⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-05 更新
Efficiency without Compromise: CLIP-aided Text-to-Image GANs with Increased Diversity
Authors:Yuya Kobayashi, Yuhta Takida, Takashi Shibuya, Yuki Mitsufuji
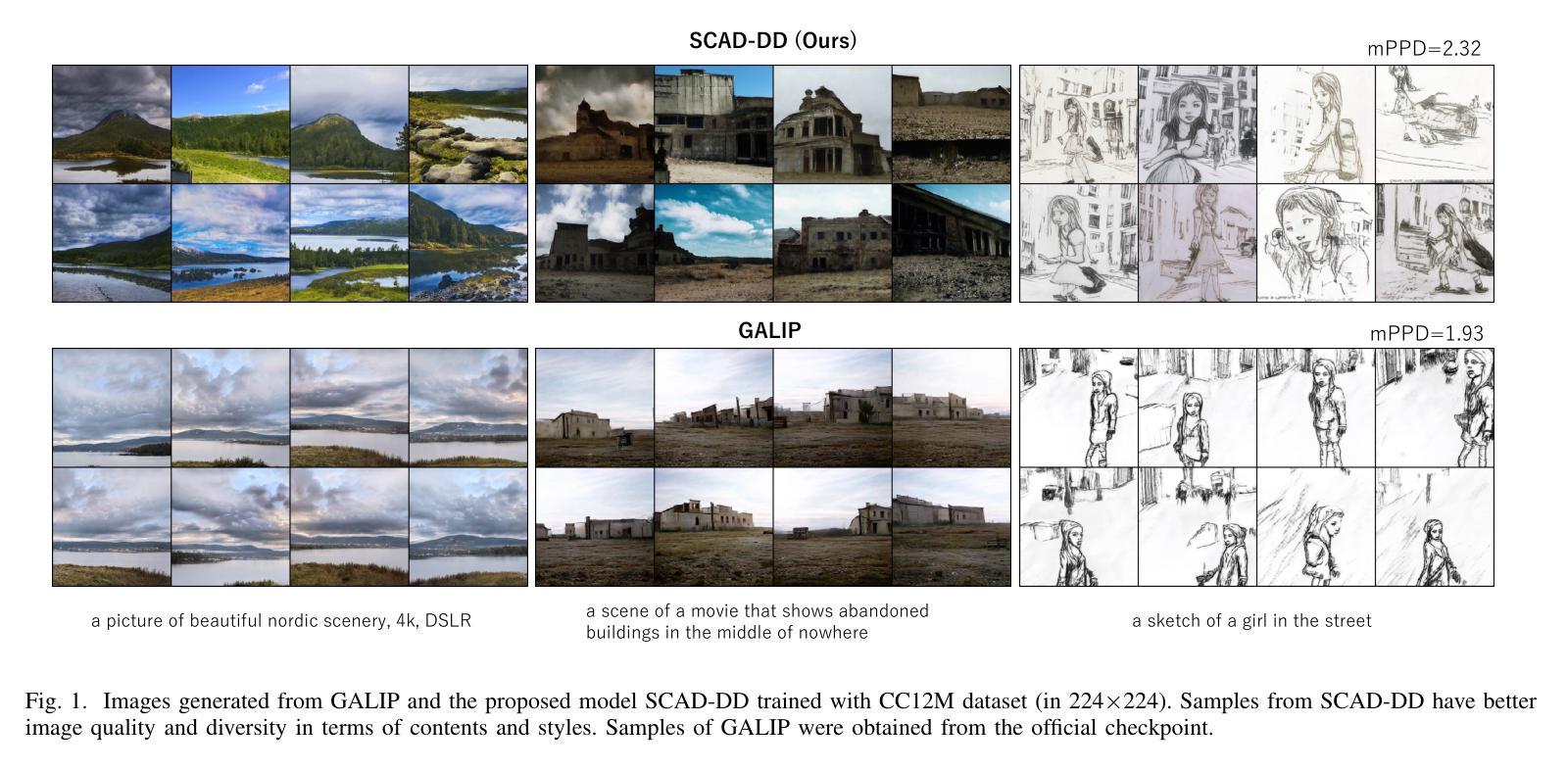
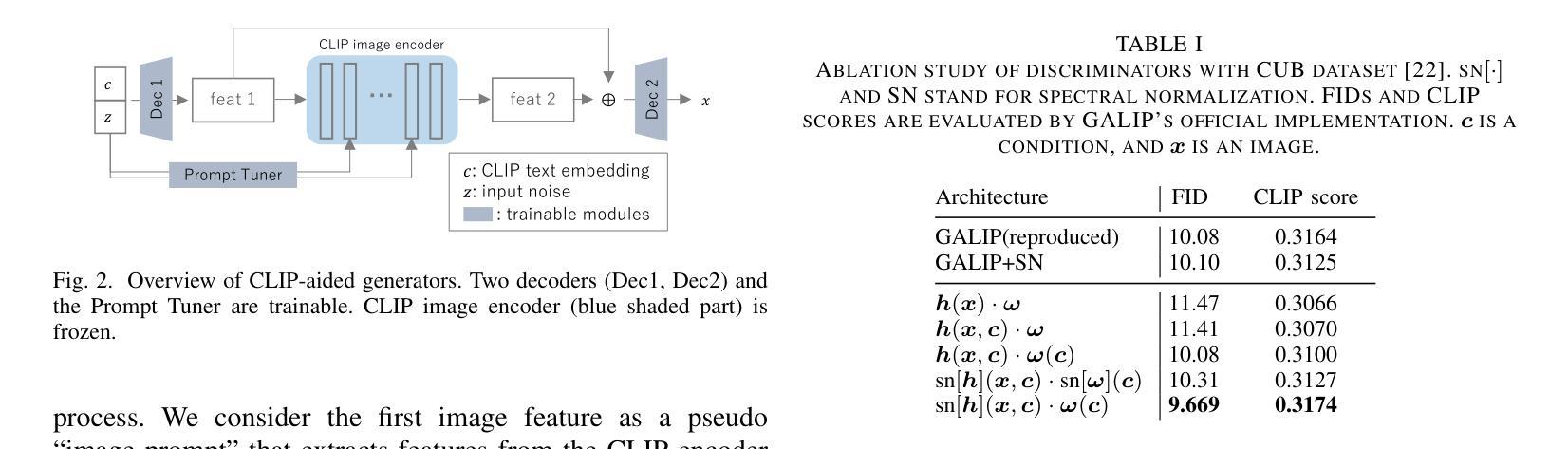
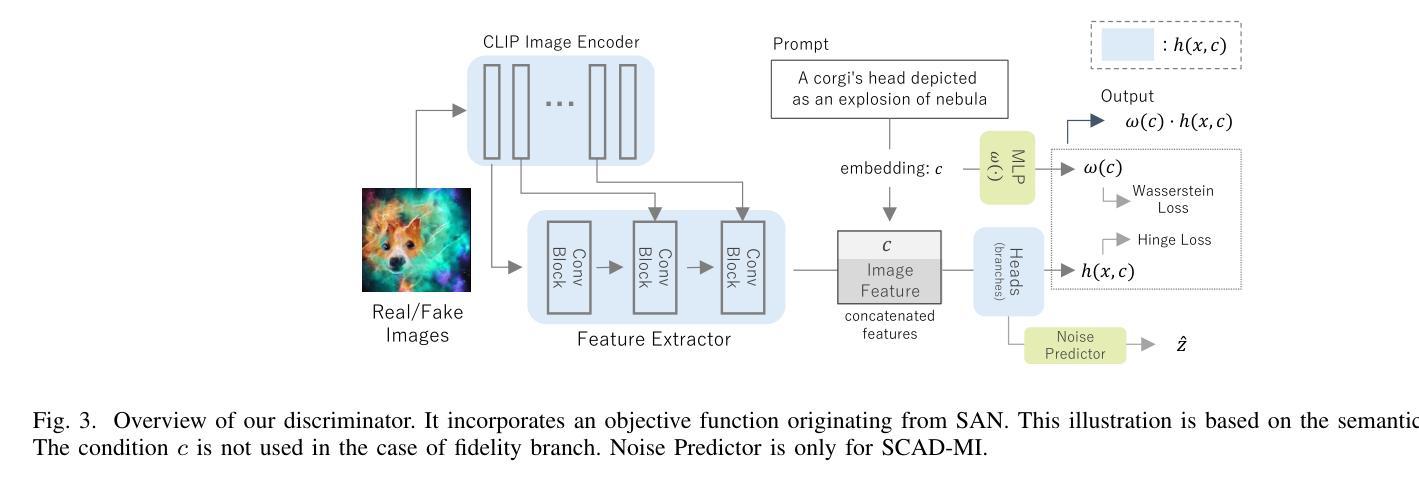
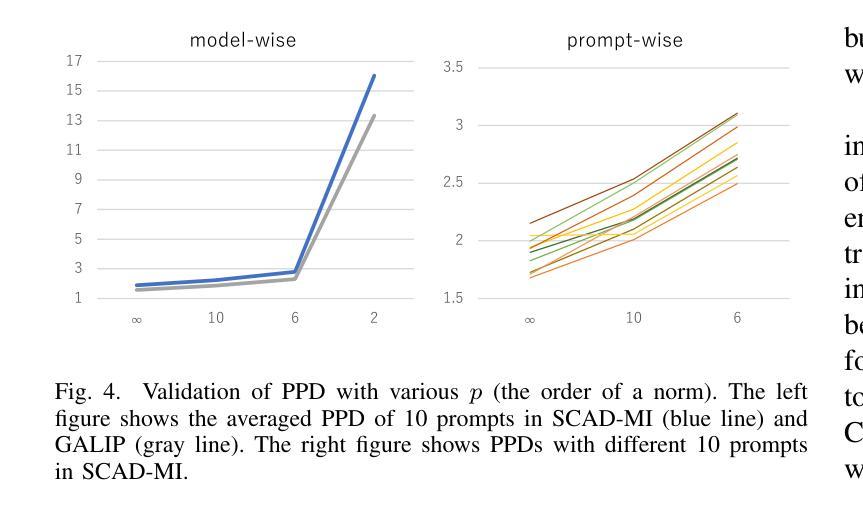
Recently, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have been successfully scaled to billion-scale large text-to-image datasets. However, training such models entails a high training cost, limiting some applications and research usage. To reduce the cost, one promising direction is the incorporation of pre-trained models. The existing method of utilizing pre-trained models for a generator significantly reduced the training cost compared with the other large-scale GANs, but we found the model loses the diversity of generation for a given prompt by a large margin. To build an efficient and high-fidelity text-to-image GAN without compromise, we propose to use two specialized discriminators with Slicing Adversarial Networks (SANs) adapted for text-to-image tasks. Our proposed model, called SCAD, shows a notable enhancement in diversity for a given prompt with better sample fidelity. We also propose to use a metric called Per-Prompt Diversity (PPD) to evaluate the diversity of text-to-image models quantitatively. SCAD achieved a zero-shot FID competitive with the latest large-scale GANs at two orders of magnitude less training cost.
最近,生成对抗网络(GANs)已成功扩展至亿级大规模文本到图像数据集。然而,训练此类模型需要很高的训练成本,这限制了某些应用和研究的使用。为了降低成本,一个前景广阔的方向是融入预训练模型。现有方法利用预训练模型作为生成器大大减少了与其他大规模GAN的训练成本相比,但我们发现该模型在给定的提示下丧失了很大的生成多样性。为了构建高效且高保真度的文本到图像GAN而不妥协,我们建议使用两个针对文本到图像任务进行改编的切片对抗网络(SANs)作为专用鉴别器。我们提出的模型,称为SCAD,在给定提示下显著提高了多样性,并具有更好的样本保真度。我们还建议使用称为每提示多样性(PPD)的指标来定量评估文本到图像模型的多样性。SCAD实现了与最新大规模GAN相当的零FID,并且训练成本降低了两个数量级。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IJCNN 2025
Summary
本文介绍了利用预训练模型结合切片对抗网络(SANs)的文本到图像生成对抗网络(GAN)的新模型SCAD。该模型在降低训练成本的同时,显著提高了给定提示下的生成多样性,实现了高效且高保真度的文本到图像转换。通过引入一个新的评价指标PPD(Per-Prompt Diversity),SCAD模型在两阶训练成本内达到了最新大规模GAN的竞争水平。
Key Takeaways
- GANs已成功应用于大规模文本到图像数据集。
- 利用预训练模型可降低训练成本,但会损失生成的多样性。
- SCAD模型结合了SANs技术,旨在实现高效且高保真度的文本到图像转换。
- SCAD模型通过引入两个专用鉴别器,提高了给定提示下的生成多样性。
- SCAD模型使用PPD这一新评价指标来定量评估文本到图像模型的多样性。
- SCAD模型实现了零启动FID(Fréchet Inception Distance)与最新大规模GAN相当的训练效果。
点此查看论文截图

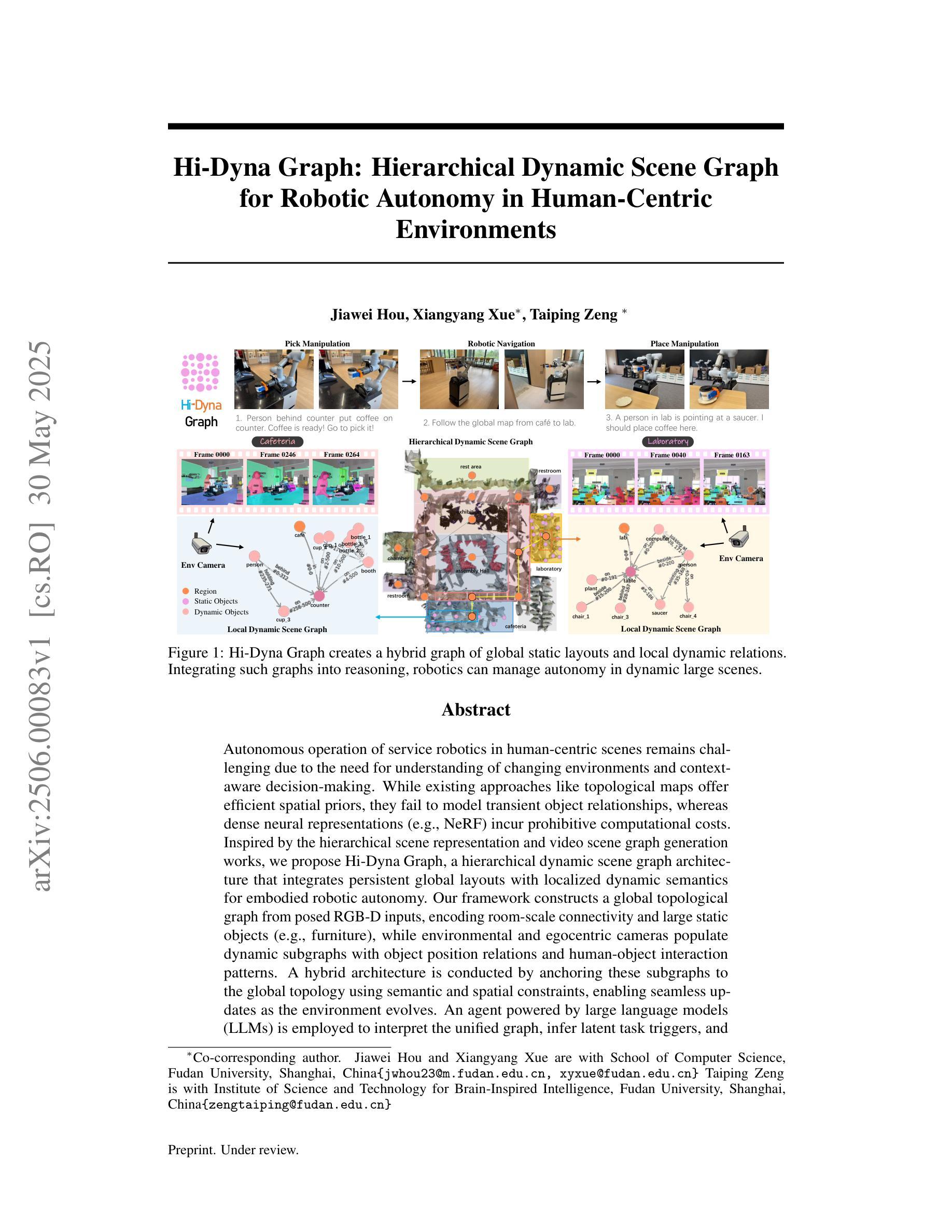
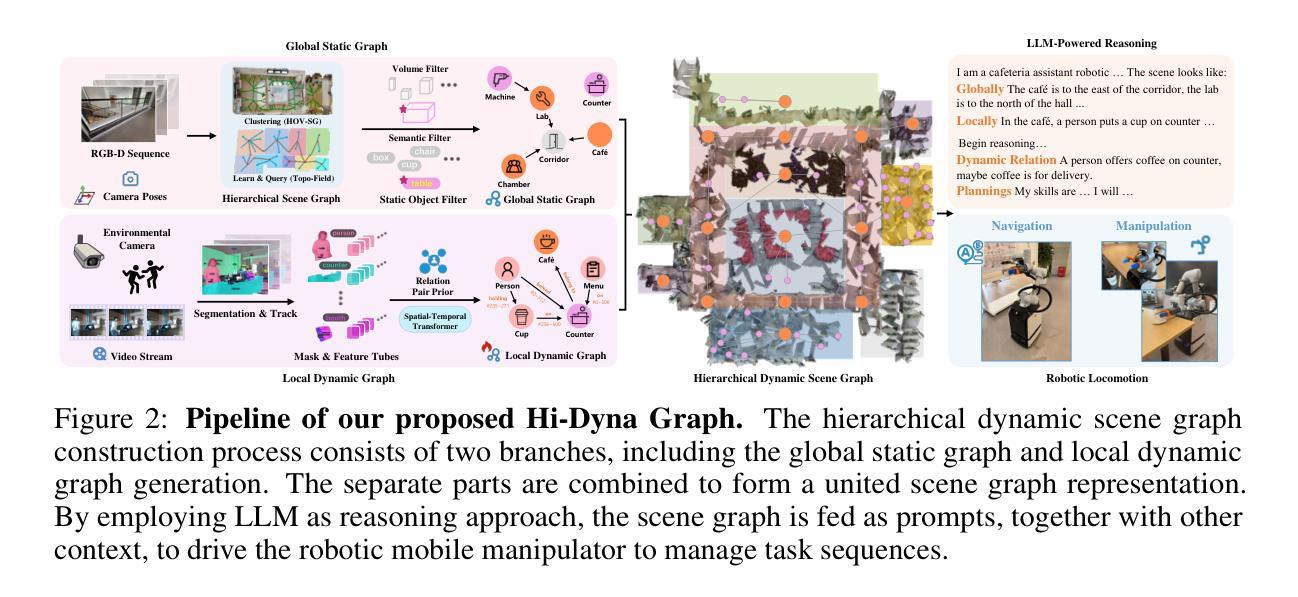
Hi-Dyna Graph: Hierarchical Dynamic Scene Graph for Robotic Autonomy in Human-Centric Environments
Authors:Jiawei Hou, Xiangyang Xue, Taiping Zeng
Autonomous operation of service robotics in human-centric scenes remains challenging due to the need for understanding of changing environments and context-aware decision-making. While existing approaches like topological maps offer efficient spatial priors, they fail to model transient object relationships, whereas dense neural representations (e.g., NeRF) incur prohibitive computational costs. Inspired by the hierarchical scene representation and video scene graph generation works, we propose Hi-Dyna Graph, a hierarchical dynamic scene graph architecture that integrates persistent global layouts with localized dynamic semantics for embodied robotic autonomy. Our framework constructs a global topological graph from posed RGB-D inputs, encoding room-scale connectivity and large static objects (e.g., furniture), while environmental and egocentric cameras populate dynamic subgraphs with object position relations and human-object interaction patterns. A hybrid architecture is conducted by anchoring these subgraphs to the global topology using semantic and spatial constraints, enabling seamless updates as the environment evolves. An agent powered by large language models (LLMs) is employed to interpret the unified graph, infer latent task triggers, and generate executable instructions grounded in robotic affordances. We conduct complex experiments to demonstrate Hi-Dyna Grap’s superior scene representation effectiveness. Real-world deployments validate the system’s practicality with a mobile manipulator: robotics autonomously complete complex tasks with no further training or complex rewarding in a dynamic scene as cafeteria assistant. See https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Hi-Dyna-Graph-B326 for video demonstration and more details.
服务机器人在以人为中心的环境中进行自主操作仍然具有挑战性,这需要对变化的环境和基于上下文进行决策的理解。虽然现有的拓扑地图等方法提供了有效的空间先验信息,但它们无法对瞬态对象关系进行建模,而密集神经表示(例如NeRF)则带来了过高的计算成本。受分层场景表示和视频场景图生成工作的启发,我们提出了Hi-Dyna Graph,这是一种分层动态场景图架构,它结合了持久全局布局和局部动态语义,以实现机器人在环境中的自主能力。我们的框架从姿势RGB-D输入构建全局拓扑图,编码房间规模的连接和大静态物体(例如家具),而环境和以自我为中心的相机则利用对象位置关系和人与对象交互模式填充动态子图。通过语义和空间约束将这些子图锚定到全局拓扑上,构建混合架构,使环境演变时能够无缝更新。使用大型语言模型驱动的代理来解读统一图,推断潜在任务触发器,并生成基于机器人可用性的可执行指令。我们进行了复杂的实验,以展示Hi-Dyna Graph在场景表示方面的卓越效果。在现实世界的应用部署中,使用移动操纵器验证了系统的实用性:机器人能够在动态场景中无需进一步训练或复杂的奖励机制即可自主完成复杂任务,例如在自助餐厅担任助理。有关视频演示和更多详细信息,请访问:https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Hi-Dyna-Graph-B326。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了Hi-Dyna Graph,这是一种分层动态场景图架构,旨在提高服务机器人在人类中心场景中执行任务的自主性。Hi-Dyna Graph结合了全局拓扑图和动态子图,可以应对环境变化和人类交互。它利用RGB-D输入构建全局拓扑图,并生成动态子图来捕捉物体位置关系和人类交互模式。此外,该架构还融合了大型语言模型,用于解释统一图、推断潜在任务触发因素并生成可执行指令。实验证明,Hi-Dyna Graph在动态场景中实现机器人自主完成复杂任务方面具有优越效果。
Key Takeaways
- Hi-Dyna Graph是一种分层动态场景图架构,结合了全局拓扑图和动态子图,旨在提高服务机器人在人类中心场景中的自主性。
- 该架构利用RGB-D输入构建全局拓扑图,反映房间规模的连通性和大型静态物体。
- 环境相机和egocentric相机生成动态子图,捕捉物体位置关系和人类交互模式。
- Hi-Dyna Graph融合了大型语言模型,用于解释统一图、推断潜在任务触发因素并生成可执行指令。
- 实验证明Hi-Dyna Graph在动态场景中实现机器人自主完成复杂任务方面具有优越效果。
- 该系统具有实用性,已在移动机械臂等机器人上得到验证。
点此查看论文截图
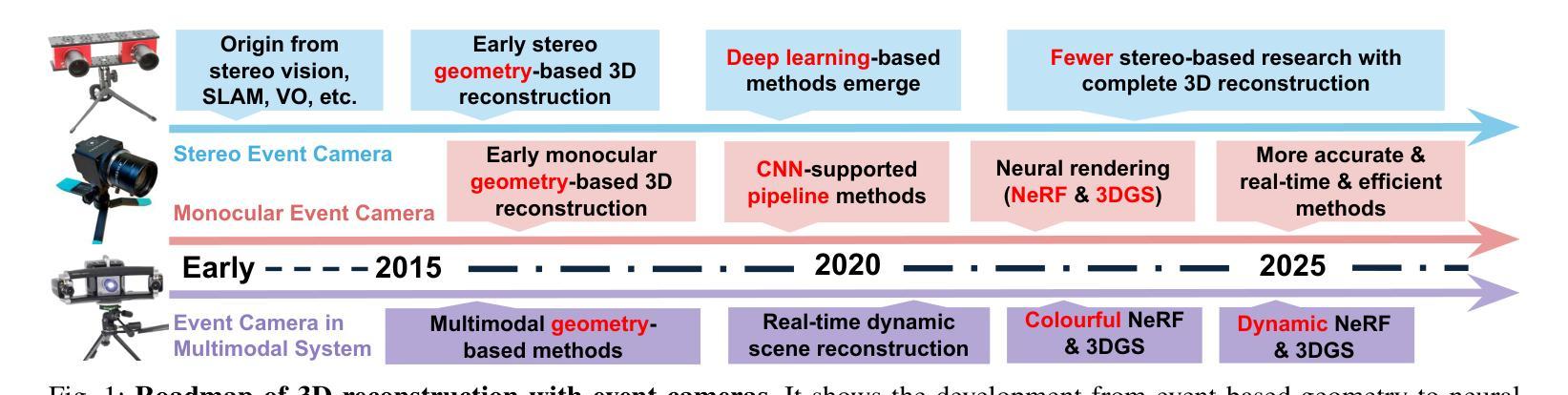
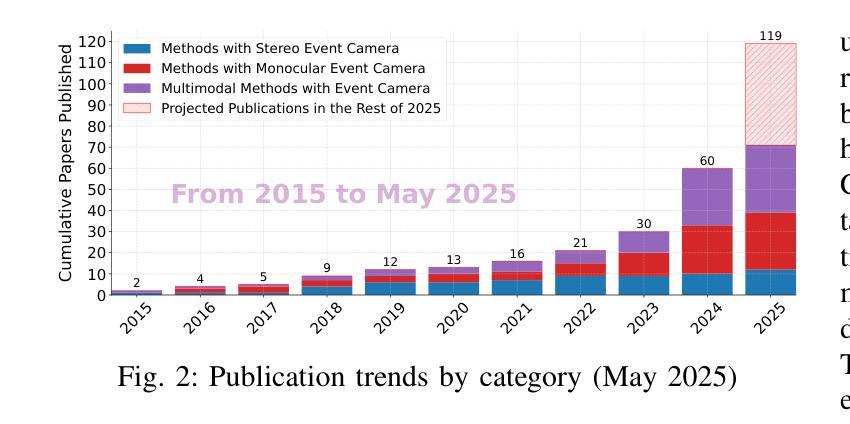
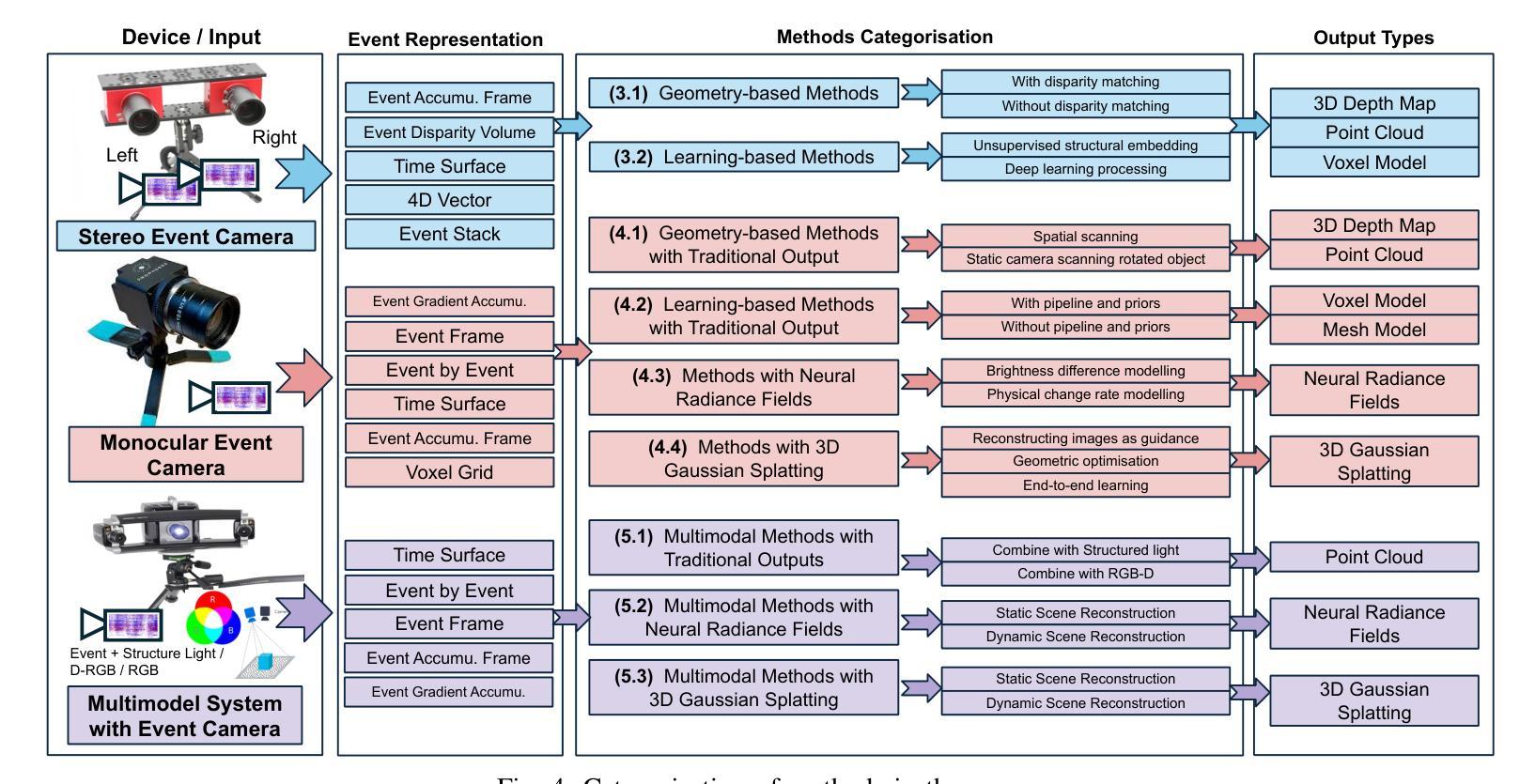
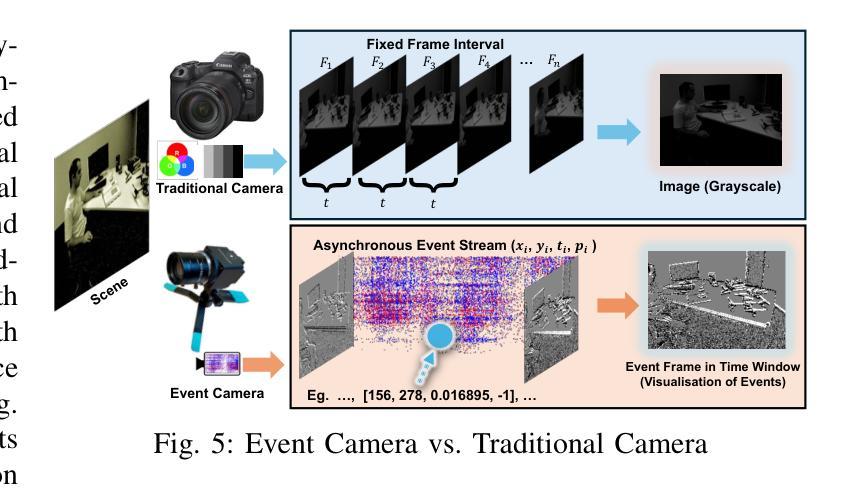
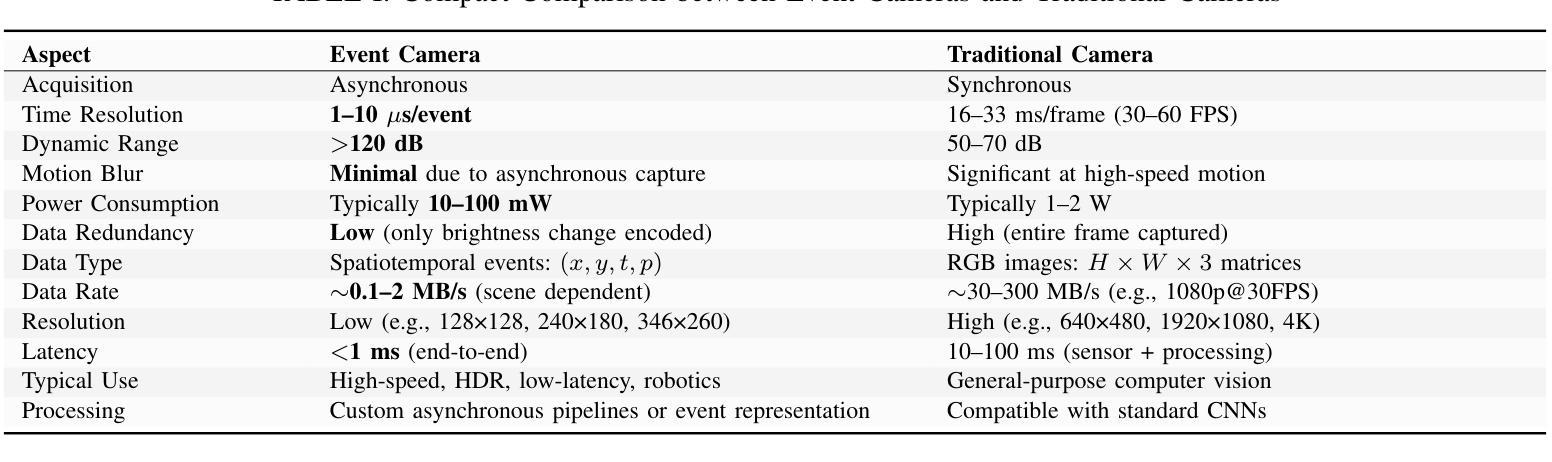
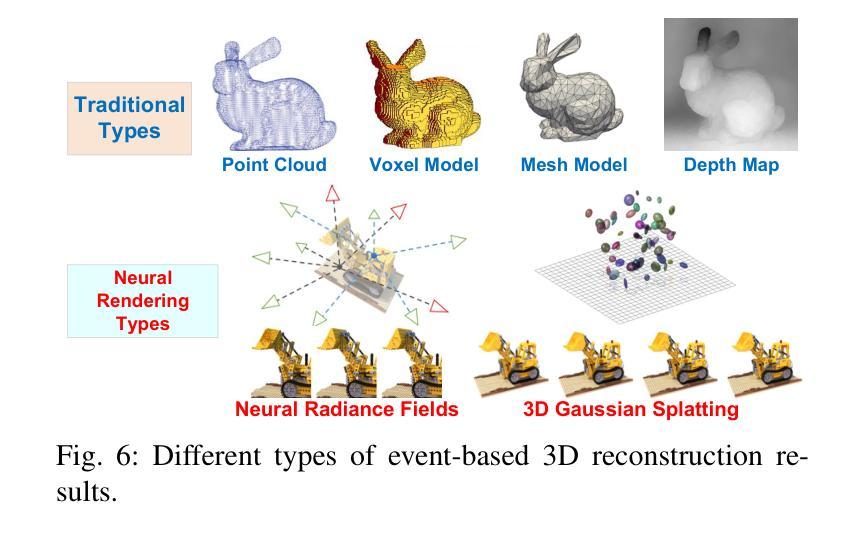
A Survey of 3D Reconstruction with Event Cameras
Authors:Chuanzhi Xu, Haoxian Zhou, Langyi Chen, Haodong Chen, Ying Zhou, Vera Chung, Qiang Qu, Weidong Cai
Event cameras are rapidly emerging as powerful vision sensors for 3D reconstruction, uniquely capable of asynchronously capturing per-pixel brightness changes. Compared to traditional frame-based cameras, event cameras produce sparse yet temporally dense data streams, enabling robust and accurate 3D reconstruction even under challenging conditions such as high-speed motion, low illumination, and extreme dynamic range scenarios. These capabilities offer substantial promise for transformative applications across various fields, including autonomous driving, robotics, aerial navigation, and immersive virtual reality. In this survey, we present the first comprehensive review exclusively dedicated to event-based 3D reconstruction. Existing approaches are systematically categorised based on input modality into stereo, monocular, and multimodal systems, and further classified according to reconstruction methodologies, including geometry-based techniques, deep learning approaches, and neural rendering techniques such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Within each category, methods are chronologically organised to highlight the evolution of key concepts and advancements. Furthermore, we provide a detailed summary of publicly available datasets specifically suited to event-based reconstruction tasks. Finally, we discuss significant open challenges in dataset availability, standardised evaluation, effective representation, and dynamic scene reconstruction, outlining insightful directions for future research. This survey aims to serve as an essential reference and provides a clear and motivating roadmap toward advancing the state of the art in event-driven 3D reconstruction.
事件相机作为强大的视觉传感器,正在迅速崭露头角,用于三维重建。它具有独特的异步捕获像素亮度变化的能力。与传统基于帧的相机相比,事件相机产生稀疏但时间上密集的数据流,即使在高速运动、低光照和极端动态范围等挑战条件下,也能实现稳健和准确的三维重建。这些能力为自主驾驶、机器人技术、空中导航和沉浸式虚拟现实等各个领域的应用提供了巨大潜力。在本文中,我们对基于事件的三维重建进行了首次全面综述。根据输入模式,现有方法被系统地分为立体、单目和多模态系统,并进一步根据重建方法分类,包括基于几何的技术、深度学习方法以及神经渲染技术,如神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯溅射(3DGS)。在每个类别中,方法按时间顺序组织,以突出关键概念和进展的演变。此外,我们详细总结了专门适用于基于事件的重构任务的公开可用数据集。最后,我们讨论了数据集可用性、标准化评估、有效表示和动态场景重建等方面的重要开放挑战,并指出了未来研究的有见地的方向。本综述旨在作为重要的参考,并为推动事件驱动三维重建的最新发展提供一个清晰而有动力的路线图。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 16 figures, 11 tables
Summary
事件相机作为强大的视觉传感器正在迅速崛起,在3D重建领域具有独特的优势。与传统基于帧的相机相比,事件相机能够异步捕获像素级的亮度变化,产生稀疏但时间密集的数据流。这使得在高速运动、低光照和极端动态范围等挑战条件下,仍能进行稳健准确的3D重建。事件相机在自动驾驶、机器人技术、空中导航和沉浸式虚拟现实等多个领域具有巨大的应用潜力。本文首次全面综述了基于事件的3D重建技术,对现有方法进行分类,并详细介绍了神经渲染技术如神经辐射场和3D高斯喷涂在事件相机3D重建中的应用。此外,本文还总结了适用于基于事件的重建任务的可公开数据集,并讨论了数据集可用性、标准化评估、有效表示和动态场景重建等存在的挑战及未来研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 事件相机能够异步捕获像素级的亮度变化,为3D重建提供了独特优势。
- 事件相机在挑战条件下如高速运动、低光照和极端动态范围场景,能实现稳健准确的3D重建。
- 事件相机在多个领域具有巨大的应用潜力,包括自动驾驶、机器人技术、空中导航和虚拟现实等。
- 现有基于事件的3D重建方法被分为立体、单目和多媒体系统,并基于重建方法进一步分类,包括基于几何的技术、深度学习方法以及神经渲染技术。
- 文章详细总结了适用于基于事件的重建任务的可公开数据集。
- 数据集可用性、标准化评估、有效表示和动态场景重建等仍是当前面临的主要挑战。
点此查看论文截图


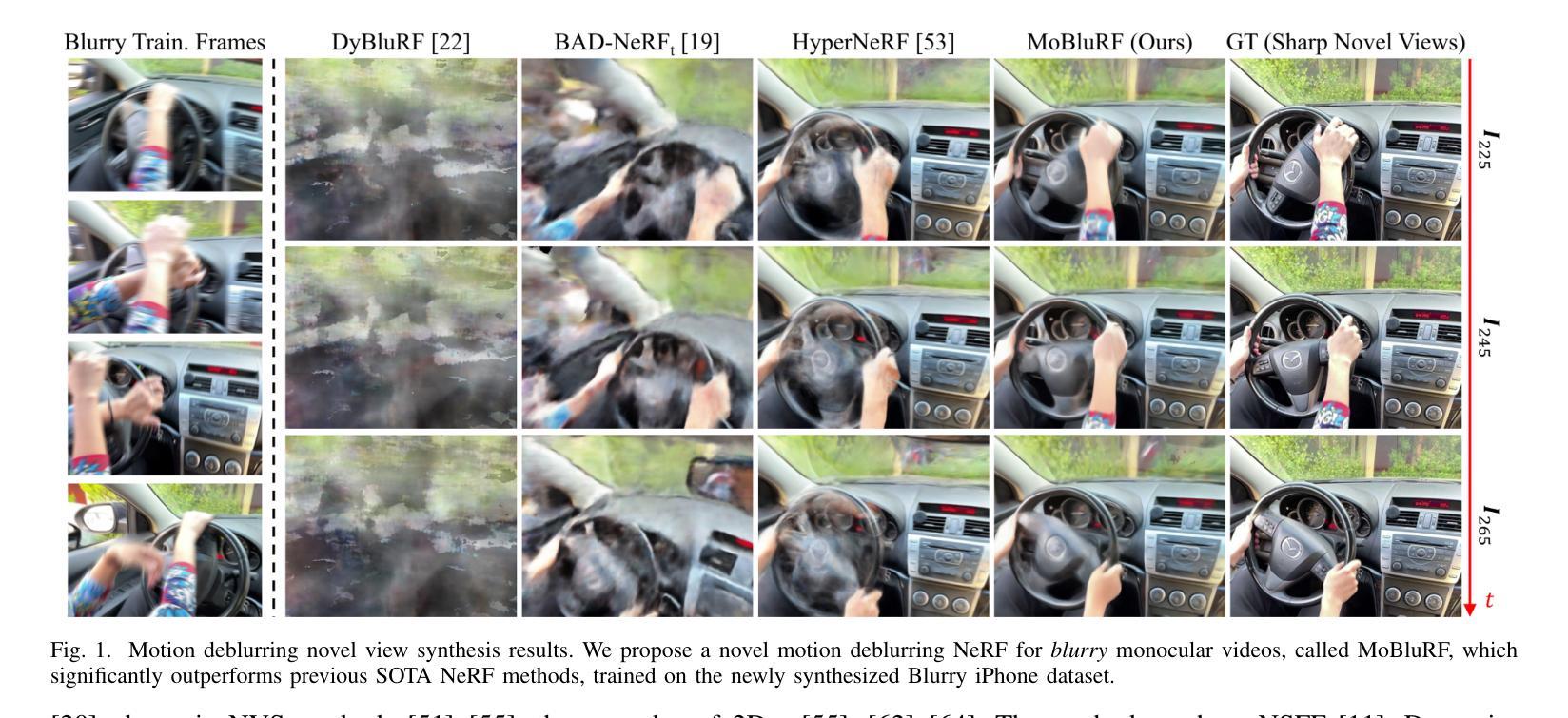
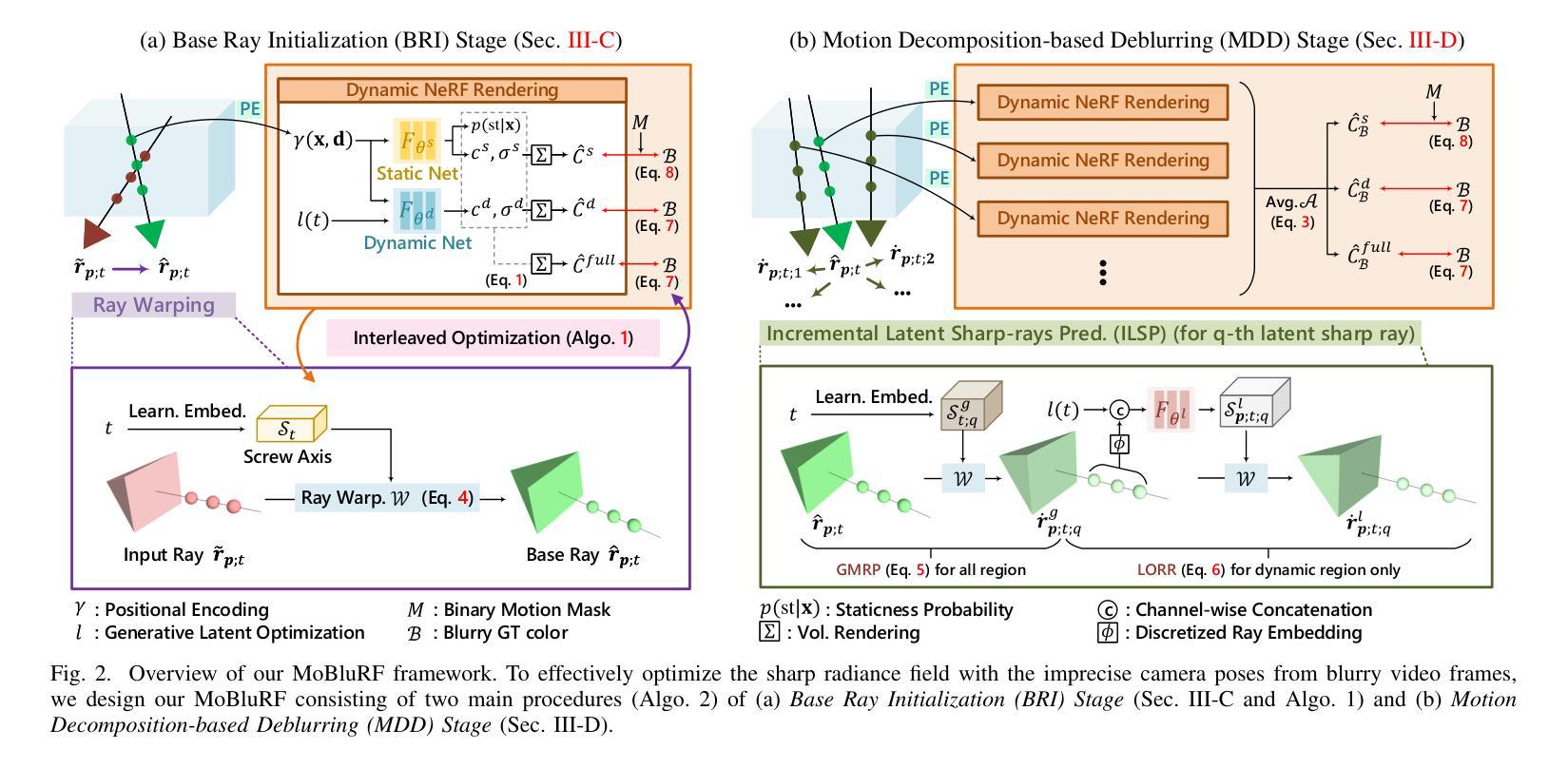
MoBluRF: Motion Deblurring Neural Radiance Fields for Blurry Monocular Video
Authors:Minh-Quan Viet Bui, Jongmin Park, Jihyong Oh, Munchurl Kim
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), initially developed for static scenes, have inspired many video novel view synthesis techniques. However, the challenge for video view synthesis arises from motion blur, a consequence of object or camera movements during exposure, which hinders the precise synthesis of sharp spatio-temporal views. In response, we propose a novel motion deblurring NeRF framework for blurry monocular video, called MoBluRF, consisting of a Base Ray Initialization (BRI) stage and a Motion Decomposition-based Deblurring (MDD) stage. In the BRI stage, we coarsely reconstruct dynamic 3D scenes and jointly initialize the base rays which are further used to predict latent sharp rays, using the inaccurate camera pose information from the given blurry frames. In the MDD stage, we introduce a novel Incremental Latent Sharp-rays Prediction (ILSP) approach for the blurry monocular video frames by decomposing the latent sharp rays into global camera motion and local object motion components. We further propose two loss functions for effective geometry regularization and decomposition of static and dynamic scene components without any mask supervision. Experiments show that MoBluRF outperforms qualitatively and quantitatively the recent state-of-the-art methods with large margins.
神经辐射场(NeRF)最初是为静态场景开发的,已经启发了很多视频新视角合成技术。然而,视频视角合成的挑战来自于运动模糊,这是曝光过程中物体或相机移动的结果,阻碍了精确合成清晰的空间时间视图。为了应对这一问题,我们提出了一种用于模糊单目视频的新型运动去模糊NeRF框架,称为MoBluRF,它包含基础光线初始化(BRI)阶段和运动分解去模糊(MDD)阶段。在BRI阶段,我们粗略重建动态3D场景,并联合初始化基础光线,这些光线进一步用于预测潜在清晰光线,使用的是给定模糊帧的不准确相机姿态信息。在MDD阶段,我们引入了一种新型增量潜在清晰光线预测(ILSP)方法,通过将潜在清晰光线分解为全局相机运动和局部物体运动成分,来对模糊单目视频帧进行处理。我们还进一步提出了两种损失函数,以实现有效的几何正则化和静态与动态场景组件的分解,而无需任何掩膜监督。实验表明,MoBluRF在定性和定量上均大大优于最近的最先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2025. The first two authors contributed equally to this work (equal contribution). The last two authors are co-corresponding authors. Please visit our project page at https://kaist-viclab.github.io/moblurf-site/
Summary
神经网络辐射场(NeRF)最初用于静态场景,现已激发许多视频新视角合成技术。针对视频视角合成中的运动模糊问题,提出一种名为MoBluRF的新型运动去模糊NeRF框架,包含基础光线初始化(BRI)阶段和运动分解去模糊(MDD)阶段。BRI阶段粗略重建动态3D场景并联合初始化基础光线,用于预测潜在清晰光线;MDD阶段采用新型增量潜在清晰光线预测(ILSP)方法,将潜在清晰光线分解为全局相机运动和局部物体运动成分。还提出两种损失函数,实现有效的几何正则化和静态与动态场景成分的分解,无需遮罩监督。实验表明,MoBluRF在质量和数量上都大幅超越了最近的最先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF技术已用于视频新视角合成,面临运动模糊的挑战。
- 提出了MoBluRF框架,包含BRI和MDD两个阶段以解决运动模糊问题。
- BRI阶段粗略重建动态3D场景并初始化基础光线。
- MDD阶段采用ILSP方法预测潜在清晰光线,并分解为全局和局部运动成分。
- 提出了两种损失函数,实现几何正则化和场景成分分解。
- MoBluRF在实验中大幅超越了现有技术。
点此查看论文截图