⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-03 更新
Speech Token Prediction via Compressed-to-fine Language Modeling for Speech Generation
Authors:Wenrui Liu, Qian Chen, Wen Wang, Yafeng Chen, Jin Xu, Zhifang Guo, Guanrou Yang, Weiqin Li, Xiaoda Yang, Tao Jin, Minghui Fang, Jialong Zuo, Bai Jionghao, Zemin Liu
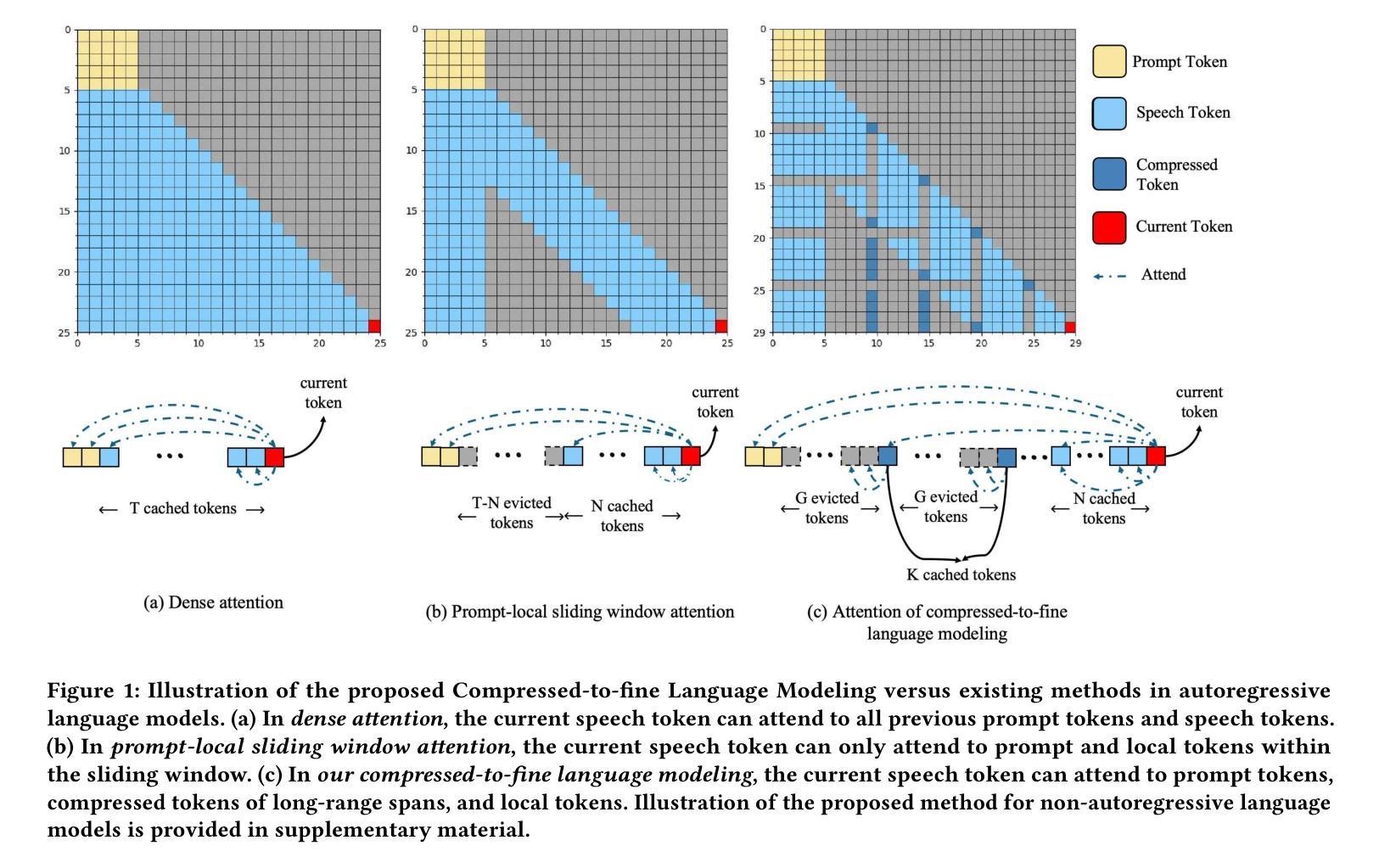
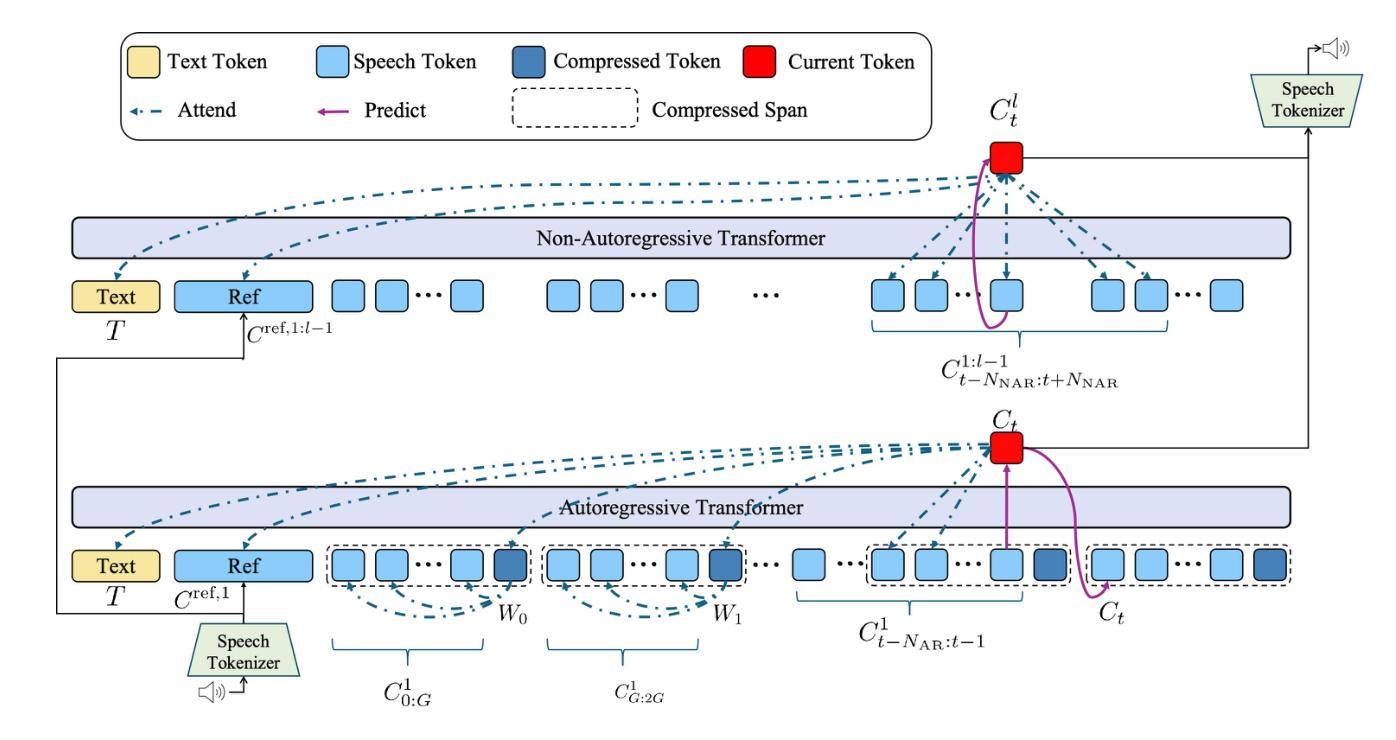
Neural audio codecs, used as speech tokenizers, have demonstrated remarkable potential in the field of speech generation. However, to ensure high-fidelity audio reconstruction, neural audio codecs typically encode audio into long sequences of speech tokens, posing a significant challenge for downstream language models in long-context modeling. We observe that speech token sequences exhibit short-range dependency: due to the monotonic alignment between text and speech in text-to-speech (TTS) tasks, the prediction of the current token primarily relies on its local context, while long-range tokens contribute less to the current token prediction and often contain redundant information. Inspired by this observation, we propose a \textbf{compressed-to-fine language modeling} approach to address the challenge of long sequence speech tokens within neural codec language models: (1) \textbf{Fine-grained Initial and Short-range Information}: Our approach retains the prompt and local tokens during prediction to ensure text alignment and the integrity of paralinguistic information; (2) \textbf{Compressed Long-range Context}: Our approach compresses long-range token spans into compact representations to reduce redundant information while preserving essential semantics. Extensive experiments on various neural audio codecs and downstream language models validate the effectiveness and generalizability of the proposed approach, highlighting the importance of token compression in improving speech generation within neural codec language models. The demo of audio samples will be available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/SpeechTokenPredictionViaCompressedToFinedLM.
神经音频编解码器作为语音标记器,在语音生成领域表现出了显著潜力。然而,为了确保高保真音频重建,神经音频编解码器通常将音频编码成较长的语音标记序列,这对下游语言模型在长时间上下文建模方面构成了重大挑战。我们发现语音标记序列表现出短距离依赖性:在文本到语音(TTS)任务中,由于文本和语音之间的单调对齐,当前标记的预测主要依赖于其局部上下文,而远距离标记对当前标记预测的贡献较小且往往包含冗余信息。受此观察启发,我们提出了一种“由粗到细的语言建模”方法来解决神经编解码器语言模型中长序列语音标记的挑战:(1)精细的初始和短距离信息:我们的方法在预测时保留提示和局部标记,以确保文本对齐和副语言信息的完整性;(2)压缩的长距离上下文:我们的方法将长距离标记跨度压缩成紧凑的表示形式,以减少冗余信息同时保留必要的语义。在各种神经音频编解码器和下游语言模型上的大量实验验证了所提出方法的有效性和通用性,强调了标记压缩在改进神经编解码器语言模型中的语音生成中的重要性。音频样本演示将可在https://anonymous.4open.science/r/SpeechTokenPredictionViaCompressedToFinedLM上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经网络音频编码在语音生成领域展现出显著潜力,但音频重建的高保真度对下游语言模型提出了长序列建模的挑战。观察到语音令牌序列展现出短距离依赖特性,我们提出了“压缩到精细的语言建模”方法来解决神经编码语言模型中的长序列语音令牌挑战。方法包括保留精细的初始和短距离信息,同时压缩长距离上下文以减少冗余信息,兼顾语义的完整性。经过大量实验验证,该方法在提高神经编码语言模型的语音生成性能中展现了显著效果和泛化能力。相关音频样本可在相关链接中查看。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络音频编码在语音生成中具有显著潜力。
- 高保真音频重建对下游语言模型提出长序列建模挑战。
- 语音令牌序列展现短距离依赖特性。
- 提出“压缩到精细的语言建模”方法来解决长序列语音令牌挑战。
- 方法保留初始和短距离信息,同时压缩长距离上下文以减少冗余信息。
- 实验验证了该方法的显著效果和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

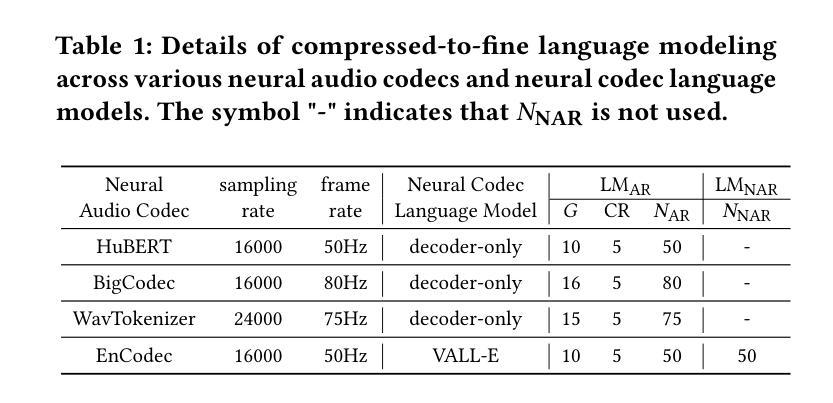
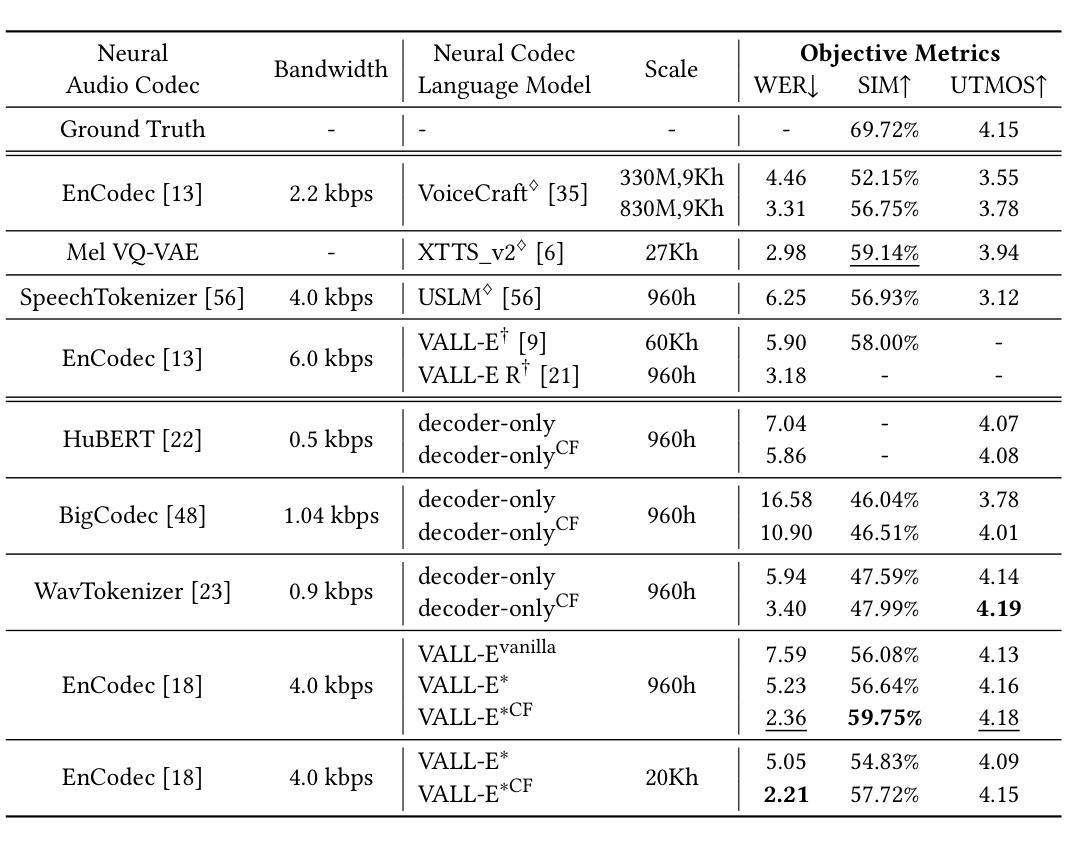
Can Emotion Fool Anti-spoofing?
Authors:Aurosweta Mahapatra, Ismail Rasim Ulgen, Abinay Reddy Naini, Carlos Busso, Berrak Sisman
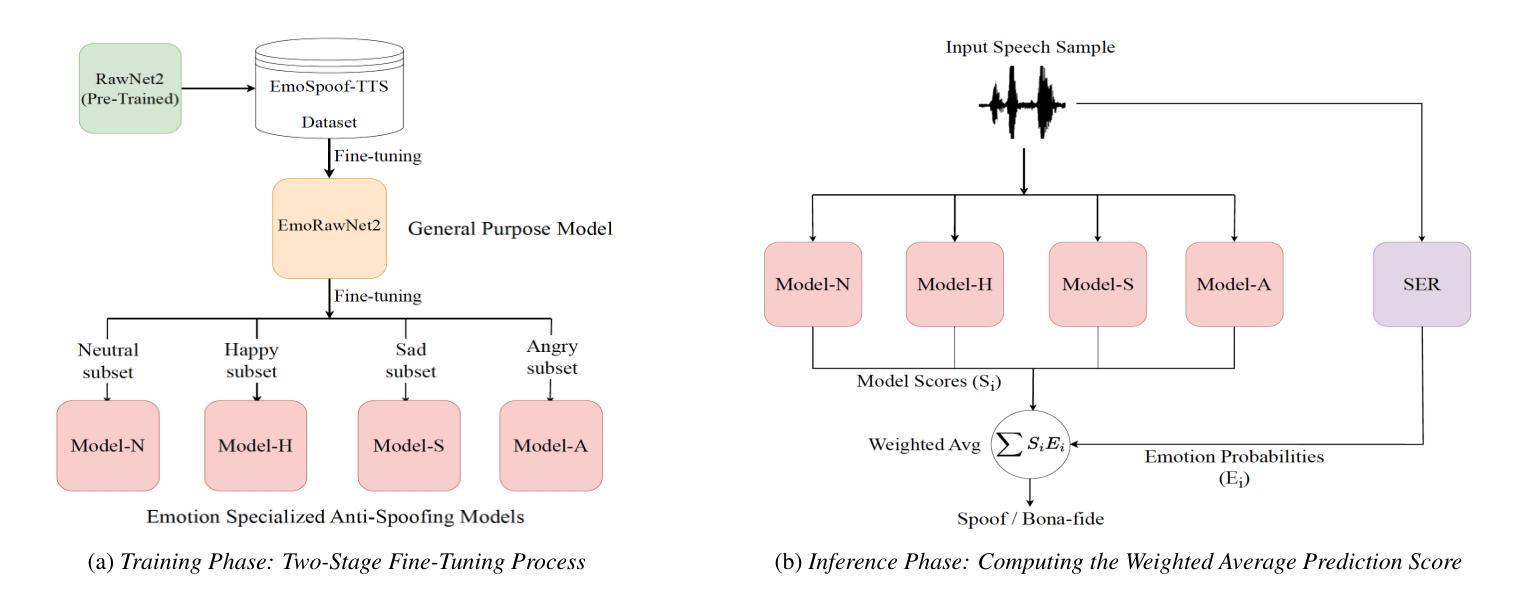
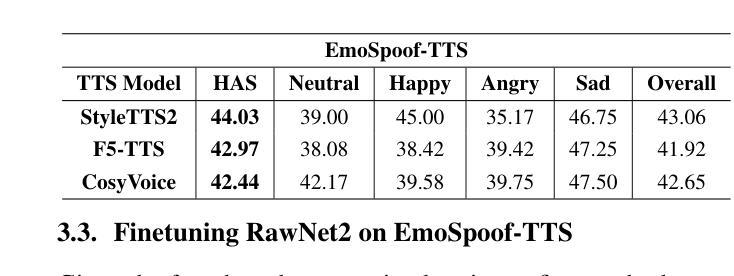
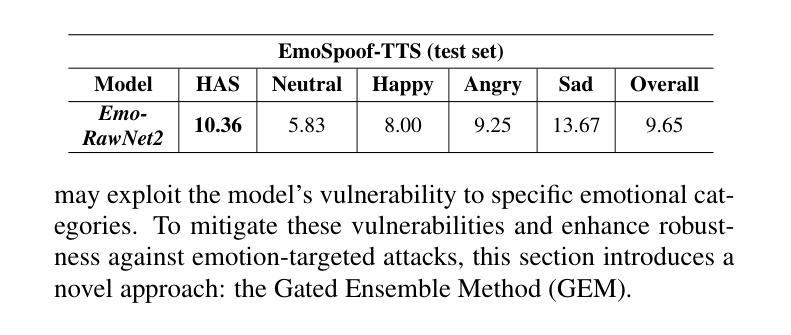
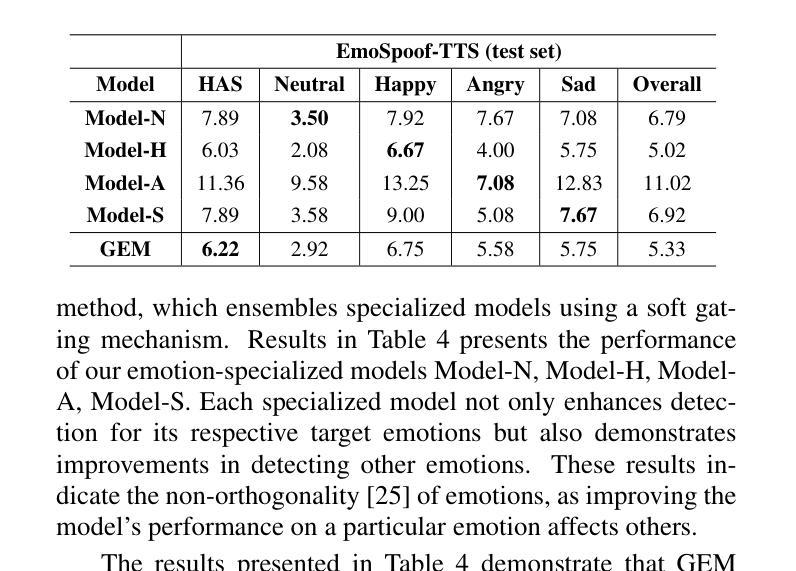
Traditional anti-spoofing focuses on models and datasets built on synthetic speech with mostly neutral state, neglecting diverse emotional variations. As a result, their robustness against high-quality, emotionally expressive synthetic speech is uncertain. We address this by introducing EmoSpoof-TTS, a corpus of emotional text-to-speech samples. Our analysis shows existing anti-spoofing models struggle with emotional synthetic speech, exposing risks of emotion-targeted attacks. Even trained on emotional data, the models underperform due to limited focus on emotional aspect and show performance disparities across emotions. This highlights the need for emotion-focused anti-spoofing paradigm in both dataset and methodology. We propose GEM, a gated ensemble of emotion-specialized models with a speech emotion recognition gating network. GEM performs effectively across all emotions and neutral state, improving defenses against spoofing attacks. We release the EmoSpoof-TTS Dataset: https://emospoof-tts.github.io/Dataset/
传统的抗欺骗技术主要关注基于中性状态合成语音的模型和数据集,忽视了多样化的情绪变化。因此,它们对于高质量、情感丰富的合成语音的稳健性尚不确定。我们通过引入EmoSpoof-TTS来解决这个问题,这是一个情感文本到语音样本的语料库。我们的分析表明,现有的抗欺骗模型在处理情感合成语音时面临困难,存在针对情感目标的攻击风险。即使在情感数据上进行训练,这些模型的表现也不尽如人意,因为它们在情感方面的关注有限,并且在不同情感之间的表现存在差异。这强调了数据集和方法论中都需要以情感为中心的抗欺骗范式。我们提出了GEM,这是一个带有语音情感识别门控网络的情感专业化模型的门控集合。GEM在所有情感和中性状态下都能有效运行,提高了对欺骗攻击的防御能力。我们公开了EmoSpoof-TTS数据集:https://emospoof-tts.github.io/Dataset/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文介绍了传统反欺骗技术主要关注中性状态下的合成语音模型和数据集,忽视了情感变化多样性所带来的问题。为解决此问题,提出了EmoSpoof-TTS情绪文本转语音样本库。分析表明,现有反欺骗模型难以应对情感合成语音,存在被情感目标攻击的风险。即使采用情感数据训练,模型表现仍然受限,性能在不同情感之间存在差异。为此,提出了采用情绪专门化模型的门控集成方法GEM,并配备语音情感识别门控网络。GEM在所有情感和中性状态下表现优异,提高了对欺骗攻击的防御能力。同时,发布EmoSpoof-TTS数据集。
Key Takeaways
- 传统反欺骗技术主要集中在中性状态的合成语音上,忽视了情感变化多样性。
- 现有反欺骗模型难以应对情感合成语音,存在风险。
- 情感数据训练虽然能提高性能,但仍有局限性。
- 不同情感状态下的反欺骗性能存在差异。
- 需要建立情感专门化的反欺骗模型以提高性能。
- 提出了采用情绪专门化模型的门控集成方法GEM。
点此查看论文截图

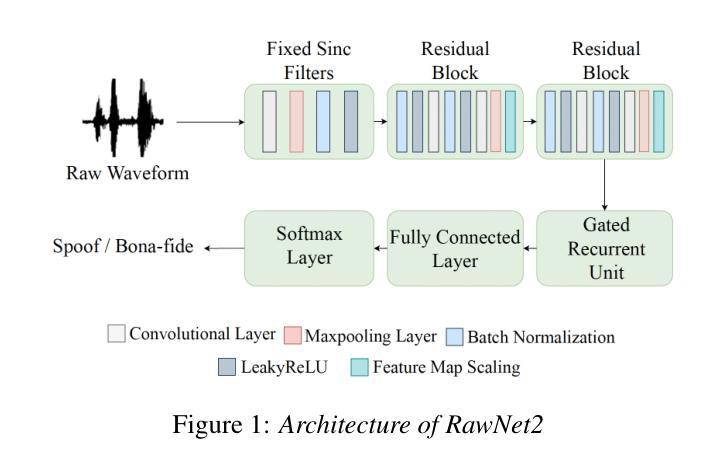
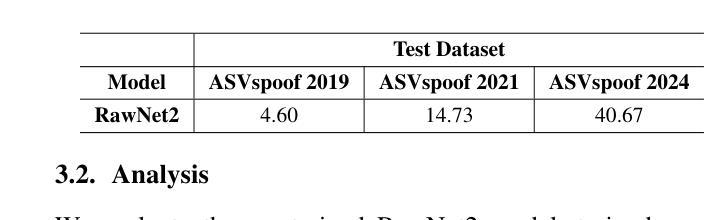
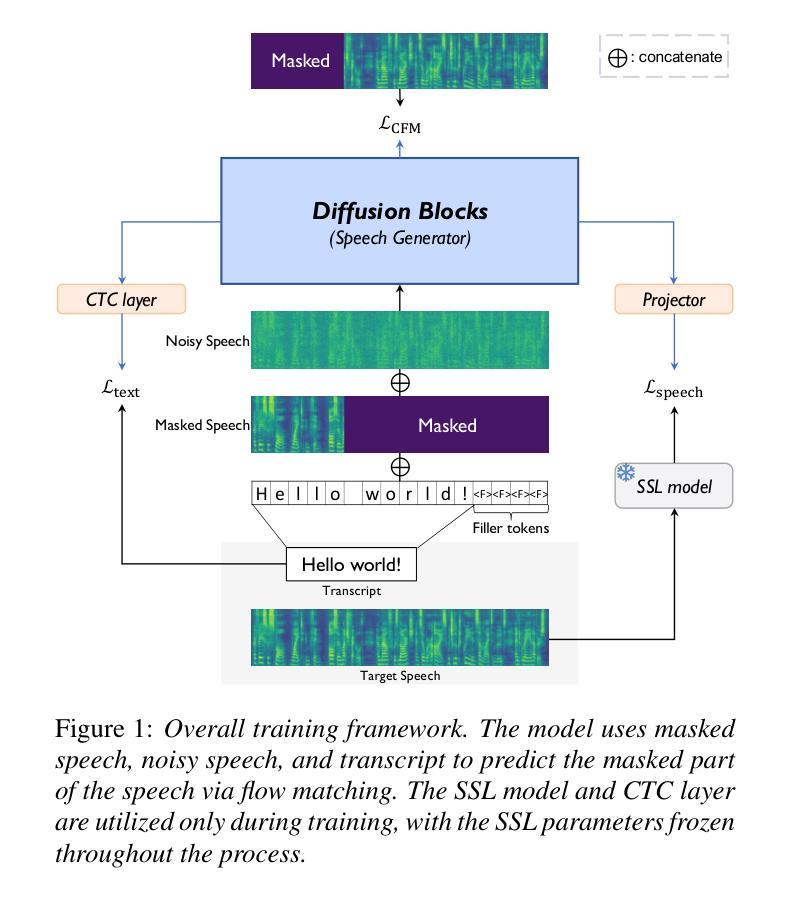
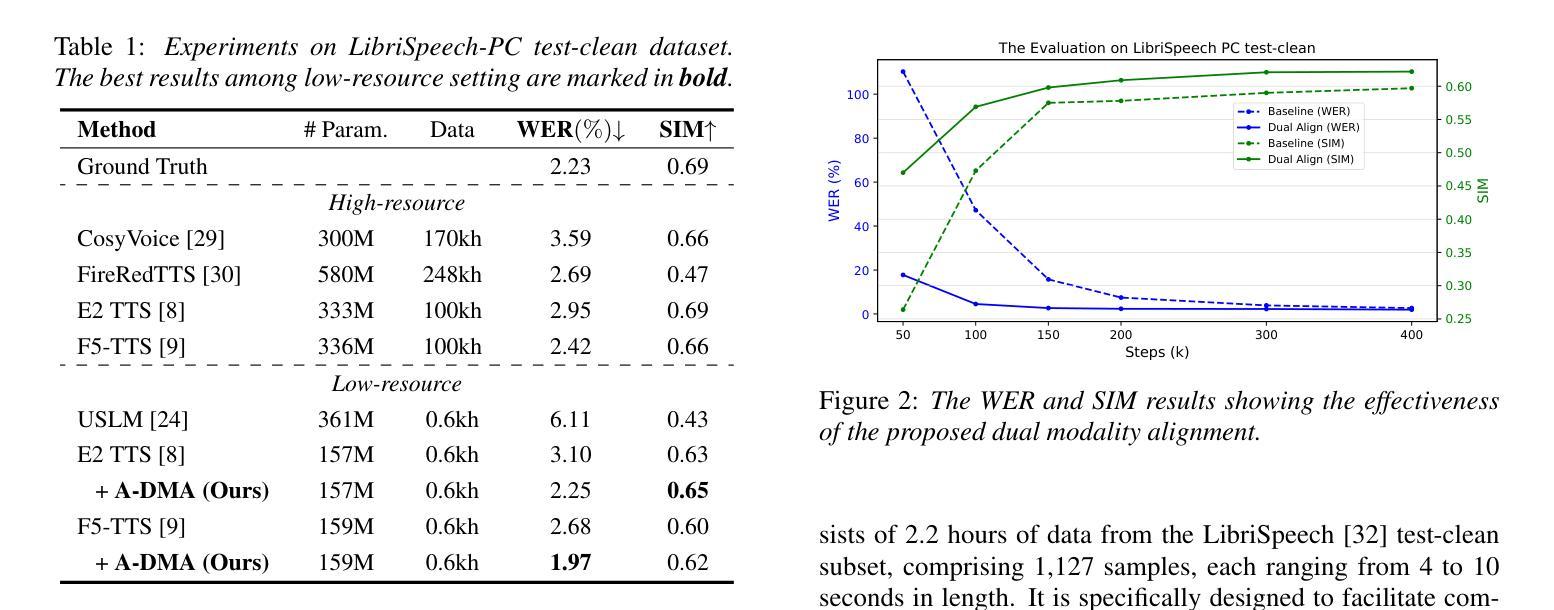
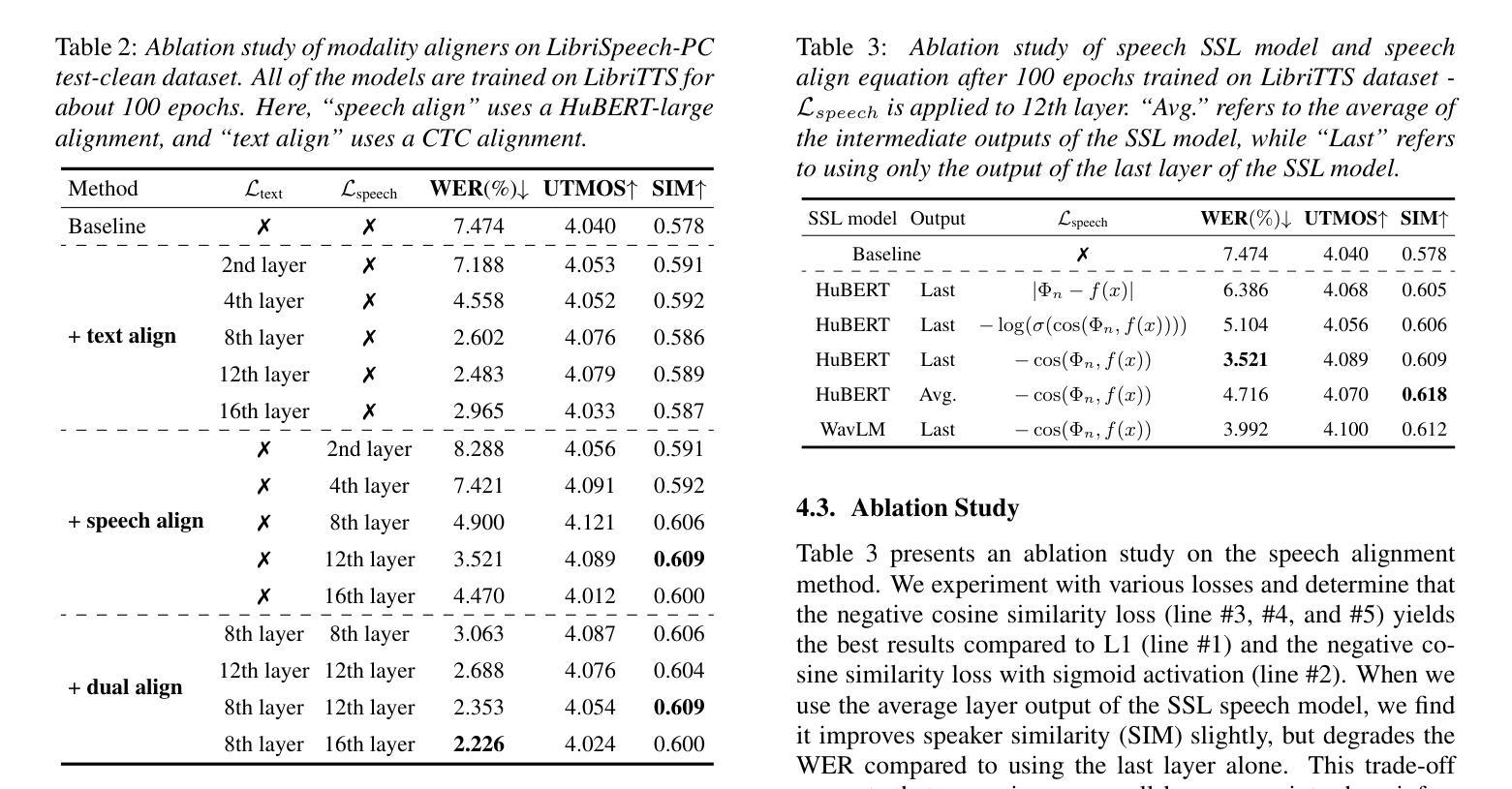
Accelerating Diffusion-based Text-to-Speech Model Training with Dual Modality Alignment
Authors:Jeongsoo Choi, Zhikang Niu, Ji-Hoon Kim, Chunhui Wang, Joon Son Chung, Xie Chen
The goal of this paper is to optimize the training process of diffusion-based text-to-speech models. While recent studies have achieved remarkable advancements, their training demands substantial time and computational costs, largely due to the implicit guidance of diffusion models in learning complex intermediate representations. To address this, we propose A-DMA, an effective strategy for Accelerating training with Dual Modality Alignment. Our method introduces a novel alignment pipeline leveraging both text and speech modalities: text-guided alignment, which incorporates contextual representations, and speech-guided alignment, which refines semantic representations. By aligning hidden states with discriminative features, our training scheme reduces the reliance on diffusion models for learning complex representations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that A-DMA doubles the convergence speed while achieving superior performance over baselines. Code and demo samples are available at: https://github.com/ZhikangNiu/A-DMA
本文的目标是优化基于扩散的文本到语音模型的训练过程。虽然最近的研究取得了显著的进步,但它们的训练需要大量的时间和计算成本,这主要是因为扩散模型在学习复杂中间表示时的隐性指导。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了A-DMA,一种利用双模态对齐加速训练的有效策略。我们的方法引入了一个利用文本和语音两种模式的新型对齐管道:文本引导对齐,它结合了上下文表示,以及语音引导对齐,它改进了语义表示。通过对隐藏状态与判别特征进行对齐,我们的训练方案减少了扩散模型在学习复杂表示方面的依赖。大量实验表明,A-DMA的收敛速度提高了一倍,同时相比基线实现了优越的性能。代码和演示样本可在:https://github.com/ZhikangNiu/A-DMA找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文旨在优化基于扩散的文本转语音模型的训练过程。针对扩散模型在训练过程中存在的隐式指导和高时间成本问题,提出了A-DMA策略,通过双重模态对齐的方式加速训练。该方法结合文本和语音两种模态,实现了文本引导的对齐和语音引导的对齐,减少了扩散模型对复杂表示的依赖。实验证明,A-DMA策略不仅使收敛速度翻倍,而且实现了超越基准的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文针对文本转语音模型的训练过程进行优化,旨在降低时间和计算成本。
- 论文提出了A-DMA策略,通过双重模态对齐的方式加速训练过程。
- A-DMA策略包括文本引导的对齐和语音引导的对齐,分别用于结合文本和语音信息。
- 通过对齐隐藏状态和判别特征,A-DMA策略减少了扩散模型对复杂表示的依赖。
- 实验证明,A-DMA策略可以显著提高训练速度并超越基准性能。
- 该策略的代码和演示样本已公开在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图

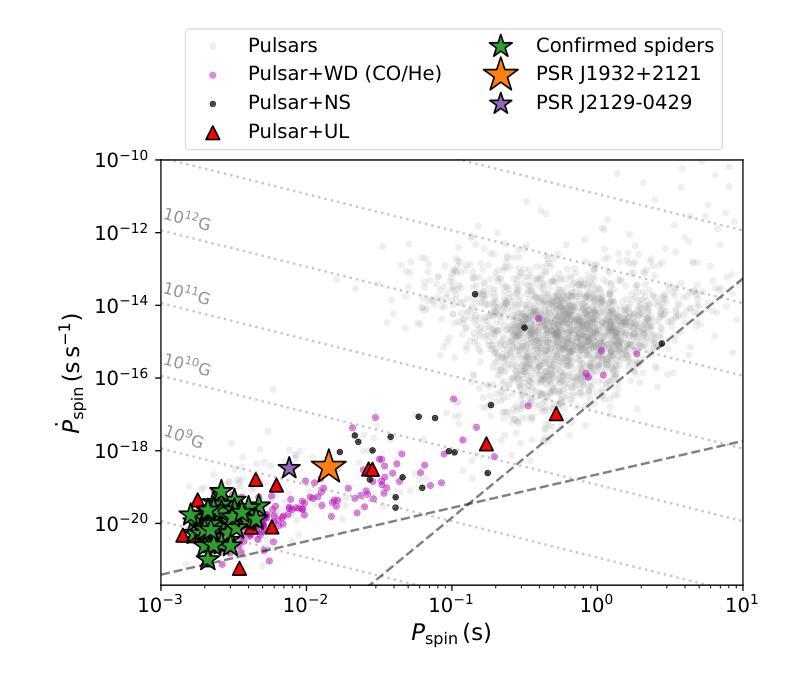
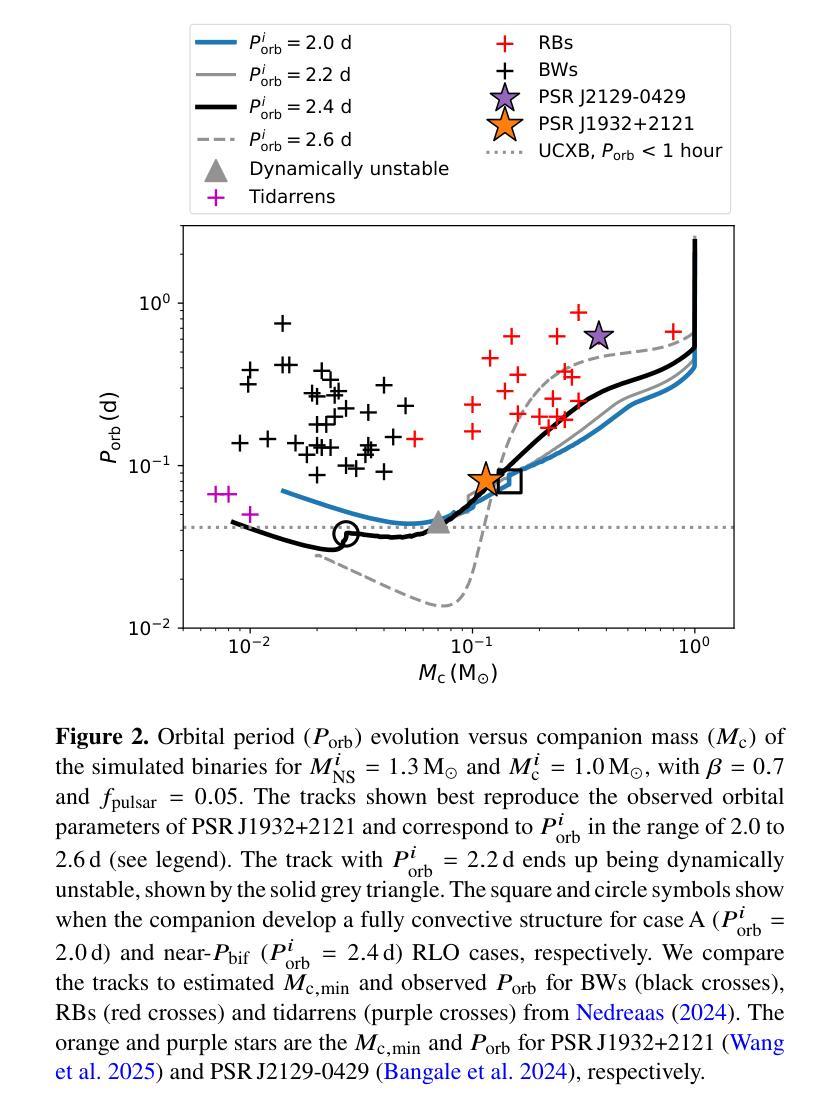
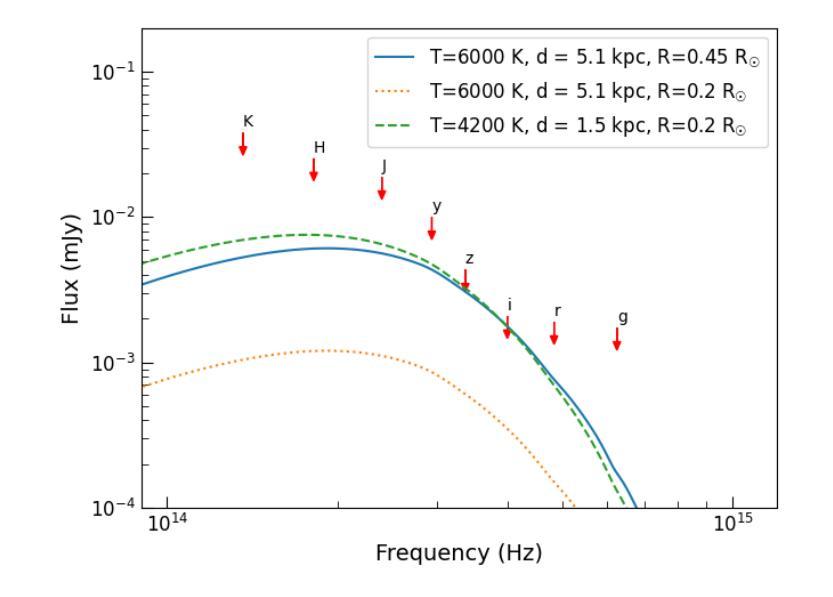
The slowest spinning Galactic-field spider PSR J1932+2121: A history of inefficient mass transfer
Authors:Devina Misra, Karri I. I. Koljonen, Manuel Linares
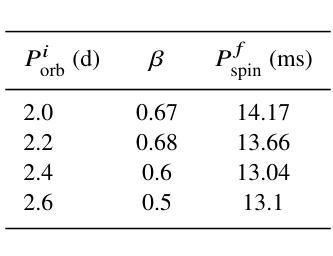
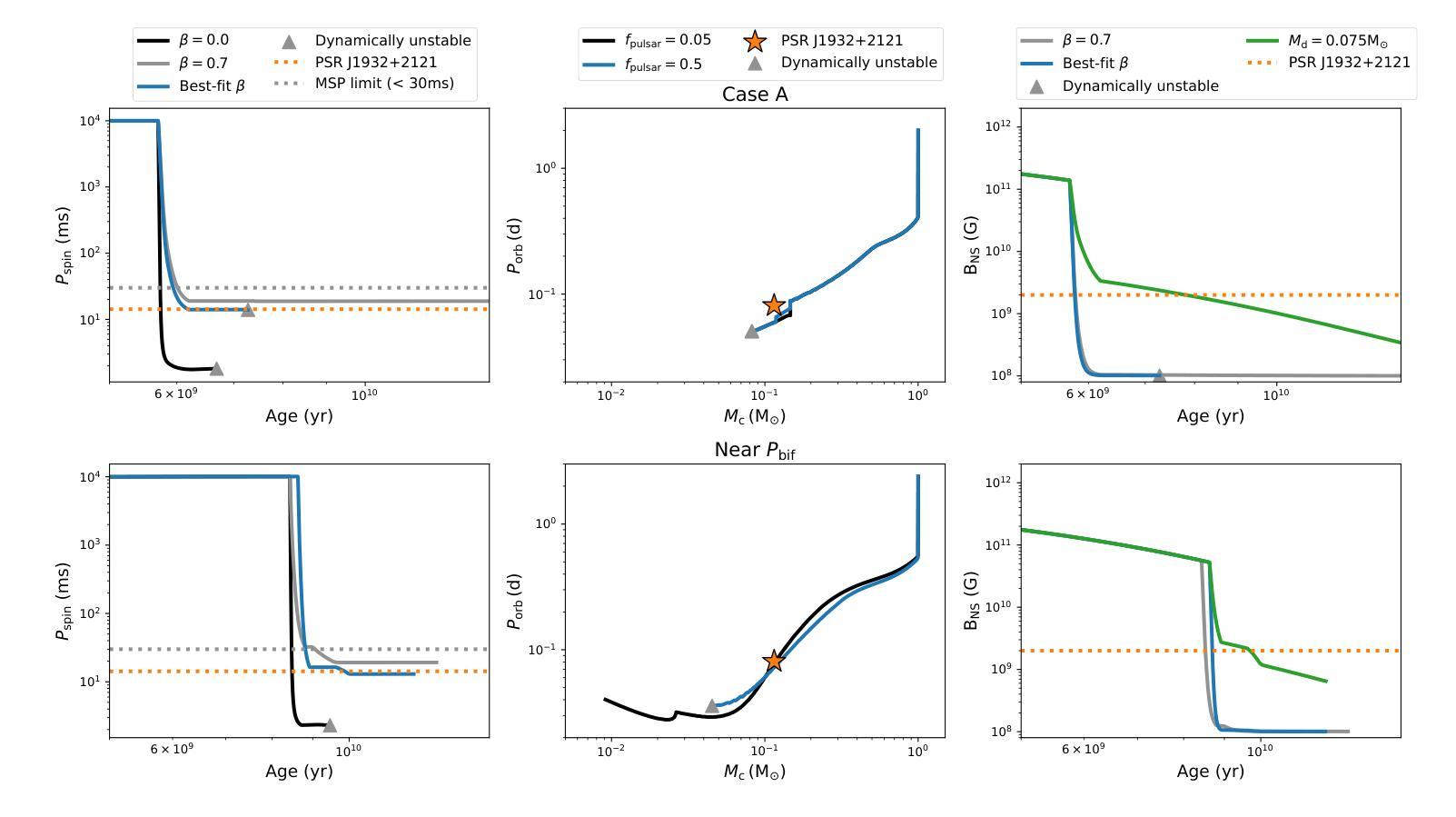
The Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope is discovering hundreds of new pulsars, including a slowly spinning compact binary millisecond pulsar (spin period $P_{\rm spin}=14.2$,ms) which showed radio eclipses and evidence of ablation of its companion: PSR J1932+2121. Its orbital period is $P_{\rm orb}=0.08$,d and the minimum companion mass is estimated as 0.12,\Msun. Hence, this pulsar is classified as part of the Galactic-field spider (redback) population. However, it spins almost an order of magnitude slower than other Galactic-field spiders. Using detailed evolutionary calculations with {\tt MESA}, we model the formation, mass-transfer and radio-pulsar phases, in order to explain the observed properties of PSR,J1932+2121. We find that PSR,J1932+2121 is a redback that has experienced an inefficient mass-transfer phase resulting in a lower accretion efficiency (in the range of 0.3 to 0.5) and subsequently slower spin compared to other spiders. We narrow down the initial range of $P_{\rm orb}$ that best reproduces its properties, to 2.0–2.6,d. Current models of accretion-induced magnetic field decay are not able to explain its unusually high surface magnetic field of $2\times 10^{9}$,G. Hence, PSR,J1932+2121 provides a unique opportunity to study inefficient accretion-induced spin up and surface magnetic field decay of pulsars.
五百米口径球状望远镜正在发现数百个新的脉冲星,其中包括一个缓慢旋转的紧凑二元毫秒脉冲星(自转周期 P_{\rm spin}=14.2 ms),它显示出射电掩星和其同伴被剥离的迹象:PSR J1932+2121。其轨道周期为 P_{\rm orb}=0.08 d,同伴星的最小质量估计为0.12\Msun。因此,该脉冲星被归类为银河场蜘蛛(redback)的一部分。然而,与其他银河场蜘蛛相比,它的自转速度几乎慢了一个数量级。我们使用{\tt MESA}进行详细的演化计算,对PSR J1932+2121的形成、质量传递和射电脉冲星阶段进行建模,以解释其观测到的特性。我们发现PSR J1932+2121是一颗经历了低效质量传递阶段的redback,导致较低的吸积效率(在0.3至0.5的范围内),自转速度较慢。我们将其轨道周期的初始范围缩小到最佳符合其特性的范围是2.0–2.6 d。当前吸积诱导磁场衰减模型无法解释其异常高的表面磁场(高达 2\times 10^{9} G)。因此,PSR J1932+2121为研究脉冲星吸积引起的自转加速和表面磁场衰减提供了独特的机会。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 4 figures. Accepted by MNRAS Letters. Referee’s comments were addressed
摘要
五百年口径望远镜发现数百颗新脉冲星,其中包括一颗缓慢旋转的致密二元毫秒脉冲星(自转周期P_{\rm spin}=14.2 ms),显示出射电掩星和其伴侣星被剥离的迹象:PSR J1932+2121。其轨道周期为P_{\rm orb}=0.08天,伴侣星最小质量估计为0.12Msun。因此,这颗脉冲星被归类为银河场蜘蛛(redback)种群的一部分。然而,它的自转速度比其他银河场蜘蛛慢几乎一个数量级。我们使用{\tt MESA}进行详细的演化计算,模拟PSR J1932+2121的形成、质量传递和射电脉冲星阶段,以解释其观测到的特性。我们发现PSR J1932+2121是一颗经历了低效质量传递阶段的redback,导致较低的吸积效率(在0.3至0.5范围内),因此自转速度较慢。我们缩小了最佳复现其属性的初始轨道周期范围,为2.0–2.6天。目前的吸积诱导磁场衰减模型无法解释其高达2× 10^9 G的表面磁场强度。因此,PSR J1932+2121为研究脉冲星吸积引起的低效自转加速和表面磁场衰减提供了独特的机会。
关键见解
- 五百公尺口径望远镜发现数百颗新脉冲星,包括一颗特殊脉冲星PSR J1932+2121。
- PSR J1932+2121展现出射电掩星和其伴侣星被剥离的迹象,属于银河场蜘蛛(redback)种群。
- PSR J1932+212的自转速度较慢,这可能与它的吸积效率低下有关。
点此查看论文截图