重建方法,以及新型视图合成(NVS)方法。另一方面,在使用等距图像时,需要克服由360度相机的投影模型造成的大畸变。在基于3DGS的方法中,360度相机模型的大畸变会产生极大的3D高斯,从而导致渲染精度较差。我们提出了基于3DGS的全方位GS(ErpGS),以实现NVS并解决这些问题。ErpGS引入了一些提高渲染精度的技术:几何正则化、尺度正则化,以及了解畸变的权重和掩膜,以抑制等距图像中障碍物的影响。在公共数据集上的实验表明,与传统方法相比,ErpGS可以更准确地进行新型视图图像的渲染。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICIP2025. Project page: https://gsisaoki.github.io/ERPGS/
Summary
基于3DGS的全方位GS(ErpGS)方法被提出,用于解决使用全景相机采集的多视角图像在3D重建中的渲染精度问题。该方法通过几何正则化、尺度正则化以及考虑畸变的权重和掩膜等技术,抑制了等距投影图像中障碍物的影响,提高了渲染精度。在公共数据集上的实验表明,ErpGS方法可以更准确地进行新型视角图像的渲染。
Key Takeaways
- 使用全景相机采集的多视角图像可以重建一个广阔的3D空间。
- 存在基于NeRF和3DGS的3D重建方法以及新型视图合成(NVS)方法。
- 使用等距投影图像时,需要克服由全景相机投影模型引起的大畸变问题。
- 在基于3DGS的方法中,全景相机模型的大畸变会导致生成极大的3D高斯,进而造成渲染精度低下。
- ErpGS是一种基于3DGS的全方位GS,旨在实现NVS并解决上述问题。
- ErpGS通过几何正则化、尺度正则化以及引入考虑畸变的权重和掩膜等技术,提高了渲染精度。
点此查看论文截图