⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-03 更新
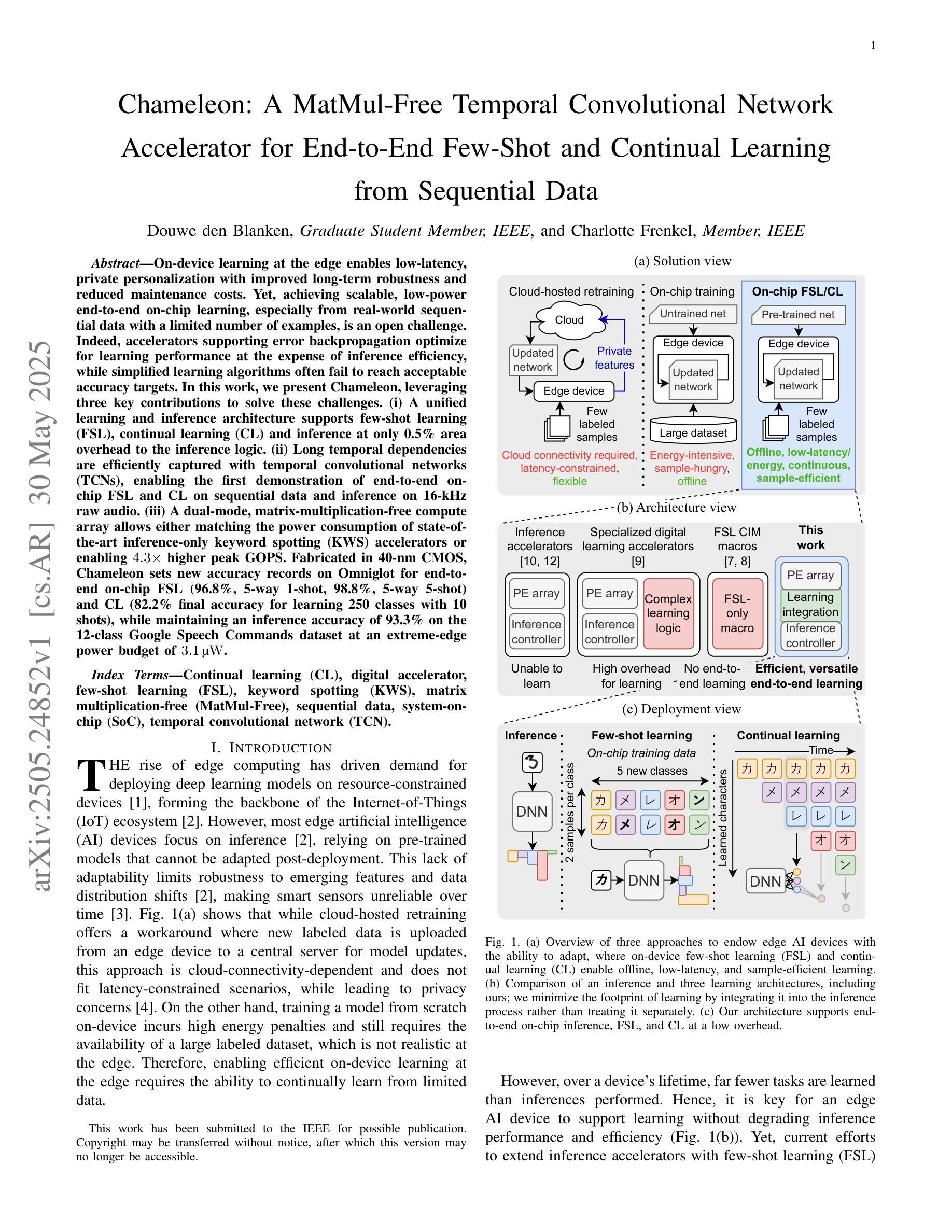
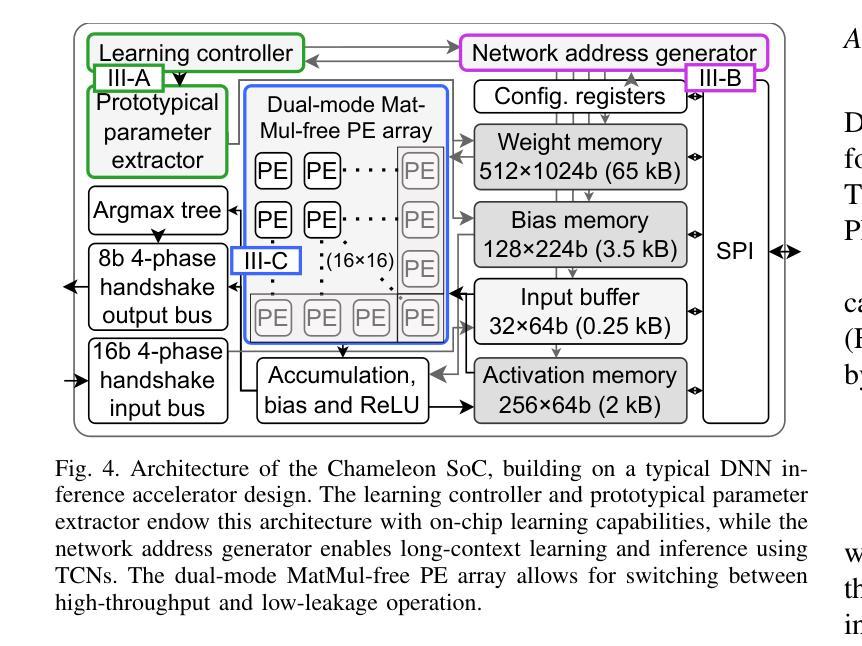
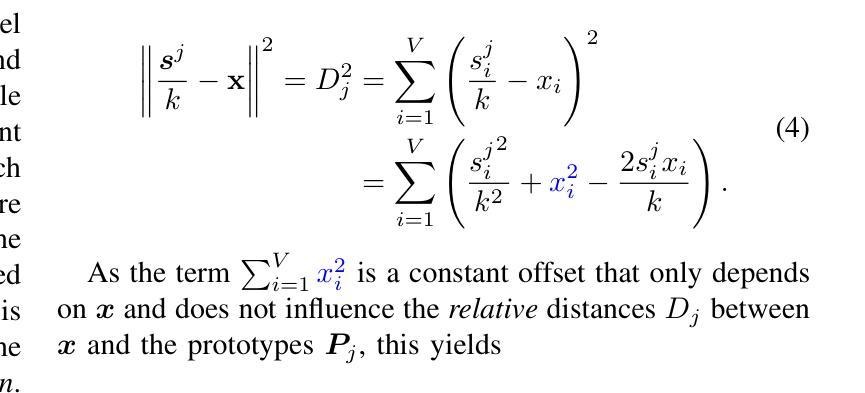
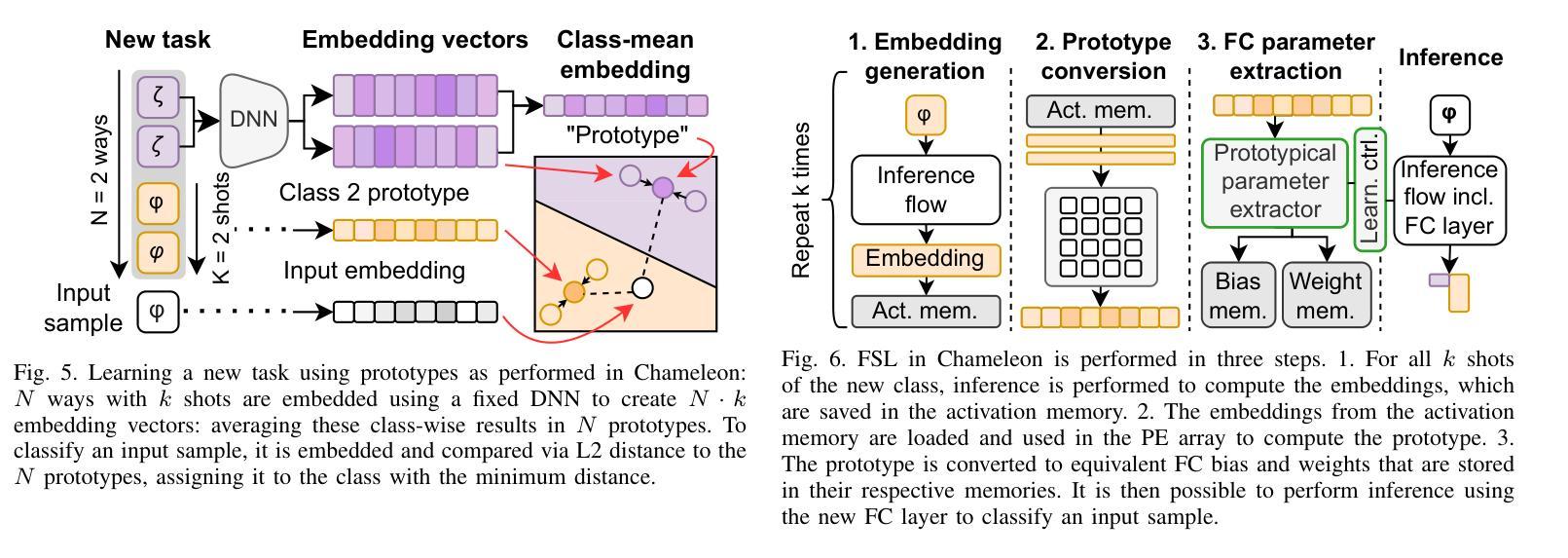
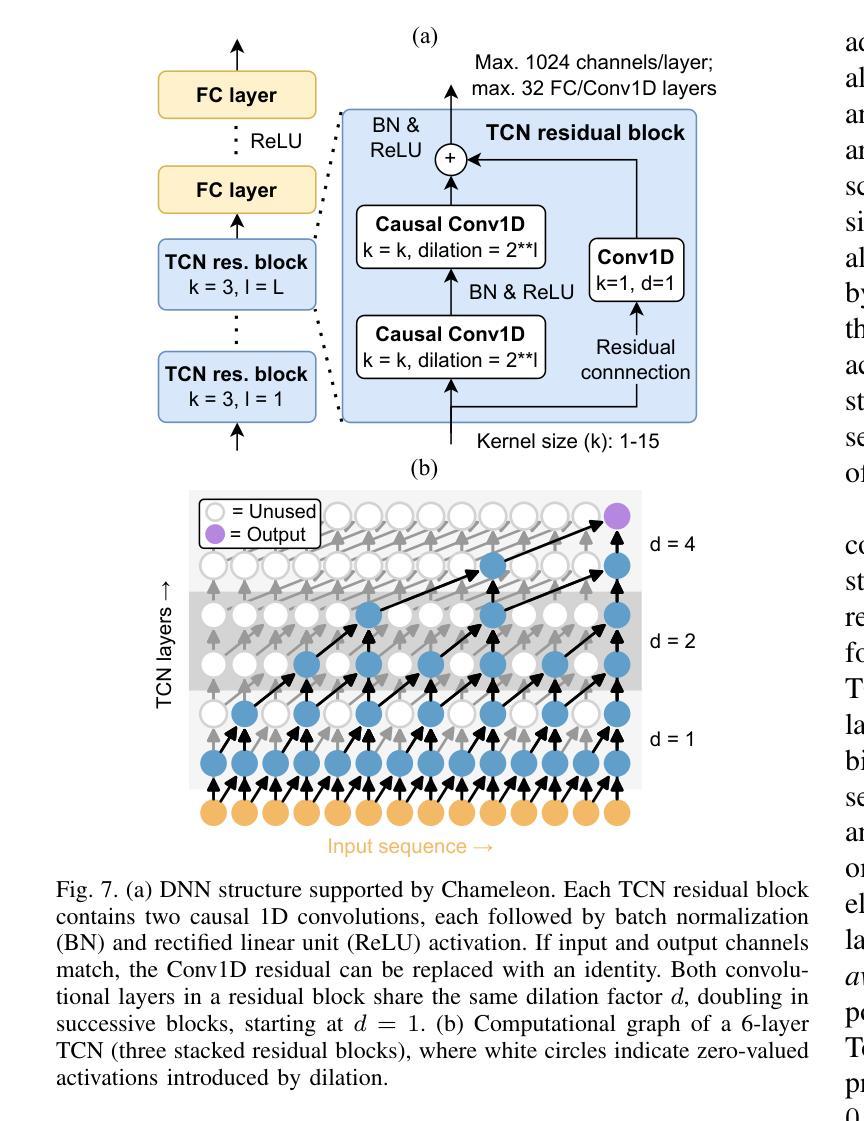
Chameleon: A MatMul-Free Temporal Convolutional Network Accelerator for End-to-End Few-Shot and Continual Learning from Sequential Data
Authors:Douwe den Blanken, Charlotte Frenkel
On-device learning at the edge enables low-latency, private personalization with improved long-term robustness and reduced maintenance costs. Yet, achieving scalable, low-power end-to-end on-chip learning, especially from real-world sequential data with a limited number of examples, is an open challenge. Indeed, accelerators supporting error backpropagation optimize for learning performance at the expense of inference efficiency, while simplified learning algorithms often fail to reach acceptable accuracy targets. In this work, we present Chameleon, leveraging three key contributions to solve these challenges. (i) A unified learning and inference architecture supports few-shot learning (FSL), continual learning (CL) and inference at only 0.5% area overhead to the inference logic. (ii) Long temporal dependencies are efficiently captured with temporal convolutional networks (TCNs), enabling the first demonstration of end-to-end on-chip FSL and CL on sequential data and inference on 16-kHz raw audio. (iii) A dual-mode, matrix-multiplication-free compute array allows either matching the power consumption of state-of-the-art inference-only keyword spotting (KWS) accelerators or enabling $4.3\times$ higher peak GOPS. Fabricated in 40-nm CMOS, Chameleon sets new accuracy records on Omniglot for end-to-end on-chip FSL (96.8%, 5-way 1-shot, 98.8%, 5-way 5-shot) and CL (82.2% final accuracy for learning 250 classes with 10 shots), while maintaining an inference accuracy of 93.3% on the 12-class Google Speech Commands dataset at an extreme-edge power budget of 3.1 $\mu$W.
在设备边缘进行在线学习可以实现低延迟、隐私个性化的体验,同时提高长期稳健性并降低维护成本。然而,实现可扩展的、低功耗的端到端片上学习,特别是从有限样本的真实序列数据中学习,仍然是一个开放性的挑战。实际上,支持反向传播的加速器以推理效率为代价优化了学习性能,而简化的学习算法往往无法达到可接受的准确度目标。在这项工作中,我们推出了Chameleon,通过三个关键贡献来解决这些挑战。(1)统一的学习和推理架构支持少样本学习(FSL)、持续学习(CL)和推理,其面积仅比推理逻辑增加了0.5%。(2)利用时序卷积网络(TCNs)有效地捕捉长期时间依赖关系,实现了对序列数据的端到端片上FSL和CL的首次演示以及对16kHz原始音频的推理。(3)双模式、无矩阵乘法计算阵列允许与最先进的仅用于推理的关键词识别(KWS)加速器的功耗相匹配,或者实现4.3倍更高的峰值GOPs。采用40纳米CMOS工艺制造的Chameleon在Omniglot数据集上创下了端到端片上FSL的新准确率纪录(5分类,每分类只用一个样本的情况下准确率为96.8%,每分类用五个样本的情况下准确率为98.8%),在持续学习方面(学习250个类别,每个类别用十个样本时的最终准确率为82.2%),同时在Google语音命令数据集上的推理准确率达到了93.3%,在极端边缘的功率预算为3.1微瓦的情况下实现了上述成果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 7 figures
摘要
本论文提出Chameleon方案来解决实际应用中面临的难题。它实现在设备上快速响应少量样本信息进行自适应学习和优化预测效果的同时控制能量消耗以及减小后续维护费用。特别是处理动态复杂连续场景(例如流媒体语音控制或实时监控图像任务等),过去系统试图依赖增设加速器和算法复杂性提高来提高性能,却难以在实时连续数据流情况下准确和快速地调整其状态以及大幅降低计算成本,故存在一定的挑战。本方案的主要优势包括采用一体化的推理与深度学习框架兼容时序数据流的变化机制并支持关键数据流的最直观抽象单元融合的策略优化方式(例如图形处理单元),通过引入卷积神经网络技术实现时序数据的长期依赖关系的高效捕捉,以及采用双模式矩阵乘法无依赖的计算阵列允许峰值运算速度的大幅提升或节能操作以适应低功耗应用的需求。实验结果展示其在多个场景中超越当前领先方案的性能表现。例如在Omniglot数据集上支持少量的学习样本就可以实现96.8%的准确率,同时Google Speech Commands数据集上的预测准确率也保持在相当高的水平。同时,Chameleon方案实现了低功耗下的高性能表现,在极端低功耗预算下仍能保持出色的性能表现。
关键见解
- 提出Chameleon方案,解决了在有限样本下实现快速响应学习的挑战,支持个性化定制且降低维护成本。
- 采用统一的学习与推理架构,实现快速学习适应并支持推理操作。引入TCN网络技术实现长期依赖的高效捕捉。在实时数据流上进行端对端学习和推理演示,实现了首个基于时序数据的少样本学习演示和推理案例应用等关键点的无缝处理操作能力显著优于之前已有模型的策略实现,以此克服既有难点并保持高速的运行表现水准。同时展示了在音频数据上的推理能力。
- 双模式计算阵列设计允许灵活调整计算性能与功耗之间的平衡,根据应用场景选择性能提升或低功耗模式,适用于不同的计算需求。具有降低能耗的同时,显著提高了计算能力的高效利用,展现了明显的能效优势并适应广泛的硬件平台环境特性优化,可以极大程度上推动算法运行速度与效能的优化发展态势与综合价值能力应用等突破提升优化提升。
点此查看论文截图

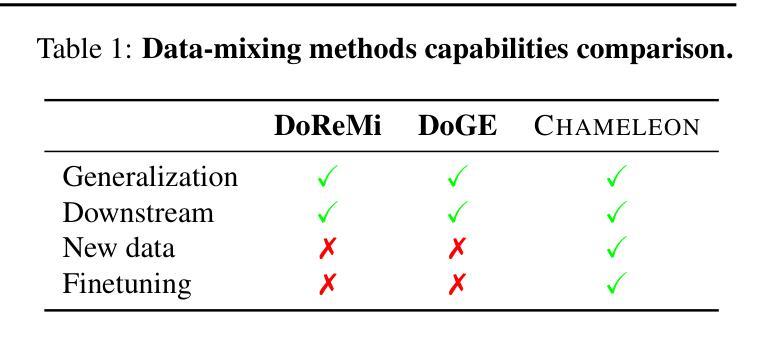
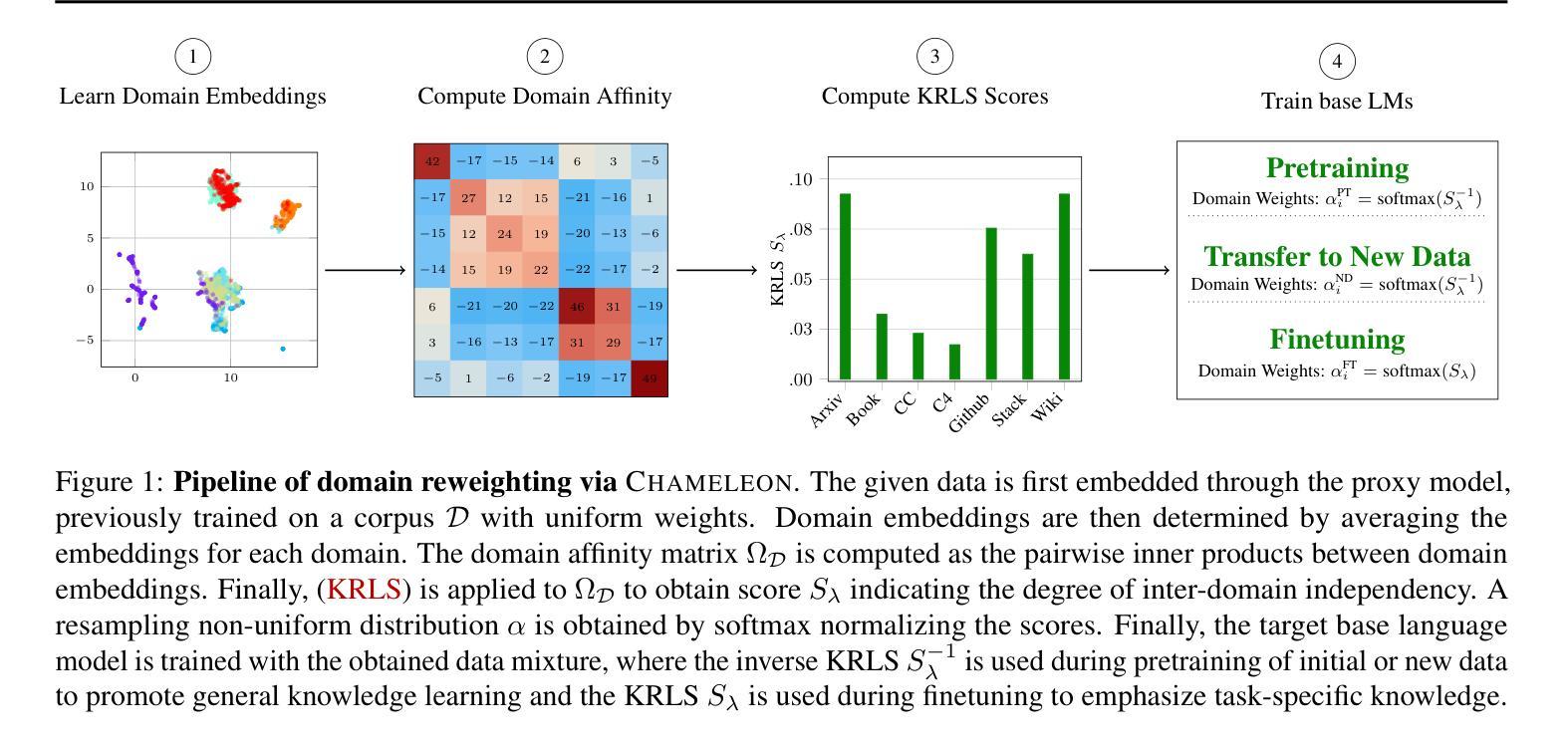
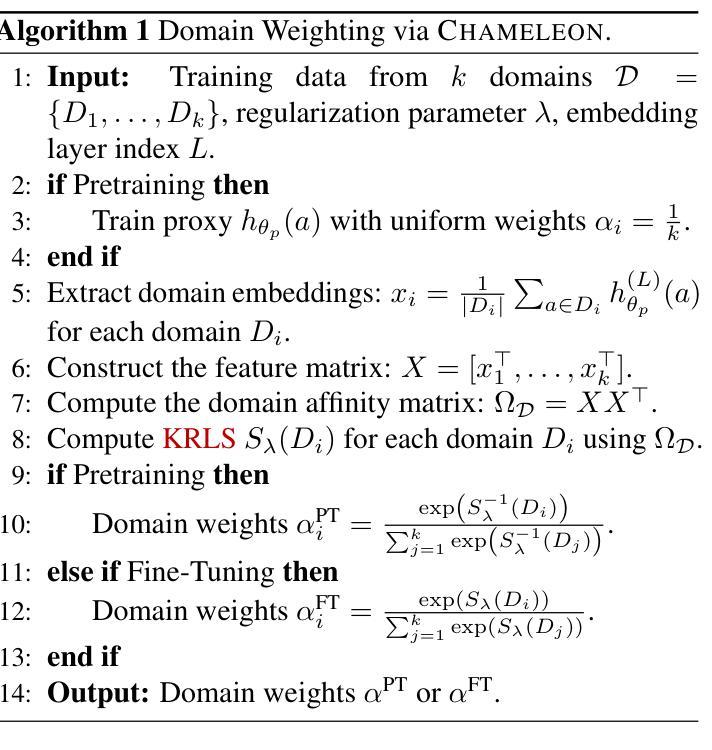
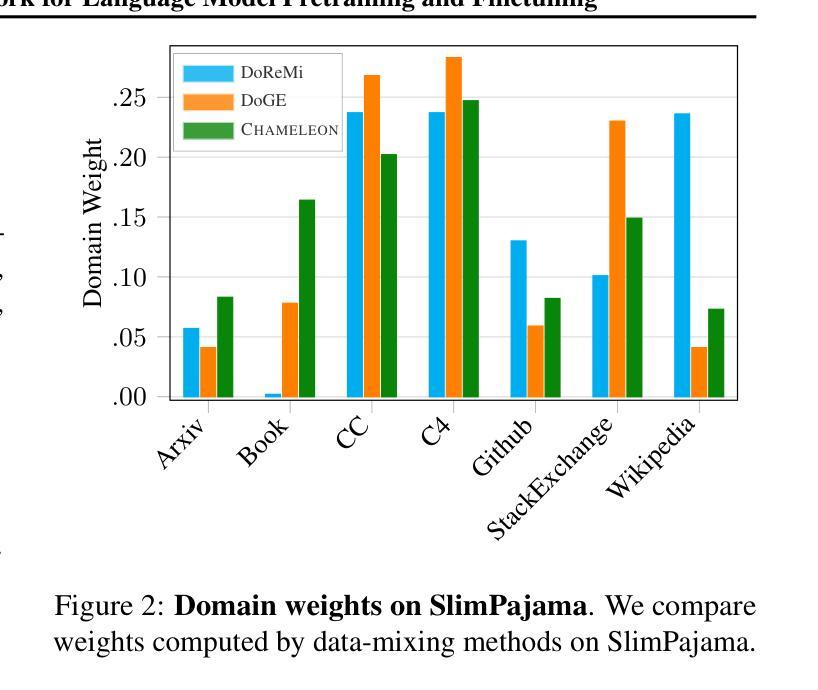
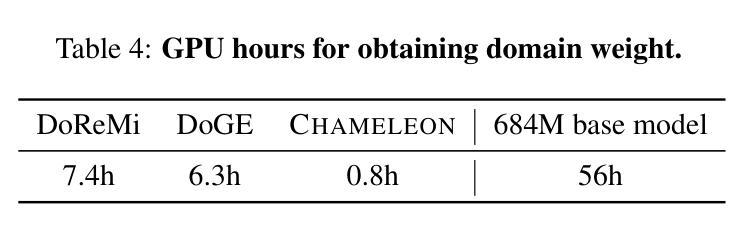
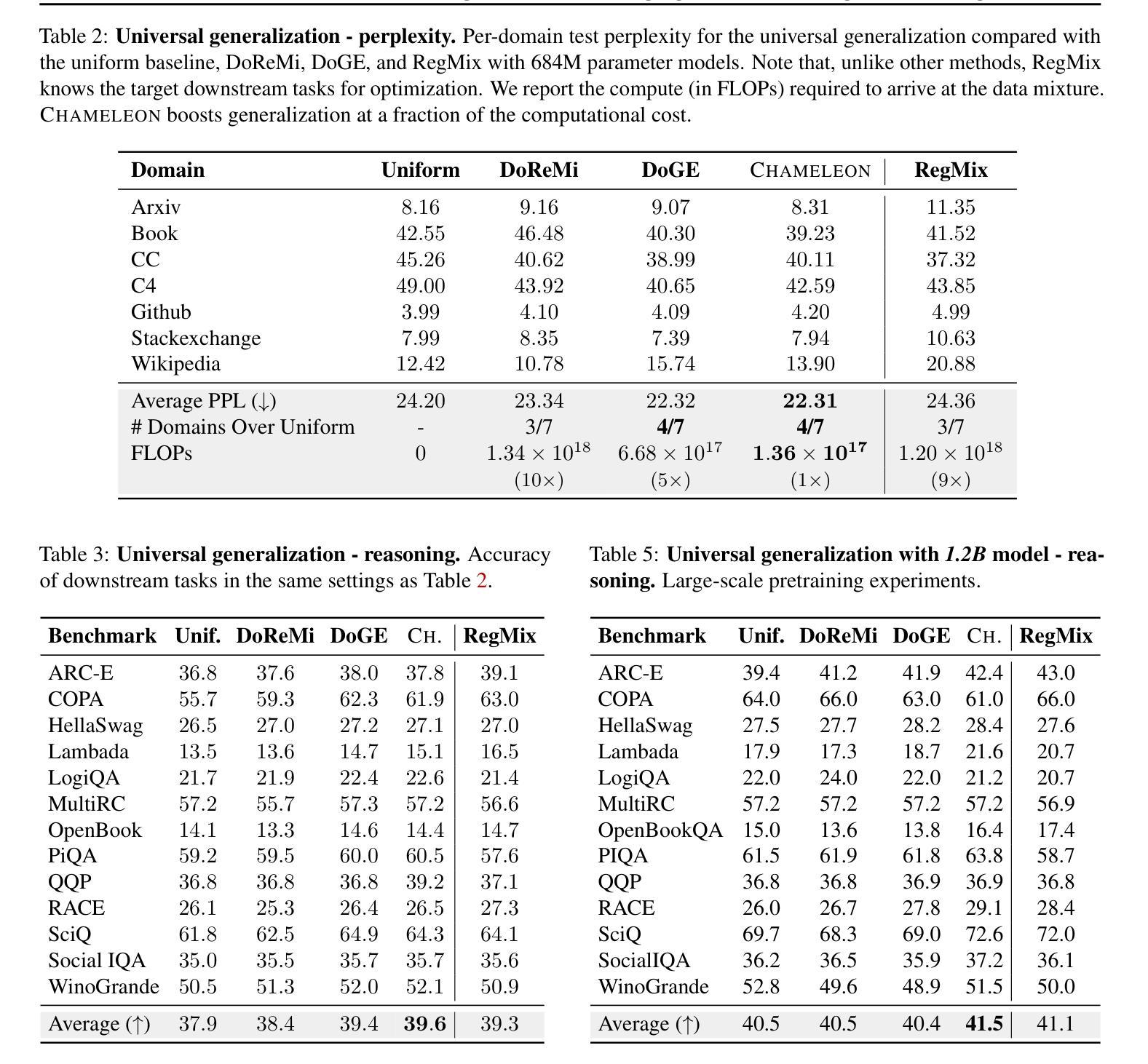
Chameleon: A Flexible Data-mixing Framework for Language Model Pretraining and Finetuning
Authors:Wanyun Xie, Francesco Tonin, Volkan Cevher
Training data mixtures greatly impact the generalization performance of large language models. Existing domain reweighting methods often rely on costly weight computations and require retraining when new data is introduced. To this end, we introduce a flexible and efficient data mixing framework, Chameleon, that employs leverage scores to quantify domain importance within a learned embedding space. We first construct a domain affinity matrix over domain embeddings. The induced leverage scores determine a mixture that upweights domains sharing common representations in embedding space. This formulation allows direct transfer to new data by computing the new domain embeddings. In experiments, we demonstrate improvements over three key scenarios: (i) our computed weights improve performance on pretraining domains with a fraction of the compute of existing methods; (ii) Chameleon can adapt to data changes without proxy retraining, boosting few-shot reasoning accuracies when transferred to new data; (iii) our method enables efficient domain reweighting in finetuning, consistently improving test perplexity on all finetuning domains over uniform mixture. Our code is available at https://github.com/LIONS-EPFL/Chameleon.
训练数据混合物对大型语言模型的泛化性能有很大影响。现有的领域重权方法通常依赖于昂贵的权重计算,并在引入新数据时需要重新训练。为此,我们引入了一个灵活高效的数据混合框架Chameleon,它利用杠杆分数来量化学习嵌入空间中的领域重要性。我们首先在域嵌入上构建域亲和矩阵。所得到的杠杆分数确定了一种混合物,该混合物会提高在嵌入空间中共享共同表示的领域的权重。这种表述允许通过计算新域嵌入直接转移到新数据上。在实验中,我们在三种关键场景中证明了改进:(i)我们计算的权重在预训练域上的性能优于现有方法,同时只使用了现有方法的一部分计算量;(ii)Chameleon能够适应数据变化而无需通过重新训练提升表现,转移到新数据时提高了少量数据的推理准确度;(iii)我们的方法在微调时的领域重权效率很高,在所有微调领域上的一致改进测试困惑度优于均匀混合物。我们的代码可在https://github.com/LIONS-EPFL/Chameleon找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
本文介绍了Chameleon数据混合框架,它通过利用杠杆得分来量化在所学嵌入空间中的领域重要性,从而提高大型语言模型的泛化性能。该框架通过构建领域亲和矩阵和计算杠杆得分来确定数据混合的比例,强调在嵌入空间中共享共同表示的领域的权重。实验表明,Chameleon在预训练、适应新数据和微调领域等三种场景下都表现出优越性。
Key Takeaways
- Chameleon框架通过数据混合提高语言模型的泛化性能。
- 利用杠杆得分量化领域在嵌入空间中的重要性。
- 构建领域亲和矩阵来确定数据混合比例。
- 框架能自适应新数据,通过计算新领域嵌入进行直接迁移。
- 在预训练领域计算权重时,Chameleon使用较少的计算资源即能提升性能。
- Chameleon在适应新数据和微调领域时均表现出优越性,提高了少样本推理的准确度并降低了测试困惑度。
点此查看论文截图

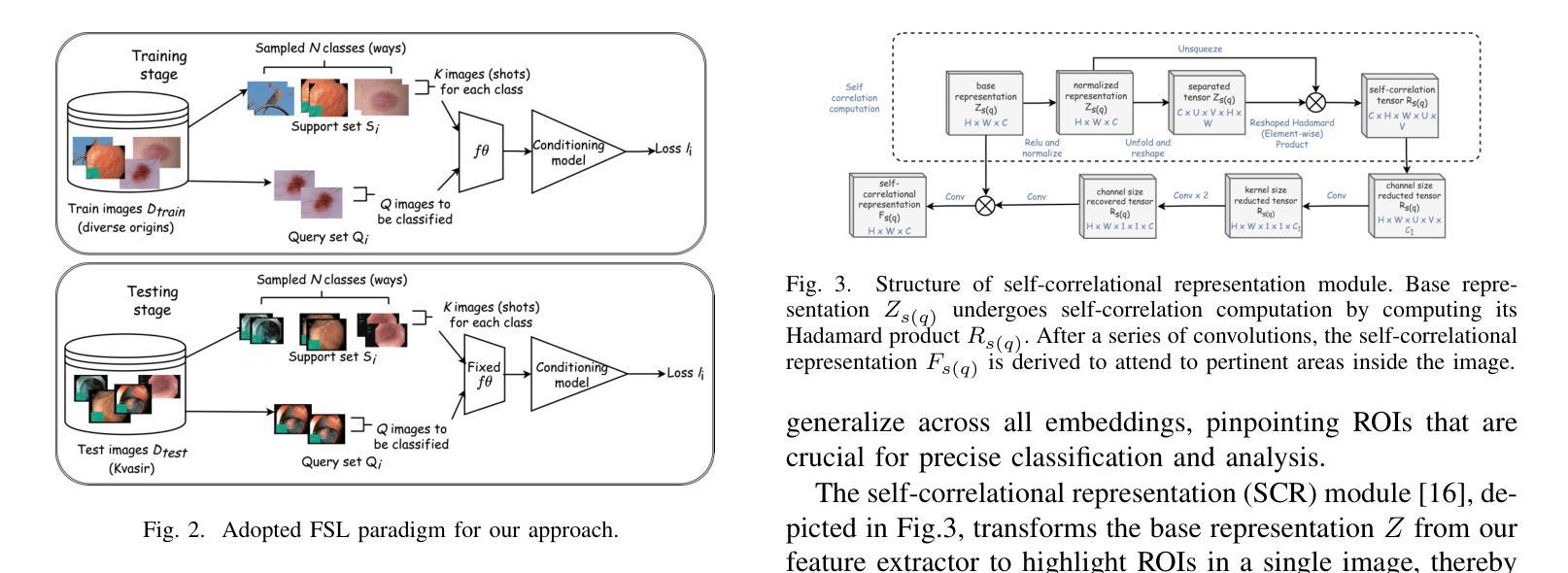
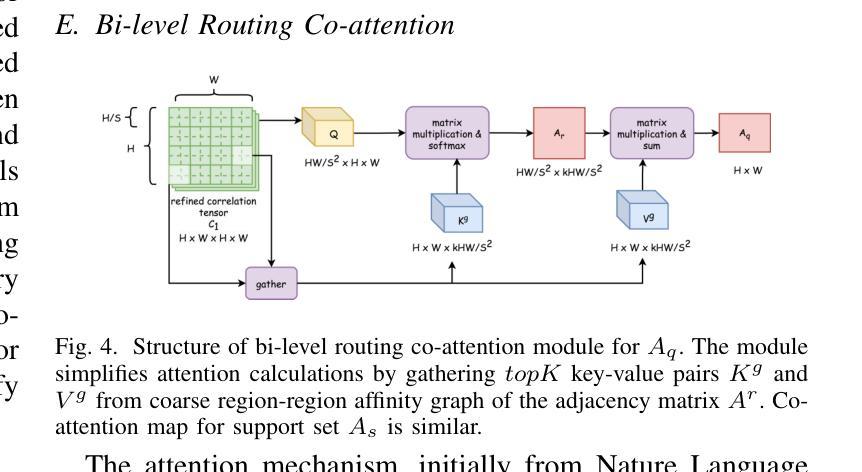
Lightweight Relational Embedding in Task-Interpolated Few-Shot Networks for Enhanced Gastrointestinal Disease Classification
Authors:Xinliu Zhong, Leo Hwa Liang, Angela S. Koh, Yeo Si Yong
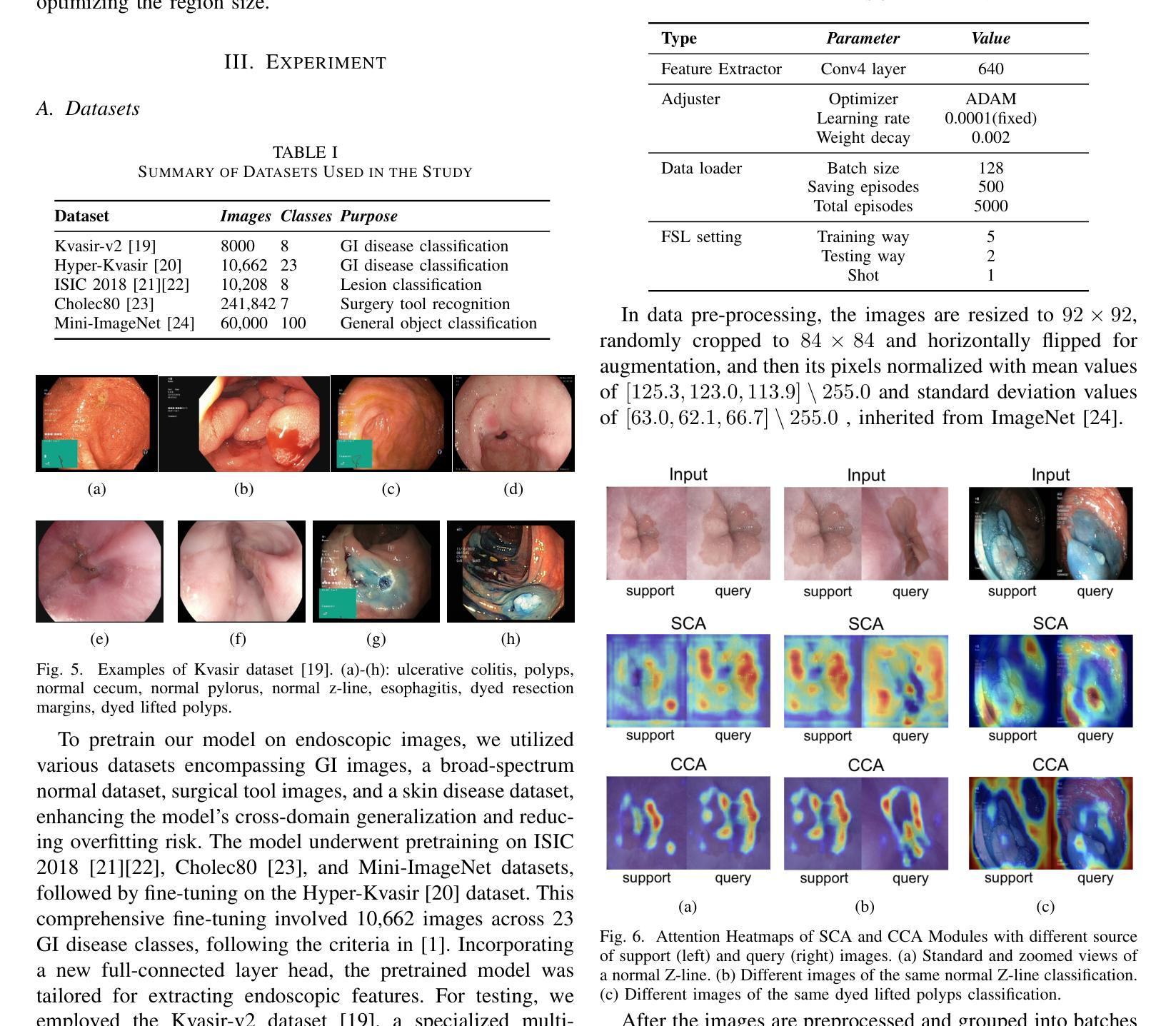
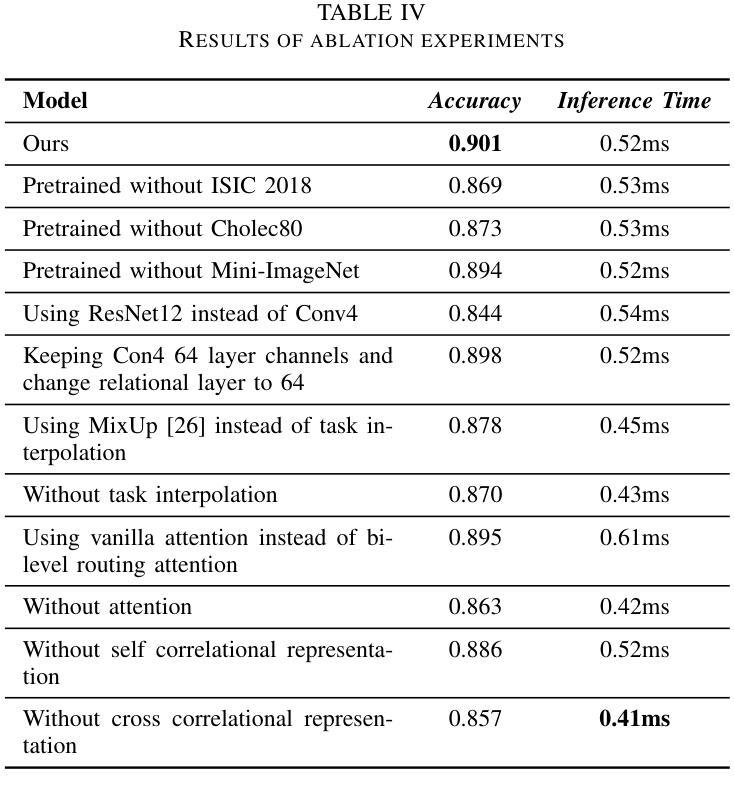
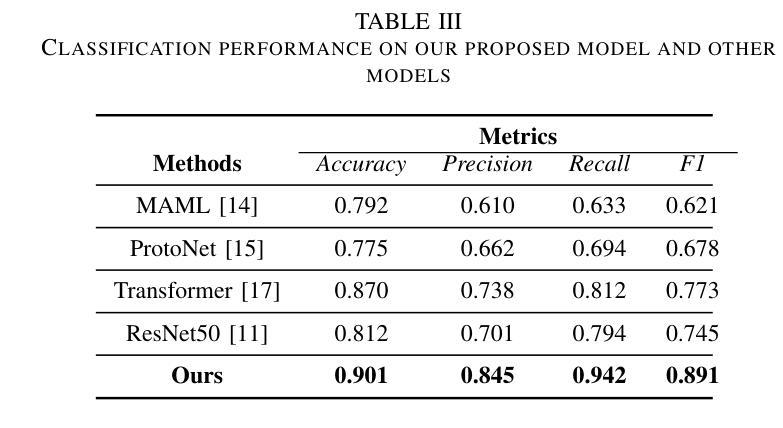
Traditional diagnostic methods like colonoscopy are invasive yet critical tools necessary for accurately diagnosing colorectal cancer (CRC). Detection of CRC at early stages is crucial for increasing patient survival rates. However, colonoscopy is dependent on obtaining adequate and high-quality endoscopic images. Prolonged invasive procedures are inherently risky for patients, while suboptimal or insufficient images hamper diagnostic accuracy. These images, typically derived from video frames, often exhibit similar patterns, posing challenges in discrimination. To overcome these challenges, we propose a novel Deep Learning network built on a Few-Shot Learning architecture, which includes a tailored feature extractor, task interpolation, relational embedding, and a bi-level routing attention mechanism. The Few-Shot Learning paradigm enables our model to rapidly adapt to unseen fine-grained endoscopic image patterns, and the task interpolation augments the insufficient images artificially from varied instrument viewpoints. Our relational embedding approach discerns critical intra-image features and captures inter-image transitions between consecutive endoscopic frames, overcoming the limitations of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). The integration of a light-weight attention mechanism ensures a concentrated analysis of pertinent image regions. By training on diverse datasets, the model’s generalizability and robustness are notably improved for handling endoscopic images. Evaluated on Kvasir dataset, our model demonstrated superior performance, achieving an accuracy of 90.1%, precision of 0.845, recall of 0.942, and an F1 score of 0.891. This surpasses current state-of-the-art methods, presenting a promising solution to the challenges of invasive colonoscopy by optimizing CRC detection through advanced image analysis.
传统诊断方法如结肠镜检查是侵入性的,但对于准确诊断结肠癌(CRC)仍是必要的关键工具。早期发现结肠癌对于提高患者存活率至关重要。然而,结肠镜检查依赖于获得充足且高质量的内窥镜图像。长时间的侵入性手术对患者来说存在固有风险,而次优或不充足的图像则会影响诊断的准确性。这些图像通常来源于视频帧,呈现出相似的模式,给鉴别带来挑战。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型的深度学习网络,该网络建立在小样学习架构之上,包括定制的特征提取器、任务插值、关系嵌入和双级路由注意力机制。小样学习范式使我们的模型能够迅速适应未见过的精细内窥镜图像模式,任务插值则从各种仪器视角人工增强不足图像。我们的关系嵌入方法能够辨别图像内的关键特征,并捕捉连续内窥镜帧之间的图像间过渡,从而克服卷积神经网络(CNN)的局限性。轻量级注意力机制的集成确保了相关图像区域的集中分析。通过多样数据集进行训练,该模型的通用性和稳健性得到了显著改善,以处理内窥镜图像。在Kvasir数据集上进行的评估显示,我们的模型表现出卓越的性能,达到了90.1%的准确率、0.845的精确度、0.942的召回率和0.891的F1分数。这超越了当前最先进的方法,通过优化CRC检测的高级图像分析,为解决侵入性结肠镜检查的挑战提供了有希望的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 15 figures
Summary
提出一种基于深度学习和少样本学习架构的模型,用于结直肠癌的早期诊断。模型包括特征提取器、任务插值、关系嵌入和双级路由注意力机制,能够迅速适应内窥镜图像模式,解决图像质量不足和模式识别困难的问题。在Kvasir数据集上的表现优于当前最先进的方法,为结直肠癌检测提供了一种有前景的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 模型基于深度学习和少样本学习架构构建,用于解决结直肠癌早期诊断中内窥镜图像的问题。
- 模型通过特征提取器、任务插值、关系嵌入和双级路由注意力机制等技术,提高诊断准确性和效率。
- 模型能够迅速适应内窥镜图像模式,解决图像质量不足和模式识别困难的问题。
- 通过在Kvasir数据集上的实验验证,模型的准确性、精确度、召回率和F1分数均表现优异。
- 模型展现出优于当前最先进方法的性能,为结直肠癌检测提供了有效解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

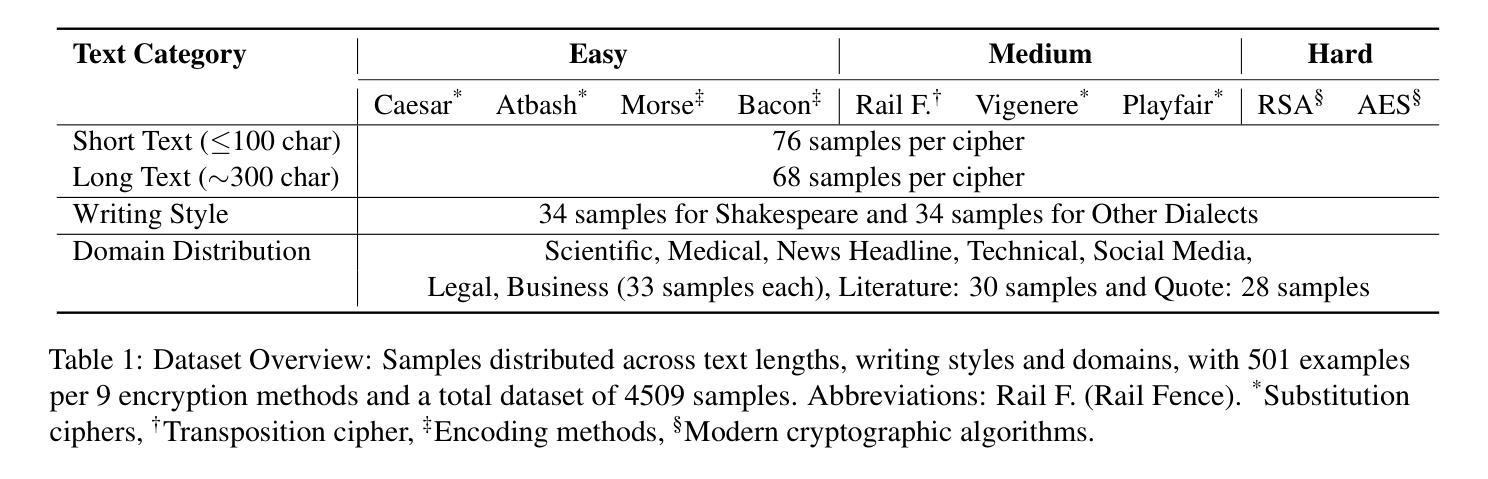
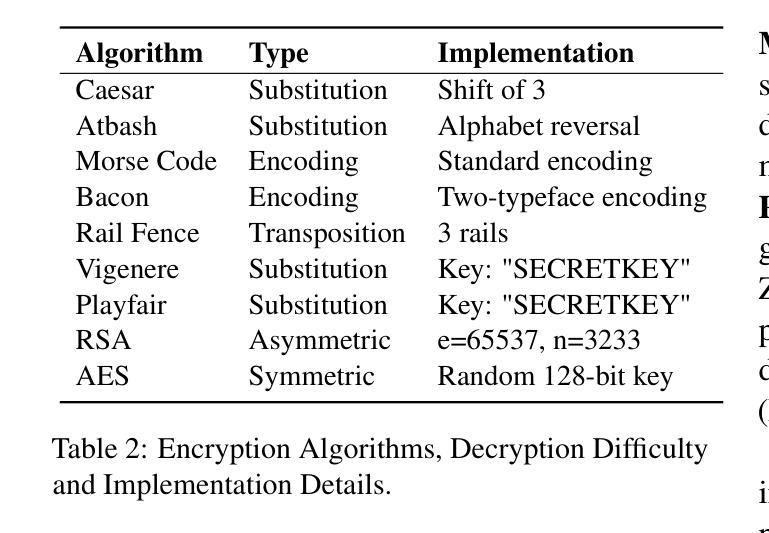
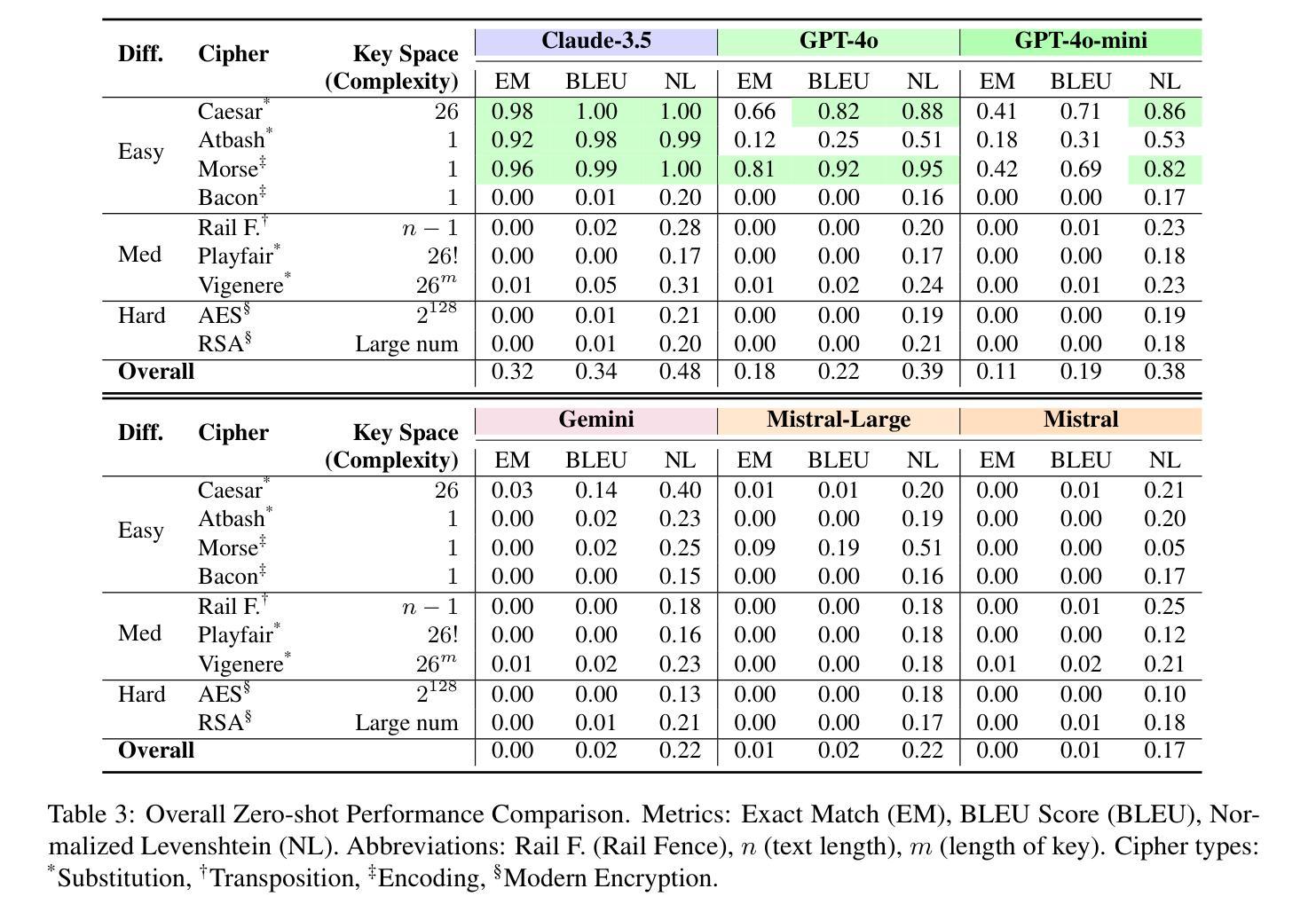
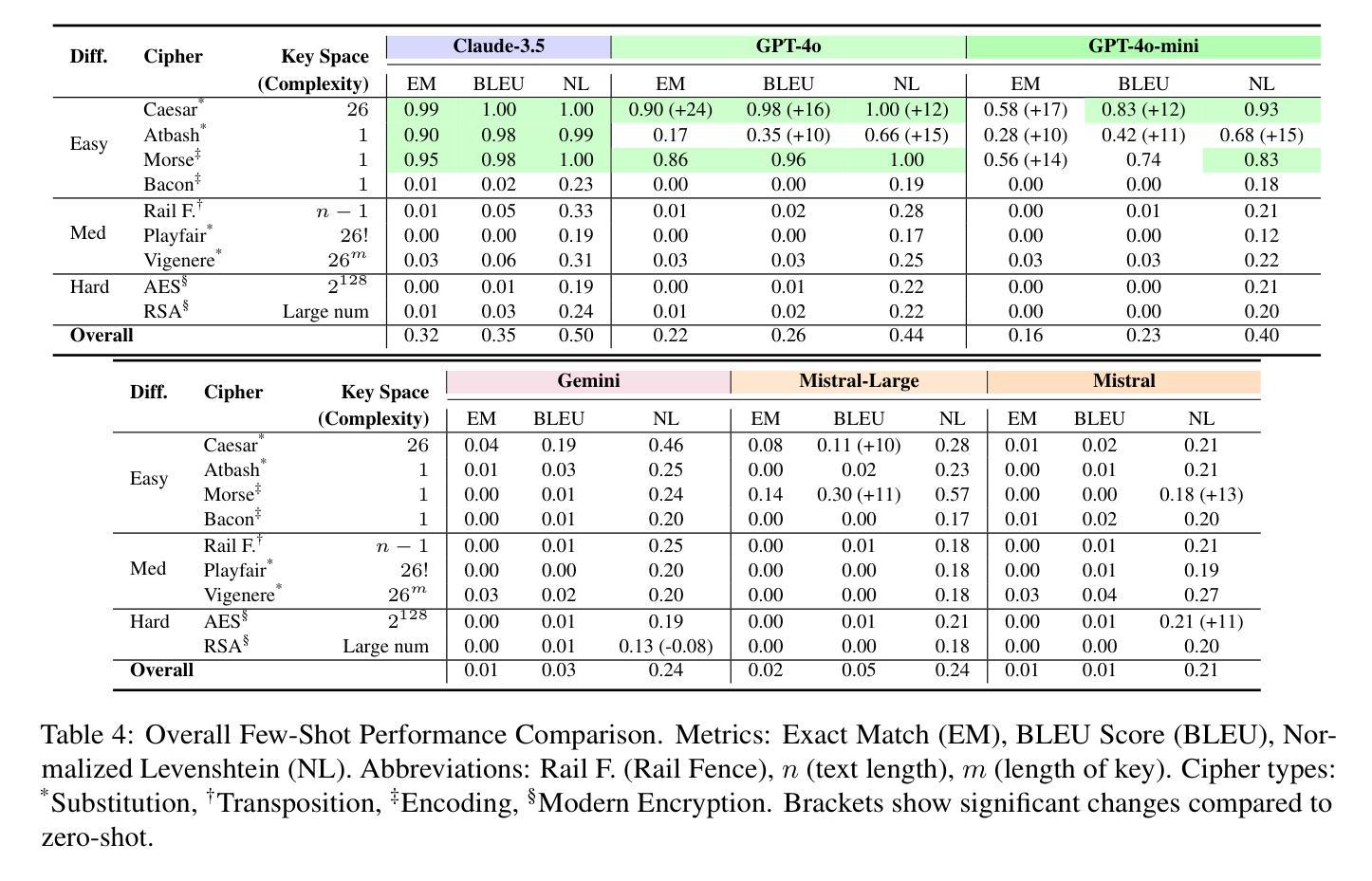
Benchmarking Large Language Models for Cryptanalysis and Mismatched-Generalization
Authors:Utsav Maskey, Chencheng Zhu, Usman Naseem
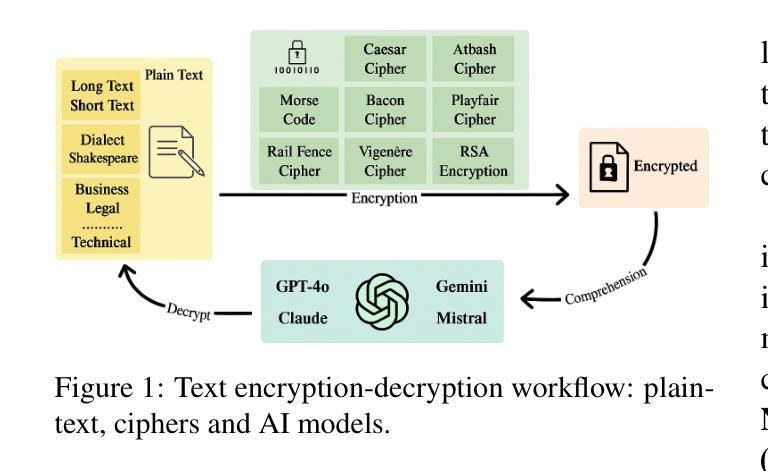
Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have transformed natural language understanding and generation, leading to extensive benchmarking across diverse tasks. However, cryptanalysis a critical area for data security and encryption has not yet been thoroughly explored in LLM evaluations. To address this gap, we evaluate cryptanalytic potential of state of the art LLMs on encrypted texts generated using a range of cryptographic algorithms. We introduce a novel benchmark dataset comprising diverse plain texts spanning various domains, lengths, writing styles, and topics paired with their encrypted versions. Using zero-shot and few shot settings, we assess multiple LLMs for decryption accuracy and semantic comprehension across different encryption schemes. Our findings reveal key insights into the strengths and limitations of LLMs in side-channel communication while raising concerns about their susceptibility to jailbreaking attacks. This research highlights the dual-use nature of LLMs in security contexts and contributes to the ongoing discussion on AI safety and security.
最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进步已经改变了自然语言的理解和生成方式,并在各种任务上进行了广泛的基准测试。然而,对于数据安全和加密至关重要的密码分析领域在LLM评估中尚未得到充分探索。为了弥补这一空白,我们评估了最先端的大型语言模型对使用多种加密算法生成的加密文本的密码分析潜力。我们引入了一个包含多种领域的普通文本及其加密版本配对的新型基准数据集。通过零样本和少样本设置,我们评估了不同加密方案下多个大型语言模型的解密准确性和语义理解能力。我们的研究揭示了大型语言模型在侧信道通信中的优势和局限性,并引发了对其容易受到越狱攻击的担忧。这项研究强调了大型语言模型在安全上下文中的双重用途性质,并为人工智能安全和保护的持续讨论做出了贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展已经改变了自然语言的理解和生成方式,并在各种任务上进行了广泛的基准测试。然而,对于数据安全和加密至关重要的密码分析领域在LLM评估中尚未得到充分探索。为了弥补这一空白,我们评估了最先进的大型语言模型对使用多种加密算法生成的加密文本的密码分析潜力。我们引入了一个包含多种领域的普通文本及其加密版本的新型基准数据集。通过零样本和少样本设置,我们评估了多个大型语言模型在不同加密方案下的解密准确性和语义理解能力。我们的研究揭示了大型语言模型在侧信道通信中的优缺点,并对其容易受到越狱攻击提出了担忧。该研究突显了大型语言模型在安全上下文中的双重用途性质,并为人工智能安全和安全性讨论做出了贡献。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在自然语言理解和生成方面的进展已在多个任务上进行基准测试。
- 密码分析在LLM评估中尚未得到充分探索。
- 引入了一个新型基准数据集,包含普通文本及其使用多种加密算法生成的加密版本。
- 通过零样本和少样本设置评估了LLMs在多种加密方案下的解密能力和语义理解。
- LLMs在侧信道通信中具有潜力和局限性。
- LLMs容易受到越狱攻击,这引发了关于其安全性的担忧。
点此查看论文截图

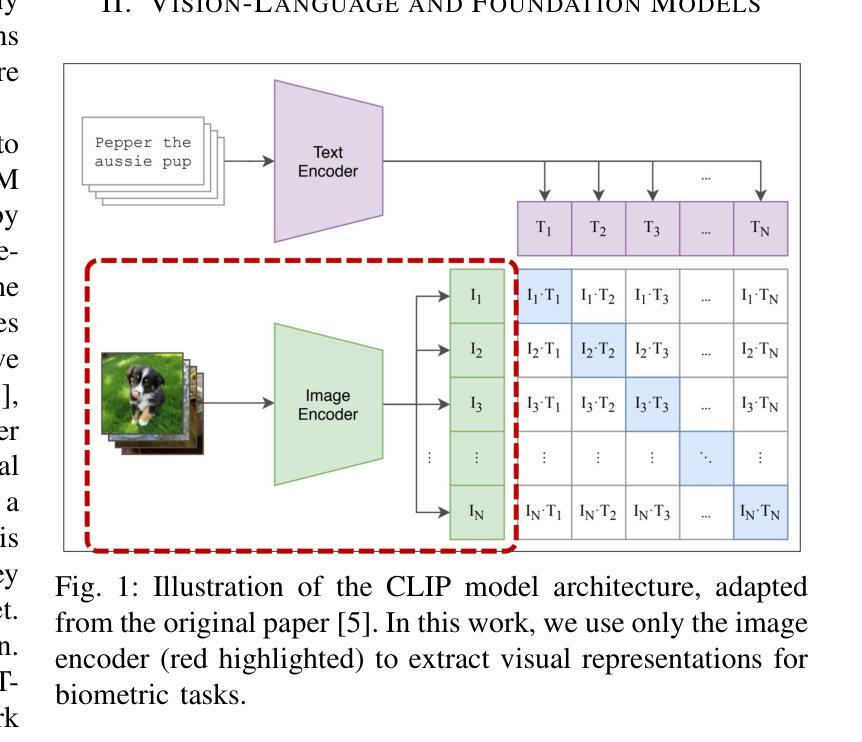
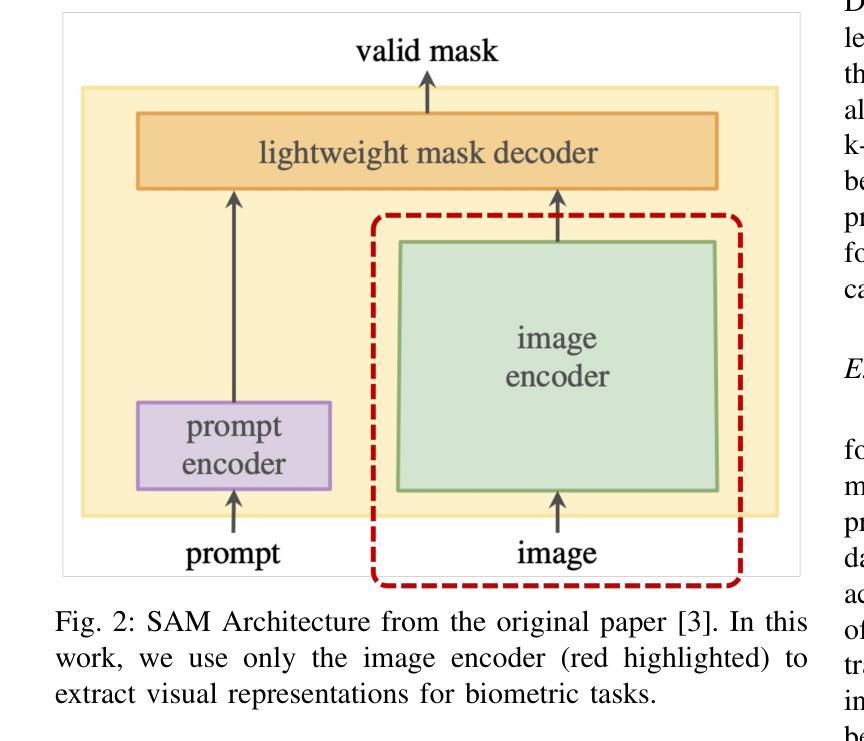
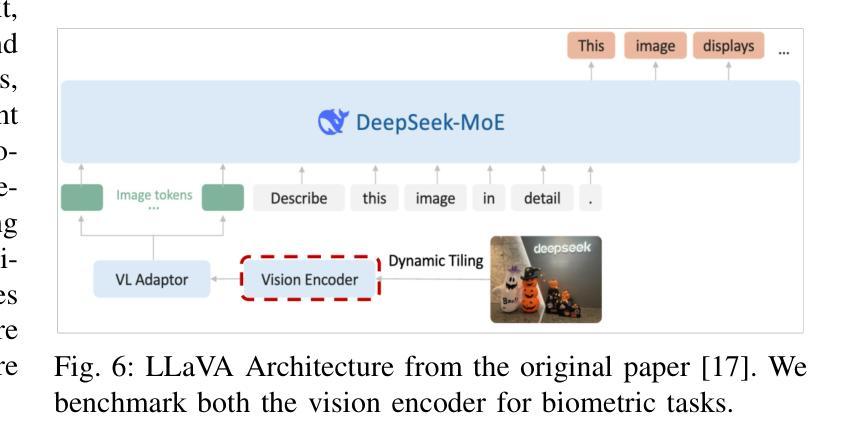
Benchmarking Foundation Models for Zero-Shot Biometric Tasks
Authors:Redwan Sony, Parisa Farmanifard, Hamzeh Alzwairy, Nitish Shukla, Arun Ross
The advent of foundation models, particularly Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs), has redefined the frontiers of artificial intelligence, enabling remarkable generalization across diverse tasks with minimal or no supervision. Yet, their potential in biometric recognition and analysis remains relatively underexplored. In this work, we introduce a comprehensive benchmark that evaluates the zero-shot and few-shot performance of state-of-the-art publicly available VLMs and MLLMs across six biometric tasks spanning the face and iris modalities: face verification, soft biometric attribute prediction (gender and race), iris recognition, presentation attack detection (PAD), and face manipulation detection (morphs and deepfakes). A total of 41 VLMs were used in this evaluation. Experiments show that embeddings from these foundation models can be used for diverse biometric tasks with varying degrees of success. For example, in the case of face verification, a True Match Rate (TMR) of 96.77 percent was obtained at a False Match Rate (FMR) of 1 percent on the Labeled Face in the Wild (LFW) dataset, without any fine-tuning. In the case of iris recognition, the TMR at 1 percent FMR on the IITD-R-Full dataset was 97.55 percent without any fine-tuning. Further, we show that applying a simple classifier head to these embeddings can help perform DeepFake detection for faces, Presentation Attack Detection (PAD) for irides, and extract soft biometric attributes like gender and ethnicity from faces with reasonably high accuracy. This work reiterates the potential of pretrained models in achieving the long-term vision of Artificial General Intelligence.
随着基础模型的兴起,特别是视觉语言模型(VLMs)和多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的出现,人工智能的边界得到了重新定义,这些模型能够在各种任务中实现显著泛化,而无需或只需很少的监督。然而,它们在生物识别分析和应用中的潜力尚未得到充分探索。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个全面的基准测试,评估了最前沿的公开可用的VLMs和MLLMs在六个跨越面部和虹膜模态的生物识别任务的零样本学习和少样本学习能力:面部验证、软生物识别属性预测(性别和种族)、虹膜识别、呈现攻击检测(PAD)和面部操作检测(形态和深度伪造)。本次评估共使用了40个VLMs。实验表明,这些基础模型的嵌入可用于各种生物识别任务,并取得不同程度的成功。例如,在面部验证方面,在野外真实场景下的面部数据集(Labeled Face in the Wild (LFW))上,以1%的误识率(False Match Rate, FMR)获得了高达96.77%的真匹配率(True Match Rate, TMR),且无需微调。在虹膜识别方面,在IITD-R-Full数据集上,以1%的误识率获得了高达97.55%的真匹配率,同样无需微调。此外,我们展示了在这些嵌入之上应用简单的分类器头部有助于检测人脸深度伪造、检测虹膜的呈现攻击,并从人脸中提取性别和种族等软生物识别属性,具有较高的准确性。这项工作再次强调了预训练模型在实现人工智能通用化长期愿景方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于预训练模型如Vision-Language Models (VLMs)和多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的进展,人工智能的边界得到了重新定义。这些模型能够在不同任务中展现出出色的泛化能力,特别是在生物识别和分析领域。本研究通过一项全面的基准测试评估了这些模型在六个生物识别任务中的零样本和少样本性能,包括面部和虹膜识别等。实验表明,这些模型的嵌入可用于多种生物识别任务,并取得了不同程度的成功。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练模型如VLMs和MLLMs推动了人工智能的发展,展现出强大的跨任务泛化能力。
- 在生物识别领域的应用潜力尚未完全挖掘。
- 本研究提供了一个全面的基准测试来评估预训练模型在六个生物识别任务中的性能。
- 实验结果表明,这些模型的嵌入可用于多种任务,并取得显著成果。
- 在面部验证任务中,LFW数据集上的True Match Rate达到了96.77%,在无需微调的情况下。
- 在虹膜识别任务中,IITD-R-Full数据集上的表现同样出色,验证了预训练模型在生物识别领域的潜力。
点此查看论文截图


Provably Improving Generalization of Few-Shot Models with Synthetic Data
Authors:Lan-Cuong Nguyen, Quan Nguyen-Tri, Bang Tran Khanh, Dung D. Le, Long Tran-Thanh, Khoat Than
Few-shot image classification remains challenging due to the scarcity of labeled training examples. Augmenting them with synthetic data has emerged as a promising way to alleviate this issue, but models trained on synthetic samples often face performance degradation due to the inherent gap between real and synthetic distributions. To address this limitation, we develop a theoretical framework that quantifies the impact of such distribution discrepancies on supervised learning, specifically in the context of image classification. More importantly, our framework suggests practical ways to generate good synthetic samples and to train a predictor with high generalization ability. Building upon this framework, we propose a novel theoretical-based algorithm that integrates prototype learning to optimize both data partitioning and model training, effectively bridging the gap between real few-shot data and synthetic data. Extensive experiments results show that our approach demonstrates superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods, outperforming them across multiple datasets.
由于缺少标记的训练样本,小样本文本分类仍然是一个挑战。通过合成数据增强样本已经成为缓解这个问题的有前途的方法,但在合成样本上训练的模型往往面临性能下降的问题,因为真实和合成分布之间存在固有的差距。为了解决这个问题,我们开发了一个理论框架,该框架对分布差异对监督学习的影响进行了量化,特别是在图像分类的上下文中。更重要的是,我们的框架提出了生成良好合成样本和训练具有出色泛化能力的预测器的实用方法。基于这个框架,我们提出了一种基于理论的新型算法,该算法结合了原型学习来优化数据分区和模型训练,有效地缩小了真实小样本数据和合成数据之间的差距。广泛的实验结果表明,我们的方法相较于最新技术表现出卓越的性能,在多个数据集上超越它们。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025. Our code will be released soon
总结
少量标注训练样本的图像分类仍然是一个挑战。使用合成数据扩增是一种解决此问题的方法,但模型在合成样本上的训练往往会出现性能下降,这是由于真实和合成分布之间存在固有差距。为了解决这一局限性,我们建立了一个理论框架,定量分析了这种分布差异对监督学习的影响,特别是在图像分类的情境中。更重要的是,我们的框架提供了生成良好合成样本和训练具有高通用化能力的预测器的实用方法。基于该框架,我们提出了一种结合原型学习的新算法,优化数据分区和模型训练,有效弥合了真实少量数据和合成数据之间的差距。大量实验结果表明,我们的方法相较于最先进的方法表现出卓越的性能,并在多个数据集上超越它们。
关键见解
- 少量标注训练样本的图像分类是一个挑战。
- 使用合成数据扩增可以缓解这个问题。
- 模型在合成样本上的训练存在性能下降的风险,原因是真实和合成数据分布之间存在差距。
- 我们建立了理论框架来分析这种分布差异对监督学习的影响。
- 该框架提供了生成良好合成样本和训练高通用预测器的方法。
- 基于该框架,我们提出了一种结合原型学习的新算法,优化数据分区和模型训练。
点此查看论文截图

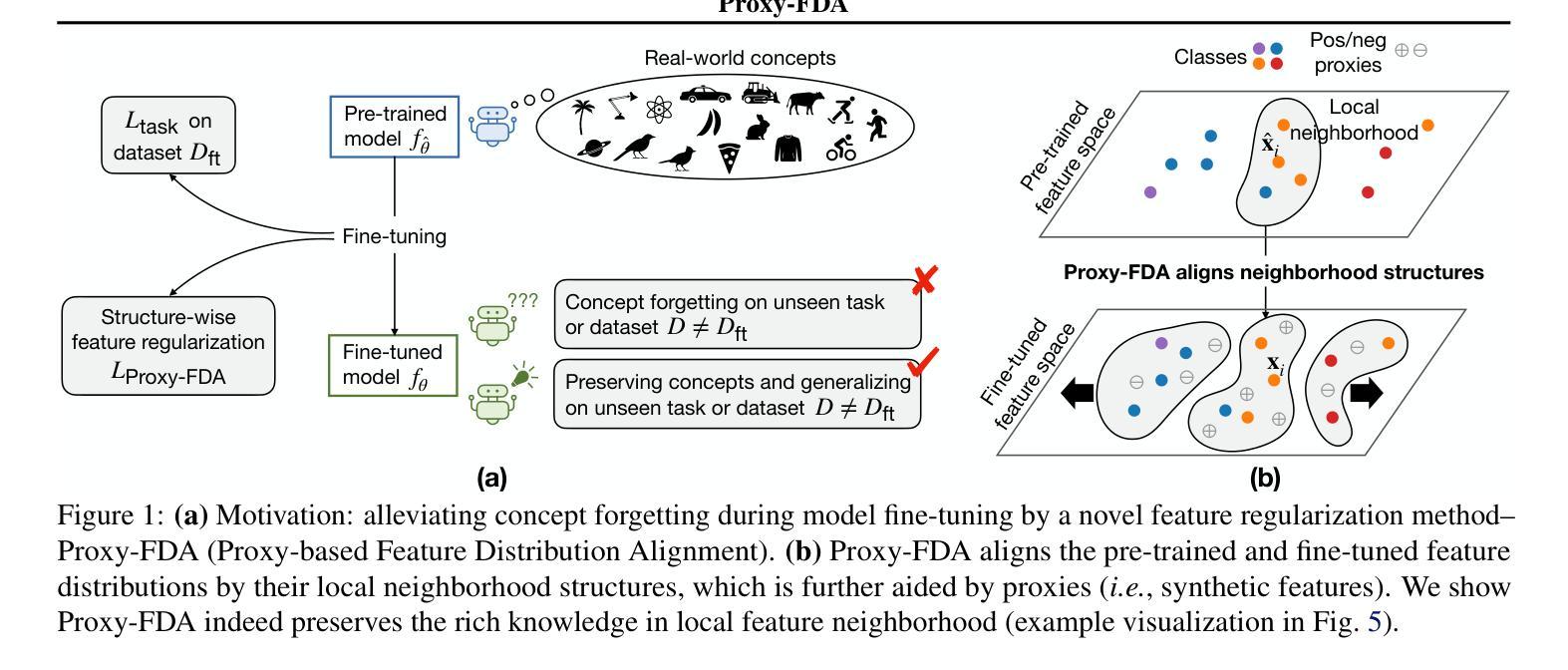
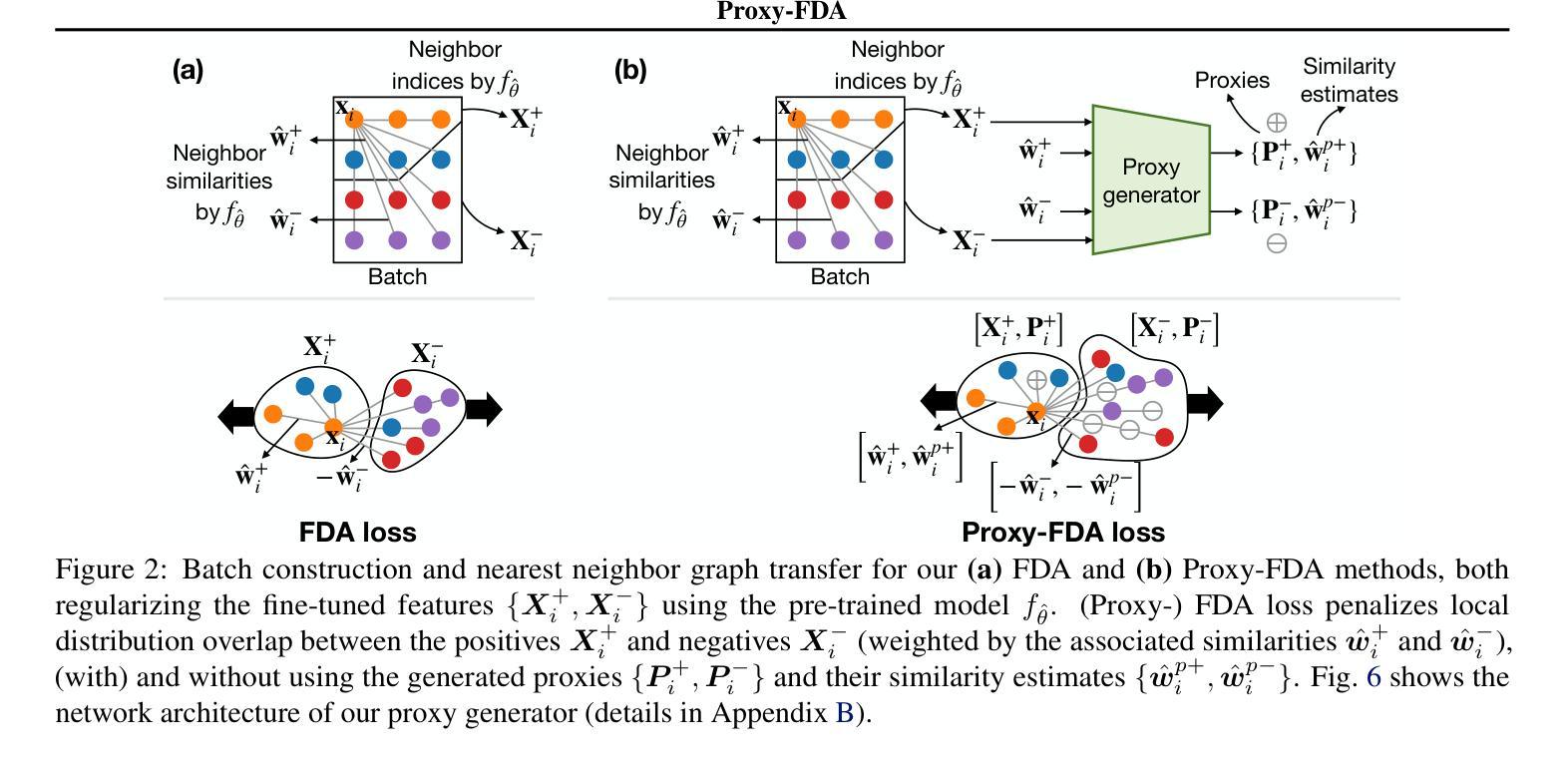
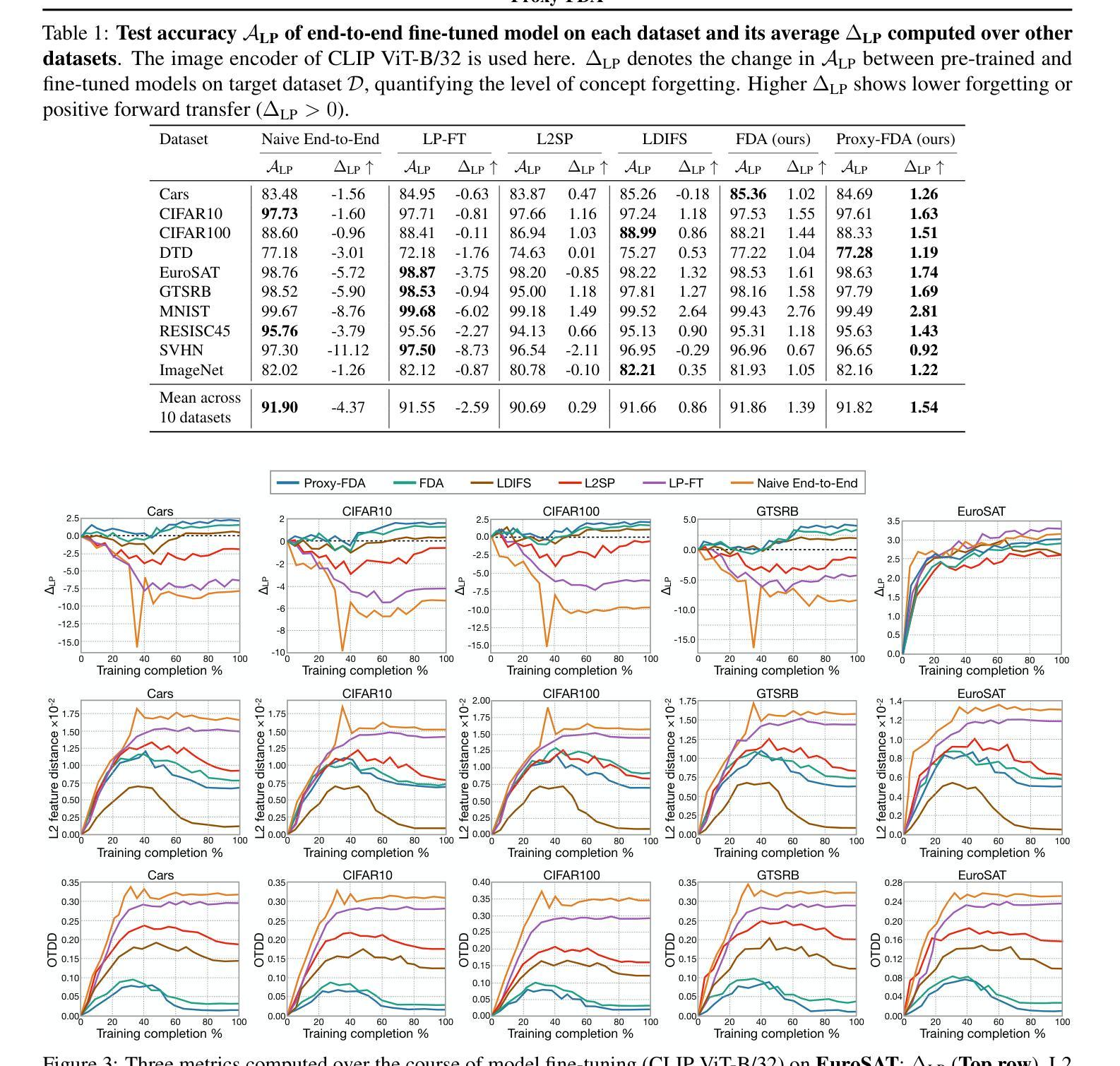
Proxy-FDA: Proxy-based Feature Distribution Alignment for Fine-tuning Vision Foundation Models without Forgetting
Authors:Chen Huang, Skyler Seto, Hadi Pouransari, Mehrdad Farajtabar, Raviteja Vemulapalli, Fartash Faghri, Oncel Tuzel, Barry-John Theobald, Josh Susskind
Vision foundation models pre-trained on massive data encode rich representations of real-world concepts, which can be adapted to downstream tasks by fine-tuning. However, fine-tuning foundation models on one task often leads to the issue of concept forgetting on other tasks. Recent methods of robust fine-tuning aim to mitigate forgetting of prior knowledge without affecting the fine-tuning performance. Knowledge is often preserved by matching the original and fine-tuned model weights or feature pairs. However, such point-wise matching can be too strong, without explicit awareness of the feature neighborhood structures that encode rich knowledge as well. We propose a novel regularization method Proxy-FDA that explicitly preserves the structural knowledge in feature space. Proxy-FDA performs Feature Distribution Alignment (using nearest neighbor graphs) between the pre-trained and fine-tuned feature spaces, and the alignment is further improved by informative proxies that are generated dynamically to increase data diversity. Experiments show that Proxy-FDA significantly reduces concept forgetting during fine-tuning, and we find a strong correlation between forgetting and a distributional distance metric (in comparison to L2 distance). We further demonstrate Proxy-FDA’s benefits in various fine-tuning settings (end-to-end, few-shot and continual tuning) and across different tasks like image classification, captioning and VQA.
预训练在大量数据上的视觉基础模型对真实世界概念进行了丰富的表示,通过微调可以适应下游任务。然而,对基础模型进行单一任务的微调常常会导致其他任务的概念遗忘问题。最近的稳健微调方法旨在减轻对先前知识的遗忘,同时不影响微调性能。知识通常通过匹配原始模型和微调后的模型权重或特征对来保留。然而,这样的点对点匹配可能过于强烈,没有明确意识到特征邻域结构也编码了丰富的知识。我们提出了一种新的正则化方法Proxy-FDA,它显式地保留特征空间中的结构知识。Proxy-FDA执行特征分布对齐(使用最近邻图)在预训练的和微调后的特征空间之间,通过对齐以及动态生成信息代理来提高数据多样性。实验表明,Proxy-FDA在微调过程中显著减少了概念遗忘,我们发现遗忘与分布距离度量之间存在强烈的相关性(与L2距离相比)。我们进一步证明了Proxy-FDA在各种微调设置(端到端、小样本和连续调整)和不同任务(如图像分类、描述和视觉问答)中的优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
预训练在大量数据上的视觉基础模型编码了丰富的现实世界概念表示,通过微调适应下游任务。然而,对基础模型进行微调会导致其他任务的概念遗忘问题。最近提出的稳健微调方法旨在减轻对先前知识的遗忘,同时不影响微调性能。知识通常通过匹配原始模型和微调模型权重或特征对来保留。然而,这种点对点匹配可能过于强烈,没有明确地意识到特征邻域结构也编码了丰富的知识。本文提出了一种新的正则化方法——Proxy-FDA,它显式地保留特征空间中的结构知识。Proxy-FDA执行特征分布对齐(使用最近邻图)和预训练与微调特征空间之间对齐,通过动态生成信息代理来提高数据多样性。实验表明,Proxy-FDA在微调过程中显著减少了概念遗忘,我们发现遗忘与分布距离度量之间存在强烈的相关性(与L2距离相比)。我们还证明了Proxy-FDA在各种微调设置(端到端、小样本和持续调整)和不同任务(如图像分类、描述和视觉问答)中的优势。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉基础模型预训练在大量数据上可编码丰富的现实世界概念表示。
- 微调基础模型会导致概念遗忘问题。
- 现有的稳健微调方法旨在减轻对先前知识的遗忘,同时保持微调性能。
- 知识保留通常通过匹配模型权重或特征对来实现,但这种方法可能过于强烈。
- Proxy-FDA方法通过显式地保留特征空间中的结构知识来解决这个问题。
- Proxy-FDA使用最近邻图执行特征分布对齐,并通过动态生成信息代理提高数据多样性。
点此查看论文截图

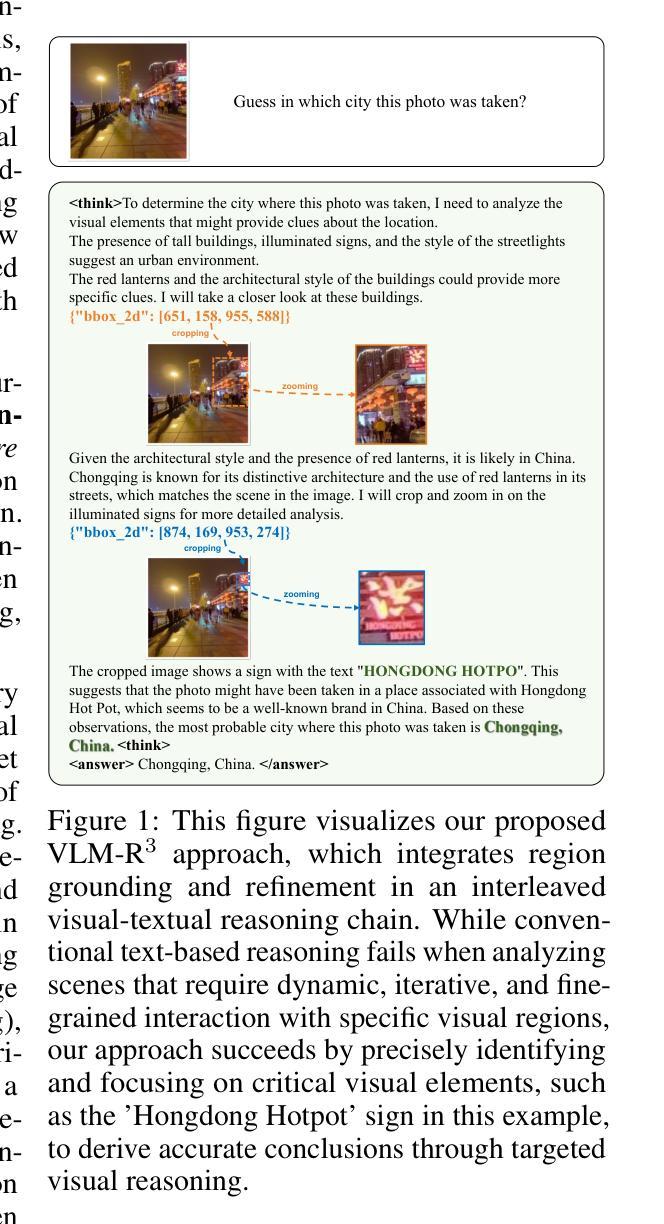
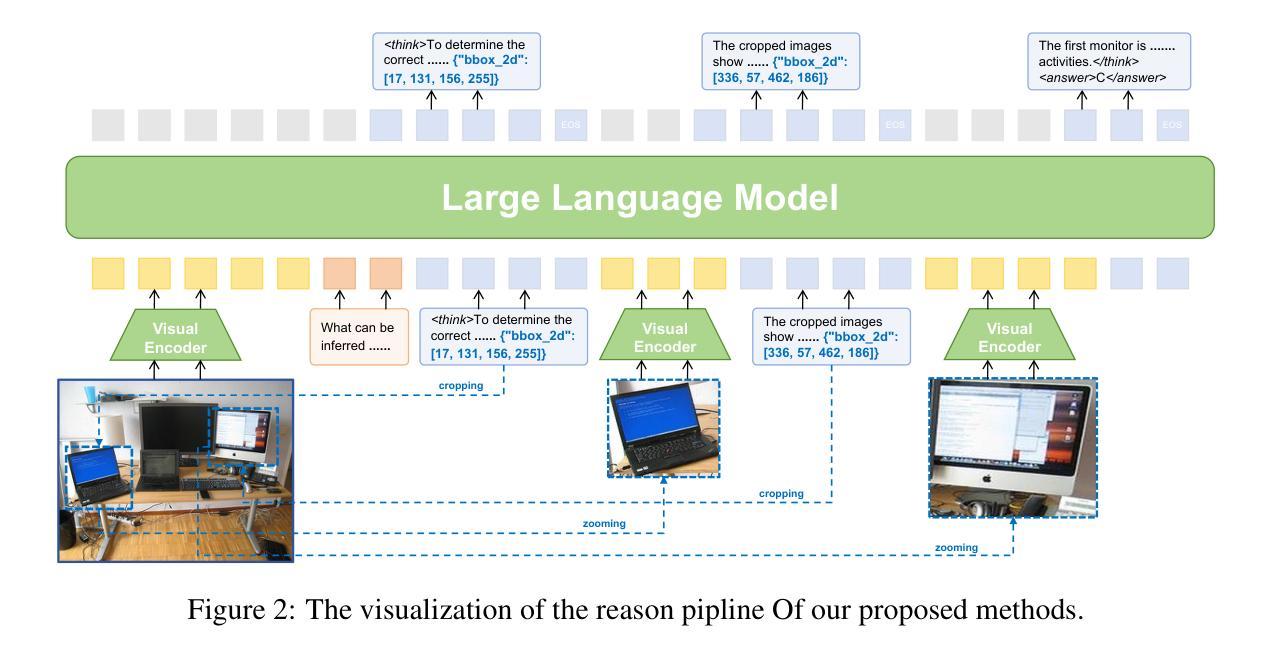
VLM-R$^3$: Region Recognition, Reasoning, and Refinement for Enhanced Multimodal Chain-of-Thought
Authors:Chaoya Jiang, Yongrui Heng, Wei Ye, Han Yang, Haiyang Xu, Ming Yan, Ji Zhang, Fei Huang, Shikun Zhang
Recently, reasoning-based MLLMs have achieved a degree of success in generating long-form textual reasoning chains. However, they still struggle with complex tasks that necessitate dynamic and iterative focusing on and revisiting of visual regions to achieve precise grounding of textual reasoning in visual evidence. We introduce \textbf{VLM-R$^3$} (\textbf{V}isual \textbf{L}anguage \textbf{M}odel with \textbf{R}egion \textbf{R}ecognition and \textbf{R}easoning), a framework that equips an MLLM with the ability to (i) decide \emph{when} additional visual evidence is needed, (ii) determine \emph{where} to ground within the image, and (iii) seamlessly weave the relevant sub-image content back into an interleaved chain-of-thought. The core of our method is \textbf{Region-Conditioned Reinforcement Policy Optimization (R-GRPO)}, a training paradigm that rewards the model for selecting informative regions, formulating appropriate transformations (e.g.\ crop, zoom), and integrating the resulting visual context into subsequent reasoning steps. To bootstrap this policy, we compile a modest but carefully curated Visuo-Lingual Interleaved Rationale (VLIR) corpus that provides step-level supervision on region selection and textual justification. Extensive experiments on MathVista, ScienceQA, and other benchmarks show that VLM-R$^3$ sets a new state of the art in zero-shot and few-shot settings, with the largest gains appearing on questions demanding subtle spatial reasoning or fine-grained visual cue extraction.
最近,基于推理的MLLMs(Masked Language Modeling)在生成长文本推理链方面取得了一定的成功。然而,它们在处理复杂的任务时仍然面临挑战,这些任务需要动态和迭代地关注并重新访问视觉区域,以实现文本推理在视觉证据中的精确定位。我们引入了VLM-R$^3$(配备区域识别和推理的视觉语言模型,简称VLM-R$^3$),这是一个框架,它为MLLM提供了以下能力:(i)决定何时需要额外的视觉证据,(ii)确定在图像中的定位位置,(iii)无缝地将相关的子图像内容重新编织成连贯的推理链。我们的方法的核心是区域条件强化策略优化(R-GRPO),这是一种训练范式,奖励模型选择信息区域、制定适当的转换(例如裁剪、放大)并将得到的视觉上下文集成到随后的推理步骤中。为了引导策略,我们整理了一个适度但精心策划的Visuo-Lingual Interleaved Rationale(VLIR)语料库,该语料库提供了关于区域选择和文本依据的步骤级监督。在MathVista、ScienceQA和其他基准测试上的大量实验表明,VLM-R$^3$在零样本和少样本设置中树立了新的技术标杆,尤其是在需要微妙的空间推理或精细的视觉线索提取的问题上,其收益最大。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于视觉语言模型的推理框架VLM-R$^3$结合了视觉识别和推理能力,实现了动态迭代关注图像区域,精确地将文本推理与视觉证据对接。通过区域条件强化政策优化(R-GRPO)训练模式,模型可自主筛选信息区域、执行适当变换并融入后续推理步骤。通过精心策划的Visuo-Lingual Interleaved Rationale语料库进行政策引导。在MathVista、ScienceQA等基准测试上表现卓越,特别是在需要精细空间推理和细微视觉线索提取的问题上展现出显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- VLM-R$^3$结合了视觉识别和推理能力,实现动态迭代关注图像区域。
- 通过R-GRPO训练模式,模型可自主筛选信息区域并执行适当变换。
- VLM-R$^3$包含Visuo-Lingual Interleaved Rationale语料库进行政策引导。
- VLM-R$^3$在多个基准测试上表现优异,特别是在需要精细空间推理和视觉线索提取的问题上。
- 模型能够在必要时获取额外的视觉证据并精准定位图像内容。
- VLM-R$^3$能无缝将相关的子图像内容融入链式思维过程。
点此查看论文截图

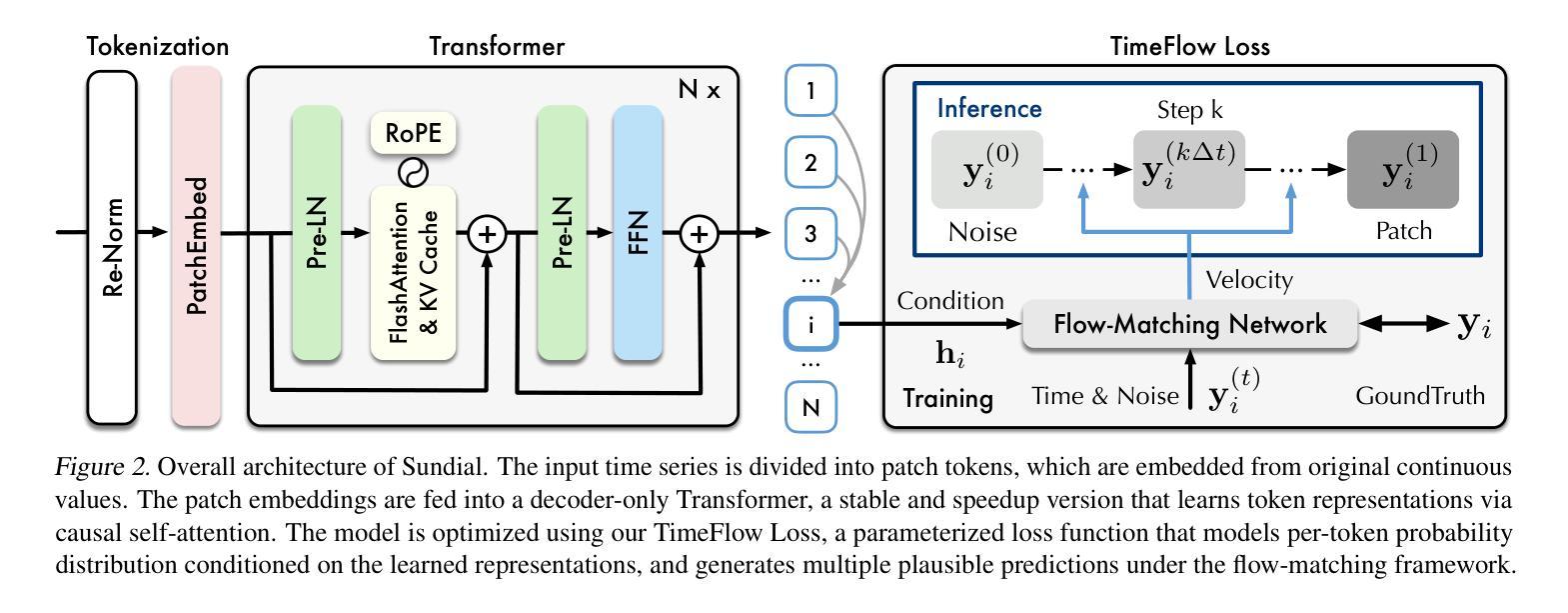
Sundial: A Family of Highly Capable Time Series Foundation Models
Authors:Yong Liu, Guo Qin, Zhiyuan Shi, Zhi Chen, Caiyin Yang, Xiangdong Huang, Jianmin Wang, Mingsheng Long
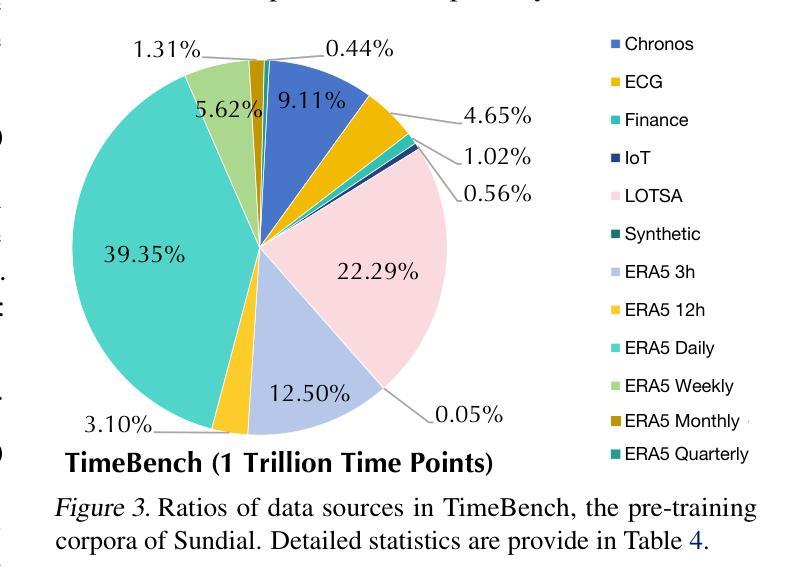
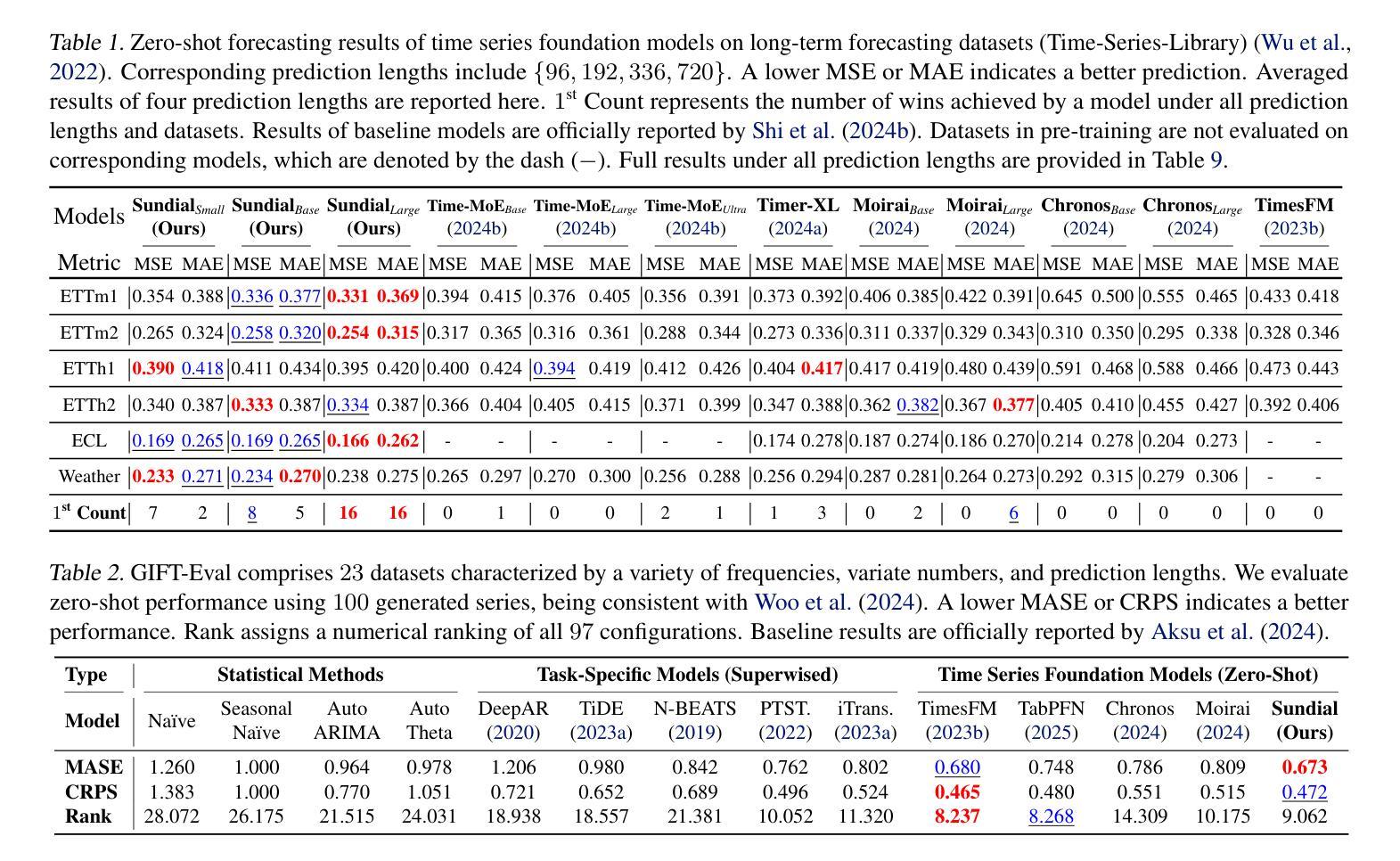
We introduce Sundial, a family of native, flexible, and scalable time series foundation models. To predict the next-patch’s distribution, we propose a TimeFlow Loss based on flow-matching, which facilitates native pre-training of Transformers on continuous-valued time series without discrete tokenization. Conditioned on arbitrary-length time series, our models are pre-trained without specifying any prior distribution and can generate multiple probable predictions, achieving more flexibility in representation learning than using parametric densities. Towards time series foundation models, we leverage minimal but crucial adaptations of Transformers and curate TimeBench with one trillion time points, comprising mostly real-world datasets and synthetic data. By mitigating mode collapse via TimeFlow Loss, we pre-train a family of Sundial models on TimeBench, which achieve unprecedented model capacity and generalization performance. In addition to excellent scalability, Sundial achieves state-of-the-art results on both point and probabilistic forecasting benchmarks with a just-in-time inference speed, i.e., making zero-shot predictions within a few milliseconds. We believe that Sundial’s pioneering generative forecasting capability can improve model reliability in real-world decision-making. Code is available at: https://github.com/thuml/Sundial.
我们介绍了Sundial,这是一系列原生、灵活且可扩展的时间序列基础模型。为了预测下一个补丁的分布,我们提出了基于流匹配的TimeFlow Loss,它促进了在连续值时间序列上对Transformer进行原生预训练,无需进行离散令牌化。我们的模型可以在任意长度的时序数据上进行预训练,无需指定任何先验分布,并且可以生成多个可能的预测结果,相较于使用参数密度的方法,在表示学习中实现了更高的灵活性。针对时间序列基础模型,我们对Transformer进行了微小但关键性的调整,并整理了包含十亿时间点的TimeBench数据集,主要由现实世界数据集和合成数据组成。通过TimeFlow Loss减轻模式崩溃问题,我们在TimeBench上对一系列Sundial模型进行了预训练,实现了前所未有的模型容量和泛化性能。除了出色的可扩展性之外,Sundial在点预测和概率预测基准测试上均达到了最新水平的结果,即时推理速度极快,即零样本预测仅需几毫秒。我们相信Sundial开创性的生成预测能力可以提高现实世界决策中的模型可靠性。代码可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/thuml/Sundial。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Sundial系列原生、灵活、可扩展的时间序列基础模型。提出基于流匹配的TimeFlow Loss预测下一个补丁的分布,实现了在无需离散标记化的情况下对连续值时间序列进行原生预训练。模型在任意长度的时间序列上预训练,无需指定任何先验分布,可生成多个可能的预测结果,提高了表示学习的灵活性。通过使用最小但关键的Transformer适应策略和大规模数据集TimeBench,我们训练了Sundial模型家族,该模型具有良好的可扩展性,并且在点和概率预测方面都达到了最佳效果,还具有即时推理速度,可在毫秒内实现零射击预测。我们认为Sundial开创性的生成预测能力能够提高实际决策中的模型可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- Sundial是一个原生、灵活、可扩展的时间序列基础模型家族。
- 提出TimeFlow Loss方法预测下一个补丁的分布,该方法基于流匹配且适用于连续值时间序列的预训练。
- 模型能够在任意长度的时间序列上预训练,无需指定先验分布,并能生成多个可能的预测结果。
- 利用最小但关键的Transformer适应策略和大规模数据集TimeBench训练了Sundial模型家族。
- Sundial具有良好的可扩展性,在点和概率预测方面均达到了最佳效果,且能实现快速的即时推理。
- 该模型展现出可靠的生成预测能力,有望提升实际决策中的模型可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

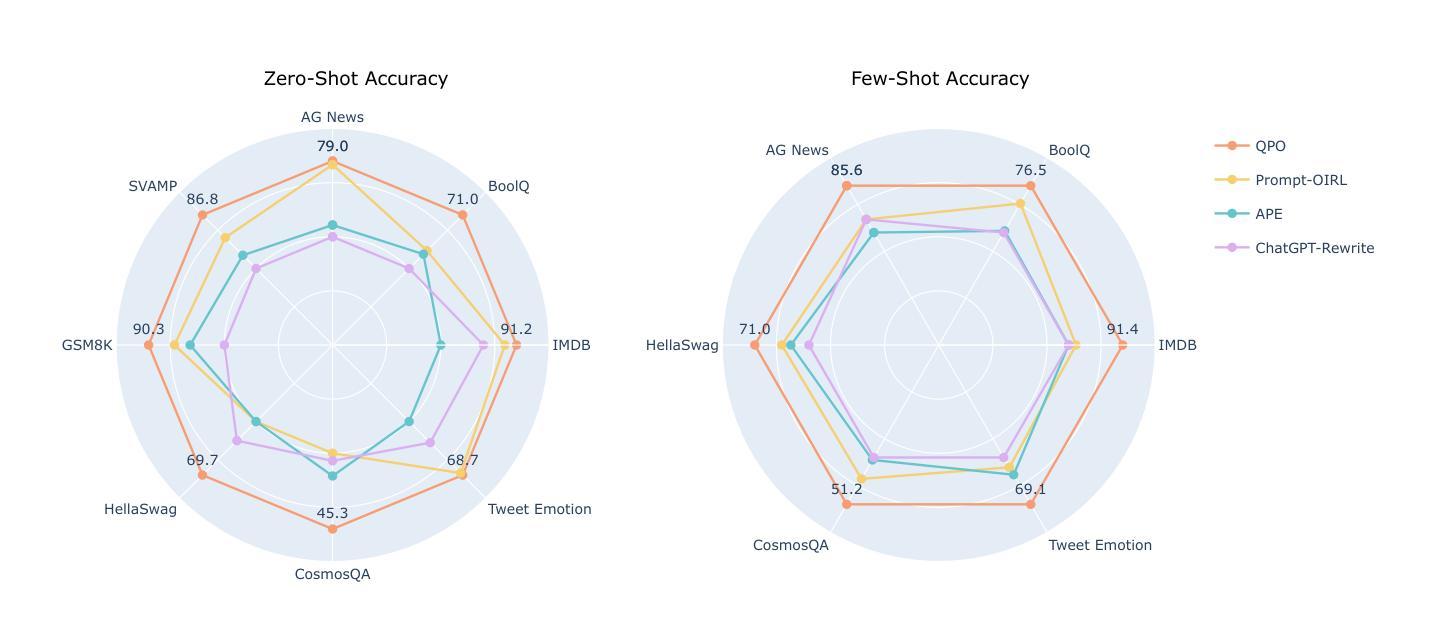
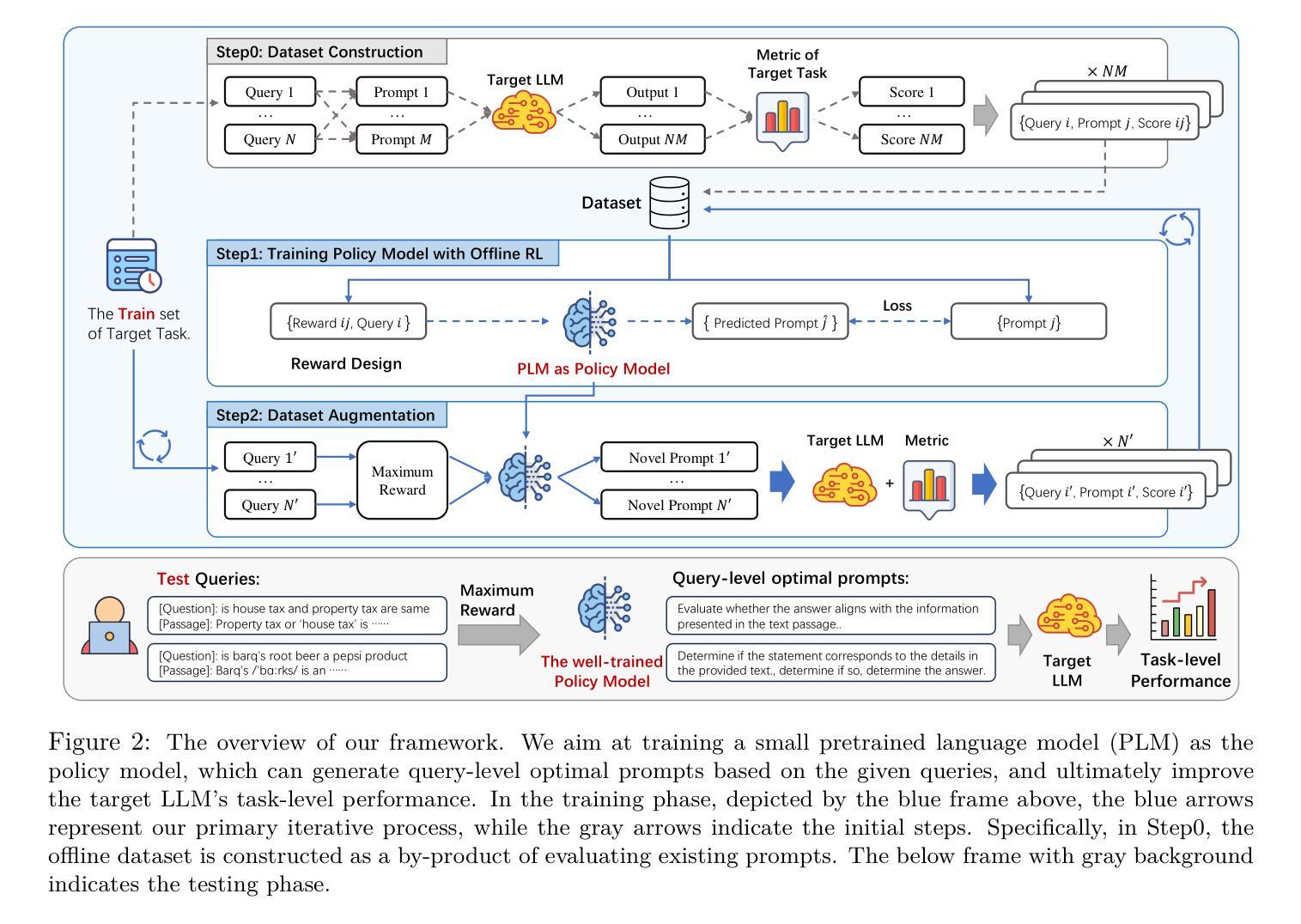
QPO: Query-dependent Prompt Optimization via Multi-Loop Offline Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Yilun Kong, Hangyu Mao, Qi Zhao, Bin Zhang, Jingqing Ruan, Li Shen, Yongzhe Chang, Xueqian Wang, Rui Zhao, Dacheng Tao
Prompt engineering has demonstrated remarkable success in enhancing the performance of large language models (LLMs) across diverse tasks. However, most existing prompt optimization methods only focus on the task-level performance, overlooking the importance of query-preferred prompts, which leads to suboptimal performances. Additionally, these methods rely heavily on frequent interactions with LLMs to obtain feedback for guiding the optimization process, incurring substantial redundant interaction costs. In this paper, we introduce Query-dependent Prompt Optimization (QPO), which leverages multi-loop offline reinforcement learning to iteratively fine-tune a small pretrained language model to generate optimal prompts tailored to the input queries, thus significantly improving the prompting effect on the large target LLM. We derive insights from offline prompting demonstration data, which already exists in large quantities as a by-product of benchmarking diverse prompts on open-sourced tasks, thereby circumventing the expenses of online interactions. Furthermore, we continuously augment the offline dataset with the generated prompts in each loop, as the prompts from the fine-tuned model are supposed to outperform the source prompts in the original dataset. These iterative loops bootstrap the model towards generating optimal prompts. Experiments on various LLM scales and diverse NLP and math tasks demonstrate the efficacy and cost-efficiency of our method in both zero-shot and few-shot scenarios.
提示工程在提升大型语言模型(LLM)在各种任务上的性能上取得了显著的成功。然而,现有的大多数提示优化方法只关注任务级别的性能,忽视了查询偏好提示的重要性,从而导致性能不佳。此外,这些方法还严重依赖于与LLM的频繁交互来获得反馈以指导优化过程,产生了大量的冗余交互成本。在本文中,我们引入了查询依赖提示优化(QPO),它利用多循环离线强化学习来迭代微调一个小的预训练语言模型,以生成针对输入查询的定制最优提示,从而显著提高在大目标LLM上的提示效果。我们从离线提示演示数据中获得见解,这些数据作为在开源任务上评估各种提示的副产品而大量存在,从而避免了在线交互的费用。此外,我们还在每个循环中不断扩充离线数据集与生成的提示,因为微调模型产生的提示应该优于原始数据集中的源提示。这些迭代循环使模型朝着生成最佳提示的方向发展。在各种规模的LLM和不同的NLP和数学任务上的实验证明了我们方法在零击和少击场景中的有效性和成本效益。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Transactions on Machine Learning Research (TMLR)
Summary
本文提出一种查询依赖的提示优化(QPO)方法,利用多循环离线强化学习来微调小型预训练语言模型,以生成针对输入查询量身定制的最优提示。该方法不仅提高了在大目标语言模型上的提示效果,而且通过利用离线提示演示数据来降低成本,并持续用生成提示扩充离线数据集以提高模型性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提示工程在提升大型语言模型性能方面表现显著。
- 现有提示优化方法主要关注任务级别性能,忽略了查询偏好提示的重要性,导致性能不佳。
- QPO方法利用多循环离线强化学习来微调预训练语言模型,生成针对输入查询的最优提示。
- QPO通过利用离线提示演示数据来降低在线交互成本。
- QPO方法持续使用生成提示扩充离线数据集,提高模型性能。
- QPO在零样本和少样本场景下均表现出有效性和成本效益。
点此查看论文截图