⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-05 更新
Zero-Shot Tree Detection and Segmentation from Aerial Forest Imagery
Authors:Michelle Chen, David Russell, Amritha Pallavoor, Derek Young, Jane Wu
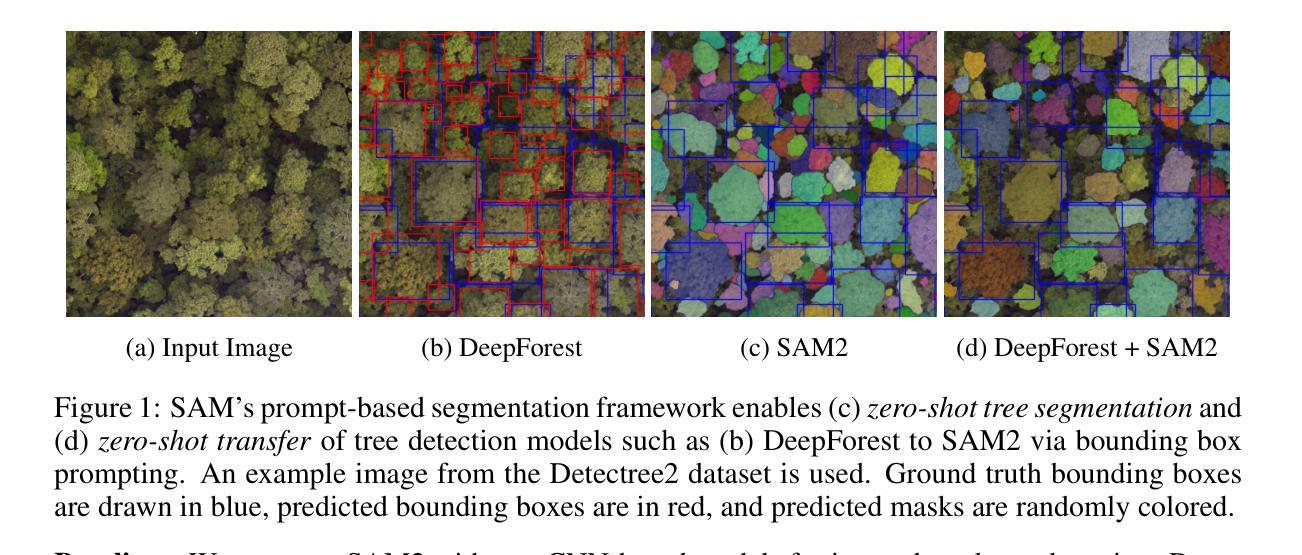
Large-scale delineation of individual trees from remote sensing imagery is crucial to the advancement of ecological research, particularly as climate change and other environmental factors rapidly transform forest landscapes across the world. Current RGB tree segmentation methods rely on training specialized machine learning models with labeled tree datasets. While these learning-based approaches can outperform manual data collection when accurate, the existing models still depend on training data that’s hard to scale. In this paper, we investigate the efficacy of using a state-of-the-art image segmentation model, Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2), in a zero-shot manner for individual tree detection and segmentation. We evaluate a pretrained SAM2 model on two tasks in this domain: (1) zero-shot segmentation and (2) zero-shot transfer by using predictions from an existing tree detection model as prompts. Our results suggest that SAM2 not only has impressive generalization capabilities, but also can form a natural synergy with specialized methods trained on in-domain labeled data. We find that applying large pretrained models to problems in remote sensing is a promising avenue for future progress. We make our code available at: https://github.com/open-forest-observatory/tree-detection-framework.
从遥感影像大规模勾画单棵树对于生态研究的进步至关重要,特别是随着气候变化和其他环境因素迅速改变全球森林景观。当前的RGB树分割方法依赖于使用带有标签的树数据集训练专门的机器学习模型。虽然这些基于学习的方法在准确时可以表现出超越手动数据收集的效能,但现有模型仍然依赖于难以扩展的训练数据。在本文中,我们调查了使用最先进的图像分割模型——Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)进行零样本个人树木检测和分割的效用。我们评估了预训练的SAM2模型在该领域的两个任务:(1)零样本分割和(2)使用现有树木检测模型的预测结果作为提示进行零样本迁移。我们的结果表明,SAM2不仅具有令人印象深刻的泛化能力,而且可以与在领域标签数据上训练的专用方法形成自然的协同作用。我们发现将大型预训练模型应用于遥感问题是一个很有前途的未来发展方向。我们的代码可在:https://github.com/open-forest-observatory/tree-detection-framework找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/open-forest-observatory/tree-detection-framework
Summary
在大规模遥感影像中精准勾画出树木个体对于生态研究至关重要,特别是随着气候变化和环境因素快速改变全球森林景观。当前RGB树分割方法依赖于使用标记树数据集训练专门的机器学习模型。虽然这些基于学习的方法在准确性方面可以超越手动数据收集,但现有模型仍然依赖于难以扩展的训练数据。本文调查了使用最新图像分割模型Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)进行零样本个人树木检测和分割的有效性。我们在两个任务上评估了预训练的SAM2模型:(1)零样本分割和(2)使用现有树木检测模型的预测结果作为提示进行零样本迁移。结果表明,SAM2不仅具有良好的泛化能力,而且可以与在域内标记数据上训练的专门方法形成自然协同。我们发现将大型预训练模型应用于遥感问题是一个值得未来关注的途径。我们提供的代码可以在https://github.com/open-forest-observatory/tree-detection-framework找到。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模从遥感影像中勾画树木对生态研究至关重要,尤其在气候变化影响森林景观的背景下。
- 当前RGB树分割方法依赖于训练有标签的机器学习模型,但这种方法难以扩展。
- Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2)模型在零样本个人树木检测和分割上表现出良好效果。
- SAM2模型具有显著泛化能力,并能与针对特定数据训练的专门方法协同工作。
- 使用预训练的的大型模型处理遥感问题是未来研究的一个有前途的方向。
- 本文评估了两种任务:零样本分割和零样本迁移,后者通过使用现有树木检测模型的预测结果作为提示来实现。
点此查看论文截图


Hierarchical Self-Prompting SAM: A Prompt-Free Medical Image Segmentation Framework
Authors:Mengmeng Zhang, Xingyuan Dai, Yicheng Sun, Jing Wang, Yueyang Yao, Xiaoyan Gong, Fuze Cong, Feiyue Wang, Yisheng Lv
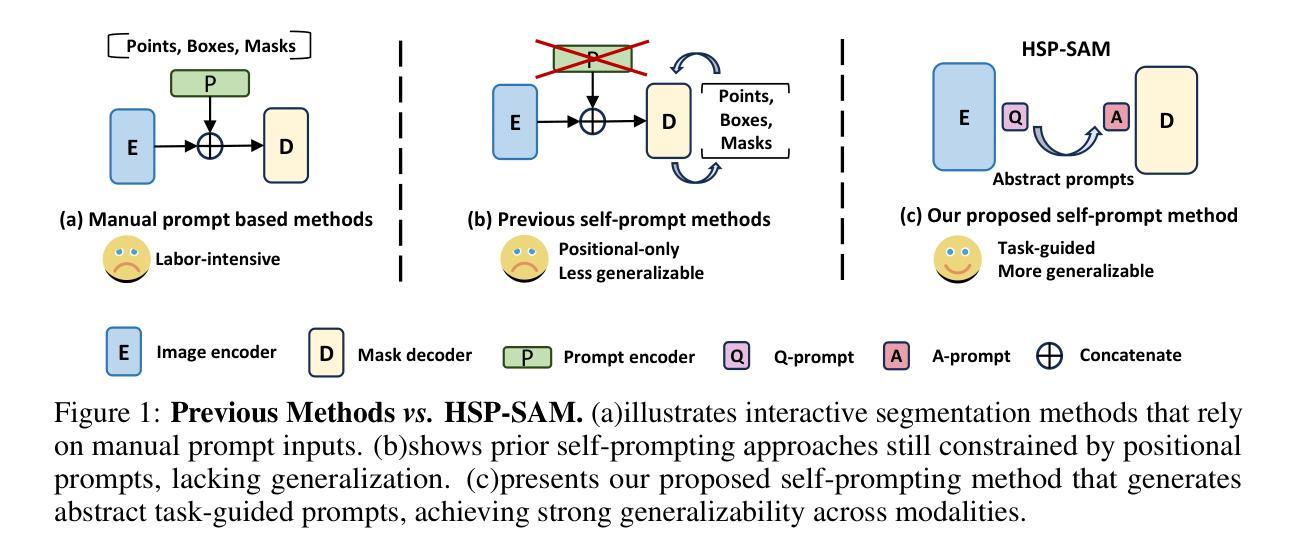
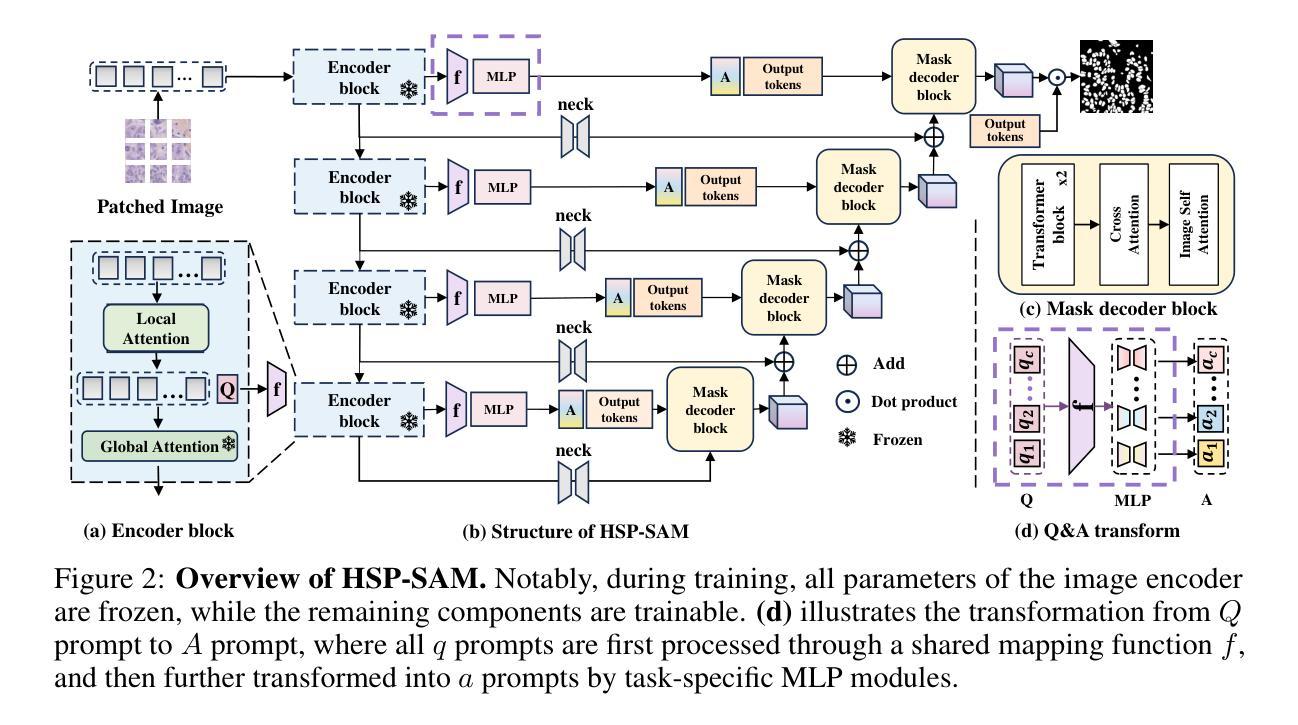
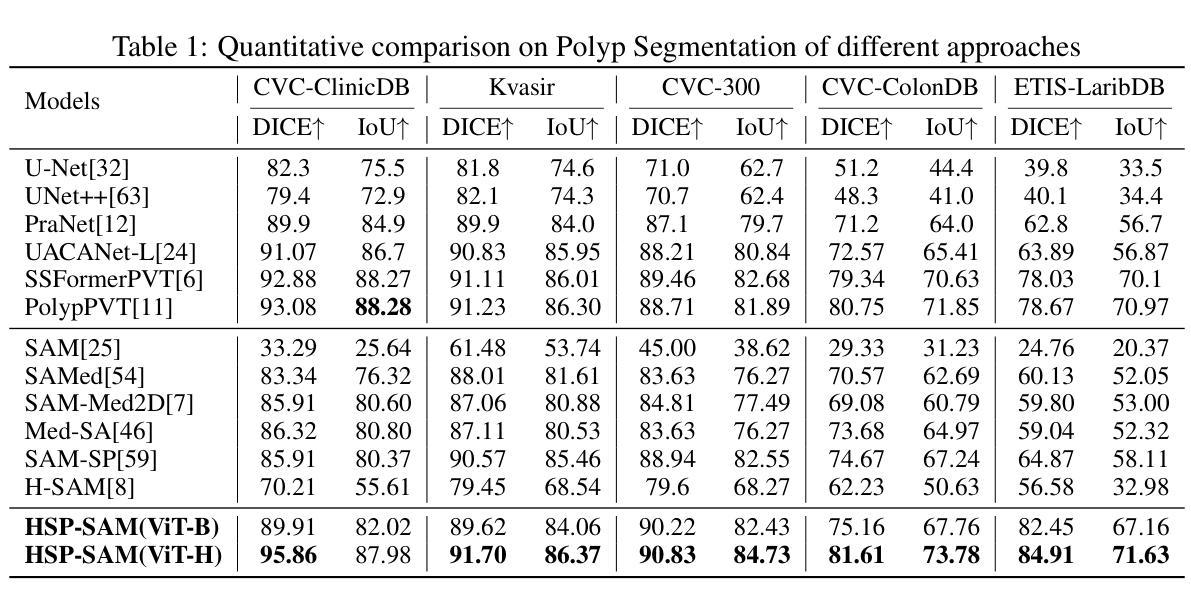
Although the Segment Anything Model (SAM) is highly effective in natural image segmentation, it requires dependencies on prompts, which limits its applicability to medical imaging where manual prompts are often unavailable. Existing efforts to fine-tune SAM for medical segmentation typically struggle to remove this dependency. We propose Hierarchical Self-Prompting SAM (HSP-SAM), a novel self-prompting framework that enables SAM to achieve strong performance in prompt-free medical image segmentation. Unlike previous self-prompting methods that remain limited to positional prompts similar to vanilla SAM, we are the first to introduce learning abstract prompts during the self-prompting process. This simple and intuitive self-prompting framework achieves superior performance on classic segmentation tasks such as polyp and skin lesion segmentation, while maintaining robustness across diverse medical imaging modalities. Furthermore, it exhibits strong generalization to unseen datasets, achieving improvements of up to 14.04% over previous state-of-the-art methods on some challenging benchmarks. These results suggest that abstract prompts encapsulate richer and higher-dimensional semantic information compared to positional prompts, thereby enhancing the model’s robustness and generalization performance. All models and codes will be released upon acceptance.
尽管Segment Anything Model(SAM)在自然图像分割中效果显著,但它依赖于提示,这在手动提示通常不可用的医学成像中限制了其适用性。现有的针对医学分割的SAM微调努力通常难以消除这种依赖。我们提出了分层自提示SAM(HSP-SAM),这是一种新型的自提示框架,使SAM在无提示医学图像分割中实现了强大的性能。与以往仅限于位置提示的自提示方法(类似于普通SAM)不同,我们是第一个在自提示过程中引入抽象提示的。这种简单直观的自提示框架在经典分割任务(如息肉和皮肤病变分割)上实现了卓越的性能,同时在多种医学成像模态中保持了稳健性。此外,它在未见数据集上表现出强大的泛化能力,在一些具有挑战性的基准测试上较之前的最先进方法提高了高达14.04%。这些结果表明,与位置提示相比,抽象提示封装了更丰富、更高维度的语义信息,从而增强了模型的稳健性和泛化性能。所有模型和代码将在接受后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Segment Anything Model(SAM)在自然图像分割中的出色表现,但其在医学图像分割应用中受限于需要提示的问题。为解决此问题,我们提出了分层自提示框架HSP-SAM,使SAM在无提示医学图像分割中表现出强劲性能。HSP-SAM引入抽象提示学习,实现超越经典分割任务如息肉和皮肤病变分割的优异表现,同时适用于多种医学影像模态。其展现出对未见数据集的强大泛化能力,在一些具有挑战性的基准测试中较先前最先进的方法提升了最多达14.04%。这些结果暗示抽象提示包含更丰富和高维度的语义信息,增强了模型的稳健性和泛化性能。
Key Takeaways
- HSP-SAM是一个新颖的分层自提示框架,旨在解决Segment Anything Model在医学图像分割中对提示的依赖问题。
- 与现有的自提示方法不同,HSP-SAM首次引入了抽象提示学习过程。
- HSP-SAM框架超越了经典分割任务如息肉和皮肤病变分割的优异表现。
- HSP-SAM在各种医学影像模态上展现出稳健性。
- HSP-SAM具有强大的泛化能力,对未见数据集表现良好。
- 与先前最先进的方法相比,HSP-SAM在某些挑战性基准测试中提高了最多达14.04%的性能。
- 结果表明,抽象提示较传统位置提示包含了更丰富、更高维度的语义信息。
点此查看论文截图

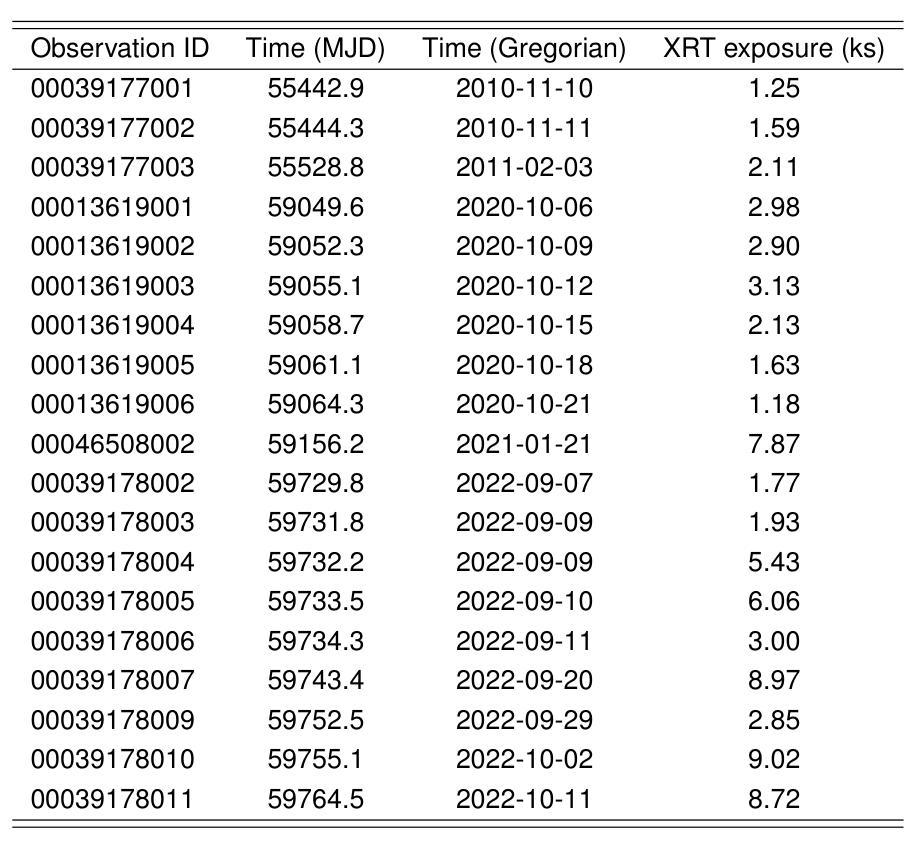
Multi-wavelength analysis of FSRQ B2 1348+30B: Constraints on the jet power
Authors:Sajad Ahanger, Sunder Sahayanathan, Sitha K. Jagan, Shah Zahir, Naseer Iqbal
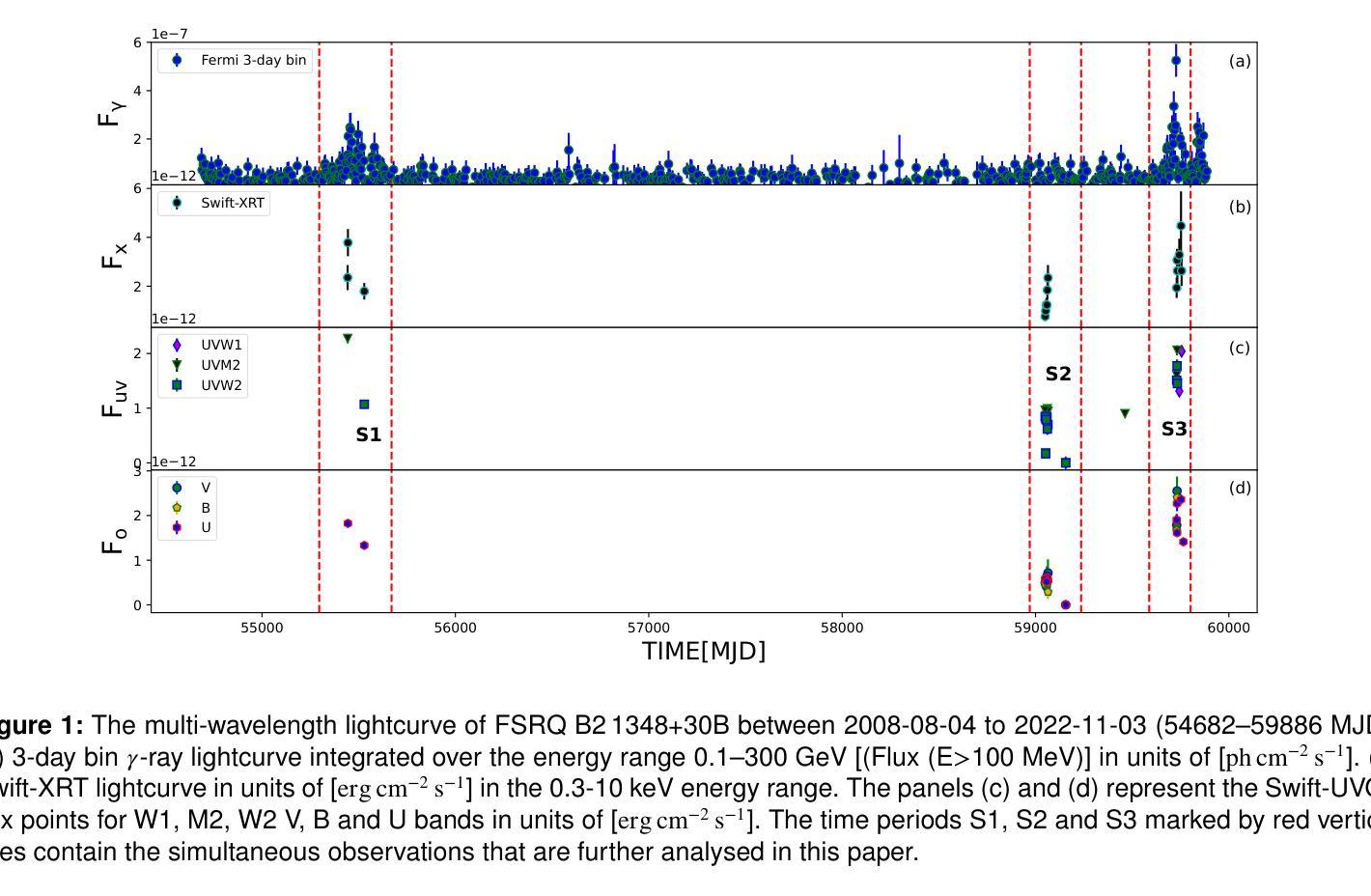
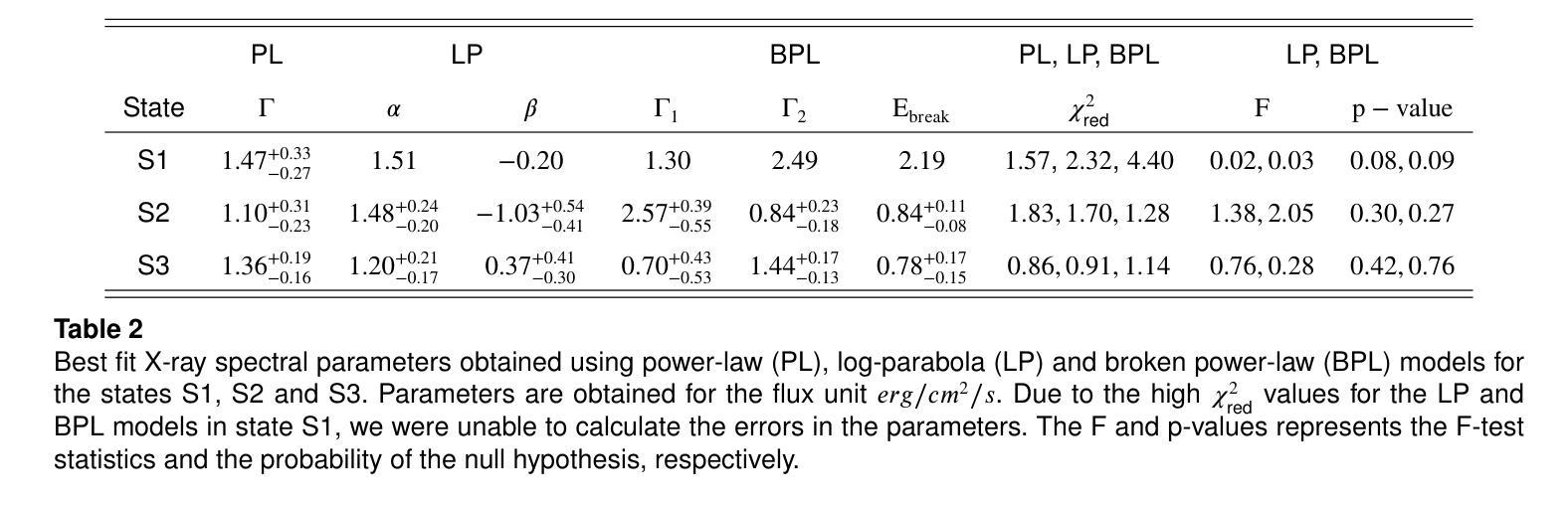
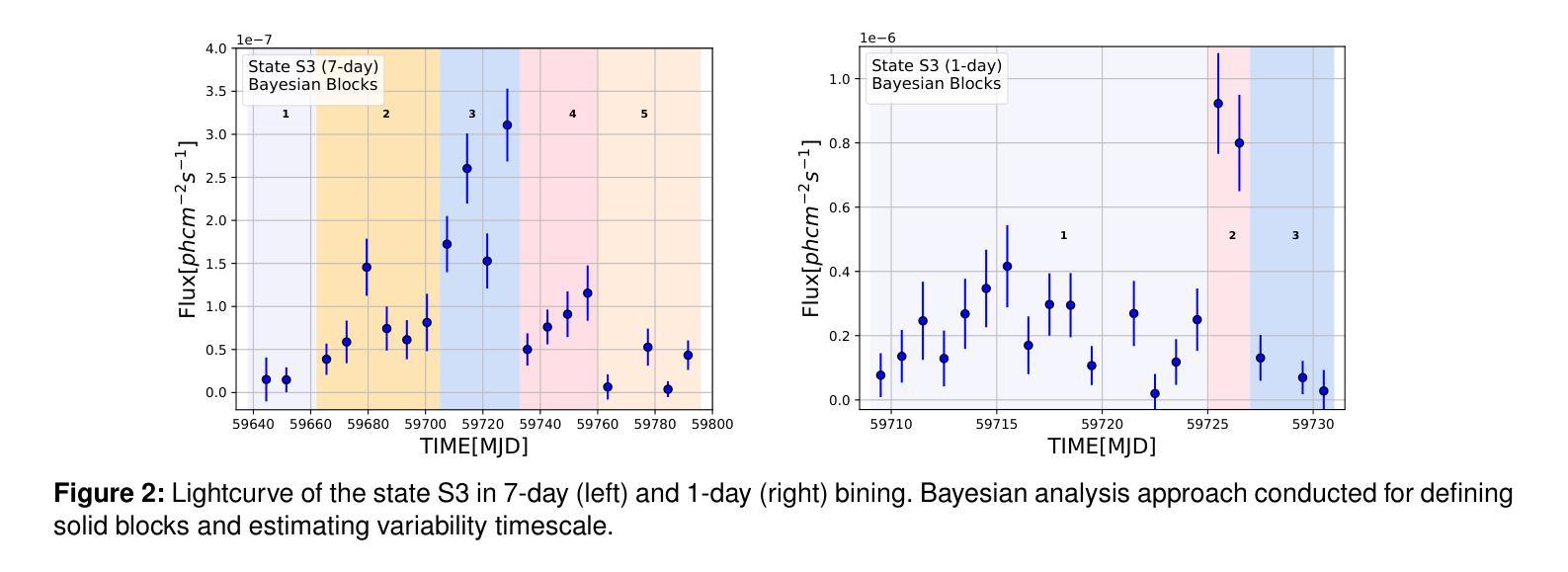
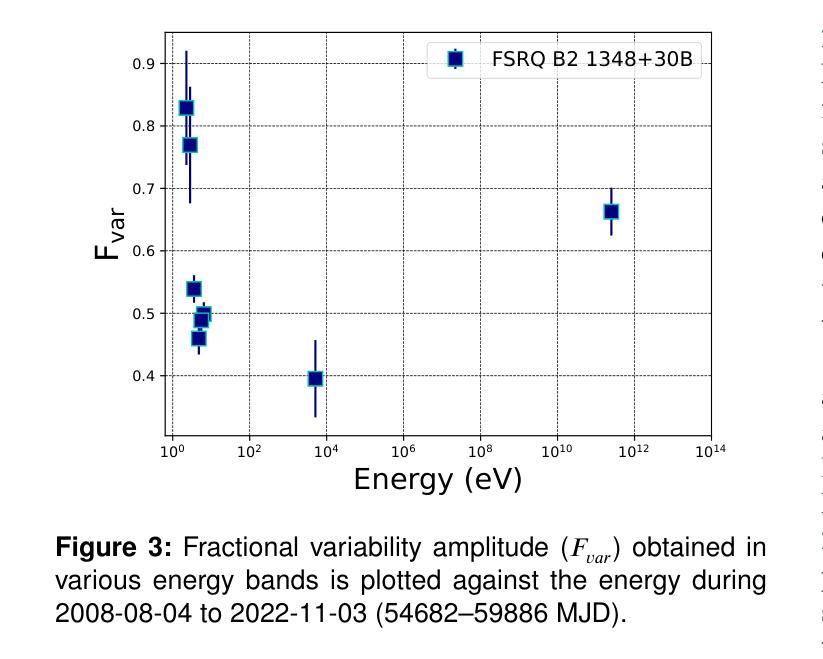
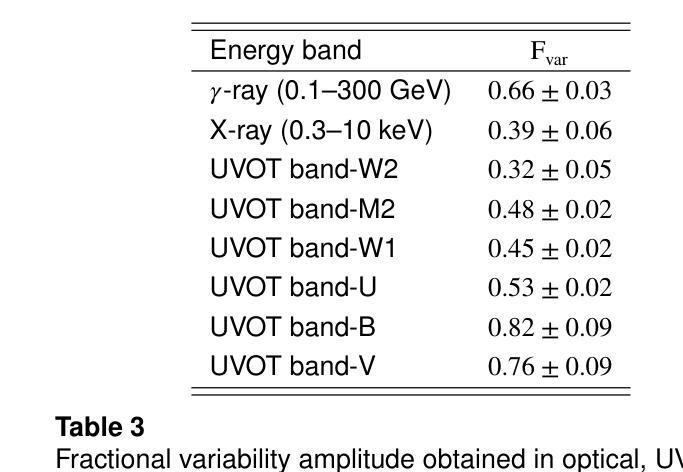
We present 14.5-year multi-wavelength analysis of flat-spectrum radio quasar B2 1348+30B using Swift-UVOT, Swift-XRT, and Fermi-LAT observations. In the gamma-ray band, the 3 day bin lightcurve reveals two major flaring events on 2010-09-19 (55458 MJD) and 2022-05-26 (59725 MJD) detected at flux levels $(2.5\pm 0.5) \times 10^{-7},\rm{ph,cm^{-2},s^{-1}}$ and $(5.2\pm 0.6) \times 10^{-7},\rm{ph,cm^{-2},s^{-1}}$. The Bayesian block analysis of the flares suggested the variability timescale to be $\leq$ 3,day. To study the dynamic nature of the source, multi-wavelength spectrum was obtained for three flux states which includes the two flaring state and a relative low state. The $\gamma$-ray spectra of the source in all the states are well fitted by a power-law model with maximum photon energy < 20 GeV. In X-ray, a power-law model can explain the flaring state spectra while a broken power-law with extremely hard high energy component was required to model the low flux state. This indicates the presence of the low energy cutoff in the Compton spectral component. A simple one-zone leptonic model involving synchrotron, synchrotron self Compton and external Compton mechanism can successfully reproduce the broad-band spectral energy distribution of all the flux states. The model parameters suggest significant increase in the jet Lorentz factor during the high flux states. Further, the best fit parameters are used to constrain the minimum energy of the emitting electron distribution from the hard high energy spectrum of the low flux state. This analysis was extended to draw limits on the kinetic power of the blazar jet and was compared with the Eddington luminosity of the central black hole.
我们利用Swift-UVOT、Swift-XRT和Fermi-LAT观测数据,对平谱射电类星体B2 1348+30B进行了长达14.5年的多波长分析。在伽马射线波段,为期3天的光变曲线显示,在历元时刻55458 MJD(即2010年9月19日)和历元时刻59725 MJD(即2022年5月26日)发生了两次主要耀发事件,流量水平分别为(2.5±0.5)× 10^-7 ph cm^-2 s^-1和(5.2±0.6)× 10^-7 ph cm^-2 s^-1。耀发事件的贝叶斯块分析表明其变化时间尺度不超过3天。为了研究源动态特性,我们获得了三种流量状态下的多波长光谱,包括两次耀发状态和一次相对低状态。源在所有状态下的伽马射线光谱均可用幂律模型很好地拟合,最大光子能量小于20 GeV。在X射线波段,幂律模型可以解释耀发状态的光谱,而对低流量状态则需要一个具有极硬高能分量的截断幂律模型来描述。这表明康普顿光谱分量中存在低能截断。一个涉及同步辐射、同步自康普顿和外部康普顿机制的简单单区轻子模型能够成功地再现所有流量状态的宽频谱能量分布。模型参数表明在高流量状态下洛伦兹因子显著增加。此外,最佳拟合参数被用来限制低流量状态硬高能谱发射电子分布的最小能量。这一分析被用来对喷流的动力学功率设置限制,并与中心黑洞的艾丁顿光度进行比较。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 6 figures, 5 tables, Accepted for publication in JHEAP
Summary
在长达14.5年的研究中,我们对具有平坦光谱的射电类星体B2 1348+30B进行了多波长分析,使用了Swift-UVOT、Swift-XRT和Fermi-LAT观测数据。在伽马射线波段,发现了两个主要耀斑事件,其光变曲线揭示了耀斑活动的动态特征。多波长光谱分析表明,源在不同流量状态下的光谱特征有所不同,这支持了使用简单的一区莱普顿模型来解释其谱能量分布的观点。此外,该分析还提供了对喷流洛伦兹因子和电子分布最小能量的了解,并进一步对类星体喷流的动力进行了限制和比较。
Key Takeaways
- 使用Swift-UVOT、Swift-XRT和Fermi-LAT观测数据对平谱射电类星体B2 1348+30B进行了长达14.5年的多波长分析。
- 在伽马射线波段发现两个主要耀斑事件,揭示了耀斑活动的动态特征。
- 通过多波长光谱分析发现不同流量状态下的源具有不同的光谱特性。
- 简单的一区莱普顿模型成功地再现了所有流量状态的谱能量分布。
- 源在低流量状态下的高能谱需要硬的高能成分来解释,暗示了Compton谱成分的低能截断的存在。
- 源的喷流洛伦兹因子在高流量状态下显著增加。
点此查看论文截图

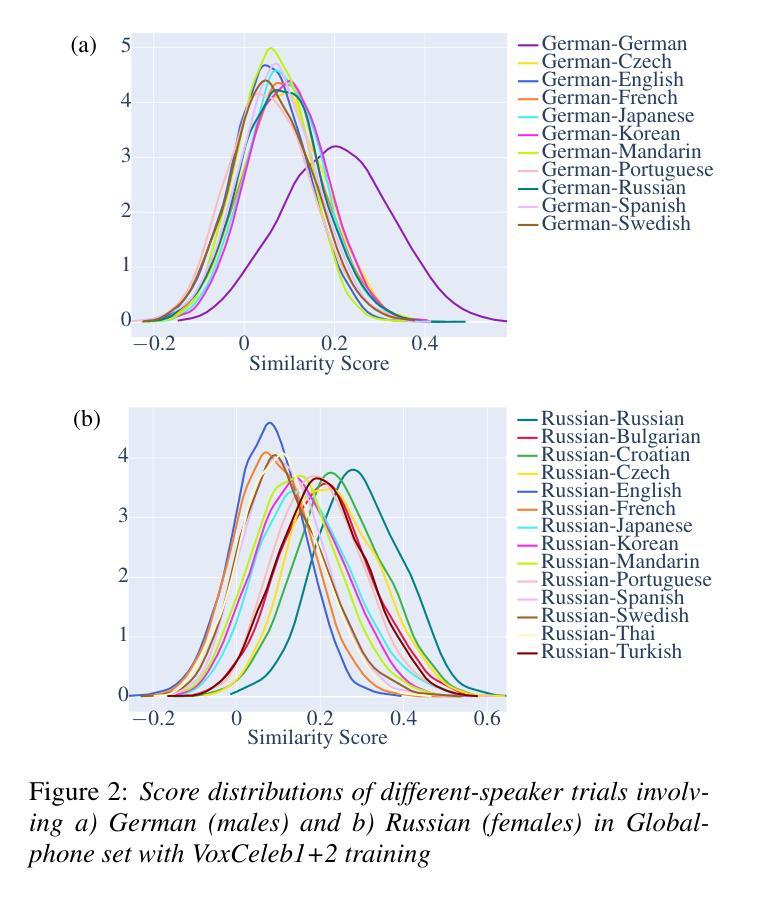
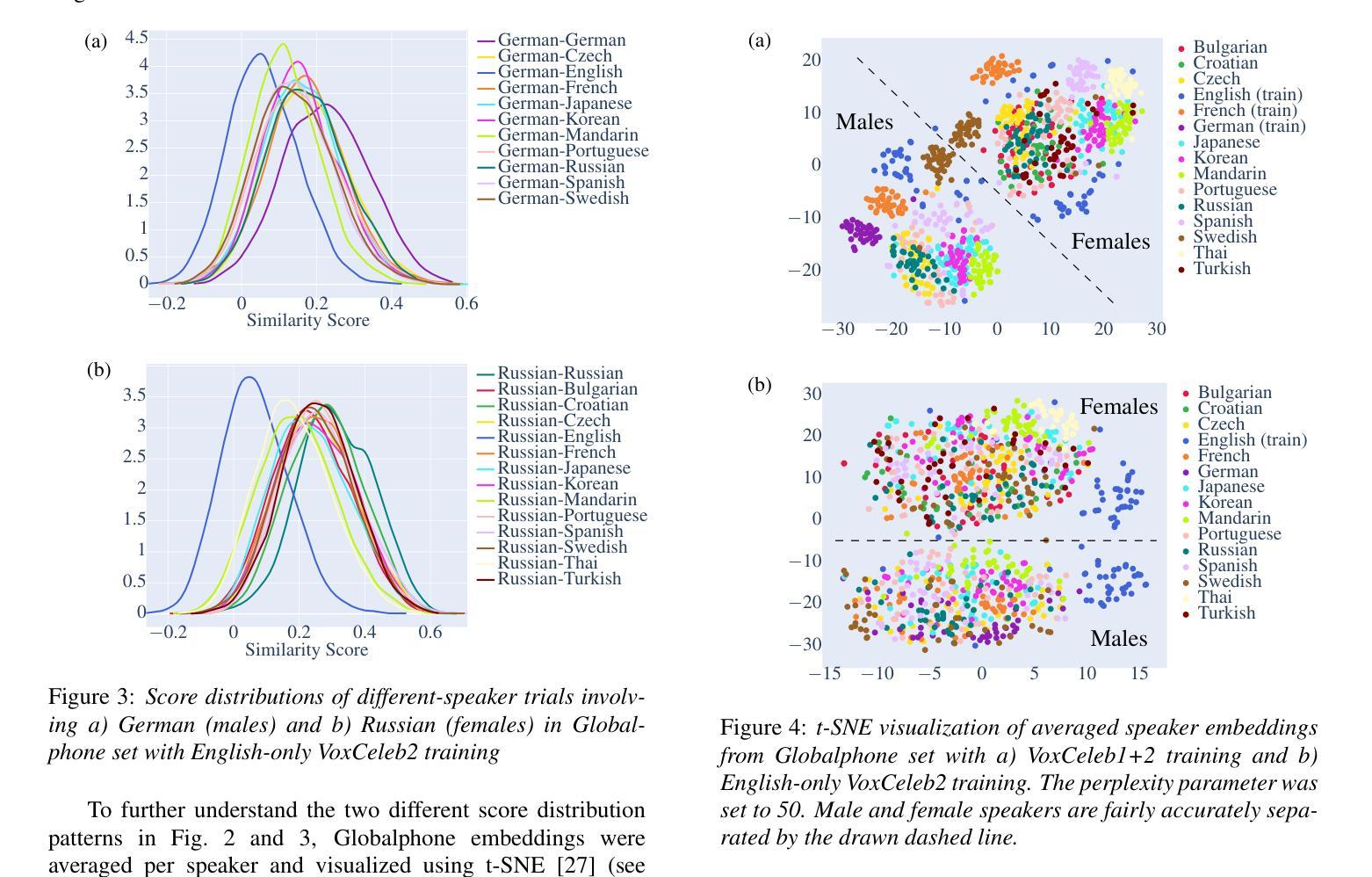
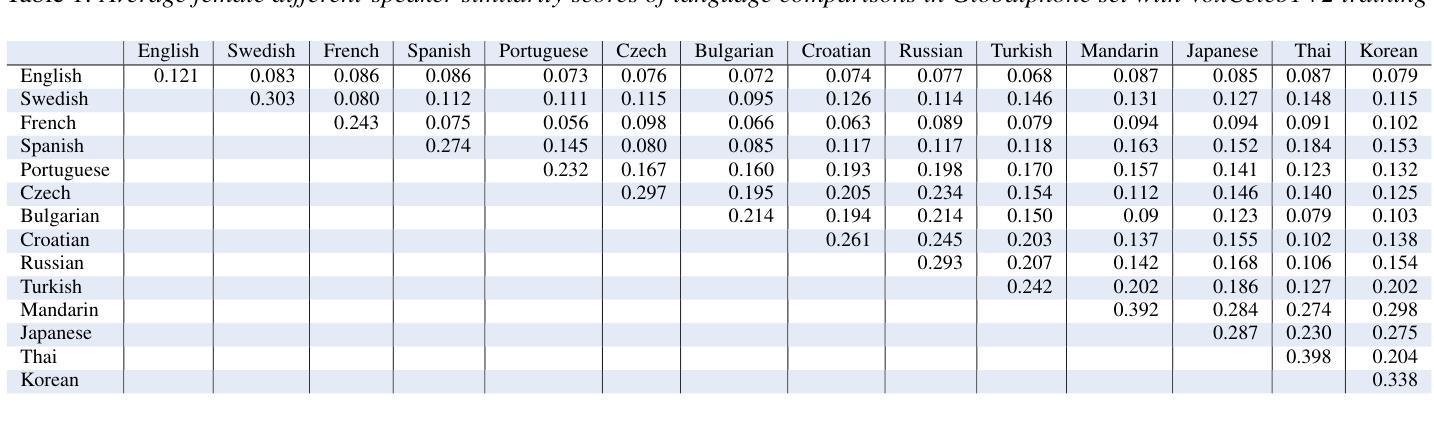
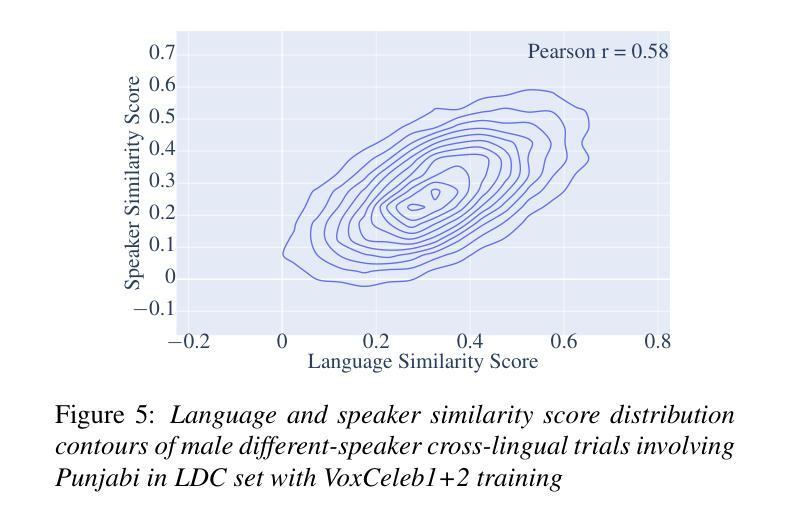
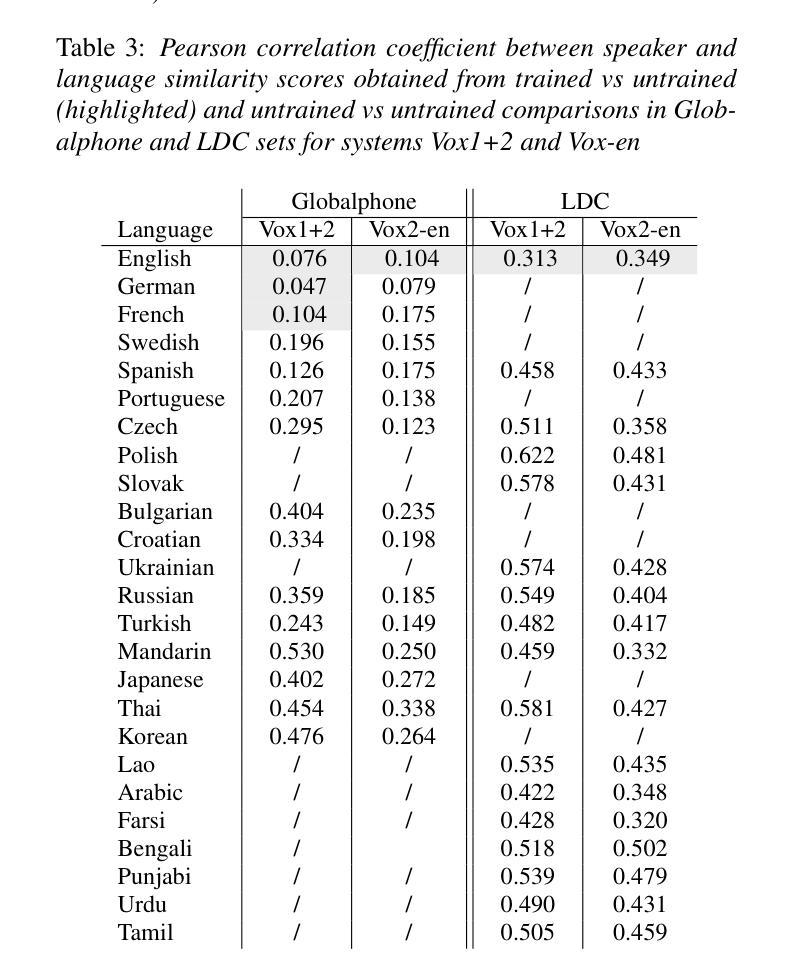
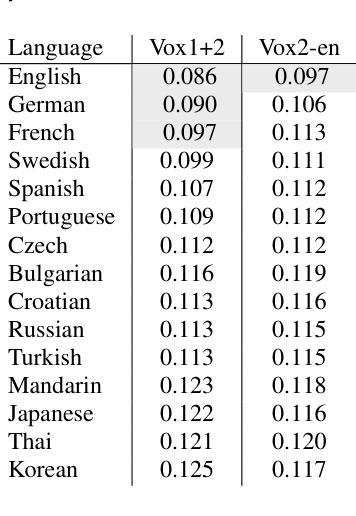
On the influence of language similarity in non-target speaker verification trials
Authors:Paul M. Reuter, Michael Jessen
In this paper, we investigate the influence of language similarity in cross-lingual non-target speaker verification trials using a state-of-the-art speaker verification system, ECAPA-TDNN, trained on multilingual and monolingual variants of the VoxCeleb dataset. Our analysis of the score distribution patterns on multilingual Globalphone and LDC CTS reveals a clustering effect in speaker comparisons involving a training language, whereby the choice of comparison language only minimally impacts scores. Conversely, we observe a language similarity effect in trials involving languages not included in the training set of the speaker verification system, with scores correlating with language similarity measured by a language classification system, especially when using multilingual training data.
本文中,我们研究语言相似性对使用最前沿说话人验证系统ECAPA-TDNN进行的跨语言非目标说话人验证试验的影响。该系统是在VoxCeleb数据集的多语种和单语种变体上进行训练的。我们对多语种Globalphone和LDC CTS上的得分分布模式进行分析,发现在涉及训练语言的说话人比较中出现了聚类效应,所选的比较语言对得分的影响微乎其微。相反,在涉及不在说话人验证系统训练集中的语言的试验中,我们观察到语言相似性效应,得分与由语言分类系统测得的语言相似性相关,特别是在使用多语种训练数据时。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted to Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文探讨了语言相似性对跨语种非目标说话人验证试验的影响。研究使用了基于最前沿的说话人验证系统ECAPA-TDNN,该系统在VoxCeleb数据集的多语种和单语种变体上进行训练。分析Globalphone和LDC CTS上的得分分布模式显示,在涉及训练语言的说话人比较中,对比语言的选择对得分影响甚微,但在涉及不在验证系统训练集中的语言的试验中,观察到语言相似性对得分有显著影响,尤其是使用多语种训练数据时,得分与语言分类系统的语言相似性度量相关。
Key Takeaways
- 研究了跨语种非目标说话人验证中语言相似性的影响。
- 采用ECAPA-TDNN这一先进的说话人验证系统进行分析。
- 在涉及训练语言的说话人比较中,对比语言的选择对得分影响较小。
- 在涉及非训练语言时,观察到语言相似性对得分有显著影响。
- 多语种训练数据在衡量语言相似性时尤为重要。
- 得分分布模式在跨语种验证中呈现出语言聚类效应。
点此查看论文截图

Simple, Good, Fast: Self-Supervised World Models Free of Baggage
Authors:Jan Robine, Marc Höftmann, Stefan Harmeling
What are the essential components of world models? How far do we get with world models that are not employing RNNs, transformers, discrete representations, and image reconstructions? This paper introduces SGF, a Simple, Good, and Fast world model that uses self-supervised representation learning, captures short-time dependencies through frame and action stacking, and enhances robustness against model errors through data augmentation. We extensively discuss SGF’s connections to established world models, evaluate the building blocks in ablation studies, and demonstrate good performance through quantitative comparisons on the Atari 100k benchmark.
世界模型的必要组成部分是什么?在不使用RNN、transformer、离散表示和图像重建的情况下,我们能走多远?本文介绍了SGF,这是一种简单、良好和快速的世界模型,它采用自监督表示学习,通过帧和动作堆叠捕捉短期依赖性,并通过数据增强提高模型误差的稳健性。我们深入讨论了SGF与现有世界模型之间的联系,在消融研究中评估了各个组成部分,并在Atari 100k基准测试上通过定量比较展示了良好的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2025. Code is available at https://github.com/jrobine/sgf
Summary
世界模型的必要组成部分是什么?不使用RNNs、transformers、离散表示和图像重建的世界模型能走多远?本文介绍了一种简单、良好和快速的SGF世界模型,该模型采用自监督表示学习,通过帧和动作堆叠捕捉短期依赖关系,并通过数据增强提高模型误差的稳健性。本文广泛讨论了SGF与现有世界模型的关联,通过局部消融研究评估了构建块,并在Atari 100k基准测试中通过定量比较展示了良好的性能。
Key Takeaways
- SGF是一种简单、良好和快速的世界模型。
- SGF采用自监督表示学习。
- SGF通过帧和动作堆叠捕捉短期依赖关系。
- SGF通过数据增强提高模型误差的稳健性。
- SGF与现有世界模型的关联被广泛讨论。
- 消融研究评估了SGF的构建块。
点此查看论文截图

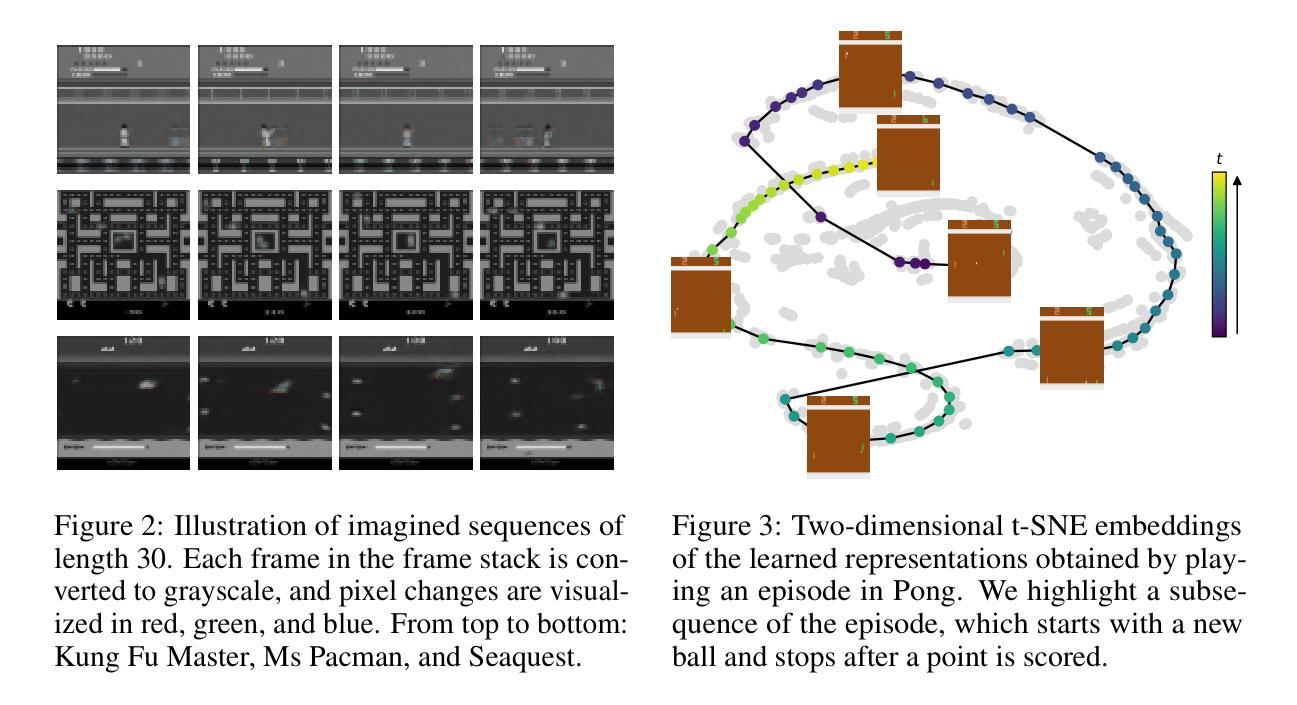
Insight into the origin of multiwavelength emissions of PKS 1510-089 through modeling 12 SEDs from 2008 to 2015
Authors:Maichang Lei, Yuan Zheng, Jianfu Zhang, Yuhai Yuan, Jiancheng Wang
PKS,1510$-$089 is one of the most peculiar sources among the FSRQs, exhibiting a notable big blue bump (BBB). This provides an unique opportunity to explore the coupling between the activity of the central engine and the relativistic jet, offering further insight into the origin of the multiwavelength emissions. To this end, we collected multiwavelength data spanning four periods from 2008 to 2015 and performed the spectral energy distribution (SED) modeling using a one-zone homogeneous leptonic model. In the model, a multichromatic accretion disk (AD) is used to fit the optical/UV data sets, while the external radiation fields from the broad-line region (BLR) and dusty torus (DT) are properly considered to produce the high-energy $\gamma$-ray emissions. Our best fit to 12 SEDs yields the following results: (i) The innermost stable orbit ($R_{\rm ISO}$) of the AD is not stable but varies between $3,R_{\rm S}$ and $18,R_{\rm S}$ during these observations. (ii) The high-energy hump of the SED is well dominated by Compton scattering of the BLR photons, while the X-ray flux may be comprised of multiple radiation components. (iii) The $\gamma$-ray emitting regions are generally matter-dominated, with low magnetization, and are located beyond the BLR but within the DT. At such distance, the multiwavelength emissions are likely to originate from shock accelerations; (iv) For the energization of the relativistic jet, our study supports the Blandford$-$Znajek (BZ) mechanism, instead of the Blandford$-$Payne (BP) mechanism, as the latter fails to power the jet.
PKS 1510-089是FSRQs中最特殊的源之一,表现出显著的大蓝包(BBB)。这为探索中心发动机活动与相对论喷流之间的耦合提供了独特的机会,为进一步深入了解多波长发射的起源提供了启示。为此,我们收集了2008年至2015年的四期多波长数据,并使用单一区域均匀轻子模型进行了谱能量分布(SED)建模。在模型中,使用多色吸积盘(AD)来拟合光学/紫外数据集,同时适当考虑了来自宽线区(BLR)和尘埃环(DT)的外部辐射场,以产生高能伽马射线发射。我们对12个SED的最佳拟合得出以下结果:(i)AD的最内稳定轨道(RISO)不稳定,在这些观测期间在3Rs和18Rs之间变化。(ii)SED的高能峰主要由BLR光子的康普顿散射占据主导地位,而X射线流量可能由多个辐射成分组成。(iii)伽马射线发射区域通常是物质主导的,具有低磁化强度,位于BLR之外但在DT之内。在这样的距离下,多波长发射很可能源于冲击加速;(iv)关于相对论喷流的能量化,我们的研究支持Blandford-Znajek(BZ)机制,而不是Blandford-Payne(BP)机制,因为后者无法为喷流提供动力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 33 pages, 13 figure, 5 Tables. Accepted for publication in ApJ
Summary
PKS 1510$-$089是FSRQs中最奇特的源之一,具有显著的大蓝包(BBB)。通过对其的研究,可以更好地了解中心引擎活动与相对论喷流的耦合关系,进而深入研究多波长发射的起源。研究使用单一区域均匀莱普顿模型进行谱能量分布(SED)建模,发现AD的最内稳定轨道不稳定,高能量凸起主要由BLR光子的康普顿散射主导,伽马射线发射区域通常物质占主导,且位于BLR之外但DT之内。研究支持BZ机制为相对论喷流提供能量。
Key Takeaways
- PKS 1510$-$089是一个具有显著大蓝包(BBB)的FSRQs特殊源,为研究中心引擎活动与相对论喷流耦合关系提供了独特机会。
- 通过SED建模发现AD最内稳定轨道不稳定,且在不同观察时期有所变化。
- 高能凸起主要由BLR光子的康普顿散射主导。
- 伽马射线发射区域通常物质占主导,且位于BLR之外但DT之内,多波长发射可能源于冲击加速。
- 研究结果支持BZ机制为相对论喷流提供能量,而BP机制可能无法提供足够的能量。
- X射线流量可能由多种辐射成分组成。
点此查看论文截图

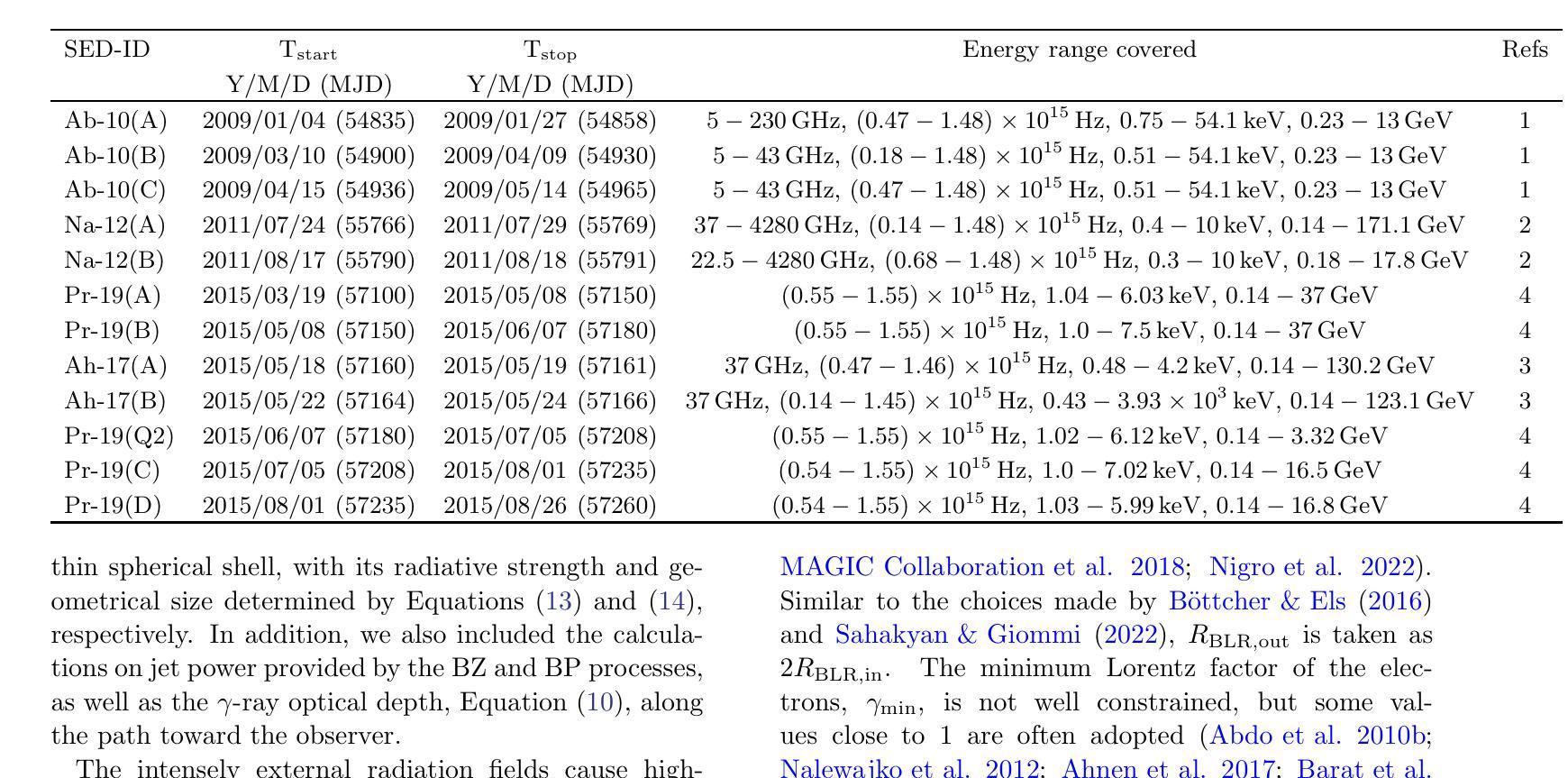
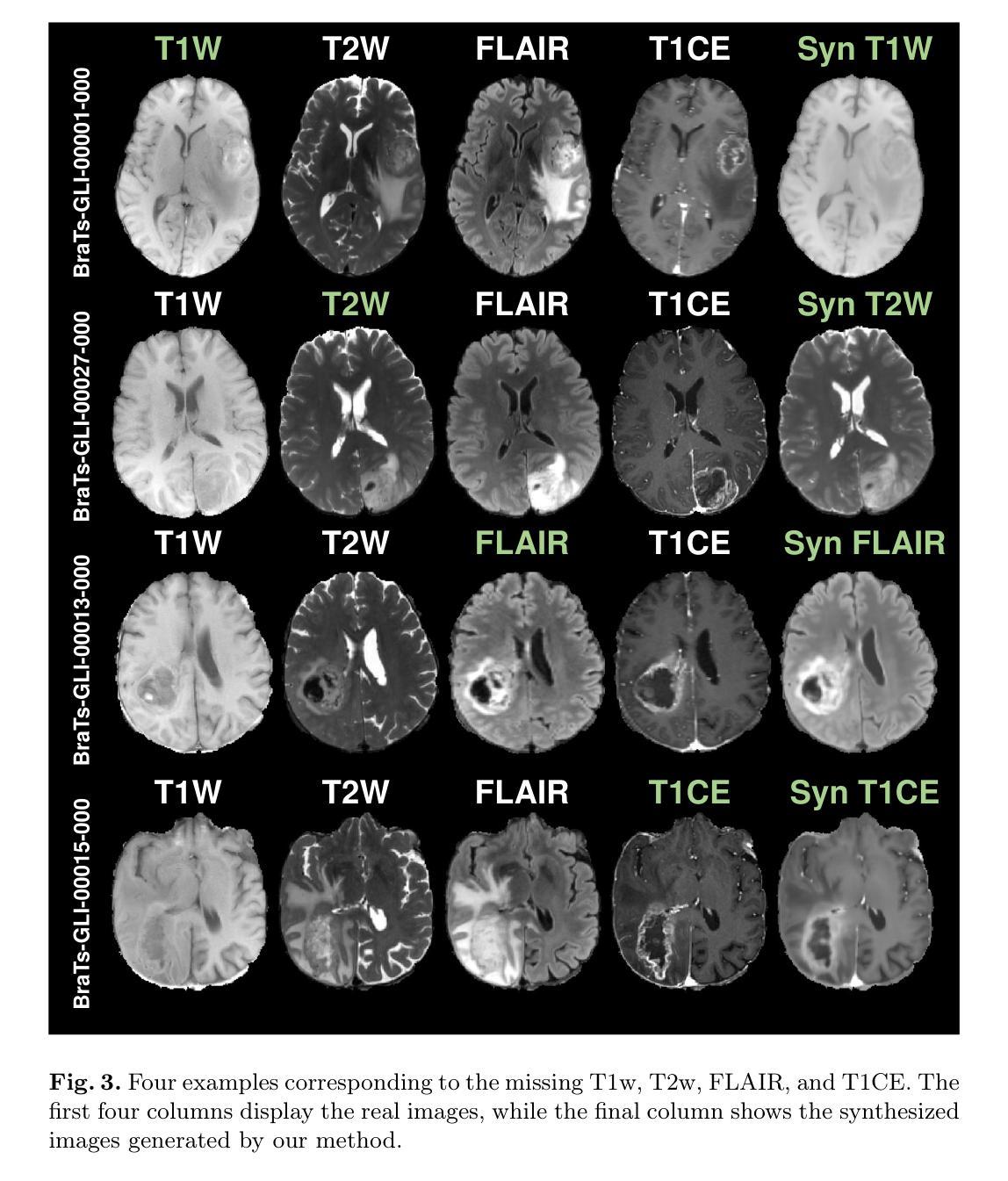
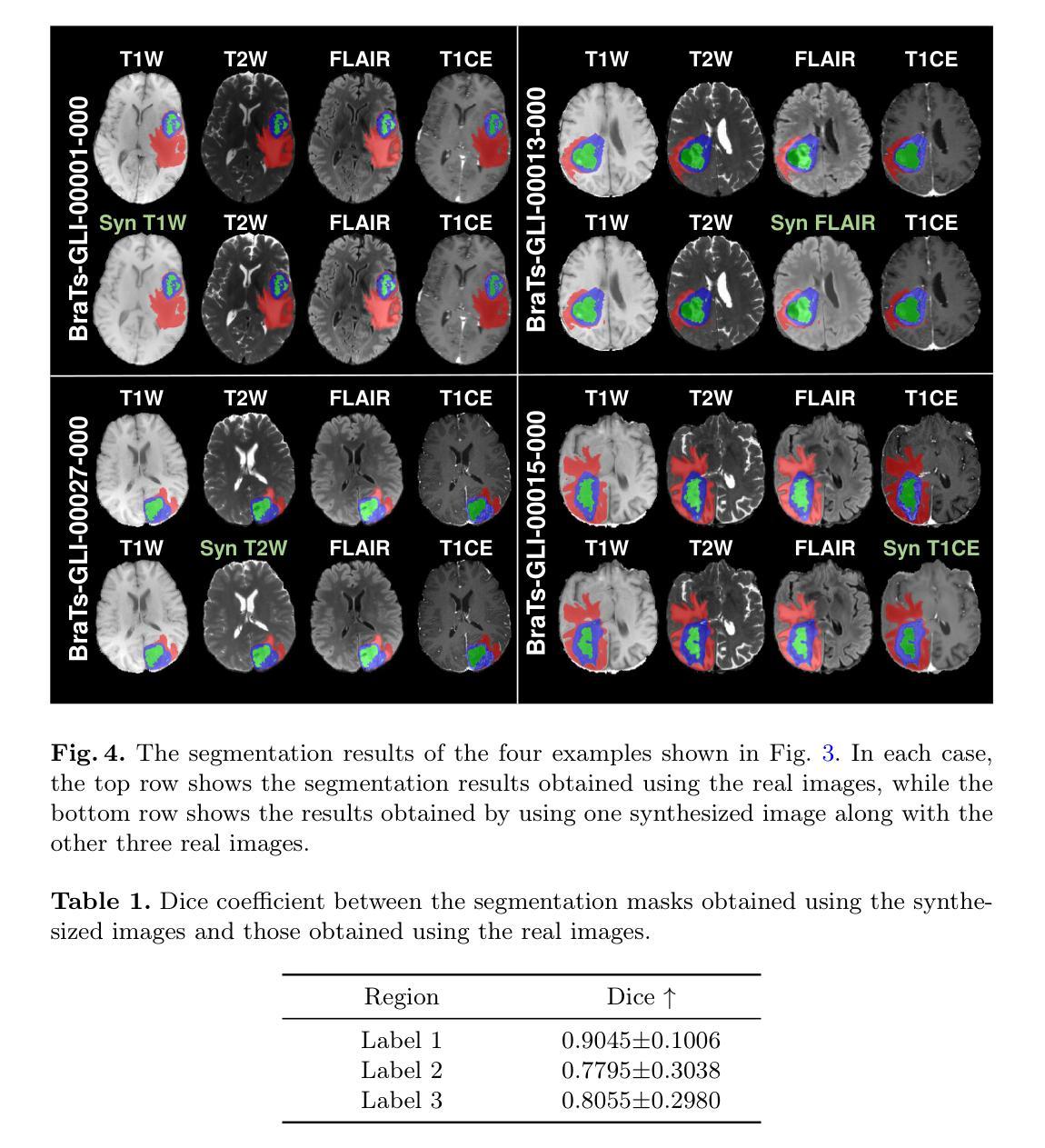
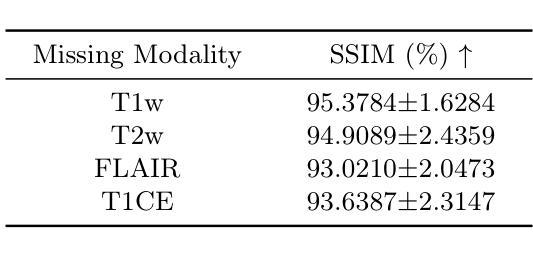
Multi-modal brain MRI synthesis based on SwinUNETR
Authors:Haowen Pang, Weiyan Guo, Chuyang Ye
Multi-modal brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays a crucial role in clinical diagnostics by providing complementary information across different imaging modalities. However, a common challenge in clinical practice is missing MRI modalities. In this paper, we apply SwinUNETR to the synthesize of missing modalities in brain MRI. SwinUNETR is a novel neural network architecture designed for medical image analysis, integrating the strengths of Swin Transformer and convolutional neural networks (CNNs). The Swin Transformer, a variant of the Vision Transformer (ViT), incorporates hierarchical feature extraction and window-based self-attention mechanisms, enabling it to capture both local and global contextual information effectively. By combining the Swin Transformer with CNNs, SwinUNETR merges global context awareness with detailed spatial resolution. This hybrid approach addresses the challenges posed by the varying modality characteristics and complex brain structures, facilitating the generation of accurate and realistic synthetic images. We evaluate the performance of SwinUNETR on brain MRI datasets and demonstrate its superior capability in generating clinically valuable images. Our results show significant improvements in image quality, anatomical consistency, and diagnostic value.
多模态脑磁共振成像(MRI)在临床诊断中扮演着重要角色,因为它能够提供不同成像模式之间的补充信息。然而,临床实践中的一个常见挑战是MRI模式缺失。在本文中,我们将SwinUNETR应用于脑MRI中缺失模式的合成。SwinUNETR是一种新型的神经网络架构,专为医学图像分析而设计,融合了Swin Transformer和卷积神经网络(CNN)的优势。Swin Transformer是Vision Transformer(ViT)的一种变体,结合了分层特征提取和基于窗口的自注意力机制,能够有效地捕捉局部和全局上下文信息。通过将Swin Transformer与CNN相结合,SwinUNETR融合了全局上下文感知和详细的空间分辨率。这种混合方法解决了由不同的模态特征和复杂的脑结构所带来的挑战,促进了准确且逼真的合成图像的产生。我们在脑MRI数据集上评估了SwinUNETR的性能,并展示了其在生成具有临床价值图像方面的卓越能力。我们的结果在图像质量、解剖一致性和诊断价值方面显示出显著改善。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 5 figures
Summary
多模态脑磁共振成像(MRI)在临床诊断中扮演重要角色,能提供不同成像模式的信息互补。针对临床实践中缺失MRI模态的问题,本文应用SwinUNETR进行脑MRI缺失模态的合成。SwinUNETR是一种结合了Swin Transformer和卷积神经网络(CNN)优势的新型神经网络架构,用于医学图像分析。它通过结合Swin Transformer的分层特征提取和基于窗口的自注意力机制,有效捕捉局部和全局上下文信息。将Swin Transformer与CNN相结合,SwinUNETR融合了全局上下文感知和详细的空间分辨率。这种混合方法解决了不同模态特征和复杂脑结构带来的挑战,能够生成准确且逼真的合成图像。在脑MRI数据集上评估SwinUNETR的性能,证明了其在生成具有临床价值图像方面的卓越能力。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态脑磁共振成像(MRI)对于临床诊断至关重要,能融合不同成像模式的信息。
- 缺失MRI模态是临床实践中一个常见问题。
- SwinUNETR是一种用于医学图像分析的神经网络架构,结合了Swin Transformer和卷积神经网络(CNN)。
- SwinUNETR能够生成准确且逼真的合成图像,解决不同模态特征和复杂脑结构带来的挑战。
- SwinUNETR在脑MRI数据集上的性能表现优异,能生成具有临床价值的图像。
- SwinUNETR通过结合全局上下文感知和详细的空间分辨率,提高了图像质量和诊断价值。
点此查看论文截图

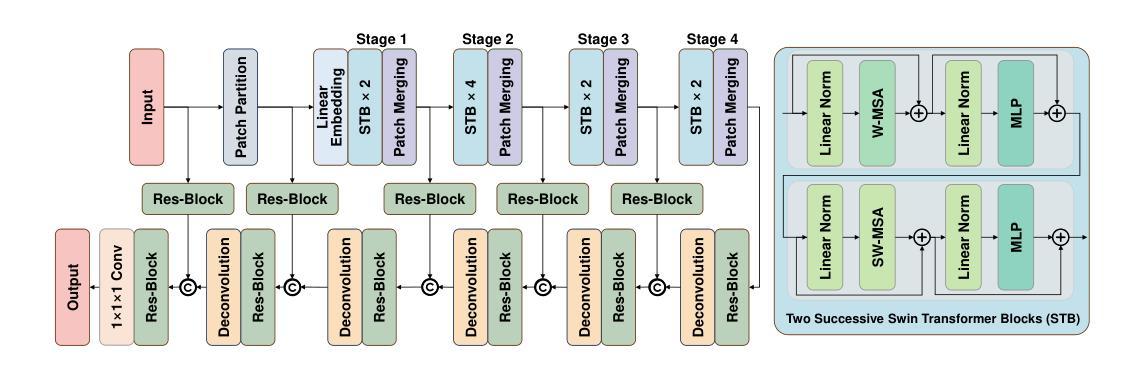
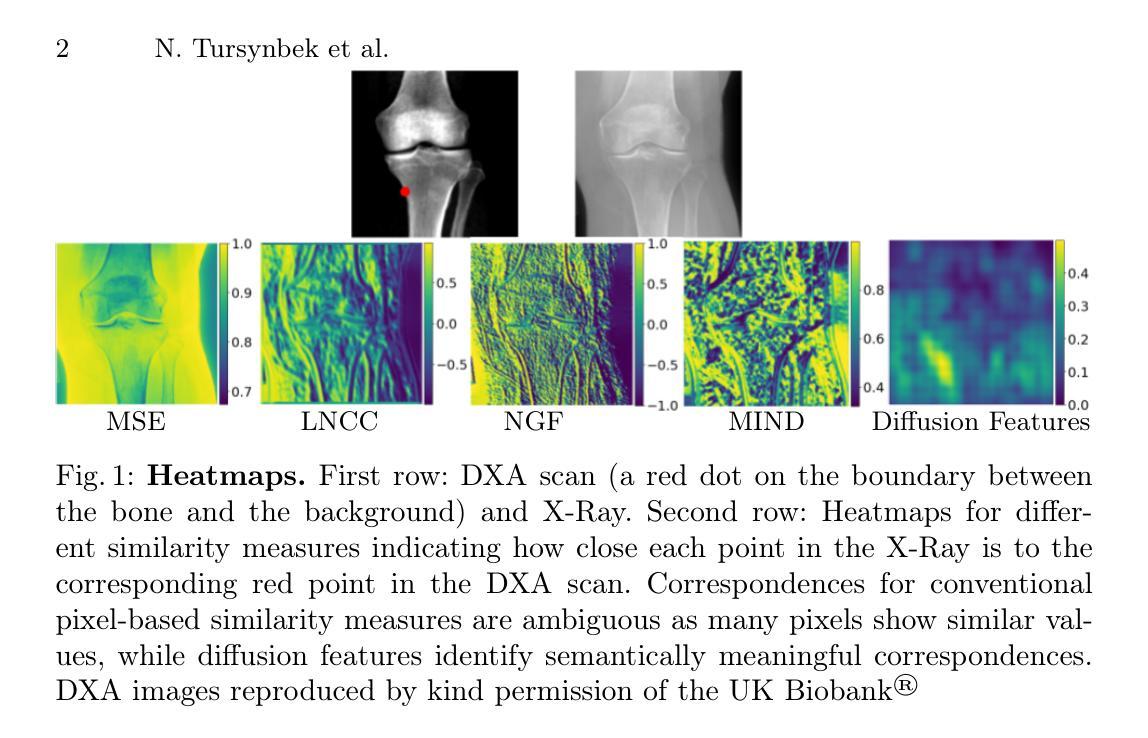
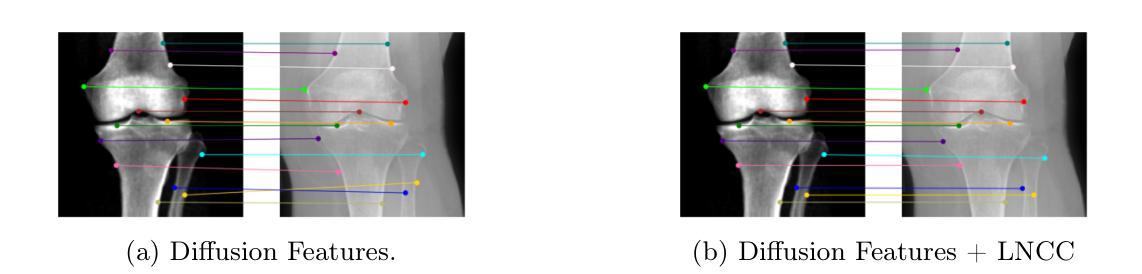
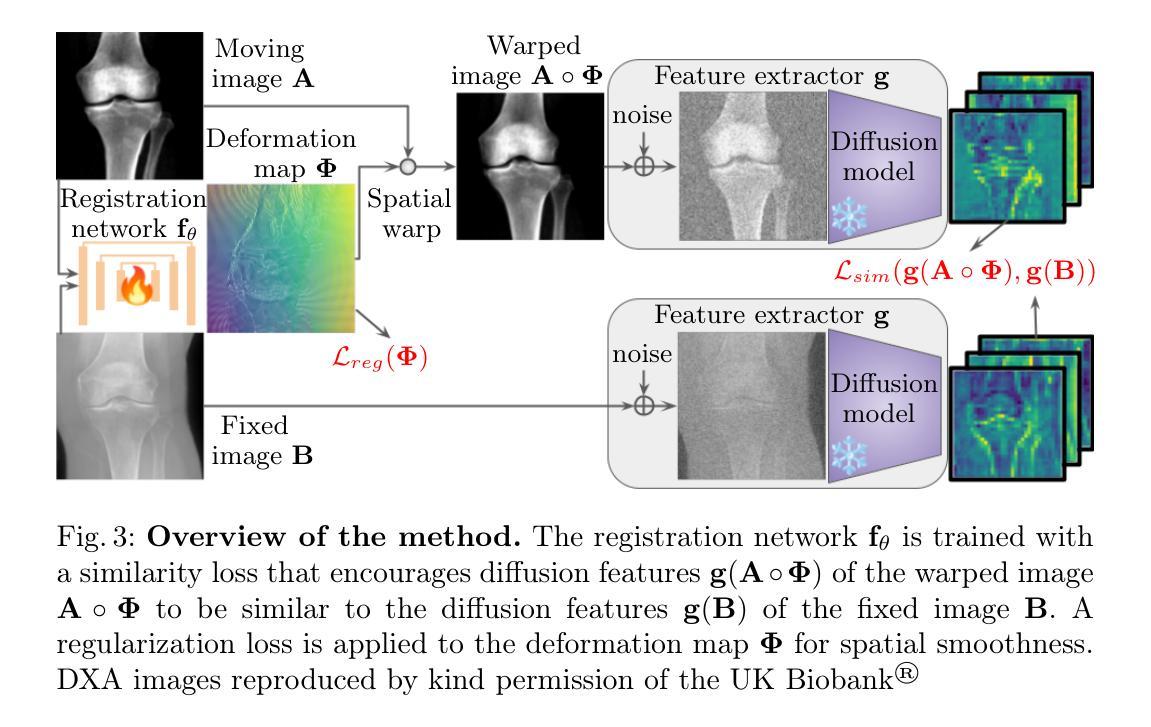
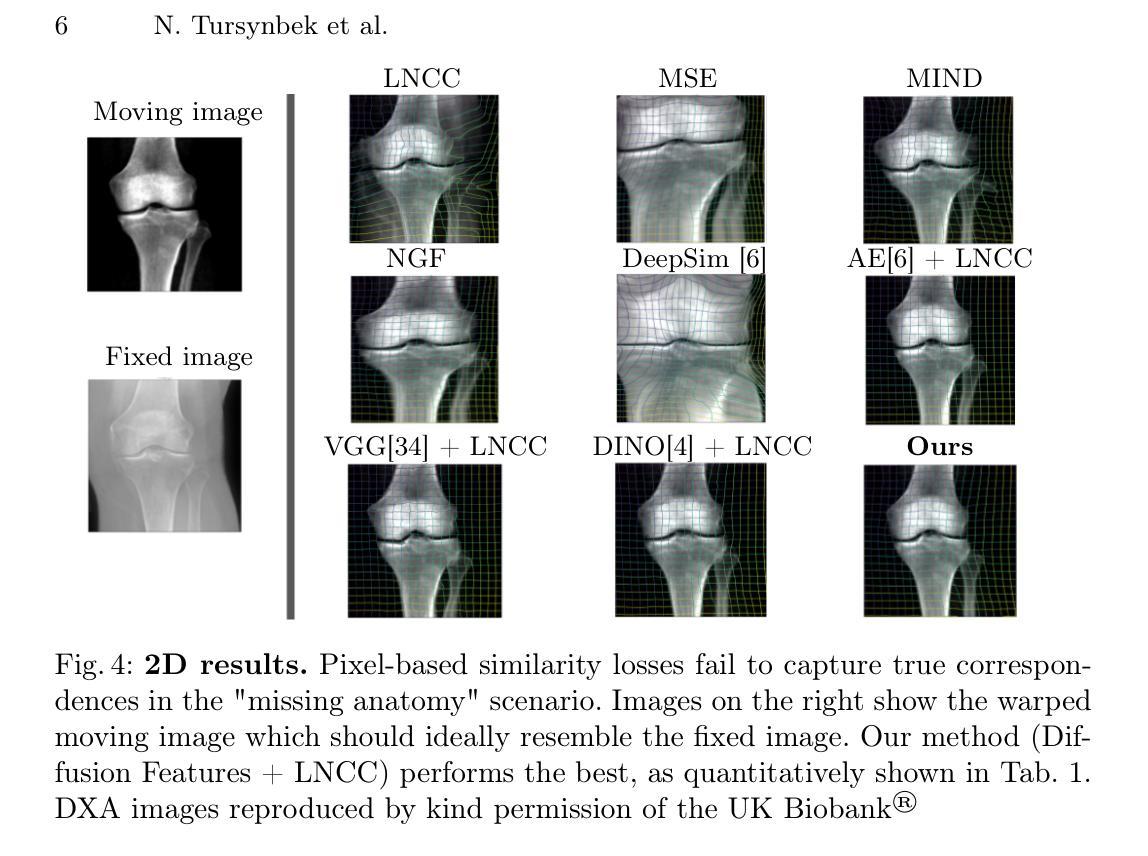
Guiding Registration with Emergent Similarity from Pre-Trained Diffusion Models
Authors:Nurislam Tursynbek, Hastings Greer, Basar Demir, Marc Niethammer
Diffusion models, while trained for image generation, have emerged as powerful foundational feature extractors for downstream tasks. We find that off-the-shelf diffusion models, trained exclusively to generate natural RGB images, can identify semantically meaningful correspondences in medical images. Building on this observation, we propose to leverage diffusion model features as a similarity measure to guide deformable image registration networks. We show that common intensity-based similarity losses often fail in challenging scenarios, such as when certain anatomies are visible in one image but absent in another, leading to anatomically inaccurate alignments. In contrast, our method identifies true semantic correspondences, aligning meaningful structures while disregarding those not present across images. We demonstrate superior performance of our approach on two tasks: multimodal 2D registration (DXA to X-Ray) and monomodal 3D registration (brain-extracted to non-brain-extracted MRI). Code: https://github.com/uncbiag/dgir
扩散模型虽然被训练用于图像生成,但已逐渐成为下游任务的强大基础特征提取器。我们发现,专为生成自然RGB图像而训练的即用型扩散模型可以识别医学图像中的语义对应。基于这一观察,我们提出利用扩散模型特征作为相似度度量来指导可变形图像配准网络。我们显示,常用的基于强度的相似度损失在具有挑战性的场景中经常失败,例如在一种图像中可见某些解剖结构而在另一种图像中缺失时,这会导致解剖上不准确的对齐。相比之下,我们的方法能够识别真正的语义对应,对齐有意义的结构,同时忽略那些在不同图像中不存在的结构。我们在两个任务上展示了我们的方法的优越性:多模态二维配准(DXA到X射线)和单模态三维配准(提取大脑与非提取大脑的MRI)。代码:https://github.com/uncbiag/dgir
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
Summary
扩散模型虽被训练用于图像生成,但已成为强大的下游任务基础特征提取器。本研究发现,现成的扩散模型能够识别医学图像中的语义对应关系。基于此,研究提出利用扩散模型特征作为相似度度量,以指导可变形图像配准网络。在特定解剖结构在一图中可见而在另一图中缺失等挑战场景中,常见的基于强度的相似度损失常失效,而本研究方法能识别真正的语义对应关系,对齐有意义结构,同时忽略不同图像中不存在的内容。在两种任务上,本研究方法表现优越:多模态二维配准(DXA到X光)和单模态三维配准(提取大脑与未提取大脑的MRI)。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型可作为强大的下游任务特征提取器,不仅用于图像生成。
- 扩散模型能够识别医学图像中的语义对应关系。
- 在挑战场景中,常见的基于强度的相似度损失可能会失效。
- 研究提出利用扩散模型特征来指导可变形图像配准网络。
- 本研究方法能识别真正的语义对应关系,对齐有意义结构。
- 本研究在两种任务上表现优越:多模态二维配准和单模态三维配准。
点此查看论文截图

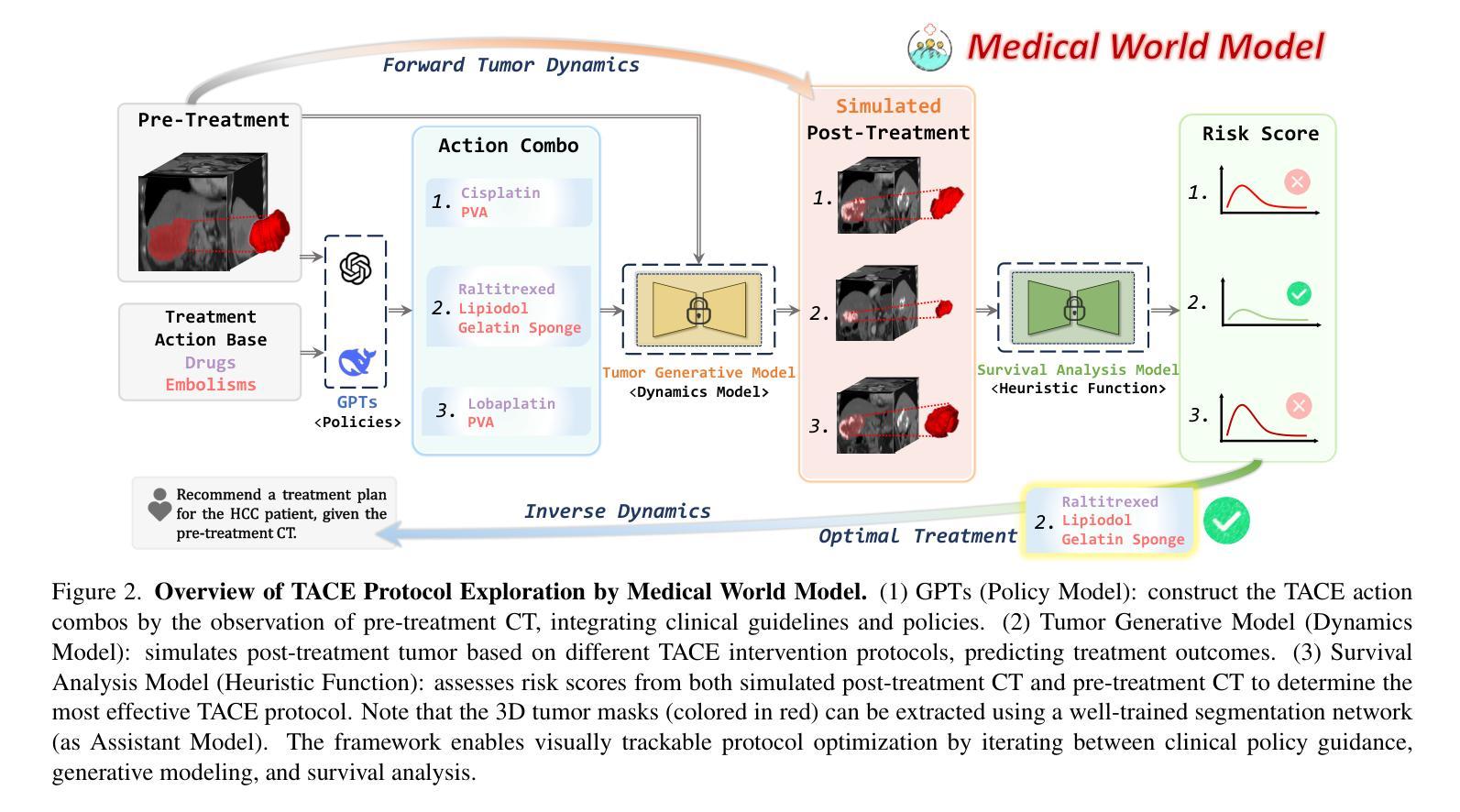
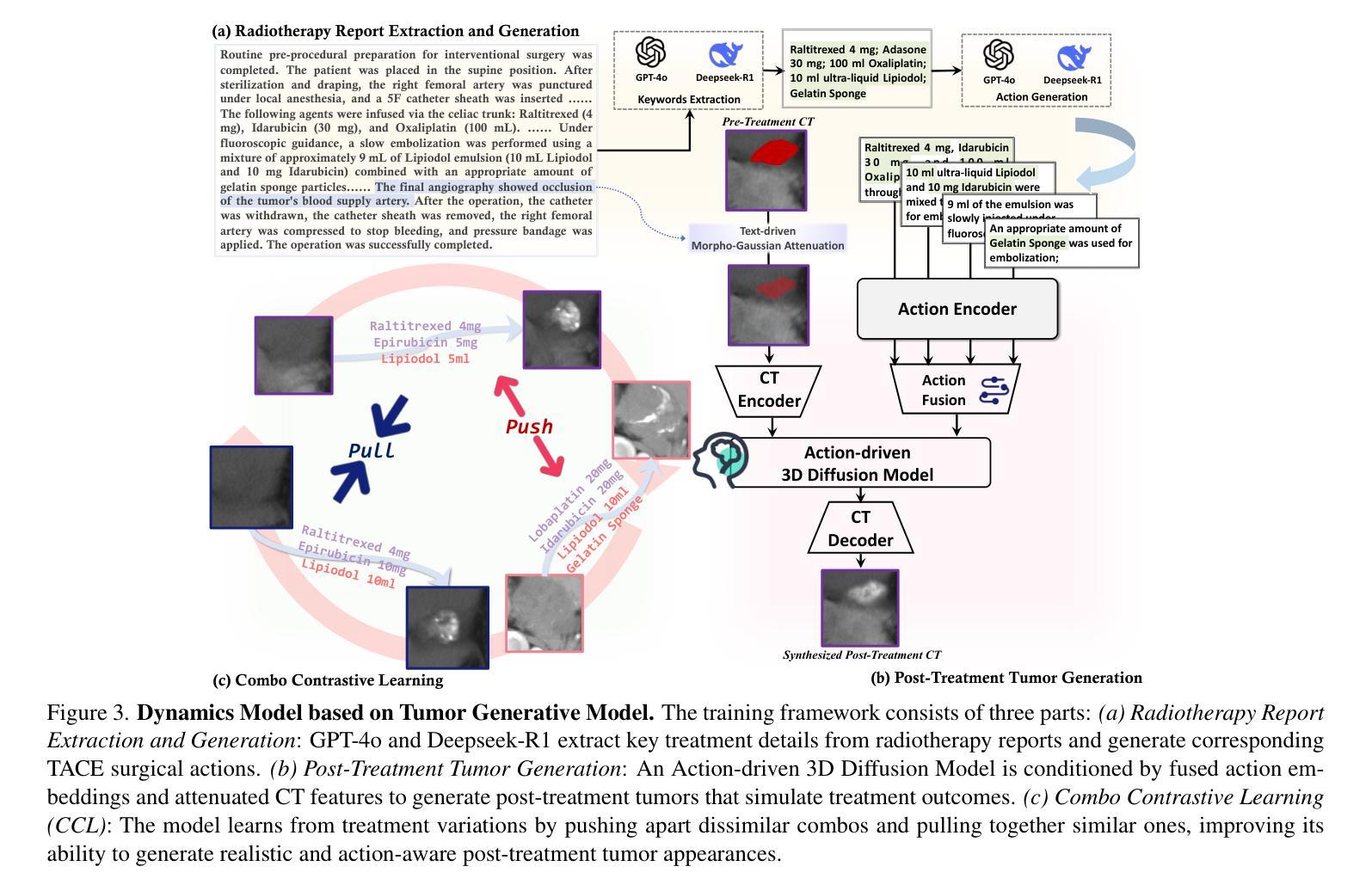
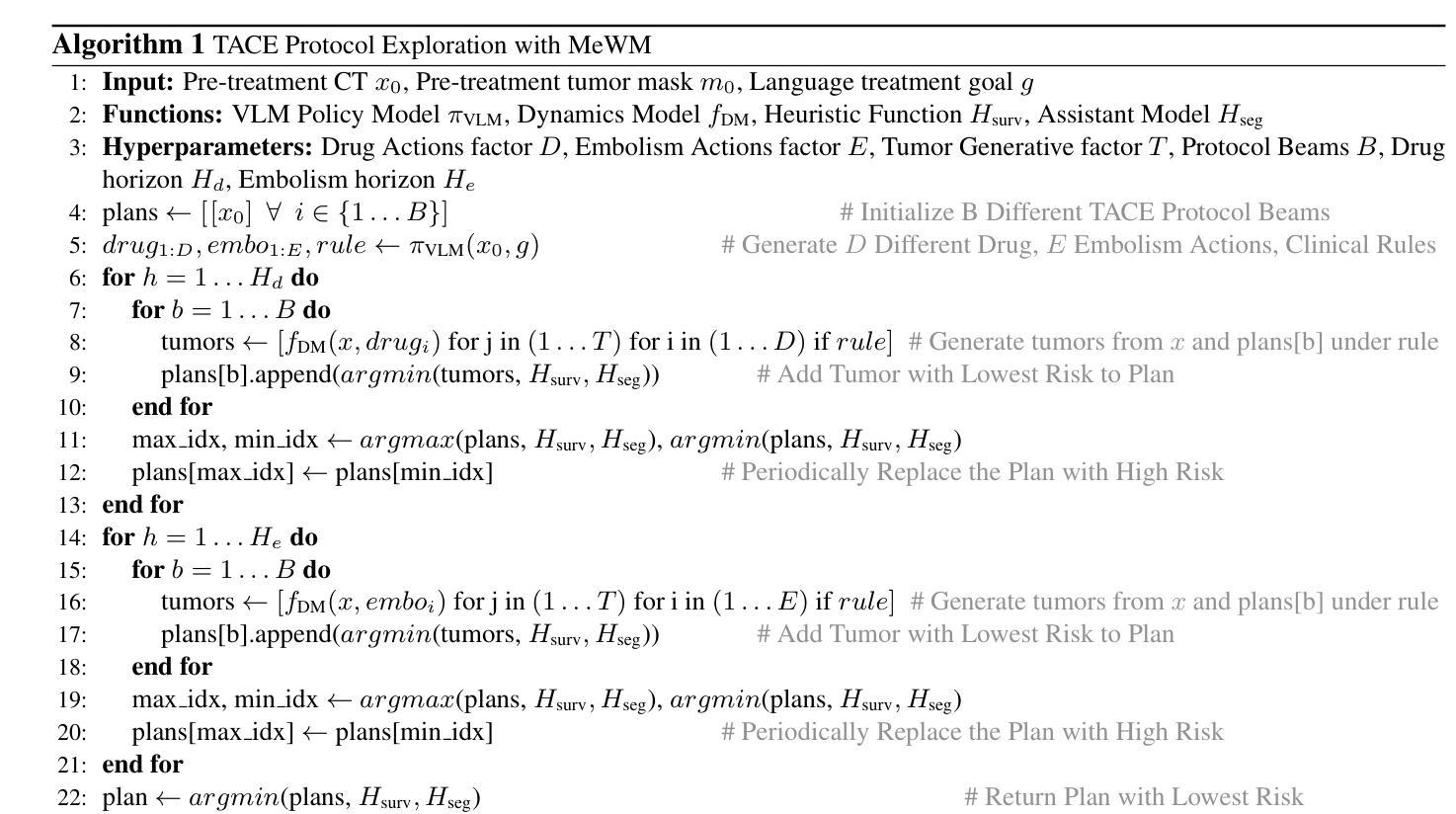
Medical World Model: Generative Simulation of Tumor Evolution for Treatment Planning
Authors:Yijun Yang, Zhao-Yang Wang, Qiuping Liu, Shuwen Sun, Kang Wang, Rama Chellappa, Zongwei Zhou, Alan Yuille, Lei Zhu, Yu-Dong Zhang, Jieneng Chen
Providing effective treatment and making informed clinical decisions are essential goals of modern medicine and clinical care. We are interested in simulating disease dynamics for clinical decision-making, leveraging recent advances in large generative models. To this end, we introduce the Medical World Model (MeWM), the first world model in medicine that visually predicts future disease states based on clinical decisions. MeWM comprises (i) vision-language models to serve as policy models, and (ii) tumor generative models as dynamics models. The policy model generates action plans, such as clinical treatments, while the dynamics model simulates tumor progression or regression under given treatment conditions. Building on this, we propose the inverse dynamics model that applies survival analysis to the simulated post-treatment tumor, enabling the evaluation of treatment efficacy and the selection of the optimal clinical action plan. As a result, the proposed MeWM simulates disease dynamics by synthesizing post-treatment tumors, with state-of-the-art specificity in Turing tests evaluated by radiologists. Simultaneously, its inverse dynamics model outperforms medical-specialized GPTs in optimizing individualized treatment protocols across all metrics. Notably, MeWM improves clinical decision-making for interventional physicians, boosting F1-score in selecting the optimal TACE protocol by 13%, paving the way for future integration of medical world models as the second readers.
在现代医学和临床护理中,提供有效的治疗方法和做出明智的临床决策是不可或缺的目标。我们感兴趣的是利用大型生成模型的最新进展来模拟疾病动态以辅助临床决策。为此,我们引入了医学世界模型(MeWM),这是医学领域中的首个世界模型,能够基于临床决策视觉预测未来的疾病状态。MeWM包括(i)视觉语言模型,用作策略模型,(ii)肿瘤生成模型,用作动态模型。策略模型生成行动计划,如临床治疗,而动态模型模拟在给定的治疗条件下的肿瘤进展或消退。在此基础上,我们提出了逆向动态模型,对模拟的肿瘤进行生存分析以评估治疗效果和选择最佳的临床行动计划。因此,所提出的MeWM通过合成治疗后的肿瘤来模拟疾病动态,其在图灵测试中表现出最新的特异性水平并得到放射科的评估验证。同时,其逆向动态模型在优化个体化治疗方案方面优于医学专用GPT模型的所有指标。值得注意的是,MeWM提高了介入医师的临床决策能力,在选择最佳TACE协议时提高了F1分数达13%,为未来的医学世界模型作为第二诊断医师的整合铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学世界模型(MeWM)利用大型生成模型,模拟疾病动态以辅助临床决策。MeWM包括策略模型和动态模型两部分,分别生成治疗计划和模拟肿瘤发展。其逆动态模型应用生存分析评估治疗效果,优化治疗方案选择。MeWM在肿瘤模拟上具有先进特异性,在医生评估中表现优异,优化个体化治疗协议,提高医生决策准确性。
Key Takeaways
- MeWM是首个用于医学领域的世界模型,可通过视觉预测未来疾病状态,辅助临床决策。
- MeWM包括策略模型和动态模型,分别负责生成治疗计划和模拟肿瘤发展。
- MeWM的逆动态模型应用生存分析评估治疗效果,优化治疗方案选择。
- MeWM在模拟疾病动态方面具有先进特异性,在医生评估中表现优异。
- 与医疗专业GPT相比,MeWM在优化个体化治疗协议方面表现出更高的性能。
- MeWM提高了医生在临床决策中的准确性,特别是在选择最佳TACE协议方面。
点此查看论文截图

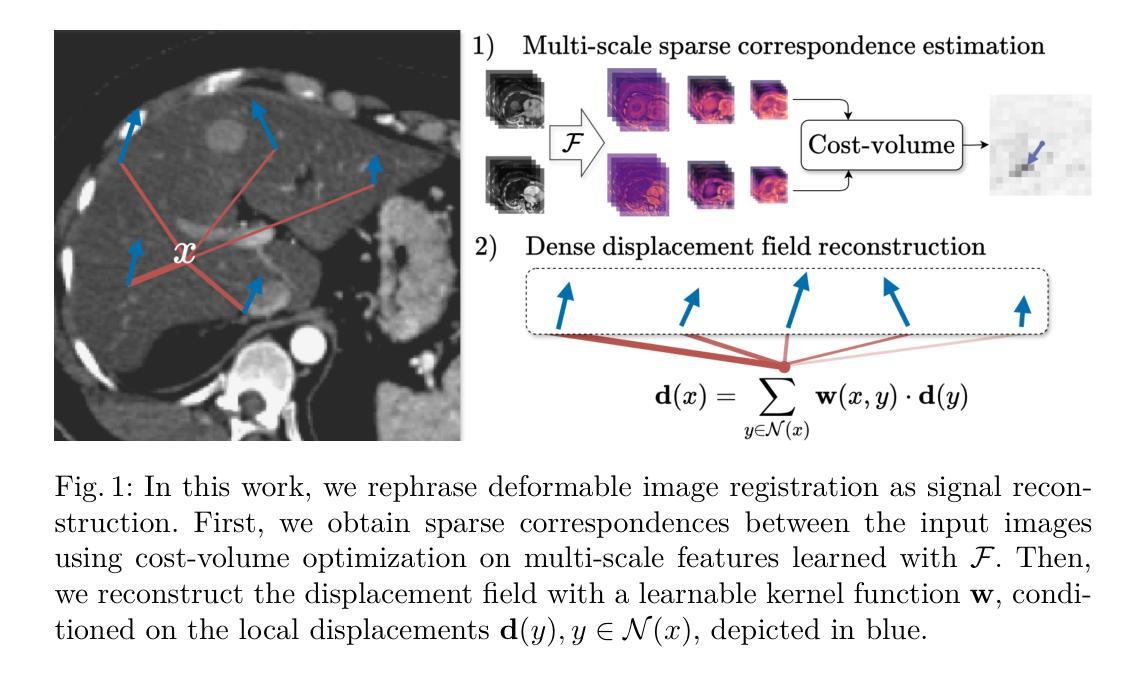
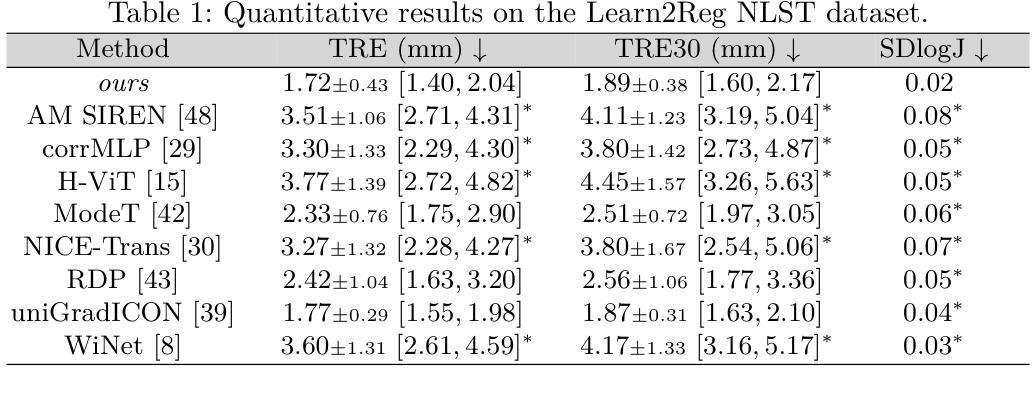
Implicit Deformable Medical Image Registration with Learnable Kernels
Authors:Stefano Fogarollo, Gregor Laimer, Reto Bale, Matthias Harders
Deformable medical image registration is an essential task in computer-assisted interventions. This problem is particularly relevant to oncological treatments, where precise image alignment is necessary for tracking tumor growth, assessing treatment response, and ensuring accurate delivery of therapies. Recent AI methods can outperform traditional techniques in accuracy and speed, yet they often produce unreliable deformations that limit their clinical adoption. In this work, we address this challenge and introduce a novel implicit registration framework that can predict accurate and reliable deformations. Our insight is to reformulate image registration as a signal reconstruction problem: we learn a kernel function that can recover the dense displacement field from sparse keypoint correspondences. We integrate our method in a novel hierarchical architecture, and estimate the displacement field in a coarse-to-fine manner. Our formulation also allows for efficient refinement at test time, permitting clinicians to easily adjust registrations when needed. We validate our method on challenging intra-patient thoracic and abdominal zero-shot registration tasks, using public and internal datasets from the local University Hospital. Our method not only shows competitive accuracy to state-of-the-art approaches, but also bridges the generalization gap between implicit and explicit registration techniques. In particular, our method generates deformations that better preserve anatomical relationships and matches the performance of specialized commercial systems, underscoring its potential for clinical adoption.
可变形医学图像配准是计算机辅助干预中的一项重要任务。这个问题在肿瘤治疗中尤其重要,因为需要精确的图像对齐以追踪肿瘤生长情况、评估治疗效果,并确保准确的治疗方案实施。虽然最近的AI方法在准确性和速度方面可以超越传统技术,但它们通常会产生不可靠的变形,限制了其在临床上的采用。在这项工作中,我们解决了这一挑战,并引入了一种新型隐式配准框架,可以预测准确且可靠的变形。我们的见解是将图像配准重新表述为信号重建问题:我们学习一个内核函数,可以从稀疏关键点对应关系恢复密集位移场。我们将该方法集成到一种新型分层架构中,以从粗到细的方式估计位移场。我们的公式还允许在测试时进行高效的优化调整,使临床医生能够根据需要轻松调整配准。我们在具有挑战性的患者内部胸腔和腹部零射击配准任务上验证了我们的方法,使用了公共和本地大学医院的内部数据集。我们的方法不仅展示了与最新技术相竞争准确性,而且弥合了隐式和显式配准技术之间的泛化差距。特别是,我们的方法生成的变形更好地保留了解剖关系,并匹配了专业商业系统的性能,突显了其临床采用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025 Provisional Accept
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的隐式注册框架,用于解决医学图像变形注册的问题。该框架将图像注册重新构建为信号重建问题,通过学习从稀疏关键点对应关系中恢复密集位移场。该框架结合了分层架构,并以从粗到细的方式估计位移场。此外,它允许在测试时进行高效的调整,使临床医生能够根据需要轻松调整注册。本文的方法在具有挑战性的患者内部胸腔和腹部零射击注册任务上进行了验证,并表现出与最新技术相当的准确性,同时在隐式和显式注册技术之间建立了桥梁。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了隐式注册框架来解决医学图像变形注册问题。
- 将图像注册重新构建为信号重建问题,学习从稀疏关键点对应关系中恢复密集位移场。
- 结合分层架构,以从粗到细的方式估计位移场。
- 方法允许在测试时进行高效的调整,方便临床医生按需调整注册。
- 方法在挑战性的患者内部胸腔和腹部零射击注册任务上进行了验证。
- 与最新技术相比,该方法表现出相当的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

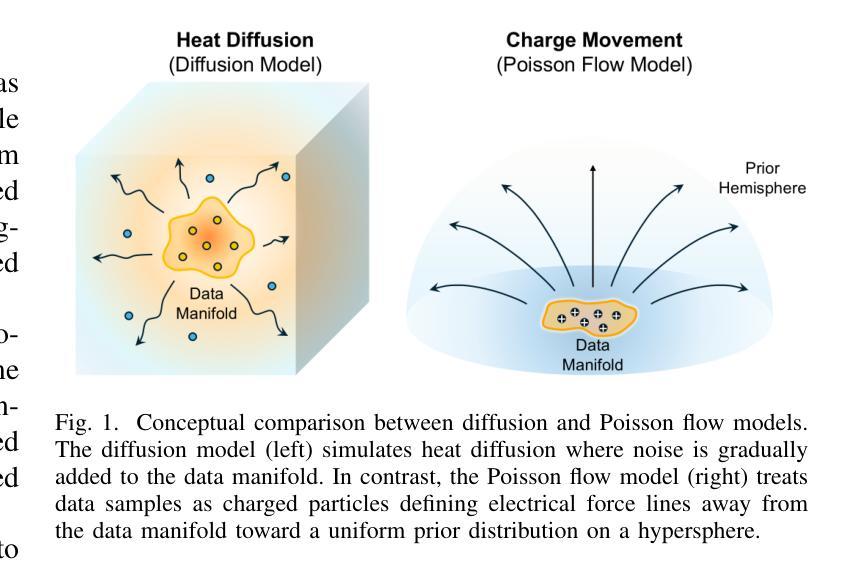
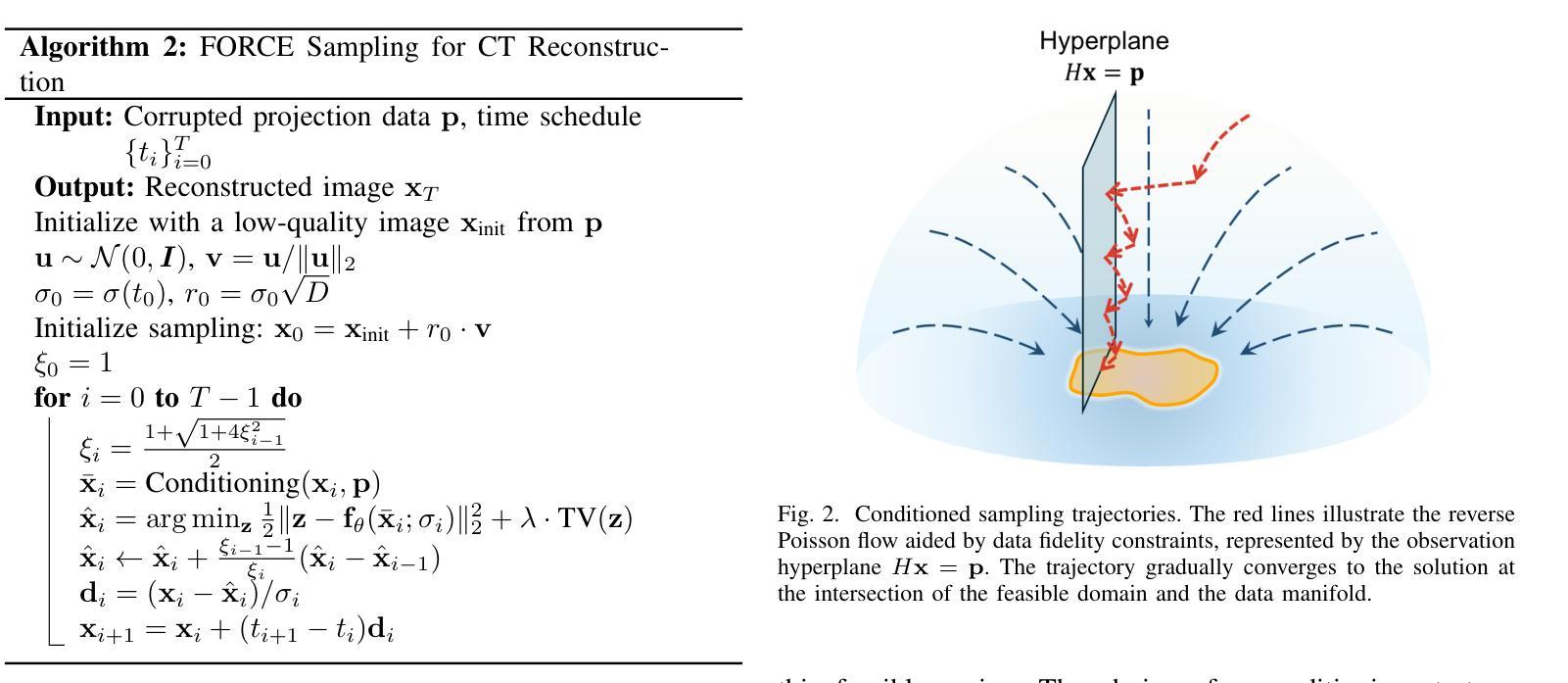
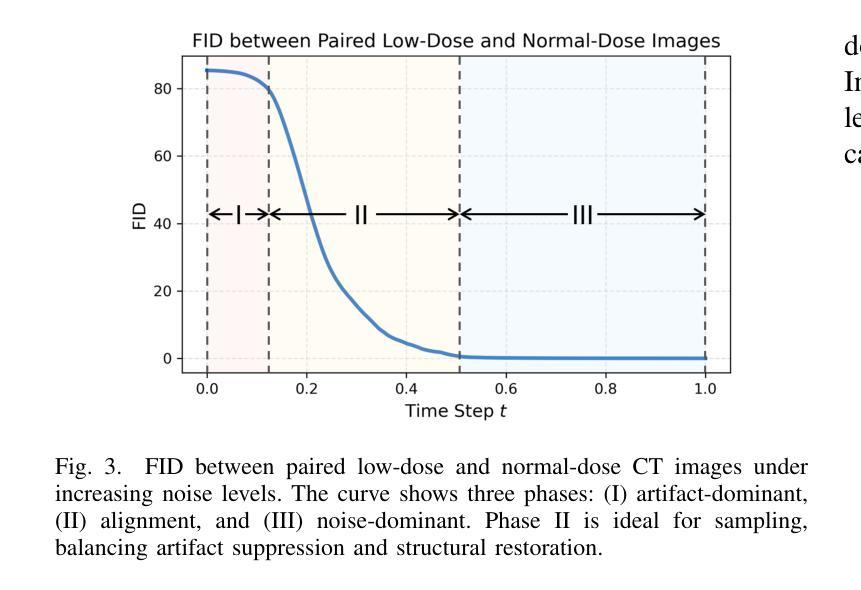
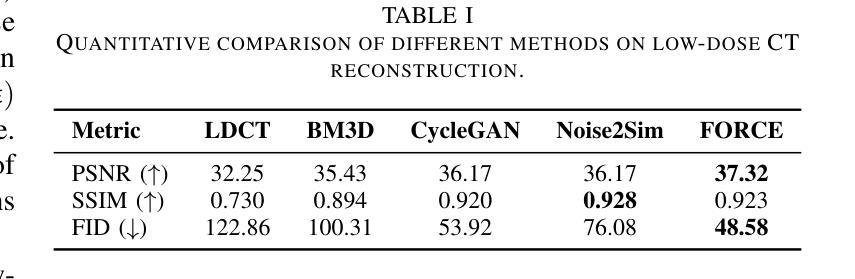
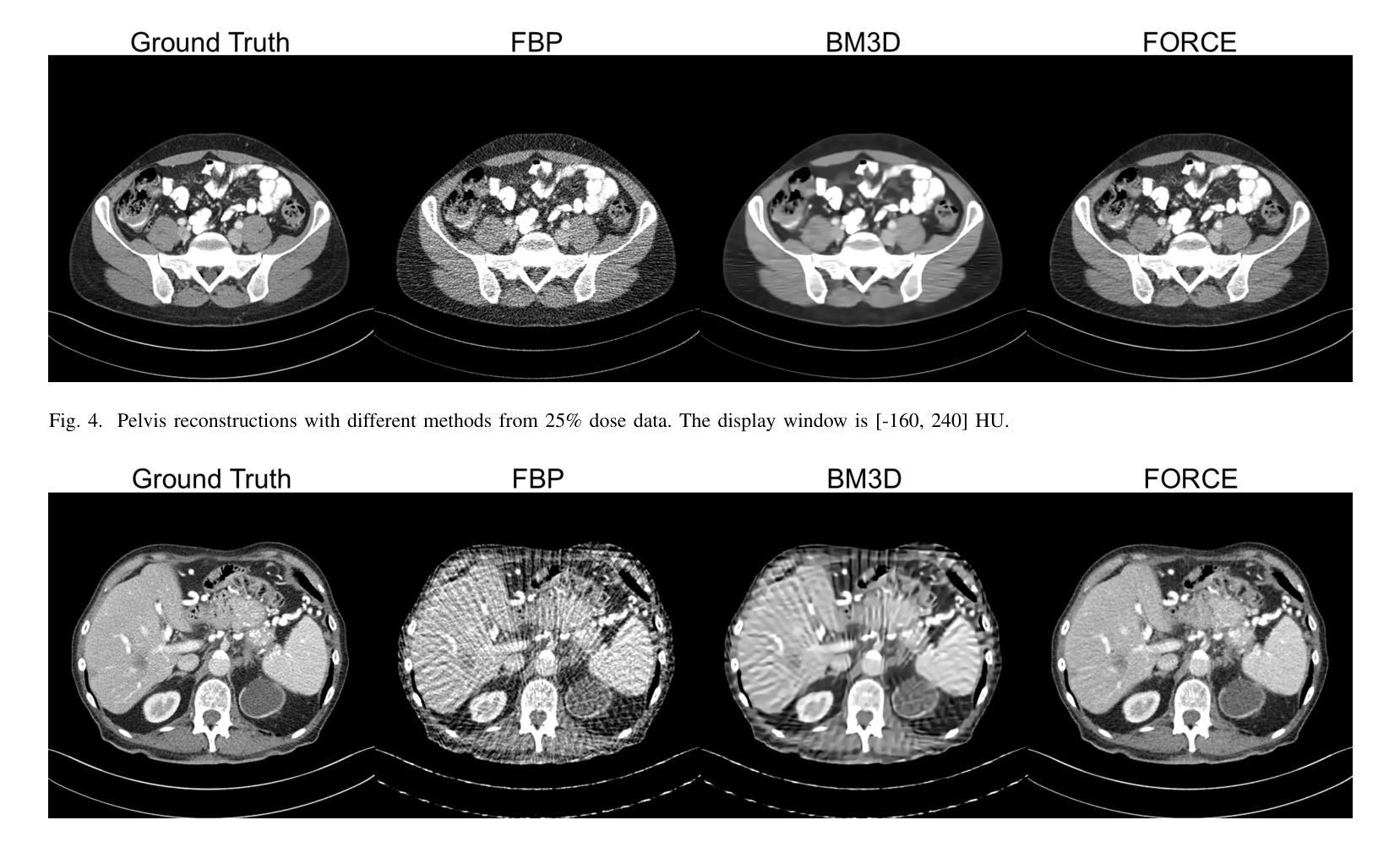
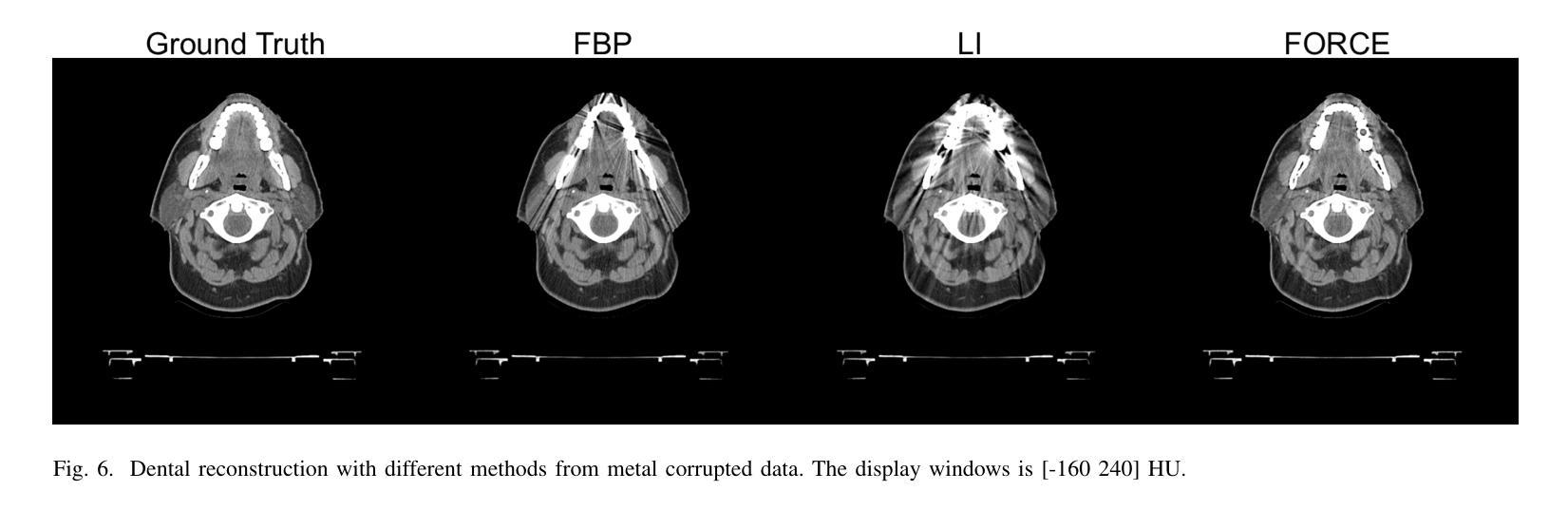
Tomographic Foundation Model – FORCE: Flow-Oriented Reconstruction Conditioning Engine
Authors:Wenjun Xia, Chuang Niu, Ge Wang
Computed tomography (CT) is a major medical imaging modality. Clinical CT scenarios, such as low-dose screening, sparse-view scanning, and metal implants, often lead to severe noise and artifacts in reconstructed images, requiring improved reconstruction techniques. The introduction of deep learning has significantly advanced CT image reconstruction. However, obtaining paired training data remains rather challenging due to patient motion and other constraints. Although deep learning methods can still perform well with approximately paired data, they inherently carry the risk of hallucination due to data inconsistencies and model instability. In this paper, we integrate the data fidelity with the state-of-the-art generative AI model, referred to as the Poisson flow generative model (PFGM) with a generalized version PFGM++, and propose a novel CT framework: Flow-Oriented Reconstruction Conditioning Engine (FORCE). In our experiments, the proposed method shows superior performance in various CT imaging tasks, outperforming existing unsupervised reconstruction approaches.
计算机断层扫描(CT)是一种主要的医学成像模式。在临床CT场景中,如低剂量筛查、稀疏视图扫描和金属植入物,重建的图像往往会产生严重的噪声和伪影,这要求改进重建技术。深度学习引入到CT图像重建中取得了显著进展。然而,由于患者移动和其他约束条件,获取配对训练数据仍然相当具有挑战性。尽管深度学习方法仍然可以在近似配对数据上表现良好,但由于数据不一致和模型不稳定,它们天生存在出现幻觉的风险。在本文中,我们将数据保真度与最新生成的人工智能模型相结合,称为Poisson流生成模型(PFGM)及其通用版本PFGM++,并提出了一种新型的CT框架:面向流动的重建调节引擎(FORCE)。在我们的实验中,该方法在各种CT成像任务中表现出卓越的性能,超越了现有的无监督重建方法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了基于深度学习和生成式AI模型的医学CT图像重建技术。由于临床CT场景中常常存在噪声和伪影问题,需要改进重建技术。作者提出了一个名为FORCE的新型CT框架,结合了数据保真度和最新的生成式AI模型——Poisson流生成模型(PFGM)及其广义版本PFGM++。实验表明,该方法在多种CT成像任务上表现出卓越性能,优于现有的无监督重建方法。
关键见解
- CT图像重建技术在临床应用中面临噪声和伪影问题,需要改进。
- 深度学习在CT图像重建中的应用受到配对训练数据获取的挑战。
- 患者运动和其他约束是获取配对训练数据的主要难题。
- 深度学习方法在大约配对数据上表现良好,但存在数据不一致和模型不稳定的风险。
- 作者提出了结合数据保真度和生成式AI模型的FORCE框架。
- FORCE框架使用了Poisson流生成模型(PFGM)及其广义版本PFGM++。
- 实验表明,FORCE框架在多种CT成像任务上的性能优于现有的无监督重建方法。
点此查看论文截图


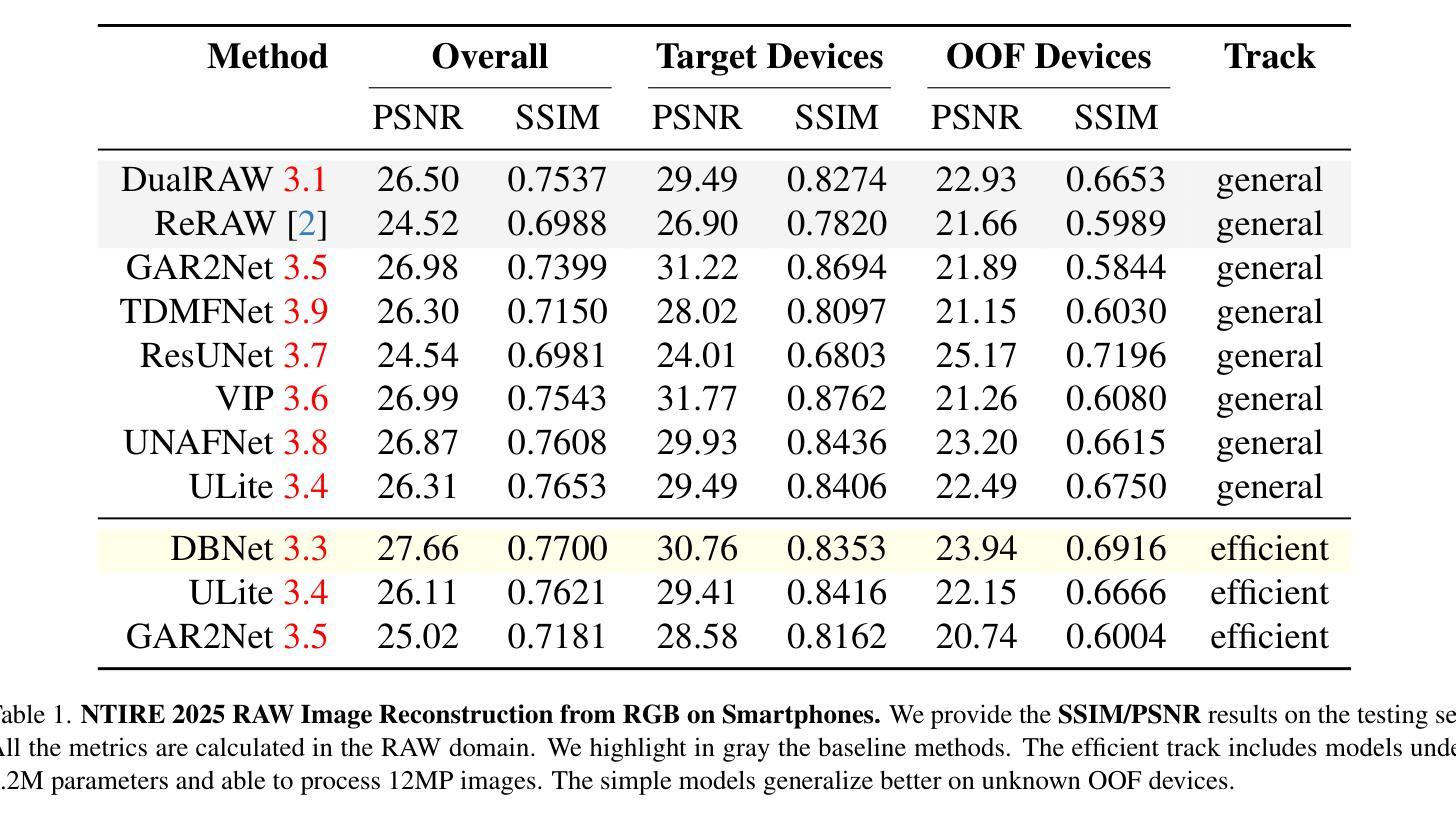
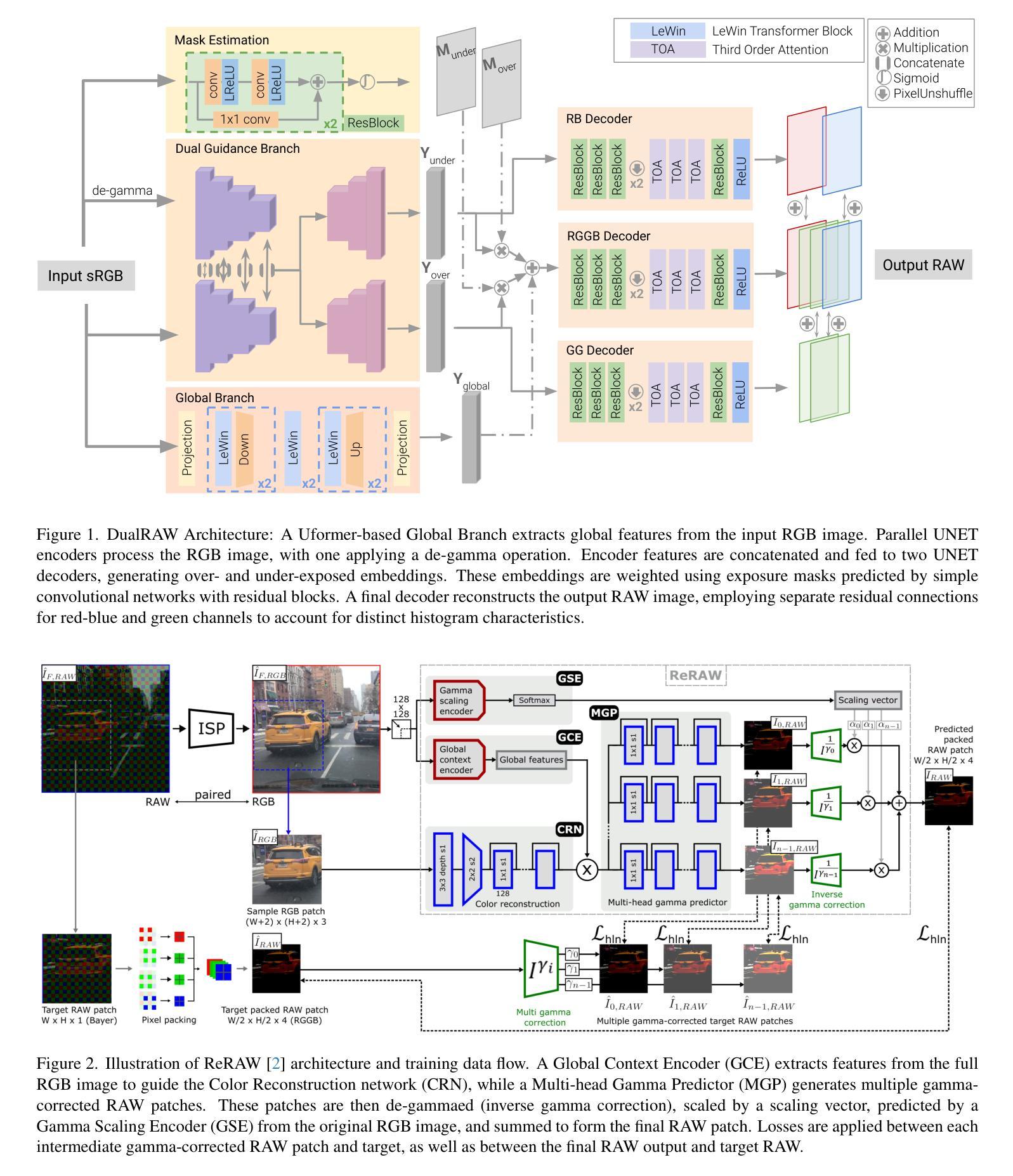
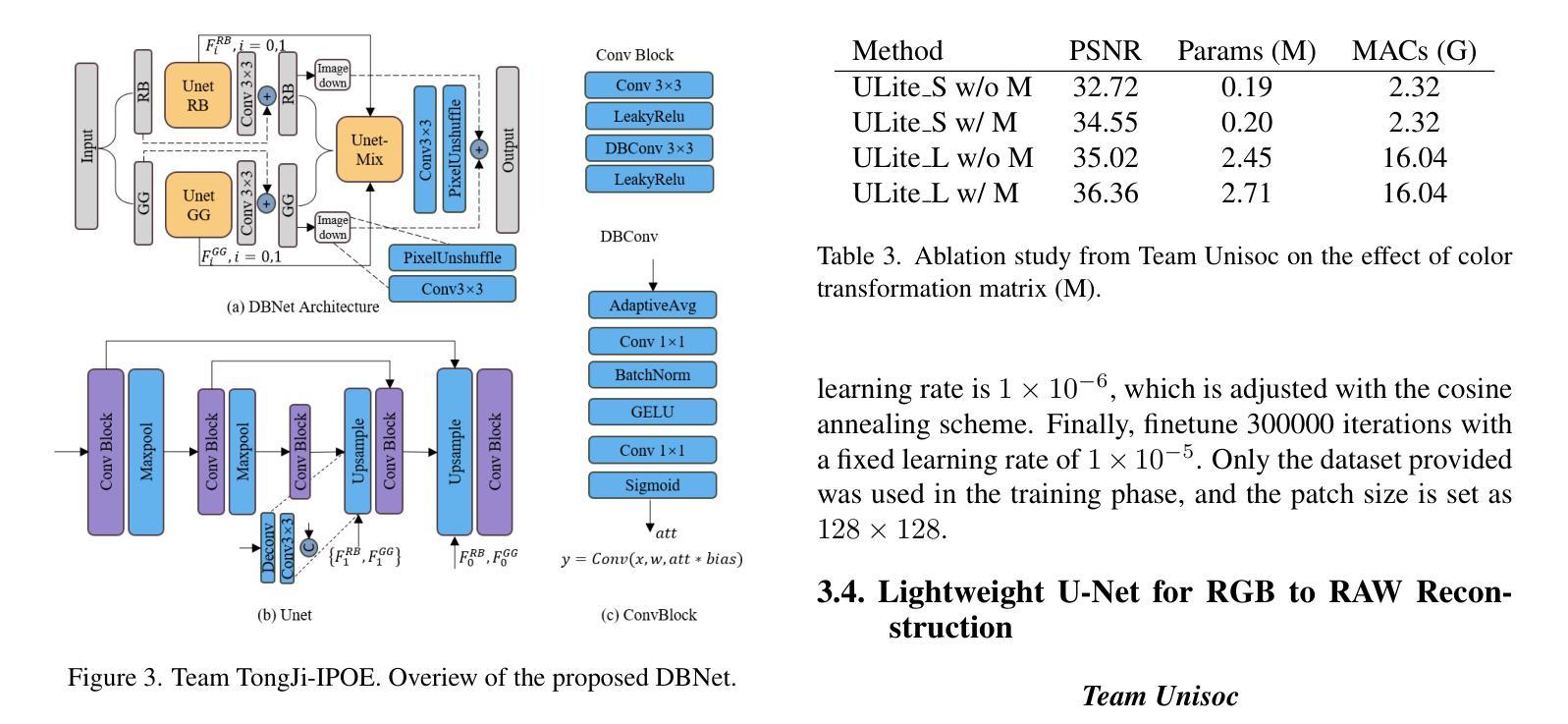
RAW Image Reconstruction from RGB on Smartphones. NTIRE 2025 Challenge Report
Authors:Marcos V. Conde, Radu Timofte, Radu Berdan, Beril Besbinar, Daisuke Iso, Pengzhou Ji, Xiong Dun, Zeying Fan, Chen Wu, Zhansheng Wang, Pengbo Zhang, Jiazi Huang, Qinglin Liu, Wei Yu, Shengping Zhang, Xiangyang Ji, Kyungsik Kim, Minkyung Kim, Hwalmin Lee, Hekun Ma, Huan Zheng, Yanyan Wei, Zhao Zhang, Jing Fang, Meilin Gao, Xiang Yu, Shangbin Xie, Mengyuan Sun, Huanjing Yue, Jingyu Yang Huize Cheng, Shaomeng Zhang, Zhaoyang Zhang, Haoxiang Liang
Numerous low-level vision tasks operate in the RAW domain due to its linear properties, bit depth, and sensor designs. Despite this, RAW image datasets are scarce and more expensive to collect than the already large and public sRGB datasets. For this reason, many approaches try to generate realistic RAW images using sensor information and sRGB images. This paper covers the second challenge on RAW Reconstruction from sRGB (Reverse ISP). We aim to recover RAW sensor images from smartphones given the corresponding sRGB images without metadata and, by doing this, ``reverse” the ISP transformation. Over 150 participants joined this NTIRE 2025 challenge and submitted efficient models. The proposed methods and benchmark establish the state-of-the-art for generating realistic RAW data.
由于RAW域的线性属性、位深度和传感器设计,许多低级视觉任务都在RAW域中进行。尽管如此,RAW图像数据集非常稀缺,且收集成本高于已经大量存在的公开sRGB数据集。因此,许多方法试图利用传感器信息和sRGB图像生成逼真的RAW图像。本文涉及从sRGB进行RAW重建(反向ISP)的第二个挑战。我们的目标是在没有元数据的情况下,根据相应的sRGB图像恢复来自智能手机的RAW传感器图像,并因此“反向”ISP转换。超过150名参与者加入了这一NTIRE 2025挑战赛,并提交了高效模型。所提出的方法和基准测试建立了生成逼真RAW数据的最新技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025 - New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement (NTIRE)
Summary
本文介绍了在RAW域进行低层次视觉任务的重要性,但由于RAW图像数据集稀缺且收集成本较高,许多方法尝试利用传感器信息和sRGB图像生成逼真的RAW图像。本文重点介绍了从sRGB图像重建RAW传感器图像的第二个挑战(反向ISP)。目标是利用对应的sRGB图像恢复RAW传感器图像,无需元数据参与。超过150名参与者参加了NTIRE 2025挑战赛,并提出了有效的模型,为生成逼真的RAW数据建立了最新标准。
Key Takeaways
- RAW域因其线性特性、位深度和传感器设计而被用于众多低层次视觉任务。
- RAW图像数据集稀缺且收集成本较高,因此有研究尝试用sRGB图像和传感器信息生成逼真的RAW图像。
- 本文关注从sRGB图像重建RAW传感器图像的第二个挑战,即反向ISP。
- 目标是仅使用对应的sRGB图像恢复RAW传感器图像,无需元数据参与。
- 超过150名参与者参与了NTIRE 2025挑战赛,提出了多种高效模型。
点此查看论文截图


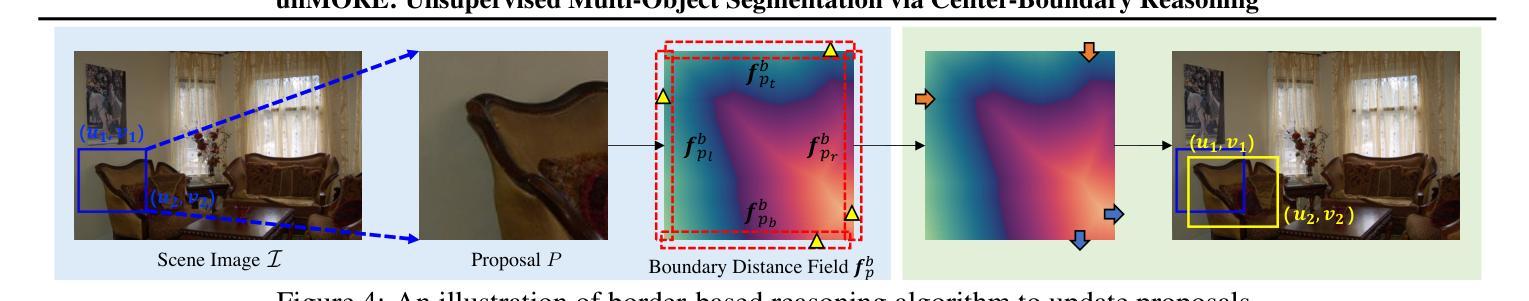
unMORE: Unsupervised Multi-Object Segmentation via Center-Boundary Reasoning
Authors:Yafei Yang, Zihui Zhang, Bo Yang
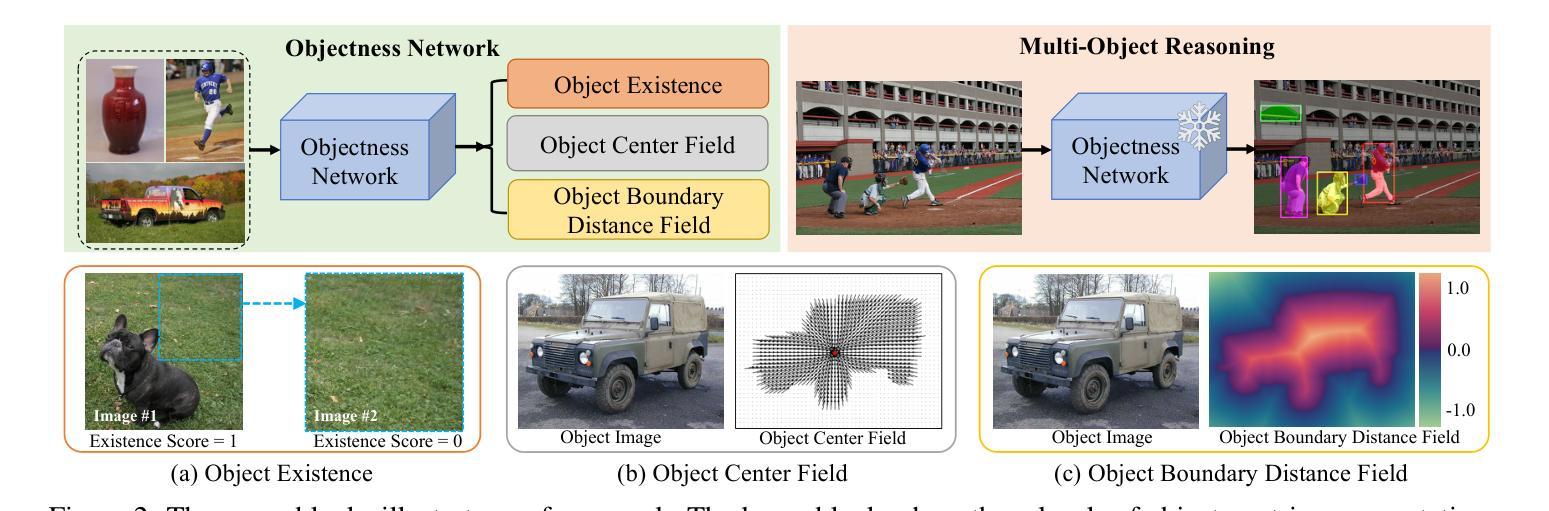
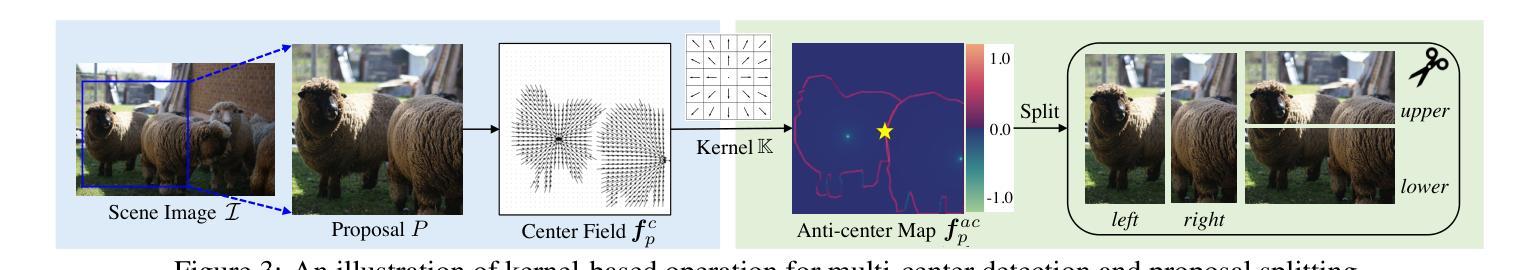
We study the challenging problem of unsupervised multi-object segmentation on single images. Existing methods, which rely on image reconstruction objectives to learn objectness or leverage pretrained image features to group similar pixels, often succeed only in segmenting simple synthetic objects or discovering a limited number of real-world objects. In this paper, we introduce unMORE, a novel two-stage pipeline designed to identify many complex objects in real-world images. The key to our approach involves explicitly learning three levels of carefully defined object-centric representations in the first stage. Subsequently, our multi-object reasoning module utilizes these learned object priors to discover multiple objects in the second stage. Notably, this reasoning module is entirely network-free and does not require human labels. Extensive experiments demonstrate that unMORE significantly outperforms all existing unsupervised methods across 6 real-world benchmark datasets, including the challenging COCO dataset, achieving state-of-the-art object segmentation results. Remarkably, our method excels in crowded images where all baselines collapse.
我们研究了单图像的无监督多目标分割这一具有挑战性的问题。现有方法往往依赖于图像重建目标来学习对象性,或者利用预训练的图像特征来将相似的像素组合在一起,但它们通常仅在分割简单合成对象或发现有限数量的真实世界对象时成功。在本文中,我们介绍了unMORE,这是一种新型的两阶段流程,旨在识别真实世界图像中的多个复杂对象。我们的方法的关键在于在第一阶段显式地学习三个层次精心定义的以对象为中心的表示。随后,我们的多目标推理模块利用这些学习到的对象先验知识在第二阶段发现多个对象。值得注意的是,该推理模块完全无需网络且不需要人工标签。大量实验表明,在包括具有挑战性的COCO数据集在内的六个真实世界基准数据集上,unMORE显著优于所有现有无监督方法,实现了最先进的对象分割结果。值得注意的是,我们的方法在拥挤的图像中的表现尤为出色,而所有基线方法均在此处失效。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025. Code and data are available at: https://github.com/vLAR-group/unMORE
Summary
本文研究了单图像的无监督多目标分割问题。针对现有方法(如依赖图像重建目标来学习对象性,或利用预训练图像特征来分组相似像素)在分割复杂现实世界对象时的局限性,本文提出了一种新型的两阶段管道unMORE。该方法第一阶段通过显式学习三个层次的对象中心表示,第二阶段利用多目标推理模块发现多个对象,无需网络且无需人为标签。在六个现实世界基准数据集上的实验表明,unMORE在包括具有挑战性的COCO数据集上实现了最先进的目标分割结果。特别地,该方法在拥挤图像中的表现超越了所有基线。
Key Takeaways
- 研究无监督多目标分割在单图像的问题。
- 现有方法在分割复杂现实世界对象时存在局限性。
- 引入了一种新型的两阶段管道unMORE来解决这个问题。
- 第一阶段通过显式学习三个层次的对象中心表示。
- 第二阶段利用多目标推理模块发现多个对象,无需网络和人为标签。
- 在多个现实世界数据集上的实验表明,unMORE显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

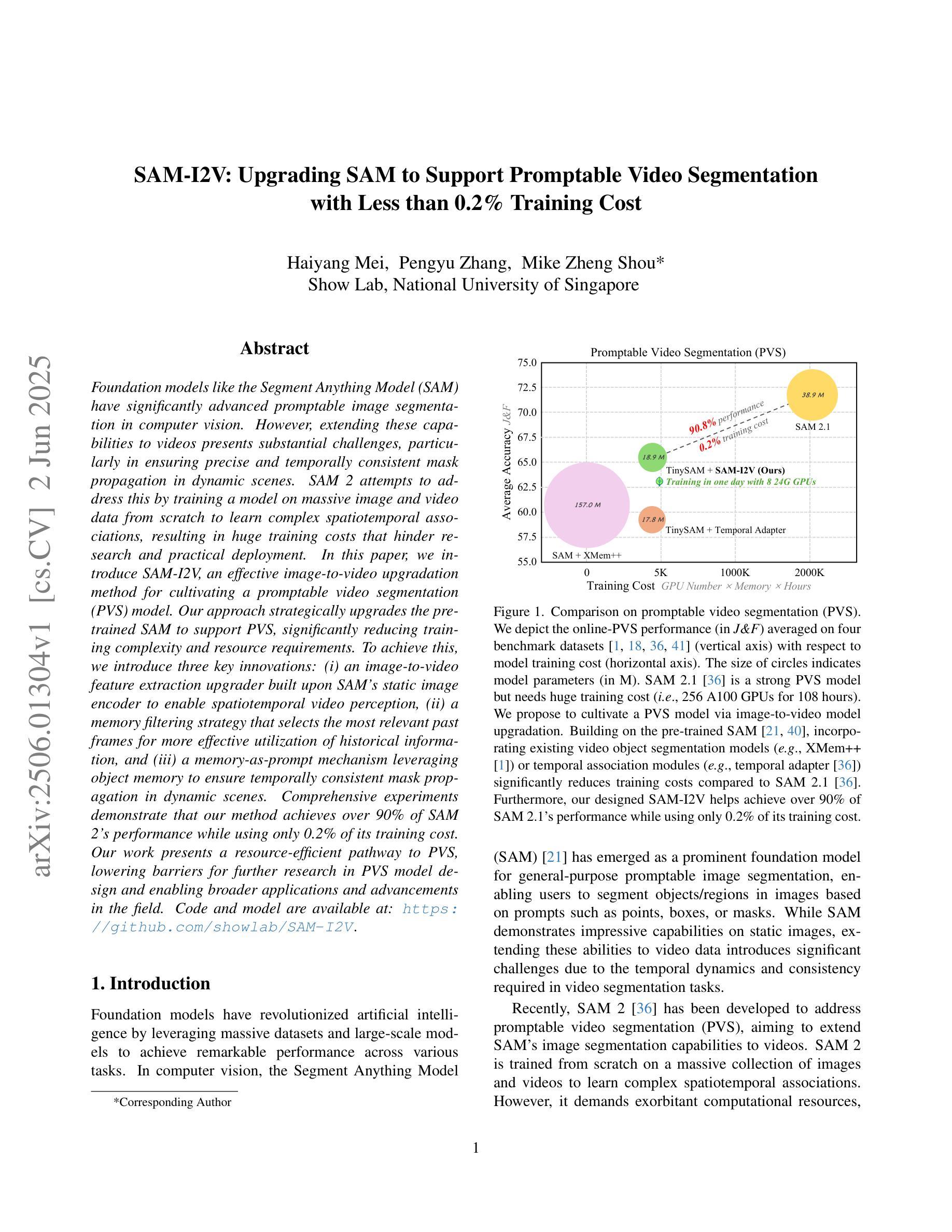
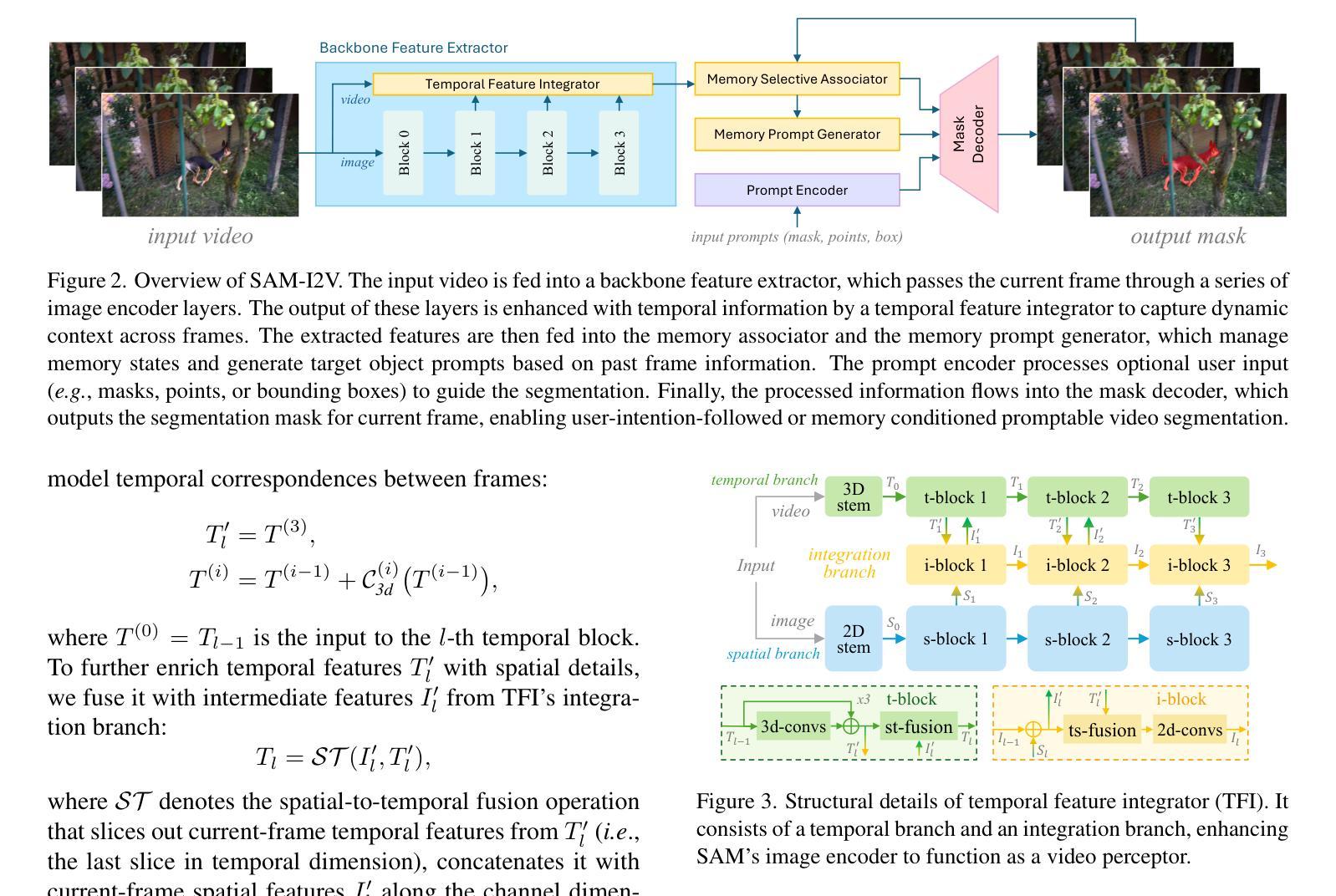
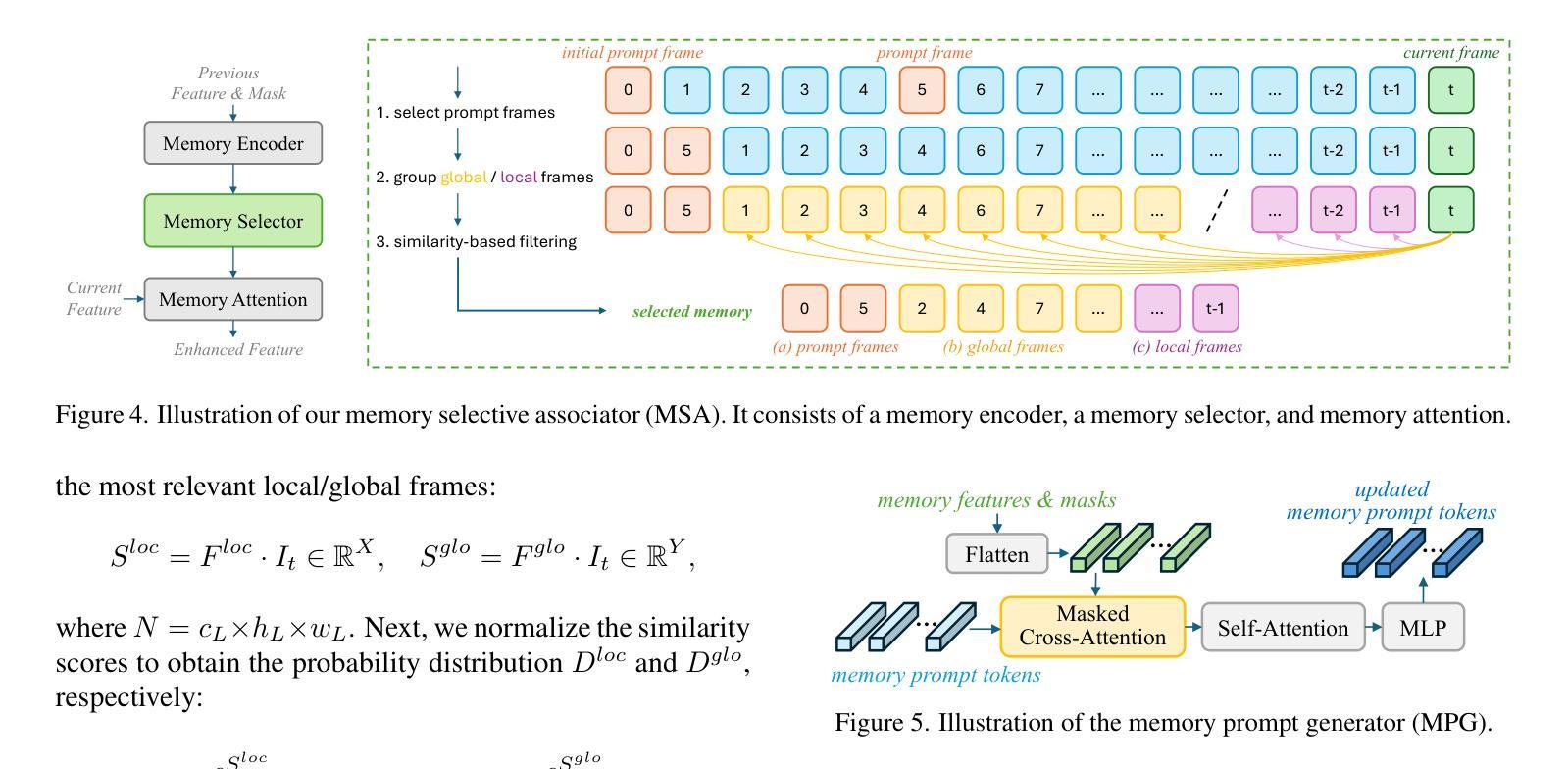
SAM-I2V: Upgrading SAM to Support Promptable Video Segmentation with Less than 0.2% Training Cost
Authors:Haiyang Mei, Pengyu Zhang, Mike Zheng Shou
Foundation models like the Segment Anything Model (SAM) have significantly advanced promptable image segmentation in computer vision. However, extending these capabilities to videos presents substantial challenges, particularly in ensuring precise and temporally consistent mask propagation in dynamic scenes. SAM 2 attempts to address this by training a model on massive image and video data from scratch to learn complex spatiotemporal associations, resulting in huge training costs that hinder research and practical deployment. In this paper, we introduce SAM-I2V, an effective image-to-video upgradation method for cultivating a promptable video segmentation (PVS) model. Our approach strategically upgrades the pre-trained SAM to support PVS, significantly reducing training complexity and resource requirements. To achieve this, we introduce three key innovations: (i) an image-to-video feature extraction upgrader built upon SAM’s static image encoder to enable spatiotemporal video perception, (ii) a memory filtering strategy that selects the most relevant past frames for more effective utilization of historical information, and (iii) a memory-as-prompt mechanism leveraging object memory to ensure temporally consistent mask propagation in dynamic scenes. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves over 90% of SAM 2’s performance while using only 0.2% of its training cost. Our work presents a resource-efficient pathway to PVS, lowering barriers for further research in PVS model design and enabling broader applications and advancements in the field. Code and model are available at: https://github.com/showlab/SAM-I2V.
类似Segment Anything Model(SAM)这样的基础模型已经在计算机视觉的可提示图像分割方面取得了显著进展。然而,将这些能力扩展到视频却面临着巨大挑战,特别是在确保动态场景中的精确和时间上一致的掩膜传播方面。SAM 2 通过在大量图像和视频数据上进行模型训练来学习复杂的时空关联,以解决这一问题,但这也导致了巨大的训练成本,阻碍了研究和实际应用部署。在本文中,我们介绍了一种有效的图像到视频的升级方法SAM-I2V,用于培养可提示视频分割(PVS)模型。我们的方法通过升级预训练的SAM来支持PVS,显著降低了训练复杂性和资源需求。为实现这一目标,我们引入了三项关键创新:(i)基于SAM的静态图像编码器构建图像到视频特征提取升级器,以实现时空视频感知;(ii)一种记忆过滤策略,选择最相关的过去帧,以更有效地利用历史信息;(iii)一种记忆提示机制,利用对象内存确保动态场景中的时间上一致的掩膜传播。大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了SAM 2性能的90%以上,同时仅使用其0.2%的训练成本。我们的工作为PVS提供了一条资源高效的路径,降低了PVS模型设计的进一步研究障碍,并启用了该领域的更广泛应用和进展。代码和模型可在[https://github.com/showlab/SAM-I2V找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
SAM-I2V方法利用预训练的SAM图像模型,通过引入三项关键技术创新,实现了视频分割的升级,显著降低了训练复杂度和资源需求。该技术包括:基于SAM静态图像编码器的图像到视频特征提取升级器、记忆过滤策略以及利用对象记忆的内存提示机制。实验证明,该方法实现了超过90%的SAM 2性能,同时仅使用其0.2%的训练成本。
Key Takeaways
- SAM-I2V是Segment Anything Model(SAM)的视频分割升级方法。
- SAM-I2V解决了将图像分割模型应用于视频时面临的挑战,如精确且时间一致的掩膜传播。
- 通过三项关键技术创新实现视频分割的升级:图像到视频特征提取升级器、记忆过滤策略和内存提示机制。
- 实验证明,SAM-I2V实现了超过90%的SAM 2性能,同时大幅降低了训练成本和资源需求。
- SAM-I2V工作为可提示视频分割(PVS)提供了资源高效的途径,降低了进一步研究PVS模型设计的门槛,并促进了该领域的广泛应用和进一步发展。
点此查看论文截图
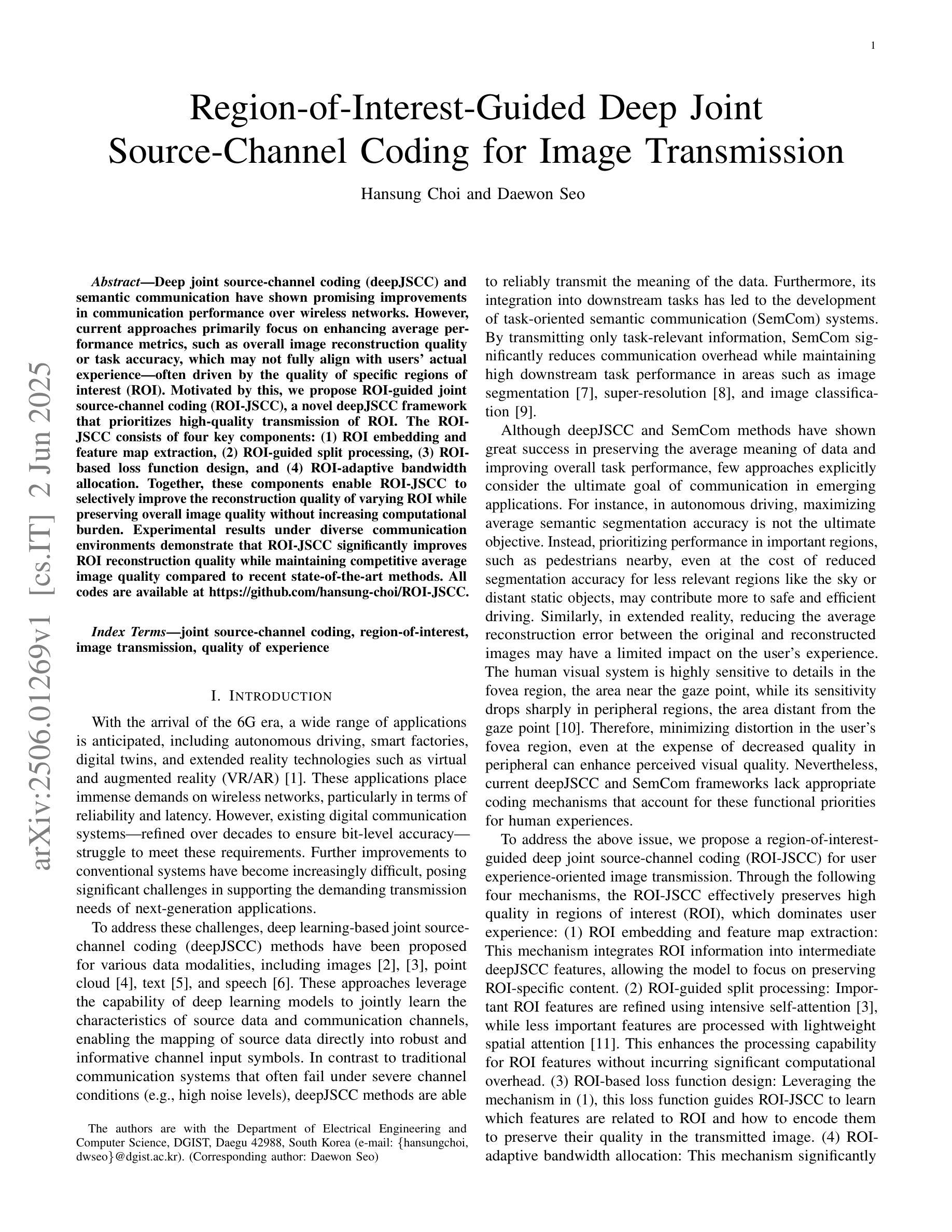
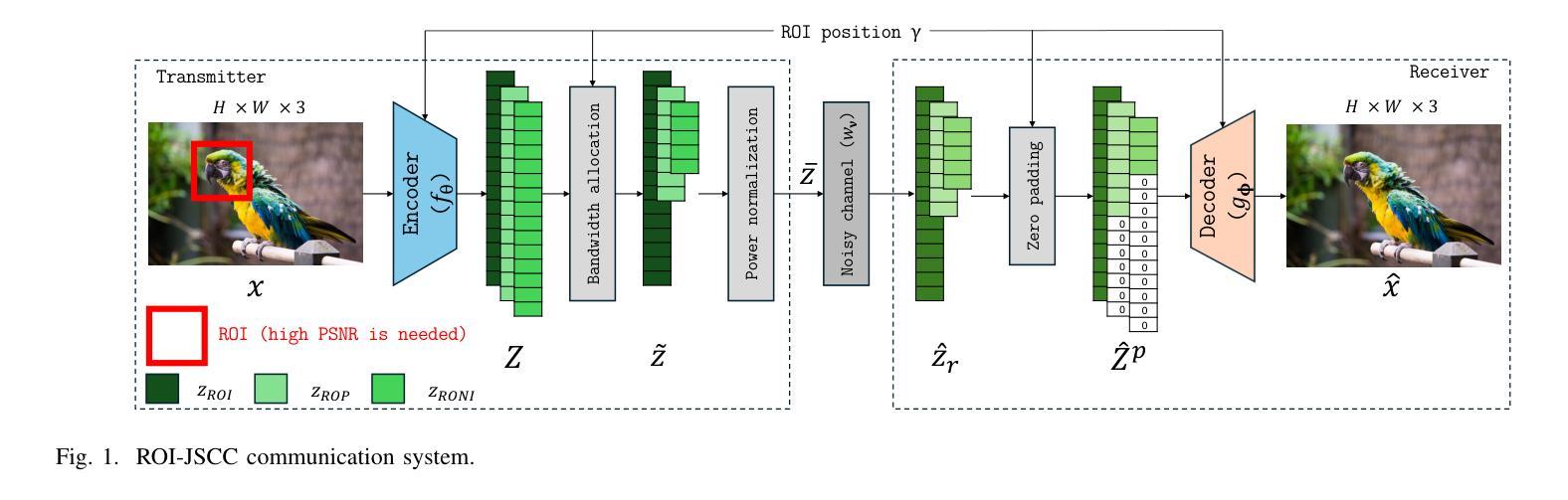
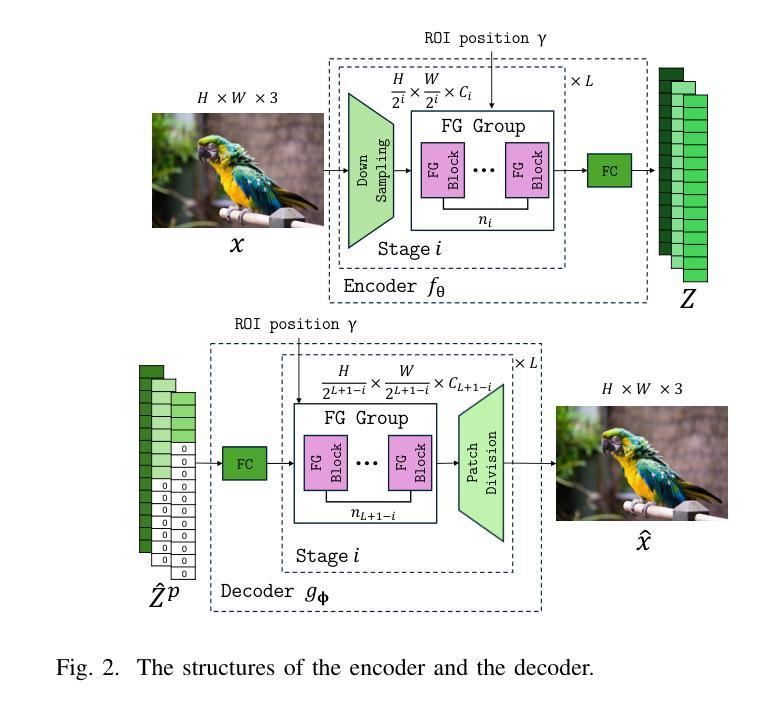
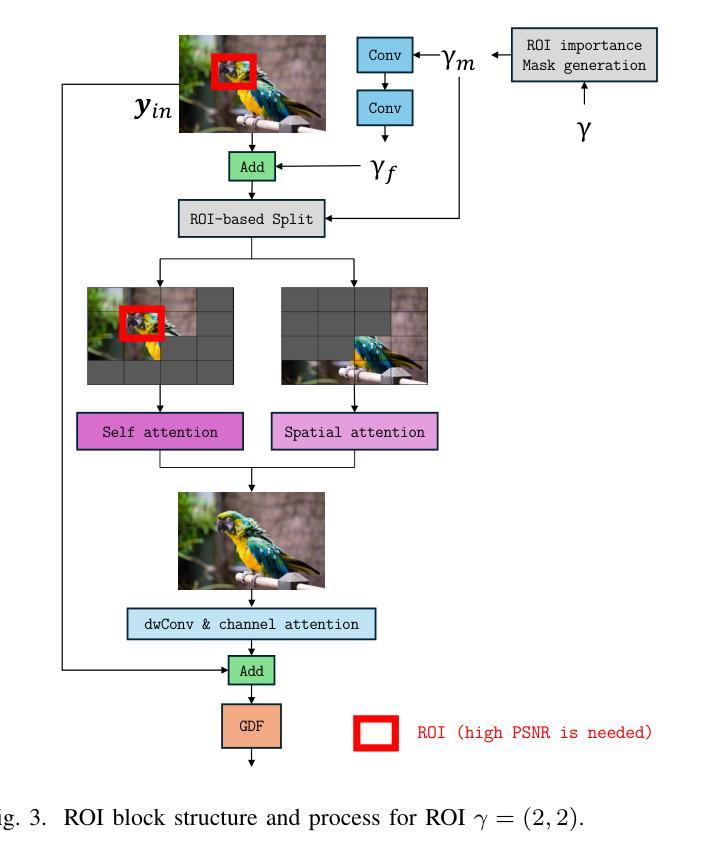
Region-of-Interest-Guided Deep Joint Source-Channel Coding for Image Transmission
Authors:Hansung Choi, Daewon Seo
Deep joint source-channel coding (deepJSCC) and semantic communication have shown promising improvements in communication performance over wireless networks. However, current approaches primarily focus on enhancing average performance metrics, such as overall image reconstruction quality or task accuracy, which may not fully align with users’ actual experience – often driven by the quality of specific regions of interest (ROI). Motivated by this, we propose ROI-guided joint source-channel coding (ROI-JSCC), a novel deepJSCC framework that prioritizes high-quality transmission of ROI. The ROI-JSCC consists of four key components: (1) ROI embedding and feature map extraction, (2) ROI-guided split processing, (3) ROI-based loss function design, and (4) ROI-adaptive bandwidth allocation. Together, these components enable ROI-JSCC to selectively improve the reconstruction quality of varying ROI while preserving overall image quality without increasing computational burden. Experimental results under diverse communication environments demonstrate that ROI-JSCC significantly improves ROI reconstruction quality while maintaining competitive average image quality compared to recent state-of-the-art methods. All codes are available at https://github.com/hansung-choi/ROI-JSCC.
深度联合源信道编码(deepJSCC)和语义通信在无线网络的通信性能上显示出有前景的改进。然而,当前的方法主要集中在提高平均性能指标,如整体图像重建质量或任务准确性,这可能无法完全与用户实际体验对齐,用户实际体验通常是由感兴趣区域(ROI)的质量驱动的。因此,我们提出了ROI引导联合源信道编码(ROI-JSCC),这是一种新型deepJSCC框架,优先高质量传输ROI。ROI-JSCC由四个关键组件构成:(1)ROI嵌入和特征映射提取,(2)ROI引导分裂处理,(3)基于ROI的损失函数设计,以及(4)ROI自适应带宽分配。这些组件共同作用,使ROI-JSCC能够在保持整体图像质量的同时,有选择地提高不同ROI的重建质量,且不增加计算负担。在多种通信环境下的实验结果表明,ROI-JSCC在保持平均图像质量竞争力的同时,显著提高了ROI的重建质量,与最近的最先进方法相比表现优异。所有代码可在https://github.com/hansung-choi/ROI-JSCC获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像通信中,深层联合源信道编码(deepJSCC)和语义通信已显示出在提高通信性能方面的潜力。当前方法主要关注平均性能指标,如整体图像重建质量或任务准确性,但可能无法完全与用户关注的特定感兴趣区域(ROI)的质量相匹配。因此,提出ROI引导的联合源信道编码(ROI-JSCC),优先传输ROI的高质量。它包括ROI嵌入、特征映射提取、ROI引导的分步处理、ROI基础的损失函数设计和ROI自适应的带宽分配等四个关键组件。实验结果表明,ROI-JSCC在保持整体图像质量的同时,显著提高ROI的重建质量。
Key Takeaways
- DeepJSCC和语义通信在医学图像通信中可提高性能。
- 当前方法主要关注平均性能指标,如整体图像重建质量。
- 用户实际关注的重点是特定感兴趣区域(ROI)的质量。
- ROI-JSCC是一种优先传输ROI高质量的新型deepJSCC框架。
- ROI-JSCC包括四个关键组件:ROI嵌入、特征映射、分步处理和损失函数设计。
- ROI-JSCC能够选择性提高不同ROI的重建质量,同时保持整体图像质量,且不增加计算负担。
点此查看论文截图

Revolutionizing Radiology Workflow with Factual and Efficient CXR Report Generation
Authors:Pimchanok Sukjai, Apiradee Boonmee
The escalating demand for medical image interpretation underscores the critical need for advanced artificial intelligence solutions to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of radiological diagnoses. This paper introduces CXR-PathFinder, a novel Large Language Model (LLM)-centric foundation model specifically engineered for automated chest X-ray (CXR) report generation. We propose a unique training paradigm, Clinician-Guided Adversarial Fine-Tuning (CGAFT), which meticulously integrates expert clinical feedback into an adversarial learning framework to mitigate factual inconsistencies and improve diagnostic precision. Complementing this, our Knowledge Graph Augmentation Module (KGAM) acts as an inference-time safeguard, dynamically verifying generated medical statements against authoritative knowledge bases to minimize hallucinations and ensure standardized terminology. Leveraging a comprehensive dataset of millions of paired CXR images and expert reports, our experiments demonstrate that CXR-PathFinder significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art medical vision-language models across various quantitative metrics, including clinical accuracy (Macro F1 (14): 46.5, Micro F1 (14): 59.5). Furthermore, blinded human evaluation by board-certified radiologists confirms CXR-PathFinder’s superior clinical utility, completeness, and accuracy, establishing its potential as a reliable and efficient aid for radiological practice. The developed method effectively balances high diagnostic fidelity with computational efficiency, providing a robust solution for automated medical report generation.
随着医学图像解读需求的不断增长,对先进的人工智能解决方案的需求也愈发迫切,以提高放射诊断的效率和准确性。本文介绍了CXR-PathFinder,这是一种新型的大型语言模型(LLM)为中心的基础模型,专门用于自动生成胸部X光(CXR)报告。我们提出了一种独特的训练范式——临床医生指导的对抗微调(CGAFT),它将专家临床反馈精心集成到对抗性学习框架中,以减轻事实上的不一致性并提高诊断精度。作为补充,我们的知识图谱增强模块(KGAM)充当推理时的安全卫士,动态验证生成的医学陈述与权威知识库的一致性,以最小化幻觉并确保标准化术语。利用数百万对CXR图像和专家报告的综合数据集,我们的实验表明,CXR-PathFinder在各种定量指标上显著优于现有的最先进的医疗视觉语言模型,包括临床准确性(宏观F1(14):46.5,微观F1(14):59.5)。此外,经过认证的放射科医生进行的盲态人类评估证实了CXR-PathFinder在临床实用性、完整性和准确性方面的优越性,证明了其在放射实践中作为可靠且高效的辅助工具的潜力。所开发的方法有效地平衡了高诊断保真度和计算效率,为自动医学报告生成提供了稳健的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文提出一种名为CXR-PathFinder的新型大型语言模型(LLM)为中心的基础模型,用于自动生成胸部X光(CXR)报告。通过独特的训练范式Clinician-Guided Adversarial Fine-Tuning(CGAFT)和Knowledge Graph Augmentation Module(KGAM),该模型提高了诊断的准确性和精确性,减少了事实上的不一致性,并确保标准化术语。实验表明,CXR-PathFinder在多种定量指标上显著优于现有的最先进的医疗视觉语言模型,并在放射实践领域展现出可靠且高效的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像解读需求不断增长,强调对先进人工智能解决方案的需求,以提高放射诊断的效率和准确性。
- 介绍了CXR-PathFinder模型,该模型是一种专门用于自动生成胸部X光报告的大型语言模型。
- CXR-PathFinder采用独特的训练范式Clinician-Guided Adversarial Fine-Tuning (CGAFT),将专家临床反馈纳入对抗性学习框架,以提高诊断的准确性和精确性。
- Knowledge Graph Augmentation Module (KGAM) 作为推理时的安全保障,动态验证生成的医疗陈述,确保标准化术语并减少虚构情况。
- 实验表明,CXR-PathFinder在各种定量指标上显著优于其他先进模型,包括临床精度(Macro F1 (14): 46.5, Micro F1 (14): 59.5)。
- 盲态人类评估(由认证放射学家进行)证实了CXR-PathFinder在临床实用性、完整性和准确性方面的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

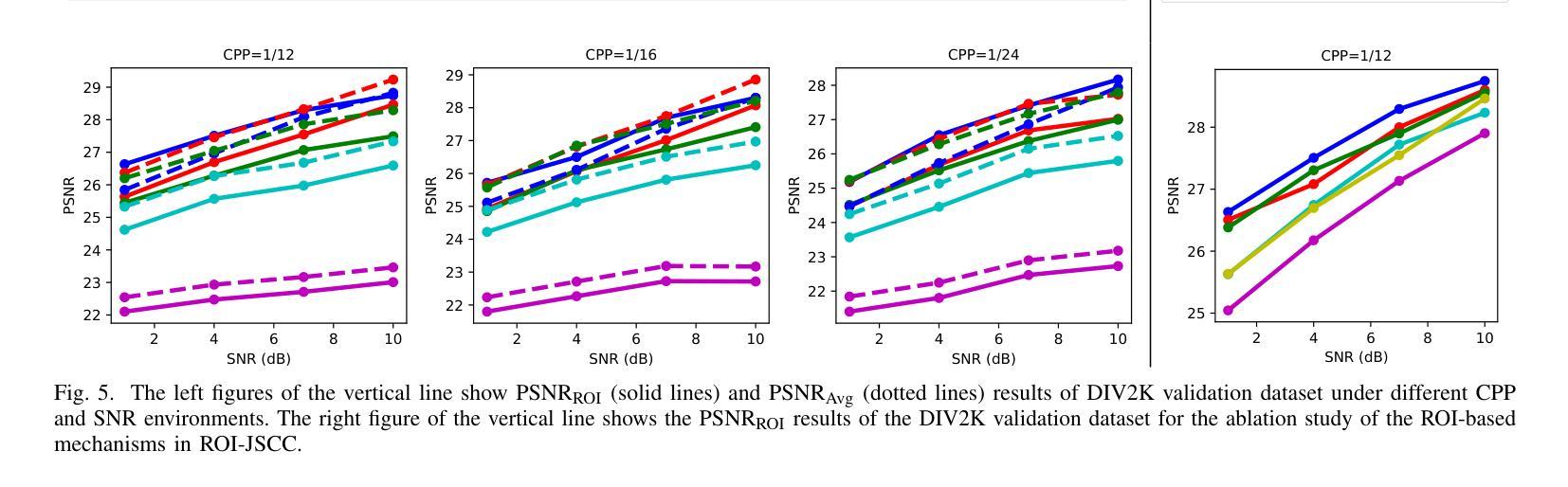
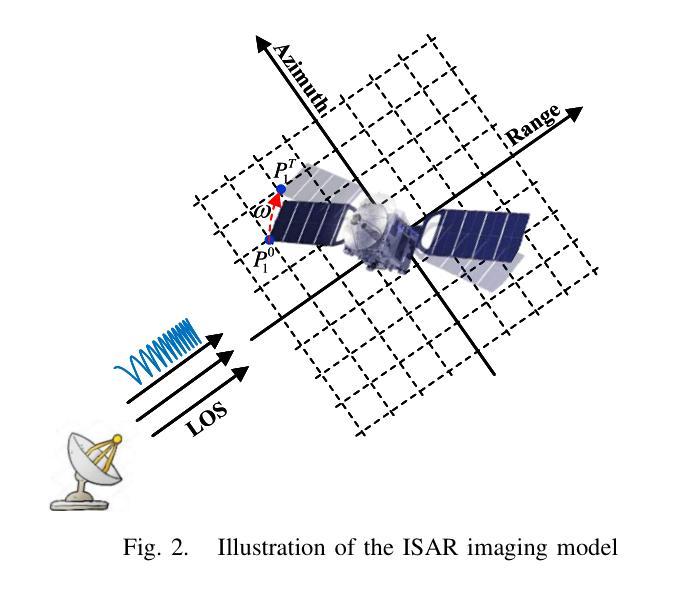
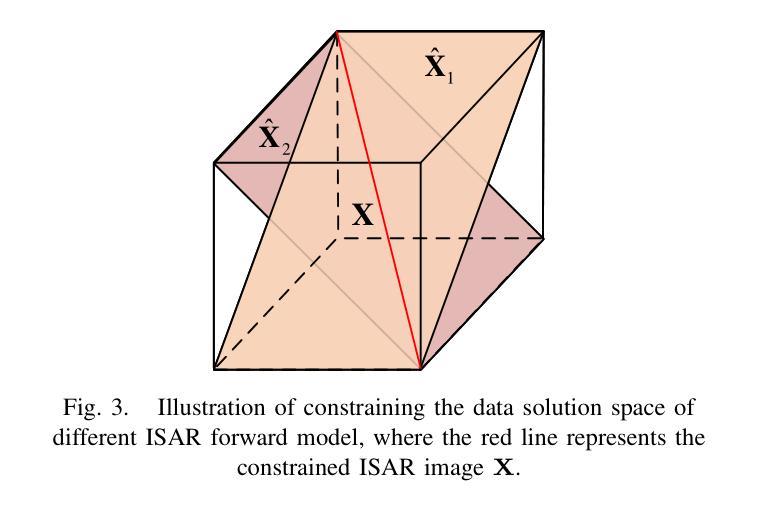
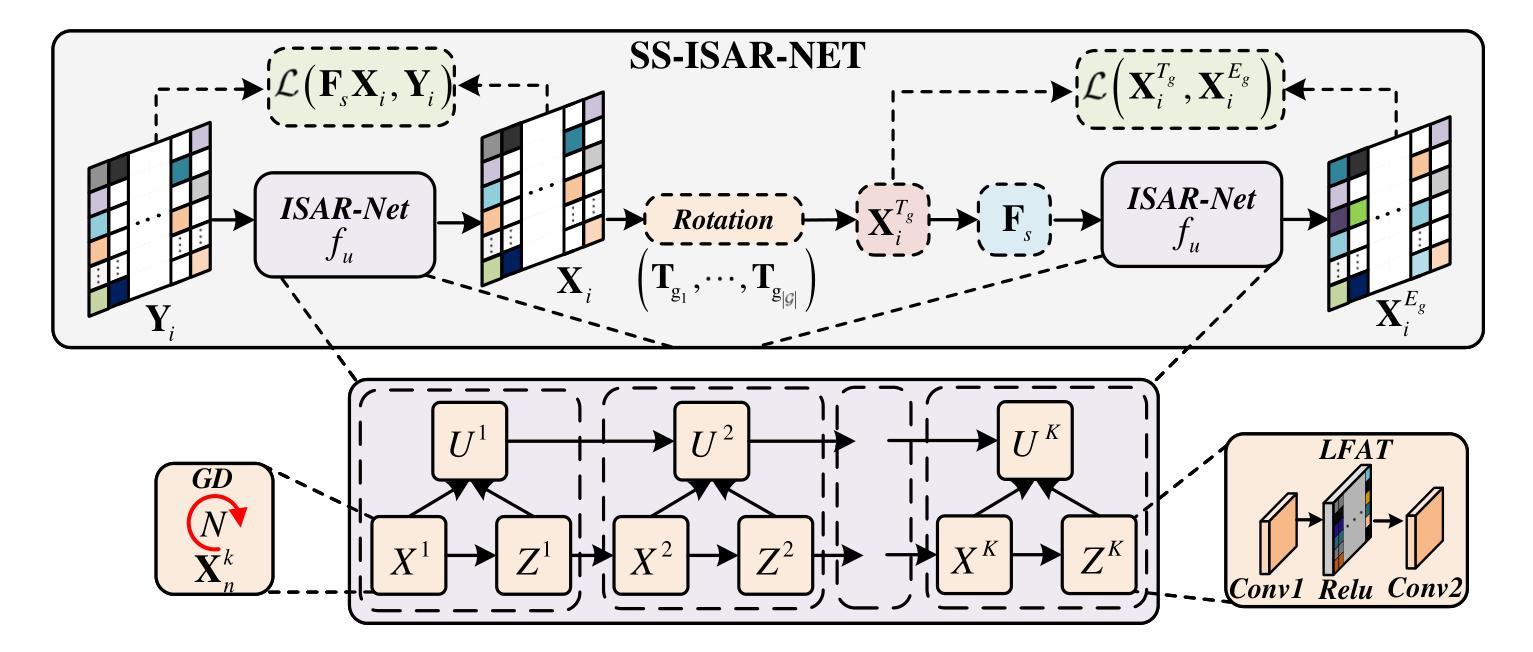
Self-Supervised-ISAR-Net Enables Fast Sparse ISAR Imaging
Authors:Ziwen Wang, Jianping wang, Pucheng Li, Yifan Wu, Zegang Ding
Numerous sparse inverse synthetic aperture radar (ISAR) imaging methods based on unfolded neural networks have been developed for high-quality image reconstruction with sparse measurements. However, their training typically requires paired ISAR images and echoes, which are often difficult to obtain. Meanwhile, one property can be observed that for a certain sparse measurement configuration of ISAR, when a target is rotated around its center of mass, only the image of the target undergoes the corresponding rotation after ISAR imaging, while the grating lobes do not follow this rotation and are solely determined by the sparse-sampling pattern. This property is mathematically termed as the equivariant property. Taking advantage of this property, an unfolded neural network for sparse ISAR imaging with self-supervised learning, named SS-ISAR-Net is proposed. It effectively mitigates grating lobes caused by sparse radar echo, allowing high-quality training to be achieved using only sparse radar echo data. The superiority of the proposed SS-ISAR-Net, compared to existing methods, is verified through experiments with both synthetic and real-world measurement data.
基于展开神经网络的稀疏逆合成孔径雷达(ISAR)成像方法已经被开发出来,用于利用稀疏测量进行高质量图像重建。然而,它们的训练通常需要成对的ISAR图像和回波,而这些通常很难获得。同时,可以观察到这样一个特性:对于ISAR的某种稀疏测量配置,当目标围绕其质量中心旋转时,只有在ISAR成像后,目标图像会进行相应的旋转,而光栅瓣并不遵循这种旋转,而是仅由稀疏采样模式决定。这一特性在数学上被称为等变属性。利用这一特性,提出了一种具有自监督学习功能的稀疏ISAR成像展开神经网络,名为SS-ISAR-Net。它有效地减轻了由稀疏雷达回波引起的光栅瓣问题,仅使用稀疏雷达回波数据即可实现高质量训练。通过合成数据和真实世界测量数据的实验验证了所提出的SS-ISAR-Net相比现有方法的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于展开式神经网络的稀疏逆合成孔径雷达(ISAR)成像方法已被开发用于高质量图像重建,但通常需要配对的ISAR图像和回波数据,获取困难。观察到一种特性,即ISAR特定的稀疏测量配置下,目标绕质心旋转时,成像后的目标会相应旋转,而栅瓣不会随旋转改变,仅由稀疏采样模式决定。利用这一特性,提出了一种具有自监督学习能力的稀疏ISAR成像展开神经网络SS-ISAR-Net。该方法有效减轻了稀疏雷达回波引起的栅瓣问题,并能仅使用稀疏雷达回波数据进行高质量训练。通过实验验证,与现有方法相比,SS-ISAR-Net表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 基于展开神经网络的稀疏逆合成孔径雷达成像用于高质量图像重建。
- 获取配对的ISAR图像和回波数据通常很困难。
- 目标在ISAR成像过程中绕质心旋转时,图像中的目标会相应旋转,而栅瓣不随旋转改变。
- 利用上述特性提出了SS-ISAR-Net网络模型。
- SS-ISAR-Net能有效减轻稀疏雷达回波引起的栅瓣问题。
- 仅使用稀疏雷达回波数据即可实现高质量训练。
- 实验验证了SS-ISAR-Net相较于现有方法的优越性,无论是在合成数据还是真实测量数据上。
点此查看论文截图

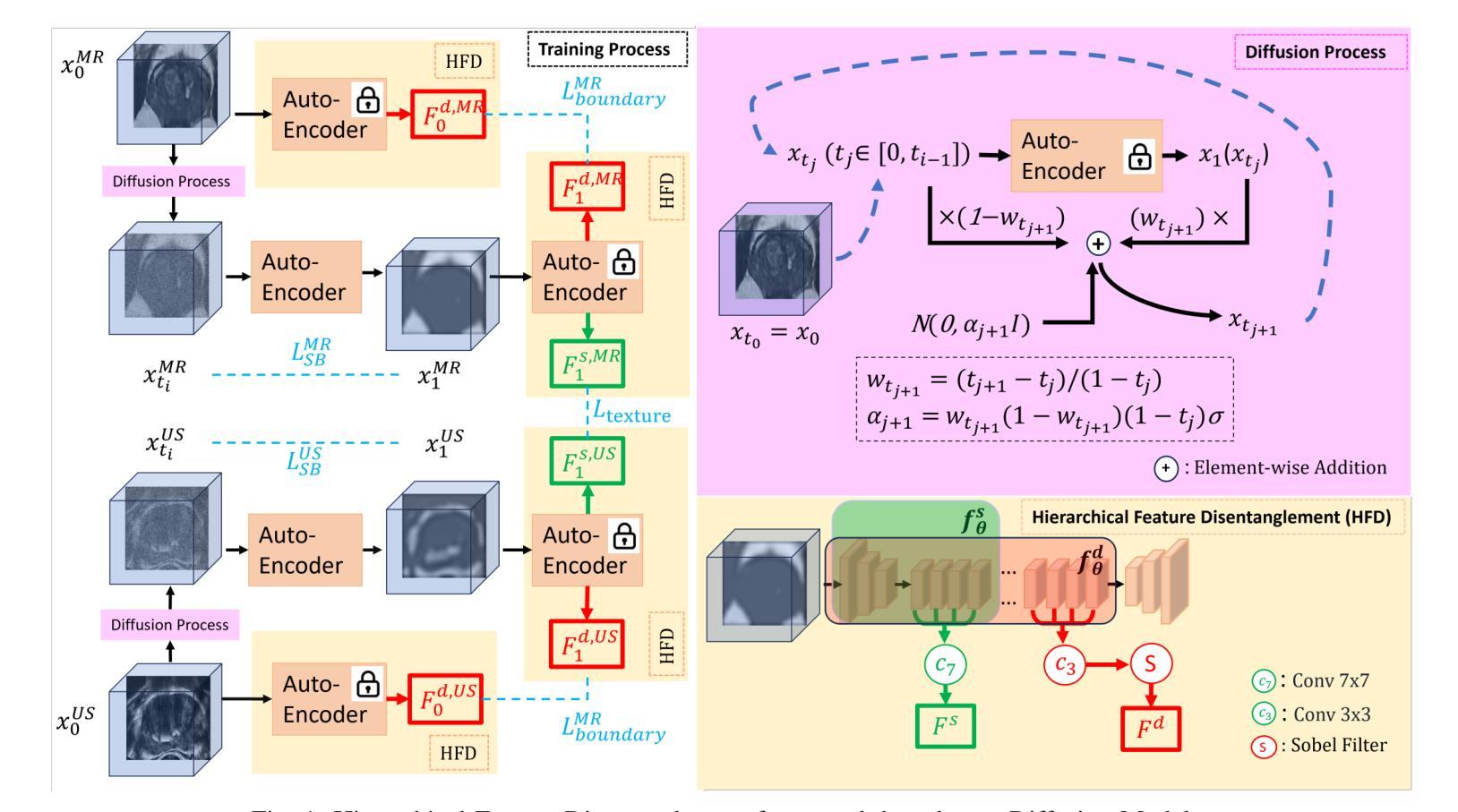
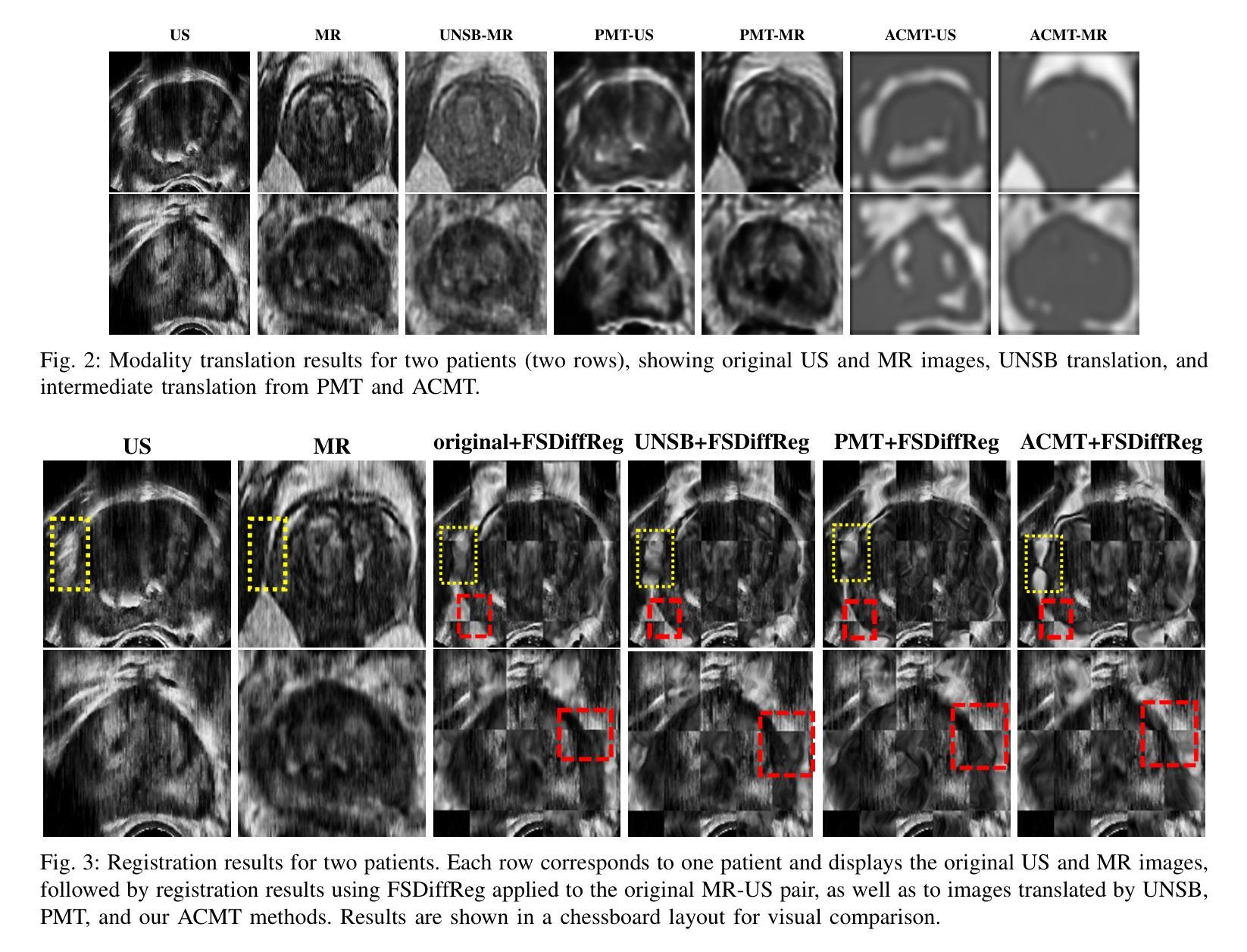
Modality Translation and Registration of MR and Ultrasound Images Using Diffusion Models
Authors:Xudong Ma, Nantheera Anantrasirichai, Stefanos Bolomytis, Alin Achim
Multimodal MR-US registration is critical for prostate cancer diagnosis. However, this task remains challenging due to significant modality discrepancies. Existing methods often fail to align critical boundaries while being overly sensitive to irrelevant details. To address this, we propose an anatomically coherent modality translation (ACMT) network based on a hierarchical feature disentanglement design. We leverage shallow-layer features for texture consistency and deep-layer features for boundary preservation. Unlike conventional modality translation methods that convert one modality into another, our ACMT introduces the customized design of an intermediate pseudo modality. Both MR and US images are translated toward this intermediate domain, effectively addressing the bottlenecks faced by traditional translation methods in the downstream registration task. Experiments demonstrate that our method mitigates modality-specific discrepancies while preserving crucial anatomical boundaries for accurate registration. Quantitative evaluations show superior modality similarity compared to state-of-the-art modality translation methods. Furthermore, downstream registration experiments confirm that our translated images achieve the best alignment performance, highlighting the robustness of our framework for multi-modal prostate image registration.
多模态MR-US注册对前列腺癌诊断至关重要。然而,由于模态之间的差异很大,这项任务仍然具有挑战性。现有方法往往无法在关键边界对齐的同时,又过于敏感地关注不相关的细节。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于层次特征分解设计的解剖连贯性模态翻译(ACMT)网络。我们利用浅层特征实现纹理一致性,利用深层特征实现边界保留。不同于将一种模态转换为另一种模态的传统模态翻译方法,我们的ACMT引入了中间伪模态的定制设计。MR和US图像都向这个中间域进行转换,有效地解决了传统翻译方法在下游注册任务中所面临的瓶颈。实验表明,我们的方法减轻了模态特定的差异,同时保留了关键解剖边界,以实现准确的注册。定量评估表明,与最先进的模态翻译方法相比,我们的模态相似性更高。此外,下游注册实验证实,我们的翻译图像实现了最佳的对齐性能,凸显了我们框架在多模态前列腺图像注册的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于层次特征分离设计的解剖学一致性模态翻译(ACMT)网络,用于解决多模态MR-US在前列腺癌诊断中的注册问题。通过利用浅层特征实现纹理一致性和深层特征进行边界保留,有效地解决了传统模态翻译方法在下游注册任务中遇到的瓶颈。实验表明,该方法在减轻模态特定差异的同时,保留了关键解剖边界,实现了准确的注册。与最先进的模态翻译方法相比,该方法在模态相似性方面表现出优越性,并在下游注册实验中证实了其最佳对齐性能,凸显了其在多模态前列腺图像注册中的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态MR-US注册对前列腺癌诊断至关重要,但存在显著模态差异的挑战。
- 现有方法往往难以对齐关键边界,同时过于敏感于无关细节。
- 提出了一种基于层次特征分离设计的解剖学一致性模态翻译(ACMT)网络。
- ACMT网络利用浅层特征实现纹理一致性和深层特征进行边界保留。
- 引入了一种中间伪模态的定制设计,使MR和US图像都向此中间领域翻译,解决传统翻译方法在下游注册任务中的瓶颈。
- 实验表明,该方法在模态相似性方面优于最先进的模态翻译方法。
点此查看论文截图

SSAM: Self-Supervised Association Modeling for Test-Time Adaption
Authors:Yaxiong Wang, Zhenqiang Zhang, Lechao Cheng, Zhun Zhong, Dan Guo, Meng Wang
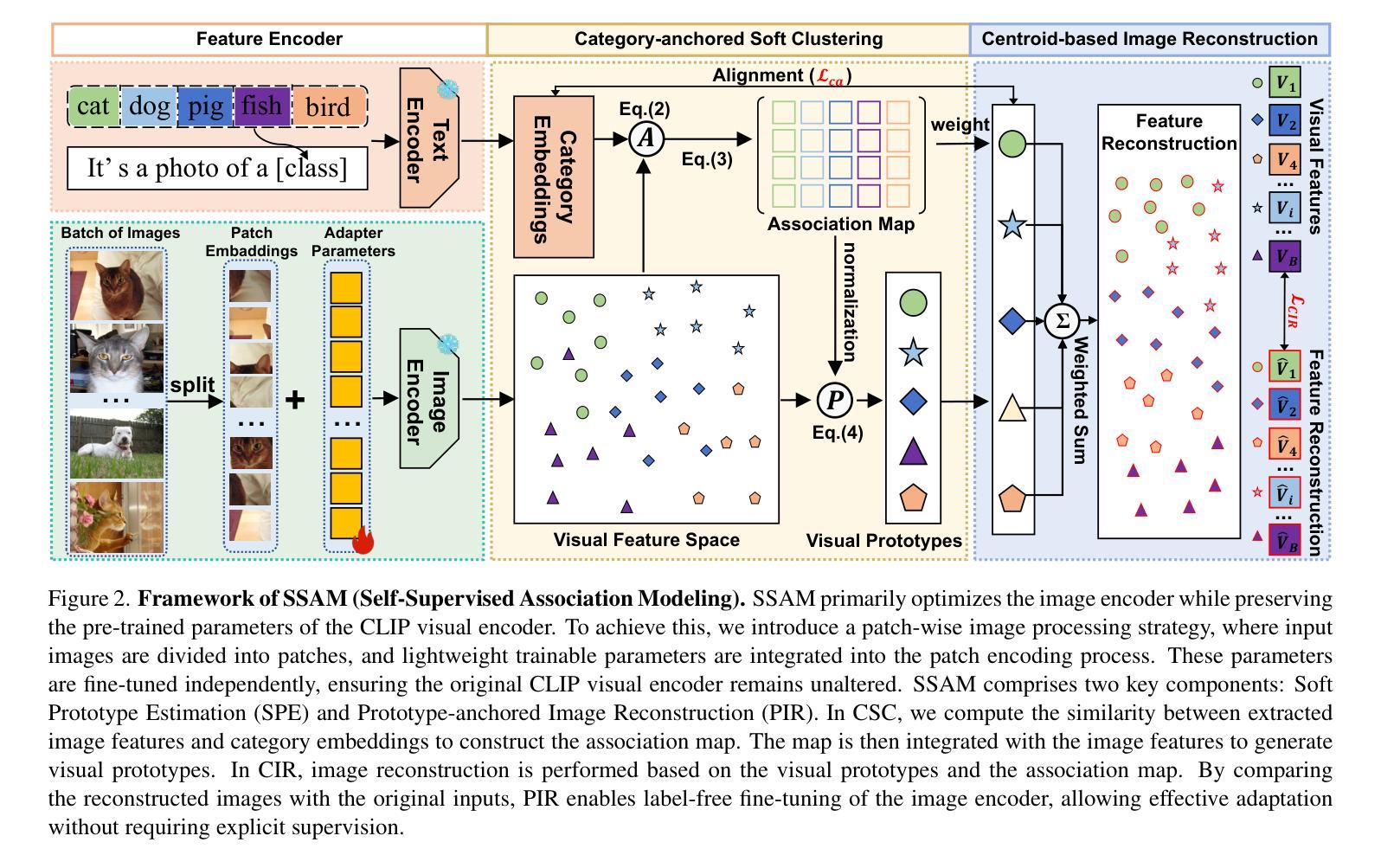
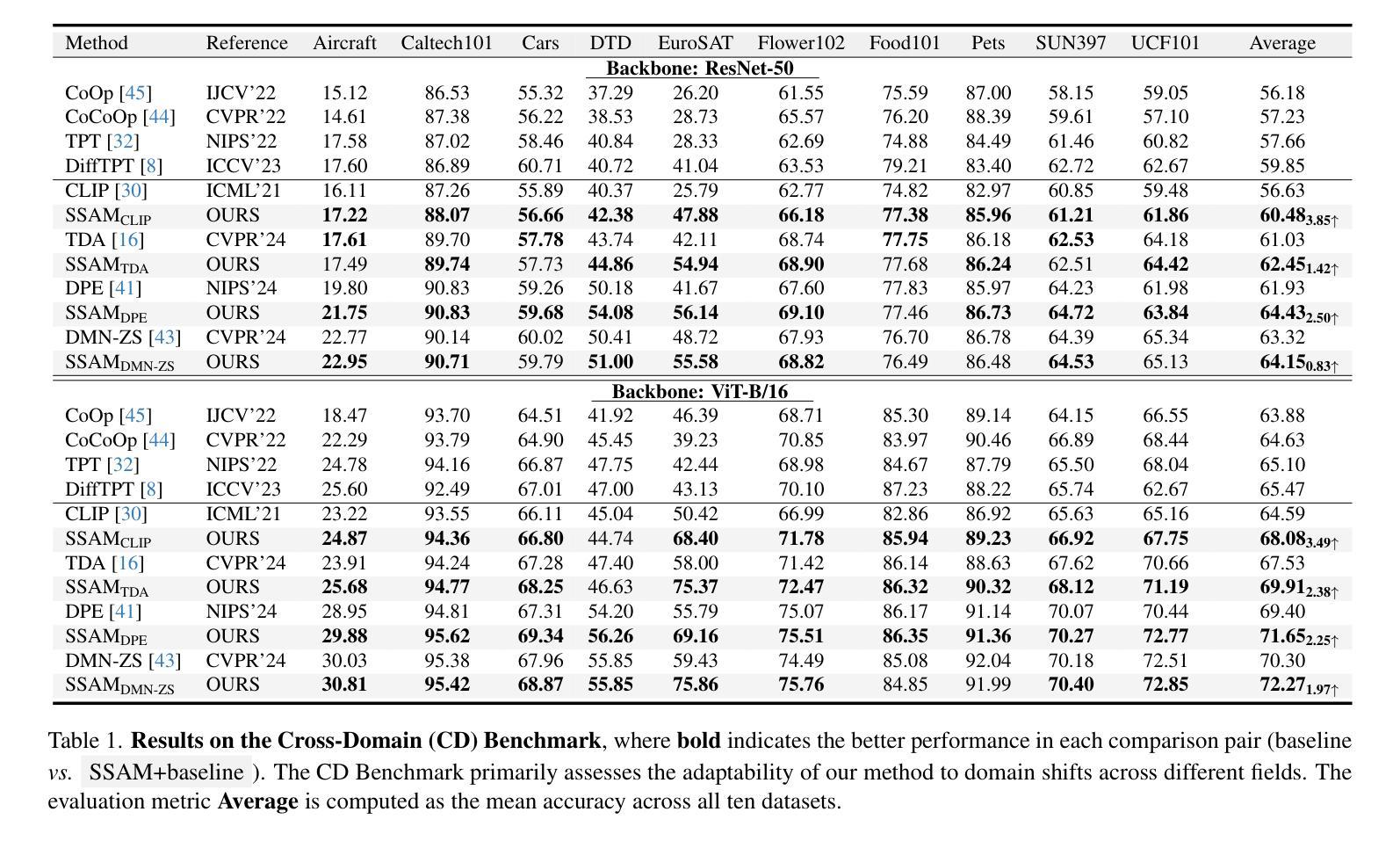
Test-time adaption (TTA) has witnessed important progress in recent years, the prevailing methods typically first encode the image and the text and design strategies to model the association between them. Meanwhile, the image encoder is usually frozen due to the absence of explicit supervision in TTA scenarios. We identify a critical limitation in this paradigm: While test-time images often exhibit distribution shifts from training data, existing methods persistently freeze the image encoder due to the absence of explicit supervision during adaptation. This practice overlooks the image encoder’s crucial role in bridging distribution shift between training and test. To address this challenge, we propose SSAM (Self-Supervised Association Modeling), a new TTA framework that enables dynamic encoder refinement through dual-phase association learning. Our method operates via two synergistic components: 1) Soft Prototype Estimation (SPE), which estimates probabilistic category associations to guide feature space reorganization, and 2) Prototype-anchored Image Reconstruction (PIR), enforcing encoder stability through cluster-conditional image feature reconstruction. Comprehensive experiments across diverse baseline methods and benchmarks demonstrate that SSAM can surpass state-of-the-art TTA baselines by a clear margin while maintaining computational efficiency. The framework’s architecture-agnostic design and minimal hyperparameter dependence further enhance its practical applicability.
近年来,测试时适应(TTA)技术取得了重要进展。目前主流的方法通常首先对图像和文本进行编码,并设计策略对它们之间的关联进行建模。同时,由于TTA场景中缺乏明确的监督信息,图像编码器通常被冻结。我们发现了这一模式的关键局限:虽然测试时的图像往往表现出与训练数据不同的分布,但由于适应过程中缺乏明确的监督,现有方法仍然坚持冻结图像编码器。这种做法忽视了图像编码器在弥合训练和测试之间分布转移方面的关键作用。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了SSAM(自监督关联建模),这是一种新的TTA框架,通过双阶段关联学习实现动态编码器优化。我们的方法由两个协同组件组成:1)软原型估计(SPE),它估计概率类别关联以引导特征空间重组;2)以原型为中心的图像重建(PIR),通过聚类条件图像特征重建来加强编码器的稳定性。在多种基准方法和基准测试上的综合实验表明,SSAM可以明显超越最新的TTA基准测试,同时保持计算效率。该框架的架构无关设计和较小的超参数依赖性进一步增强了其实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 papges
Summary
本文提出一种新型的测试时适应(TTA)框架SSAM(Self-Supervised Association Modeling),通过双阶段关联学习实现动态编码器优化,解决现有方法忽略图像编码器在适应训练与测试数据分布变化中的重要性。SSAM包含两个协同组件:Soft Prototype Estimation(SPE)和Prototype-anchored Image Reconstruction(PIR),分别用于引导特征空间重组和强化编码器稳定性。实验表明,SSAM在多种基准方法和基准测试上超越了现有TTA方法,具有显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时适应(TTA)框架SSAM通过双阶段关联学习实现动态编码器优化。
- SSAM解决了现有方法忽略图像编码器在适应训练与测试数据分布变化中的重要性。
- SSAM包含两个协同组件:Soft Prototype Estimation(SPE)和Prototype-anchored Image Reconstruction(PIR)。
- SPE通过估计概率类别关联来引导特征空间重组。
- PIR通过集群条件图像特征重建来强化编码器稳定性。
- 实验表明,SSAM在多个基准方法和基准测试上超越了现有TTA方法。
点此查看论文截图