⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-04 更新
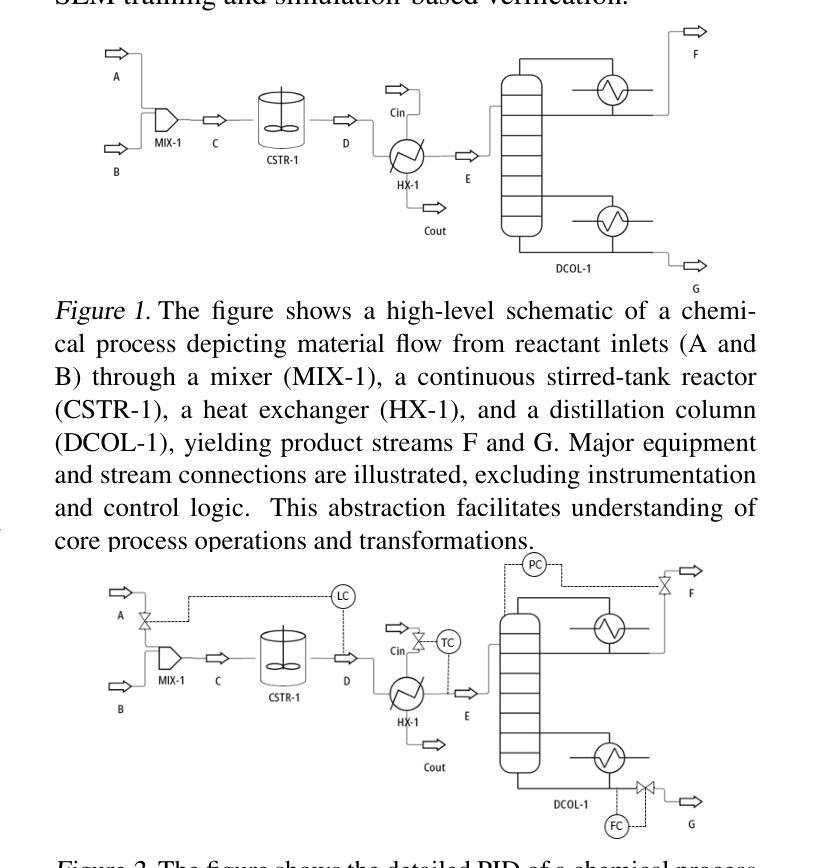
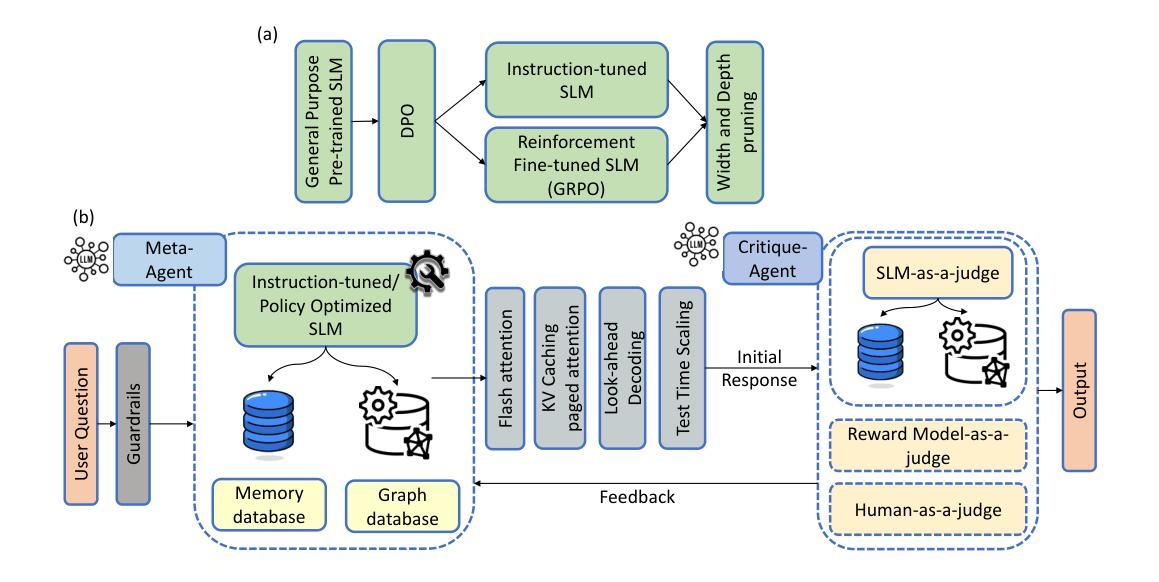
AutoChemSchematic AI: A Closed-Loop, Physics-Aware Agentic Framework for Auto-Generating Chemical Process and Instrumentation Diagrams
Authors:Sakhinana Sagar Srinivas, Shivam Gupta, Venkataramana Runkana
Recent advancements in generative AI have accelerated the discovery of novel chemicals and materials; however, transitioning these discoveries to industrial-scale production remains a critical bottleneck, as it requires the development of entirely new chemical manufacturing processes. Current AI methods cannot auto-generate PFDs or PIDs, despite their critical role in scaling chemical processes, while adhering to engineering constraints. We present a closed loop, physics aware framework for the automated generation of industrially viable PFDs and PIDs. The framework integrates domain specialized small scale language models (SLMs) (trained for chemical process QA tasks) with first principles simulation, leveraging three key components: (1) a hierarchical knowledge graph of process flow and instrumentation descriptions for 1,020+ chemicals, (2) a multi-stage training pipeline that fine tunes domain specialized SLMs on synthetic datasets via Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), and Retrieval-Augmented Instruction Tuning (RAIT), and (3) DWSIM based simulator in the loop validation to ensure feasibility. To improve both runtime efficiency and model compactness, the framework incorporates advanced inference time optimizations including FlashAttention, Lookahead Decoding, PagedAttention with KV-cache quantization, and Test Time Inference Scaling and independently applies structural pruning techniques (width and depth) guided by importance heuristics to reduce model size with minimal accuracy loss. Experiments demonstrate that the framework generates simulator-validated process descriptions with high fidelity, outperforms baseline methods in correctness, and generalizes to unseen chemicals. By bridging AI-driven design with industrial-scale feasibility, this work significantly reduces R&D timelines from lab discovery to plant deployment.
最近生成式人工智能的进步加速了新型化学物质和材料的发现,然而,将这些发现转化为工业规模的生产仍然是一个关键的瓶颈,因为这需要开发全新的化学制造工艺。尽管当前的AI方法在扩展化学过程中起着关键作用,但它们无法自动生成工艺流程图(PFDs)或工艺流程说明(PIDs)。我们提出了一个闭环的物理感知框架,用于自动生成可行的工艺流程图(PFDs)和工艺流程说明(PIDs)。该框架结合了针对化学工艺问答任务训练的领域专业化小型语言模型(SLM)与基于基本原理的仿真,利用三个关键组件:(1)包含超过1020种化学物质的工艺流程和仪器描述层次知识图谱;(2)一个多阶段训练管道,通过监督微调(SFT)、直接偏好优化(DPO)和检索增强指令调整(RAIT)在合成数据集上微调领域专业化SLM;(3)基于DWSIM的仿真器循环验证以确保可行性。为了提高运行效率和模型紧凑性,该框架采用了先进的推理时间优化技术,包括FlashAttention、前瞻性解码、分页注意力与KV缓存量化以及测试时间推理缩放技术,并独立应用结构修剪技术(宽度和深度),以重要性启发式为指导减少模型大小,同时尽量减少精度损失。实验表明,该框架生成了仿真验证的高保真工艺流程描述,在正确性方面优于基线方法,并能推广到未见过的化学物质。通过弥合了人工智能驱动的设计与工业规模可行性之间的鸿沟,这项工作显著缩短了从实验室发现到工厂部署的研发时间。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了利用先进的生成式AI技术加速新型化学物质和材料发现的过程,但工业规模生产阶段仍是瓶颈。当前AI方法无法自动生成工艺流程图(PFDs)和工艺流程指示图(PIDs),本文提出了一种闭环、物理感知的框架来解决这一问题。该框架结合了专业领域的小型语言模型(SLMs)和基于第一原理的仿真技术,通过三个关键组件实现自动化生成具有工业可行性的PFDs和PIDs。实验证明,该框架生成的工艺流程描述具有高度的保真度和正确性,并能推广到未见过的化学物质。这一工作显著缩短了从实验室发现到工厂部署的研发时间。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式AI在新型化学物质和材料发现方面取得进展,但工业规模生产仍是挑战。
- 当前AI方法无法自动生成工艺流程图(PFDs)和工艺流程指示图(PIDs)。
- 提出一种闭环、物理感知的框架,结合小型语言模型(SLMs)和基于第一原理的仿真技术,自动化生成具有工业可行性的PFDs和PIDs。
- 框架包含三个关键组件:层次化的知识图谱、多阶段训练管道和DWSIM模拟器验证。
- 框架采用多种推理时间优化技术和结构剪枝技术,以提高运行效率和模型紧凑性。
- 实验证明,该框架生成的工艺流程描述具有高度的保真度和正确性。
点此查看论文截图

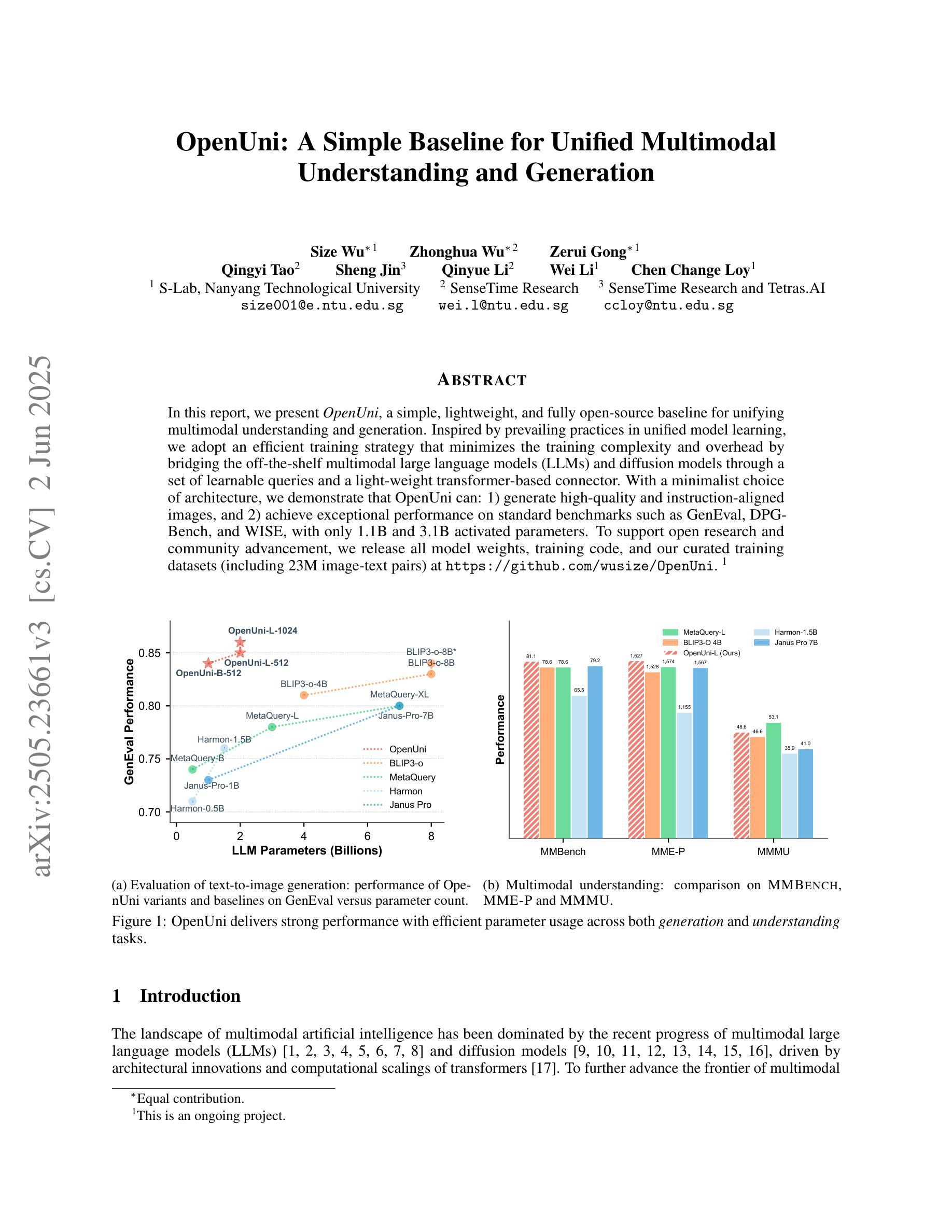
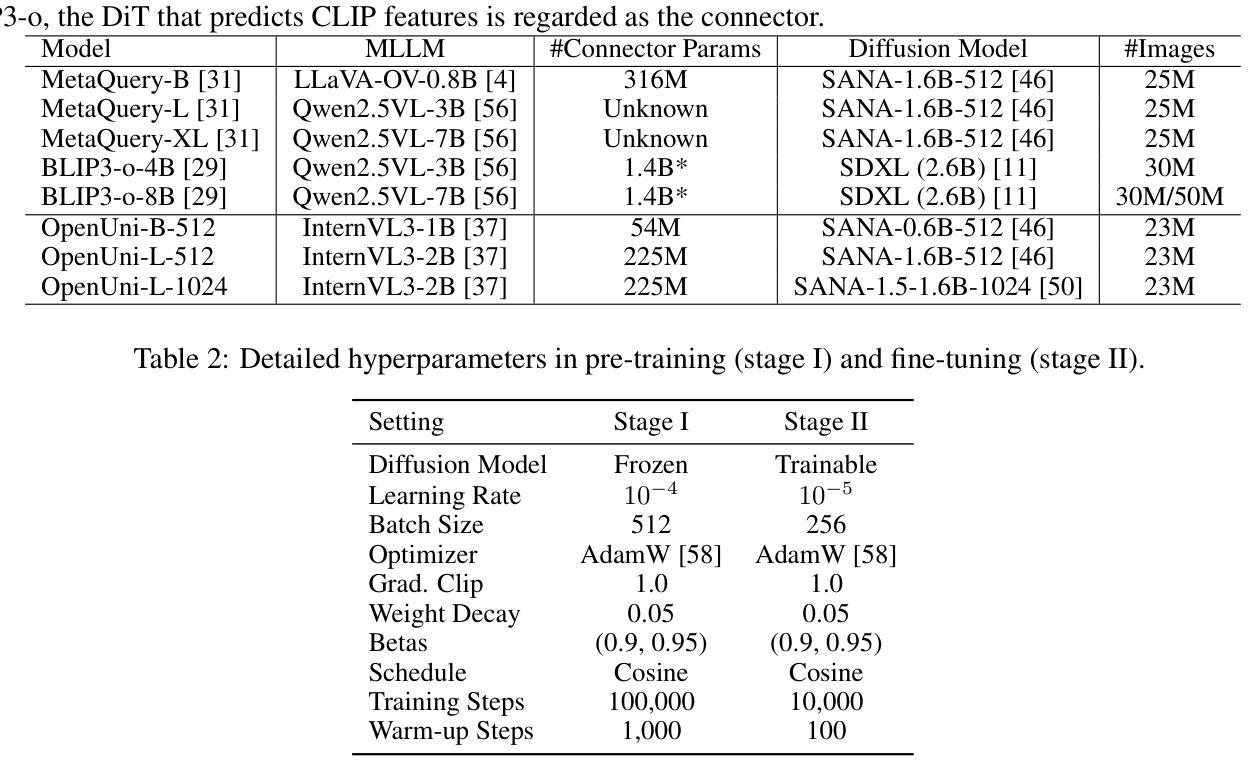
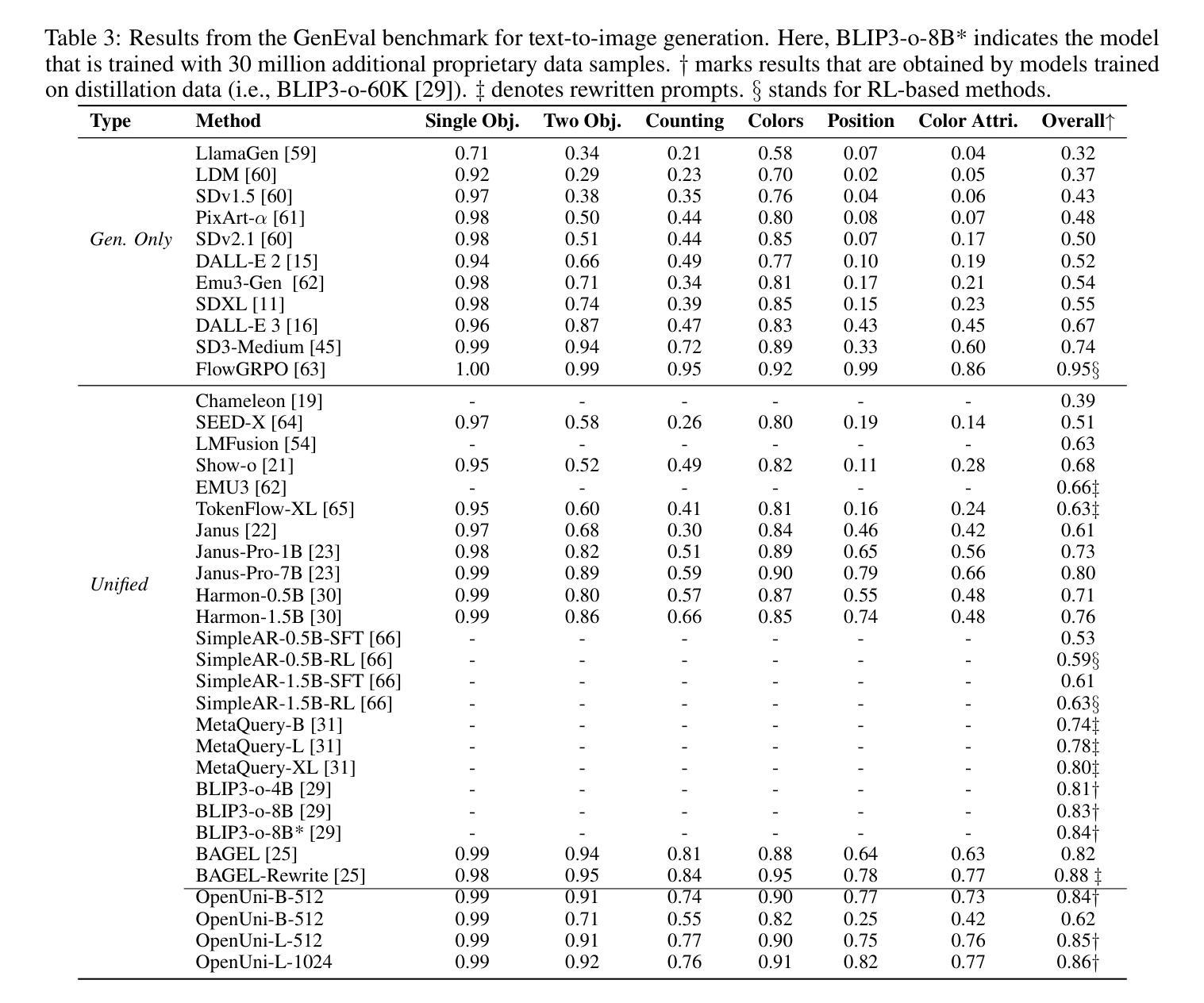
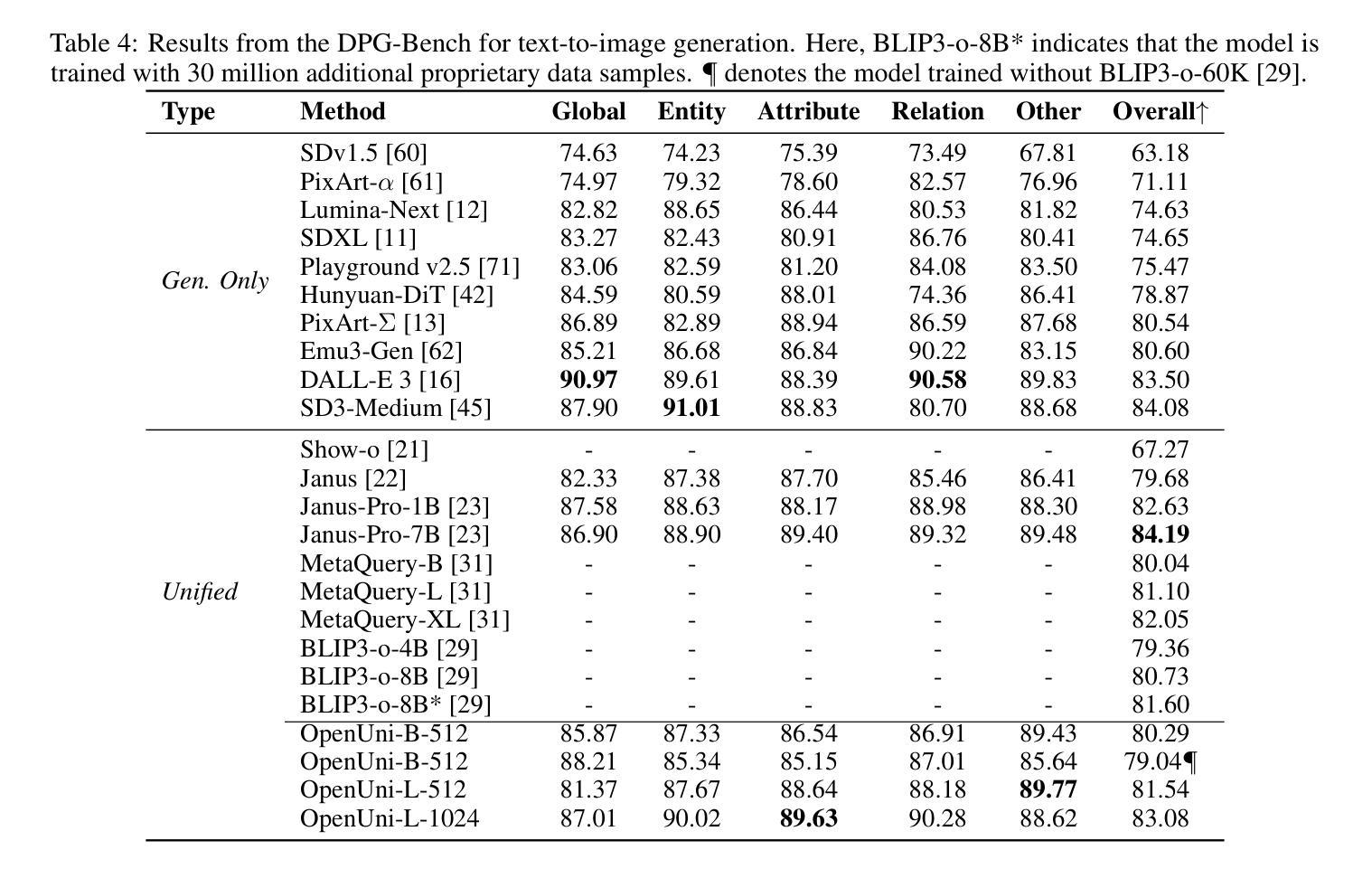
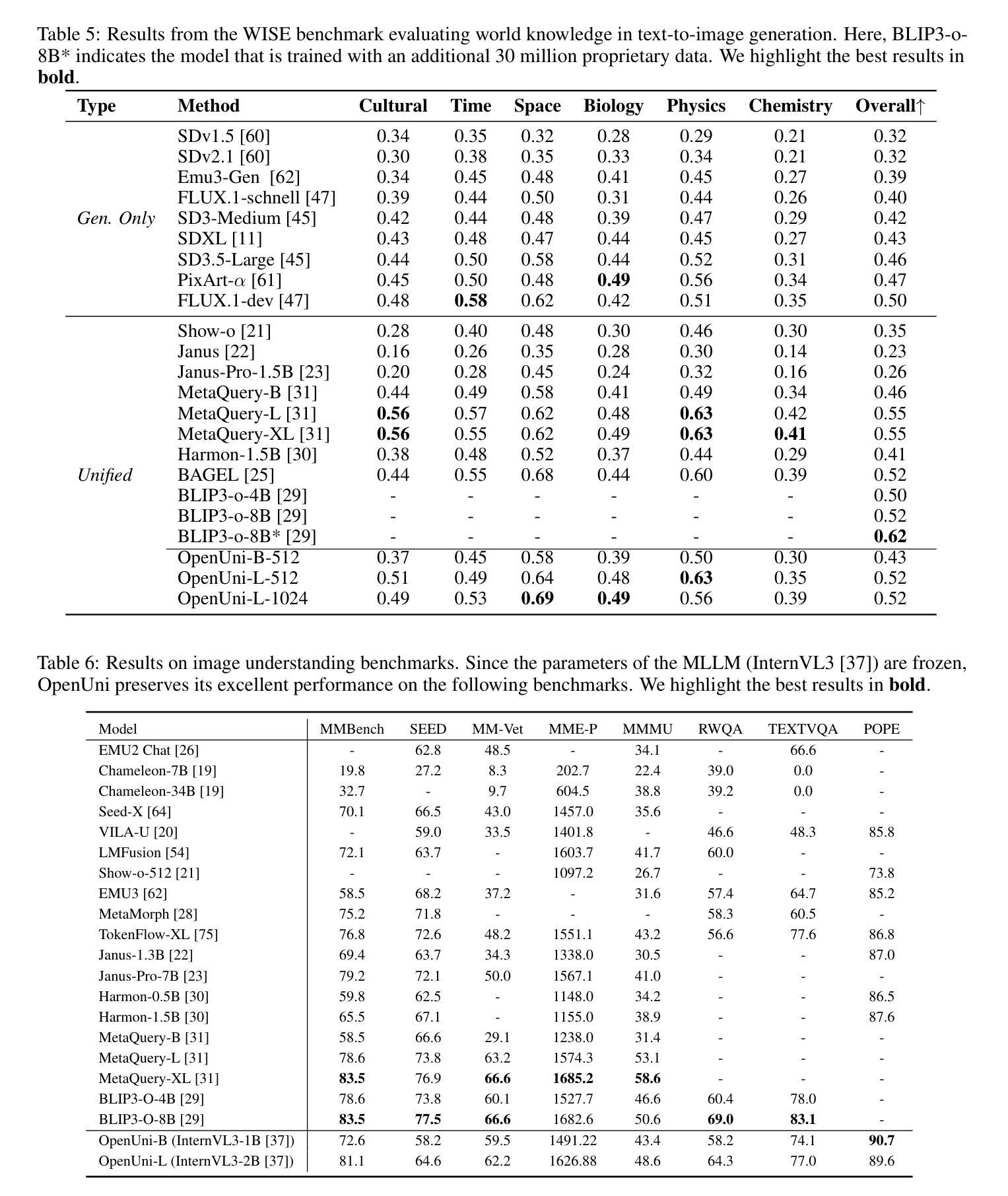
OpenUni: A Simple Baseline for Unified Multimodal Understanding and Generation
Authors:Size Wu, Zhonghua Wu, Zerui Gong, Qingyi Tao, Sheng Jin, Qinyue Li, Wei Li, Chen Change Loy
In this report, we present OpenUni, a simple, lightweight, and fully open-source baseline for unifying multimodal understanding and generation. Inspired by prevailing practices in unified model learning, we adopt an efficient training strategy that minimizes the training complexity and overhead by bridging the off-the-shelf multimodal large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models through a set of learnable queries and a light-weight transformer-based connector. With a minimalist choice of architecture, we demonstrate that OpenUni can: 1) generate high-quality and instruction-aligned images, and 2) achieve exceptional performance on standard benchmarks such as GenEval, DPG- Bench, and WISE, with only 1.1B and 3.1B activated parameters. To support open research and community advancement, we release all model weights, training code, and our curated training datasets (including 23M image-text pairs) at https://github.com/wusize/OpenUni.
在报告中,我们介绍了OpenUni,这是一个简单、轻量级、完全开源的基线系统,用于统一多模态理解和生成。我们借鉴了当前流行的统一模型学习实践,采用了一种高效的训练策略,通过一组可学习的查询和一个基于轻量级变压器的连接器,将现成的多模态大型语言模型(LLM)和扩散模型连接起来,从而降低了训练复杂性和开销。在架构上选择简洁明了,我们证明OpenUni可以:1)生成高质量、指令一致的图像;2)在GenEval、DPG-Bench和WISE等标准基准测试上实现卓越性能,激活参数只有1.1B和3.1B。为了支持开放研究和社区发展,我们在https://github.com/wusize/OpenUni上发布了所有模型权重、训练代码和我们精选的训练数据集(包括2300万张图像文本对)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
开源项目OpenUni旨在实现多模态理解和生成的一体化。通过有效的训练策略,该项目充分利用现有的多模态大型语言模型(LLM)和扩散模型,通过可学习的查询和轻量级基于转换器的连接器实现训练复杂性和开销的最小化。该项目展示了其能够生成高质量、符合指令的图像,并在GenEval、DPG Bench和WISE等标准基准测试中表现出卓越性能。所有模型权重、训练代码和精选的训练数据集(包括2.3亿个图像文本对)均已发布在GitHub上,以支持开放研究和社区发展。
Key Takeaways
- OpenUni是一个简单、轻量级、完全开源的项目,旨在统一多模态理解和生成。
- 它采用了一种高效的训练策略,通过连接现有的多模态大型语言模型(LLM)和扩散模型来实现性能优化。
- 该项目具有生成高质量、符合指令的图像的能力。
- OpenUni在多个标准基准测试中表现出卓越性能,如GenEval、DPG Bench和WISE。
- 它支持通过可学习的查询和轻量级基于转换器的连接器进行灵活应用。
- 该项目将所有模型权重、训练代码和训练数据集公开发布在GitHub上,以促进开放研究和社区发展。
点此查看论文截图
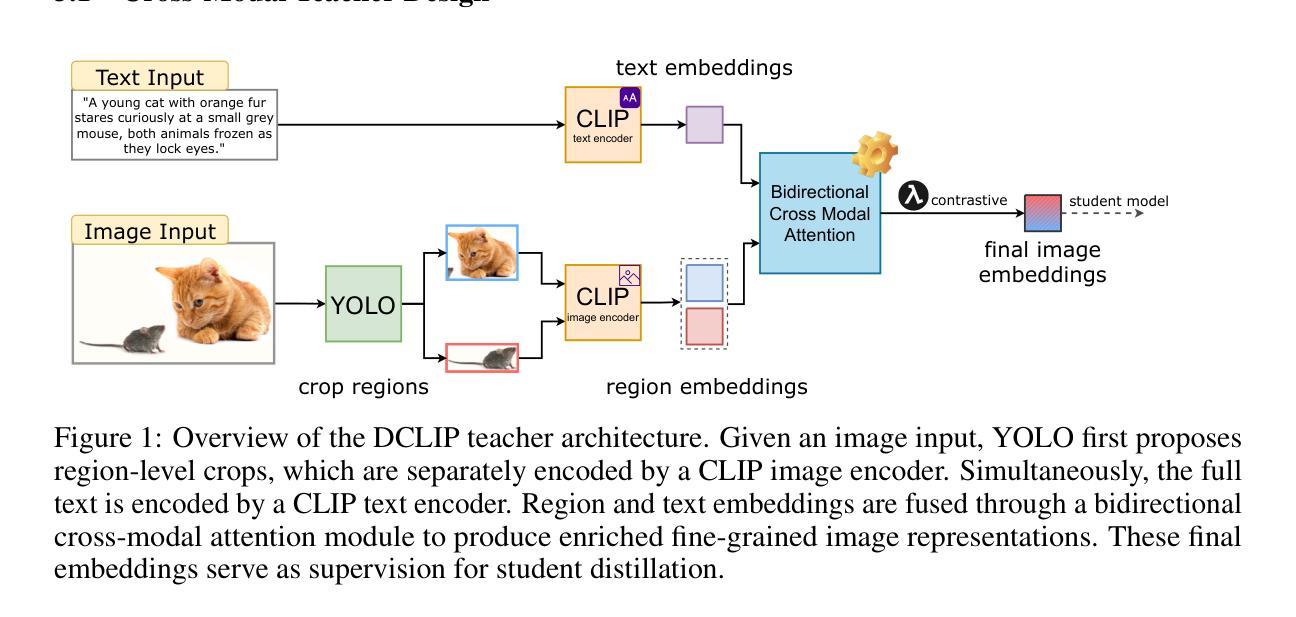
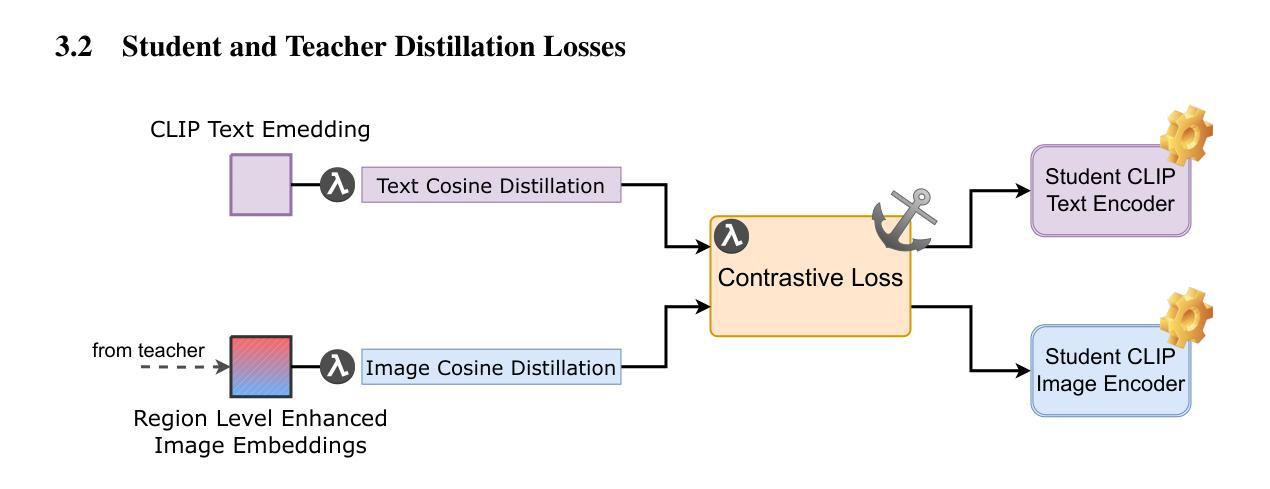
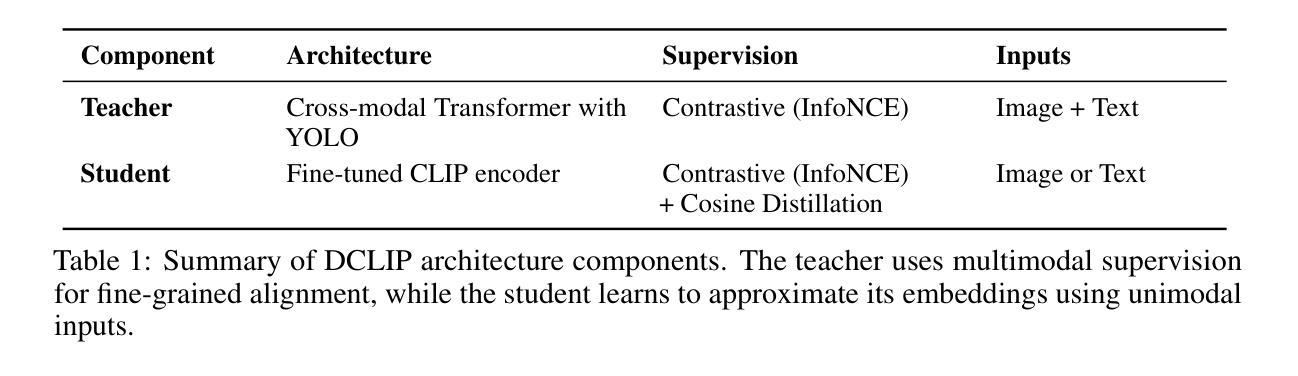
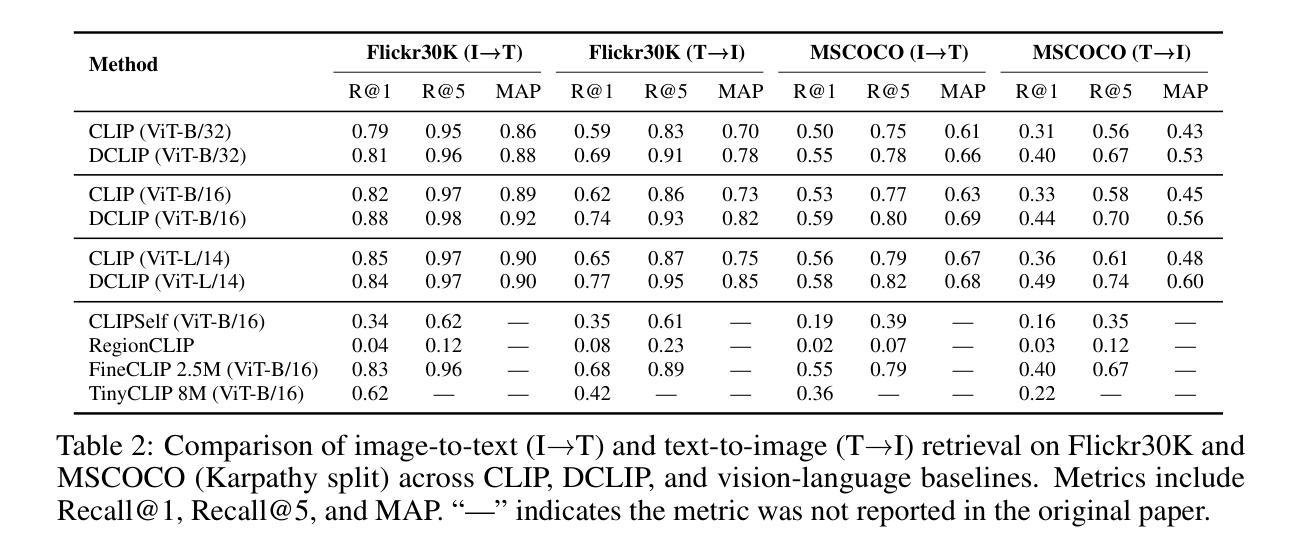
Distill CLIP (DCLIP): Enhancing Image-Text Retrieval via Cross-Modal Transformer Distillation
Authors:Daniel Csizmadia, Andrei Codreanu, Victor Sim, Vighnesh Prabhu, Michael Lu, Kevin Zhu, Sean O’Brien, Vasu Sharma
We present Distill CLIP (DCLIP), a fine-tuned variant of the CLIP model that enhances multimodal image-text retrieval while preserving the original model’s strong zero-shot classification capabilities. CLIP models are typically constrained by fixed image resolutions and limited context, which can hinder their effectiveness in retrieval tasks that require fine-grained cross-modal understanding. DCLIP addresses these challenges through a meta teacher-student distillation framework, where a cross-modal transformer teacher is fine-tuned to produce enriched embeddings via bidirectional cross-attention between YOLO-extracted image regions and corresponding textual spans. These semantically and spatially aligned global representations guide the training of a lightweight student model using a hybrid loss that combines contrastive learning and cosine similarity objectives. Despite being trained on only ~67,500 samples curated from MSCOCO, Flickr30k, and Conceptual Captions-just a fraction of CLIP’s original dataset-DCLIP significantly improves image-text retrieval metrics (Recall@K, MAP), while retaining approximately 94% of CLIP’s zero-shot classification performance. These results demonstrate that DCLIP effectively mitigates the trade-off between task specialization and generalization, offering a resource-efficient, domain-adaptive, and detail-sensitive solution for advanced vision-language tasks. Code available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DCLIP-B772/README.md.
我们提出了Distill CLIP(DCLIP),它是CLIP模型的一种微调变体,增强了多模态图像文本检索功能,同时保留了原始模型强大的零样本分类能力。CLIP模型通常受到固定图像分辨率和有限上下文的限制,这可能会阻碍它们在需要精细跨模态理解的任务中的有效性。DCLIP通过元教师学生蒸馏框架来解决这些挑战,其中跨模态变压器教师经过微调,通过YOLO提取的图像区域和相应文本跨度之间的双向交叉注意力产生丰富的嵌入。这些语义和空间对齐的全局表示通过使用结合对比学习和余弦相似性目标的混合损失来指导轻量级学生模型的训练。尽管仅使用从MSCOCO、Flickr30k和Conceptual Captions中精选的约67,500个样本进行训练,这些样本仅占CLIP原始数据集的一部分,但DCLIP显著提高了图像文本检索指标(Recall@K,MAP),同时保留了CLIP大约94%的零样本分类性能。这些结果表明,DCLIP有效地缓解了任务专门化与通用化之间的权衡,为高级视觉语言任务提供了资源高效、领域自适应和细节敏感的解决方案。代码可用https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DCLIP-B772/README.md。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Distill CLIP(DCLIP)是CLIP模型的精细调整变体,旨在增强多模态图像文本检索功能,同时保留原始模型的强大零样本分类能力。DCLIP通过元教师-学生蒸馏框架解决CLIP模型在图像分辨率和上下文方面的局限性,通过跨模态变压器教师模型产生丰富的嵌入,通过YOLO提取的图像区域和相应文本跨度之间的双向交叉注意力实现。这些语义和空间对齐的全局表示通过混合损失引导轻量级学生模型的训练,该损失结合了对比学习和余弦相似性目标。尽管仅在MSCOCO、Flickr30k和Conceptual Captions等数据集的部分样本上进行训练,但DCLIP显著提高了图像文本检索指标(Recall@K,MAP),同时保留了CLIP的零样本分类性能的约94%。这些结果表明,DCLIP有效地缓解了任务特异性和通用性之间的权衡,为高级视觉语言任务提供了资源高效、域自适应和细节敏感的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- DCLIP是CLIP模型的改进版本,旨在增强多模态图像文本检索能力。
- DCLIP解决了CLIP模型在图像分辨率和上下文方面的局限性。
- DCLIP使用跨模态变压器教师模型产生丰富的嵌入。
- YOLO提取的图像区域和文本跨度之间的双向交叉注意力增强了模型性能。
- DCLIP通过混合损失函数训练轻量级学生模型。
- DCLIP在少量数据集上训练,但显著提高了图像文本检索性能。
点此查看论文截图

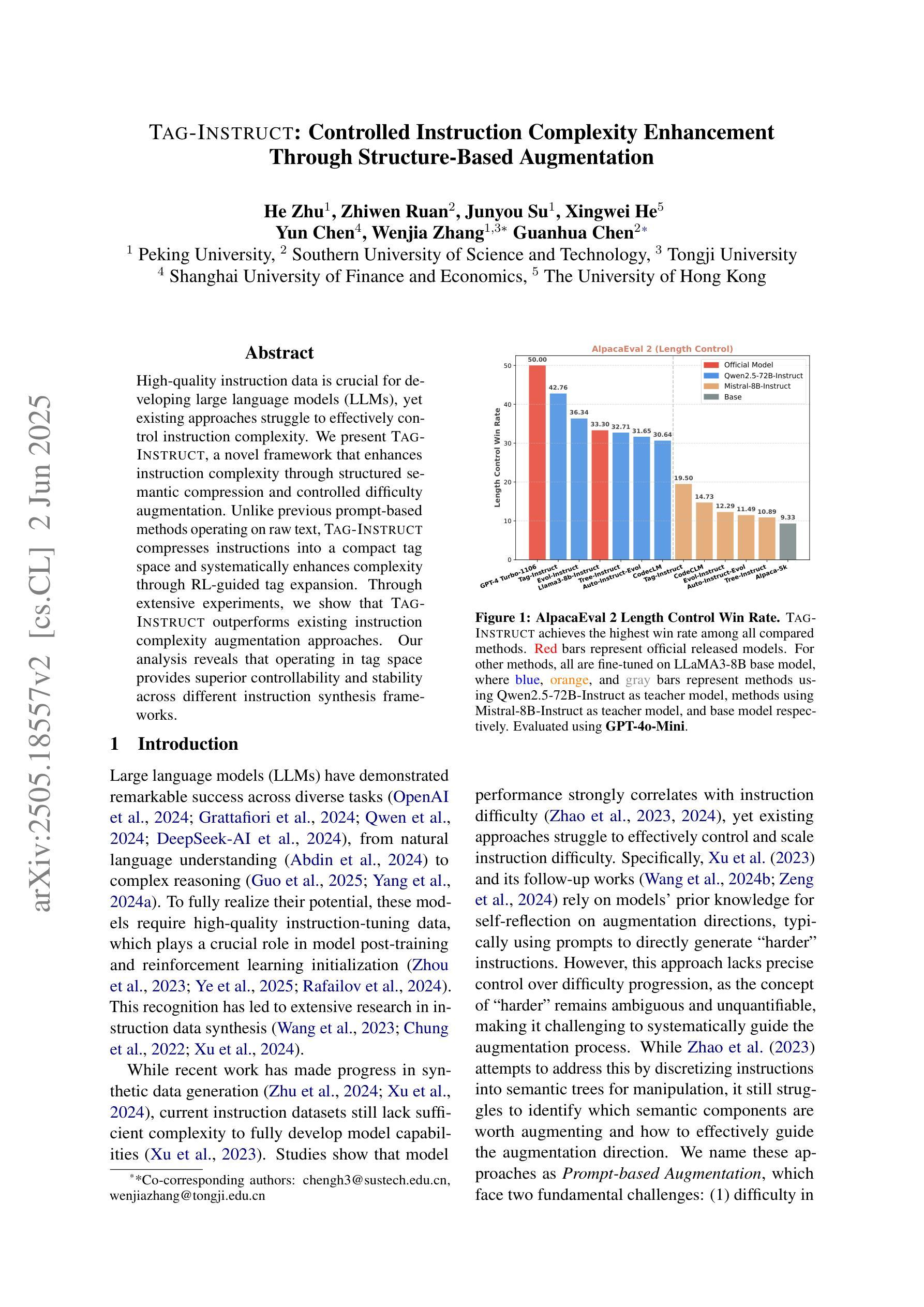
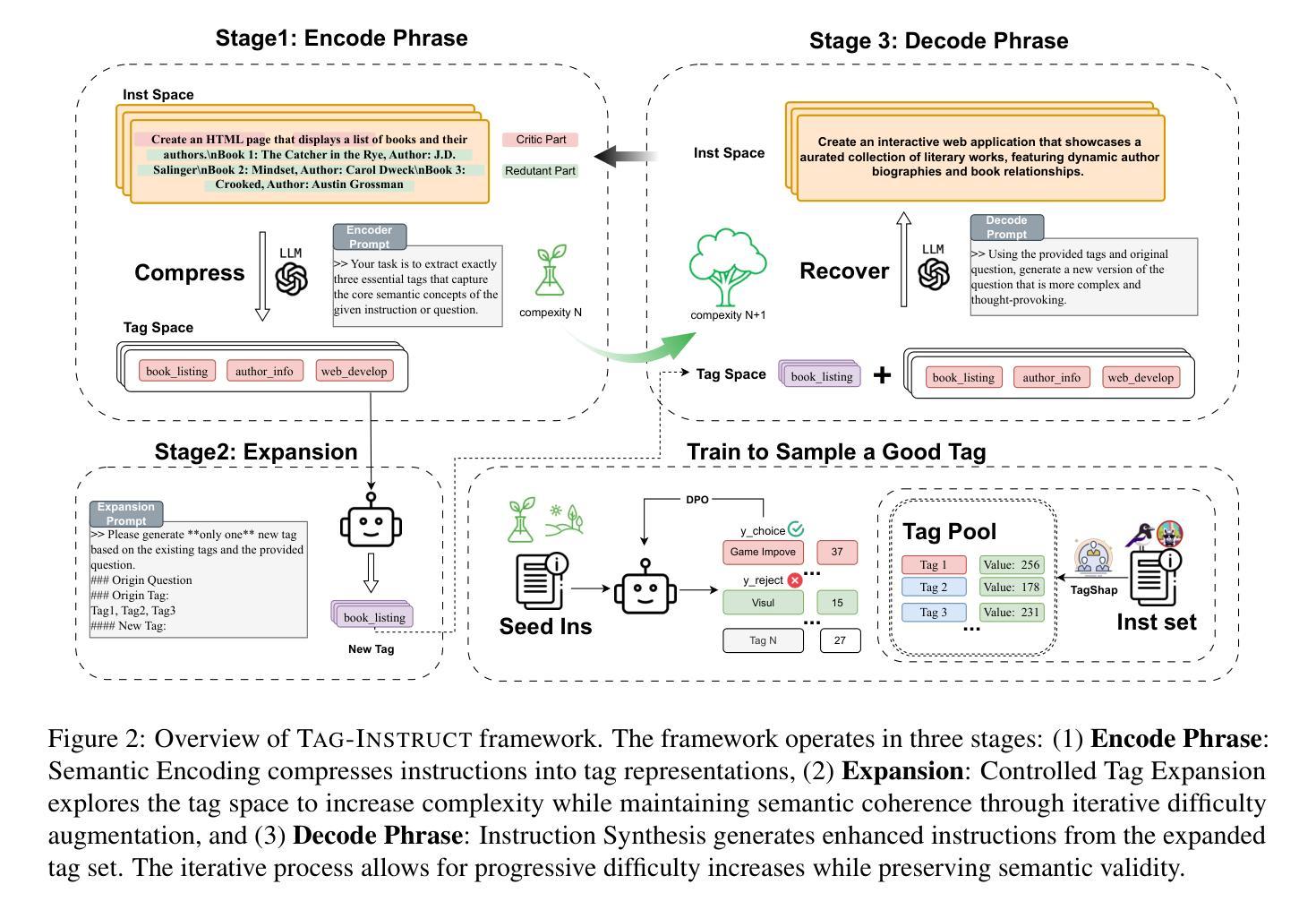
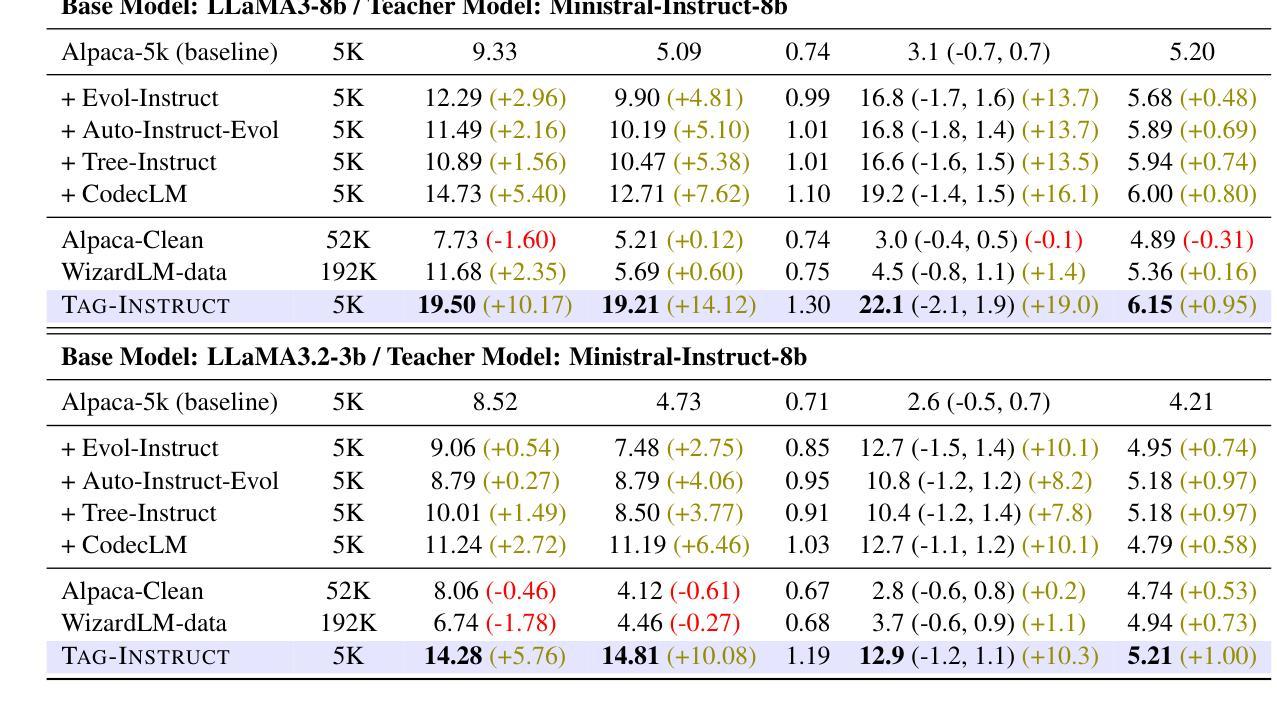
TAG-INSTRUCT: Controlled Instruction Complexity Enhancement through Structure-based Augmentation
Authors:He Zhu, Zhiwen Ruan, Junyou Su, Xingwei He, Yun Chen, Wenjia Zhang, Guanhua Chen
High-quality instruction data is crucial for developing large language models (LLMs), yet existing approaches struggle to effectively control instruction complexity. We present TAG-INSTRUCT, a novel framework that enhances instruction complexity through structured semantic compression and controlled difficulty augmentation. Unlike previous prompt-based methods operating on raw text, TAG-INSTRUCT compresses instructions into a compact tag space and systematically enhances complexity through RL-guided tag expansion. Through extensive experiments, we show that TAG-INSTRUCT outperforms existing instruction complexity augmentation approaches. Our analysis reveals that operating in tag space provides superior controllability and stability across different instruction synthesis frameworks.
高质量指令数据对于开发大型语言模型(LLM)至关重要,然而现有方法难以有效控制指令复杂性。我们提出了TAG-INSTRUCT这一新型框架,它通过结构化语义压缩和受控难度增强来提升指令复杂性。与之前在原始文本上操作的基于提示的方法不同,TAG-INSTRUCT将指令压缩到一个紧凑的标签空间中,并通过RL引导的标签扩展来系统地增强复杂性。通过大量实验,我们证明了TAG-INSTRUCT优于现有的指令复杂性增强方法。我们的分析表明,在标签空间中进行操作提供了出色的可控性和稳定性,适用于不同的指令合成框架。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在开发大型语言模型(LLM)中高质量指令数据的重要性。现有方法难以有效控制指令复杂性,因此提出了TAG-INSTRUCT这一新型框架。该框架通过结构化语义压缩和受控难度增强来提高指令复杂性。与基于提示的方法不同,它在紧凑的标签空间内压缩指令,并通过强化学习引导标签扩展进行系统性的增强。实验证明,TAG-INSTRUCT在指令复杂性增强方面优于现有方法。分析表明,在标签空间中进行操作提供了出色的可控性和稳定性,适用于不同的指令合成框架。
Key Takeaways
- 高质量指令数据对开发大型语言模型(LLM)至关重要。
- 现有方法难以有效控制指令复杂性。
- TAG-INSTRUCT是一种新型框架,旨在提高指令复杂性。
- 该框架通过结构化语义压缩和受控难度增强来实现目标。
- 与基于提示的方法不同,TAG-INSTRUCT在紧凑的标签空间内操作。
- 通过强化学习引导标签扩展,增强指令复杂性。
点此查看论文截图
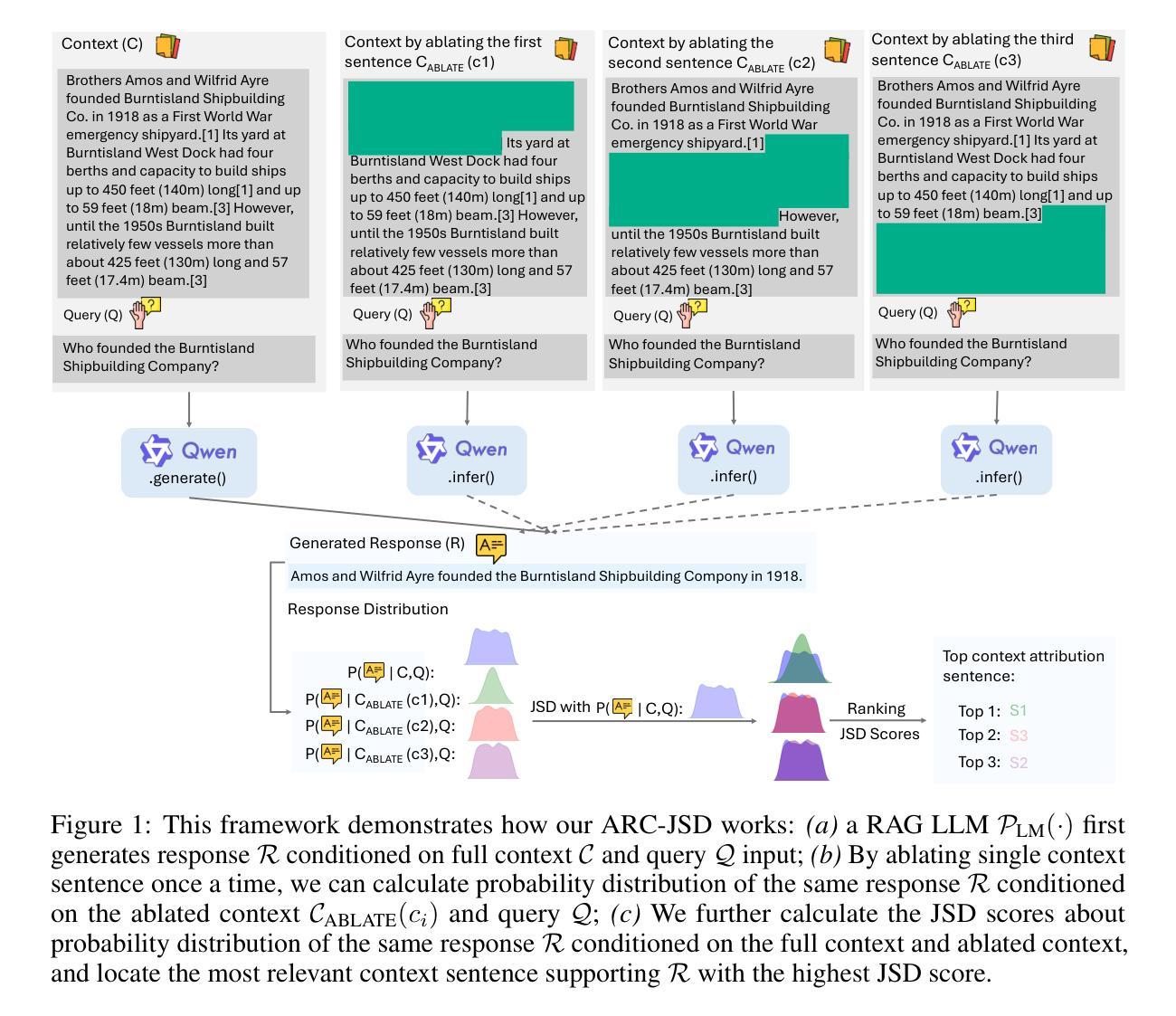
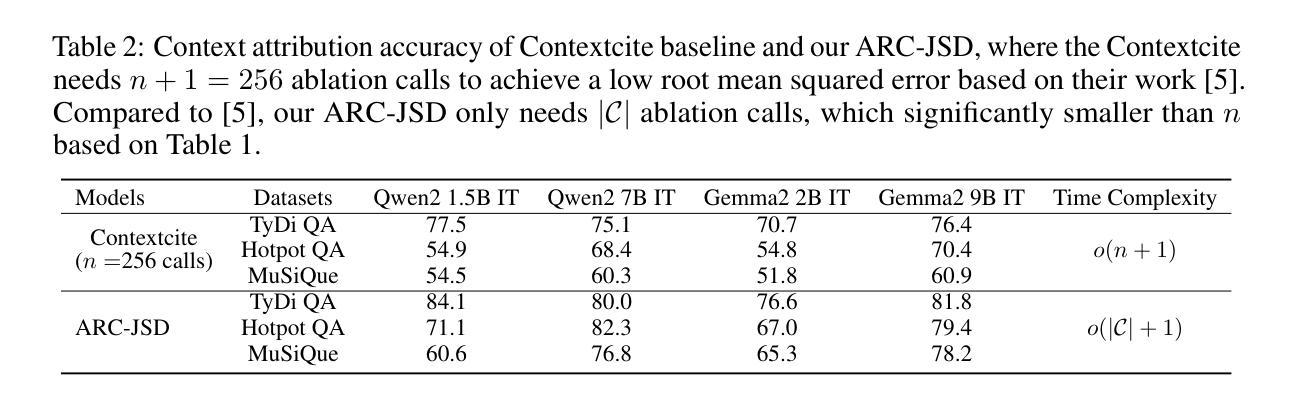
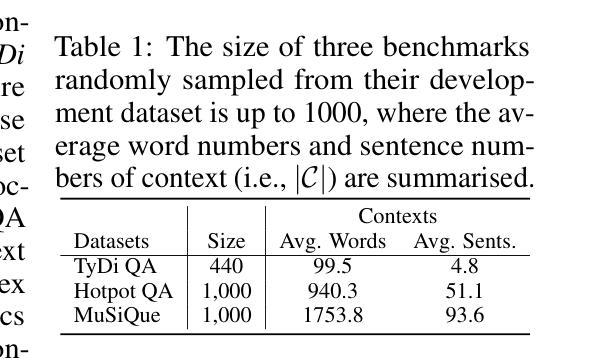
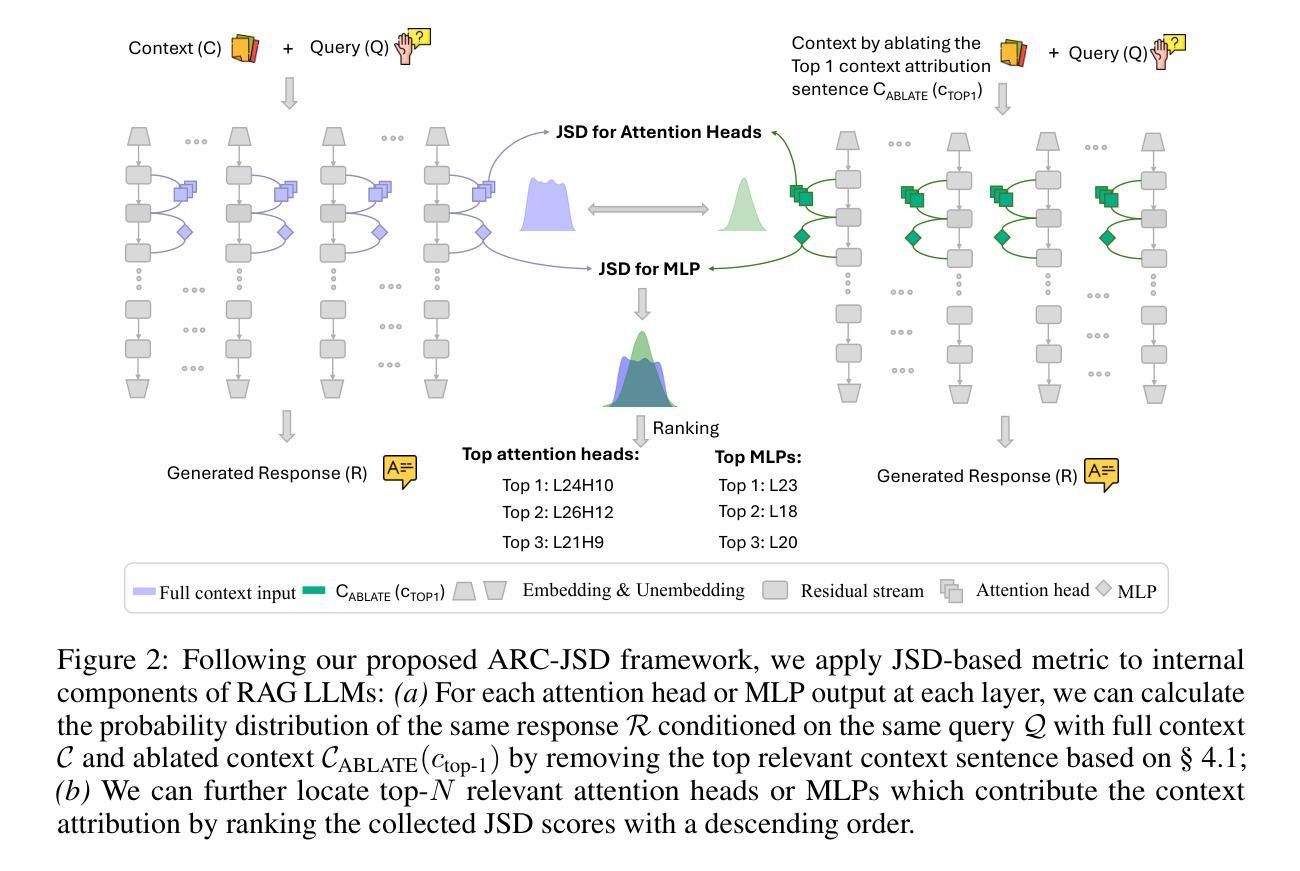
Attributing Response to Context: A Jensen-Shannon Divergence Driven Mechanistic Study of Context Attribution in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Authors:Ruizhe Li, Chen Chen, Yuchen Hu, Yanjun Gao, Xi Wang, Emine Yilmaz
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) leverages large language models (LLMs) combined with external contexts to enhance the accuracy and reliability of generated responses. However, reliably attributing generated content to specific context segments, context attribution, remains challenging due to the computationally intensive nature of current methods, which often require extensive fine-tuning or human annotation. In this work, we introduce a novel Jensen-Shannon Divergence driven method to Attribute Response to Context (ARC-JSD), enabling efficient and accurate identification of essential context sentences without additional fine-tuning or surrogate modelling. Evaluations on a wide range of RAG benchmarks, such as TyDi QA, Hotpot QA, and Musique, using instruction-tuned LLMs in different scales demonstrate superior accuracy and significant computational efficiency improvements compared to the previous surrogate-based method. Furthermore, our mechanistic analysis reveals specific attention heads and multilayer perceptron (MLP) layers responsible for context attribution, providing valuable insights into the internal workings of RAG models. Our code is available at https://github.com/ruizheliUOA/ARC_JSD
检索增强生成(RAG)利用大型语言模型(LLM)和外部上下文相结合,提高生成响应的准确性和可靠性。然而,由于当前方法的计算密集特性,将生成内容可靠地归因于特定的上下文片段,即上下文归因,仍然是一个挑战,这通常需要大量的微调或人工标注。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新型的基于Jensen-Shannon散度的方法——基于语境响应归因(ARC-JSD),能够在无需额外微调或替代建模的情况下,高效准确地识别出关键上下文句子。在多种RAG基准测试上的评估,如TyDi QA、Hotpot QA和Musique,使用不同规模指令调整LLM的评估,显示出相较于之前的基于替代方法具有更高的准确性和显著的计算效率改进。此外,我们的机制分析揭示了负责上下文归因的特定注意力头和多层感知器(MLP)层,为理解RAG模型的内部工作原理提供了有价值的见解。我们的代码可在https://github.com/ruizheliUOA/ARC_JSD找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in process
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)与外部环境结合生成响应,但其计算量大使得区分响应内容对应的特定语境变得困难。现介绍一种新型基于杰森-香农散度驱动的方法ARC-JSD进行语境识别,其准确高效无需额外的微调或替代建模。其在各类检索增强型生成任务上展现出色优势。通过解析注意力层和多层感知机层揭示了语境识别的内部机制。具体实现方法见代码仓库。
Key Takeaways
- RAG技术结合大型语言模型与外部上下文提高生成响应的准确性和可靠性。
- 语境识别是RAG的一个挑战,现有方法计算量大且效率不高。
- ARC-JSD方法使用杰森-香农散度技术解决语境识别问题,准确高效且无需额外微调或替代建模。
- ARC-JSD在多种RAG任务上表现优越,包括TyDi QA、Hotpot QA和Musique等。
- 通过内部机制分析,揭示了特定注意力层和多层感知机层在语境识别中的作用。
点此查看论文截图

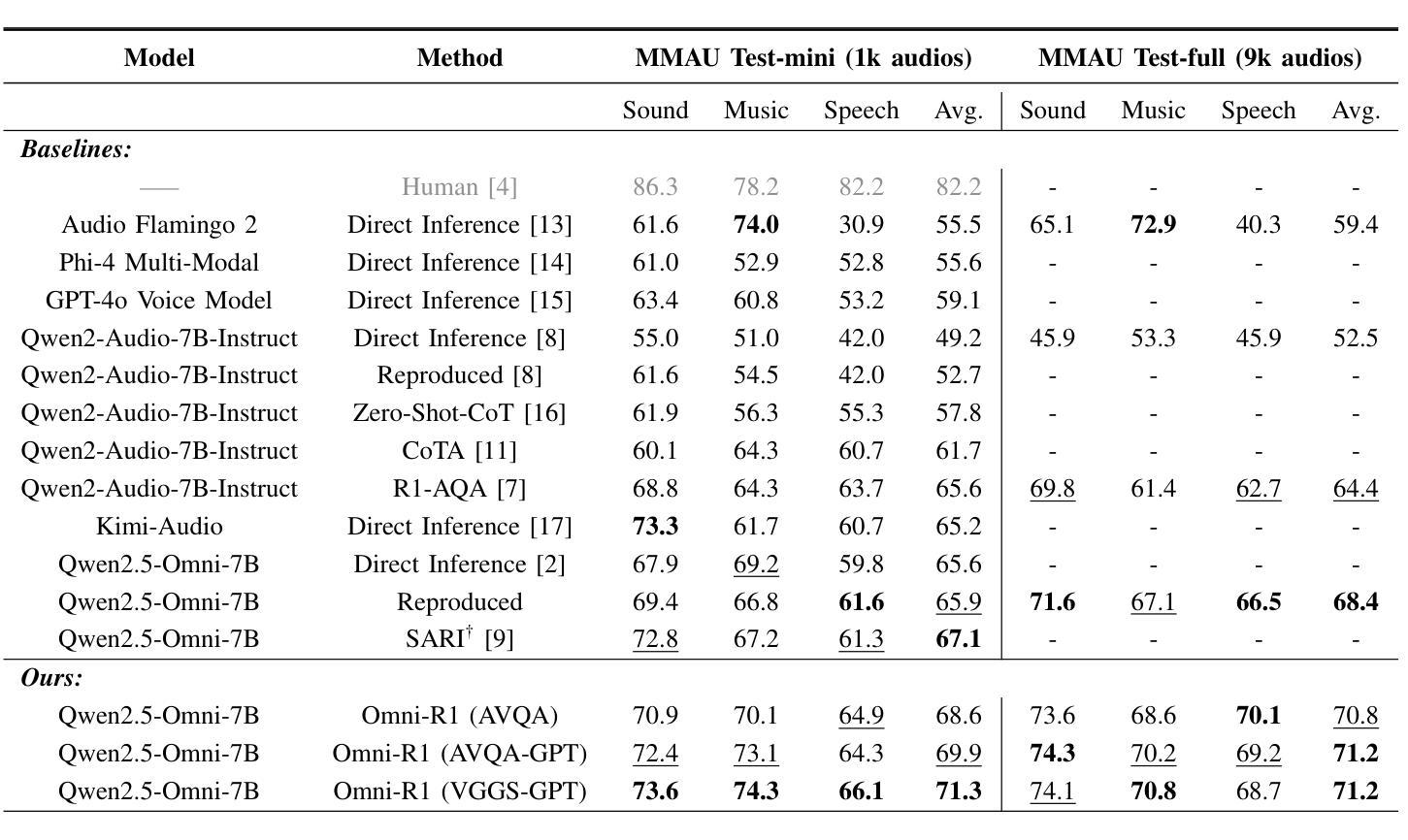
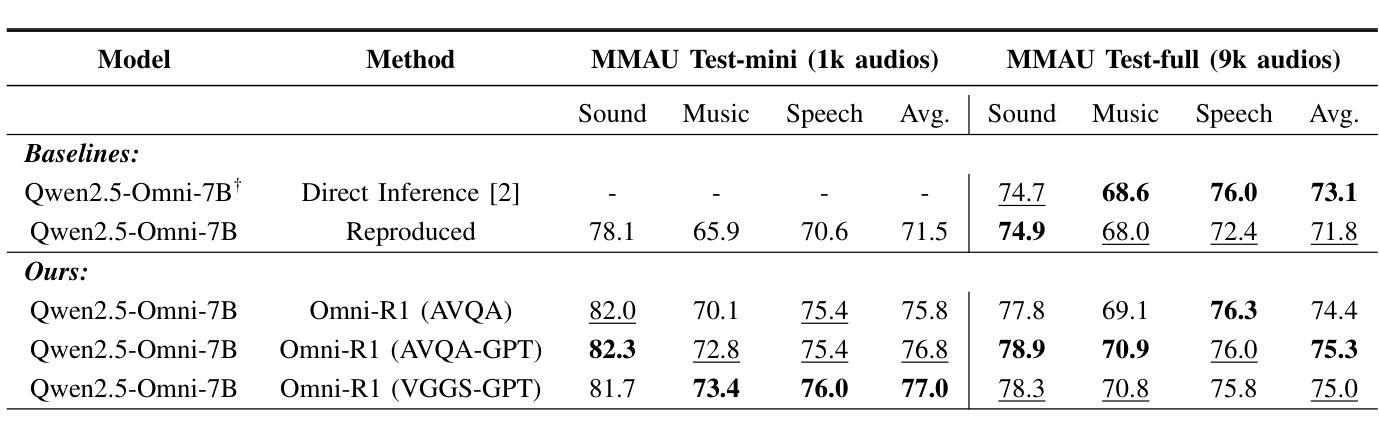
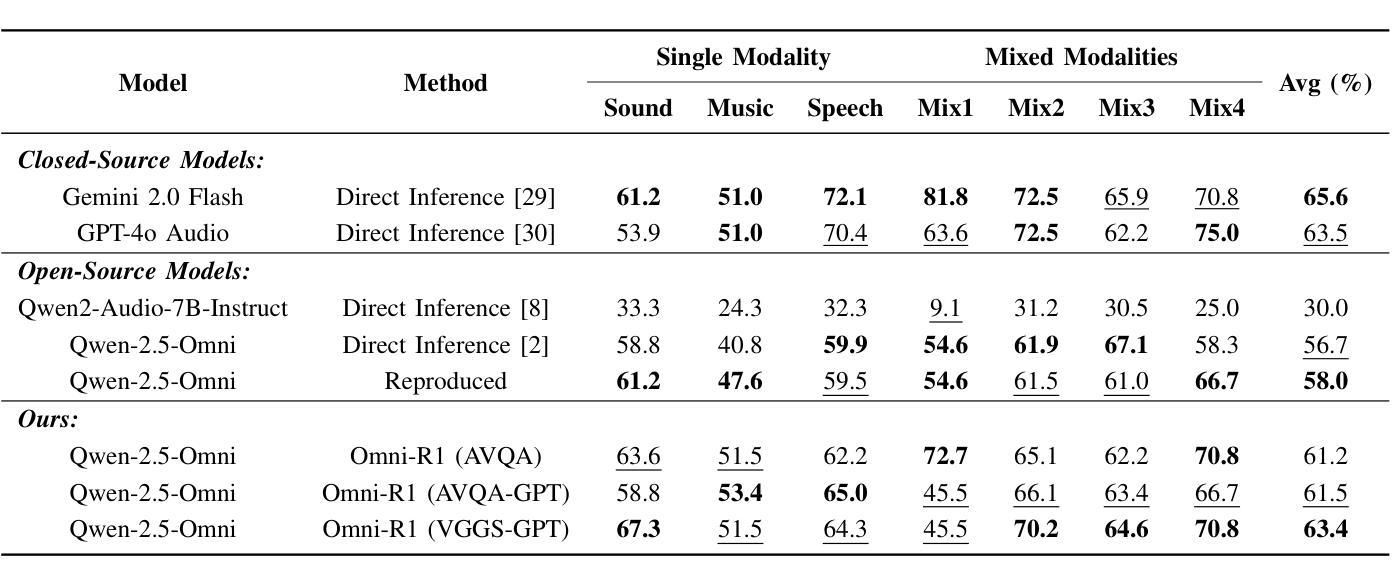
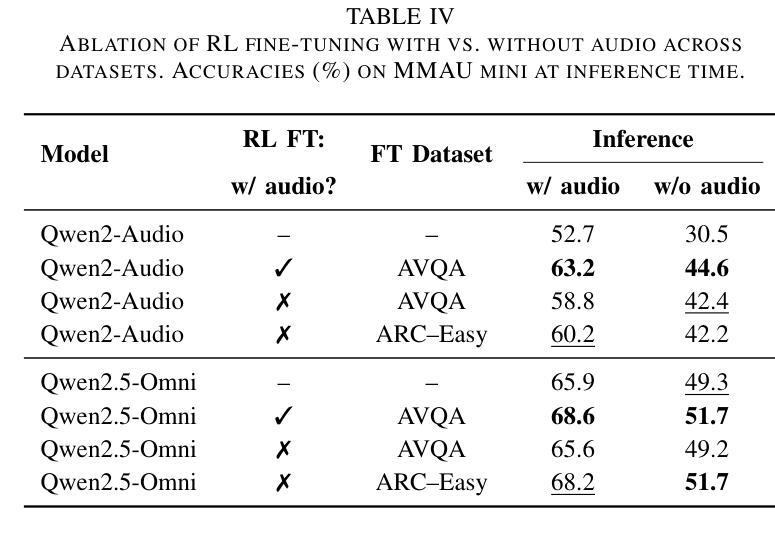
Omni-R1: Do You Really Need Audio to Fine-Tune Your Audio LLM?
Authors:Andrew Rouditchenko, Saurabhchand Bhati, Edson Araujo, Samuel Thomas, Hilde Kuehne, Rogerio Feris, James Glass
We propose Omni-R1 which fine-tunes a recent multi-modal LLM, Qwen2.5-Omni, on an audio question answering dataset with the reinforcement learning method GRPO. This leads to new State-of-the-Art performance on the recent MMAU and MMAR benchmarks. Omni-R1 achieves the highest accuracies on the sounds, music, speech, and overall average categories, both on the Test-mini and Test-full splits. To understand the performance improvement, we tested models both with and without audio and found that much of the performance improvement from GRPO could be attributed to better text-based reasoning. We also made a surprising discovery that fine-tuning without audio on a text-only dataset was effective at improving the audio-based performance.
我们提出了Omni-R1,它通过强化学习法GRPO对近期的多模式LLM,Qwen2.5-Omni进行微调,该模型在音频问答数据集上进行训练。这实现了在最新的MMAU和MMAR基准测试上的最新国家技术水准性能。Omni-R1在声音、音乐、演讲和总体平均类别上均达到了最高的准确度,无论是在Test-mini还是Test-full分割上。为了了解性能提升的原因,我们对带有和不带音频的模型进行了测试,发现GRPO的大部分性能提升是由于基于文本推理的改进。我们还意外地发现,在纯文本数据集上进行不带音频的微调,对于提高基于音频的性能也是有效的。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Omni-R1通过微调多模态大型语言模型Qwen2.5-Omni,并结合强化学习算法GRPO,在音频问答数据集上取得了最新最先进的性能表现。在MMAU和MMAR基准测试中,Omni-R1在声音、音乐、语音和总体平均类别上均达到了最高准确率,无论是在测试集的小型分割还是全分割中都表现优异。通过对模型有无音频的测试,发现GRPO的大部分性能提升主要归功于基于文本推理的改进。令人惊讶的是,即使在只有文本的数据集上进行微调,也能有效提高基于音频的性能。
Key Takeaways
- Omni-R1通过微调多模态大型语言模型并结合强化学习在音频问答数据集上实现了卓越性能。
- Omni-R1在声音、音乐、语音和总体平均类别上达到了最高准确率。
- 在测试模型有无音频的情况下,发现大部分性能提升来源于基于文本推理的改进。
- GRPO算法对模型性能的提升起到了关键作用。
- 在只有文本的数据集上进行微调也能有效提高基于音频的性能。
- Omni-R1的成功验证了多模态大型语言模型在音频领域的潜力。
点此查看论文截图


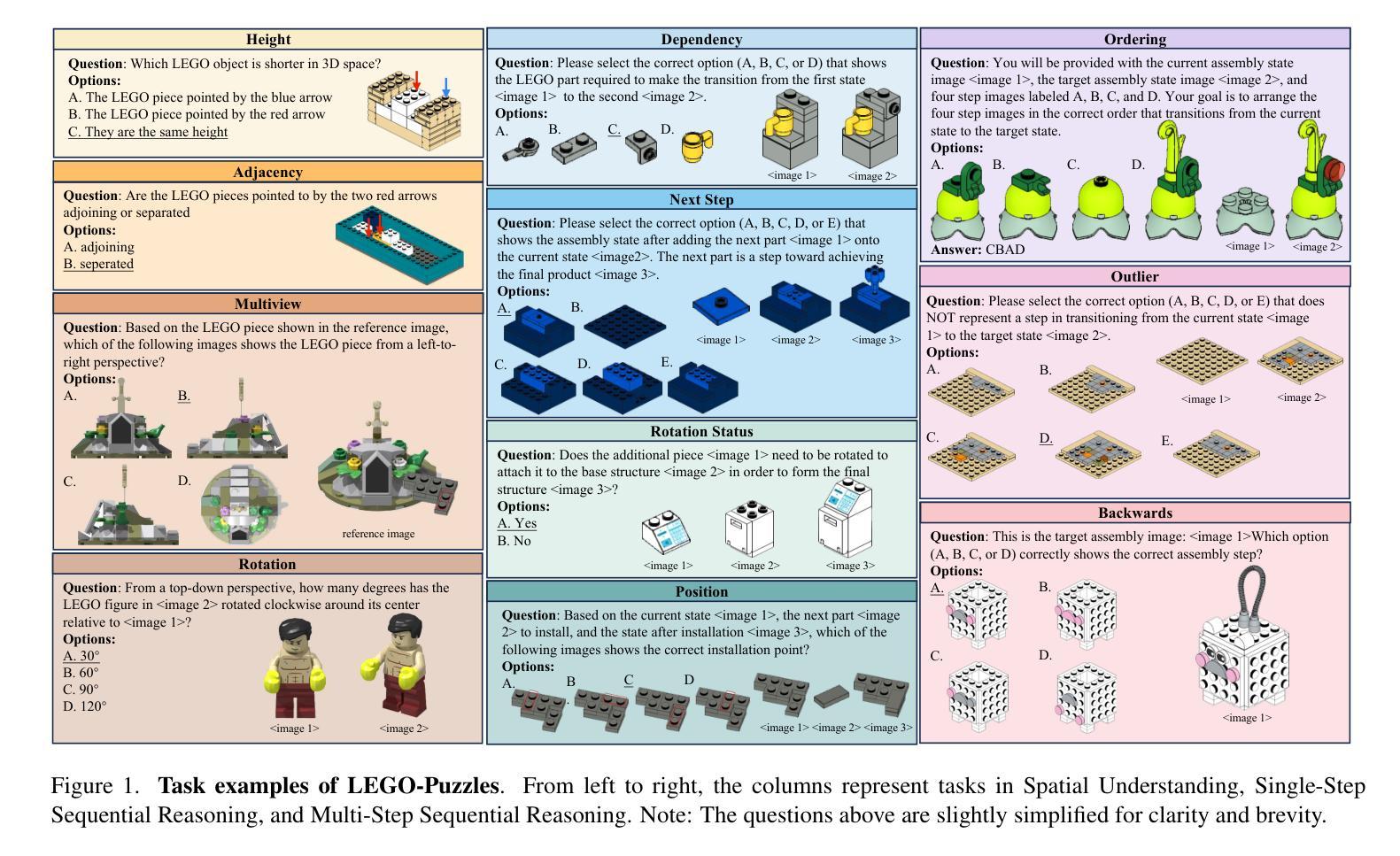
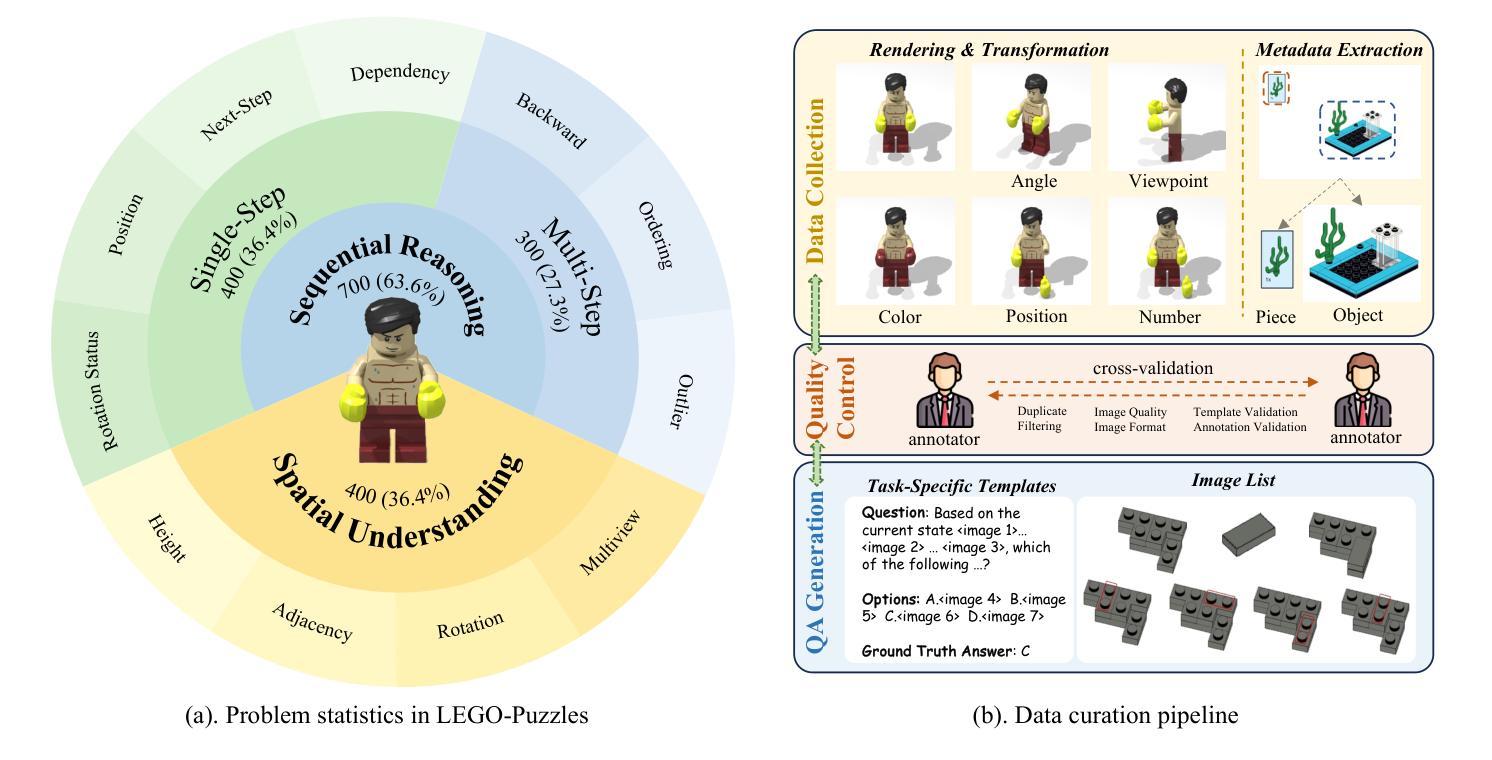
LEGO-Puzzles: How Good Are MLLMs at Multi-Step Spatial Reasoning?
Authors:Kexian Tang, Junyao Gao, Yanhong Zeng, Haodong Duan, Yanan Sun, Zhening Xing, Wenran Liu, Kaifeng Lyu, Kai Chen
Multi-step spatial reasoning entails understanding and reasoning about spatial relationships across multiple sequential steps, which is crucial for tackling complex real-world applications, such as robotic manipulation, autonomous navigation, and automated assembly. To assess how well current Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have acquired this fundamental capability, we introduce LEGO-Puzzles, a scalable benchmark designed to evaluate both spatial understanding and sequential reasoning in MLLMs through LEGO-based tasks. LEGO-Puzzles consists of 1,100 carefully curated visual question-answering (VQA) samples spanning 11 distinct tasks, ranging from basic spatial understanding to complex multi-step reasoning. Based on LEGO-Puzzles, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of 20 state-of-the-art MLLMs and uncover significant limitations in their spatial reasoning capabilities: even the most powerful MLLMs can answer only about half of the test cases, whereas human participants achieve over 90% accuracy. Furthermore, based on LEGO-Puzzles, we design generation tasks to investigate whether MLLMs can transfer their spatial understanding and reasoning abilities to image generation. Our experiments show that only GPT-4o and Gemini-2.0-Flash exhibit a limited ability to follow these instructions, while other MLLMs either replicate the input image or generate completely irrelevant outputs. Overall, LEGO-Puzzles exposes critical deficiencies in existing MLLMs’ spatial understanding and sequential reasoning capabilities, and underscores the need for further advancements in multimodal spatial reasoning.
多步空间推理涉及理解和推理跨多个连续步骤的空间关系,这对于解决复杂现实世界应用至关重要,例如机器人操作、自主导航和自动化组装。为了评估当前的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在获取这种基本能力方面的表现,我们引入了乐高拼图(LEGO-Puzzles),这是一个可扩展的基准测试,旨在通过基于乐高的任务来评估MLLMs的空间理解和顺序推理能力。乐高拼图包含1100个精心策划的视觉问答(VQA)样本,涵盖11个不同的任务,从基本空间理解到复杂的多步推理。基于乐高拼图,我们对20个最新MLLMs进行了全面评估,并发现了它们在空间推理能力方面的重大局限性:即使是最强大的MLLM也只能回答大约一半的测试用例,而人类参与者的准确率超过90%。此外,基于乐高拼图,我们设计了生成任务来调查MLLMs是否能够将他们的空间理解和推理能力转移到图像生成。我们的实验表明,只有GPT-4o和Gemini-2.0-Flash表现出有限的能力来遵循这些指令,而其他MLLMs要么复制输入图像,要么生成完全不相关的输出。总体而言,乐高拼图揭示了现有MLLMs在空间理解和顺序推理能力方面的关键缺陷,并强调了在多模态空间推理方面需要进一步的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 figures
Summary
LEGO-Puzzles是一个用于评估多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的空间理解和推理能力的大规模基准测试。它由包含多种复杂空间任务的1100个视觉问答(VQA)样本组成。评估发现,当前最先进的MLLMs只能回答一半左右的问题,而人类参与者的准确率超过90%。同时,在图像生成任务中,仅有GPT-4o和Gemini-2.0-Flash能有限地遵循空间理解和推理指令。总体来说,LEGO-Puzzles揭示了现有MLLMs在空间理解和顺序推理能力上的不足,并强调了进一步改进多模态空间推理的必要性。
Key Takeaways
- 多步空间推理对于处理现实世界应用如机器人操控、自主导航和自动化装配至关重要。
- LEGO-Puzzles是一个用于评估MLLMs空间理解和顺序推理能力的大规模基准测试。
- 当前最先进的MLLMs在LEGO-Puzzles测试中只能回答一半左右的问题,表明其在空间推理能力上存在局限性。
- 人类参与者在LEGO-Puzzles测试中的准确率超过90%。
- 在图像生成任务中,仅有部分MLLMs(如GPT-4o和Gemini-2.0-Flash)能遵循空间理解和推理指令。
- LEGO-Puzzles揭示了现有MLLMs在空间理解和推理能力上的不足。
点此查看论文截图

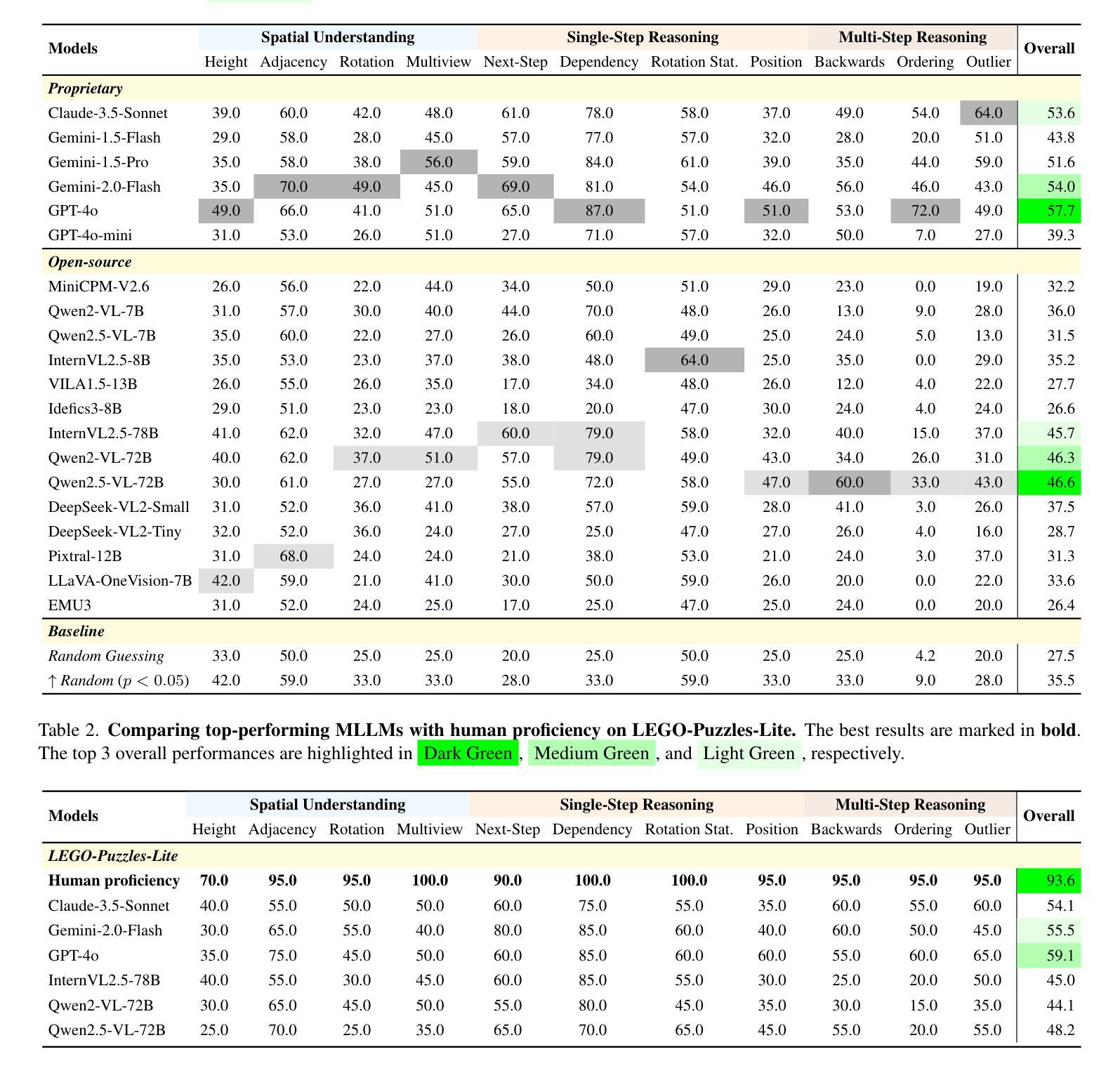
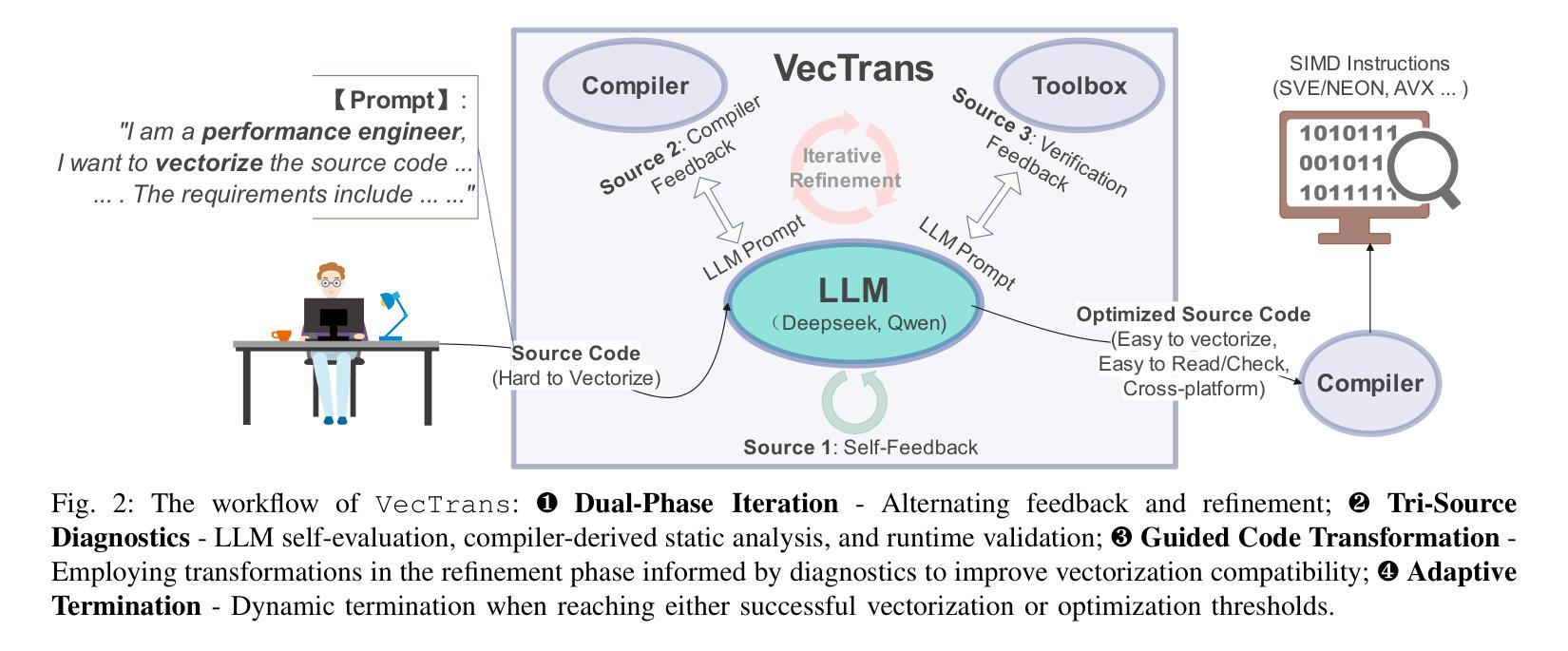
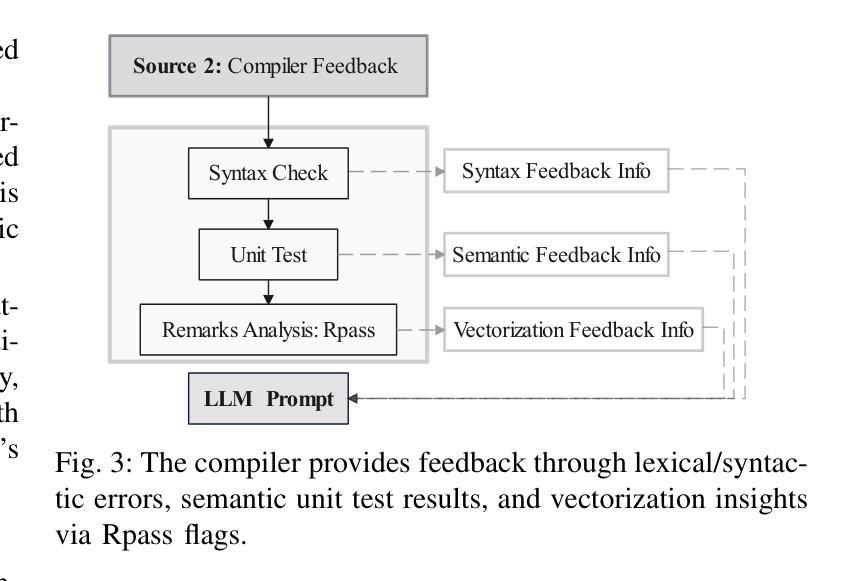
VecTrans: Enhancing Compiler Auto-Vectorization through LLM-Assisted Code Transformations
Authors:Zhongchun Zheng, Kan Wu, Long Cheng, Lu Li, Rodrigo C. O. Rocha, Tianyi Liu, Wei Wei, Jianjiang Zeng, Xianwei Zhang, Yaoqing Gao
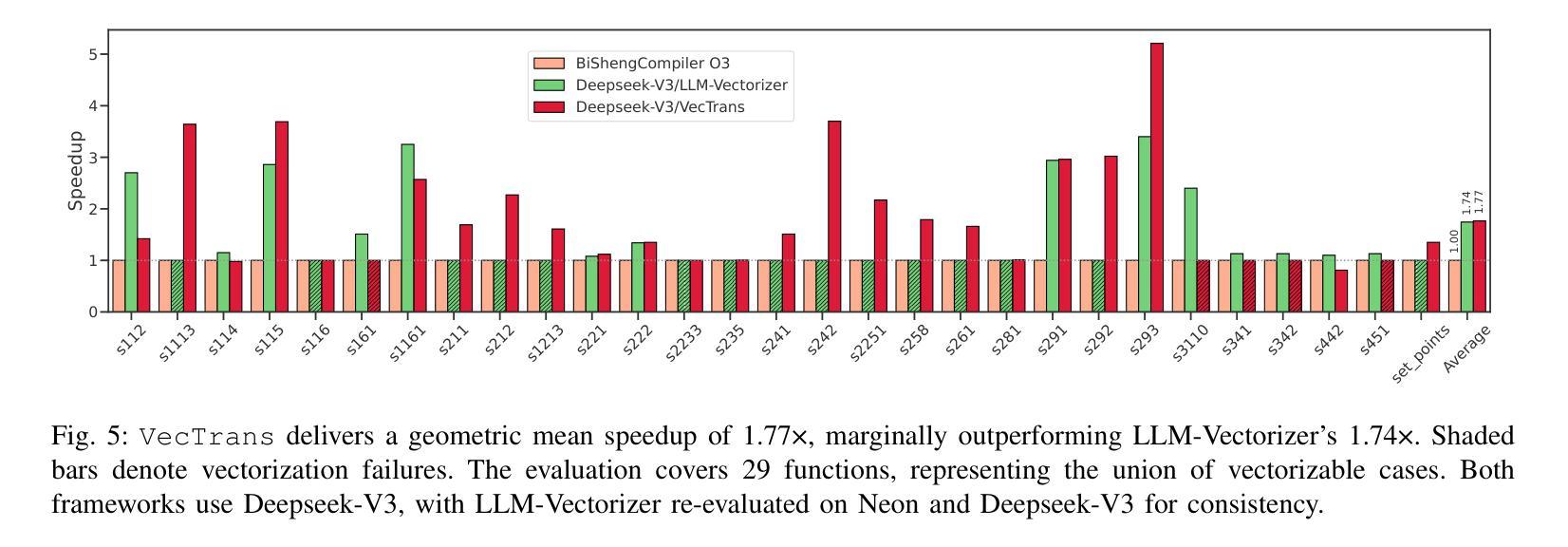
Auto-vectorization is a fundamental optimization for modern compilers to exploit SIMD parallelism. However, state-of-the-art approaches still struggle to handle intricate code patterns, often requiring manual hints or domain-specific expertise. Large language models (LLMs), with their ability to capture intricate patterns, provide a promising solution, yet their effective application in compiler optimizations remains an open challenge due to issues such as hallucinations and a lack of domain-specific reasoning. In this paper, we present VecTrans, a novel framework that leverages LLMs to enhance compiler-based code vectorization. VecTrans first employs compiler analysis to identify potentially vectorizable code regions. It then utilizes an LLM to refactor these regions into patterns that are more amenable to the compilers auto-vectorization. To ensure semantic correctness, VecTrans further integrates a hybrid validation mechanism at the intermediate representation (IR) level. With the above efforts, VecTrans combines the adaptability of LLMs with the precision of compiler vectorization, thereby effectively opening up the vectorization opportunities. experimental results show that among all TSVC functions unvectorizable by GCC, ICC, Clang, and BiSheng Compiler, VecTrans achieves an geomean speedup of 1.77x and successfully vectorizes 24 of 51 test cases. This marks a significant advancement over state-of-the-art approaches while maintaining a cost efficiency of $0.012 per function optimization for LLM API usage.
自动矢量化是现代编译器利用SIMD并行性的基本优化。然而,最先进的技术在处理复杂的代码模式时仍面临困难,通常需要手动提示或特定领域的专业知识。大型语言模型(LLM)具有捕捉复杂模式的能力,提供了有前景的解决方案,但由于幻想和缺乏特定领域的推理等问题,它们在编译器优化中的有效应用仍然是一个开放性的挑战。在本文中,我们提出了VecTrans,一个利用LLM增强基于编译器的代码矢量化的新型框架。VecTrans首先使用编译器分析来识别可能可向量化的代码区域。然后,它利用LLM将这些区域重构为更易于编译器自动矢量化的模式。为了确保语义正确性,VecTrans进一步在中间表示(IR)级别集成了一种混合验证机制。通过以上努力,VecTrans结合了LLM的适应性和编译器矢量化的精确性,从而有效地开辟了矢量化机会。实验结果表明,在所有不被GCC、ICC、Clang和BiSheng编译器矢量化的TSVC函数中,VecTrans实现了1.77倍的几何平均加速,并成功矢量化了51个测试用例中的24个。这标志着在保持成本效益的同时,相较于最先进的技术取得了重大进展,每个函数优化的LLM API使用成本为0.012美元。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了VecTrans框架,该框架利用大型语言模型(LLM)增强基于编译器的代码向量化。VecTrans首先通过编译器分析识别潜在的可向量化代码区域,然后使用LLM对这些区域进行重构,以便编译器自动进行向量化。为确保语义正确性,VecTrans在中间表示(IR)级别进一步集成了混合验证机制。实验结果表明,VecTrans在所有未被GCC、ICC、Clang和BiSheng编译器向量化的TSVC函数中实现了平均加速比提高1.77倍,成功向量化24个测试案例中的51个。相较于当前最佳方法,这一进展具有显著优势,并且每次函数优化的LLM API使用成本为每人节省美元的费用成本达到控制的目标标准水准每人低工时付出足够廉价的开支级别最低人力成本支出效率也极高。总体而言,VecTrans结合了LLM的适应性和编译器向量化的精确性,有效开启了向量化的可能性。它不仅对改善编程效率和软件性能有重要意义,而且具有巨大的应用潜力。这项研究对于利用大型语言模型在编译器优化方面的应用具有里程碑意义。随着技术的不断进步和应用的推广,我们期待看到更多关于此类技术的创新和改进。
Key Takeaways
以下是基于文本的关键见解:
点此查看论文截图

SPILL: Domain-Adaptive Intent Clustering based on Selection and Pooling with Large Language Models
Authors:I-Fan Lin, Faegheh Hasibi, Suzan Verberne
In this paper, we propose Selection and Pooling with Large Language Models (SPILL), an intuitive and domain-adaptive method for intent clustering without fine-tuning. Existing embeddings-based clustering methods rely on a few labeled examples or unsupervised fine-tuning to optimize results for each new dataset, which makes them less generalizable to multiple datasets. Our goal is to make these existing embedders more generalizable to new domain datasets without further fine-tuning. Inspired by our theoretical derivation and simulation results on the effectiveness of sampling and pooling techniques, we view the clustering task as a small-scale selection problem. A good solution to this problem is associated with better clustering performance. Accordingly, we propose a two-stage approach: First, for each utterance (referred to as the seed), we derive its embedding using an existing embedder. Then, we apply a distance metric to select a pool of candidates close to the seed. Because the embedder is not optimized for new datasets, in the second stage, we use an LLM to further select utterances from these candidates that share the same intent as the seed. Finally, we pool these selected candidates with the seed to derive a refined embedding for the seed. We found that our method generally outperforms directly using an embedder, and it achieves comparable results to other state-of-the-art studies, even those that use much larger models and require fine-tuning, showing its strength and efficiency. Our results indicate that our method enables existing embedders to be further improved without additional fine-tuning, making them more adaptable to new domain datasets. Additionally, viewing the clustering task as a small-scale selection problem gives the potential of using LLMs to customize clustering tasks according to the user’s goals.
本文提出了基于大语言模型的选择池化(SPILL)方法,这是一种直观且适用于特定领域的意图聚类方法,无需微调。现有的基于嵌入的聚类方法依赖于少量带标签的样本或基于无监督学习的微调,以便为每新数据集优化结果,这导致它们在多个数据集上的通用性较差。我们的目标是在无需进一步微调的情况下,使现有嵌入技术更具通用性,以适应新的领域数据集。通过我们对采样和池技术的有效性进行理论推导和模拟验证得到的启发,我们将聚类任务视为一个小规模的选择问题。良好的解决方案与更好的聚类性能相关。因此,我们提出了一个两阶段的方法:首先,针对每个句子(称为种子),我们使用现有的嵌入技术得到其嵌入表示。然后,我们使用距离度量选择一个与种子接近的候选池。由于嵌入技术并不是针对新数据集进行优化的,在第二阶段,我们使用大型语言模型从这些候选中进一步选择与种子具有相同意图的句子。最后,我们将这些选择的候选与种子合并,得到种子的精细嵌入表示。我们发现,我们的方法通常优于直接使用嵌入技术的方法,并且与其他最新研究的结果相当,即使这些研究使用更大的模型并需要微调。这显示了其强大和高效性。我们的结果表明,我们的方法能够在无需额外微调的情况下进一步改进现有嵌入技术,使其更适应新的领域数据集。此外,将聚类任务视为小规模的选择问题具有使用大型语言模型根据用户目标定制聚类任务的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型辅助的意图聚类方法无需微调。本文提出了基于选择池化的大语言模型(SPILL)方法,该方法直观且适应于领域需求,无需微调即可进行意图聚类。通过对采样和池化技术的理论推导和仿真验证,将聚类任务视为小规模选择问题,提出了一种两阶段的方法,通过利用现有嵌入器和大语言模型的优势,提高聚类性能。该方法一般优于直接使用嵌入器的方法,且与现有的顶尖研究成果表现相当。此方法的优点在于可进一步提高现有嵌入器的性能而无需额外的微调,使其更能适应新领域数据集,具有广泛的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- SPILL方法基于选择池化技术,通过理论推导和仿真验证实现无需微调进行意图聚类。
- 提出一种两阶段方法,利用现有嵌入器和大语言模型的优势提高聚类性能。
- SPILL方法通过选择接近种子的候选集进行池化,进一步提高了种子嵌入的精度。
- 与直接使用嵌入器的方法相比,SPILL方法表现更优,且与顶尖研究成果表现相当。
- SPILL方法能进一步提升现有嵌入器的性能,无需额外微调,对新领域数据集的适应能力更强。
- 通过将聚类任务视为小规模选择问题,SPILL方法具有广泛的实用性。
点此查看论文截图

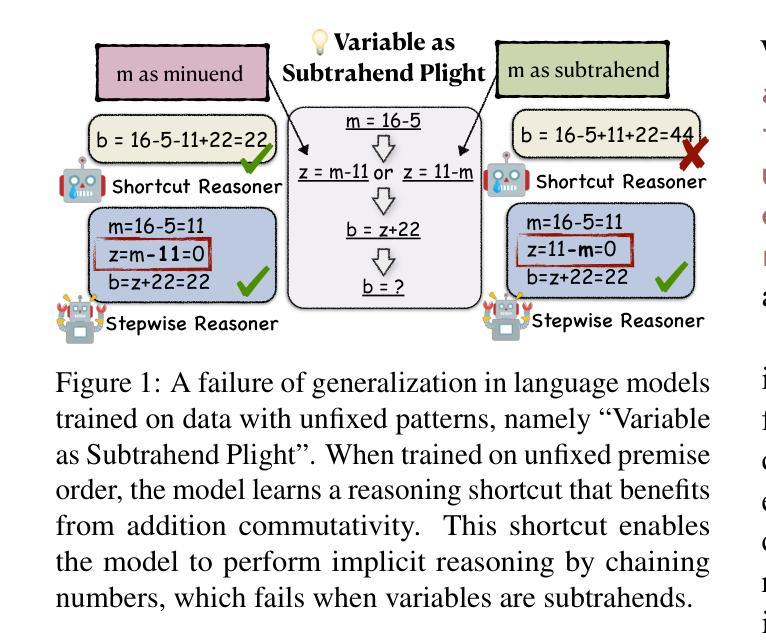
Implicit Reasoning in Transformers is Reasoning through Shortcuts
Authors:Tianhe Lin, Jian Xie, Siyu Yuan, Deqing Yang
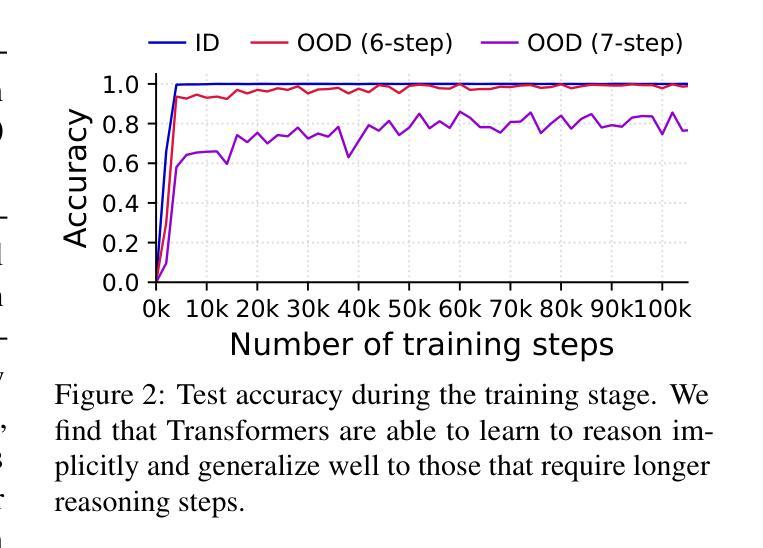
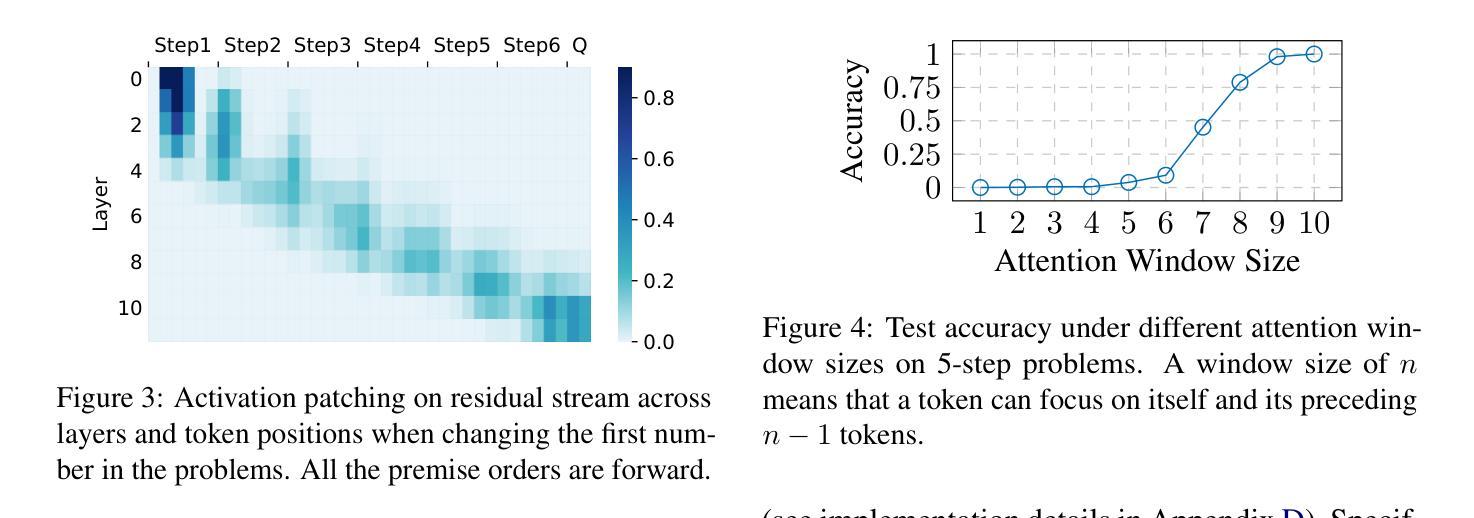
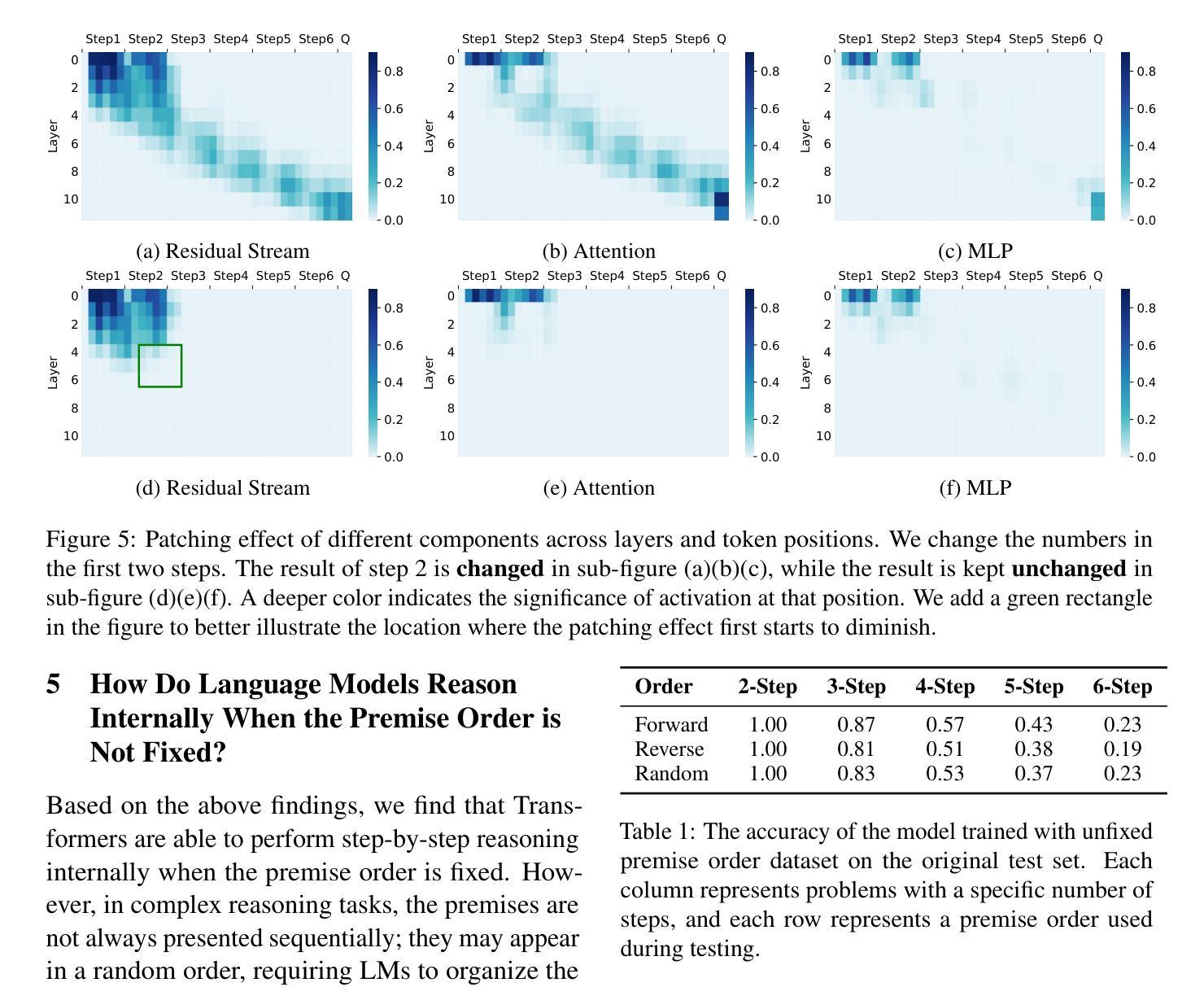
Test-time compute is emerging as a new paradigm for enhancing language models’ complex multi-step reasoning capabilities, as demonstrated by the success of OpenAI’s o1 and o3, as well as DeepSeek’s R1. Compared to explicit reasoning in test-time compute, implicit reasoning is more inference-efficient, requiring fewer generated tokens. However, why does the advanced reasoning capability fail to emerge in the implicit reasoning style? In this work, we train GPT-2 from scratch on a curated multi-step mathematical reasoning dataset and conduct analytical experiments to investigate how language models perform implicit reasoning in multi-step tasks. Our findings reveal: 1) Language models can perform step-by-step reasoning and achieve high accuracy in both in-domain and out-of-domain tests via implicit reasoning. However, this capability only emerges when trained on fixed-pattern data. 2) Conversely, implicit reasoning abilities emerging from training on unfixed-pattern data tend to overfit a specific pattern and fail to generalize further. Notably, this limitation is also observed in state-of-the-art large language models. These findings suggest that language models acquire implicit reasoning through shortcut learning, enabling strong performance on tasks with similar patterns while lacking generalization.
测试时的计算正成为一种新兴的模式,用于增强语言模型的复杂多步推理能力,OpenAI的o1和o3以及DeepSeek的R1的成功也证明了这一点。与测试时的显式推理相比,隐式推理的推理效率更高,产生的标记更少。然而,为什么高级推理能力没有在隐式推理风格中出现呢?在这项工作中,我们从零开始训练GPT-2,目标是在筛选过的多步数学推理数据集上,并通过分析实验来研究语言模型在多步任务中进行隐式推理的表现。我们的研究结果揭示了以下几点:1)语言模型可以通过隐式推理进行逐步推理,并在领域内外测试中实现高准确率。但这种能力只在固定模式的数据训练下才会出现。2)相反,从非固定模式数据训练中出现的隐式推理能力往往过于适应特定模式,无法进一步推广。值得注意的是,这一局限性在最新的大型语言模型中也被观察到。这些发现表明,语言模型通过捷径学习获得隐式推理能力,能够在具有相似模式的任务上表现出强大的性能,但缺乏泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 Findings
Summary
本文主要探讨了测试时计算(test-time compute)这一新兴范式对增强语言模型复杂多步骤推理能力的作用。通过实验分析,发现语言模型在固定模式数据训练下可通过隐式推理完成步骤式推理,且在不同领域测试中均表现出高准确率。然而,在非标定模式数据训练下,隐式推理能力往往过于拟合特定模式,缺乏泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时计算是一种新兴范式,用于增强语言模型的复杂多步骤推理能力。
- OpenAI的o1和o3以及DeepSeek的R1的成功演示了这一点。
- 隐式推理相比显式推理更加推理高效,需要生成的标记更少。
- 语言模型可以在固定模式数据训练下通过隐式推理进行逐步推理,并在域内和域外测试中获得高准确率。
- 在非标定模式数据训练下,隐式推理能力倾向于过度拟合特定模式,缺乏泛化能力。
- 语言模型的隐式推理能力是通过“捷径学习”获得的。
点此查看论文截图

TESS 2: A Large-Scale Generalist Diffusion Language Model
Authors:Jaesung Tae, Hamish Ivison, Sachin Kumar, Arman Cohan
We introduce TESS 2, a general instruction-following diffusion language model that outperforms contemporary instruction-tuned diffusion models, as well as matches and sometimes exceeds strong autoregressive (AR) models. We train TESS 2 by first adapting a strong AR model via continued pretraining with the usual cross-entropy as diffusion loss, and then performing further instruction tuning. We find that adaptation training as well as the choice of the base model is crucial for training good instruction-following diffusion models. We further propose reward guidance, a novel and modular inference-time guidance procedure to align model outputs without needing to train the underlying model. Finally, we show that TESS 2 further improves with increased inference-time compute, highlighting the utility of diffusion LMs in having fine-grained controllability over the amount of compute used at inference time. Code and models are available at https://github.com/hamishivi/tess-2.
我们介绍了TESS 2,这是一个通用指令遵循扩散语言模型,它超越了当代指令优化扩散模型,与强大的自回归(AR)模型相匹配,有时甚至超过它们。我们通过首先使用强大的AR模型进行持续预训练,以常规的交叉熵作为扩散损失,然后进一步进行指令调整来训练TESS 2。我们发现适应训练以及基础模型的选择对于训练良好的指令遵循扩散模型至关重要。我们进一步提出了奖励指导,这是一种新的模块化推理时间指导程序,可以在不需要训练底层模型的情况下对齐模型输出。最后,我们证明TESS 2随着推理时间的计算增加可以进一步提高性能,这突显了扩散LM在推理时间使用的计算量方面具有精细控制的有用性。代码和模型可在https://github.com/hamishivi/tess-2找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 camera-ready
摘要
本文介绍了TESS 2,这是一种通用指令遵循扩散语言模型,它超越了当代指令调整扩散模型的表现,并可与强大的自回归(AR)模型相匹敌,甚至在某些情况下表现更佳。我们通过先使用常规交叉熵作为扩散损失对强大AR模型进行持续预训练,然后进行进一步的指令调整来训练TESS 2。我们发现适应训练以及基础模型的选择对于训练良好的指令遵循扩散模型至关重要。我们还提出了奖励指导,这是一种新型模块化推理时间指导程序,可在无需训练底层模型的情况下对齐模型输出。最后,我们证明了TESS 2随着推理时间计算量的增加而进一步改进,这凸显了扩散语言模型在推理时间使用计算量的精细控制能力。模型和代码可通过https://github.com/hamishivi/tess-2获取。
要点摘要
- TESS 2是一种通用指令遵循扩散语言模型,表现超越当代指令调整扩散模型,可与强大的自回归(AR)模型相匹敌。
- TESS 2通过持续预训练和进一步的指令调整进行训练,其中适应训练和基础模型的选择是关键。
- 提出了奖励指导,这是一种新的推理时间指导程序,可在无需训练底层模型的情况下对齐模型输出。
- TESS 2随着推理时间计算量的增加进一步改进,体现了扩散语言模型的精细可控性。
- TESS 2的发布和代码库可用于进一步研究和开发。
- 扩散语言模型在指令遵循任务上具有潜在优势,未来研究可能进一步优化这类模型的性能和结构。
点此查看论文截图

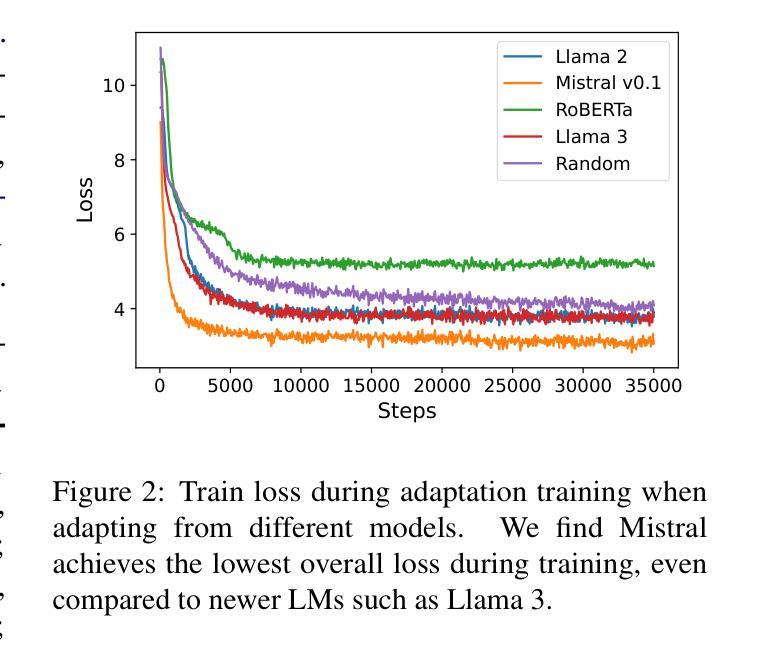
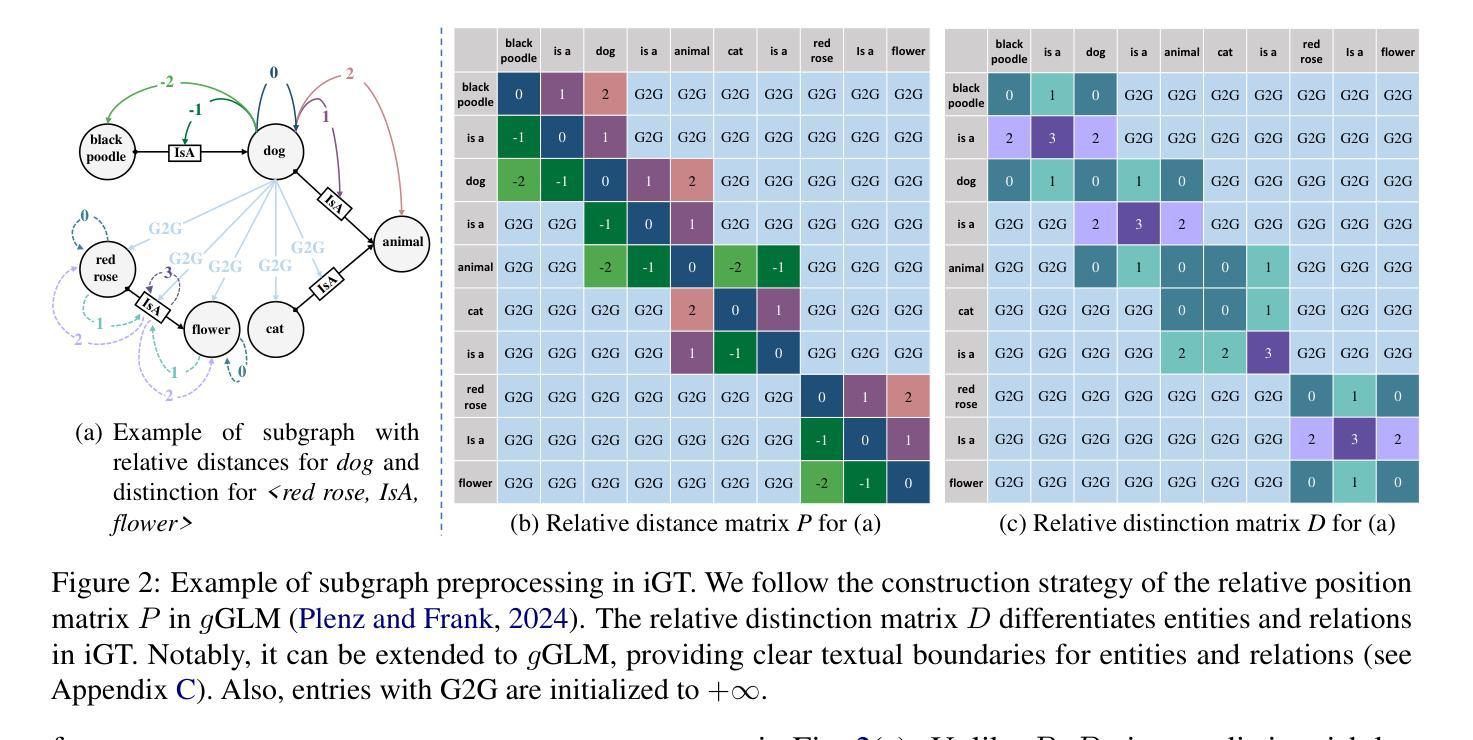
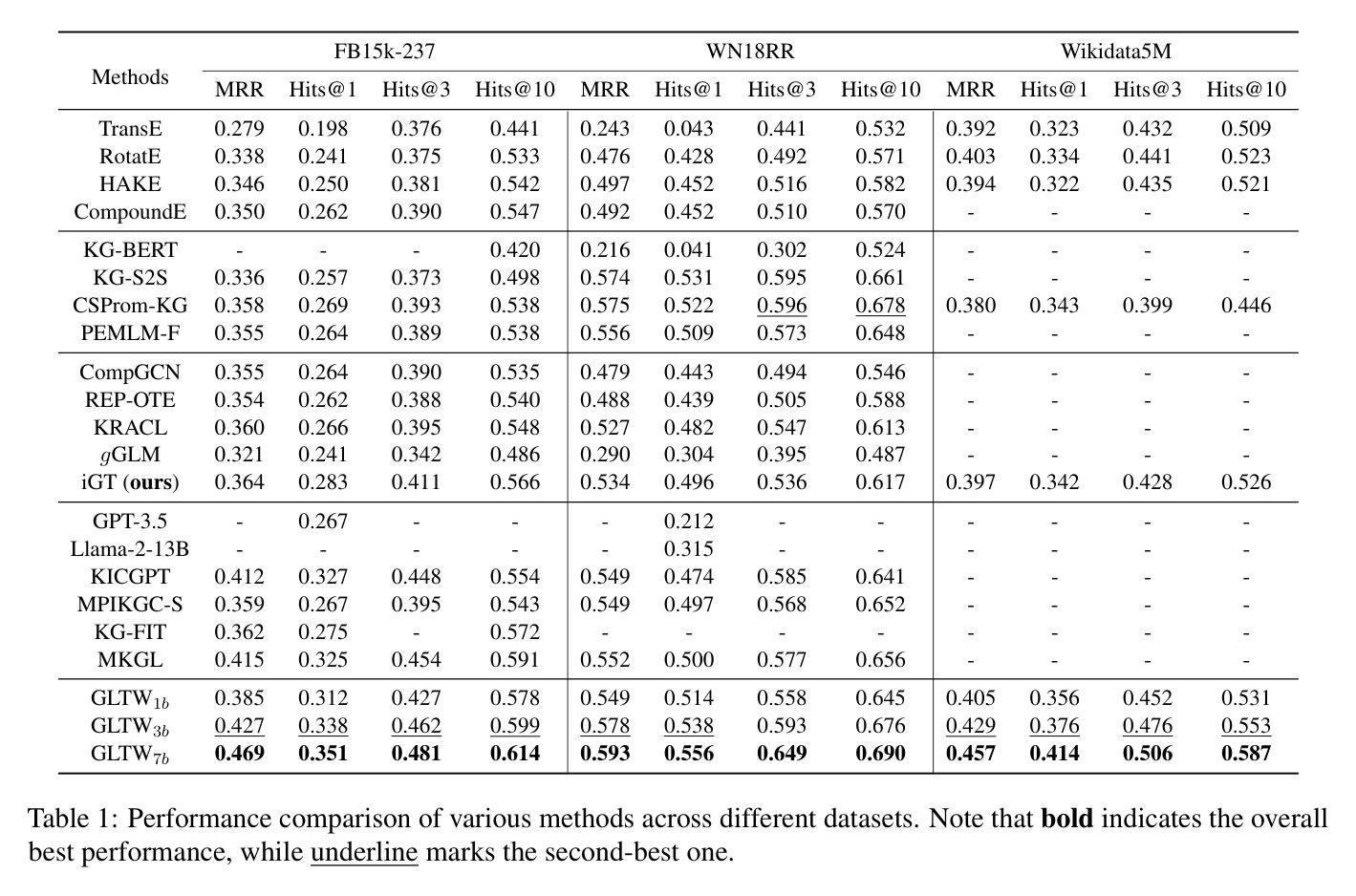
GLTW: Joint Improved Graph Transformer and LLM via Three-Word Language for Knowledge Graph Completion
Authors:Kangyang Luo, Yuzhuo Bai, Cheng Gao, Shuzheng Si, Yingli Shen, Zhu Liu, Zhitong Wang, Cunliang Kong, Wenhao Li, Yufei Huang, Ye Tian, Xuantang Xiong, Lei Han, Maosong Sun
Knowledge Graph Completion (KGC), which aims to infer missing or incomplete facts, is a crucial task for KGs. However, integrating the vital structural information of KGs into Large Language Models (LLMs) and outputting predictions deterministically remains challenging. To address this, we propose a new method called GLTW, which encodes the structural information of KGs and merges it with LLMs to enhance KGC performance. Specifically, we introduce an improved Graph Transformer (iGT) that effectively encodes subgraphs with both local and global structural information and inherits the characteristics of language model, bypassing training from scratch. Also, we develop a subgraph-based multi-classification training objective, using all entities within KG as classification objects, to boost learning efficiency.Importantly, we combine iGT with an LLM that takes KG language prompts as input.Our extensive experiments on various KG datasets show that GLTW achieves significant performance gains compared to SOTA baselines.
知识图谱补全(KGC)旨在推断缺失或不完整的事实,是知识图谱(KG)中的一项关键任务。然而,将知识图谱中的重要结构信息整合到大型语言模型(LLM)中并确定性地输出预测仍然是一个挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新的方法,称为GLTW,它将知识图谱的结构信息编码并与LLM合并,以提高KGC的性能。具体来说,我们引入了一种改进的图变换器(iGT),它能够有效编码包含局部和全局结构信息的子图,并继承语言模型的特性,无需从零开始训练。此外,我们开发了一种基于子图的多元分类训练目标,使用知识图谱中的所有实体作为分类对象,以提高学习效率。重要的是,我们将iGT与接受知识图谱语言提示作为输入的LLM相结合。我们在各种知识图谱数据集上的广泛实验表明,与最新基线相比,GLTW实现了显著的性能提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACL2025(Findings)
Summary:针对知识图谱补全(KGC)中融入知识图谱的结构信息并确定性输出预测的挑战,我们提出了名为GLTW的新方法。该方法通过改进的图变压器(iGT)有效编码子图的结构信息,并与大型语言模型(LLM)结合,提高KGC性能。同时,我们开发了一种基于子图的多分类训练目标,利用知识图谱中的所有实体作为分类对象,提高学习效率。结合语言提示的LLM与iGT相结合,在各种知识图谱数据集上的实验表明,GLTW相比最新基线实现了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways:
- 知识图谱补全(KGC)是知识图谱(KG)中的关键任务,旨在推断缺失或不完整的事实。
- 整合知识图谱的结构信息到大型语言模型(LLM)并确定性输出预测具有挑战性。
- 提出的新方法GLTW通过改进的图变压器(iGT)编码子图的结构信息,并与LLM结合,以提高KGC性能。
- iGT能有效编码子图的局部和全局结构信息,并继承语言模型的特性,无需从零开始训练。
- 开发了一种基于子图的多分类训练目标,利用知识图谱中的所有实体提高学习效率。
- GLTW结合语言提示的LLM与iGT。
点此查看论文截图

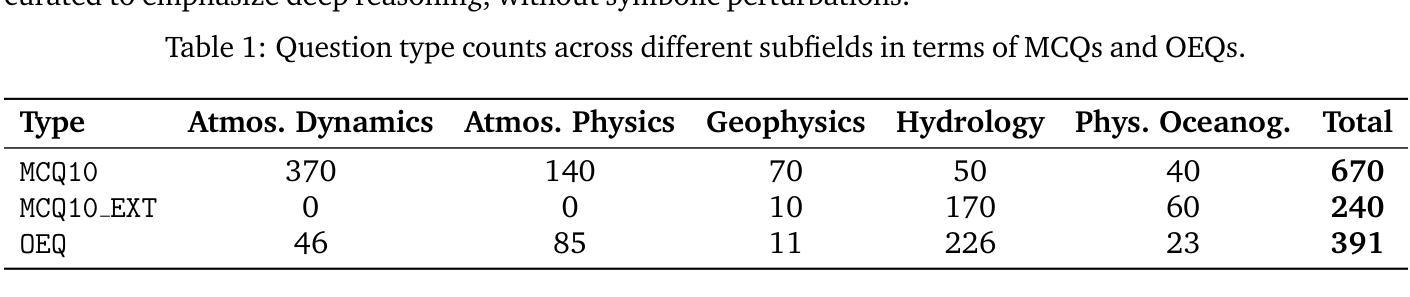
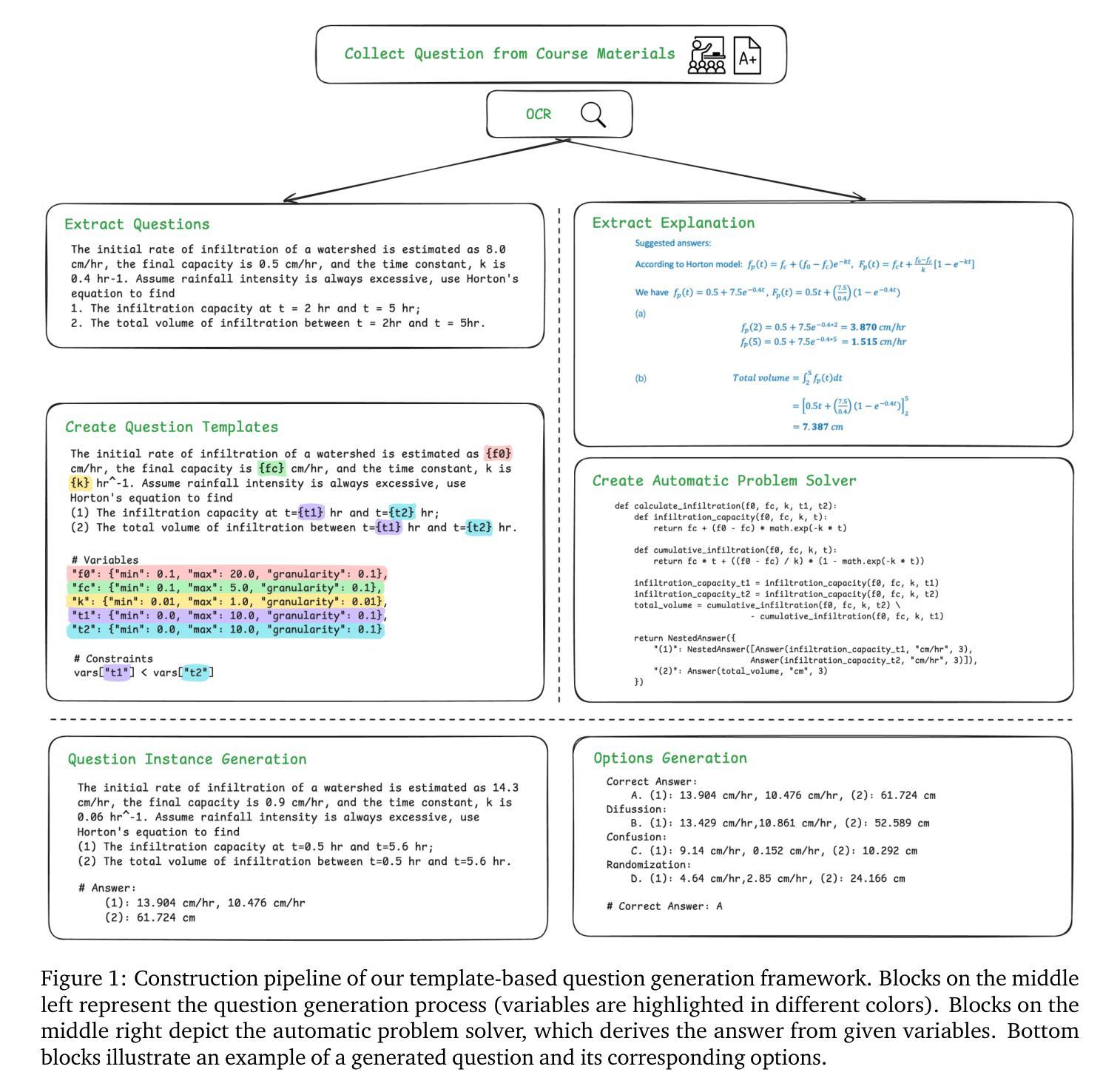
AtmosSci-Bench: Evaluating the Recent Advance of Large Language Model for Atmospheric Science
Authors:Chenyue Li, Wen Deng, Mengqian Lu, Binhang Yuan
The rapid advancements in large language models (LLMs), particularly in their reasoning capabilities, hold transformative potential for addressing complex challenges in atmospheric science. However, leveraging LLMs effectively in this domain requires a robust and comprehensive evaluation benchmark. Toward this end, we present AtmosSci-Bench, a novel benchmark designed to systematically assess LLM performance across five core categories of atmospheric science problems: hydrology, atmospheric dynamics, atmospheric physics, geophysics, and physical oceanography. AtmosSci-Bench features a dual-format design comprising both multiple-choice questions (MCQs) and open-ended questions (OEQs), enabling scalable automated evaluation alongside deeper analysis of conceptual understanding. We employ a template-based MCQ generation framework to create diverse, graduate-level problems with symbolic perturbation, while OEQs are used to probe open-ended reasoning. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation of representative LLMs, categorized into four groups: instruction-tuned models, advanced reasoning models, math-augmented models, and domain-specific climate models. Our analysis provides some interesting insights into the reasoning and problem-solving capabilities of LLMs in atmospheric science. We believe AtmosSci-Bench can serve as a critical step toward advancing LLM applications in climate service by offering a standard and rigorous evaluation framework. Our source codes are currently available at Our source codes are currently available at https://github.com/Relaxed-System-Lab/AtmosSci-Bench.
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,特别是在其推理能力方面,为解决大气科学中的复杂挑战带来了变革性潜力。然而,要在这一领域有效地利用LLM,需要进行稳健而全面的评估基准测试。为此,我们推出了AtmosSci-Bench,这是一个新颖的基准测试,旨在系统评估LLM在五个大气科学核心类别的问题上的性能:水文、大气动力学、大气物理学、地球物理学和海洋物理学。AtmosSci-Bench采用双格式设计,包括多项选择题(MCQs)和开放性问题(OEQs),既能够进行可扩展的自动化评估,又能对概念理解进行深入分析。我们采用基于模板的多项选择题生成框架,创建具有符号扰动性的多样化、研究生水平的问题,而开放性问题则用于探索开放式推理。我们对具有代表性的LLM进行了全面评估,将它们分为四个类别:指令调整模型、高级推理模型、数学增强模型和特定领域的气候模型。我们的分析对LLM在大气科学中的推理和问题解决能力提供了一些有趣的见解。我们相信,通过提供标准和严格的评估框架,AtmosSci-Bench将成为推动LLM在气候服务中应用的关键步骤。我们的源代码目前可通过https://github.com/Relaxed-System-Lab/AtmosSci-Bench获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 33 pages, 4 figures, 7 tables
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在气象科学领域具有巨大的潜力,但需要一个全面评估基准来实现其有效应用。为此,我们提出了AtmosSci-Bench基准,用于系统评估LLM在五大核心气象科学问题领域的能力。AtmosSci-Bench采用双重格式设计,包括多项选择题和开放性问题,以实现规模化自动评估和对概念理解的深入分析。对现有LLM的评估显示,其在气象科学中的推理和问题解决能力颇具见解。我们相信AtmosSci-Bench能为气候服务中的LLM应用提供一个标准和严格的评估框架。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在气象科学领域具有变革性潜力。
- AtmosSci-Bench是一个用于评估LLM在气象科学领域能力的全新基准。
- AtmosSci-Bench包含五大核心气象科学问题领域。
- 该基准采用双重格式设计,包括多项选择题和开放性问题。
- AtmosSci-Bench可实现规模化自动评估和对概念理解的深入分析。
- 对现有LLM的评估显示出其在气象科学中的推理和问题解决能力。
点此查看论文截图

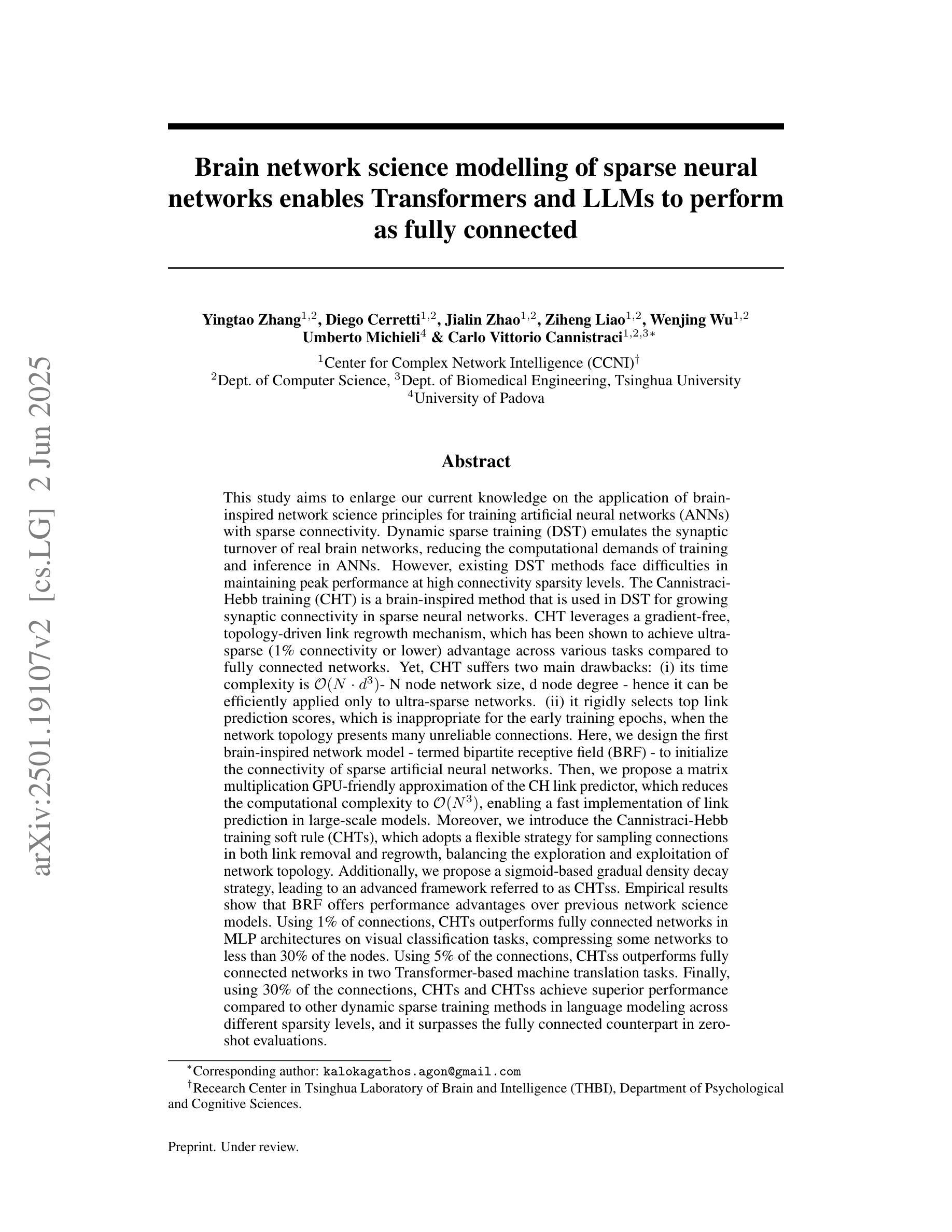
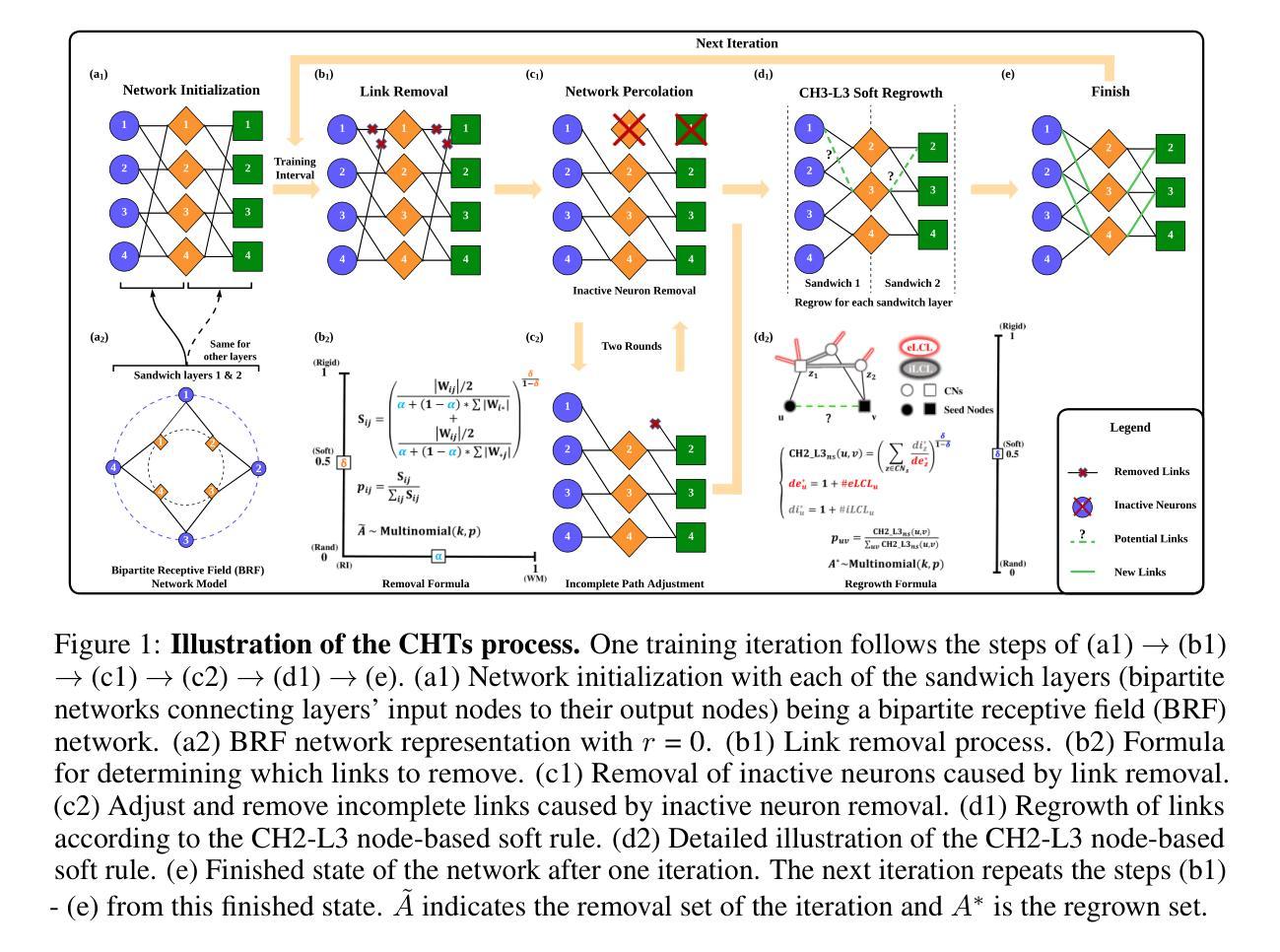
Brain network science modelling of sparse neural networks enables Transformers and LLMs to perform as fully connected
Authors:Yingtao Zhang, Diego Cerretti, Jialin Zhao, Wenjing Wu, Ziheng Liao, Umberto Michieli, Carlo Vittorio Cannistraci
Dynamic sparse training (DST) can reduce the computational demands in ANNs, but faces difficulties in keeping peak performance at high sparsity levels. The Cannistraci-Hebb training (CHT) is a brain-inspired method for growing connectivity in DST. CHT leverages a gradient-free, topology-driven link regrowth, which has shown ultra-sparse (less than 1% connectivity) advantage across various tasks compared to fully connected networks. Yet, CHT suffers two main drawbacks: (i) its time complexity is $O(Nd^3)$ - N node network size, d node degree - restricting it to ultra-sparse regimes. (ii) it selects top link prediction scores, which is inappropriate for the early training epochs, when the network presents unreliable connections. Here, we design the first brain-inspired network model - termed bipartite receptive field (BRF) - to initialize the connectivity of sparse artificial neural networks. We further introduce a GPU-friendly matrix-based approximation of CH link prediction, reducing complexity to $O(N^3)$. We introduce the Cannistraci-Hebb training soft rule (CHTs), which adopts a flexible strategy for sampling connections in both link removal and regrowth, balancing the exploration and exploitation of network topology. Additionally, we integrate CHTs with a sigmoid gradual density decay (CHTss). Empirical results show that BRF offers performance advantages over previous network science models. Using 1% of connections, CHTs outperforms fully connected networks in MLP architectures on image classification tasks, compressing some networks to less than 30% of the nodes. Using 5% of the connections, CHTss outperforms fully connected networks in two Transformer-based machine translation tasks. Finally, at 30% connectivity, both CHTs and CHTss outperform other DST methods in language modeling and even exceed fully connected baselines in zero-shot tasks.
动态稀疏训练(DST)可以减少人工神经网络(ANN)的计算需求,但在保持高稀疏级别的峰值性能时面临困难。Cannistraci-Hebb训练(CHT)是一种用于在DST中增加连接的大脑启发方法。CHT利用无梯度、拓扑驱动的连接再生长,与全连接网络相比,在各种任务中显示出超稀疏(小于1%的连接率)的优势。然而,CHT存在两个主要缺点:(i)其时间复杂度为O(Nd^3)(N为节点网络大小,d为节点度),限制其在超稀疏环境中的使用。(ii)它选择顶部连接预测分数,这在网络呈现不可靠连接的早期训练周期中是不合适的。在这里,我们设计了第一个大脑启发网络模型——称为二部接收场(BRF)——来初始化稀疏人工神经网络的连接。我们进一步引入了基于GPU友好的矩阵近似CH连接预测,将复杂度降低到O(N^3)。我们引入了Cannistraci-Hebb训练的软规则(CHTs),它采用灵活的策略进行连接删除和再生长的采样,平衡网络拓扑的探索和利用。此外,我们将CHTs与Sigmoid逐渐密度衰减(CHTss)相结合。经验结果表明,BRF在之前的网络科学模型中表现出性能优势。使用1%的连接,CHTs在多层感知器架构的图像分类任务上优于全连接网络,压缩某些网络至不到30%的节点。使用5%的连接,CHTss在基于Transformer的机器翻译任务中优于全连接网络。最后,在30%的连接率下,CHTs和CHTss在语言建模中都优于其他DST方法,甚至在零样本任务中超过全连接基线。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
动态稀疏训练(DST)可以降低人工神经网络(ANN)的计算需求,但在保持高稀疏性水平的峰值性能方面面临困难。Cannistraci-Hebb训练(CHT)是一种受大脑启发的在DST中增加连接性的方法。CHT利用梯度自由、拓扑驱动的连接再生,与全连接网络相比,在各种任务中显示出超稀疏(少于1%的连接)的优势。然而,CHT存在两个主要缺点:一是其时间复杂度为O(Nd^3),限制了其在超稀疏状态下的应用;二是在网络呈现不可靠连接时,选择顶部链接预测分数是不恰当的。为解决这些问题,我们设计了首个受大脑启发的网络模型——二分接收场(BRF),以初始化稀疏人工神经网络的连接性。我们还引入了CH链接预测的GPU友好矩阵近似方法,将复杂度降低到O(N^3)。此外,我们引入了Cannistraci-Hebb训练软规则(CHTs),采用灵活的策略进行链接的删除和再生采样,平衡网络拓扑的探索与利用。将CHTs与Sigmoid逐步衰减(CHTsS)相结合后,实证结果表明BRF优于之前的网络科学模型。在仅使用1%的连接情况下,CHTs在多层感知器架构上的图像分类任务中表现出超越全连接网络的优势,压缩部分网络至不到30%的节点。使用5%的连接时,CHTsS在基于Transformer的机器翻译任务中优于全连接网络。最后,在30%的连接性下,CHTs和CHTsS在语言建模中都优于其他DST方法,甚至在零射击任务中超过全连接基线。
Key Takeaways
- DST能有效降低ANN的计算需求,但在高稀疏性时面临性能挑战。
- CHT是一种受大脑启发的训练方式,适用于DST中的连接增长。
- CHT具有两个主要缺点:高时间复杂度和不适当的早期训练连接选择。
- BRF模型被设计来解决CHT的问题,通过初始化稀疏ANN的连通性。
- 引入CHT软规则和Sigmoid逐步衰减策略以提高性能。
- BRF和CHTs在图像分类和语言建模任务中表现出优势。
点此查看论文截图
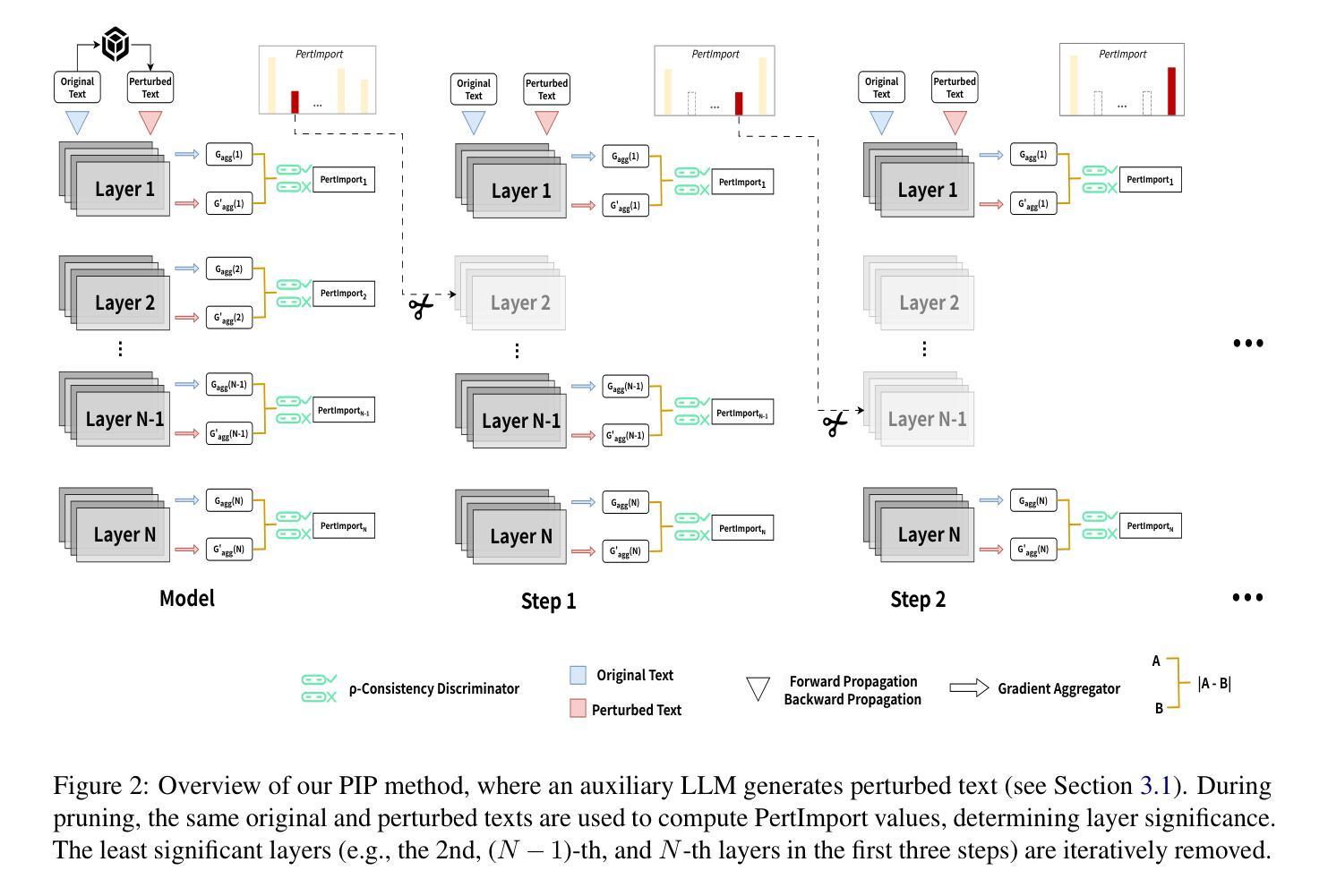
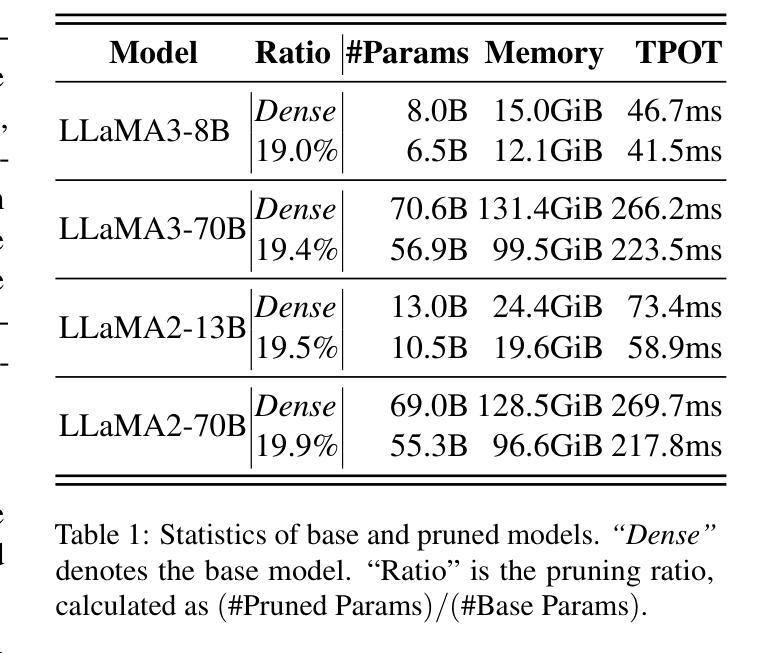
PIP: Perturbation-based Iterative Pruning for Large Language Models
Authors:Yi Cao, Wei-Jie Xu, Yucheng Shen, Weijie Shi, Chi-Min Chan, Jianfeng Qu, Jiajie Xu
The rapid increase in the parameter counts of Large Language Models (LLMs), reaching billions or even trillions, presents significant challenges for their practical deployment, particularly in resource-constrained environments. To ease this issue, we propose PIP (Perturbation-based Iterative Pruning), a novel double-view structured pruning method to optimize LLMs, which combines information from two different views: the unperturbed view and the perturbed view. With the calculation of gradient differences, PIP iteratively prunes those that struggle to distinguish between these two views. Our experiments show that PIP reduces the parameter count by approximately 20% while retaining over 85% of the original model’s accuracy across varied benchmarks. In some cases, the performance of the pruned model is within 5% of the unpruned version, demonstrating PIP’s ability to preserve key aspects of model effectiveness. Moreover, PIP consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) structured pruning methods, establishing it as a leading technique for optimizing LLMs in environments with constrained resources.
大型语言模型(LLM)的参数数量迅速增加,达到数十亿甚至更多,为其在实际环境中的部署带来了重大挑战,尤其是在资源受限的环境中。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了PIP(基于扰动的迭代剪枝)方法,这是一种用于优化LLM的新型双视图结构化剪枝方法。它结合了两种不同的视图:未扰动视图和扰动视图的信息。通过计算梯度差异,PIP通过迭代剪枝那些在区分这两种视图时遇到困难的部分。我们的实验表明,PIP能够在减少约20%的参数的同时,在各种基准测试中保留原始模型85%以上的准确性。在某些情况下,修剪模型的性能与未修剪的版本相差不到5%,这表明PIP能够保留模型的关键有效性方面。此外,PIP始终优于现有的最新(SOTA)结构化剪枝方法,使其成为在资源受限环境中优化LLM的领先技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的参数数量迅速增加,达到数十亿甚至更多,为其在实际部署中带来挑战,特别是在资源受限的环境中。为此,我们提出PIP(基于扰动的迭代剪枝)方法,这是一种新型的双视角结构剪枝方法,旨在优化LLM。它结合了两个不同视角的信息:未扰动视角和扰动视角。通过计算梯度差异,PIP迭代地剪去那些在两种视角间难以区分的部分。实验表明,PIP能够在减少约20%参数的同时,在多种基准测试中保留超过85%的原始模型精度。在某些情况下,剪枝模型的性能与未剪枝版本相差不到5%,证明PIP在保留模型关键有效性方面表现出色。此外,PIP持续超越现有的最先进的结构剪枝方法,成为资源受限环境中优化LLM的领先技术。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)参数数量激增带来实际部署挑战,特别是在资源受限环境中。
- PIP方法是一种双视角结构剪枝方法,旨在优化LLM。
- PIP结合未扰动视角和扰动视角的信息,通过计算梯度差异进行迭代剪枝。
- 实验显示,PIP能在减少约20%参数的同时保留超过85%的原始模型精度。
- PIP在某些情况下剪枝模型的性能与未剪枝版本相近,差距在5%以内。
- PIP在保留模型关键有效性方面表现出色。
点此查看论文截图

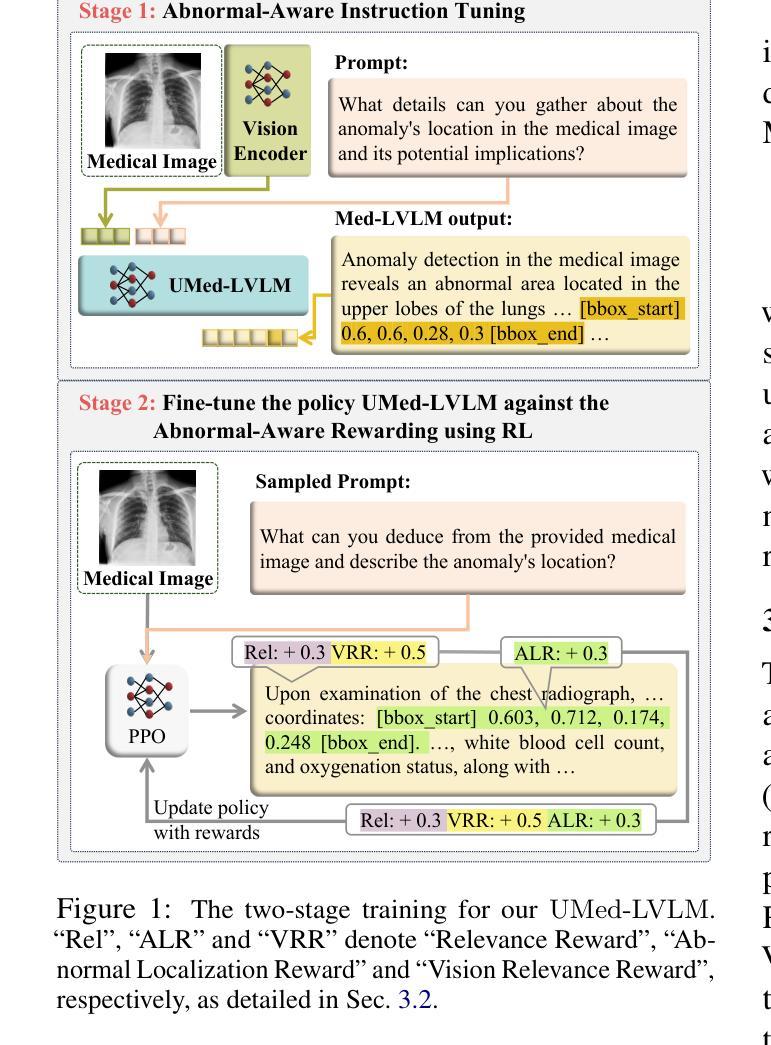
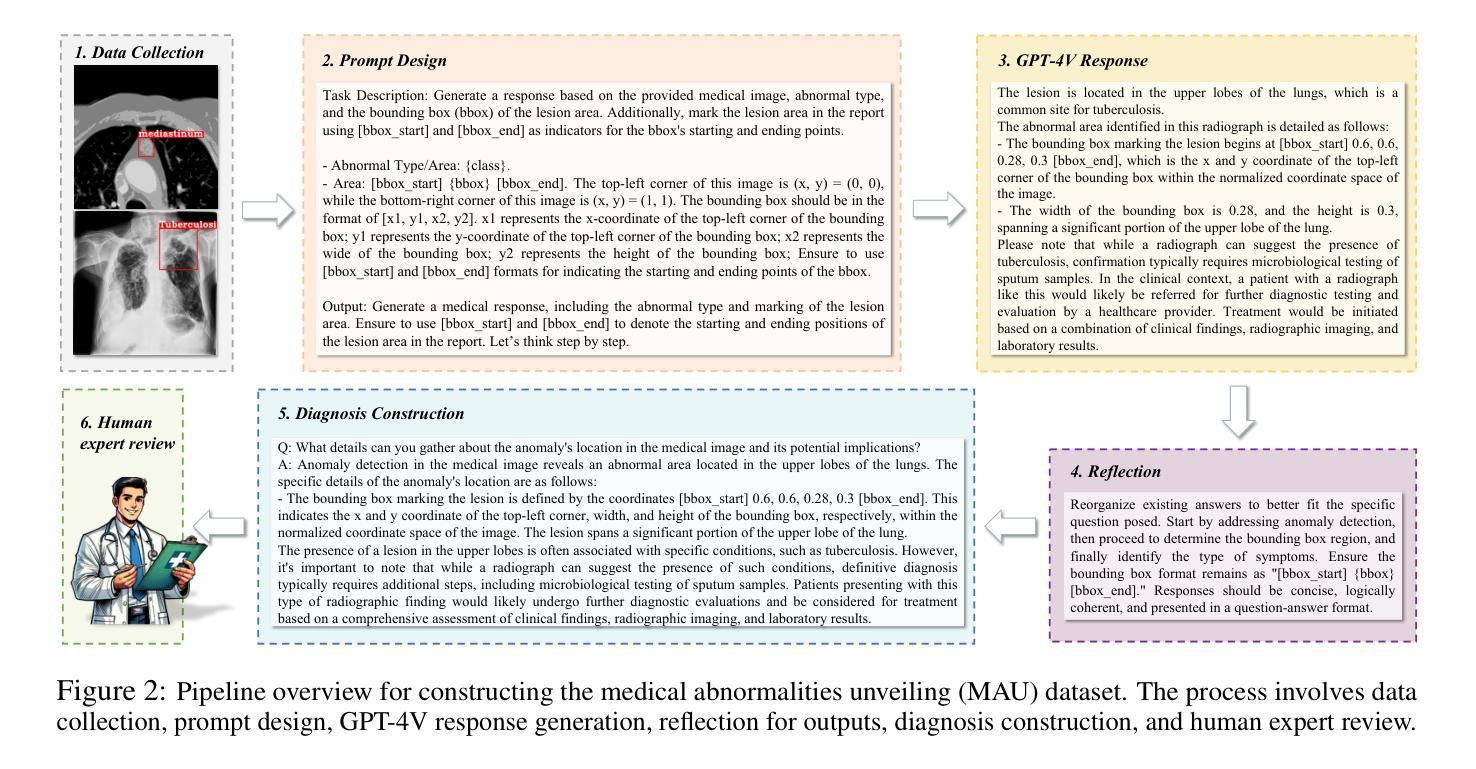
Improving Medical Large Vision-Language Models with Abnormal-Aware Feedback
Authors:Yucheng Zhou, Lingran Song, Jianbing Shen
Existing Medical Large Vision-Language Models (Med-LVLMs), encapsulating extensive medical knowledge, demonstrate excellent capabilities in understanding medical images. However, there remain challenges in visual localization in medical images, which is crucial for abnormality detection and interpretation. To address these issues, we propose a novel UMed-LVLM designed to unveil medical abnormalities. Specifically, we collect a Medical Abnormalities Unveiling (MAU) dataset and propose a two-stage training method for UMed-LVLM training. To collect MAU dataset, we propose a prompt method utilizing the GPT-4V to generate diagnoses based on identified abnormal areas in medical images. Moreover, the two-stage training method includes Abnormal-Aware Instruction Tuning and Abnormal-Aware Rewarding, comprising Relevance Reward, Abnormal Localization Reward and Vision Relevance Reward. Experimental results demonstrate that our UMed-LVLM significantly outperforms existing Med-LVLMs in identifying and understanding medical abnormalities, achieving a 58% improvement over the baseline. In addition, this work shows that enhancing the abnormality detection capabilities of Med-LVLMs significantly improves their understanding of medical images and generalization capability.
现有的医疗大型视觉语言模型(Med-LVLMs)包含了丰富的医学知识,在理解医学图像方面表现出卓越的能力。然而,在医学图像的视觉定位方面仍存在挑战,这对于异常检测和解释至关重要。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型的UMed-LVLM模型,旨在揭示医学异常。具体来说,我们收集了医学异常揭示(MAU)数据集,并针对UMed-LVLM模型训练提出了两阶段训练方法。为了收集MAU数据集,我们提出了一种利用GPT-4V提示方法生成基于医学图像中识别出的异常区域的诊断结果。此外,两阶段训练方法包括异常感知指令调整和异常感知奖励机制,包括相关性奖励、异常定位奖励和视觉相关性奖励。实验结果表明,我们的UMed-LVLM在识别和了解医学异常方面显著优于现有的Med-LVLMs,较基线模型提高了58%。此外,这项工作表明,增强Med-LVLMs的异常检测能力可以显著提高其对医学图像的理解和泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages
Summary
本文介绍了现有的医疗大型视觉语言模型(Med-LVLMs)在理解医学图像方面表现出卓越的能力,但在医学图像视觉定位方面仍存在挑战。为应对这些挑战,提出了一种新型UMed-LVLM模型,旨在揭示医学异常。该模型采用两阶段训练法,收集医疗异常揭示(MAU)数据集并运用GPT-4V进行提示生成诊断结果。实验证明,UMed-LVLM在识别和了解医学异常方面显著优于现有Med-LVLMs,相较于基线有58%的提升。此外,该研究指出增强Med-LVLMs的异常检测能力可显著提高其对医学图像的理解和泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- Med-LVLMs在理解和解释医学图像方面表现出卓越的能力,但在医学图像的视觉定位方面仍面临挑战。
- 提出一种新型UMed-LVLM模型,旨在解决视觉定位问题,更好地揭示医学异常。
- 采用两阶段训练法来训练UMed-LVLM模型,包括异常感知指令调整和异常感知奖励机制。
- 收集医疗异常揭示(MAU)数据集,利用GPT-4V提示方法生成诊断结果。
- UMed-LVLM模型在识别和了解医学异常方面显著优于现有Med-LVLMs,实现了较高的性能提升。
- 增强Med-LVLMs的异常检测能力有助于提高其医学图像的理解和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

RecLM: Recommendation Instruction Tuning
Authors:Yangqin Jiang, Yuhao Yang, Lianghao Xia, Da Luo, Kangyi Lin, Chao Huang
Modern recommender systems aim to deeply understand users’ complex preferences through their past interactions. While deep collaborative filtering approaches using Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) excel at capturing user-item relationships, their effectiveness is limited when handling sparse data or zero-shot scenarios, primarily due to constraints in ID-based embedding functions. To address these challenges, we propose a model-agnostic recommendation instruction-tuning paradigm that seamlessly integrates large language models with collaborative filtering. Our proposed $\underline{Rec}$ommendation $\underline{L}$anguage $\underline{M}$odel (RecLM) enhances the capture of user preference diversity through a carefully designed reinforcement learning reward function that facilitates self-augmentation of language models. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate significant advantages of our approach across various settings, and its plug-and-play compatibility with state-of-the-art recommender systems results in notable performance enhancements. The implementation of our RecLM framework is publicly available at: https://github.com/HKUDS/RecLM.
现代推荐系统旨在通过用户过去的交互来深入了解用户的复杂偏好。虽然使用图神经网络(GNNs)的深度协同过滤方法在捕捉用户-项目关系方面表现出色,但在处理稀疏数据或零射击场景时,其有效性受到限制,这主要是因为基于ID的嵌入函数存在约束。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种模型无关的推荐指令微调范式,该范式能够无缝地将大型语言模型与协同过滤集成在一起。我们提出的推荐语言模型(RecLM)通过精心设计的强化学习奖励函数增强了对用户偏好多样性的捕捉,该奖励函数有助于语言模型的自我增强。全面的评估表明,我们的方法在各种设置中具有显著的优势,并且其与最新推荐系统的即插即用兼容性导致了显著的性能提升。我们的RecLM框架的实现可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/HKUDS/RecLM。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is accepted by ACL 2025 main conference
Summary
融合图神经网络和推荐语言模型的推荐系统改进方案。针对现有推荐系统在处理稀疏数据或零样本场景时的局限性,提出一种模型无关的推荐指令调整范式,将大型语言模型与协同过滤无缝集成。通过精心设计强化学习奖励函数,增强对用户偏好多样性的捕捉,促进语言模型的自我增强。在多种设置下的综合评估显示,该方法具有显著优势,且与最新推荐系统的即插即用兼容性可实现显著的性能提升。RecLM框架的实现在GitHub上公开可用。
Key Takeaways
- 推荐系统通过用户的过去交互来深入理解其复杂偏好。
- 图神经网络在捕捉用户-物品关系方面表现出色。
- 现有方法在处理稀疏数据或零样本场景时存在局限性。
- 提出了一种模型无关的推荐指令调整范式,结合大型语言模型与协同过滤。
- 通过强化学习奖励函数增强对用户偏好多样性的捕捉。
- 综合评估显示所提方法在各种设置下具有显著优势。
点此查看论文截图

Enhancing LLM-based Hatred and Toxicity Detection with Meta-Toxic Knowledge Graph
Authors:Yibo Zhao, Jiapeng Zhu, Can Xu, Yao Liu, Xiang Li
The rapid growth of social media platforms has raised significant concerns regarding online content toxicity. When Large Language Models (LLMs) are used for toxicity detection, two key challenges emerge: 1) the absence of domain-specific toxic knowledge leads to false negatives; 2) the excessive sensitivity of LLMs to toxic speech results in false positives, limiting freedom of speech. To address these issues, we propose a novel method called MetaTox, leveraging graph search on a meta-toxic knowledge graph to enhance hatred and toxicity detection. First, we construct a comprehensive meta-toxic knowledge graph by utilizing LLMs to extract toxic information through a three-step pipeline, with toxic benchmark datasets serving as corpora. Second, we query the graph via retrieval and ranking processes to supplement accurate, relevant toxic knowledge. Extensive experiments and in-depth case studies across multiple datasets demonstrate that our MetaTox significantly decreases the false positive rate while boosting overall toxicity detection performance. Our code is available at https://github.com/YiboZhao624/MetaTox.
社交媒体平台的快速发展引发了人们对网络内容毒性的重大关注。当大型语言模型(LLM)用于毒性检测时,会出现两个关键挑战:1)缺乏特定领域的毒性知识会导致假阴性结果;2)LLM对有毒言论过于敏感,导致假阳性结果,限制言论自由。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新方法,称为MetaTox,利用元毒性知识图谱上的图搜索来增强仇恨和毒性检测。首先,我们通过一个三步骤的管道,利用LLM提取毒性信息,以毒性基准数据集作为语料库,构建了一个全面的元毒性知识图谱。其次,我们通过检索和排名过程查询图谱,以补充准确、相关的毒性知识。在多个数据集上的广泛实验和深入个案研究结果表明,我们的MetaTox方法显著降低了误报率,同时提高了总体毒性检测性能。我们的代码可在https://github.com/YiboZhao624/MetaTox获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages of content
Summary
社交媒体平台的快速发展引发了人们对网络内容毒性的关注。在使用大型语言模型(LLM)进行毒性检测时,存在两个主要挑战:缺乏特定领域的毒性知识和过度敏感导致误报。为解决这些问题,我们提出了一种名为MetaTox的新方法,利用元毒性知识图谱上的图搜索来增强仇恨和毒性检测。通过构建全面的元毒性知识图谱,通过检索和排名过程查询图谱,以补充准确、相关的毒性知识。实验和案例研究表明,MetaTox能显著降低误报率,提高整体毒性检测性能。
Key Takeaways
- 社交媒体平台的快速发展引发了对网络内容毒性的关注。
- 使用大型语言模型(LLM)进行毒性检测存在两个主要挑战:缺乏特定领域的毒性知识和过度敏感导致误报。
- MetaTox方法通过构建元毒性知识图谱来解决这些问题。
- MetaTox利用大型语言模型提取毒性信息,通过三步管道构建元毒性知识图谱,并利用毒性基准数据集作为语料库。
- MetaTox通过检索和排名过程查询元毒性知识图谱,以补充准确、相关的毒性知识。
- 实验和案例研究表明,MetaTox能显著降低误报率。
点此查看论文截图

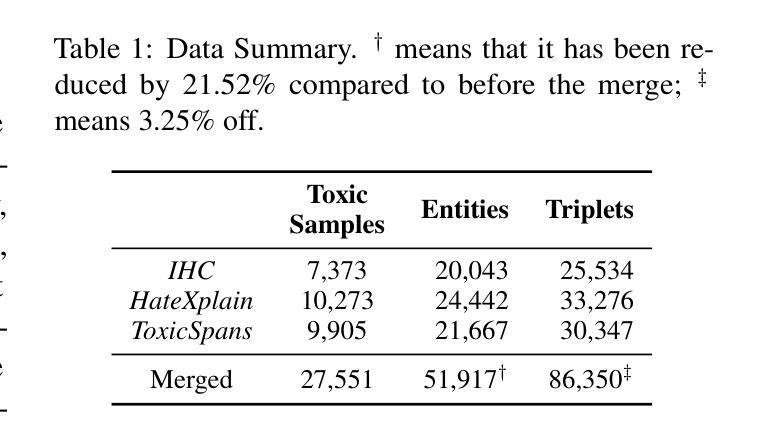
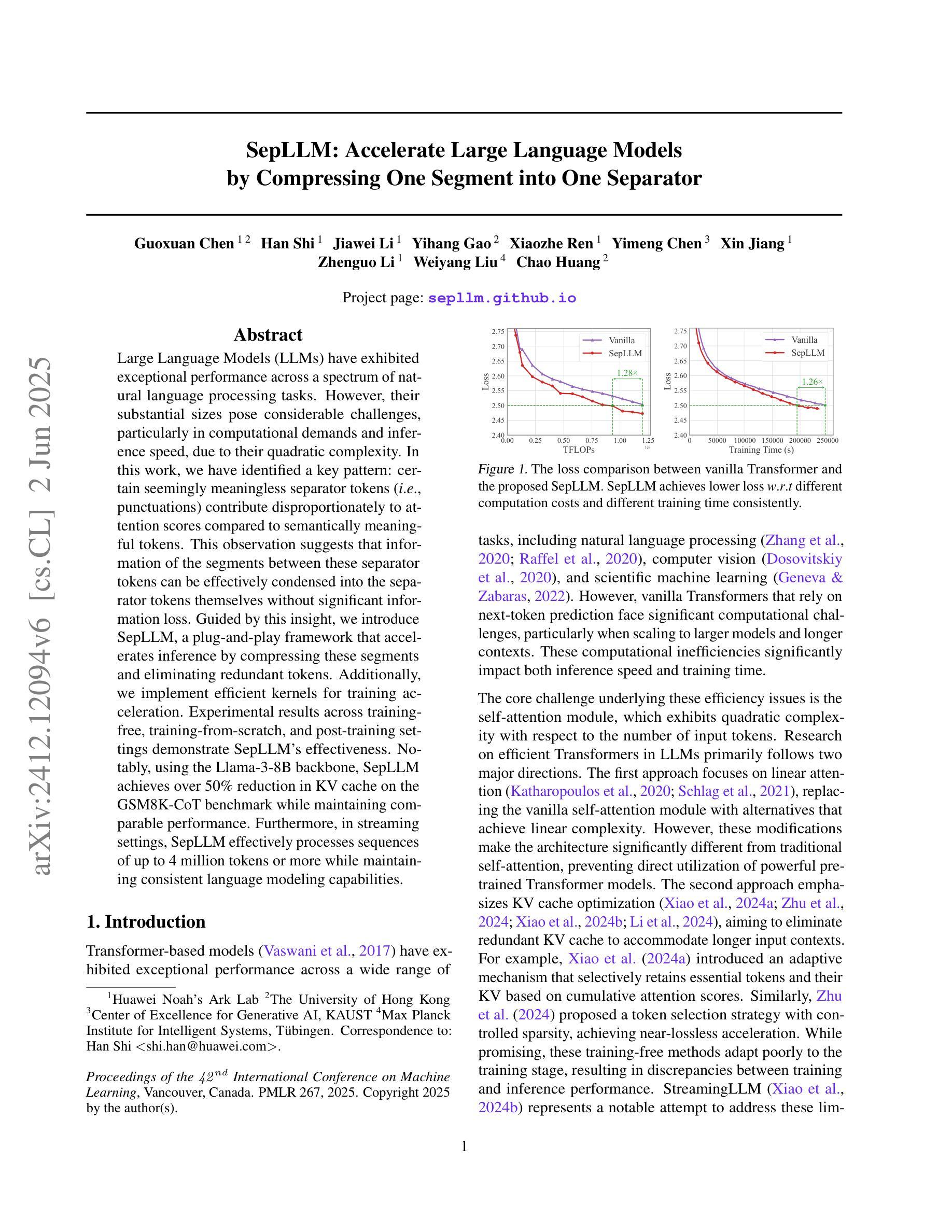
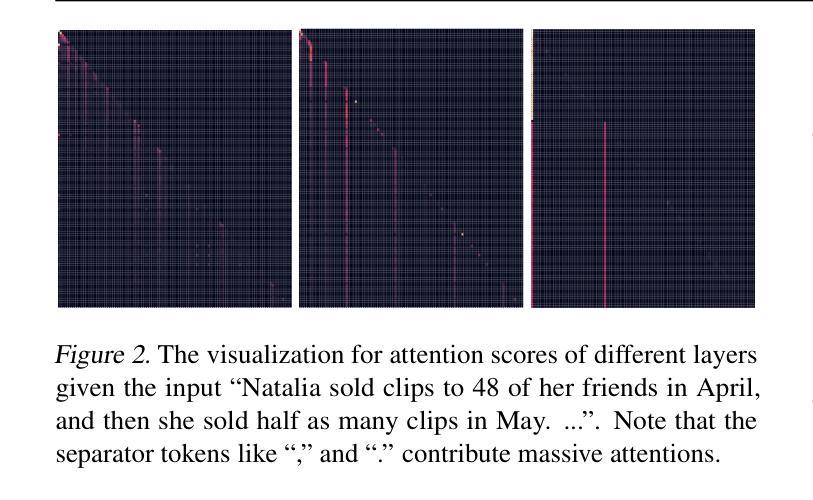
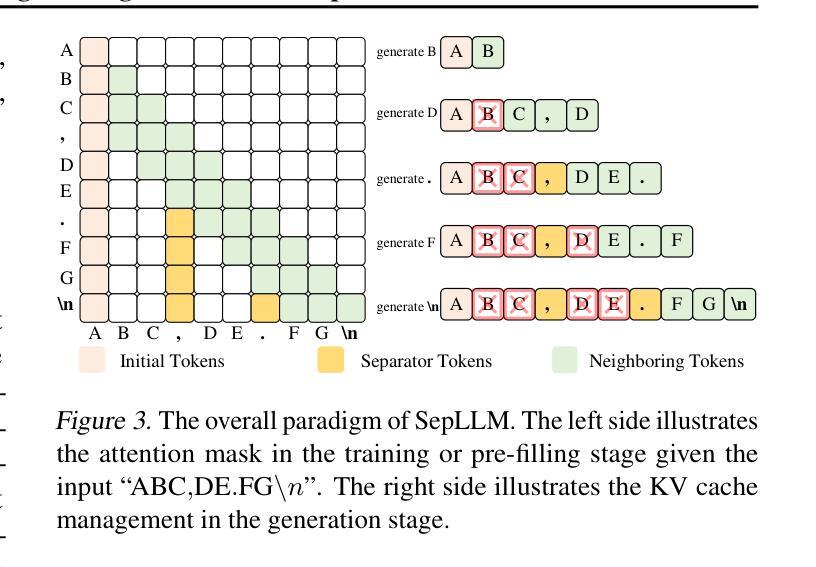
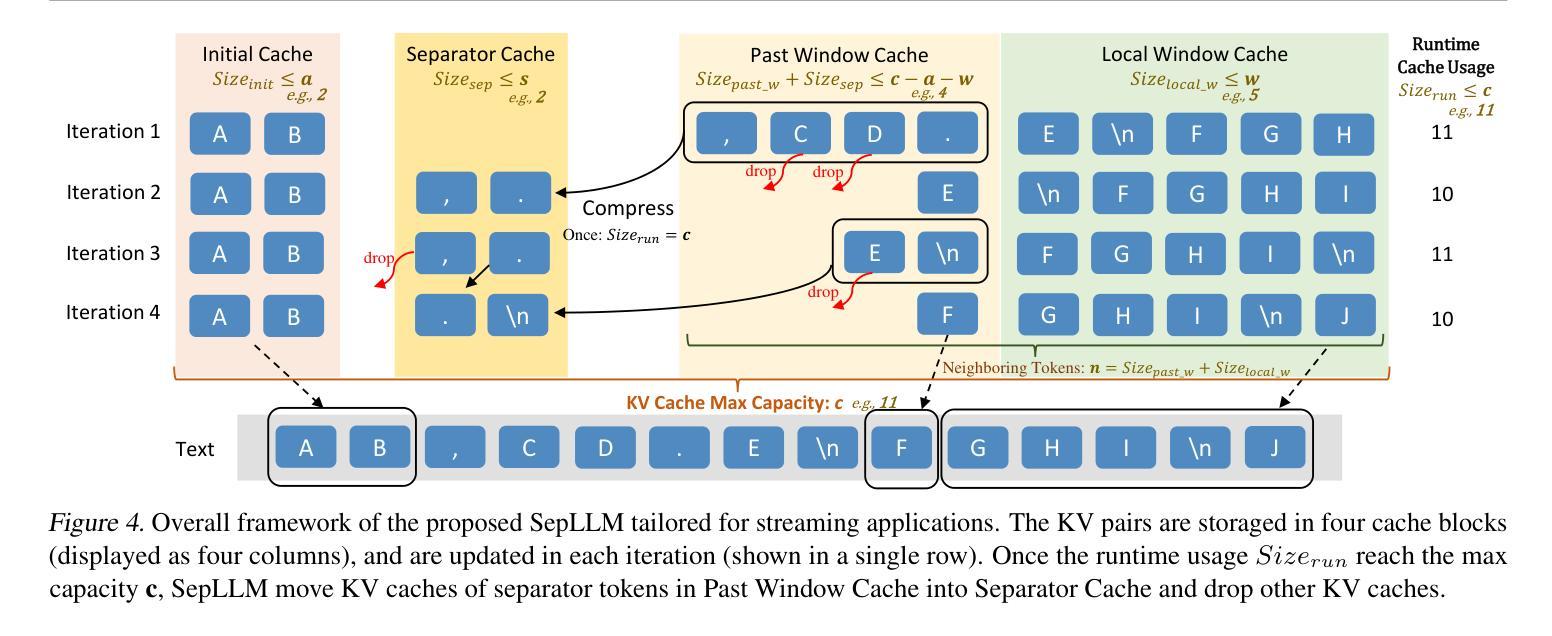
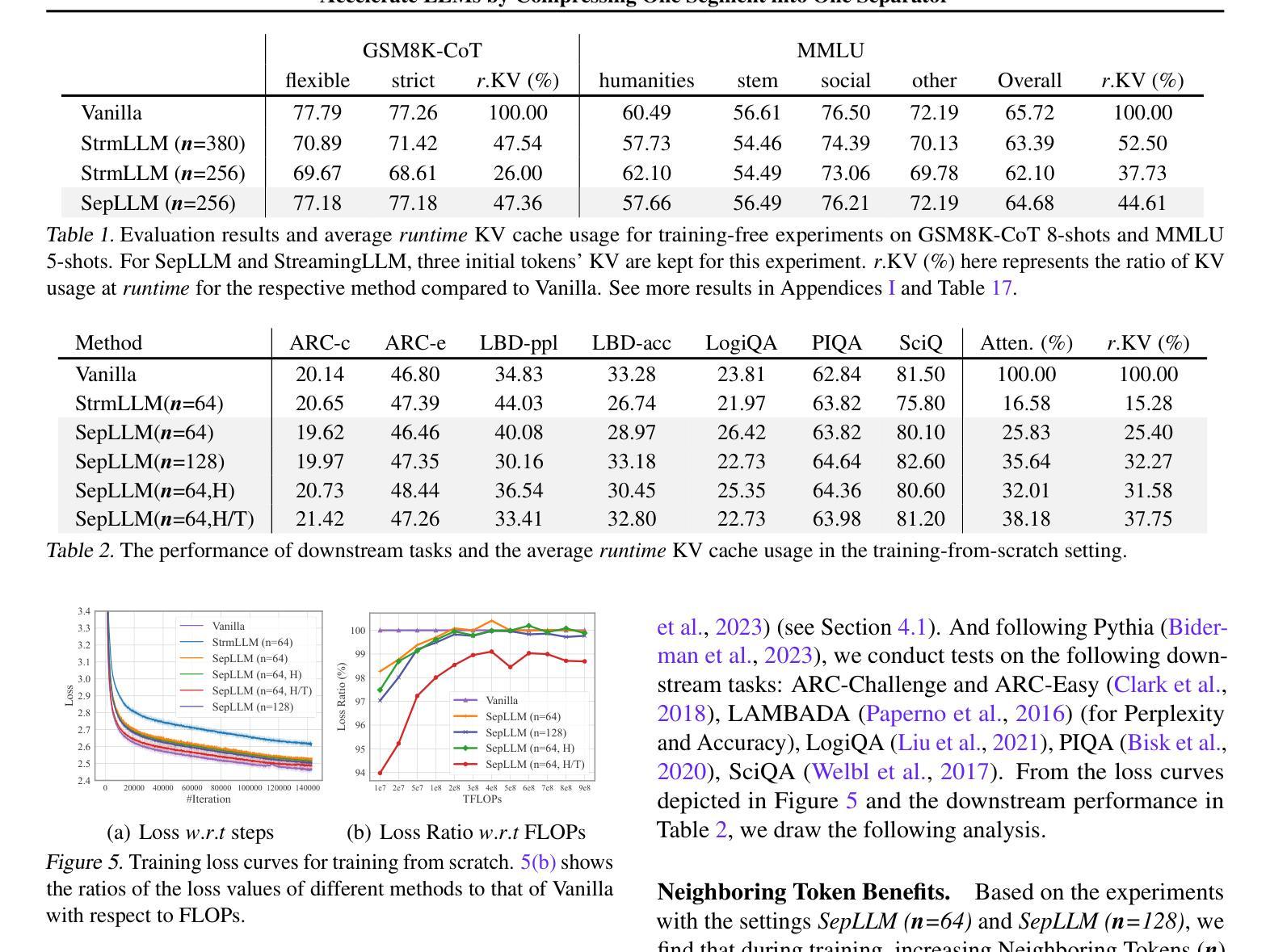
SepLLM: Accelerate Large Language Models by Compressing One Segment into One Separator
Authors:Guoxuan Chen, Han Shi, Jiawei Li, Yihang Gao, Xiaozhe Ren, Yimeng Chen, Xin Jiang, Zhenguo Li, Weiyang Liu, Chao Huang
Large Language Models (LLMs) have exhibited exceptional performance across a spectrum of natural language processing tasks. However, their substantial sizes pose considerable challenges, particularly in computational demands and inference speed, due to their quadratic complexity. In this work, we have identified a key pattern: certain seemingly meaningless separator tokens (i.e., punctuations) contribute disproportionately to attention scores compared to semantically meaningful tokens. This observation suggests that information of the segments between these separator tokens can be effectively condensed into the separator tokens themselves without significant information loss. Guided by this insight, we introduce SepLLM, a plug-and-play framework that accelerates inference by compressing these segments and eliminating redundant tokens. Additionally, we implement efficient kernels for training acceleration. Experimental results across training-free, training-from-scratch, and post-training settings demonstrate SepLLM’s effectiveness. Notably, using the Llama-3-8B backbone, SepLLM achieves over 50% reduction in KV cache on the GSM8K-CoT benchmark while maintaining comparable performance. Furthermore, in streaming settings, SepLLM effectively processes sequences of up to 4 million tokens or more while maintaining consistent language modeling capabilities.
大型语言模型(LLM)在多种自然语言处理任务中表现出了卓越的性能。然而,它们庞大的规模带来了相当大的挑战,特别是在计算需求和推理速度方面,因为它们具有二次方的复杂性。在这项工作中,我们发现了一个关键模式:某些看似无意义的分隔符(如标点符号)与语义上有意义的标记相比,对注意力分数的影响极为显著。这一观察结果表明,这些分隔符之间的片段信息可以有效地浓缩到分隔符本身中,而不会损失重要信息。基于这一见解,我们引入了SepLLM,这是一个即插即用的框架,通过压缩这些片段并消除冗余标记来加速推理。此外,我们还为训练加速实现了高效的内核。在无需训练、从头开始训练和后续训练设置中的实验结果表明SepLLM的有效性。值得注意的是,使用Llama-3-8B骨干网,SepLLM在GSM8K-CoT基准测试上实现了KV缓存超过50%的减少,同时保持性能相当。此外,在流式环境中,SepLLM能够有效地处理长达4百万个标记以上的序列,同时保持一致的语言建模能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICML 2025
Summary
本文介绍了Large Language Models(LLMs)在处理自然语言任务时的出色表现,但其庞大的规模带来了计算需求和推理速度的挑战。研究团队发现分隔符(如标点符号)对于注意力分数的影响远超其他语义上有意义的标记,据此提出SepLLM框架,通过压缩分隔符间的片段和消除冗余标记来加速推理。实验结果显示SepLLM在不同设置下均有效,使用Llama-3-8B模型在GSM8K-CoT基准测试中实现了超过50%的KV缓存减少,同时保持性能。在流式处理场景中,SepLLM能处理超过4百万个标记的序列,保持稳定的语言建模能力。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在自然语言处理任务中表现出色,但其庞大的规模导致计算需求和推理速度的挑战。
- 分隔符(如标点符号)对注意力分数的影响显著,超过语义上有意义的标记。
- SepLLM框架通过压缩分隔符间的片段和消除冗余标记来加速LLM的推理。
- SepLLM在多种设置下的实验结果显示其有效性。
- 使用Llama-3-8B模型,SepLLM在GSM8K-CoT基准测试中实现超过50%的KV缓存减少,同时保持性能。
- SepLLM能处理大规模的序列,在流式处理场景中表现出稳定的语言建模能力。
点此查看论文截图
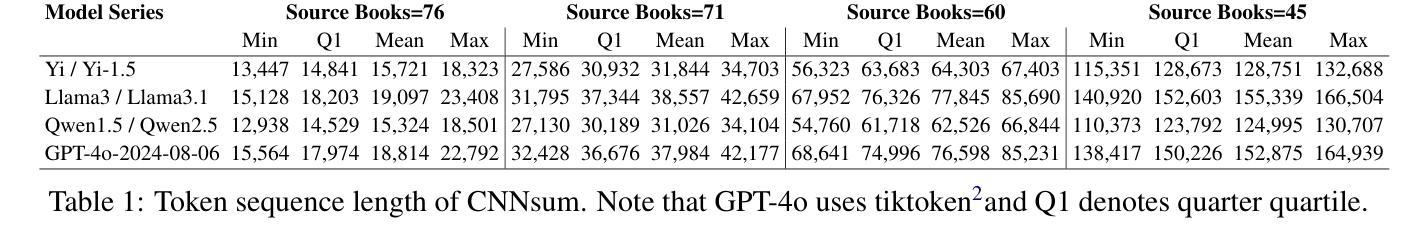
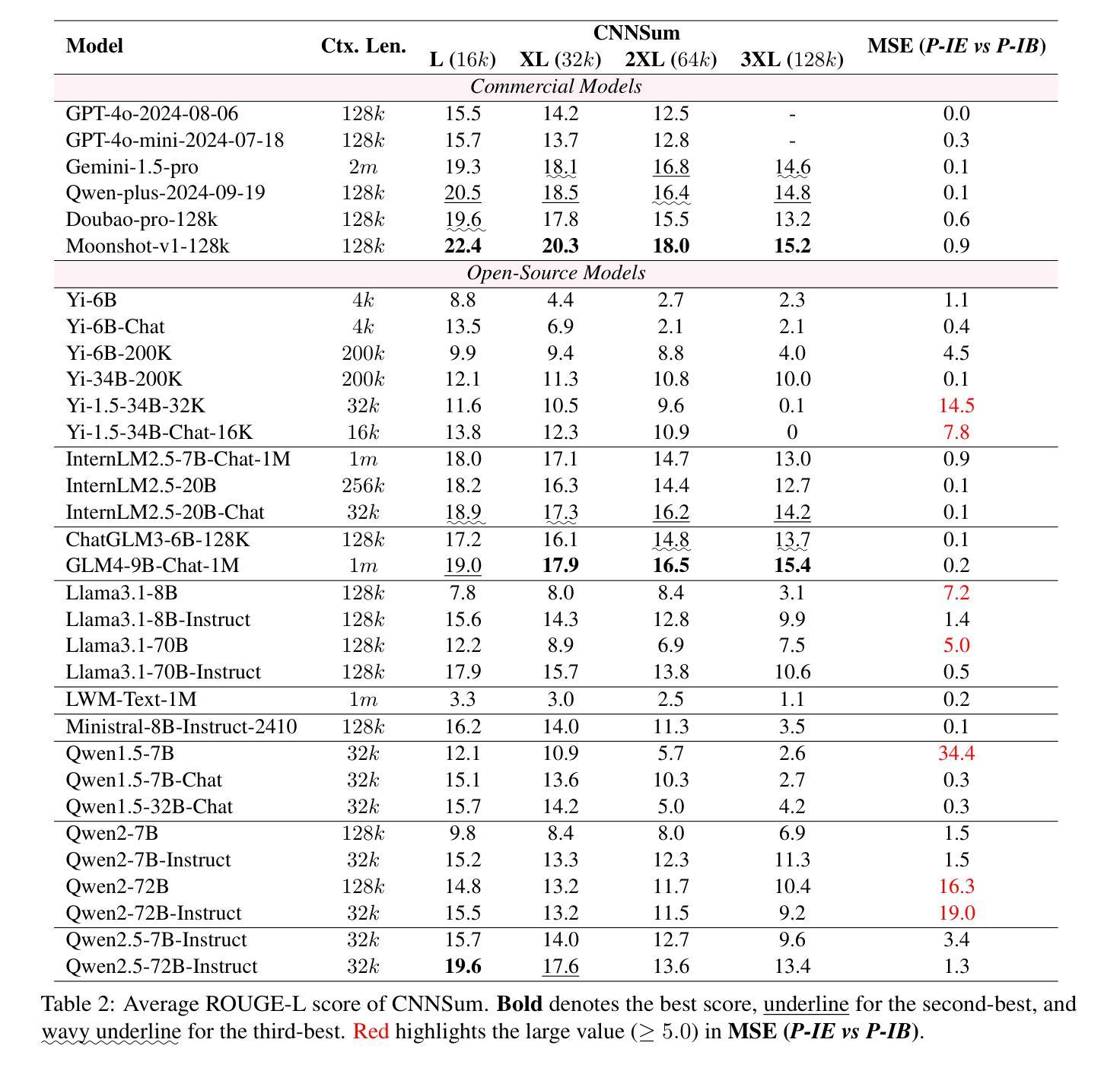
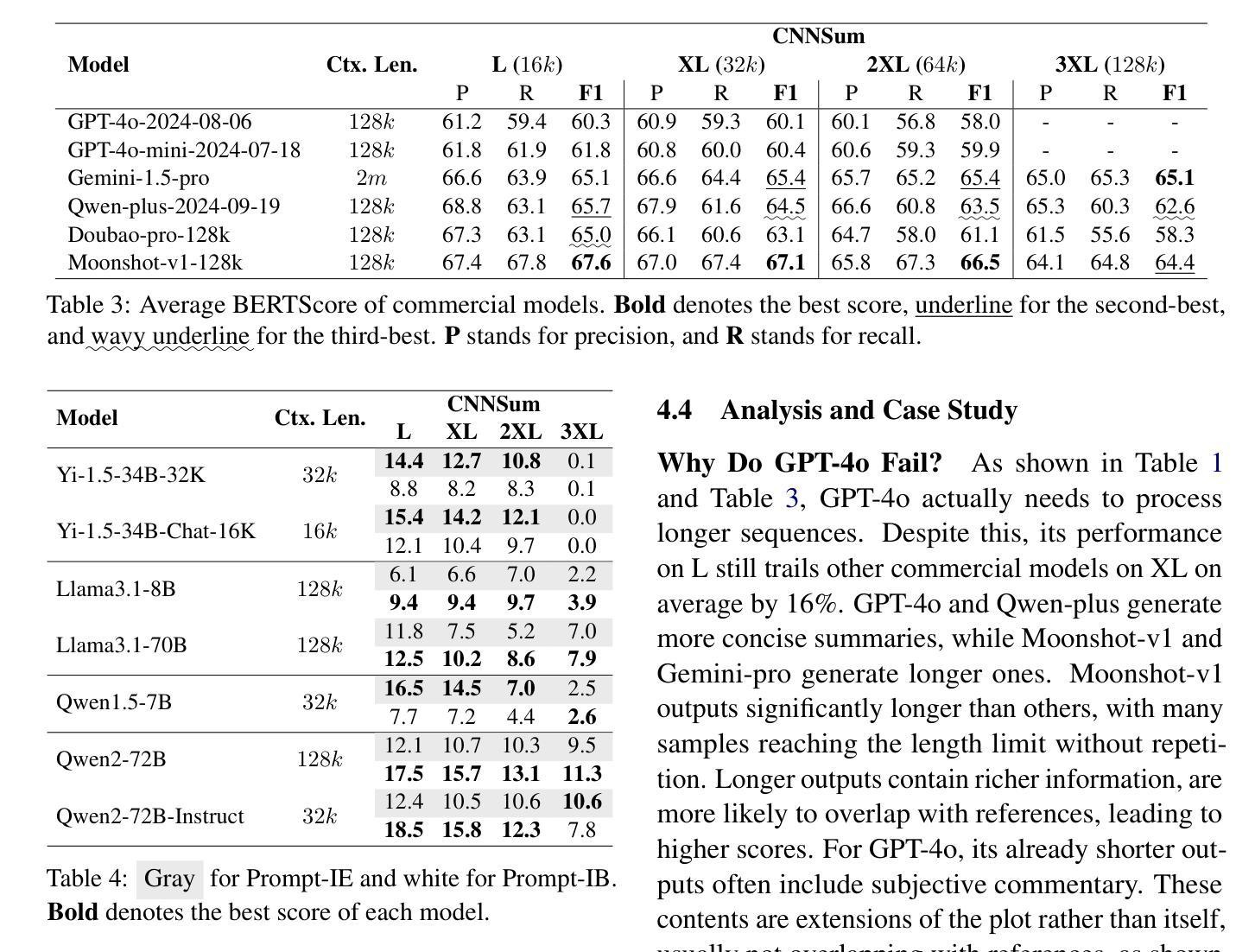
CNNSum: Exploring Long-Context Summarization with Large Language Models in Chinese Novels
Authors:Lingxiao Wei, He Yan, Xiangju Lu, Junmin Zhu, Jun Wang, Wei Zhang
Large language models (LLMs) have been well-researched in various long-context tasks. However, the scarcity of long-context summarization datasets hinders progress in this area. To address this, we introduce CNNSum, a multi-scale long-context summarization benchmark based on Chinese novels, featuring human-driven annotations across four subsets totaling 695 samples, with lengths ranging from 16k to 128k. We benchmark numerous LLMs and conduct detailed human assessments to summarize abnormal output types. Furthermore, we extensively explore how to improve long-context summarization. In our study: (1) Advanced LLMs may generate much subjective commentary, leading to vague summaries. (2) Currently, long-context summarization mainly relies on memory ability. The advantages of Large LLMs are hard to utilize, thus small LLMs are more cost-effective. (3) Different prompt types paired with various version models may cause large performance gaps. In further fine-tuning, these can be mitigated, and the Base version models perform better. (4) LLMs with RoPE-base scaled exhibit strong extrapolation potential; using short-context data can significantly improve long-context summarization performance. However, further applying other interpolation methods requires careful selection. (5) CNNSum provides more reliable evaluation results than other benchmarks. We release CNNSum to advance future research.(https://github.com/CxsGhost/CNNSum)
长语言模型(LLM)在各种长文本任务中已得到深入研究。然而,长文本摘要数据集缺乏阻碍了该领域的进展。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了基于中文小说的多尺度长文本摘要基准测试CNNSum。它拥有四个子集共695个样本的人类驱动标注,长度从16k到128k不等。我们对众多LLM进行基准测试,并进行详细的人类评估,以总结异常输出类型。此外,我们还深入探讨了如何改进长文本摘要。在我们的研究中发现:(1)高级LLM可能会产生大量主观评论,导致摘要模糊不清。(2)目前,长文本摘要主要依赖于记忆能力。大型LLM的优势难以发挥,因此小型LLM更具成本效益。(3)不同的提示类型与各种版本模型的配对可能会导致较大的性能差距。在进一步微调中,这些差距可以得到缓解,基础版本模型表现更好。(4)基于RoPE的大型LLM表现出强大的外推潜力;使用短文本数据可以显著提高长文本摘要的性能。但是,进一步应用其他内插方法需要谨慎选择。(5)相较于其他基准测试,CNNSum提供了更可靠的评价结果。我们发布CNNSum以推动未来的研究(https://github.com/CxsGhost/CNNSum)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACL 2025 (Findings)
摘要
LLM在处理长文本上下文任务方面的研究进展良好,但由于缺乏长文本摘要数据集,该领域的进展受到阻碍。为解决这一问题,研究团队推出了基于中文小说的多尺度长文本上下文摘要基准CNNSum,包含四个子集共695个样本,长度从1万到几十万字不等。研究团队对多个LLM进行了基准测试,并对异常输出类型进行了详细的人类评估总结。同时,该研究深入探讨了如何改进长文本上下文摘要技术。研究发现:(1)高级LLM可能产生大量主观评论,导致摘要模糊;(2)目前长文本上下文摘要主要依赖记忆能力,高级LLM的优势难以发挥;(3)不同的提示类型与各种版本模型的结合会导致较大性能差异;(4)带有RoPE-base的大模型展现出强大的外推潜力,使用短文本数据可以显著提高长文本上下文摘要性能;(5)CNNSum相较于其他基准测试提供了更可靠的结果评估。(链接在此)。整个项目成果促进了LLM研究的发展。期待借助这个项目未来的持续优化改进能为AI大语言模型带来更多的实用性与功能性价值。为这一研究领域开启新篇章。(具体可参考以下内容摘要简化版:“中国科研团队针对大型语言模型在应对长文本上下文的缺点而开发了CNNSum基准测试平台。该平台基于中文小说构建多尺度数据集,并发现高级LLM可能产生模糊摘要的问题。研究还指出不同提示类型及版本模型的性能差异与LLM的实际性能有紧密关联。”)。我们的目的是提升这个领域的进一步研究发展。[注:考虑到在人工智能大语言模型的相关研究和趋势日益兴盛的大环境下对该平台的适用性前景方面的情况太过泛泛或宽泛化的探讨实际意义有限或者并无法实现相关内容被潜对有关业内者的判断(不同技术侧重的差异性往往形成障碍和主观误解)这一点与摘要是根据正文产生的必然规律不相符或说有矛盾的层面在内。(一个有待具体解答的问题可能是:“基于该基准测试平台的结果和发现,我们能如何更好地推动人工智能大语言模型的发展”)]。目前项目成果已经公开在GitHub上供公众查阅和使用。期待未来有更多的研究者和开发者能够参与到这个项目中来共同推动人工智能的发展。
关键见解
一、LLM在长文本上下文任务中的研究已取得进展,但缺乏相应的长文本摘要数据集限制了该领域的进步。
二、推出了基于中文小说的多尺度长文本上下文摘要基准CNNSum,包含四个子集共695个样本。
三、高级LLM可能产生大量主观评论导致模糊摘要的问题。
点此查看论文截图