⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-05 更新
EDITOR: Effective and Interpretable Prompt Inversion for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Mingzhe Li, Gehao Zhang, Zhenting Wang, Shiqing Ma, Siqi Pan, Richard Cartwright, Juan Zhai
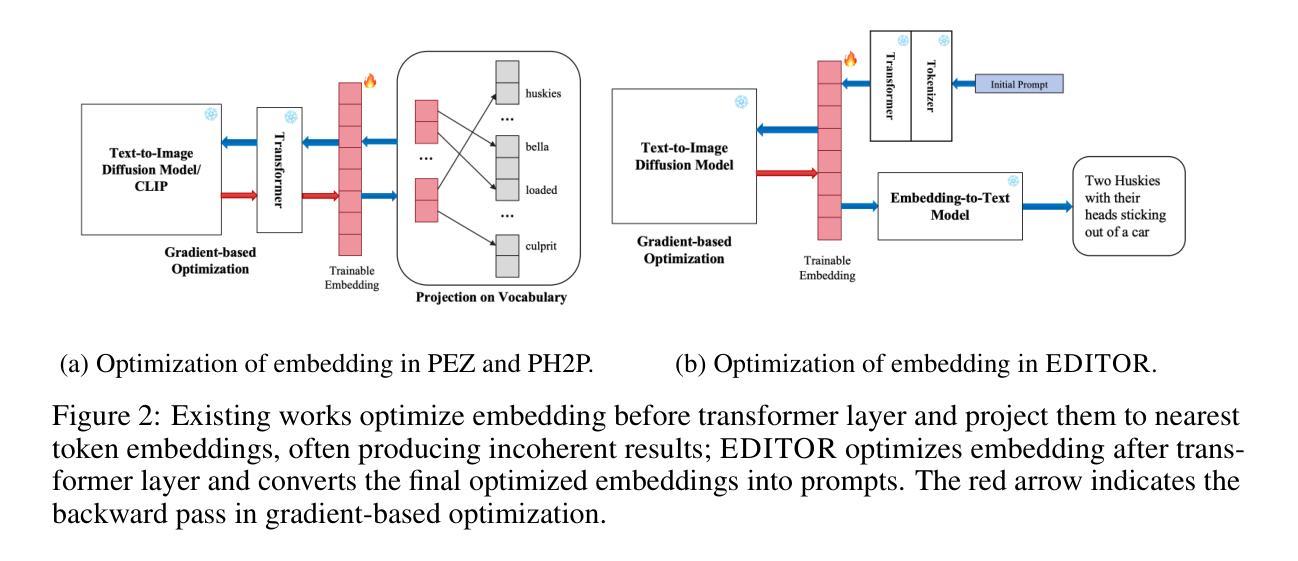
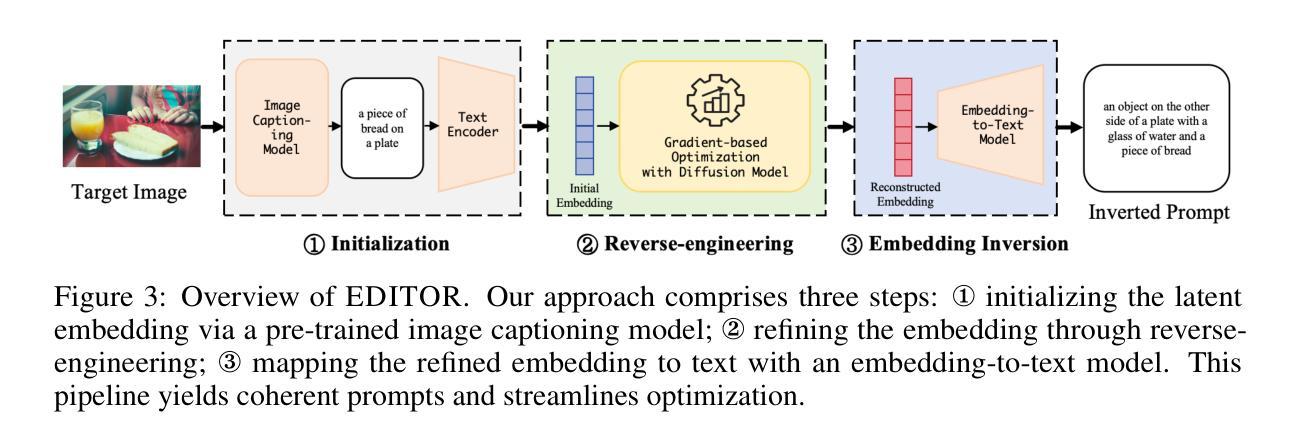
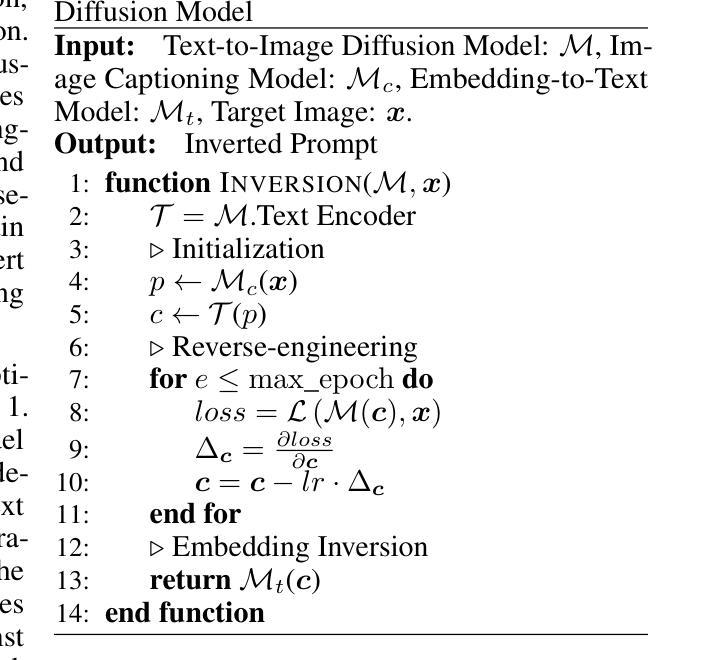
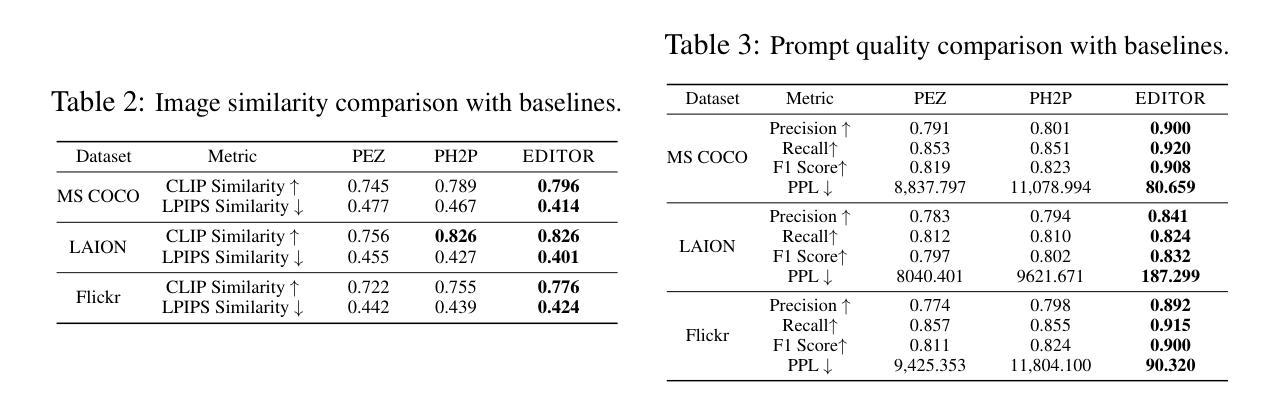
Text-to-image generation models~(e.g., Stable Diffusion) have achieved significant advancements, enabling the creation of high-quality and realistic images based on textual descriptions. Prompt inversion, the task of identifying the textual prompt used to generate a specific artifact, holds significant potential for applications including data attribution, model provenance, and watermarking validation. Recent studies introduced a delayed projection scheme to optimize for prompts representative of the vocabulary space, though challenges in semantic fluency and efficiency remain. Advanced image captioning models or visual large language models can generate highly interpretable prompts, but they often lack in image similarity. In this paper, we propose a prompt inversion technique called \sys for text-to-image diffusion models, which includes initializing embeddings using a pre-trained image captioning model, refining them through reverse-engineering in the latent space, and converting them to texts using an embedding-to-text model. Our experiments on the widely-used datasets, such as MS COCO, LAION, and Flickr, show that our method outperforms existing methods in terms of image similarity, textual alignment, prompt interpretability and generalizability. We further illustrate the application of our generated prompts in tasks such as cross-concept image synthesis, concept manipulation, evolutionary multi-concept generation and unsupervised segmentation.
文本到图像生成模型(例如Stable Diffusion)已经取得了重大进展,能够根据文本描述创建高质量和逼真的图像。提示反转(prompt inversion)是识别用于生成特定艺术品的文本提示的任务,对于数据归属、模型来源和水印验证等应用具有巨大潜力。最近的研究引入了一种延迟投影方案,以优化代表词汇空间的提示,尽管在语义流畅性和效率方面仍存在挑战。高级图像描述模型或视觉大型语言模型可以生成高度可解释的提示,但它们往往缺乏图像相似性。在本文中,我们提出了一种针对文本到图像扩散模型的提示反转技术,称为\sys,它使用预训练的图像描述模型进行嵌入初始化,通过反向工程在潜在空间中进行优化,并使用嵌入到文本模型将其转换为文本。我们在MS COCO、LAION和Flickr等常用数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法在图像相似性、文本对齐、提示可解释性和通用性方面优于现有方法。我们进一步说明了所生成的提示在跨概念图像合成、概念操作、进化多概念生成和无监督分割等任务中的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
文本转图像生成模型(如Stable Diffusion)已取得显著进展,能够根据文本描述生成高质量、逼真的图像。本文提出了一种针对文本转图像扩散模型的提示反转技术,通过预训练图像描述模型进行嵌入初始化,在潜在空间进行反向工程优化,并使用嵌入到文本的模型进行转换。实验证明,该方法在图像相似性、文本对齐、提示可解释性和通用性方面优于现有方法,并展示了在跨概念图像合成、概念操作、进化多概念生成和无监督分割任务中的应用。
Key Takeaways:
- 文本转图像生成模型如Stable Diffusion已能生成高质量、逼真的图像。
- 提示反转技术可用于确定生成特定工件所使用的文本提示。
- 现有挑战包括语义流畅性和效率问题。
- 该研究提出了一种新的提示反转技术\sys,用于文本转图像扩散模型。
- \sys技术包括使用预训练图像描述模型进行嵌入初始化,潜在空间反向工程优化,以及使用嵌入到文本的模型进行转换。
- 实验证明,该方法在图像相似性、文本对齐、提示可解释性和通用性方面优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


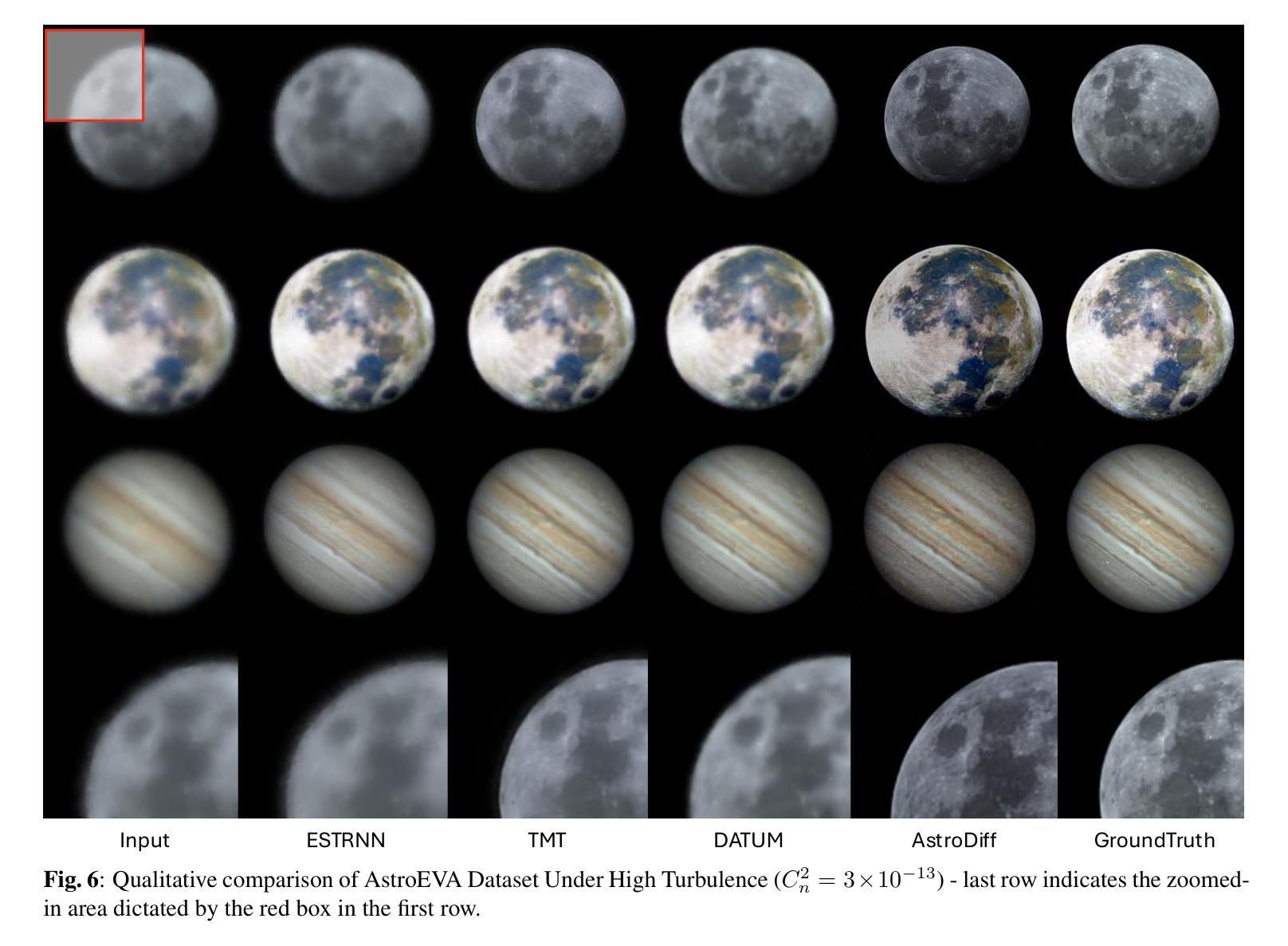
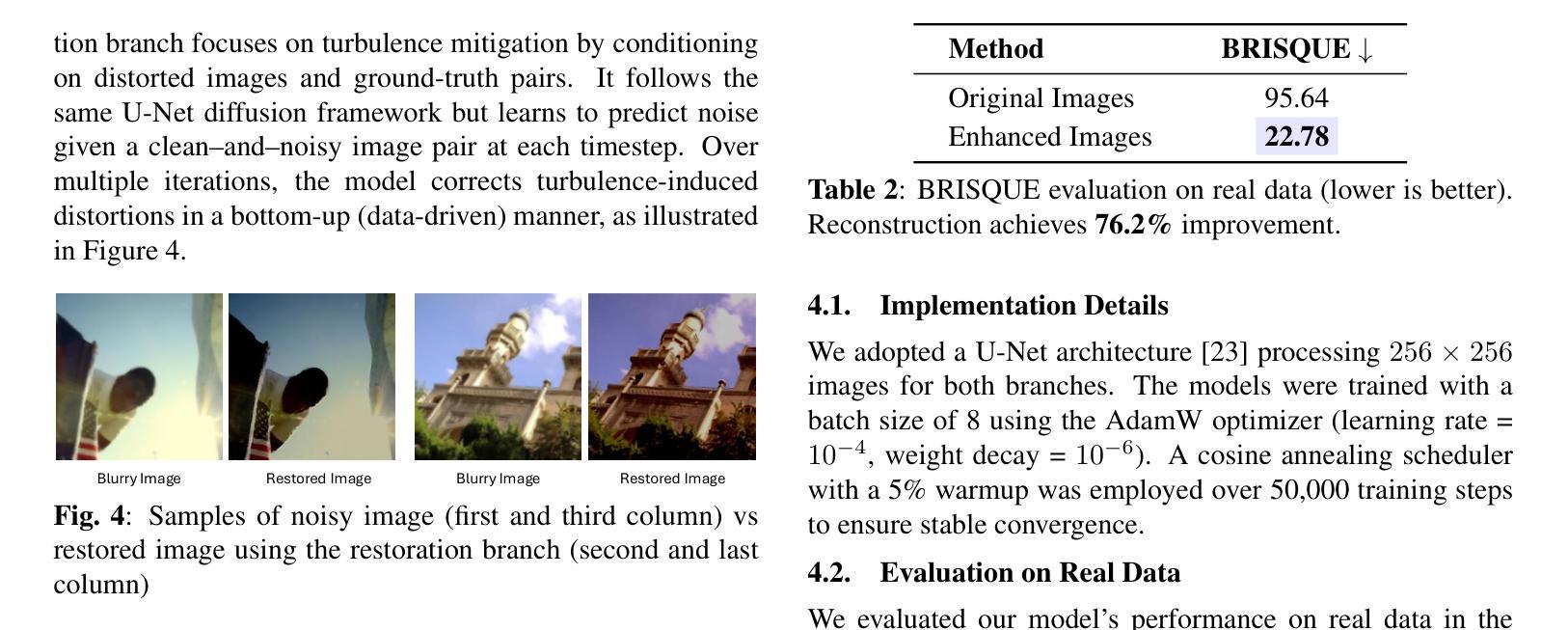
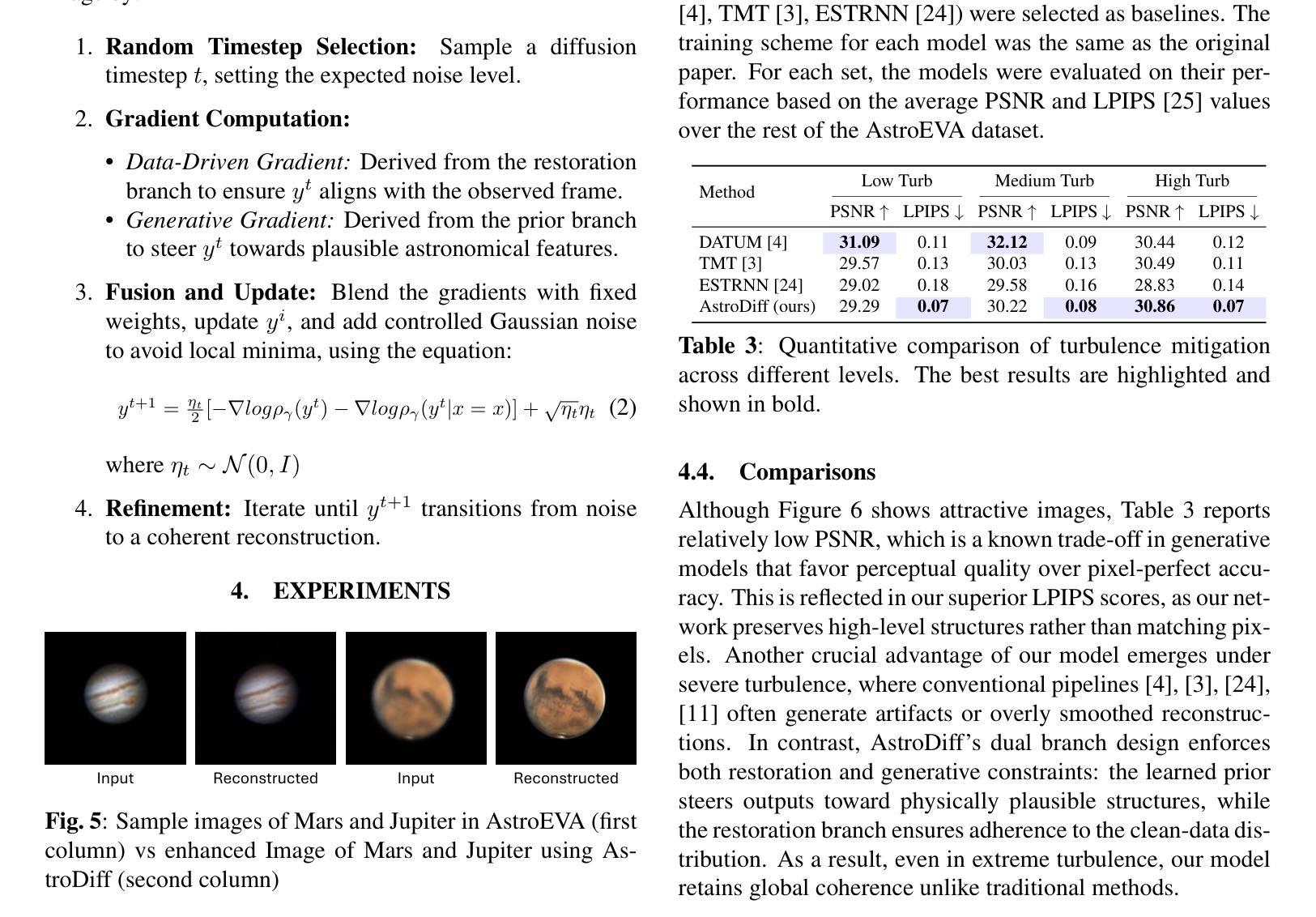
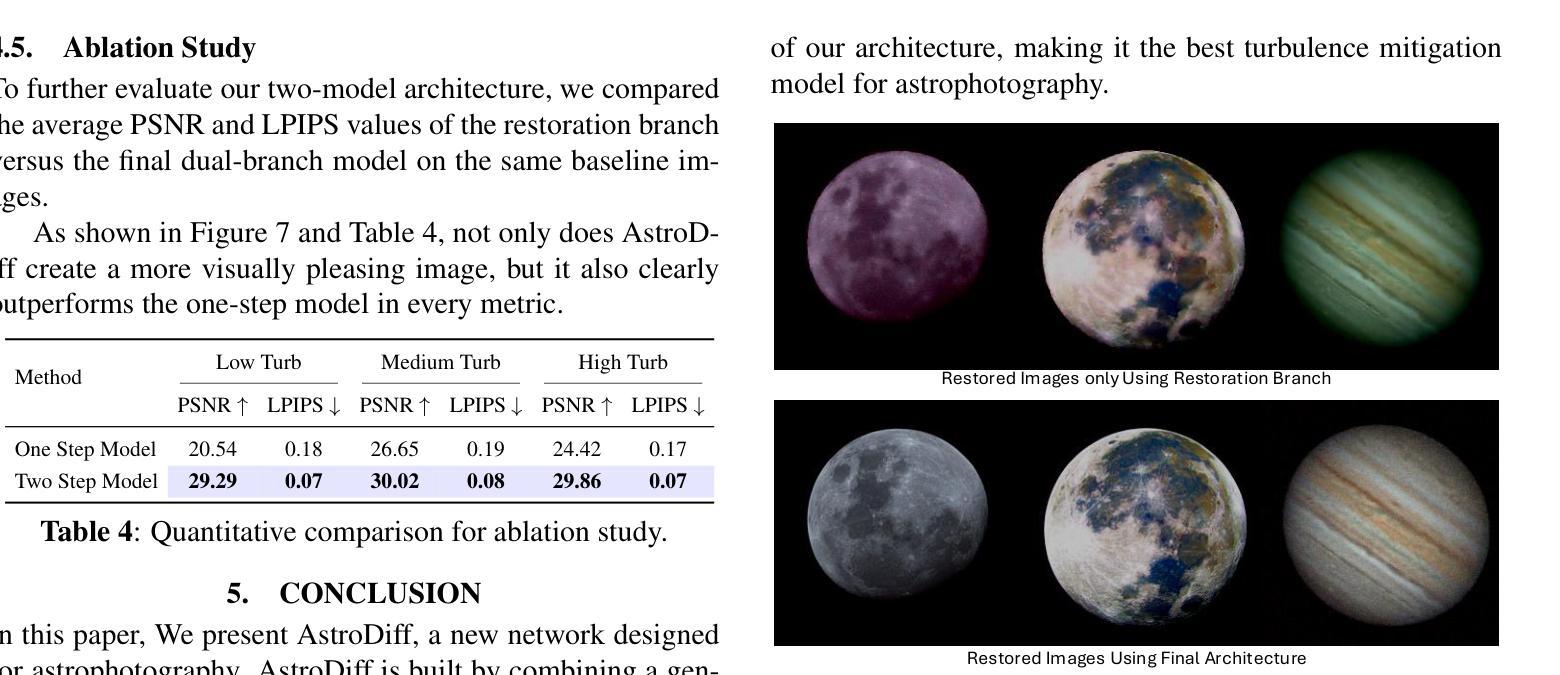
Astrophotography turbulence mitigation via generative models
Authors:Joonyeoup Kim, Yu Yuan, Xingguang Zhang, Xijun Wang, Stanley Chan
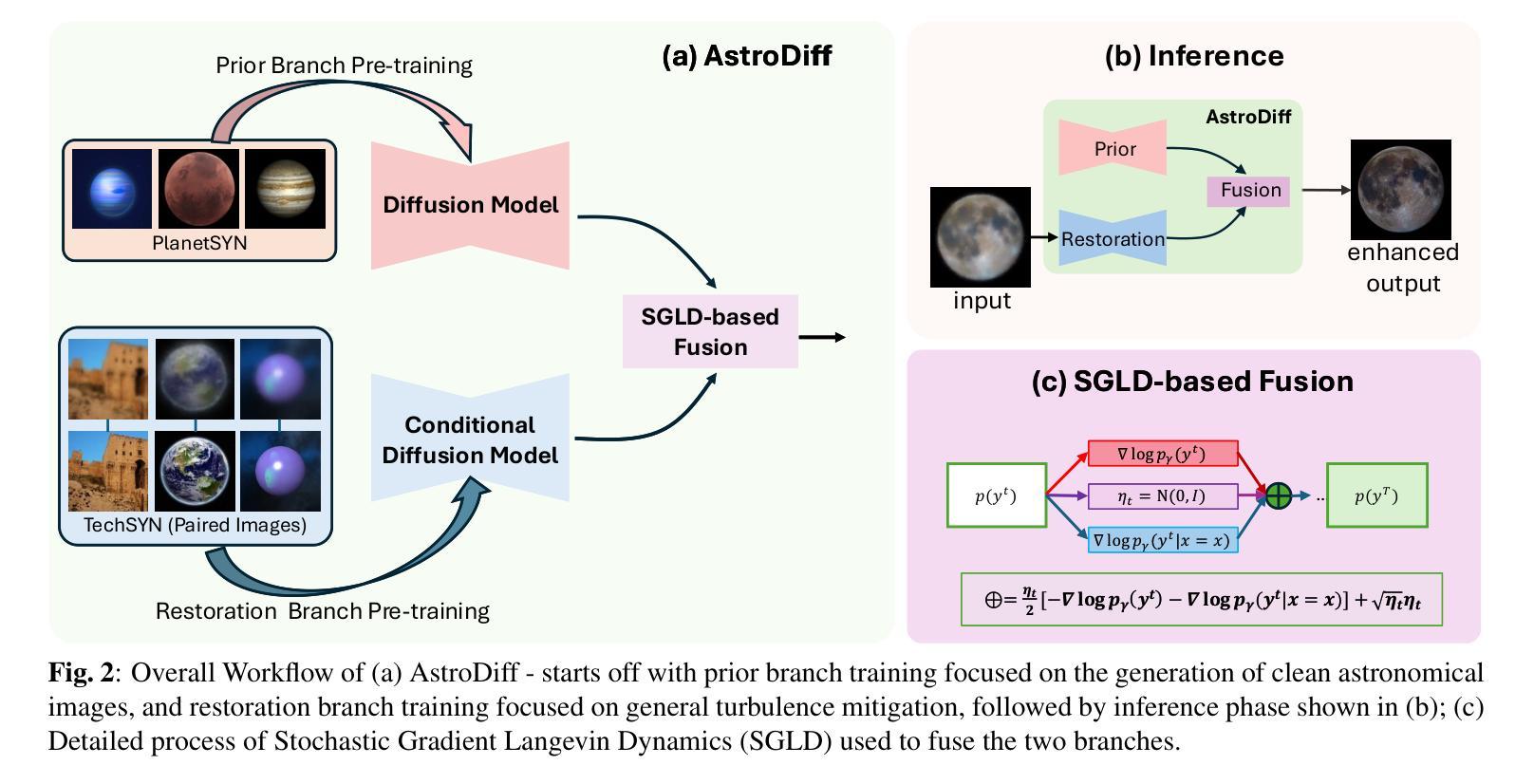
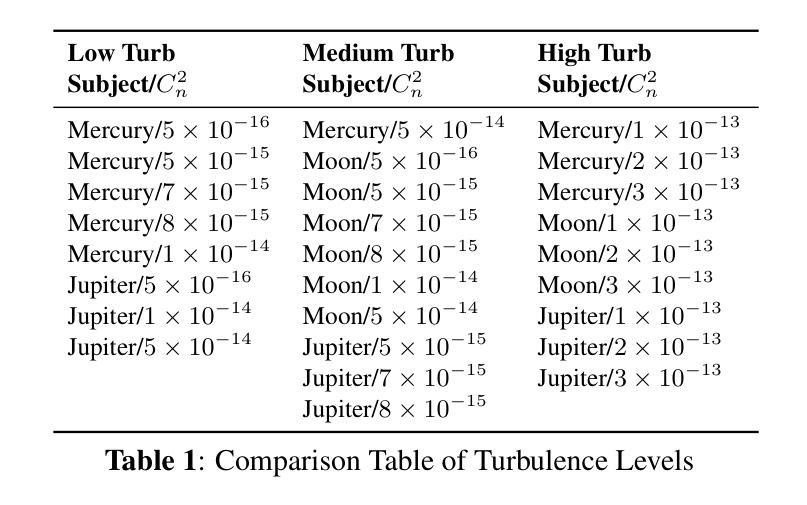
Photography is the cornerstone of modern astronomical and space research. However, most astronomical images captured by ground-based telescopes suffer from atmospheric turbulence, resulting in degraded imaging quality. While multi-frame strategies like lucky imaging can mitigate some effects, they involve intensive data acquisition and complex manual processing. In this paper, we propose AstroDiff, a generative restoration method that leverages both the high-quality generative priors and restoration capabilities of diffusion models to mitigate atmospheric turbulence. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AstroDiff outperforms existing state-of-the-art learning-based methods in astronomical image turbulence mitigation, providing higher perceptual quality and better structural fidelity under severe turbulence conditions. Our code and additional results are available at https://web-six-kappa-66.vercel.app/
摄影是现代天文学和空间研究的核心。然而,大多数由地面望远镜拍摄的天文图像受到大气湍流的影响,导致成像质量下降。虽然像幸运成像这样的多帧策略可以减轻一些影响,但它们涉及大量的数据获取和复杂的手动处理。在本文中,我们提出了AstroDiff,这是一种利用扩散模型的高质生成优先权和恢复能力来减轻大气湍流影响的生成恢复方法。大量实验表明,AstroDiff在天文图像湍流抑制方面超越了现有的最先进的学习型方法,在严重的湍流条件下提供了更高的感知质量和更好的结构保真度。我们的代码和额外结果可在[https://web-six-kappa-6 6.vercel.app/]找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了天文学研究中面临的挑战,特别是地面望远镜拍摄的天文图像受到大气扰动的影响。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的生成恢复方法——AstroDiff。该方法利用扩散模型的高质量和恢复能力,有效减轻大气扰动的影响。实验证明,AstroDiff在天文图像去噪领域优于现有方法,特别是在严重扰动条件下,其感知质量更高,结构保真度更好。
Key Takeaways
- 天文学研究中,地面望远镜拍摄的天文图像受到大气扰动的影响。
- 多帧成像策略如幸运成像可以部分缓解这一问题,但需要大量数据获取和复杂的后期处理。
- AstroDiff是一种基于扩散模型的生成恢复方法,旨在解决大气扰动问题。
- 扩散模型具有高质量和恢复能力,有助于改善天文图像的质量。
- AstroDiff在天文图像去噪领域实验表现出色,具有更高的感知质量和结构保真度。
- 该方法的代码和更多实验结果可以在相关网站找到。
点此查看论文截图




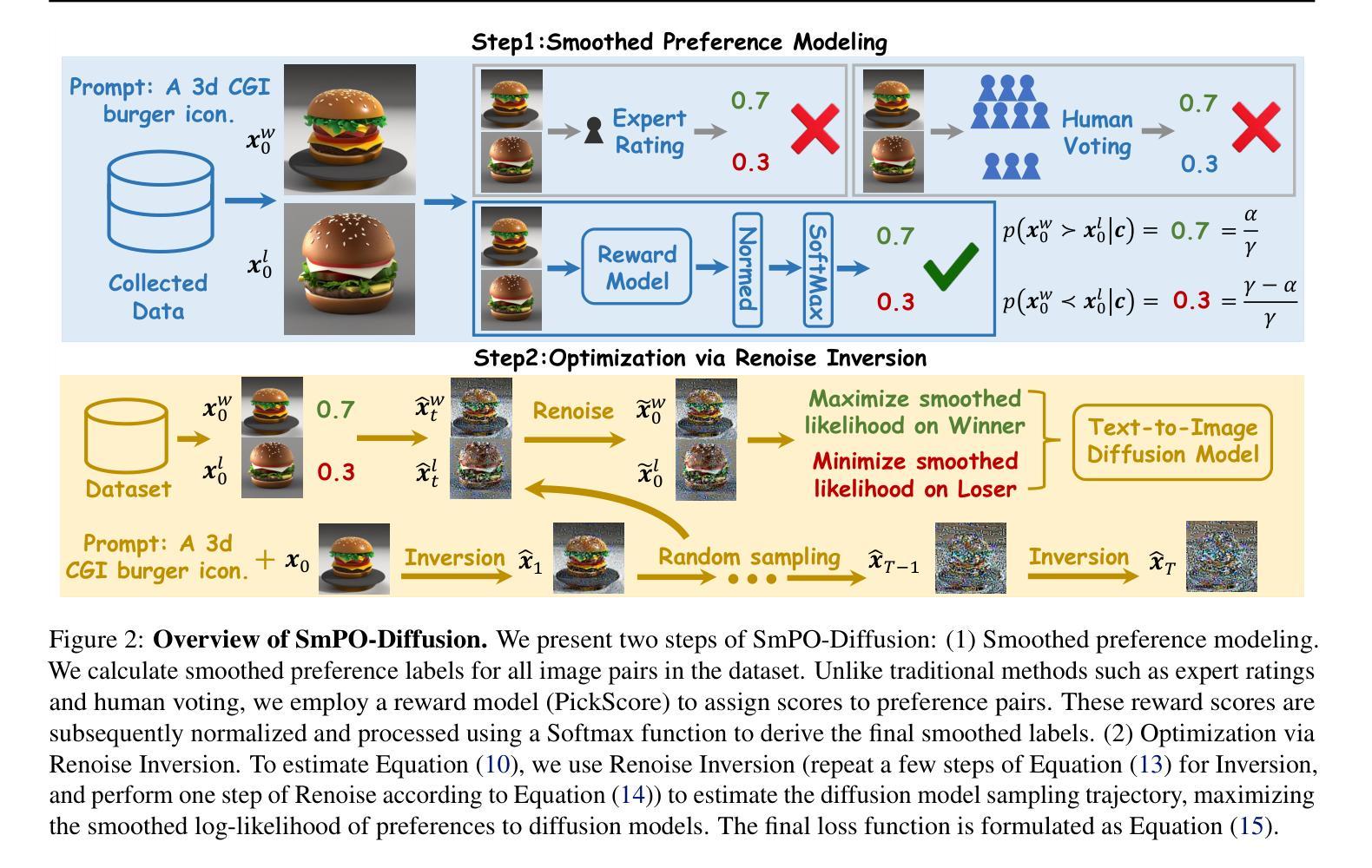
Smoothed Preference Optimization via ReNoise Inversion for Aligning Diffusion Models with Varied Human Preferences
Authors:Yunhong Lu, Qichao Wang, Hengyuan Cao, Xiaoyin Xu, Min Zhang
Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) aligns text-to-image (T2I) generation models with human preferences using pairwise preference data. Although substantial resources are expended in collecting and labeling datasets, a critical aspect is often neglected: \textit{preferences vary across individuals and should be represented with more granularity.} To address this, we propose SmPO-Diffusion, a novel method for modeling preference distributions to improve the DPO objective, along with a numerical upper bound estimation for the diffusion optimization objective. First, we introduce a smoothed preference distribution to replace the original binary distribution. We employ a reward model to simulate human preferences and apply preference likelihood averaging to improve the DPO loss, such that the loss function approaches zero when preferences are similar. Furthermore, we utilize an inversion technique to simulate the trajectory preference distribution of the diffusion model, enabling more accurate alignment with the optimization objective. Our approach effectively mitigates issues of excessive optimization and objective misalignment present in existing methods through straightforward modifications. Our SmPO-Diffusion achieves state-of-the-art performance in preference evaluation, outperforming baselines across metrics with lower training costs. The project page is https://jaydenlyh.github.io/SmPO-project-page/.
直接偏好优化(DPO)使用成对偏好数据将文本到图像(T2I)生成模型与人类偏好对齐。虽然收集和标注数据集需要耗费大量资源,但一个关键方面往往被忽视:*不同个体的偏好各不相同,应以更精细的方式表示。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了SmPO-Diffusion,这是一种建模偏好分布以改进DPO目标的新方法,以及一种对扩散优化目标的数值上限估计。首先,我们引入平滑的偏好分布来替换原始的二进分布。我们使用奖励模型来模拟人类偏好,并应用偏好可能性平均法来改进DPO损失,从而使损失函数在偏好相似时接近零。此外,我们运用反演技术模拟扩散模型的轨迹偏好分布,使与优化目标的对齐更加准确。我们的方法通过简单的修改有效地缓解了现有方法中过度优化和目标不对齐的问题。SmPO-Diffusion在偏好评估方面实现了最先进的性能,在指标上优于基线,并且降低了训练成本。项目页面是https://jaydenlyh.github.io/SmPO-project-page/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025
Summary
本文介绍了Direct Preference Optimization(DPO)在文本到图像生成模型中的应用,并指出了现有方法中的不足。为了改进DPO,提出了一种新的方法SmPO-Diffusion,通过模拟人类偏好分布来优化DPO目标,并引入了平滑偏好分布和奖励模型。此外,还利用反演技术模拟扩散模型的轨迹偏好分布,提高了优化目标的准确性。SmPO-Diffusion在偏好评估方面取得了最先进的性能,以更低的训练成本超越了基线。
Key Takeaways
- Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) 用于文本到图像生成模型中,利用成对偏好数据对齐人类偏好。
- 现有方法忽视了个人偏好的多样性,应该更细致地表示这些偏好。
- SmPO-Diffusion方法引入平滑偏好分布来改进DPO目标,并模拟人类偏好。
- 利用奖励模型和改进的DPO损失来提高性能,当偏好相似时损失函数接近零。
- 使用反演技术模拟扩散模型的轨迹偏好分布,提高与优化目标的对齐精度。
- SmPO-Diffusion有效缓解了现有方法中的过度优化和目标不对齐问题。
点此查看论文截图



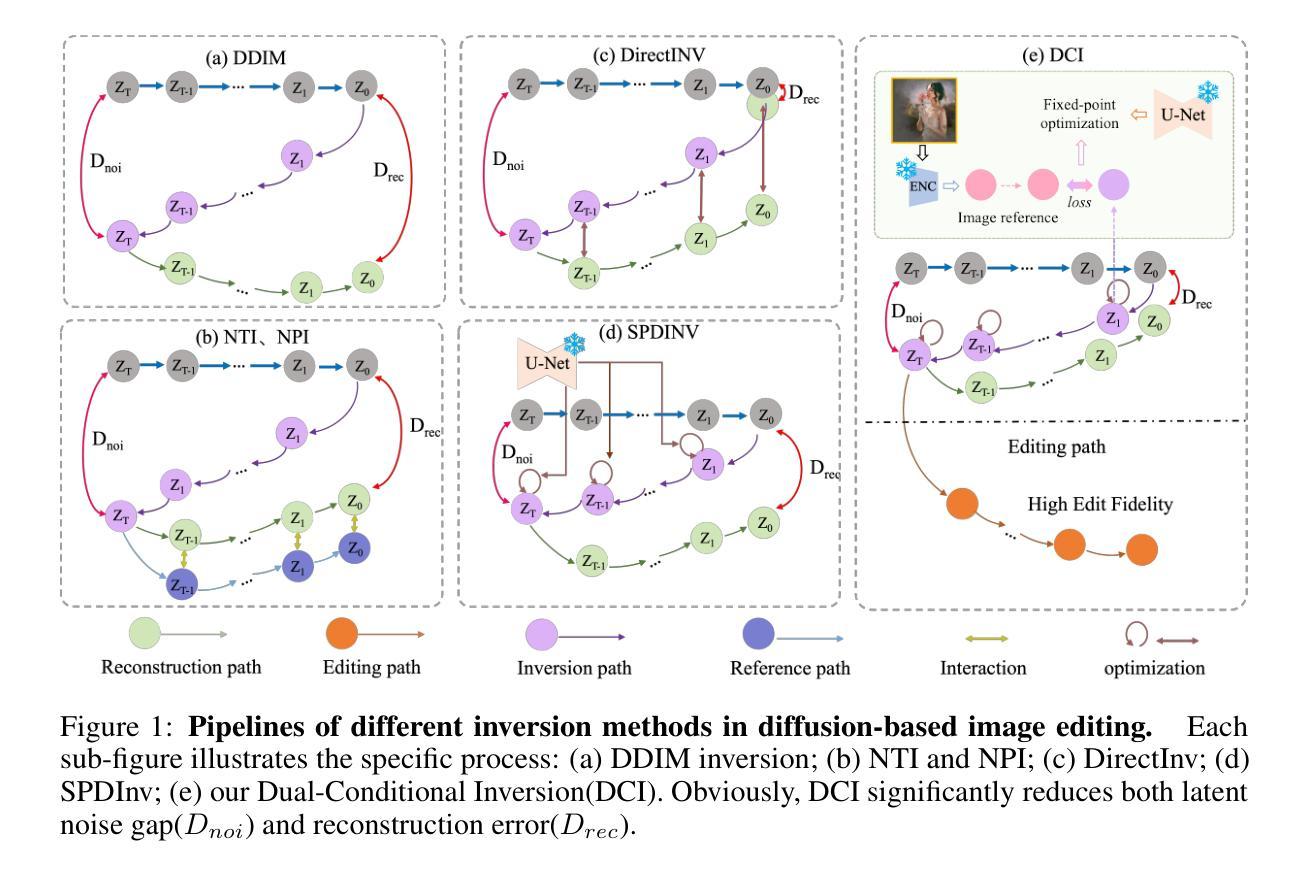
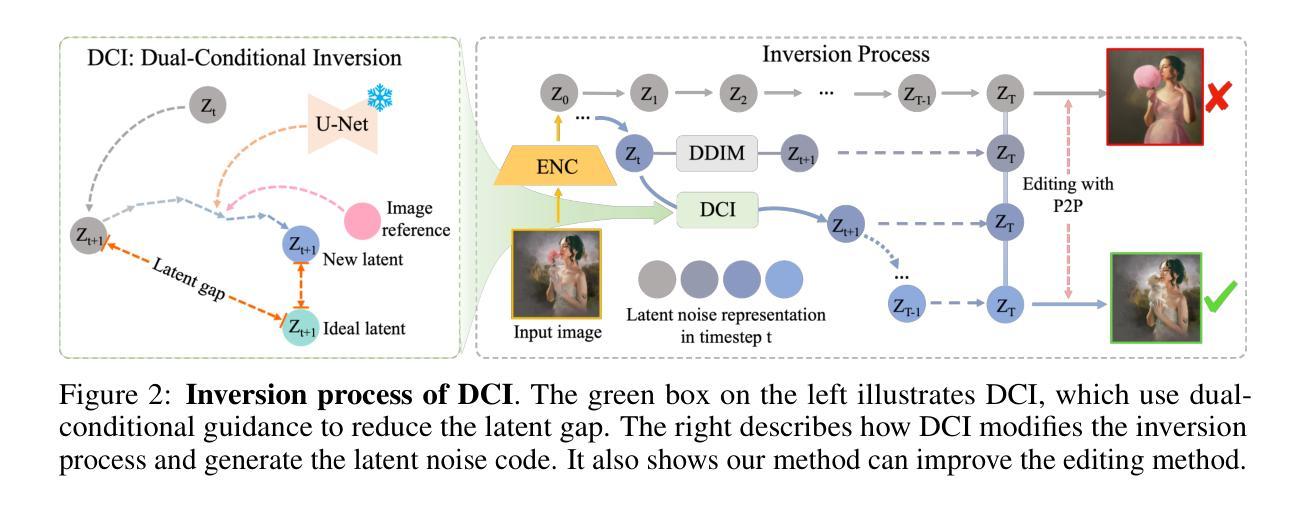
DCI: Dual-Conditional Inversion for Boosting Diffusion-Based Image Editing
Authors:Zixiang Li, Haoyu Wang, Wei Wang, Chuangchuang Tan, Yunchao Wei, Yao Zhao
Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in image generation and editing tasks. Inversion within these models aims to recover the latent noise representation for a real or generated image, enabling reconstruction, editing, and other downstream tasks. However, to date, most inversion approaches suffer from an intrinsic trade-off between reconstruction accuracy and editing flexibility. This limitation arises from the difficulty of maintaining both semantic alignment and structural consistency during the inversion process. In this work, we introduce Dual-Conditional Inversion (DCI), a novel framework that jointly conditions on the source prompt and reference image to guide the inversion process. Specifically, DCI formulates the inversion process as a dual-condition fixed-point optimization problem, minimizing both the latent noise gap and the reconstruction error under the joint guidance. This design anchors the inversion trajectory in both semantic and visual space, leading to more accurate and editable latent representations. Our novel setup brings new understanding to the inversion process. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DCI achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple editing tasks, significantly improving both reconstruction quality and editing precision. Furthermore, we also demonstrate that our method achieves strong results in reconstruction tasks, implying a degree of robustness and generalizability approaching the ultimate goal of the inversion process.
扩散模型在图像生成和编辑任务中取得了显著的成功。这些模型中的反演旨在恢复真实或生成图像的潜在噪声表示,从而实现重建、编辑和其他下游任务。然而,迄今为止,大多数反演方法面临着重建精度和编辑灵活性之间的内在权衡。这一局限性源于在反演过程中保持语义对齐和结构性一致性的困难。在这项工作中,我们引入了Dual-Conditional Inversion(DCI)这一新型框架,它联合基于源提示和参考图像进行条件设定,以指导反演过程。具体而言,DCI将反演过程制定为一个双条件固定点优化问题,在联合指导下最小化潜在噪声差距和重建误差。这种设计在语义和视觉空间上锚定了反演轨迹,从而得到更准确和可编辑的潜在表示。我们新颖的设置带来了对反演过程的新理解。大量实验表明,DCI在多个编辑任务中达到了最先进的性能,显著提高了重建质量和编辑精度。此外,我们还证明我们的方法在重建任务中取得了强大的结果,这暗示了反演过程的稳健性和通用性接近最终目标。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型在图像生成和编辑任务中的出色表现。文章提出了一种新的方法——双重条件反转(DCI),通过同时考虑源提示和参考图像来指导反转过程,从而解决了以往反转方法存在的重建精度与编辑灵活性之间的权衡问题。DCI将反转过程制定为双重条件下的固定点优化问题,通过最小化潜在噪声差距和重建误差,使反转轨迹在语义和视觉空间中得以固定,从而获得更准确且可编辑的潜在表示。实验表明,DCI在多个编辑任务上取得了最佳性能,显著提高了重建质量和编辑精度。同时,该方法在重建任务中也表现出强大的结果,展现出其稳健性和泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成和编辑任务中表现卓越。
- 现有反转方法面临重建精度与编辑灵活性之间的权衡问题。
- DCI(双重条件反转)方法提出,通过同时考虑源提示和参考图像来解决此问题。
- DCI将反转过程视为双重条件下的固定点优化问题,最小化潜在噪声差距和重建误差。
- DCI使反转轨迹在语义和视觉空间中固定,产生更准确且可编辑的潜在表示。
- 实验证明,DCI在多个编辑任务上达到最佳性能,显著提高重建质量和编辑精度。
点此查看论文截图

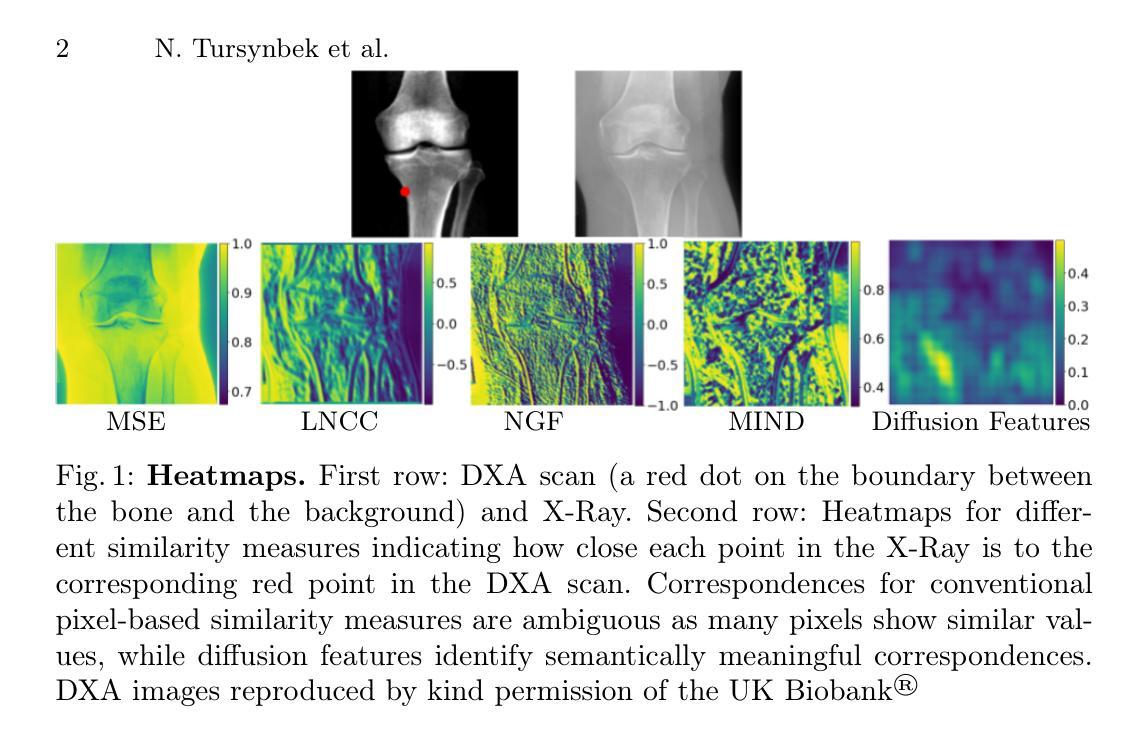
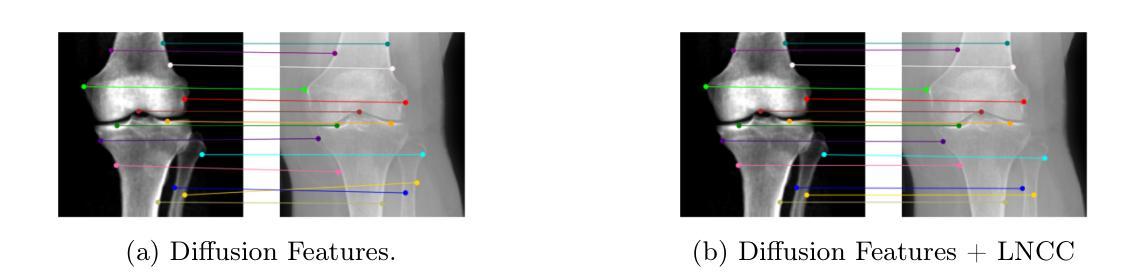
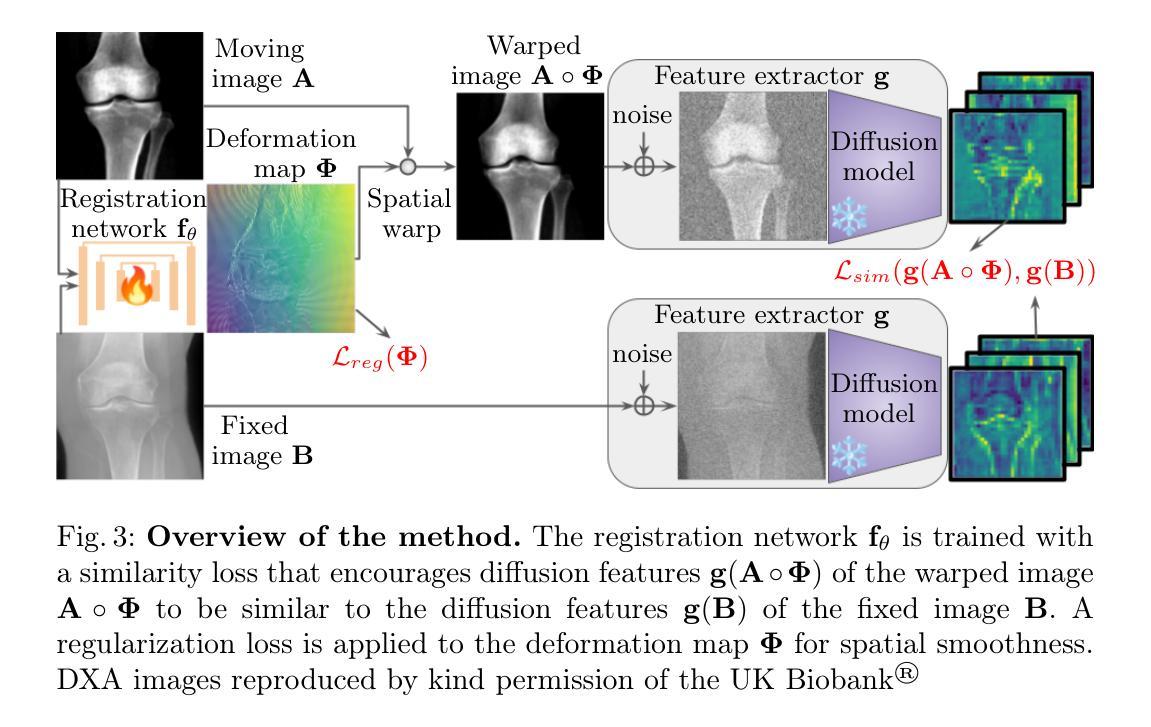
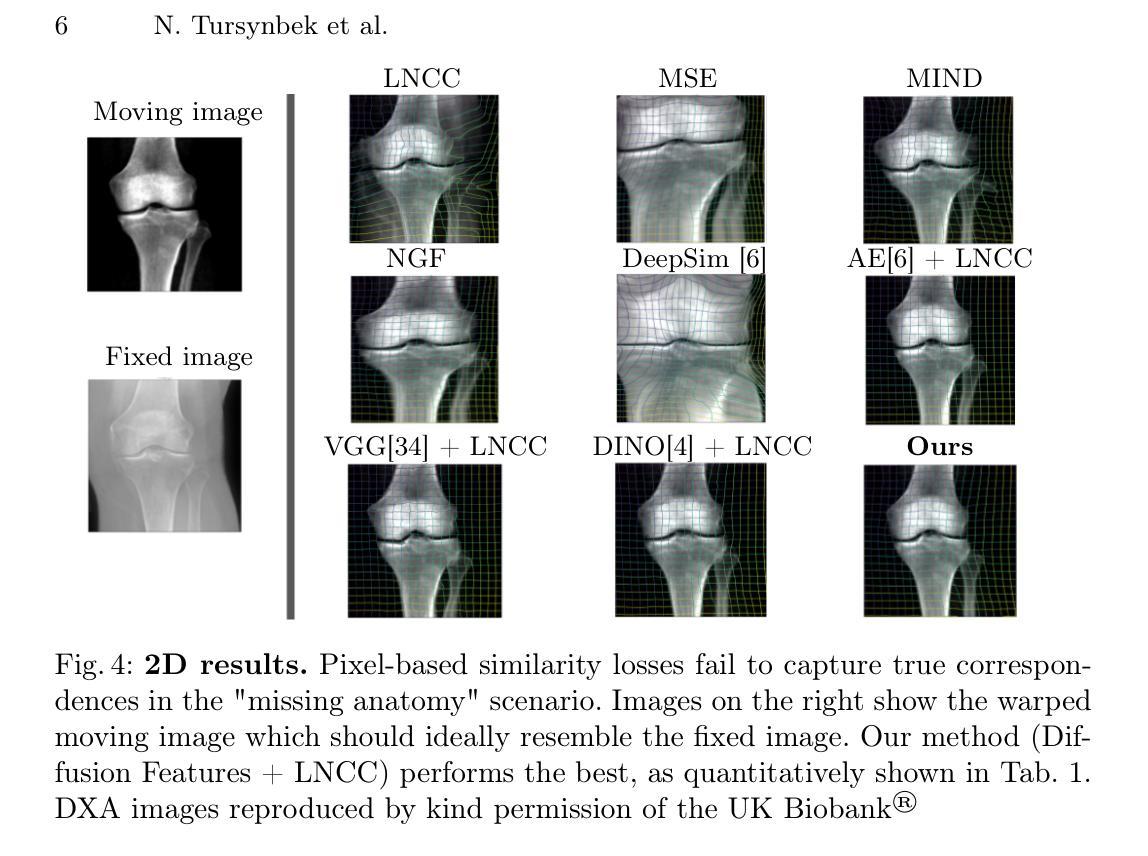
Guiding Registration with Emergent Similarity from Pre-Trained Diffusion Models
Authors:Nurislam Tursynbek, Hastings Greer, Basar Demir, Marc Niethammer
Diffusion models, while trained for image generation, have emerged as powerful foundational feature extractors for downstream tasks. We find that off-the-shelf diffusion models, trained exclusively to generate natural RGB images, can identify semantically meaningful correspondences in medical images. Building on this observation, we propose to leverage diffusion model features as a similarity measure to guide deformable image registration networks. We show that common intensity-based similarity losses often fail in challenging scenarios, such as when certain anatomies are visible in one image but absent in another, leading to anatomically inaccurate alignments. In contrast, our method identifies true semantic correspondences, aligning meaningful structures while disregarding those not present across images. We demonstrate superior performance of our approach on two tasks: multimodal 2D registration (DXA to X-Ray) and monomodal 3D registration (brain-extracted to non-brain-extracted MRI). Code: https://github.com/uncbiag/dgir
扩散模型虽然被训练用于图像生成,但已作为下游任务的强大基础特征提取器而出现。我们发现,专为生成自然RGB图像而训练的即用型扩散模型可以识别医学图像中的语义对应物。基于这一观察,我们提出利用扩散模型特征作为相似性度量来指导可变形图像配准网络。我们表明,基于强度的常见相似性损失在具有挑战性的场景中常常失败,例如在一张图像中可见某些解剖结构而在另一张图像中缺失时,会导致解剖结构不准确的对齐。与之相反,我们的方法能够识别真正的语义对应关系,对齐有意义的结构,同时忽略那些在不同图像中不存在的部分。我们在两个任务上展示了我们的方法的优越性:多模态二维配准(DXA到X射线)和单模态三维配准(提取大脑与非提取大脑的MRI)。代码:https://github.com/uncbiag/dgir
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
Summary
扩散模型最初是为图像生成而设计的,但现在已成为下游任务的基础特征提取器。研究发现,现成的扩散模型,在仅用于生成自然RGB图像的情况下,能够在医学图像中识别出语义上对应的内容。基于此观察,我们提议利用扩散模型特征作为相似度度量,以指导可变形图像配准网络。常见的基于强度的相似度损失在特定场景下会失效,如某些解剖结构在一幅图像中可见而在另一幅中缺失时,会导致解剖结构对应不准确。与之相比,我们的方法能够识别真正的语义对应关系,对齐有意义的结构,同时忽略那些在不同图像中不存在的部分。我们在两种任务上展示了其卓越性能:多模态的二维配准(DXA到X光)和单模态的三维配准(提取大脑与未提取大脑的MRI)。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已被发现可以作为强大的特征提取器用于下游任务,不仅在图像生成上有优势。
- 扩散模型能够在医学图像中识别语义上的对应关系。
- 扩散模型特征被提议用作相似度度量,以改进可变形图像配准网络。
- 在特定场景下,常见的基于强度的相似度损失会失效,导致解剖结构对应不准确。
- 与传统方法相比,利用扩散模型的方法能够更准确地识别并对齐有意义的结构。
- 该方法在两种不同类型的图像配准任务上展示了卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

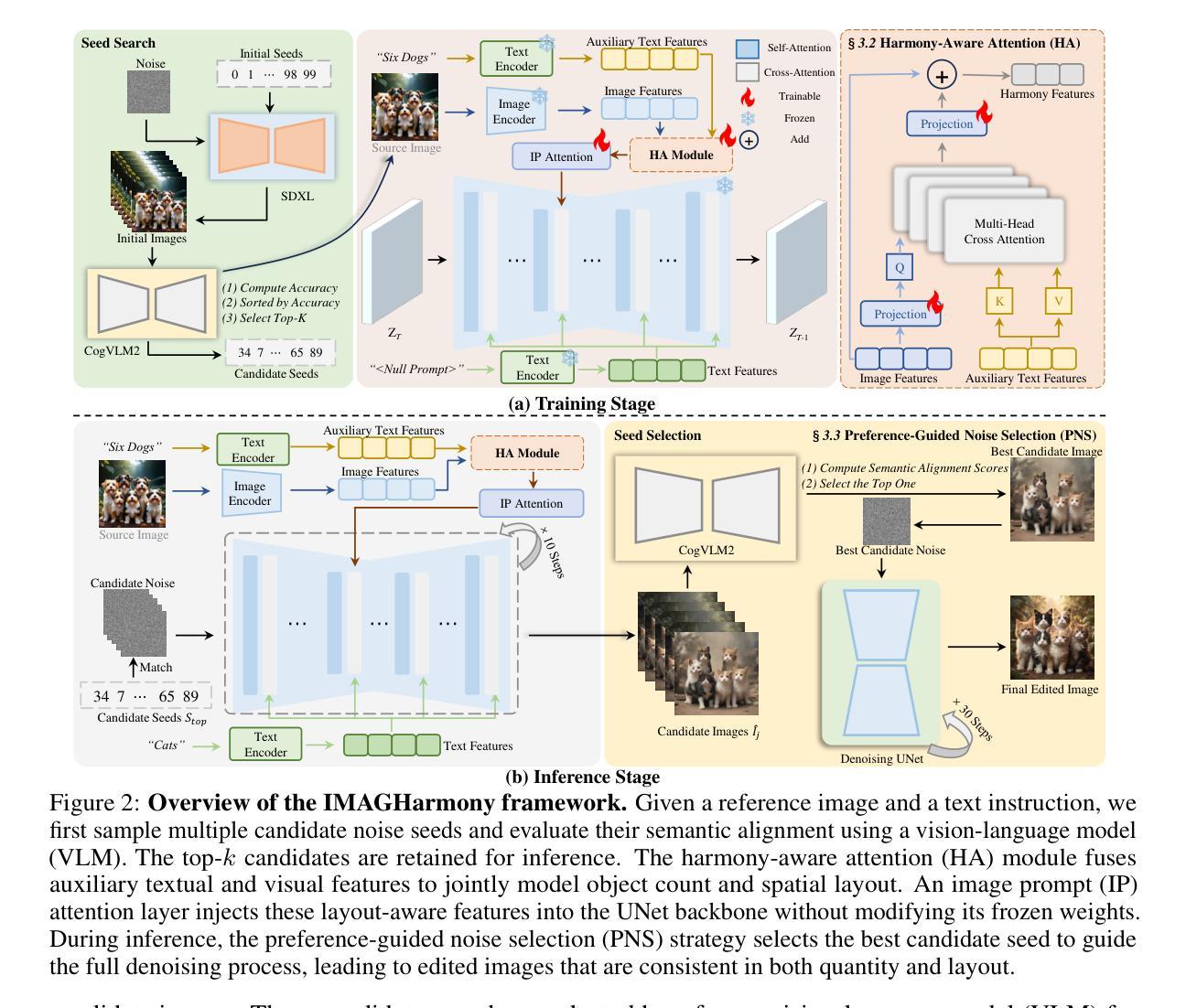
IMAGHarmony: Controllable Image Editing with Consistent Object Quantity and Layout
Authors:Fei Shen, Xiaoyu Du, Yutong Gao, Jian Yu, Yushe Cao, Xing Lei, Jinhui Tang
Recent diffusion models have advanced image editing by enhancing visual quality and control, supporting broad applications across creative and personalized domains. However, current image editing largely overlooks multi-object scenarios, where precise control over object categories, counts, and spatial layouts remains a significant challenge. To address this, we introduce a new task, quantity-and-layout consistent image editing (QL-Edit), which aims to enable fine-grained control of object quantity and spatial structure in complex scenes. We further propose IMAGHarmony, a structure-aware framework that incorporates harmony-aware attention (HA) to integrate multimodal semantics, explicitly modeling object counts and layouts to enhance editing accuracy and structural consistency. In addition, we observe that diffusion models are susceptible to initial noise and exhibit strong preferences for specific noise patterns. Motivated by this, we present a preference-guided noise selection (PNS) strategy that chooses semantically aligned initial noise samples based on vision-language matching, thereby improving generation stability and layout consistency in multi-object editing. To support evaluation, we construct HarmonyBench, a comprehensive benchmark covering diverse quantity and layout control scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that IMAGHarmony consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in structural alignment and semantic accuracy. The code and model are available at https://github.com/muzishen/IMAGHarmony.
近期扩散模型通过提高视觉质量和控制力,推动了图像编辑的进展,并广泛支持创意和个性化领域的应用。然而,当前图像编辑大多忽视了多目标场景,对目标类别、数量和空间布局的精细控制仍然是一个重大挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了一项新任务——数量与布局一致图像编辑(QL-Edit),旨在实现对复杂场景中目标数量和空间结构的精细控制。我们进一步提出了IMAGHarmony,这是一个结构感知的框架,它结合了和谐感知注意力(HA)来整合多模式语义,显式地建模目标数量和布局,以提高编辑精度和结构一致性。此外,我们观察到扩散模型对初始噪声敏感,并表现出对特定噪声模式的强烈偏好。受此启发,我们提出了一种偏好引导噪声选择(PNS)策略,它基于视觉语言匹配选择语义对齐的初始噪声样本,从而提高多目标编辑中的生成稳定性和布局一致性。为了支持评估,我们构建了HarmonyBench,这是一个涵盖多种数量和布局控制场景的全面基准测试集。大量实验表明,IMAGHarmony在结构对齐和语义准确性方面始终优于最新方法。代码和模型可在https://github.com/muzishen/IMAGHarmony找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期扩散模型在图像编辑领域取得进展,支持创意和个人化应用的广泛应用。然而,多目标场景下的图像编辑仍面临精确控制目标类别、数量和空间布局的难题。为此,引入QL-Edit任务,旨在实现复杂场景中目标数量和空间结构的精细控制。提出IMAGHarmony结构感知框架,结合和谐感知注意力(HA)整合多模式语义,显式建模目标数量和布局提高编辑精度和结构一致性。此外,发现扩散模型易受初始噪声影响并偏好特定噪声模式,因此提出基于偏好引导的噪声选择(PNS)策略,通过视觉语言匹配选择语义对齐的初始噪声样本,提高多目标编辑中的生成稳定性和布局一致性。建立HarmonyBench综合基准测试平台,涵盖多种数量和布局控制场景。实验表明,IMAGHarmony在结构对齐和语义准确性方面表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像编辑中取得进展,支持创意和个人化应用。
- 当前图像编辑在多目标场景的控制上存在挑战。
- 引入QL-Edit任务以实现目标数量和空间结构的精细控制。
- 提出IMAGHarmony框架,结合和谐感知注意力整合多模式语义。
- 扩散模型易受初始噪声影响并具有噪声模式偏好。
- 提出PNS策略,通过视觉语言匹配选择语义对齐的初始噪声样本。
点此查看论文截图



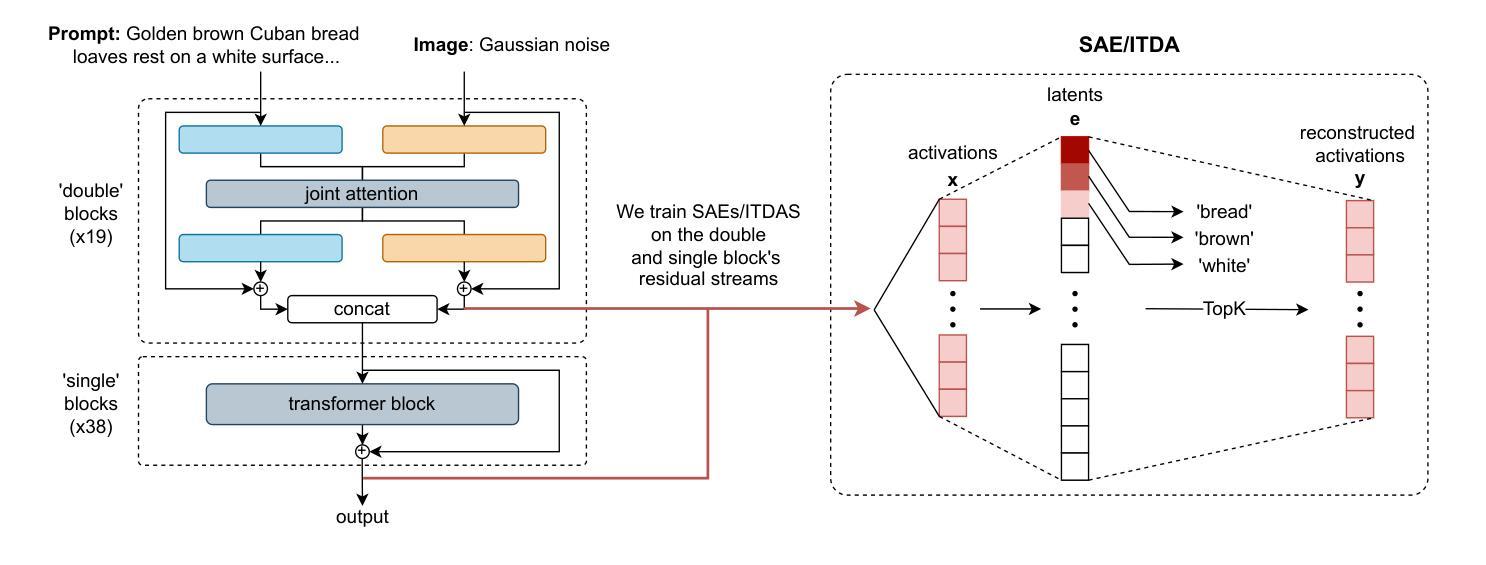
Interpreting Large Text-to-Image Diffusion Models with Dictionary Learning
Authors:Stepan Shabalin, Ayush Panda, Dmitrii Kharlapenko, Abdur Raheem Ali, Yixiong Hao, Arthur Conmy
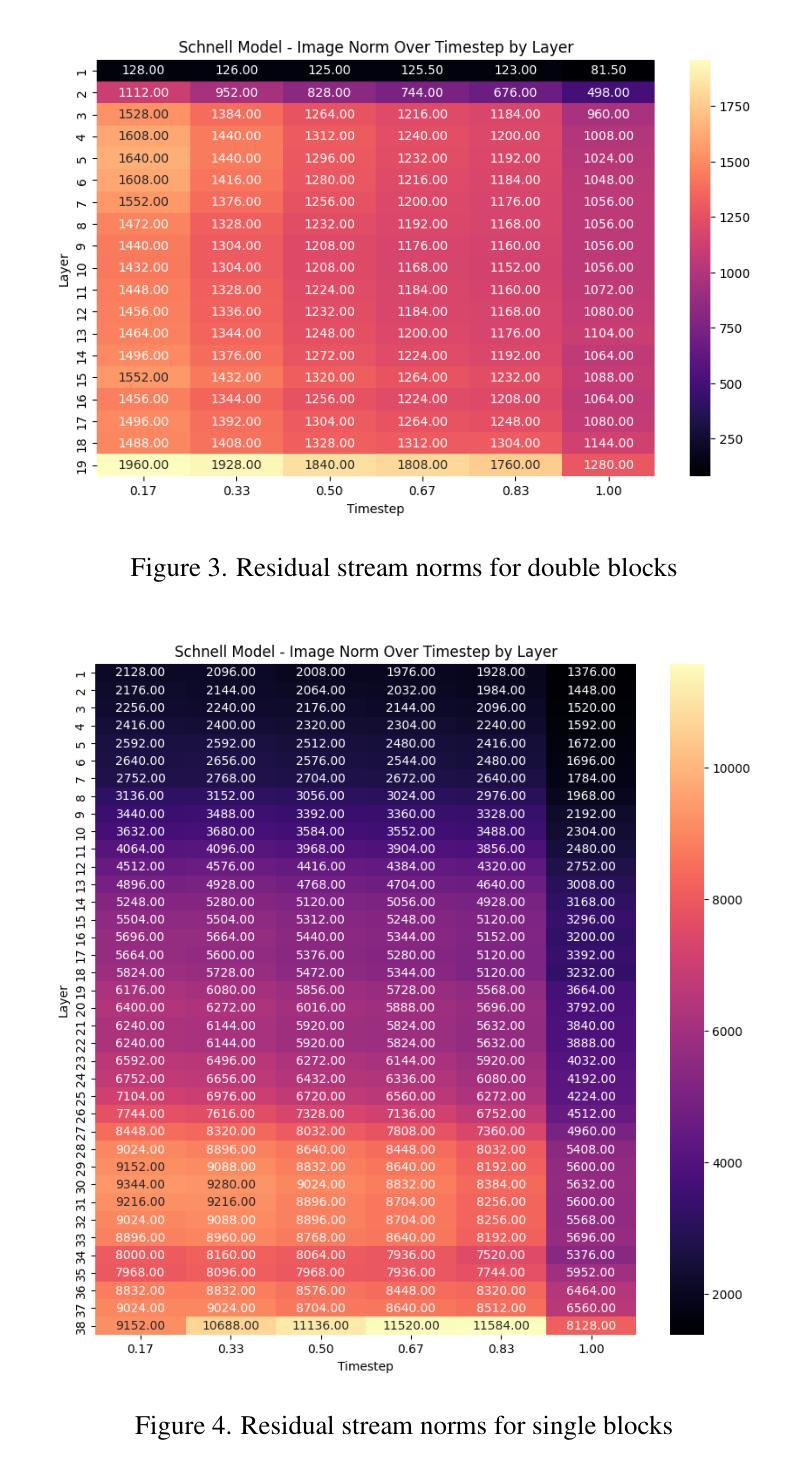
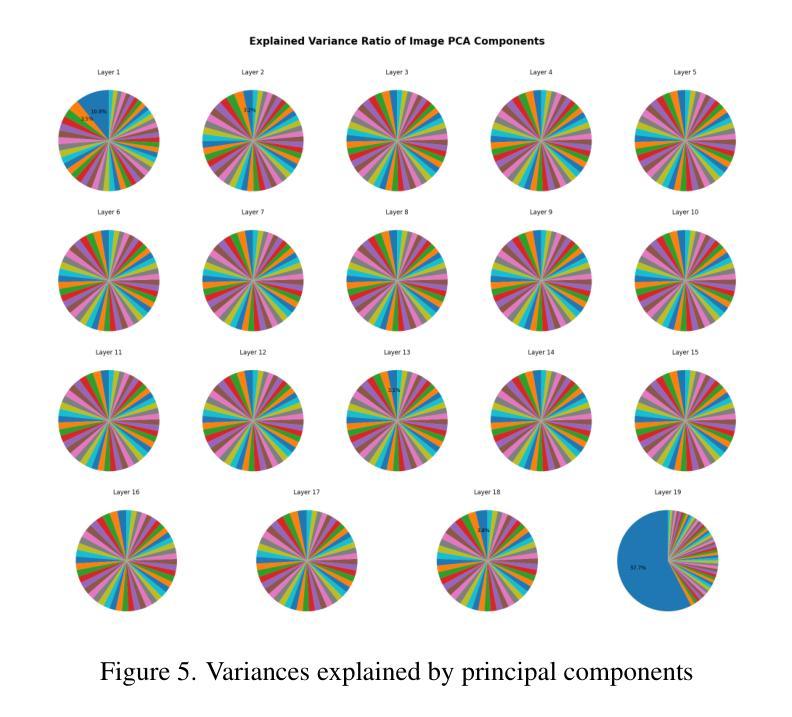
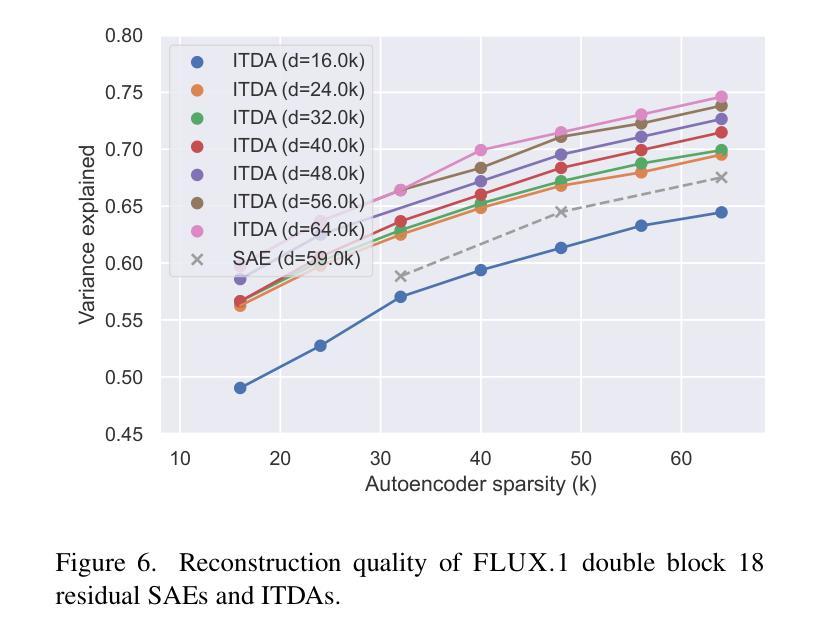
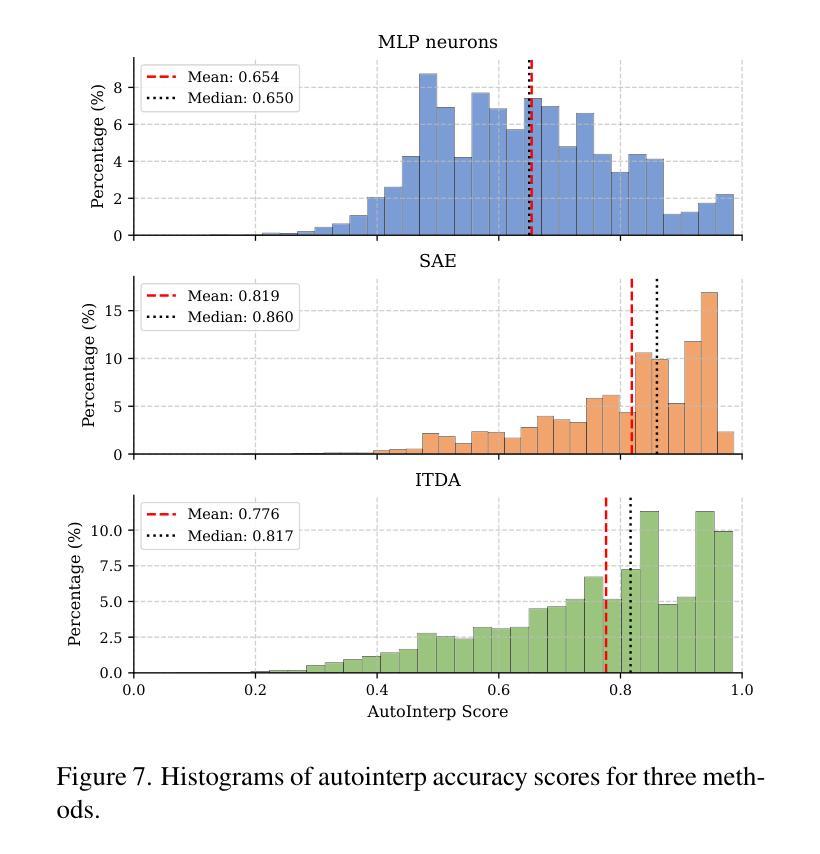
Sparse autoencoders are a promising new approach for decomposing language model activations for interpretation and control. They have been applied successfully to vision transformer image encoders and to small-scale diffusion models. Inference-Time Decomposition of Activations (ITDA) is a recently proposed variant of dictionary learning that takes the dictionary to be a set of data points from the activation distribution and reconstructs them with gradient pursuit. We apply Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) and ITDA to a large text-to-image diffusion model, Flux 1, and consider the interpretability of embeddings of both by introducing a visual automated interpretation pipeline. We find that SAEs accurately reconstruct residual stream embeddings and beat MLP neurons on interpretability. We are able to use SAE features to steer image generation through activation addition. We find that ITDA has comparable interpretability to SAEs.
稀疏自动编码器是一种有前景的新方法,用于分解语言模型的激活以进行解释和控制。它们已成功应用于视觉转换器图像编码器和小型扩散模型。激活的推理时间分解(ITDA)是字典学习的一个新近提出的变体,它将字典视为激活分布中的数据点集,并通过梯度追求进行重建。我们将稀疏自动编码器(SAE)和ITDA应用于大型文本到图像的扩散模型Flux 1,并通过引入视觉自动化解释管道考虑两者的嵌入解释性。我们发现SAE能够准确重建残差流嵌入,并在解释性方面优于MLP神经元。我们能够使用SAE特性通过激活添加来引导图像生成。我们发现ITDA的解释性与SAE相当。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 10 figures, Mechanistic Interpretability for Vision at CVPR 2025
Summary
稀疏自编码器是分解语言模型激活以进行解释和控制的一种新兴、有前景的方法。已成功应用于视觉转换器图像编码器和小型扩散模型。我们应用稀疏自编码器和推理时间激活分解(ITDA)到大型文本到图像扩散模型Flux 1,并通过引入视觉自动化解释管道考虑两者的嵌入解释性。研究发现,SAE能够准确重建残差流嵌入,并在解释性方面优于MLP神经元。我们还能够使用SAE特性通过激活添加来操控图像生成。ITDA的解释性与SAE相当。
Key Takeaways
- 稀疏自编码器是分解语言模型激活的新兴方法,用于解释和控制。
- 稀疏自编码器已成功应用于视觉转换器图像编码器和小型扩散模型。
- 推理时间分解激活(ITDA)是字典学习的一种变体,能够重建激活分布的数据点。
- 在大型文本到图像扩散模型Flux 1上应用了SAE和ITDA。
- SAE能够准确重建残差流嵌入,且在解释性方面优于MLP神经元。
- SAE特性可用于操控图像生成。
点此查看论文截图

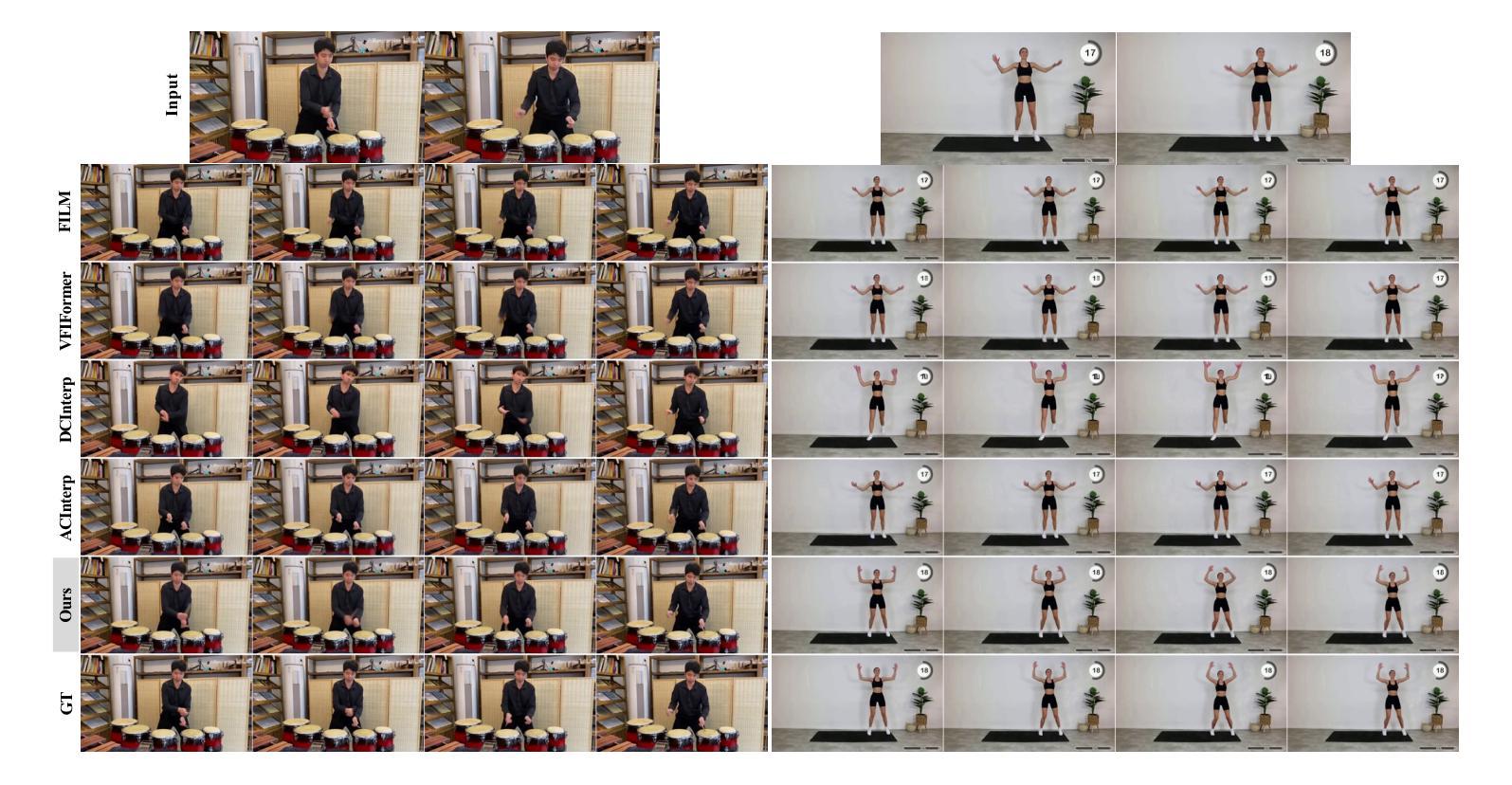
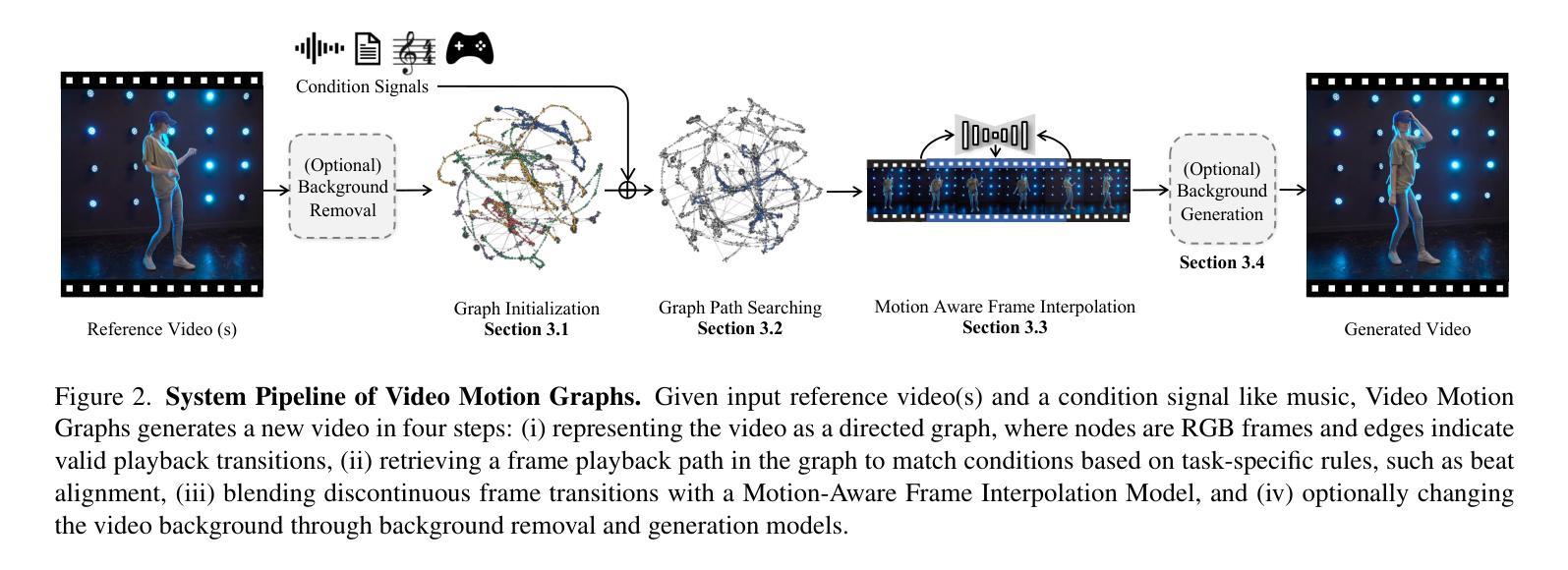
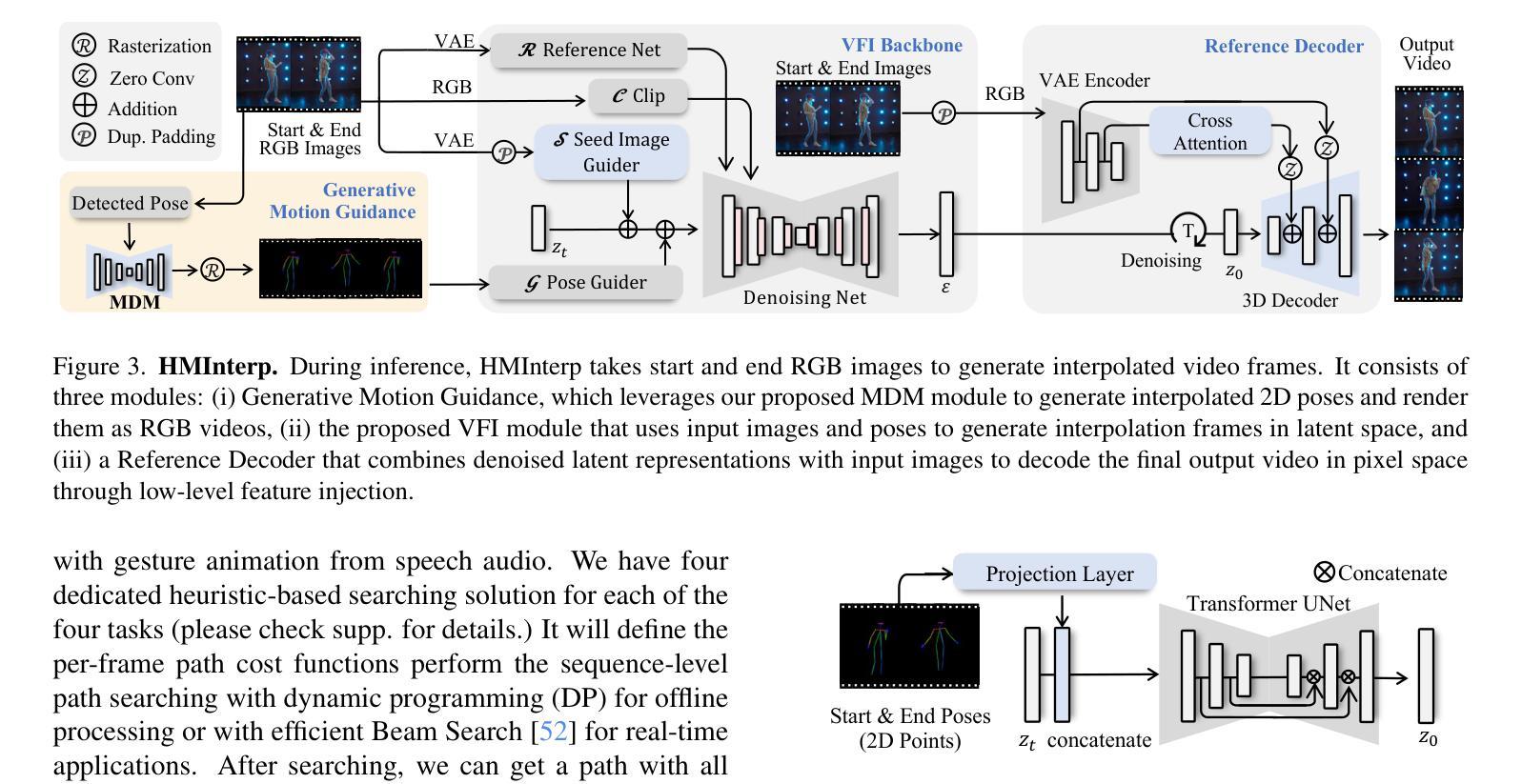
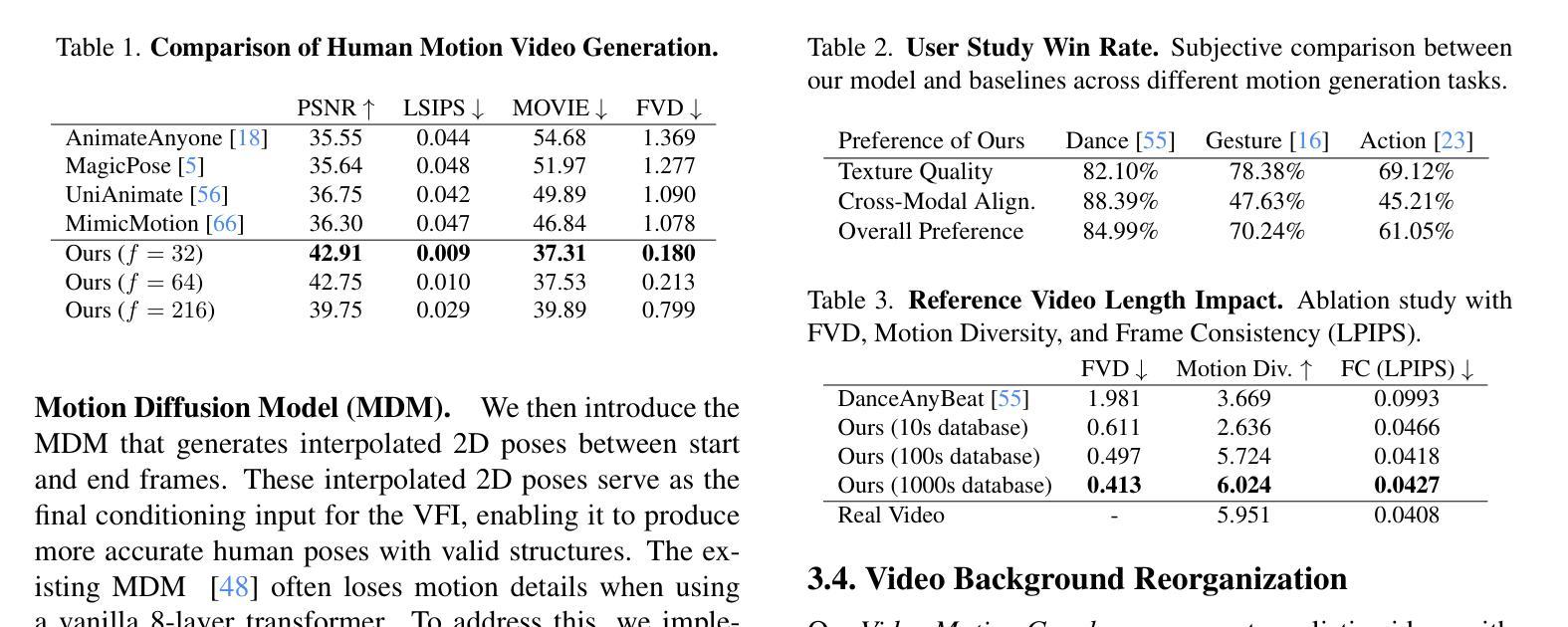
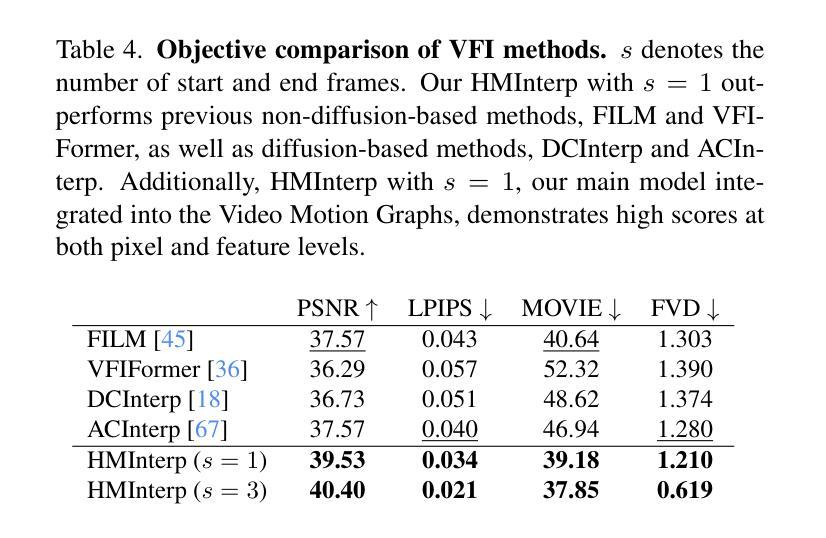
Video Motion Graphs
Authors:Haiyang Liu, Zhan Xu, Fa-Ting Hong, Hsin-Ping Huang, Yi Zhou, Yang Zhou
We present Video Motion Graphs, a system designed to generate realistic human motion videos. Using a reference video and conditional signals such as music or motion tags, the system synthesizes new videos by first retrieving video clips with gestures matching the conditions and then generating interpolation frames to seamlessly connect clip boundaries. The core of our approach is HMInterp, a robust Video Frame Interpolation (VFI) model that enables seamless interpolation of discontinuous frames, even for complex motion scenarios like dancing. HMInterp i) employs a dual-branch interpolation approach, combining a Motion Diffusion Model for human skeleton motion interpolation with a diffusion-based video frame interpolation model for final frame generation. ii) adopts condition progressive training to effectively leverage identity strong and weak conditions, such as images and pose. These designs ensure both high video texture quality and accurate motion trajectory. Results show that our Video Motion Graphs outperforms existing generative- and retrieval-based methods for multi-modal conditioned human motion video generation. Project page can be found at https://h-liu1997.github.io/Video-Motion-Graphs/
我们提出了视频运动图(Video Motion Graphs)系统,旨在生成逼真的人类运动视频。该系统使用参考视频和条件信号(如音乐或运动标签)来合成新视频。它首先检索与条件匹配的视频片段,然后生成插帧以无缝连接片段边界。我们的方法的核心是HMInterp,这是一个强大的视频帧插值(VFI)模型,即使对于跳舞等复杂运动场景,也能实现无缝插值。HMInterp采用双分支插值方法,结合用于人体骨架运动插值的运动扩散模型与基于扩散的视频帧插值模型进行最终帧生成。它采用条件渐进训练,有效利用强条件和弱条件(如图像和姿态)。这些设计确保了视频纹理质量高且运动轨迹准确。结果表明,我们的视频运动图系统在多模态条件下的人类运动视频生成中优于现有的生成型和检索型方法。项目页面可访问:[https://h-liu1997.github.io/Video-Motion-Graphs/]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages,10 figures
Summary
本文介绍了Video Motion Graphs系统,该系统能够根据参考视频、音乐或动作标签等条件信号生成逼真的人类运动视频。它通过检索匹配条件的视频片段,并利用HMInterp进行插帧,生成流畅的新视频。HMInterp是一个强大的视频帧插值模型,能在复杂动作场景如舞蹈中无缝插值断帧。采用双分支插值方法,结合人体骨架运动插值的Motion Diffusion Model和最终帧生成的扩散式视频帧插值模型。并采用条件渐进训练,有效利用身份强弱条件如图像和姿态。结果证明Video Motion Graphs在多模态条件下的人类运动视频生成中表现优于现有生成和检索方法。
Key Takeaways
- Video Motion Graphs系统能够根据条件信号生成逼真的人类运动视频。
- 系统通过检索匹配条件的视频片段并插帧来生成新视频。
- HMInterp是一个强大的视频帧插值模型,支持复杂运动场景的无缝插值。
- HMInterp采用双分支插值方法,结合Motion Diffusion Model和扩散式视频帧插值模型。
- 条件渐进训练技术被用来有效利用不同的条件信息。
- Video Motion Graphs在多项测试中表现优于现有方法。
- 项目页面提供了更多详细信息。
点此查看论文截图


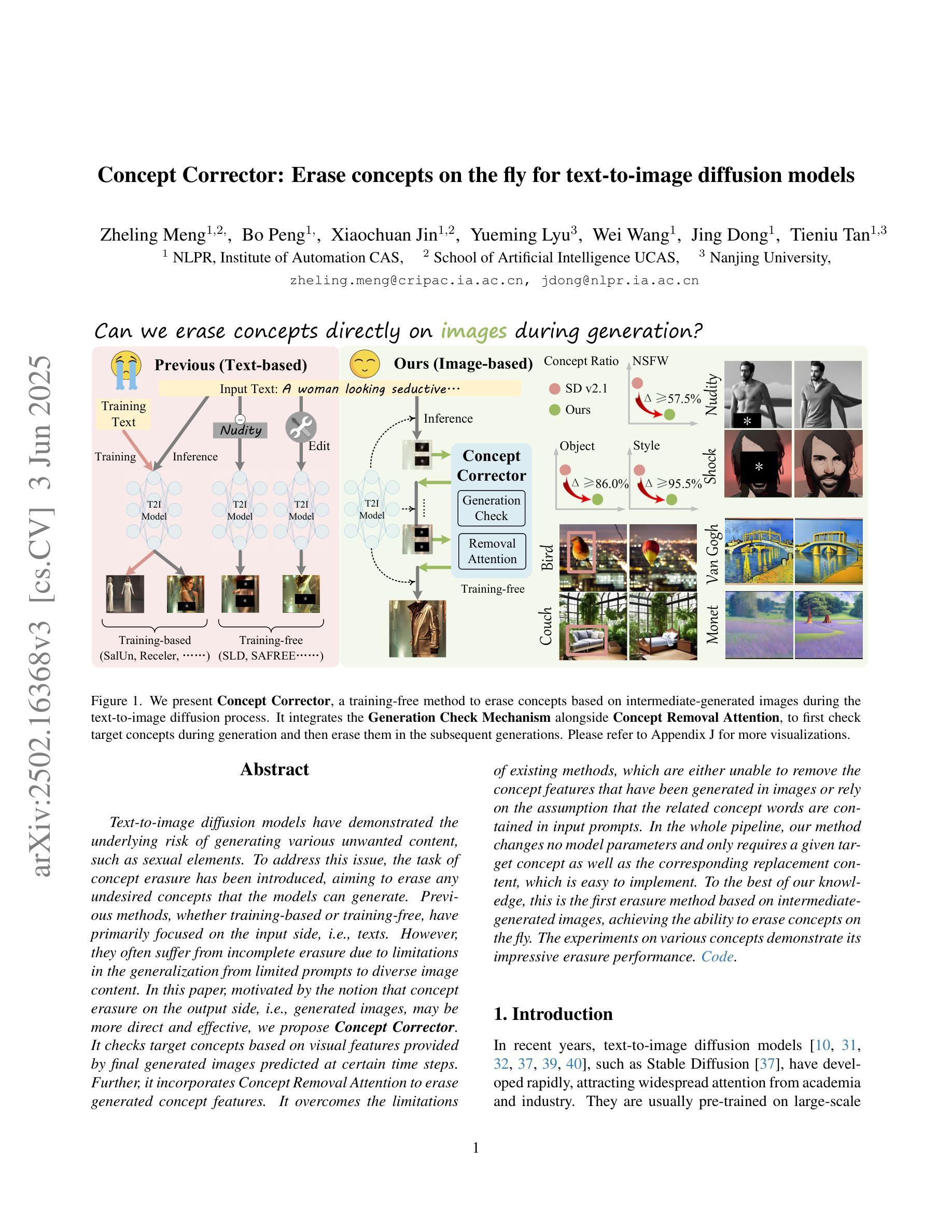
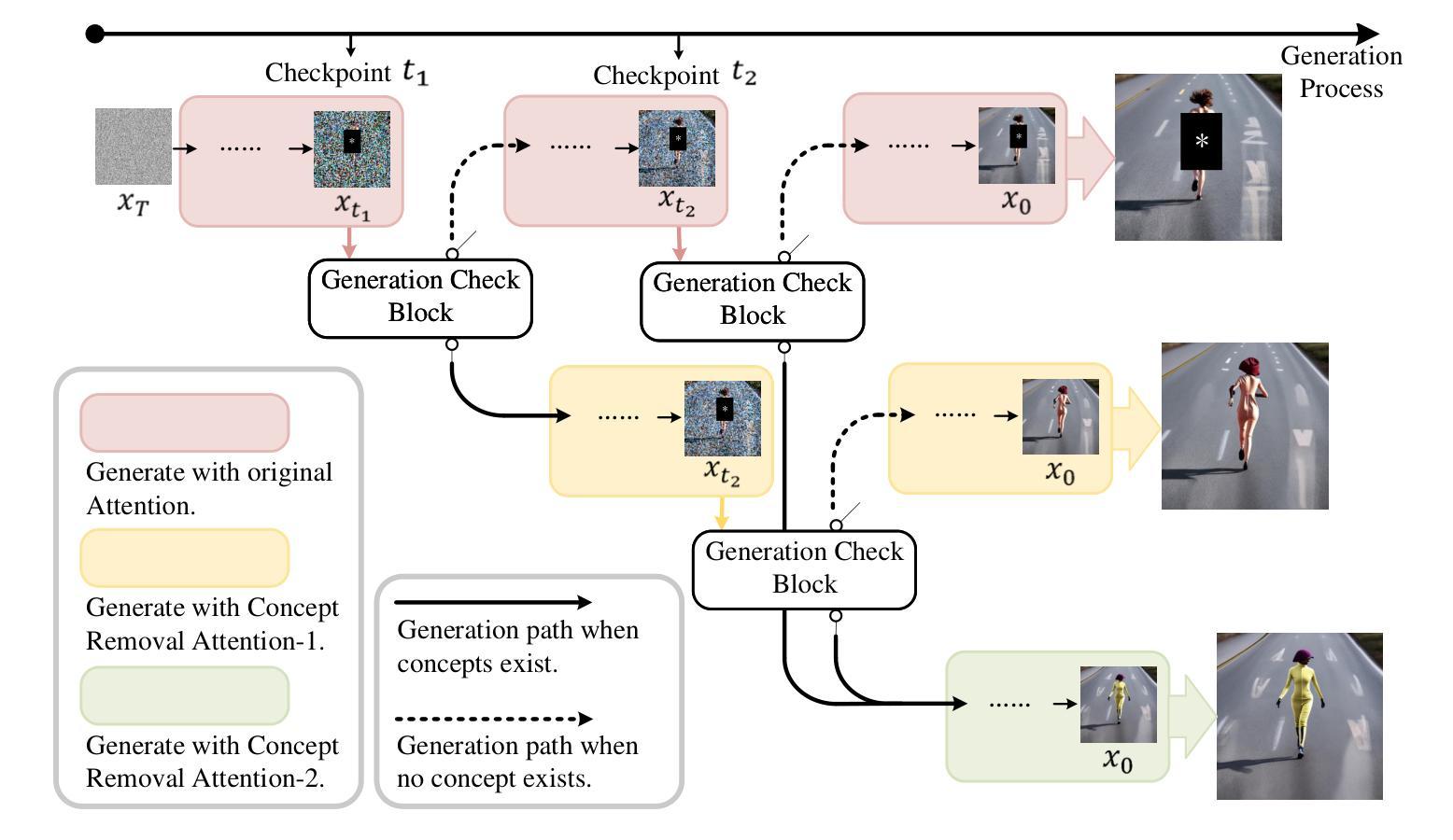
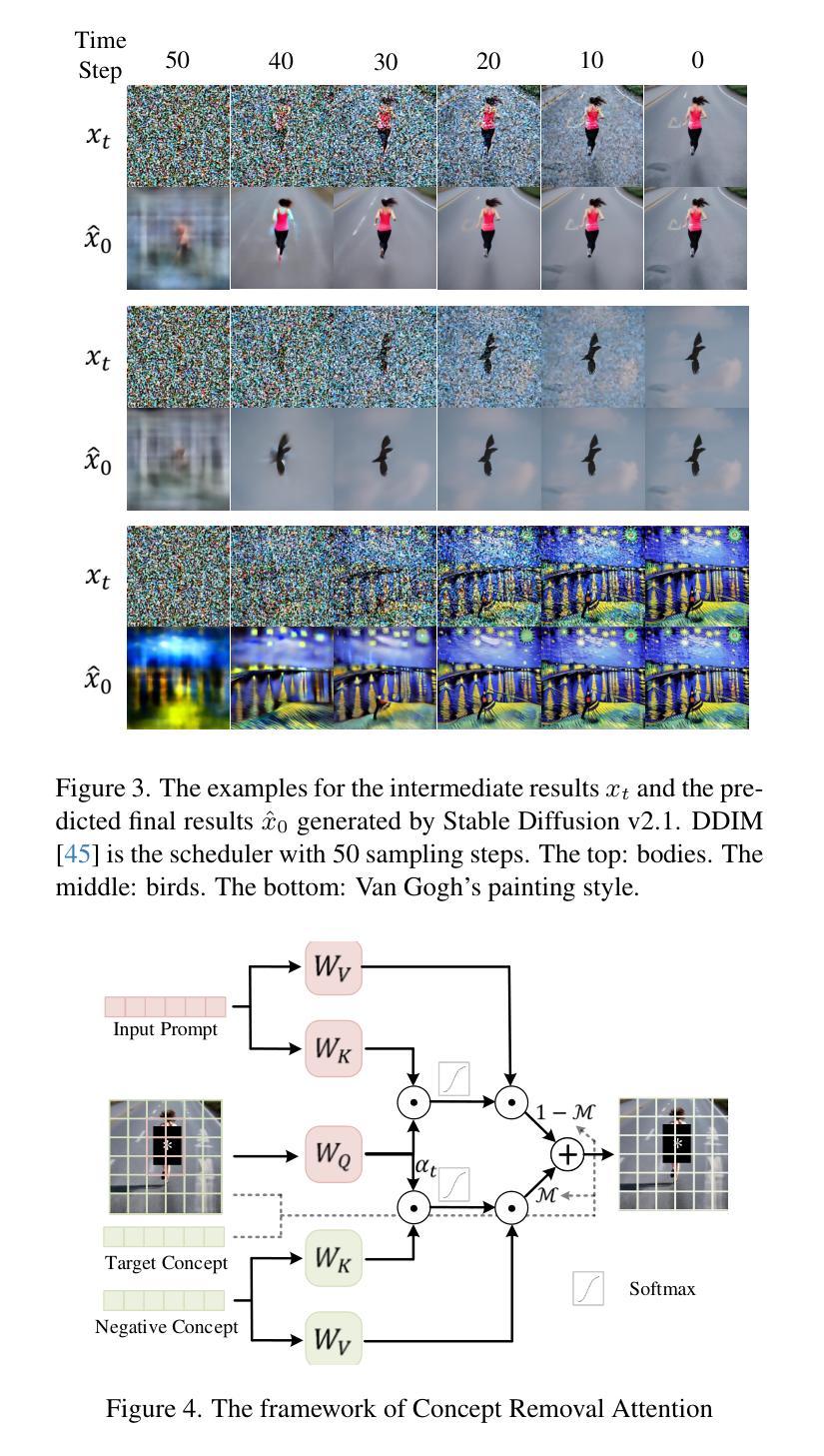
Concept Corrector: Erase concepts on the fly for text-to-image diffusion models
Authors:Zheling Meng, Bo Peng, Xiaochuan Jin, Yueming Lyu, Wei Wang, Jing Dong, Tieniu Tan
Text-to-image diffusion models have demonstrated the underlying risk of generating various unwanted content, such as sexual elements. To address this issue, the task of concept erasure has been introduced, aiming to erase any undesired concepts that the models can generate. Previous methods, whether training-based or training-free, have primarily focused on the input side, i.e., texts. However, they often suffer from incomplete erasure due to limitations in the generalization from limited prompts to diverse image content. In this paper, motivated by the notion that concept erasure on the output side, i.e., generated images, may be more direct and effective, we propose Concept Corrector. It checks target concepts based on visual features provided by final generated images predicted at certain time steps. Further, it incorporates Concept Removal Attention to erase generated concept features. It overcomes the limitations of existing methods, which are either unable to remove the concept features that have been generated in images or rely on the assumption that the related concept words are contained in input prompts. In the whole pipeline, our method changes no model parameters and only requires a given target concept as well as the corresponding replacement content, which is easy to implement. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first erasure method based on intermediate-generated images, achieving the ability to erase concepts on the fly. The experiments on various concepts demonstrate its impressive erasure performance.
文本到图像的扩散模型已经显示出生成各种不想要内容(如性元素)的潜在风险。为了解决这个问题,引入了概念消除的任务,旨在消除模型可能生成的不需要的概念。以前的方法,无论是基于训练的,还是非训练的,主要关注输入方面,即文本。然而,由于从有限的提示推广到多样化的图像内容的局限性,它们经常遭受不完全消除的问题。本文受到输出侧(即生成的图像)概念消除可能更直接和有效的概念的启发,我们提出了概念修正器。它基于最终生成的图像在特定时间步长预测的视觉特征来检查目标概念。此外,它结合了概念去除注意力来消除生成的概念特征。它克服了现有方法的局限性,这些方法要么无法消除已生成图像中的概念特征,要么依赖于相关概念词包含在输入提示中的假设。在整个流程中,我们的方法不会更改任何模型参数,只需给定目标概念以及相应的替换内容即可,易于实现。据我们所知,这是一种基于中间生成的图像的首个消除方法,实现了即时消除概念的能力。对各种概念的实验证明了其令人印象深刻的消除性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于生成图像的概念修正器(Concept Corrector),旨在解决文本到图像扩散模型生成不想要内容(如性元素等)的问题。该方法通过检查特定时间步长生成的图像的视觉特征来验证目标概念,并结合概念移除注意力机制来消除生成的概念特征。此方法克服了现有方法的局限性,无需修改模型参数,仅需要目标概念及其替换内容,易于实现,且在各种概念上的实验证明了其出色的消除性能。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像扩散模型存在生成不想要内容的潜在风险,如性元素等。
- 概念消除任务旨在消除模型中生成的不想要的概念。
- 现有方法主要关注输入侧的概念消除,但存在从有限提示推广到多样图像内容的局限性。
- 本文提出的Concept Corrector基于生成图像的概念修正,通过检查生成的图像的视觉特征来验证和消除目标概念。
- Concept Corrector结合了概念移除注意力机制,能够克服现有方法的局限性。
- 该方法无需修改模型参数,仅需要目标概念及其替换内容,易于实现。
点此查看论文截图
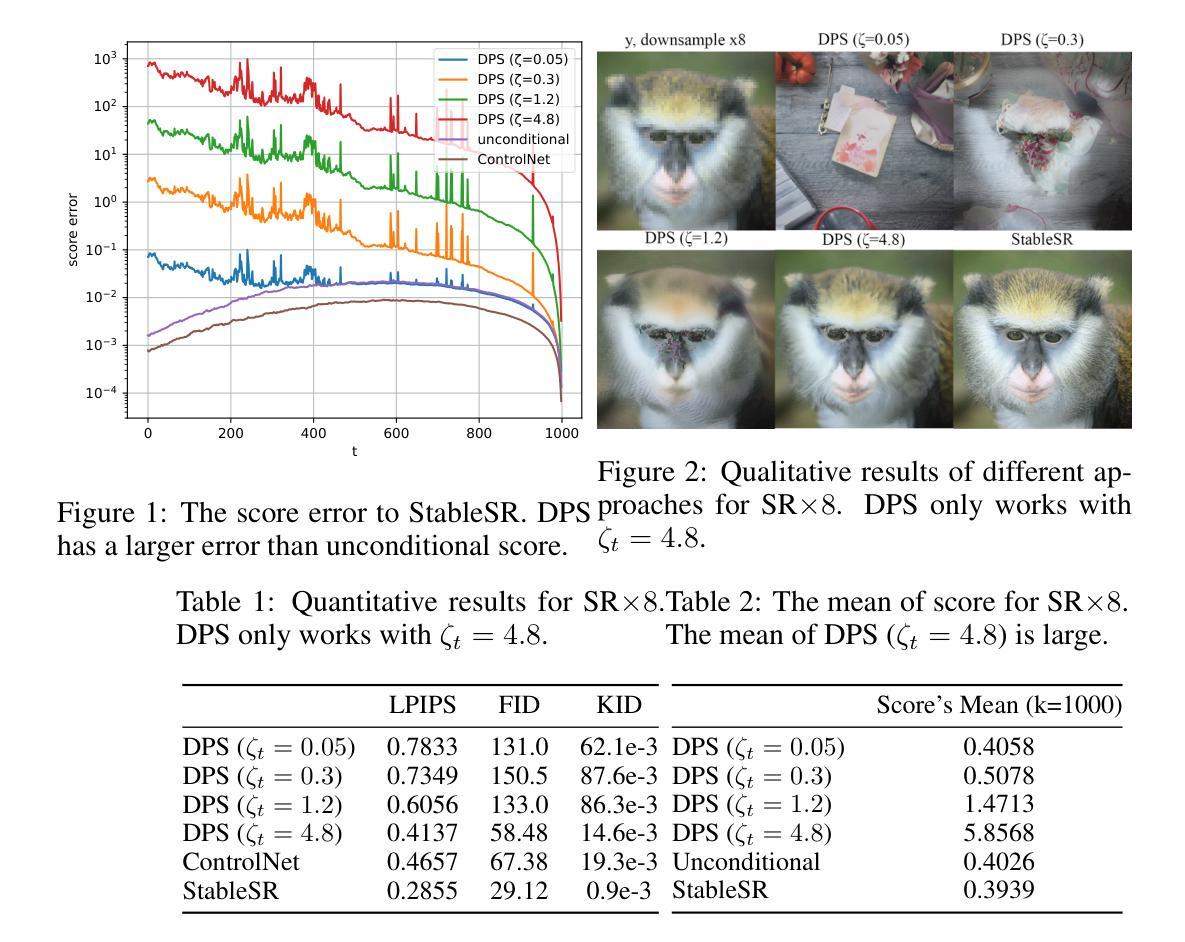
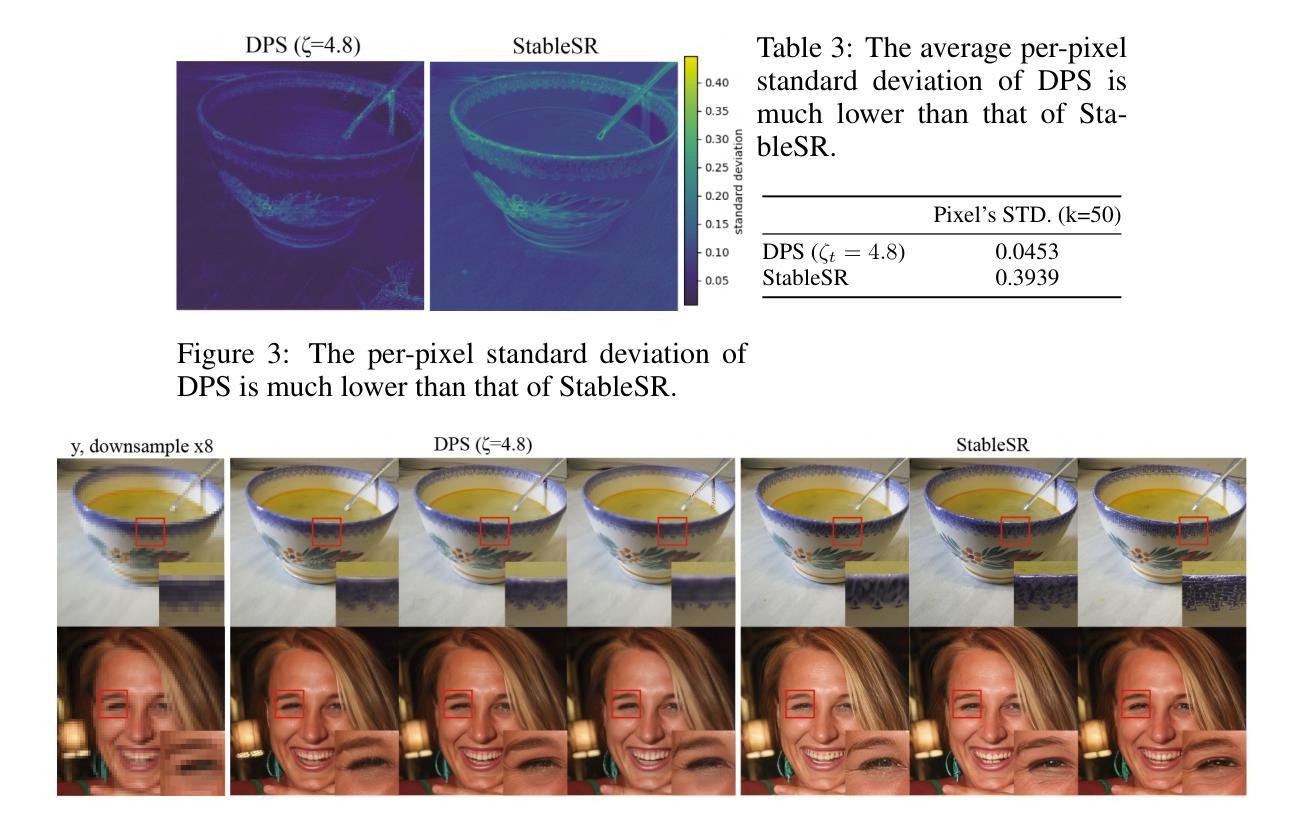
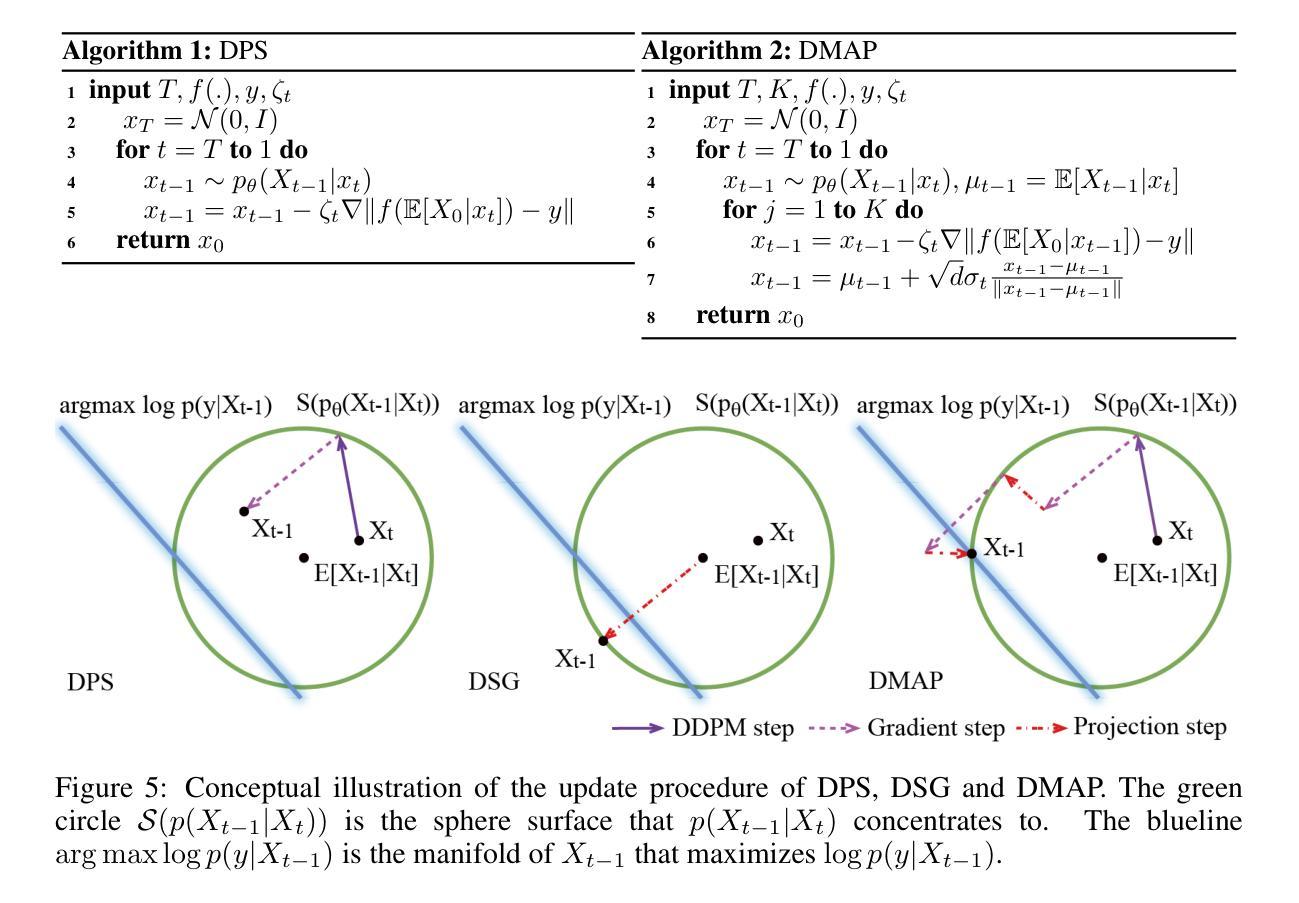
Rethinking Diffusion Posterior Sampling: From Conditional Score Estimator to Maximizing a Posterior
Authors:Tongda Xu, Xiyan Cai, Xinjie Zhang, Xingtong Ge, Dailan He, Ming Sun, Jingjing Liu, Ya-Qin Zhang, Jian Li, Yan Wang
Recent advancements in diffusion models have been leveraged to address inverse problems without additional training, and Diffusion Posterior Sampling (DPS) (Chung et al., 2022a) is among the most popular approaches. Previous analyses suggest that DPS accomplishes posterior sampling by approximating the conditional score. While in this paper, we demonstrate that the conditional score approximation employed by DPS is not as effective as previously assumed, but rather aligns more closely with the principle of maximizing a posterior (MAP). This assertion is substantiated through an examination of DPS on 512x512 ImageNet images, revealing that: 1) DPS’s conditional score estimation significantly diverges from the score of a well-trained conditional diffusion model and is even inferior to the unconditional score; 2) The mean of DPS’s conditional score estimation deviates significantly from zero, rendering it an invalid score estimation; 3) DPS generates high-quality samples with significantly lower diversity. In light of the above findings, we posit that DPS more closely resembles MAP than a conditional score estimator, and accordingly propose the following enhancements to DPS: 1) we explicitly maximize the posterior through multi-step gradient ascent and projection; 2) we utilize a light-weighted conditional score estimator trained with only 100 images and 8 GPU hours. Extensive experimental results indicate that these proposed improvements significantly enhance DPS’s performance. The source code for these improvements is provided in https://github.com/tongdaxu/Rethinking-Diffusion-Posterior-Sampling-From-Conditional-Score-Estimator-to-Maximizing-a-Posterior.
近期扩散模型的新进展已被用于解决无需额外训练的反问题,其中扩散后采样(DPS)(Chung等人,2022a)是最受欢迎的方法之一。之前的分析表明,DPS通过后验采样实现条件评分的近似。然而,本文我们证明DPS所采用的条件评分近似并不像之前假设的那样有效,而更接近于最大后验(MAP)的原则。通过对DPS在512x512 ImageNet图像上的研究,我们发现:1)DPS的条件评分估计与训练良好的条件扩散模型的评分存在显著差异,甚至不如无条件评分;2)DPS的条件评分估计均值偏离零,使其成为无效的评分估计;3)虽然DPS可以生成高质量的样本,但样本多样性显著降低。鉴于上述发现,我们认为DPS更接近MAP而非条件评分估计器,并据此对DPS提出以下改进:1)我们通过多步梯度上升和投影来显式地最大化后验;2)我们使用轻量级的条件评分估计器,仅使用100张图像和8个GPU小时进行训练。大量的实验结果表明,这些改进显著提高了DPS的性能。相关源代码可访问https://github.com/tongdaxu/Rethinking-Diffusion-Posterior-Sampling-From-Conditional-Score-Estimator-to-Maximizing-a-Posterior。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
摘要
最近,扩散模型的新进展被用来解决无需额外训练的反问题,其中Diffusion Posterior Sampling(DPS)是最受欢迎的方法之一。本文通过对DPS的深入分析,指出其采用的条件分数近似并不像先前认为的那样有效,而是更符合最大后验概率(MAP)的原理。通过对512x512 ImageNet图像上的DPS研究,发现其存在的几个问题:其一,DPS的条件分数估计与训练良好的条件扩散模型的分数存在显著差异,甚至不如无条件分数;其二,DPS的条件分数估计均值偏离零,使其成为一个无效的分数估计;其三,DPS生成的样本质量高但多样性显著降低。基于此,本文提出对DPS的改进方案:一是通过多步梯度上升和投影显式最大化后验概率;二是使用轻量级的条件分数估计器,仅使用100张图像和8 GPU小时进行训练。实验结果表明,这些改进显著提升了DPS的性能。改进代码的源代码可在https://github.com/tongdaxu/Rethinking-Diffusion-Posterior-Sampling-From-Conditional-Score-Estimator-to-Maximizing-a-Posterior找到。
关键见解
- Diffusion Posterior Sampling (DPS) 被用来解决无需额外训练的反问题。
- 本文发现DPS的条件分数估计存在问题,与训练良好的条件扩散模型的分数存在显著差异。
- DPS的条件分数估计均值偏离零,使其成为一个无效的分数估计。
- DPS生成的样本虽然质量高但多样性不足。
- 本文提出通过多步梯度上升和投影来显式最大化后验概率的方法改进DPS。
- 使用轻量级的条件分数估计器,训练成本降低。
点此查看论文截图

Constant Rate Scheduling: Constant-Rate Distributional Change for Efficient Training and Sampling in Diffusion Models
Authors:Shuntaro Okada, Kenji Doi, Ryota Yoshihashi, Hirokatsu Kataoka, Tomohiro Tanaka
We propose a general approach to optimize noise schedules for training and sampling in diffusion models. Our approach optimizes the noise schedules to ensure a constant rate of change in the probability distribution of diffused data throughout the diffusion process. Any distance metric for measuring the probability-distributional change is applicable to our approach, and we introduce three distance metrics. We evaluated the effectiveness of our approach on unconditional and class-conditional image-generation tasks using the LSUN (Horse, Bedroom, Church), ImageNet, FFHQ, and CIFAR10 datasets. Through extensive experiments, we confirmed that our approach broadly improves the performance of pixel-space and latent-space diffusion models regardless of the dataset, sampler, and number of function evaluations ranging from 5 to 250. Notably, by using our approach for optimizing both training and sampling schedules, we achieved a state-of-the-art FID score of 2.03 without sacrificing mode coverage on LSUN Horse 256 $\times$ 256.
我们提出了一种针对扩散模型训练和采样的噪声调度优化的一般方法。我们的方法优化噪声调度,以确保扩散数据概率分布在整个扩散过程中的变化速率恒定。任何用于衡量概率分布变化的距离度量都适用于我们的方法,我们介绍了三种距离度量。我们在LSUN(马、卧室、教堂)、ImageNet、FFHQ和CIFAR10数据集上,对无条件和类别条件图像生成任务评估了我们的方法的有效性。通过大量实验,我们证实了我们方法广泛提高了像素空间和潜在空间扩散模型性能,无论数据集、采样器和功能评估次数(从5到250次)如何。值得注意的是,通过采用我们的方法来优化训练和采样调度,我们在LSUN Horse 256 x 256上实现了前所未有的FID分数2.03,同时没有牺牲模式覆盖。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 44 pages, 20 figures, 25 tables
Summary
本文提出了一种优化扩散模型训练和采样过程中噪声调度的一般方法。该方法通过优化噪声调度来确保扩散数据概率分布在扩散过程中的变化速率恒定。文中介绍了三种适用于该方法的距离度量指标,并在LSUN(马、卧室、教堂)、ImageNet、FFHQ和CIFAR10等数据集的图像生成任务中验证了该方法的有效性。实验表明,该方法可广泛提高像素空间和潜在空间扩散模型的性能,适用于不同的数据集、采样器和功能评估次数。特别是在LSUN Horse 256×256数据集上,通过优化训练和采样调度,实现了无模式丢失的FID分数为2.03。
Key Takeaways
- 文中提出了一种优化扩散模型的噪声调度方法,确保在整个扩散过程中概率分布的变化速率恒定。
- 介绍了三种适用于该方法的距离度量指标,用于测量概率分布的变化。
- 在多个数据集(如LSUN、ImageNet、FFHQ和CIFAR10)上进行了实验验证,证明了该方法的有效性。
- 该方法可广泛应用于像素空间和潜在空间的扩散模型,适用于不同的数据集、采样器和功能评估次数。
- 通过优化训练和采样调度,实现了在LSUN Horse 256×256数据集上的先进FID分数。
- 该方法能够提高图像生成任务的性能,并在不牺牲模式覆盖的情况下达到最佳效果。
点此查看论文截图

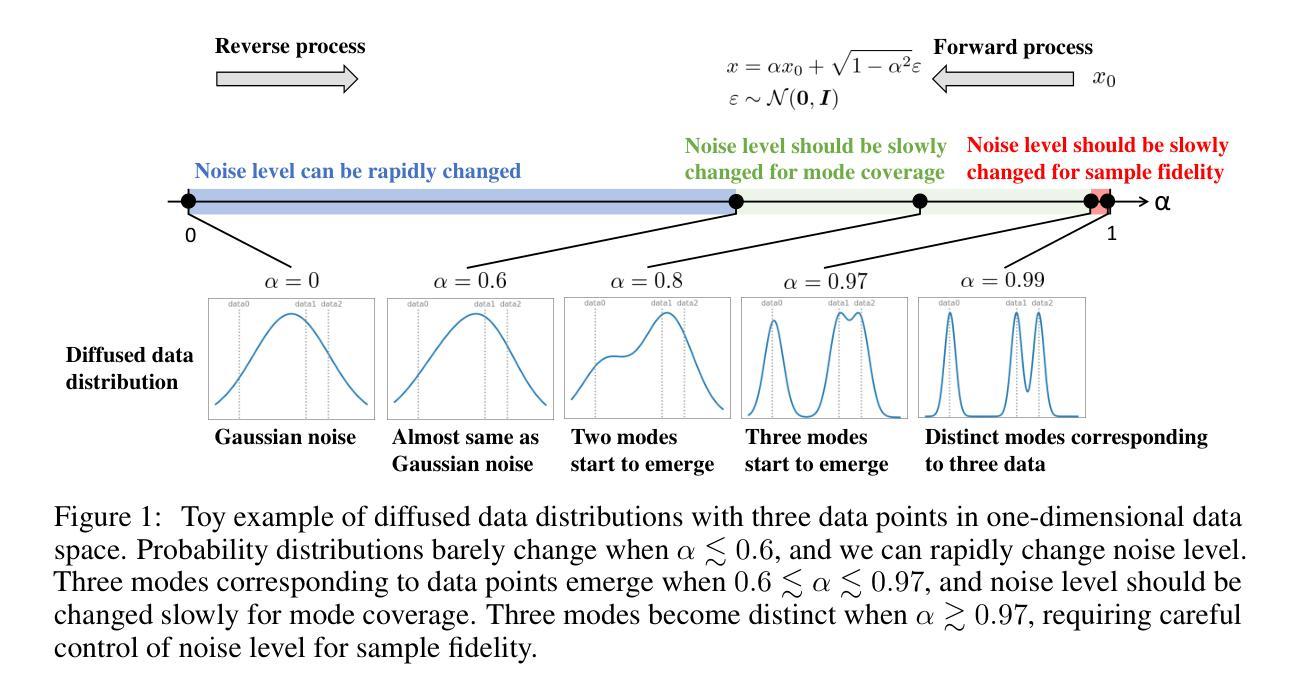
DeepSPV: A Deep Learning Pipeline for 3D Spleen Volume Estimation from 2D Ultrasound Images
Authors:Zhen Yuan, David Stojanovski, Lei Li, Alberto Gomez, Haran Jogeesvaran, Esther Puyol-Antón, Baba Inusa, Andrew P. King
Splenomegaly, the enlargement of the spleen, is an important clinical indicator for various associated medical conditions, such as sickle cell disease (SCD). Spleen length measured from 2D ultrasound is the most widely used metric for characterising spleen size. However, it is still considered a surrogate measure, and spleen volume remains the gold standard for assessing spleen size. Accurate spleen volume measurement typically requires 3D imaging modalities, such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, but these are not widely available, especially in the Global South which has a high prevalence of SCD. In this work, we introduce a deep learning pipeline, DeepSPV, for precise spleen volume estimation from single or dual 2D ultrasound images. The pipeline involves a segmentation network and a variational autoencoder for learning low-dimensional representations from the estimated segmentations. We investigate three approaches for spleen volume estimation and our best model achieves 86.62%/92.5% mean relative volume accuracy (MRVA) under single-view/dual-view settings, surpassing the performance of human experts. In addition, the pipeline can provide confidence intervals for the volume estimates as well as offering benefits in terms of interpretability, which further support clinicians in decision-making when identifying splenomegaly. We evaluate the full pipeline using a highly realistic synthetic dataset generated by a diffusion model, achieving an overall MRVA of 83.0% from a single 2D ultrasound image. Our proposed DeepSPV is the first work to use deep learning to estimate 3D spleen volume from 2D ultrasound images and can be seamlessly integrated into the current clinical workflow for spleen assessment.
脾肿大即脾脏增大,是多种相关疾病(如镰状细胞病)的重要临床指标。脾脏长度通过二维超声测量是表征脾脏大小最常用的指标。然而,这仍然被视为一种替代测量手段,脾脏体积仍然是评估脾脏大小的金标准。准确的脾脏体积测量通常需要三维成像模式,如计算机断层扫描或磁共振成像,但这些并不普遍可用,特别是在全球南部地区,镰状细胞病发病率较高。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个深度学习管道DeepSPV,用于从单个或两个二维超声图像中精确估计脾脏体积。该管道包括一个分割网络和一个变分自动编码器,用于从估计的分割中学习低维表示。我们研究了三种估计脾脏体积的方法,我们的最佳模型在单视图/双视图设置下达到86.62%/92.5%的平均相对体积精度(MRVA),超过了人类专家的表现。此外,该管道可以为体积估计提供置信区间,并在可解释性方面带来好处,这有助于临床医生在诊断脾肿大时做出决策。我们使用通过扩散模型生成的高度逼真的合成数据集对全流程进行了评估,从单个二维超声图像达到的总体平均相对体积精度为83.0%。我们提出的DeepSPV是第一个使用深度学习从二维超声图像估计三维脾脏体积的工作,可以无缝集成到当前的脾脏评估临床工作流程中。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2308.08038
Summary
本研究利用深度学习技术,从单或双2D超声图像中精确估计脾脏体积。提出DeepSPV管道,包含分割网络和变分自编码器,用于学习估计分割的低维表示。研究三种脾脏体积估计方法,最佳模型在单视图/双视图设置下达到86.62%/92.5%的平均相对体积精度(MRVA),超越人类专家的性能。此外,该管道可为体积估计提供置信区间,提高可解释性,支持医生在识别脾肿大时的决策。使用扩散模型生成的高度现实合成数据集评估整体管道,从单个2D超声图像获得总体MRVA为83.0%。DeepSPV是首个利用深度学习从2D超声图像估计3D脾脏体积的工作,可无缝集成到当前临床工作流程中进行脾脏评估。
Key Takeaways
- 脾肿大是重要的临床指标,涉及多种医学状况如镰状细胞病(SCD)。
- 脾脏长度通常通过二维超声测量,但脾脏体积是金标准。
- 三维成像技术如计算机断层扫描或磁共振成像用于精确测量脾脏体积,但在全球南部地区普及程度较低。
- 引入深度学习管道DeepSPV,可从单个或双个二维超声图像精确估计脾脏体积。
- DeepSPV包括分割网络和变分自编码器,并调查了三种脾脏体积估计方法。
- 最佳模型表现超过人类专家,为体积估计提供置信区间,并提高可解释性以辅助医生决策。
点此查看论文截图

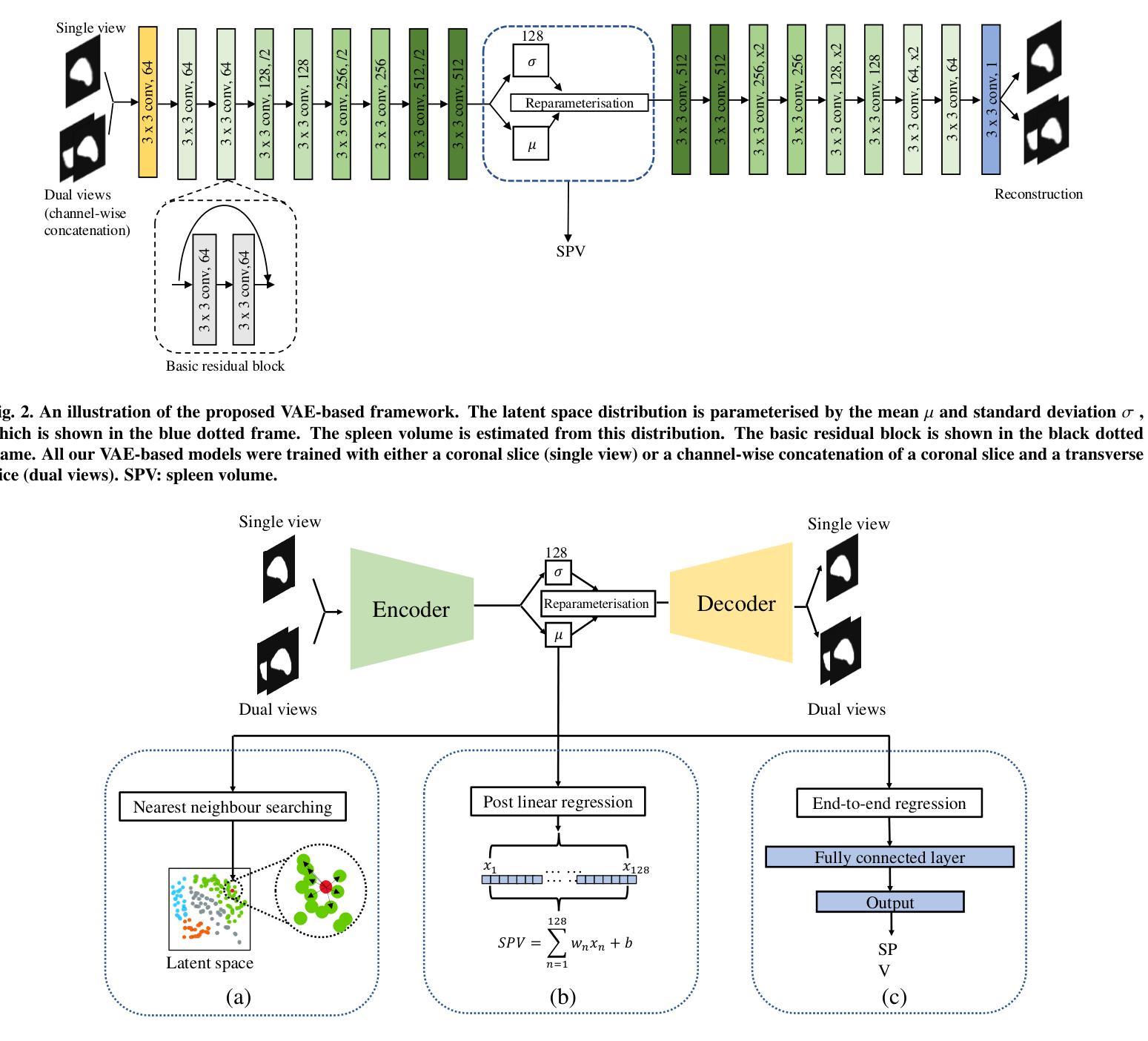
Shallow Diffuse: Robust and Invisible Watermarking through Low-Dimensional Subspaces in Diffusion Models
Authors:Wenda Li, Huijie Zhang, Qing Qu
The widespread use of AI-generated content from diffusion models has raised significant concerns regarding misinformation and copyright infringement. Watermarking is a crucial technique for identifying these AI-generated images and preventing their misuse. In this paper, we introduce Shallow Diffuse, a new watermarking technique that embeds robust and invisible watermarks into diffusion model outputs. Unlike existing approaches that integrate watermarking throughout the entire diffusion sampling process, Shallow Diffuse decouples these steps by leveraging the presence of a low-dimensional subspace in the image generation process. This method ensures that a substantial portion of the watermark lies in the null space of this subspace, effectively separating it from the image generation process. Our theoretical and empirical analyses show that this decoupling strategy greatly enhances the consistency of data generation and the detectability of the watermark. Extensive experiments further validate that our Shallow Diffuse outperforms existing watermarking methods in terms of robustness and consistency. The codes will be released at https://github.com/liwd190019/Shallow-Diffuse.
随着扩散模型生成的AI内容广泛应用,关于误导信息和版权侵犯的担忧日益加剧。水印技术是识别这些AI生成图像并防止其被滥用的一种关键技术。在本文中,我们介绍了Shallow Diffuse,这是一种新的水印技术,能将稳健且不可见的水印嵌入到扩散模型的输出中。与在整个扩散采样过程中整合水印的现有方法不同,Shallow Diffuse通过利用图像生成过程中存在的低维子空间来解耦这些步骤。这种方法确保大部分水印位于该子空间的零空间中,从而有效地将其与图像生成过程分离。我们的理论和实证分析表明,这种解耦策略大大提高了数据生成的一致性和水印的可检测性。进一步的广泛实验验证,我们的Shallow Diffuse在稳健性和一致性方面超越了现有的水印方法。代码将在https://github.com/liwd190019/Shallow-Diffuse发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Shallow Diffuse的新水印技术,该技术能够将稳健且不可见的水印嵌入到扩散模型输出中。与其他在整个扩散采样过程中集成水印的方法不同,Shallow Diffuse利用图像生成过程中的低维子空间,将水印与图像生成过程分离。该方法既增强了数据生成的一致性,又提高了水印的可检测性。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成内容的普及引发了关于误导信息和版权侵犯的担忧,因此水印技术对于识别AI生成的图像和防止其滥用至关重要。
- Shallow Diffuse是一种新的水印技术,可以嵌入到扩散模型的输出中,且嵌入的水印既稳健又不可见。
- 与其他方法不同,Shallow Diffuse利用图像生成过程中的低维子空间,将水印嵌入步骤与图像生成过程分离。
- 这种分离策略提高了数据生成的一致性和水印的可检测性。
- Shallow Diffuse在稳健性和一致性方面超越了现有的水印方法。
- 该技术的代码将在https://github.com/liwd190019/Shallow-Diffuse上发布。
- 该技术对于保护版权和维护信息的真实性具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

Eliminating Oversaturation and Artifacts of High Guidance Scales in Diffusion Models
Authors:Seyedmorteza Sadat, Otmar Hilliges, Romann M. Weber
Classifier-free guidance (CFG) is crucial for improving both generation quality and alignment between the input condition and final output in diffusion models. While a high guidance scale is generally required to enhance these aspects, it also causes oversaturation and unrealistic artifacts. In this paper, we revisit the CFG update rule and introduce modifications to address this issue. We first decompose the update term in CFG into parallel and orthogonal components with respect to the conditional model prediction and observe that the parallel component primarily causes oversaturation, while the orthogonal component enhances image quality. Accordingly, we propose down-weighting the parallel component to achieve high-quality generations without oversaturation. Additionally, we draw a connection between CFG and gradient ascent and introduce a new rescaling and momentum method for the CFG update rule based on this insight. Our approach, termed adaptive projected guidance (APG), retains the quality-boosting advantages of CFG while enabling the use of higher guidance scales without oversaturation. APG is easy to implement and introduces practically no additional computational overhead to the sampling process. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that APG is compatible with various conditional diffusion models and samplers, leading to improved FID, recall, and saturation scores while maintaining precision comparable to CFG, making our method a superior plug-and-play alternative to standard classifier-free guidance.
无分类器引导(CFG)对于提高扩散模型的生成质量和输入条件与最终输出之间的对齐性至关重要。虽然通常需要较高的引导尺度来增强这些方面,但它也会导致过饱和和不切实际的伪影。在本文中,我们重新审视了CFG的更新规则,并进行了修改以解决此问题。我们首先将CFG的更新术语分解为相对于条件模型预测并行和正交的分量,并观察到并行分量主要导致过饱和,而正交分量提高了图像质量。因此,我们通过降低并行分量的权重,实现了高质量生成而不出现过饱和。此外,我们将CFG与梯度上升联系起来,并基于这一见解为CFG更新规则引入了一种新的重新缩放和动量方法。我们的方法称为自适应投影引导(APG),保留了CFG提高质量的好处,同时能够在不使用更高引导尺度的情况下实现过饱和。APG易于实现,几乎不会给采样过程增加额外的计算开销。通过大量实验,我们证明了APG与各种条件扩散模型和采样器兼容,在提高FID、召回率和饱和度得分的同时,保持与CFG相当的精度,这使得我们的方法成为标准无分类器引导的一种优越的可插拔替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2025
Summary
本论文提出一种改进方案——自适应投影指导(APG),旨在解决分类器指导在扩散模型中生成高质量输出和输入对齐时的不足。研究指出,通过分解指导更新规则中的并行和正交成分,可有效调整生成图像的质量和饱和度,实现更高质量的生成且不会出现过度饱和现象。新方法结合梯度上升思路,实施简便且几乎不增加计算开销。实验证明,APG在不同条件扩散模型和采样器中表现优异,显著提高FID、召回率和饱和度得分,同时保持与CFG相当的精度,成为标准分类器自由指导的卓越替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 分类器自由指导(CFG)对扩散模型的生成质量和输入与输出对齐至关重要。
- 高指导尺度虽能提升生成质量和对齐度,但会导致过度饱和和不现实的艺术品。
- 通过分解CFG的更新规则,发现并行成分主要导致过度饱和,而正交成分能提高图像质量。
- 提出自适应投影指导(APG)方法,通过下调并行成分权重实现高质量生成且避免过度饱和。
- APG与梯度上升相结合,为CFG更新规则引入新的重新缩放和动量方法。
- APG方法易于实施,几乎不增加采样过程的计算开销。
点此查看论文截图



Ensemble Kalman Diffusion Guidance: A Derivative-free Method for Inverse Problems
Authors:Hongkai Zheng, Wenda Chu, Austin Wang, Nikola Kovachki, Ricardo Baptista, Yisong Yue
When solving inverse problems, one increasingly popular approach is to use pre-trained diffusion models as plug-and-play priors. This framework can accommodate different forward models without re-training while preserving the generative capability of diffusion models. Despite their success in many imaging inverse problems, most existing methods rely on privileged information such as derivative, pseudo-inverse, or full knowledge about the forward model. This reliance poses a substantial limitation that restricts their use in a wide range of problems where such information is unavailable, such as in many scientific applications. We propose Ensemble Kalman Diffusion Guidance (EnKG), a derivative-free approach that can solve inverse problems by only accessing forward model evaluations and a pre-trained diffusion model prior. We study the empirical effectiveness of EnKG across various inverse problems, including scientific settings such as inferring fluid flows and astronomical objects, which are highly non-linear inverse problems that often only permit black-box access to the forward model. We open-source our code at https://github.com/devzhk/enkg-pytorch.
在解决反问题时,越来越流行的一种方法是使用预训练的扩散模型作为即插即用的先验。该框架可以在不重新训练的情况下适应不同的前向模型,同时保留扩散模型的生成能力。尽管它们在许多成像反问题中取得了成功,但大多数现有方法依赖于特权信息,如导数、伪逆或关于前向模型的全知。这种依赖构成了巨大的局限性,限制了它们在广泛的问题中的使用,尤其是在没有此类信息的情况下,如在许多科学应用中。我们提出了无导数的集合卡尔曼扩散引导(EnKG)方法,该方法只需访问前向模型评估和预训练的扩散模型先验来解决反问题。我们研究了EnKG在各种反问题上的经验有效性,包括科学环境下的流体流动和天文对象推断等高度非线性反问题,这些问题通常只允许对前向模型的黑箱访问。我们的代码开源在https://github.com/devzhk/enkg-pytorch。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练扩散模型作为即插即用先验在解决反问题中越来越受欢迎。该框架能够兼容不同的前向模型而无需重新训练,同时保留扩散模型的生成能力。针对大多数现有方法依赖于派生信息、伪逆或前向模型的完全知识等局限性,我们提出无导数的集合卡尔曼扩散引导(EnKG)方法,仅通过访问前向模型评估和预训练扩散模型先验来解决反问题。我们在各种反问题上研究了EnKG的实证有效性,包括科学设置如推断流体流动和天文对象等高度非线性反问题。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型被越来越多地用于解决反问题,作为即插即用先验使用。
- 扩散模型框架可以适应不同的前向模型,无需重新训练,同时保留生成能力。
- 现有方法大多依赖于派生信息或前向模型的完全知识,这在许多科学应用中不可用。
- 提出了一种无导数的集合卡尔曼扩散引导(EnKG)方法来解决反问题。
- EnKG仅通过访问前向模型评价和扩散模型先验工作。
- EnKG在包括流体流动和天文对象推断在内的高度非线性反问题上具有实证有效性。
- 公开了EnKG的开源代码。
点此查看论文截图

Diffusion Models for Tabular Data Imputation and Synthetic Data Generation
Authors:Mario Villaizán-Vallelado, Matteo Salvatori, Carlos Segura, Ioannis Arapakis
Data imputation and data generation have important applications for many domains, like healthcare and finance, where incomplete or missing data can hinder accurate analysis and decision-making. Diffusion models have emerged as powerful generative models capable of capturing complex data distributions across various data modalities such as image, audio, and time series data. Recently, they have been also adapted to generate tabular data. In this paper, we propose a diffusion model for tabular data that introduces three key enhancements: (1) a conditioning attention mechanism, (2) an encoder-decoder transformer as the denoising network, and (3) dynamic masking. The conditioning attention mechanism is designed to improve the model’s ability to capture the relationship between the condition and synthetic data. The transformer layers help model interactions within the condition (encoder) or synthetic data (decoder), while dynamic masking enables our model to efficiently handle both missing data imputation and synthetic data generation tasks within a unified framework. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation by comparing the performance of diffusion models with transformer conditioning against state-of-the-art techniques, such as Variational Autoencoders, Generative Adversarial Networks and Diffusion Models, on benchmark datasets. Our evaluation focuses on the assessment of the generated samples with respect to three important criteria, namely: (1) Machine Learning efficiency, (2) statistical similarity, and (3) privacy risk mitigation. For the task of data imputation, we consider the efficiency of the generated samples across different levels of missing features.
数据补全和数据生成在许多领域都有重要应用,如医疗和金融,其中不完整或缺失的数据可能会阻碍准确的分析和决策。扩散模型作为强大的生成模型,能够捕捉图像、音频和时间序列数据等不同数据模态的复杂数据分布。最近,它们也被改编为生成表格数据。在本文中,我们提出了一种用于表格数据的扩散模型,该模型引入了三个关键改进:(1)条件注意力机制,(2)编码器-解码器转换器作为去噪网络,以及(3)动态掩码。条件注意力机制旨在提高模型捕捉条件与合成数据之间关系的能力。转换器层有助于对条件(编码器)或合成数据(解码器)内的交互进行建模,而动态掩码使我们的模型能够在统一框架内高效地处理缺失数据补全和合成数据生成任务。我们通过将具有转换器条件的扩散模型性能与最新技术进行比较,进行了全面的评估。我们在基准数据集上与变分自动编码器、生成对抗网络和扩散模型等最新技术进行了比较。我们的评估重点是根据三个重要标准对生成的样本进行评估,即:(1)机器学习效率,(2)统计相似性,(3)隐私风险缓解。对于数据补全任务,我们考虑了不同缺失特征级别下生成样本的效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 7 figures, 6 tables
摘要
本文提出了一种用于处理表格数据的扩散模型,并引入三大增强机制:条件注意机制、编码解码器转换器和动态掩码。该模型能够捕捉条件与合成数据之间的关系,通过转换器层在条件或合成数据内部进行交互建模,并能在统一框架内处理缺失数据填充和合成数据生成任务。模型经过全面的评估,并与当前技术主流的技术如变分自编码器、生成对抗网络和扩散模型进行了比较。评估的重点是生成的样本在机器学习效率、统计相似性和隐私风险缓解方面的表现。对于数据填充任务,模型在不同程度的特征缺失下的效率也被考虑在内。
关键见解
- 扩散模型已用于生成图像、音频和时间序列数据等复杂数据分布,现在也被应用于表格数据的生成和处理。
- 本文提出的扩散模型引入三大增强机制:条件注意机制、编码解码器转换器和动态掩码,以改善数据生成和处理效果。
- 条件注意机制有助于提高模型捕捉条件与合成数据之间关系的能力。
- 编码解码器转换器有助于在条件(编码器)或合成数据(解码器)内部进行交互建模。
- 动态掩码使模型能够在一个统一的框架内处理缺失数据填充和合成数据生成任务。
- 模型经过全面的评估,与变分自编码器、生成对抗网络和扩散模型等主流技术进行了比较,表现优异。
- 评估集中在生成的样本的机器学习效率、统计相似性和隐私风险缓解方面,同时考虑了不同水平的特征缺失下的数据填充效率。
点此查看论文截图