⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-03 更新
ReasonGen-R1: CoT for Autoregressive Image generation models through SFT and RL
Authors:Yu Zhang, Yunqi Li, Yifan Yang, Rui Wang, Yuqing Yang, Dai Qi, Jianmin Bao, Dongdong Chen, Chong Luo, Lili Qiu
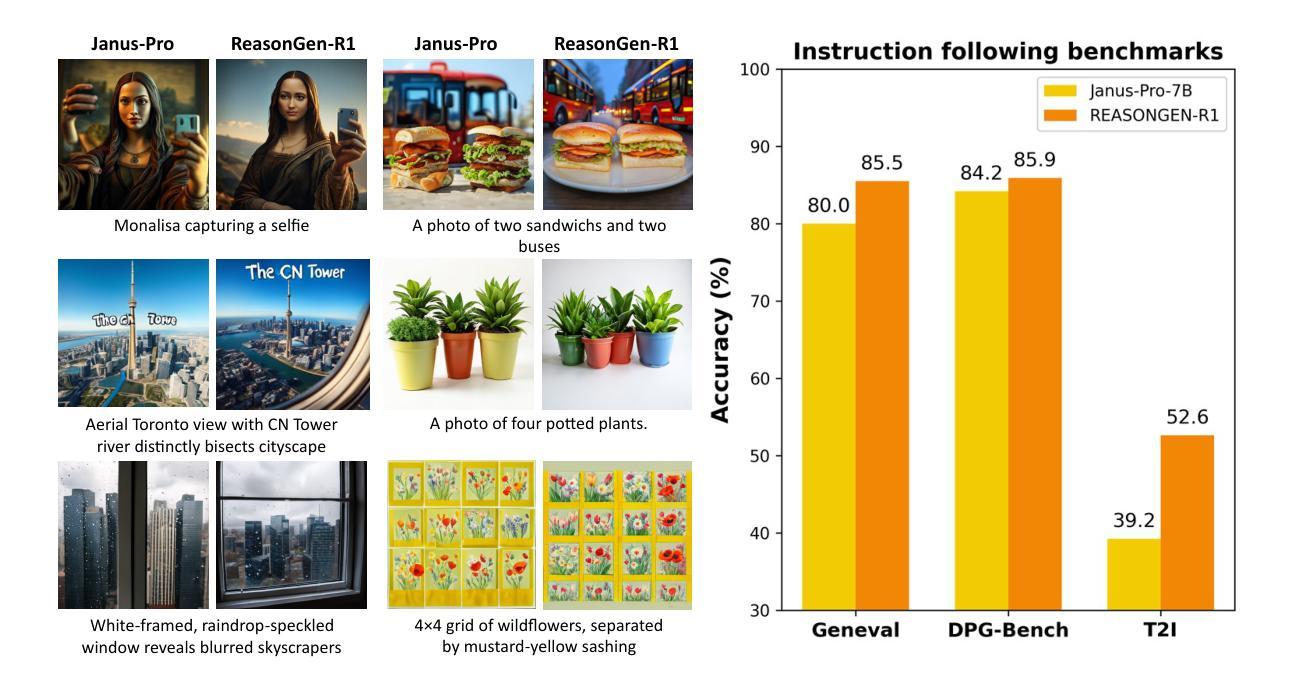
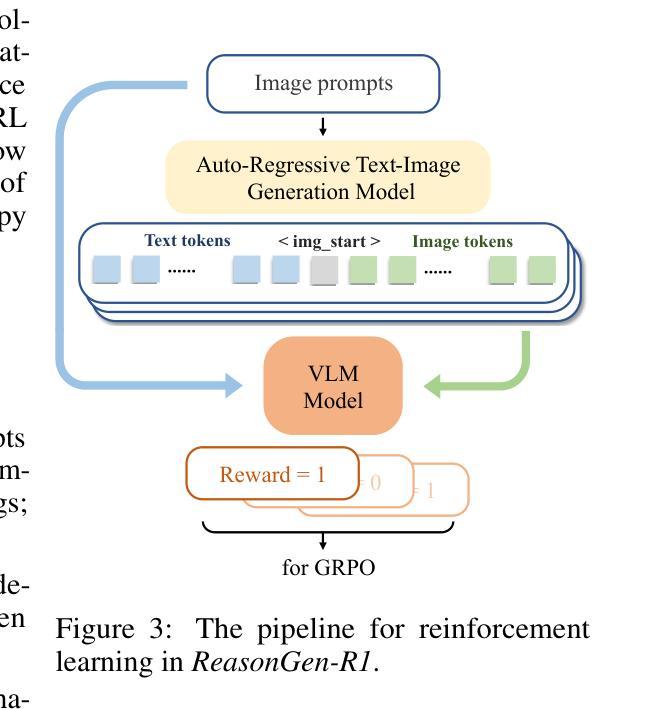
Although chain-of-thought reasoning and reinforcement learning (RL) have driven breakthroughs in NLP, their integration into generative vision models remains underexplored. We introduce ReasonGen-R1, a two-stage framework that first imbues an autoregressive image generator with explicit text-based “thinking” skills via supervised fine-tuning on a newly generated reasoning dataset of written rationales, and then refines its outputs using Group Relative Policy Optimization. To enable the model to reason through text before generating images, We automatically generate and release a corpus of model crafted rationales paired with visual prompts, enabling controlled planning of object layouts, styles, and scene compositions. Our GRPO algorithm uses reward signals from a pretrained vision language model to assess overall visual quality, optimizing the policy in each update. Evaluations on GenEval, DPG, and the T2I benchmark demonstrate that ReasonGen-R1 consistently outperforms strong baselines and prior state-of-the-art models. More: aka.ms/reasongen.
尽管思维链推理和强化学习(RL)在自然语言处理(NLP)领域取得了突破,但它们融入生成式视觉模型的研究仍然不足。我们引入了ReasonGen-R1,这是一个两阶段框架,首先通过在新生成的基于文本推理数据集上进行监督微调,赋予自回归图像生成器明确的基于文本的“思考”技能,然后使用群体相对策略优化来优化其输出。为了能够让模型在生成图像之前通过文本进行推理,我们自动生成并发布了一系列与视觉提示配对的人工构造理由语料库,从而实现对象布局、风格和场景组成的受控规划。我们的GRPO算法使用来自预训练视觉语言模型的奖励信号来评估整体视觉质量,并在每次更新中优化策略。在GenEval、DPG和T2I基准测试上的评估结果表明,ReasonGen-R1持续超越强劲的基准线和先前的最先进的模型。更多信息请访问aka.ms/reasongen。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了ReasonGen-R1模型,这是一个将链式思维推理与强化学习结合的两阶段框架,用于生成具有文本基础的“思考”技能的图像生成器。首先通过在新生成的推理数据集上进行监督微调,使模型具备推理能力,然后使用集团相对策略优化算法对其输出进行精炼。模型通过文本进行推理后生成图像,并自动生成与视觉提示配对的数据集,以控制对象布局、风格和场景构图。评价结果表明,ReasonGen-R1在GenEval、DPG和T2I基准测试上均优于强大的基准模型和先前最先进的模型。
Key Takeaways
- ReasonGen-R1结合了链式思维推理和强化学习,成功应用于生成具有文本基础的“思考”技能的图像生成器。
- 通过在新生成的推理数据集上进行监督微调,模型获得了文本驱动的推理能力。
- 使用集团相对策略优化算法(GRPO)精炼模型输出,以提高图像质量。
- 模型能够先通过文本进行推理再生成图像,提供了更多的创造性和控制力。
- 自动生成与视觉提示配对的数据集,有助于控制对象布局、风格和场景构图。
- 评价结果证明了ReasonGen-R1在多个基准测试上的优越性能。
点此查看论文截图

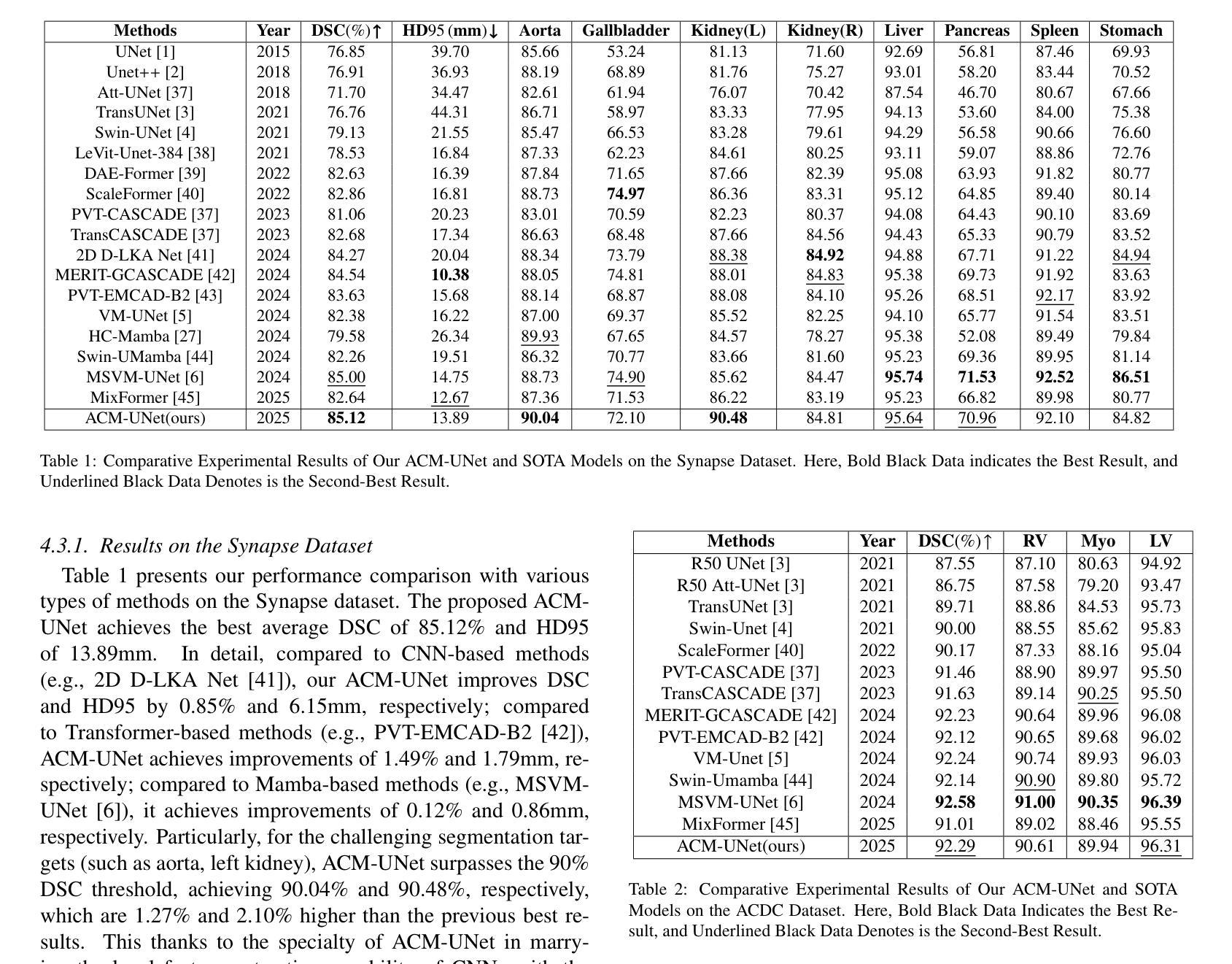
ACM-UNet: Adaptive Integration of CNNs and Mamba for Efficient Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Jing Huang, Yongkang Zhao, Yuhan Li, Zhitao Dai, Cheng Chen, Qiying Lai
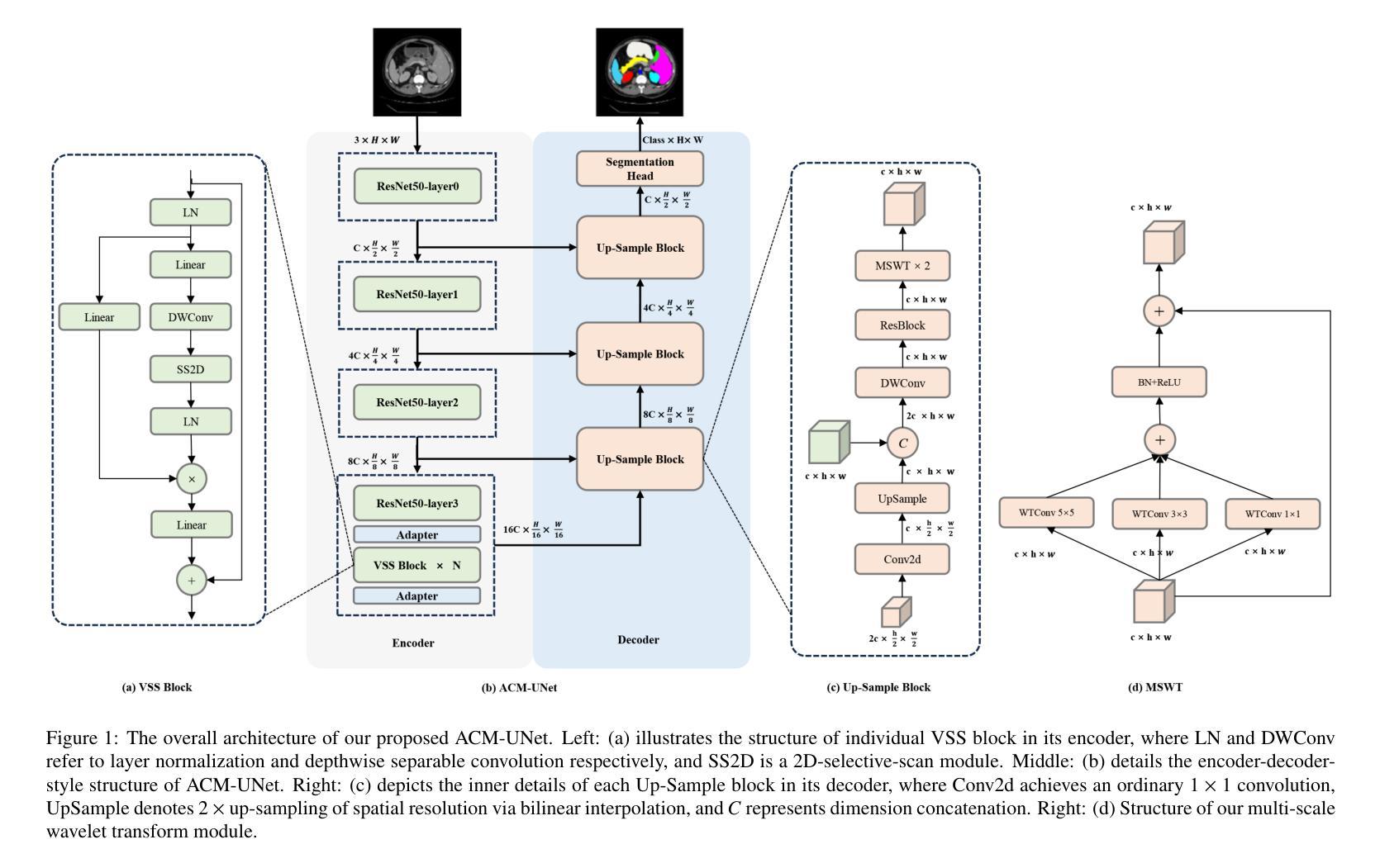
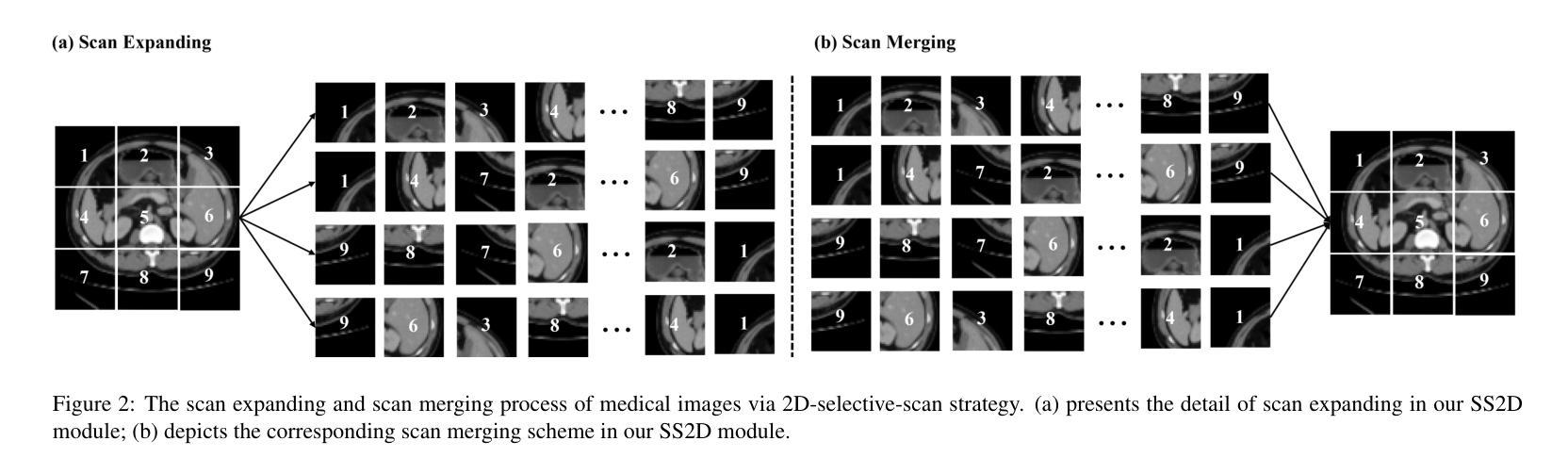
The U-shaped encoder-decoder architecture with skip connections has become a prevailing paradigm in medical image segmentation due to its simplicity and effectiveness. While many recent works aim to improve this framework by designing more powerful encoders and decoders, employing advanced convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for local feature extraction, Transformers or state space models (SSMs) such as Mamba for global context modeling, or hybrid combinations of both, these methods often struggle to fully utilize pretrained vision backbones (e.g., ResNet, ViT, VMamba) due to structural mismatches. To bridge this gap, we introduce ACM-UNet, a general-purpose segmentation framework that retains a simple UNet-like design while effectively incorporating pretrained CNNs and Mamba models through a lightweight adapter mechanism. This adapter resolves architectural incompatibilities and enables the model to harness the complementary strengths of CNNs and SSMs-namely, fine-grained local detail extraction and long-range dependency modeling. Additionally, we propose a hierarchical multi-scale wavelet transform module in the decoder to enhance feature fusion and reconstruction fidelity. Extensive experiments on the Synapse and ACDC benchmarks demonstrate that ACM-UNet achieves state-of-the-art performance while remaining computationally efficient. Notably, it reaches 85.12% Dice Score and 13.89mm HD95 on the Synapse dataset with 17.93G FLOPs, showcasing its effectiveness and scalability. Code is available at: https://github.com/zyklcode/ACM-UNet.
具有跳跃连接的U形编码器-解码器架构因其简单性和有效性已成为医学图像分割中的主流范式。虽然最近许多工作旨在通过设计更强大的编码器和解码器、使用先进的卷积神经网络(CNN)进行局部特征提取、使用变压器或状态空间模型(SSM)如Mamba进行全局上下文建模,或两者的混合组合来改进此框架,但这些方法往往难以充分利用预训练的视觉主干(例如ResNet、ViT、VMamba)由于结构不匹配。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了ACM-UNet,这是一个通用分割框架,它保留了简单的UNet设计,同时通过轻量级适配器机制有效地结合了预训练的CNN和Mamba模型。该适配器解决了架构不兼容的问题,使模型能够利用CNN和SSM的互补优势,即精细的局部细节提取和长距离依赖建模。此外,我们在解码器中提出了分层多尺度小波变换模块,以增强特征融合和重建保真度。在Synapse和ACDC基准测试上的广泛实验表明,ACM-UNet在保持计算效率的同时实现了最先进的性能。值得注意的是,它在Synapse数据集上达到了85.12%的Dice分数和13.89mm的HD98(可能误打,应为HD95),展示了其有效性和可扩展性。代码可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/zyklcode/ACM-UNet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 3 figures, 5 tables
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为ACM-UNet的通用医学图像分割框架,它采用简单的UNet设计,并通过轻量级适配器有效结合预训练的CNN和Mamba模型。该适配器解决了架构不兼容问题,使模型能够利用CNN和SSM的互补优势。此外,还提出了层次化的多尺度小波变换模块,以增强特征融合和重建的保真度。在Synapse和ACDC基准测试上,ACM-UNet实现了最先进的性能,同时保持了计算效率。
Key Takeaways
- ACM-UNet是一种医学图像分割框架,基于U型编码器-解码器架构并带有skip连接。
- 它通过轻量级适配器有效结合预训练的CNN和Mamba模型,解决架构不匹配问题。
- ACM-UNet结合CNN和SSM的互补优势,分别擅长细粒度局部细节提取和长距离依赖建模。
- 框架中引入了层次化的多尺度小波变换模块,增强特征融合和重建的保真度。
- 在Synapse和ACDC基准测试中,ACM-UNet实现了最先进的性能。
- ACM-UNet达到85.12%的Dice得分和13.89mm HD95,同时保持17.93G FLOPs的计算效率。
- 代码已公开在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图

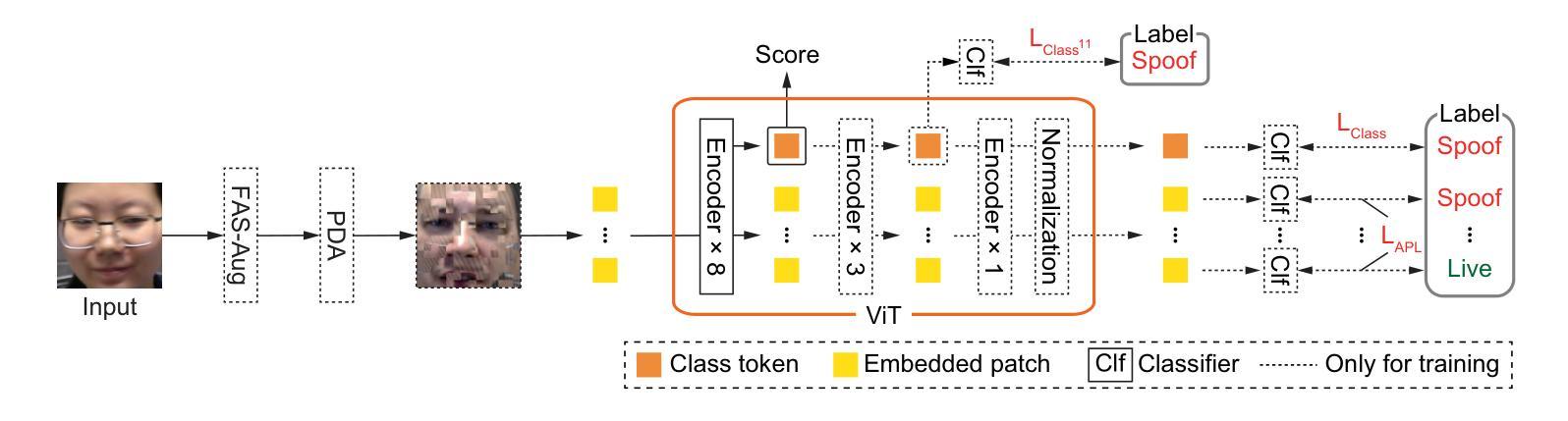
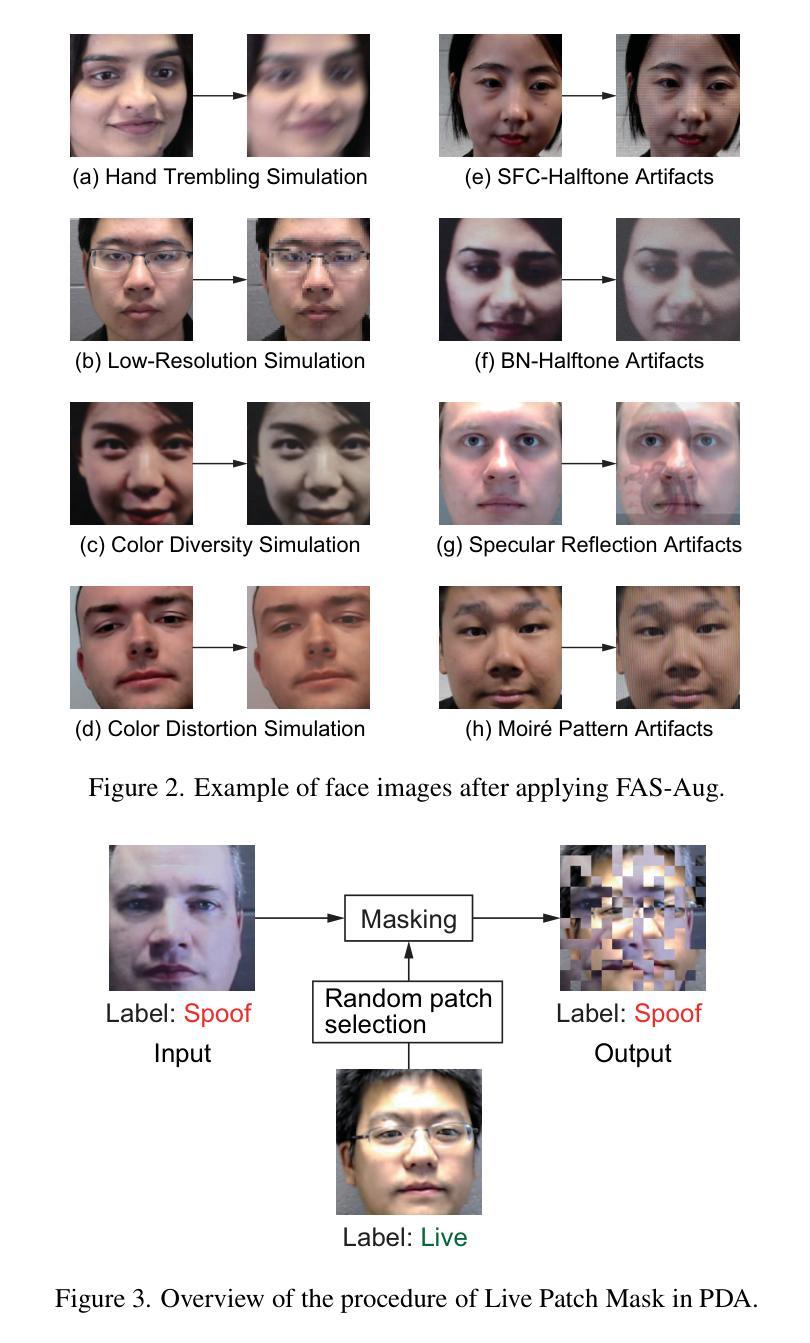
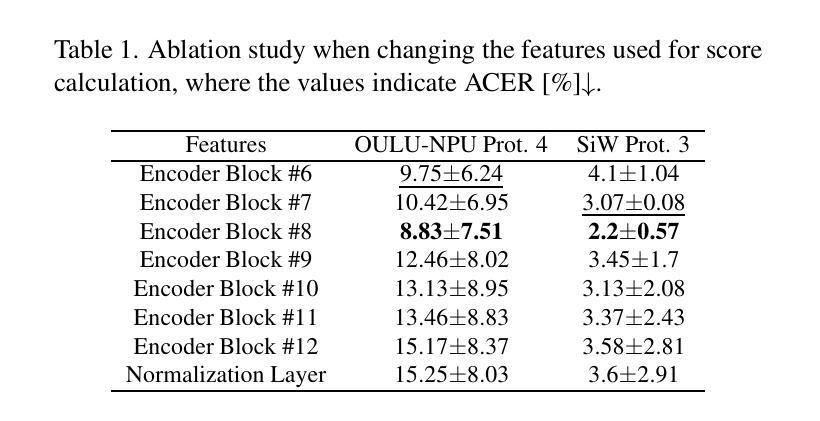
Leveraging Intermediate Features of Vision Transformer for Face Anti-Spoofing
Authors:Mika Feng, Koichi Ito, Takafumi Aoki, Tetsushi Ohki, Masakatsu Nishigaki
Face recognition systems are designed to be robust against changes in head pose, illumination, and blurring during image capture. If a malicious person presents a face photo of the registered user, they may bypass the authentication process illegally. Such spoofing attacks need to be detected before face recognition. In this paper, we propose a spoofing attack detection method based on Vision Transformer (ViT) to detect minute differences between live and spoofed face images. The proposed method utilizes the intermediate features of ViT, which have a good balance between local and global features that are important for spoofing attack detection, for calculating loss in training and score in inference. The proposed method also introduces two data augmentation methods: face anti-spoofing data augmentation and patch-wise data augmentation, to improve the accuracy of spoofing attack detection. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method through experiments using the OULU-NPU and SiW datasets.
人脸识别系统设计时考虑到对头部姿态、照明和图像捕捉过程中的模糊变化的稳健性。如果恶意人员出示注册用户的面部照片,他们可能会非法绕过认证过程。必须在人脸识别之前检测到这种欺骗攻击。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的欺骗攻击检测方法,以检测实时和伪造面部图像之间的微小差异。该方法利用ViT的中间特征,这些特征在局部和全局特征之间具有良好的平衡,对于欺骗攻击检测很重要,用于计算训练和推理中的损失和得分。该方法还引入两种数据增强方法:面部防欺骗数据增强和补丁级数据增强,以提高欺骗攻击检测的准确性。我们通过使用OULU-NPU和SiW数据集的实验证明了该方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2025 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW)
摘要
本文提出了一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的防伪攻击检测法,用于识别真实与伪造人脸图像之间的细微差异。该方法利用ViT的中间特征,兼顾局部和全局特征,有利于防伪攻击检测。此外,引入两种数据增强方法——面部防伪数据增强和块级数据增强,提高防伪攻击检测的准确性。通过实验在OULU-NPU和SiW数据集上的验证,证明了该方法的有效性。
关键见解
- 伪造人脸照片可能绕过身份验证过程,存在安全隐患。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)可用于检测真实与伪造人脸图像之间的差异。
- ViT的中间特征兼顾局部和全局信息,对防伪攻击检测至关重要。
- 引入数据增强方法提高防伪攻击检测的准确性。
- 提出的检测法采用损失计算训练并得分推理。
- 实验在OULU-NPU和SiW数据集上验证了方法的有效性。
- 该方法可提高人脸识别系统的安全性,对抗伪造攻击。
点此查看论文截图

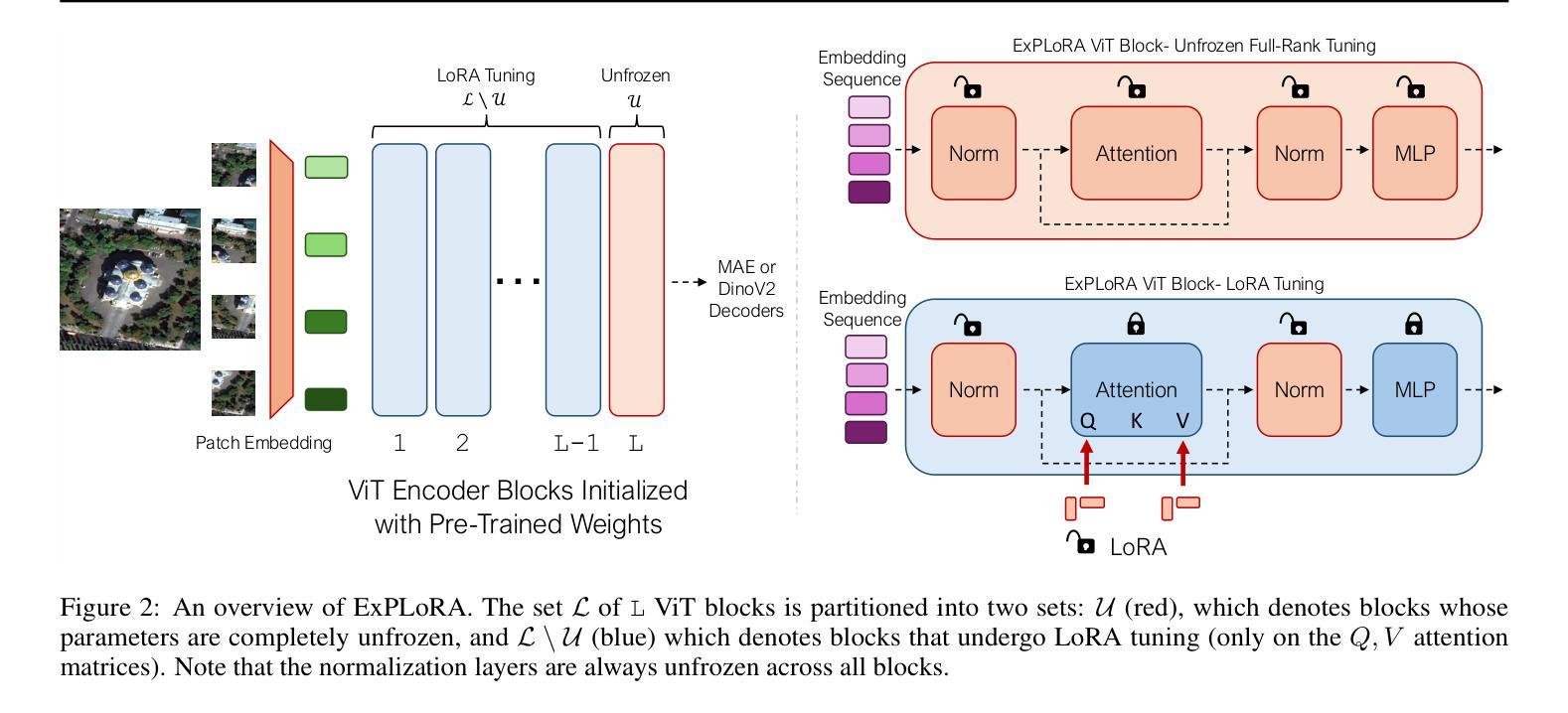
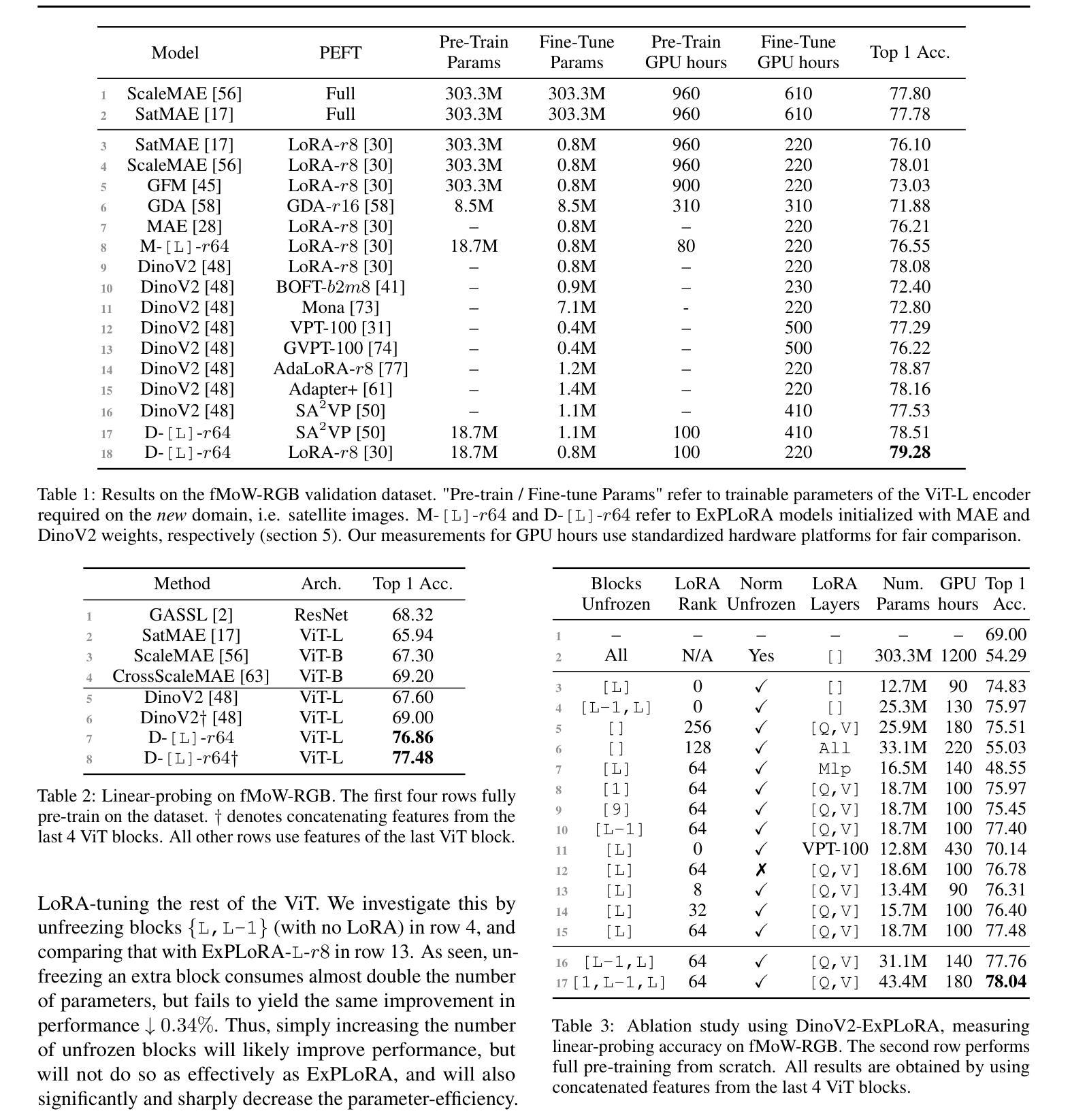
ExPLoRA: Parameter-Efficient Extended Pre-Training to Adapt Vision Transformers under Domain Shifts
Authors:Samar Khanna, Medhanie Irgau, David B. Lobell, Stefano Ermon
Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) techniques such as low-rank adaptation (LoRA) can effectively adapt large pre-trained foundation models to downstream tasks using only a small fraction (0.1%-10%) of the original trainable weights. An under-explored question of PEFT is in extending the pre-training phase without supervised labels; that is, can we adapt a pre-trained foundation model to a new domain via efficient self-supervised pre-training on this domain? In this work, we introduce ExPLoRA, a highly effective technique to improve transfer learning of pre-trained vision transformers (ViTs) under domain shifts. Initializing a ViT with pre-trained weights on large, natural-image datasets such as from DinoV2 or MAE, ExPLoRA continues the unsupervised pre-training objective on a new domain, unfreezing 1-2 pre-trained ViT blocks and tuning all other layers with LoRA. We then fine-tune the resulting model only with LoRA on this new domain for supervised learning. Our experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art results on satellite imagery, even outperforming fully pre-training and fine-tuning ViTs. Using the DinoV2 training objective, we demonstrate up to 8% improvement in linear probing top-1 accuracy on downstream tasks while using <10% of the number of parameters that are used in prior fully-tuned state-of-the art approaches. Our ablation studies confirm the efficacy of our approach over other baselines such as PEFT. Code is available on the project website: https://samar-khanna.github.io/ExPLoRA/
参数效率微调(PEFT)技术,如低秩适应(LoRA),可以有效地使大型预训练基础模型适应下游任务,仅使用原始可训练权重的很小一部分(0.1%-10%)。PEFT的一个尚未探索的问题是扩展预训练阶段而无需监督标签;也就是说,我们是否可以通过在此领域进行有效的自我监督预训练,将预训练的基础模型适应到新领域?在这项工作中,我们引入了ExPLoRA,这是一种有效提高预训练视觉转换器(ViT)在领域转移中的迁移学习能力的高效技术。ExPLoRA以大型自然图像数据集(如DinoV2或MAE)上的预训练权重初始化ViT,继续在新领域进行无监督的预训练目标,解冻1-2个预训练的ViT块,并用LoRA调整所有其他层的参数。然后,我们仅使用LoRA在此新领域上进行监督学习对模型进行微调。我们的实验在卫星图像上展示了卓越的结果,甚至超越了完全预训练和微调ViT。使用DinoV2的训练目标,我们在下游任务的线性探测top-1准确率上提高了高达8%,同时使用的参数数量不到先前完全调整过的最先进的方法的10%。我们的消融研究证实了我们的方法在其他基线(如PEFT)上的有效性。代码可在项目网站上找到:https://samar-khanna.github.io/ExPLoRA/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at ICML 2025
Summary
使用参数高效的微调技术如LoRA能够实现对大型预训练基础模型的有效适应下游任务,仅使用原始可训练权重的极小部分(0.1%-10%)。本研究介绍了ExPLoRA技术,该技术能有效提高预训练视觉Transformer(ViT)在不同领域间的迁移学习能力。通过初始化大型自然图像数据集如DinoV2或MAE上的预训练权重,ExPLoRA在新的领域上继续无监督的预训练目标,并只解冻少量预训练的ViT块并用LoRA对其它所有层进行微调。实验结果证明了该技术在卫星图像上的领先水平,甚至超过了完全预训练和微调ViT的方法。使用DinoV2训练目标,我们在下游任务上实现了高达8%的线性探测top-1准确率提升,同时仅使用了少量参数。该技术的优势得到了我们的实验验证。
Key Takeaways
- ExPLoRA是一种改进预训练视觉Transformer(ViT)在不同领域迁移学习性能的技术。
- ExPLoRA技术在无监督预训练阶段通过解冻部分预训练ViT块并应用LoRA技术进行微调。
- 该技术能在新的领域上实现高效迁移学习,并优于完全预训练和微调ViT的方法。
- 在下游任务上实现了高达8%的准确率提升,同时使用的参数更少。
- 该技术适用于卫星图像等特定领域的应用场景。
点此查看论文截图