⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-05 更新
Revisiting Continuity of Image Tokens for Cross-domain Few-shot Learning
Authors:Shuai Yi, Yixiong Zou, Yuhua Li, Ruixuan Li
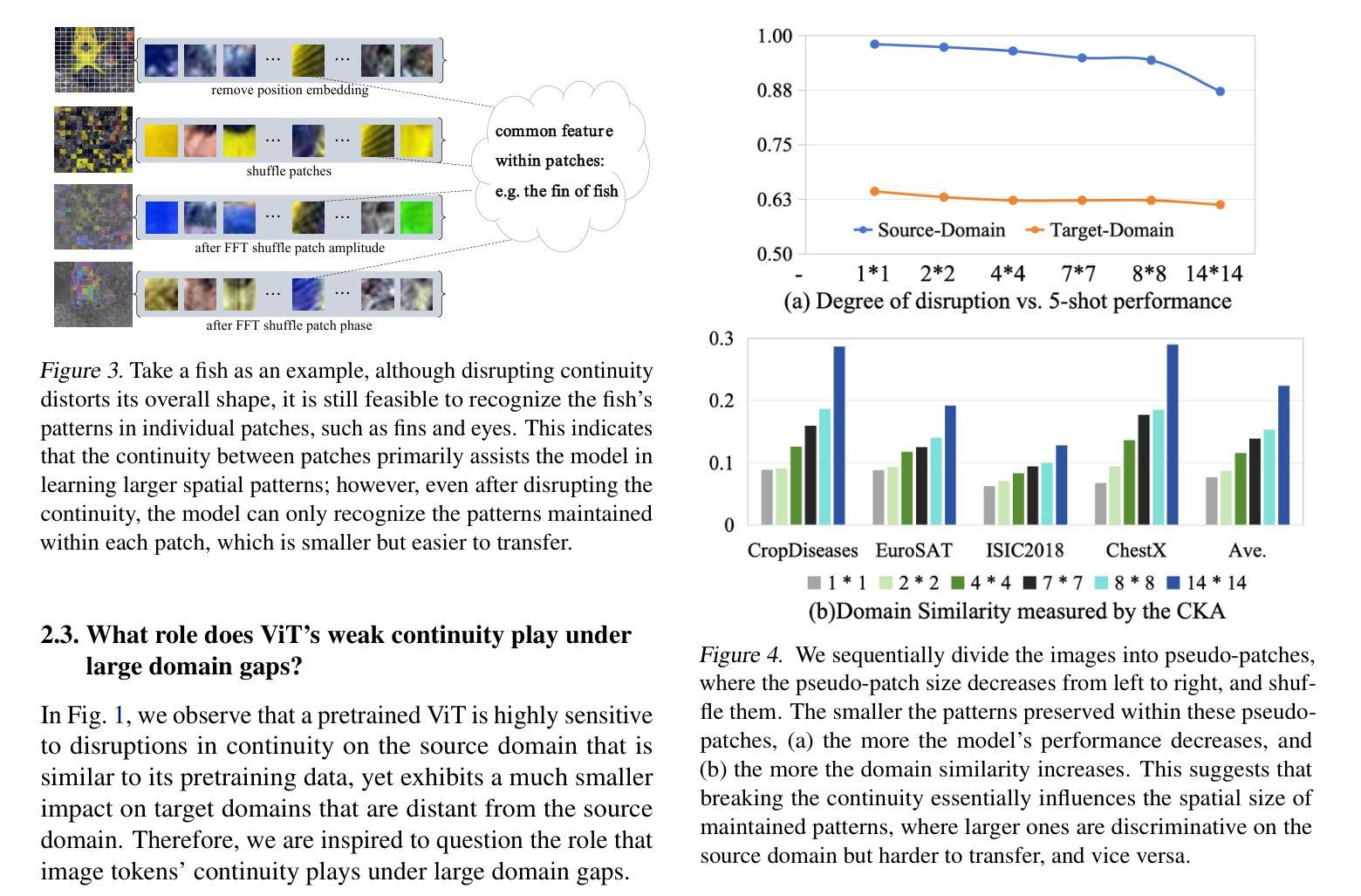
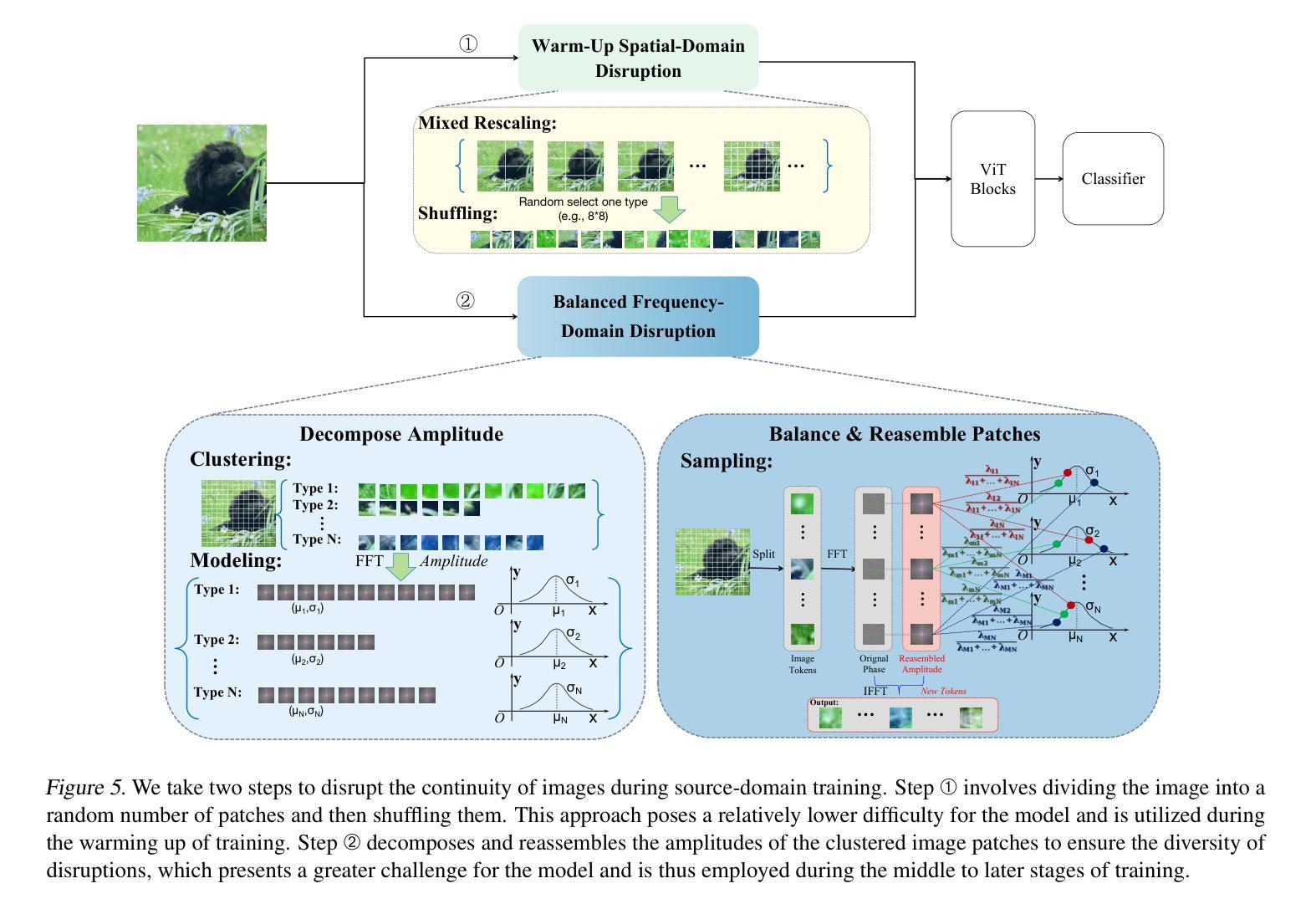
Vision Transformer (ViT) has achieved remarkable success due to its large-scale pretraining on general domains, but it still faces challenges when applying it to downstream distant domains that have only scarce training data, which gives rise to the Cross-Domain Few-Shot Learning (CDFSL) task. Inspired by Self-Attention’s insensitivity to token orders, we find an interesting phenomenon neglected in current works: disrupting the continuity of image tokens (i.e., making pixels not smoothly transited across patches) in ViT leads to a noticeable performance decline in the general (source) domain but only a marginal decrease in downstream target domains. This questions the role of image tokens’ continuity in ViT’s generalization under large domain gaps. In this paper, we delve into this phenomenon for an interpretation. We find continuity aids ViT in learning larger spatial patterns, which are harder to transfer than smaller ones, enlarging domain distances. Meanwhile, it implies that only smaller patterns within each patch could be transferred under extreme domain gaps. Based on this interpretation, we further propose a simple yet effective method for CDFSL that better disrupts the continuity of image tokens, encouraging the model to rely less on large patterns and more on smaller ones. Extensive experiments show the effectiveness of our method in reducing domain gaps and outperforming state-of-the-art works. Codes and models are available at https://github.com/shuaiyi308/ReCIT.
Vision Transformer(ViT)由于在通用领域的大规模预训练而取得了显著的成功,但在应用于只有少量训练数据的下游远距离领域时,仍然面临挑战,这引发了跨域小样本学习(CDFSL)任务的出现。受自注意力对令牌顺序的不敏感性的启发,我们发现当前工作中忽略了一个有趣的现象:破坏图像令牌的连续性(即在ViT中使像素在补丁之间不平稳过渡)会导致在通用(源)领域性能显著下降,而在下游目标领域仅出现轻微下降。这一现象对图像令牌连续性在ViT跨越大领域差距时的推广作用提出了质疑。本文深入探讨了这一现象,以对其进行解释。我们发现连续性有助于ViT学习更大的空间模式,这些模式比小的模式更难迁移,从而扩大了领域距离。同时,它暗示在极端领域差异下,每个补丁内的小模式都可以进行迁移。基于这一解释,我们进一步提出了针对CDFSL的简单而有效的方法,更好地破坏了图像令牌的连续性,鼓励模型更少地依赖大模式,更多地依赖小模式。大量实验表明,我们的方法在减少领域差距和超越最新作品方面非常有效。代码和模型可在https://github.com/shuaiyi308/ReCIT上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025(spotlight)
Summary
本文探讨了Vision Transformer(ViT)在处理跨域小样本学习任务(CDFSL)时的局限性,发现扰乱图像标记的连续性在源域性能下降较小目标域时会出现显著的性能下降。研究指出连续性有助于ViT学习更大的空间模式,这些模式在跨域转移时较难转移。基于此,提出了一种简单有效的方法来更好地破坏图像标记的连续性,鼓励模型更多地依赖小模式而非大模式,从而减少域差距并超越现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer (ViT) 在处理跨域小样本学习任务(CDFSL)时面临挑战。
- 扰乱图像标记的连续性对ViT在源域的性能有显著影响,但对目标域的影响较小。
- 连续性有助于ViT学习更大的空间模式,这些模式在跨域转移时较难转移。
- 更小的模式可能在极端跨域情况下更容易被转移。
- 提出了一种简单有效的方法来破坏图像标记的连续性,以减少对大型模式的依赖并增加对小模式的依赖。
- 此方法在减少域差距方面表现出良好的效果。
点此查看论文截图

Leveraging Information Retrieval to Enhance Spoken Language Understanding Prompts in Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Pierre Lepagnol, Sahar Ghannay, Thomas Gerald, Christophe Servan, Sophie Rosset
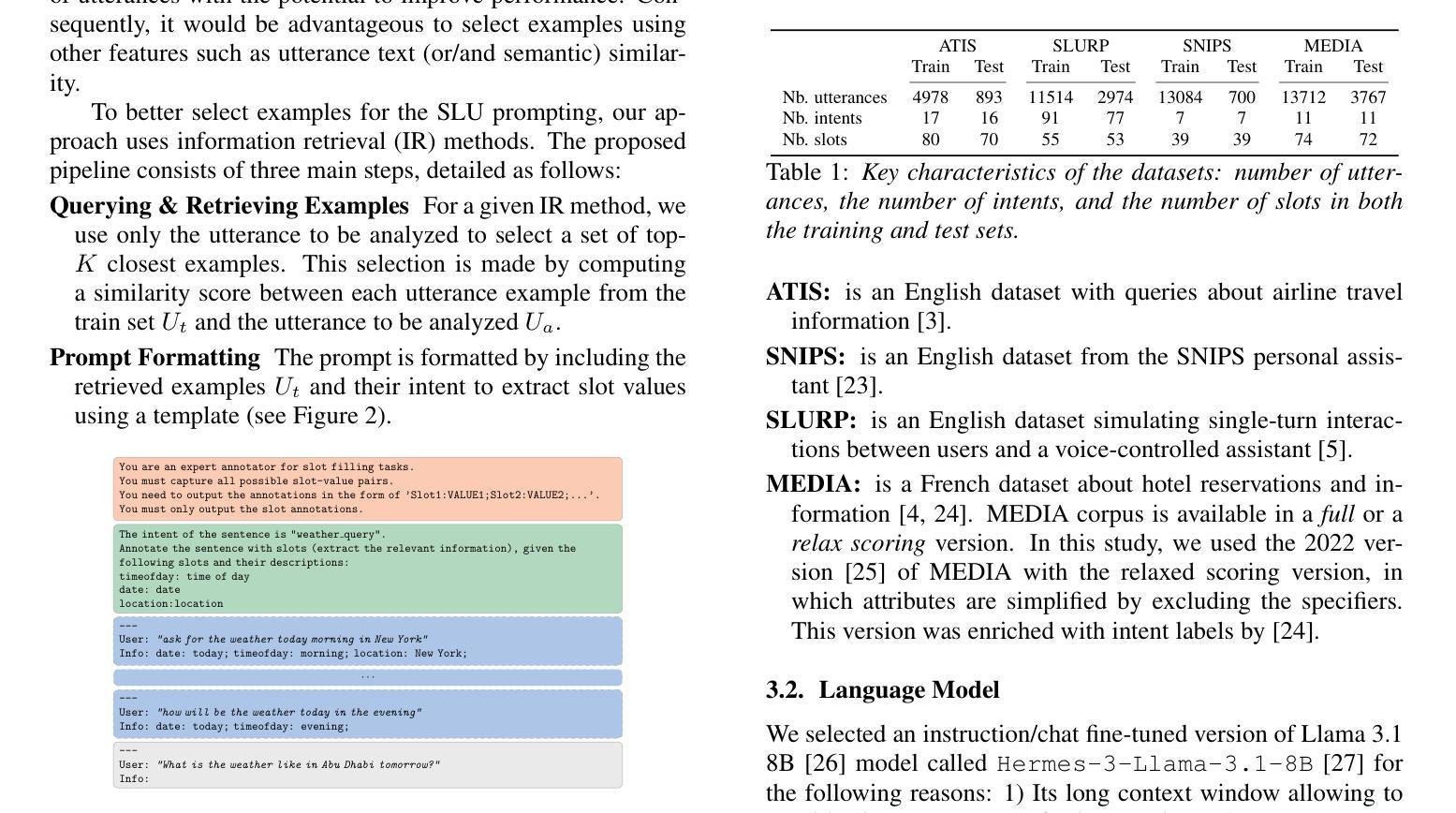
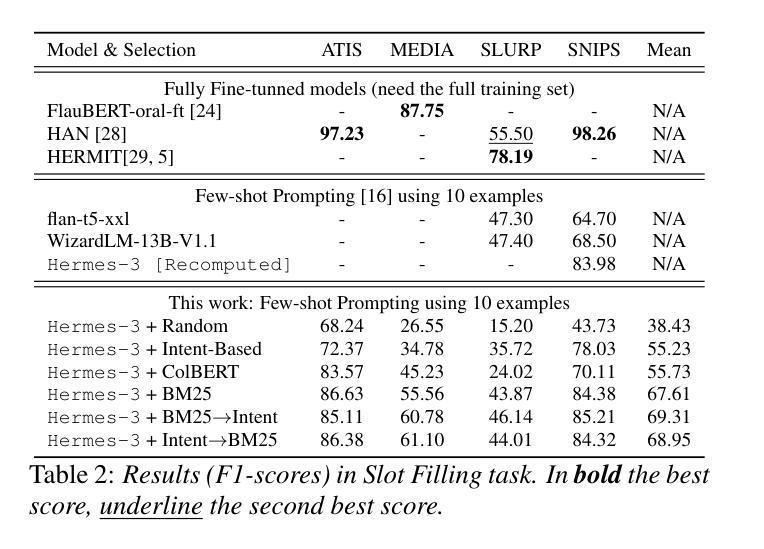
Understanding user queries is fundamental in many applications, such as home assistants, booking systems, or recommendations. Accordingly, it is crucial to develop accurate Spoken Language Understanding (SLU) approaches to ensure the reliability of the considered system. Current State-of-the-Art SLU techniques rely on large amounts of training data; however, only limited annotated examples are available for specific tasks or languages. In the meantime, instruction-tuned large language models (LLMs) have shown exceptional performance on unseen tasks in a few-shot setting when provided with adequate prompts. In this work, we propose to explore example selection by leveraging Information retrieval (IR) approaches to build an enhanced prompt that is applied to an SLU task. We evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method on several SLU benchmarks. Experimental results show that lexical IR methods significantly enhance performance without increasing prompt length.
在诸多应用(如家用助手、预订系统或推荐系统)中,理解用户查询是根本所在。因此,为了确保相关系统的可靠性,开发准确的口语理解(SLU)方法至关重要。当前最先进的SLU技术依赖于大量的训练数据;然而,对于特定任务或语言来说,可用的带标注的例子却相对较少。同时,通过提供适当提示,经过指令训练的 大型语言模型(LLM)在未见任务的少量样本场景中表现出了卓越性能。在这项工作中,我们提出通过利用信息检索(IR)方法进行示例选择,以构建用于SLU任务的增强提示。我们在多个SLU基准测试上对所用方法的有效性进行了评估。实验结果表明,词法IR方法可显著增强性能,而无需增加提示长度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Conference paper accepted to INTERSPEECH 2025
Summary
本文探讨了基于信息检索方法的选择性示例在增强自然语言理解任务中的重要性。文章提出利用信息检索(IR)方法构建增强提示,并将其应用于自然语言理解任务中的口语理解(SLU)。实验结果表明,词汇信息检索方法在不增加提示长度的情况下显著提高了性能。
Key Takeaways
- 用户查询理解在许多应用中至关重要,如家庭助手、预订系统和推荐系统等。
- 准确的语言理解技术对于确保系统的可靠性至关重要。当前先进的自然语言理解技术依赖于大量的训练数据。
- 在有限标注示例的情况下,指令优化的大型语言模型在少数场景下的性能表现优异。
- 通过利用信息检索方法,本文提出了示例选择以增强自然语言理解任务的性能。
- 实验证明,词汇信息检索方法在不增加提示长度的情况下提高了口语理解的性能。
- 此方法在各种自然语言理解基准测试中表现出良好的效果。
点此查看论文截图


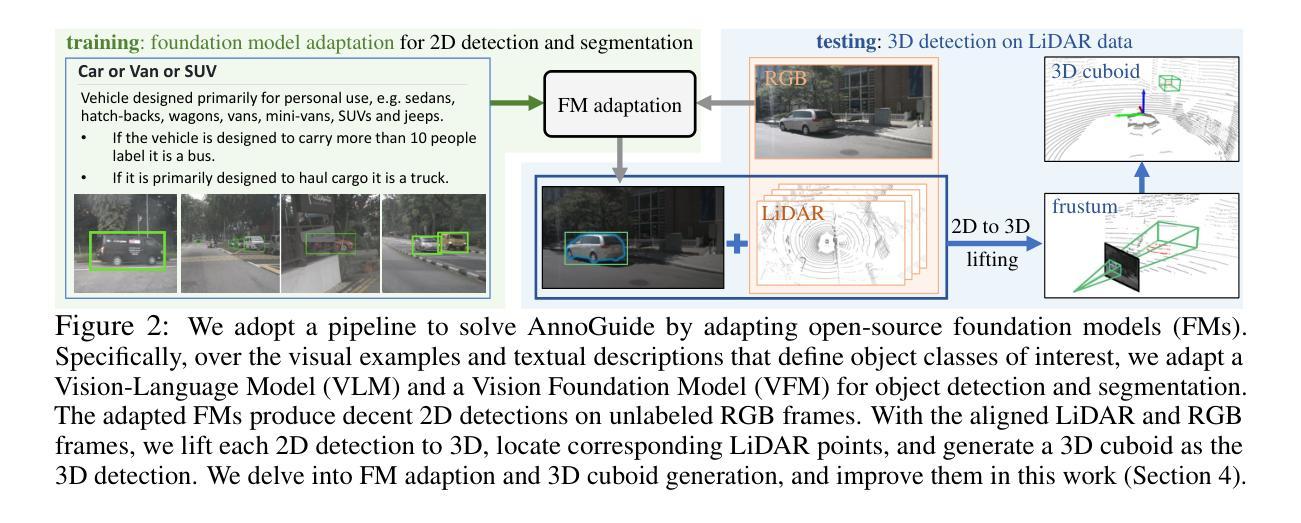
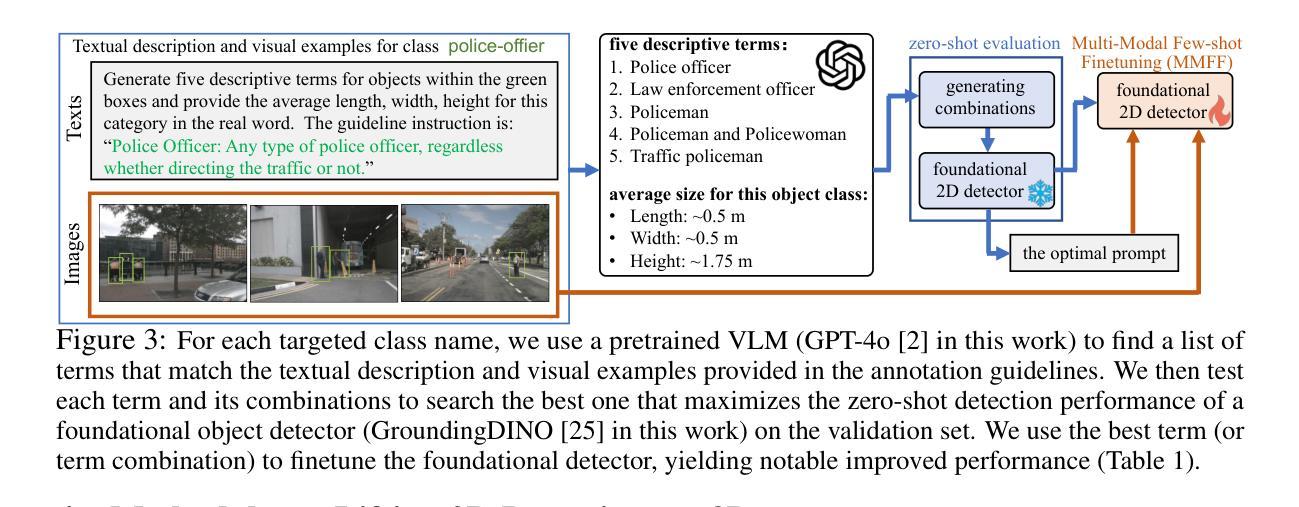
Towards Auto-Annotation from Annotation Guidelines: A Benchmark through 3D LiDAR Detection
Authors:Yechi Ma, Wei Hua, Shu Kong
A crucial yet under-appreciated prerequisite in machine learning solutions for real-applications is data annotation: human annotators are hired to manually label data according to detailed, expert-crafted guidelines. This is often a laborious, tedious, and costly process. To study methods for facilitating data annotation, we introduce a new benchmark AnnoGuide: Auto-Annotation from Annotation Guidelines. It aims to evaluate automated methods for data annotation directly from expert-defined annotation guidelines, eliminating the need for manual labeling. As a case study, we repurpose the well-established nuScenes dataset, commonly used in autonomous driving research, which provides comprehensive annotation guidelines for labeling LiDAR point clouds with 3D cuboids across 18 object classes. These guidelines include a few visual examples and textual descriptions, but no labeled 3D cuboids in LiDAR data, making this a novel task of multi-modal few-shot 3D detection without 3D annotations. The advances of powerful foundation models (FMs) make AnnoGuide especially timely, as FMs offer promising tools to tackle its challenges. We employ a conceptually straightforward pipeline that (1) utilizes open-source FMs for object detection and segmentation in RGB images, (2) projects 2D detections into 3D using known camera poses, and (3) clusters LiDAR points within the frustum of each 2D detection to generate a 3D cuboid. Starting with a non-learned solution that leverages off-the-shelf FMs, we progressively refine key components and achieve significant performance improvements, boosting 3D detection mAP from 12.1 to 21.9! Nevertheless, our results highlight that AnnoGuide remains an open and challenging problem, underscoring the urgent need for developing LiDAR-based FMs. We release our code and models at GitHub: https://annoguide.github.io/annoguide3Dbenchmark
在真实应用中的机器学习解决方案中一个关键但常被低估的前提是数据标注。需要雇佣人类标注者根据详细的专业制定的指导方针来手动标注数据。这通常是一个繁琐、乏味且成本高昂的过程。为了研究促进数据标注的方法,我们引入了一个新的基准测试AnnoGuide:直接从标注指南进行自动标注。它的目标是评估直接从专家定义的标注指南进行数据标注的自动化方法,从而消除对手动标注的需求。作为案例研究,我们对自主驾驶研究中常用的成熟数据集nuScenes进行重新定位,该数据集提供了关于激光雷达点云与跨越18个对象类别的三维边界框的详细标注指南。这些指南包括少数视觉示例和文本描述,但没有激光雷达数据中的标记三维边界框,这使得成为一项新颖的多模态少样本三维检测任务但不涉及三维注释。强大的基础模型(FMs)的发展使AnnoGuide尤为及时,因为FMs提供了解决其挑战的有前途的工具。我们采用了一个概念上简单的管道,该管道(1)利用用于对象检测和分割的开源FMs在RGB图像中,(2)使用已知的相机姿态将二维检测投影到三维空间,(3)在每个二维检测的视锥内对激光雷达点进行聚类以生成三维边界框。从一个利用现成的FMs的非学习解决方案开始,我们逐步改进关键组件并实现了显著的性能提升,将三维检测mAP从12.1提高到21.9!尽管如此,我们的结果突显出AnnoGuide仍然是一个开放且具有挑战性的问题,强调迫切需要在激光雷达基础上开发FMs。我们在GitHub上发布我们的代码和模型:https://annoguide.github.io/annoguide3Dbenchmark。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
机器学习解决方案在实际应用中的一个重要但被忽视的前提是数据标注,需要人工根据详细的专家制定的指南进行标注,这是一个繁琐且成本高昂的过程。为简化数据标注过程,我们引入了新的基准测试AnnoGuide:直接从标注指南进行自动标注。以自动驾驶研究中常用的nuScenes数据集为例,它在LiDAR点云上使用18类对象的3D框提供全面的标注指南,但没有提供LiDAR数据的3D标注。利用强大的基础模型,我们采用了简单的管道将RGB图像中的对象检测和分割用于LiDAR点云中的3D检测,逐步改进关键组件并取得显著的性能提升,将3D检测的mAP从12.1提升至21.9。然而,我们的结果突显了AnnoGuide仍然是一个开放且具有挑战性的问题,迫切需要开发基于LiDAR的基础模型。
Key Takeaways
- 数据标注是机器学习解决方案实际应用中的关键前提,但常被忽视。
- 数据标注是一个繁琐、耗时且成本高昂的过程。
- 引入新的基准测试AnnoGuide,旨在从标注指南直接进行自动标注,简化流程。
- 以nuScenes数据集为例,展示在LiDAR点云上的多模态少样本3D检测任务。
- 利用基础模型采用简单管道实现RGB图像中的对象检测和分割,并将其应用于LiDAR点云中的3D检测。
- 通过逐步改进关键组件,显著提升性能,将3D检测的mAP从12.1提升至21.9。
点此查看论文截图


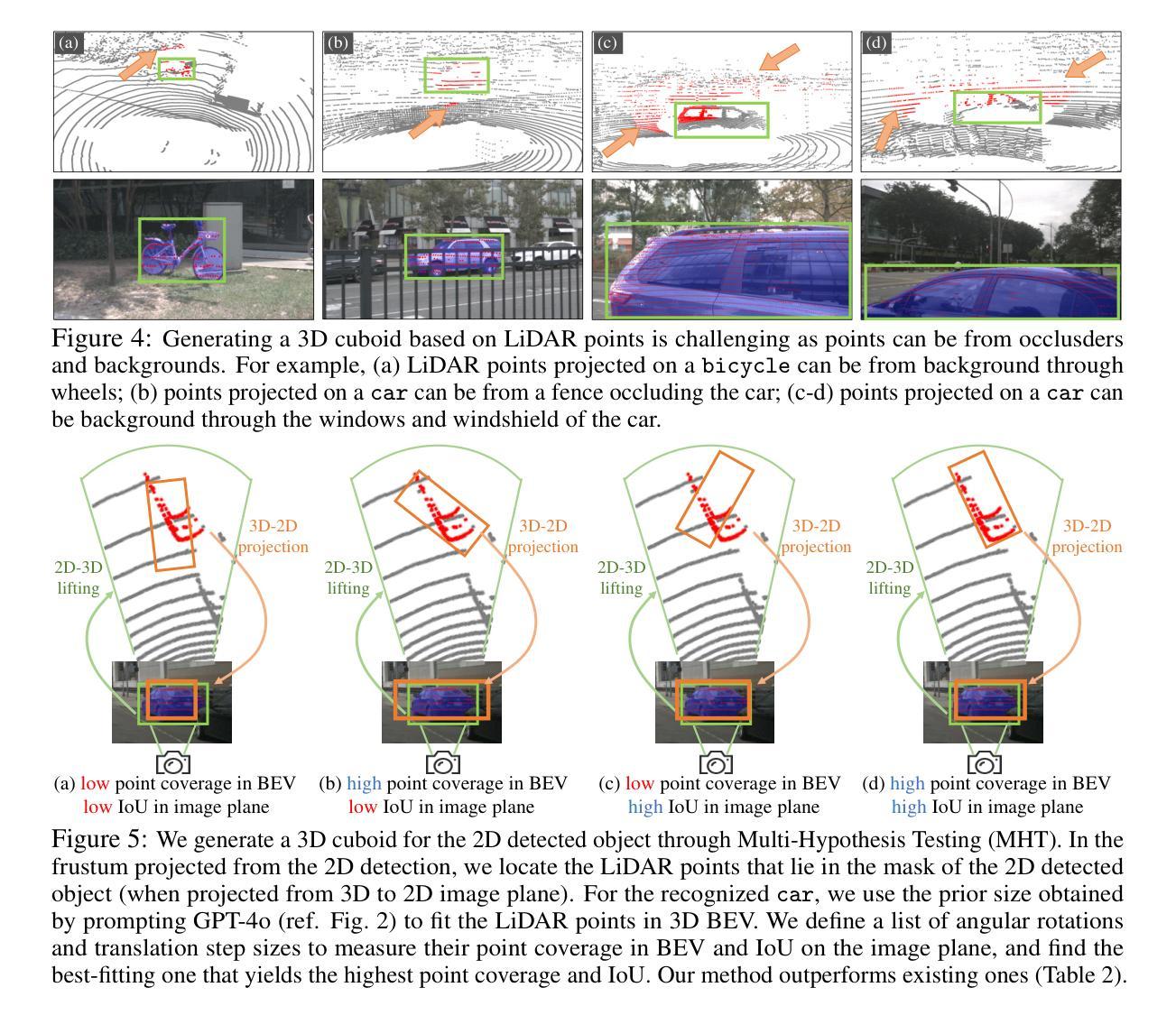
Token and Span Classification for Entity Recognition in French Historical Encyclopedias
Authors:Ludovic Moncla, Hédi Zeghidi
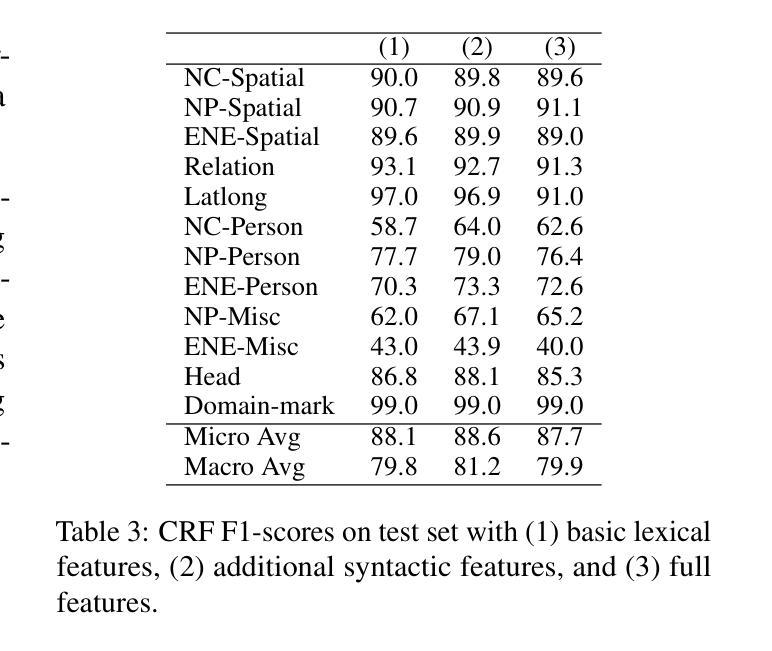
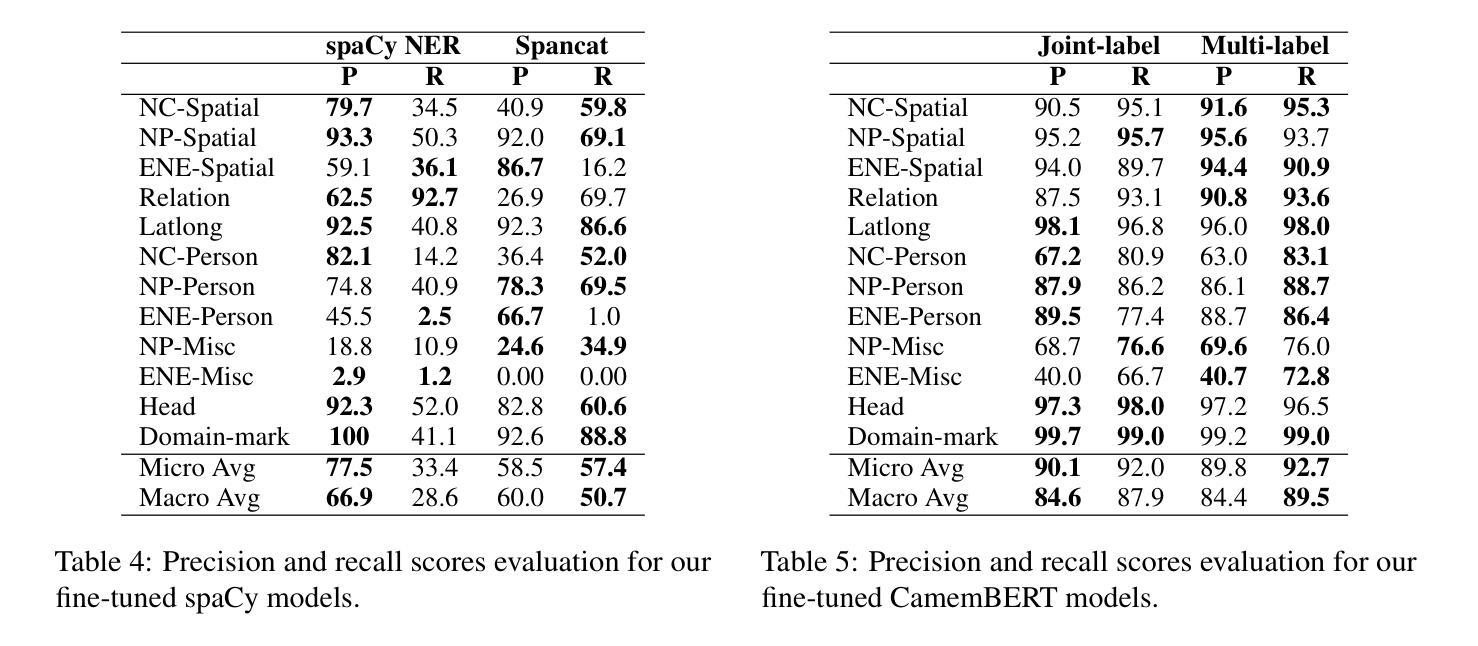
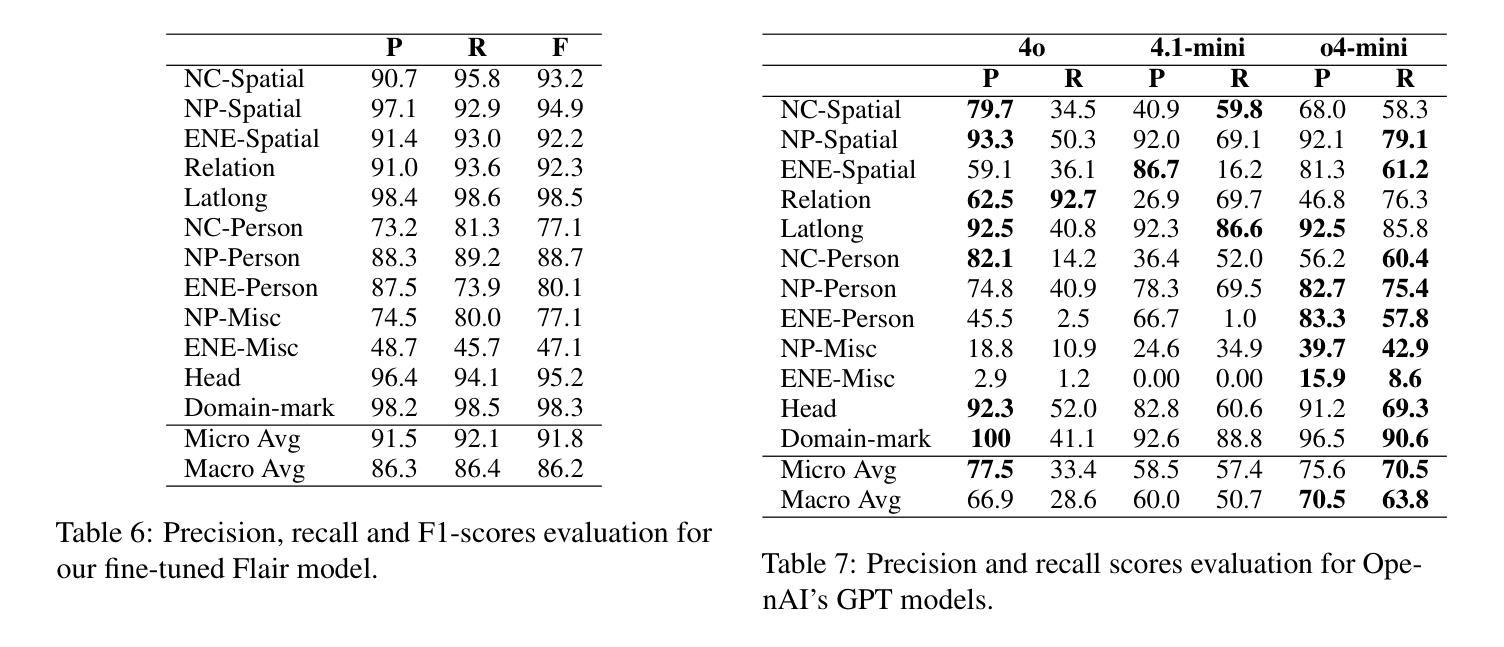
Named Entity Recognition (NER) in historical texts presents unique challenges due to non-standardized language, archaic orthography, and nested or overlapping entities. This study benchmarks a diverse set of NER approaches, ranging from classical Conditional Random Fields (CRFs) and spaCy-based models to transformer-based architectures such as CamemBERT and sequence-labeling models like Flair. Experiments are conducted on the GeoEDdA dataset, a richly annotated corpus derived from 18th-century French encyclopedias. We propose framing NER as both token-level and span-level classification to accommodate complex nested entity structures typical of historical documents. Additionally, we evaluate the emerging potential of few-shot prompting with generative language models for low-resource scenarios. Our results demonstrate that while transformer-based models achieve state-of-the-art performance, especially on nested entities, generative models offer promising alternatives when labeled data are scarce. The study highlights ongoing challenges in historical NER and suggests avenues for hybrid approaches combining symbolic and neural methods to better capture the intricacies of early modern French text.
在历史文本中的命名实体识别(NER)面临独特的挑战,这主要是由于语言非标准化、古老的正字法以及嵌套或重叠的实体。本研究对一系列NER方法进行了基准测试,这些方法包括经典的基于条件随机场(CRF)和spaCy模型的方法,以及基于转换器的架构(如CamemBERT)和序列标签模型(如Flair)。实验是在GeoEDdA数据集上进行的,该数据集是从18世纪法国百科全书派生的丰富注释语料库。我们提出将NER视为词级和跨度级的分类,以适应历史文档中典型的复杂嵌套实体结构。此外,我们还评估了在低资源情况下生成语言模型的少量提示的潜在新兴能力。我们的结果表明,虽然基于转换器的模型在嵌套实体方面取得了最先进的性能,但在标记数据稀缺的情况下,生成模型提供了有前景的替代方案。该研究突出了历史NER中的持续挑战,并建议结合符号方法和神经方法的混合方法,以更好地捕捉早期现代法语文本的复杂性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了在历史文本中进行命名实体识别(NER)面临的挑战,包括非标准语言、古老的正字法以及嵌套或重叠的实体等问题。文章评估了一系列NER方法,从传统的条件随机场(CRF)和spaCy模型到基于变压器的架构(如CamemBERT)和序列标签模型(如Flair)。在GeoEDdA数据集上进行的实验表明,基于变压器的模型在识别嵌套实体方面达到了最新水平,而生成模型在数据稀缺的情况下展现出巨大潜力。研究强调了历史文本NER的当前挑战,并建议结合符号方法和神经网络方法的混合方法,以更好地捕捉早期现代法语文本的复杂性。
Key Takeaways
- 历史文本NER面临非标准语言、古老正字法和嵌套实体的挑战。
- 评估了多种NER方法,包括条件随机场、spaCy模型、基于变压器的架构和序列标签模型。
- 基于变压器的模型在识别嵌套实体方面表现出最新水平的技术。
- 生成模型在数据稀缺的情况下展现出巨大潜力。
- 历史文本NER仍存在挑战。
- 混合方法结合符号方法和神经网络方法可能更好地捕捉早期现代法语文本的复杂性。
点此查看论文截图

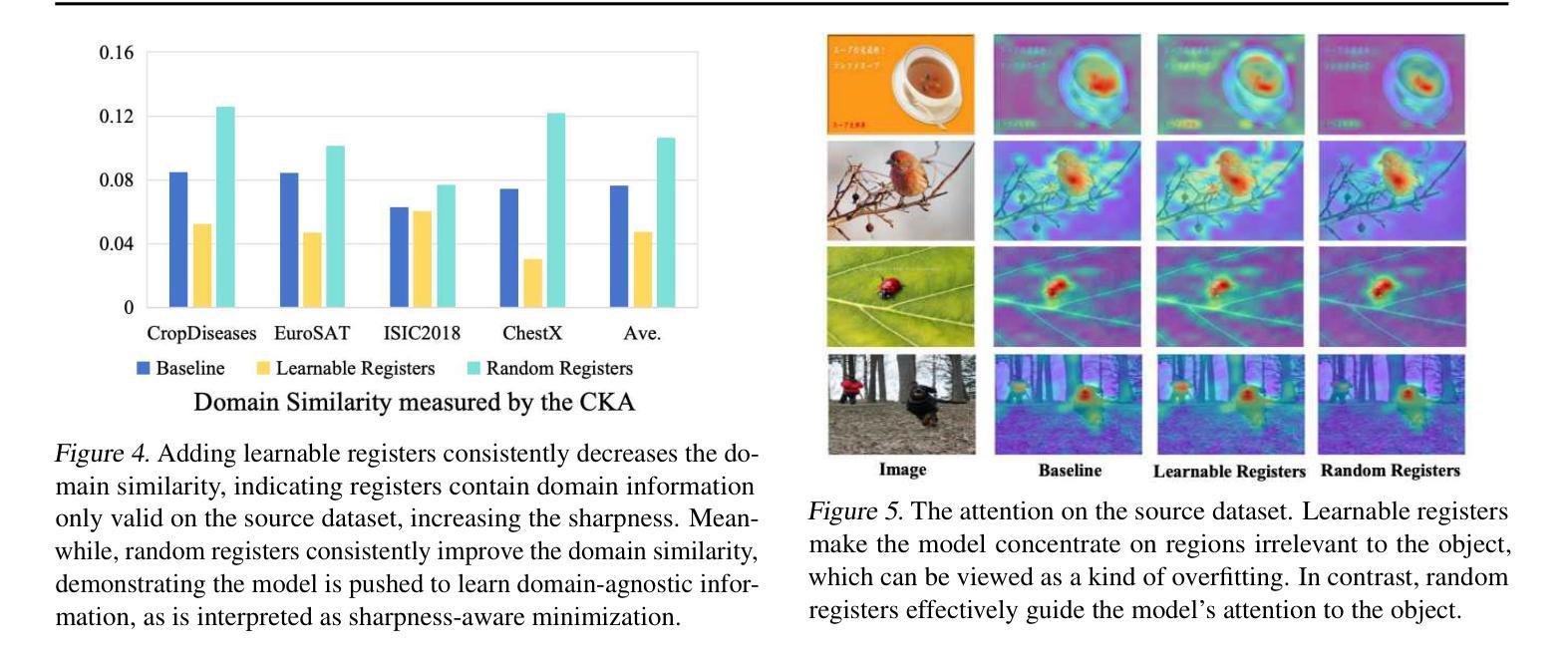
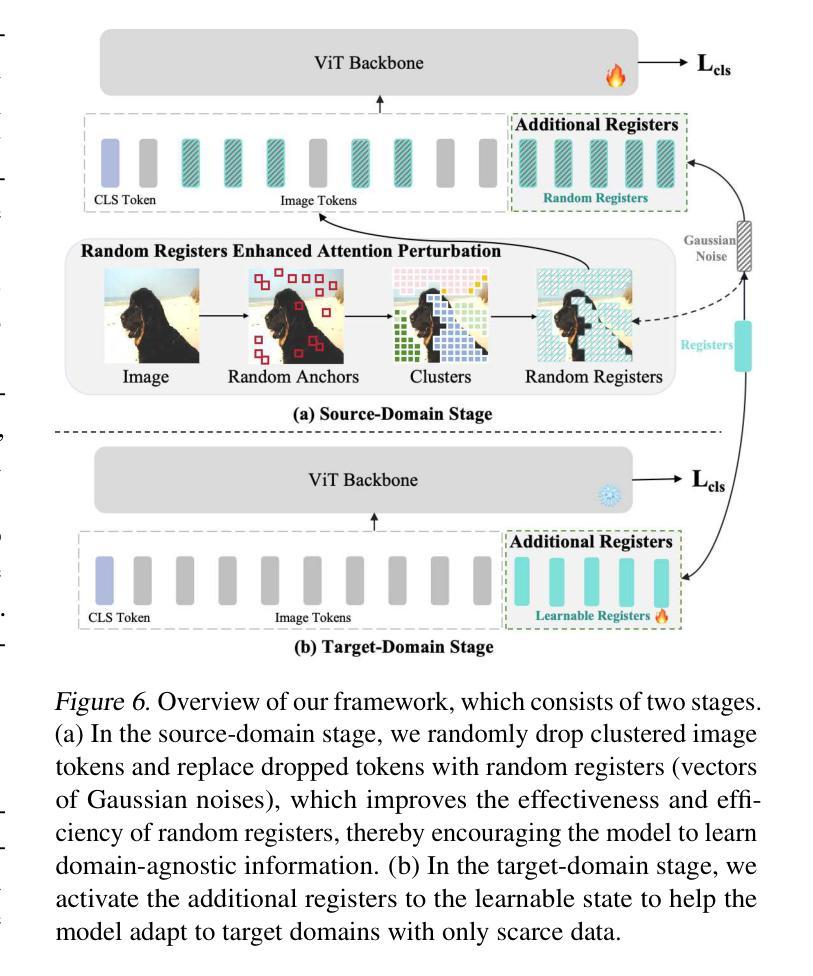
Random Registers for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Shuai Yi, Yixiong Zou, Yuhua Li, Ruixuan Li
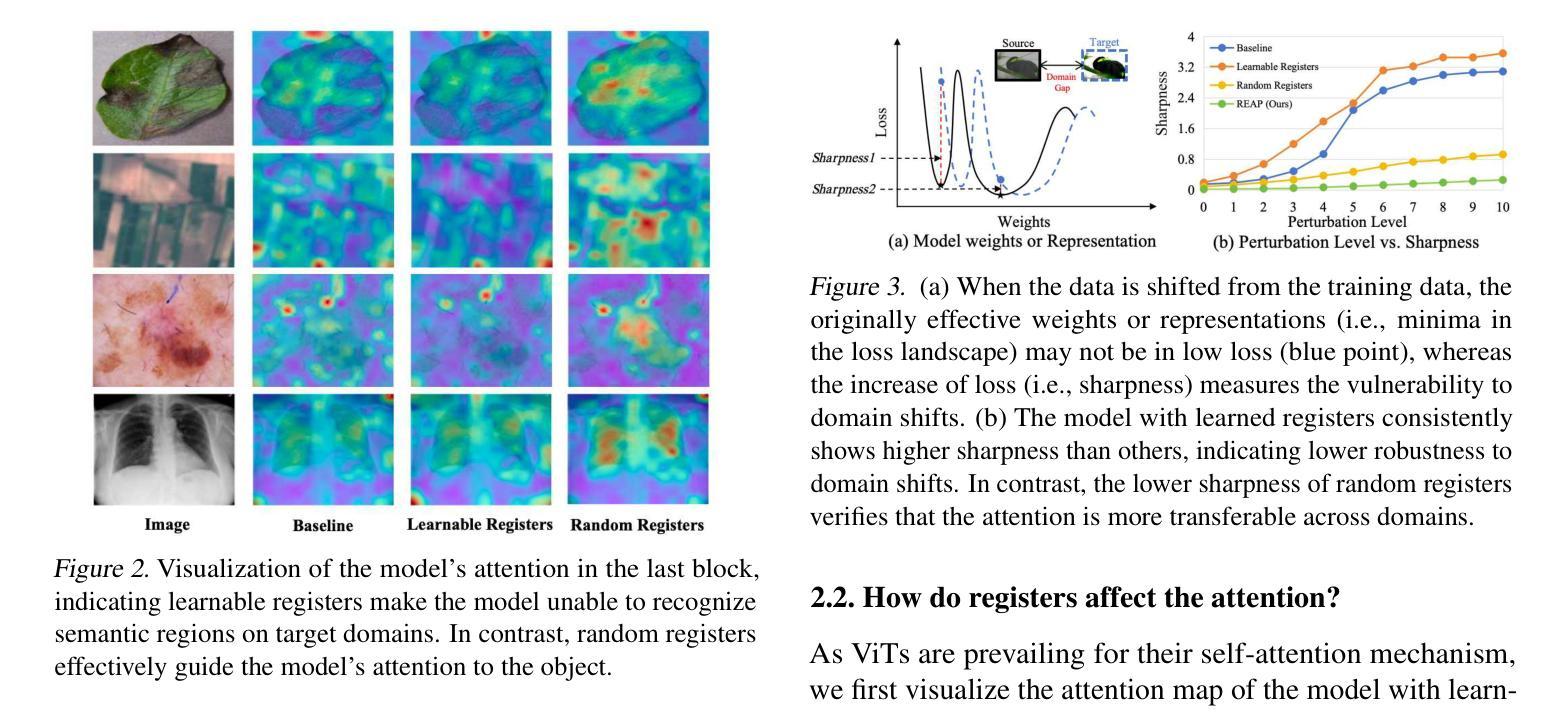
Cross-domain few-shot learning (CDFSL) aims to transfer knowledge from a data-sufficient source domain to data-scarce target domains. Although Vision Transformer (ViT) has shown superior capability in many vision tasks, its transferability against huge domain gaps in CDFSL is still under-explored. In this paper, we find an intriguing phenomenon: during the source-domain training, prompt tuning, as a common way to train ViT, could be harmful for the generalization of ViT in target domains, but setting them to random noises (i.e., random registers) could consistently improve target-domain performance. We then delve into this phenomenon for an interpretation. We find that learnable prompts capture domain information during the training on the source dataset, which views irrelevant visual patterns as vital cues for recognition. This can be viewed as a kind of overfitting and increases the sharpness of the loss landscapes. In contrast, random registers are essentially a novel way of perturbing attention for the sharpness-aware minimization, which helps the model find a flattened minimum in loss landscapes, increasing the transferability. Based on this phenomenon and interpretation, we further propose a simple but effective approach for CDFSL to enhance the perturbation on attention maps by adding random registers on the semantic regions of image tokens, improving the effectiveness and efficiency of random registers. Extensive experiments on four benchmarks validate our rationale and state-of-the-art performance. Codes and models are available at https://github.com/shuaiyi308/REAP.
跨域小样本学习(CDFSL)旨在将知识从数据充足来源域转移到数据稀缺目标域。尽管视觉转换器(ViT)在许多视觉任务中显示出卓越的能力,但其在CDFSL中面对巨大域差距的可转移性仍然未被充分探索。在本文中,我们发现了一个有趣的现象:在源域训练过程中,作为训练ViT的一种常见方法,提示调整可能会损害ViT在目标域中的泛化能力,但将其设置为随机噪声(即随机寄存器)可以持续提高目标域的性能。我们深入研究了这一现象并进行了解释。我们发现,在源数据集上进行训练时,可学习的提示会捕获域信息,将不相关的视觉模式视为识别的关键线索。这可以被视为一种过度拟合,并增加了损失景观的尖锐度。相比之下,随机寄存器本质上是通过对注意力进行扰动来实现锐度感知最小化的一种新方法,这有助于模型在损失景观中找到一个平坦的最小值,从而提高可转移性。基于这种现象和解释,我们进一步为CDFSL提出了一种简单有效的方法,通过在图像标记的语义区域上添加随机寄存器来增加注意力图的扰动,从而提高随机寄存器的有效性和效率。在四个基准测试上的大量实验验证了我们方法的合理性并达到了最新技术水平。相关代码和模型可在https://github.com/shuaiyi308/REAP上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025
Summary
本文探讨了跨域小样本学习(CDFSL)中,使用视觉转换器(ViT)时遇到的一个有趣现象。研究发现,在源域训练过程中,常见的提示调整方式可能对目标域的泛化能力产生负面影响,而将设置转为随机噪声(即随机寄存器)能够持续提高目标域性能。对此现象进行深入了解后发现,可学习的提示在源数据集训练时会捕获域信息,将不相关的视觉模式视为重要识别线索,造成过度拟合和损失景观的尖锐化。相反,随机寄存器本质上是一种扰动注意力机制的新方法,有助于模型在损失景观中找到平坦最小值,提高迁移能力。基于此现象和解释,文章进一步提出了一种简单有效的方法来增强CDFSL中的注意力映射扰动,通过在图像标记的语义区域上添加随机寄存器来提高其有效性和效率。经过四个基准测试的实验验证,该研究达到了业界领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 跨域小样本学习(CDFSL)旨在从数据充足的源域迁移知识到数据稀缺的目标域。
- 视觉转换器(ViT)在CDFSL中的迁移能力尚未完全探索。
- 提示调整在源域训练中可能对ViT在目标域的泛化能力产生负面影响。
- 随机噪声(随机寄存器)能够提高目标域性能。
- 可学习的提示会捕获源数据集中的域信息,可能导致过度拟合和损失景观的尖锐化。
- 随机寄存器通过扰动注意力机制帮助模型找到损失景观中的平坦最小值,提高迁移能力。
点此查看论文截图

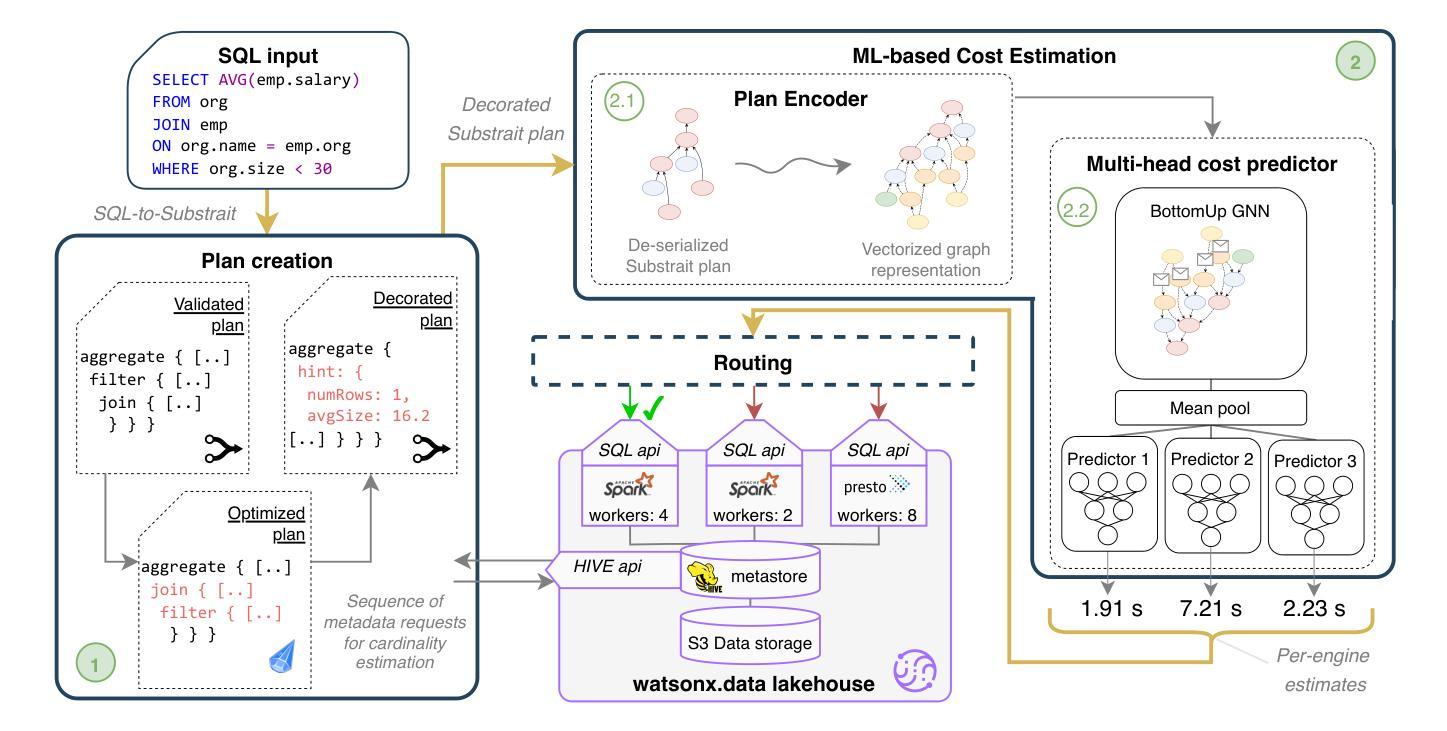
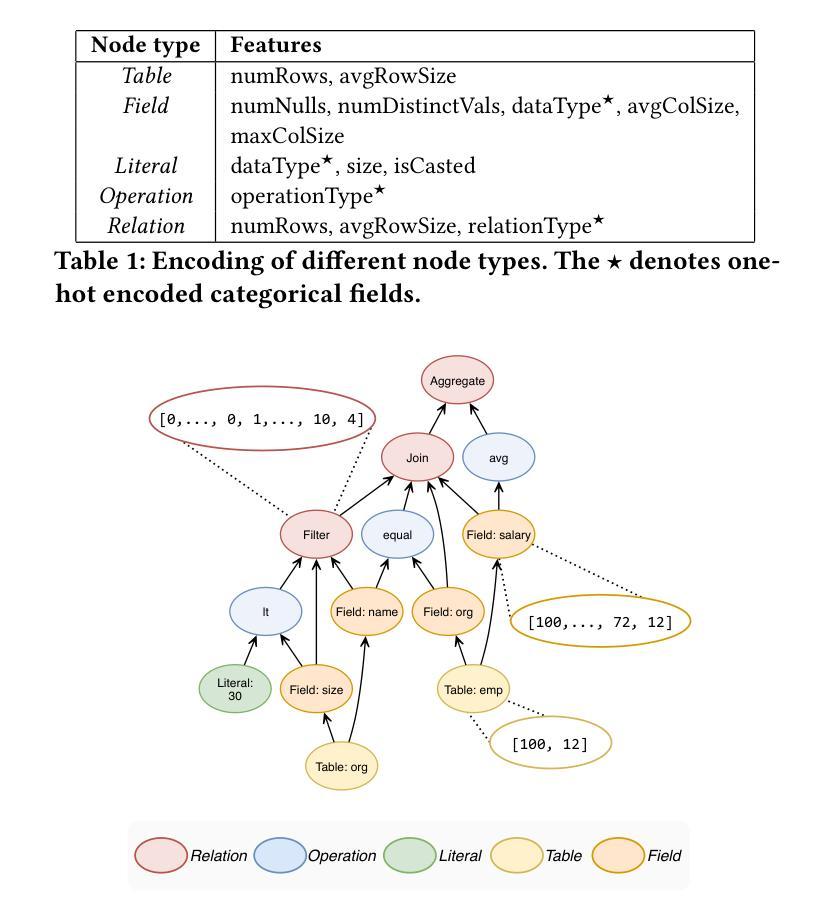
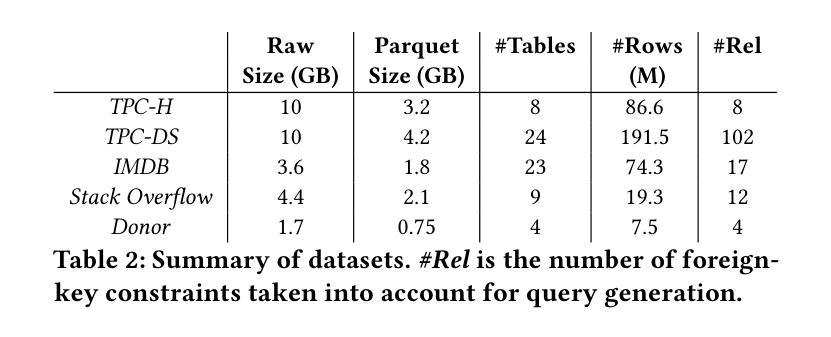
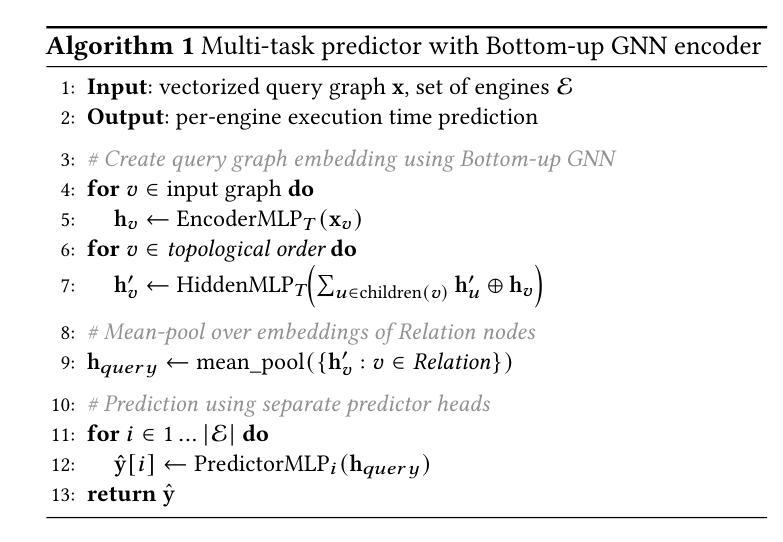
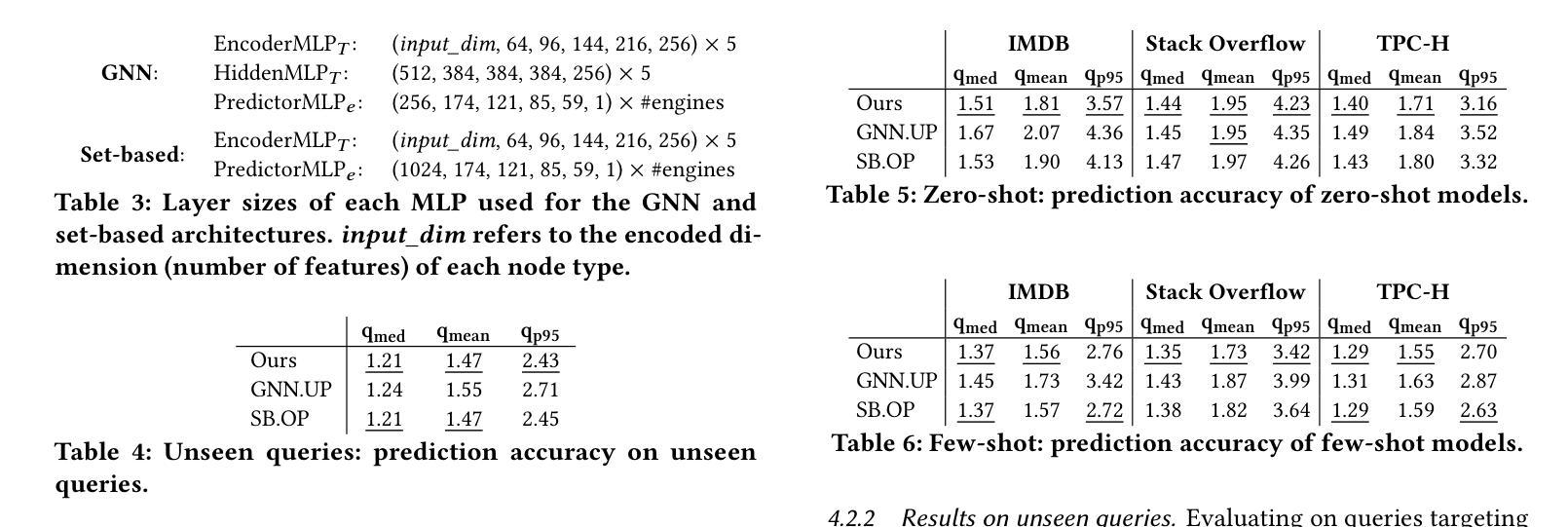
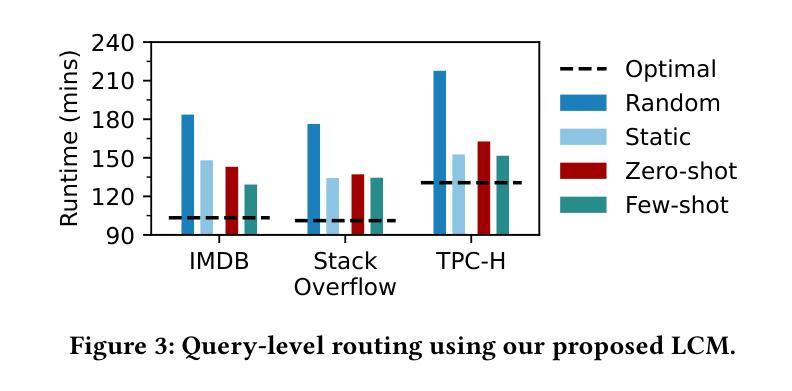
A Learned Cost Model-based Cross-engine Optimizer for SQL Workloads
Authors:András Strausz, Niels Pardon, Ioana Giurgiu
Lakehouse systems enable the same data to be queried with multiple execution engines. However, selecting the engine best suited to run a SQL query still requires a priori knowledge of the query computational requirements and an engine capability, a complex and manual task that only becomes more difficult with the emergence of new engines and workloads. In this paper, we address this limitation by proposing a cross-engine optimizer that can automate engine selection for diverse SQL queries through a learned cost model. Optimized with hints, a query plan is used for query cost prediction and routing. Cost prediction is formulated as a multi-task learning problem, and multiple predictor heads, corresponding to different engines and provisionings, are used in the model architecture. This eliminates the need to train engine-specific models and allows the flexible addition of new engines at a minimal fine-tuning cost. Results on various databases and engines show that using a query optimized logical plan for cost estimation decreases the average Q-error by even 12.6% over using unoptimized plans as input. Moreover, the proposed cross-engine optimizer reduces the total workload runtime by up to 25.2% in a zero-shot setting and 30.4% in a few-shot setting when compared to random routing.
湖仓系统允许使用多个执行引擎查询相同的数据。然而,选择最适合运行SQL查询的引擎仍然需要预先了解查询计算要求以及引擎能力,这是一项随着新引擎和工作负载的出现而变得越来越复杂的手动任务。在本文中,我们通过提出一种跨引擎优化器来解决这一限制,该优化器可以通过学习成本模型来自动为各种SQL查询选择引擎。该优化器通过提示进行优化,使用查询计划进行查询成本预测和路由。成本预测被制定为多任务学习问题,模型架构中使用了与不同引擎和配置相对应的多个预测器头。这消除了需要训练特定于引擎的模型的需求,并允许灵活地添加新引擎,而只需最小的微调成本。在各种数据库和引擎上的结果表明,使用经过优化的查询逻辑计划进行成本估计,可以将平均Q误差降低12.6%,超过使用未优化的计划作为输入。此外,与随机路由相比,所提出的跨引擎优化器在零样本设置下减少了高达25.2%的总工作量运行时间,在少数样本设置下减少了30.4%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages
Summary
本文提出了一种跨引擎优化器,通过采用学习成本模型自动选择适合运行不同SQL查询的引擎。该优化器利用提示和优化后的查询计划进行成本预测和路由选择。成本预测被转化为多任务学习问题,模型架构中采用多个预测器头,对应不同的引擎和配置。此方法无需训练特定引擎的模型,可灵活添加新引擎并降低微调成本。实验结果显示,使用优化后的查询逻辑计划进行成本估计可降低平均Q误差,且跨引擎优化器可减少总工作量运行时间。
Key Takeaways
- Lakehouse systems enable querying the same data with multiple execution engines.
- 自动化引擎选择对于运行不同SQL查询至关重要。
- 跨引擎优化器通过采用学习成本模型来解决自动化引擎选择问题。
- 查询计划用于预测查询成本和路由选择。
- 成本预测被转化为多任务学习问题。
- 使用优化后的查询逻辑计划可降低平均Q误差,并减少总工作量运行时间。
点此查看论文截图

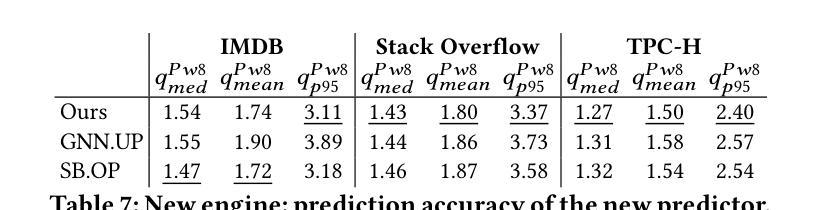
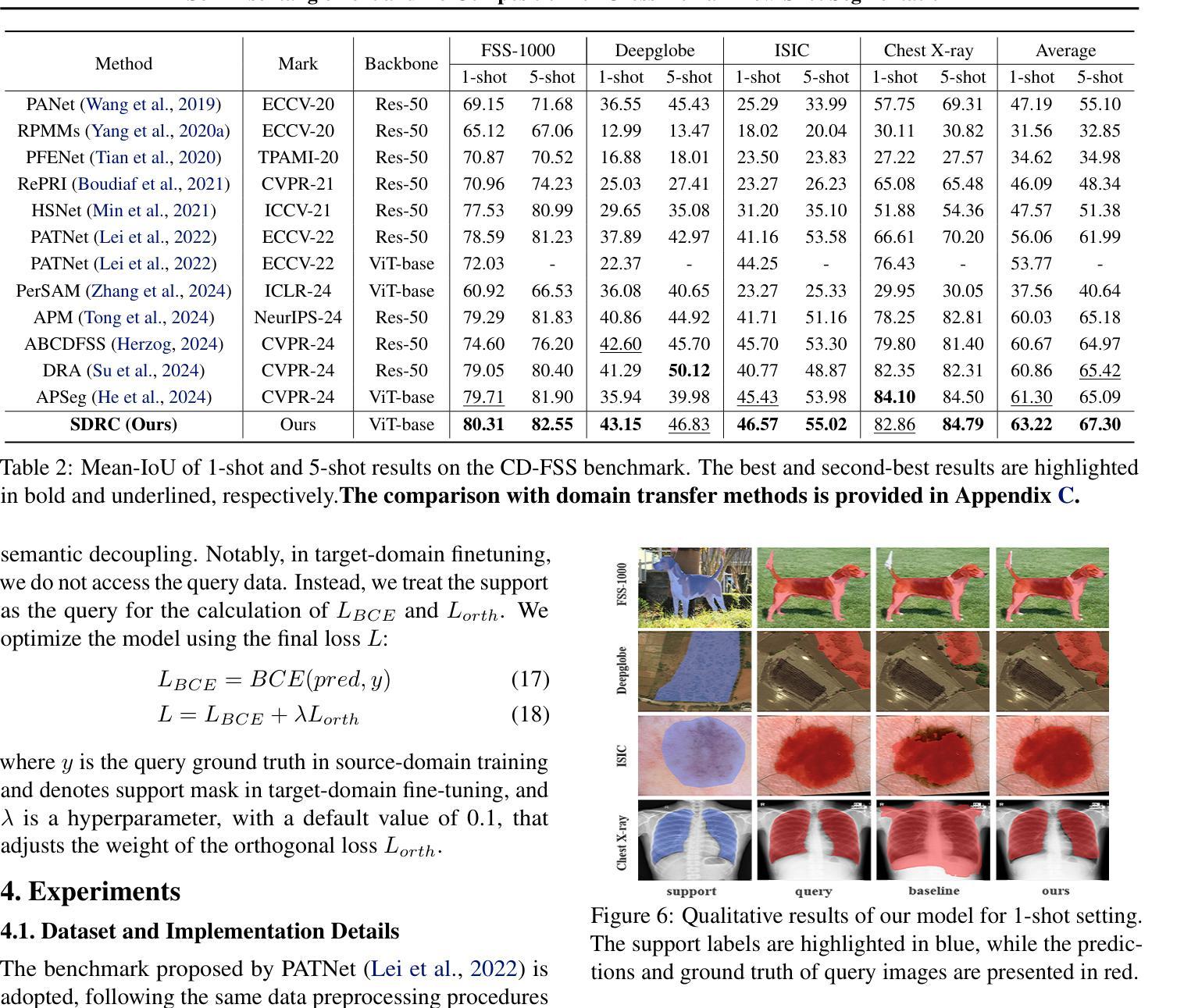
Self-Disentanglement and Re-Composition for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Segmentation
Authors:Jintao Tong, Yixiong Zou, Guangyao Chen, Yuhua Li, Ruixuan Li
Cross-Domain Few-Shot Segmentation (CD-FSS) aims to transfer knowledge from a source-domain dataset to unseen target-domain datasets with limited annotations. Current methods typically compare the distance between training and testing samples for mask prediction. However, we find an entanglement problem exists in this widely adopted method, which tends to bind sourcedomain patterns together and make each of them hard to transfer. In this paper, we aim to address this problem for the CD-FSS task. We first find a natural decomposition of the ViT structure, based on which we delve into the entanglement problem for an interpretation. We find the decomposed ViT components are crossly compared between images in distance calculation, where the rational comparisons are entangled with those meaningless ones by their equal importance, leading to the entanglement problem. Based on this interpretation, we further propose to address the entanglement problem by learning to weigh for all comparisons of ViT components, which learn disentangled features and re-compose them for the CD-FSS task, benefiting both the generalization and finetuning. Experiments show that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art CD-FSS method by 1.92% and 1.88% in average accuracy under 1-shot and 5-shot settings, respectively.
跨域小样本分割(CD-FSS)旨在将源域数据集的知识转移到未见过的目标域数据集上,且目标域数据集带有有限的注释。当前的方法通常通过比较训练和测试样本之间的距离来进行掩膜预测。然而,我们发现广泛采用的方法中存在纠缠问题,这一问题倾向于将源域模式绑定在一起,使得每个模式都难以转移。本文旨在解决CD-FSS任务的这个问题。首先,我们找到了ViT结构的自然分解,并在此基础上深入研究纠缠问题以进行解释。我们发现分解的ViT组件在距离计算中会交叉比较图像,其中合理比较与无意义比较纠缠在一起,它们的重要性相等,导致了纠缠问题。基于此解释,我们进一步提出通过为所有ViT组件的比较学习权重来解决纠缠问题,这些组件学习解耦的特征并重新组合它们以用于CD-FSS任务,有利于泛化和微调。实验表明,我们的模型在平均准确率上分别超出最新CD-FSS方法1.92%和1.88%,在单样本和五样本设置下均如此。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025
Summary
基于跨域小样本分割(CD-FSS)的目标是在具有有限标注的未见目标域数据集上转移源域数据集的知识。当前方法主要通过比较训练和测试样本之间的距离进行掩膜预测,但存在纠缠问题,倾向于将源域模式绑定在一起,使得每个模式的转移都变得更加困难。本文旨在解决CD-FSS任务中的这一问题。我们首先找到ViT结构的自然分解,并在此基础上深入研究纠缠问题以进行解释。我们发现分解的ViT组件在距离计算时相互比较图像,其中合理的比较与无意义的比较纠缠在一起,导致纠缠问题。基于此解释,我们进一步提出通过学习为所有ViT组件的比较进行加权来解决纠缠问题,学习解纠缠特征并重新组合它们以用于CD-FSS任务,这有利于模型的泛化和微调。
Key Takeaways
- CD-FSS旨在从源域数据集转移知识到目标域数据集,面对有限标注的挑战。
- 当前方法通过比较训练和测试样本之间的距离进行掩膜预测,但存在纠缠问题。
- 纠缠问题源于ViT组件在距离计算时的比较方式,合理的比较与无意义的比较纠缠在一起。
- 提出通过学习为ViT组件的比较进行加权来解决纠缠问题。
- 解纠缠特征的学习有助于提高模型的泛化和微调能力。
- 实验结果显示,与现有CD-FSS方法相比,新模型在1-shot和5-shot设置下的平均准确度分别提高了1.92%和1.88%。
点此查看论文截图

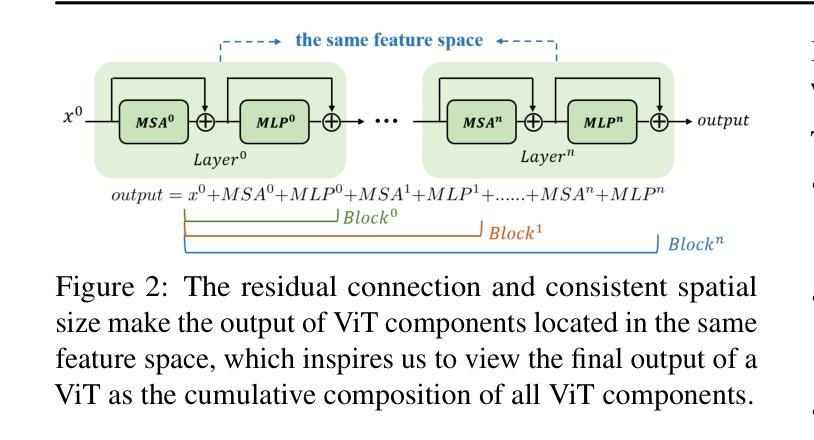
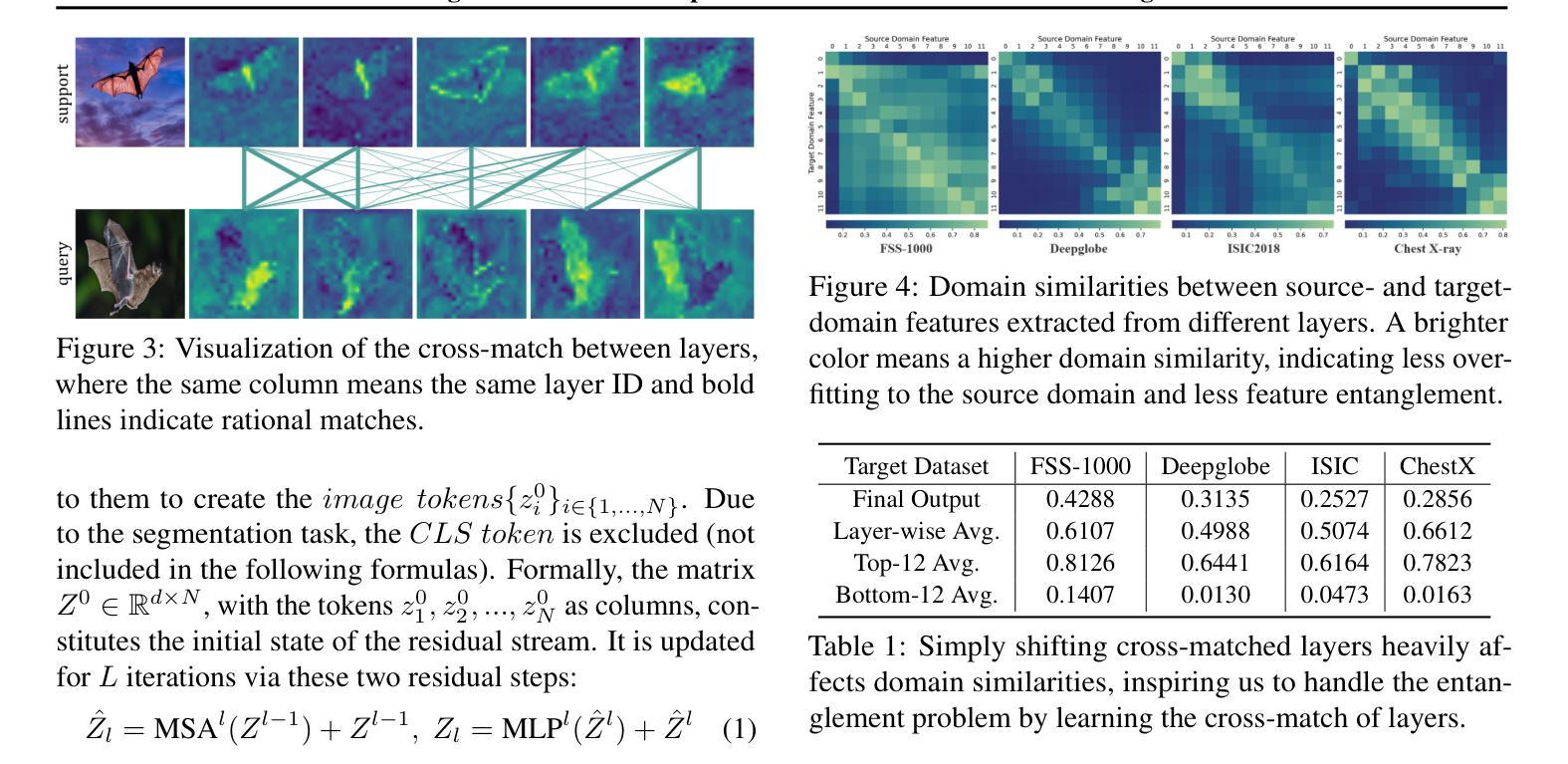
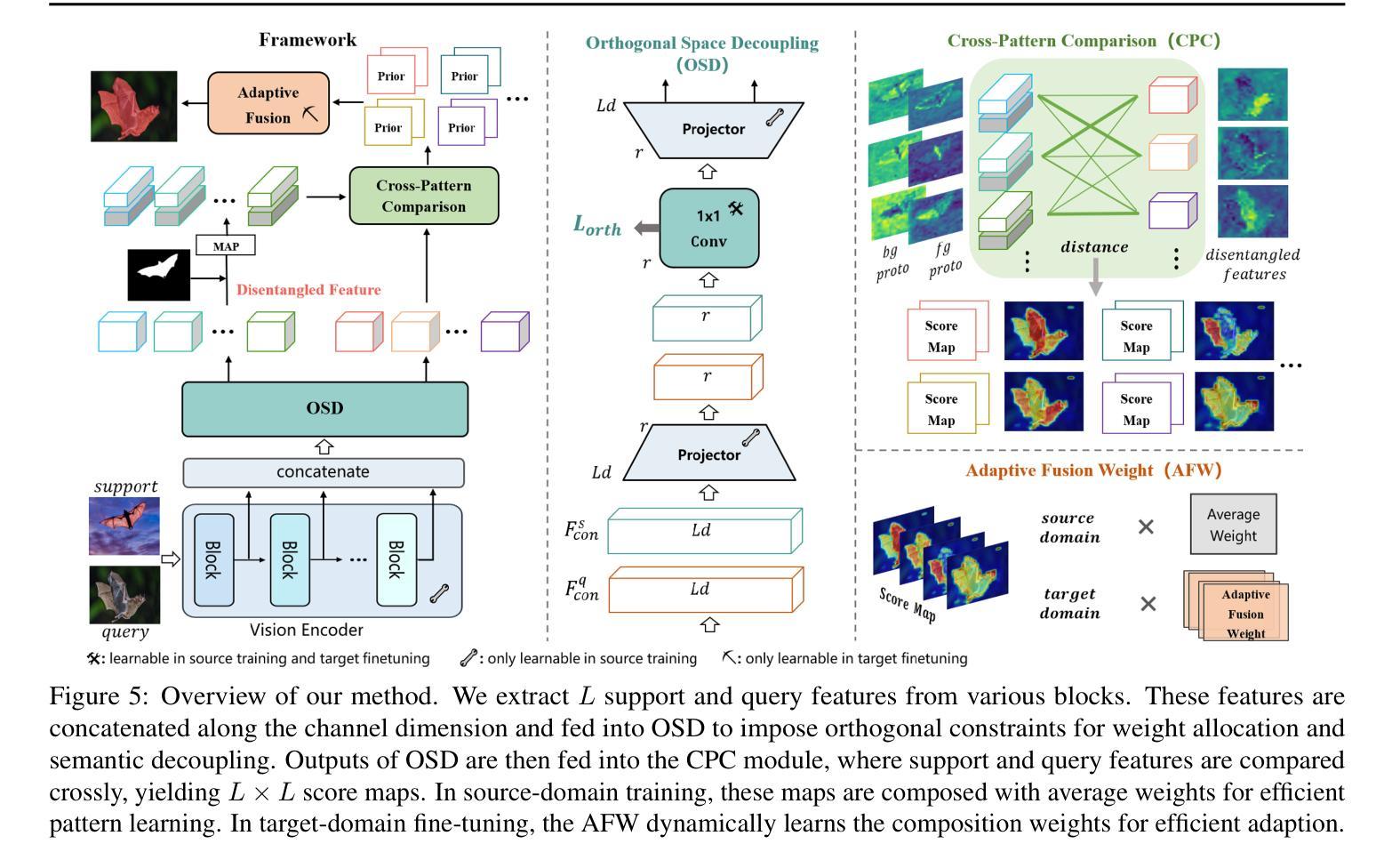
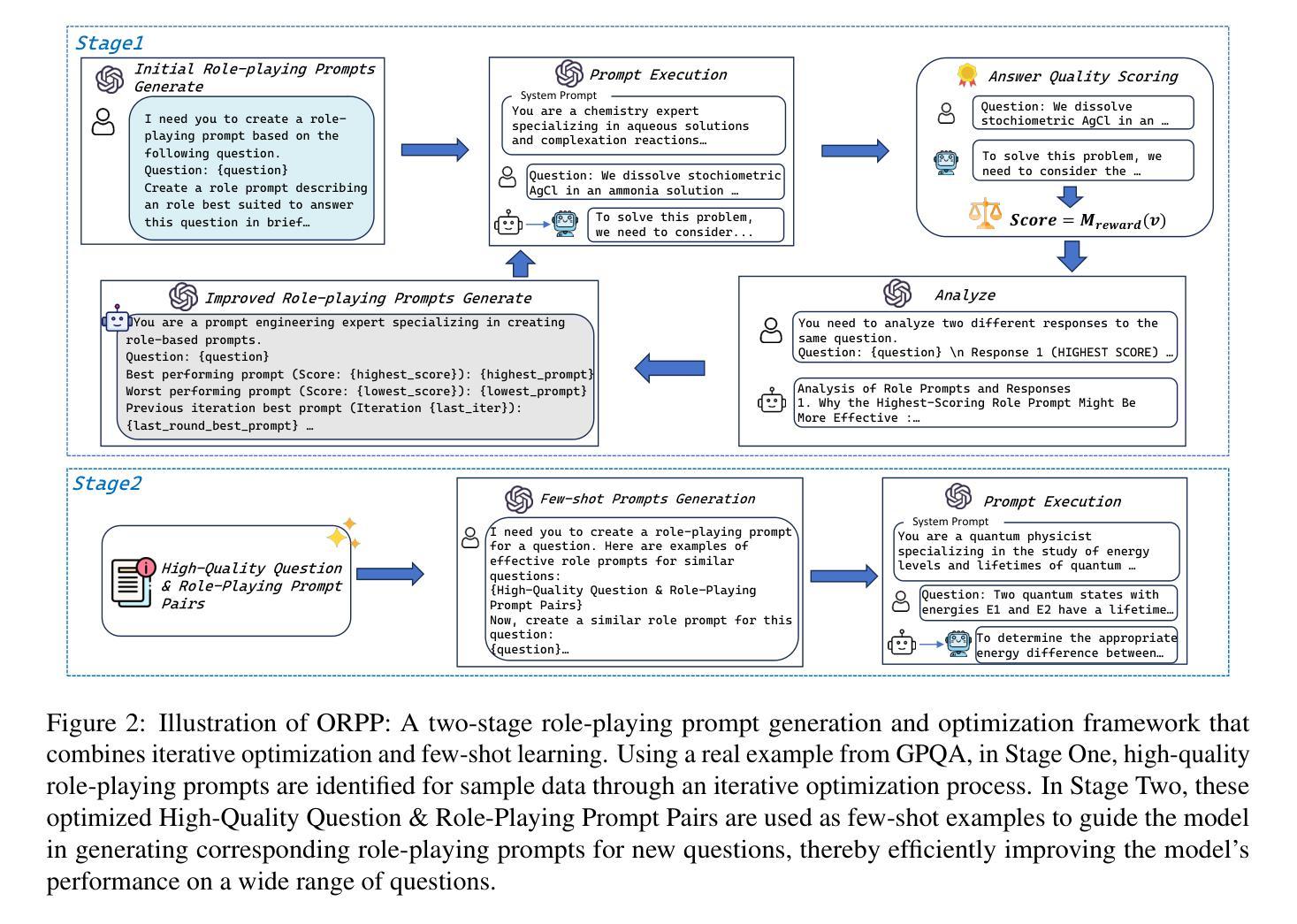
ORPP: Self-Optimizing Role-playing Prompts to Enhance Language Model Capabilities
Authors:Yifan Duan, Yihong Tang, Kehai Chen, Liqiang Nie, Min Zhang
High-quality prompts are crucial for eliciting outstanding performance from large language models (LLMs) on complex tasks. Existing research has explored model-driven strategies for prompt optimization. However, these methods often suffer from high computational overhead or require strong optimization capabilities from the model itself, which limits their broad applicability.To address these challenges, we propose ORPP (Optimized Role-Playing Prompt),a framework that enhances model performance by optimizing and generating role-playing prompts. The core idea of ORPP is to confine the prompt search space to role-playing scenarios, thereby fully activating the model’s intrinsic capabilities through carefully crafted, high-quality role-playing prompts. Specifically, ORPP first performs iterative optimization on a small subset of training samples to generate high-quality role-playing prompts. Then, leveraging the model’s few-shot learning capability, it transfers the optimization experience to efficiently generate suitable prompts for the remaining samples.Our experimental results show that ORPP not only matches but in most cases surpasses existing mainstream prompt optimization methods in terms of performance. Notably, ORPP demonstrates superior “plug-and-play” capability. In most cases, it can be integrated with various other prompt methods and further enhance their effectiveness.
高质量提示对于激发大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂任务上的卓越性能至关重要。现有研究已经探索了基于模型的提示优化策略。然而,这些方法通常面临高计算开销或需要模型本身的强大优化能力,这限制了它们的广泛应用。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了ORPP(优化角色扮演提示)框架,它通过优化和生成角色扮演提示来提高模型性能。ORPP的核心思想是将提示搜索空间限制在角色扮演场景上,通过精心构建的高质量角色扮演提示,充分激活模型的内在能力。具体来说,ORPP首先对训练样本的一个小子集进行迭代优化,生成高质量的角色扮演提示。然后,利用模型的少样本学习能力,将优化经验转移到为其余样本生成合适的提示。我们的实验结果表明,ORPP不仅在性能上达到了现有主流提示优化方法的水准,而且在大多数情况下超过了它们。值得注意的是,ORPP展示了出色的“即插即用”能力。在大多数情况下,它可以与其他提示方法相结合,进一步提高其有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在高质量提示的引导下,能在复杂任务上表现出卓越性能。现有研究已探索了基于模型的提示优化策略,但这些方法往往存在计算开销大或需要模型自身强大的优化能力,限制了其广泛应用。为解决这些挑战,我们提出ORPP(优化角色扮演提示)框架,通过优化和生成角色扮演提示来提高模型性能。ORPP的核心思想是将提示搜索空间限制在角色扮演场景上,通过精心构建的高质量角色扮演提示,充分激活模型的内在能力。实验结果表明,ORPP不仅在性能上达到甚至超越了主流提示优化方法,而且具有出色的“即插即用”能力,能够与其他提示方法相结合,进一步提升其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 高质量提示对大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂任务上的性能至关重要。
- 现有提示优化方法存在计算开销大或需要模型自身强大优化能力的局限性。
- ORPP框架通过优化和生成角色扮演提示来提高模型性能。
- ORPP将提示搜索空间限制在角色扮演场景,充分激活模型的内在能力。
- ORPP通过迭代优化一小部分训练样本来生成高质量的角色扮演提示。
- 利用模型的少样本学习能力,ORPP将优化经验转移到其他样本上,生成合适的提示。
点此查看论文截图


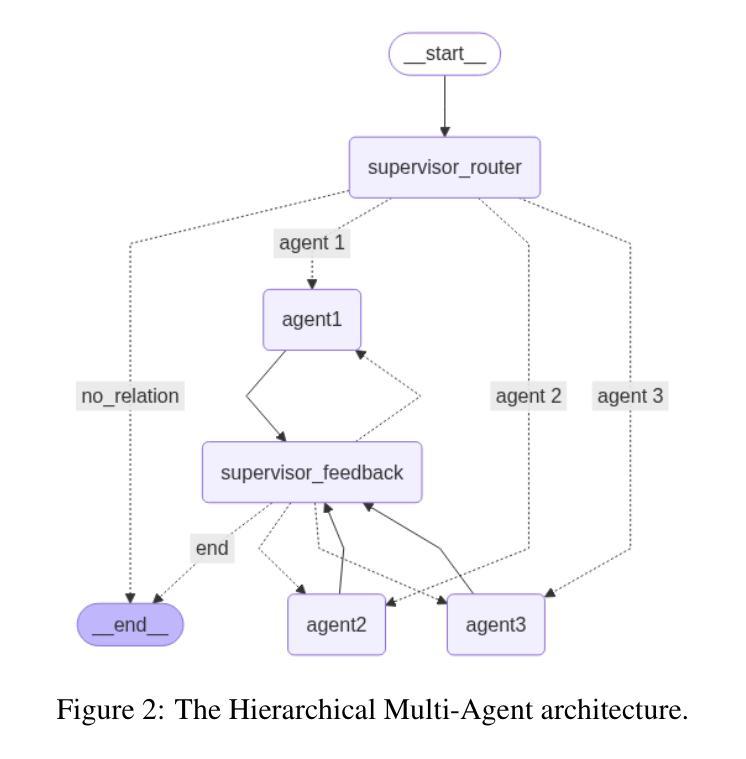
Comparative Analysis of AI Agent Architectures for Entity Relationship Classification
Authors:Maryam Berijanian, Kuldeep Singh, Amin Sehati
Entity relationship classification remains a challenging task in information extraction, especially in scenarios with limited labeled data and complex relational structures. In this study, we conduct a comparative analysis of three distinct AI agent architectures designed to perform relation classification using large language models (LLMs). The agentic architectures explored include (1) reflective self-evaluation, (2) hierarchical task decomposition, and (3) a novel multi-agent dynamic example generation mechanism, each leveraging different modes of reasoning and prompt adaptation. In particular, our dynamic example generation approach introduces real-time cooperative and adversarial prompting. We systematically compare their performance across multiple domains and model backends. Our experiments demonstrate that multi-agent coordination consistently outperforms standard few-shot prompting and approaches the performance of fine-tuned models. These findings offer practical guidance for the design of modular, generalizable LLM-based systems for structured relation extraction. The source codes and dataset are available at \href{https://github.com/maryambrj/ALIEN.git}{https://github.com/maryambrj/ALIEN.git}.
实体关系分类在信息提取中仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务,特别是在标签数据有限和关系结构复杂的情况下。在这项研究中,我们对三种旨在利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行关系分类的独特AI代理架构进行了比较分析。所探讨的代理架构包括(1)反思自我评价、(2)层次任务分解和(3)一种新型的多代理动态示例生成机制,每种机制都利用不同的推理模式和提示适应性。特别是,我们的动态示例生成方法引入了实时合作和对抗性提示。我们系统地比较了它们在多个领域和模型后端的表现。我们的实验表明,多代理协调始终优于标准的小样本提示,并接近微调模型的性能。这些发现为设计模块化、可推广的基于LLM的结构化关系提取系统提供了实际指导。源代码和数据集可通过链接https://github.com/maryambrj/ALIEN.git获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了实体关系分类在信息提取中的挑战,特别是在标签数据有限和关系结构复杂的情况下。文章对比分析了三种用于关系分类的AI代理架构,包括反思自我评价、层次任务分解和新型多代理动态示例生成机制。其中,动态示例生成方法引入了实时合作和对抗性提示。实验表明,多代理协同一致地超越了标准少样本提示,并接近微调模型的性能。这为设计模块化的、通用的大语言模型基础的系统进行结构化关系提取提供了实际指导。
Key Takeaways
- 实体关系分类是信息提取中的一项挑战,尤其在数据有限和关系结构复杂的情况下。
- 分析了三种AI代理架构:反思自我评价、层次任务分解和新型多代理动态示例生成机制。
- 多代理动态示例生成方法结合了实时合作和对抗性提示。
- 实验结果显示,多代理协同在关系分类任务上表现最佳,超越了标准少样本提示方法。
- 多代理协同性能接近微调模型的性能。
- 该研究为设计模块化的、通用的大语言模型基础的系统进行结构化关系提取提供了实践指导。
点此查看论文截图

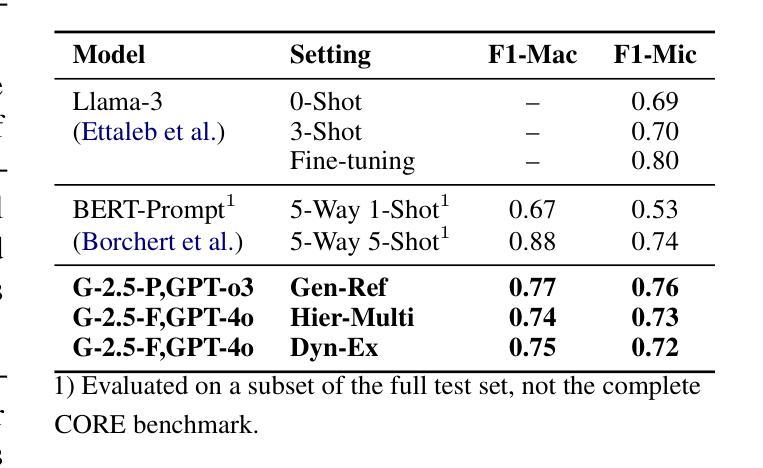
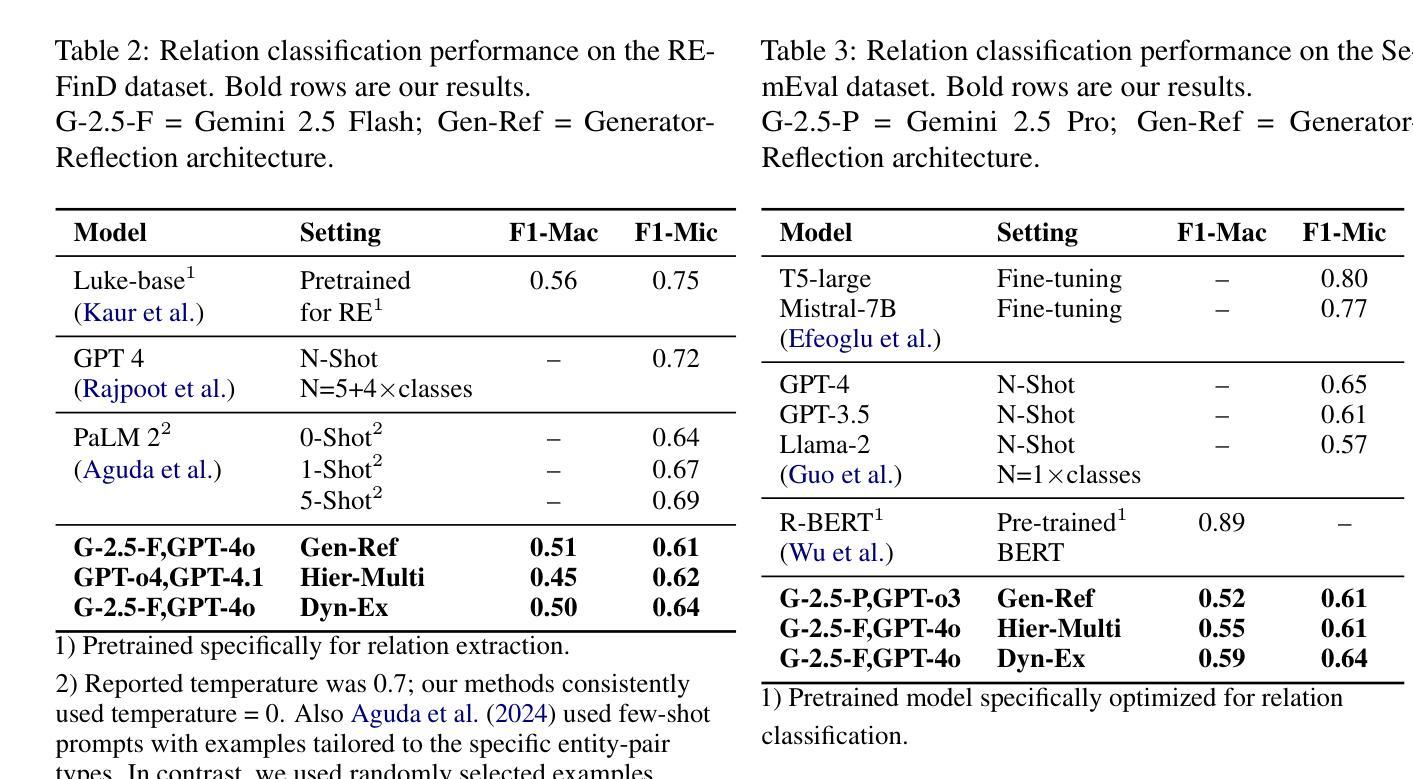
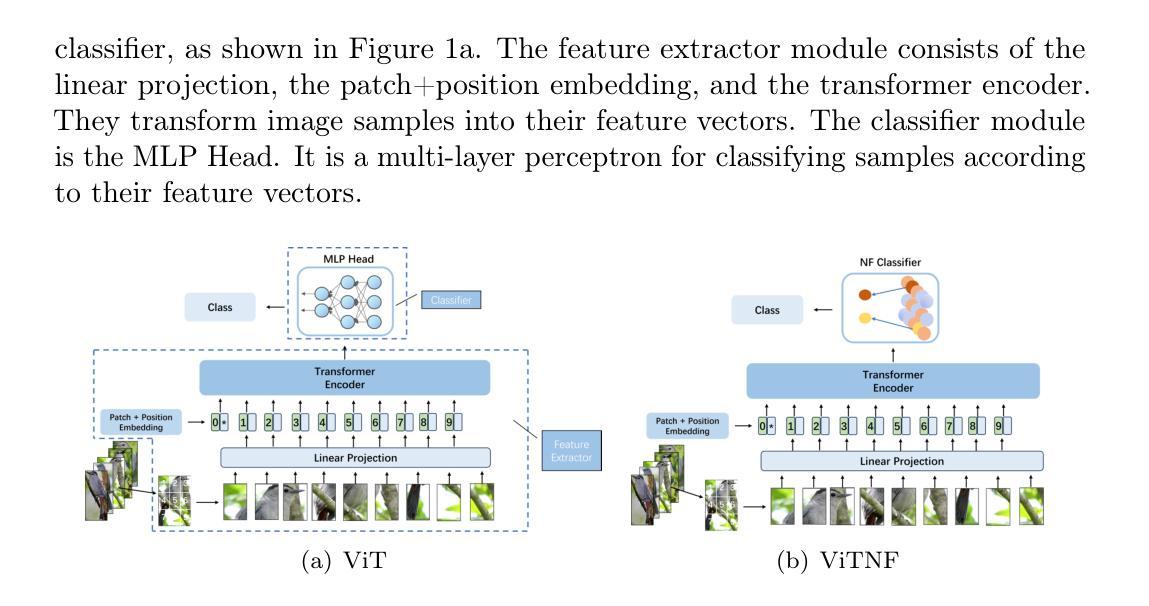
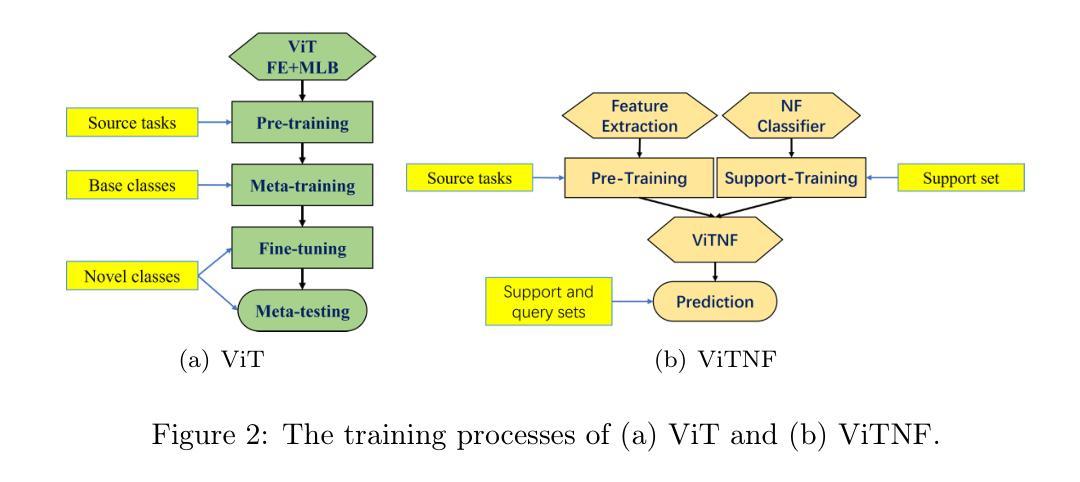
ViTNF: Leveraging Neural Fields to Boost Vision Transformers in Generalized Category Discovery
Authors:Jiayi Su, Dequan Jin
Generalized category discovery (GCD) is a highly popular task in open-world recognition, aiming to identify unknown class samples using known class data. By leveraging pre-training, meta-training, and fine-tuning, ViT achieves excellent few-shot learning capabilities. Its MLP head is a feedforward network, trained synchronously with the entire network in the same process, increasing the training cost and difficulty without fully leveraging the power of the feature extractor. This paper proposes a new architecture by replacing the MLP head with a neural field-based one. We first present a new static neural field function to describe the activity distribution of the neural field and then use two static neural field functions to build an efficient few-shot classifier. This neural field-based (NF) classifier consists of two coupled static neural fields. It stores the feature information of support samples by its elementary field, the known categories by its high-level field, and the category information of support samples by its cross-field connections. We replace the MLP head with the proposed NF classifier, resulting in a novel architecture ViTNF, and simplify the three-stage training mode by pre-training the feature extractor on source tasks and training the NF classifier with support samples in meta-testing separately, significantly reducing ViT’s demand for training samples and the difficulty of model training. To enhance the model’s capability in identifying new categories, we provide an effective algorithm to determine the lateral interaction scale of the elementary field. Experimental results demonstrate that our model surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods on CIFAR-100, ImageNet-100, CUB-200, and Standard Cars, achieving dramatic accuracy improvements of 19% and 16% in new and all classes, respectively, indicating a notable advantage in GCD.
广义类别发现(GCD)是开放世界识别中非常受欢迎的任务,旨在利用已知类别的数据来识别未知类别的样本。通过利用预训练、元训练和微调,ViT实现了出色的少样本学习能力。其MLP头是前馈网络,与整个网络在同一进程中同步训练,增加了训练成本和难度,而没有充分利用特征提取器的力量。本文提出了一种新的架构,用基于神经场的头来替换MLP头。我们首先提出了一种新的静态神经场函数来描述神经场的活动分布,然后使用两个静态神经场函数来构建有效的少样本分类器。这个基于神经场(NF)的分类器由两个耦合的静态神经场组成。它通过基本场存储支持样本的特征信息,通过高级场存储已知类别的信息,并通过跨场连接存储支持样本的类别信息。我们用提出的NF分类器替换MLP头,得到了新型架构ViTNF,通过预训练特征提取器在源任务上,以及在元测试中用支持样本分别训练NF分类器,简化了三阶段训练模式,大大降低了ViT对训练样本的需求和模型训练的难度。为了提高模型识别新类别的能力,我们提供了一种确定基本场横向交互尺度的有效算法。实验结果表明,我们的模型在CIFAR-100、ImageNet-100、CUB-200和Standard Cars等数据集上超越了现有的最先进的方法,新类别和所有类别的准确率分别提高了19%和16%,在GCD中显示出显著的优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本文提出了一个新的架构ViTNF,它通过利用神经网络场替换ViT中的MLP头来实现更高效的少样本分类。新架构通过两个耦合的静态神经网络场来存储支持样本的特征信息、已知类别的信息以及支持样本的类别信息。此外,还提供了一个确定基本场横向交互尺度的有效算法,用于提高模型识别新类别的能力。实验结果表明,该模型在CIFAR-100、ImageNet-100、CUB-200和Standard Cars等数据集上的表现优于现有最先进的模型,在新类和所有类的准确率分别提高了19%和16%,在广义类别发现任务中具有显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- 文中介绍了广义类别发现(GCD)任务,旨在利用已知类别数据识别未知类别样本。
- 论文提出了一种新的架构ViTNF,通过替换ViT中的MLP头,利用神经网络场实现少样本学习。
- ViTNF架构通过两个耦合的静态神经网络场存储支持样本和已知类别的特征信息。
- 提供了确定基本场横向交互尺度的有效算法,以提高模型识别新类别的能力。
- 实验结果表明,ViTNF在多个数据集上的表现优于现有模型,准确率的提高证明了其在GCD任务中的优势。
- ViTNF简化了训练模式,通过预训练特征提取器和在元测试阶段分别训练NF分类器与支持样本,降低了ViT对训练样本的需求和模型训练的难度。
- ViTNF架构的引入有助于推动少样本学习领域的发展。
点此查看论文截图

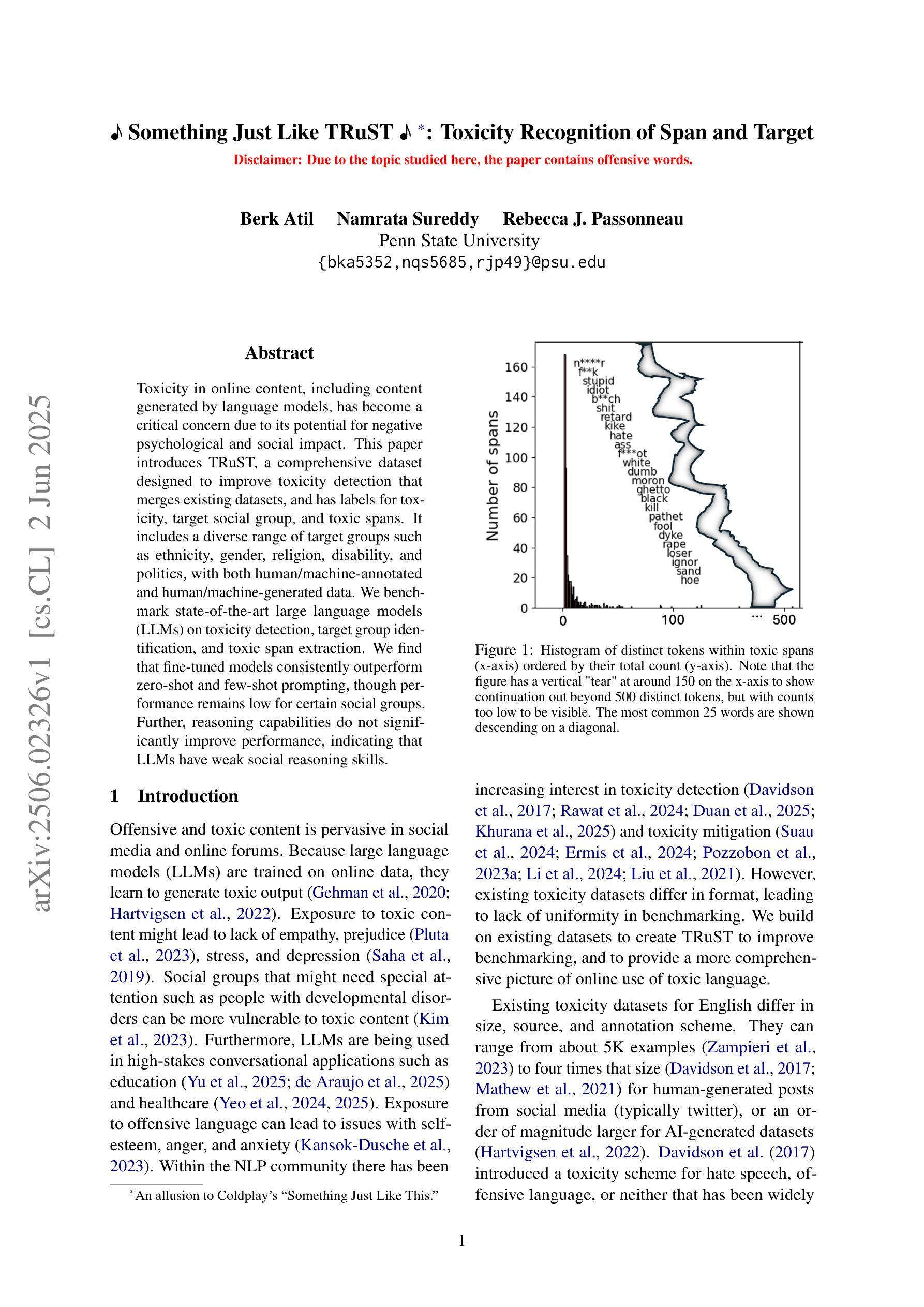
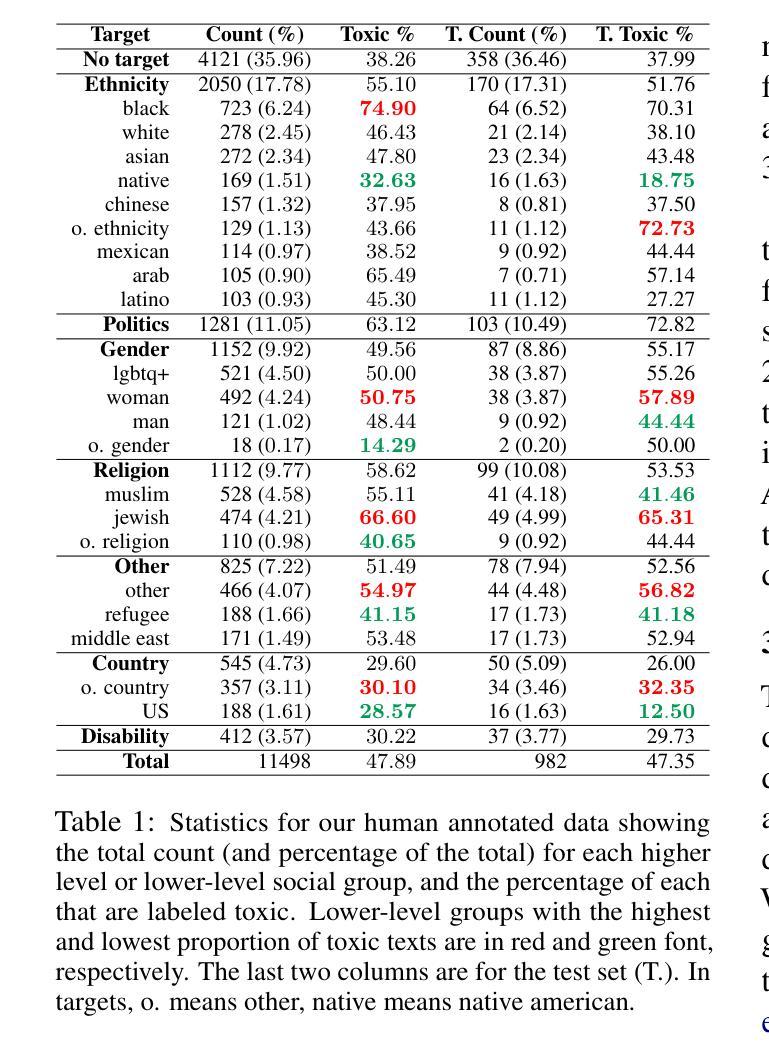
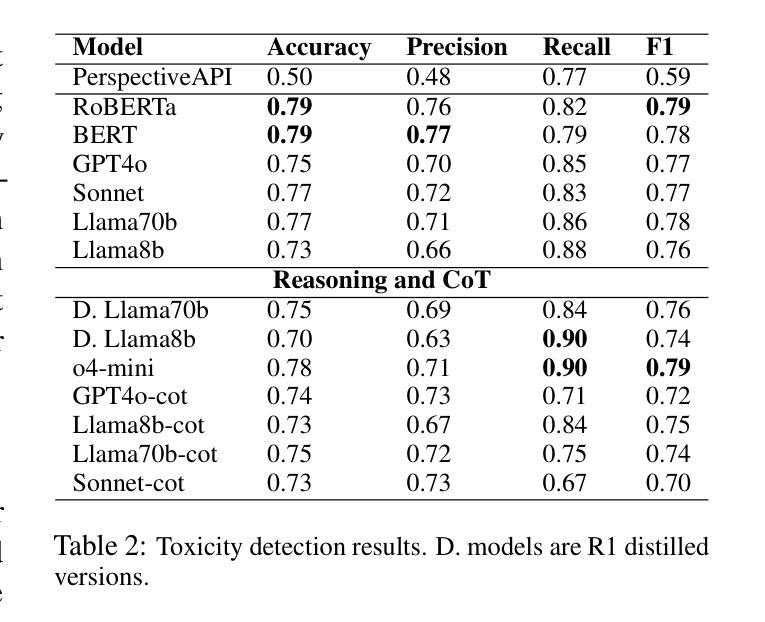
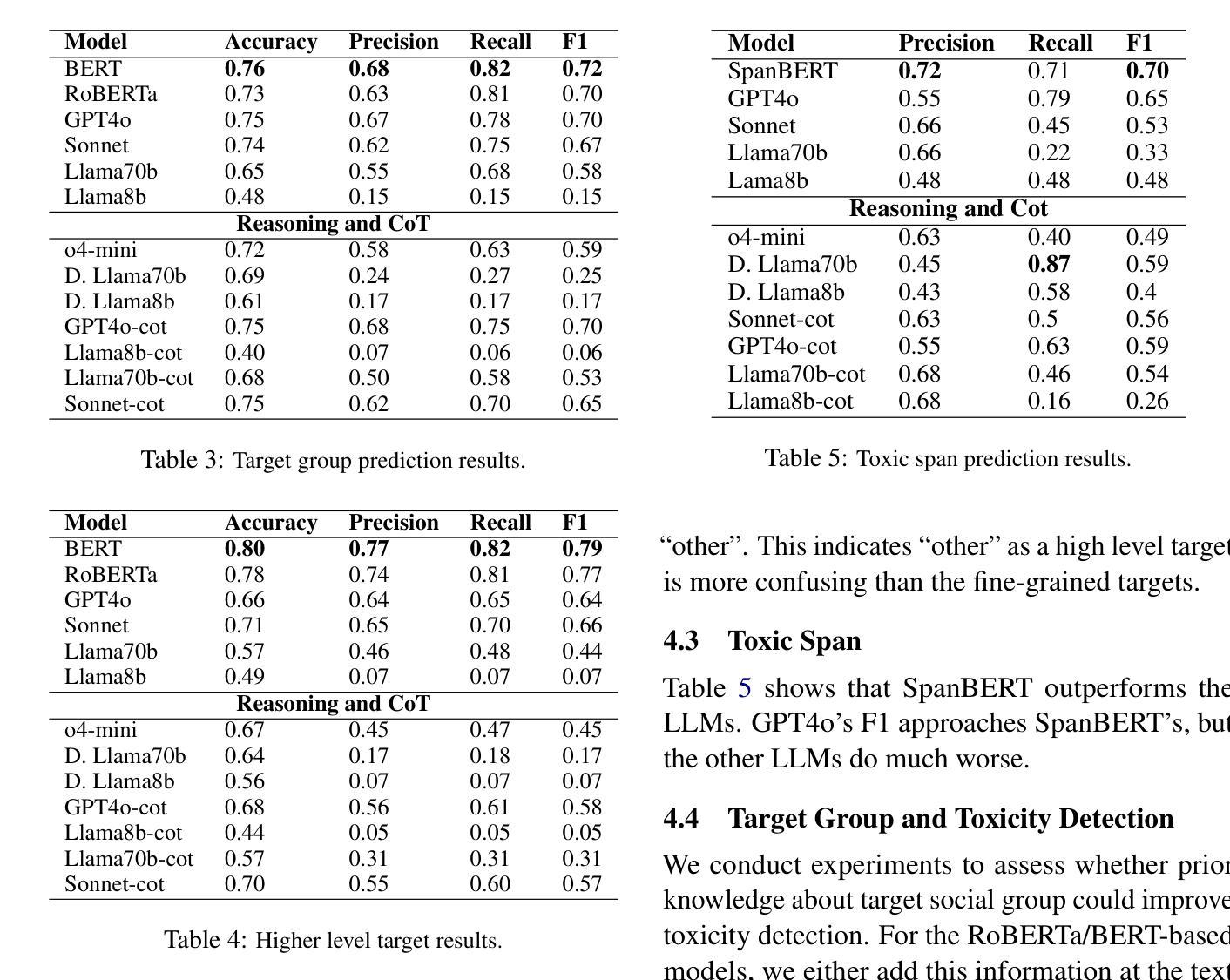
Something Just Like TRuST : Toxicity Recognition of Span and Target
Authors:Berk Atil, Namrata Sureddy, Rebecca J. Passonneau
Toxicity in online content, including content generated by language models, has become a critical concern due to its potential for negative psychological and social impact. This paper introduces TRuST, a comprehensive dataset designed to improve toxicity detection that merges existing datasets, and has labels for toxicity, target social group, and toxic spans. It includes a diverse range of target groups such as ethnicity, gender, religion, disability, and politics, with both human/machine-annotated and human machine-generated data. We benchmark state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) on toxicity detection, target group identification, and toxic span extraction. We find that fine-tuned models consistently outperform zero-shot and few-shot prompting, though performance remains low for certain social groups. Further, reasoning capabilities do not significantly improve performance, indicating that LLMs have weak social reasoning skills.
网络内容中的毒性,包括由语言模型生成的内容,由于其可能产生的负面心理和社会影响,已成为人们关注的重点。本文介绍了TRuST数据集,这是一个为了改善毒性检测而设计的综合数据集,它合并了现有数据集,并为毒性、目标社会群体和有毒跨度提供了标签。它涵盖了广泛的目标群体,如种族、性别、宗教、残疾和政治等,包括人机标注和人机生成的数据。我们对最先进的大型语言模型(LLM)在毒性检测、目标群体识别和有毒跨度提取方面进行了基准测试。我们发现微调模型始终优于零样本和少样本提示,尽管某些社会群体的性能仍然较低。此外,推理能力并没有显著提高性能,这表明大型语言模型的社会推理能力较弱。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注在线内容中的毒性问题,包括由语言模型生成的内容。文章介绍了一个综合数据集TRuST,该数据集旨在提高毒性检测能力,它通过合并现有数据集,并为毒性、目标社会群体和毒性跨度提供标签。文章还评估了最先进的大型语言模型(LLMs)在毒性检测、目标群体识别和毒性跨度提取方面的表现。研究发现,微调模型始终优于零样本和少样本提示,但对某些社会群体的表现仍然较低。此外,推理能力并没有显著提高性能,表明LLMs在社交推理方面存在不足。
Key Takeaways
- 在线内容的毒性问题日益严重,需要关注。
- TRuST数据集旨在提高毒性检测能力,包括多种目标群体,如种族、性别、宗教、残疾和政治等。
- 数据集包含人类/机器注释和由机器生成的数据。
- 评估了大型语言模型(LLMs)在三个任务上的表现:毒性检测、目标群体识别和毒性跨度提取。
- 微调模型在任务上的表现优于零样本和少样本提示。
- 对于某些社会群体的性能仍然较低,表明语言模型在某些方面的表现有待提升。
点此查看论文截图
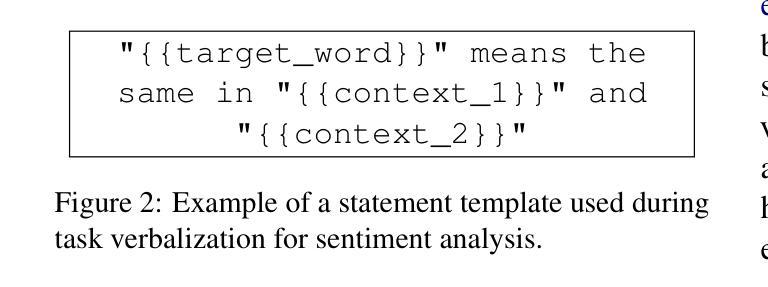
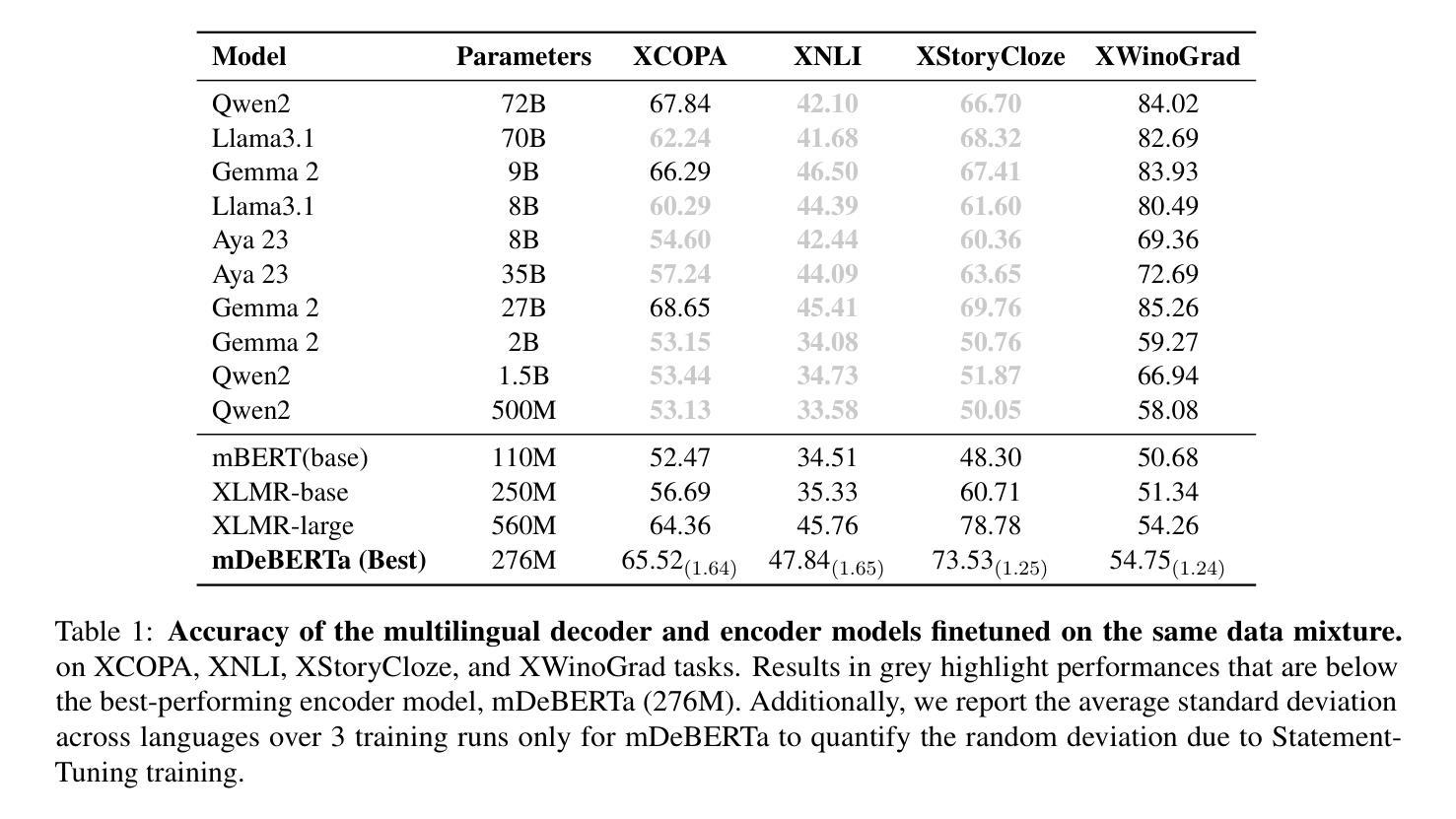
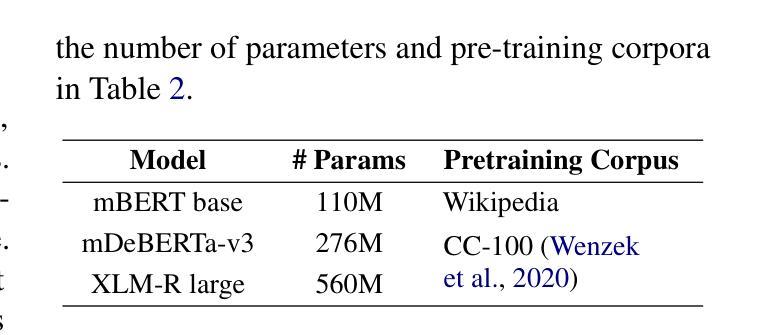
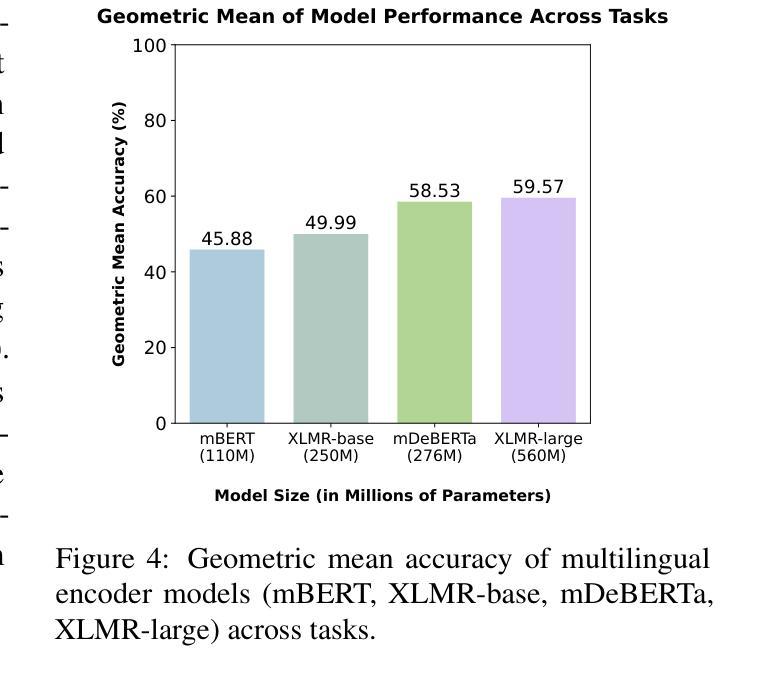
Statement-Tuning Enables Efficient Cross-lingual Generalization in Encoder-only Models
Authors:Ahmed Elshabrawy, Thanh-Nhi Nguyen, Yeeun Kang, Lihan Feng, Annant Jain, Faadil Abdullah Shaikh, Jonibek Mansurov, Mohamed Fazli Mohamed Imam, Jesus-German Ortiz-Barajas, Rendi Chevi, Alham Fikri Aji
Large Language Models (LLMs) excel in zero-shot and few-shot tasks, but achieving similar performance with encoder-only models like BERT and RoBERTa has been challenging due to their architecture. However, encoders offer advantages such as lower computational and memory costs. Recent work adapts them for zero-shot generalization using Statement Tuning, which reformulates tasks into finite templates. We extend this approach to multilingual NLP, exploring whether encoders can achieve zero-shot cross-lingual generalization and serve as efficient alternatives to memory-intensive LLMs for low-resource languages. Our results show that state-of-the-art encoder models generalize well across languages, rivaling multilingual LLMs while being more efficient. We also analyze multilingual Statement Tuning dataset design, efficiency gains, and language-specific generalization, contributing to more inclusive and resource-efficient NLP models. We release our code and models.
大型语言模型(LLMs)在零样本和少样本任务上表现出色,但由于其架构特点,使用编码器模型(如BERT和RoBERTa)实现类似性能一直是一个挑战。然而,编码器具有计算和内存成本低的优势。最近的工作通过Statement Tuning将其适应于零样本泛化,将任务重新格式化为有限的模板。我们将此方法扩展到多语种自然语言处理,探索编码器是否可以实现零样本跨语言泛化,并作为内存密集型大型语言模型的高效替代方案,用于低资源语言。我们的结果表明,最先进的编码器模型在跨语言方面的泛化效果很好,与多语种的大型语言模型相比具有更高的效率。我们还分析了多语种Statement Tuning数据集的设计、效率提升和语言特定泛化,为构建更具包容性和资源效率的自然语言处理模型做出贡献。我们公开了我们的代码和模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACL 2025 (Findings)
Summary
大语言模型(LLMs)在零样本和少样本任务上表现出卓越性能,但由于架构限制,使用编码器模型(如BERT和RoBERTa)实现类似性能一直具有挑战性。然而,编码器具有低计算和内存成本的优势。最近的工作使用语句调整法将其适应于零样本泛化,将任务重新制定为有限模板。我们将其扩展到多语言自然语言处理(NLP),探讨编码器是否可以实现零样本跨语言泛化,并作为内存密集型LLMs的替代方案,在低资源语言中实现高效服务。我们的结果表明,最先进的编码器模型跨语言泛化效果良好,可与多语言LLMs相抗衡,同时效率更高。我们还分析了多语言语句调整数据集的设计、效率增益和语言特定泛化,为更具包容性和资源效率的自然语言处理模型做出贡献。我们公开了代码和模型。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型在零样本和少样本任务上表现出卓越性能,但编码器模型实现类似性能具有挑战性。
- 编码器模型具有低计算和内存成本的优势。
- 语句调整法被用于适应编码器模型的零样本泛化,将任务转化为有限模板。
- 将编码器模型扩展到多语言NLP,实现零样本跨语言泛化。
- 最先进的编码器模型在多语言环境下表现出良好的泛化性能,效率高于多语言大型语言模型。
- 分析表明,多语言语句调整数据集设计、效率增益和语言特定泛化是改进NLP模型的重要方向。
点此查看论文截图

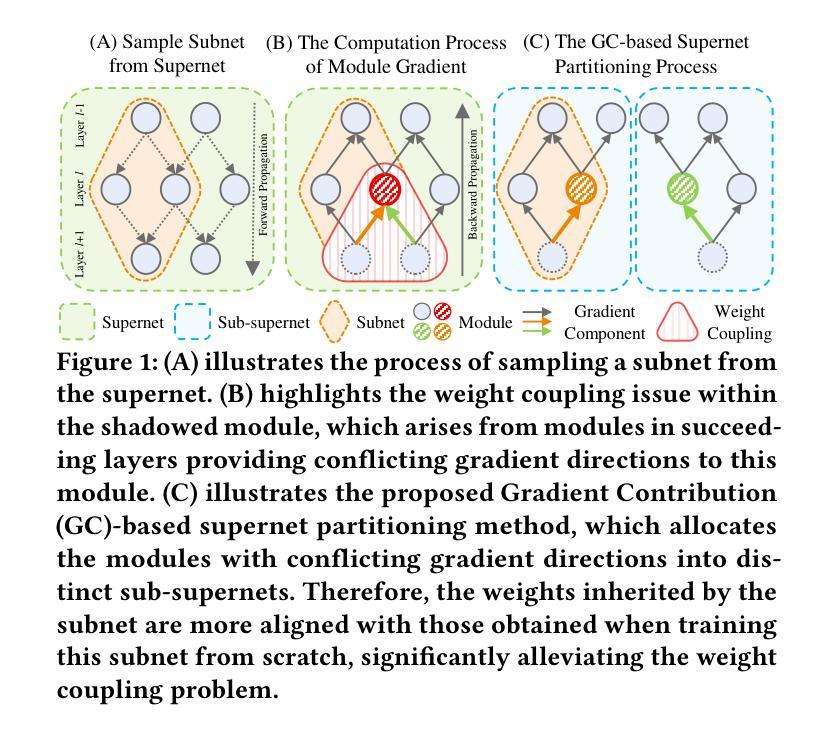
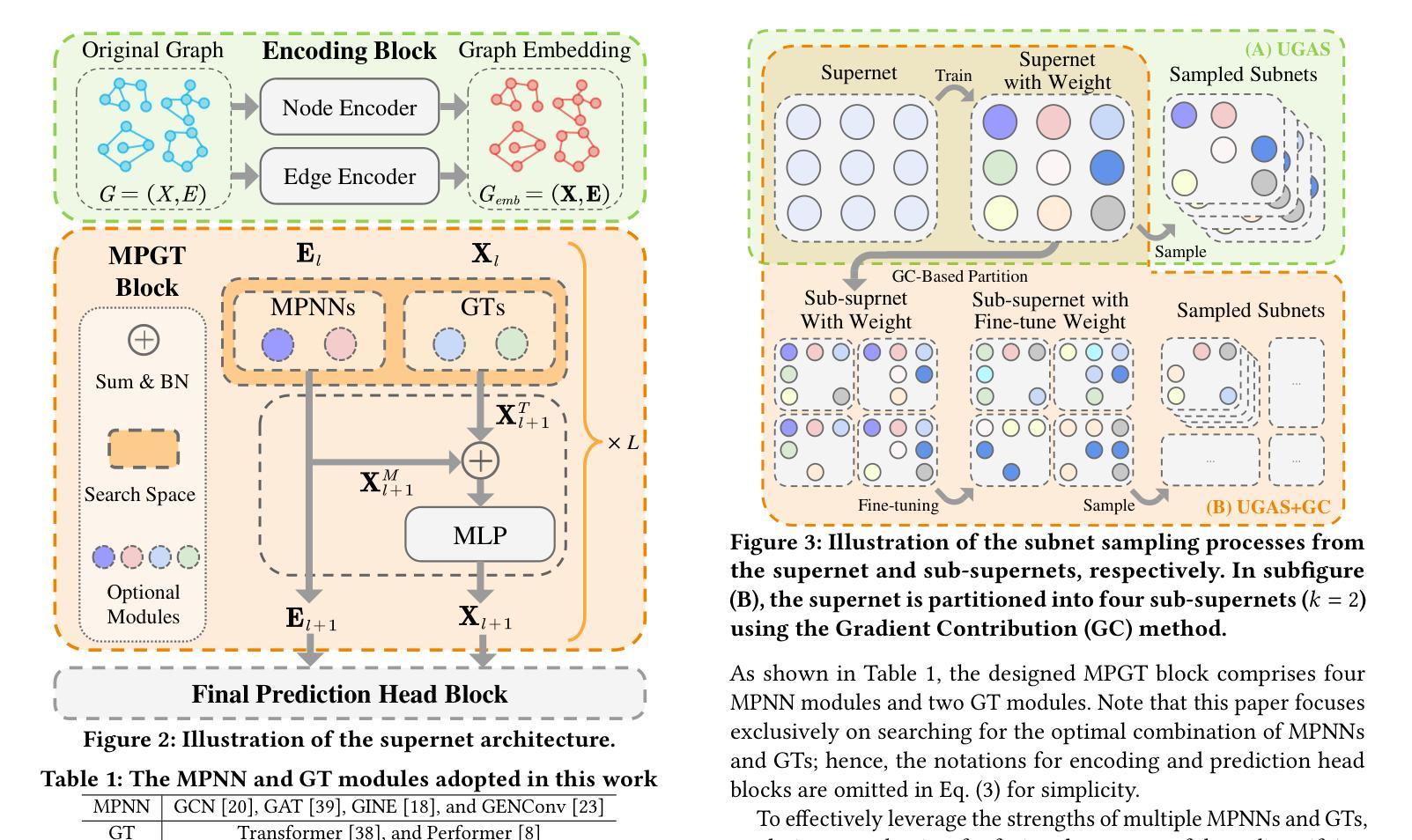
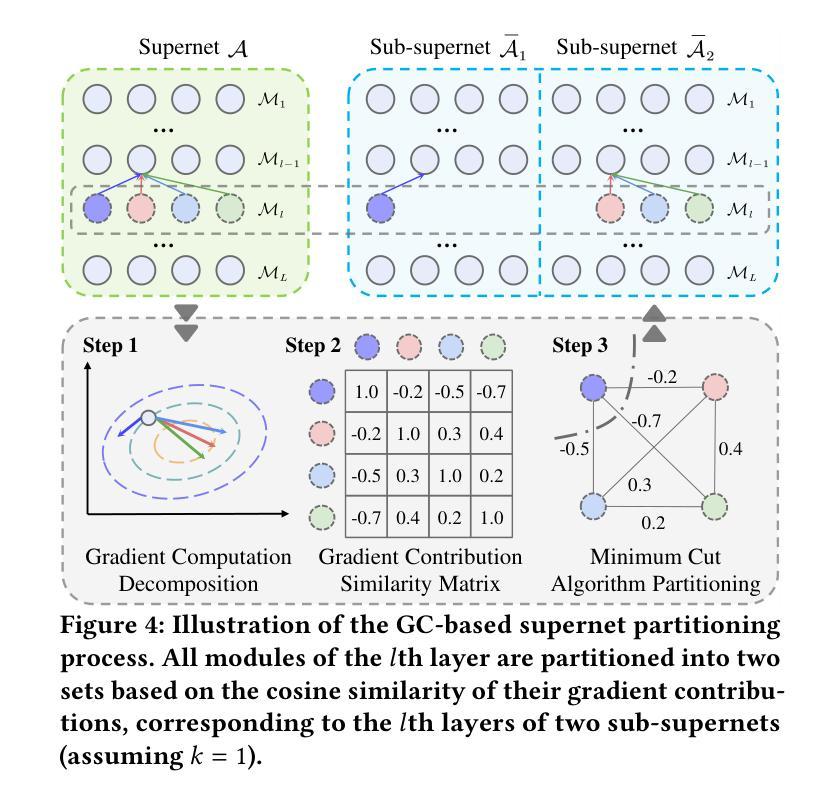
Towards Efficient Few-shot Graph Neural Architecture Search via Partitioning Gradient Contribution
Authors:Wenhao Song, Xuan Wu, Bo Yang, You Zhou, Yubin Xiao, Yanchun Liang, Hongwei Ge, Heow Pueh Lee, Chunguo Wu
To address the weight coupling problem, certain studies introduced few-shot Neural Architecture Search (NAS) methods, which partition the supernet into multiple sub-supernets. However, these methods often suffer from computational inefficiency and tend to provide suboptimal partitioning schemes. To address this problem more effectively, we analyze the weight coupling problem from a novel perspective, which primarily stems from distinct modules in succeeding layers imposing conflicting gradient directions on the preceding layer modules. Based on this perspective, we propose the Gradient Contribution (GC) method that efficiently computes the cosine similarity of gradient directions among modules by decomposing the Vector-Jacobian Product during supernet backpropagation. Subsequently, the modules with conflicting gradient directions are allocated to distinct sub-supernets while similar ones are grouped together. To assess the advantages of GC and address the limitations of existing Graph Neural Architecture Search methods, which are limited to searching a single type of Graph Neural Networks (Message Passing Neural Networks (MPNNs) or Graph Transformers (GTs)), we propose the Unified Graph Neural Architecture Search (UGAS) framework, which explores optimal combinations of MPNNs and GTs. The experimental results demonstrate that GC achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in supernet partitioning quality and time efficiency. In addition, the architectures searched by UGAS+GC outperform both the manually designed GNNs and those obtained by existing NAS methods. Finally, ablation studies further demonstrate the effectiveness of all proposed methods.
为了解决权重耦合问题,一些研究引入了小样本神经网络架构搜索(NAS)方法,将超网分割成多个子超网。然而,这些方法通常存在计算效率低下的问题,并且往往提供次优的分割方案。为了更有效地解决这个问题,我们从一个新的角度分析了权重耦合问题,其主要源于后续层中的不同模块对前一层模块施加冲突的梯度方向。基于此,我们提出了梯度贡献(GC)方法,它通过分解超网反向传播中的向量-雅可比乘积,有效地计算了模块之间梯度方向的余弦相似性。随后,具有冲突梯度方向的模块被分配到不同的子超网中,而相似的模块则组合在一起。为了评估GC的优势,并解决现有图神经网络架构搜索方法的局限性(这些方法仅限于搜索单一类型的图神经网络,如消息传递神经网络(MPNNs)或图转换器(GTs)),我们提出了统一图神经网络架构搜索(UGAS)框架,该框架探索了MPNNs和GTs的最佳组合。实验结果表明,GC在超网分割质量和时间效率方面达到了最新水平。此外,通过UGAS+GC搜索的架构在性能上超过了手动设计的GNNs和现有NAS方法得到的架构。最后,消融研究进一步证明了所有提出方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by SIGKDD 2025
Summary
本文研究了基于神经网络架构搜索(NAS)的权重耦合问题,并提出了全新的视角和方法来解决该问题。通过分解向量雅可比乘积,提出了梯度贡献(GC)方法来计算模块间的梯度方向相似性,优化网络结构中的子超网划分,从而提升了网络的性能和效率。此外,为解决现有图形神经网络架构搜索方法只针对单一类型的图形神经网络的局限性,本文提出了统一图形神经网络架构搜索(UGAS)框架,结合消息传递神经网络和图形转换器,以寻找最佳组合方式。实验结果表明,GC方法在超网划分质量和时间效率方面达到了最优水平,而UGAS+GC搜索到的架构在性能上超过了手动设计的GNN和现有NAS方法。最后的消融研究进一步验证了所有方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 研究针对神经网络架构搜索中的权重耦合问题,提出了全新的视角和方法来解决该问题。
- 通过梯度贡献(GC)方法计算模块间的梯度方向相似性,优化子超网划分。
- GC方法提高了超网划分质量和时间效率,达到最优水平。
- UGAS框架结合了消息传递神经网络和图形转换器,以寻找最佳组合方式,解决了现有图形神经网络架构搜索方法的局限性。
- UGAS+GC搜索到的架构性能超过了手动设计的GNN和现有NAS方法。
点此查看论文截图


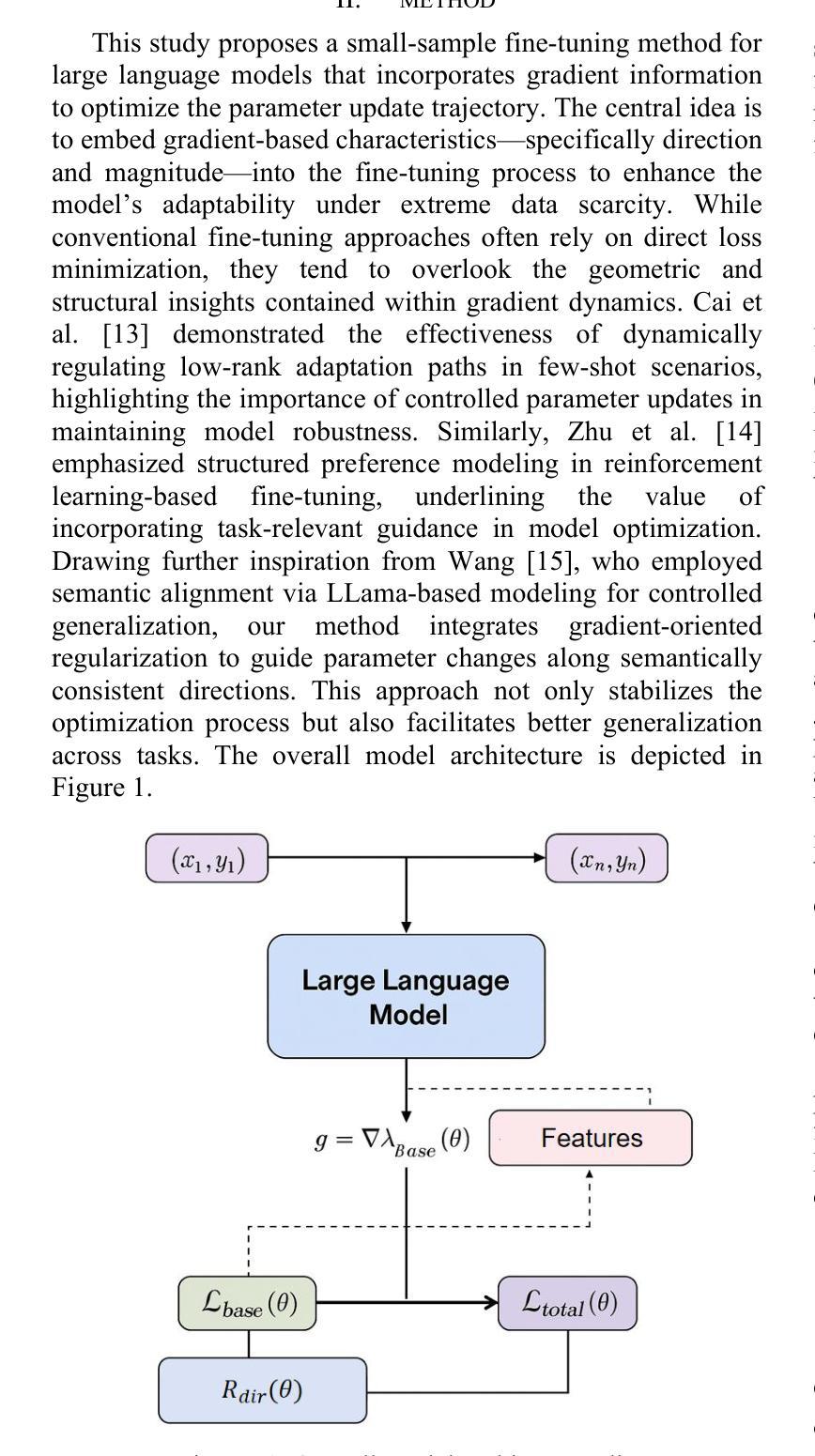
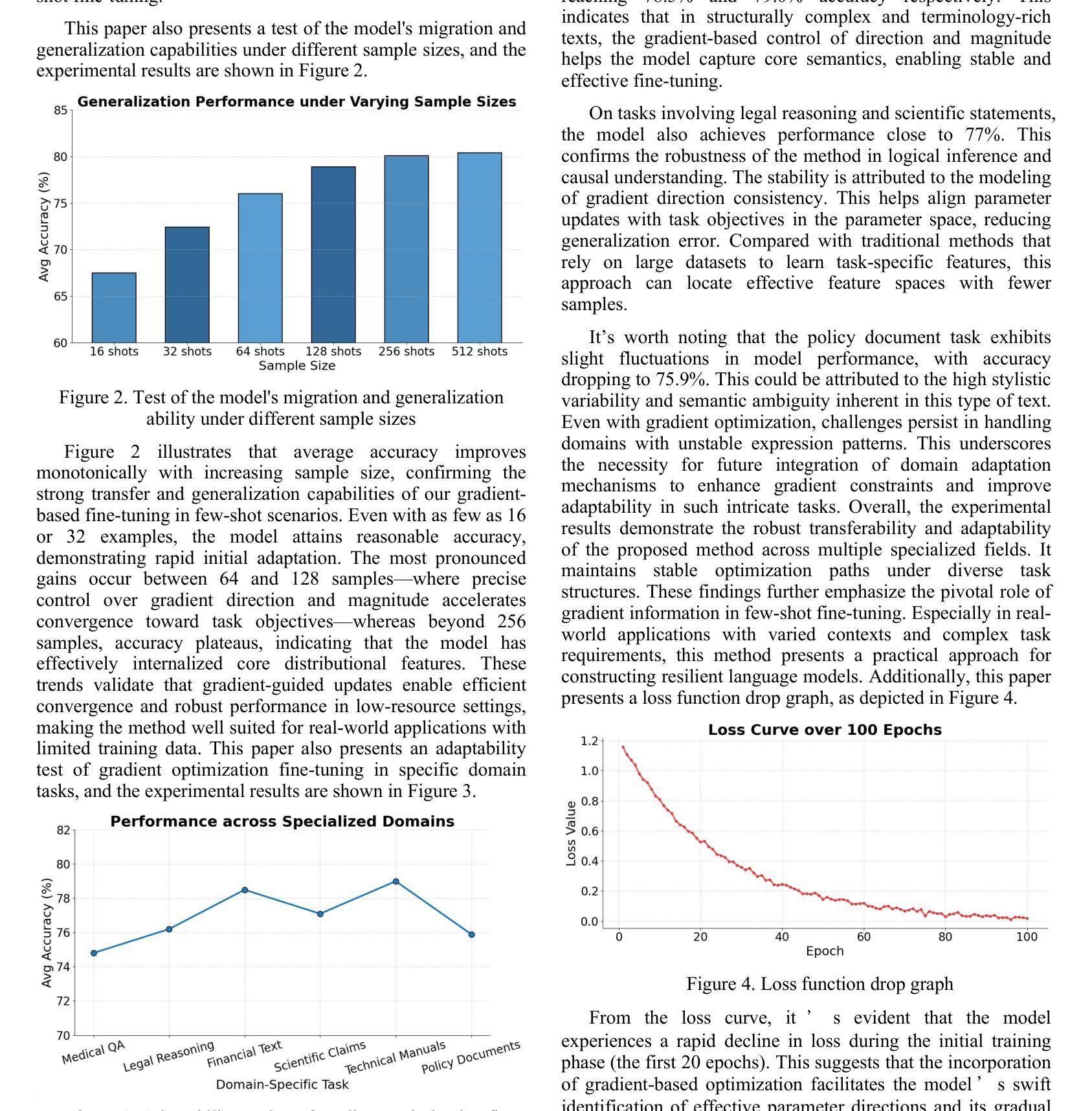
Structured Gradient Guidance for Few-Shot Adaptation in Large Language Models
Authors:Hongye Zheng, Yichen Wang, Ray Pan, Guiran Liu, Binrong Zhu, Hanlu Zhang
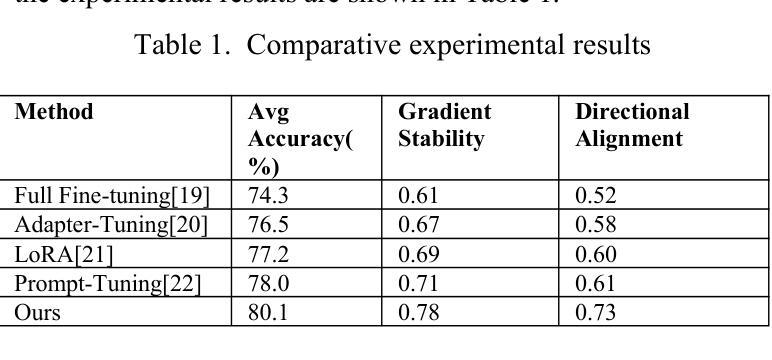
This paper presents a gradient-informed fine-tuning method for large language models under few-shot conditions. The goal is to enhance task adaptability and training stability when data is limited. The method builds on a base loss function and introduces two gradient-related regularization terms. The first enforces gradient direction consistency to guide parameter updates along task-relevant directions and prevent drift. The second controls gradient magnitude to avoid abnormal updates. Together, these components support a more efficient and stable optimization path. To further improve cross-task generalization, the method incorporates a gradient alignment mechanism. This mechanism measures the consistency between optimization directions of the source and target tasks. It enhances fine-tuning performance in multi-task and cross-domain scenarios. Across various natural language understanding tasks, the method outperforms existing fine-tuning strategies in average accuracy, gradient stability, and directional alignment. Empirical evaluations under different sample sizes and domain-specific tasks confirm the method’s robustness and broad applicability in low-resource environments. In particular, the method shows clear advantages in controlling parameter update paths. The results demonstrate that a gradient-based fine-tuning framework can effectively leverage the representational power of large language models. It ensures training stability while reducing dependence on large volumes of labeled data.
本文提出了一种基于梯度的微调方法,用于在少量样本条件下对大语言模型进行微调。目标是提高任务适应性和训练稳定性,特别是在数据有限的情况下。该方法基于基础损失函数,并引入两个与梯度相关的正则化项。第一项强制执行梯度方向一致性,以引导参数更新沿着任务相关方向进行,防止漂移。第二项控制梯度幅度,以避免异常更新。这两项共同支持更高效稳定的优化路径。为了进一步提高跨任务的泛化能力,该方法还融入了一种梯度对齐机制。该机制衡量源任务和目标任务优化方向的一致性,在多任务和跨域场景中提高了微调性能。在各种自然语言理解任务中,该方法在平均准确率、梯度稳定性和方向对齐方面均优于现有的微调策略。在不同样本量和特定领域的任务上的实证评估证明了该方法在低资源环境下的稳健性和广泛适用性。尤其是,该方法在控制参数更新路径方面显示出明显优势。结果表明,基于梯度的微调框架可以有效地利用大型语言模型的表示能力,确保训练稳定性,同时减少对大量标记数据的依赖。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于梯度的微调方法,用于在数据有限的情况下对大型语言模型进行微调。该方法旨在提高任务适应性和训练稳定性,通过基础损失函数和两个与梯度相关的正则化项来实现。第一个项通过强制梯度方向一致性来引导参数更新沿着任务相关方向进行,防止漂移;第二个项控制梯度幅度,避免异常更新。此外,该方法还引入了一种梯度对齐机制,以提高跨任务的泛化能力。在多个自然语言理解任务上,该方法在平均准确率、梯度稳定性和方向对齐方面优于现有的微调策略。该方法在不同样本量和特定领域的任务上表现出稳健性和广泛的应用性,特别是在控制参数更新路径方面显示出明显优势。研究结果表明,基于梯度的微调框架可以有效地利用大型语言模型的表示能力,确保训练稳定性,同时减少对大量标记数据的依赖。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种基于梯度的微调方法,适用于数据有限情况下的大型语言模型。
- 方法建立在基础损失函数上,并引入两个与梯度相关的正则化项,以提高任务适应性和训练稳定性。
- 梯度方向一致性的强制实施引导参数更新沿任务相关方向进行,防止参数漂移。
- 梯度幅度的控制避免了异常更新,确保了更稳定和高效的优化路径。
- 引入的梯度对齐机制提高了跨任务的泛化能力,尤其在多任务和跨域场景中表现优异。
- 在多个自然语言理解任务上,该方法在平均准确率、梯度稳定性和方向对齐方面超越现有微调策略。
点此查看论文截图

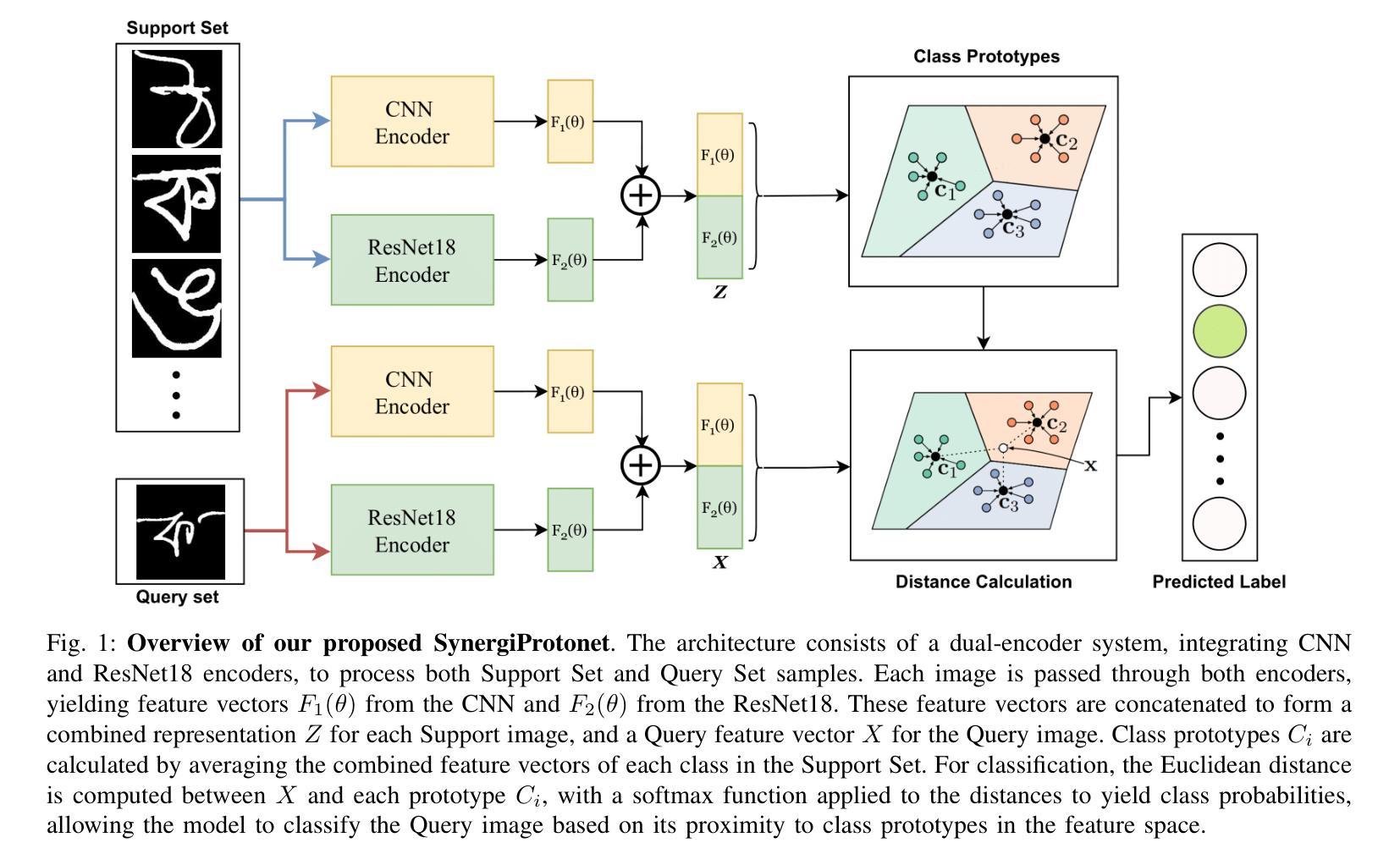
Performance Analysis of Few-Shot Learning Approaches for Bangla Handwritten Character and Digit Recognition
Authors:Mehedi Ahamed, Radib Bin Kabir, Tawsif Tashwar Dipto, Mueeze Al Mushabbir, Sabbir Ahmed, Md. Hasanul Kabir
This study investigates the performance of few-shot learning (FSL) approaches in recognizing Bangla handwritten characters and numerals using limited labeled data. It demonstrates the applicability of these methods to scripts with intricate and complex structures, where dataset scarcity is a common challenge. Given the complexity of Bangla script, we hypothesize that models performing well on these characters can generalize effectively to languages of similar or lower structural complexity. To this end, we introduce SynergiProtoNet, a hybrid network designed to improve the recognition accuracy of handwritten characters and digits. The model integrates advanced clustering techniques with a robust embedding framework to capture fine-grained details and contextual nuances. It leverages multi-level (both high- and low-level) feature extraction within a prototypical learning framework. We rigorously benchmark SynergiProtoNet against several state-of-the-art few-shot learning models: BD-CSPN, Prototypical Network, Relation Network, Matching Network, and SimpleShot, across diverse evaluation settings including Monolingual Intra-Dataset Evaluation, Monolingual Inter-Dataset Evaluation, Cross-Lingual Transfer, and Split Digit Testing. Experimental results show that SynergiProtoNet consistently outperforms existing methods, establishing a new benchmark in few-shot learning for handwritten character and digit recognition. The code is available on GitHub: https://github.com/MehediAhamed/SynergiProtoNet.
本研究探讨了小样学习(FSL)方法在利用有限标记数据识别孟加拉语手写字符和数字时的性能。它证明了这些方法对于具有复杂结构的脚本的适用性,其中数据集稀缺是一个常见的挑战。考虑到孟加拉脚本的复杂性,我们假设在这些字符上表现良好的模型可以有效地推广到结构相似或较低的语言。为此,我们引入了SynergiProtoNet,这是一个混合网络,旨在提高手写字符和数字的识别准确率。该模型将先进的聚类技术与稳健的嵌入框架相结合,以捕捉细微的细节和上下文细微差别。它在原型学习框架内利用多层次(高级和低级)特征提取。我们对SynergiProtoNet与几种最先进的小样学习模型进行了严格的基准测试,包括BD-CSPN、原型网络、关系网络、匹配网络和SimpleShot,在不同的评估环境设置下,包括单语内数据集评估、单语间数据集评估、跨语言迁移和分割数字测试。实验结果表明,SynergiProtoNet始终优于现有方法,在手写字符和数字的小样学习识别方面建立了新的基准。代码可在GitHub上找到:https://github.com/MehediAhamed/SynergiProtoNet。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了小样本学习(FSL)方法在识别孟加拉语手写字符和数字方面的性能,并利用有限标记数据进行了实验。研究展示了这些方法在具有复杂结构的脚本中的应用,其中数据集稀缺是一个常见挑战。针对孟加拉语脚本的复杂性,研究假设在字符上表现良好的模型可以推广到结构相似或较低的语言。为此,研究提出了一种名为SynergiProtoNet的混合网络,旨在提高手写字符和数字的识别准确性。该模型结合了先进的聚类技术和稳健的嵌入框架,以捕捉细微的细节和上下文细微差别。它在原型学习框架内利用多层次(高低层次)的特征提取。本研究对SynergiProtoNet与几种先进的小样本学习模型进行了严格的基准测试,包括BD-CSPN、原型网络、关系网络、匹配网络和SimpleShot等。实验结果表明,SynergiProtoNet在多种评估设置下均表现优异,为手写字符和数字识别的小样本学习树立了新基准。相关代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 研究探讨了小样本学习(FSL)在识别孟加拉语手写字符和数字方面的应用。
- 提出了一种名为SynergiProtoNet的混合网络模型,用于提高手写字符和数字的识别准确性。
- SynergiProtoNet结合了先进的聚类技术和稳健的嵌入框架,捕捉细微的细节和上下文信息。
- 该模型在原型学习框架内利用多层次特征提取。
- 研究对SynergiProtoNet与多种先进的小样本学习模型进行了基准测试。
- 实验结果表明,SynergiProtoNet在手写字符和数字识别的性能上超越了现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

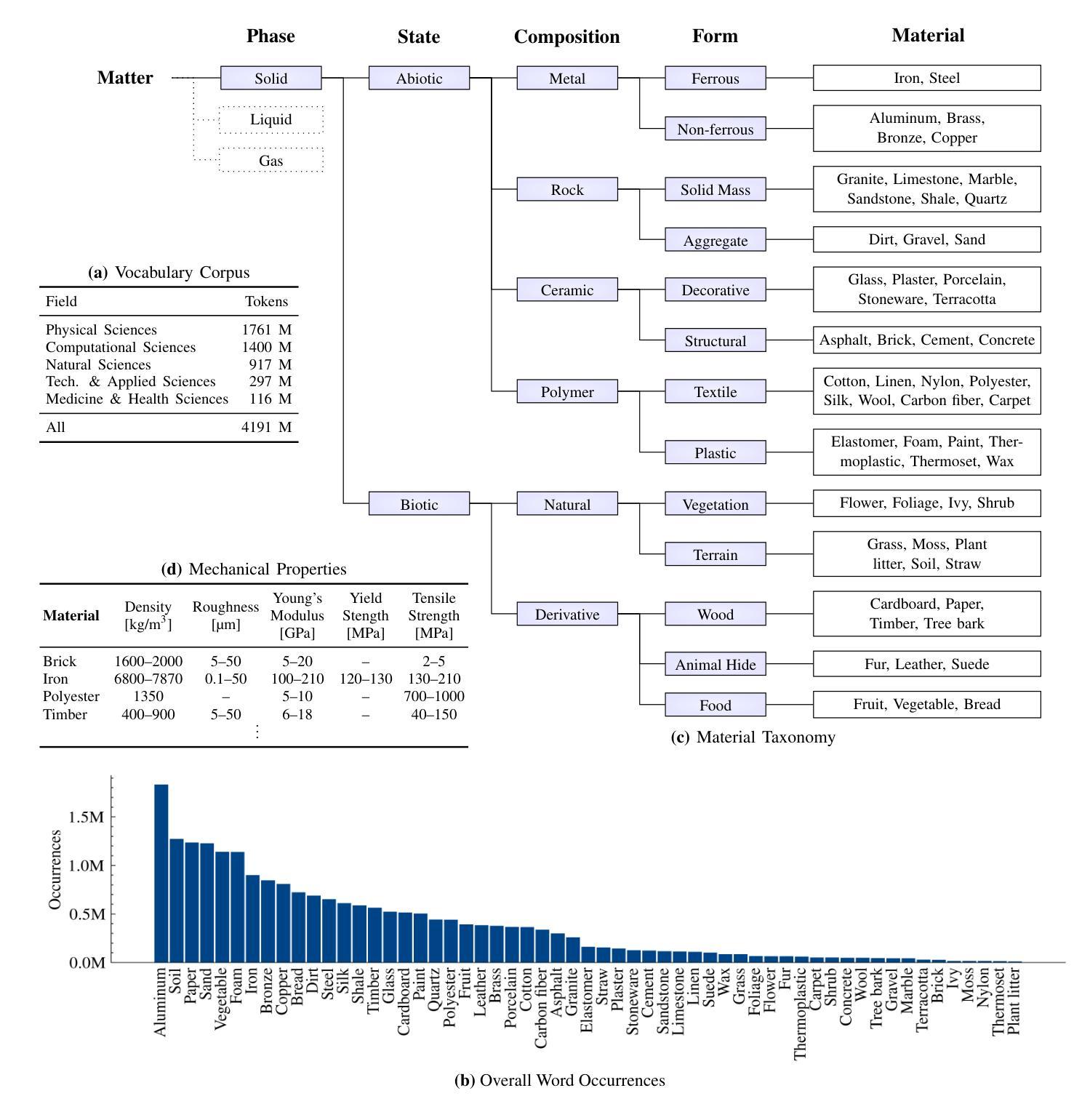
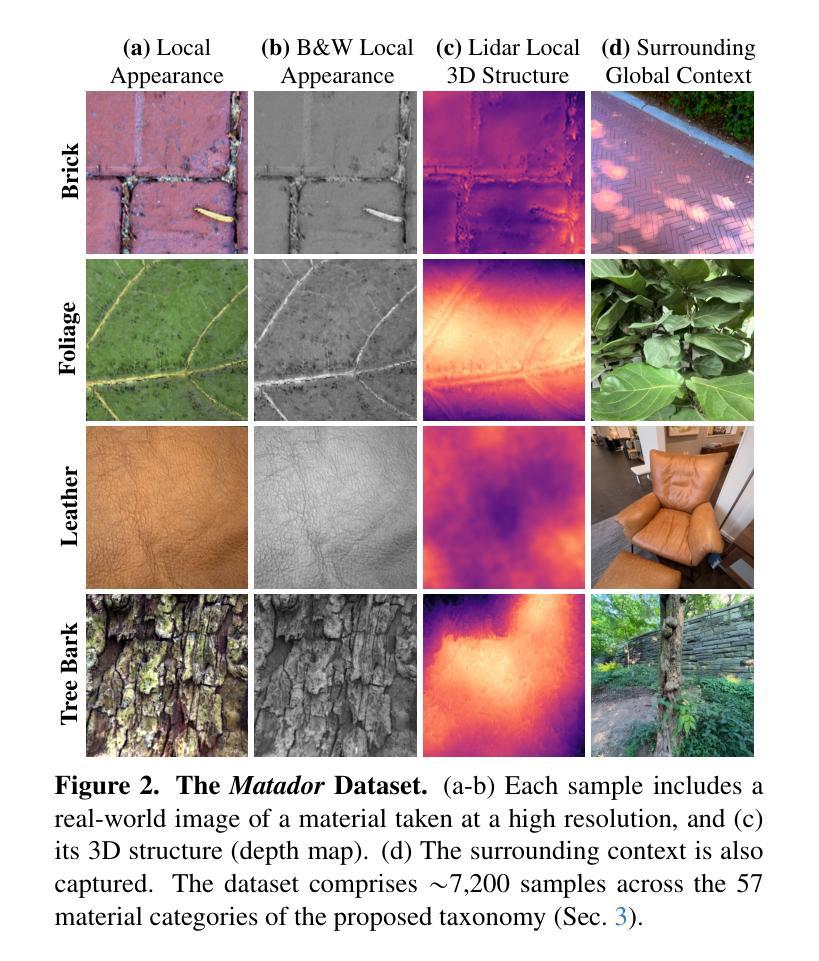
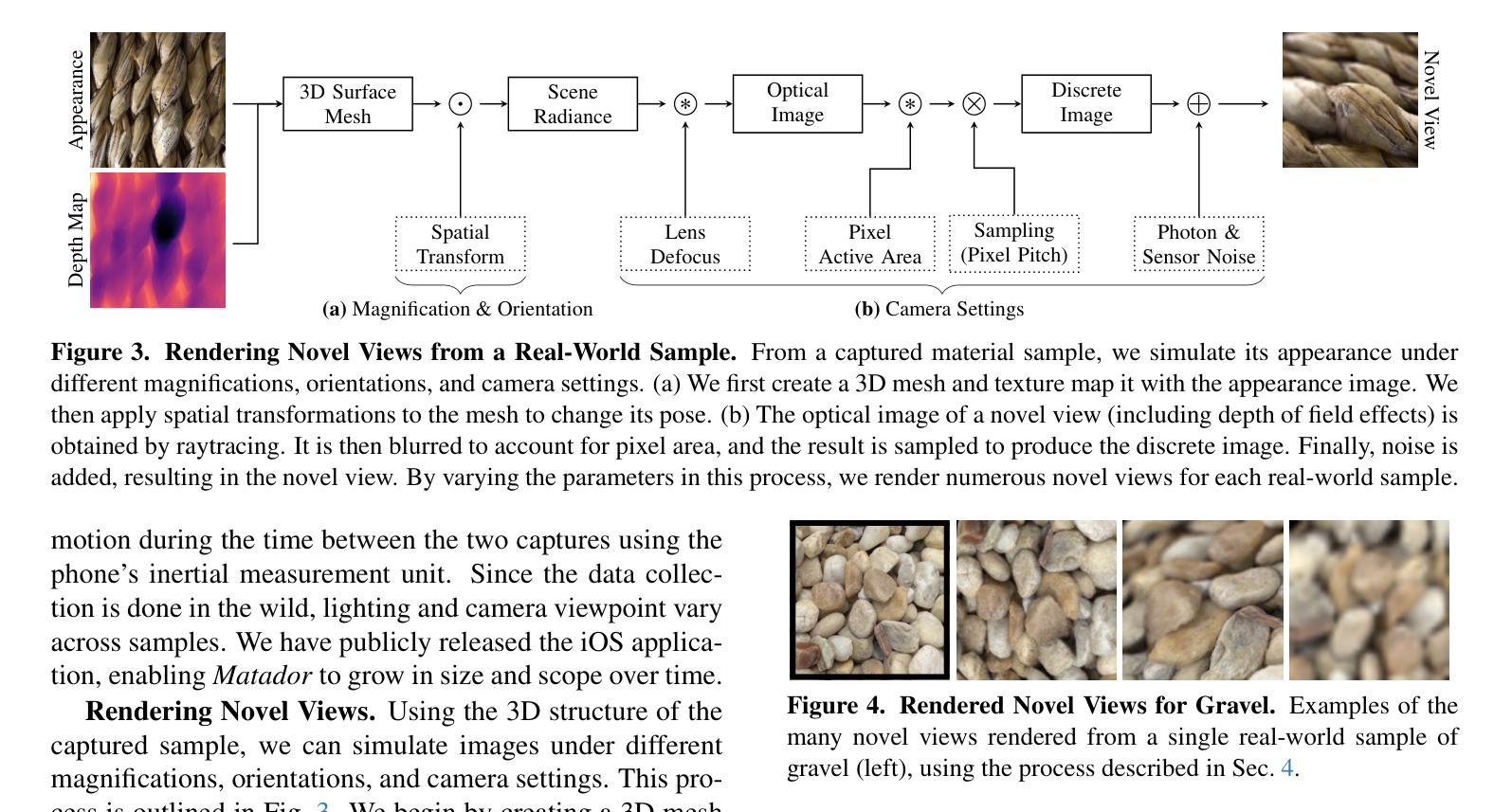
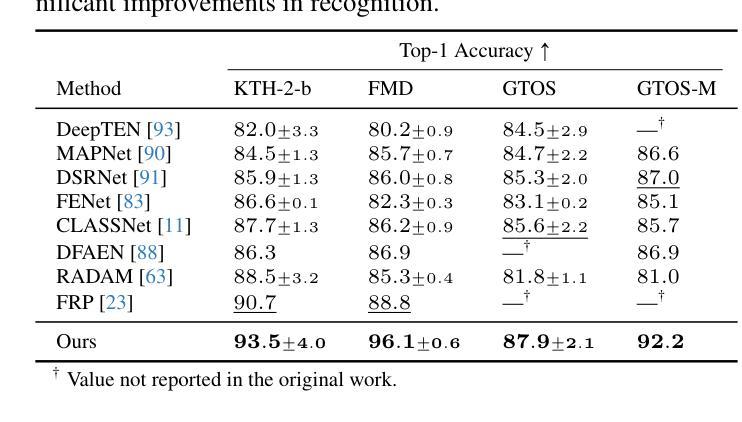
Hierarchical Material Recognition from Local Appearance
Authors:Matthew Beveridge, Shree K. Nayar
We introduce a taxonomy of materials for hierarchical recognition from local appearance. Our taxonomy is motivated by vision applications and is arranged according to the physical traits of materials. We contribute a diverse, in-the-wild dataset with images and depth maps of the taxonomy classes. Utilizing the taxonomy and dataset, we present a method for hierarchical material recognition based on graph attention networks. Our model leverages the taxonomic proximity between classes and achieves state-of-the-art performance. We demonstrate the model’s potential to generalize to adverse, real-world imaging conditions, and that novel views rendered using the depth maps can enhance this capability. Finally, we show the model’s capacity to rapidly learn new materials in a few-shot learning setting.
我们介绍了一种基于局部外观进行层次识别的材料分类法。我们的分类法受到视觉应用的启发,并根据材料的物理特征进行排列。我们贡献了一个包含分类图像和深度图的多样化、野外数据集。利用分类法和数据集,我们提出了一种基于图注意力网络的层次材料识别方法。我们的模型利用类之间的分类接近性,实现了最先进的性能。我们证明了该模型在恶劣的、真实世界的成像条件下具有泛化潜力,并且使用深度图呈现的新视角可以增强这种能力。最后,我们展示了该模型在少量学习条件下快速学习新材料的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于局部外观的用于层次识别的材料分类体系。该分类体系受视觉应用的启发,根据材料的物理特征进行排列组合。此外,本文贡献了一个包含分类图像和深度图的野生数据集。基于该分类体系和数据集,提出了一种基于图注意力网络的层次材料识别方法。该方法利用类之间的分类邻近性,实现了最先进的性能。展示了该模型在恶劣的、真实世界的成像条件下泛化的潜力,并使用深度图渲染的新视角可以增强这一能力。最后,展示了该模型在少样本学习环境下快速学习新材料的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种基于物理特性的材料分类体系,适用于视觉应用。
- 提供了一个包含图像和深度图的真实世界数据集,用于材料的层次识别。
- 提出了一种基于图注意力网络的层次材料识别方法。
- 模型利用类之间的分类邻近性,实现了卓越的性能。
- 模型在恶劣的、真实世界的成像条件下具有良好的泛化能力。
- 使用深度图渲染的新视角可以增强模型的识别能力。
点此查看论文截图

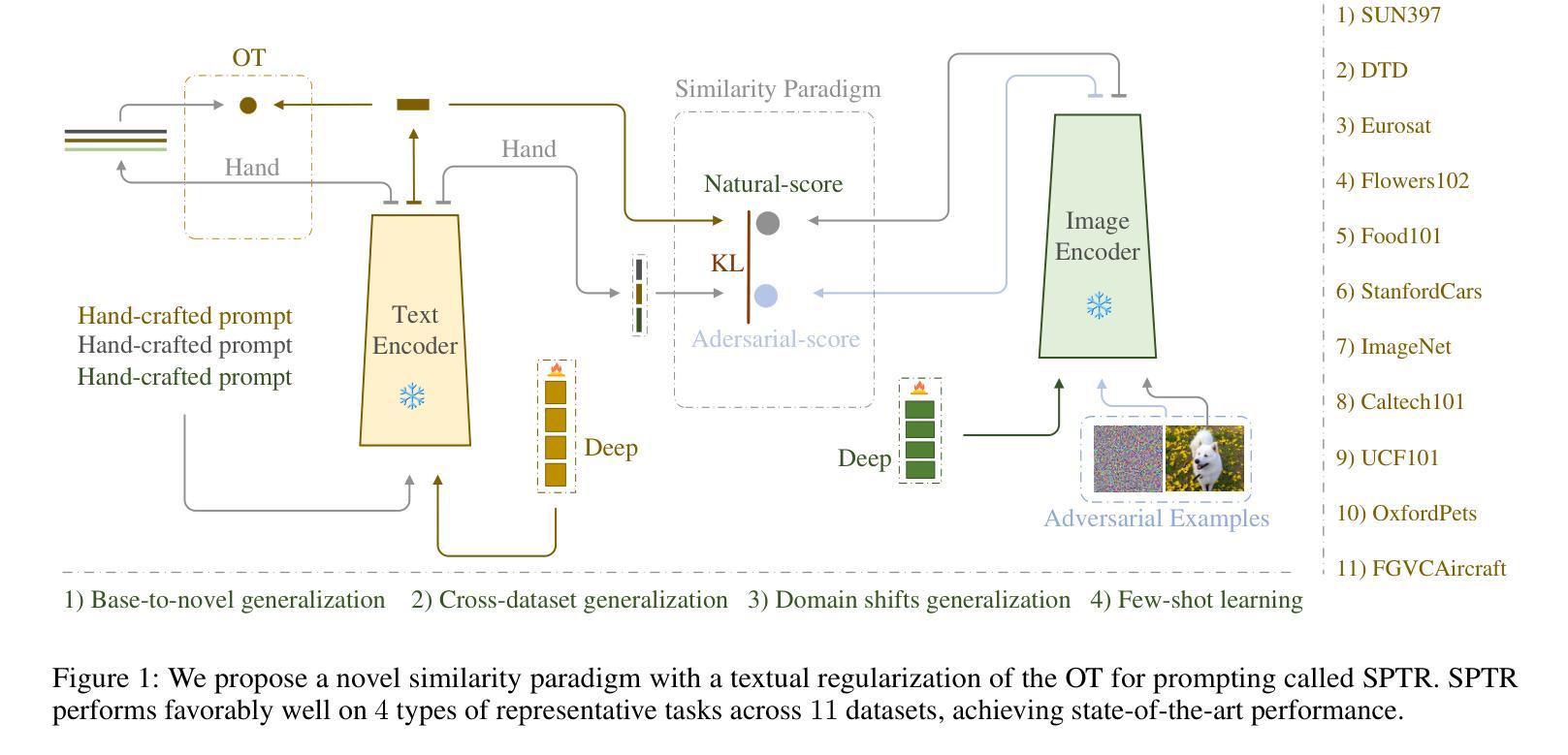
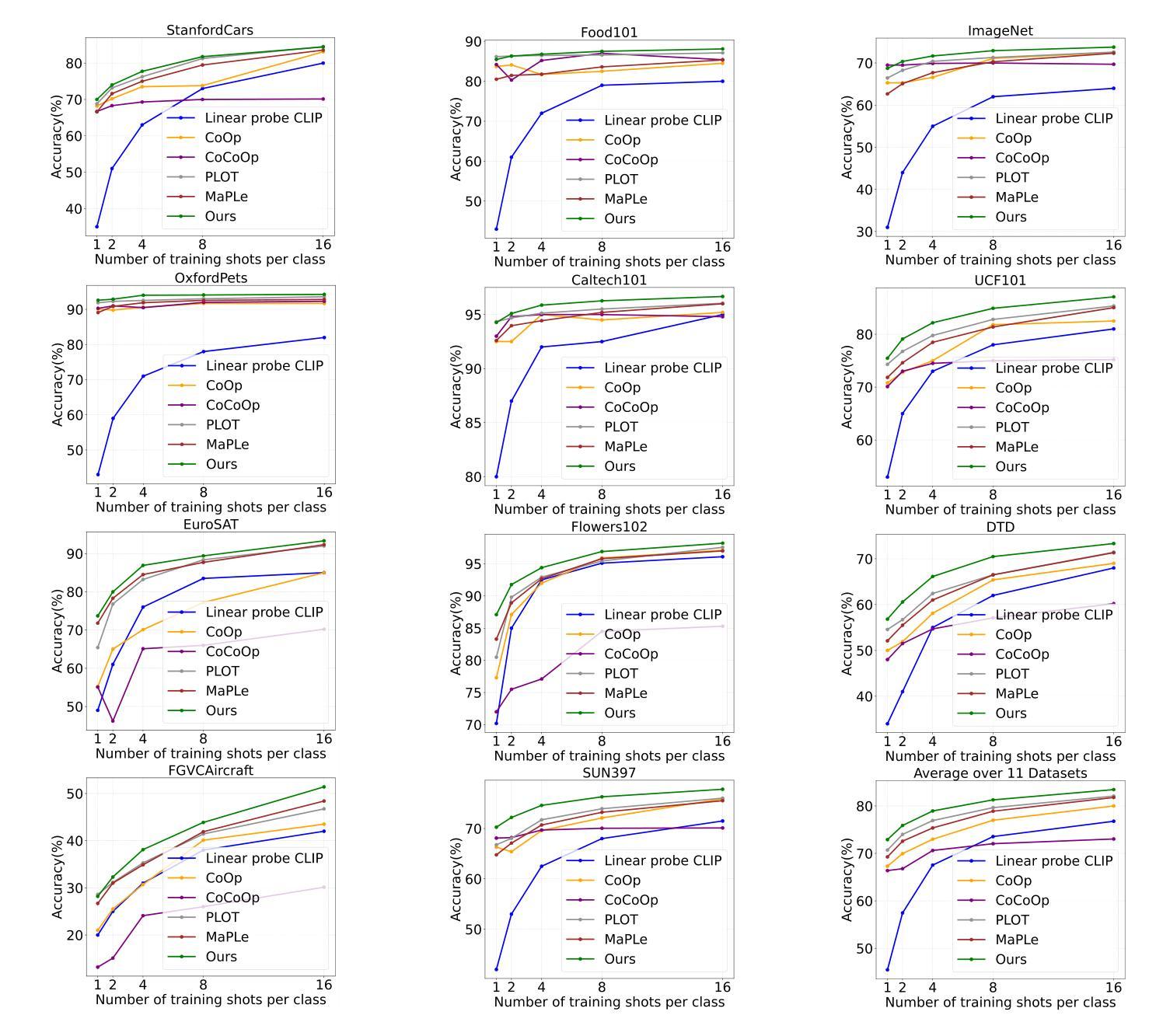
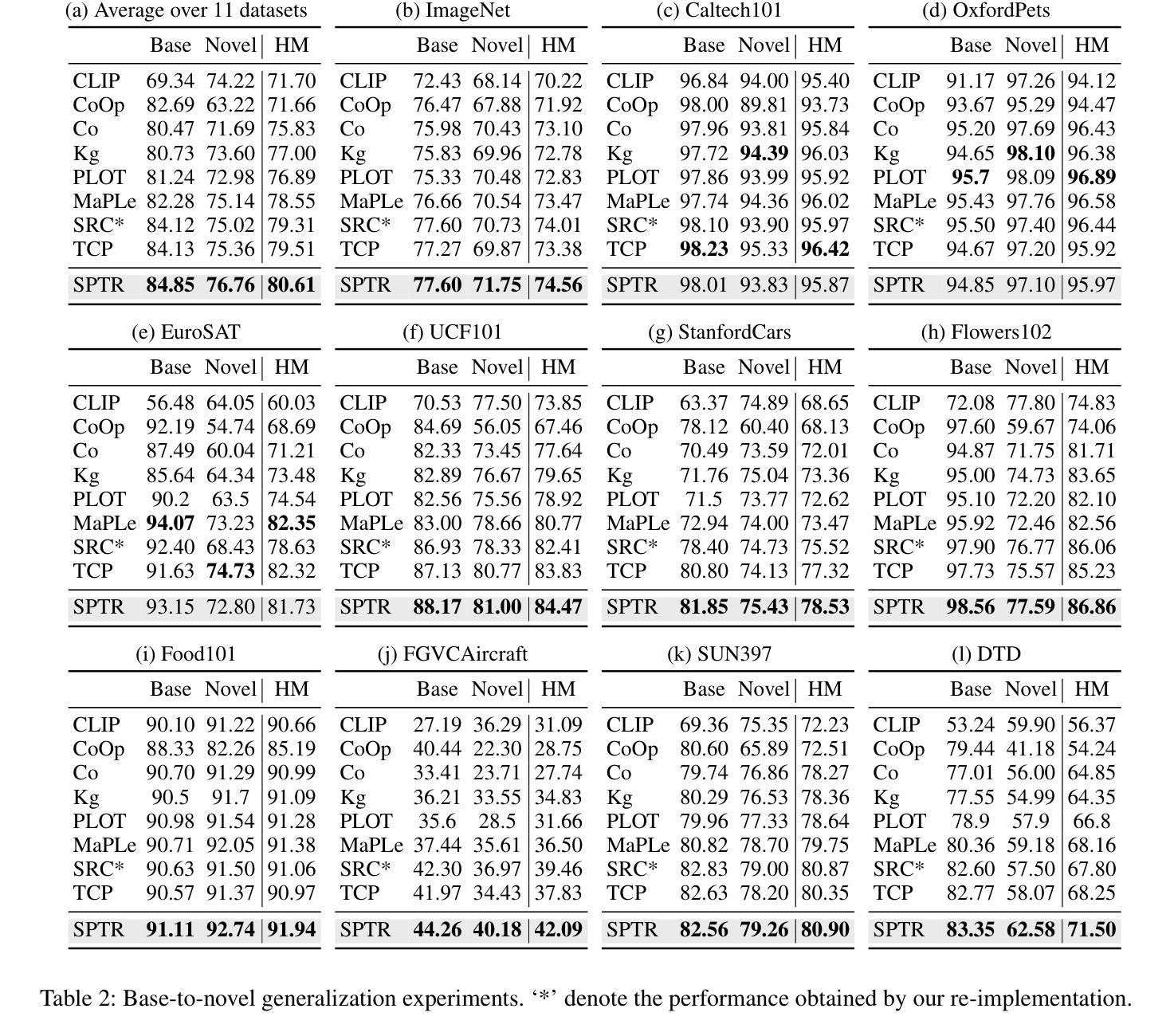
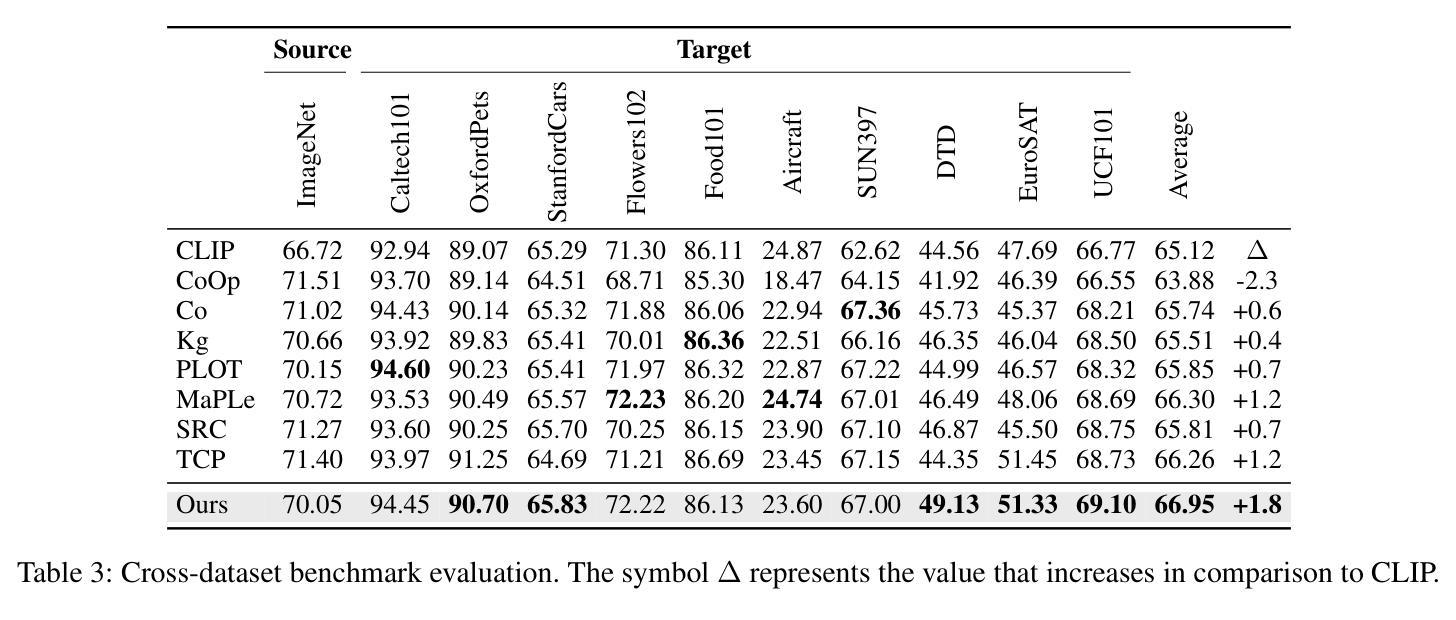
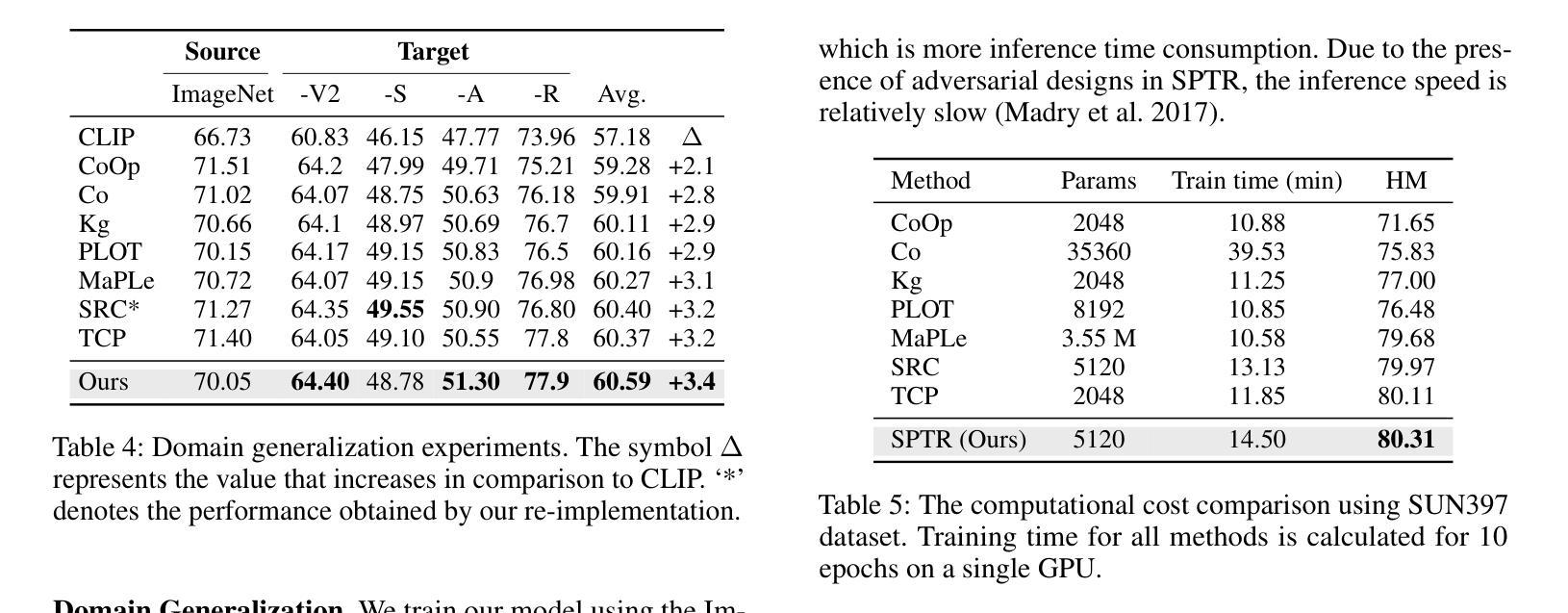
A Similarity Paradigm Through Textual Regularization Without Forgetting
Authors:Fangming Cui, Jan Fong, Rongfei Zeng, Xinmei Tian, Jun Yu
Prompt learning has emerged as a promising method for adapting pre-trained visual-language models (VLMs) to a range of downstream tasks. While optimizing the context can be effective for improving performance on specific tasks, it can often lead to poor generalization performance on unseen classes or datasets sampled from different distributions. It may be attributed to the fact that textual prompts tend to overfit downstream data distributions, leading to the forgetting of generalized knowledge derived from hand-crafted prompts. In this paper, we propose a novel method called Similarity Paradigm with Textual Regularization (SPTR) for prompt learning without forgetting. SPTR is a two-pronged design based on hand-crafted prompts that is an inseparable framework. 1) To avoid forgetting general textual knowledge, we introduce the optimal transport as a textual regularization to finely ensure approximation with hand-crafted features and tuning textual features. 2) In order to continuously unleash the general ability of multiple hand-crafted prompts, we propose a similarity paradigm for natural alignment score and adversarial alignment score to improve model robustness for generalization. Both modules share a common objective in addressing generalization issues, aiming to maximize the generalization capability derived from multiple hand-crafted prompts. Four representative tasks (i.e., non-generalization few-shot learning, base-to-novel generalization, cross-dataset generalization, domain generalization) across 11 datasets demonstrate that SPTR outperforms existing prompt learning methods.
提示学习已成为将预训练的视觉语言模型(VLM)适应多种下游任务的一种有前途的方法。虽然优化上下文对于提高特定任务的性能可能是有效的,但它往往会导致对来自不同分布的未见类别或数据集的泛化性能不佳。这可能是由于文本提示倾向于过度拟合下游数据分布,导致忘记手工制作的提示中得出的通用知识。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为基于文本正则化的相似性范式(SPTR)的新型提示学习方法,以实现无遗忘的提示学习。SPTR是一个基于手工制作的提示的两面设计,是一个不可分割的框架。首先,为了避免忘记一般的文本知识,我们引入了最优传输作为文本正则化来精细地确保与手工制作的功能的近似和调整文本特征。其次,为了不断释放多个手工制作的提示的通用能力,我们提出了自然对齐得分和对抗性对齐得分的相似性范式,以提高模型的泛化能力。这两个模块的共同目标是解决泛化问题,旨在从多个手工制作的提示中最大化泛化能力。在跨越11个数据集的四个代表性任务(即非泛化的小样本学习、基础到新颖的泛化、跨数据集泛化和域泛化)上证明了SPTR优于现有的提示学习方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文探讨了在预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)中使用提示学习(Prompt Learning)方法时遇到的挑战。尽管优化上下文对于提高特定任务的性能可能有效,但它可能导致在未见的类别或数据集上的泛化性能下降。文章提出了一种名为相似性范式下的文本正则化(SPTR)的新型方法来解决提示学习中的遗忘问题。该方法包括两部分,采用手写提示形式的不分离框架:首先引入最佳传输作为文本正则化,确保手写特征和调整文本特征的近似匹配;其次提出相似性范式来改进模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力。该方法的目的是从多个手写提示中最大限度地提高泛化能力。在跨越多个数据集的四项代表性任务上进行的实验表明,SPTR优于现有的提示学习方法。
Key Takeaways
以下是文本中七个重要的观点或发现:
- 提示学习在视觉语言模型适应下游任务中展现出巨大潜力。
- 优化上下文虽然能提高特定任务的性能,但可能导致泛化性能下降。
- SPTR方法旨在解决提示学习中的遗忘问题。
- SPTR包含两个关键部分:文本正则化和相似性范式。
- 文本正则化确保手写特征和调整文本特征的近似匹配。
- 相似性范式旨在提高模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

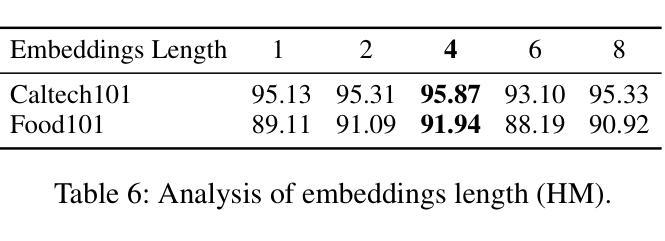
Are Transformers Able to Reason by Connecting Separated Knowledge in Training Data?
Authors:Yutong Yin, Zhaoran Wang
Humans exhibit remarkable compositional reasoning by integrating knowledge from various sources. For example, if someone learns ( B = f(A) ) from one source and ( C = g(B) ) from another, they can deduce ( C=g(B)=g(f(A)) ) even without encountering ( ABC ) together, showcasing the generalization ability of human intelligence. In this paper, we introduce a synthetic learning task, “FTCT” (Fragmented at Training, Chained at Testing), to validate the potential of Transformers in replicating this skill and interpret its inner mechanism. In the training phase, data consist of separated knowledge fragments from an overall causal graph. During testing, Transformers must infer complete causal graph traces by integrating these fragments. Our findings demonstrate that few-shot Chain-of-Thought prompting enables Transformers to perform compositional reasoning on FTCT by revealing correct combinations of fragments, even if such combinations were absent in the training data. Furthermore, the emergence of compositional reasoning ability is strongly correlated with the model complexity and training-testing data similarity. We propose, both theoretically and empirically, that Transformers learn an underlying generalizable program from training, enabling effective compositional reasoning during testing.
人类能够通过整合来自不同来源的知识展现出惊人的组合推理能力。例如,如果有人从某一来源学习到(B=f(A))并从另一来源学习到(C=g(B)),他们即使在没有同时遇到(ABC)的情况下,也能推导出(C=g(B)=g(f(A))),这展现了人类智力的泛化能力。在本文中,我们引入了一项合成学习任务“FTCT”(训练时片段化,测试时链接),以验证Transformer复制这项技能的潜力并解释其内在机制。在训练阶段,数据由来自整体因果图的分离知识片段组成。在测试阶段,Transformer必须通过整合这些片段来推断完整的因果图轨迹。我们的研究发现,即使在训练数据中未出现正确的片段组合,通过少量思维链提示的Transformer也能在FTCT上表现出组合推理能力。此外,组合推理能力的出现与模型复杂度和训练-测试数据相似性之间存在强烈相关性。我们从理论和实践两方面提出,Transformer从训练中学习了一个通用的基础程序,从而在测试过程中实现了有效的组合推理。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICLR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了人类具备将不同来源的知识进行整合进行推理的出色能力。通过引入一种名为“FTCT”(训练时碎片化,测试时链接)的合成学习任务,验证了Transformer模型在复制此技能方面的潜力并解释了其内在机制。训练阶段数据来自整体的因果图中的知识片段,而在测试阶段,Transformer必须通过整合这些片段来推断完整的因果图轨迹。研究发现,即使是只使用少数Chain-of-Thought提示也能让Transformer在FTCT上执行组合推理,揭示正确的片段组合,即便这些组合在训练数据中不存在。此外,模型的复杂性和训练测试数据的相似性对组合推理能力的出现有强烈影响。作者认为Transformer能从训练中学习到一个可概括的底层程序,并在测试阶段进行有效的组合推理。
Key Takeaways
- 人类具备强大的组合推理能力,能从不同来源的知识中整合信息并进行推理。
- “FTCT”任务被设计用于验证Transformer模型是否具备这种组合推理能力。
- 在FTCT任务中,Transformer在测试阶段能通过整合训练阶段获得的知识片段来推断完整的因果图轨迹。
- 通过使用少量Chain-of-Thought提示,Transformer能执行组合推理并揭示正确的知识片段组合。
- 组合推理能力的出现与模型的复杂性和训练测试数据的相似性密切相关。
- Transformer在训练过程中可能学习到一个可概括的底层程序,该程序有助于在测试阶段进行有效的组合推理。
点此查看论文截图

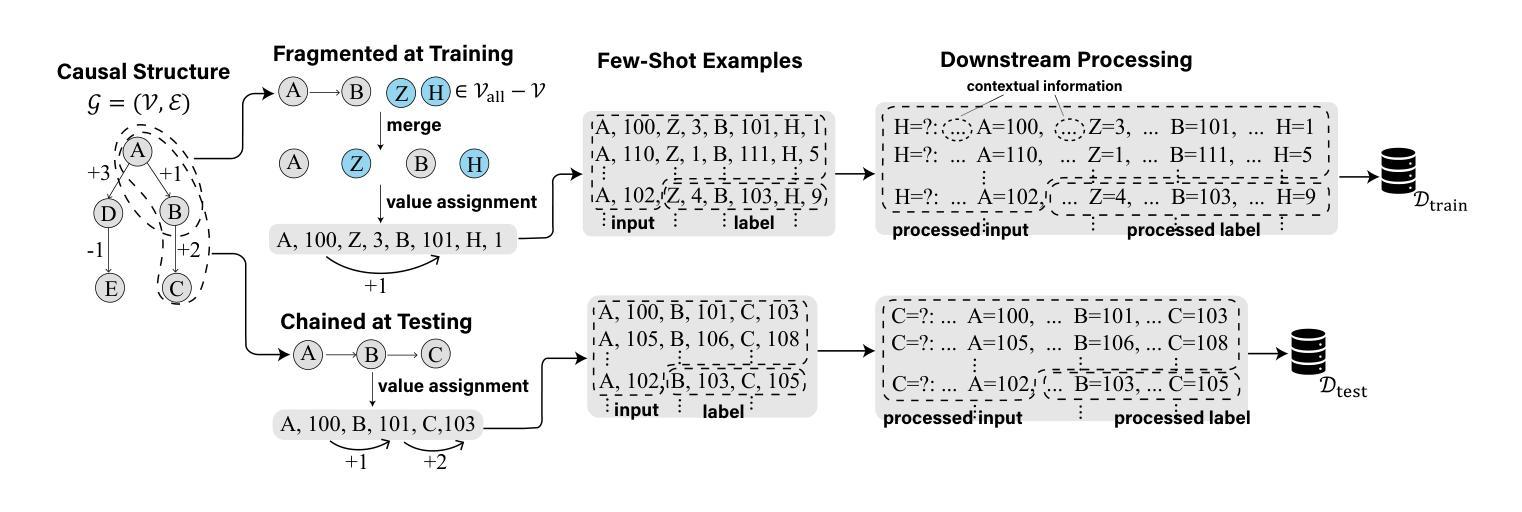
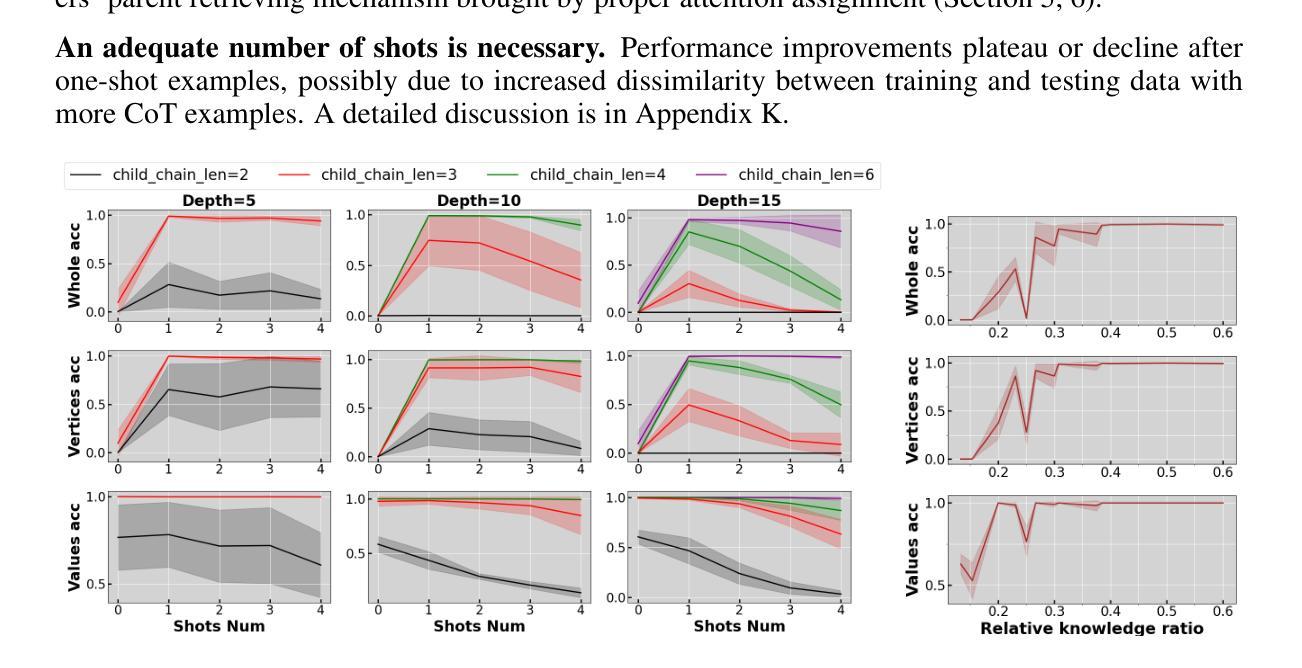
Can Input Attributions Explain Inductive Reasoning in In-Context Learning?
Authors:Mengyu Ye, Tatsuki Kuribayashi, Goro Kobayashi, Jun Suzuki
Interpreting the internal process of neural models has long been a challenge. This challenge remains relevant in the era of large language models (LLMs) and in-context learning (ICL); for example, ICL poses a new issue of interpreting which example in the few-shot examples contributed to identifying/solving the task. To this end, in this paper, we design synthetic diagnostic tasks of inductive reasoning, inspired by the generalization tests typically adopted in psycholinguistics. Here, most in-context examples are ambiguous w.r.t. their underlying rule, and one critical example disambiguates it. The question is whether conventional input attribution (IA) methods can track such a reasoning process, i.e., identify the influential example, in ICL. Our experiments provide several practical findings; for example, a certain simple IA method works the best, and the larger the model, the generally harder it is to interpret the ICL with gradient-based IA methods.
神经网络模型的内部过程解释一直是一个挑战。这个挑战在大型语言模型(LLM)和上下文学习(ICL)的时代仍然具有现实意义。例如,ICL提出了一个新的问题,即解释少数例子中的哪一个例子对识别/解决任务有所贡献。为此,本文设计了基于心理语言学中通常采用的概括测试的归纳推理的合成诊断任务。在这里,大多数上下文例子在基础规则方面都是模糊的,只有一个关键例子可以消除歧义。问题是传统的输入归因(IA)方法是否能够追踪这样的推理过程,即识别出上下文学习中的关键例子。我们的实验得出了几个实际发现:例如,某种简单的IA方法效果最佳,模型越大,基于梯度的IA方法来解释其语境含义往往更加困难。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Findings of ACL 2025
Summary
本文设计了一系列合成诊断任务,以探索大型语言模型在上下文中进行学习时的内部推理过程。研究发现,传统的输入归因方法可能无法有效追踪这些推理过程,一个简单的输入归因方法表现最佳,并且模型规模越大,使用基于梯度的输入归因方法来解释其在上下文中的学习难度通常越高。
Key Takeaways
- 设计合成诊断任务以探索大型语言模型在上下文学习中的内部推理过程。
- 大多数上下文示例对于其隐含的规则是模糊的,一个关键示例起到了澄清作用。
- 传统的输入归因方法可能无法追踪推理过程,需要更有效的方法来识别影响性的示例。
- 一个简单的输入归因方法表现最佳。
- 模型规模越大,使用基于梯度的输入归因方法来解释其在上下文中的学习难度越高。
- 上下文学习中的解释性挑战仍然存在,需要更多研究来探索有效的解释方法。
点此查看论文截图

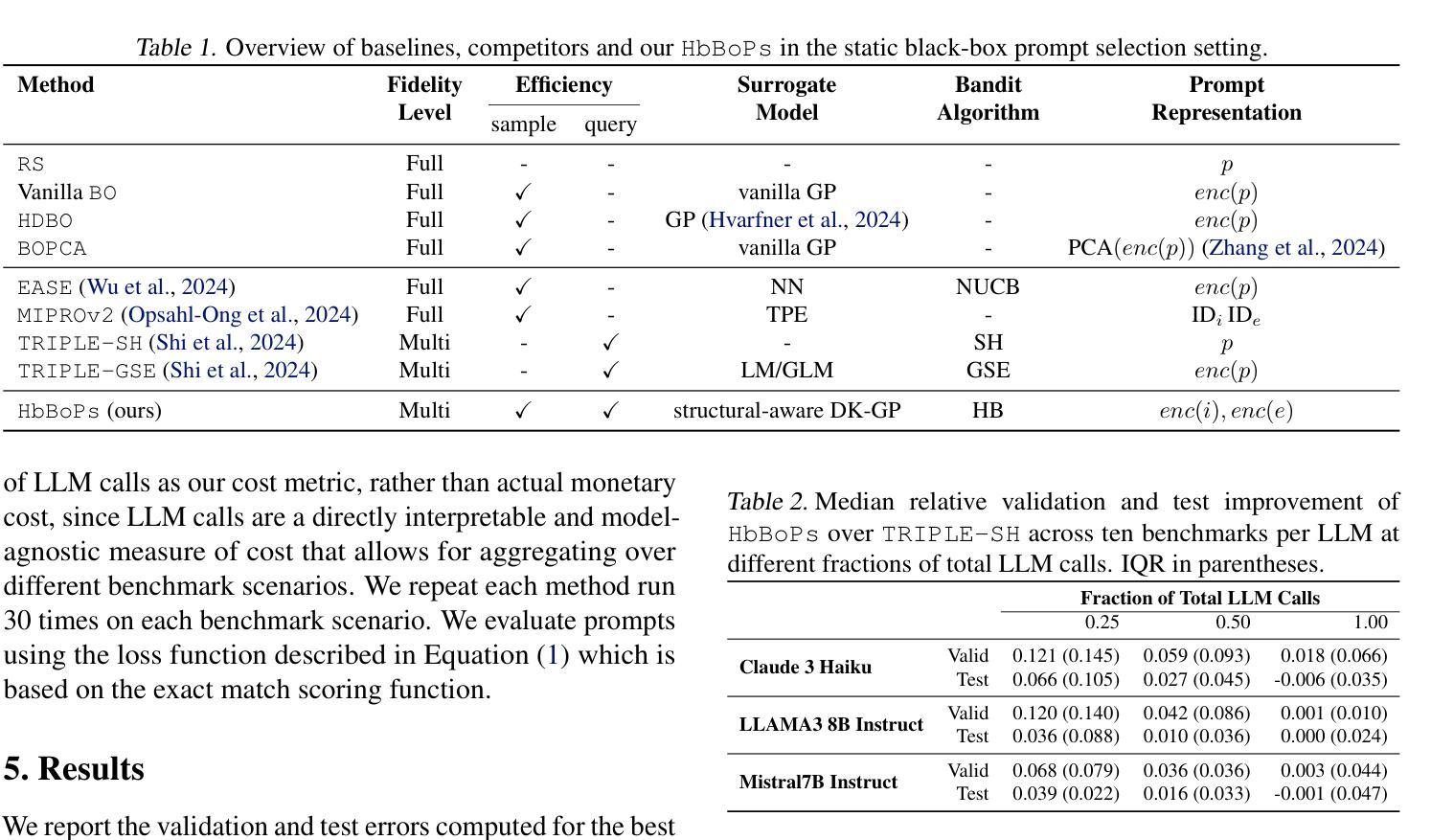
Hyperband-based Bayesian Optimization for Black-box Prompt Selection
Authors:Lennart Schneider, Martin Wistuba, Aaron Klein, Jacek Golebiowski, Giovanni Zappella, Felice Antonio Merra
Optimal prompt selection is crucial for maximizing large language model (LLM) performance on downstream tasks, especially in black-box settings where models are only accessible via APIs. Black-box prompt selection is challenging due to potentially large, combinatorial search spaces, absence of gradient information, and high evaluation cost of prompts on a validation set. We propose HbBoPs, a novel method that combines a structural-aware deep kernel Gaussian Process with Hyperband as a multi-fidelity scheduler to efficiently select prompts. HbBoPs uses embeddings of instructions and few-shot exemplars, treating them as modular components within prompts. This enhances the surrogate model’s ability to predict which prompt to evaluate next in a sample-efficient manner. Hyperband improves query-efficiency by adaptively allocating resources across different fidelity levels, reducing the number of validation instances required for evaluating prompts. Extensive experiments across ten diverse benchmarks and three LLMs demonstrate that HbBoPs outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both performance and efficiency.
最优提示选择对于最大化下游任务中的大型语言模型(LLM)性能至关重要,特别是在只能通过API访问模型的黑箱环境中更是如此。黑箱提示选择具有挑战性,原因在于潜在的庞大组合搜索空间、缺少梯度信息以及提示在验证集上的高评估成本。我们提出了HbBoPs,这是一种将结构感知深度内核高斯过程与Hyperband多保真调度器相结合的新型方法,以高效选择提示。HbBoPs使用指令和少量示例的嵌入,将它们视为提示中的模块化组件。这增强了替代模型以样本高效的方式预测应评估哪个提示的能力。Hyperband通过自适应地在不同保真度级别上分配资源来提高查询效率,减少了评估提示所需的验证实例数量。在十个不同基准测试和三个LLM上的广泛实验表明,HbBoPs在性能和效率方面都优于最新技术方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICML 2025. 26 pages, 11 tables, 7 figures
Summary
本文主要探讨了在大型语言模型(LLM)下游任务中,最优提示选择的重要性,特别是在只能通过API访问模型的黑箱设置中。针对黑箱提示选择面临的挑战,如搜索空间可能很大、缺少梯度信息和提示验证成本高等问题,本文提出了一种新型的提示选择方法HbBoPs。该方法结合了结构感知深度核高斯过程与Hyperband多保真调度器,以高效选择提示。HbBoPs使用指令和少量范例的嵌入,将其作为提示中的模块化组件。这增强了替代模型以样本高效的方式预测应评估哪个提示的能力。Hyperband通过自适应分配不同保真度级别的资源来提高查询效率,减少了评估提示所需的验证实例数量。在十个不同基准测试和三个大型语言模型上的广泛实验表明,HbBoPs在性能和效率方面都优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 文本强调大型语言模型(LLM)下游任务中,最优提示选择的重要性。
- 黑箱环境中进行提示选择面临搜索空间巨大、缺乏梯度信息和验证成本高昂等挑战。
- 提出了一种新型提示选择方法HbBoPs,结合了结构感知深度核高斯过程和Hyperband多保真调度器。
- HbBoPs使用指令和少量范例的嵌入作为提示中的模块化组件,提高预测准确性。
- Hyperband提高了查询效率,通过自适应分配资源减少了评估提示所需的验证实例数量。
- 实验结果表明,HbBoPs在多个基准测试和大型语言模型上在性能和效率方面都超越了现有技术。
点此查看论文截图