⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-04 更新
CTRL-GS: Cascaded Temporal Residue Learning for 4D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Karly Hou, Wanhua Li, Hanspeter Pfister
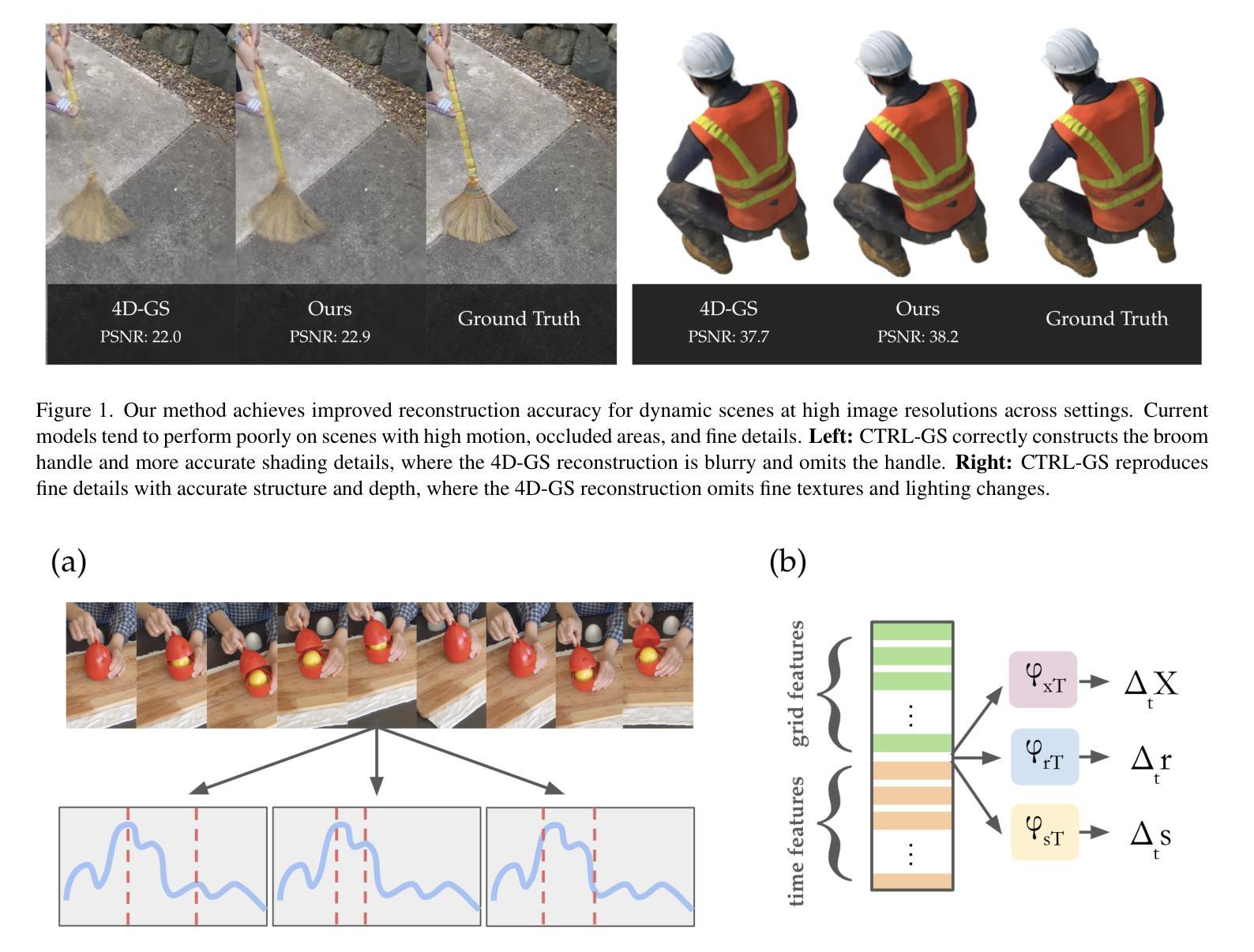
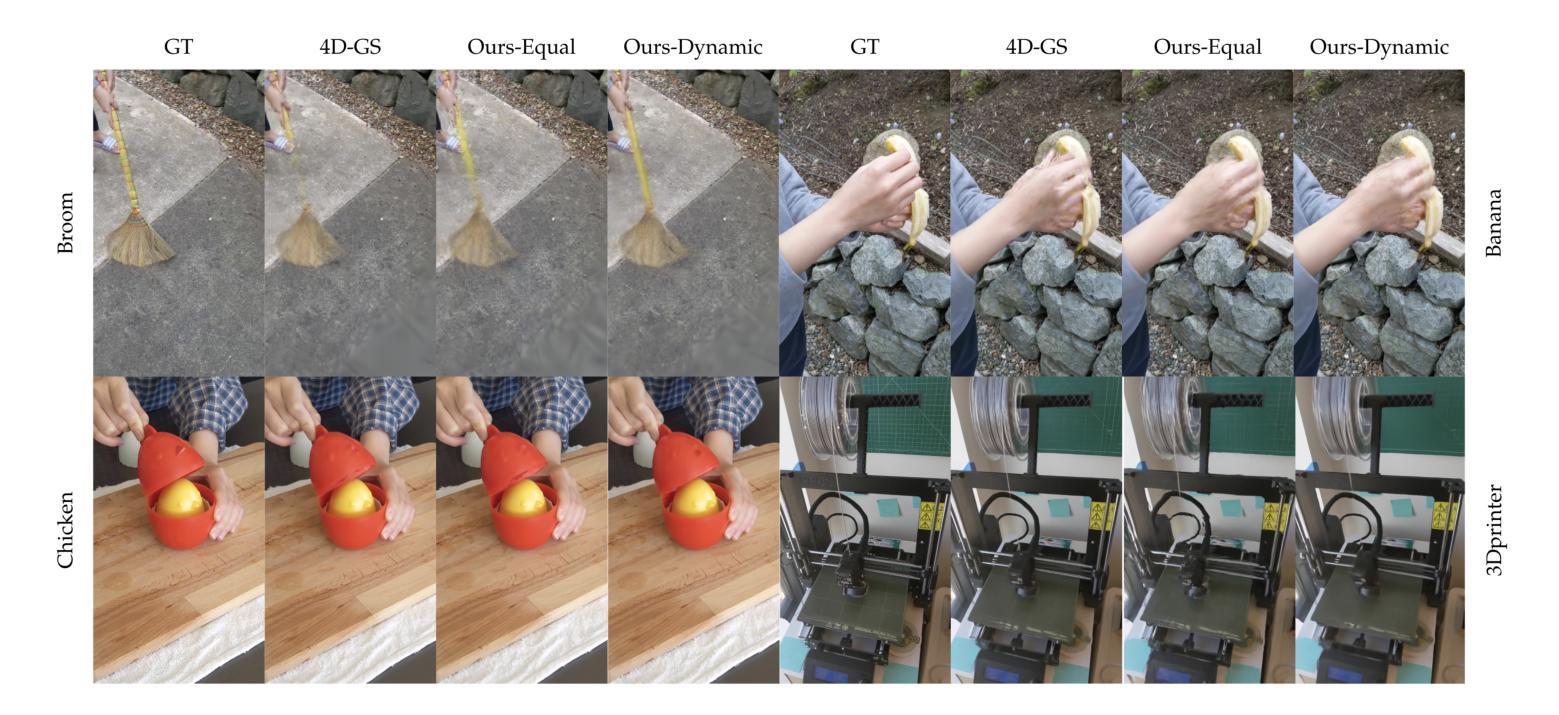
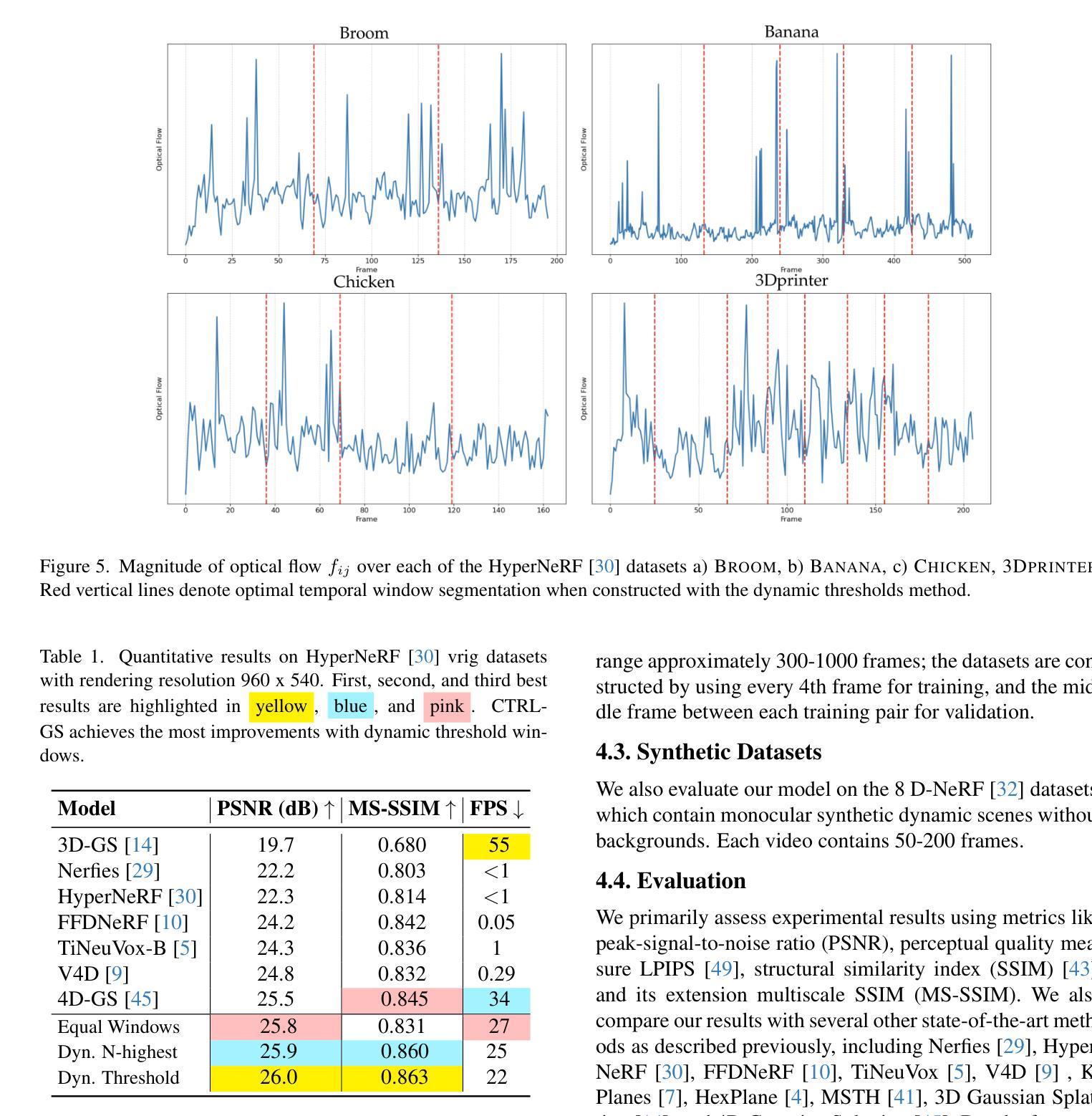
Recently, Gaussian Splatting methods have emerged as a desirable substitute for prior Radiance Field methods for novel-view synthesis of scenes captured with multi-view images or videos. In this work, we propose a novel extension to 4D Gaussian Splatting for dynamic scenes. Drawing on ideas from residual learning, we hierarchically decompose the dynamic scene into a “video-segment-frame” structure, with segments dynamically adjusted by optical flow. Then, instead of directly predicting the time-dependent signals, we model the signal as the sum of video-constant values, segment-constant values, and frame-specific residuals, as inspired by the success of residual learning. This approach allows more flexible models that adapt to highly variable scenes. We demonstrate state-of-the-art visual quality and real-time rendering on several established datasets, with the greatest improvements on complex scenes with large movements, occlusions, and fine details, where current methods degrade most.
最近,高斯摊铺方法已成为先前辐射场方法的一种理想替代方法,用于对使用多视角图像或视频捕获的场景进行新颖视角合成。在这项工作中,我们提出了针对动态场景的4D高斯摊铺新方法。我们借鉴残差学习的思想,将动态场景层次地分解为“视频段帧”结构,并通过光流动态调整段。然后,我们不是直接预测时间相关信号,而是受残差学习成功的启发,将信号建模为视频恒定值、段恒定值和特定帧残差的总和。这种方法允许更灵活的模型,能够适应高度可变的场景。我们在几个公认的数据集上展示了最先进的视觉质量和实时渲染效果,在具有大动作、遮挡和精细细节等复杂场景上的改进最为显著,这是当前方法退化最严重的地方。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to 4D Vision Workshop @ CVPR 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于四维高斯拼贴技术的新型动态场景扩展方法。该方法借鉴残差学习的思想,将动态场景分解为“视频片段帧”结构,通过光流动态调整片段。建模时,将信号视为视频恒定值、片段恒定值和帧特定残差之和,以灵活适应高度可变的场景。在多个数据集上实现了最先进的视觉质量和实时渲染效果,特别是在具有大动作、遮挡和细节丰富的复杂场景中表现尤为出色。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于四维高斯拼贴技术的动态场景扩展方法。
- 通过借鉴残差学习的思想,将动态场景分解为“视频片段帧”结构。
- 通过光流动态调整片段,以提高模型的适应能力。
- 建模时将信号视为视频恒定值、片段恒定值和帧特定残差之和。
- 方法实现了灵活的模型,能够适应高度可变的场景。
- 在多个数据集上实现了先进的视觉质量和实时渲染效果。
点此查看论文截图


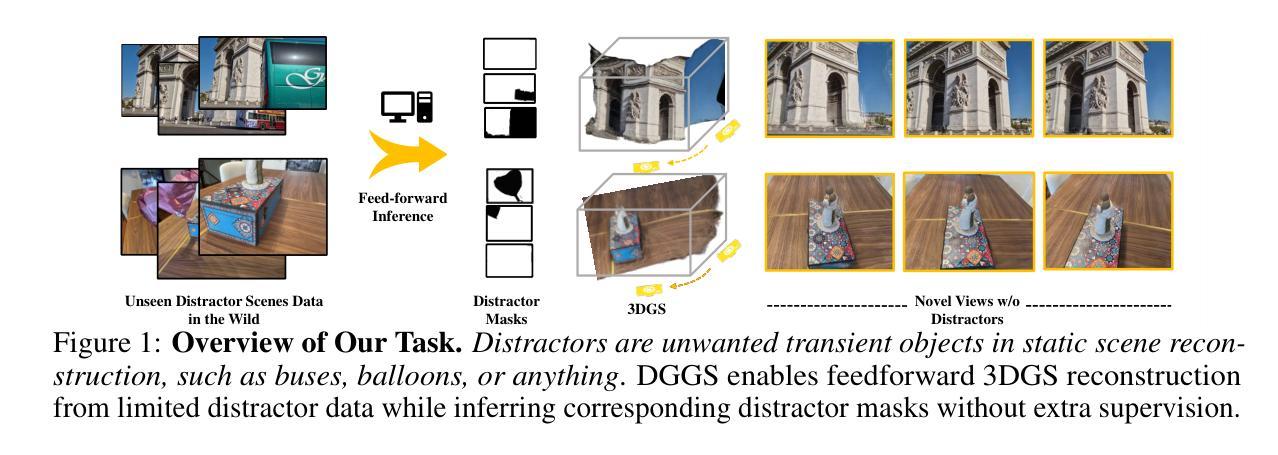
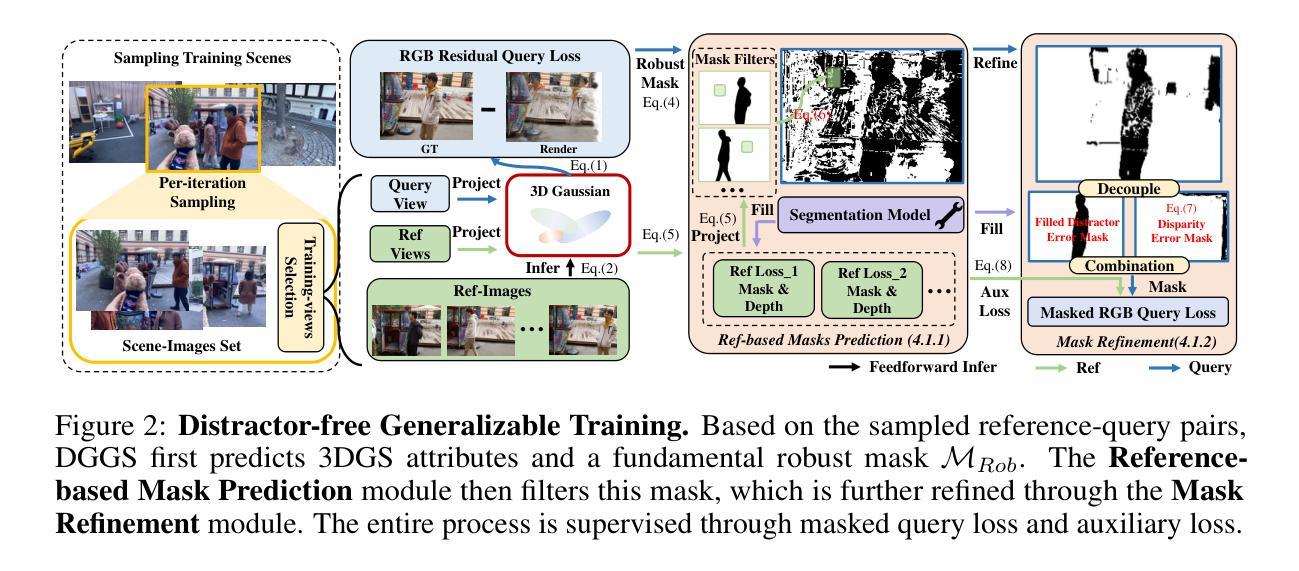
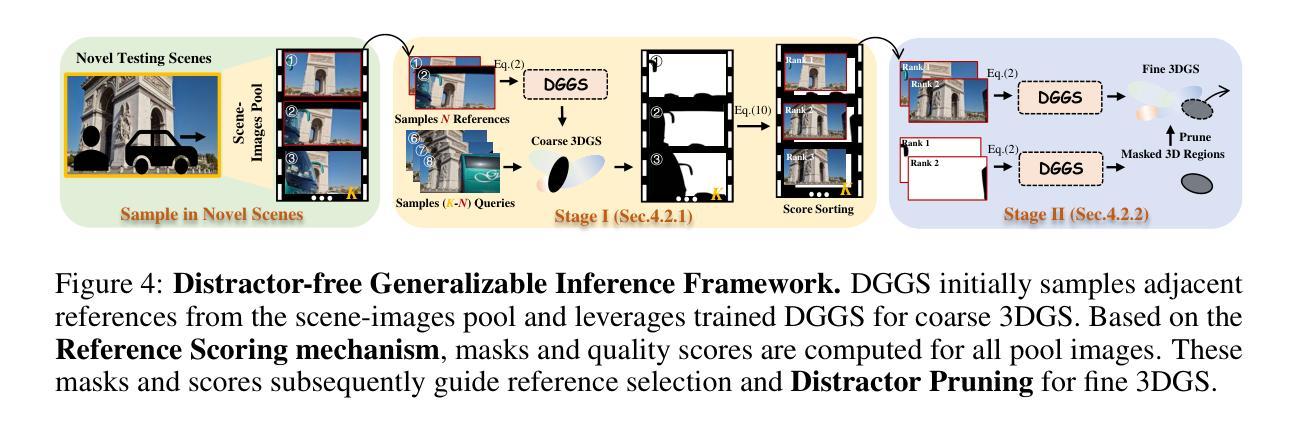
Distractor-free Generalizable 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yanqi Bao, Jing Liao, Jing Huo, Yang Gao
We present DGGS, a novel framework that addresses the previously unexplored challenge: $\textbf{Distractor-free Generalizable 3D Gaussian Splatting}$ (3DGS). It mitigates 3D inconsistency and training instability caused by distractor data in the cross-scenes generalizable train setting while enabling feedforward inference for 3DGS and distractor masks from references in the unseen scenes. To achieve these objectives, DGGS proposes a scene-agnostic reference-based mask prediction and refinement module during the training phase, effectively eliminating the impact of distractor on training stability. Moreover, we combat distractor-induced artifacts and holes at inference time through a novel two-stage inference framework for references scoring and re-selection, complemented by a distractor pruning mechanism that further removes residual distractor 3DGS-primitive influences. Extensive feedforward experiments on the real and our synthetic data show DGGS’s reconstruction capability when dealing with novel distractor scenes. Moreover, our generalizable mask prediction even achieves an accuracy superior to existing scene-specific training methods. Homepage is https://github.com/bbbbby-99/DGGS.
我们提出了DGGS,这是一种新型框架,解决了以前未被探索的挑战:无干扰物可泛化的三维高斯融合(3DGS)。它缓解了由干扰数据导致的三维不一致性和训练不稳定问题,这在跨场景泛化训练设置中,同时实现了对3DGS和未见场景中参考干扰掩膜的前馈推理。为了实现这些目标,DGGS在训练阶段提出了基于场景的参考掩膜预测和细化模块,有效地消除了干扰数据对训练稳定性的影响。此外,我们通过一个新的两阶段推理框架对参考评分和重新选择进行推断,解决了干扰数据引起的伪影和空洞问题,辅以干扰剔除机制,进一步消除了残余干扰物对3DGS原始影响。在真实和我们合成数据上的大量前馈实验表明,DGGS在处理新型干扰场景时的重建能力。此外,我们的可泛化的掩膜预测甚至达到了超过现有场景特定训练方法的准确性。主页是https://github.com/bbbbby-99/DGGS。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
DGGS是一个新颖框架,专注于解决此前尚未探索的挑战:无干扰物的一般化3D高斯喷绘(3DGS)。它减轻了由干扰物数据引起的3D不一致性和训练不稳定问题,同时实现了对未见场景的参考的前向推理和干扰物掩膜的预测。DGGS通过场景无关的参考掩膜预测和训练阶段的细化模块,有效消除了干扰物对训练稳定性的影响。此外,DGGS还通过参考评分和重新选择的双阶段推理框架以及干扰物修剪机制,解决了干扰物引起的伪像和空洞问题,进一步消除了残留的干扰物影响。对真实和合成数据的向前实验表明,DGGS在处理新型干扰物场景时的重建能力出众,且其通用的掩膜预测精度超过了现有的场景特定训练方法。
Key Takeaways
- DGGS是一个针对无干扰物的一般化3D高斯喷绘(3DGS)的新框架。
- DGGS解决了由干扰物数据引起的3D不一致性和训练不稳定问题。
- DGGS实现了基于参考的前向推理和干扰物掩膜的预测。
- DGGS通过场景无关的参考掩膜预测和细化模块,消除了干扰物对训练稳定性的影响。
- DGGS采用双阶段推理框架和干扰物修剪机制,解决干扰物引起的伪像和空洞问题。
- DGGS在真实和合成数据上的实验表现出其出色的重建能力和较高的掩膜预测精度。
- DGGS的通用性超越了现有的场景特定训练方法。
点此查看论文截图


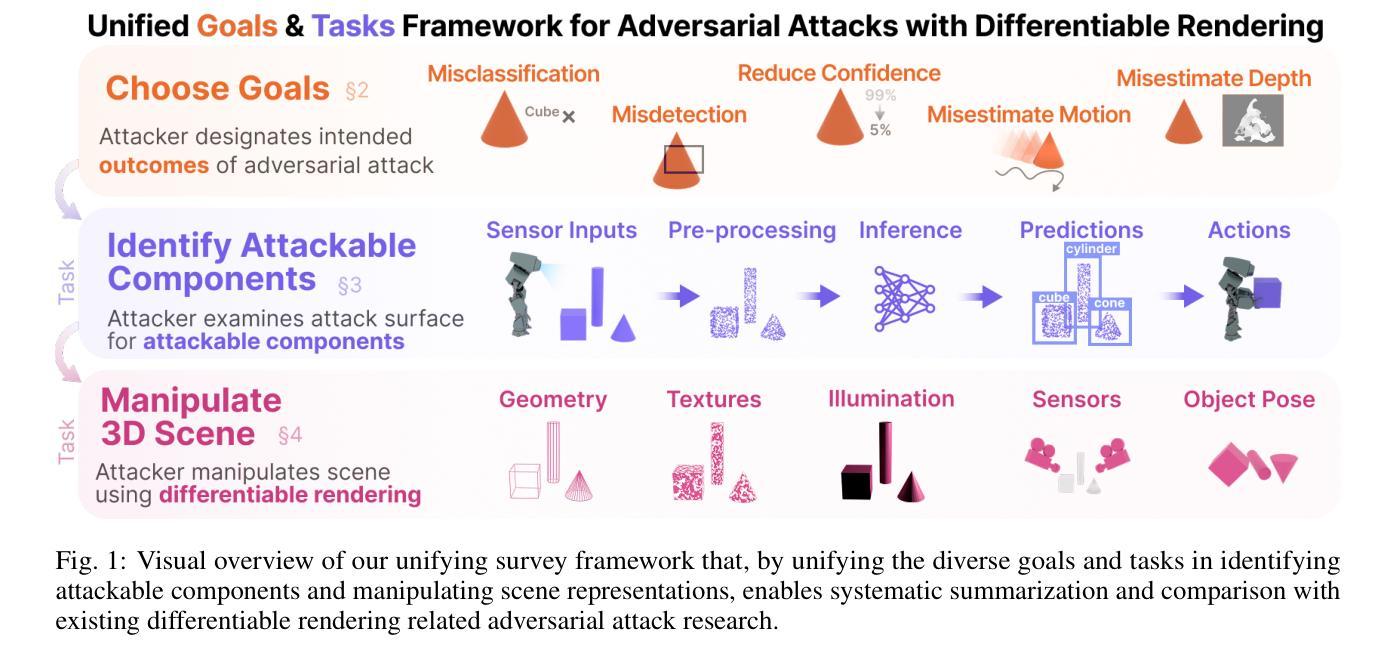
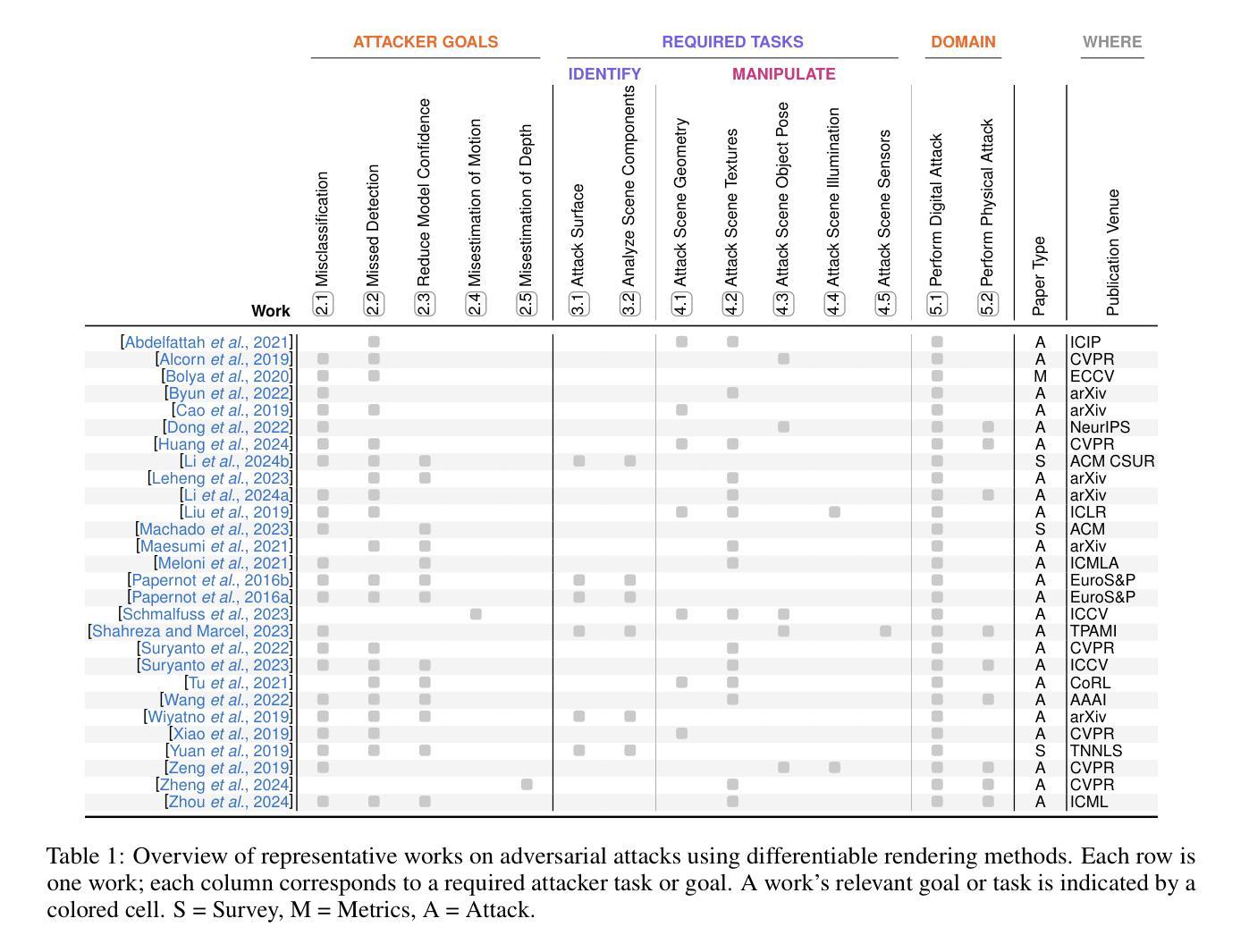
RenderBender: A Survey on Adversarial Attacks Using Differentiable Rendering
Authors:Matthew Hull, Haoran Wang, Matthew Lau, Alec Helbling, Mansi Phute, Chao Zhang, Zsolt Kira, Willian Lunardi, Martin Andreoni, Wenke Lee, Polo Chau
Differentiable rendering techniques like Gaussian Splatting and Neural Radiance Fields have become powerful tools for generating high-fidelity models of 3D objects and scenes. Their ability to produce both physically plausible and differentiable models of scenes are key ingredient needed to produce physically plausible adversarial attacks on DNNs. However, the adversarial machine learning community has yet to fully explore these capabilities, partly due to differing attack goals (e.g., misclassification, misdetection) and a wide range of possible scene manipulations used to achieve them (e.g., alter texture, mesh). This survey contributes the first framework that unifies diverse goals and tasks, facilitating easy comparison of existing work, identifying research gaps, and highlighting future directions - ranging from expanding attack goals and tasks to account for new modalities, state-of-the-art models, tools, and pipelines, to underscoring the importance of studying real-world threats in complex scenes.
像高斯填充(Gaussian Splatting)和神经辐射场(Neural Radiance Fields)这样的可微渲染技术已成为生成三维物体和场景高保真模型的有力工具。它们能够产生物理上可信且可微的场景模型,是生成针对深度神经网络(DNNs)的物理可信对抗攻击的关键要素。然而,对抗机器学习社区尚未充分探索这些能力,部分原因是攻击目标的不同(例如,误分类、误检测),以及为实现这些目标而使用的场景操作范围广泛(例如,改变纹理、网格)。本文贡献了一个统一的框架,该框架融合了各种目标和任务,促进了现有工作的轻松比较,确定了研究空白,并突出了未来研究方向——从扩大攻击目标和任务以适应新模态、最新模型、工具和流程,到强调在复杂场景中研究现实世界威胁的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 1 figure, 2 tables, IJCAI ‘25 Survey Track
Summary
本文介绍了可微渲染技术如高斯混色和神经辐射场在生成三维物体和场景高保真模型方面的强大功能。这些技术能够产生物理上可信和可微的场景模型,成为制作物理上可信的对深度神经网络(DNNs)的对抗攻击的关键要素。然而,对抗机器学习社区尚未充分利用这些能力,部分原因在于攻击目标的不同(如误分类、误检测)以及实现这些目标所使用的场景操纵手段的差异(如改变纹理、网格)。本文提出的首个统一框架有助于对各种目标和任务进行比较,识别研究空白,并强调未来的研究方向,包括扩展攻击目标和任务以适应新模态、最新模型、工具和流程,并强调在复杂场景中研究真实威胁的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 可微渲染技术如高斯混色和神经辐射场能生成高保真度的3D场景模型。
- 这些技术为制作物理上可信的对深度神经网络的对抗攻击提供了关键工具。
- 对抗机器学习社区尚未充分利用可微渲染技术,部分原因是攻击目标和手段的差异。
- 提出的统一框架有助于比较各种攻击目标,识别研究空白。
- 未来的研究方向包括扩展攻击目标和任务,以适应新模态、最新模型和流程。
- 该框架强调研究复杂场景中的真实威胁的重要性。
点此查看论文截图


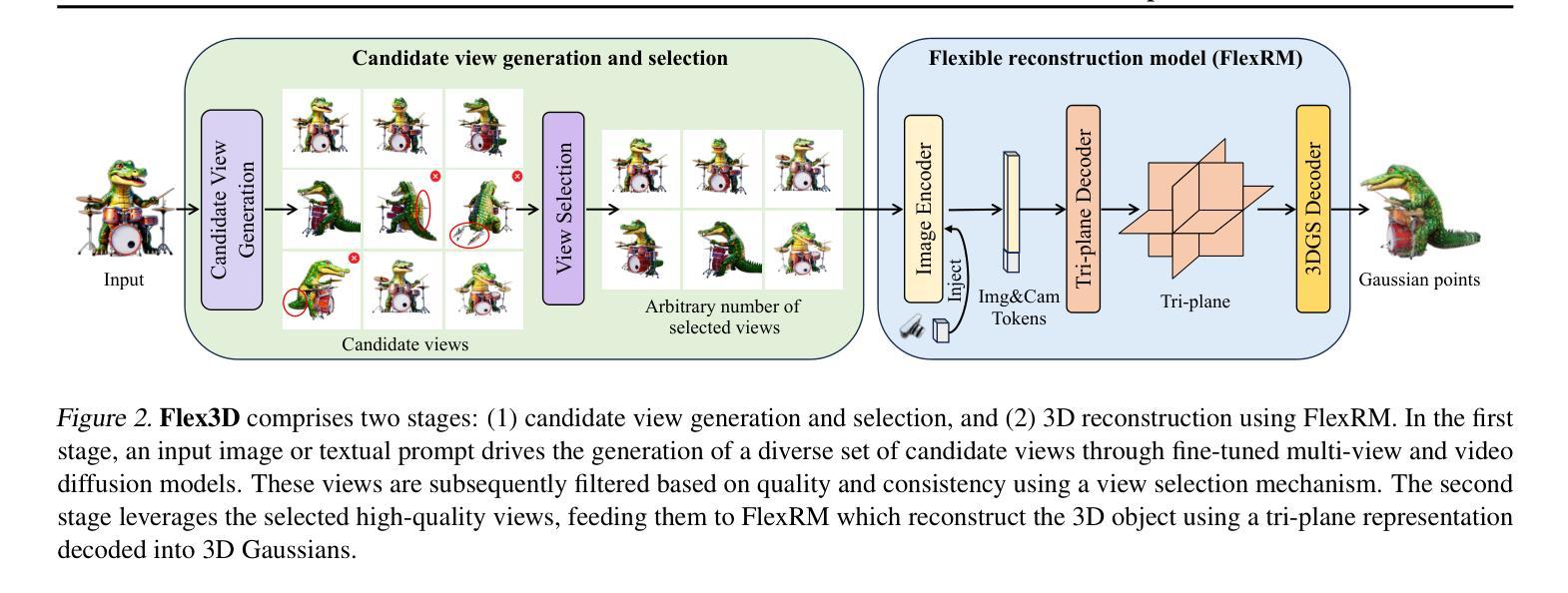
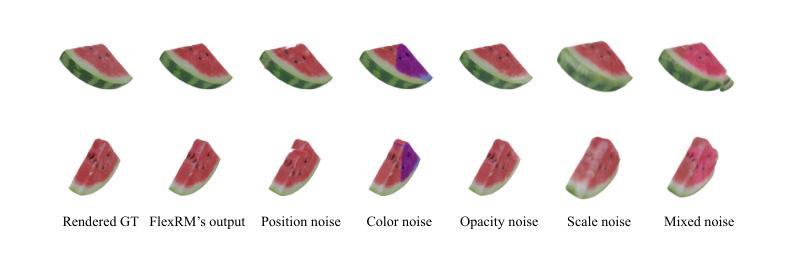
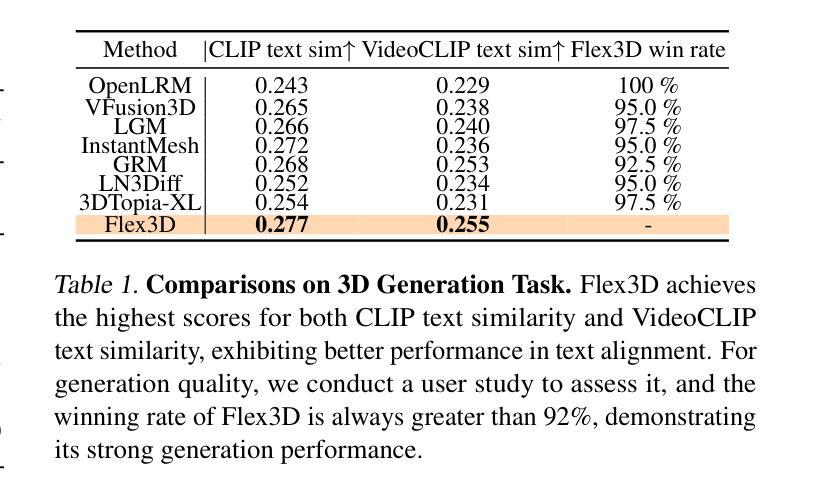
Flex3D: Feed-Forward 3D Generation with Flexible Reconstruction Model and Input View Curation
Authors:Junlin Han, Jianyuan Wang, Andrea Vedaldi, Philip Torr, Filippos Kokkinos
Generating high-quality 3D content from text, single images, or sparse view images remains a challenging task with broad applications. Existing methods typically employ multi-view diffusion models to synthesize multi-view images, followed by a feed-forward process for 3D reconstruction. However, these approaches are often constrained by a small and fixed number of input views, limiting their ability to capture diverse viewpoints and, even worse, leading to suboptimal generation results if the synthesized views are of poor quality. To address these limitations, we propose Flex3D, a novel two-stage framework capable of leveraging an arbitrary number of high-quality input views. The first stage consists of a candidate view generation and curation pipeline. We employ a fine-tuned multi-view image diffusion model and a video diffusion model to generate a pool of candidate views, enabling a rich representation of the target 3D object. Subsequently, a view selection pipeline filters these views based on quality and consistency, ensuring that only the high-quality and reliable views are used for reconstruction. In the second stage, the curated views are fed into a Flexible Reconstruction Model (FlexRM), built upon a transformer architecture that can effectively process an arbitrary number of inputs. FlemRM directly outputs 3D Gaussian points leveraging a tri-plane representation, enabling efficient and detailed 3D generation. Through extensive exploration of design and training strategies, we optimize FlexRM to achieve superior performance in both reconstruction and generation tasks. Our results demonstrate that Flex3D achieves state-of-the-art performance, with a user study winning rate of over 92% in 3D generation tasks when compared to several of the latest feed-forward 3D generative models.
从文本、单张图像或稀疏视图图像生成高质量3D内容仍然是一项具有广泛应用挑战性的任务。现有方法通常采用多视图扩散模型合成多视图图像,然后进行前向传播过程进行3D重建。然而,这些方法通常受限于输入视图的数量和固定性,难以捕捉不同视角,更糟糕的是,如果合成的视图质量不佳,还会导致生成结果不理想。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了Flex3D,这是一种新型的两阶段框架,能够利用任意数量的高质量输入视图。第一阶段包括候选视图生成和筛选管道。我们采用微调的多视图图像扩散模型和视频扩散模型来生成候选视图池,实现对目标3D对象的丰富表示。随后,视图选择管道根据质量和一致性过滤这些视图,确保仅使用高质量和可靠的视图进行重建。在第二阶段,精选的视图被输入到灵活重建模型(FlexRM)中,该模型基于能够有效处理任意数量输入的变压器架构。FlexRM直接输出利用三平面表示的3D高斯点,实现高效且详细的3D生成。通过对设计和训练策略的广泛探索,我们优化了FlexRM,在重建和生成任务中都实现了卓越的性能。我们的结果表明,Flex3D在生成任务方面达到了最新水平,在用户研究中相较于几种最新的前馈3D生成模型的胜率超过92%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 25. Project page: https://junlinhan.github.io/projects/flex3d/
Summary
本文提出了一种名为Flex3D的新型两阶段框架,用于从文本、单张图像或稀疏视图图像生成高质量3D内容。该框架通过候选视图生成和筛选管道,利用微调的多视图图像扩散模型和视频扩散模型生成候选视图池,丰富目标3D对象的表示。然后,视图选择管道根据质量和一致性过滤这些视图,确保仅使用高质量和可靠的视图进行重建。在第二阶段,精选的视图被输入到基于变压器架构的灵活重建模型(FlexRM)中,该模型可直接输出利用三角平面表示形式的3D高斯点,从而实现高效且详细的3D生成。经过对设计和训练策略的广泛探索,FlexRM在重建和生成任务中均实现了卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- Flex3D是一个两阶段框架,旨在解决从文本、单张图像或稀疏视图图像生成高质量3D内容的问题。
- 第一阶段包括候选视图生成和筛选管道,利用多视图图像扩散模型和视频扩散模型生成丰富的目标3D对象表示。
- 视图选择管道确保仅使用高质量和可靠的视图进行重建。
- 第二阶段使用基于变压器架构的灵活重建模型(FlexRM),可直接输出3D高斯点,实现高效且详细的3D生成。
- FlexRM的优化设计使其在重建和生成任务中均表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图


WaterSplatting: Fast Underwater 3D Scene Reconstruction Using Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Huapeng Li, Wenxuan Song, Tianao Xu, Alexandre Elsig, Jonas Kulhanek
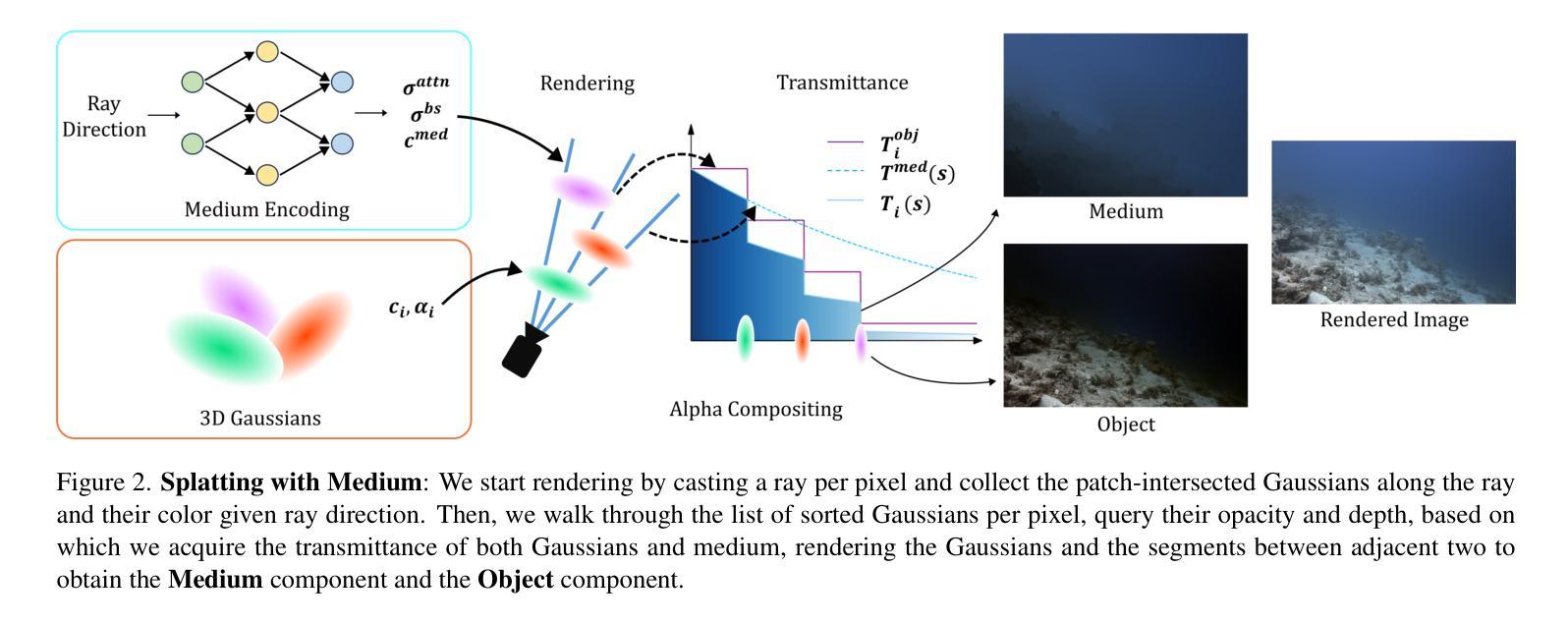
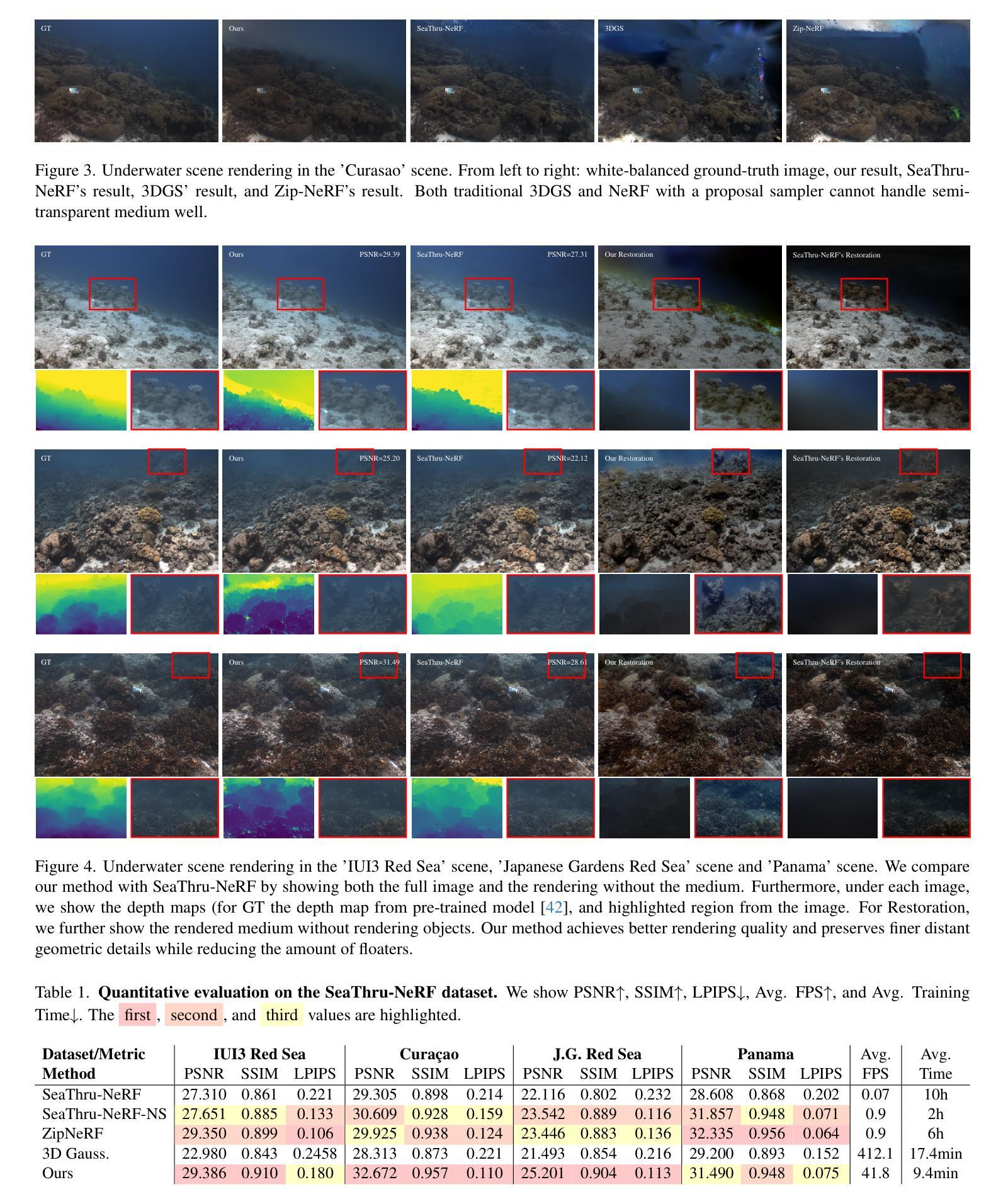
The underwater 3D scene reconstruction is a challenging, yet interesting problem with applications ranging from naval robots to VR experiences. The problem was successfully tackled by fully volumetric NeRF-based methods which can model both the geometry and the medium (water). Unfortunately, these methods are slow to train and do not offer real-time rendering. More recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) method offered a fast alternative to NeRFs. However, because it is an explicit method that renders only the geometry, it cannot render the medium and is therefore unsuited for underwater reconstruction. Therefore, we propose a novel approach that fuses volumetric rendering with 3DGS to handle underwater data effectively. Our method employs 3DGS for explicit geometry representation and a separate volumetric field (queried once per pixel) for capturing the scattering medium. This dual representation further allows the restoration of the scenes by removing the scattering medium. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art NeRF-based methods in rendering quality on the underwater SeaThru-NeRF dataset. Furthermore, it does so while offering real-time rendering performance, addressing the efficiency limitations of existing methods. Web: https://water-splatting.github.io
水下三维场景重建是一个充满挑战但很有趣的问题,其应用从海军机器人到虚拟现实体验都有。基于全容积的NeRF方法成功解决了这个问题,该方法可以同时对几何和介质(水)进行建模。然而,这些方法训练速度慢,无法实现实时渲染。最近,3D高斯喷射(3DGS)方法为NeRF提供了一种快速替代方案。然而,由于它是一种只渲染几何的显式方法,不能渲染介质,因此不适合水下重建。因此,我们提出了一种融合体积渲染和3DGS的新方法,以有效处理水下数据。我们的方法采用3DGS进行明确的几何表示,并使用一个单独的体积场(每个像素查询一次)来捕捉散射介质。这种双重表示还可以通过对场景进行散射介质的消除来恢复场景。我们的方法在海底SeaThru-NeRF数据集上的渲染质量优于最先进的基于NeRF的方法。此外,它在提供实时渲染性能的同时实现了这一点,解决了现有方法的效率限制。网址:https://water-splatting.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Web: https://water-splatting.github.io
Summary
水下三维场景重建是一个充满挑战但有趣的问题,具有广泛的应用领域,如海军机器人到虚拟现实体验。近期提出了一种融合体积渲染与3DGS的新方法,该方法采用3DGS进行显式几何表示,并采用单独体积场捕捉散射介质信息。此方法可以重建水下场景,通过消除散射介质进行场景修复,同时提供了高质量的渲染效果以及实时的渲染性能。该方法超越了基于NeRF的现有方法的渲染质量限制并解决了效率问题。如需更多信息,请访问网站:https://water-splatting.github.io。
Key Takeaways
- 水下三维场景重建是一个涵盖多个领域且具有挑战性的课题。
- 完全基于体积的NeRF方法能够建模几何和介质(如水),但训练时间长且无法实现实时渲染。
- 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) 方法提供了一个快速的替代方案,但它只能渲染几何,无法处理介质,因此不适用于水下重建。
- 新提出的方法融合了体积渲染与3DGS,采用双重表示法处理水下数据:使用3DGS进行显式几何表示,并使用体积场捕捉散射介质。
- 该方法能够去除散射介质的影响以恢复场景,提供超越现有NeRF方法的渲染质量,并实现了实时渲染性能。
点此查看论文截图

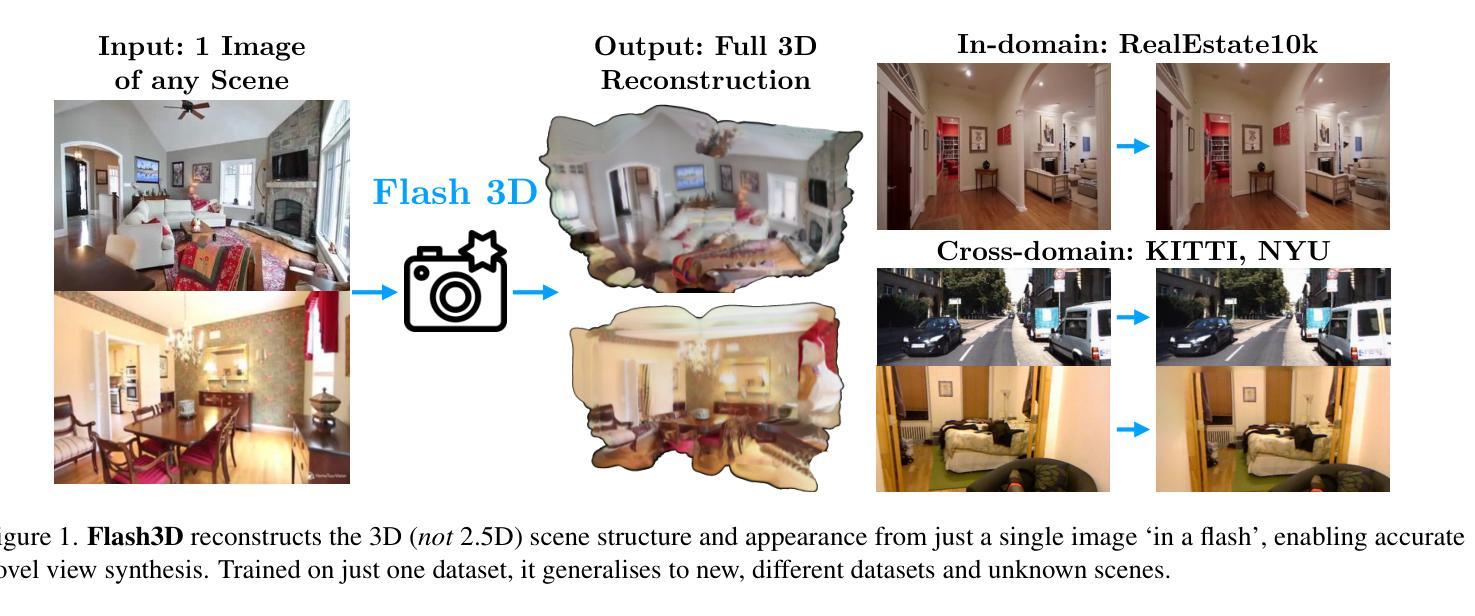
Flash3D: Feed-Forward Generalisable 3D Scene Reconstruction from a Single Image
Authors:Stanislaw Szymanowicz, Eldar Insafutdinov, Chuanxia Zheng, Dylan Campbell, João F. Henriques, Christian Rupprecht, Andrea Vedaldi
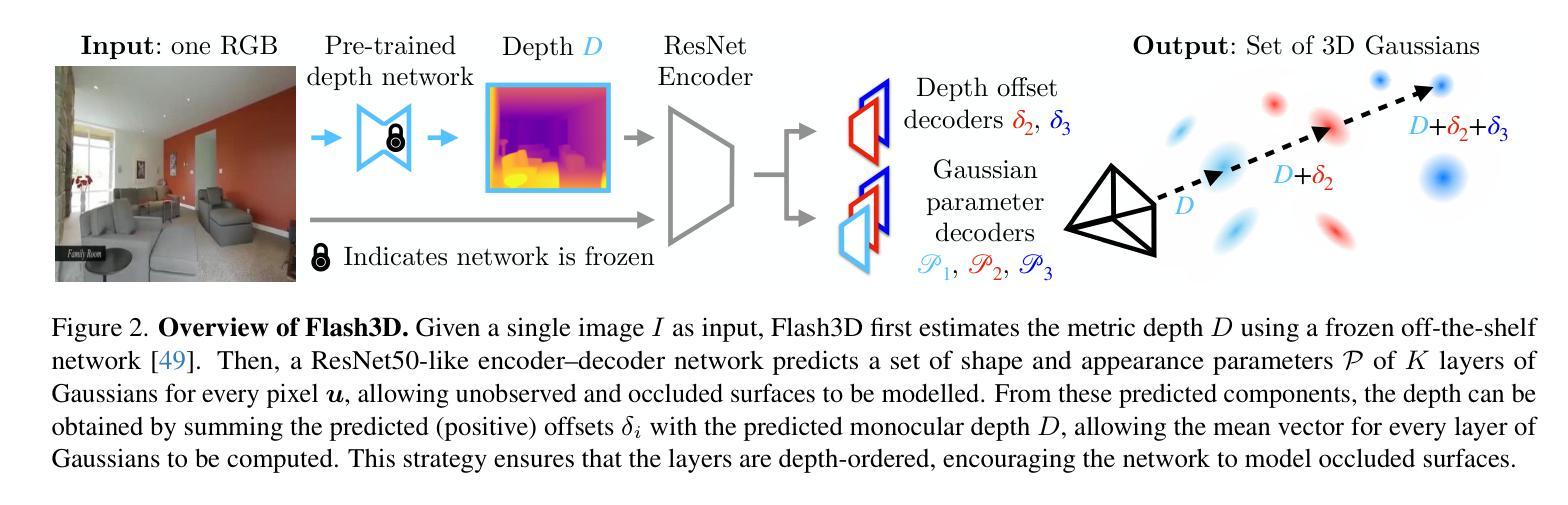
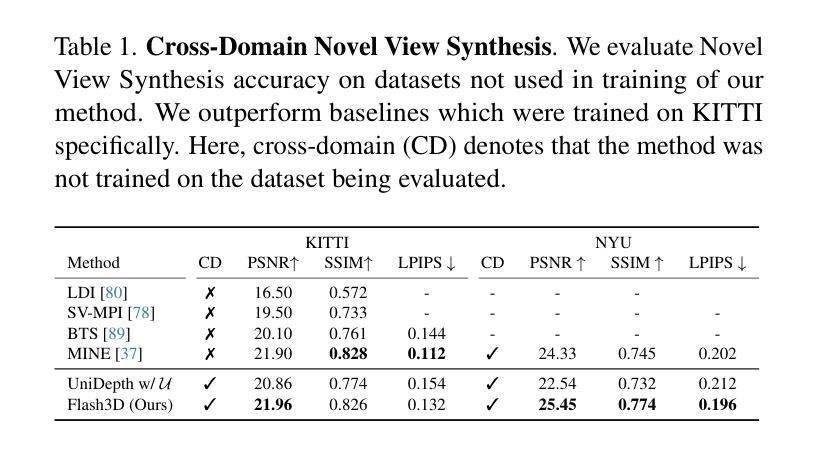
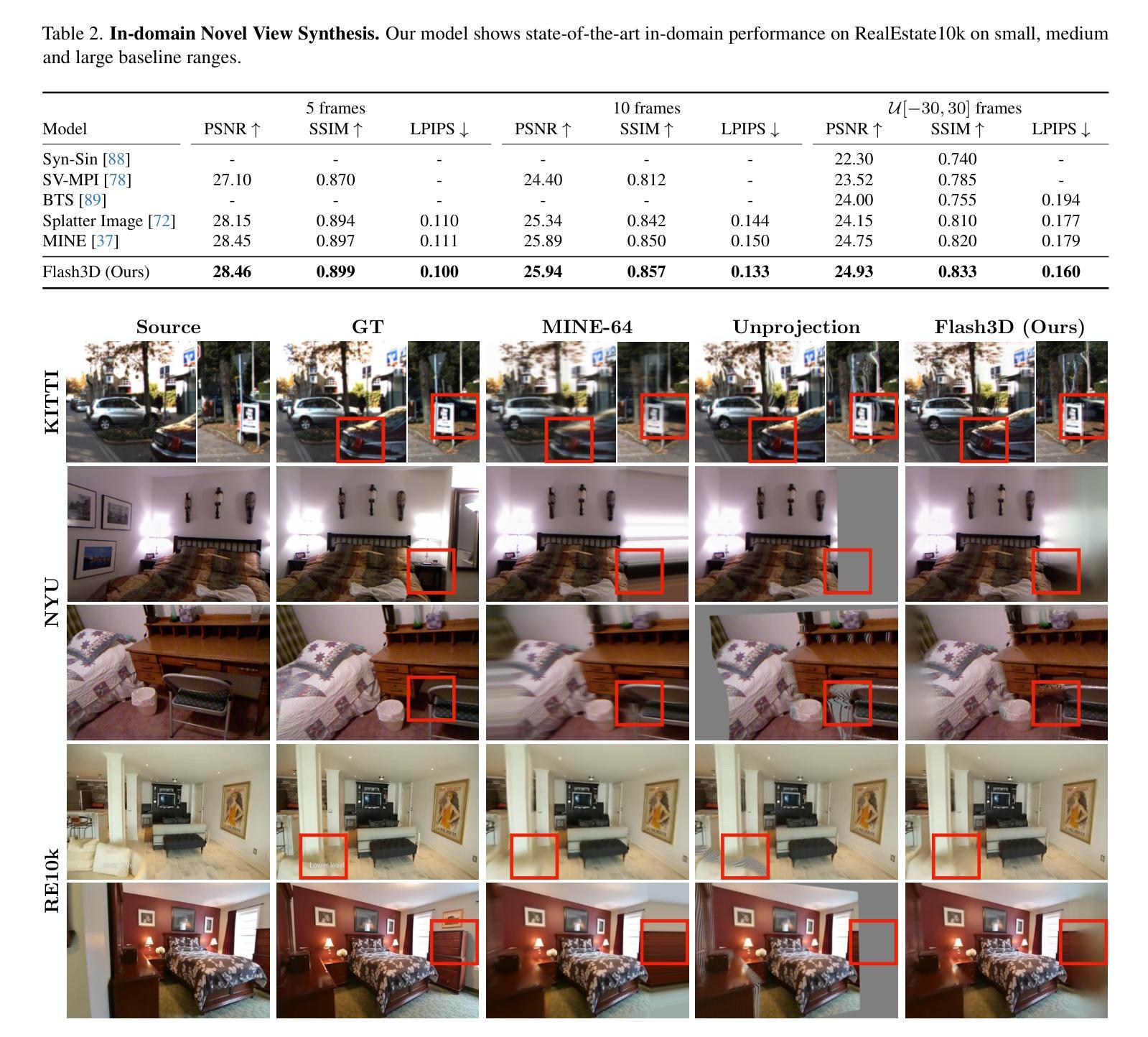
We propose Flash3D, a method for scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis from a single image which is both very generalisable and efficient. For generalisability, we start from a “foundation” model for monocular depth estimation and extend it to a full 3D shape and appearance reconstructor. For efficiency, we base this extension on feed-forward Gaussian Splatting. Specifically, we predict a first layer of 3D Gaussians at the predicted depth, and then add additional layers of Gaussians that are offset in space, allowing the model to complete the reconstruction behind occlusions and truncations. Flash3D is very efficient, trainable on a single GPU in a day, and thus accessible to most researchers. It achieves state-of-the-art results when trained and tested on RealEstate10k. When transferred to unseen datasets like NYU it outperforms competitors by a large margin. More impressively, when transferred to KITTI, Flash3D achieves better PSNR than methods trained specifically on that dataset. In some instances, it even outperforms recent methods that use multiple views as input. Code, models, demo, and more results are available at https://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/research/flash3d/.
我们提出了Flash3D,这是一种从单幅图像中进行场景重建和新颖视角合成的方法,既具有高度的通用性,又非常高效。在通用性方面,我们从用于单目深度估计的“基础”模型开始,并将其扩展到完整的3D形状和外观重建模型。在效率方面,我们的扩展基于前馈高斯展布技术。具体来说,我们在预测的深度处预测第一层3D高斯,然后添加在空间中有偏移的额外高斯层,使模型能够完成遮挡和截断部分的重建。Flash3D非常高效,可以在单GPU上训练一天,因此大多数研究人员都可以使用。在RealEstate10k上进行训练和测试时,它达到了最先进的水平。当转移到未见过的数据集(如NYU)时,它的性能大大超过了竞争对手。更值得一提的是,当转移到KITTI时,Flash3D的PSNR超过了在该数据集上专门训练的方法。在某些情况下,它甚至超越了以多视角作为输入的最新方法。代码、模型、演示和更多结果可在https://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/research/flash3d/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/research/flash3d/
Summary
Flash3D是一种从单张图像进行场景重建和新颖视角合成的方法,具有极高的通用性和效率。该方法以单目深度估计的“基础”模型为起点,扩展为完整的3D形状和外观重建器。基于前馈高斯飞溅技术,提高了效率。通过预测位于预测深度处的第一层3D高斯,并添加在空间上偏移的额外高斯层,使模型能够完成遮挡和截断后的重建。Flash3D在RealEstate10k上训练,表现出卓越的性能。在NYU等未见数据集上的表现远超竞争对手,在KITTI上的表现甚至超过了专门训练的方法,且在某些情况下胜过使用多视角输入的方法。
Key Takeaways
- Flash3D是一种从单张图像进行场景重建和新颖视角合成的方法。
- Flash3D方法具有高通用性和高效率。
- Flash3D以单目深度估计的“基础”模型为起点,并扩展为完整的3D形状和外观重建器。
- 基于前馈高斯飞溅技术提高了效率。
- Flash3D通过添加在空间上偏移的额外高斯层,能够完成遮挡和截断后的重建。
- Flash3D在RealEstate10k数据集上表现卓越,且在NYU和KITTI等数据集上的表现优于竞争对手。
- Flash3D在某些情况下甚至胜过使用多视角输入的方法。
点此查看论文截图