⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-05 更新
Revisiting Continuity of Image Tokens for Cross-domain Few-shot Learning
Authors:Shuai Yi, Yixiong Zou, Yuhua Li, Ruixuan Li
Vision Transformer (ViT) has achieved remarkable success due to its large-scale pretraining on general domains, but it still faces challenges when applying it to downstream distant domains that have only scarce training data, which gives rise to the Cross-Domain Few-Shot Learning (CDFSL) task. Inspired by Self-Attention’s insensitivity to token orders, we find an interesting phenomenon neglected in current works: disrupting the continuity of image tokens (i.e., making pixels not smoothly transited across patches) in ViT leads to a noticeable performance decline in the general (source) domain but only a marginal decrease in downstream target domains. This questions the role of image tokens’ continuity in ViT’s generalization under large domain gaps. In this paper, we delve into this phenomenon for an interpretation. We find continuity aids ViT in learning larger spatial patterns, which are harder to transfer than smaller ones, enlarging domain distances. Meanwhile, it implies that only smaller patterns within each patch could be transferred under extreme domain gaps. Based on this interpretation, we further propose a simple yet effective method for CDFSL that better disrupts the continuity of image tokens, encouraging the model to rely less on large patterns and more on smaller ones. Extensive experiments show the effectiveness of our method in reducing domain gaps and outperforming state-of-the-art works. Codes and models are available at https://github.com/shuaiyi308/ReCIT.
Vision Transformer(ViT)由于在通用领域的大规模预训练而取得了显著的成功,但在应用于只有少量训练数据的下游领域时仍面临挑战,这引发了跨域小样本学习(CDFSL)的任务。受自注意力对令牌顺序的不敏感性的启发,我们发现当前工作中忽略了一个有趣的现象:破坏图像令牌连续性(即,使像素在补丁之间不平稳过渡)在ViT中会导致在一般(源)领域的性能显著下降,但在下游目标领域只会导致轻微的性能下降。这质疑了图像令牌连续性在ViT跨大领域差距时的通用化作用。本文深入探讨了这一现象以进行解释。我们发现连续性有助于ViT学习更大的空间模式,这些模式比小的模式更难迁移,从而扩大了领域间的距离。同时,它暗示在极端的领域差距下,每个补丁内的小模式可能会发生转移。基于这一解释,我们进一步提出了一种简单有效的CDFSL方法,更好地破坏了图像令牌的连续性,鼓励模型更少地依赖大模式,更多地依赖小模式。大量实验表明,我们的方法在减少领域差距和性能上优于最新技术。相关代码和模型可在https://github.com/shuaiyi308/ReCIT上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025(spotlight)
Summary
ViT在大规模通用域预训练上取得了显著成功,但在应用于下游的远距离领域时仍面临挑战,特别是在训练数据稀缺的情况下。本文研究了ViT中图像标记的连续性对跨域少样本学习的影响,发现破坏图像标记的连续性有助于提高模型在目标领域的性能。通过深入研究这一现象,本文提出了一种简单而有效的方法,通过更好地破坏图像标记的连续性来减少领域差距,并超越现有的前沿工作。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer (ViT) 在大规模预训练方面取得了成功,但在应用于下游的远距离领域时仍面临挑战。
- 破坏图像标记的连续性(即像素在补丁之间不平稳过渡)在一般(源)域会导致性能显著下降,但在下游目标域仅导致轻微下降。
- 图像标记的连续性有助于ViT学习更大的空间模式,这些模式在极端领域差异下难以转移。这意味着在极端领域差异下,每个补丁内的小模式可能被转移。
- 基于这一发现,本文提出了一种简单而有效的方法,通过更好地破坏图像标记的连续性来鼓励模型更少地依赖大模式,更多地依赖小模式。
- 该方法在减少领域差距方面表现出色,并超越了现有的前沿工作。
- 论文提供了相关的代码和模型链接供研究者和开发者使用。
点此查看论文截图

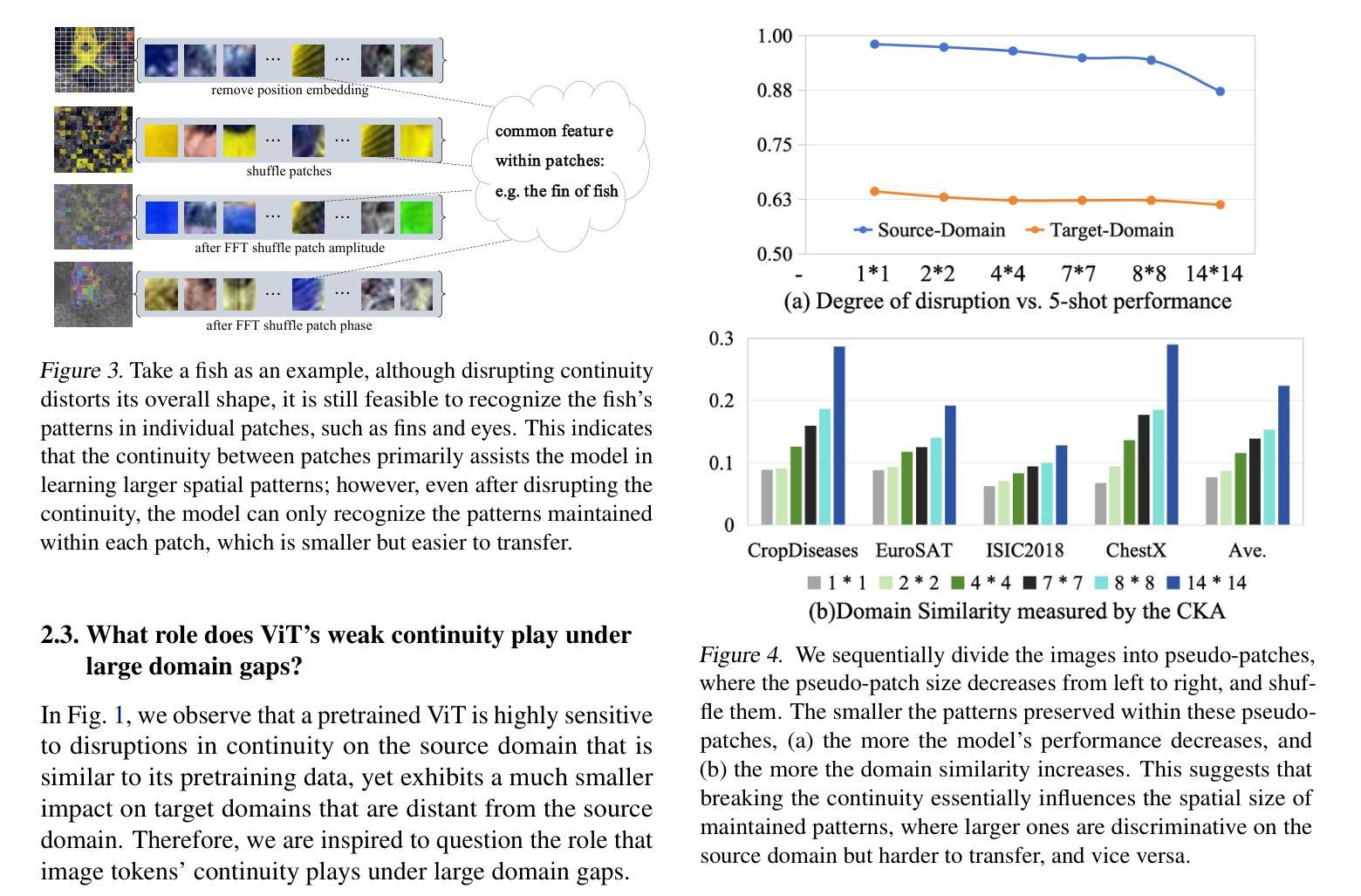
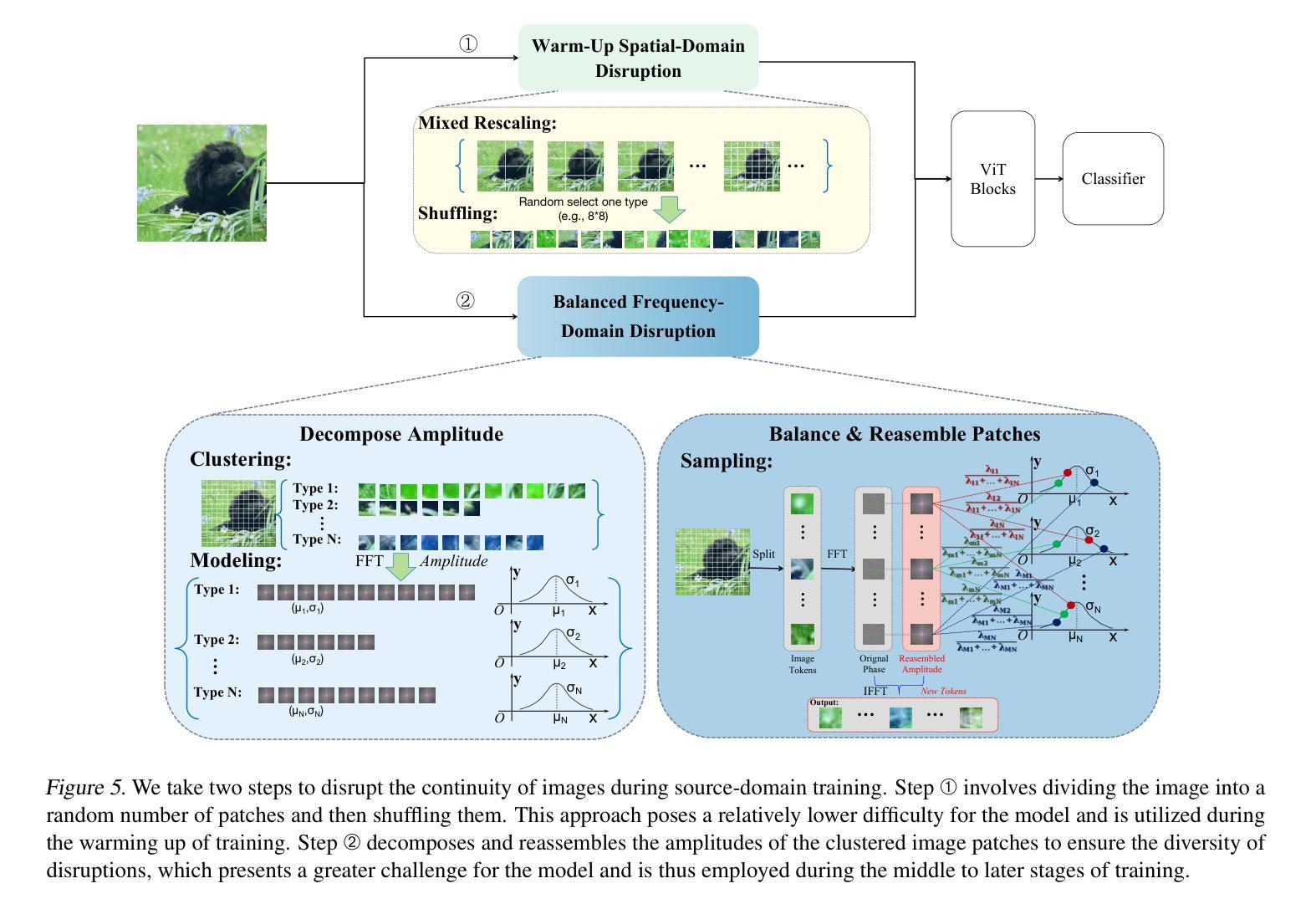
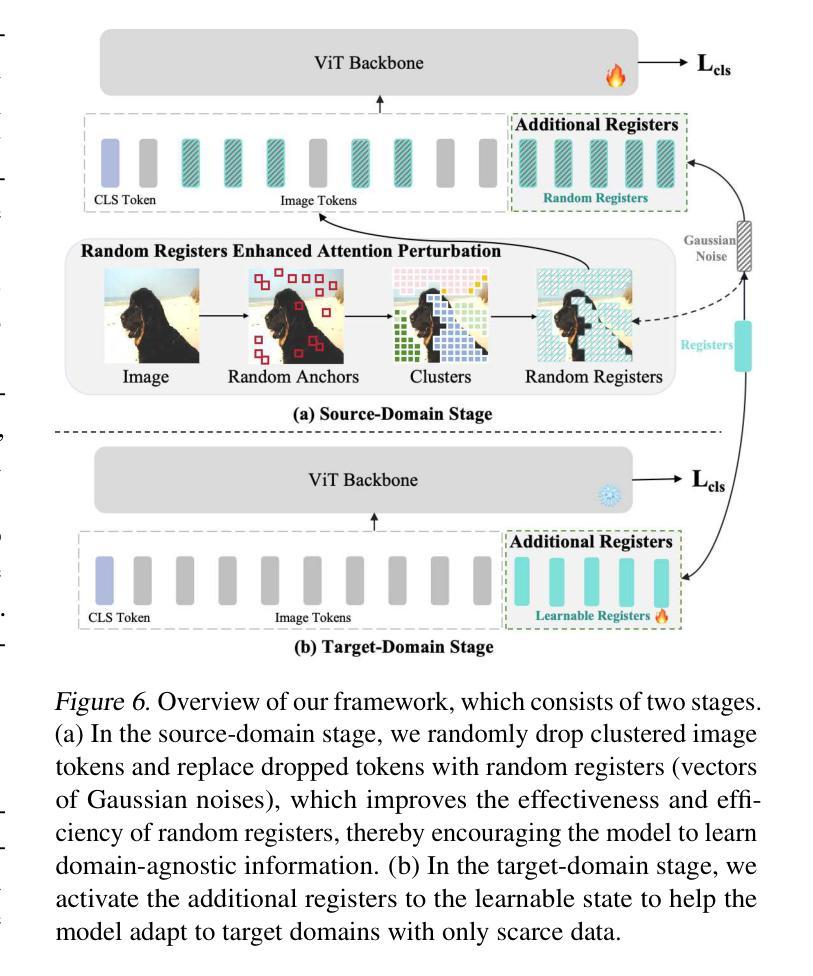
Random Registers for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Shuai Yi, Yixiong Zou, Yuhua Li, Ruixuan Li
Cross-domain few-shot learning (CDFSL) aims to transfer knowledge from a data-sufficient source domain to data-scarce target domains. Although Vision Transformer (ViT) has shown superior capability in many vision tasks, its transferability against huge domain gaps in CDFSL is still under-explored. In this paper, we find an intriguing phenomenon: during the source-domain training, prompt tuning, as a common way to train ViT, could be harmful for the generalization of ViT in target domains, but setting them to random noises (i.e., random registers) could consistently improve target-domain performance. We then delve into this phenomenon for an interpretation. We find that learnable prompts capture domain information during the training on the source dataset, which views irrelevant visual patterns as vital cues for recognition. This can be viewed as a kind of overfitting and increases the sharpness of the loss landscapes. In contrast, random registers are essentially a novel way of perturbing attention for the sharpness-aware minimization, which helps the model find a flattened minimum in loss landscapes, increasing the transferability. Based on this phenomenon and interpretation, we further propose a simple but effective approach for CDFSL to enhance the perturbation on attention maps by adding random registers on the semantic regions of image tokens, improving the effectiveness and efficiency of random registers. Extensive experiments on four benchmarks validate our rationale and state-of-the-art performance. Codes and models are available at https://github.com/shuaiyi308/REAP.
跨域小样本学习(CDFSL)旨在将从数据充足来源域的知识转移到数据稀缺的目标域。尽管Vision Transformer(ViT)在许多视觉任务中表现出了卓越的能力,但在CDFSL中针对巨大的域差异的可转移性仍然未被充分探索。在本文中,我们发现了一个有趣的现象:在源域训练过程中,作为训练ViT的一种常见方法,提示调整可能会损害ViT在目标域中的泛化能力,但将其设置为随机噪声(即随机寄存器)可以持续提高目标域的性能。然后,我们深入研究了这一现象并进行了解释。我们发现,在源数据集上进行训练时,可学习的提示会捕获域信息,将不相关的视觉模式视为识别的关键线索。这可以被视为一种过拟合,并增加了损失景观的尖锐度。相比之下,随机寄存器本质上是扰动注意力的一种新型方式,用于尖锐度感知最小化,有助于模型在损失景观中找到平坦的最小值,从而提高可转移性。基于这种现象和解释,我们进一步提出了针对CDFSL的简单有效方法,通过在图像令牌的语义区域上添加随机寄存器来加强对注意力图的扰动,提高了随机寄存器的有效性和效率。在四个基准测试上的大量实验验证了我们理论的合理性并达到了最新技术水平。相关代码和模型可访问https://github.com/shuaiyi308/REAP。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025
Summary
本文探讨了跨域小样本学习(CDFSL)中,Vision Transformer(ViT)在源域训练时的prompt tuning对目标域泛化性能的影响。研究发现,相较于使用prompt tuning,将模型设置为随机噪声(即随机寄存器)可以提高目标域的性能。本文进一步探究其原因,发现学习到的提示在源数据集训练时会捕获域信息,这可能使模型对特定模式的视觉图案过于敏感而降低泛化性能。与此相反,随机寄存器本质上是一种对注意力进行扰动的方法,有助于模型在损失景观中找到平坦的最小值,从而提高迁移能力。基于此现象和解释,本文提出了一种针对CDFSL的简单有效的随机寄存器强化注意力图的方案,实现较高的效果。同时有众多实验验证了该方案的有效性。相关代码和模型已在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer在跨域小样本学习中的迁移能力尚未得到充分研究。
- 提示训练可能会捕获源域的特定信息,导致模型在目标域的泛化性能下降。
- 随机噪声(随机寄存器)的设定有助于模型提高目标域的性能表现。这种噪声可以使模型注意力得以扰动并降低过拟合风险。
- 通过随机寄存器强化注意力图的方法可以进一步提升模型在CDFSL中的表现。
- 该方法在不同基准测试上的表现均优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

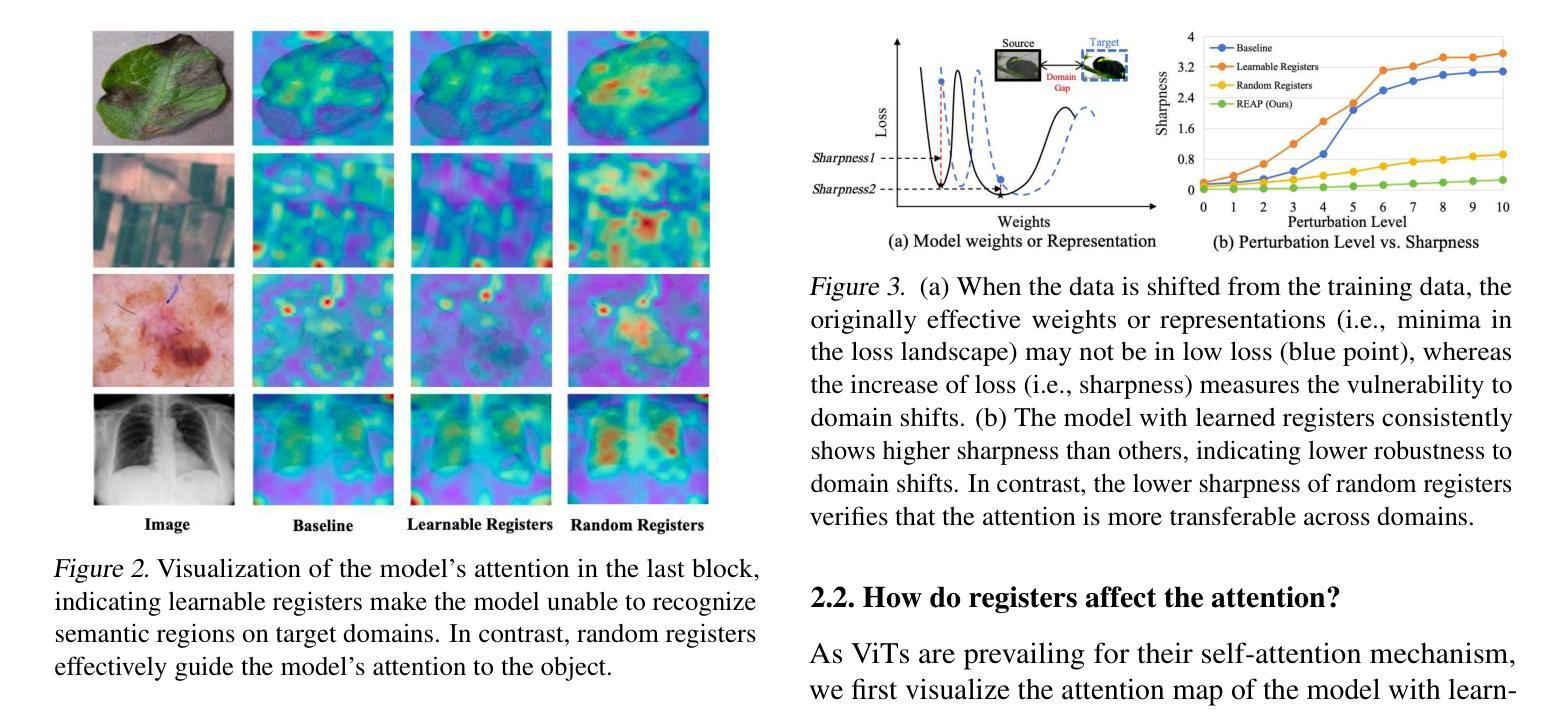
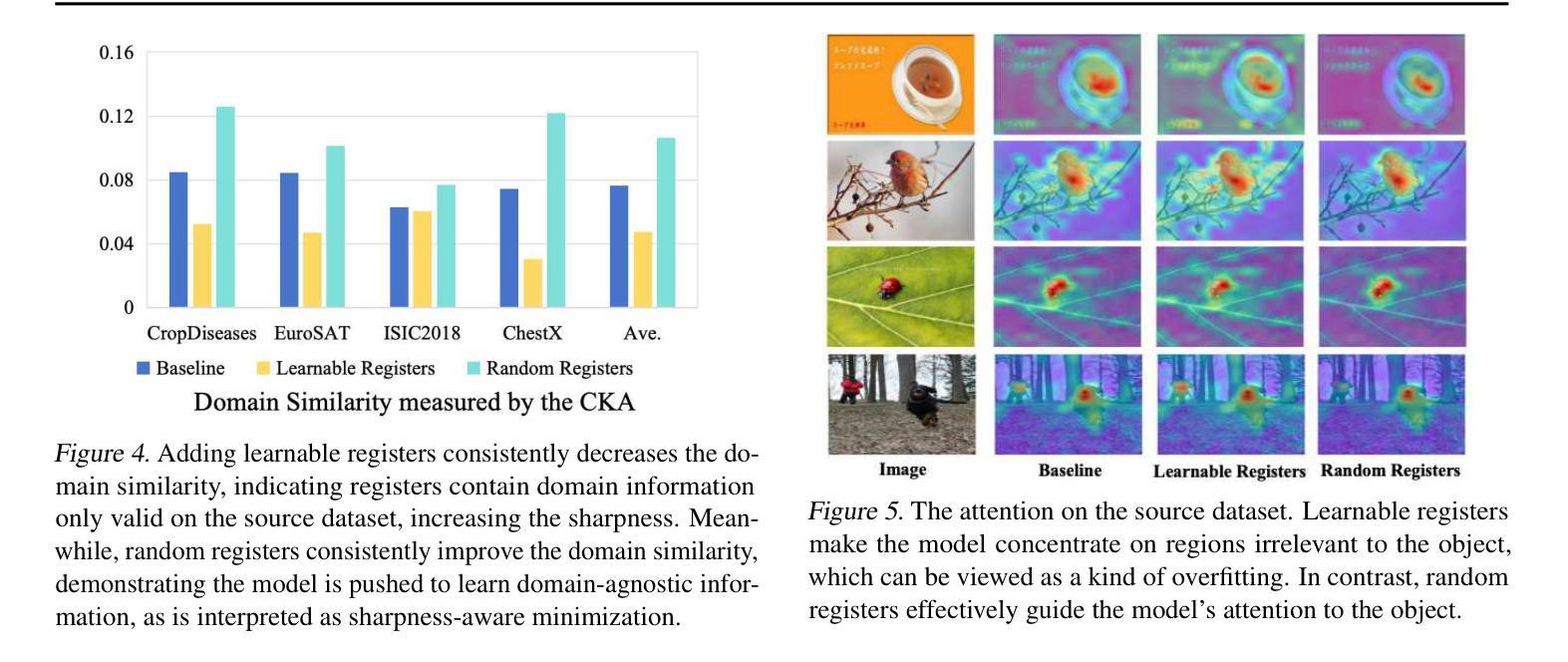
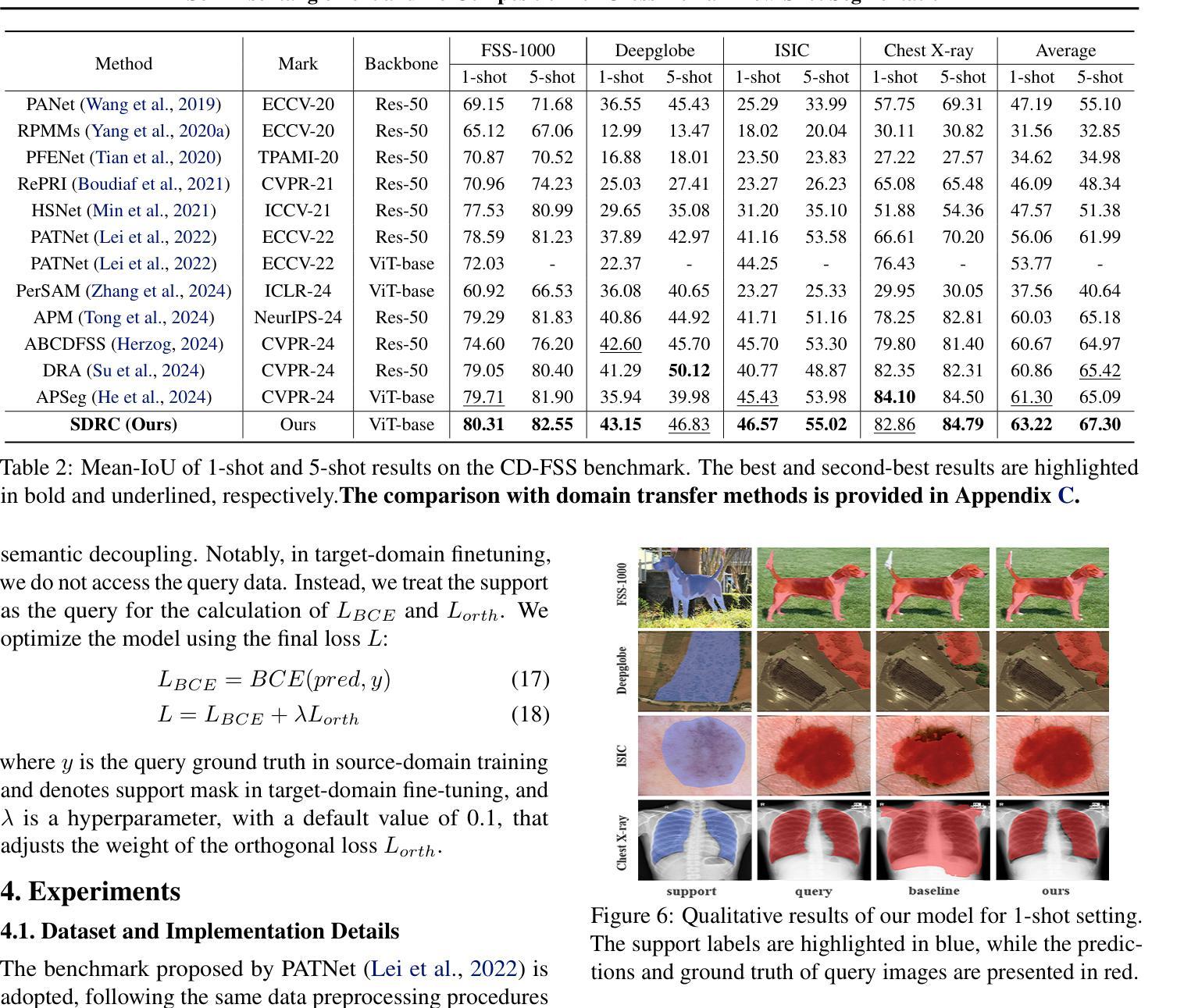
Self-Disentanglement and Re-Composition for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Segmentation
Authors:Jintao Tong, Yixiong Zou, Guangyao Chen, Yuhua Li, Ruixuan Li
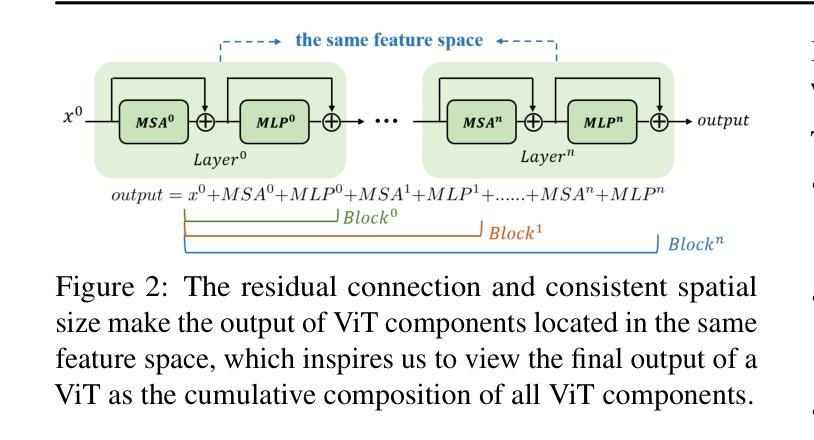
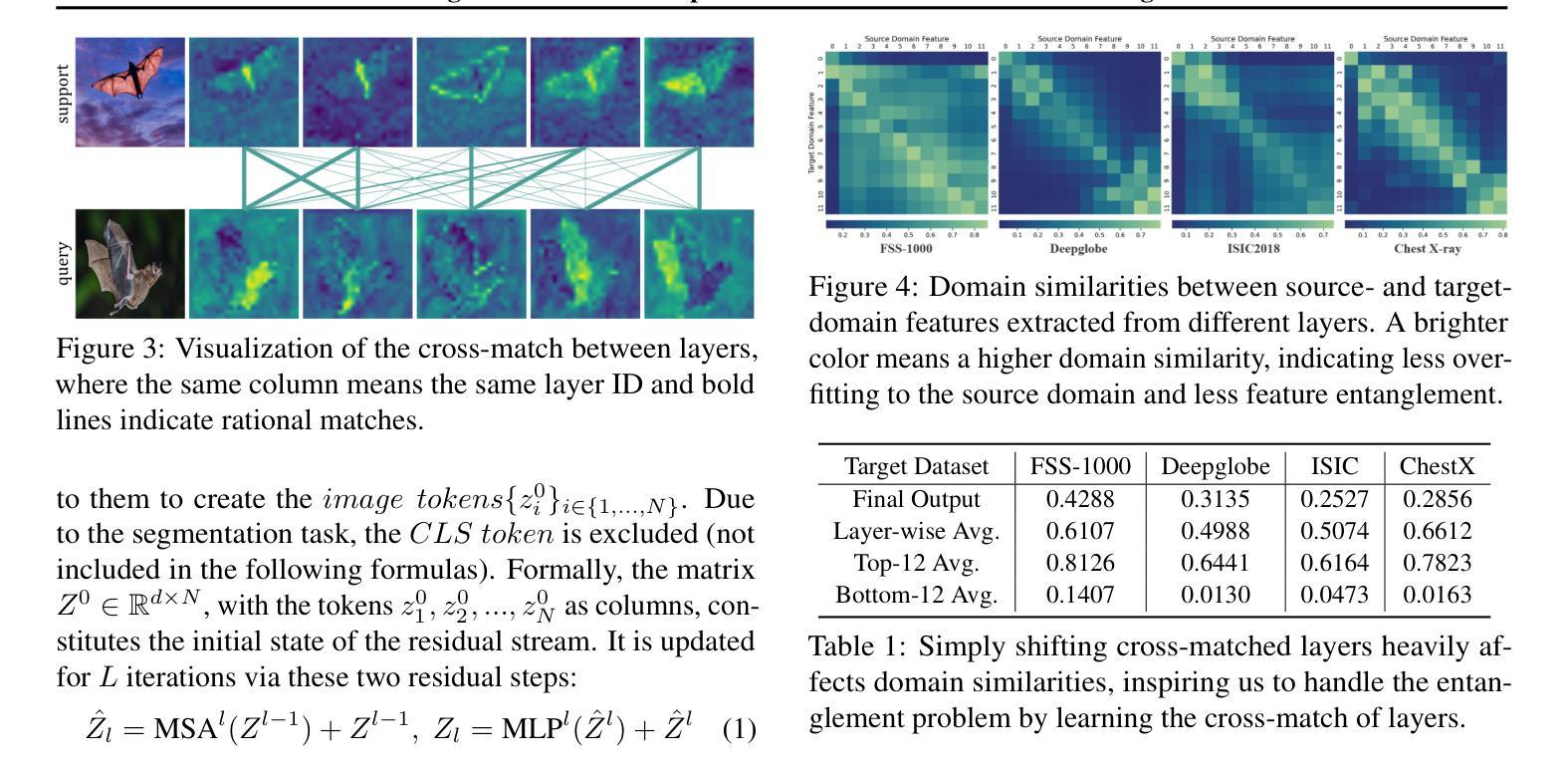
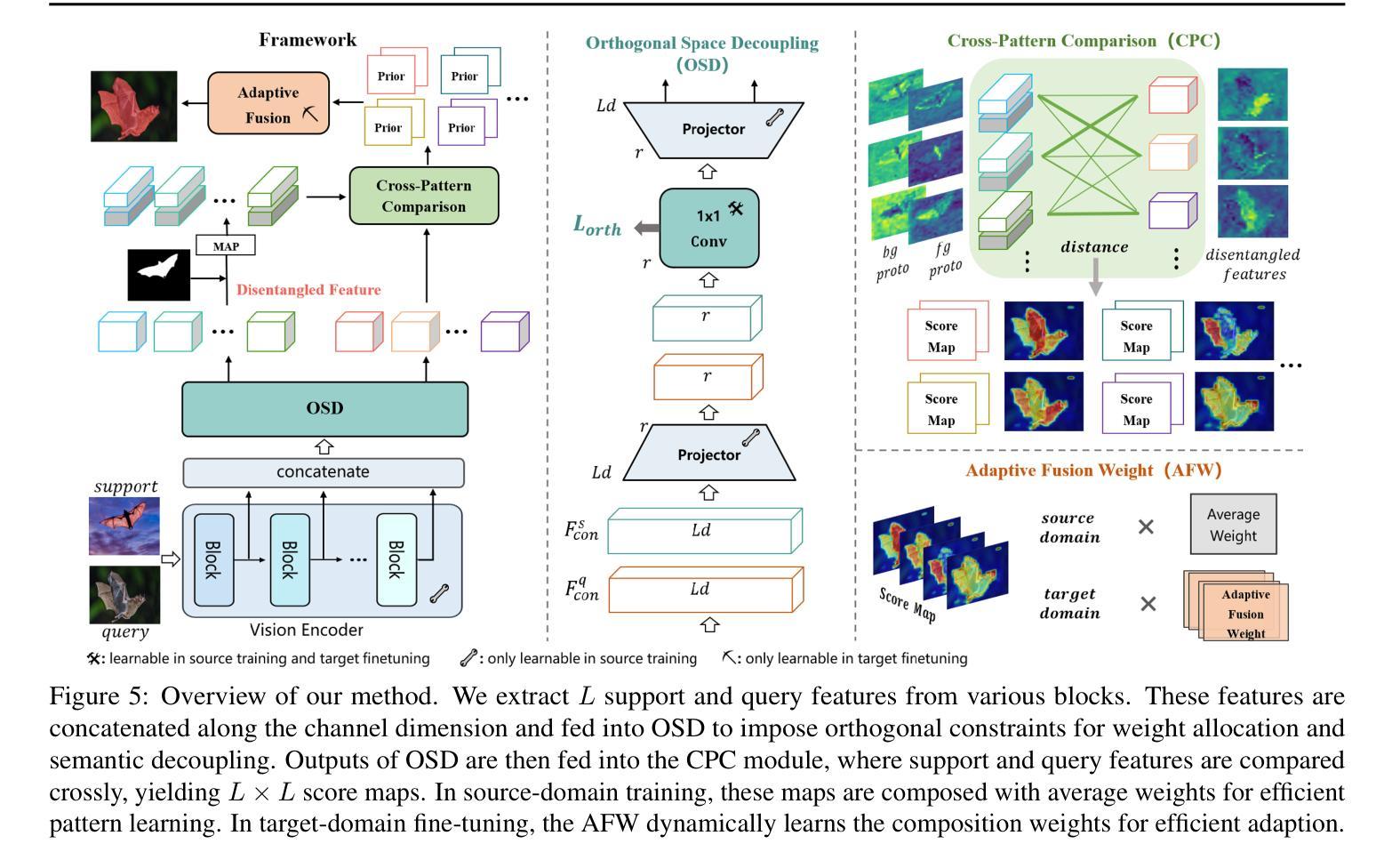
Cross-Domain Few-Shot Segmentation (CD-FSS) aims to transfer knowledge from a source-domain dataset to unseen target-domain datasets with limited annotations. Current methods typically compare the distance between training and testing samples for mask prediction. However, we find an entanglement problem exists in this widely adopted method, which tends to bind sourcedomain patterns together and make each of them hard to transfer. In this paper, we aim to address this problem for the CD-FSS task. We first find a natural decomposition of the ViT structure, based on which we delve into the entanglement problem for an interpretation. We find the decomposed ViT components are crossly compared between images in distance calculation, where the rational comparisons are entangled with those meaningless ones by their equal importance, leading to the entanglement problem. Based on this interpretation, we further propose to address the entanglement problem by learning to weigh for all comparisons of ViT components, which learn disentangled features and re-compose them for the CD-FSS task, benefiting both the generalization and finetuning. Experiments show that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art CD-FSS method by 1.92% and 1.88% in average accuracy under 1-shot and 5-shot settings, respectively.
跨域小样本分割(CD-FSS)旨在将源域数据集的知识转移到未见过的目标域数据集上,且目标域数据集标注有限。当前的方法通常通过比较训练和测试样本之间的距离来进行掩膜预测。然而,我们发现广泛采用的这种方法中存在纠缠问题,它倾向于将源域模式绑定在一起,使得每个模式都难以转移。本文旨在解决CD-FSS任务中的这个问题。首先,我们找到了ViT结构的自然分解,并在此基础上深入研究了纠缠问题以进行解释。我们发现分解后的ViT组件在距离计算时会进行图像间的交叉比较,其中合理的比较与无意义的比较纠缠在一起,具有同等重要性,导致了纠缠问题。基于这一解释,我们进一步提出通过为所有ViT组件的比较学习权重来解决纠缠问题,这些组件学习解耦的特征并重新组合它们以用于CD-FSS任务,有益于泛化和微调。实验表明,我们的模型在平均准确率上超过了最新的CD-FSS方法,在1次和5次拍摄设置下分别提高了1.92%和1.88%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025
Summary
本文研究了跨域小样本分割(CD-FSS)任务中的纠缠问题,并对此提出了解决方案。文章首先基于ViT结构进行了自然分解,发现了纠缠问题的存在,然后提出了通过学习为ViT组件的对比进行加权来解决纠缠问题的方法。该方法能够学习解纠缠特征并重新组合,有助于提高CD-FSS任务的泛化和微调能力。实验表明,该方法在平均准确率上超过了现有CD-FSS方法。
Key Takeaways
- CD-FSS任务旨在从源域数据集向未见过的目标域数据集进行知识迁移,且目标数据集标注有限。
- 当前方法主要通过比较训练和测试样本之间的距离来进行掩膜预测,但存在纠缠问题,即源域模式相互绑定,难以进行迁移。
- 文章基于ViT结构进行了自然分解,发现了纠缠问题的存在,并对此进行了详细解释。
- 文章指出,ViT组件在距离计算中进行交叉比较时,有意义的比较和无意义的比较纠缠在一起,导致纠缠问题。
- 为了解决纠缠问题,文章提出了通过学习为ViT组件的对比进行加权的方法,该方法能够学习解纠缠特征并重新组合。
- 该方法有助于提高CD-FSS任务的泛化和微调能力。
点此查看论文截图

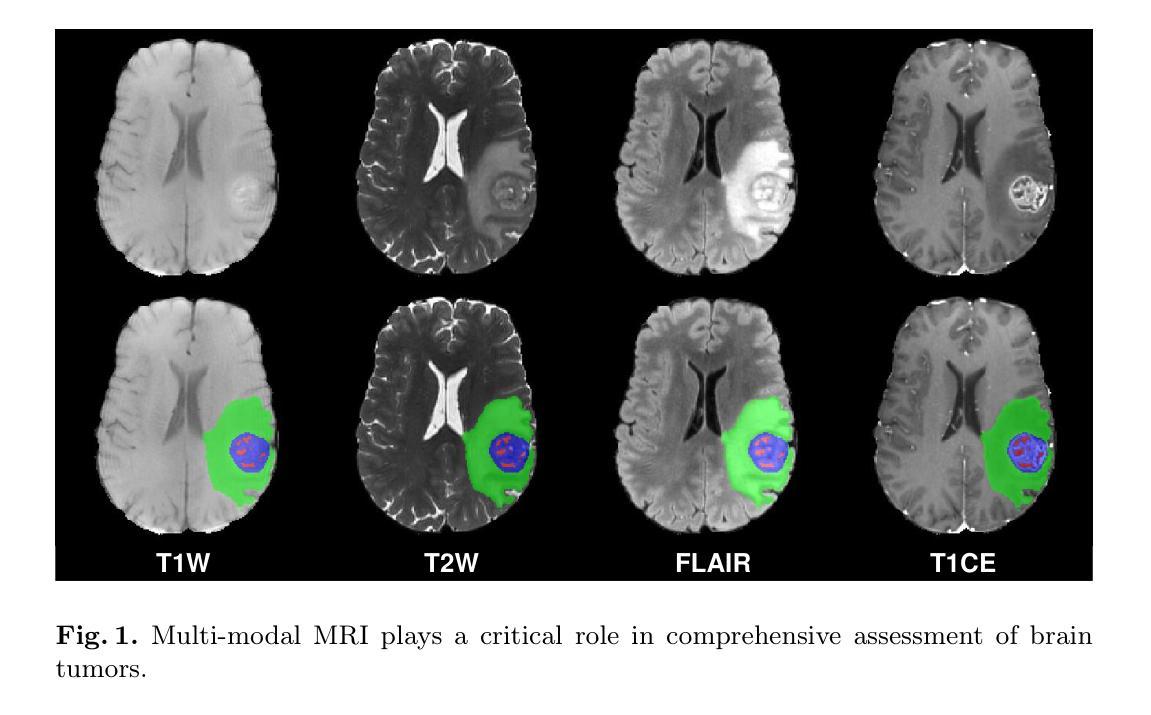
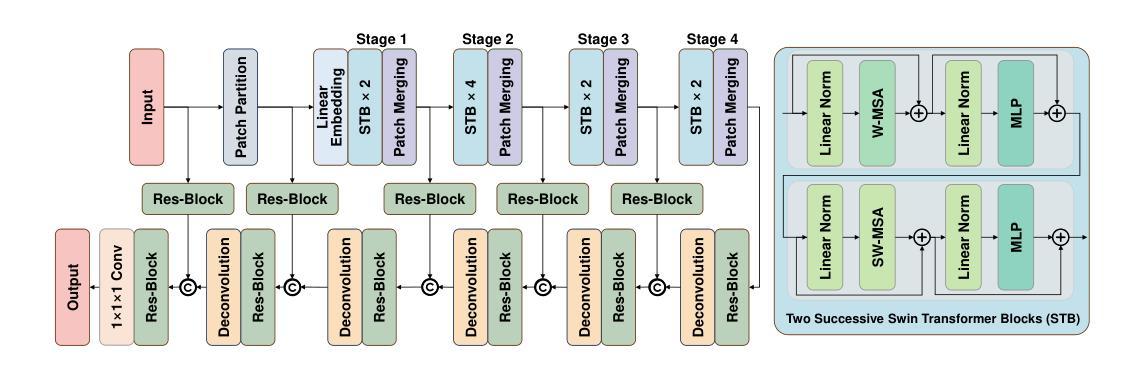
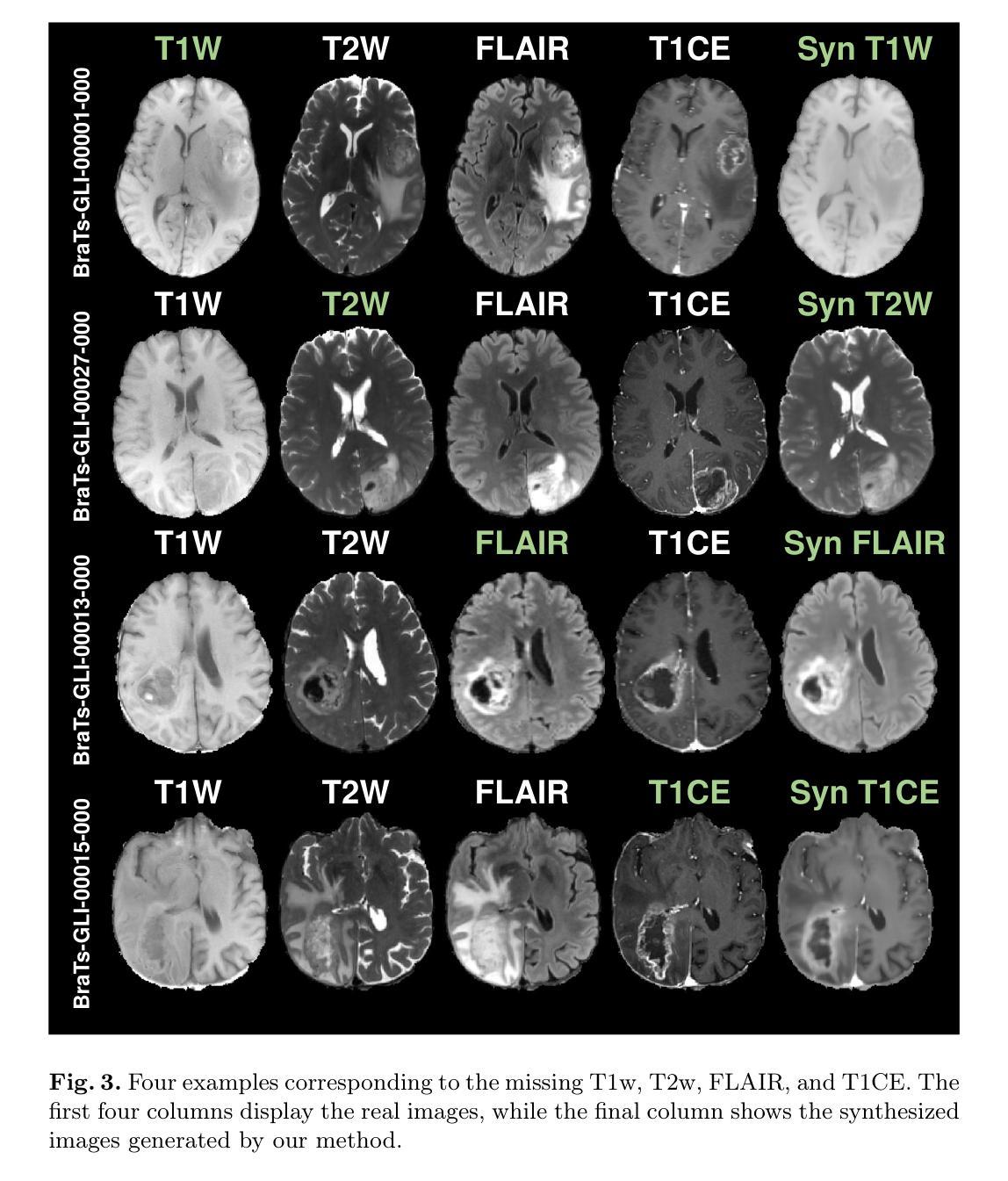
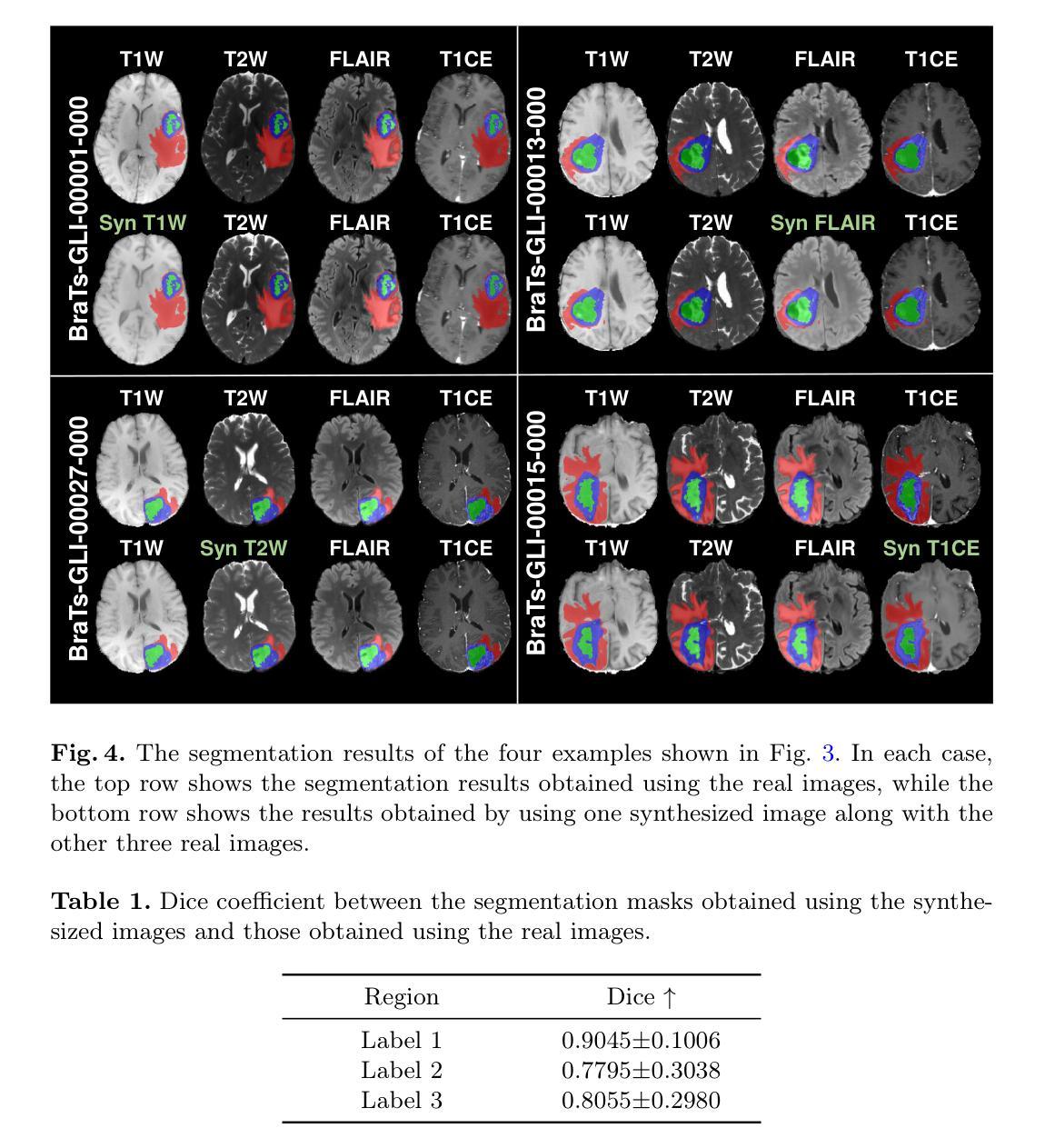
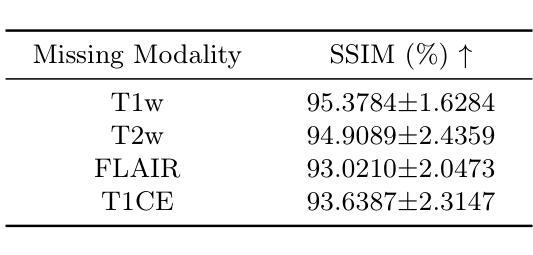
Multi-modal brain MRI synthesis based on SwinUNETR
Authors:Haowen Pang, Weiyan Guo, Chuyang Ye
Multi-modal brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays a crucial role in clinical diagnostics by providing complementary information across different imaging modalities. However, a common challenge in clinical practice is missing MRI modalities. In this paper, we apply SwinUNETR to the synthesize of missing modalities in brain MRI. SwinUNETR is a novel neural network architecture designed for medical image analysis, integrating the strengths of Swin Transformer and convolutional neural networks (CNNs). The Swin Transformer, a variant of the Vision Transformer (ViT), incorporates hierarchical feature extraction and window-based self-attention mechanisms, enabling it to capture both local and global contextual information effectively. By combining the Swin Transformer with CNNs, SwinUNETR merges global context awareness with detailed spatial resolution. This hybrid approach addresses the challenges posed by the varying modality characteristics and complex brain structures, facilitating the generation of accurate and realistic synthetic images. We evaluate the performance of SwinUNETR on brain MRI datasets and demonstrate its superior capability in generating clinically valuable images. Our results show significant improvements in image quality, anatomical consistency, and diagnostic value.
多模态脑磁共振成像(MRI)在临床诊断中扮演着至关重要的角色,因为它能提供不同成像模式之间的互补信息。然而,在临床实践中,一个常见的挑战是缺失MRI模式。在本文中,我们将SwinUNETR应用于脑MRI中缺失模式的合成。SwinUNETR是一种为医学图像分析设计的新型神经网络架构,融合了Swin Transformer和卷积神经网络(CNN)的优势。Swin Transformer是Vision Transformer(ViT)的一种变体,结合了分层特征提取和基于窗口的自注意力机制,能够有效地捕捉局部和全局上下文信息。通过将Swin Transformer与CNN相结合,SwinUNETR融合了全局上下文意识和详细的空间分辨率。这种混合方法解决了不同模态特征和复杂脑结构所带来的挑战,有利于生成准确和逼真的合成图像。我们在脑MRI数据集上评估了SwinUNETR的性能,并展示了其在生成具有临床价值图像方面的卓越能力。我们的结果在图像质量、解剖一致性和诊断价值方面都有显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 5 figures
Summary
基于多模态脑磁共振成像(MRI)在临床诊断中的重要作用,本文利用SwinUNETR合成缺失模态的脑MRI。SwinUNETR是一种用于医学图像分析的新型神经网络架构,结合了Swin Transformer和卷积神经网络(CNN)的优势。该架构融合了全局上下文感知和精细的空间分辨率,能有效应对不同模态特征和复杂脑结构带来的挑战,生成准确逼真的合成图像。在脑MRI数据集上的评估结果表明,SwinUNETR在图像质量、解剖一致性和诊断价值方面表现出卓越的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态MRI在临床诊断中提供不同成像模态的互补信息,对缺失模态的合成具有挑战。
- SwinUNETR是一种结合了Swin Transformer和CNN的新型神经网络架构,用于医学图像分析。
- Swin Transformer是Vision Transformer(ViT)的一种变体,具有层次化特征提取和基于窗口的自注意力机制,能捕捉局部和全局上下文信息。
- SwinUNETR将全局上下文感知与精细的空间分辨率相结合,应对不同模态特征和复杂脑结构的挑战。
- SwinUNETR在脑MRI数据集上的性能评估表明其在图像质量、解剖一致性和诊断价值方面的卓越能力。
- SwinUNETR生成的合成图像具有准确性和逼真性。
- 该方法在临床应用中有潜力提高诊断的准确性和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

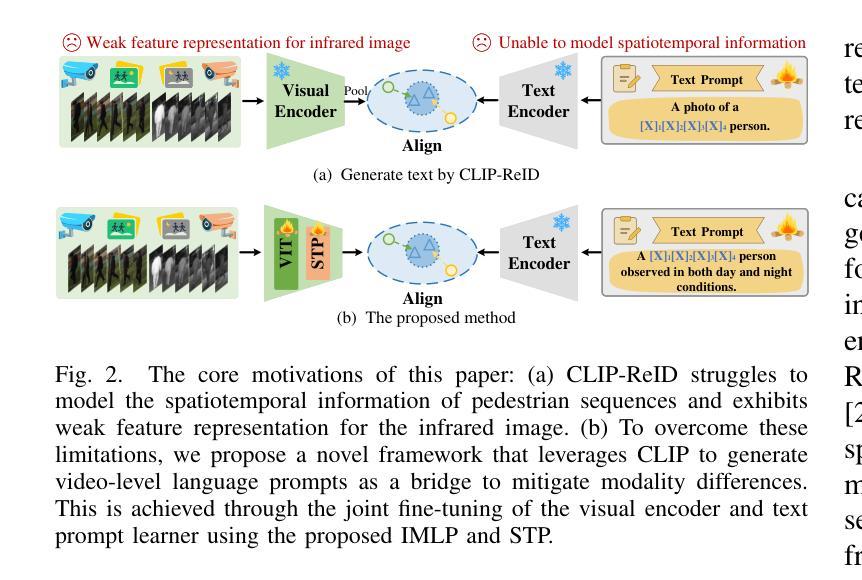
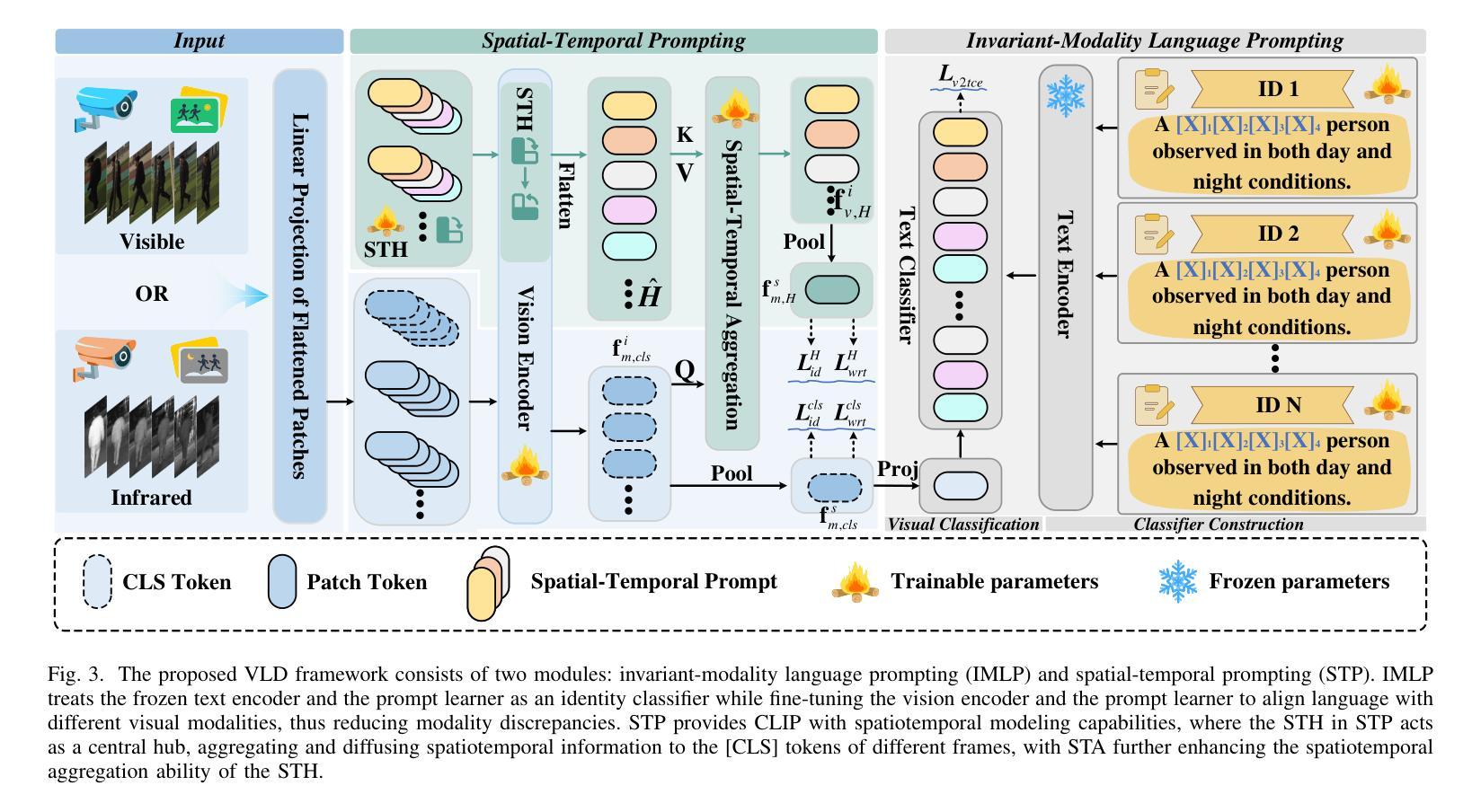
Video-Level Language-Driven Video-Based Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification
Authors:Shuang Li, Jiaxu Leng, Changjiang Kuang, Mingpi Tan, Xinbo Gao
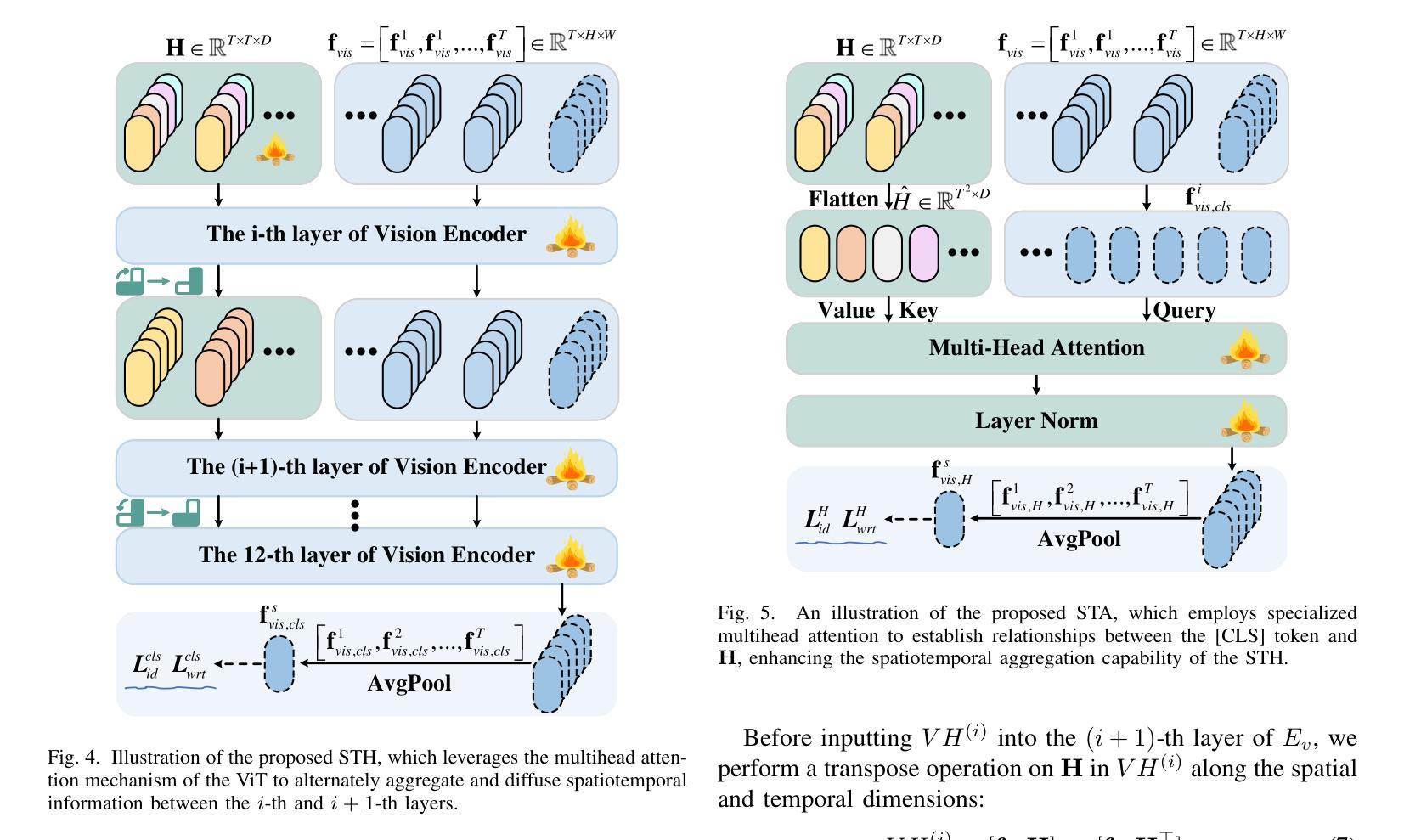
Video-based Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification (VVI-ReID) aims to match pedestrian sequences across modalities by extracting modality-invariant sequence-level features. As a high-level semantic representation, language provides a consistent description of pedestrian characteristics in both infrared and visible modalities. Leveraging the Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) model to generate video-level language prompts and guide the learning of modality-invariant sequence-level features is theoretically feasible. However, the challenge of generating and utilizing modality-shared video-level language prompts to address modality gaps remains a critical problem. To address this problem, we propose a simple yet powerful framework, video-level language-driven VVI-ReID (VLD), which consists of two core modules: invariant-modality language prompting (IMLP) and spatial-temporal prompting (STP). IMLP employs a joint fine-tuning strategy for the visual encoder and the prompt learner to effectively generate modality-shared text prompts and align them with visual features from different modalities in CLIP’s multimodal space, thereby mitigating modality differences. Additionally, STP models spatiotemporal information through two submodules, the spatial-temporal hub (STH) and spatial-temporal aggregation (STA), which further enhance IMLP by incorporating spatiotemporal information into text prompts. The STH aggregates and diffuses spatiotemporal information into the [CLS] token of each frame across the vision transformer (ViT) layers, whereas STA introduces dedicated identity-level loss and specialized multihead attention to ensure that the STH focuses on identity-relevant spatiotemporal feature aggregation. The VLD framework achieves state-of-the-art results on two VVI-ReID benchmarks. The code will be released at https://github.com/Visuang/VLD.
基于视频的可见光-红外行人再识别(VVI-ReID)旨在通过提取跨模态的序列级特征来匹配跨模态的行人序列。作为一种高级语义表示,语言为红外和可见光两种模态下的行人特征提供了连贯的描述。利用对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型生成视频级语言提示并引导学习跨模态的序列级特征在理论上可行。然而,生成和利用跨模态共享的视频级语言提示来解决模态差异的挑战仍然是关键性问题。针对这一问题,我们提出了一个简单而强大的框架,即视频级语言驱动VVI-ReID(VLD),它包含两个核心模块:不变模态语言提示(IMLP)和空间时间提示(STP)。IMLP采用联合微调策略,对视觉编码器和提示学习者进行有效训练,以生成跨模态共享文本提示,并将它们与CLIP多模态空间中的不同模态的视觉特征对齐,从而减轻模态差异。此外,STP通过两个子模块,即空间时间中心(STH)和空间时间聚合(STA),对时空信息进行建模,通过将时空信息融入文本提示来进一步增强IMLP。STH将每帧的时空信息聚合并扩散到视觉转换器(ViT)各层的[CLS]标记中,而STA引入专用的身份级损失和特殊的多头注意力,以确保STH专注于身份相关的时空特征聚合。VLD框架在两个VVI-ReID基准测试中达到了最新水平的结果。代码将在https://github.com/Visuang/VLD上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE TIFS
摘要
基于视频的多模态行人再识别(VVI-ReID)旨在通过提取跨模态的序列级特征来匹配不同模态下的行人序列。本研究提出一种简洁而强大的框架,即视频级语言驱动的VVI-ReID(VLD),该框架包括两个核心模块:不变模态语言提示(IMLP)和时空提示(STP)。IMLP采用联合微调策略,对视觉编码器和提示学习者进行有效训练,生成跨模态共享文本提示,并将它们与不同模态的视觉特征对齐到CLIP的多模态空间中,从而减轻模态差异。STP模块通过两个子模块(时空中心和时空聚合)将时空信息融入文本提示中,进一步增强IMLP的效果。该框架在两项VVI-ReID基准测试中取得了最新成果。代码将发布在https://github.com/Visuang/VLD。
要点提炼
- VVI-ReID的目标是匹配跨模态的行人序列,通过提取序列级特征来进行识别。
- 利用Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP)模型生成视频级语言提示,为解决模态差异问题提供了理论可行性。
- 提出的视频级语言驱动框架(VLD)包含两个核心模块:不变模态语言提示(IMLP)和时空提示(STP)。
- IMLP模块通过联合微调策略生成跨模态共享文本提示,并减轻模态差异。
- STP模块通过时空中心和时空聚合两个子模块融入时空信息,进一步增强识别效果。
- 该框架在VVI-ReID的基准测试中取得了最新成果。
点此查看论文截图

Dual-Process Image Generation
Authors:Grace Luo, Jonathan Granskog, Aleksander Holynski, Trevor Darrell
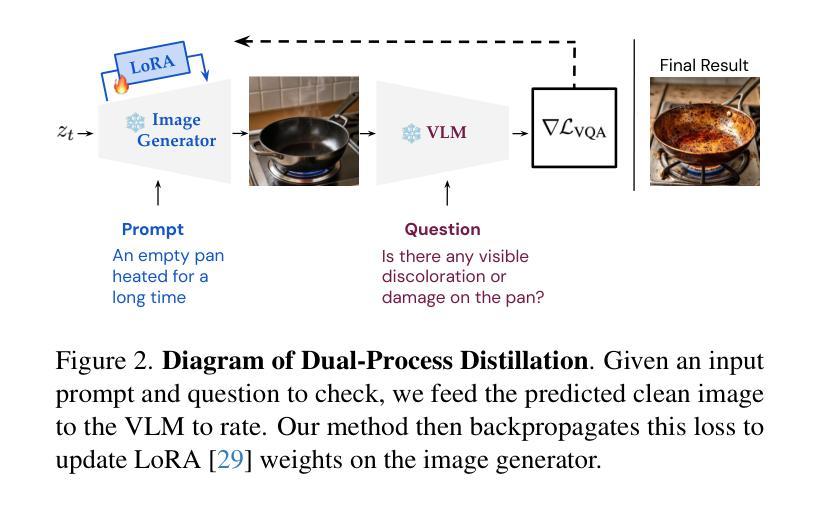
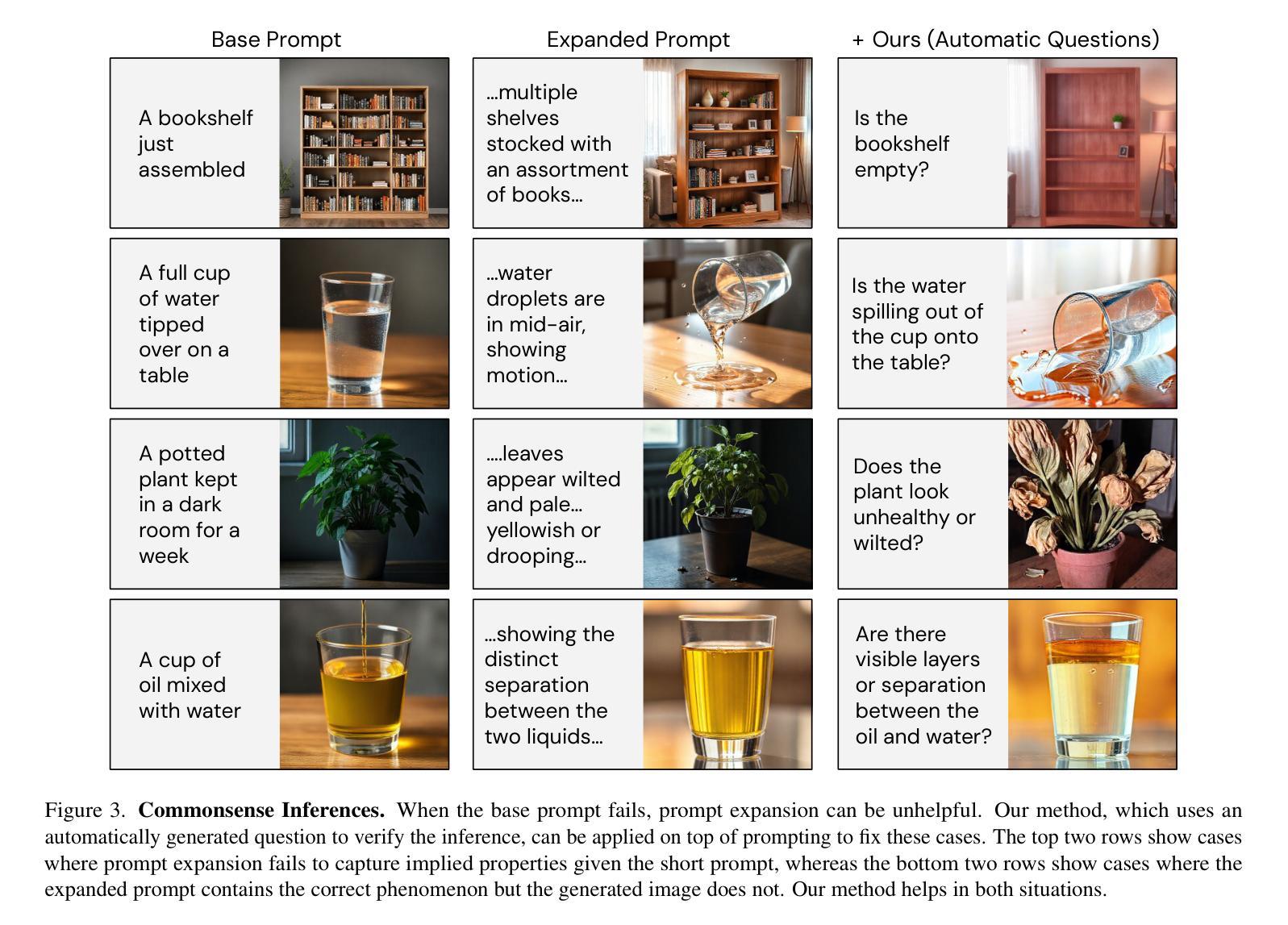
Prior methods for controlling image generation are limited in their ability to be taught new tasks. In contrast, vision-language models, or VLMs, can learn tasks in-context and produce the correct outputs for a given input. We propose a dual-process distillation scheme that allows feed-forward image generators to learn new tasks from deliberative VLMs. Our scheme uses a VLM to rate the generated images and backpropagates this gradient to update the weights of the image generator. Our general framework enables a wide variety of new control tasks through the same text-and-image based interface. We showcase a handful of applications of this technique for different types of control signals, such as commonsense inferences and visual prompts. With our method, users can implement multimodal controls for properties such as color palette, line weight, horizon position, and relative depth within a matter of minutes. Project page: https://dual-process.github.io.
先前控制图像生成的方法在教授新任务方面的能力有限。相比之下,视觉语言模型(VLM)可以在上下文中学习任务并为给定输入产生正确的输出。我们提出了一种双过程蒸馏方案,该方案允许前馈图像生成器从深思熟虑的VLM中学习新任务。我们的方案使用VLM对生成的图像进行评分,并将此梯度反向传播以更新图像生成器的权重。我们的通用框架通过相同的文本和图像接口支持多种新控制任务。我们展示了该技术在不同类型的控制信号方面的几个应用,如常识推理和视觉提示。使用我们的方法,用户可以在几分钟内实现颜色调、线条粗细、地平位置以及相对深度等多模式控制。项目页面:https://dual-process.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种双过程蒸馏方案,该方案允许前馈图像生成器从深思熟虑的视界语言模型(VLMs)学习新任务。通过利用VLM对生成的图像进行评分并将梯度反向传播以更新图像生成器的权重,该方案实现了文本和图像基于接口的多样化新控制任务。该技术可快速实现多种控制信号的应用,如常识推理和视觉提示,用户可以在几分钟内实现颜色调色板、线条粗细、地平线位置和相对深度的多模式控制。
Key Takeaways
- 现有图像生成控制方法存在无法学习新任务的局限性。
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)可以在上下文中学习新任务并为给定输入产生正确输出。
- 提出的双过程蒸馏方案允许前馈图像生成器从深思熟虑的VLMs学习新任务。
- 该方案使用VLM对生成的图像进行评分,并通过反向传播更新图像生成器的权重。
- 该框架通过文本和图像接口支持多种新控制任务。
- 该技术可以快速实现多种控制信号的应用,如常识推理和视觉提示。
- 用户可以迅速实现颜色调色板、线条粗细、地平线位置和相对深度的多模式控制。
点此查看论文截图


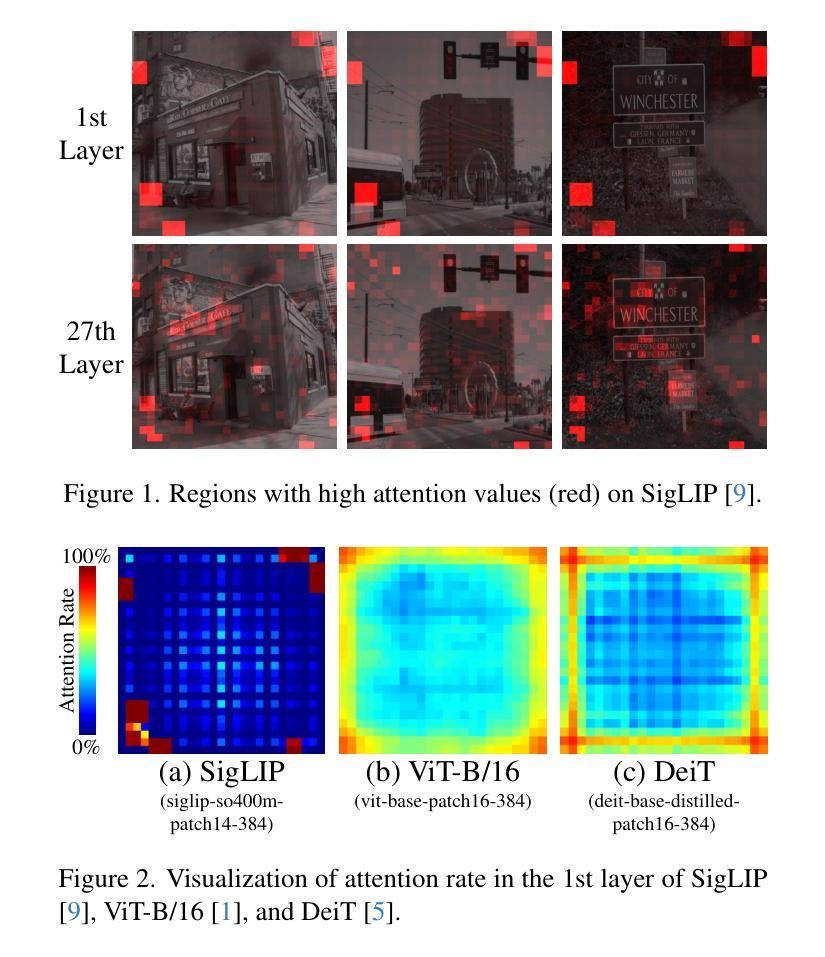
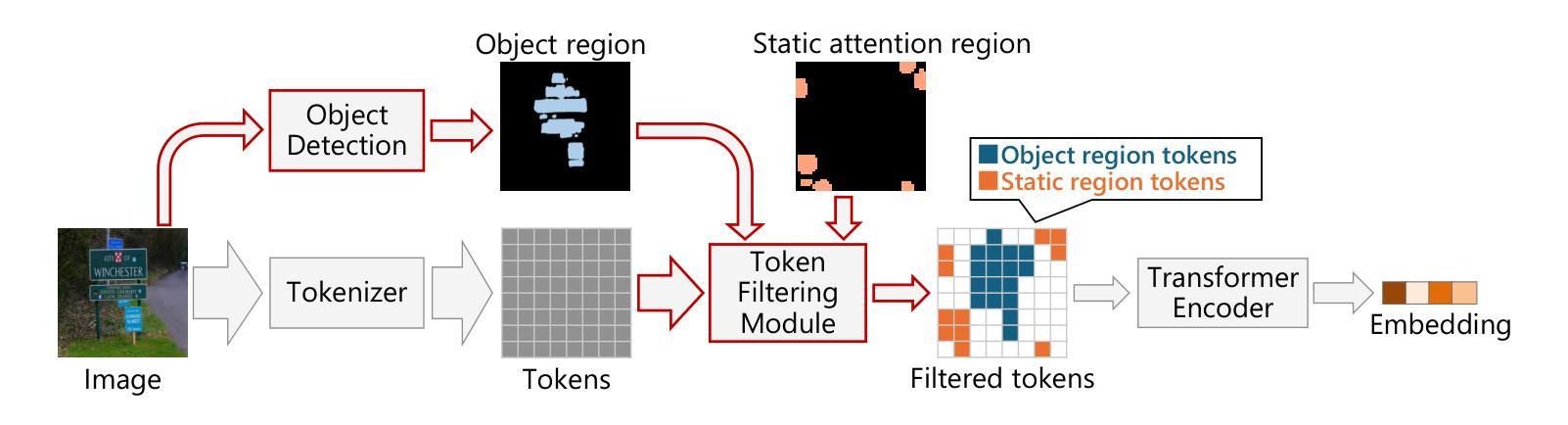
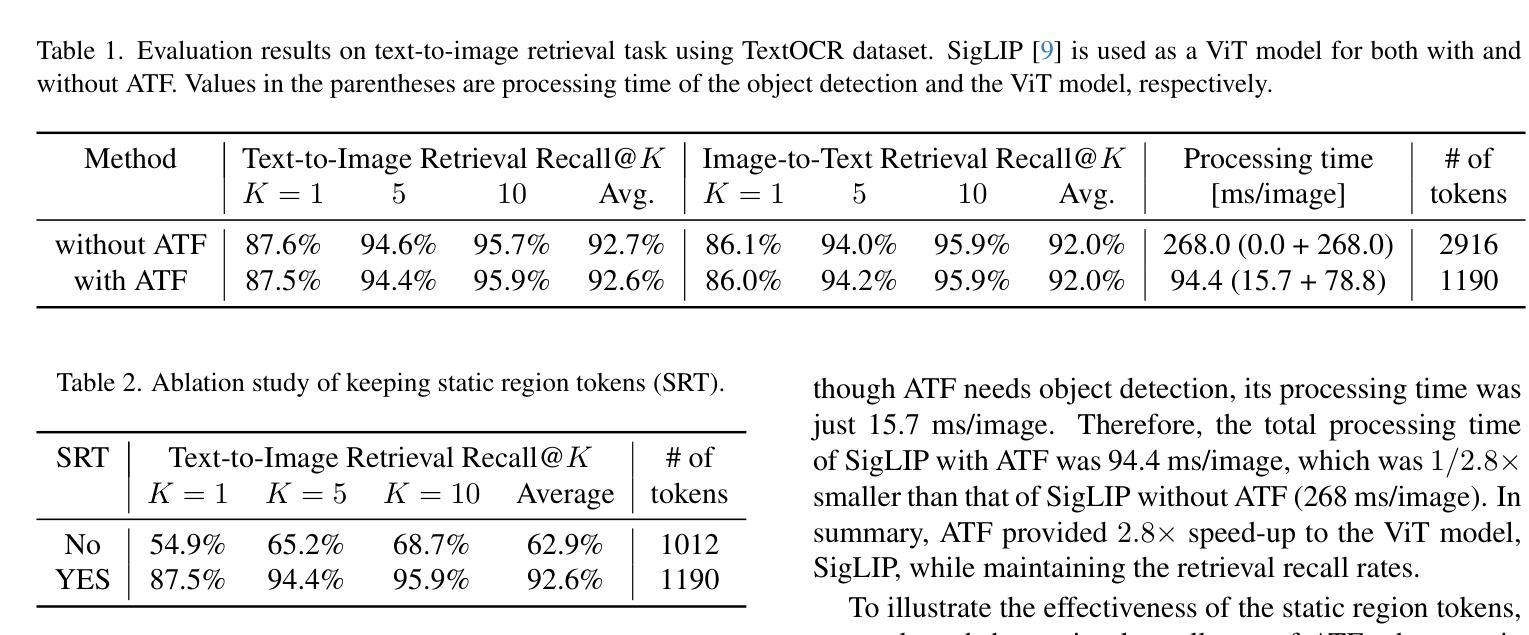
Speed-up of Vision Transformer Models by Attention-aware Token Filtering
Authors:Takahiro Naruko, Hiroaki Akutsu
Vision Transformer (ViT) models have made breakthroughs in image embedding extraction, which provide state-of-the-art performance in tasks such as zero-shot image classification. However, the models suffer from a high computational burden. In this paper, we propose a novel speed-up method for ViT models called Attention-aware Token Filtering (ATF). ATF consists of two main ideas: a novel token filtering module and a filtering strategy. The token filtering module is introduced between a tokenizer and a transformer encoder of the ViT model, without modifying or fine-tuning of the transformer encoder. The module filters out tokens inputted to the encoder so that it keeps tokens in regions of specific object types dynamically and keeps tokens in regions that statically receive high attention in the transformer encoder. This filtering strategy maintains task accuracy while filtering out tokens inputted to the transformer encoder. Evaluation results on retrieval tasks show that ATF provides $2.8\times$ speed-up to a ViT model, SigLIP, while maintaining the retrieval recall rate.
Vision Transformer(ViT)模型在图像嵌入提取方面取得了突破,其在零样本图像分类等任务中达到了最先进的性能。然而,这些模型面临着计算负担较大的问题。在本文中,我们提出了一种用于加速ViT模型的新型方法,称为注意力感知令牌过滤(ATF)。ATF主要包括两个主要思想:一个新颖的令牌过滤模块和过滤策略。令牌过滤模块被引入到ViT模型的令牌器和变压器编码器之间,无需修改或微调变压器编码器。该模块过滤掉输入到编码器的令牌,以便动态地保留特定对象类型区域的令牌,并保留在变压器编码器中静态接收高注意力的区域的令牌。这种过滤策略在过滤掉输入到变压器编码器的令牌的同时保持了任务准确性。在检索任务上的评估结果表明,ATF在保持检索召回率的同时,为ViT模型SigLIP提供了2.8倍的速度提升。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在视觉转换器(ViT)模型中,针对图像嵌入提取取得了突破性进展,其在零样本图像分类等任务中表现出卓越性能。然而,这些模型计算负担较高。本文提出了一种名为注意力感知令牌过滤(ATF)的ViT模型加速方法。ATF主要包括两个核心理念:新颖令牌过滤模块和过滤策略。令牌过滤模块被引入ViT模型的令牌器和转换器编码器之间,无需修改或微调转换器编码器。该模块动态保留特定对象区域的令牌并保留静态接收转换器编码器中高关注度的区域的令牌。此过滤策略在过滤输入到转换器编码器的令牌的同时保持任务准确性。在检索任务上的评估结果表明,ATF能在保持检索召回率的同时,将ViT模型SigLIP的速度提高2.8倍。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer (ViT) 在图像嵌入提取方面取得突破,适用于零样本图像分类等任务。
- ViT模型面临高计算负担问题。
- 提出了名为ATF的ViT模型加速方法,包括新颖的令牌过滤模块和过滤策略。
- 令牌过滤模块位于ViT模型的令牌器和转换器编码器之间,无需修改或微调转换器编码器。
- ATF通过动态保留特定对象区域的令牌和静态高关注度区域的令牌进行过滤。
6.ATF能在保持任务准确性的同时,减少输入到转换器编码器的令牌数量。
点此查看论文截图

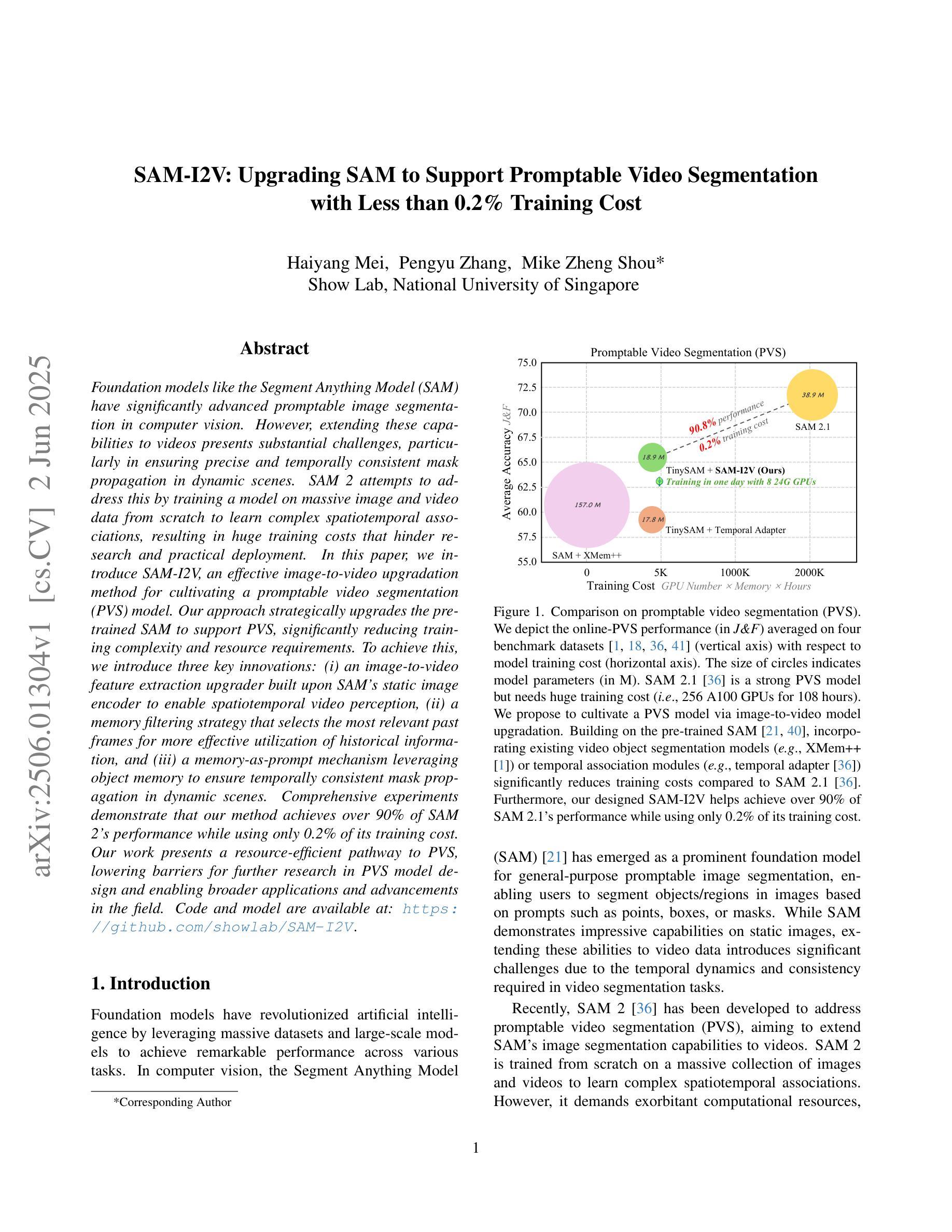
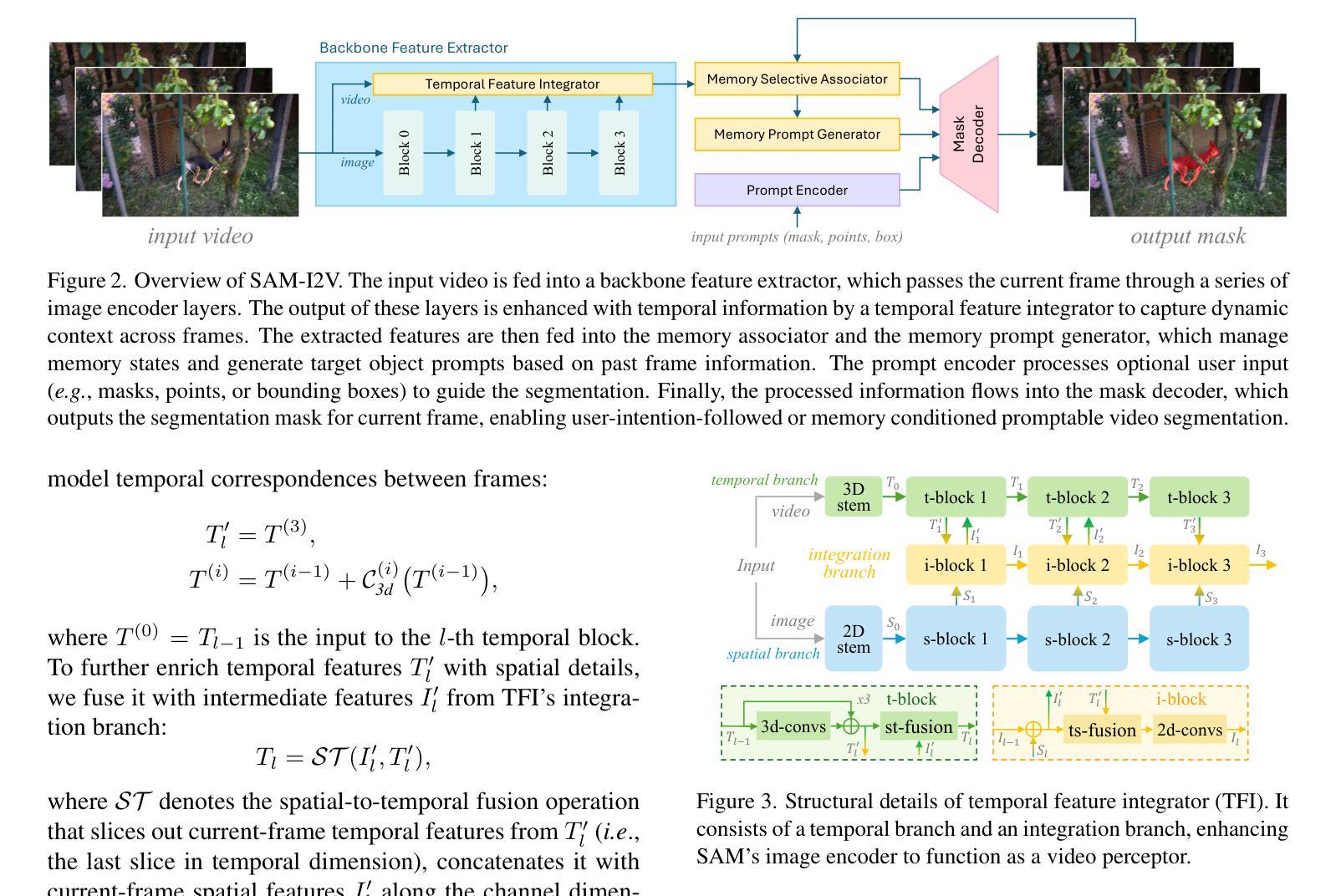
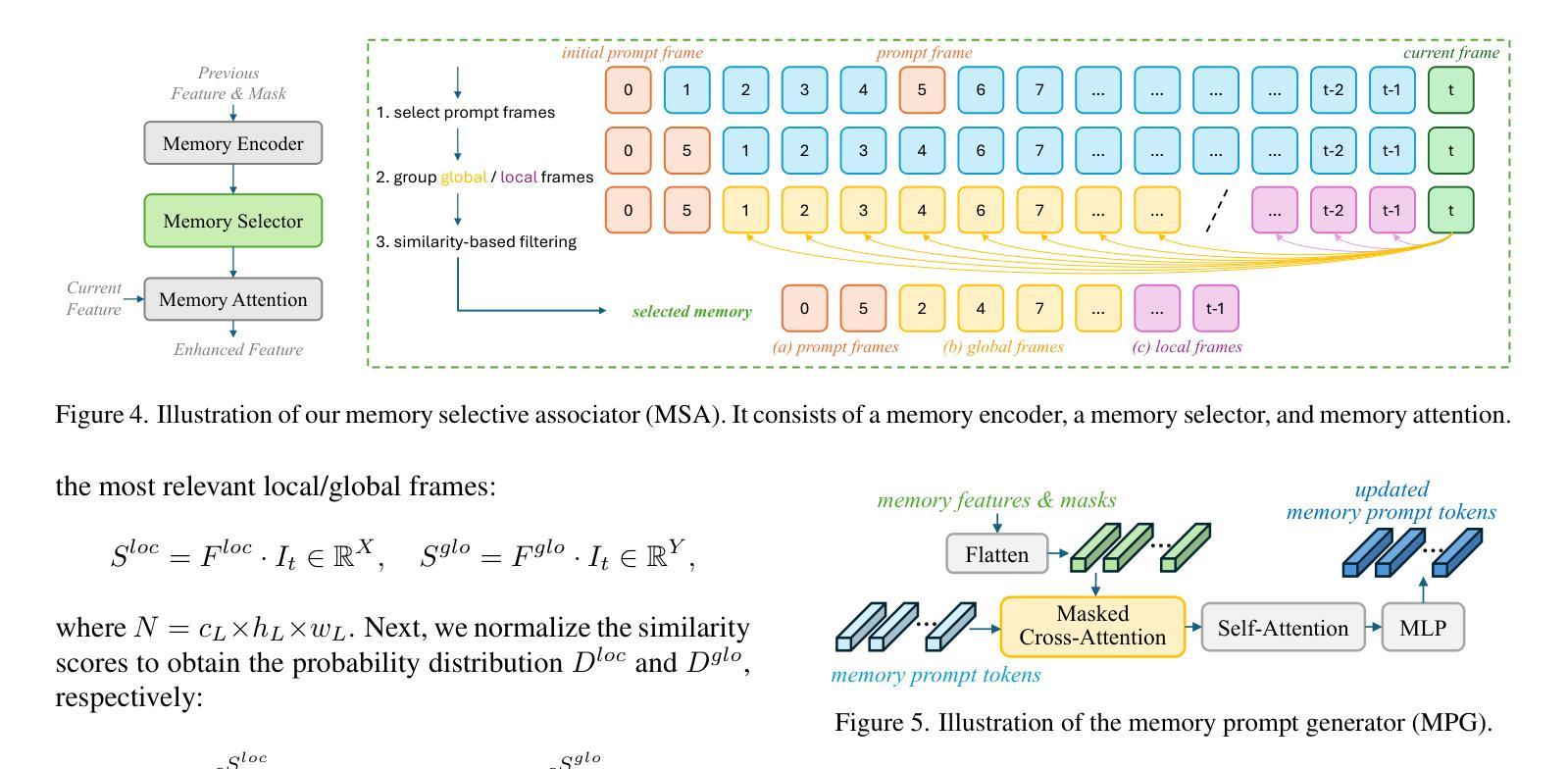
SAM-I2V: Upgrading SAM to Support Promptable Video Segmentation with Less than 0.2% Training Cost
Authors:Haiyang Mei, Pengyu Zhang, Mike Zheng Shou
Foundation models like the Segment Anything Model (SAM) have significantly advanced promptable image segmentation in computer vision. However, extending these capabilities to videos presents substantial challenges, particularly in ensuring precise and temporally consistent mask propagation in dynamic scenes. SAM 2 attempts to address this by training a model on massive image and video data from scratch to learn complex spatiotemporal associations, resulting in huge training costs that hinder research and practical deployment. In this paper, we introduce SAM-I2V, an effective image-to-video upgradation method for cultivating a promptable video segmentation (PVS) model. Our approach strategically upgrades the pre-trained SAM to support PVS, significantly reducing training complexity and resource requirements. To achieve this, we introduce three key innovations: (i) an image-to-video feature extraction upgrader built upon SAM’s static image encoder to enable spatiotemporal video perception, (ii) a memory filtering strategy that selects the most relevant past frames for more effective utilization of historical information, and (iii) a memory-as-prompt mechanism leveraging object memory to ensure temporally consistent mask propagation in dynamic scenes. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves over 90% of SAM 2’s performance while using only 0.2% of its training cost. Our work presents a resource-efficient pathway to PVS, lowering barriers for further research in PVS model design and enabling broader applications and advancements in the field. Code and model are available at: https://github.com/showlab/SAM-I2V.
像Segment Anything Model(SAM)这样的基础模型已经在计算机视觉中推动了可提示的图像分割的显著进步。然而,将这些能力扩展到视频却面临着巨大的挑战,特别是在动态场景中确保精确和时空一致的遮罩传播方面。SAM 2 通过在大量图像和视频数据上从头开始训练模型以学习复杂的时空关联来解决这个问题,这导致了巨大的训练成本,阻碍了研究和实际应用部署。在本文中,我们介绍了SAM-I2V,这是一种有效的从图像到视频的升级方法,用于培养可提示的视频分割(PVS)模型。我们的方法通过升级预训练的SAM来支持PVS,大大降低了训练复杂度和资源需求。为此,我们引入了三个关键创新点:(i)一种基于SAM静态图像编码器的图像到视频特征提取升级器,以实现时空视频感知;(ii)一种记忆过滤策略,用于选择最相关的过去帧以更有效地利用历史信息;(iii)一种利用对象记忆的记忆即提示机制,以确保动态场景中的时空一致遮罩传播。综合实验表明,我们的方法达到了SAM 2性能的90%以上,同时仅使用其0.2%的训练成本。我们的工作为PVS提供了一条资源高效的途径,降低了PVS模型设计的进一步研究障碍,并启用了该领域的更广泛应用和进展。代码和模型可在https://github.com/showlab/SAM-I2V 获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary:基于SAM模型的可提示视频分割技术(SAM-I2V)研究介绍了一种有效的图像到视频的升级方法,用于构建可提示视频分割(PVS)模型。该方法通过升级预训练的SAM模型来支持PVS,显著降低了训练复杂性和资源需求。引入三项关键技术创新,包括基于SAM静态图像编码器的图像到视频特征提取升级器、记忆过滤策略以及利用对象记忆的提示机制。实验表明,该方法实现了超过90%的SAM 2性能,同时仅使用其0.2%的训练成本。为PVS设计提供了资源高效的途径,降低了进一步研究和实践应用的门槛。代码和模型已公开。
Key Takeaways:
- SAM模型在提示图像分割方面表现出卓越性能,但将其扩展到视频面临挑战,特别是确保动态场景中的精确和时序一致的掩膜传播。
- SAM 2模型通过大规模图像和视频数据从头开始训练来学习复杂的时空关联,但带来了巨大的训练成本,阻碍了研究和实际应用部署。
- SAM-I2V方法介绍了一种有效的图像到视频的升级策略,以支持提示视频分割(PVS)。该方法显著降低了训练复杂性和资源需求。
- SAM-I2V引入了三项关键创新:图像到视频特征提取升级器、记忆过滤策略和记忆提示机制,确保动态场景中的时空一致掩膜传播。
- 实验表明,SAM-I2V方法实现了与SAM 2相当的性能表现,同时大幅降低了训练成本。
- 公开的代码和模型为资源受限环境下的研究提供了便利,促进了视频分割领域的进一步研究和应用发展。
点此查看论文截图
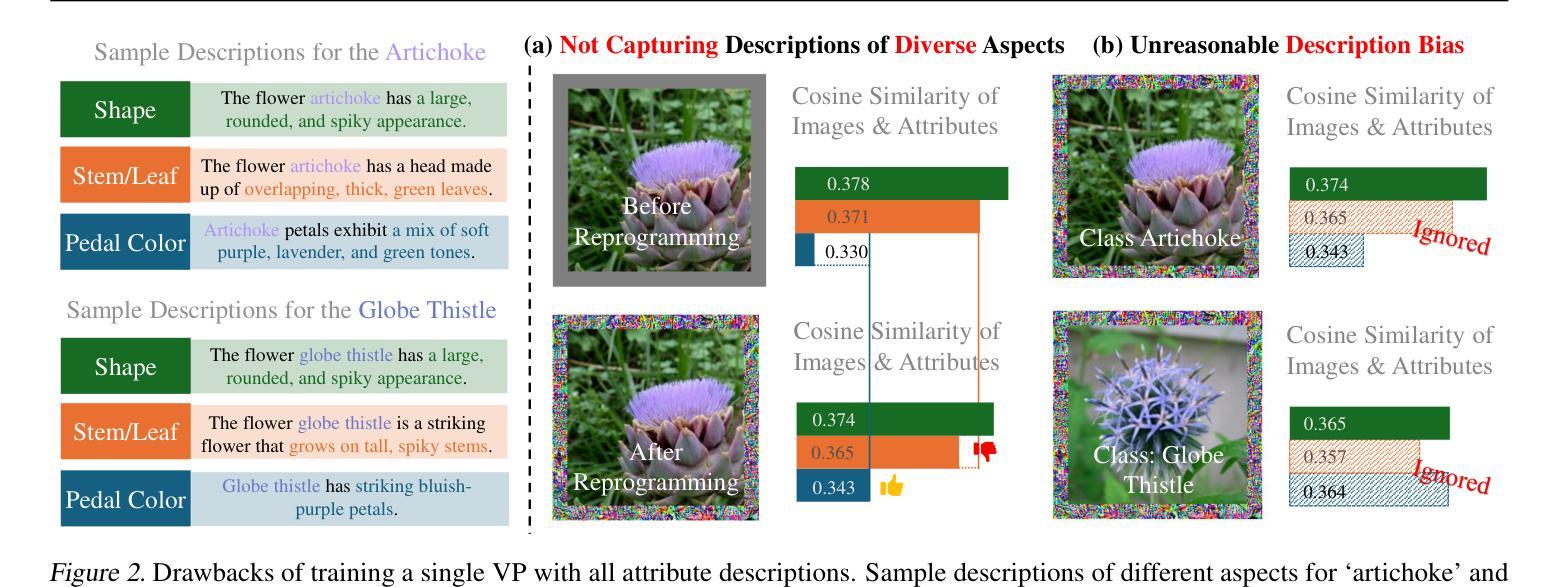
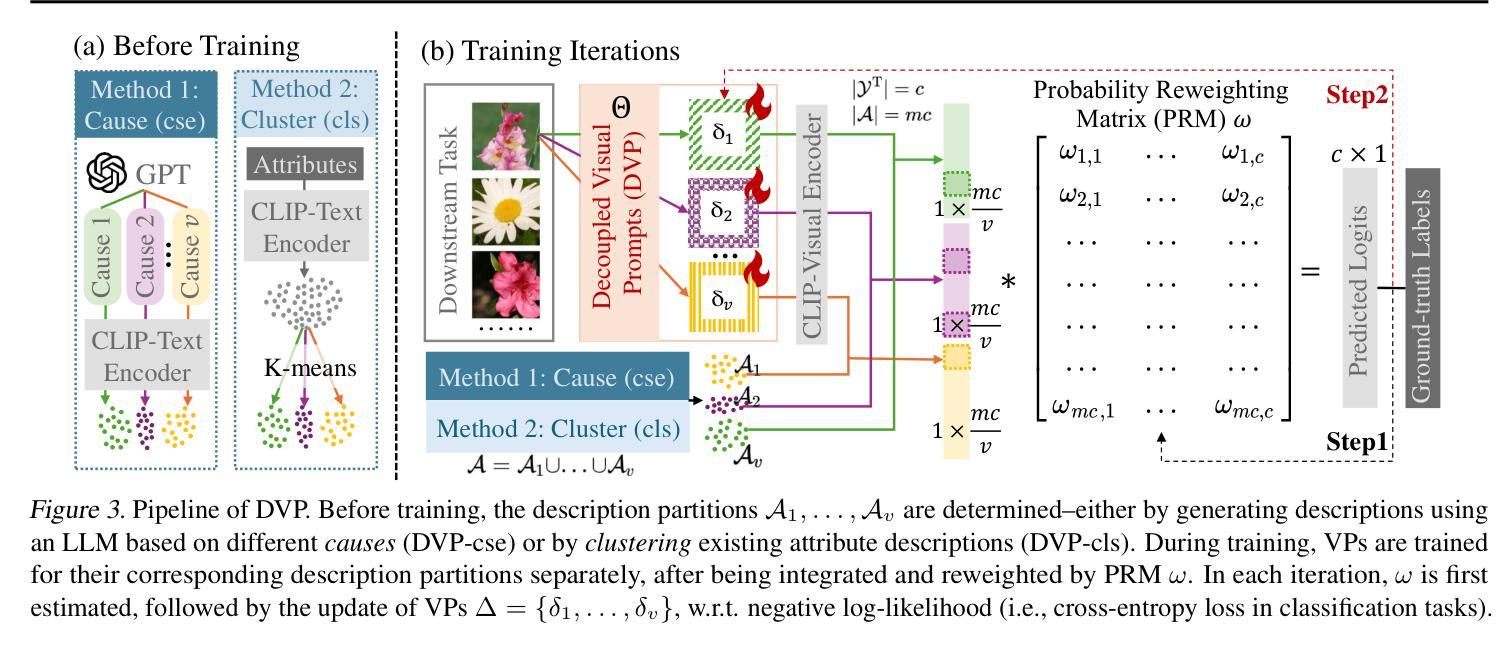
Understanding Model Reprogramming for CLIP via Decoupling Visual Prompts
Authors:Chengyi Cai, Zesheng Ye, Lei Feng, Jianzhong Qi, Feng Liu
Model reprogramming adapts pretrained models to downstream tasks by modifying only the input and output spaces. Visual reprogramming (VR) is one instance for vision tasks that adds a trainable noise pattern (i.e., a visual prompt) to input images to facilitate downstream classification. The existing VR approaches for CLIP train a single visual prompt using all descriptions of different downstream classes. However, the limited learning capacity may result in (1) a failure to capture diverse aspects of the descriptions (e.g., shape, color, and texture), and (2) a possible bias toward less informative attributes that do not help distinguish between classes. In this paper, we introduce a decoupling-and-reweighting framework. Our decoupled visual prompts (DVP) are optimized using descriptions grouped by explicit causes (DVP-cse) or unsupervised clusters (DVP-cls). Then, we integrate the outputs of these visual prompts with a probabilistic reweighting matrix (PRM) that measures their contributions to each downstream class. Theoretically, DVP lowers the empirical risk bound. Experimentally, DVP outperforms baselines on average across 11 downstream datasets. Notably, the DVP-PRM integration enables insights into how individual visual prompts influence classification decisions, providing a probabilistic framework for understanding reprogramming. Our code is available at https://github.com/tmlr-group/DecoupledVP.
模型重构通过仅修改输入和输出空间来适应预训练模型以适应下游任务。视觉重构(VR)是视觉任务的一个实例,它向输入图像添加可训练的噪声模式(即视觉提示)以促进下游分类。现有的CLIP的VR方法使用不同下游类别的所有描述来训练一个单一视觉提示。然而,有限的学习能力可能导致(1)无法捕捉描述的各个方面(例如形状、颜色和纹理);(2)偏向于可能不具有区分不同类别能力的信息较少的属性。在本文中,我们引入了一个解耦和加权框架。我们的解耦视觉提示(DVP)使用按明确原因分组(DVP-cse)的描述或无监督聚类(DVP-cls)进行优化。然后,我们使用概率加权矩阵(PRM)整合这些视觉提示的输出,该矩阵衡量它们对下游每个类别的贡献。理论上,DVP降低了经验风险界限。实验上,DVP在平均意义上优于在11个下游数据集上的基准测试。值得注意的是,DVP-PRM集成提供了关于单个视觉提示如何影响分类决策的信息,提供了一个理解重构的概率框架。我们的代码可在https://github.com/tmlr-group/DecoupledVP找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了视觉重编程(VR)的一种新方法——解耦和重权框架下的视觉提示(DVP)。该框架通过对不同下游类别的描述进行分组优化视觉提示,降低经验风险界限。在多个下游数据集上的实验表明,DVP优于基准方法。特别是,DVP-PRM集成提供了对单个视觉提示如何影响分类决策的理解,为重新编程提供了一个概率框架。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉重编程(VR)是一种用于适应预训练模型的方法,只修改输入和输出空间。通过向输入图像添加可训练的噪声模式(即视觉提示)来适应下游分类任务。现有的VR方法可能无法捕捉描述的各个方面,并且可能偏向于没有帮助区分类的信息较少的属性。为了解决这些问题,提出了一个解耦和重权框架下的视觉提示(DVP)。通过此框架优化的视觉提示被称为解耦的视觉提示(DVP)。
- DVP通过两种方式优化视觉提示:一种是基于明确的因果分组进行优化(DVP-cse),另一种是基于无监督聚类进行优化(DVP-cls)。通过这两种方式优化的视觉提示可以更有效地捕获描述中的信息并适应下游任务。理论而言,该框架有助于降低经验风险界限。因此相对于基线方法有更优的表现。在多个下游数据集上的实验验证了这一点。
- DVP与概率重权矩阵(PRM)的结合使得我们能够理解单个视觉提示如何影响分类决策,并为模型重新编程提供了一个新的视角和理解框架。这对于解释和改进模型的性能非常重要。对于理解和改进模型性能非常重要。此代码的开源实现为用户提供了一个了解和运用该方法的机会。
点此查看论文截图

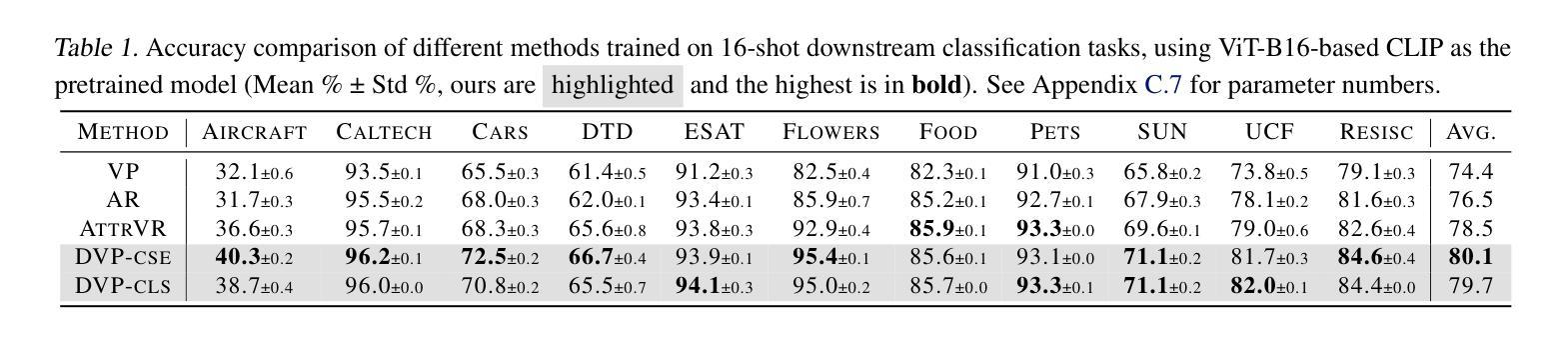
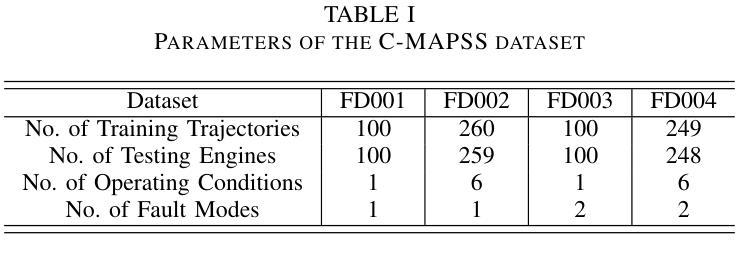
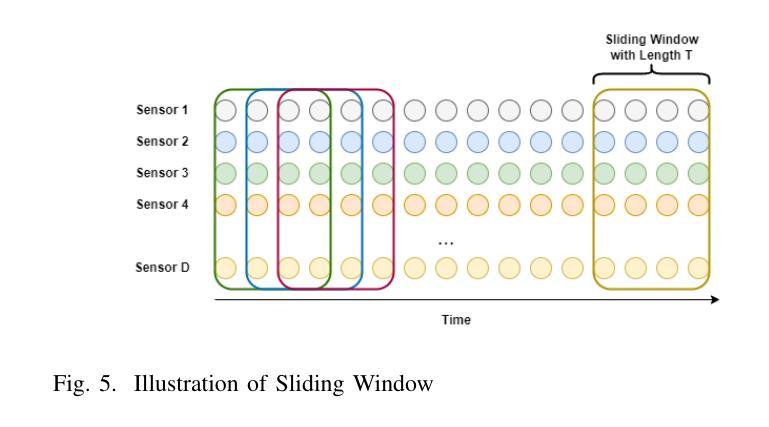
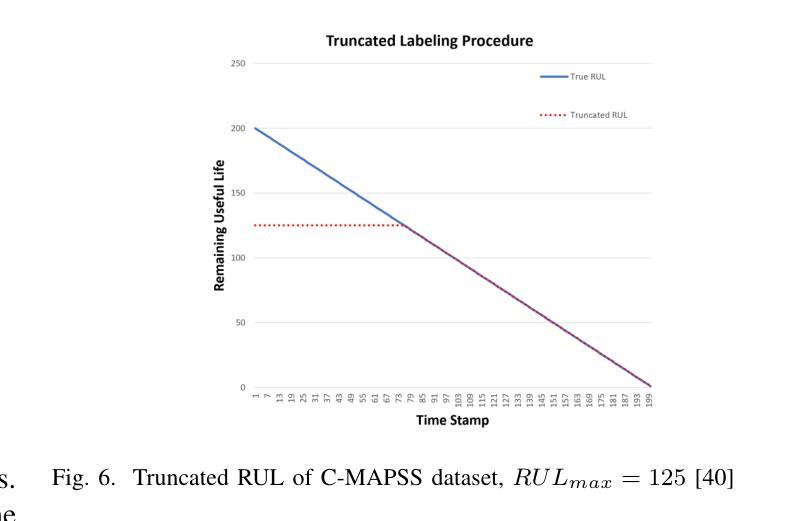
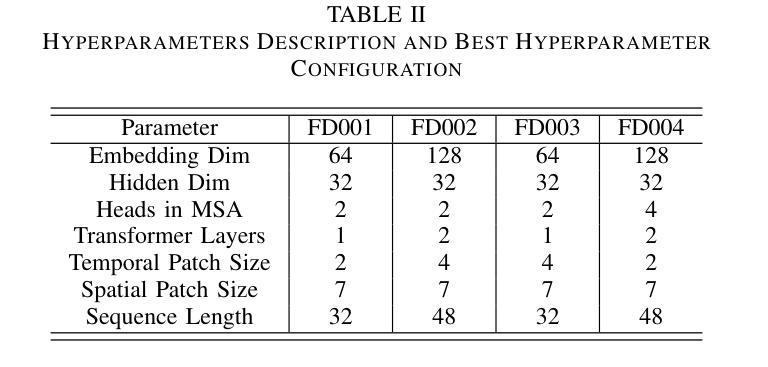
PerFormer: A Permutation Based Vision Transformer for Remaining Useful Life Prediction
Authors:Zhengyang Fan, Wanru Li, Kuo-chu Chang, Ting Yuan
Accurately estimating the remaining useful life (RUL) for degradation systems is crucial in modern prognostic and health management (PHM). Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), initially developed for tasks like image and video recognition, have proven highly effectively in RUL prediction, demonstrating remarkable performance. However, with the emergence of the Vision Transformer (ViT), a Transformer model tailored for computer vision tasks such as image classification, and its demonstrated superiority over CNNs, there is a natural inclination to explore its potential in enhancing RUL prediction accuracy. Nonetheless, applying ViT directly to multivariate sensor data for RUL prediction poses challenges, primarily due to the ambiguous nature of spatial information in time series data. To address this issue, we introduce the PerFormer, a permutation-based vision transformer approach designed to permute multivariate time series data, mimicking spatial characteristics akin to image data, thereby making it suitable for ViT. To generate the desired permutation matrix, we introduce a novel permutation loss function aimed at guiding the convergence of any matrix towards a permutation matrix. Our experiments on NASA’s C-MAPSS dataset demonstrate the PerFormer’s superior performance in RUL prediction compared to state-of-the-art methods employing CNNs, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), and various Transformer models. This underscores its effectiveness and potential in PHM applications.
对退化系统的剩余使用寿命(RUL)进行准确估计是现代预测与健康管理(PHM)中的关键。卷积神经网络(CNN)最初被开发用于图像和视频识别等任务,已经证明在RUL预测中的高度有效性,表现出卓越的性能。然而,随着用于图像分类等计算机视觉任务的定制Transformer模型——视觉Transformer(ViT)的出现,以及其相较于CNN的优越性证明,人们自然倾向于探索其在提高RUL预测精度方面的潜力。然而,直接将ViT应用于多元传感器数据的RUL预测却存在挑战,这主要是因为时间序列数据中空间信息的模糊性。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了PerFormer,这是一种基于排列的愿景转换器方法,旨在排列多元时间序列数据,模仿类似于图像数据的空间特征,从而使其适合ViT。为了生成所需的排列矩阵,我们引入了一种新型排列损失函数,旨在引导任何矩阵向排列矩阵收敛。我们在NASA的C-MAPSS数据集上的实验表明,PerFormer在RUL预测方面的性能优于采用CNN、循环神经网络(RNN)和各种Transformer模型的最先进方法。这突显了其在PHM应用中的有效性和潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
卷积神经网络(CNN)在剩余使用寿命(RUL)预测中表现出卓越的性能,但随着针对计算机视觉任务的定制版Vision Transformer(ViT)的出现,其在RUL预测中的潜力备受关注。然而,直接应用ViT于多元传感器数据进行RUL预测存在挑战。为此,我们引入了PerFormer,一种基于排列的Vision Transformer方法,可对多元时间序列数据进行排列,模拟图像数据的空间特征。通过引入新型排列损失函数,指导排列矩阵的收敛。在NASA的C-MAPSS数据集上的实验表明,PerFormer在RUL预测方面的性能优于采用CNN、循环神经网络(RNN)和各种Transformer模型的最先进方法,突显其在预后与健康管理(PHM)应用中的有效性及潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)在剩余使用寿命(RUL)预测中已有卓越表现。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)的出现为RUL预测带来了新的潜力。
- 直接应用ViT于多元传感器数据存在挑战,因时间序列数据的空间信息不明确。
- 引入PerFormer,一种基于排列的Vision Transformer方法,能排列多元时间序列数据,模拟图像数据的空间特征。
- 新型排列损失函数用于生成排列矩阵,并引导其收敛。
- 在NASA的C-MAPSS数据集上的实验显示,PerFormer在RUL预测方面性能卓越,优于其他模型。
点此查看论文截图

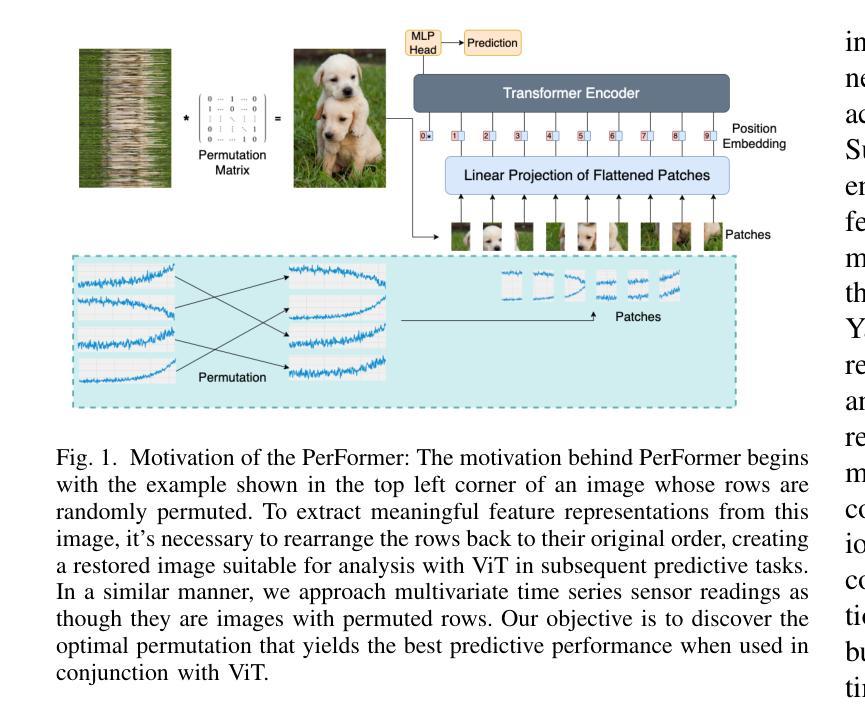
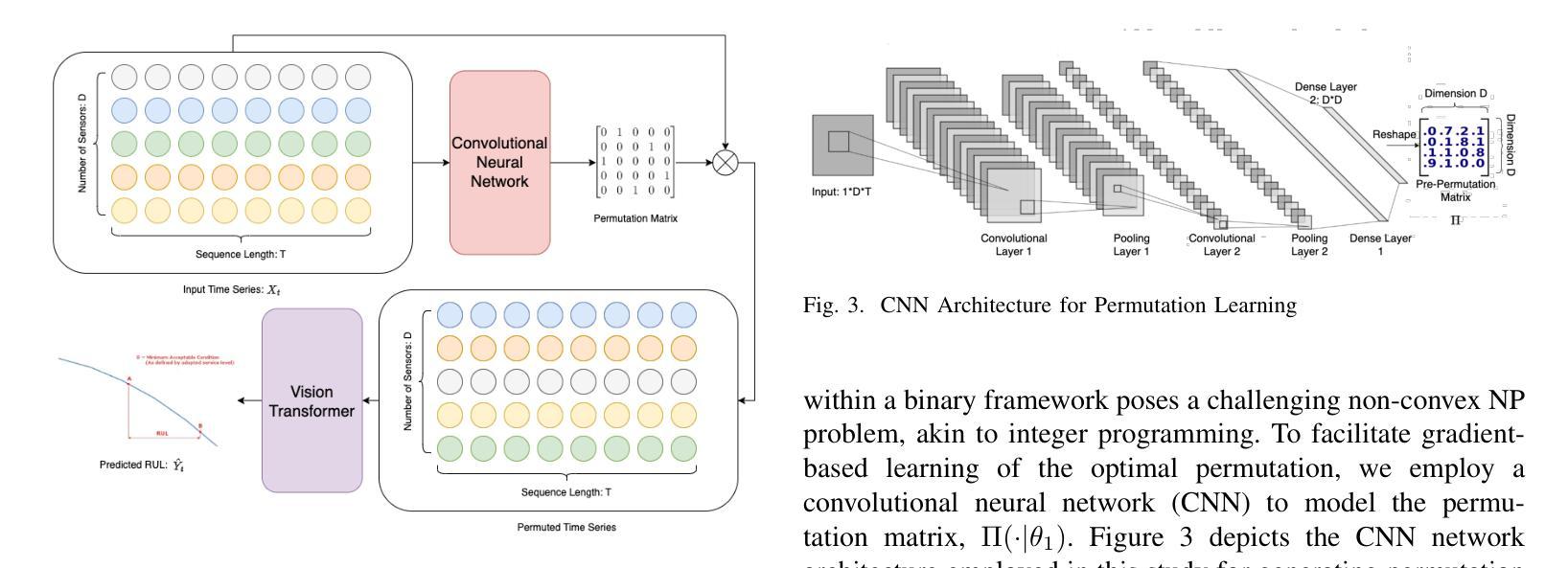
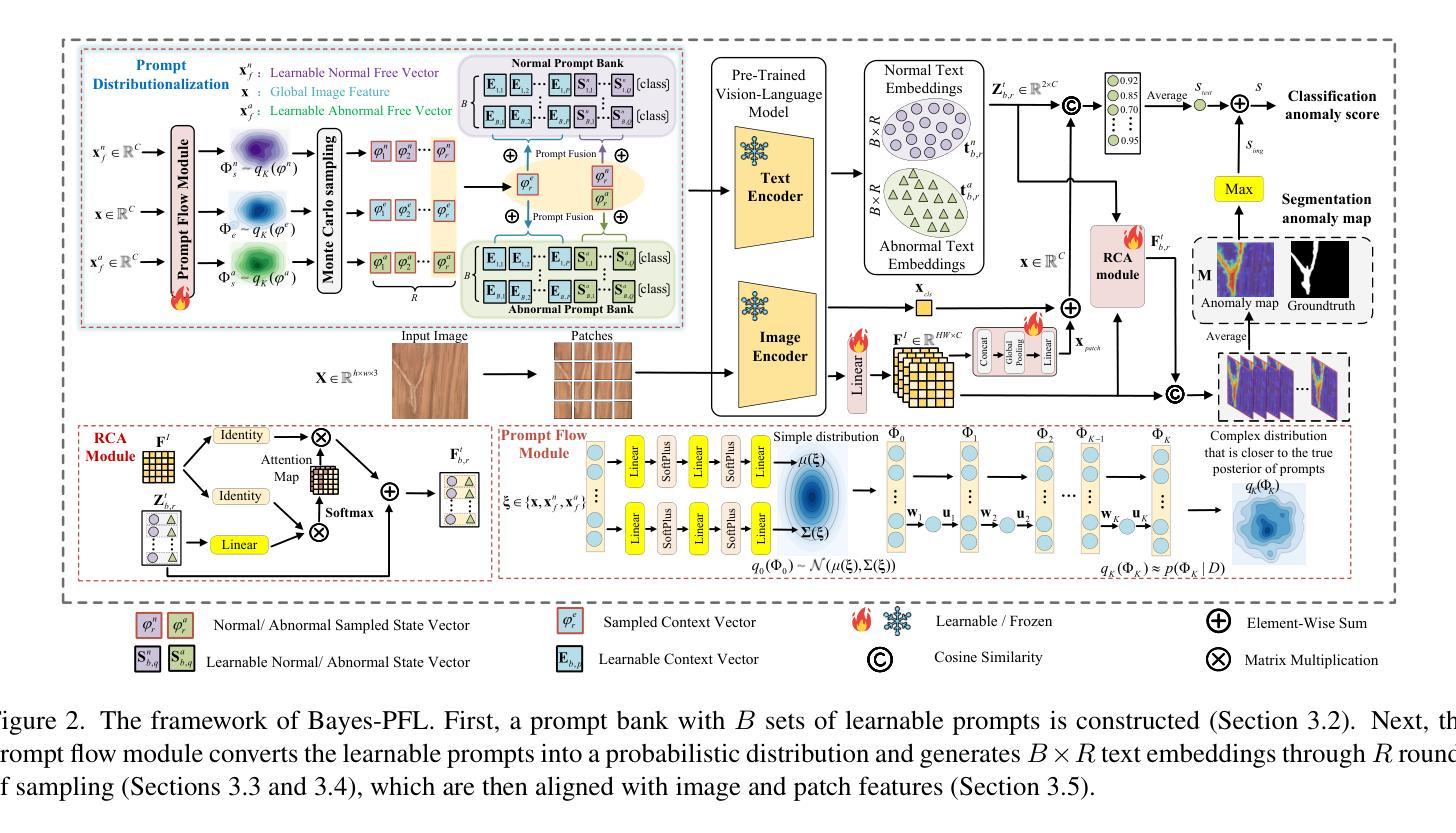
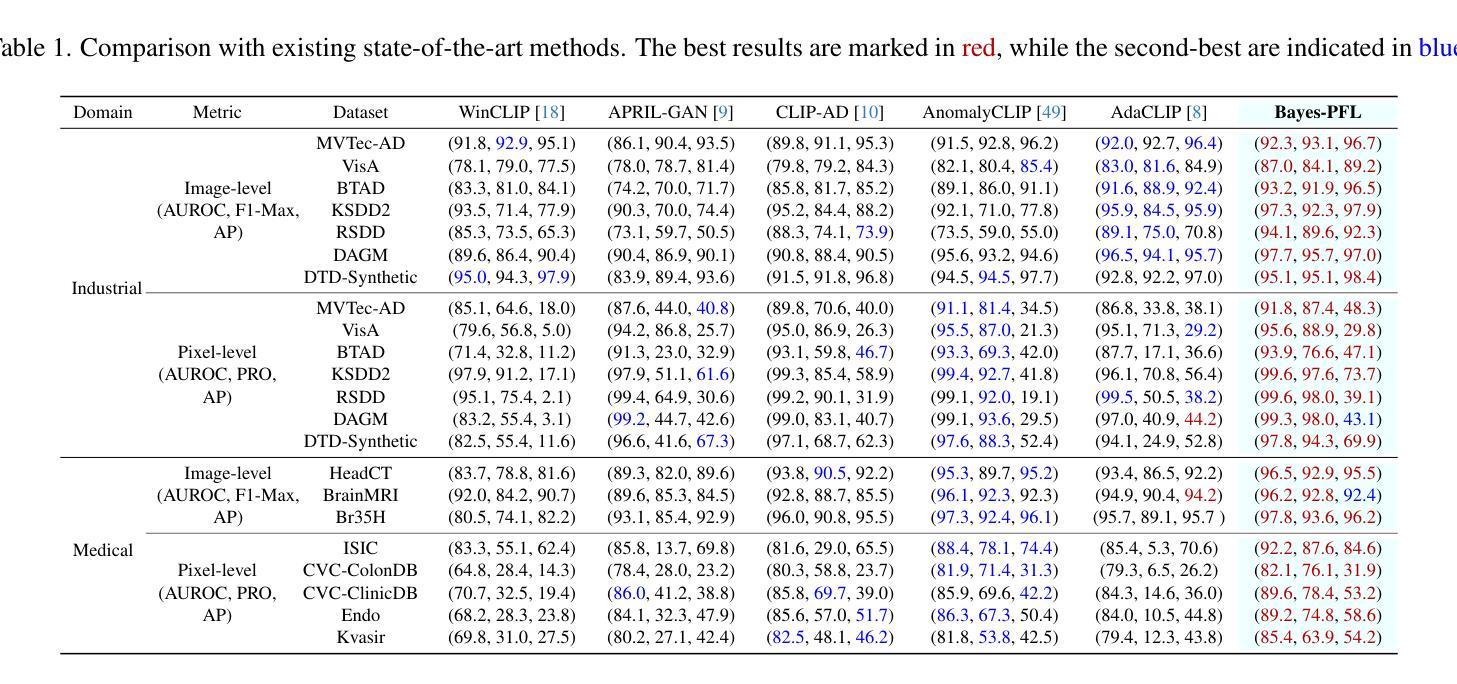
Bayesian Prompt Flow Learning for Zero-Shot Anomaly Detection
Authors:Zhen Qu, Xian Tao, Xinyi Gong, Shichen Qu, Qiyu Chen, Zhengtao Zhang, Xingang Wang, Guiguang Ding
Recently, vision-language models (e.g. CLIP) have demonstrated remarkable performance in zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD). By leveraging auxiliary data during training, these models can directly perform cross-category anomaly detection on target datasets, such as detecting defects on industrial product surfaces or identifying tumors in organ tissues. Existing approaches typically construct text prompts through either manual design or the optimization of learnable prompt vectors. However, these methods face several challenges: 1) handcrafted prompts require extensive expert knowledge and trial-and-error; 2) single-form learnable prompts struggle to capture complex anomaly semantics; and 3) an unconstrained prompt space limits generalization to unseen categories. To address these issues, we propose Bayesian Prompt Flow Learning (Bayes-PFL), which models the prompt space as a learnable probability distribution from a Bayesian perspective. Specifically, a prompt flow module is designed to learn both image-specific and image-agnostic distributions, which are jointly utilized to regularize the text prompt space and improve the model’s generalization on unseen categories. These learned distributions are then sampled to generate diverse text prompts, effectively covering the prompt space. Additionally, a residual cross-model attention (RCA) module is introduced to better align dynamic text embeddings with fine-grained image features. Extensive experiments on 15 industrial and medical datasets demonstrate our method’s superior performance. The code is available at https://github.com/xiaozhen228/Bayes-PFL.
最近,视觉语言模型(例如CLIP)在零样本异常检测(ZSAD)中表现出了卓越的性能。这些模型通过利用训练过程中的辅助数据,可以直接对目标数据集进行跨类别异常检测,如检测工业产品表面的缺陷或识别组织中的肿瘤。现有方法通常通过手动设计或优化可学习的提示向量来构建文本提示。然而,这些方法面临几个挑战:1)手工制作的提示需要广泛的专业知识和试错;2)单一形式的可学习提示难以捕捉复杂的异常语义;3)无约束的提示空间限制了未见类别的泛化能力。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了贝叶斯提示流学习(Bayes-PFL),它从贝叶斯角度将提示空间建模为可学习的概率分布。具体来说,设计了一个提示流模块来学习图像特定和图像通用的分布,这些分布被共同用来规范文本提示空间,提高模型在未见类别上的泛化能力。这些学习到的分布然后被采样以生成多样化的文本提示,有效地覆盖了提示空间。此外,还引入了一个残差跨模型注意力(RCA)模块,以更好地将动态文本嵌入与精细图像特征对齐。在15个工业和医疗数据集上的大量实验证明了我们方法的优越性。代码可用在https://github.com/xiaozhen228/Bayes-PFL。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为贝叶斯提示流学习(Bayes-PFL)的方法,用于解决视觉语言模型在零样本异常检测(ZSAD)中的挑战。该方法通过从贝叶斯视角对提示空间进行建模,解决了手工提示需要大量专业知识和反复试验的问题,以及单一形式的学习提示难以捕捉复杂的异常语义和不受约束的提示空间限制了未见类别的泛化能力的问题。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在零样本异常检测(ZSAD)中表现出卓越性能。
- 现有方法通过手动设计或优化学习提示向量来构建文本提示,但存在挑战。
- 贝叶斯提示流学习(Bayes-PFL)方法提出,将提示空间建模为可从贝叶斯视角学习的概率分布。
- Bayes-PFL设计了一个提示流模块来学习图像特定和图像通用的分布,以规范文本提示空间并提高模型对未见类别的泛化能力。
- 通过采样学习到的分布来生成多样化的文本提示,有效覆盖提示空间。
- 引入残差跨模型注意力(RCA)模块,以更好地对齐动态文本嵌入和细粒度图像特征。
点此查看论文截图

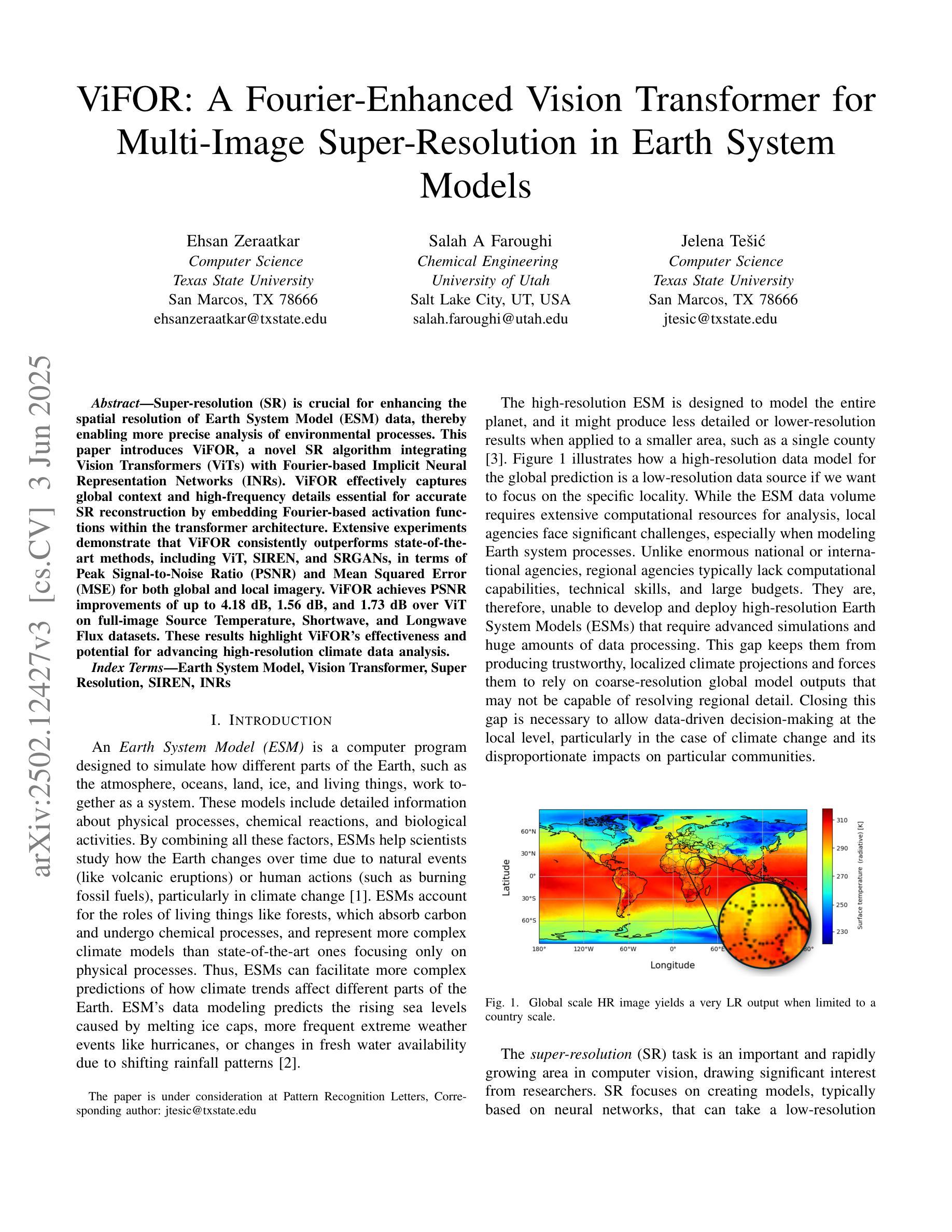
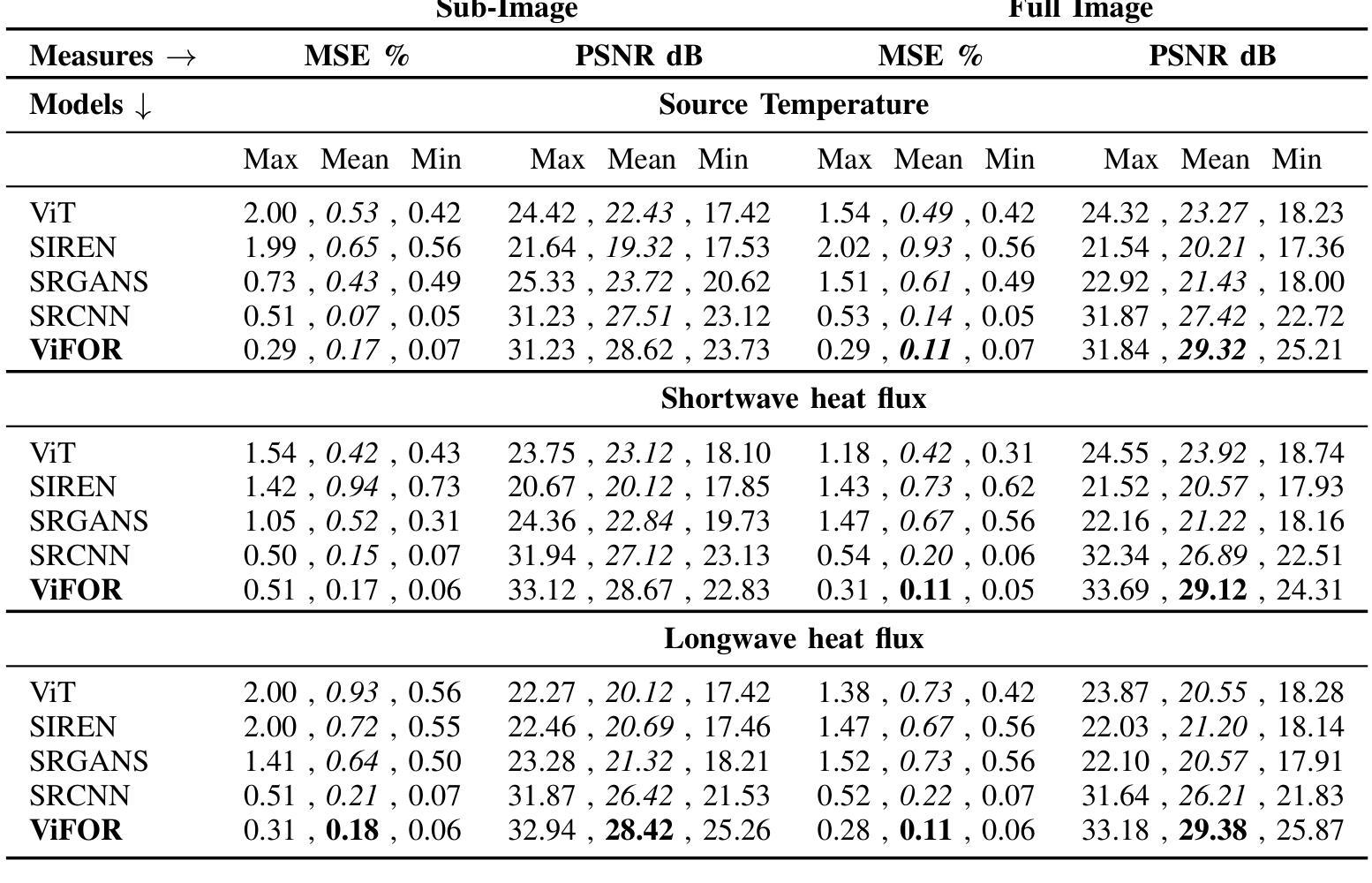
ViFOR: A Fourier-Enhanced Vision Transformer for Multi-Image Super-Resolution in Earth System
Authors:Ehsan Zeraatkar, Salah A Faroughi, Jelena Tešić
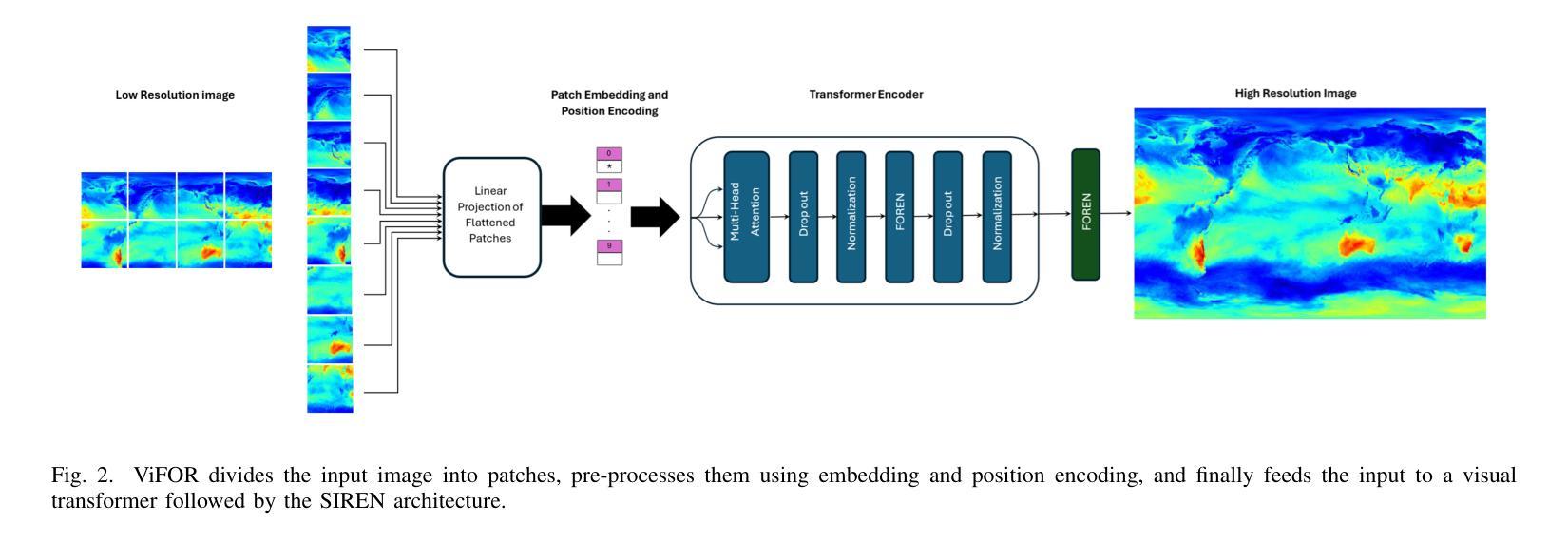
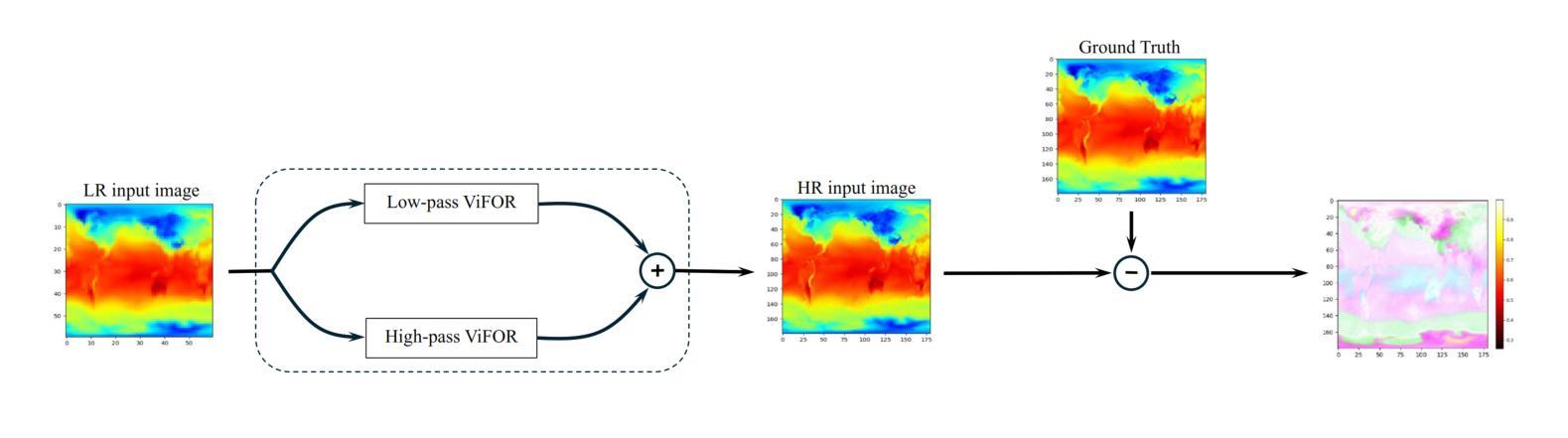
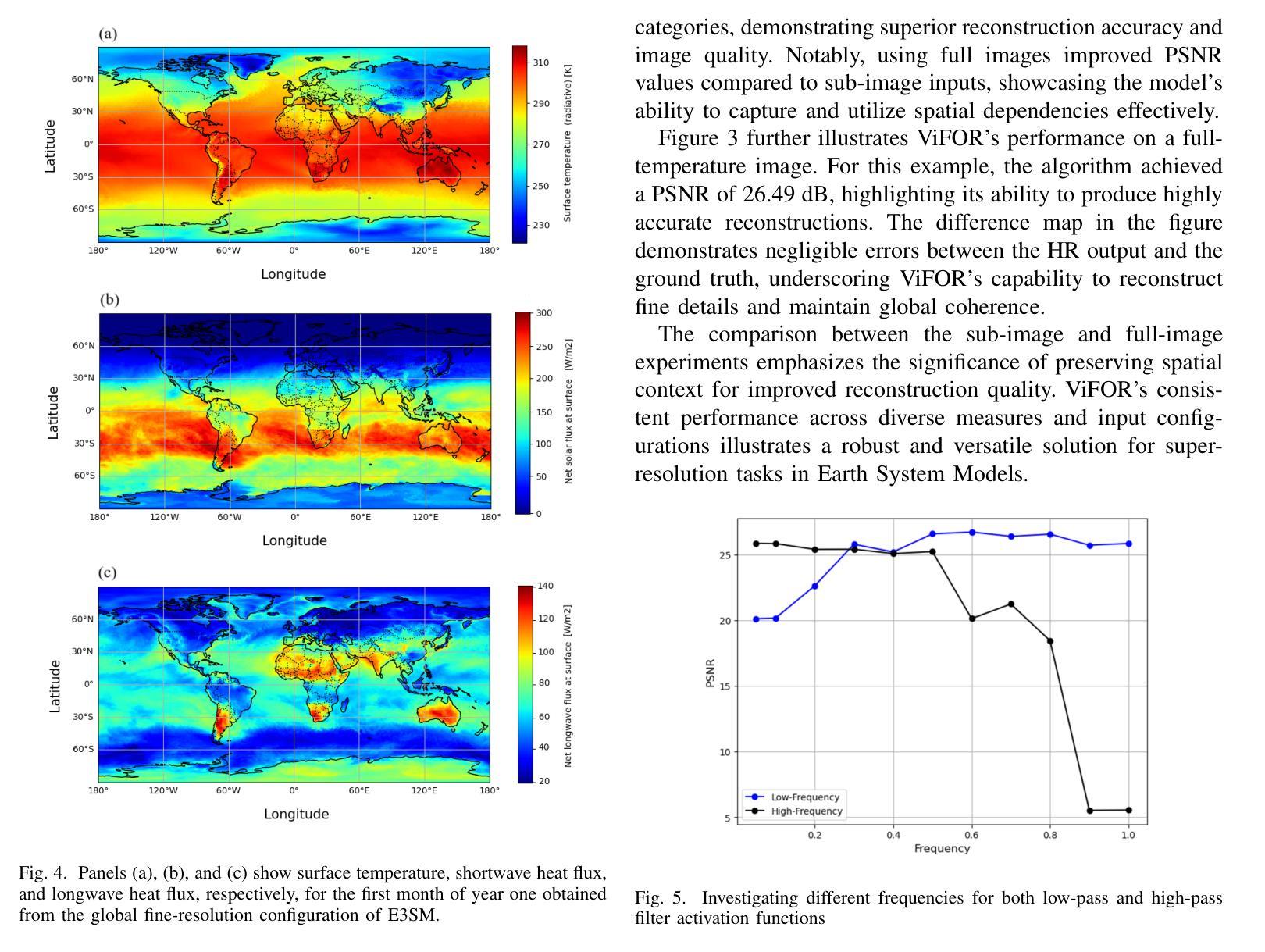
Super-resolution (SR) is crucial for enhancing the spatial resolution of Earth System Model (ESM) data, thereby enabling more precise analysis of environmental processes. This paper introduces ViFOR, a novel SR algorithm integrating Vision Transformers (ViTs) with Fourier-based Implicit Neural Representation Networks (INRs). ViFOR effectively captures global context and high-frequency details essential for accurate SR reconstruction by embedding Fourier-based activation functions within the transformer architecture. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ViFOR consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods, including ViT, SIREN, and SRGANs, in terms of Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Mean Squared Error (MSE) for both global and local imagery. ViFOR achieves PSNR improvements of up to 4.18 dB, 1.56 dB, and 1.73 dB over ViT on full-image Source Temperature, Shortwave, and Longwave Flux datasets. These results highlight ViFOR’s effectiveness and potential for advancing high-resolution climate data analysis.
超分辨率(SR)对于提高地球系统模型(ESM)数据的空间分辨率至关重要,从而能够更精确地分析环境过程。本文介绍了ViFOR,这是一种新型SR算法,它将视觉转换器(ViTs)与基于傅里叶隐式神经网络表示(INRs)相结合。ViFOR通过将基于傅里叶的激活函数嵌入到转换器架构中,有效地捕获全局上下文和对于准确SR重建至关重要的高频细节。大量实验表明,无论是在全局还是局部图像方面,ViFOR在峰值信噪比(PSNR)和均方误差(MSE)方面均优于包括ViT、SIREN和SRGANs等最新方法。ViFOR在全图像源温度、短波和长波通量数据集上的PSNR分别比ViT提高了4.18 dB、1.56 dB和1.73 dB。这些结果突出了ViFOR的有效性以及其在推进高分辨率气候数据分析方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了ViFOR,这是一种新型的超分辨率算法,结合了基于Vision Transformer的模型和基于傅立叶变换的隐神经表示网络。ViFOR通过将傅立叶激活函数嵌入到Transformer架构中,有效地捕捉全局上下文和高频细节,对于准确的超分辨率重建至关重要。实验表明,ViFOR在峰值信噪比(PSNR)和均方误差(MSE)方面,全面超越了包括ViT、SIREN和SRGAN等在内的最新方法,无论是在全局还是局部图像上均表现优异。特别是对于全图像源温度、短波和长波流量数据集,ViFOR相比ViT的PSNR提升分别达到了4.18分贝、1.56分贝和1.73分贝。这显示了ViFOR在推进高分辨率气候数据分析方面的潜力和有效性。
Key Takeaways
- ViFOR是一种结合了Vision Transformer和基于傅立叶变换的隐神经表示网络的新型超分辨率算法。
- ViFOR通过将傅立叶激活函数嵌入到Transformer架构中,以捕捉全局上下文和高频细节,这对于准确超分辨率重建至关重要。
- 实验表明,ViFOR在峰值信噪比(PSNR)和均方误差(MSE)方面超越了其他最新方法。
- ViFOR在全图像源温度、短波和长波流量数据集上的表现优于ViT,PSNR提升显著。
- ViFOR算法在推进高分辨率气候数据分析方面具有潜力和有效性。
- ViFOR算法能够有效结合全球视野和细节信息,这对于环境过程的精确分析至关重要。
点此查看论文截图