⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-04 更新
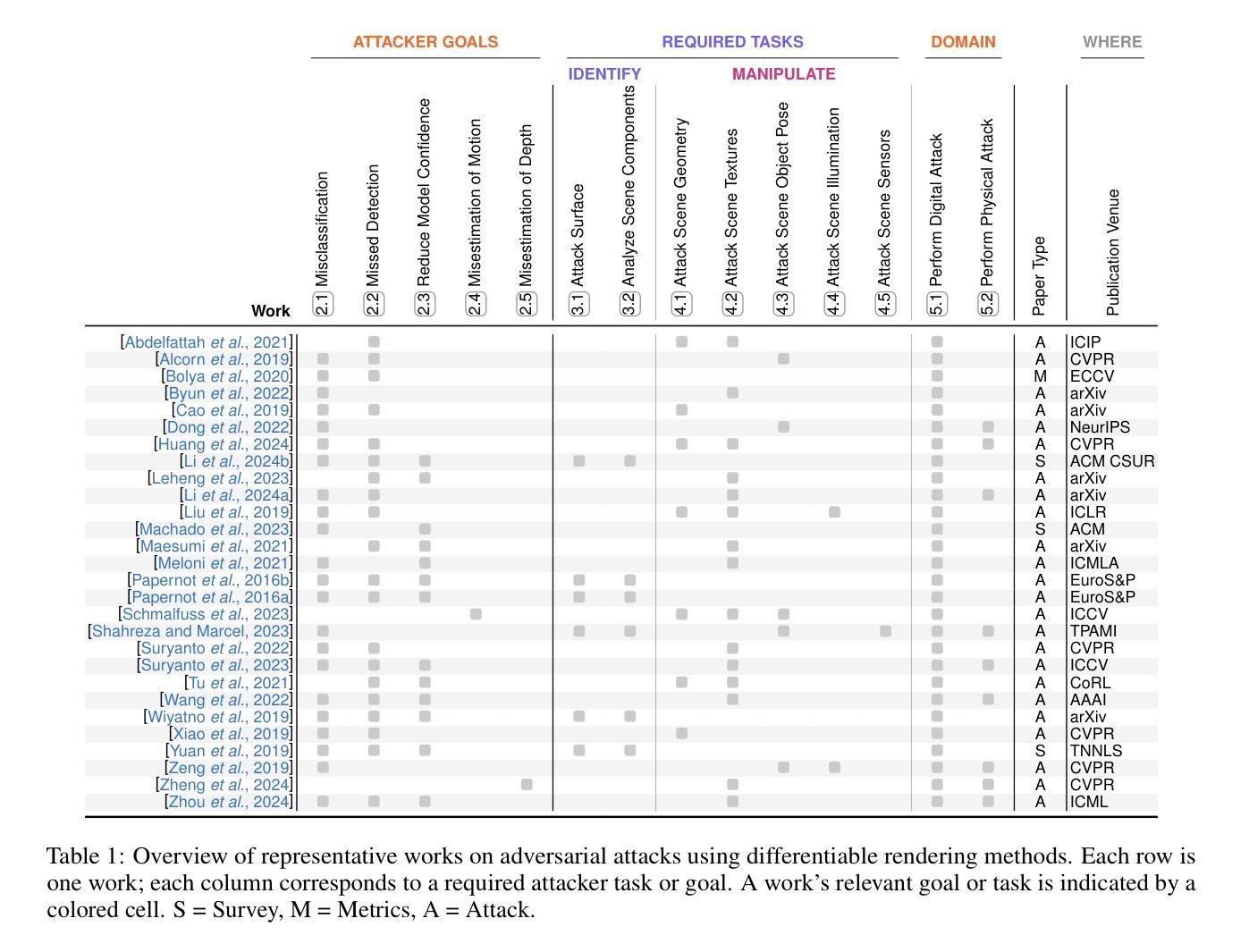
RenderBender: A Survey on Adversarial Attacks Using Differentiable Rendering
Authors:Matthew Hull, Haoran Wang, Matthew Lau, Alec Helbling, Mansi Phute, Chao Zhang, Zsolt Kira, Willian Lunardi, Martin Andreoni, Wenke Lee, Polo Chau
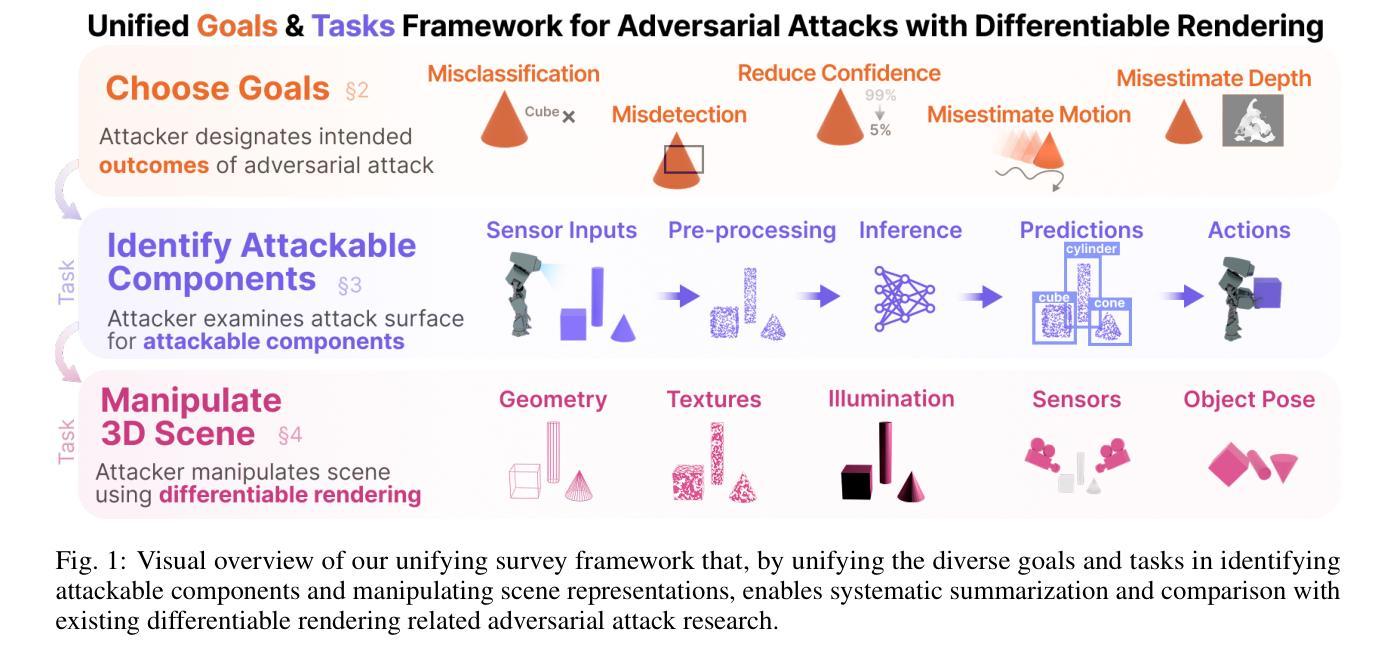
Differentiable rendering techniques like Gaussian Splatting and Neural Radiance Fields have become powerful tools for generating high-fidelity models of 3D objects and scenes. Their ability to produce both physically plausible and differentiable models of scenes are key ingredient needed to produce physically plausible adversarial attacks on DNNs. However, the adversarial machine learning community has yet to fully explore these capabilities, partly due to differing attack goals (e.g., misclassification, misdetection) and a wide range of possible scene manipulations used to achieve them (e.g., alter texture, mesh). This survey contributes the first framework that unifies diverse goals and tasks, facilitating easy comparison of existing work, identifying research gaps, and highlighting future directions - ranging from expanding attack goals and tasks to account for new modalities, state-of-the-art models, tools, and pipelines, to underscoring the importance of studying real-world threats in complex scenes.
像高斯Splatting和神经辐射场这样的可微分渲染技术已成为生成3D对象和场景高保真模型的有力工具。它们能够产生物理上可信和可区分的场景模型,是产生对深度神经网络(DNNs)进行物理可信对抗攻击的关键要素。然而,对抗性机器学习社区尚未充分探索这些能力,部分原因是攻击目标不同(例如,误分类、误检测),以及为实现这些目标而使用的场景操纵手段多种多样(例如,改变纹理、网格)。本文提出了第一个统一的框架,涵盖了各种目标和任务,促进了现有工作的轻松比较,识别了研究空白,并突出了未来的研究方向——从扩大攻击目标和任务以适应新模态、最新模型、工具和管道,到强调在复杂场景中研究现实世界威胁的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 1 figure, 2 tables, IJCAI ‘25 Survey Track
Summary
神经网络渲染技术如高斯拼贴和神经辐射场已成为生成高质量三维物体和场景模型的有力工具。它们能够生成物理上可行和可区分的场景模型,是生成对深度神经网络进行物理上可行的对抗性攻击的关键成分。然而,对抗性机器学习社区尚未充分利用这些技术,部分原因在于攻击目标(如误分类、误检测)的差异以及为实现这些目标所使用的各种可能的场景操作(如更改纹理、网格)。本次调研贡献了一个统一的框架,整合了不同的目标和任务,便于现有工作的比较,发现了研究空白并突出了未来研究方向,包括扩大攻击目标和任务以适应新模态、最新模型、工具和流程,以及强调在复杂场景中研究真实威胁的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络渲染技术如高斯拼贴和神经辐射场可生成高质量的三维物体和场景模型。
- 这些技术对于生成物理上可行和可区分的场景模型至关重要,可用于深度神经网络的对抗性攻击。
- 对抗性机器学习社区尚未充分利用这些渲染技术,原因在于攻击目标和场景操作方式的多样性。
- 本次调研提出了一个统一的框架,整合不同的攻击目标和任务,便于比较现有工作。
- 研究空白存在于对新的攻击目标、任务、模态和最新模型的探索上。
- 未来研究方向包括扩大攻击目标和任务范围,以适应新的技术和流程。
点此查看论文截图


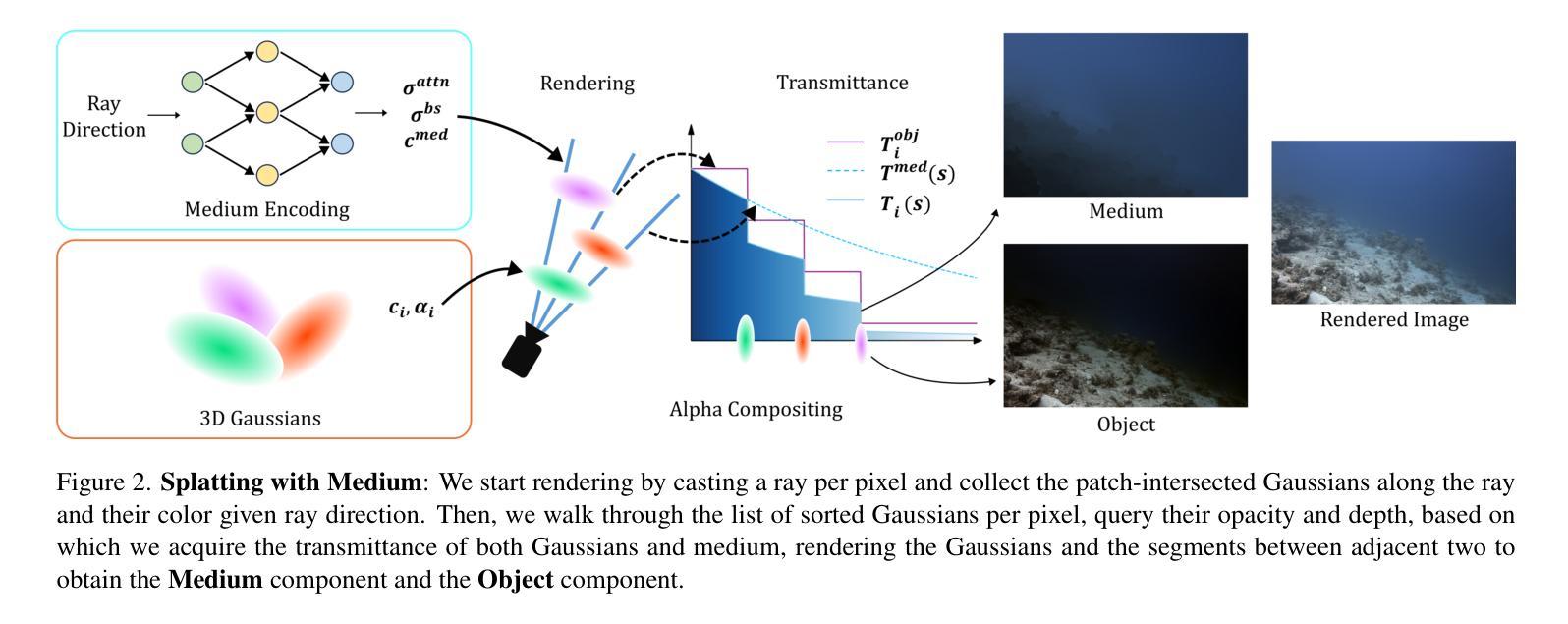
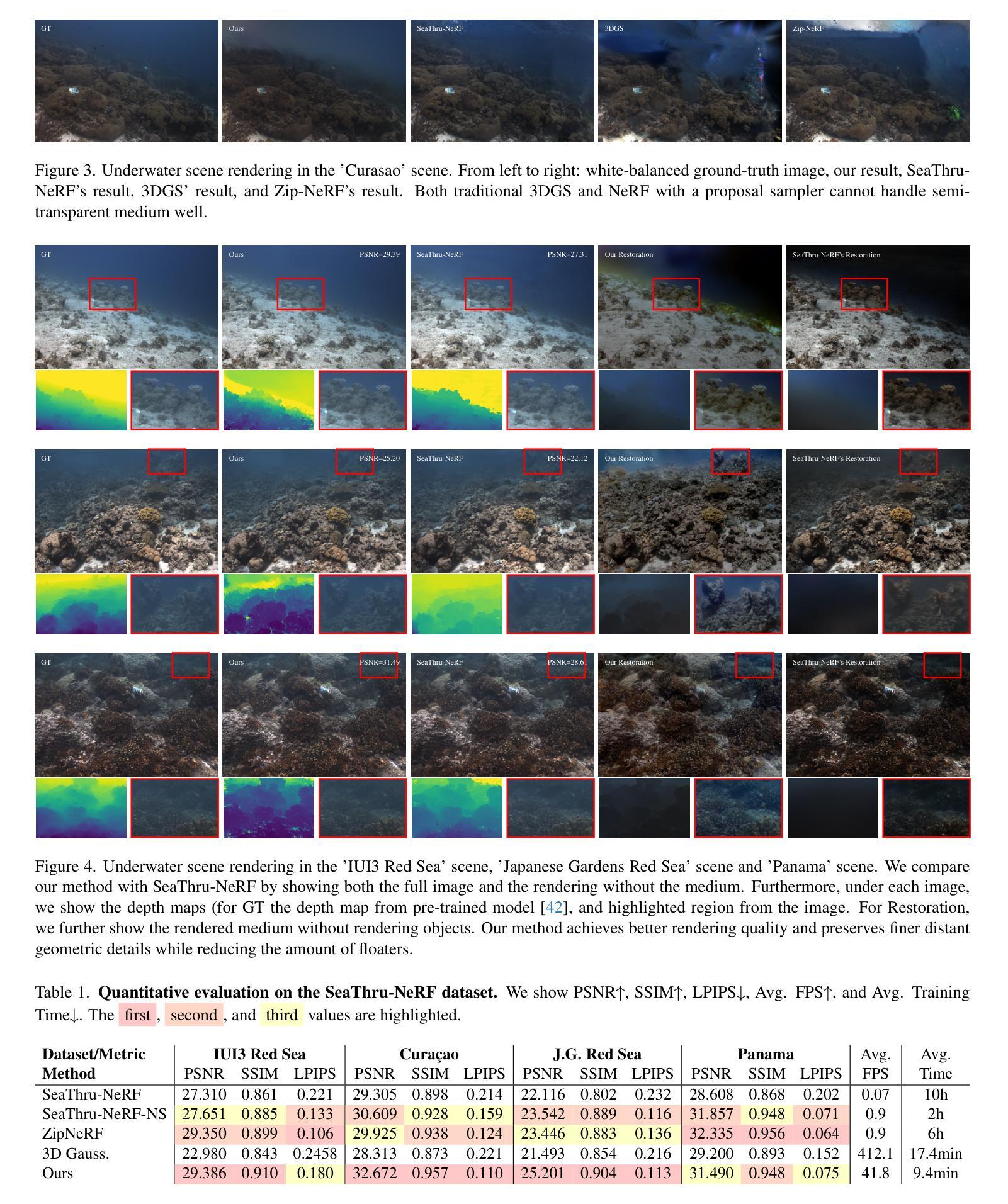
WaterSplatting: Fast Underwater 3D Scene Reconstruction Using Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Huapeng Li, Wenxuan Song, Tianao Xu, Alexandre Elsig, Jonas Kulhanek
The underwater 3D scene reconstruction is a challenging, yet interesting problem with applications ranging from naval robots to VR experiences. The problem was successfully tackled by fully volumetric NeRF-based methods which can model both the geometry and the medium (water). Unfortunately, these methods are slow to train and do not offer real-time rendering. More recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) method offered a fast alternative to NeRFs. However, because it is an explicit method that renders only the geometry, it cannot render the medium and is therefore unsuited for underwater reconstruction. Therefore, we propose a novel approach that fuses volumetric rendering with 3DGS to handle underwater data effectively. Our method employs 3DGS for explicit geometry representation and a separate volumetric field (queried once per pixel) for capturing the scattering medium. This dual representation further allows the restoration of the scenes by removing the scattering medium. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art NeRF-based methods in rendering quality on the underwater SeaThru-NeRF dataset. Furthermore, it does so while offering real-time rendering performance, addressing the efficiency limitations of existing methods. Web: https://water-splatting.github.io
水下三维场景重建是一个充满挑战但有趣的问题,其应用从海军机器人到虚拟现实体验都有。基于完全体积的NeRF方法成功解决了这个问题,该方法可以对几何和介质(水)进行建模。然而,这些方法的训练速度较慢,并不提供实时渲染。最近,三维高斯涂抹(3DGS)方法为NeRF提供了一个快速替代方案。然而,由于它是一种只渲染几何的显式方法,因此无法渲染介质,从而不适合水下重建。因此,我们提出了一种新型方法,将体积渲染与3DGS相结合,以有效处理水下数据。我们的方法采用3DGS进行明确的几何表示,并使用一个单独的体积场(每个像素查询一次)来捕捉散射介质。这种双重表示还可以进一步通过去除散射介质来恢复场景。我们的方法在水下SeaThru-NeRF数据集上的渲染质量超过了最先进的NeRF方法。此外,它还提供实时渲染性能,解决了现有方法的效率限制。网站:https://water-splatting.github.io
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Web: https://water-splatting.github.io
Summary
水下三维场景重建是一个既具挑战性又充满趣味的问题,涉及军事机器人、虚拟现实体验等多个应用领域。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种融合体积渲染与3D高斯溅射的新方法,旨在有效处理水下数据。该方法采用明确的几何表示和散射介质捕获的双重表示方式,能够恢复场景并消除散射介质的影响。相较于现有的NeRF方法,本文提出的方法在海底渲染质量上更胜一筹,且实现了实时渲染性能。同时,为解决NeRF的局限性提供了一种解决方案。感兴趣可访问网址进行更多了解:https://water-splatting.github.io。
Key Takeaways
- 水下三维场景重建是一个重要的研究方向,在多个领域都有实际应用价值。
- 目前针对该问题已有多种方法尝试解决,但仍存在挑战。比如,需要找到既快又好地渲染的方法等。
- 全卷积NeRF方法可以建模几何和介质(如水),但训练慢且无法实现实时渲染。
- 3D高斯溅射方法作为一种快速替代方案无法渲染介质。本文则提出了融合这两种方法的策略来处理水下数据。
点此查看论文截图