⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-03 更新
Open CaptchaWorld: A Comprehensive Web-based Platform for Testing and Benchmarking Multimodal LLM Agents
Authors:Yaxin Luo, Zhaoyi Li, Jiacheng Liu, Jiacheng Cui, Xiaohan Zhao, Zhiqiang Shen
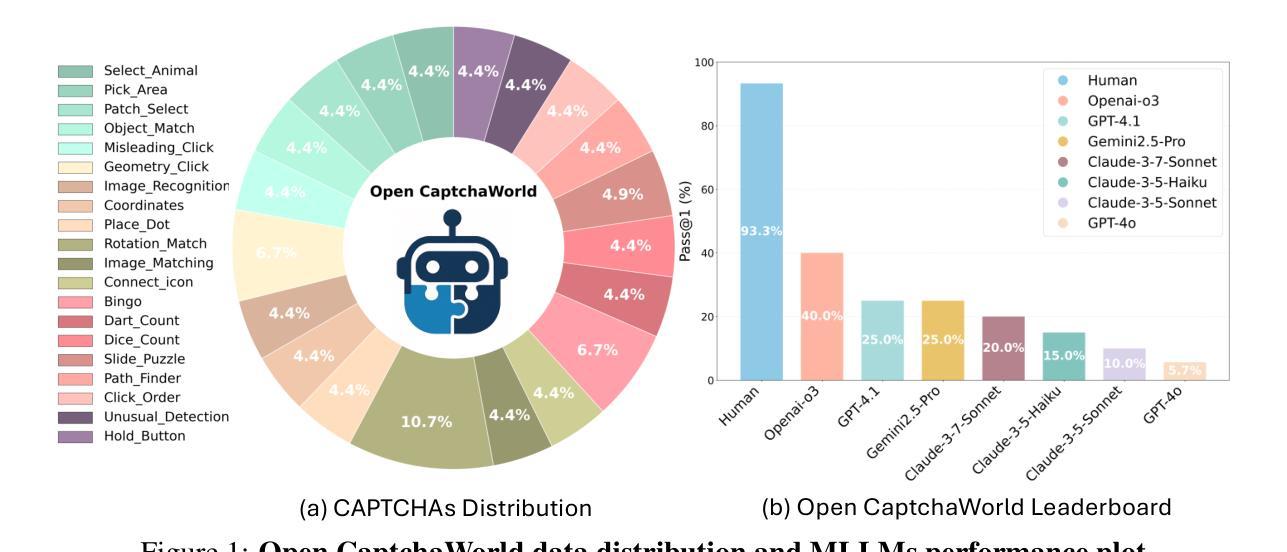
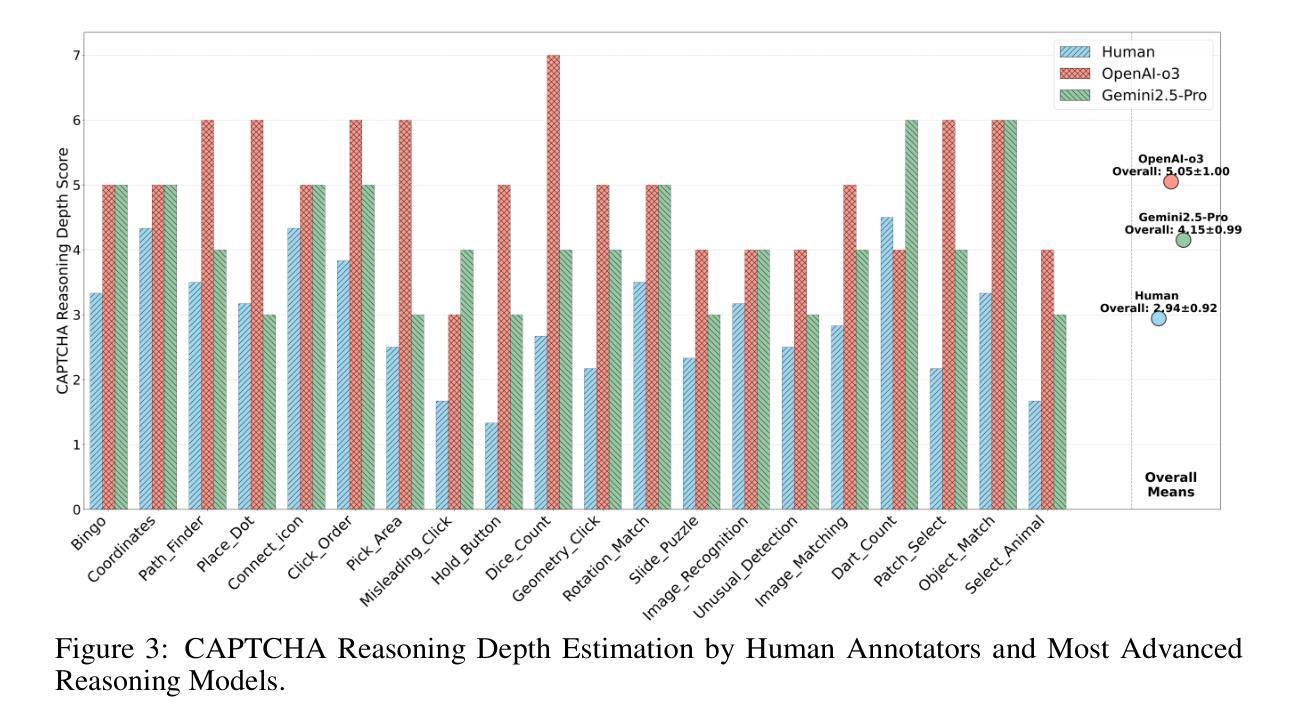
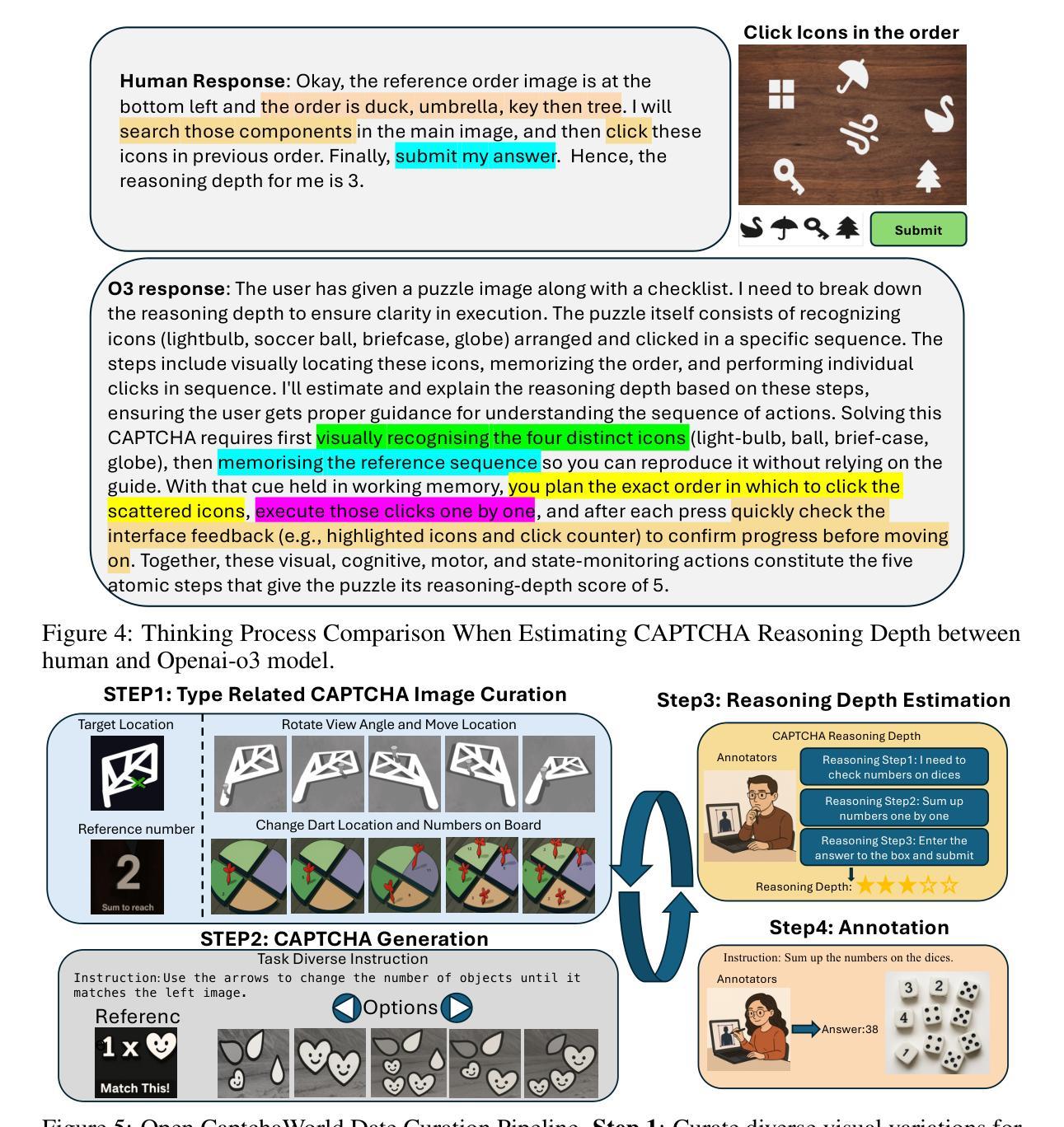
CAPTCHAs have been a critical bottleneck for deploying web agents in real-world applications, often blocking them from completing end-to-end automation tasks. While modern multimodal LLM agents have demonstrated impressive performance in static perception tasks, their ability to handle interactive, multi-step reasoning challenges like CAPTCHAs is largely untested. To address this gap, we introduce Open CaptchaWorld, the first web-based benchmark and platform specifically designed to evaluate the visual reasoning and interaction capabilities of MLLM-powered agents through diverse and dynamic CAPTCHA puzzles. Our benchmark spans 20 modern CAPTCHA types, totaling 225 CAPTCHAs, annotated with a new metric we propose: CAPTCHA Reasoning Depth, which quantifies the number of cognitive and motor steps required to solve each puzzle. Experimental results show that humans consistently achieve near-perfect scores, state-of-the-art MLLM agents struggle significantly, with success rates at most 40.0% by Browser-Use Openai-o3, far below human-level performance, 93.3%. This highlights Open CaptchaWorld as a vital benchmark for diagnosing the limits of current multimodal agents and guiding the development of more robust multimodal reasoning systems. Code and Data are available at this https URL.
CAPTCHA一直是现实世界应用中部署网络代理的关键瓶颈,经常阻止它们完成端到端的自动化任务。虽然现代的多模式LLM代理在静态感知任务中表现出了令人印象深刻的表现,但它们处理像CAPTCHA这样的交互式、多步骤推理挑战的能力却很少得到测试。为了弥补这一空白,我们推出了Open CaptchaWorld,这是第一个专门为评估MLLM驱动代理的视觉推理和交互能力而设计的网络基准测试平台和工具,通过多样化和动态的CAPTCHA谜题来实现。我们的基准测试涵盖了20种现代CAPTCHA类型,总共225个CAPTCHA,通过我们提出的新指标进行注释:CAPTCHA推理深度,该指标量化了解答每个谜题所需的认知和行动步骤数量。实验结果表明,人类始终取得近乎完美的成绩,而最先进的MLLM代理则面临巨大挑战,Browser-Use Openai-o3的成功率最高只有40.0%,远低于人类的表现水平93.3%。这凸显了Open CaptchaWorld作为一个基准测试的重要性,可以诊断当前多模式代理的局限性,并引导开发更稳健的多模式推理系统。代码和数据可在以下URL网址找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code at: https://github.com/MetaAgentX/OpenCaptchaWorld
Summary
推出首个针对多模态LLM代理人的网络基准测试平台Open CaptchaWorld,通过225个不同类型的CAPTCHA谜题评估其视觉推理和交互能力。实验结果显显示人类表现优异,而当前最先进的MLLM代理人解决率最高仅达40%,远低于人类水平。Open CaptchaWorld成为诊断当前多模态代理人局限性的重要基准,并引导开发更稳健的多模态推理系统。
Key Takeaways
- CAPTCHAs是部署网络代理在实际应用中的关键瓶颈,经常阻止其完成端到端自动化任务。
- 现代多模态LLM代理在静态感知任务中表现出色,但在处理交互式、多步骤推理挑战方面能力尚未得到充分测试。
- Open CaptchaWorld是首个专门设计用于评估多模态LLM代理的视觉推理和交互能力的网络基准测试平台。
- 平台包含225个不同类型的CAPTCHA谜题,并提出了一个新的评估指标:CAPTCHA推理深度,用于量化解决每个谜题所需的认知和动作步骤数量。
- 实验结果显示,人类表现接近完美,而最先进的MLLM代理人的解决率远低于人类水平,最高仅达40%。
- Open CaptchaWorld是一个重要的基准测试,有助于诊断当前多模态代理人的局限性。
点此查看论文截图

MoDoMoDo: Multi-Domain Data Mixtures for Multimodal LLM Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Yiqing Liang, Jielin Qiu, Wenhao Ding, Zuxin Liu, James Tompkin, Mengdi Xu, Mengzhou Xia, Zhengzhong Tu, Laixi Shi, Jiacheng Zhu
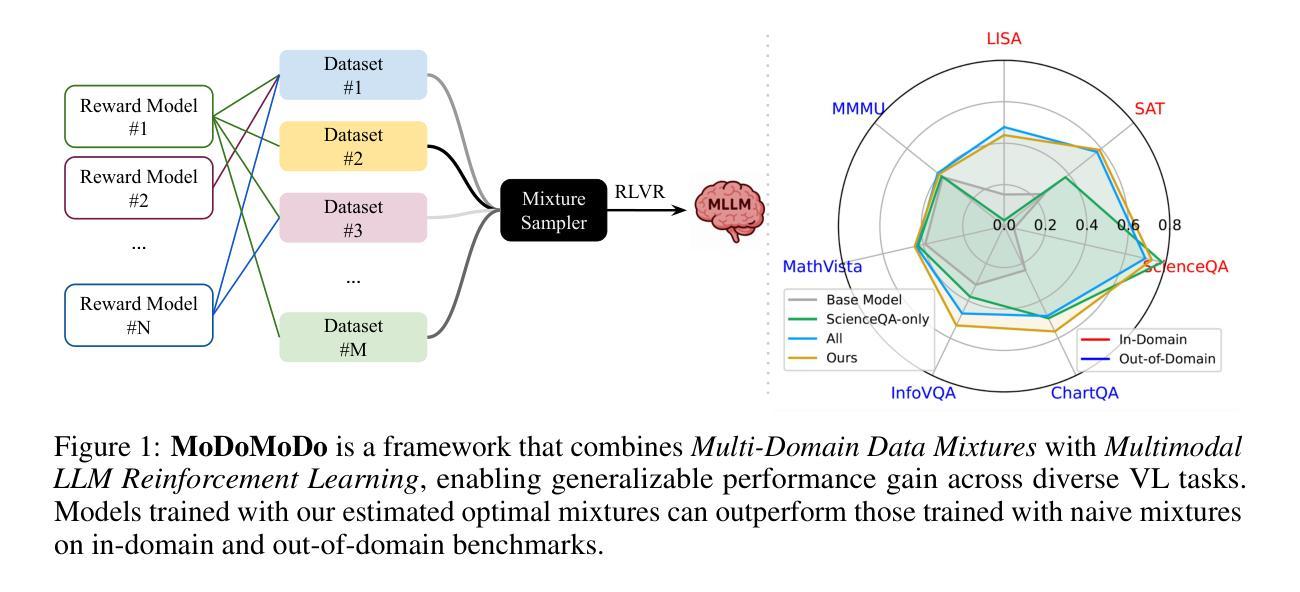
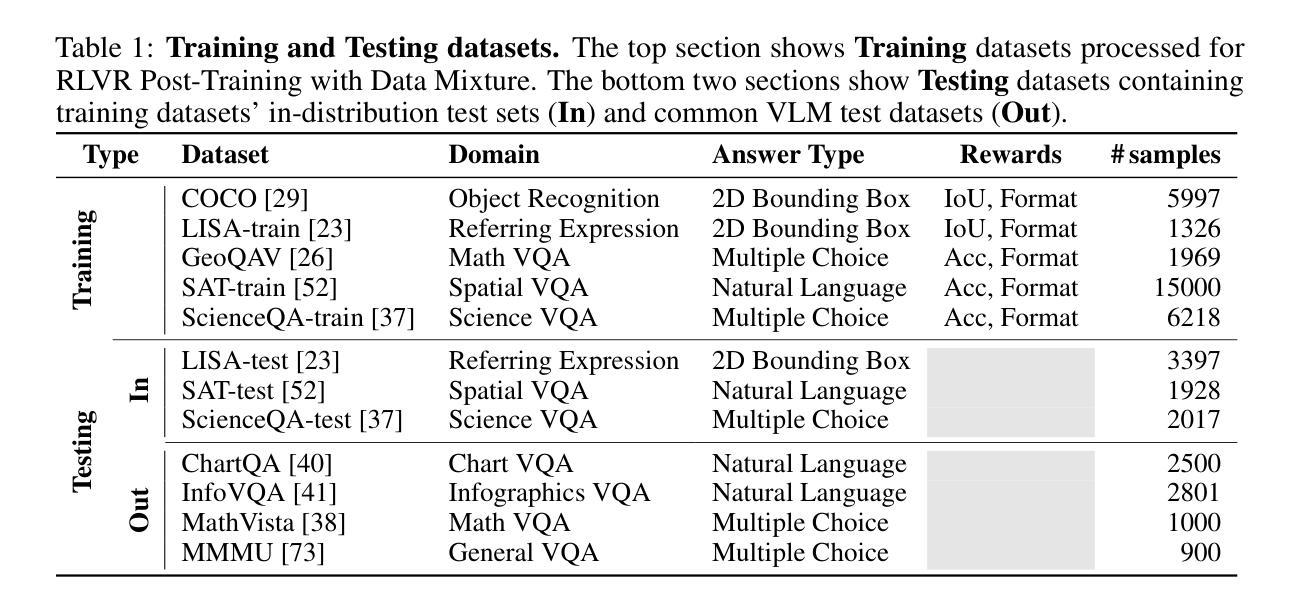
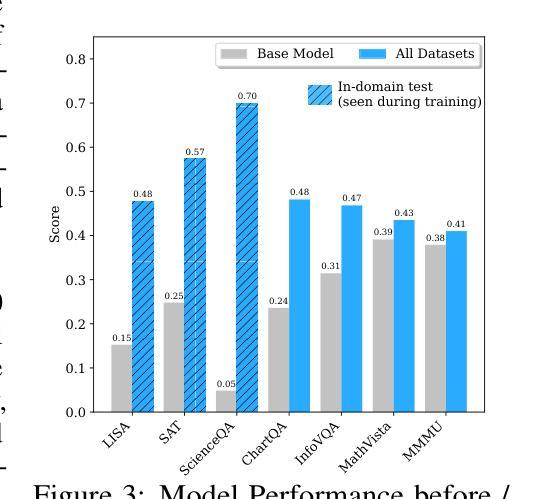
Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has recently emerged as a powerful paradigm for post-training large language models (LLMs), achieving state-of-the-art performance on tasks with structured, verifiable answers. Applying RLVR to Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) presents significant opportunities but is complicated by the broader, heterogeneous nature of vision-language tasks that demand nuanced visual, logical, and spatial capabilities. As such, training MLLMs using RLVR on multiple datasets could be beneficial but creates challenges with conflicting objectives from interaction among diverse datasets, highlighting the need for optimal dataset mixture strategies to improve generalization and reasoning. We introduce a systematic post-training framework for Multimodal LLM RLVR, featuring a rigorous data mixture problem formulation and benchmark implementation. Specifically, (1) We developed a multimodal RLVR framework for multi-dataset post-training by curating a dataset that contains different verifiable vision-language problems and enabling multi-domain online RL learning with different verifiable rewards; (2) We proposed a data mixture strategy that learns to predict the RL fine-tuning outcome from the data mixture distribution, and consequently optimizes the best mixture. Comprehensive experiments showcase that multi-domain RLVR training, when combined with mixture prediction strategies, can significantly boost MLLM general reasoning capacities. Our best mixture improves the post-trained model’s accuracy on out-of-distribution benchmarks by an average of 5.24% compared to the same model post-trained with uniform data mixture, and by a total of 20.74% compared to the pre-finetuning baseline.
强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)作为一种强大的范式,最近出现在训练大型语言模型(LLM)之后,其在具有结构化、可验证答案的任务上实现了最先进的性能。将RLVR应用于多模态LLM(MLLM)带来了巨大的机会,但由于需要微妙的视觉、逻辑和空间能力的视觉语言任务的广泛性和异质性,其应用变得复杂。因此,使用RLVR在多数据集上训练MLLM可能是有益的,但创建了来自不同数据集之间交互的相互冲突目标所带来的挑战,这强调了需要最佳的数据集混合策略来提高泛化和推理能力。我们为Multimodal LLM RLVR引入了系统的后训练框架,其中包括严格的数据混合问题公式和基准实现。具体来说,(1)我们开发了一个多模态RLVR框架,用于多数据集的后训练,通过整理包含不同可验证的视听语言问题的数据集,并启用具有不同可验证奖励的多域在线RL学习;(2)我们提出了一种数据混合策略,该策略可以从数据混合分布中学习预测RL微调结果,从而优化最佳的混合。综合实验表明,当结合混合预测策略时,多域RLVR训练可以显着提高MLLM的通用推理能力。我们的最佳混合与采用均匀数据混合进行后训练的模型相比,提高了其在超出分布基准测试上的平均准确率5.24%,与预微调基准相比,提高了总准确率20.74%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Webpage: https://modomodo-rl.github.io/
摘要
强化学习可验证奖励(RLVR)在训练大型语言模型(LLM)后成为一种强大的范式,其在具有结构化、可验证答案的任务上取得了最先进的性能。虽然将RLVR应用于多模态LLM(MLLM)存在广泛的机遇,但由于需要微妙的视觉、逻辑和空间能力,视觉语言任务的广泛性和异质性使其复杂化。对多个数据集使用RLVR训练MLLM可能有益,但不同数据集之间交互产生的目标冲突突显了需要优化数据集混合策略以提高泛化和推理能力。我们为Multimodal LLM RLVR引入了一种系统的后训练框架,其中包括严格的数据混合问题公式和基准实现。具体来说,我们:(1)开发了一种多模态RLVR框架,用于通过包含不同可验证的视觉语言问题来筛选数据集的数据集训练后的训练阶段;(2) 提出了一种数据混合策略,该策略能够预测数据混合分布下的RL精细调整结果,从而优化最佳混合。综合实验表明,当结合混合预测策略时,多域RLVR训练可以显著提高MLLM的通用推理能力。与我们以前微调基准相比,最佳混合可以提高模型在超出分布基准测试上的准确率平均提高5.24%,并且相对于统一数据混合的后训练模型平均提高了高达高达高达20.74%。我们的方法显著提高了模型的泛化能力和推理能力。我们的最佳混合策略为未来的多模态LLM训练提供了新的视角和潜在的改进方向。
关键见解
- 强化学习可验证奖励(RLVR)在大型语言模型(LLM)的后训练中表现出强大的性能,特别是在具有结构化答案的任务上。
- 将RLVR应用于多模态LLM(MLLM)面临挑战,主要由于视觉语言任务的广泛性和异质性。
点此查看论文截图

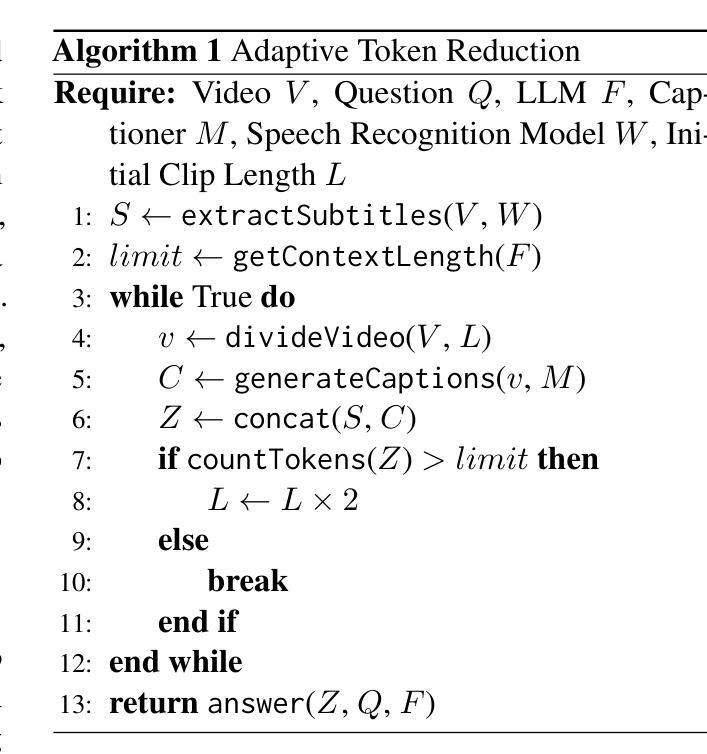
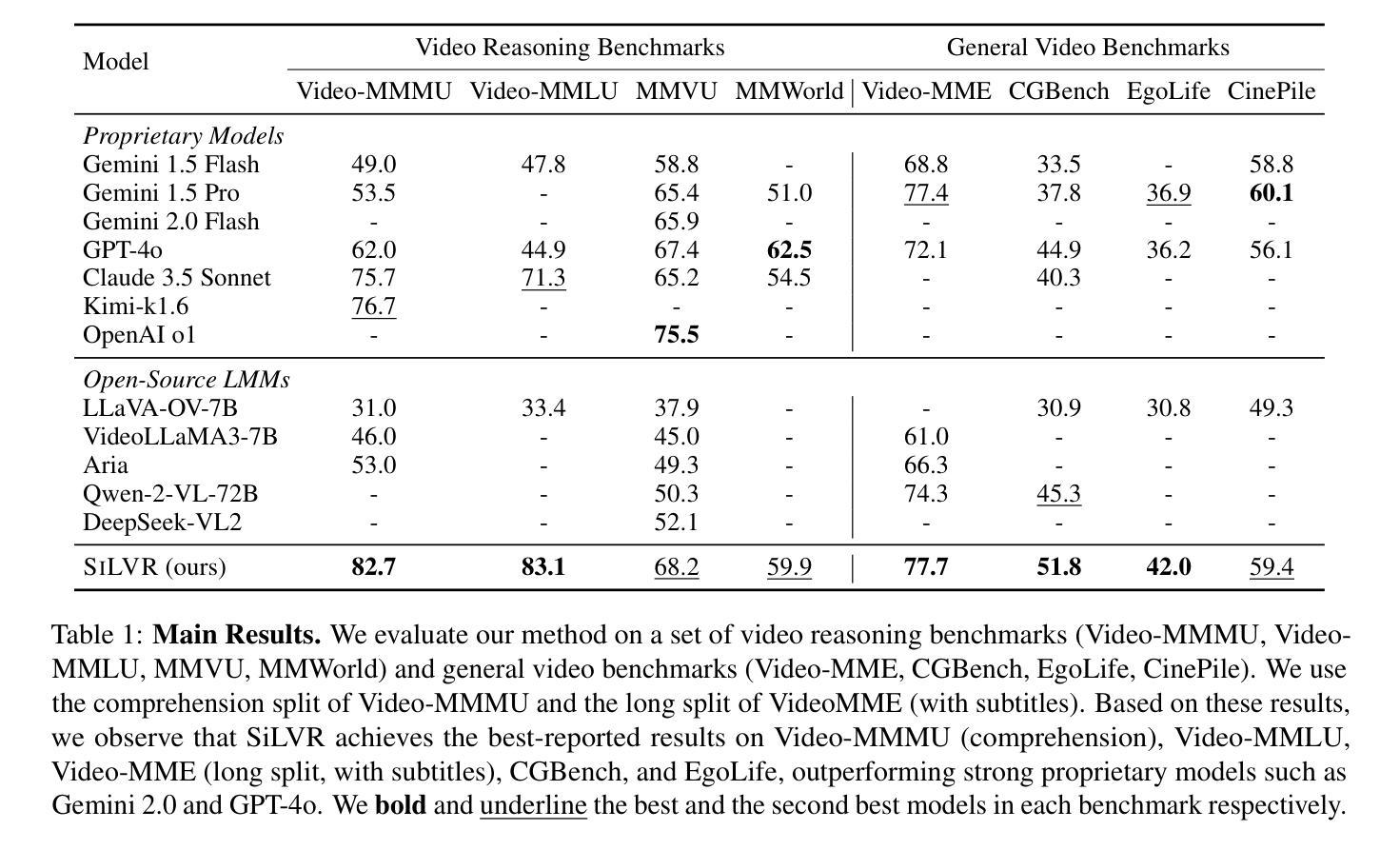
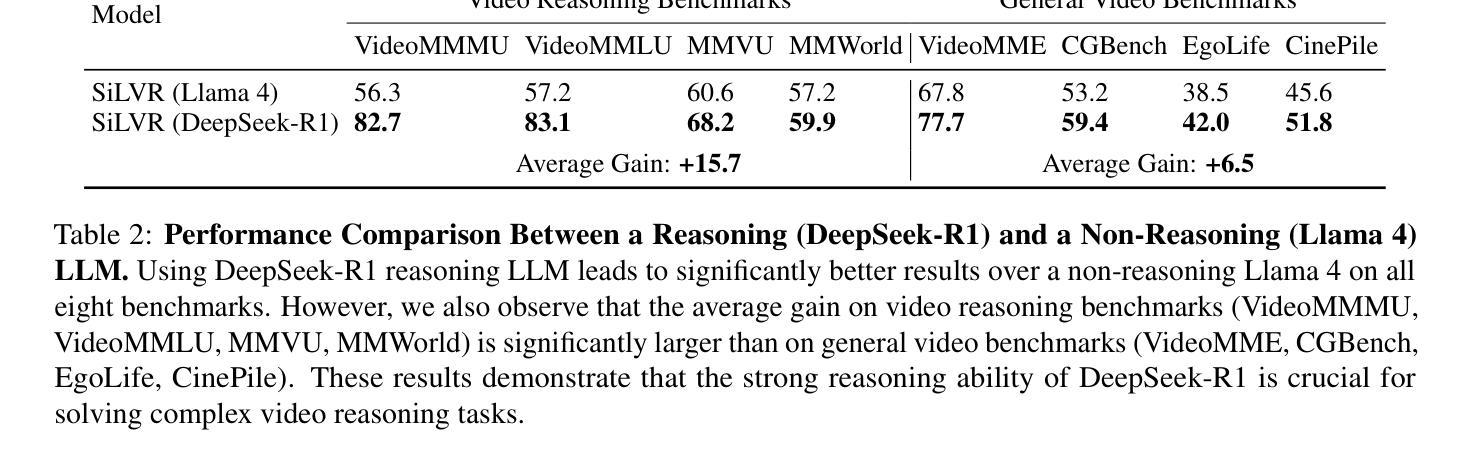
SiLVR: A Simple Language-based Video Reasoning Framework
Authors:Ce Zhang, Yan-Bo Lin, Ziyang Wang, Mohit Bansal, Gedas Bertasius
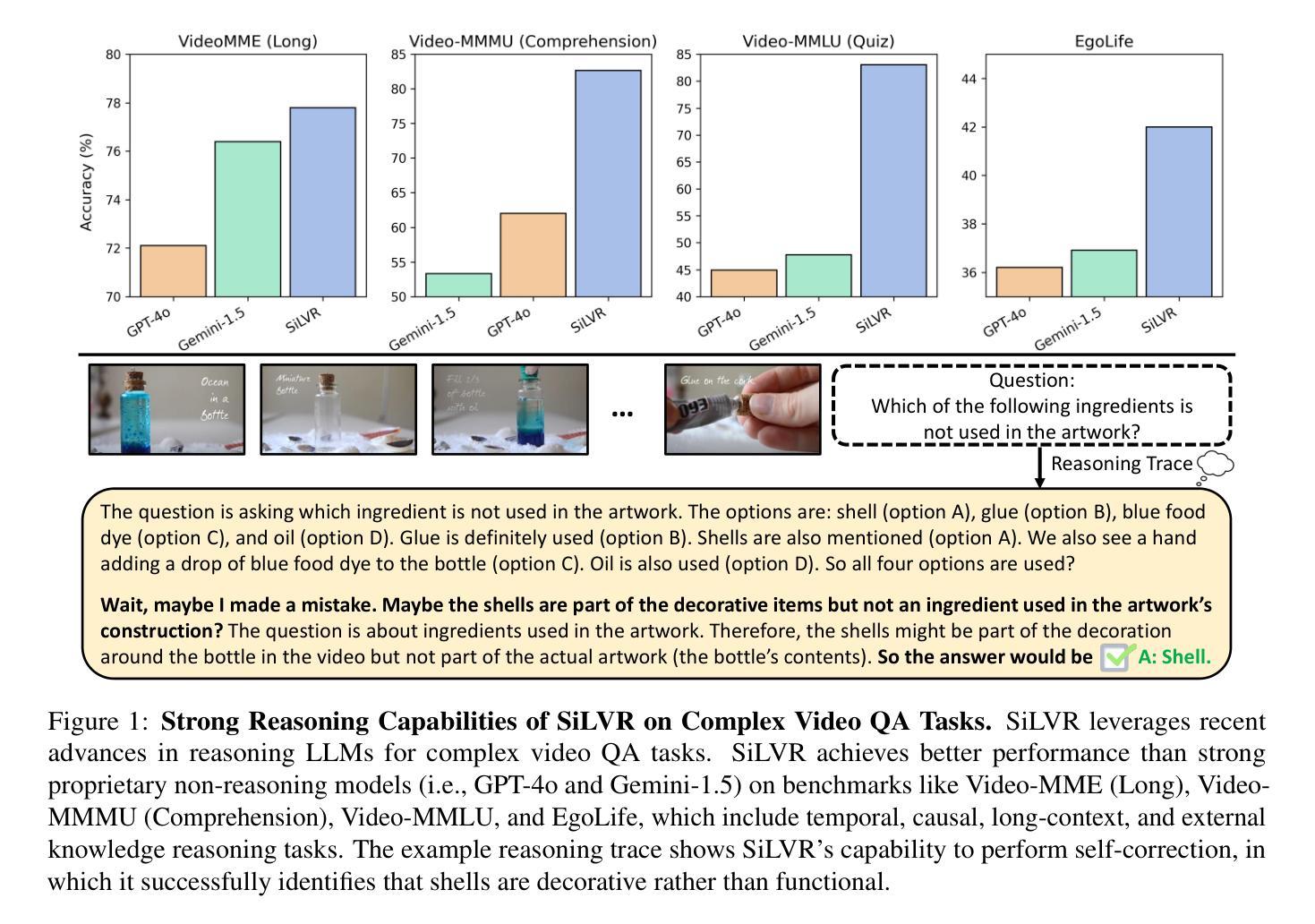
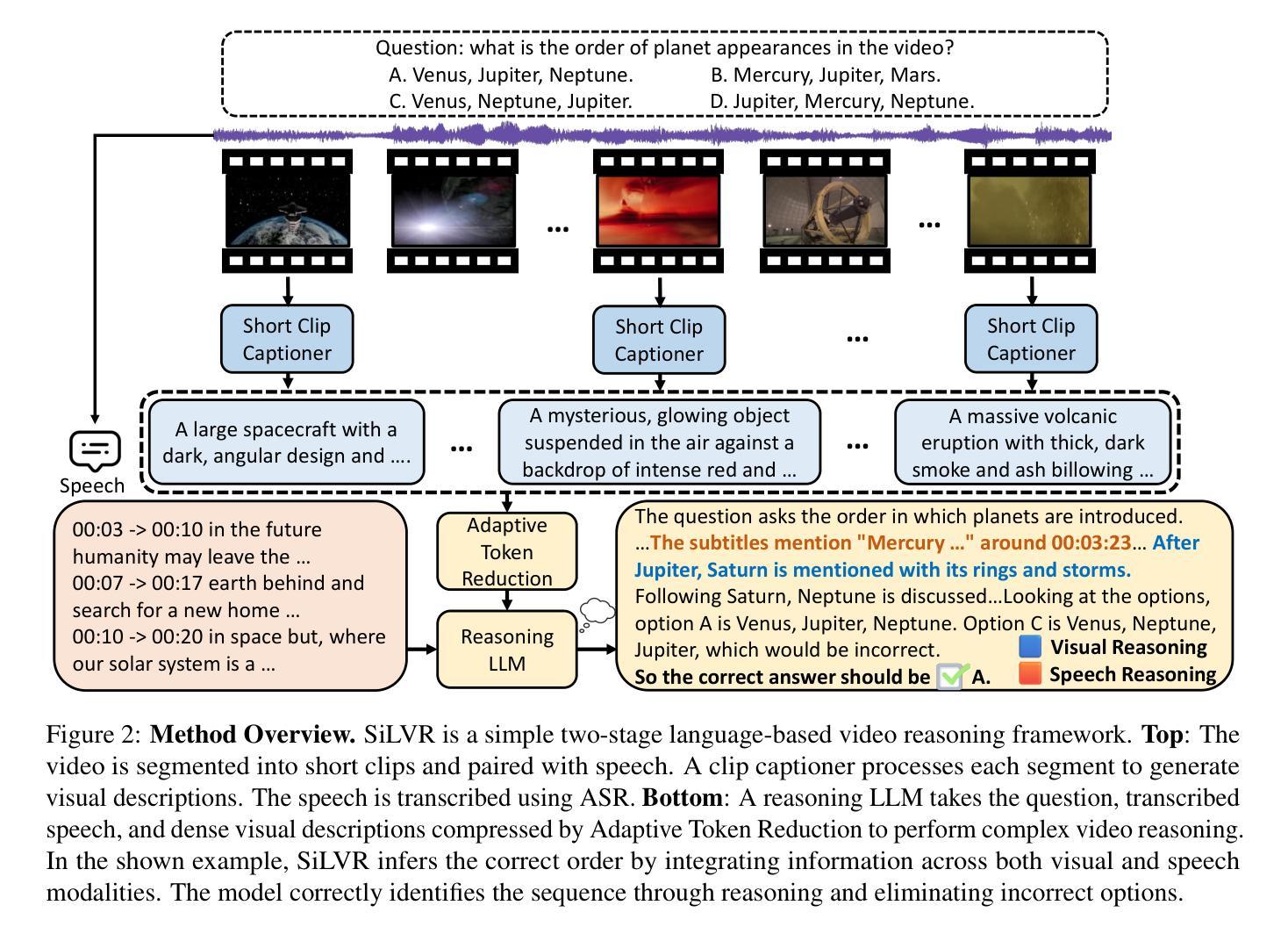
Recent advances in test-time optimization have led to remarkable reasoning capabilities in Large Language Models (LLMs), enabling them to solve highly complex problems in math and coding. However, the reasoning capabilities of multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) still significantly lag, especially for complex video-language tasks. To address this issue, we present SiLVR, a Simple Language-based Video Reasoning framework that decomposes complex video understanding into two stages. In the first stage, SiLVR transforms raw video into language-based representations using multisensory inputs, such as short clip captions and audio/speech subtitles. In the second stage, language descriptions are fed into a powerful reasoning LLM to solve complex video-language understanding tasks. To handle long-context multisensory inputs, we use an adaptive token reduction scheme, which dynamically determines the temporal granularity with which to sample the tokens. Our simple, modular, and training-free video reasoning framework achieves the best-reported results on Video-MME (long), Video-MMMU (comprehension), Video-MMLU, CGBench, and EgoLife. Furthermore, our empirical study focused on video reasoning capabilities shows that, despite not being explicitly trained on video, strong reasoning LLMs can effectively aggregate multisensory input information from video, speech, and audio for complex temporal, causal, long-context, and knowledge acquisition reasoning tasks in video. Code is available at https://github.com/CeeZh/SILVR.
最近测试时间优化的进展为大型语言模型(LLM)带来了显著的推理能力,使其能够解决数学和编码中的高度复杂问题。然而,多模态LLM(MLLM)的推理能力仍有很大差距,尤其是在复杂的视频语言任务中。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了基于简单语言的视频推理框架SiLVR,它将复杂的视频理解分为两个阶段。在第一阶段,SiLVR使用多感官输入(如短视频字幕和音频/语音字幕)将原始视频转换为基于语言的表示形式。在第二阶段,将语言描述输入到强大的推理LLM中,以解决复杂的视频语言理解任务。为了处理长上下文多感官输入,我们采用自适应令牌缩减方案,该方案动态确定令牌的时序粒度。我们简单、模块化、无需训练的视频推理框架在Video-MME(长)、Video-MMMU(理解)、Video-MMLU、CGBench和EgoLife上取得了最佳报告结果。此外,我们的以视频推理能力为研究重点的实证研究表明,尽管未对视频进行明确训练,强大的推理LLM可以有效地聚合来自视频、语音和音频的多感官输入信息,用于处理复杂的时序、因果、长上下文和知识获取视频推理任务。代码可在https://github.com/CeeZh/SILVR获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型(LLM)在测试时的优化进步显著,能够解决数学和编码中的高度复杂问题。但对于多模态LLM(MLLM)来说,其在复杂视频语言任务上的推理能力仍有显著差距。为解决这一问题,提出了基于简单语言视频推理框架SiLVR,将复杂视频理解分为两个阶段。第一阶段使用多感官输入将原始视频转换为语言表示,第二阶段将语言描述输入强大的推理LLM来解决复杂视频语言理解任务。采用自适应令牌缩减方案处理长上下文多感官输入,并实现了在多个基准测试上的最佳结果。此外,实证研究还表明,强大的推理LLM可以有效地聚合来自视频、语音和音频的多感官输入信息,以完成复杂的时空、因果、长期上下文和知识获取视频推理任务。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在测试时的优化增强了其解决复杂问题的能力,特别是在数学和编码领域。
- 多模态LLM(MLLM)在视频语言任务上的推理能力仍有提升空间。
- SiLVR框架被提出以解决MLLM在视频理解上的挑战,其通过两阶段过程将复杂视频转化为语言表示。
- SiLVR使用多感官输入如短视频字幕和音频/语音字幕来生成语言表示。
- 自适应令牌缩减方案被用于处理长上下文多感官输入。
- SiLVR框架在多个基准测试上取得了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

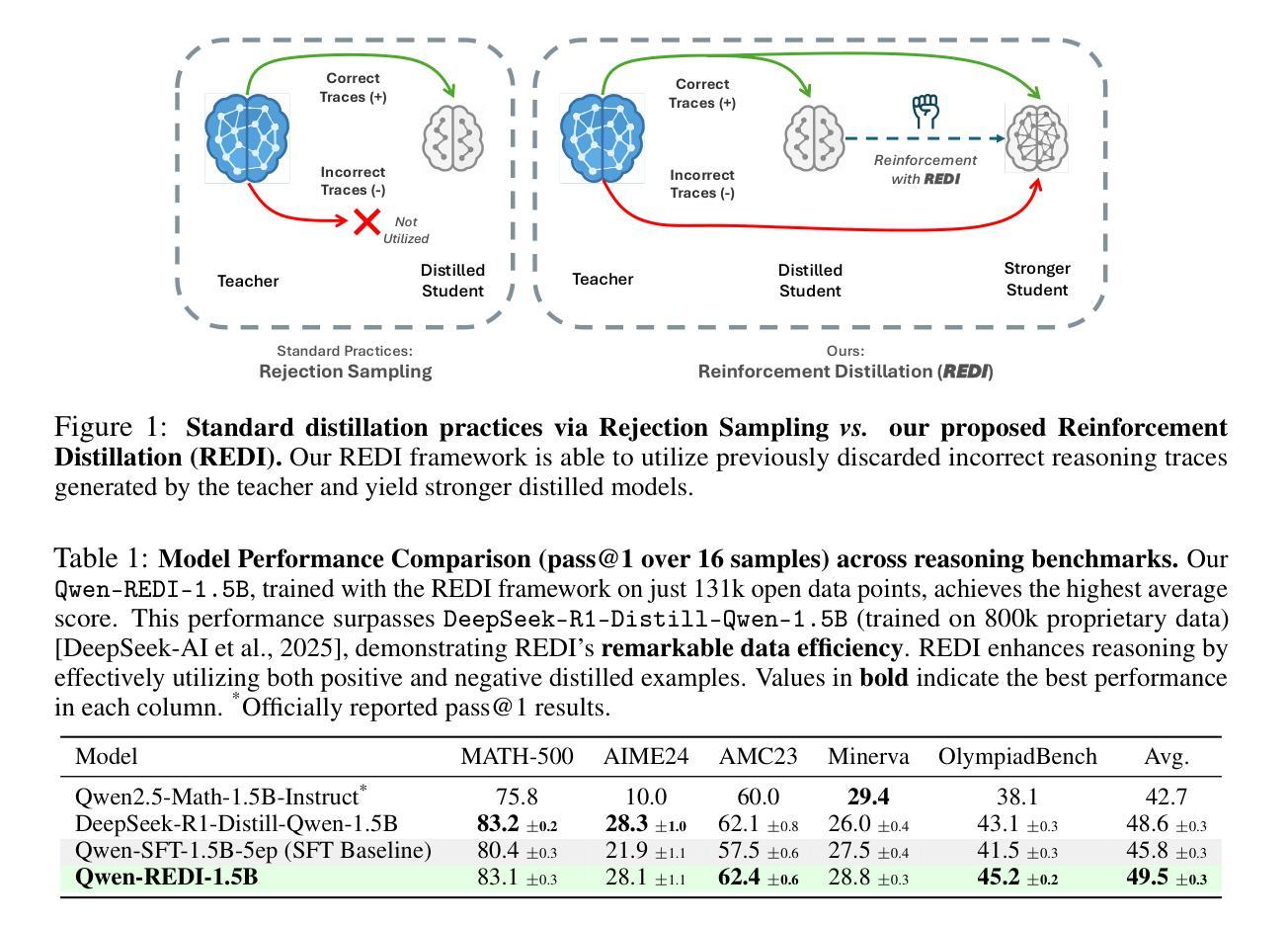
Harnessing Negative Signals: Reinforcement Distillation from Teacher Data for LLM Reasoning
Authors:Shuyao Xu, Cheng Peng, Jiangxuan Long, Weidi Xu, Wei Chu, Yuan Qi
Recent advances in model distillation demonstrate that data from advanced reasoning models (e.g., DeepSeek-R1, OpenAI’s o1) can effectively transfer complex reasoning abilities to smaller, efficient student models. However, standard practices employ rejection sampling, discarding incorrect reasoning examples – valuable, yet often underutilized data. This paper addresses the critical question: How can both positive and negative distilled reasoning traces be effectively leveraged to maximize LLM reasoning performance in an offline setting? To this end, We propose Reinforcement Distillation (REDI), a two-stage framework. Stage 1 learns from positive traces via Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT). Stage 2 further refines the model using both positive and negative traces through our proposed REDI objective. This novel objective is a simple, reference-free loss function that outperforms established methods like DPO and SimPO in this distillation context. Our empirical evaluations demonstrate REDI’s superiority over baseline Rejection Sampling SFT or SFT combined with DPO/SimPO on mathematical reasoning tasks. Notably, the Qwen-REDI-1.5B model, post-trained on just 131k positive and negative examples from the open Open-R1 dataset, achieves an 83.1% score on MATH-500 (pass@1). Its performance matches or surpasses that of DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B (a model post-trained on 800k proprietary data) across various mathematical reasoning benchmarks, establishing a new state-of-the-art for 1.5B models post-trained offline with openly available data.
近期模型蒸馏技术的进展表明,来自高级推理模型(例如DeepSeek-R1、OpenAI的o1)的数据可以有效地将复杂的推理能力传递给更小、更高效的学生模型。然而,标准实践采用拒绝采样,丢弃错误的推理示例——这些有价值但却经常被忽视的数据。本文旨在解决一个关键问题:如何有效利用正负蒸馏推理痕迹,以最大化离线设置中大型语言模型(LLM)的推理性能?为此,我们提出了强化蒸馏(REDI)这一两阶段框架。第一阶段通过监督微调(SFT)从正面痕迹中学习。第二阶段则进一步使用我们提出的REDI目标,通过正面和负面痕迹对模型进行精炼。这一新颖目标是一个简单、无参考的损失函数,在蒸馏环境中优于DPO和SimPO等方法。我们的经验评估表明,REDI在数学推理任务上优于基于拒绝采样的SFT或结合DPO/SimPO的方法。值得注意的是,仅在公开开放的Open-R1数据集上训练了13.1万个正负样本的Qwen-REDI-1.5B模型,在MATH-500(pass@1)上的得分达到83.1%。其性能匹配或超越了DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B(一个在80万专有数据上训练的模型)在各种数学推理基准测试上的表现,为使用公开数据离线训练的1.5B模型建立了新的最先进的水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 10 figures. Code available at https://github.com/Tim-Siu/reinforcement-distillation
摘要
最新模型蒸馏技术显示,高级推理模型(如DeepSeek-R1、OpenAI的o1)的数据可有效将复杂推理能力转移至更小、更高效的学生模型。然而,标准实践采用拒绝采样,丢弃错误的推理示例,这些宝贵但常常未被充分利用的数据。本文旨在解决关键问题:如何有效利用正负蒸馏推理轨迹,以最大化离线设置中LLM的推理性能?为此,我们提出强化蒸馏(REDI),一个两阶段框架。第一阶段通过监督微调(SFT)学习正面轨迹。第二阶段则使用我们提出的REDI目标,进一步精炼模型,同时利用正面和负面轨迹。此新颖目标是一个简单、无参考的损失函数,在此蒸馏环境中优于DPO和SimPO等既定方法。实证评估显示,REDI在数学推理任务上优于基于拒绝采样的SFT或结合DPO/SimPO的SFT。值得注意的是,仅对Open-R1数据集的131k正负样本进行后训练的Qwen-REDI-1.5B模型,在MATH-500上的得分为83.1%(pass@1),其性能匹配或超越了在800k专有数据上后训练的DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B模型,在多种数学推理基准测试中建立了新的离线后训练1.5B模型的最佳状态。
关键见解
- 先进模型的数据可有效转移复杂推理能力至学生模型。
- 标准实践常通过拒绝采样丢弃错误推理示例,但这种方法可能忽略了有价值的数据。
- 强化蒸馏(REDI)是一个两阶段框架,旨在解决有效利用正负蒸馏推理轨迹的问题。
- REDI的第一阶段通过监督微调(SFT)学习正面轨迹,第二阶段则利用正面和负面轨迹进行精炼。
- REDI框架采用一个新颖的无参考损失函数作为蒸馏目标,优于现有方法如DPO和SimPO。
- 实证评估显示REDI在数学推理任务上的性能优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

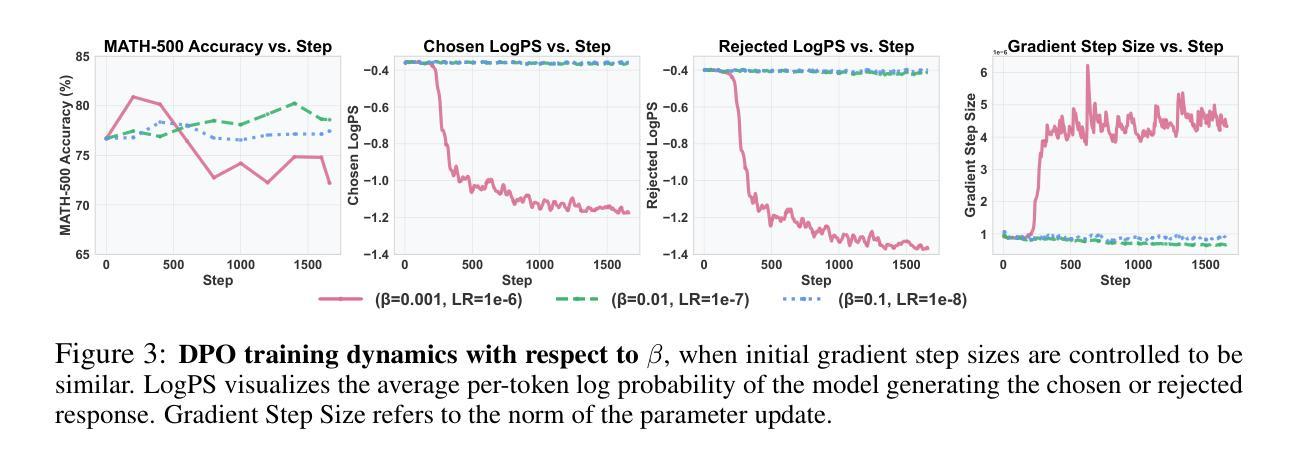
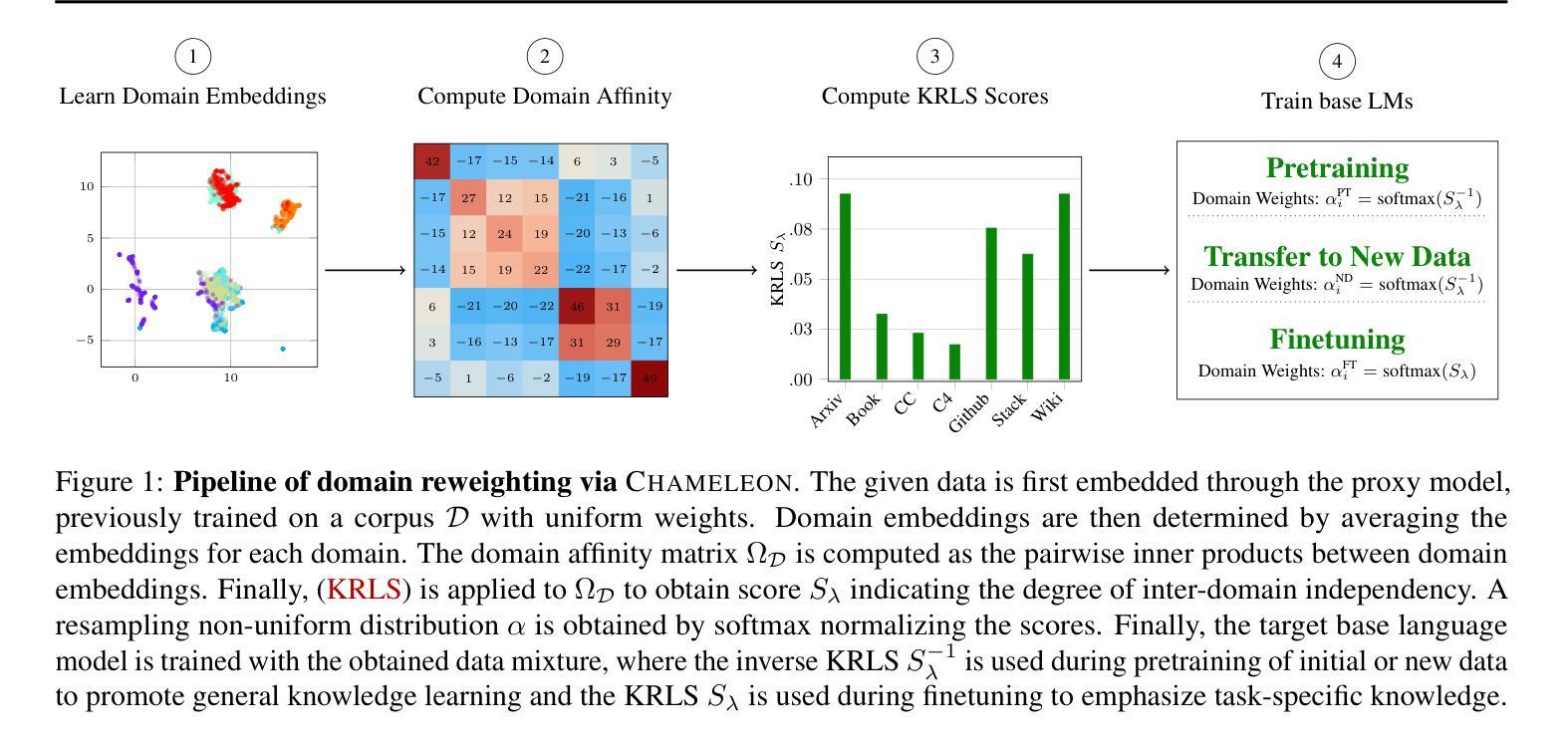
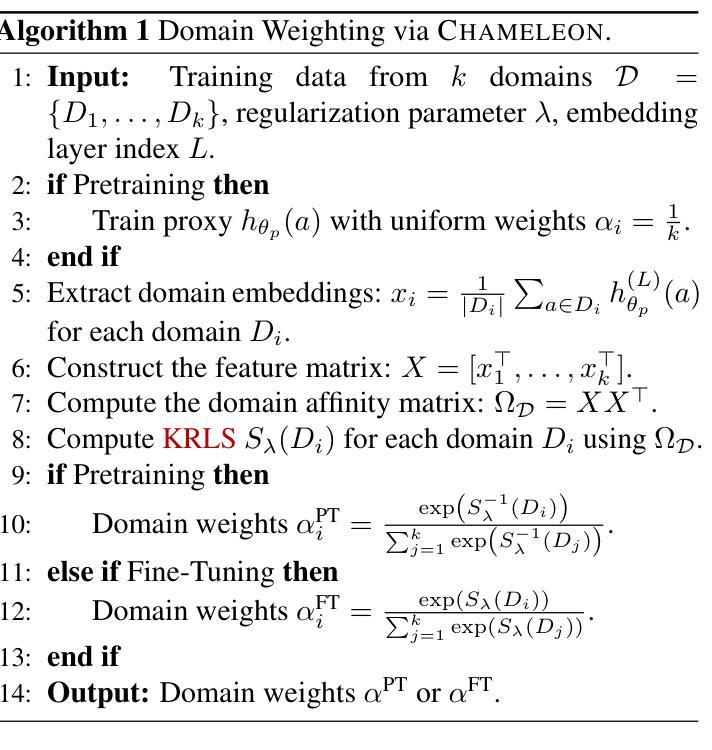
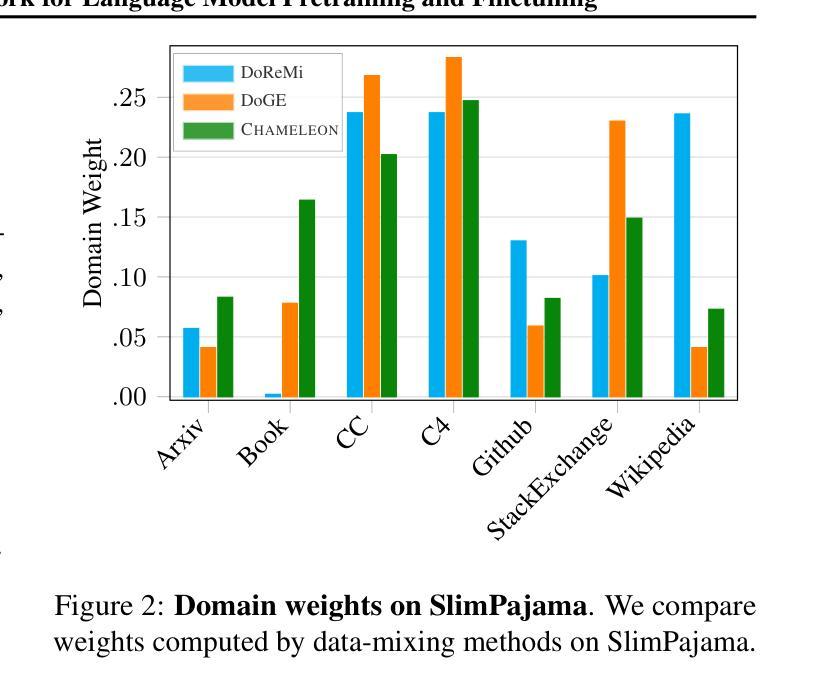
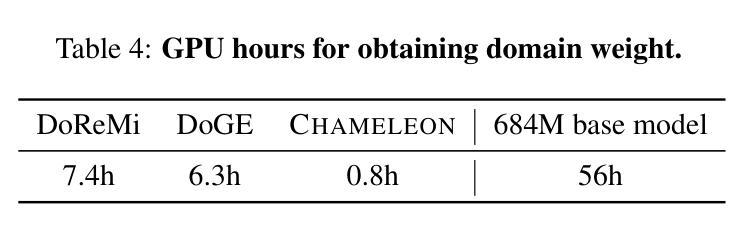
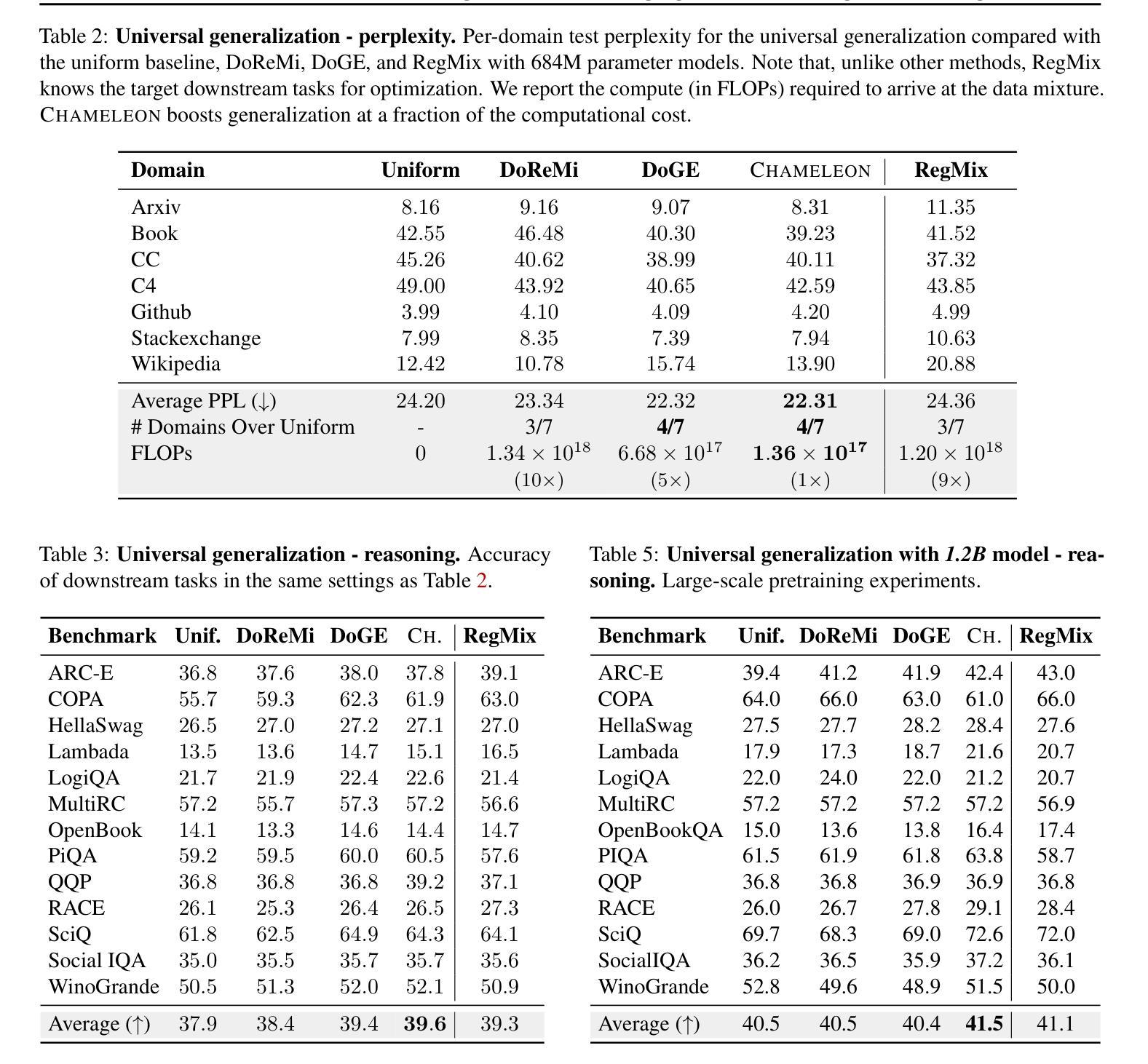
Chameleon: A Flexible Data-mixing Framework for Language Model Pretraining and Finetuning
Authors:Wanyun Xie, Francesco Tonin, Volkan Cevher
Training data mixtures greatly impact the generalization performance of large language models. Existing domain reweighting methods often rely on costly weight computations and require retraining when new data is introduced. To this end, we introduce a flexible and efficient data mixing framework, Chameleon, that employs leverage scores to quantify domain importance within a learned embedding space. We first construct a domain affinity matrix over domain embeddings. The induced leverage scores determine a mixture that upweights domains sharing common representations in embedding space. This formulation allows direct transfer to new data by computing the new domain embeddings. In experiments, we demonstrate improvements over three key scenarios: (i) our computed weights improve performance on pretraining domains with a fraction of the compute of existing methods; (ii) Chameleon can adapt to data changes without proxy retraining, boosting few-shot reasoning accuracies when transferred to new data; (iii) our method enables efficient domain reweighting in finetuning, consistently improving test perplexity on all finetuning domains over uniform mixture. Our code is available at https://github.com/LIONS-EPFL/Chameleon.
训练数据混合物对大型语言模型的泛化性能产生很大影响。现有的领域重权方法通常依赖于昂贵的权重计算,并在引入新数据时需要重新训练。为此,我们引入了一个灵活高效的数据混合框架——变色龙(Chameleon),它利用杠杆分数来衡量学习嵌入空间内的领域重要性。我们首先在领域嵌入之上构建领域亲和矩阵。由此产生的杠杆分数确定了一种混合物,该混合物会提高在嵌入空间中共享共同表示的领域的权重。这种表述方式可以通过计算新的领域嵌入来直接迁移到新的数据上。在实验中,我们在三种关键场景中展示了改进:(i)我们计算的权重在预训练域上的性能优于现有方法,且计算成本只有其一小部分;(ii)变色龙能够适应数据变化,无需代理重新训练,在转移到新数据时提高了少样本推理的准确性;(iii)我们的方法在微调领域的重权效率很高,在所有微调领域的测试困惑度上均优于均匀混合物。我们的代码可在https://github.com/LIONS-EPFL/Chameleon找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
训练数据混合对大型语言模型的泛化性能具有重要影响。现有领域重权方法通常依赖昂贵的权重计算,并在引入新数据时需要重新训练。为此,我们引入了灵活高效的数据混合框架Chameleon,该框架利用杠杆得分在学习的嵌入空间中量化领域重要性。我们首先构建领域亲和矩阵基于领域嵌入。诱导的杠杆得分确定了一种混合,这种混合会提高在嵌入空间中共享共同表示的领域的权重。这种表述允许通过计算新领域嵌入直接转移到新数据。在实验中,我们证明了我们计算出的权重能在预训练领域上提高性能,相较于现有方法使用更少的计算量;Chameleon能够适应数据变化而无需代理重新训练,在转移到新数据时提升了少样本推理的准确性;我们的方法在微调中实现了有效的领域重权,在所有微调领域的测试困惑度上均优于均匀混合。
Key Takeaways
- 训练数据混合对大型语言模型的泛化性能有重要影响。
- 现有领域重权方法成本高且需要频繁重新训练。
- Chameleon框架利用杠杆得分在嵌入空间中量化领域重要性。
- Chameleon通过构建领域亲和矩阵来处理数据混合。
- Chameleon能提高共享共同表示的领域的权重。
- Chameleon允许直接转移到新数据,无需重新训练。
- 在实验测试中,Chameleon在预训练、适应新数据和微调领域上均表现出优势。
点此查看论文截图

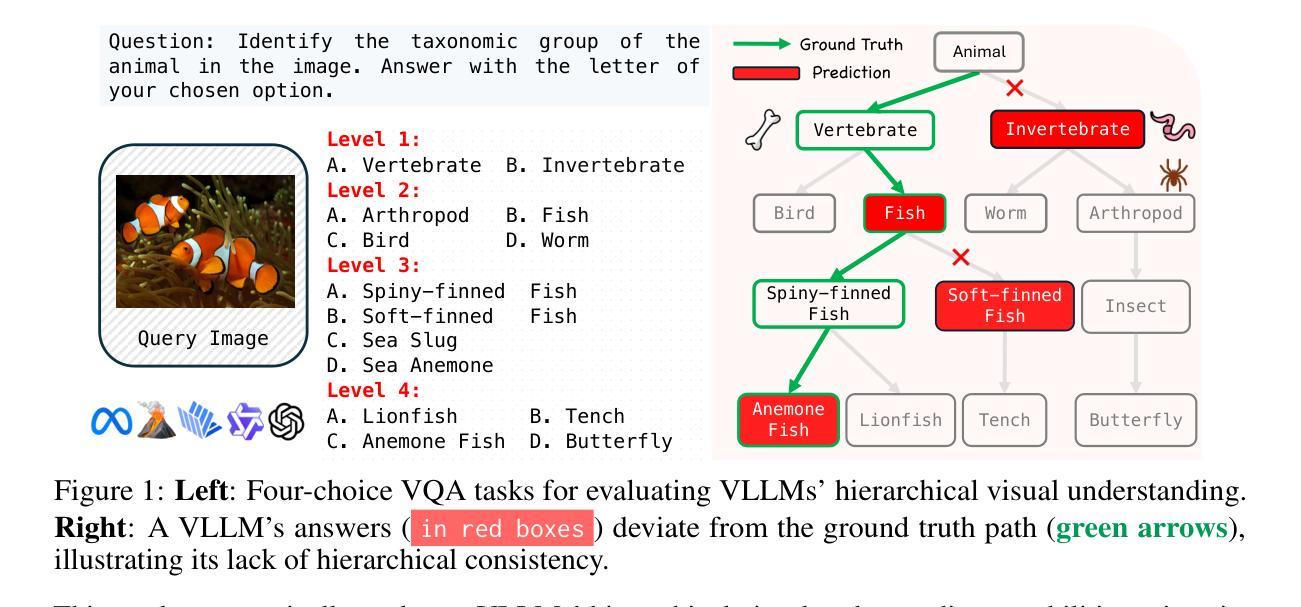
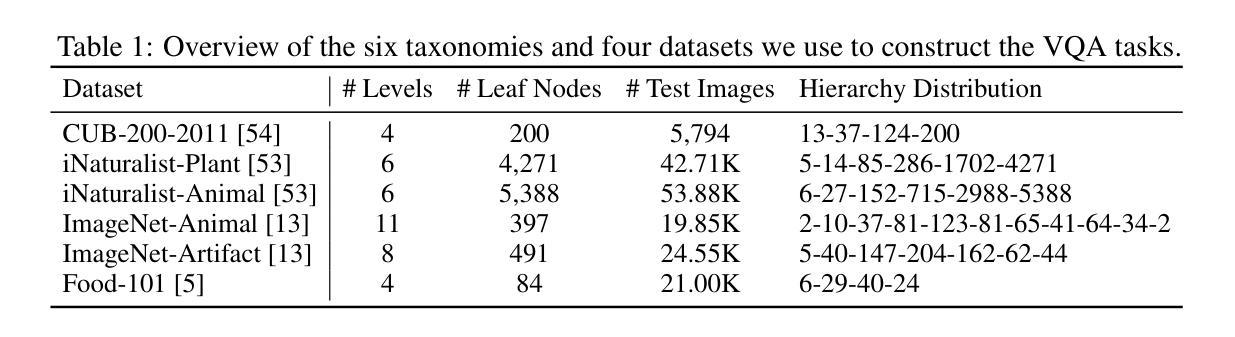
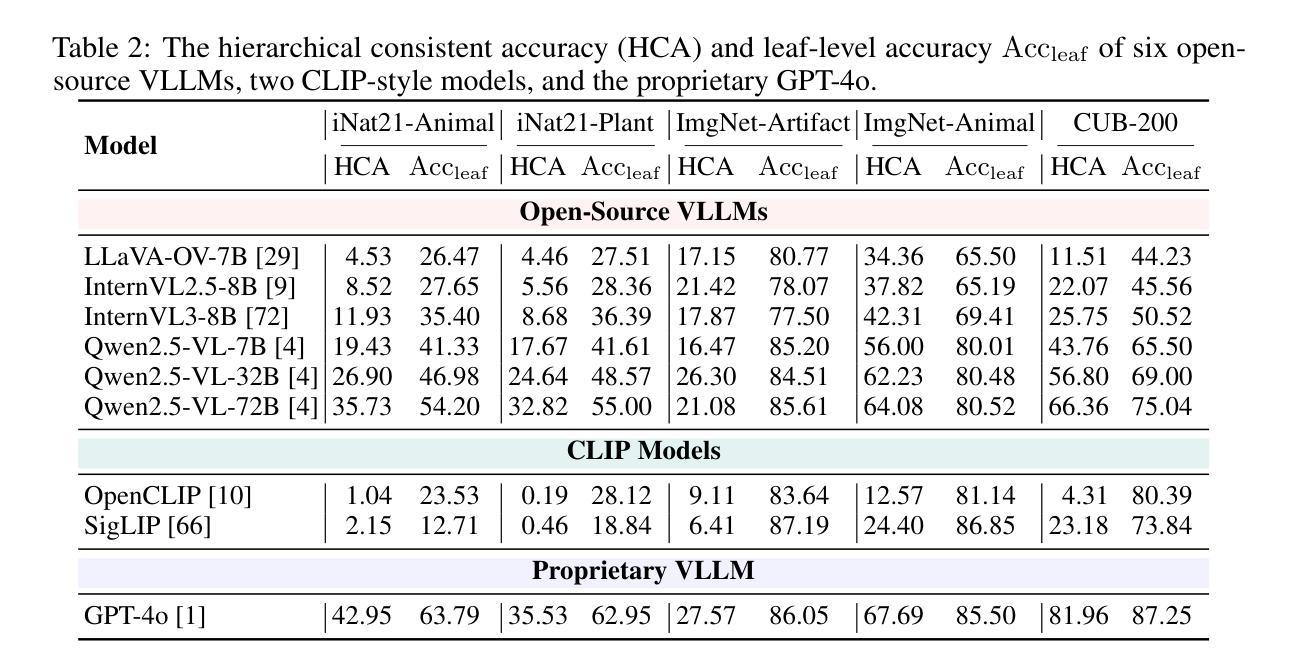
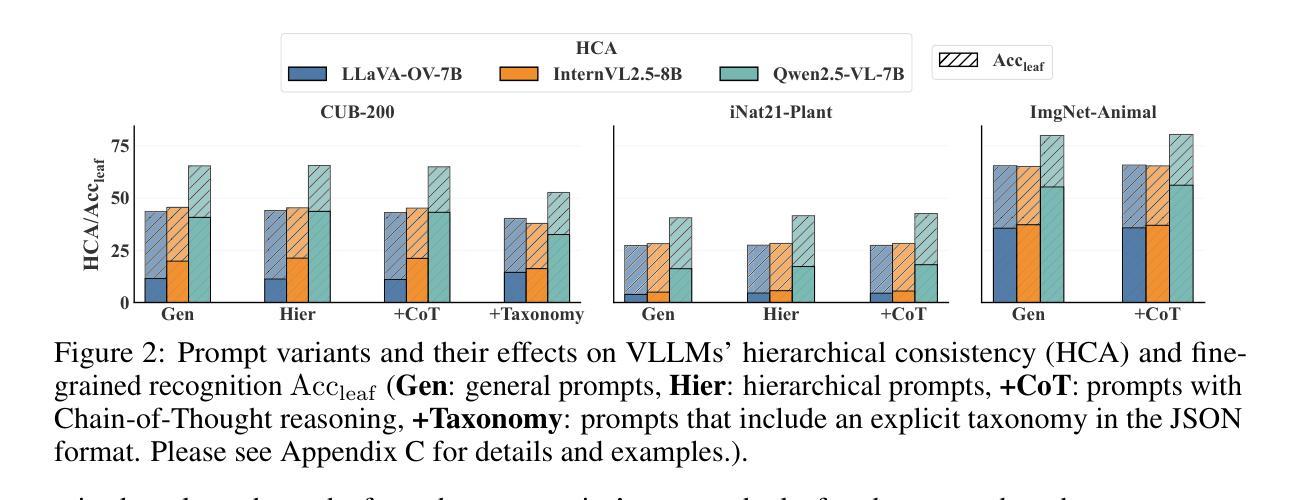
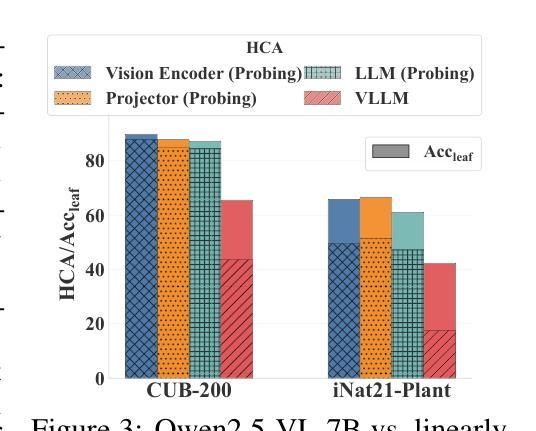
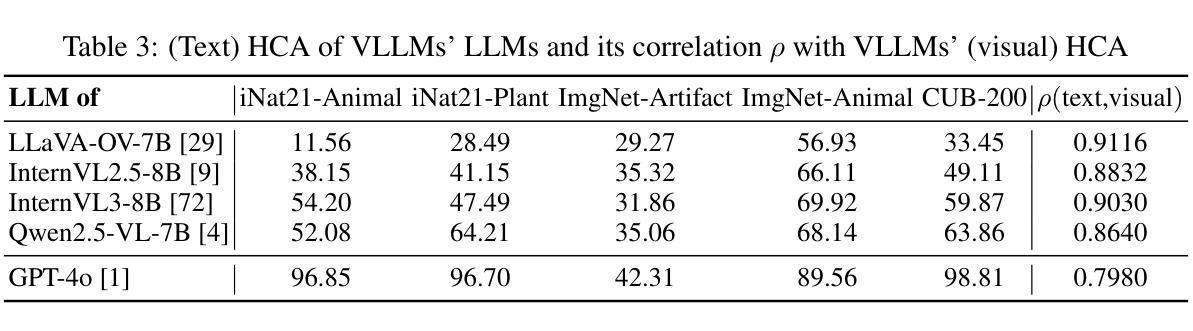
Vision LLMs Are Bad at Hierarchical Visual Understanding, and LLMs Are the Bottleneck
Authors:Yuwen Tan, Yuan Qing, Boqing Gong
This paper reveals that many state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) lack hierarchical knowledge about our visual world, unaware of even well-established biology taxonomies. This shortcoming makes LLMs a bottleneck for vision LLMs’ hierarchical visual understanding (e.g., recognizing Anemone Fish but not Vertebrate). We arrive at these findings using about one million four-choice visual question answering (VQA) tasks constructed from six taxonomies and four image datasets. Interestingly, finetuning a vision LLM using our VQA tasks reaffirms LLMs’ bottleneck effect to some extent because the VQA tasks improve the LLM’s hierarchical consistency more than the vision LLM’s. We conjecture that one cannot make vision LLMs understand visual concepts fully hierarchical until LLMs possess corresponding taxonomy knowledge.
本文揭示了许多最先进的大型语言模型(LLM)缺乏关于我们视觉世界的分层知识,甚至不了解已经确立的生物分类学。这一缺陷使得LLM成为限制视觉LLM分层视觉理解(例如,能识别鳃鳐鱼但不认识脊椎动物)的瓶颈。我们使用从六个分类法和四个图像数据集中构建的约一百万道四选一的视觉问答(VQA)任务得出这些发现。有趣的是,使用我们的VQA任务对视觉LLM进行微调,在一定程度上再次证实了LLM的瓶颈效应,因为VQA任务提高了LLM的层次一致性,但超过了视觉LLM的层次。我们猜想,在LLM拥有相应的分类学知识之前,无法使其完全理解视觉概念的层次结构。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 13 figures
总结
这篇论文揭示了目前最先进的大型语言模型(LLM)缺乏对我们视觉世界的层次知识,甚至对已经确立的生物分类学也不了解。这一缺陷使得LLM成为视觉LLM的层次化视觉理解(例如,识别海鲂鱼但不知道它是脊椎动物)的瓶颈。通过对六种分类法和四种图像数据集构建的约一百万个四选一的视觉问答任务的研究得出了这些发现。有趣的是,使用我们的VQA任务对视觉LLM进行微调,在一定程度上再次确认了LLM的瓶颈效应,因为VQA任务提高了LLM的层次一致性,但超过了对视觉LLM的提高。我们推测,除非LLM拥有相应的分类知识,否则无法使其完全层次化地理解视觉概念。
关键见解
- 先进的LLM缺乏视觉世界的层次知识,对生物分类学也不了解。
- LLM成为视觉LLM在层次化视觉理解方面的瓶颈。
- 通过约一百万个视觉问答任务发现这一缺陷,这些任务是基于六种分类法和四个图像数据集构建的。
- 使用VQA任务微调视觉LLM在一定程度上再次确认了LLM的瓶颈效应。
- VQA任务提高了LLM的层次一致性,但对视觉LLM的提升有限。
- LLM无法完全层次化地理解视觉概念,除非它们拥有相应的分类知识。
点此查看论文截图

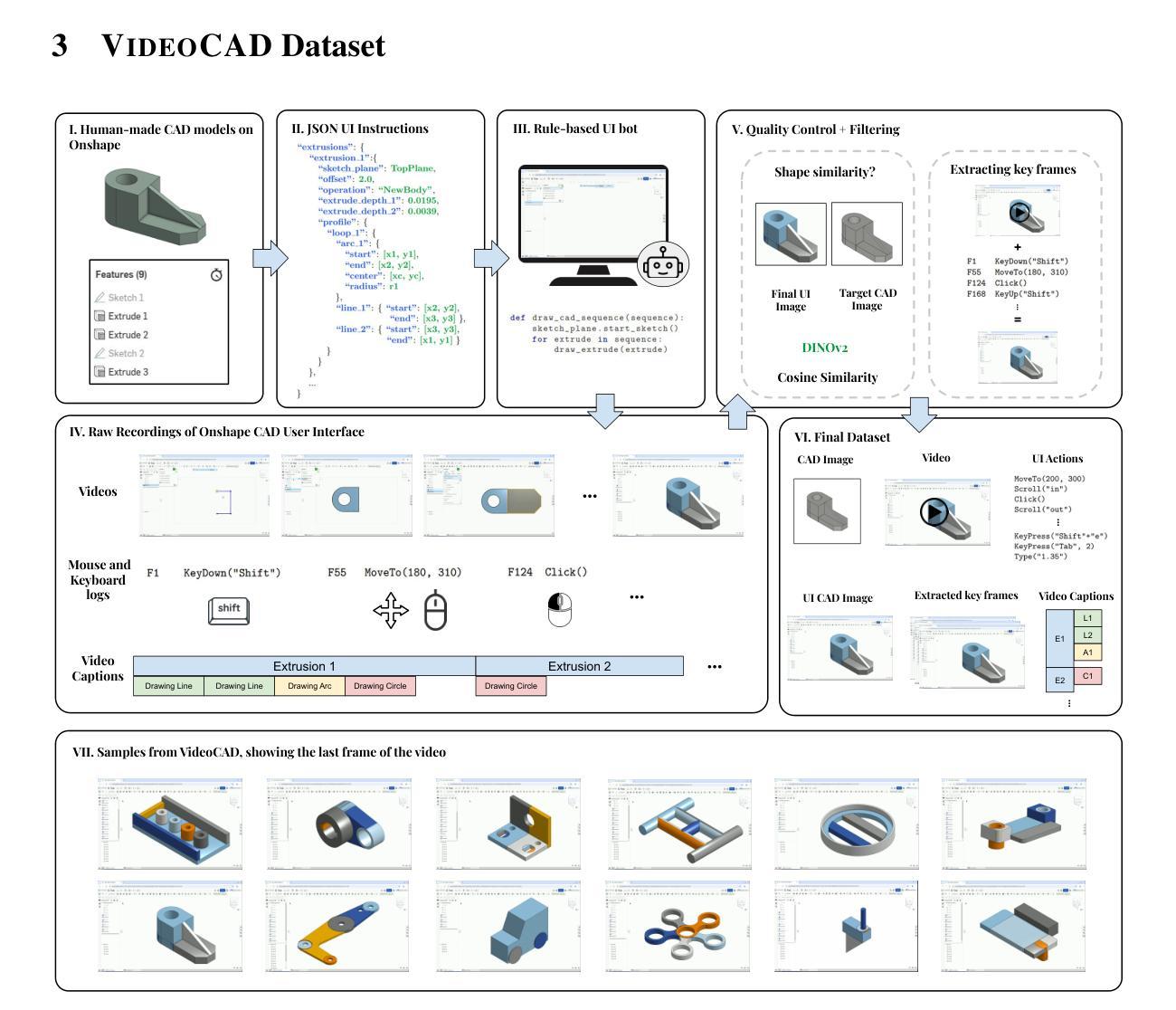
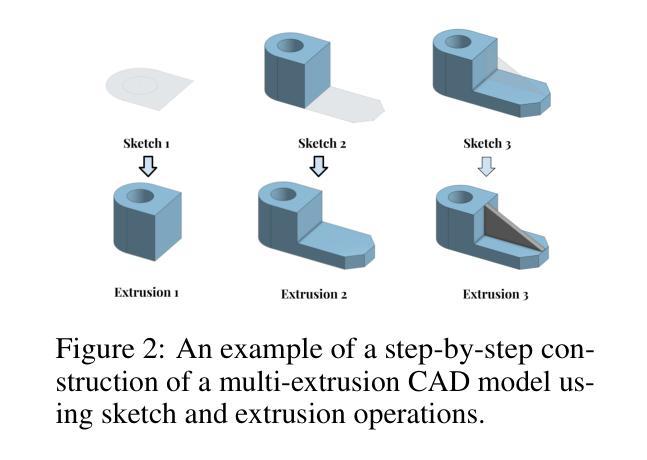
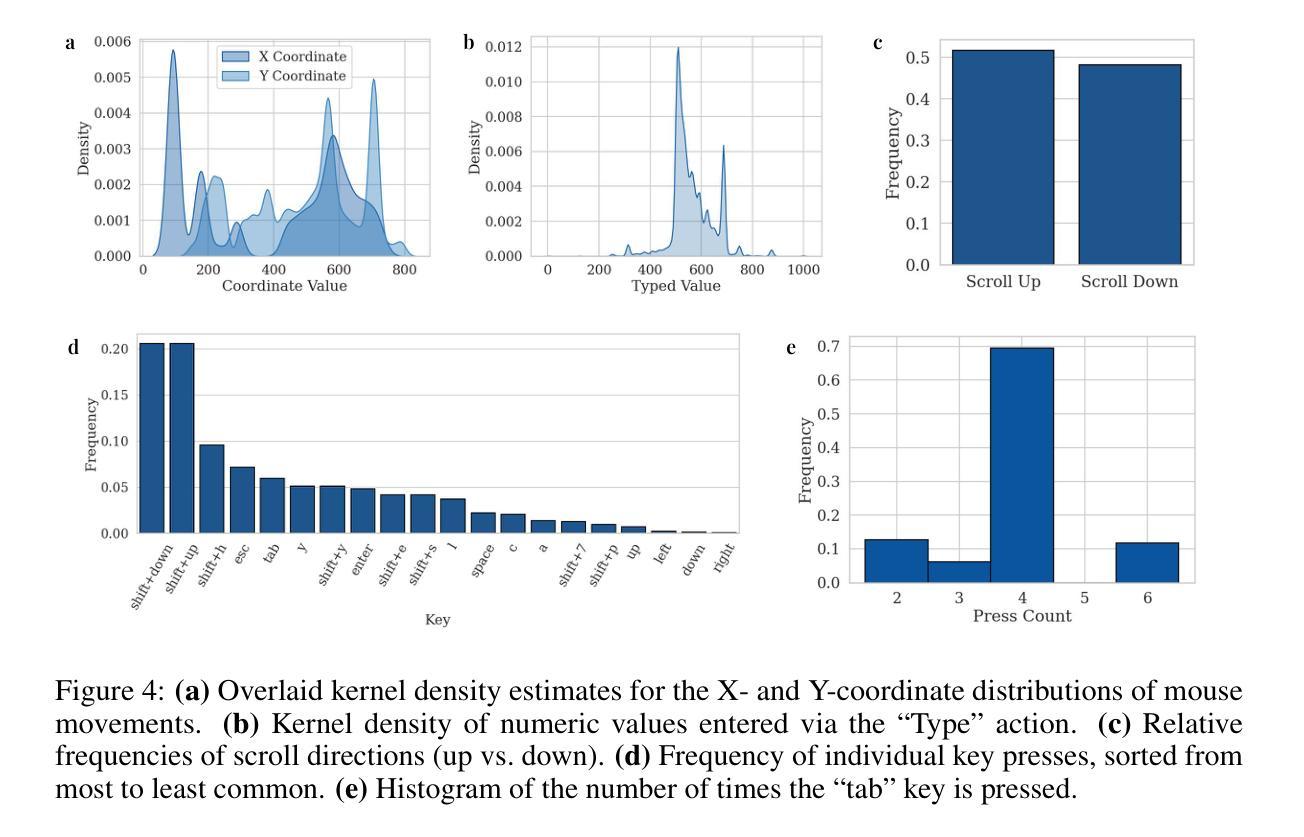
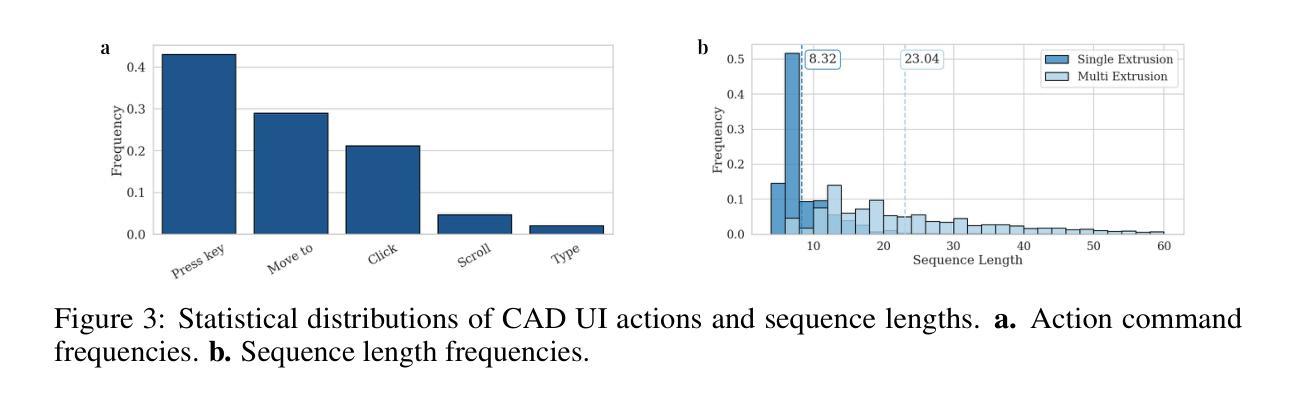
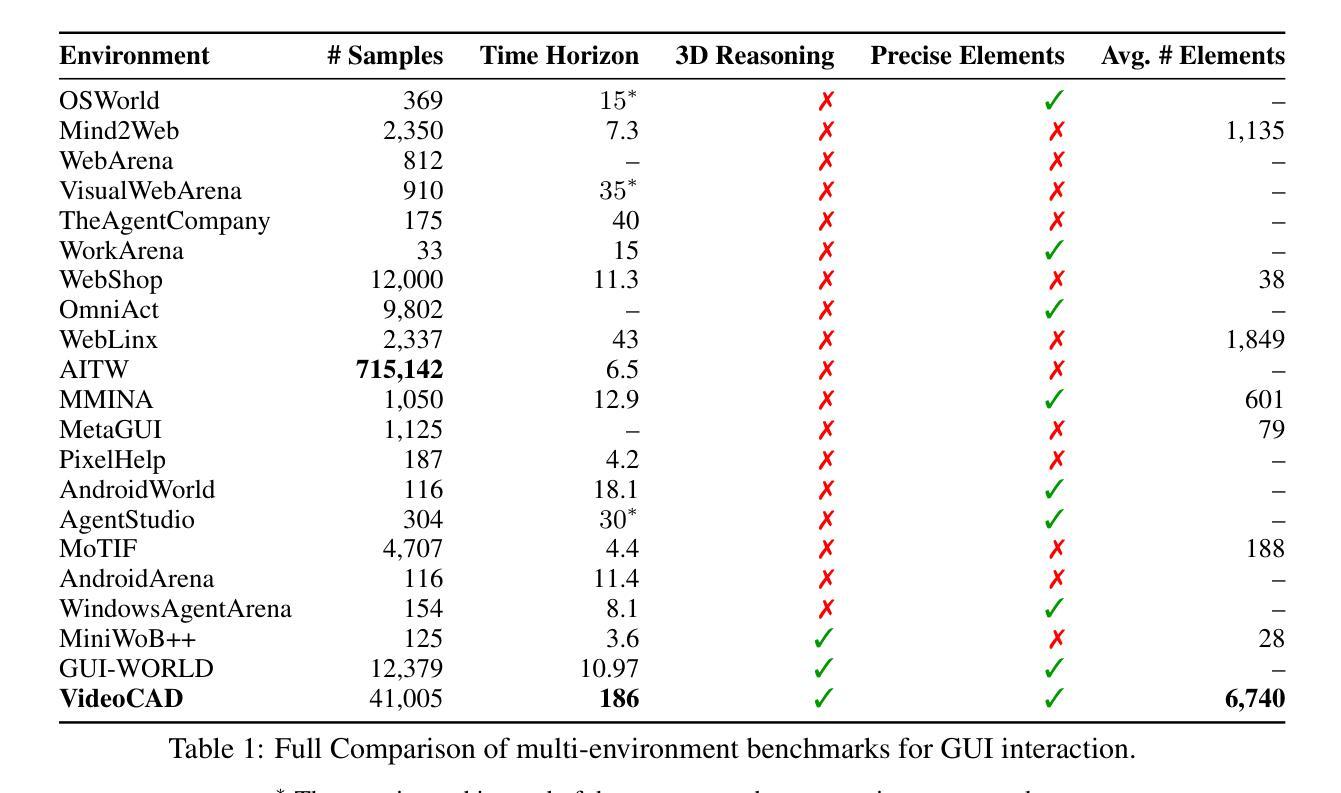
VideoCAD: A Large-Scale Video Dataset for Learning UI Interactions and 3D Reasoning from CAD Software
Authors:Brandon Man, Ghadi Nehme, Md Ferdous Alam, Faez Ahmed
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is a time-consuming and complex process, requiring precise, long-horizon user interactions with intricate 3D interfaces. While recent advances in AI-driven user interface (UI) agents show promise, most existing datasets and methods focus on short, low-complexity tasks in mobile or web applications, failing to capture the demands of professional engineering tools. In this work, we introduce VideoCAD, the first attempt at engineering UI interaction learning for precision tasks. Specifically, VideoCAD is a large-scale synthetic dataset consisting of over 41K annotated video recordings of CAD operations, generated using an automated framework for collecting high-fidelity UI action data from human-made CAD designs. Compared to existing datasets, VideoCAD offers an order of magnitude higher complexity in UI interaction learning for real-world engineering tasks, having up to a 20x longer time horizon than other datasets. We show two important downstream applications of VideoCAD: learning UI interactions from professional precision 3D CAD tools and a visual question-answering (VQA) benchmark designed to evaluate multimodal large language models’ (LLM) spatial reasoning and video understanding abilities. To learn the UI interactions, we propose VideoCADFormer - a state-of-the-art model in learning CAD interactions directly from video, which outperforms multiple behavior cloning baselines. Both VideoCADFormer and the VQA benchmark derived from VideoCAD reveal key challenges in the current state of video-based UI understanding, including the need for precise action grounding, multi-modal and spatial reasoning, and long-horizon dependencies.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)是一个耗时且复杂的过程,需要用户与复杂的3D界面进行精确、长时间的交互。尽管最近人工智能驱动的用户界面(UI)智能体的进步显示出希望,但大多数现有数据集和方法都专注于移动或网页应用程序中的简短、低复杂度任务,未能捕捉到专业工程工具的需求。在这项工作中,我们引入了VideoCAD,这是首次尝试为精密任务进行工程用户界面交互学习。具体来说,VideoCAD是一个大规模合成数据集,包含超过41K个标注的CAD操作视频记录,这些记录是通过自动化框架从人为设计的CAD中收集高保真UI动作数据生成的。与现有数据集相比,VideoCAD在现实世界工程任务的UI交互学习中提供了更高复杂度的数据,时间跨度比其他数据集长达20倍。我们展示了VideoCAD的两个重要下游应用:从专业精密3D CAD工具学习UI交互以及设计用于评估多模态大型语言模型(LLM)空间推理和视频理解能力的视觉问答(VQA)基准测试。为了学习UI交互,我们提出了VideoCADFormer——一个直接从视频学习CAD交互的最新模型,它超越了多个行为克隆基线。VideoCADFormer和从VideoCAD衍生的VQA基准测试揭示了当前视频型用户界面理解的关键挑战,包括精确动作定位、多模态和空间推理以及长期依赖关系的需求。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
CAD设计过程耗时且复杂,需要用户与精细的3D界面进行精确的长周期交互。虽然AI驱动的UI代理展现出潜力,但现有数据集和方法主要关注移动或Web应用程序中的短、低复杂性任务,未能捕捉到专业工程工具的需求。本研究推出VideoCAD,首次尝试工程UI交互学习精确任务。具体来说,VideoCAD是一个大规模合成数据集,包含超过4.1万份经注释的CAD操作视频记录,由一个自动化框架生成,用于从人工CAD设计中收集高保真UI动作数据。相较于现有数据集,VideoCAD在现实世界工程任务的UI交互学习中提供了更高复杂度的数据,时间跨度是其他数据集的20倍。我们展示了VideoCAD的两个重要下游应用:从专业精确3D CAD工具学习UI交互和视觉问答(VQA)基准测试,旨在评估多模态大型语言模型的空间推理和视频理解能力。为了学习UI交互,我们提出了VideoCADFormer——直接从视频学习CAD交互的先进模型,其表现优于多个行为克隆基线。VideoCADFormer和基于VideoCAD的VQA基准测试揭示了当前视频型UI理解的关键挑战,包括精确动作定位、多模态和空间推理以及长周期依赖关系。
关键见解
- VideoCAD是首个针对工程UI交互学习的数据集,专为精确任务设计。
- VideoCAD包含超过4.1万份经注释的CAD操作视频,复杂度高于现有数据集。
- VideoCAD提供了一个评估多模态大型语言模型空间推理和视频理解能力的VQA基准测试。
- VideoCADFormer模型表现出强大的性能,能够直接从视频中学习CAD交互。
- 当前视频型UI理解面临的关键挑战包括精确动作定位、多模态和空间推理以及长周期依赖关系。
- VideoCAD数据集和VideoCADFormer模型有助于推动CAD设计领域的进一步发展。
点此查看论文截图

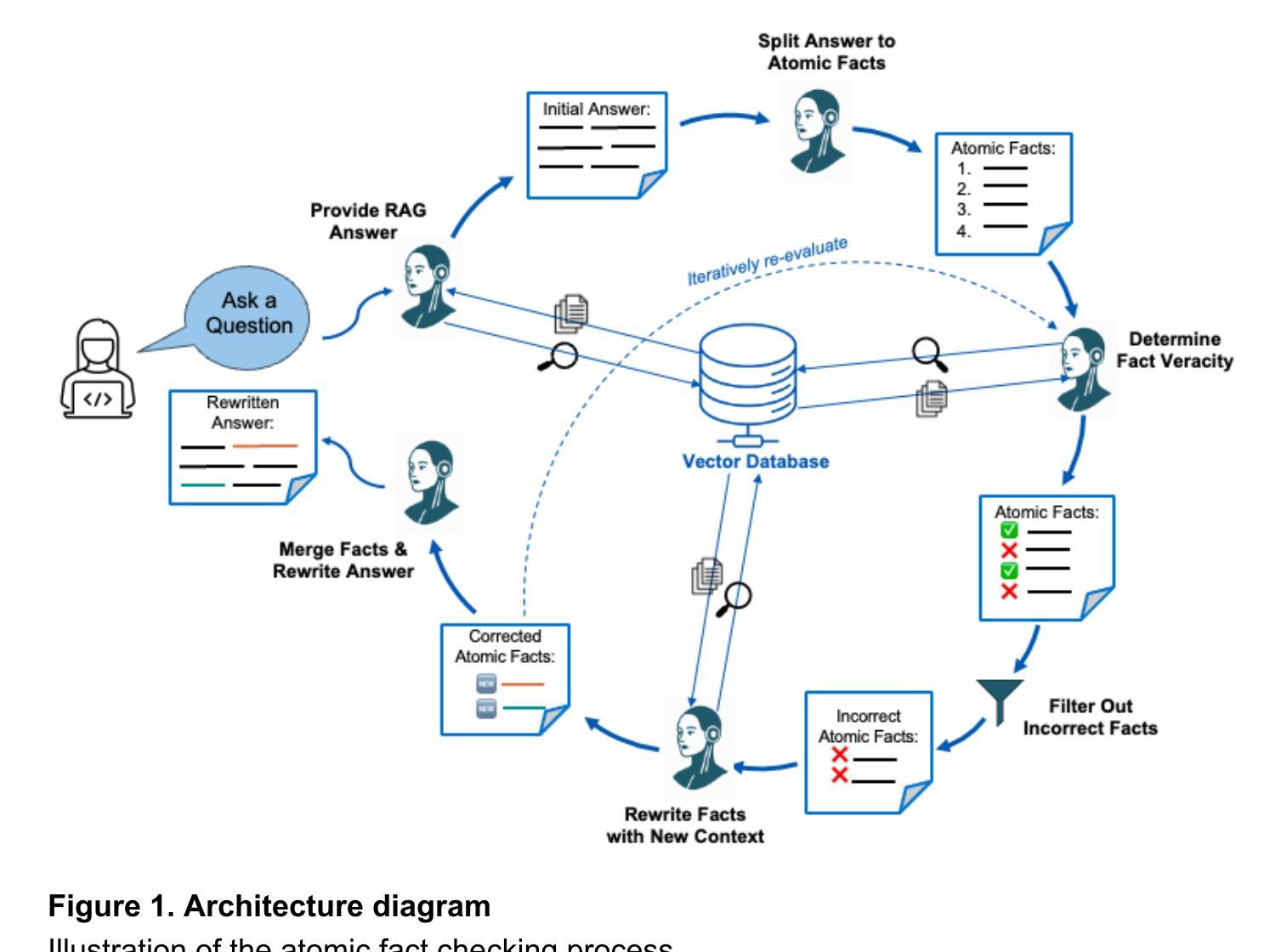
Improving Reliability and Explainability of Medical Question Answering through Atomic Fact Checking in Retrieval-Augmented LLMs
Authors:Juraj Vladika, Annika Domres, Mai Nguyen, Rebecca Moser, Jana Nano, Felix Busch, Lisa C. Adams, Keno K. Bressem, Denise Bernhardt, Stephanie E. Combs, Kai J. Borm, Florian Matthes, Jan C. Peeken
Large language models (LLMs) exhibit extensive medical knowledge but are prone to hallucinations and inaccurate citations, which pose a challenge to their clinical adoption and regulatory compliance. Current methods, such as Retrieval Augmented Generation, partially address these issues by grounding answers in source documents, but hallucinations and low fact-level explainability persist. In this work, we introduce a novel atomic fact-checking framework designed to enhance the reliability and explainability of LLMs used in medical long-form question answering. This method decomposes LLM-generated responses into discrete, verifiable units called atomic facts, each of which is independently verified against an authoritative knowledge base of medical guidelines. This approach enables targeted correction of errors and direct tracing to source literature, thereby improving the factual accuracy and explainability of medical Q&A. Extensive evaluation using multi-reader assessments by medical experts and an automated open Q&A benchmark demonstrated significant improvements in factual accuracy and explainability. Our framework achieved up to a 40% overall answer improvement and a 50% hallucination detection rate. The ability to trace each atomic fact back to the most relevant chunks from the database provides a granular, transparent explanation of the generated responses, addressing a major gap in current medical AI applications. This work represents a crucial step towards more trustworthy and reliable clinical applications of LLMs, addressing key prerequisites for clinical application and fostering greater confidence in AI-assisted healthcare.
大型语言模型(LLM)虽然展现出丰富的医学知识,但容易出现幻觉和不准确的引用,这对它们在临床上的应用和合规性构成挑战。当前的方法,如检索增强生成法,通过基于源文档的答案来部分解决这些问题,但幻觉和较低的事实层面解释性仍然存在。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 4 figures
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在医学领域展现出丰富的知识,但存在易产生幻觉和引用不准确的问题,这对其在临床应用和法规遵循方面带来挑战。现有方法如检索增强生成技术虽能部分解决这些问题,但幻觉和事实层面解释性不足的问题依然存在。本研究引入了一种新型原子事实核查框架,旨在提高用于医学长文本问答的LLM的可靠性和解释性。该方法将LLM生成的回答分解成离散的可验证单位,即原子事实,每个原子事实都会与权威医学准则知识库进行独立验证。此方法能够针对性纠正错误并直接追溯至源文献,从而提高医学问答的准确度和解释性。经医学专家多读者评估和自动化开放问答基准测试显示,该方法在事实准确度和解释性方面有显著提高,整体回答改善率最高达40%,幻觉检测率高达50%。本框架将每个原子事实追溯至最相关的数据库片段,为生成回答提供了精细、透明的解释,解决了当前医学人工智能应用中的主要缺口。本研究是向临床应用中更可靠、更值得信赖的LLM应用迈出重要一步,满足了临床应用的关键先决条件,为人工智能辅助医疗保健领域带来更大信心。
Key Takeaways
- LLM展现出丰富的医学知识,但存在幻觉和引用不准确的问题。
- 现有方法如检索增强生成技术虽能解决部分问题,但幻觉和事实解释性不足仍然存在。
- 新型原子事实核查框架旨在提高LLM在医学长文本问答中的可靠性和解释性。
- 框架将回答分解成离散的可验证单位(原子事实),并与权威医学准则知识库进行独立验证。
- 该方法能提高医学问答的准确度和解释性,通过追溯至源文献减少错误。
- 评估显示,框架整体回答改善率最高达40%,幻觉检测率高达50%。
点此查看论文截图

LegalEval-Q: A New Benchmark for The Quality Evaluation of LLM-Generated Legal Text
Authors:Li yunhan, Wu gengshen
As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used in legal applications, current evaluation benchmarks tend to focus mainly on factual accuracy while largely neglecting important linguistic quality aspects such as clarity, coherence, and terminology. To address this gap, we propose three steps: First, we develop a regression model to evaluate the quality of legal texts based on clarity, coherence, and terminology. Second, we create a specialized set of legal questions. Third, we analyze 49 LLMs using this evaluation framework. Our analysis identifies three key findings: First, model quality levels off at 14 billion parameters, with only a marginal improvement of $2.7%$ noted at 72 billion parameters. Second, engineering choices such as quantization and context length have a negligible impact, as indicated by statistical significance thresholds above 0.016. Third, reasoning models consistently outperform base architectures. A significant outcome of our research is the release of a ranking list and Pareto analysis, which highlight the Qwen3 series as the optimal choice for cost-performance tradeoffs. This work not only establishes standardized evaluation protocols for legal LLMs but also uncovers fundamental limitations in current training data refinement approaches. Code and models are available at: https://github.com/lyxx3rd/LegalEval-Q.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)在法律应用中的使用越来越普遍,当前的评估基准往往主要关注事实准确性,而很大程度上忽视了重要的语言质量方面,如清晰度、连贯性和术语。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了三个步骤:首先,我们开发了一个回归模型,基于清晰度、连贯性和术语来评估法律文本的质量。其次,我们创建了一套专门的法律问题。最后,我们使用此评估框架分析了49个LLM。我们的分析得出了三个关键发现:首先,模型质量在14亿参数时达到稳定水平,仅在72亿参数时观察到2.7%的边际改进。其次,工程选择如量化和上下文长度的影响微乎其微,如统计显著性阈值高于0.016所示。第三,推理模型始终优于基础架构。我们研究的重大成果之一是发布排名列表和帕累托分析,这突显了Qwen3系列在成本性能权衡方面的最佳选择。这项工作不仅为法律LLM建立了标准化的评估协议,还揭示了当前训练数据改进方法的基本局限性。代码和模型可在以下网址找到:[https://github.com/lyxx3rd/LegalEval-Q。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 11 figures
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)在法律应用中的评价现状,当前评价基准主要集中在事实准确性上,而忽视了语言质量的关键要素如清晰度、连贯性和术语等。本文提出了一个全面的评估框架,旨在解决这一问题。首先,通过回归模型评估法律文本质量;其次,制定专业法律问题集;最后,对49个LLM进行分析评价。研究发现模型质量在达到一定参数规模后趋于稳定,工程选择如量化和上下文长度对性能影响甚微,而推理模型表现较好。本研究不仅建立了标准化的法律LLM评估协议,还揭示了当前训练数据优化方法的基本局限性。
Key Takeaways
- 当前LLM在法律应用中的评价主要关注事实准确性,忽视了语言质量的关键要素。
- 提出的评估框架包含回归模型评估法律文本质量、制定专业法律问题集以及对LLM进行分析评价。
- 模型质量在达到一定参数规模后趋于稳定,增加参数带来的性能提升有限。
- 工程选择如量化和上下文长度对LLM性能的影响不显著。
- 推理模型在法律文本处理中表现较好。
- 研究建立了标准化的法律LLM评估协议。
- 揭示了当前训练数据优化方法的基本局限性。
点此查看论文截图


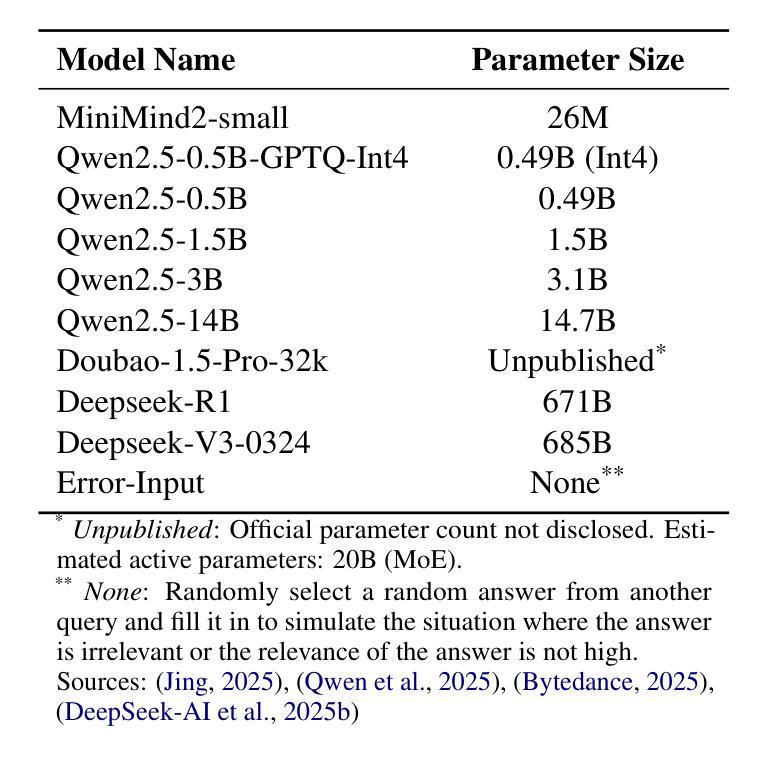
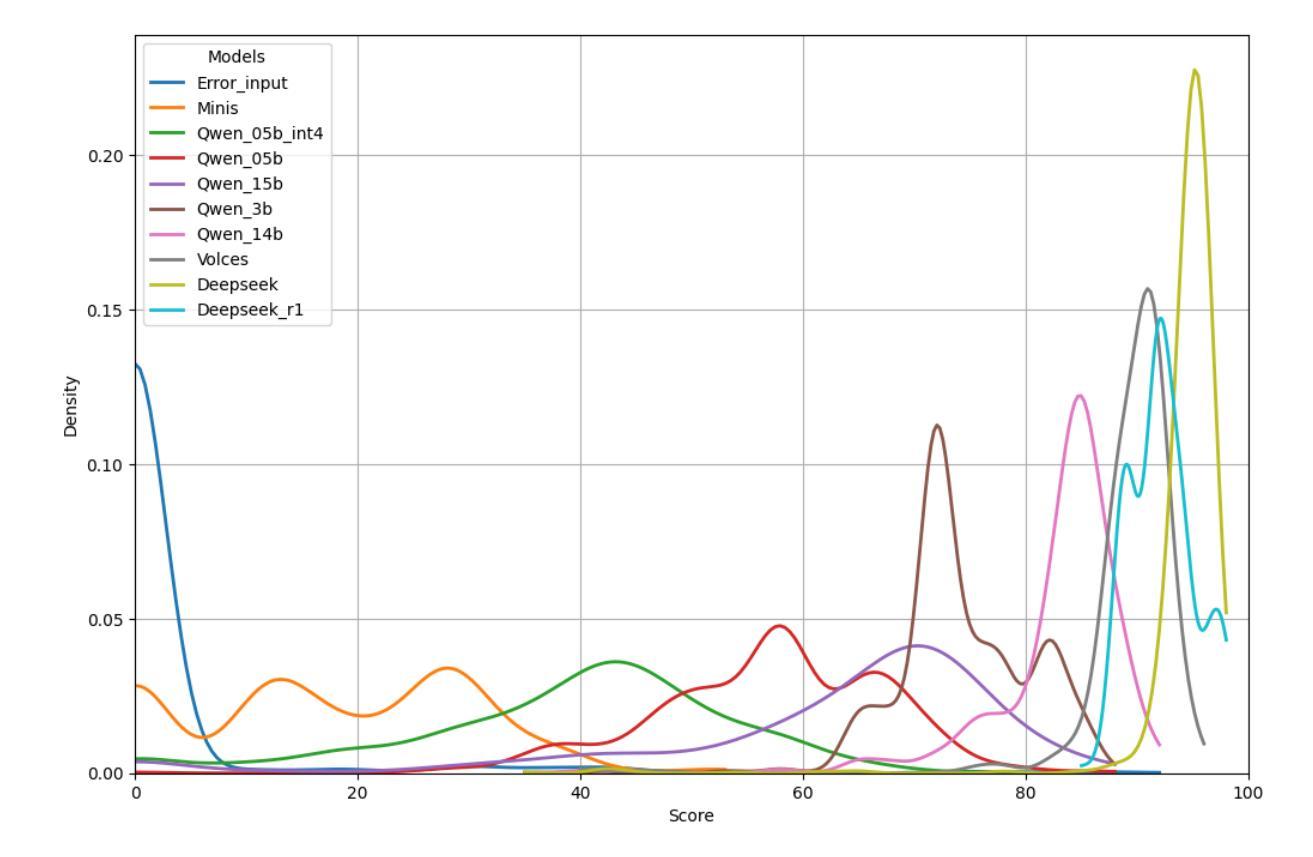
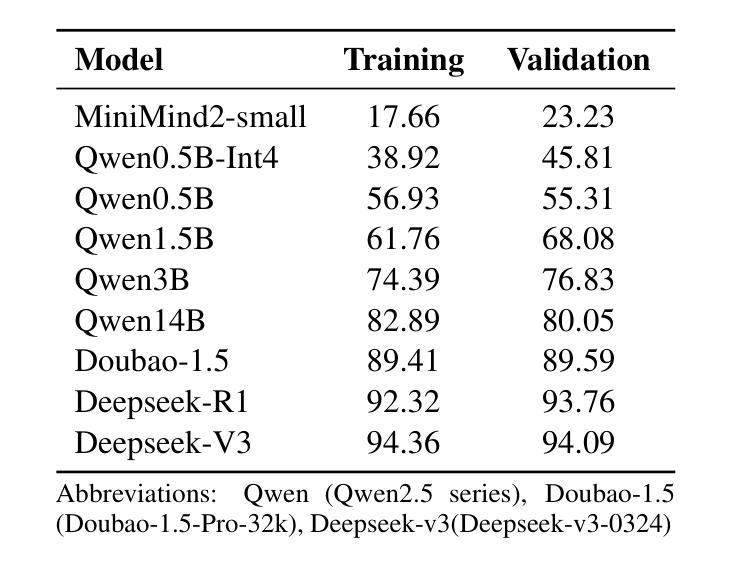
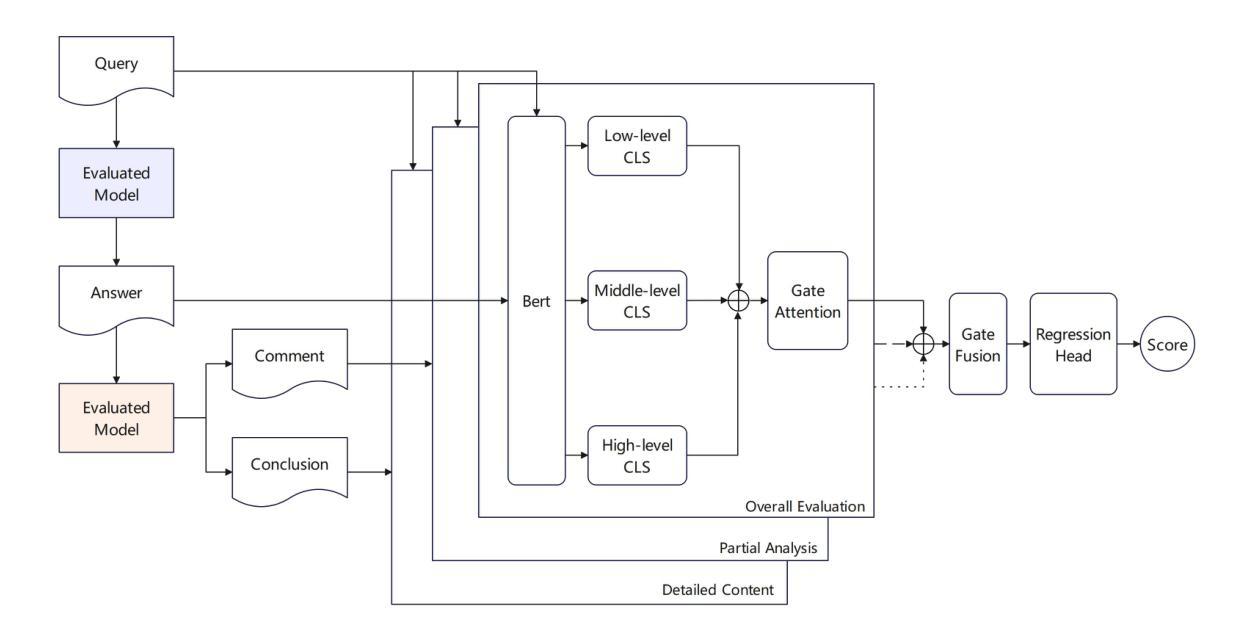
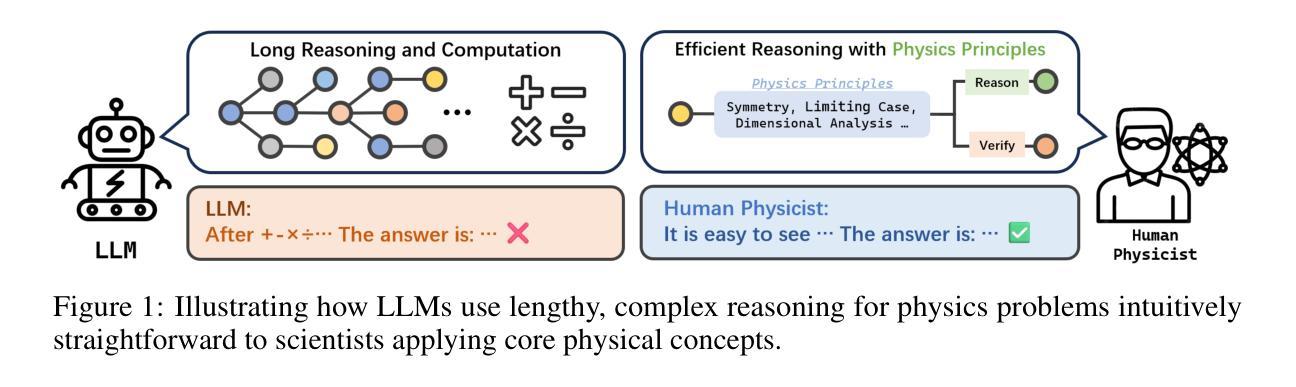
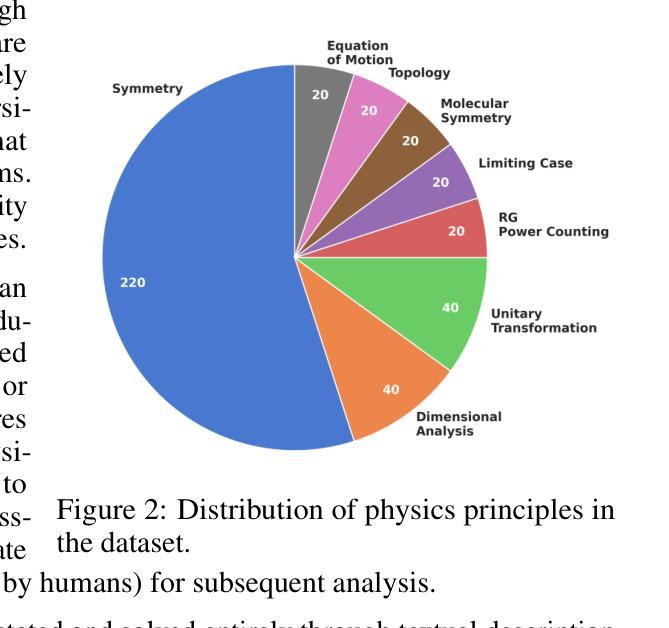
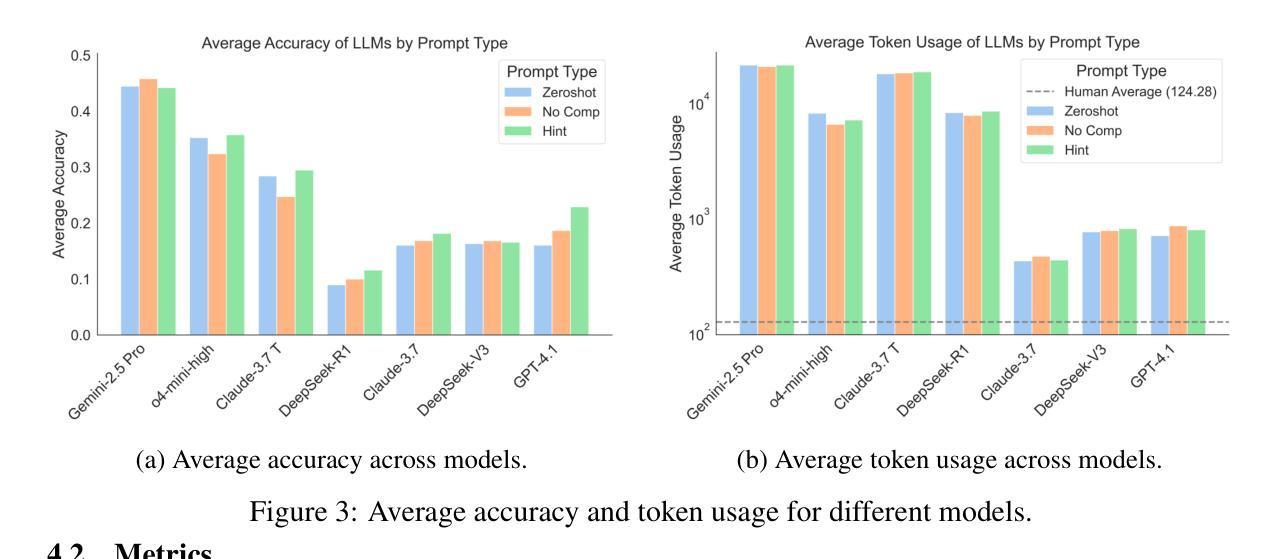
PhySense: Principle-Based Physics Reasoning Benchmarking for Large Language Models
Authors:Yinggan Xu, Yue Liu, Zhiqiang Gao, Changnan Peng, Di Luo
Large language models (LLMs) have rapidly advanced and are increasingly capable of tackling complex scientific problems, including those in physics. Despite this progress, current LLMs often fail to emulate the concise, principle-based reasoning characteristic of human experts, instead generating lengthy and opaque solutions. This discrepancy highlights a crucial gap in their ability to apply core physical principles for efficient and interpretable problem solving. To systematically investigate this limitation, we introduce PhySense, a novel principle-based physics reasoning benchmark designed to be easily solvable by experts using guiding principles, yet deceptively difficult for LLMs without principle-first reasoning. Our evaluation across multiple state-of-the-art LLMs and prompt types reveals a consistent failure to align with expert-like reasoning paths, providing insights for developing AI systems with efficient, robust and interpretable principle-based scientific reasoning.
大型语言模型(LLM)迅速进步,越来越能够解决复杂的科学问题,包括物理学问题。尽管取得了这样的进展,但当前的大型语言模型通常无法模仿人类专家的简洁、基于原则的逻辑推理,而是生成冗长且晦涩的解决方案。这种差异突显了它们在应用核心物理原理进行高效、可解释的问题解决能力上的重要差距。为了系统地研究这一局限性,我们引入了PhySense,这是一个基于原则的物理推理基准测试,专家使用指导原则可以轻松解决,而对于没有先进行原则推理的大型语言模型来说却具有欺骗性难度。我们在多个尖端的大型语言模型和提示类型上的评估显示,它们无法与类似专家的推理路径保持一致,这为开发具有高效、稳健和可解释的原则基础的AI系统提供了见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在解决复杂的科学问题,包括物理问题方面取得了快速进展。然而,它们往往无法模仿人类专家的简洁、基于原则的逻辑推理,而是生成冗长且晦涩的解决方案。为解决这一差距,我们引入了PhySense,这是一个新的基于原则的物理推理基准测试,易于专家通过遵循原则解决,但对缺乏原则优先推理的LLM来说却具有欺骗性难度。对多个先进的LLM和提示类型的评估显示,它们无法按照专家式的推理路径进行对齐,这为开发具有高效、稳健和可解释的基于原则的科学推理的AI系统提供了见解。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在解决复杂的科学问题,包括物理问题上取得了显著进展。
- LLMs在模拟人类专家的简洁、基于原则的逻辑推理方面存在差距。
- PhySense是一个新的基于原则的物理推理基准测试,旨在评估LLMs在遵循核心物理原则方面的能力。
- PhySense对于人类专家来说易于解决,但对LLMs来说具有欺骗性难度。
- 对多个先进的LLM的评估显示,它们在遵循专家式的推理路径方面存在困难。
- 这一研究为开发具有高效、稳健和可解释的基于原则的科学推理的AI系统提供了见解。
点此查看论文截图

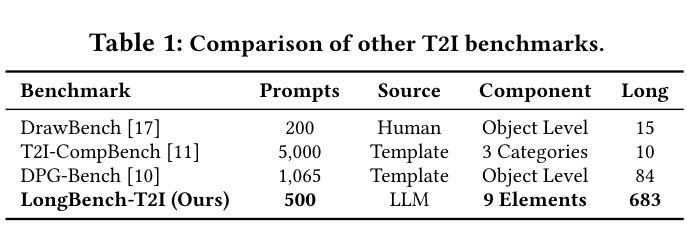
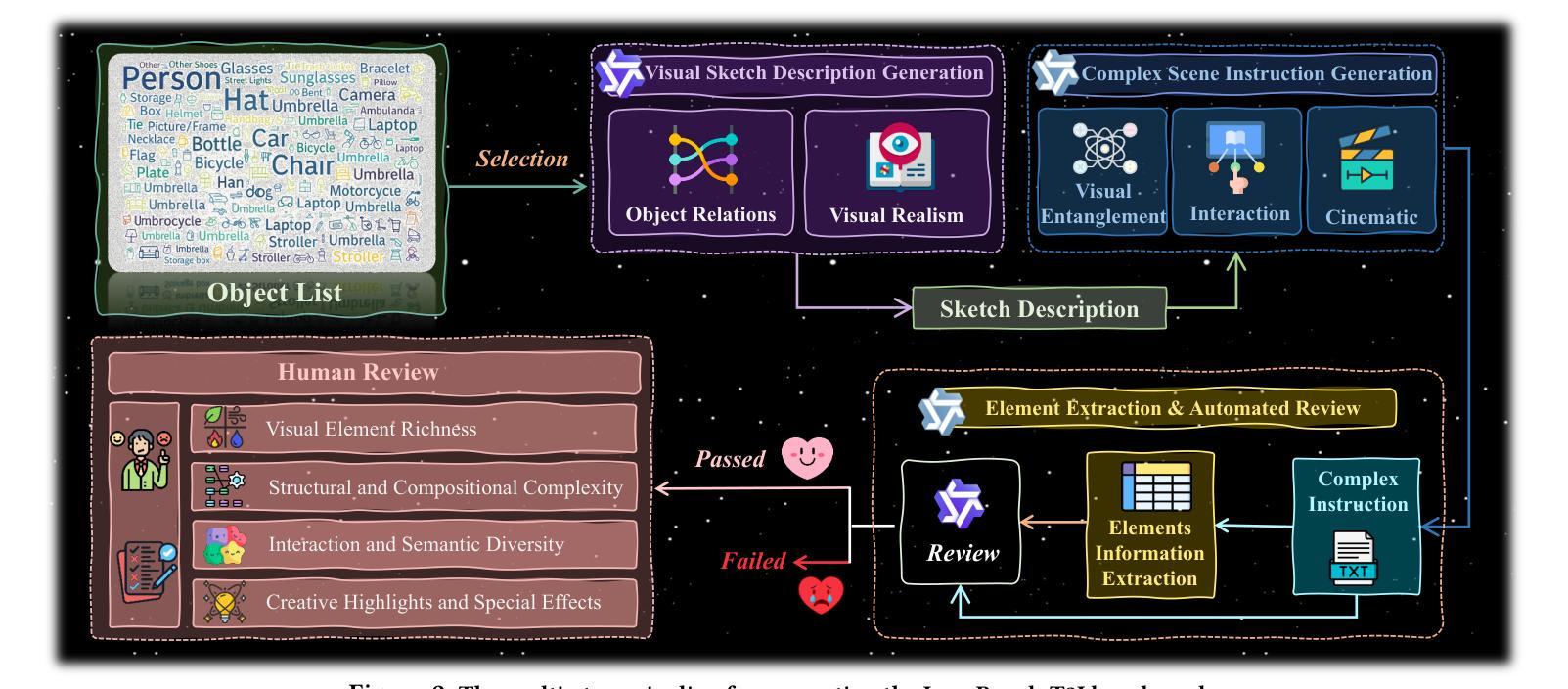
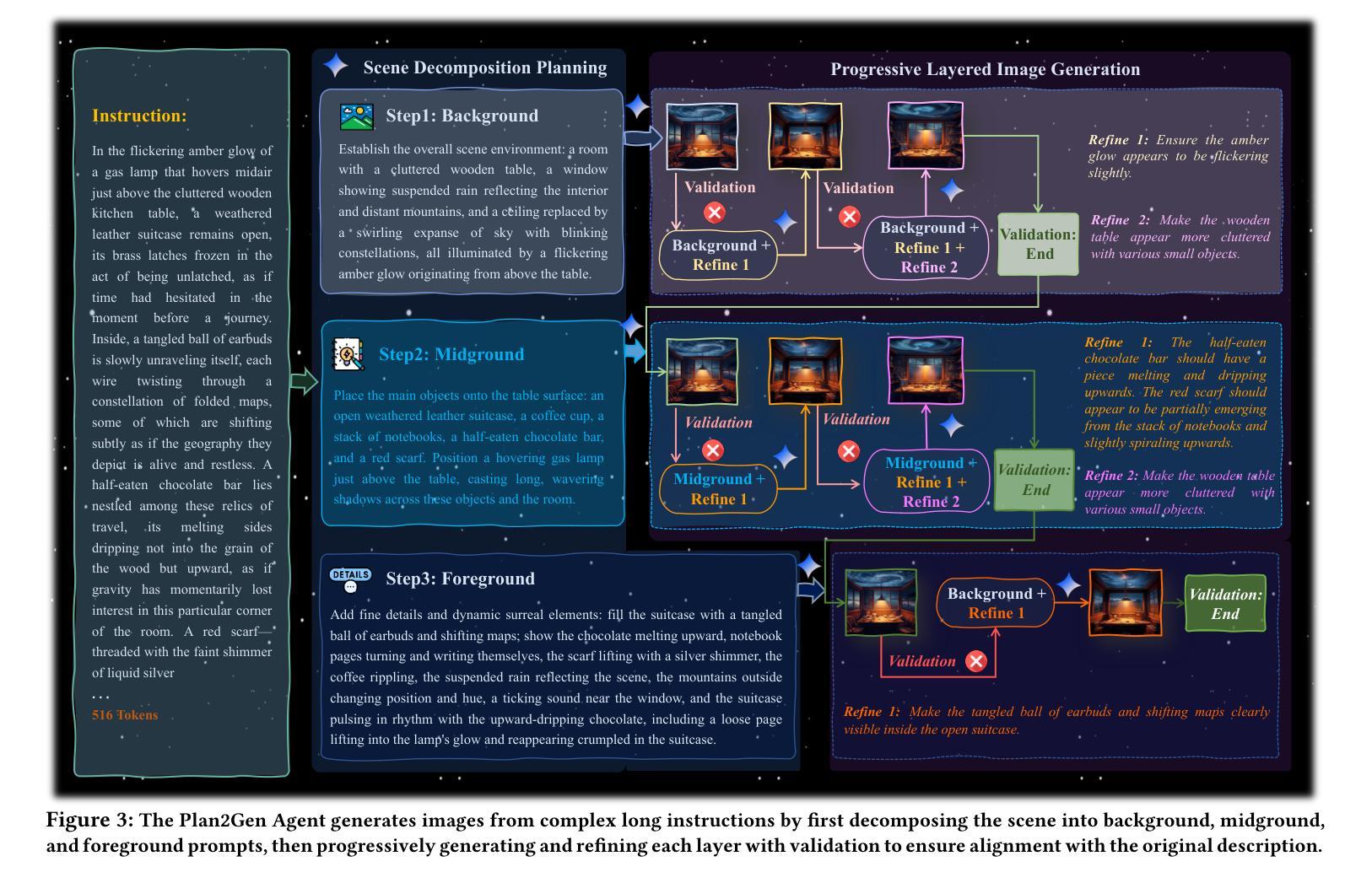
Draw ALL Your Imagine: A Holistic Benchmark and Agent Framework for Complex Instruction-based Image Generation
Authors:Yucheng Zhou, Jiahao Yuan, Qianning Wang
Recent advancements in text-to-image (T2I) generation have enabled models to produce high-quality images from textual descriptions. However, these models often struggle with complex instructions involving multiple objects, attributes, and spatial relationships. Existing benchmarks for evaluating T2I models primarily focus on general text-image alignment and fail to capture the nuanced requirements of complex, multi-faceted prompts. Given this gap, we introduce LongBench-T2I, a comprehensive benchmark specifically designed to evaluate T2I models under complex instructions. LongBench-T2I consists of 500 intricately designed prompts spanning nine diverse visual evaluation dimensions, enabling a thorough assessment of a model’s ability to follow complex instructions. Beyond benchmarking, we propose an agent framework (Plan2Gen) that facilitates complex instruction-driven image generation without requiring additional model training. This framework integrates seamlessly with existing T2I models, using large language models to interpret and decompose complex prompts, thereby guiding the generation process more effectively. As existing evaluation metrics, such as CLIPScore, fail to adequately capture the nuances of complex instructions, we introduce an evaluation toolkit that automates the quality assessment of generated images using a set of multi-dimensional metrics. The data and code are released at https://github.com/yczhou001/LongBench-T2I.
近期文本到图像(T2I)生成技术的进展使得模型能够从文本描述中生成高质量图像。然而,这些模型在处理涉及多个对象、属性和空间关系的复杂指令时常常遇到困难。现有的评估T2I模型的基准测试主要关注于文本与图像的一般对齐,无法捕捉到复杂、多角度提示的细微要求。鉴于此,我们推出了LongBench-T2I,这是一个专为在复杂指令下评估T2I模型而设计的全面基准测试。LongBench-T2I包含500个精心设计提示,涵盖九个不同的视觉评估维度,能够对模型遵循复杂指令的能力进行全面评估。除了基准测试,我们还提出了一个代理框架(Plan2Gen),它可以在不需要额外模型训练的情况下,促进复杂指令驱动的图像生成。该框架无缝集成到现有的T2I模型中,利用大型语言模型来解释和分解复杂的提示,从而更有效地指导生成过程。由于现有的评估指标(如CLIPScore)无法充分捕捉复杂指令的细微差别,我们引入了一个评估工具包,该工具包使用一套多维度指标自动评估生成图像的质量。数据和代码已发布在https://github.com/yczhou001/LongBench-T2I。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
近期文本到图像生成技术的进展使得模型能够从文本描述生成高质量图像。然而,当面对涉及多个物体、属性和空间关系的复杂指令时,这些模型往往表现不佳。当前评估文本到图像模型的基准测试主要关注文本与图像的总体对齐,忽略了复杂、多面提示的细微要求。针对这一差距,我们推出LongBench-T2I基准测试,旨在评估文本到图像模型在复杂指令下的表现。LongBench-T2I包含500个精心设计的提示,涵盖九个不同的视觉评估维度,全面评估模型遵循复杂指令的能力。此外,我们还提出了一个代理框架(Plan2Gen),可在无需额外模型训练的情况下,促进复杂指令驱动的图像生成。该框架可无缝集成现有文本到图像模型,利用大型语言模型解释和分解复杂提示,更有效地引导生成过程。由于现有评估指标如CLIPScore无法充分捕捉复杂指令的细微差别,我们推出一个评估工具包,使用多维度指标自动评估生成图像的质量。相关数据和代码已发布在https://github.com/yczhou001/LongBench-T2I。
关键见解
- 文本到图像生成技术虽然能从文本描述生成高质量图像,但在处理涉及多个物体、属性和空间关系的复杂指令时表现欠佳。
- 当前评估文本到图像模型的基准测试主要关注文本与图像的总体对齐,忽略了复杂提示的细微要求。
- LongBench-T2I基准测试旨在全面评估模型在复杂指令下的表现,包含500个精心设计的提示和九个视觉评估维度。
- 推出Plan2Gen代理框架,可在无需额外模型训练的情况下促进复杂指令驱动的图像生成。
- Plan2Gen框架利用大型语言模型解释和分解复杂提示,更有效地引导生成过程。
- 现有评估指标如CLIPScore无法充分捕捉复杂指令的细微差别,因此需要新的评估工具包。
点此查看论文截图

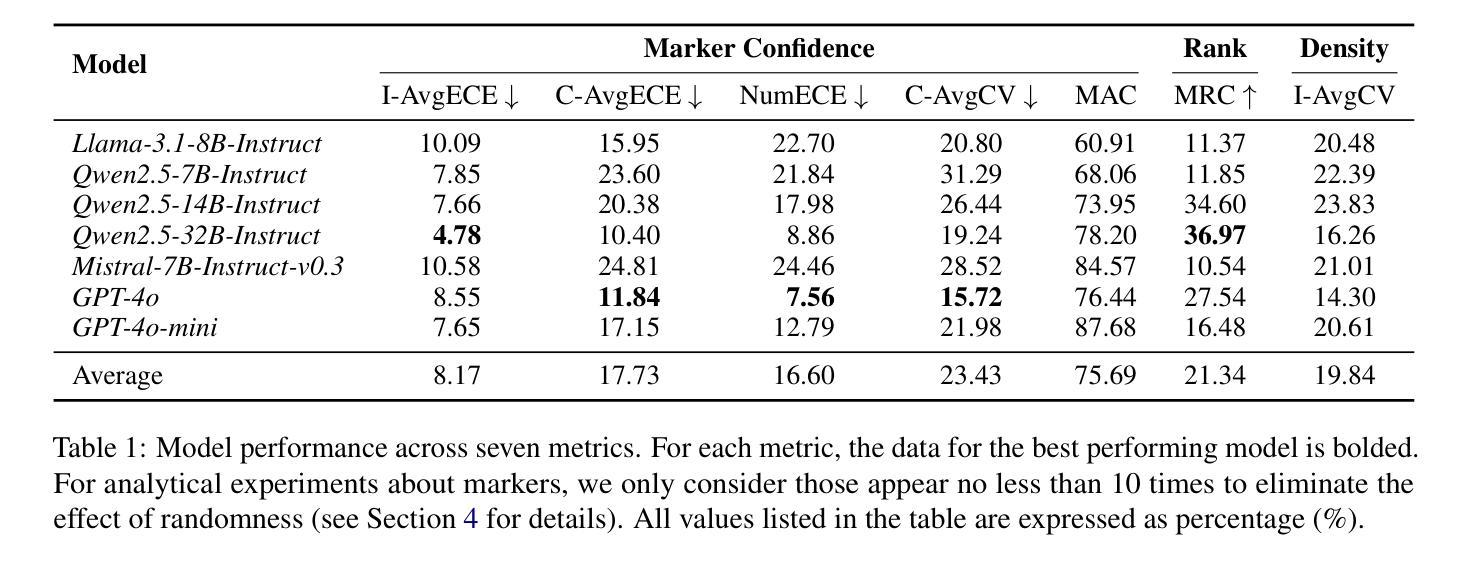
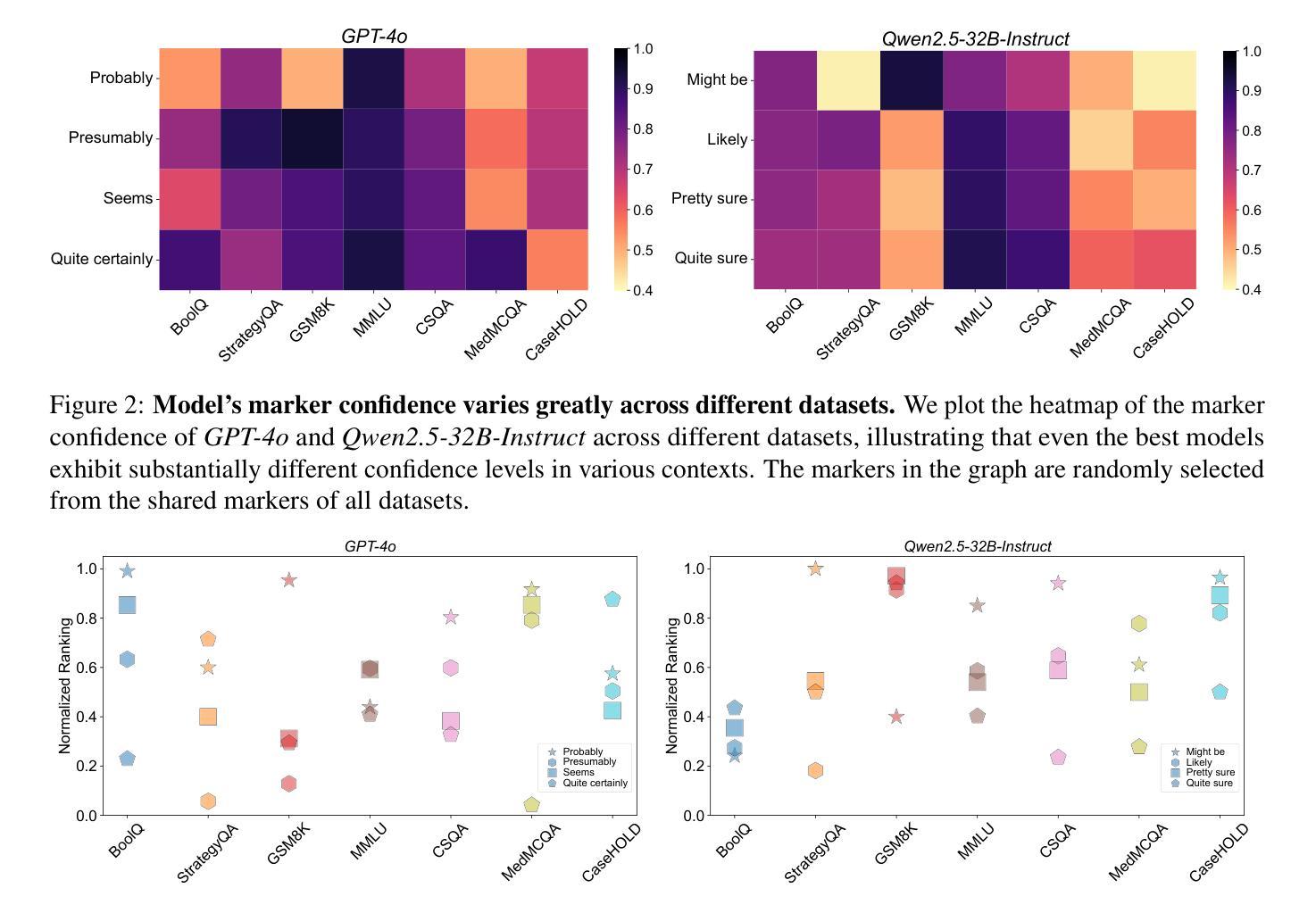
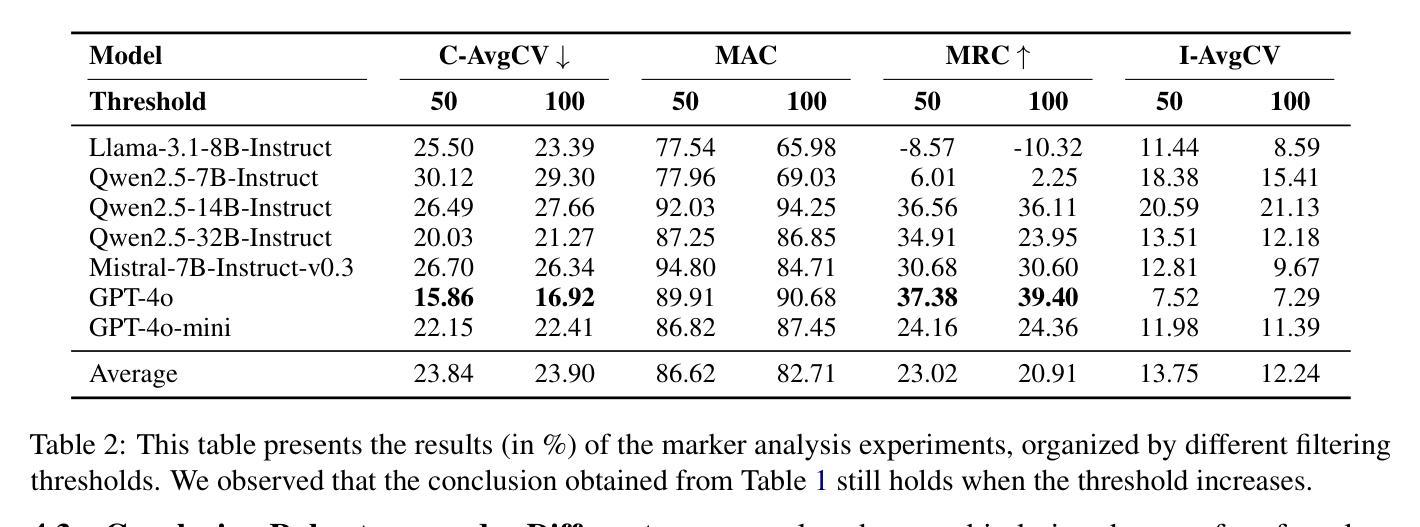
Revisiting Epistemic Markers in Confidence Estimation: Can Markers Accurately Reflect Large Language Models’ Uncertainty?
Authors:Jiayu Liu, Qing Zong, Weiqi Wang, Yangqiu Song
As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used in high-stakes domains, accurately assessing their confidence is crucial. Humans typically express confidence through epistemic markers (e.g., “fairly confident”) instead of numerical values. However, it remains unclear whether LLMs consistently use these markers to reflect their intrinsic confidence due to the difficulty of quantifying uncertainty associated with various markers. To address this gap, we first define marker confidence as the observed accuracy when a model employs an epistemic marker. We evaluate its stability across multiple question-answering datasets in both in-distribution and out-of-distribution settings for open-source and proprietary LLMs. Our results show that while markers generalize well within the same distribution, their confidence is inconsistent in out-of-distribution scenarios. These findings raise significant concerns about the reliability of epistemic markers for confidence estimation, underscoring the need for improved alignment between marker based confidence and actual model uncertainty. Our code is available at https://github.com/HKUST-KnowComp/MarCon.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)在高风险领域的应用日益增多,准确评估其信心至关重要。人类通常通过认识标记(例如“相当有信心”)而不是数值来表达信心。然而,由于与各种标记相关的不确定性的量化困难,尚不清楚LLM是否一致地使用这些标记来反映其内在信心。为了弥补这一差距,我们首先将标记信心定义为模型使用认识标记时的观察准确率。我们评估了开源和专有LLM在分布式内和分布式外的多个问答数据集上其稳定性的表现。我们的结果表明,虽然这些标记在同一分布内具有良好的通用性,但它们在分布式外的信心却是不一致的。这些发现引发了人们对认识标记在信心估计方面的可靠性的重大担忧,并强调需要在标记信心和实际模型不确定性之间实现更好的对齐。我们的代码可在https://github.com/HKUST-KnowComp/MarCon找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL2025
Summary
大语言模型(LLM)在高风险领域应用日益广泛,评估其置信度至关重要。人类通过认识性标记(如“相当有信心”)而非数值来表达信心。然而,尚不清楚LLM是否一致使用这些标记来反映其内在信心,这归因于与各种标记相关的不确定性的量化难度。为填补这一空白,研究首先定义标记信心为模型使用认识性标记时的观察准确率。研究评估了开源和专有LLM在内外分布设置多个问答数据集中的稳定性。结果表明,虽然标记在相同分布内通用性良好,但在外部分布场景中其信心不一致。这引发对认识性标记用于置信度估计可靠性的担忧,并强调需要改进标记信心和实际模型不确定性之间的对齐。相关研究代码已上传至:https://github.com/HKUST-KnowComp/MarCon 。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型(LLM)在高风险领域的广泛应用使得准确评估其置信度至关重要。
- 人类通过认识性标记表达信心,但LLM是否一致使用这些标记来反映其内在信心尚不清楚。
- 研究定义标记信心为模型使用认识性标记时的观察准确率。
- 评估了LLM在内外分布设置多个问答数据集中的稳定性。
- 标记在相同分布内通用性良好,但在外部分布场景中其信心不一致。
- 认识性标记用于置信度估计的可靠性引发担忧。
点此查看论文截图

AFLoRA: Adaptive Federated Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models with Resource-Aware Low-Rank Adaption
Authors:Yajie Zhou, Xiaoyi Pang, Zhibo Wang
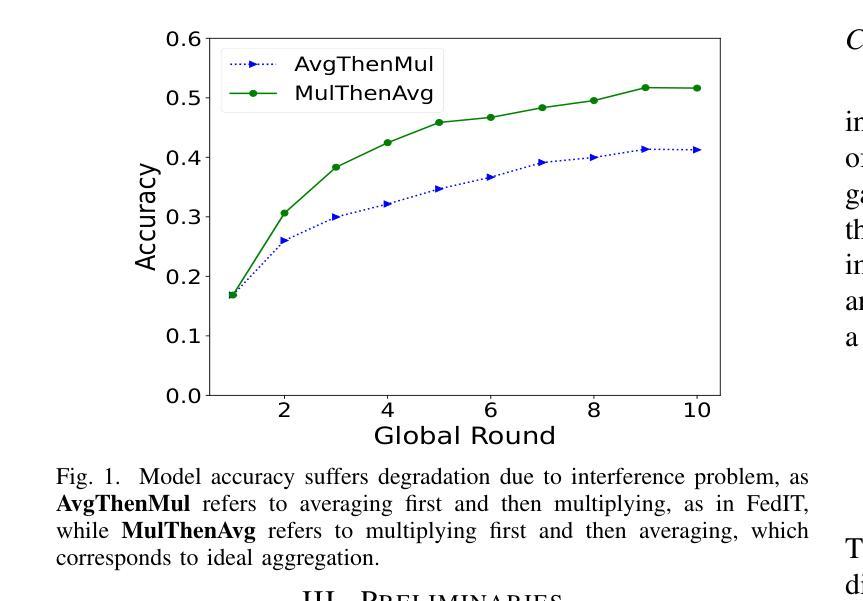
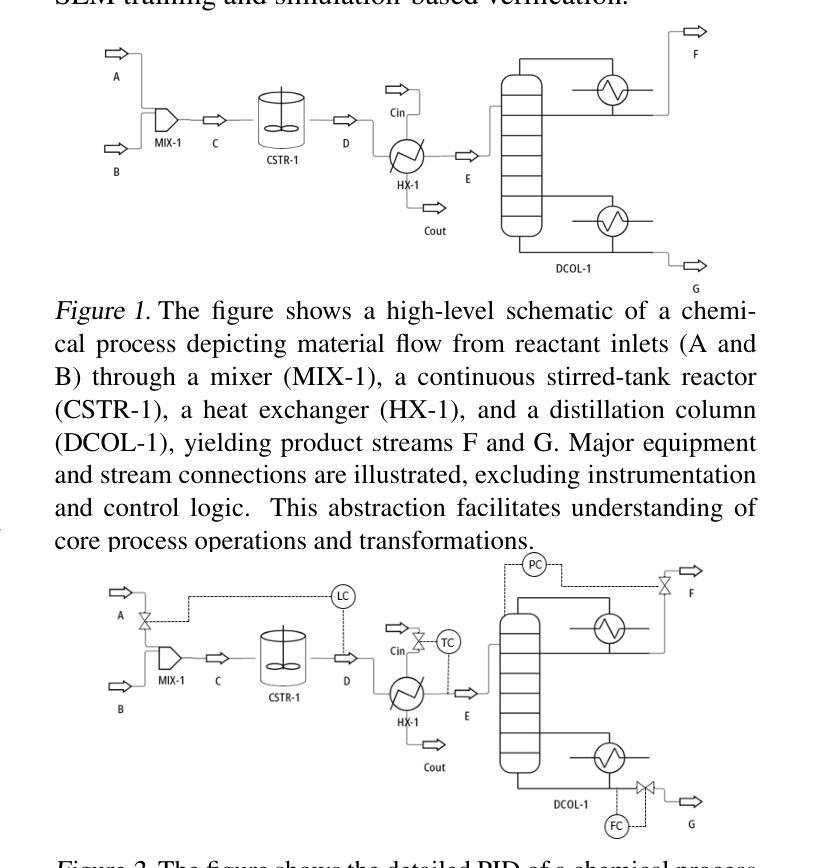
Federated fine-tuning has emerged as a promising approach to adapt foundation models to downstream tasks using decentralized data. However, real-world deployment remains challenging due to the high computational and communication demands of fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) on clients with data and system resources that are heterogeneous and constrained. In such settings, the global model’s performance is often bottlenecked by the weakest clients and further degraded by the non-IID nature of local data. Although existing methods leverage parameter-efficient techniques such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to reduce communication and computation overhead, they often fail to simultaneously ensure accurate aggregation of low-rank updates and maintain low system costs, thereby hindering overall performance. To address these challenges, we propose AFLoRA, an adaptive and lightweight federated fine-tuning framework for LLMs. AFLoRA decouples shared and client-specific updates to reduce overhead and improve aggregation accuracy, incorporates diagonal matrix-based rank pruning to better utilize local resources, and employs rank-aware aggregation with public data refinement to strengthen generalization under data heterogeneity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AFLoRA outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both accuracy and efficiency, providing a practical solution for efficient LLM adaptation in heterogeneous environments in the real world.
联邦微调(Federated Fine-tuning)作为一种使用分散数据适应基础模型以执行下游任务的方法,展现出了巨大的潜力。然而,由于需要在具有异质且受限数据和系统资源的客户端上对大型语言模型(LLM)进行微调,这使得其在现实世界中的部署仍然面临挑战。在这种环境下,全球模型的性能往往受到最弱客户的限制,并且由于本地数据的非独立同分布(non-IID)特性而进一步降低。尽管现有方法利用低秩适应(LoRA)等参数高效技术来减少通信和计算开销,但它们往往无法同时确保低秩更新的准确聚合和降低系统成本,从而阻碍了整体性能。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了AFLoRA,这是一个用于LLM的自适应和轻量级的联邦微调框架。AFLoRA通过解耦共享和客户端特定更新来降低开销并提高聚合准确性,采用基于对角矩阵的秩缩减来更好地利用本地资源,并采用秩感知聚合和公共数据细化来加强数据异质性下的泛化能力。大量实验表明,AFLoRA在准确性和效率方面都优于最新方法,为现实世界中异构环境下LLM的有效适应提供了实用解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模语言模型(LLM)的联邦微调是一种适应下游任务的有前途的方法,但在现实世界的部署中仍然面临挑战。在客户端进行微调时,由于数据和系统资源的异构性和局限性,计算和通信需求很高。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了AFLoRA,这是一种自适应的轻量级联邦微调框架。它通过解耦共享和客户端特定更新、采用基于对角矩阵的排名剪枝以及公共数据的精细化排名感知聚合等技术来提高准确性和效率。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦微调是一种适应下游任务的大型语言模型(LLM)的有效方法,但在实际部署中面临计算和通信的挑战。
- 由于数据的异构性和有限资源,全球模型的性能通常受到最弱客户的限制。
- 现有方法利用低秩适应(LoRA)等参数高效技术,但难以在准确聚合低秩更新和控制系统成本之间取得平衡,影响了整体性能。
- AFLoRA是一个自适应的轻量级联邦微调框架,旨在解决这些问题。它通过解耦共享和客户端特定更新、采用基于对角矩阵的排名剪枝以及公共数据的精细化排名感知聚合等技术来提高准确性和效率。
- AFLoRA通过减少计算和通信开销,可以更好地利用本地资源。
- AFLoRA在准确性和效率方面优于现有方法,为异构环境中有效适应LLM提供了实用解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

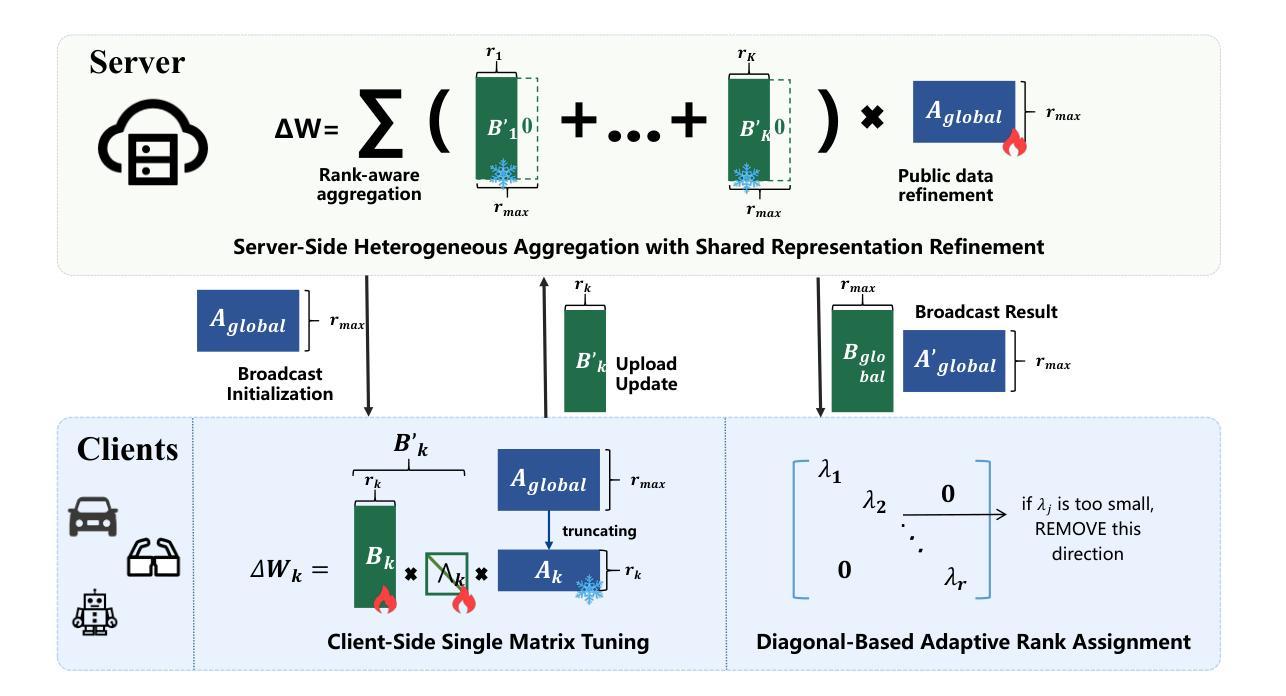
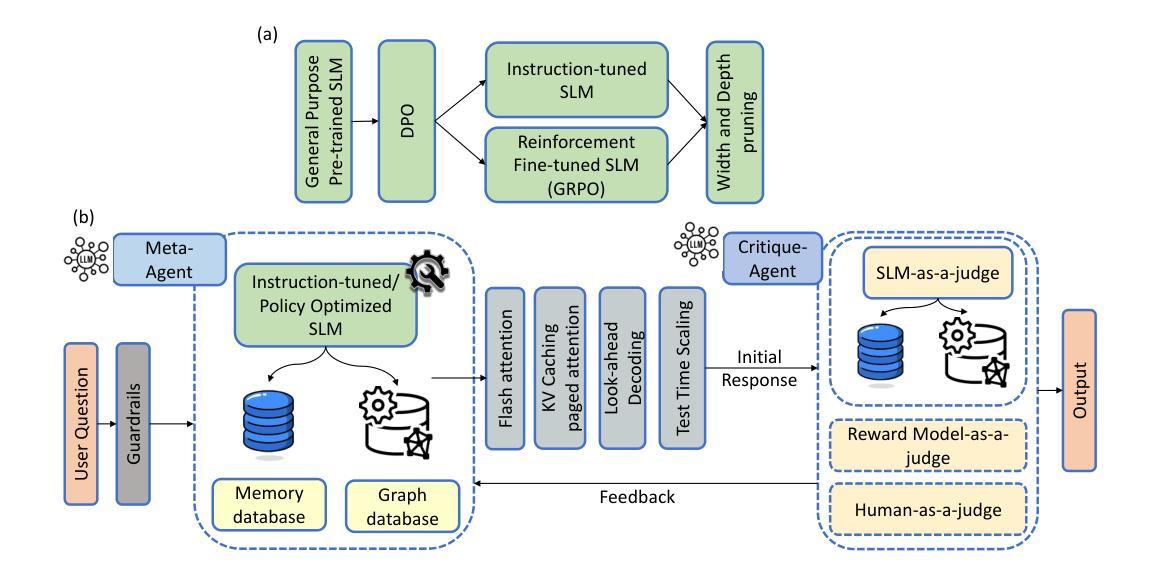
AutoChemSchematic AI: A Closed-Loop, Physics-Aware Agentic Framework for Auto-Generating Chemical Process and Instrumentation Diagrams
Authors:Sakhinana Sagar Srinivas, Shivam Gupta, Venkataramana Runkana
Recent advancements in generative AI have accelerated the discovery of novel chemicals and materials; however, transitioning these discoveries to industrial-scale production remains a critical bottleneck, as it requires the development of entirely new chemical manufacturing processes. Current AI methods cannot auto-generate PFDs or PIDs, despite their critical role in scaling chemical processes, while adhering to engineering constraints. We present a closed loop, physics aware framework for the automated generation of industrially viable PFDs and PIDs. The framework integrates domain specialized small scale language models (SLMs) (trained for chemical process QA tasks) with first principles simulation, leveraging three key components: (1) a hierarchical knowledge graph of process flow and instrumentation descriptions for 1,020+ chemicals, (2) a multi-stage training pipeline that fine tunes domain specialized SLMs on synthetic datasets via Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), and Retrieval-Augmented Instruction Tuning (RAIT), and (3) DWSIM based simulator in the loop validation to ensure feasibility. To improve both runtime efficiency and model compactness, the framework incorporates advanced inference time optimizations including FlashAttention, Lookahead Decoding, PagedAttention with KV-cache quantization, and Test Time Inference Scaling and independently applies structural pruning techniques (width and depth) guided by importance heuristics to reduce model size with minimal accuracy loss. Experiments demonstrate that the framework generates simulator-validated process descriptions with high fidelity, outperforms baseline methods in correctness, and generalizes to unseen chemicals. By bridging AI-driven design with industrial-scale feasibility, this work significantly reduces R&D timelines from lab discovery to plant deployment.
最近生成式人工智能的进步加速了新型化学物质和材料的发现。然而,将这些发现转化为工业规模的生产仍然是一个关键的瓶颈,因为这需要开发全新的化学制造工艺。尽管它们在规模化化学过程中扮演着至关重要的角色,但目前的AI方法无法自动生成工艺流程图(PFDs)或工艺流程说明(PIDs)。我们提出一个闭环、了解物理的自动化框架,用于生成具有工业可行性的工艺流程图和说明。该框架结合了针对化学工艺问答任务训练的领域专业化小型语言模型(SLM)与基于基本原理的仿真,利用三个关键组件:(1)包含1020+化学物质的工艺流程和仪器描述层次知识图谱;(2)多阶段训练管道,通过监督微调(SFT)、直接偏好优化(DPO)和检索增强指令调整(RAIT)在合成数据集上微调领域专业化SLM;(3)基于DWSIM的模拟器进行闭环验证以确保可行性。为了提高运行效率和模型紧凑性,该框架采用了先进的推理时间优化技术,包括FlashAttention、前瞻解码、带KV缓存量化的PagedAttention以及测试时间推理缩放,并独立应用结构修剪技术(宽度和深度),以重要性启发式为指导,以最小的精度损失减少模型大小。实验表明,该框架生成了经模拟器验证的高保真度工艺流程描述,在正确性方面优于基线方法,并能推广到未见过的化学物质。通过连接AI驱动的设计与工业规模可行性,这项工作显著缩短了从实验室发现到工厂部署的研发时间。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期生成式AI技术在发现新型化学物质和材料方面的进展迅速,但将这些发现转化为工业规模生产仍是关键瓶颈,需要开发全新的化学制造工艺。当前AI方法无法自动生成工程约束下的工艺流程图(PFDs)和工艺流程指示图(PIDs),而本文提出了一种闭环、物理感知的框架,用于自动生成具有工业可行性的PFDs和PIDs。该框架结合了专业领域的小规模语言模型(SLM),采用第一性原则模拟,通过三个关键组件实现:一是包含超过1020种化学物质的流程与仪器描述层次知识图谱;二是多阶段训练管道,通过监督微调(SFT)、直接偏好优化(DPO)和检索增强指令调整(RAIT)对特定领域的SLM进行微调;三是基于DWSIM的模拟循环验证以确保可行性。为提高运行效率和模型紧凑性,该框架采用了FlashAttention、前瞻解码、分页注意力与KV缓存量化等高级推理时间优化技术,并独立应用结构修剪技术(宽度和深度)以在保持精度损失最小的情况下减小模型大小。实验证明,该框架生成的工艺流程描述与模拟器验证高度一致,在正确性方面优于基准方法,并可泛化到未见过的化学物质。该工作通过桥接AI驱动的设计与工业规模可行性,显著缩短了从实验室发现到工厂部署的研发时间。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式AI在化学领域发现新型物质材料方面取得进展,但工业化生产面临瓶颈,需要新化学制造工艺。
- 当前AI无法自动生成工艺流程图(PFDs)和工艺流程指示图(PIDs),本文提出一种结合语言模型和物理模拟的闭环框架来自动生成这些图。
- 框架包含层次知识图谱、多阶段训练管道和基于DWSIM的模拟验证等技术。
- 优化技术包括高级推理时间优化和结构修剪技术,以提高运行效率和模型紧凑性。
- 实验证明该框架生成的工艺流程描述与模拟器验证高度一致,且优于基准方法。
- 该框架可泛化到未见过的化学物质,显著缩短从实验室到工厂部署的研发时间。
点此查看论文截图

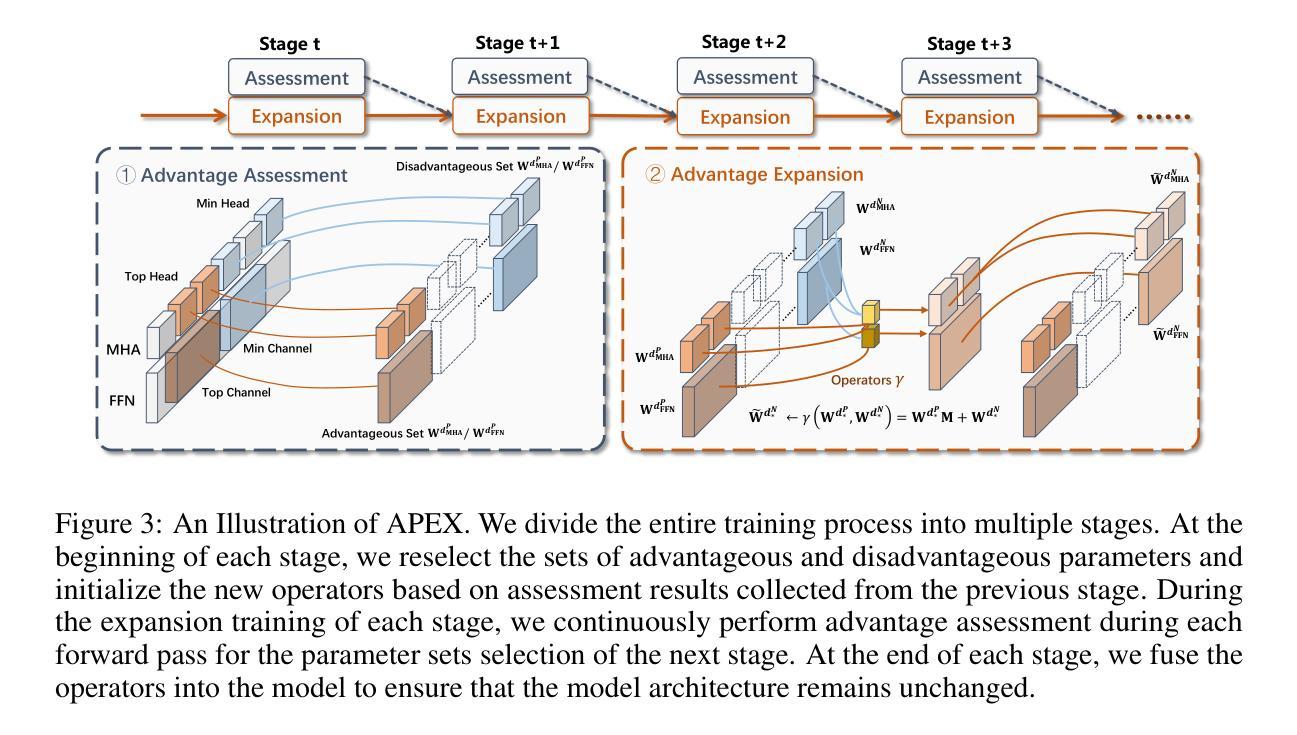
Advantageous Parameter Expansion Training Makes Better Large Language Models
Authors:Naibin Gu, Yilong Chen, Zhenyu Zhang, Peng Fu, Zheng Lin, Shuohuan Wang, Yu Sun, Hua Wu, Weiping Wang, Haifeng Wang
Although scaling up the number of trainable parameters in both pre-training and fine-tuning can effectively improve the performance of large language models, it also leads to increased computational overhead. When delving into the parameter difference, we find that a subset of parameters, termed advantageous parameters, plays a crucial role in determining model performance. Further analysis reveals that stronger models tend to possess more such parameters. In this paper, we propose Advantageous Parameter EXpansion Training (APEX), a method that progressively expands advantageous parameters into the space of disadvantageous ones, thereby increasing their proportion and enhancing training effectiveness. Further theoretical analysis from the perspective of matrix effective rank explains the performance gains of APEX. Extensive experiments on both instruction tuning and continued pre-training demonstrate that, in instruction tuning, APEX outperforms full-parameter tuning while using only 52% of the trainable parameters. In continued pre-training, APEX achieves the same perplexity level as conventional training with just 33% of the training data, and yields significant improvements on downstream tasks.
虽然预训练和微调过程中增加可训练参数的数量可以有效提高大语言模型的性能,但它也导致了计算开销的增加。在深入研究参数差异时,我们发现一部分参数,称为优势参数,在决定模型性能方面起着至关重要的作用。进一步的分析表明,性能更强的模型往往拥有更多的此类参数。在本文中,我们提出了优势参数扩展训练(APEX)方法,该方法逐步将优势参数扩展到劣势参数的空间,从而增加其比例并提高训练效果。从矩阵有效秩的角度进一步理论分析,解释了APEX的性能提升。在指令微调与持续预训练方面的广泛实验表明,在指令微调方面,APEX优于全参数调整,同时只使用52%的可训练参数。在持续预训练方面,APEX使用仅33%的训练数据即可达到与传统训练相同的困惑度水平,并在下游任务上取得了显著的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型的性能可以通过增加预训练和微调阶段的可训练参数数量来提高,但这也会增加计算开销。研究发现,被称为优势参数的参数子集对模型性能起着关键作用。更强壮的模型通常拥有更多的优势参数。本文提出了优势参数扩展训练(APEX)方法,该方法将优势参数逐步扩展到不利参数的范围内,从而提高其比例并增强训练效果。从矩阵有效秩的角度进一步分析了APEX的性能提升原因。实验表明,在指令微调方面,APEX在仅使用52%的可训练参数的情况下,性能优于全参数微调。在持续预训练方面,APEX仅使用33%的训练数据就达到了与传统训练相同的困惑度水平,并在下游任务上取得了显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 增加可训练参数数量可以提高大语言模型的性能,但也增加了计算开销。
- 优势参数对模型性能起关键作用,更强壮的模型拥有更多优势参数。
- APEX方法通过逐步扩展优势参数到不利参数的范围内,提高训练效果。
- APEX方法从矩阵有效秩的角度进行理论解释,证明了其性能提升的原因。
- 在指令微调方面,APEX在减少可训练参数使用的情况下,性能优于全参数微调。
- 在持续预训练方面,APEX在减少训练数据使用的情况下,达到了与传统训练相同的困惑度水平。
点此查看论文截图

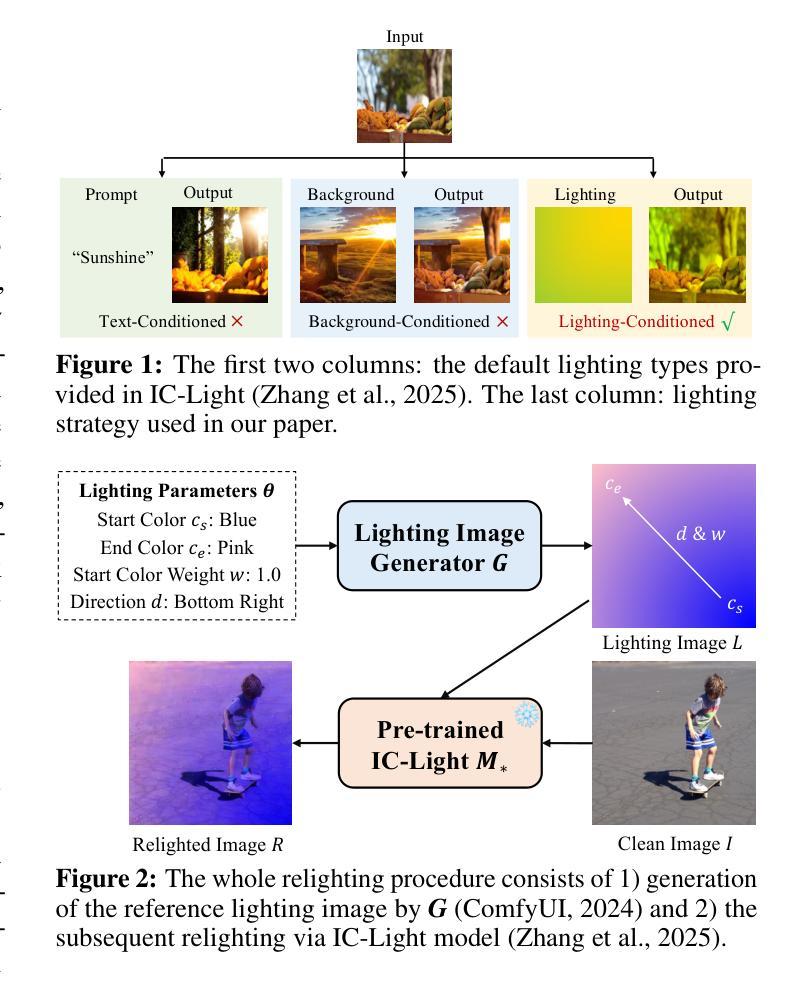
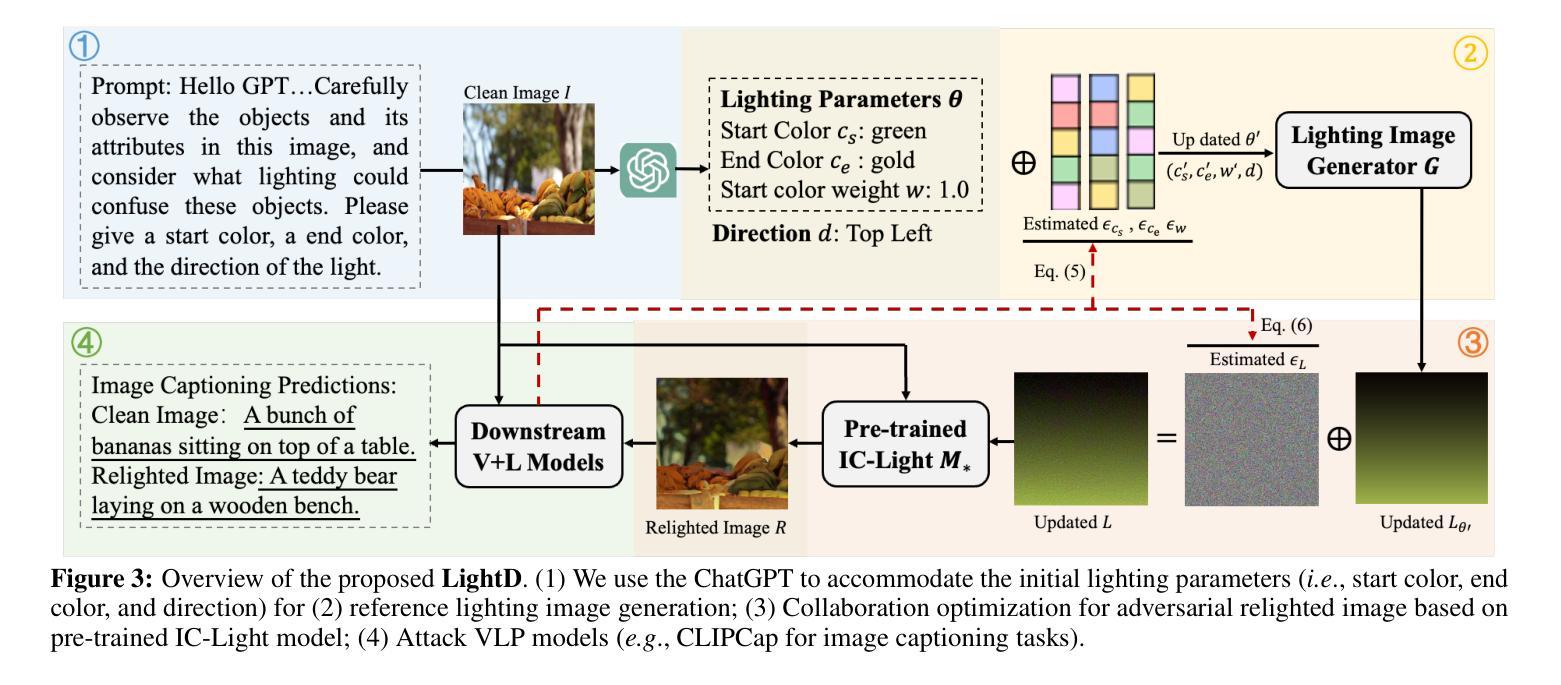
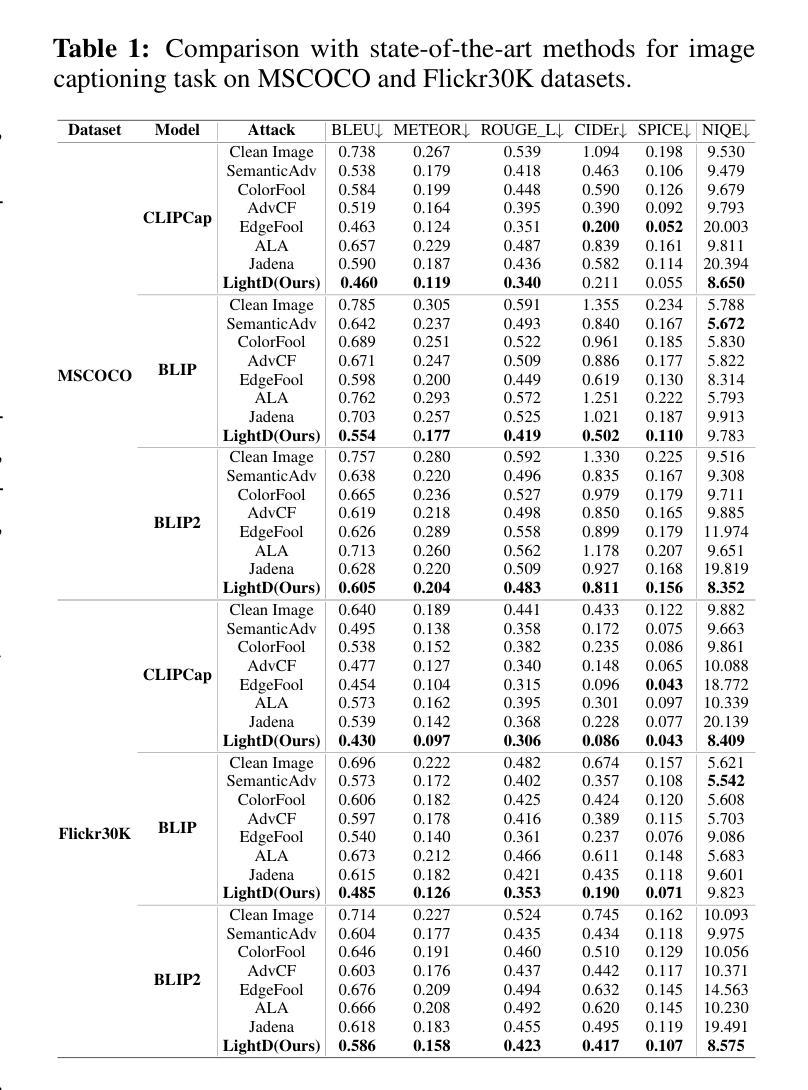
Light as Deception: GPT-driven Natural Relighting Against Vision-Language Pre-training Models
Authors:Ying Yang, Jie Zhang, Xiao Lv, Di Lin, Tao Xiang, Qing Guo
While adversarial attacks on vision-and-language pretraining (VLP) models have been explored, generating natural adversarial samples crafted through realistic and semantically meaningful perturbations remains an open challenge. Existing methods, primarily designed for classification tasks, struggle when adapted to VLP models due to their restricted optimization spaces, leading to ineffective attacks or unnatural artifacts. To address this, we propose \textbf{LightD}, a novel framework that generates natural adversarial samples for VLP models via semantically guided relighting. Specifically, LightD leverages ChatGPT to propose context-aware initial lighting parameters and integrates a pretrained relighting model (IC-light) to enable diverse lighting adjustments. LightD expands the optimization space while ensuring perturbations align with scene semantics. Additionally, gradient-based optimization is applied to the reference lighting image to further enhance attack effectiveness while maintaining visual naturalness. The effectiveness and superiority of the proposed LightD have been demonstrated across various VLP models in tasks such as image captioning and visual question answering.
虽然视觉与语言预训练(VLP)模型的对抗性攻击已被探索,但通过现实和语义上有意义的扰动生成自然对抗样本仍然是一个挑战。现有的方法主要设计用于分类任务,当适应到VLP模型时,由于优化空间有限,导致攻击效果不佳或产生不自然的伪影。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了\textbf{LightD},这是一种通过语义引导照明生成VLP模型自然对抗样本的新框架。具体来说,LightD利用ChatGPT提出与上下文相关的初始照明参数,并集成一个预训练的照明模型(IC-light)以实现各种照明调整。LightD扩大了优化空间,同时确保扰动与场景语义相符。此外,对参考照明图像应用基于梯度的优化,进一步提高攻击效果的同时保持视觉自然性。LightD的有效性和优越性在各种VLP模型的任务(如图像描述和视觉问答)中得到了验证。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
对抗样本在视觉与语言预训练模型(VLP)中的攻击已有所研究,但生成自然对抗样本仍是开放挑战。现有方法主要为分类任务设计,难以适应VLP模型,优化空间受限导致攻击无效或出现不自然伪影。为此,我们提出LightD框架,通过语义引导重光照生成自然对抗样本。LightD利用ChatGPT提出上下文感知的初始光照参数,集成预训练重光照模型IC-light实现多样化光照调整。该框架扩大了优化空间,确保扰动与场景语义一致。梯度优化参考照明图像,提高攻击有效性同时保持视觉自然性。LightD在图像描述和视觉问答等任务中展示了其有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 对抗样本在视觉与语言预训练模型(VLP)中的攻击仍是挑战。
- 现有方法难以生成自然对抗样本,优化空间受限。
- LightD框架通过语义引导重光照生成自然对抗样本。
- LightD利用ChatGPT提出上下文感知的初始光照参数。
- 集成预训练重光照模型IC-light实现多样化光照调整。
- LightD扩大了优化空间,确保扰动与场景语义一致。
点此查看论文截图

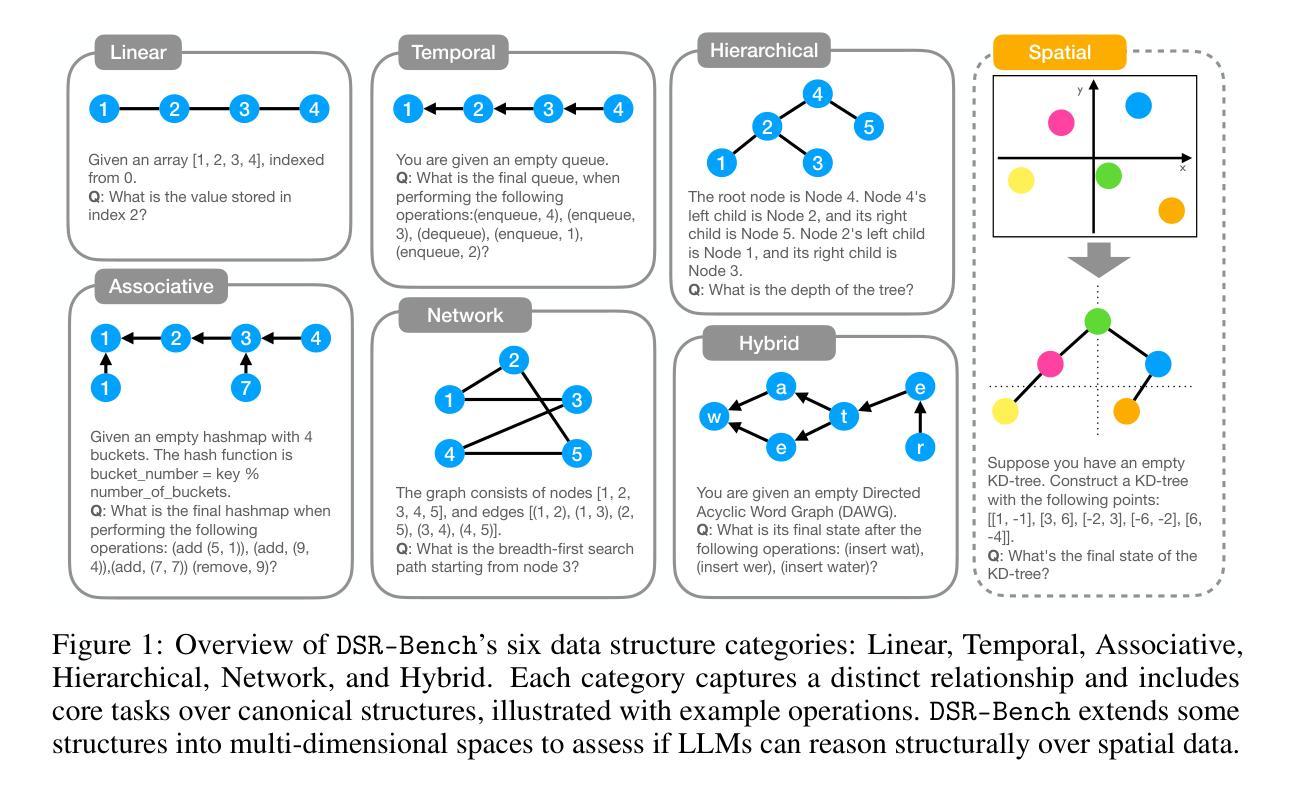
DSR-Bench: Evaluating the Structural Reasoning Abilities of LLMs via Data Structures
Authors:Yu He, Yingxi Li, Colin White, Ellen Vitercik
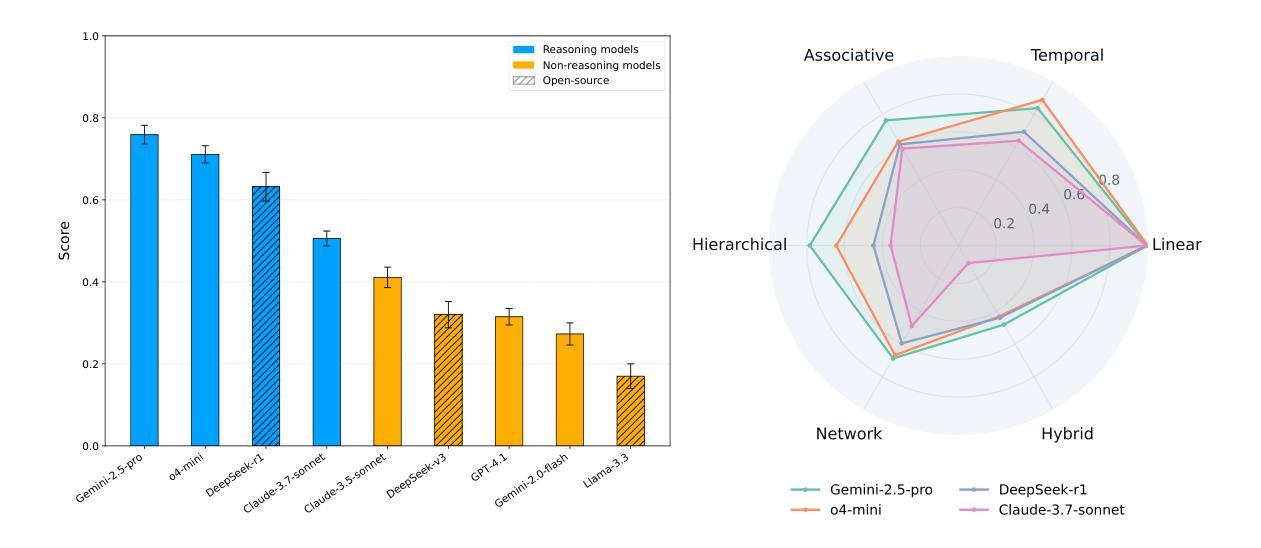
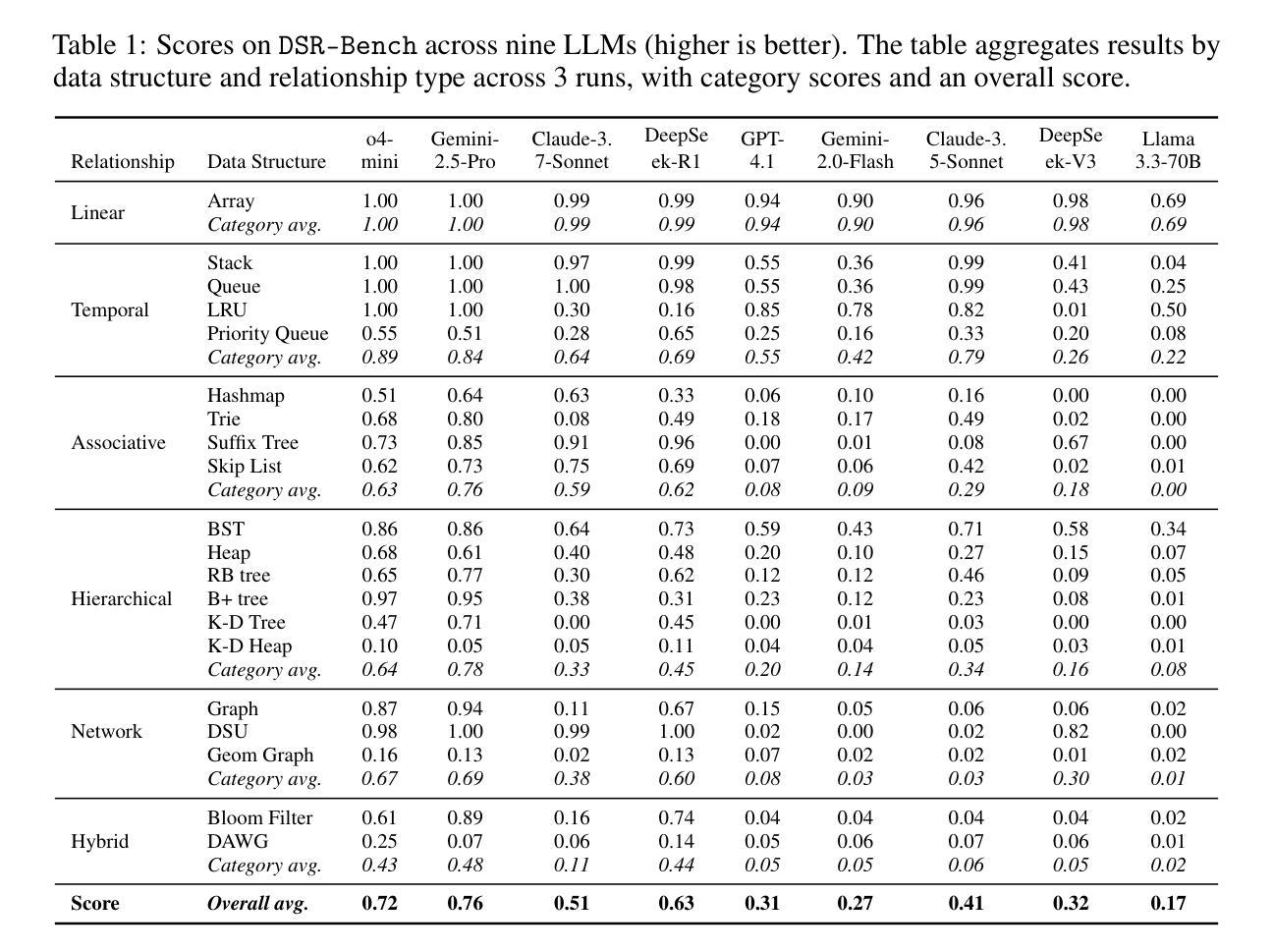
Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed for real-world tasks that fundamentally involve data manipulation. A core requirement across these tasks is the ability to perform structural reasoning–that is, to understand and reason about data relationships. For example, customer requests require a temporal ordering, which can be represented by data structures such as queues. However, existing benchmarks primarily focus on high-level, application-driven evaluations without isolating this fundamental capability. To address this gap, we introduce DSR-Bench, a novel benchmark evaluating LLMs’ structural reasoning capabilities through data structures, which provide interpretable representations of data relationships. DSR-Bench includes 20 data structures, 35 operations, and 4,140 problem instances, organized hierarchically for fine-grained analysis of reasoning limitations. Our evaluation pipeline is fully automated and deterministic, eliminating subjective human or model-based judgments. Its synthetic nature also ensures scalability and minimizes data contamination risks. We benchmark nine state-of-the-art LLMs. Our analysis shows that instruction-tuned models struggle with basic multi-attribute and multi-hop reasoning. Furthermore, while reasoning-oriented models perform better, they remain fragile on complex and hybrid structures, with the best model achieving an average score of only 47% on the challenge subset. Crucially, models often perform poorly on multi-dimensional data and natural language task descriptions, highlighting a critical gap for real-world deployment.
大型语言模型(LLM)越来越多地被部署于涉及数据操作的基础现实世界任务中。这些任务的核心要求是进行结构推理的能力,即理解和推理数据关系。例如,客户请求需要时序排序,可以通过队列等数据结构来表示。然而,现有的基准测试主要侧重于高级、应用驱动的评价,并没有孤立这种基本能力。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了DSR-Bench,这是一个新的基准测试,通过数据结构评估LLM的结构推理能力,提供数据关系的可解释表示。DSR-Bench包括20个数据结构、35个操作和4140个问题实例,按层次结构组织,用于精细分析推理局限性。我们的评估管道是完全自动化和确定的,消除了主观人为或模型基础的判断。其合成性质还确保了可扩展性,并降低了数据污染风险。我们对九种最先进的大型语言模型进行了基准测试。分析表明,指令调整模型在基本的多属性和多跳推理方面表现挣扎。此外,虽然以推理为导向的模型表现更好,但在复杂和混合结构上仍然很脆弱,其中最佳模型在挑战子集上的平均得分仅为47%。关键的是,模型在多维数据和自然语言任务描述方面的表现往往不佳,这突显了现实世界部署中的关键差距。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
大型语言模型(LLM)在实际任务中被广泛应用,要求对数据进行结构性推理,但现有的基准测试主要集中在高级应用评估上,缺乏对该核心能力的独立评估。为解决此问题,我们引入了DSR-Bench基准测试,专注于评估LLM处理数据关系的能力。该测试包括20个数据结构、35个操作和4,140个问题实例,并组织了精细的推理限制分析。我们的评估流程完全自动化且确定性强,消除了主观人为或模型基础的判断。此外,其合成性质确保了可扩展性并降低了数据污染风险。我们对九种最新LLM进行了基准测试,发现指令调整模型在基本多属性和多推理方面表现挣扎,而推理导向模型虽然在复杂和混合结构上表现更好,但在挑战子集上的平均得分仅为47%。模型在处理多维数据和自然语言任务描述时表现不佳,凸显了实际部署中的关键差距。
Key Takeaways:
- LLM在现实任务中需要处理数据操纵,其核心要求包括结构性推理能力。
- 现有基准测试主要关注高级应用评估,缺乏针对LLM结构性推理能力的独立评估。
- 为解决这一差距,引入了DSR-Bench基准测试,专注于评估LLM处理数据关系的能力,包括多种数据结构和操作。
- DSR-Bench评估流程自动化且确定性强,消除了主观判断,并确保测试的可靠性和一致性。
- 九种最新LLM在基准测试中表现不一,指令调整模型在基本多属性和多推理方面存在挑战。
- 推理导向模型在复杂和混合结构上表现较好,但在挑战子集上的平均得分较低,显示其局限性。
点此查看论文截图

Diversity of Transformer Layers: One Aspect of Parameter Scaling Laws
Authors:Hidetaka Kamigaito, Ying Zhang, Jingun Kwon, Katsuhiko Hayashi, Manabu Okumura, Taro Watanabe
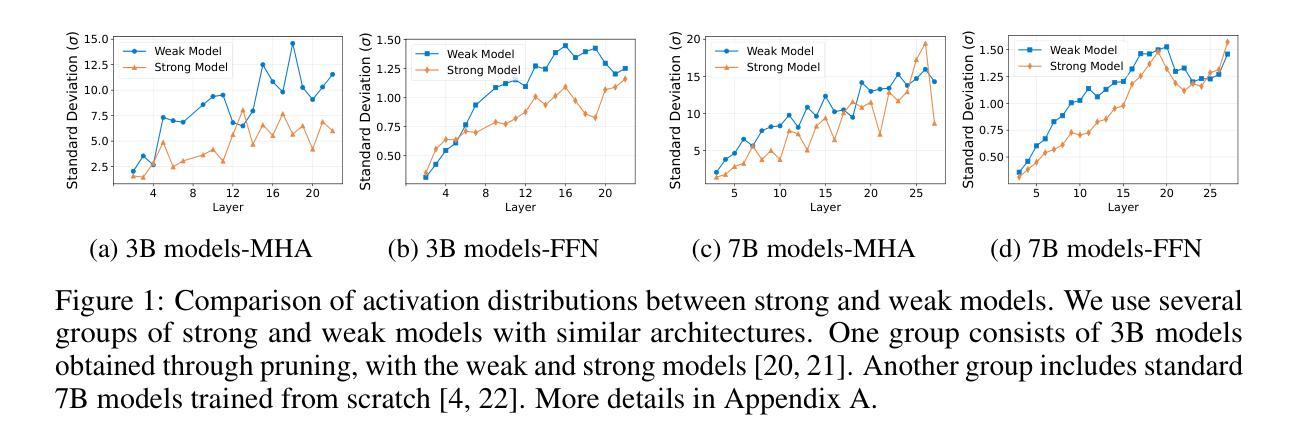
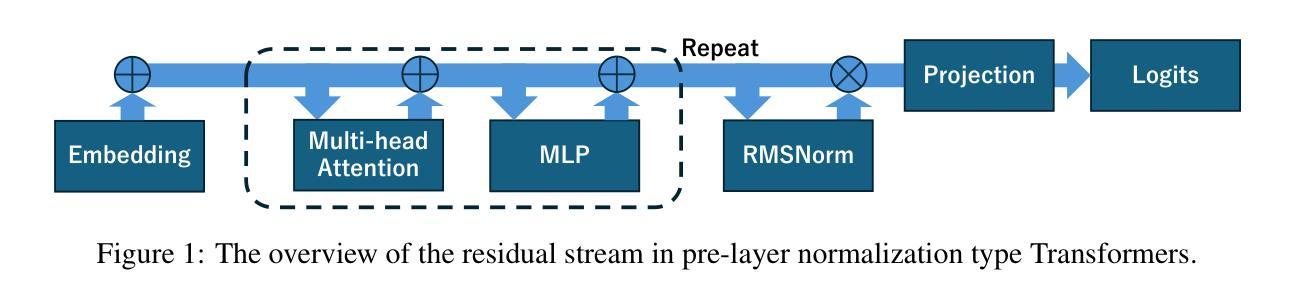
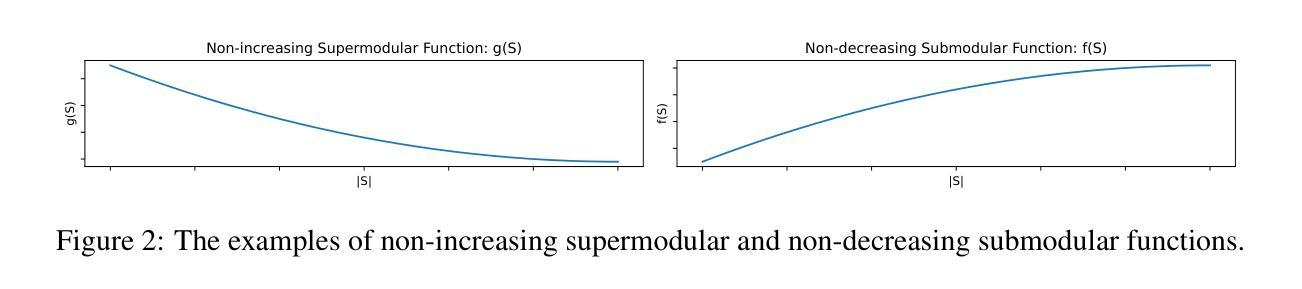
Transformers deliver outstanding performance across a wide range of tasks and are now a dominant backbone architecture for large language models (LLMs). Their task-solving performance is improved by increasing parameter size, as shown in the recent studies on parameter scaling laws. Although recent mechanistic-interpretability studies have deepened our understanding of the internal behavior of Transformers by analyzing their residual stream, the relationship between these internal mechanisms and the parameter scaling laws remains unclear. To bridge this gap, we focus on layers and their size, which mainly decide the parameter size of Transformers. For this purpose, we first theoretically investigate the layers within the residual stream through a bias-diversity decomposition. The decomposition separates (i) bias, the error of each layer’s output from the ground truth, and (ii) diversity, which indicates how much the outputs of each layer differ from each other. Analyzing Transformers under this theory reveals that performance improves when individual layers make predictions close to the correct answer and remain mutually diverse. We show that diversity becomes especially critical when individual layers’ outputs are far from the ground truth. Finally, we introduce an information-theoretic diversity and show our main findings that adding layers enhances performance only when those layers behave differently, i.e., are diverse. We also reveal the performance gains from increasing the number of layers exhibit submodularity: marginal improvements diminish as additional layers increase, mirroring the logarithmic convergence predicted by the parameter scaling laws. Experiments on multiple semantic-understanding tasks with various LLMs empirically confirm the theoretical properties derived in this study.
Transformer模型在多种任务中表现出卓越性能,现已成为大型语言模型(LLM)的主导架构。最近关于参数缩放定律的研究表明,通过增加参数规模,可以提高其任务解决性能。尽管通过解析残差流,最近的机械可解释性研究深化了我们对Transformer内部行为的理解,但这些内部机制与参数缩放定律之间的关系仍不清楚。为了填补这一空白,我们关注层及其大小,这些主要是决定Transformer参数规模的因素。为此,我们首先对残差流中的层进行理论上的偏置多样性分解研究。分解将(i)偏置(每层输出与基准值的误差)和(ii)多样性(指示每层输出之间的差异)分开。在该理论下分析Transformer显示,当各个层做出的预测接近正确答案并且彼此保持多样性时,性能会提高。我们表明,当各层输出远离基准值时,多样性变得尤为重要。最后,我们引入信息理论多样性并展示我们的主要发现:只有当这些层表现不同即具有多样性时,增加层数才会提高性能。我们还揭示了增加层数所带来性能增益的亚模性:随着额外层的增加,边际改进会减少,这与参数缩放定律预测的日志收敛相一致。在多个语义理解任务上对各种LLM进行的实验实证证实了本研究中得出的理论属性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了Transformer架构中的层数与其大小对大型语言模型(LLM)性能的影响。文章通过理论分析和实验验证,揭示了层内机制与参数缩放定律之间的关系。研究发现,当各层预测接近正确答案并保持相互多样性时,性能会提高。增加层数能提高性能,但这些层必须表现不同,即具有多样性。此外,随着层数的增加,性能改进表现出子模块性,边际改进随着额外层的增加而减少,这与参数缩放定律预测的日志收敛相一致。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer架构在多种任务上表现出卓越性能,已成为LLM的主导架构。
- 参数规模扩大能提高Transformer的任务解决性能。
- 通过对Transformer的残留流中的层进行理论研究,发现性能和层内机制和规模有关。
- 性能和层内机制的预测接近正确答案以及各层输出的多样性有关。
- 增加层数能提高性能,但这些层必须表现不同(即具有多样性)。
- 随着层数的增加,性能改进表现出子模块性,边际改进逐渐减少。
点此查看论文截图

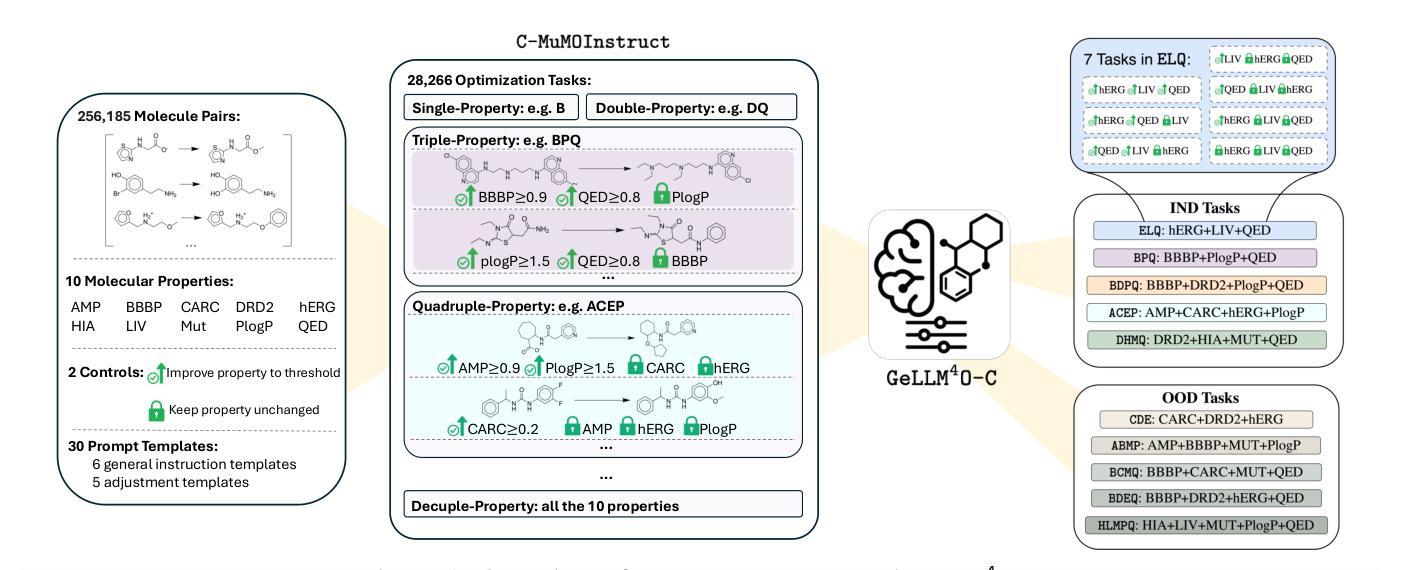
Large Language Models for Controllable Multi-property Multi-objective Molecule Optimization
Authors:Vishal Dey, Xiao Hu, Xia Ning
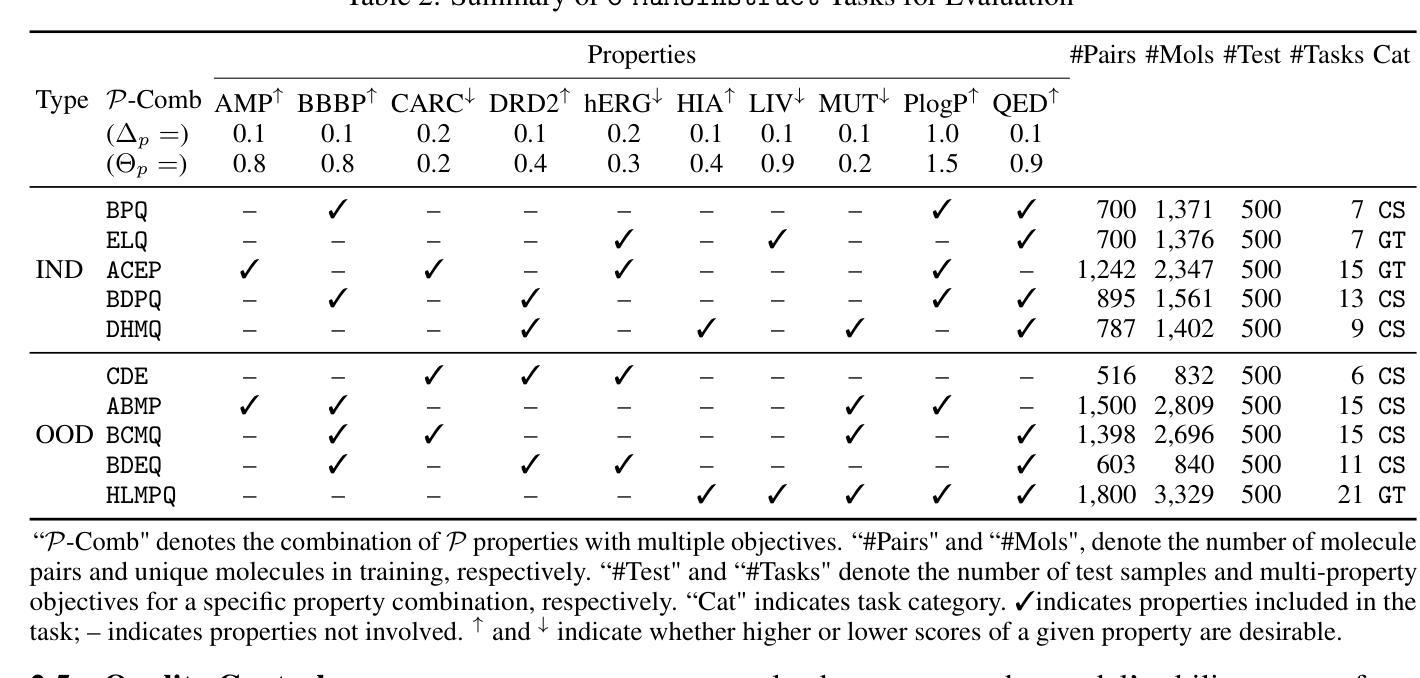
In real-world drug design, molecule optimization requires selectively improving multiple molecular properties up to pharmaceutically relevant levels, while maintaining others that already meet such criteria. However, existing computational approaches and instruction-tuned LLMs fail to capture such nuanced property-specific objectives, limiting their practical applicability. To address this, we introduce C-MuMOInstruct, the first instruction-tuning dataset focused on multi-property optimization with explicit, property-specific objectives. Leveraging C-MuMOInstruct, we develop GeLLMO-Cs, a series of instruction-tuned LLMs that can perform targeted property-specific optimization. Our experiments across 5 in-distribution and 5 out-of-distribution tasks show that GeLLMO-Cs consistently outperform strong baselines, achieving up to 126% higher success rate. Notably, GeLLMO-Cs exhibit impressive 0-shot generalization to novel optimization tasks and unseen instructions. This offers a step toward a foundational LLM to support realistic, diverse optimizations with property-specific objectives. C-MuMOInstruct and code are accessible through https://github.com/ninglab/GeLLMO-C.
在现实世界中的药物设计过程中,分子优化需要选择性改善多个分子属性以达到药物相关的水平,同时保持其他已经达到此类标准的属性。然而,现有的计算方法和指令调整的大型语言模型(LLM)无法捕捉到这种微妙的属性特定目标,从而限制了它们的实际应用性。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了C-MuMOInstruct,这是第一个专注于具有明确属性特定目标的多属性优化的指令调整数据集。利用C-MuMOInstruct,我们开发了GeLLMO-Cs系列指令调整的大型语言模型,可以执行有针对性的属性特定优化。我们在5个内部和5个外部任务上的实验表明,GeLLMO-Cs始终优于强大的基线,成功率提高了高达126%。值得注意的是,GeLLMO-Cs在新型优化任务和未见过的指令上展现出令人印象深刻的零射击泛化能力。这为支持具有属性特定目标的现实多样优化提供了基础的大型语言模型的一步。可以通过https://github.com/ninglab/GeLLMO-C访问C-MuMOInstruct和相关代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对真实药物设计中的分子优化问题,现有计算方法和指令调整的大型语言模型(LLM)无法捕捉复杂的属性特定目标,限制了其实用性。为此,研究人员引入了C-MuMOInstruct数据集,专注于具有明确属性特定目标的多属性优化。利用C-MuMOInstruct数据集,研究人员开发了GeLLMO-Cs系列指令调整LLM,能够进行有针对性的属性特定优化。实验表明,GeLLMO-Cs在5个内部和5个外部任务上表现优异,成功率高出基线达126%,并在未见过的指令和新型优化任务上展现出零样本泛化能力。这为支持真实、多样化的属性特定优化提供了基础LLM的一步。
Key Takeaways
- 真实药物设计中的分子优化需要同时提高多个分子属性至药物学相关水平,同时保持其他已达标属性的稳定性。
- 现有计算方法和指令调整的大型语言模型(LLM)无法有效处理这种复杂的属性特定优化问题。
- C-MuMOInstruct数据集的引入,专注于具有明确属性特定目标的多属性优化。
- GeLLMO-Cs系列指令调整LLM被开发出来,能够执行有针对性的属性特定优化。
- GeLLMO-Cs在多个任务上的表现超过现有基线,成功率高出达126%。
- GeLLMO-Cs展现出零样本泛化能力,可以在未见过的指令和新型优化任务上表现良好。
点此查看论文截图

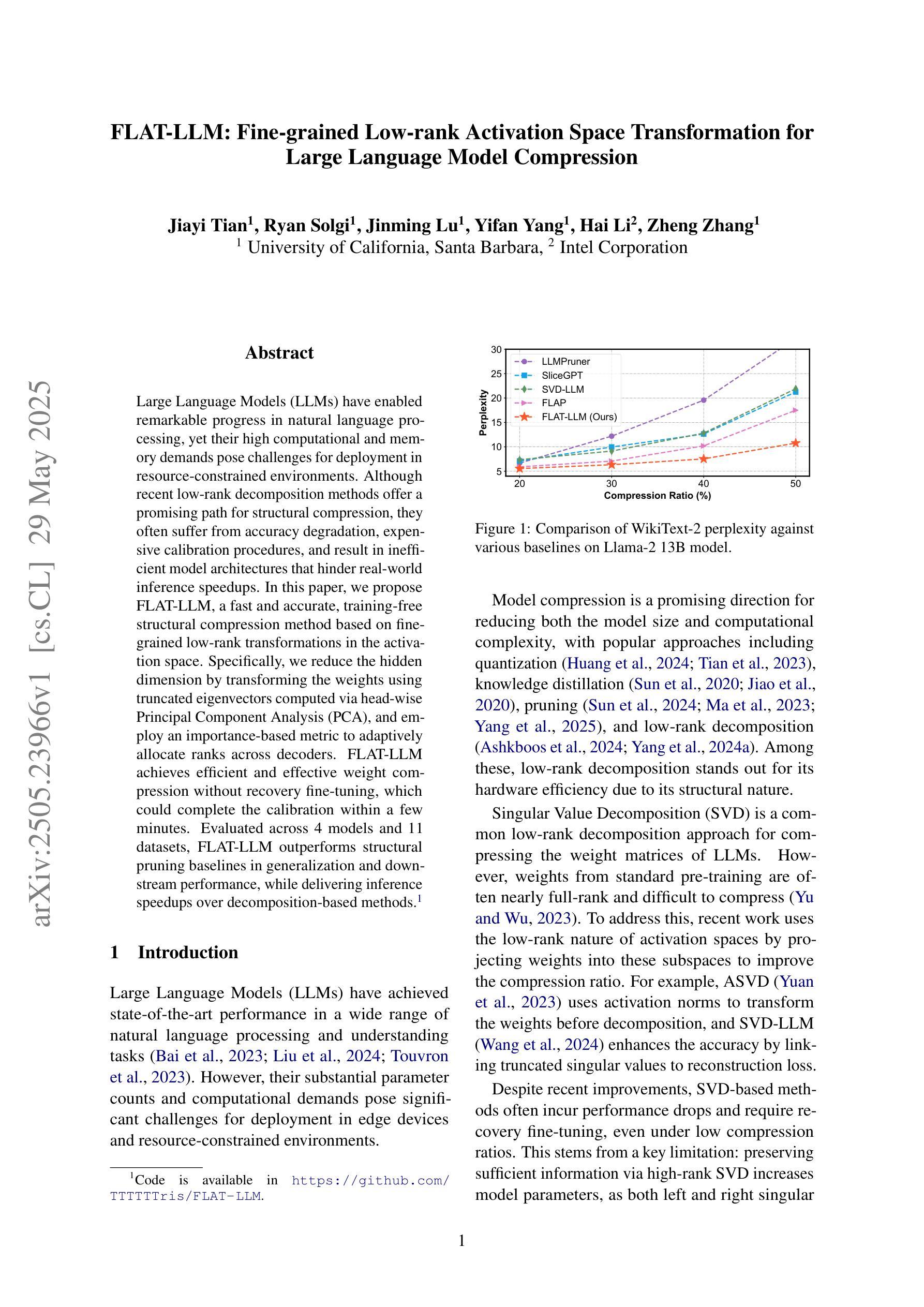
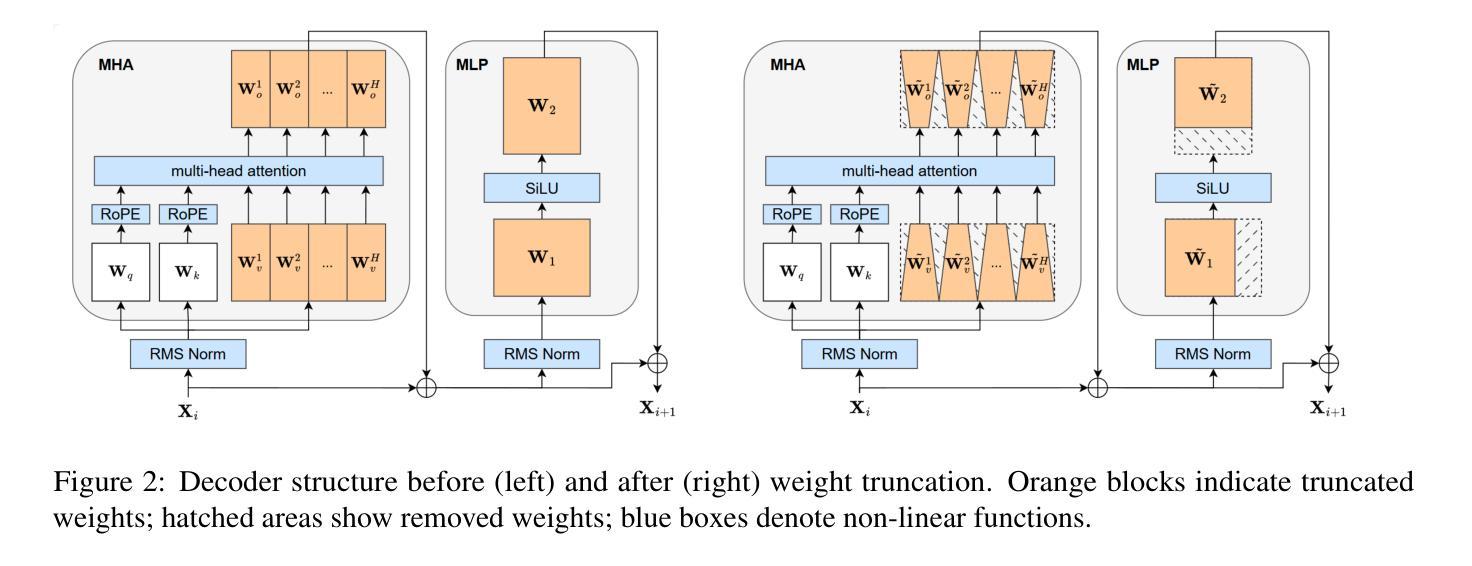
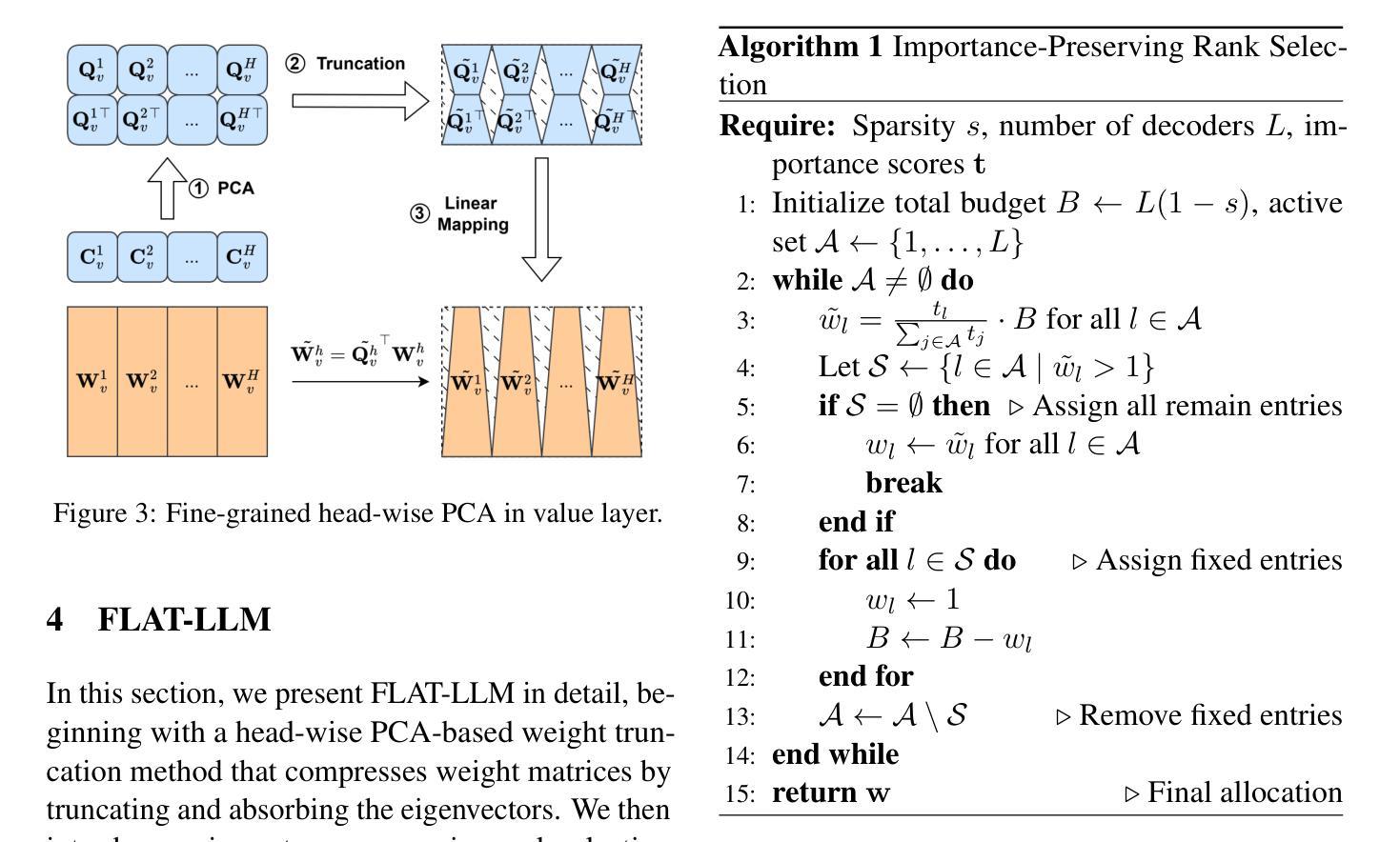
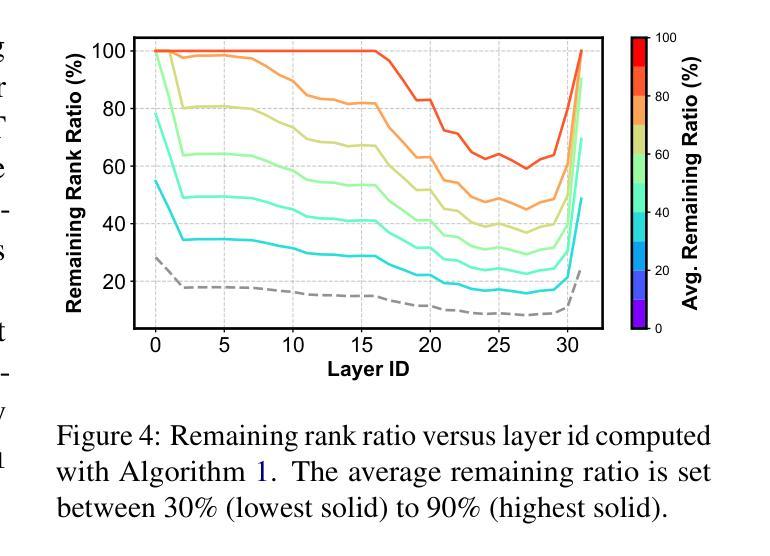
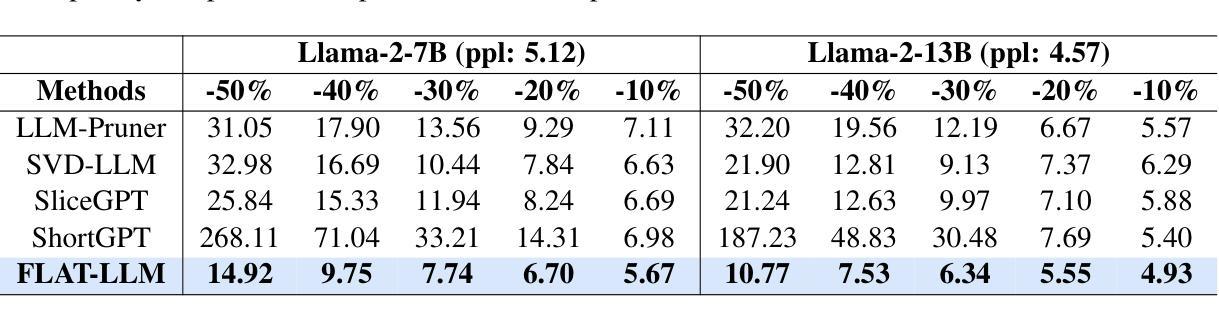
FLAT-LLM: Fine-grained Low-rank Activation Space Transformation for Large Language Model Compression
Authors:Jiayi Tian, Ryan Solgi, Jinming Lu, Yifan Yang, Hai Li, Zheng Zhang
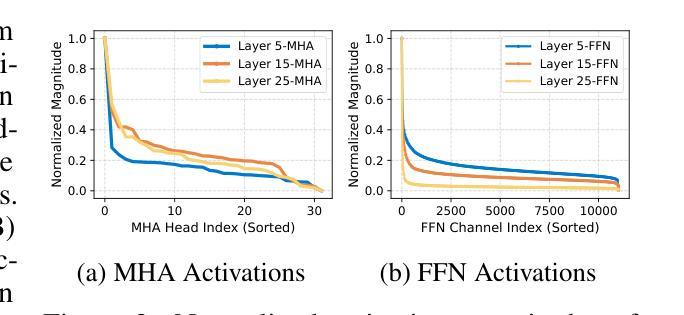
Large Language Models (LLMs) have enabled remarkable progress in natural language processing, yet their high computational and memory demands pose challenges for deployment in resource-constrained environments. Although recent low-rank decomposition methods offer a promising path for structural compression, they often suffer from accuracy degradation, expensive calibration procedures, and result in inefficient model architectures that hinder real-world inference speedups. In this paper, we propose FLAT-LLM, a fast and accurate, training-free structural compression method based on fine-grained low-rank transformations in the activation space. Specifically, we reduce the hidden dimension by transforming the weights using truncated eigenvectors computed via head-wise Principal Component Analysis (PCA), and employ an importance-based metric to adaptively allocate ranks across decoders. FLAT-LLM achieves efficient and effective weight compression without recovery fine-tuning, which could complete the calibration within a few minutes. Evaluated across 4 models and 11 datasets, FLAT-LLM outperforms structural pruning baselines in generalization and downstream performance, while delivering inference speedups over decomposition-based methods.
大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理方面取得了显著的进步,然而它们的高计算和内存需求对资源受限环境中的部署构成了挑战。尽管最近的低秩分解方法为实现结构压缩提供了有希望的途径,但它们往往存在精度下降、校准程序昂贵的问题,并导致模型架构效率低下,阻碍了现实世界的推理速度提升。在本文中,我们提出了FLAT-LLM,这是一种快速且准确的无训练结构压缩方法,基于激活空间中的精细粒度低秩变换。具体来说,我们通过头向主成分分析(PCA)计算的截断特征向量转换权重,从而减少隐藏维度,并基于重要性的度量自适应地在解码器之间分配等级。FLAT-LLM实现了高效有效的权重压缩,无需恢复微调,可以在几分钟内完成校准。在4个模型和11个数据集上的评估表明,FLAT-LLM在泛化和下游性能上超过了结构剪枝基准线,同时在基于分解的方法上实现了推理速度的提升。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLM面临计算资源和内存的挑战,现有结构压缩方法存在精度下降和校准过程复杂的问题。本文提出一种基于激活空间精细粒度低秩变换的快速准确的无训练结构压缩方法FLAT-LLM。它通过头主成分分析(PCA)计算截断特征向量,对权重进行变换,并基于重要性度量自适应分配解码器之间的秩。该方法无需恢复微调即可实现高效有效的权重压缩,可在几分钟内完成校准。在多个模型和数据集上的评估结果表明,FLAT-LLM在泛化和下游性能上优于结构剪枝基线方法,并提供比基于分解的方法更快的推理速度。
Key Takeaways
- LLM面临资源受限环境中的计算和内存挑战。
- 现有结构压缩方法存在精度下降和校准复杂的问题。
- FLAT-LLM是一种基于激活空间精细粒度低秩变换的无训练结构压缩方法。
- FLAT-LLM通过头主成分分析(PCA)进行权重变换。
- FLAT-LLM采用重要性度量自适应分配解码器之间的秩。
- FLAT-LLM无需恢复微调即可实现高效有效的权重压缩。
点此查看论文截图