⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-04 更新
MSDA: Combining Pseudo-labeling and Self-Supervision for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation in ASR
Authors:Dimitrios Damianos, Georgios Paraskevopoulos, Alexandros Potamianos
In this work, we investigate the Meta PL unsupervised domain adaptation framework for Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). We introduce a Multi-Stage Domain Adaptation pipeline (MSDA), a sample-efficient, two-stage adaptation approach that integrates self-supervised learning with semi-supervised techniques. MSDA is designed to enhance the robustness and generalization of ASR models, making them more adaptable to diverse conditions. It is particularly effective for low-resource languages like Greek and in weakly supervised scenarios where labeled data is scarce or noisy. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that Meta PL can be applied effectively to ASR tasks, achieving state-of-the-art results, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art methods, and providing more robust solutions for unsupervised domain adaptation in ASR. Our ablations highlight the necessity of utilizing a cascading approach when combining self-supervision with self-training.
在这项工作中,我们研究了用于自动语音识别(ASR)的Meta PL无监督域自适应框架。我们引入了一种多阶段域自适应管道(MSDA),这是一种样本高效的、两阶段的自适应方法,它将自监督学习与半监督技术相结合。MSDA旨在提高ASR模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力,使它们更能适应各种条件。它对低资源语言(如希腊语)以及在标签数据稀缺或嘈杂的弱监督场景中特别有效。通过大量实验,我们证明了Meta PL可以有效地应用于ASR任务,实现最先进的成果,显著优于现有方法,并为ASR中的无监督域自适应提供更稳健的解决方案。我们的消融研究强调了将自监督与自训练相结合时采用级联方法的必要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文研究了Meta PL无监督领域自适应框架在自动语音识别(ASR)中的应用。提出了一种多阶段领域自适应管道(MSDA),这是一种样本高效的、两阶段的自适应方法,结合了自监督学习与半监督技术。MSDA旨在提高ASR模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力,使其更适应不同的条件。在资源有限的语种如希腊语以及标签数据稀缺或嘈杂的弱监督场景中,该方法表现尤为出色。实验证明,Meta PL可有效应用于ASR任务,实现最新技术成果,显著优于现有方法,为ASR的无监督领域自适应提供更稳健的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了Meta PL无监督领域自适应框架在自动语音识别(ASR)中的应用。
- 提出了一种新的多阶段领域自适应管道(MSDA),结合了自监督学习与半监督技术。
- MSDA增强了ASR模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力,适应不同的条件。
- MSDA在资源有限的语种和弱监督场景中表现优异。
- 实验证明Meta PL在ASR任务上实现了最新技术成果。
- MSDA显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

Interspeech 2025 URGENT Speech Enhancement Challenge
Authors:Kohei Saijo, Wangyou Zhang, Samuele Cornell, Robin Scheibler, Chenda Li, Zhaoheng Ni, Anurag Kumar, Marvin Sach, Yihui Fu, Wei Wang, Tim Fingscheidt, Shinji Watanabe
There has been a growing effort to develop universal speech enhancement (SE) to handle inputs with various speech distortions and recording conditions. The URGENT Challenge series aims to foster such universal SE by embracing a broad range of distortion types, increasing data diversity, and incorporating extensive evaluation metrics. This work introduces the Interspeech 2025 URGENT Challenge, the second edition of the series, to explore several aspects that have received limited attention so far: language dependency, universality for more distortion types, data scalability, and the effectiveness of using noisy training data. We received 32 submissions, where the best system uses a discriminative model, while most other competitive ones are hybrid methods. Analysis reveals some key findings: (i) some generative or hybrid approaches are preferred in subjective evaluations over the top discriminative model, and (ii) purely generative SE models can exhibit language dependency.
在开发能够处理各种语音失真和录音条件的通用语音增强(SE)方面,已经付出了越来越多的努力。URGENT Challenge系列旨在通过接纳广泛的失真类型、增加数据多样性和引入广泛的评估指标来促进这种通用SE的发展。这项工作介绍了Interspeech 2025 URGENT Challenge,即该系列的第二版,旨在探索迄今为止受到有限关注的几个方面:语言依赖性、更多失真类型的普遍性、数据可扩展性以及使用带噪声训练数据的有效性。我们收到了32份提交,其中最佳系统使用的是判别模型,而其他大多数有竞争力的系统都是混合方法。分析揭示了一些关键发现:(i)在某些主观评价中,一些生成性或混合方法优于顶级判别模型;(ii)纯粹的生成性SE模型可能会表现出语言依赖性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech 2025
Summary
本段文本主要介绍了Interspeech 2025 URGENT Challenge系列的目标和成果。该挑战旨在开发通用语音增强技术,应对各种语音失真和录音条件的问题。其中引入了第二款挑战:探索语言依赖性、更多失真类型的普遍性、数据可扩展性以及使用噪声训练数据的有效性。分析结果显示,一些生成性或混合方法在某些主观评价中优于顶级判别模型,而纯粹的生成性语音增强模型可能存在语言依赖性。
Key Takeaways
- Interspeech 2025 URGENT Challenge旨在开发通用语音增强技术,以处理各种语音失真和录音条件的问题。
- 该挑战的第二版探索了语言依赖性、更多失真类型的普遍性、数据可扩展性和使用噪声训练数据的有效性等几个方面。
- 目前收到的32份提交中,最佳系统使用的是判别模型,而其他有竞争力的系统多为混合方法。
- 分析发现,在某些主观评价中,一些生成性或混合方法可能优于顶级判别模型。
- 纯粹的生成性语音增强模型可能存在语言依赖性。
- 该挑战旨在拥抱广泛的失真类型,增加数据多样性,并融入广泛的评估指标,以推动通用语音增强技术的发展。
点此查看论文截图

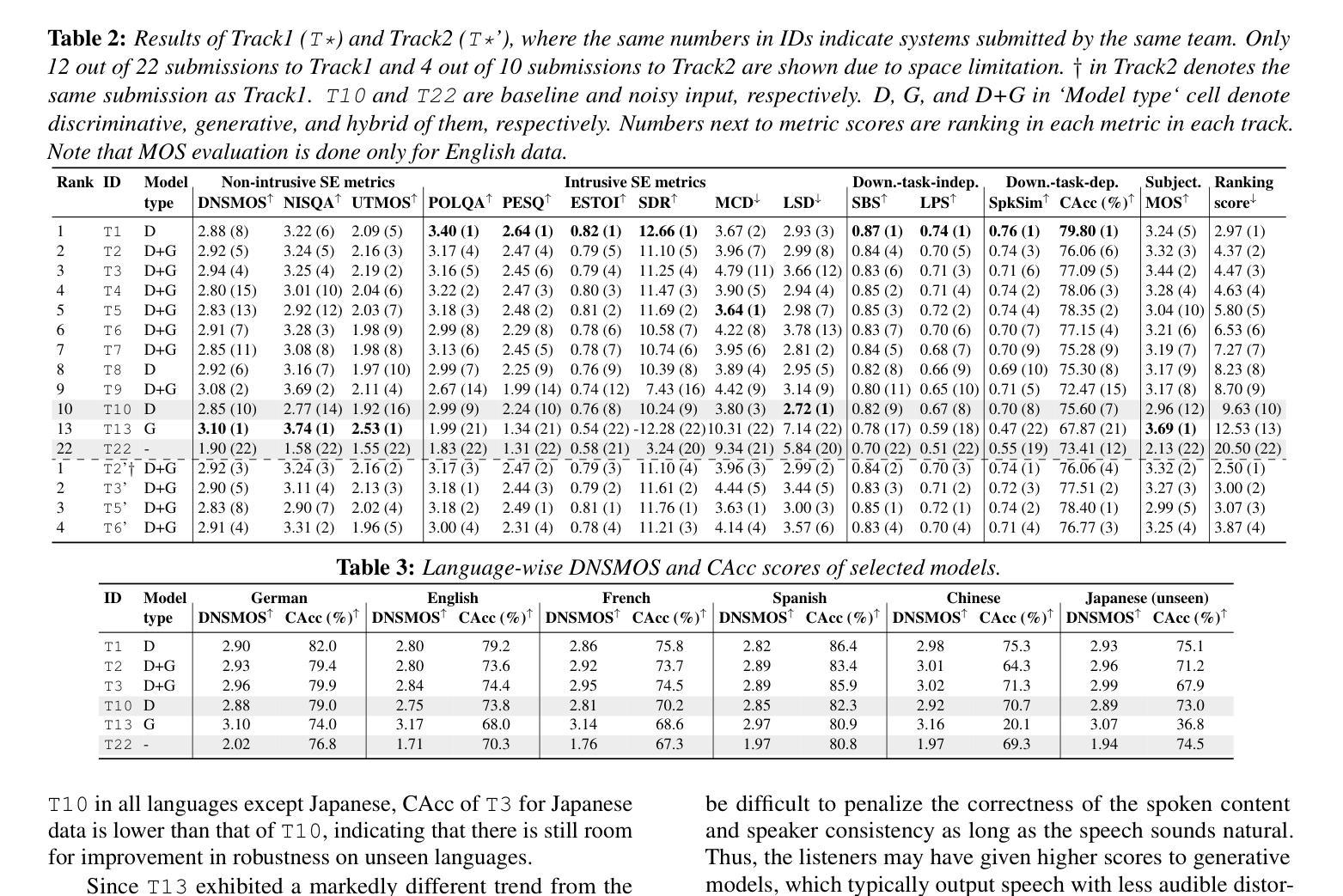
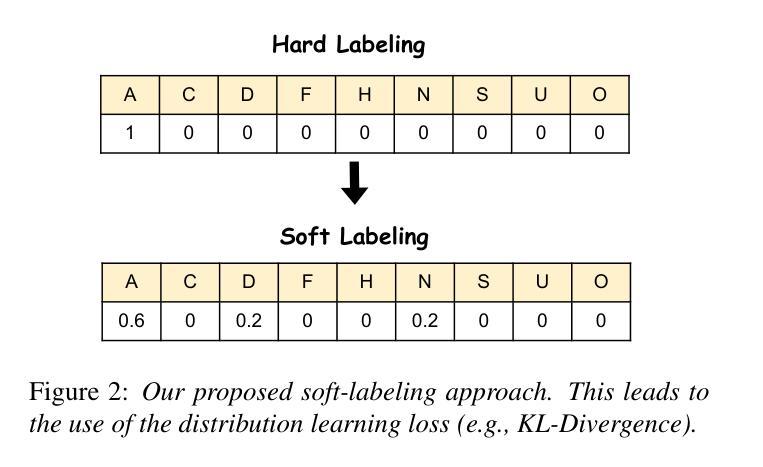
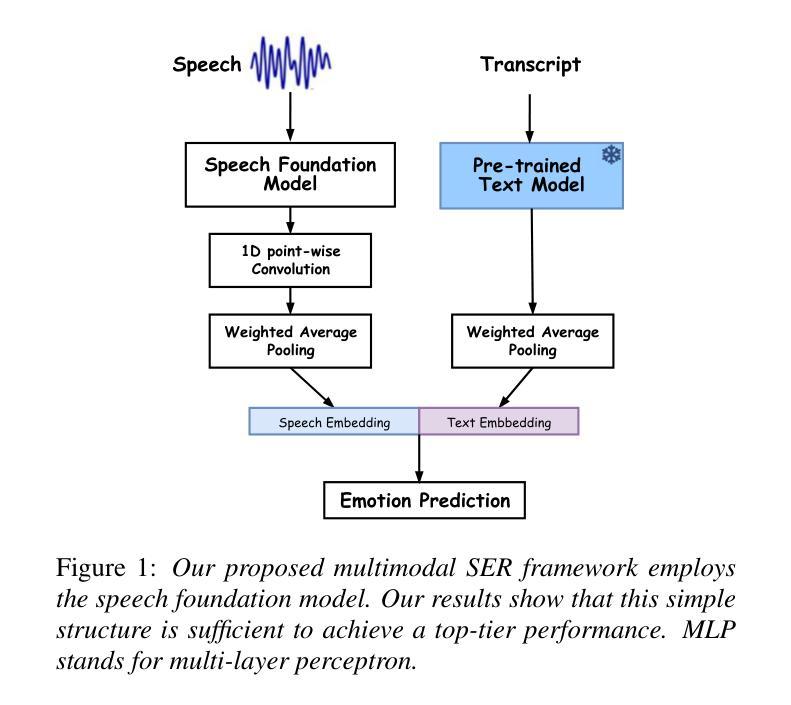
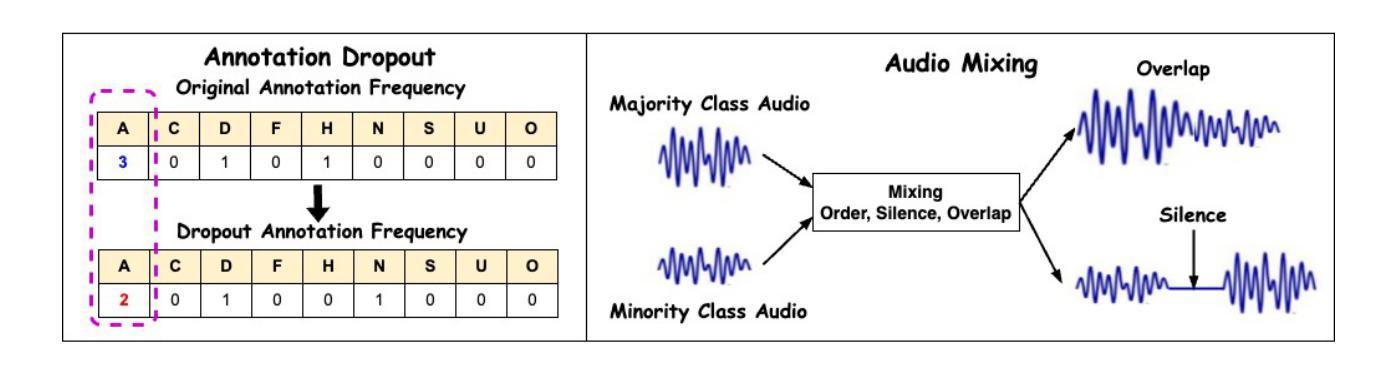
Developing a Top-tier Framework in Naturalistic Conditions Challenge for Categorized Emotion Prediction: From Speech Foundation Models and Learning Objective to Data Augmentation and Engineering Choices
Authors:Tiantian Feng, Thanathai Lertpetchpun, Dani Byrd, Shrikanth Narayanan
Speech emotion recognition (SER), particularly for naturally expressed emotions, remains a challenging computational task. Key challenges include the inherent subjectivity in emotion annotation and the imbalanced distribution of emotion labels in datasets. This paper introduces the \texttt{SAILER} system developed for participation in the INTERSPEECH 2025 Emotion Recognition Challenge (Task 1). The challenge dataset, which contains natural emotional speech from podcasts, serves as a valuable resource for studying imbalanced and subjective emotion annotations. Our system is designed to be simple, reproducible, and effective, highlighting critical choices in modeling, learning objectives, data augmentation, and engineering choices. Results show that even a single system (without ensembling) can outperform more than 95% of the submissions, with a Macro-F1 score exceeding 0.4. Moreover, an ensemble of three systems further improves performance, achieving a competitively ranked score (top-3 performing team). Our model is at: https://github.com/tiantiaf0627/vox-profile-release.
语音情感识别(SER),尤其是对自然表达情感的识别,仍然是一项具有挑战性的计算任务。主要挑战包括情感注释中的固有主观性和数据集中情感标签的不平衡分布。本文介绍了为参与INTERSPEECH 2025情感识别挑战赛(任务1)而开发的`SAILER’系统。挑战赛数据集包含来自播客的自然情感语音,是研究不平衡和主观情感注释的宝贵资源。我们的系统设计简单、可复制、有效,突出显示建模、学习目标、数据增强和工程选择中的关键选择。结果表明,即使是一个系统(无需集合)也能表现出超过95%提交的结果,宏观F1分数超过0.4。此外,三个系统的组合进一步提高了性能,取得了竞争排名分数(排名前三的团队)。我们的模型位于:https://github.com/tiantiaf0627/vox-profile-release。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to INTERSPEECH 2025
Summary
该论文针对语音情感识别(SER)面临的挑战,如情感标注的主观性和数据集情感标签的不平衡分布,提出了为参与INTERSPEECH 2025情感识别挑战赛(任务一)而开发的SAILER系统。该系统旨在设计简单、可复制和高效,强调建模、学习目标、数据增强和工程选择的重要性。实验结果显示,单一系统性能已超越大多数提交结果,宏观F1分数超过0.4。通过集成三个系统,性能进一步提升,成为排名前三的团队。
Key Takeaways
- 论文指出语音情感识别(SER)面临的挑战,包括情感标注的主观性和数据集情感标签的不平衡分布。
- 介绍了为INTERSPEECH 2025情感识别挑战赛开发的
SAILER系统。 SAILER系统的设计重点是简单性、可复制性和高效性。- 论文强调了建模、学习目标、数据增强和工程选择的重要性。
- 实验结果显示,单一系统的性能已超越大多数提交的结果,宏观F1分数超过0.4。
- 通过集成三个系统,性能进一步提升,成为竞赛中排名靠前的团队。
- 论文提供了其模型的公开访问链接。
点此查看论文截图

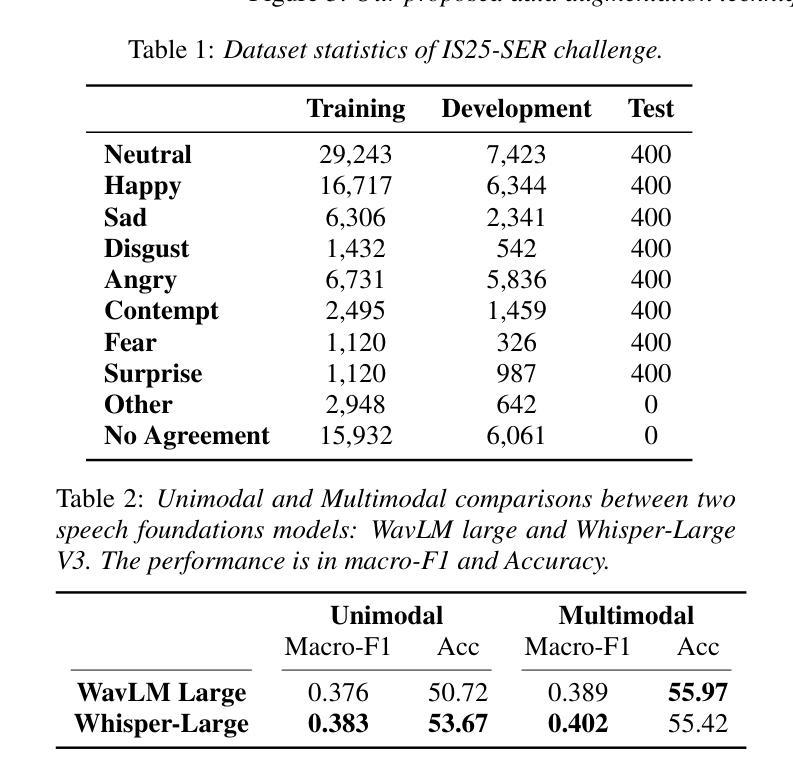
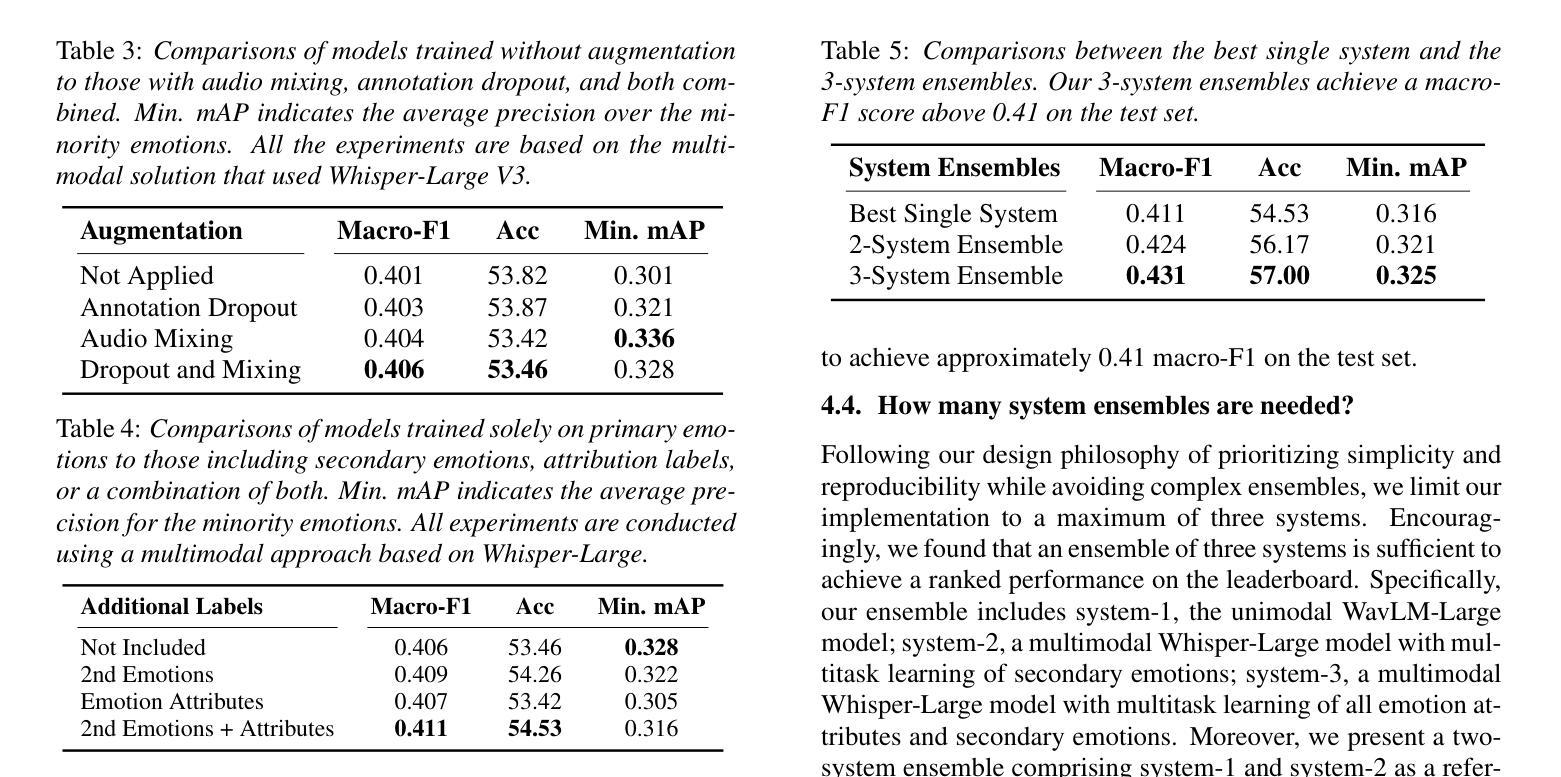
ClearSphere: Multi-Earphone Synergy for Enhanced Conversational Clarity
Authors:Lixing He
In crowded places such as conferences, background noise, overlapping voices, and lively interactions make it difficult to have clear conversations. This situation often worsens the phenomenon known as “cocktail party deafness.” We present ClearSphere, the collaborative system that enhances speech at the conversation level with multi-earphones. Real-time conversation enhancement requires a holistic modeling of all the members in the conversation, and an effective way to extract the speech from the mixture. ClearSphere bridges the acoustic sensor system and state-of-the-art deep learning for target speech extraction by making two key contributions: 1) a conversation-driven network protocol, and 2) a robust target conversation extraction model. Our networking protocol enables mobile, infrastructure-free coordination among earphone devices. Our conversation extraction model can leverage the relay audio in a bandwidth-efficient way. ClearSphere is evaluated in both real-world experiments and simulations. Results show that our conversation network obtains more than 90% accuracy in group formation, improves the speech quality by up to 8.8 dB over state-of-the-art baselines, and demonstrates real-time performance on a mobile device. In a user study with 20 participants, ClearSphere has a much higher score than baseline with good usability.
在会议等拥挤场所,背景噪音、声音重叠以及活跃的互动使得进行清晰的对话变得困难。这种情况会加剧所谓的“鸡尾酒会耳聋”现象。我们推出了ClearSphere,这是一款协作系统,通过多耳机增强对话级别的语音。实时对话增强需要对所有对话成员进行整体建模,并需要一种从混合语音中提取目标语音的有效方法。ClearSphere通过两项关键贡献——对话驱动的网络协议和稳健的目标对话提取模型,搭建了声学传感器系统和最新的深度学习目标语音提取之间的桥梁。我们的网络协议实现了耳机设备之间无需基础设施的移动协调。我们的对话提取模型能够以带宽有效的方式利用中继音频。ClearSphere在真实实验和模拟中都得到了评估。结果表明,我们的对话网络在组队方面的准确率超过90%,在最新基线的基础上改善了高达8.8分贝的语音质量,并在移动设备上实现了实时性能。在20名参与者的一项用户研究中,ClearSphere的得分远高于基线,具有良好的可用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
在会议等拥挤场合,背景噪音、声音重叠及活跃互动使得清晰交流变得困难,加剧了“鸡尾酒会耳聋”现象。为此,我们推出了ClearSphere协作系统,通过多耳机增强对话级别的语音。实时对话增强需要全面建模所有参与者的声音,并有效地从混合声音中提取目标语音。ClearSphere通过两项关键贡献——对话驱动的网络协议和稳健的目标对话提取模型,将声学传感器系统和最新的深度学习技术相结合,实现目标语音提取。网络协议可实现耳机设备之间的移动、无基础设施协调。对话提取模型能够以带宽有效的方式利用中继音频。ClearSphere在真实实验和模拟中均得到评估,结果显示,其对话网络在群体形成方面的准确率超过90%,在语音质量上比最新基线提高了高达8.8分贝,并在移动设备上实现了实时性能。在用户研究中,ClearSphere较基线产品具有更高得分和良好的可用性。
Key Takeaways:
- 在拥挤场所如会议中,背景噪音和声音重叠使得清晰交流变得困难,加剧了“鸡尾酒会耳聋”现象。
- ClearSphere是一个协作系统,旨在通过多耳机增强对话级别的语音。
- 实时对话增强需要全面建模所有参与者的声音并有效提取目标语音。
- ClearSphere通过对话驱动的网络协议和稳健的目标对话提取模型实现目标语音提取。
- 网络协议支持耳机设备间的移动、无基础设施协调。
- ClearSphere在真实实验和模拟中表现优异,对话网络准确率超过90%,语音质量显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

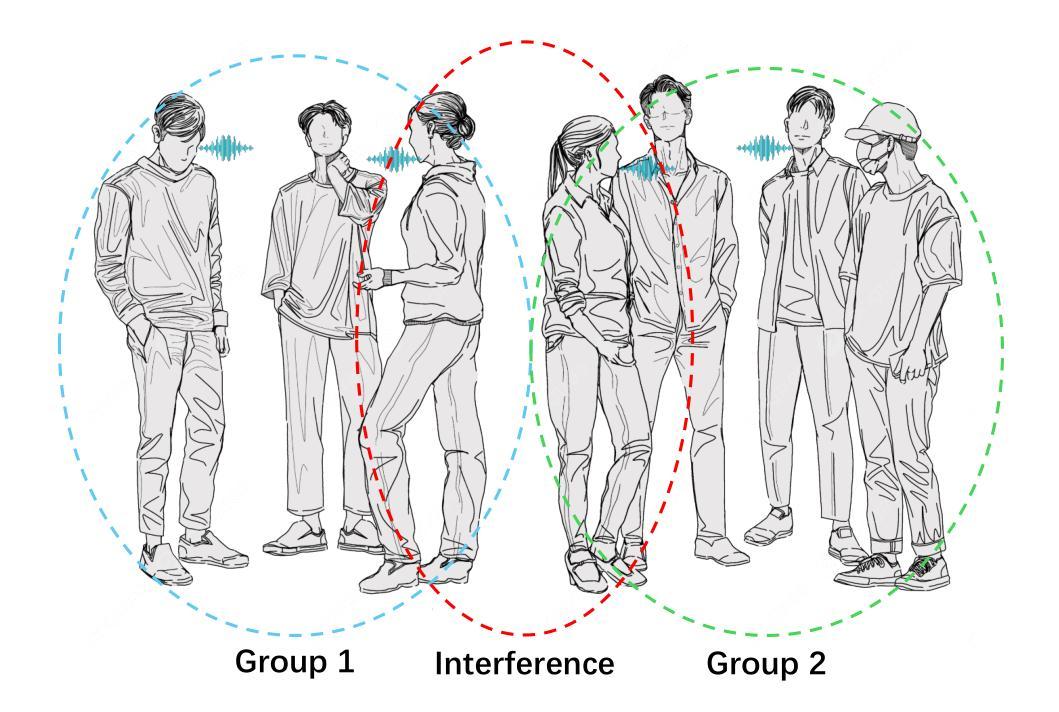
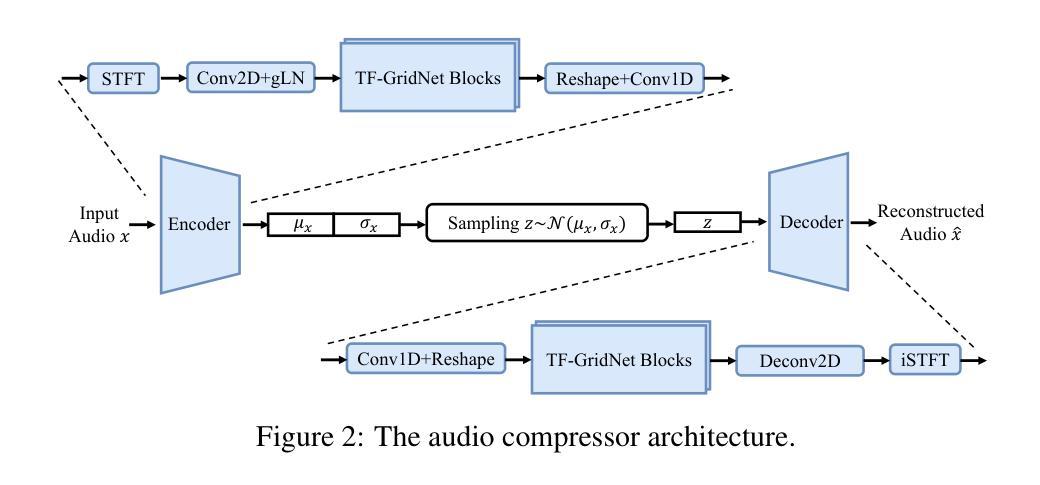
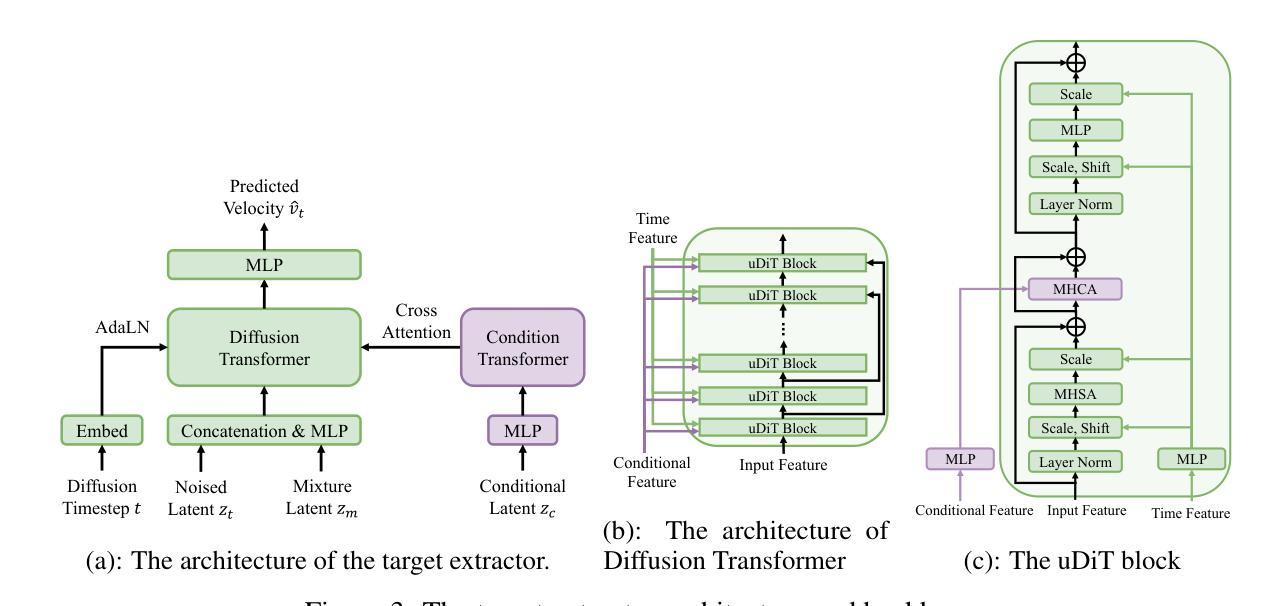
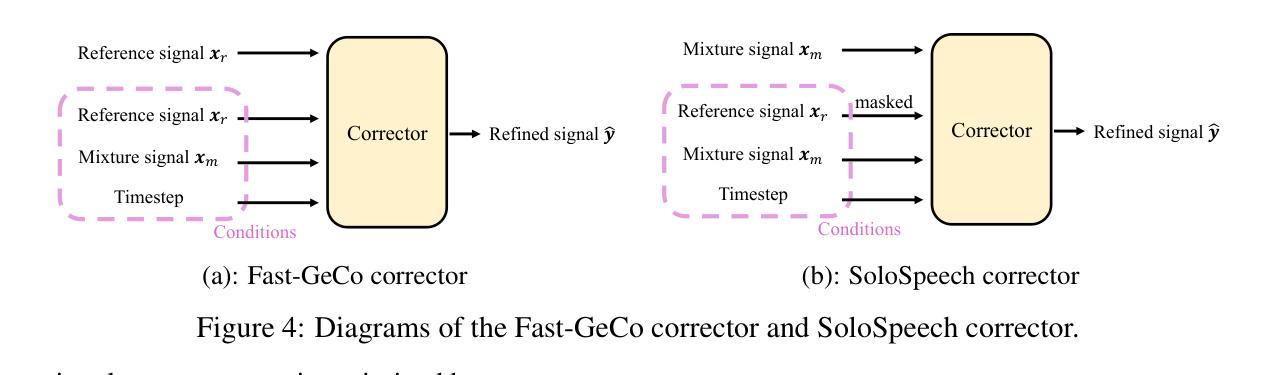
SoloSpeech: Enhancing Intelligibility and Quality in Target Speech Extraction through a Cascaded Generative Pipeline
Authors:Helin Wang, Jiarui Hai, Dongchao Yang, Chen Chen, Kai Li, Junyi Peng, Thomas Thebaud, Laureano Moro Velazquez, Jesus Villalba, Najim Dehak
Target Speech Extraction (TSE) aims to isolate a target speaker’s voice from a mixture of multiple speakers by leveraging speaker-specific cues, typically provided as auxiliary audio (a.k.a. cue audio). Although recent advancements in TSE have primarily employed discriminative models that offer high perceptual quality, these models often introduce unwanted artifacts, reduce naturalness, and are sensitive to discrepancies between training and testing environments. On the other hand, generative models for TSE lag in perceptual quality and intelligibility. To address these challenges, we present SoloSpeech, a novel cascaded generative pipeline that integrates compression, extraction, reconstruction, and correction processes. SoloSpeech features a speaker-embedding-free target extractor that utilizes conditional information from the cue audio’s latent space, aligning it with the mixture audio’s latent space to prevent mismatches. Evaluated on the widely-used Libri2Mix dataset, SoloSpeech achieves the new state-of-the-art intelligibility and quality in target speech extraction and speech separation tasks while demonstrating exceptional generalization on out-of-domain data and real-world scenarios.
目标语音提取(TSE)旨在利用特定于说话者的线索(通常作为辅助音频(即线索音频)提供)从多个说话者的混合声音中分离出目标说话者的声音。尽管最近的TSE进展主要采用了提供高感知质量的判别模型,但这些模型往往引入了不需要的伪影,降低了自然度,并且对训练和测试环境之间的差异很敏感。另一方面,TSE的生成模型在感知质量和清晰度方面有所不足。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了SoloSpeech,这是一种新型级联生成管道,它集成了压缩、提取、重建和校正过程。SoloSpeech的特点是无需说话者嵌入的目标提取器,它利用线索音频的潜在空间的条件信息,将其与混合音频的潜在空间对齐,以防止不匹配。在广泛使用的Libri2Mix数据集上,SoloSpeech在目标语音提取和语音分离任务中实现了最新的最高清晰度和质量,同时在域外数据和现实场景上表现出卓越的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
目标语音提取(TSE)旨在利用说话人特定线索从多个说话人的混合语音中分离出目标说话人的声音。虽然最近的研究主要采用提供高感知质量的判别模型,但这些模型常引入不必要的伪影、降低自然度,并对训练和测试环境的差异敏感。另一方面,生成式TSE模型在感知质量和清晰度方面滞后。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了无说话人嵌入的SoloSpeech,这是一个集成压缩、提取、重建和校正过程的新型级联生成管道。它在广泛使用的Libri2Mix数据集上实现了目标语音提取和语音分离任务的新颖性和卓越性,同时在域外数据和真实世界场景上表现出出色的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 目标语音提取(TSE)旨在从混合语音中分离出目标说话人的声音。
- 现有模型面临引入伪影、降低自然度及对环境差异敏感的挑战。
- 生成式TSE模型在感知质量和清晰度方面有待提高。
- SoloSpeech是一个新型级联生成管道,集成压缩、提取、重建和校正过程。
- SoloSpeech利用条件信息,通过潜在空间对齐,实现目标语音的精准提取。
- 在Libri2Mix数据集上,SoloSpeech达到了目标语音提取和语音分离任务的新水平。
点此查看论文截图

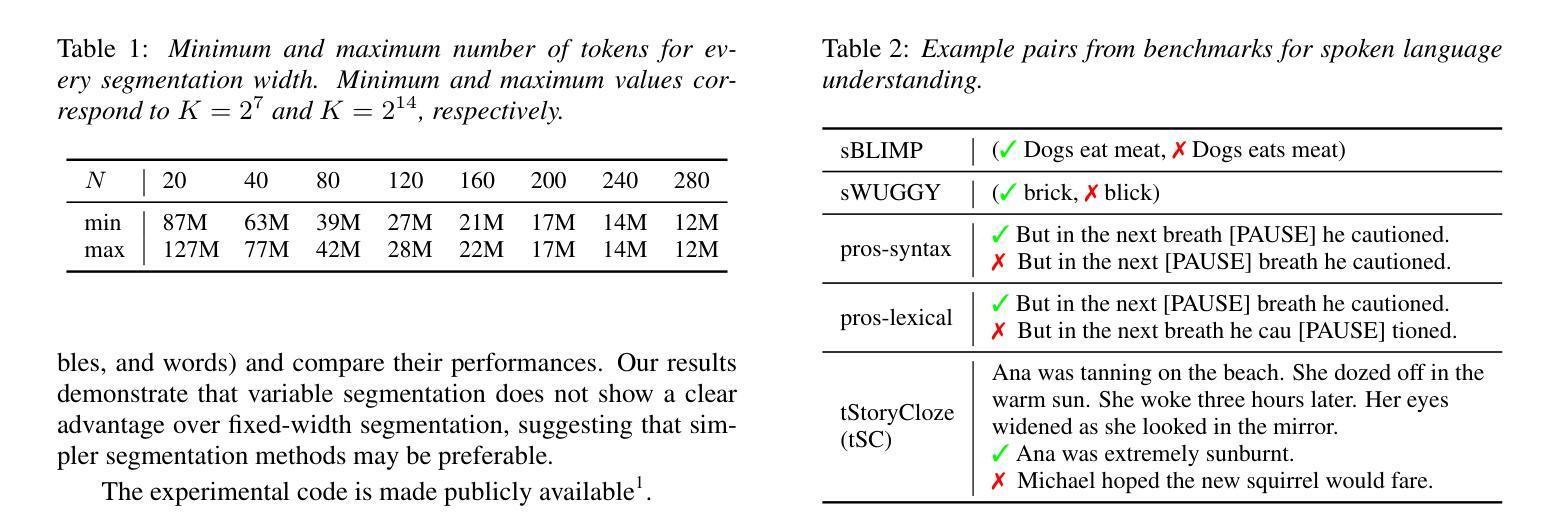
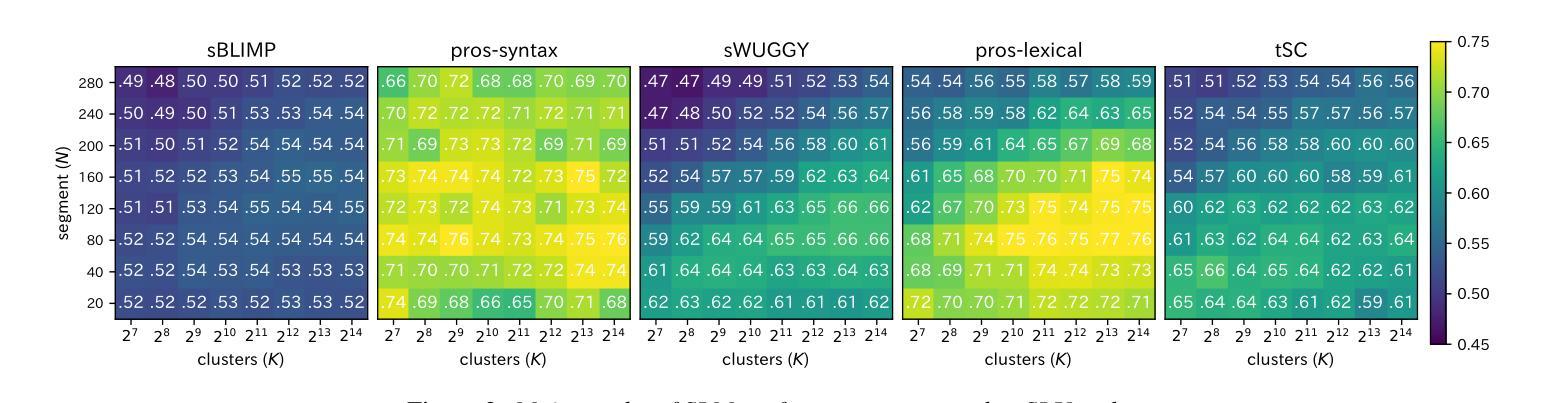
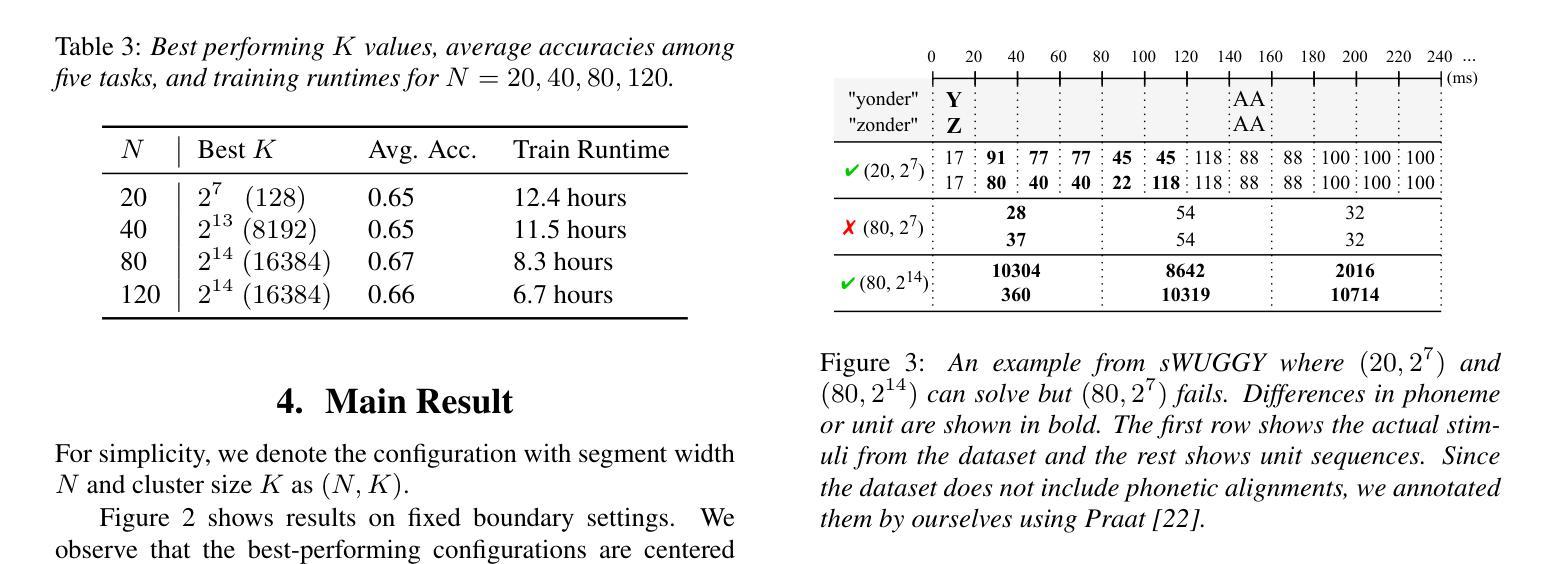
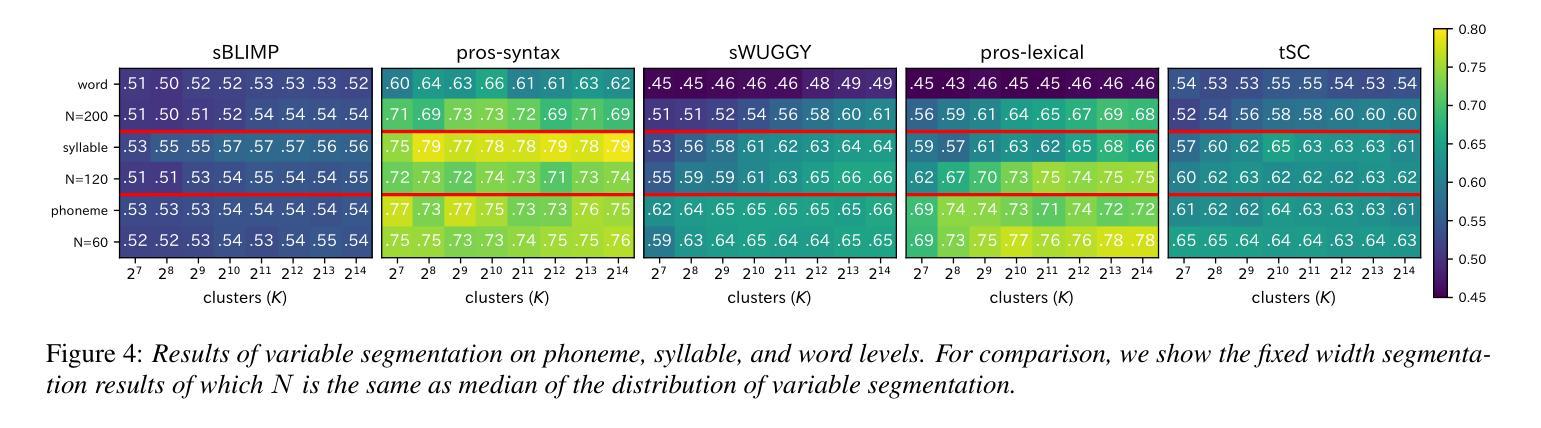
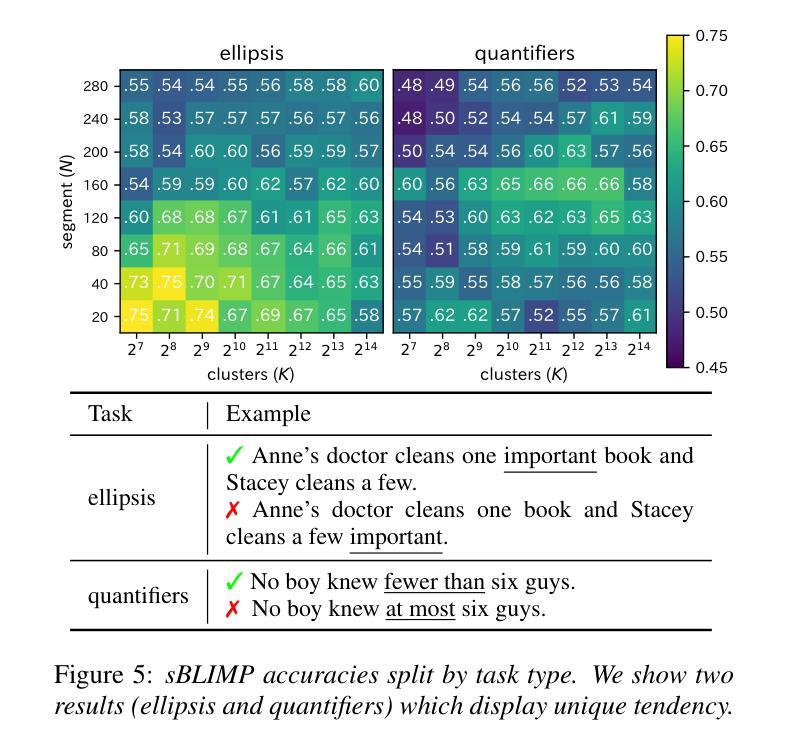
Exploring the Effect of Segmentation and Vocabulary Size on Speech Tokenization for Speech Language Models
Authors:Shunsuke Kando, Yusuke Miyao, Shinnosuke Takamichi
The purpose of speech tokenization is to transform a speech signal into a sequence of discrete representations, serving as the foundation for speech language models (SLMs). While speech tokenization has many options, their effect on the performance of SLMs remains unclear. This paper investigates two key aspects of speech tokenization: the segmentation width and the cluster size of discrete units. First, we segment speech signals into fixed/variable widths and pooled representations. We then train K-means models in multiple cluster sizes. Through the evaluation on zero-shot spoken language understanding benchmarks, we find the positive effect of moderately coarse segmentation and bigger cluster size. Notably, among the best-performing models, the most efficient one achieves a 50% reduction in training data and a 70% decrease in training runtime. Our analysis highlights the importance of combining multiple tokens to enhance fine-grained spoken language understanding.
语音切词的目的是将语音信号转换为一系列离散表示,作为语音语言模型(SLM)的基础。虽然语音切词有很多选项,但它们对SLM性能的影响仍不清楚。本文研究了语音切词的两个方面:分段宽度和离散单元簇的大小。首先,我们将语音信号分段为固定/可变宽度和池化表示。然后,我们在多个簇大小上训练K-means模型。通过对零样本口语理解基准的评估,我们发现适度粗糙的分段和较大的簇大小具有积极的影响。值得注意的是,在表现最佳的模型中,最有效的模型实现了训练数据50%的减少和训练运行时间70%的减少。我们的分析强调了结合多个令牌以增强精细口语理解的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech2025
Summary
语音标记化的目的是将语音信号转换为离散表示的序列,为语音语言模型(SLMs)打下基础。本文探讨了语音标记化的两个关键方面:分段宽度和离散单元的簇大小。研究发现,适度粗糙的分段和较大的簇大小对提升模型性能有正面效果,最高效的模型能在训练数据和训练时间上分别减少50%和70%。分析强调了结合多个标记以增强精细粒度语音语言理解的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 语音标记化是将语音信号转换为离散表示的序列的过程,为语音语言模型(SLMs)奠定基础。
- 本文研究了语音标记化的两个关键参数:分段宽度和簇大小。
- 适度粗糙的分段和较大的簇大小对SLM的性能有积极影响。
- 最高效的模型在减少训练数据和训练时间方面取得了显著成果。
- 结合多个标记有助于增强精细粒度的语音语言理解。
- 语音标记化的研究对于提高SLM的性能具有潜力,特别是在处理大规模语音数据方面。
点此查看论文截图

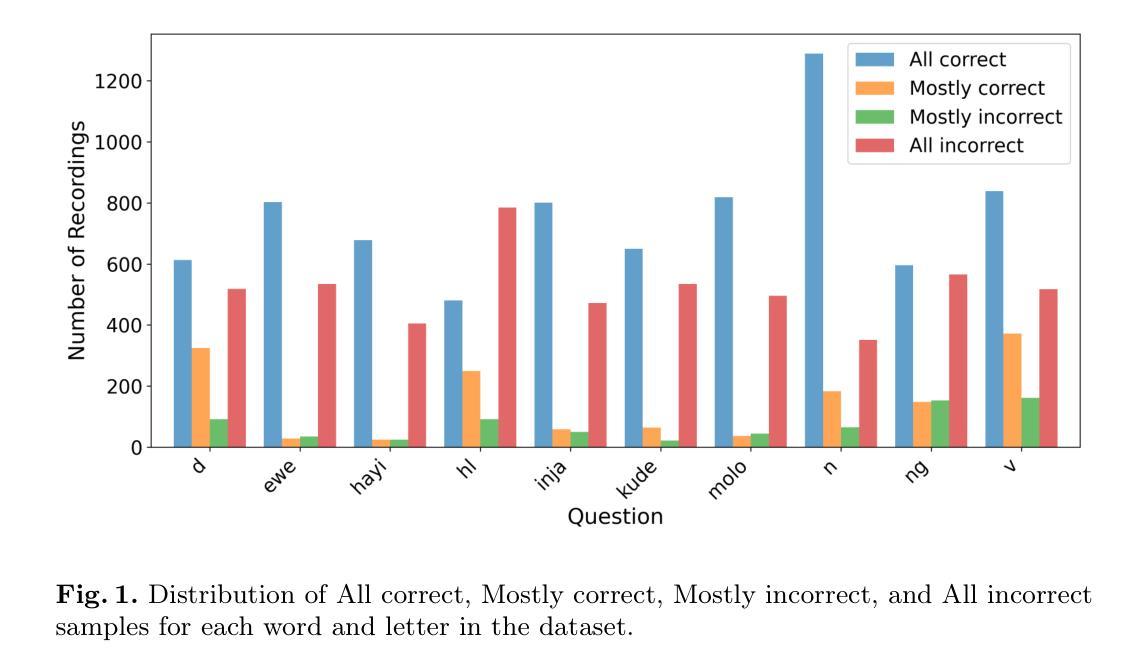
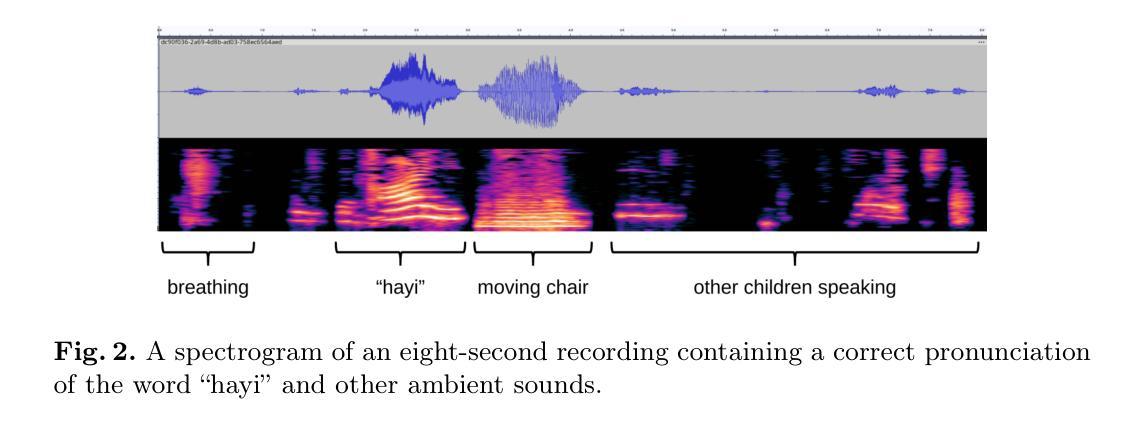
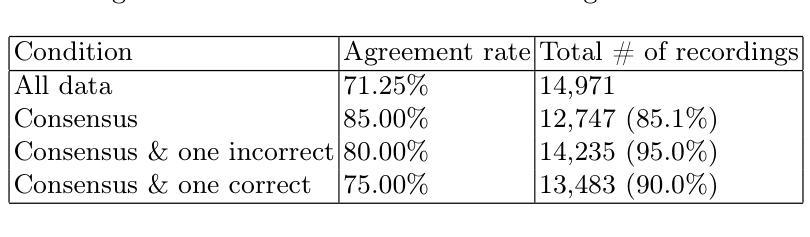
An End-to-End Approach for Child Reading Assessment in the Xhosa Language
Authors:Sergio Chevtchenko, Nikhil Navas, Rafaella Vale, Franco Ubaudi, Sipumelele Lucwaba, Cally Ardington, Soheil Afshar, Mark Antoniou, Saeed Afshar
Child literacy is a strong predictor of life outcomes at the subsequent stages of an individual’s life. This points to a need for targeted interventions in vulnerable low and middle income populations to help bridge the gap between literacy levels in these regions and high income ones. In this effort, reading assessments provide an important tool to measure the effectiveness of these programs and AI can be a reliable and economical tool to support educators with this task. Developing accurate automatic reading assessment systems for child speech in low-resource languages poses significant challenges due to limited data and the unique acoustic properties of children’s voices. This study focuses on Xhosa, a language spoken in South Africa, to advance child speech recognition capabilities. We present a novel dataset composed of child speech samples in Xhosa. The dataset is available upon request and contains ten words and letters, which are part of the Early Grade Reading Assessment (EGRA) system. Each recording is labeled with an online and cost-effective approach by multiple markers and a subsample is validated by an independent EGRA reviewer. This dataset is evaluated with three fine-tuned state-of-the-art end-to-end models: wav2vec 2.0, HuBERT, and Whisper. The results indicate that the performance of these models can be significantly influenced by the amount and balancing of the available training data, which is fundamental for cost-effective large dataset collection. Furthermore, our experiments indicate that the wav2vec 2.0 performance is improved by training on multiple classes at a time, even when the number of available samples is constrained.
儿童识字能力对其后续生命阶段的生活成果具有很强的预测作用。这指出了针对脆弱的中低收入人群进行针对性干预的必要性,以帮助缩小这些地区识字水平与高收入地区之间的差距。在这方面,阅读评估是衡量这些节目效果的重要工具,人工智能可以成为支持教育工作者完成这项任务的可靠且经济的工具。为低资源语言的孩子开发准确的自动阅读评估系统面临着重大挑战,因为数据有限且儿童的声音具有独特的声学特性。这项研究专注于南非使用的语言——科萨语,以提升儿童语音识别能力。我们展示了一个由科萨语儿童语音样本组成的新数据集。该数据集可在请求后获得,包含十个单词和字母,这些单词和字母是初级阅读评估(EGRA)系统的一部分。每个录音都通过多个标记器以在线和低成本的方式进行标记,并由独立的EGRA审查者对样本进行验证。该数据集经过三种经过微调的最先进端到端模型的评估:wav2vec 2.0、HuBERT和Whisper。结果表明,这些模型的性能可能会受到可用训练数据量和平衡性的显著影响,这对于低成本大规模数据集收集至关重要。此外,我们的实验表明,即使在可用样本数量受限的情况下,通过一次训练多个类别也可以提高wav2vec 2.0的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted on AIED 2025 containing 14 pages, 6 figures and 4 tables
摘要
儿童识字能力对其后续生活阶段的影响具有显著预测作用,这突显了对脆弱低收入和中收入群体进行针对性干预的必要性,以帮助缩小这些地区与高收入地区识字水平的差距。阅读评估是衡量这些项目成效的重要工具,而人工智能可为教育工作者提供可靠且经济的支持。在为低资源语言开发准确的自动阅读评估系统时,由于数据有限以及儿童声音的独特声学特性,面临重大挑战。本研究关注南非使用的语言——科萨语,以提升儿童语音识别能力。我们提供了一份新数据集,其中包含科萨语儿童语音样本。该数据集经请求可获得,包含早期阅读能力评估系统中的十个单词和字母。每个记录都采用了在线经济的多重标记方法进行标注,并由独立的早期阅读能力评估审查者对样本进行了验证。该数据集经过wav2vec 2.0、HuBERT和Whisper三款先进的端到端模型的微调评估。结果表明,可用训练数据的质量和平衡性对这些模型的性能有重大影响,这对于经济的大规模数据集收集至关重要。此外,我们的实验表明,即使在可用样本数量有限的情况下,通过同时训练多个类别,wav2vec 2.0的性能也能得到提升。
关键见解
- 儿童识字能力对个体后续生活阶段的影响具有预测性。
- 需要针对脆弱低收入和中收入群体进行针对性的阅读干预。
- 阅读评估是衡量阅读项目效果的重要工具,AI可支持此任务。
- 开发自动阅读评估系统时面临数据限制和儿童声音独特性挑战。
- 科萨语儿童语音数据集用于提升语音识别能力研究。
- 数据集质量及平衡性对模型性能影响显著,强调大规模数据集收集的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

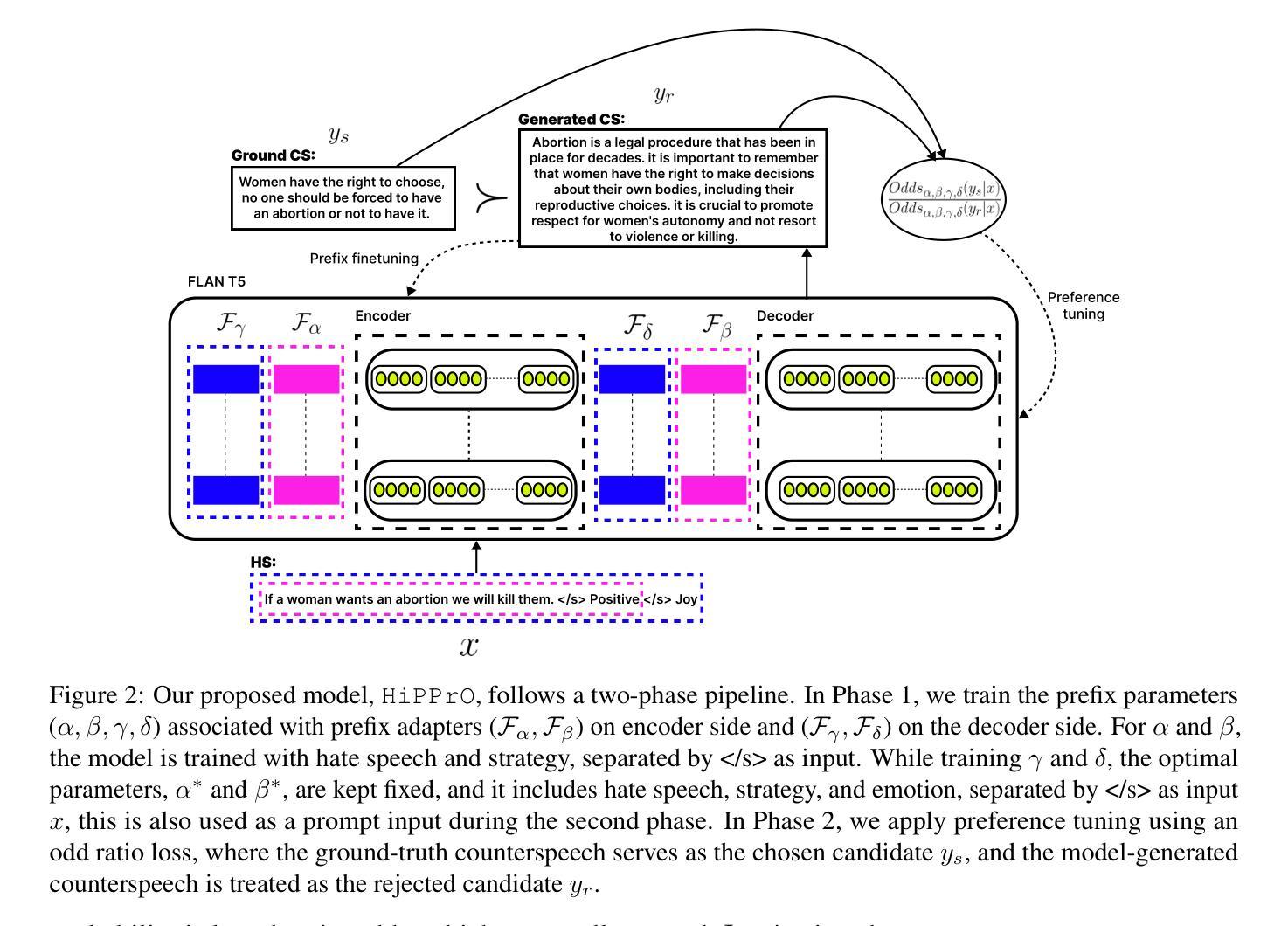
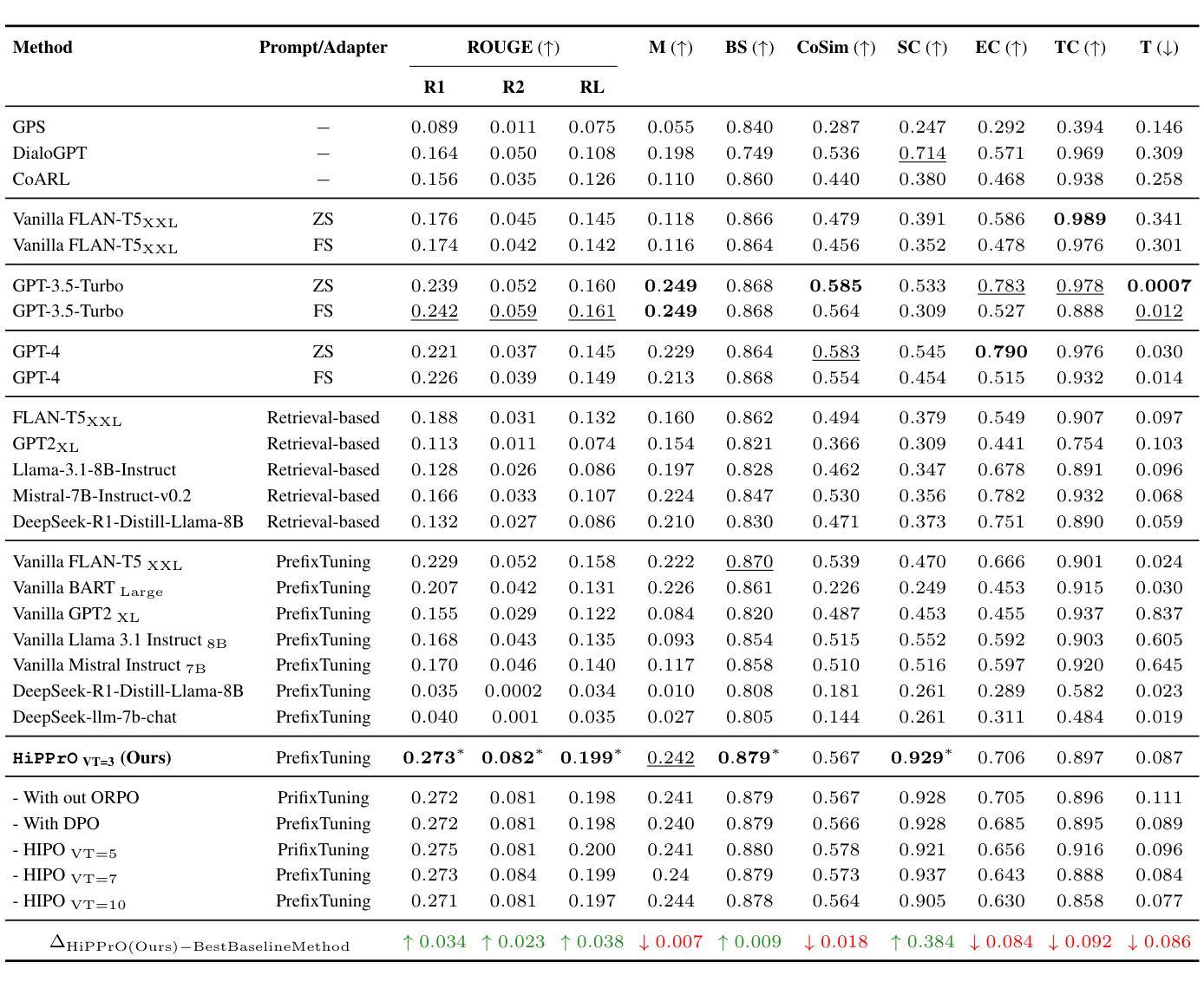
Counterspeech the ultimate shield! Multi-Conditioned Counterspeech Generation through Attributed Prefix Learning
Authors:Aswini Kumar, Anil Bandhakavi, Tanmoy Chakraborty
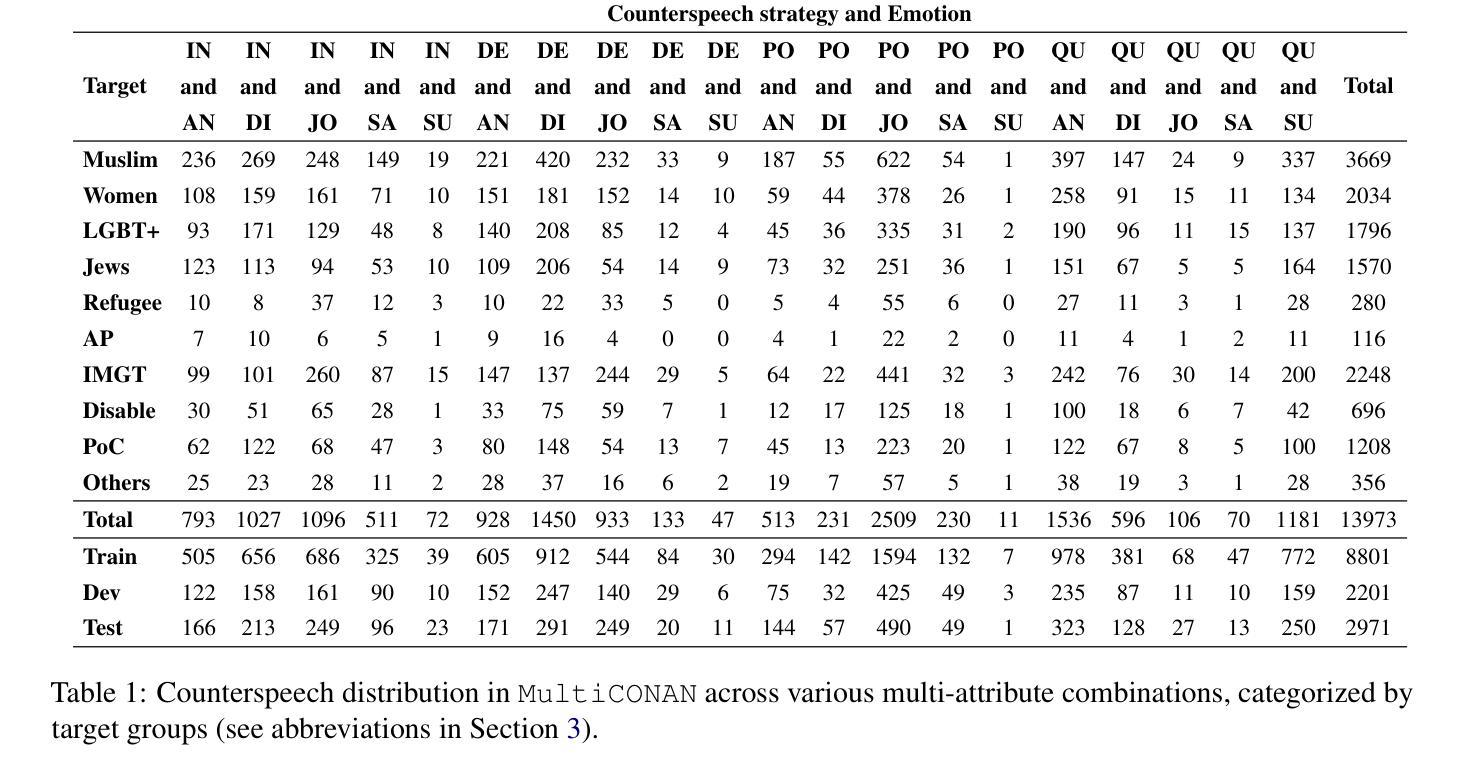
Counterspeech has proven to be a powerful tool to combat hate speech online. Previous studies have focused on generating counterspeech conditioned only on specific intents (single attributed). However, a holistic approach considering multiple attributes simultaneously can yield more nuanced and effective responses. Here, we introduce HiPPrO, Hierarchical Prefix learning with Preference Optimization, a novel two-stage framework that utilizes the effectiveness of attribute-specific prefix embedding spaces hierarchically optimized during the counterspeech generation process in the first phase. Thereafter, we incorporate both reference and reward-free preference optimization to generate more constructive counterspeech. Furthermore, we extend IntentCONANv2 by annotating all 13,973 counterspeech instances with emotion labels by five annotators. HiPPrO leverages hierarchical prefix optimization to integrate these dual attributes effectively. An extensive evaluation demonstrates that HiPPrO achieves a ~38 % improvement in intent conformity and a ~3 %, ~2 %, ~3 % improvement in Rouge-1, Rouge-2, and Rouge-L, respectively, compared to several baseline models. Human evaluations further substantiate the superiority of our approach, highlighting the enhanced relevance and appropriateness of the generated counterspeech. This work underscores the potential of multi-attribute conditioning in advancing the efficacy of counterspeech generation systems. Our code is available on Github and dataset is open-sourced on Hugging-face.
反话已被证明是打击网上仇恨言论的有力工具。以往的研究主要集中在仅针对特定意图(单一属性)生成反话。然而,同时考虑多个属性的整体方法可能会产生更微妙和有效的回应。在这里,我们介绍了HiPPrO,即带有偏好优化的分层前缀学习,这是一种新的两阶段框架,它利用属性特定前缀嵌入空间在反话生成过程中的分层优化效果。此后,我们将参考和无奖励偏好优化相结合,以生成更具建设性的反话。此外,我们对所有13973个反话实例进行了情感标签标注,由五位标注者完成。HiPPrO利用分层前缀优化有效地整合了这些双重属性。大量评估表明,与几个基准模型相比,HiPPrO在意图一致性上提高了约38%,在Rouge-1、Rouge-2和Rouge-L上分别提高了约3%、2%、3%。人类评估进一步证实了我们方法的优越性,突出了生成反话的相关性和适当性的提高。这项工作强调了多属性条件在提升反话生成系统效率方面的潜力。我们的代码已在Github上提供,数据集已在Hugging-face上开源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ACL 2025 Main Conference
Summary
本文介绍了对抗网络仇恨言论的有力工具——反话。以往的研究主要关注基于特定意图的反话生成,而本文提出一种综合考虑多种属性的全息方法,能生成更细腻和有效的回应。为此,本文引入HiPPrO框架,采用属性特定的前缀嵌入空间进行层次优化,生成更具建设性的反话。实验证明,HiPPrO在意图符合度上提高了约38%,在Rouge指标上也有显著提升。反话生成系统的多属性调节具有巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 反话是打击网络仇恨言论的有效工具。
- 以往研究主要关注基于单一意图的反话生成,本文提出综合考虑多种属性的全息方法。
- HiPPrO框架利用属性特定的前缀嵌入空间进行层次优化,生成更具建设性的反话。
- HiPPrO在意图符合度上较基线模型提高了约38%。
- 在Rouge指标上,HiPPrO较基线模型有显著提升。
- 人类评估进一步证明了HiPPrO方法的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

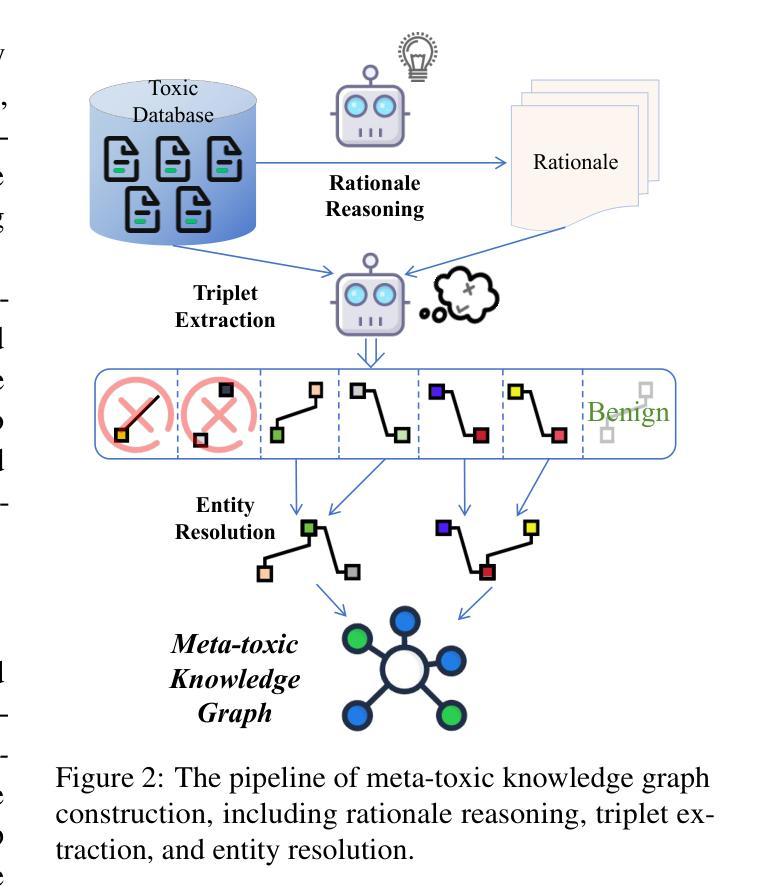
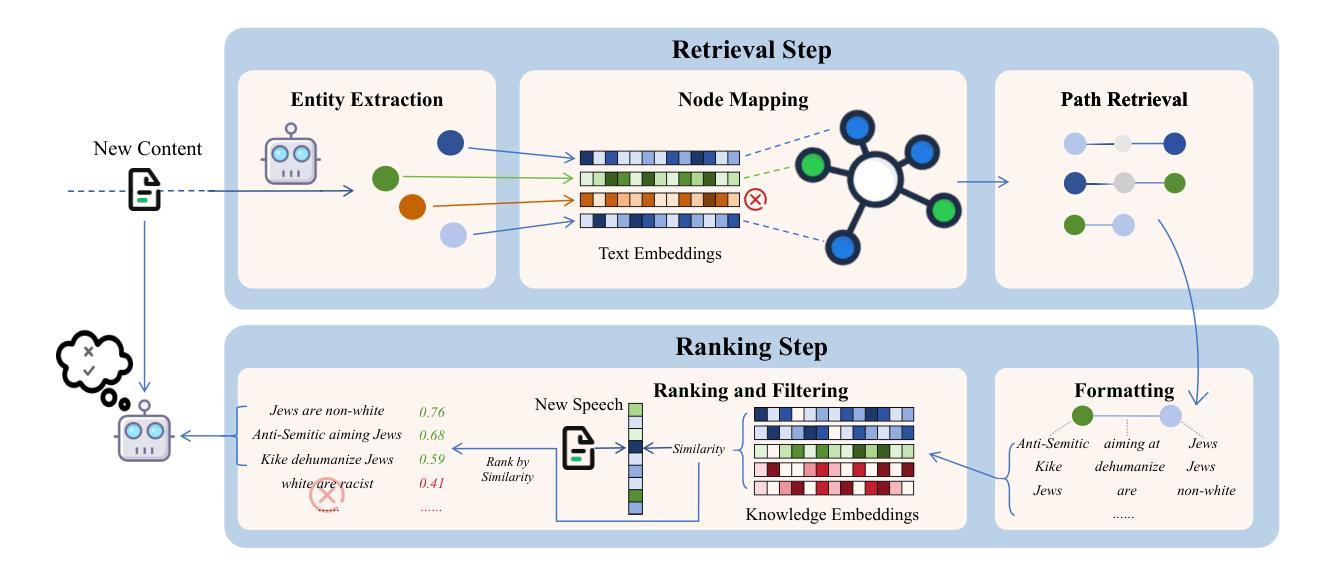
Enhancing LLM-based Hatred and Toxicity Detection with Meta-Toxic Knowledge Graph
Authors:Yibo Zhao, Jiapeng Zhu, Can Xu, Yao Liu, Xiang Li
The rapid growth of social media platforms has raised significant concerns regarding online content toxicity. When Large Language Models (LLMs) are used for toxicity detection, two key challenges emerge: 1) the absence of domain-specific toxic knowledge leads to false negatives; 2) the excessive sensitivity of LLMs to toxic speech results in false positives, limiting freedom of speech. To address these issues, we propose a novel method called MetaTox, leveraging graph search on a meta-toxic knowledge graph to enhance hatred and toxicity detection. First, we construct a comprehensive meta-toxic knowledge graph by utilizing LLMs to extract toxic information through a three-step pipeline, with toxic benchmark datasets serving as corpora. Second, we query the graph via retrieval and ranking processes to supplement accurate, relevant toxic knowledge. Extensive experiments and in-depth case studies across multiple datasets demonstrate that our MetaTox significantly decreases the false positive rate while boosting overall toxicity detection performance. Our code is available at https://github.com/YiboZhao624/MetaTox.
社交媒体平台的快速发展引发了人们对网络内容毒性的重大关注。当使用大型语言模型(LLM)进行毒性检测时,会出现两个关键挑战:1)缺乏特定领域的毒性知识会导致假阴性结果;2)LLM对有毒言论过于敏感,导致假阳性结果,限制言论自由。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种名为MetaTox的新方法,利用元毒性知识图谱上的图搜索来增强仇恨和毒性检测。首先,我们通过一个三步骤的管道,利用LLM提取毒性信息,以毒性基准数据集作为语料库,构建了一个全面的元毒性知识图谱。其次,我们通过检索和排名过程查询图谱,以补充准确且相关的毒性知识。在多个数据集上的广泛实验和深入案例研究表明,我们的MetaTox方法显著降低了误报率,同时提高了总体毒性检测性能。我们的代码可在[https://github.com/YiboZhao624/MetaTox获取。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages of content
Summary
社交媒体平台的快速发展引发了人们对网络内容毒性的关注。针对大型语言模型(LLMs)在毒性检测中的两大挑战,提出了一种新的方法MetaTox,利用元毒性知识图谱的图形搜索来增强仇恨和毒性检测。通过构建全面的元毒性知识图谱,以及通过查询图谱以补充准确且相关的毒性知识来解决这些问题。实验结果证明了MetaTox在降低误报率的同时,提高了毒性检测的总体性能。
Key Takeaways
- 社交媒体内容的毒性检测面临两大挑战:缺乏领域特定的毒性知识和过度敏感导致的误报。
- 提出了一种新的方法MetaTox,利用元毒性知识图谱的图形搜索增强毒性检测。
- MetaTox通过构建全面的元毒性知识图谱来解决缺乏领域特定知识的问题。
- 通过查询知识图谱来补充准确且相关的毒性知识,以提高检测准确性并降低误报率。
- MetaTox能够显著降低误报率,同时提高毒性检测的总体性能。
- 进行了大量的实验和深入的案例研究,证明了MetaTox的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Generative Modeling with Residual Vector Quantization-Based Tokens
Authors:Jaehyeon Kim, Taehong Moon, Keon Lee, Jaewoong Cho
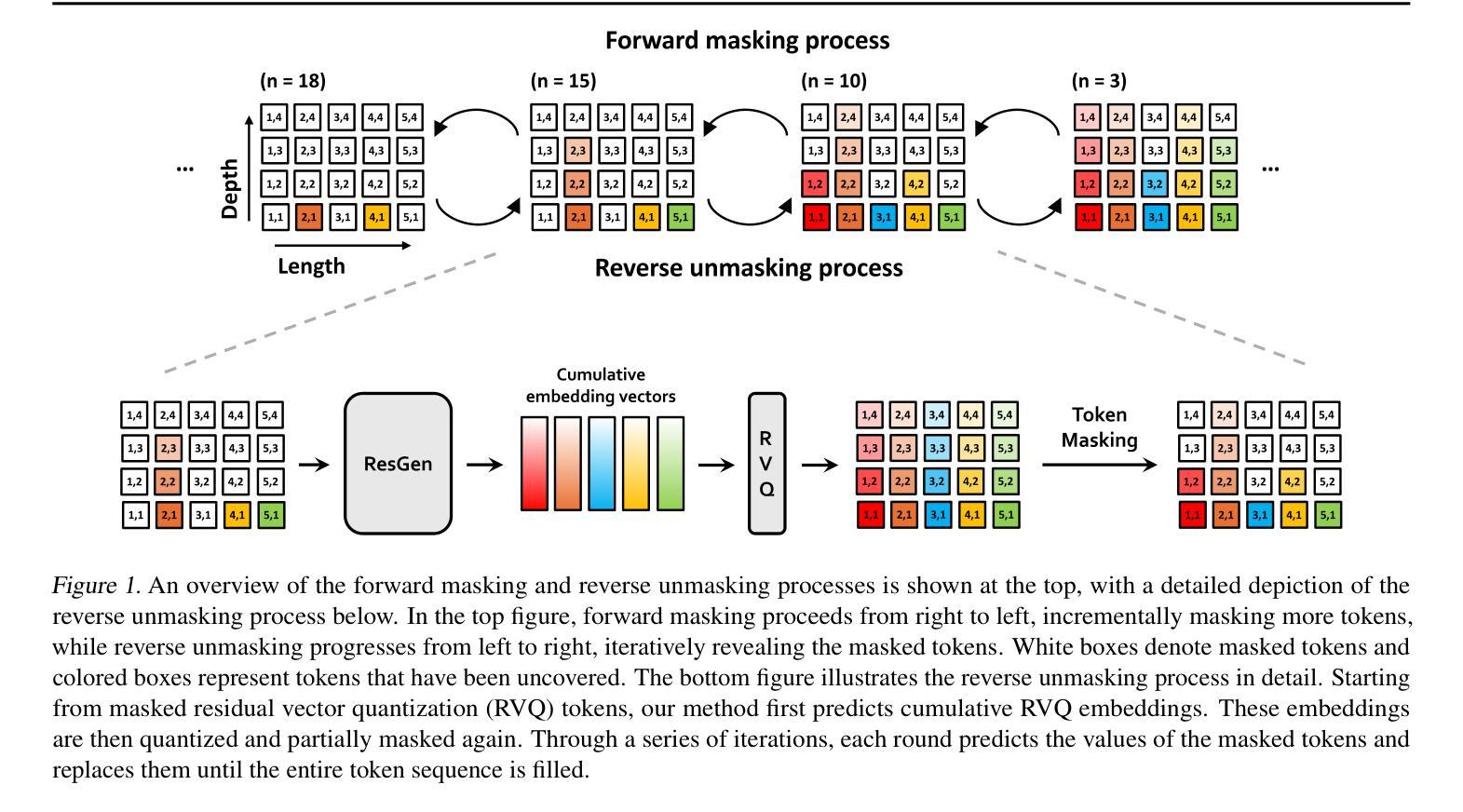
We introduce ResGen, an efficient Residual Vector Quantization (RVQ)-based generative model for high-fidelity generation with fast sampling. RVQ improves data fidelity by increasing the number of quantization steps, referred to as depth, but deeper quantization typically increases inference steps in generative models. To address this, ResGen directly predicts the vector embedding of collective tokens rather than individual ones, ensuring that inference steps remain independent of RVQ depth. Additionally, we formulate token masking and multi-token prediction within a probabilistic framework using discrete diffusion and variational inference. We validate the efficacy and generalizability of the proposed method on two challenging tasks across different modalities: conditional image generation on ImageNet 256x256 and zero-shot text-to-speech synthesis. Experimental results demonstrate that ResGen outperforms autoregressive counterparts in both tasks, delivering superior performance without compromising sampling speed. Furthermore, as we scale the depth of RVQ, our generative models exhibit enhanced generation fidelity or faster sampling speeds compared to similarly sized baseline models.
我们介绍了ResGen,这是一种基于高效的残差矢量量化(RVQ)的生成模型,用于高保真生成和快速采样。RVQ通过增加量化步骤的数量(称为深度)来提高数据保真度,但更深的量化通常会增加生成模型中的推理步骤。为了解决这一问题,ResGen直接预测集体标记的向量嵌入,而不是单个标记的向量嵌入,从而确保推理步骤与RVQ深度无关。此外,我们利用离散扩散和变分推理,在概率框架下制定标记掩码和多标记预测。我们在不同模态的两个具有挑战性的任务上验证了所提出方法的有效性和通用性:ImageNet 256x256上的条件图像生成和零样本文本到语音的合成。实验结果表明,ResGen在这两个任务上的表现均优于自回归模型,在不影响采样速度的情况下实现了卓越的性能。此外,随着我们扩展RVQ的深度,我们的生成模型与类似规模的基准模型相比,表现出更高的生成保真度或更快的采样速度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
ResGen是一种基于Residual Vector Quantization(RVQ)的高效生成模型,可实现高保真生成和快速采样。它通过增加量化步骤的数量(称为深度)来提高数据保真度,而无需增加推理步骤。ResGen直接预测集体标记的向量嵌入,而不是单独的标记,确保了推理步骤与RVQ深度无关。此外,它在概率框架下制定了标记掩码和多标记预测,采用离散扩散和变分推断方法。在ImageNet 256x256上的条件图像生成和零样本文本到语音合成等任务上验证了该方法的有效性和通用性。实验结果表明,ResGen在性能上优于自回归模型,提高了生成保真度或更快的采样速度。
Key Takeaways
- ResGen是一个基于Residual Vector Quantization(RVQ)的生成模型,可实现高保真生成和快速采样。
- RVQ通过增加量化步骤的数量提高了数据保真度,而ResGen的设计保证了推理步骤与量化深度无关。
- ResGen直接预测集体标记的向量嵌入,提高了模型效率。
- 该模型采用概率框架进行标记掩码和多标记预测,结合离散扩散和变分推断方法。
- 在条件图像生成和零样本文本到语音合成任务上,ResGen表现出优越的性能。
- ResGen相较于自回归模型,能够提高生成保真度或加快采样速度。
点此查看论文截图

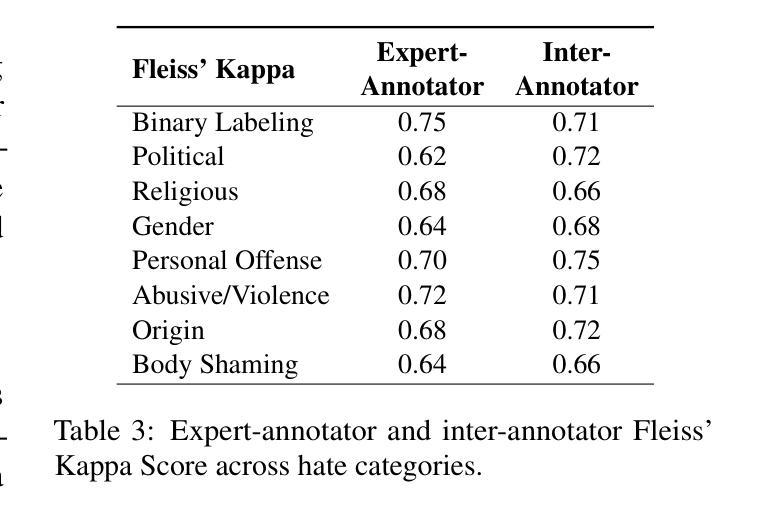
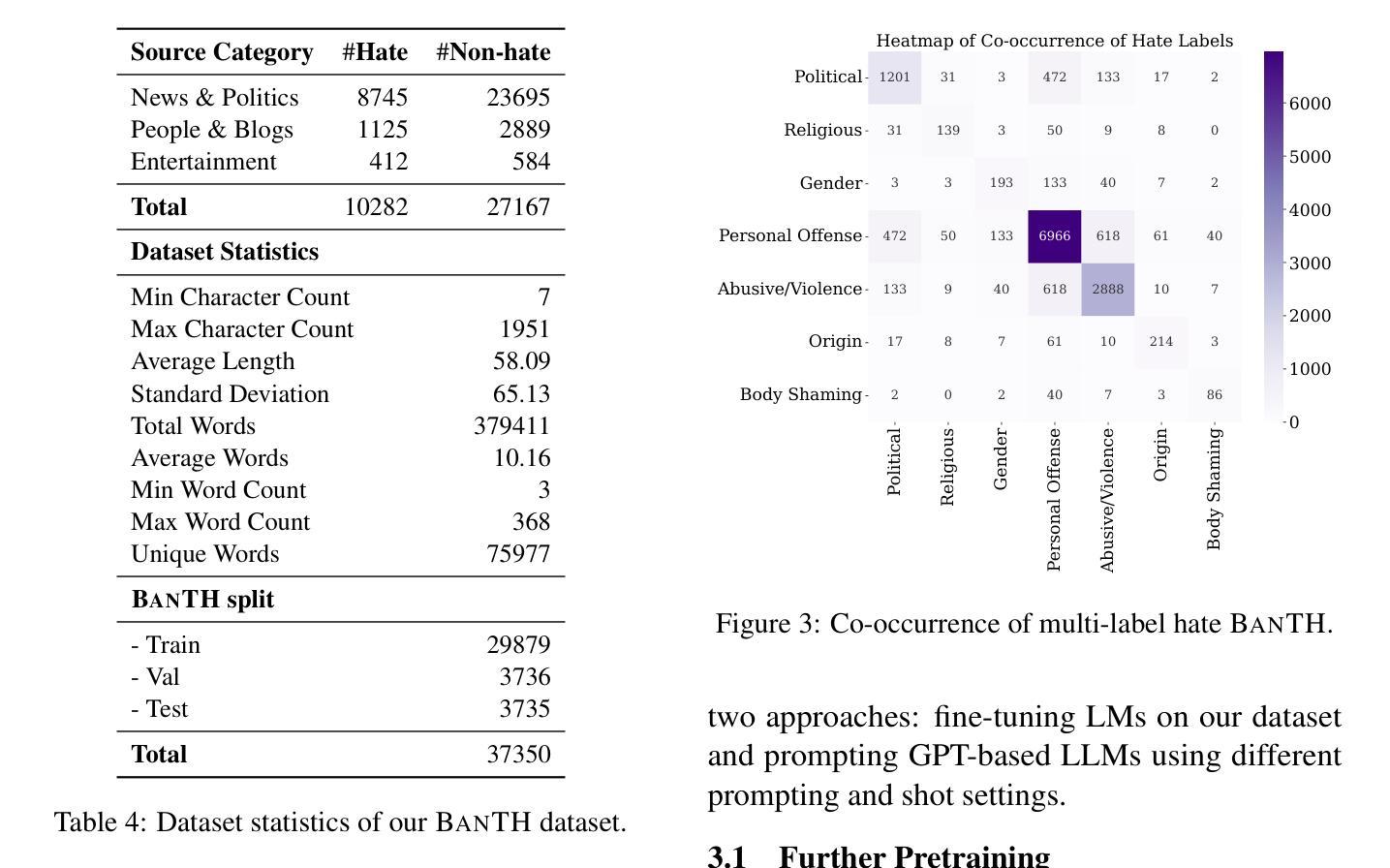
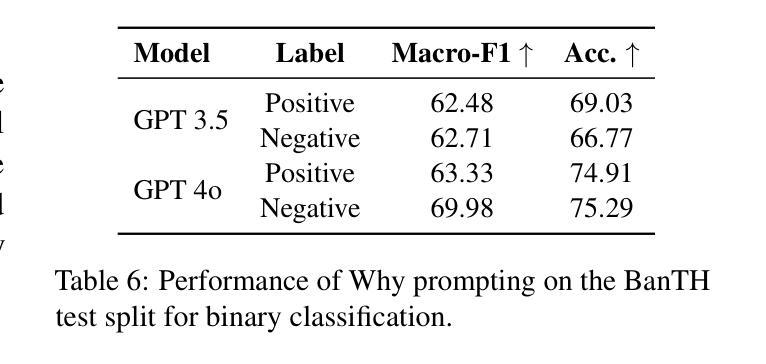
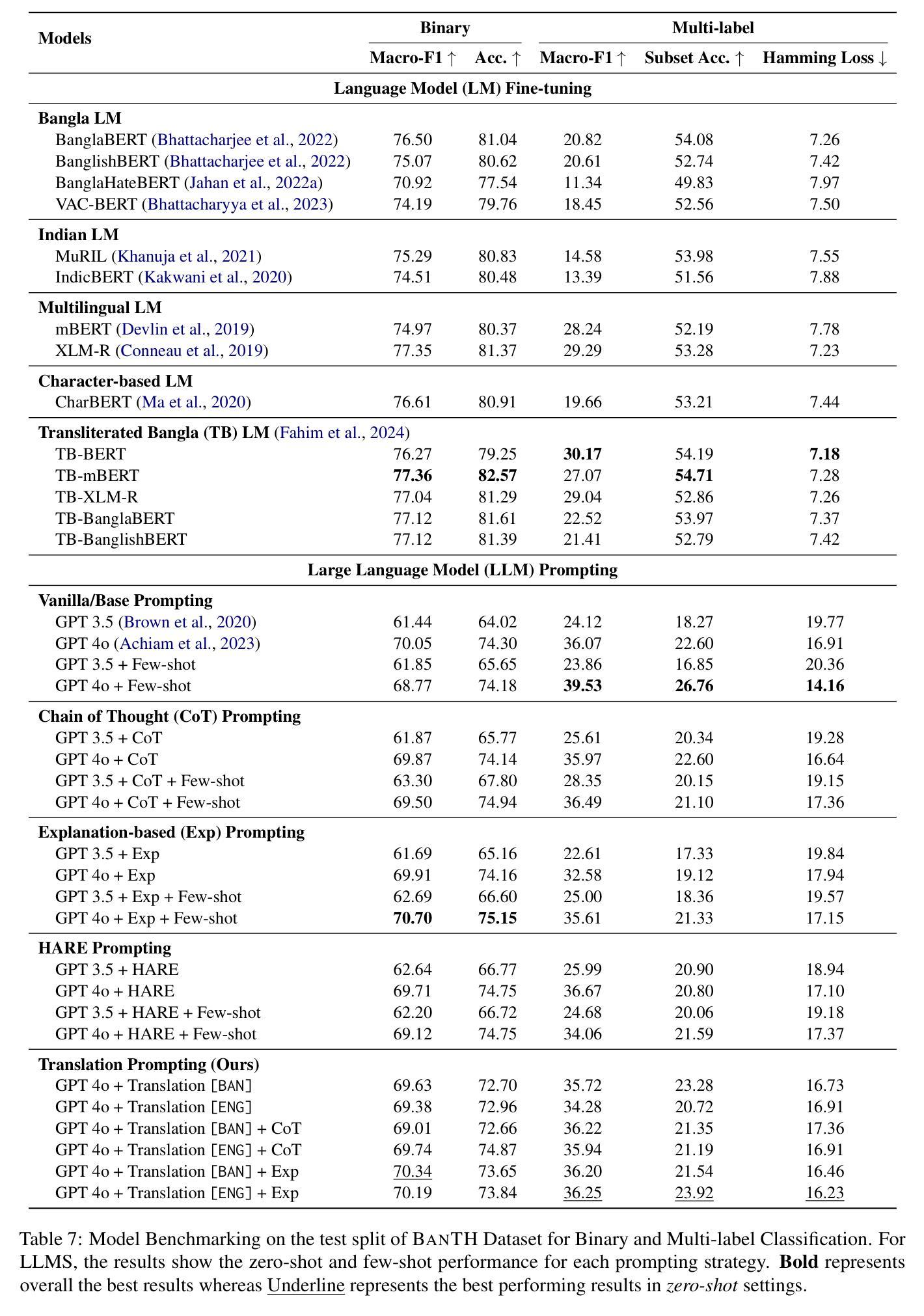
BanTH: A Multi-label Hate Speech Detection Dataset for Transliterated Bangla
Authors:Fabiha Haider, Fariha Tanjim Shifat, Md Farhan Ishmam, Deeparghya Dutta Barua, Md Sakib Ul Rahman Sourove, Md Fahim, Md Farhad Alam
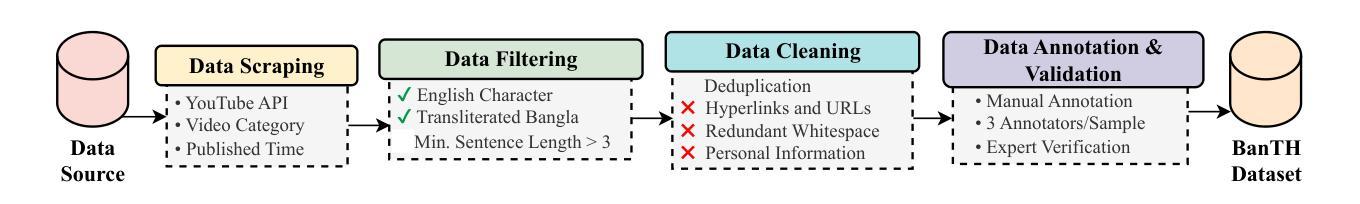
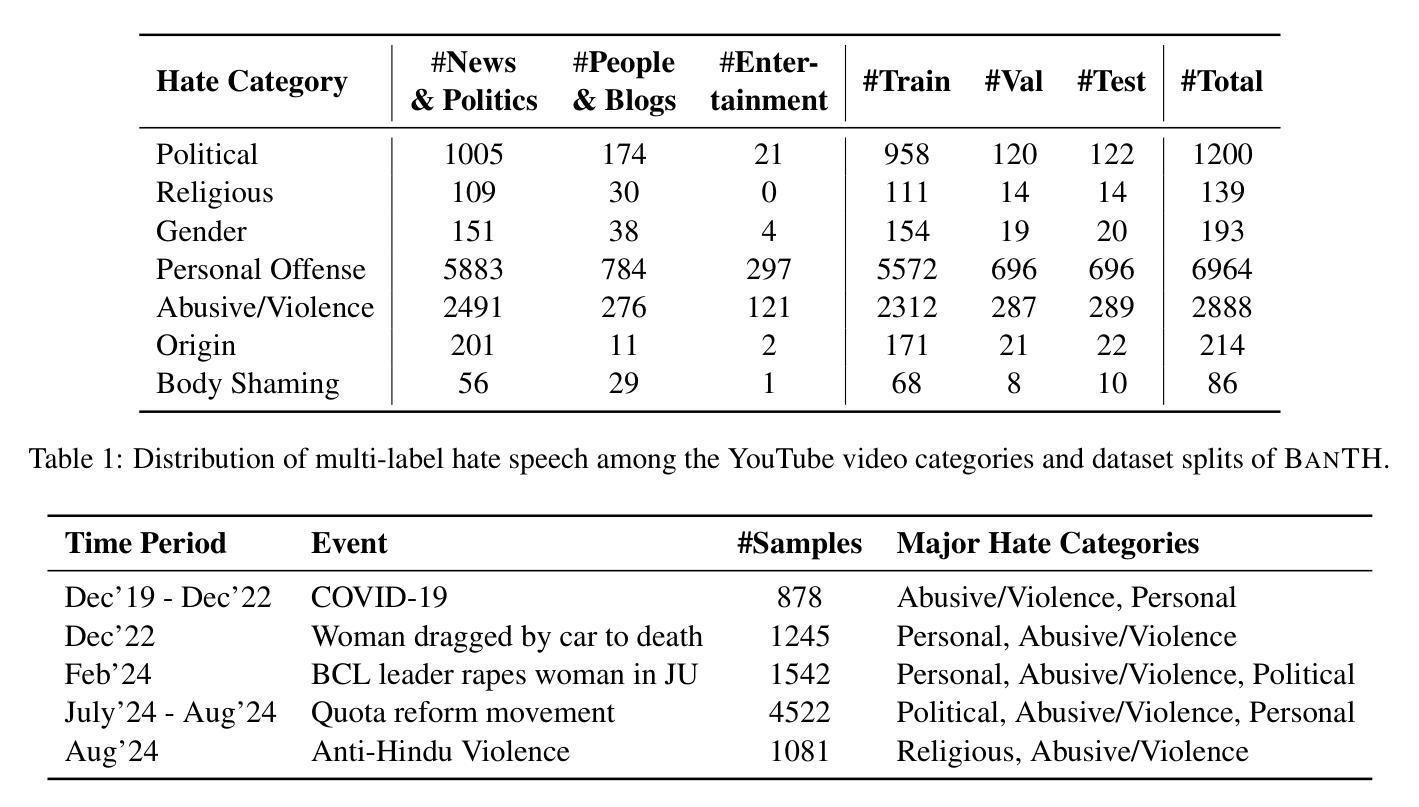
The proliferation of transliterated texts in digital spaces has emphasized the need for detecting and classifying hate speech in languages beyond English, particularly in low-resource languages. As online discourse can perpetuate discrimination based on target groups, e.g. gender, religion, and origin, multi-label classification of hateful content can help in comprehending hate motivation and enhance content moderation. While previous efforts have focused on monolingual or binary hate classification tasks, no work has yet addressed the challenge of multi-label hate speech classification in transliterated Bangla. We introduce BanTH, the first multi-label transliterated Bangla hate speech dataset comprising 37.3k samples. The samples are sourced from YouTube comments, where each instance is labeled with one or more target groups, reflecting the regional demographic. We establish novel transformer encoder-based baselines by further pre-training on transliterated Bangla corpus. We also propose a novel translation-based LLM prompting strategy for transliterated text. Experiments reveal that our further pre-trained encoders are achieving state-of-the-art performance on the BanTH dataset, while our translation-based prompting outperforms other strategies in the zero-shot setting. The introduction of BanTH not only fills a critical gap in hate speech research for Bangla but also sets the stage for future exploration into code-mixed and multi-label classification challenges in underrepresented languages.
数字空间中音译文本的激增强调了检测和非英语语言的仇恨言论分类的需求,特别是在资源较少的语言中。由于在线言论可能会使基于目标群体的歧视永久化,例如性别、宗教和出身等,仇恨内容的多标签分类有助于理解仇恨动机并增强内容管理。虽然以前的研究主要集中于单语或二元仇恨分类任务,但尚未有工作在音译孟加拉语的多标签仇恨言论分类方面提出挑战。我们介绍了BanTH,这是第一个多标签音译孟加拉仇恨言论数据集,包含37.3k样本。这些样本来源于YouTube评论,每个实例都被标记为一个或多个目标群体,反映了地区人口状况。我们通过进一步在音译孟加拉语料库上进行预训练,建立了基于新型转换器编码器的基线。我们还提出了一种基于翻译的大型语言模型提示策略,用于处理音译文本。实验表明,我们的进一步预训练编码器在BanTH数据集上达到了最先进的性能,而在零样本设置中,我们的基于翻译的方法的提示效果优于其他策略。BanTH的引入不仅填补了孟加拉仇恨言论研究中的关键空白,而且为探索未来低代表性语言的混合代码和多标签分类挑战奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in NAACL Findings 2025
Summary
随着数字空间中转译文本的普及,对非英语语言的仇恨言论检测和分类变得尤为重要,尤其是在资源较少的语言中。多标签仇恨内容分类有助于理解仇恨动机并增强内容管理。目前尚未有针对转译孟加拉语的多标签仇恨言论分类挑战的工作。我们引入了BanTH,首个多标签转译孟加拉语仇恨言论数据集,包含37.3k样本。样本来源于YouTube评论,每个实例都被标记为一个或多个目标群体,反映了区域人口统计特征。我们建立了基于转换器编码器的新基线,通过转译孟加拉语语料库进行进一步预训练。我们还提出了一种基于翻译的大型语言模型提示策略。实验表明,我们的进一步预训练编码器在BanTH数据集上实现了最新技术性能,而我们的基于翻译提示的策略在零样本设置中表现优于其他策略。BanTH的引入不仅填补了孟加拉语仇恨言论研究中的关键空白,而且为探索代码混合和多标签分类挑战在代表性不足的语言中奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 转译文本的普及强调了对非英语语言的仇恨言论检测与分类的必要性。
- 多标签仇恨内容分类有助于理解仇恨动机并增强内容管理。
- 目前尚未有针对转译孟加拉语的多标签仇恨言论分类研究。
- 引入了首个多标签转译孟加拉语仇恨言论数据集BanTH,包含37.3k样本。
- 样本来源于YouTube评论,反映区域人口特征。
- 建立了基于转换器编码器的基线模型,通过进一步预训练提升性能。
- 提出了基于翻译的大型语言模型提示策略,并在零样本设置中表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图


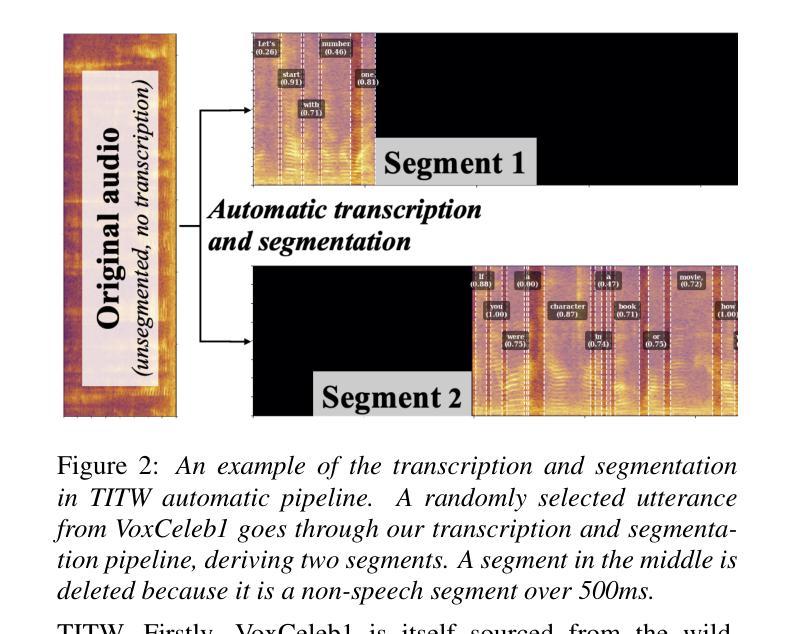
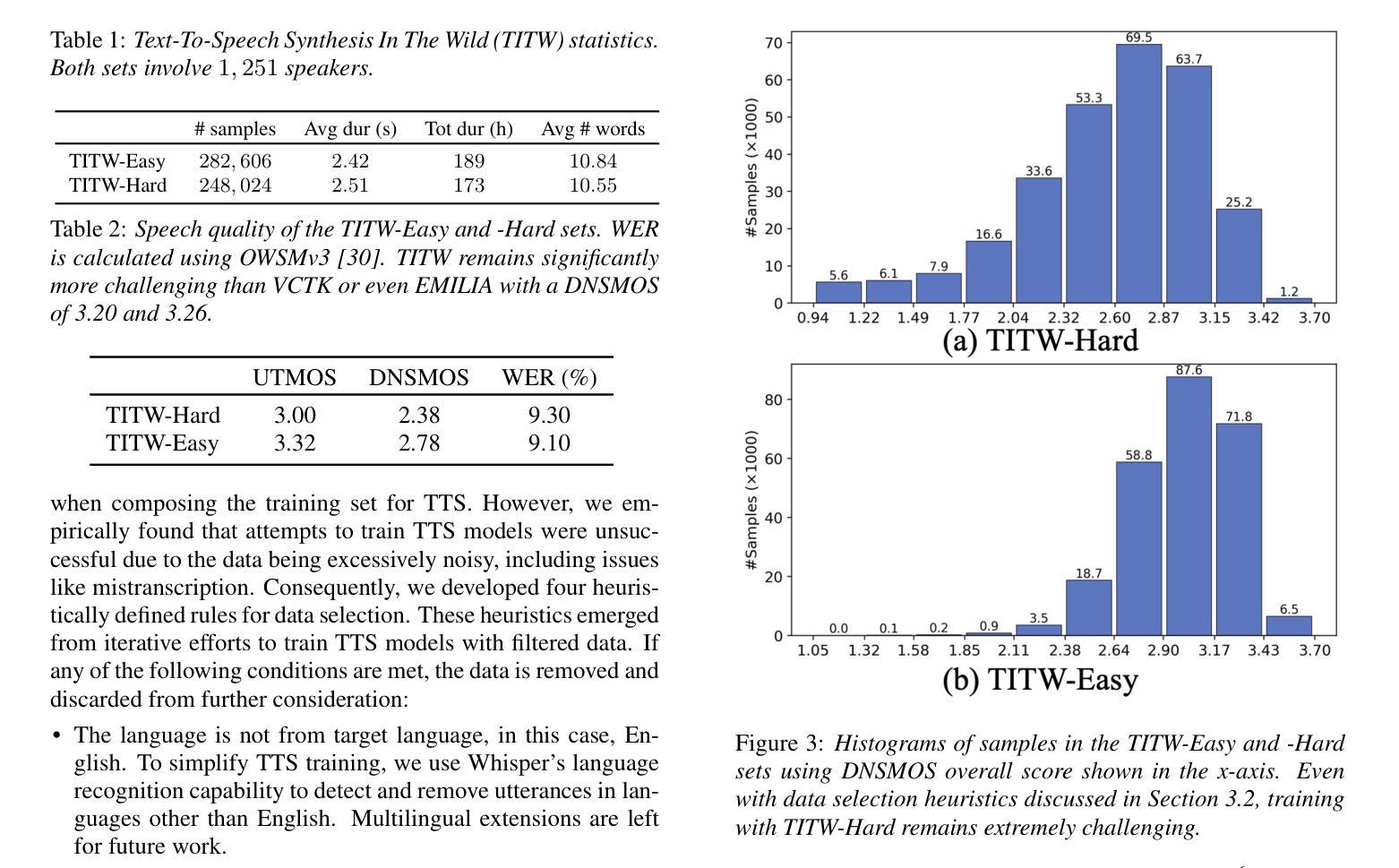
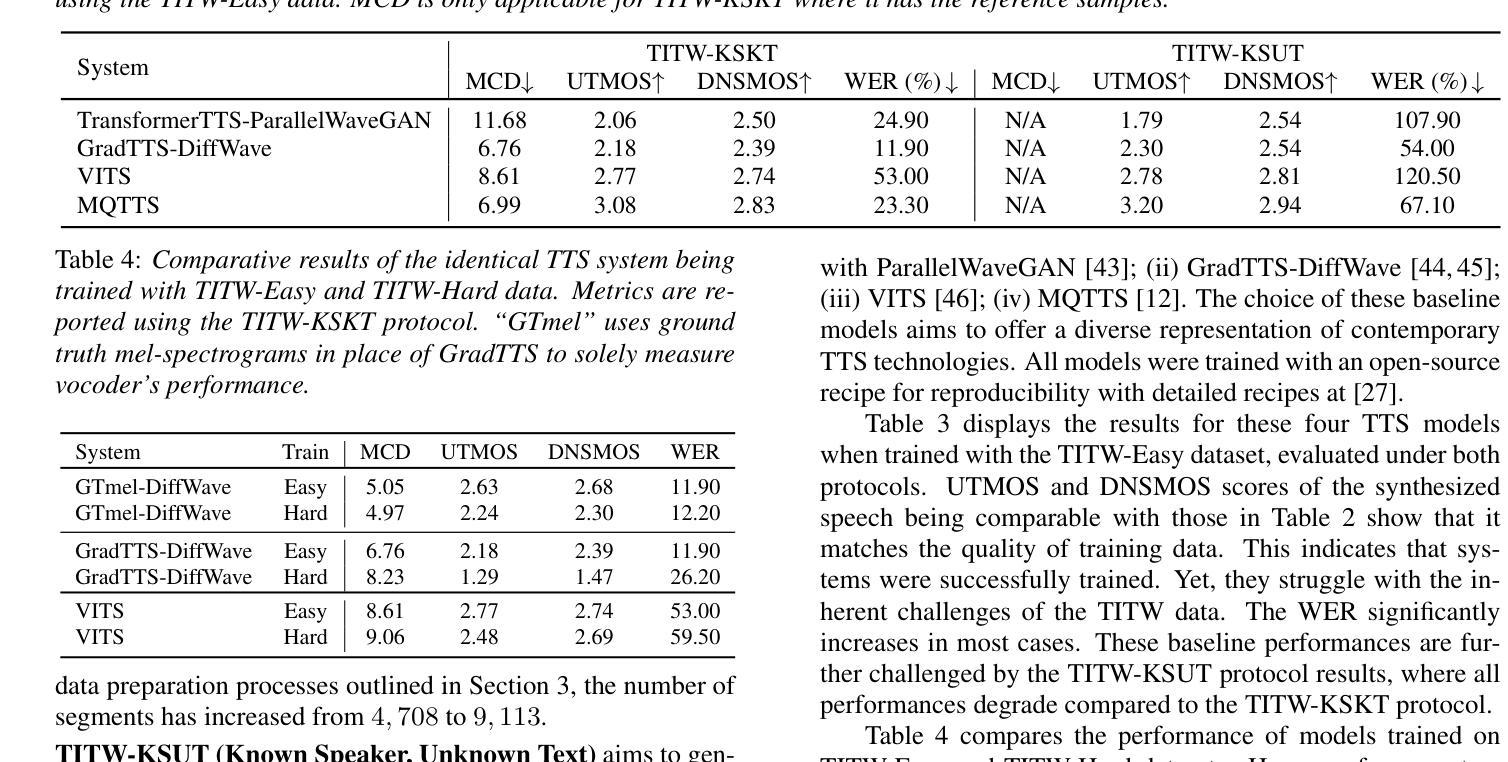
Text-To-Speech Synthesis In The Wild
Authors:Jee-weon Jung, Wangyou Zhang, Soumi Maiti, Yihan Wu, Xin Wang, Ji-Hoon Kim, Yuta Matsunaga, Seyun Um, Jinchuan Tian, Hye-jin Shim, Nicholas Evans, Joon Son Chung, Shinnosuke Takamichi, Shinji Watanabe
Traditional Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems rely on studio-quality speech recorded in controlled settings.a Recently, an effort known as noisy-TTS training has emerged, aiming to utilize in-the-wild data. However, the lack of dedicated datasets has been a significant limitation. We introduce the TTS In the Wild (TITW) dataset, which is publicly available, created through a fully automated pipeline applied to the VoxCeleb1 dataset. It comprises two training sets: TITW-Hard, derived from the transcription, segmentation, and selection of raw VoxCeleb1 data, and TITW-Easy, which incorporates additional enhancement and data selection based on DNSMOS. State-of-the-art TTS models achieve over 3.0 UTMOS score with TITW-Easy, while TITW-Hard remains difficult showing UTMOS below 2.8.
传统文本转语音(TTS)系统依赖于受控环境下的高质量语音录制。近期,一种被称为噪声TTS训练的研究方法应运而生,旨在利用野外数据。然而,缺乏专用数据集是一个重大限制。我们引入了野外文本转语音(TITW)数据集,该数据集是公开的,通过应用于VoxCeleb1数据集的完全自动化管道创建。它包含两个训练集:TITW-Hard,通过对原始VoxCeleb1数据进行转录、分段和选择而生成;TITW-Easy则基于DNSMOS进行额外的增强和数据选择。最新的TTS模型在TITW-Easy上取得了超过3.0的UTMOS分数,而TITW-Hard仍然具有挑战性,UTMOS低于2.8。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, Interspeech 2025
摘要
传统文本转语音(TTS)系统依赖于在受控环境中录制的语音数据。近期,一种名为噪声TTS训练的研究努力已经出现,旨在利用野外数据。然而,缺乏专用数据集一直是其重要限制。我们引入了野外文本转语音(TITW)数据集,该数据集已公开可用,通过对VoxCeleb1数据集应用全自动管道创建而成。它包含两个训练集:TITW-Hard,由VoxCeleb1原始数据的转录、分段和选择得出;TITW-Easy则基于DNSMOS进行了额外的增强和数据选择。使用TITW-Easy的最新TTS模型UTMOS得分超过3.0,而TITW-Hard仍然具有挑战性,UTMOS低于2.8。
要点提炼
- 传统TTS系统依赖受控环境中的高质量语音数据。
- 噪声TTS训练旨在利用野外数据。
- 缺乏专用数据集是噪声TTS训练的一个重要限制。
- 引入了TITW数据集,该数据集通过全自动管道从VoxCeleb1创建而成。
- TITW数据集包含两个训练集:TITW-Hard和TITW-Easy。
- TITW-Easy基于DNSMOS进行了额外的增强和数据选择。
- 最新TTS模型在TITW-Easy上的UTMOS得分超过3.0,而TITW-Hard具有挑战性,UTMOS低于2.8。
点此查看论文截图

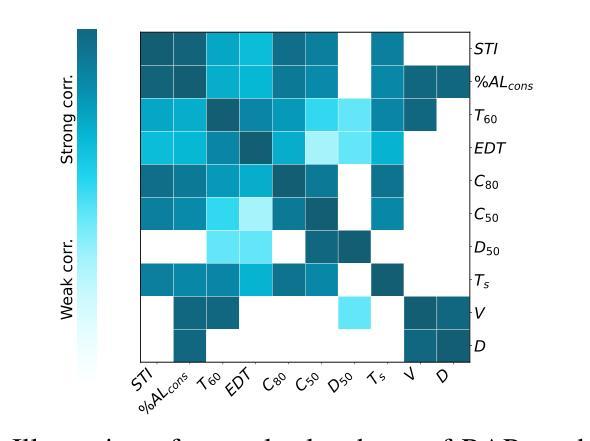
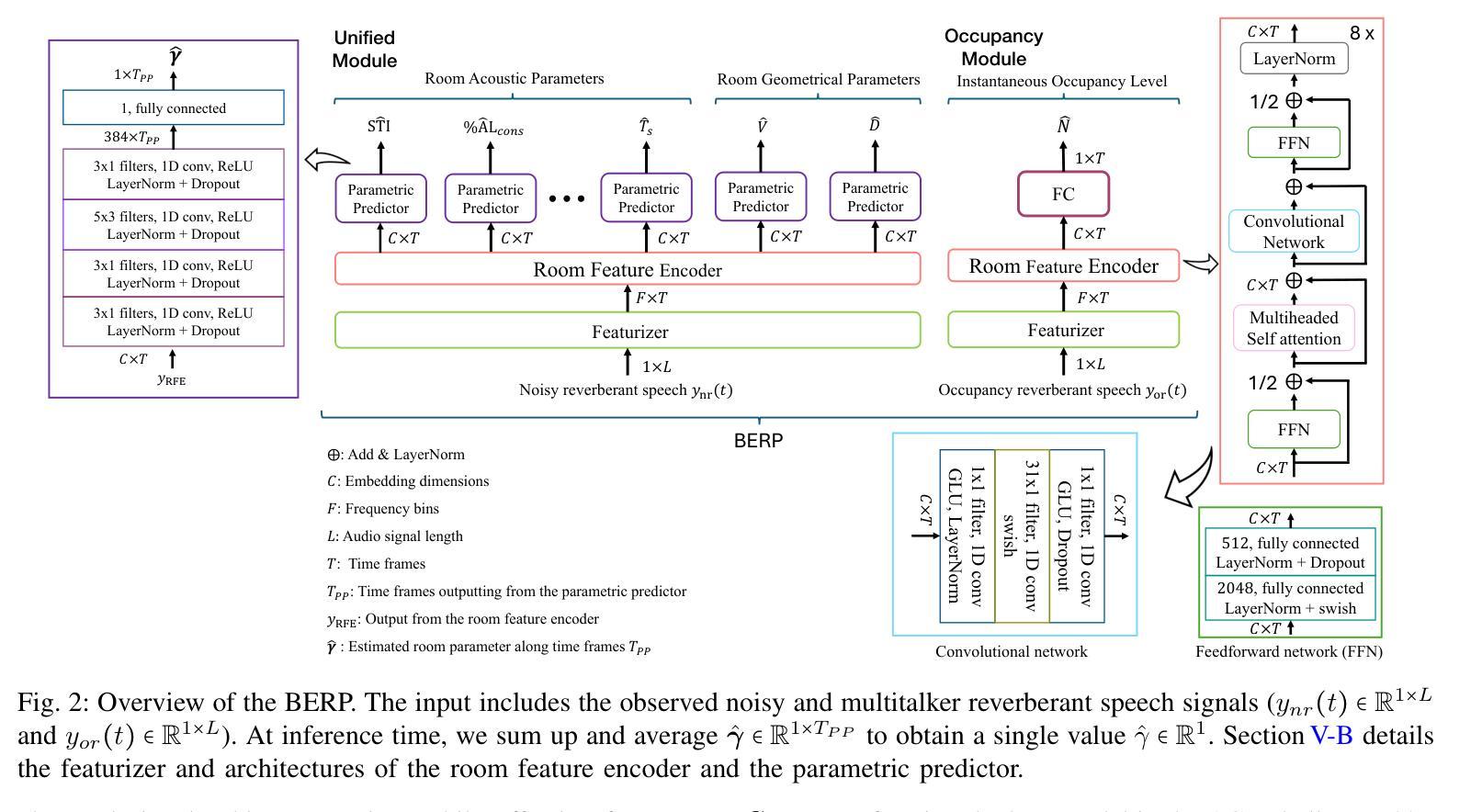
BERP: A Blind Estimator of Room Parameters for Single-Channel Noisy Speech Signals
Authors:Lijun Wang, Yixian Lu, Ziyan Gao, Kai Li, Jianqiang Huang, Yuntao Kong, Shogo Okada
Room acoustical parameters (RAPs), room geometrical parameters (RGPs) and instantaneous occupancy level are essential metrics for parameterizing the room acoustical characteristics (RACs) of a sound field around a listener’s local environment, offering comprehensive indications for various applications. Current blind estimation methods either fail to cover a broad range of real-world acoustic environments in the context of real background noise or estimate only a few RAPs and RGPs from noisy single-channel speech signals. In addition, they are limited in their ability to estimate the instantaneous occupancy level. In this paper, we propose a new universal blind estimation framework called the blind estimator of room parameters (BERP) to estimate RAPs, RGPs and occupancy level via a unified methodology. It consists of two modules: a unified room feature encoder that combines attention mechanisms with convolutional layers to learn common features across room parameters, and multiple separate parametric predictors for continuous estimation of each parameter in parallel. The combination of attention and convolutions enables the model to capture acoustic features locally and globally from speech, yielding more robust and multitask generalizable common features. Separate predictors allow the model to independently optimize for each room parameter to reduce task learning conflict and improve per-task performance. This estimation framework enables universal and efficient estimation of room parameters while maintaining satisfactory performance. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed framework, we compile a task-specific dataset from several publicly available datasets, including synthetic and real reverberant recordings. The results reveal that BERP achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance and excellent adaptability to real-world scenarios. The code and weights are available on GitHub.
房间声学参数(RAPs)、房间几何参数(RGPs)和瞬时占用水平是表征听众周围声音场的环境声学特性(RACs)的重要指标,为各种应用提供了全面的指示。当前的盲估计方法要么无法覆盖真实背景噪声环境中的广泛现实世界声学环境,要么只能从嘈杂的单通道语音信号中估计出一些RAPs和RGPs。此外,它们在估计瞬时占用水平方面的能力也有限。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的通用盲估计框架,称为房间参数盲估计器(BERP),通过统一的方法估计RAPs、RGPs和占用水平。它由两个模块组成:一个统一房间特征编码器,它将注意力机制与卷积层相结合,以学习房间参数之间的共同特征;以及多个单独的参数预测器,用于并行连续估计每个参数。注意力和卷积的结合使模型能够从语音中捕获局部和全局的声学特征,从而产生更稳健、多任务通用的共同特征。单独的预测器允许模型针对每个房间参数进行独立优化,以减少任务学习冲突并提高每项任务的性能。该估计框架能够在保持令人满意性能的同时,实现房间参数的通用和有效估计。为了评估所提出框架的有效性,我们从几个公开可用的数据集(包括合成和真实的混响录音)中编制了一个特定任务的数据集。结果表明,BERP达到了最先进的性能,并且对真实世界场景具有出色的适应性。代码和权重可在GitHub上获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16-page with supplementary materials, Accepted to IEEE Transaction on Audio Speech and Language Processing (TASLP 2025)
Summary
本文提出了一种名为BERP(房间参数盲估计器)的新通用盲估计框架,用于估计房间的声学参数(RAPs)、几何参数(RGPs)和瞬时占用级别。该框架通过结合注意力机制和卷积层,学习房间参数的通用特征,并分别对每个参数进行并行连续估计。该框架能够实现房间参数的通用和高效估计,同时保持令人满意的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 房间声学参数(RAPs)和房间几何参数(RGPs)是描述声音场特性的关键指标。
- 当前盲估计方法无法覆盖广泛的实际声学环境或仅能从带噪声的单通道语音信号中估计有限的RAPs和RGPs。
- BERP框架结合了注意力机制和卷积层,可以本地和全局捕捉语音的声学特征。
- 通过独立优化每个房间参数,BERP减少了任务学习冲突并提高了每个任务性能。
- BERP框架在任务专用数据集上的性能达到最新水平,并具有良好的适应真实世界场景的能力。
- BERP代码和权重已发布在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图

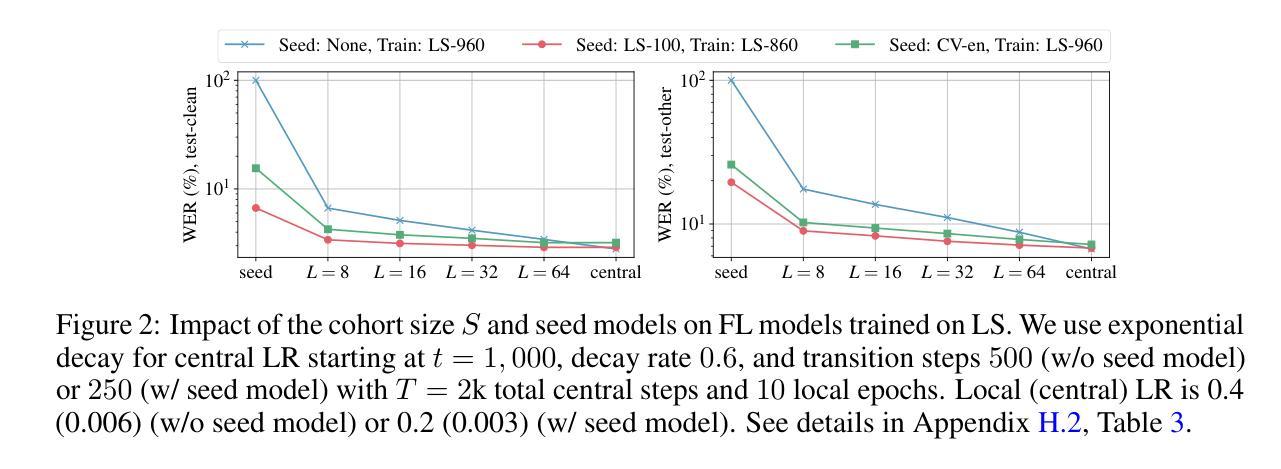
Enabling Differentially Private Federated Learning for Speech Recognition: Benchmarks, Adaptive Optimizers and Gradient Clipping
Authors:Martin Pelikan, Sheikh Shams Azam, Vitaly Feldman, Jan “Honza” Silovsky, Kunal Talwar, Christopher G. Brinton, Tatiana Likhomanenko
While federated learning (FL) and differential privacy (DP) have been extensively studied, their application to automatic speech recognition (ASR) remains largely unexplored due to the challenges in training large transformer models. Specifically, large models further exacerbate issues in FL as they are particularly susceptible to gradient heterogeneity across layers, unlike the relatively uniform gradient behavior observed in shallow models. As a result, prior works struggle to converge with standard optimization techniques, even in the absence of DP mechanisms. To the best of our knowledge, no existing work establishes a competitive, practical recipe for FL with DP in the context of ASR. To address this gap, we establish \textbf{the first benchmark for FL with DP in end-to-end ASR}. Our approach centers on per-layer clipping and layer-wise gradient normalization: theoretical analysis reveals that these techniques together mitigate clipping bias and gradient heterogeneity across layers in deeper models. Consistent with these theoretical insights, our empirical results show that FL with DP is viable under strong privacy guarantees, provided a population of at least several million users. Specifically, we achieve user-level (7.2, $10^{-9}$)-DP (resp. (4.5, $10^{-9}$)-DP) with only a 1.3% (resp. 4.6%) absolute drop in word error rate when extrapolating to high (resp. low) population scales for FL with DP in ASR. Although our experiments focus on ASR, the underlying principles we uncover - particularly those concerning gradient heterogeneity and layer-wise gradient normalization - offer broader guidance for designing scalable, privacy-preserving FL algorithms for large models across domains.
尽管联邦学习(FL)和差分隐私(DP)已经得到了广泛的研究,但它们在实际语音识别(ASR)中的应用仍然在很大程度上未被探索,这是由于训练大型变压器模型带来的挑战。具体来说,大型模型会进一步加剧联邦学习的问题,因为它们特别容易受到各层梯度异质性的影响,这与浅层模型中观察到的相对统一的梯度行为形成对比。因此,先前的工作即使在没有任何DP机制的情况下,也很难用标准优化技术实现收敛。据我们所知,目前没有任何工作建立了在ASR背景下具有DP的FL的竞争性实用方案。为了弥补这一空白,我们为具有DP的FL在端到端的ASR中建立了第一个基准测试。我们的方法以每层剪裁和逐层梯度归一化为中心:理论分析表明,这些技术相结合减轻了深层模型中剪裁偏见和各层梯度的异质性。与这些理论见解一致,我们的实证结果表明,在强大的隐私保证下,具有DP的FL是可行的,前提是有至少数百万用户。具体来说,我们在用户层面实现了(7.2,10^-9)-DP(分别在高低用户群体规模外推时实现(4.5,10^-9)-DP),词汇错误率仅绝对下降1.3%(或4.6%)。尽管我们的实验专注于ASR,但我们所揭示的基本原理,特别是关于梯度异质性和逐层梯度归一化的原理,为设计跨领域的大型模型的隐私保护联邦学习算法提供了更广泛的指导。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
摘要
本文探索了联邦学习与差分隐私在自动语音识别中的应用,针对大型模型在联邦学习中的梯度异质性挑战,提出了基于每层裁剪和层间梯度归一化的方法。建立了一个具有差分隐私的联邦学习在端到端自动语音识别中的首个基准测试,并通过理论分析和实证研究验证了该方法的可行性。在强大的隐私保障下,该方法在至少数百万用户的情况下是可行的。在保护用户隐私的同时,对自动语音识别任务的影响较小。此外,文中揭示的梯度异质性和层间梯度归一化等原理为设计跨领域的大规模、隐私保护的联邦学习算法提供了更广泛的指导。
关键见解
- 联邦学习与差分隐私在自动语音识别中的应用仍存在差距,尤其是在训练大型模型方面的挑战。
- 大型模型在联邦学习中面临梯度异质性的问题,这与浅层模型中相对统一的梯度行为不同。
- 现有工作难以在标准优化技术下收敛,甚至在不存在差分隐私机制的情况下。
- 本文建立了首个在端到端自动语音识别中具有差分隐私的联邦学习基准测试。
- 通过每层裁剪和层间梯度归一化的方法,缓解了裁剪偏差和深层模型中的梯度异质性。
- 在强大的隐私保障下,该方法的可行性已经得到实证研究验证,并且在至少数百万用户的情况下,对用户级别的隐私保护表现良好。
- 本文揭示的原理,如梯度异质性和层间梯度归一化等,为设计跨领域的大规模、隐私保护的联邦学习算法提供了指导。
点此查看论文截图