⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-03 更新
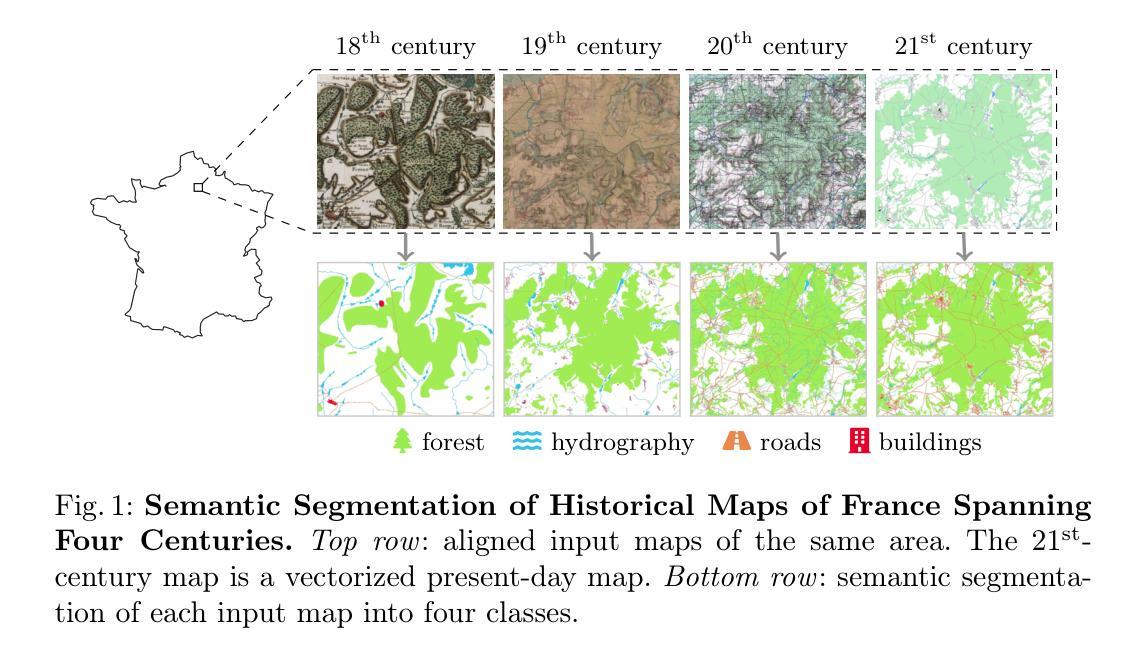
Segmenting France Across Four Centuries
Authors:Marta López-Rauhut, Hongyu Zhou, Mathieu Aubry, Loic Landrieu
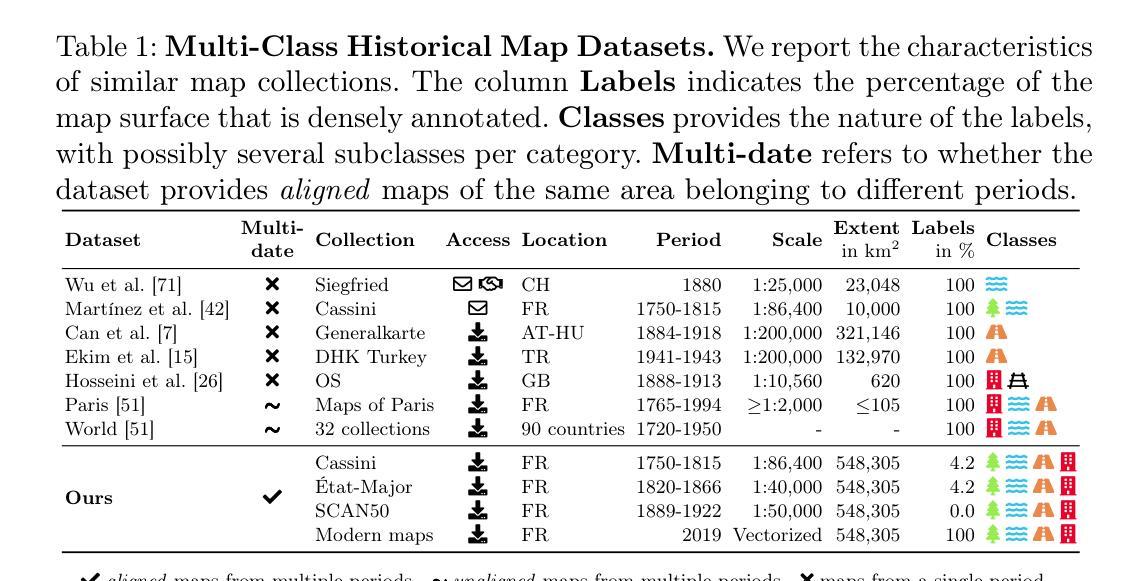
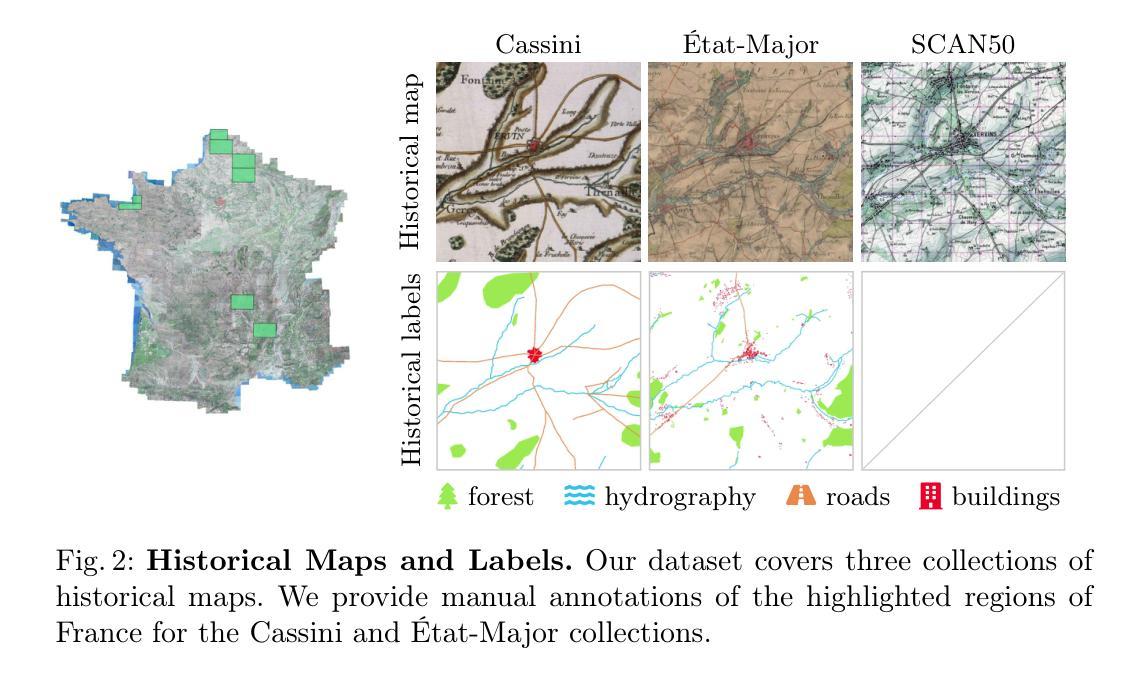
Historical maps offer an invaluable perspective into territory evolution across past centuries–long before satellite or remote sensing technologies existed. Deep learning methods have shown promising results in segmenting historical maps, but publicly available datasets typically focus on a single map type or period, require extensive and costly annotations, and are not suited for nationwide, long-term analyses. In this paper, we introduce a new dataset of historical maps tailored for analyzing large-scale, long-term land use and land cover evolution with limited annotations. Spanning metropolitan France (548,305 km^2), our dataset contains three map collections from the 18th, 19th, and 20th centuries. We provide both comprehensive modern labels and 22,878 km^2 of manually annotated historical labels for the 18th and 19th century maps. Our dataset illustrates the complexity of the segmentation task, featuring stylistic inconsistencies, interpretive ambiguities, and significant landscape changes (e.g., marshlands disappearing in favor of forests). We assess the difficulty of these challenges by benchmarking three approaches: a fully-supervised model trained with historical labels, and two weakly-supervised models that rely only on modern annotations. The latter either use the modern labels directly or first perform image-to-image translation to address the stylistic gap between historical and contemporary maps. Finally, we discuss how these methods can support long-term environment monitoring, offering insights into centuries of landscape transformation. Our official project repository is publicly available at https://github.com/Archiel19/FRAx4.git.
历史地图为几个世纪以来的地区演变提供了宝贵的视角——在卫星或遥感技术出现之前很久就开始了。深度学习的方法在历史地图分割方面已经取得了有前景的结果,但公开的数据集通常侧重于单一地图类型或时期,需要广泛且昂贵的注释,并且不适合进行全国性的长期分析。在本文中,我们介绍了一个针对大规模、长期土地利用和土地覆盖演变分析的新数据集,适用于有限注释的历史地图。跨越法国都市区(面积54万8千平方公里),我们的数据集包含了来自18世纪、19世纪和20世纪的三个地图集。我们提供了全面的现代标签,并为18世纪和19世纪的地图手动标注了历史标签,面积达2万2千平方公里。我们的数据集展示了分割任务的复杂性,具有风格不一致、解释模糊以及显著的地形变化(例如沼泽地被森林所取代)等特点。我们通过三个方法来评估这些挑战的难度:一个用历史标签训练的完全监督模型,和两个仅依靠现代注释的弱监督模型。后者要么直接使用现代标签,要么先进行图像到图像的翻译以解决历史地图和现代地图之间的风格差距。最后,我们讨论了这些方法如何支持长期环境监测,为几个世纪的景观变化提供了见解。我们的官方项目仓库可在 https://github.com/Archiel19/FRAx4.git 上公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 8 figures, 3 tables
摘要
历史地图对于研究过去几个世纪的领地演变具有宝贵价值,尤其是在卫星遥感技术出现之前。深度学习技术在历史地图分割方面展现出良好前景,但现有公开数据集通常只关注单一地图类型或时期,需要大量昂贵的标注工作,且不适用于全国范围内长期分析。本文介绍了一个针对大规模长期土地使用和土地覆盖演变分析的新数据集,该数据集包含来自法国大部的十八、十九和二十世纪三个地图集,并采用有限标注的方式。该数据集涵盖了法国的都市区域(总计约五十四万八千三百零五平方公里),并提供了现代标签的综合版本以及十八世纪和十九世纪地图的二十万八千七百七十八平方公里的手动注释历史标签。本数据集展现出复杂的分割任务特性,具有风格不一致、解释歧义及重大景观变化等特性(如沼泽地被森林所取代)。我们通过三个对比方案来评估挑战难度:一个是接受历史标签训练的全监督模型,两个是使用仅现代注释的弱监督模型采用直接应用现代标签或对历史和当代地图进行图像到图像翻译的方式解决风格差异问题。最后,我们探讨了这些方法如何支持长期环境监测,为几个世纪的景观变化提供见解。更多详细信息请参见我们的官方项目仓库:https://github.com/Archiel19/FRAx4.git。
关键见解
- 历史地图对于研究土地演变具有独特价值。
- 现有数据集无法满足大规模长期历史地图分析需求。
- 提出包含三个世纪的法国都市地图新数据集。
- 数据集含有现代与历史标注信息以应对复杂分割任务特性。
- 面对任务风格差异提出两种弱监督模型方案进行性能评估。
- 方法可为长期环境监测提供支持,揭示几个世纪的景观变化。
点此查看论文截图

pyMEAL: A Multi-Encoder Augmentation-Aware Learning for Robust and Generalizable Medical Image Translation
Authors:Abdul-mojeed Olabisi Ilyas, Adeleke Maradesa, Jamal Banzi, Jianpan Huang, Henry K. F. Mak, Kannie W. Y. Chan
Medical imaging is critical for diagnostics, but clinical adoption of advanced AI-driven imaging faces challenges due to patient variability, image artifacts, and limited model generalization. While deep learning has transformed image analysis, 3D medical imaging still suffers from data scarcity and inconsistencies due to acquisition protocols, scanner differences, and patient motion. Traditional augmentation uses a single pipeline for all transformations, disregarding the unique traits of each augmentation and struggling with large data volumes. To address these challenges, we propose a Multi-encoder Augmentation-Aware Learning (MEAL) framework that leverages four distinct augmentation variants processed through dedicated encoders. Three fusion strategies such as concatenation (CC), fusion layer (FL), and adaptive controller block (BD) are integrated to build multi-encoder models that combine augmentation-specific features before decoding. MEAL-BD uniquely preserves augmentation-aware representations, enabling robust, protocol-invariant feature learning. As demonstrated in a Computed Tomography (CT)-to-T1-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) translation study, MEAL-BD consistently achieved the best performance on both unseen- and predefined-test data. On both geometric transformations (like rotations and flips) and non-augmented inputs, MEAL-BD outperformed other competing methods, achieving higher mean peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity index measure (SSIM) scores. These results establish MEAL as a reliable framework for preserving structural fidelity and generalizing across clinically relevant variability. By reframing augmentation as a source of diverse, generalizable features, MEAL supports robust, protocol-invariant learning, advancing clinically reliable medical imaging solutions.
医学成像对于诊断至关重要,但临床应用先进的AI驱动成像面临挑战,包括患者差异性、图像伪影和模型泛化受限。深度学习虽然改变了图像处理领域,但3D医学成像仍然受到数据稀缺和不一致性的困扰,其原因在于采集协议、扫描仪差异和患者运动。传统增强方法使用单一管道处理所有转换,忽略了每种增强的独特特征,难以处理大量数据。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种多编码器增强感知学习(MEAL)框架,它利用四种不同的增强变体通过专用编码器进行处理。三种融合策略(如拼接(CC)、融合层(FL)和自适应控制器块(BD))被集成以构建多编码器模型,在解码之前组合增强特定特征。MEAL-BD独特地保留了增强感知表示,实现了稳健的协议不变特征学习。在CT到T1加权MRI的翻译研究中,MEAL-BD在未见过和预定义测试数据上始终表现出最佳性能。在几何变换(如旋转和翻转)和非增强输入方面,MEAL-BD也优于其他竞争方法,实现了更高的峰值信噪比(PSNR)和结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)得分。这些结果证明了MEAL作为一个可靠框架在保持结构保真度和泛化临床相关变化方面的能力。通过将增强重构为多样化和可泛化的特征源,MEAL支持稳健的协议不变学习,推动临床可靠的医学成像解决方案的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 36 pages, 9 figures, 2 tables
Summary
医学成像对于诊断至关重要,但临床采用先进的AI驱动成像面临患者差异性、图像伪影和模型泛化受限等挑战。深度学习虽已革新图像分析,但3D医学成像仍受数据稀缺和不一致性的影响。为解决这些问题,我们提出一种多编码器增广感知学习(MEAL)框架,利用四种不同的增广变体通过专用编码器进行处理。三种融合策略结合构建多编码器模型,在解码前结合增广特定特征。MEAL在CT到T1加权MRI的翻译研究中表现最佳,证明其作为可靠框架的价值,能够保留结构保真度并在临床上相关的变化中保持泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗成像对诊断至关重要,但AI在医疗成像领域的应用面临多方面的挑战,包括患者差异、图像伪影和模型泛化能力有限等。
- 虽然深度学习已经极大地改变了图像分析领域,但3D医学成像仍然受到数据稀缺性和不一致性的困扰。
- 提出了一种新的框架——多编码器增广感知学习(MEAL)框架,该框架利用四种不同的增广方法,并通过专门的编码器进行处理。
- MEAL框架集成了三种融合策略,包括串联、融合层和自适应控制器块,以构建多编码器模型,这些模型能够在解码之前结合增广特定的特征。
- 在CT到T1加权MRI的翻译研究中,MEAL-BD表现最佳,显示其在未见数据和预定义测试数据上的稳健性能。
- MEAL-BD在几何转换和非增强输入上的表现优于其他竞争方法,达到更高的峰值信噪比(PSNR)和结构相似性指数(SSIM)分数。
点此查看论文截图

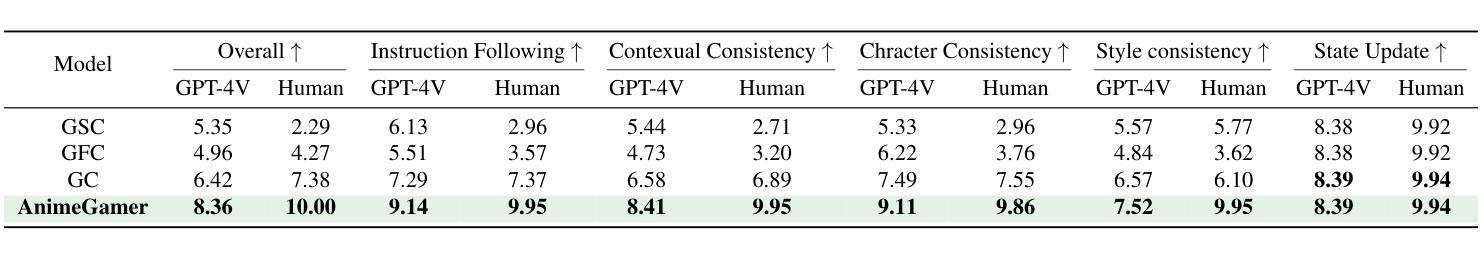
AnimeGamer: Infinite Anime Life Simulation with Next Game State Prediction
Authors:Junhao Cheng, Yuying Ge, Yixiao Ge, Jing Liao, Ying Shan
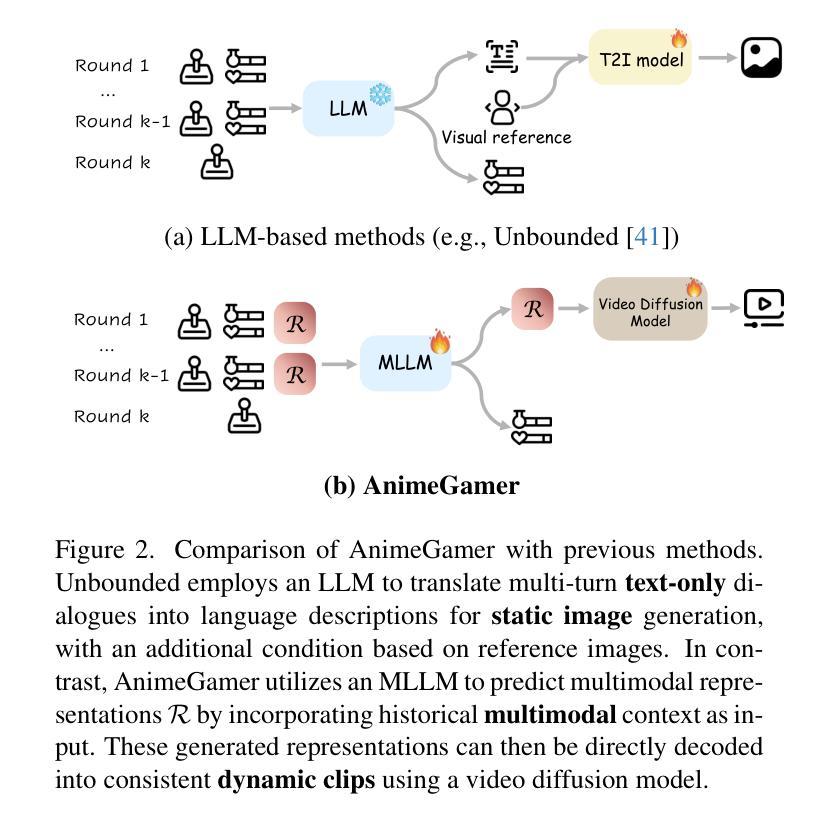
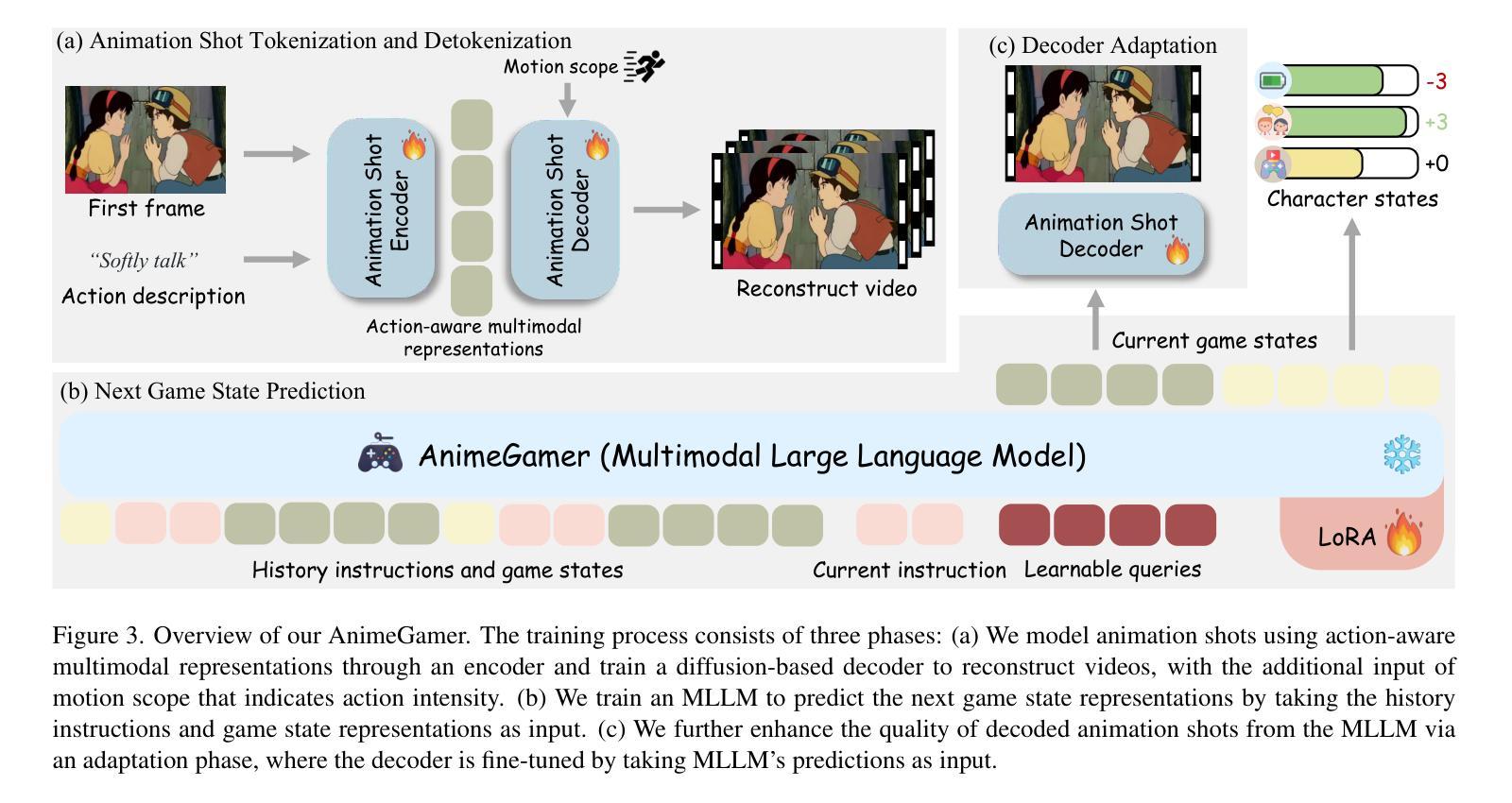
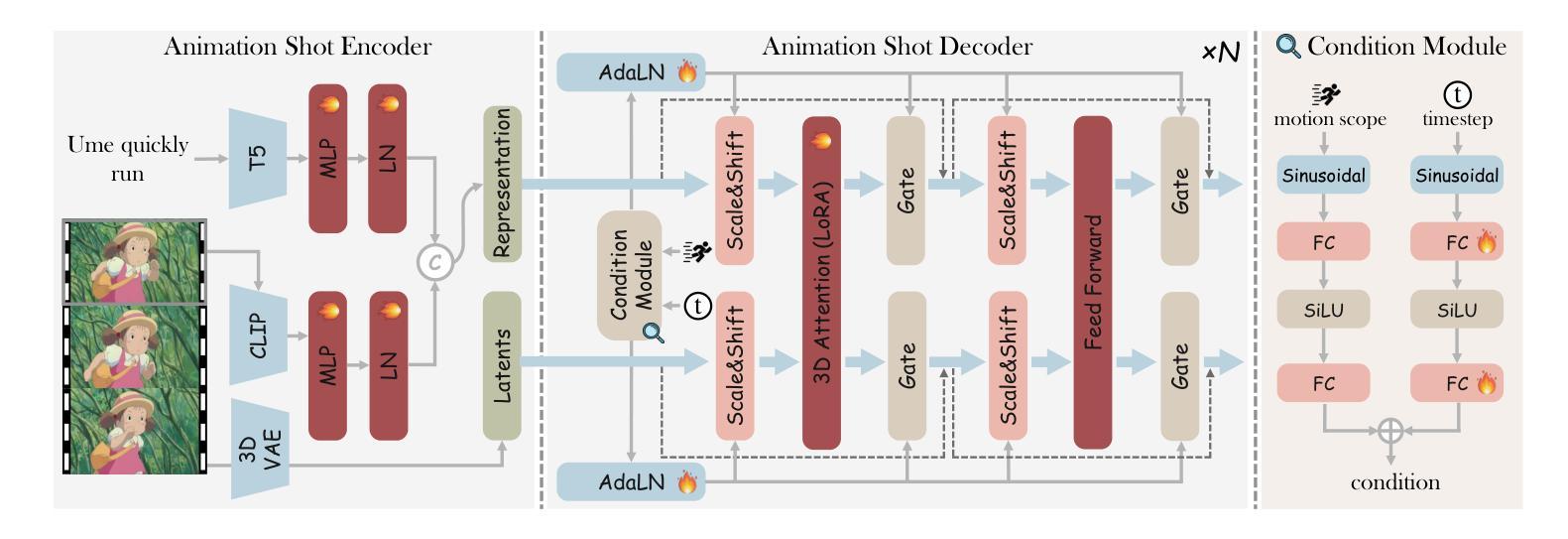
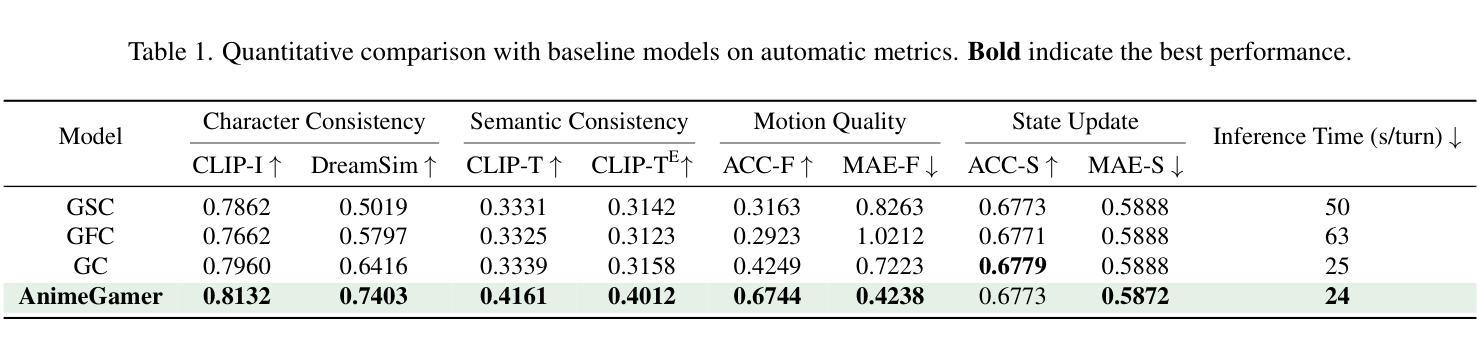
Recent advancements in image and video synthesis have opened up new promise in generative games. One particularly intriguing application is transforming characters from anime films into interactive, playable entities. This allows players to immerse themselves in the dynamic anime world as their favorite characters for life simulation through language instructions. Such games are defined as infinite game since they eliminate predetermined boundaries and fixed gameplay rules, where players can interact with the game world through open-ended language and experience ever-evolving storylines and environments. Recently, a pioneering approach for infinite anime life simulation employs large language models (LLMs) to translate multi-turn text dialogues into language instructions for image generation. However, it neglects historical visual context, leading to inconsistent gameplay. Furthermore, it only generates static images, failing to incorporate the dynamics necessary for an engaging gaming experience. In this work, we propose AnimeGamer, which is built upon Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to generate each game state, including dynamic animation shots that depict character movements and updates to character states, as illustrated in Figure 1. We introduce novel action-aware multimodal representations to represent animation shots, which can be decoded into high-quality video clips using a video diffusion model. By taking historical animation shot representations as context and predicting subsequent representations, AnimeGamer can generate games with contextual consistency and satisfactory dynamics. Extensive evaluations using both automated metrics and human evaluations demonstrate that AnimeGamer outperforms existing methods in various aspects of the gaming experience. Codes and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/TencentARC/AnimeGamer.
最近图像和视频合成的进展为生成游戏带来了新的前景。一个特别引人入胜的应用是将动漫电影中的角色转变为可互动的游戏实体。这允许玩家化身为他们最喜欢的角色,通过语言指令体验动漫世界的动态生活模拟。这类游戏被定义为无限游戏,因为它们消除了预定的边界和固定的游戏规则,玩家可以通过开放式的语言与游戏世界互动,并体验不断发展的故事线和环境。最近,一种开创性的无限动漫生活模拟方法采用大型语言模型(LLM)将多轮文本对话翻译为图像生成的语言指令。然而,它忽略了历史视觉上下文,导致游戏体验不一致。此外,它只能生成静态图像,无法融入动态元素,无法提供引人入胜的游戏体验。在这项工作中,我们提出了AnimeGamer,它建立在多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)之上,用于生成每个游戏状态,包括动态动画镜头,这些镜头描绘了角色的动作和状态更新,如图1所示。我们引入了新型的动作感知多模态表示法来表示动画镜头,可以使用视频扩散模型将其解码为高质量的视频片段。通过以历史动画镜头表示为上下文并预测后续表示,AnimeGamer可以生成具有上下文一致性和令人满意的动力学特性的游戏。通过自动化指标和人类评估的广泛评估表明,AnimeGamer在游戏体验的各个方面都优于现有方法。相关代码和检查点可在https://github.com/TencentARC/AnimeGamer获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project released at: https://howe125.github.io/AnimeGamer.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了近期图像和视频合成技术的进展,特别是在生成游戏领域的新应用。其中,将动漫角色转化为可互动实体,让玩家通过语言指令体验动漫世界的无限可能。此技术可将动漫角色转化为无限游戏的一部分,消除预设边界和规则,提供开放式的语言互动和不断演化的故事情节和环境。腾讯ARC团队提出的AnimeGamer技术基于多模态大型语言模型生成游戏状态及动态动画镜头,并使用视频扩散模型解码为高质量视频片段。此方法能够模拟上下文一致的动漫场景和游戏动态。评估结果证实AnimeGamer在游戏体验各方面均优于现有方法。相关代码和检查点已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 图像和视频合成技术的最新进展推动了生成游戏的新发展。
- 一种引人注目的应用是将动漫角色转变为互动实体,使玩家沉浸于动态的动漫世界,并作为其中角色体验生活模拟。
- 此技术将动漫角色融入无限游戏中,消除预设边界和规则,提供开放式语言互动和不断变化的故事情节和环境。
- Tencent ARC团队开发的AnimeGamer技术基于多模态大型语言模型生成游戏状态和动态动画镜头。
- AnimeGamer利用视频扩散模型将动画镜头解码为高质量视频片段,实现角色动作和状态的更新。
- AnimeGamer能够模拟上下文一致的动漫场景和游戏动态,确保游戏的一致性和动态性。
点此查看论文截图