⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-06 更新
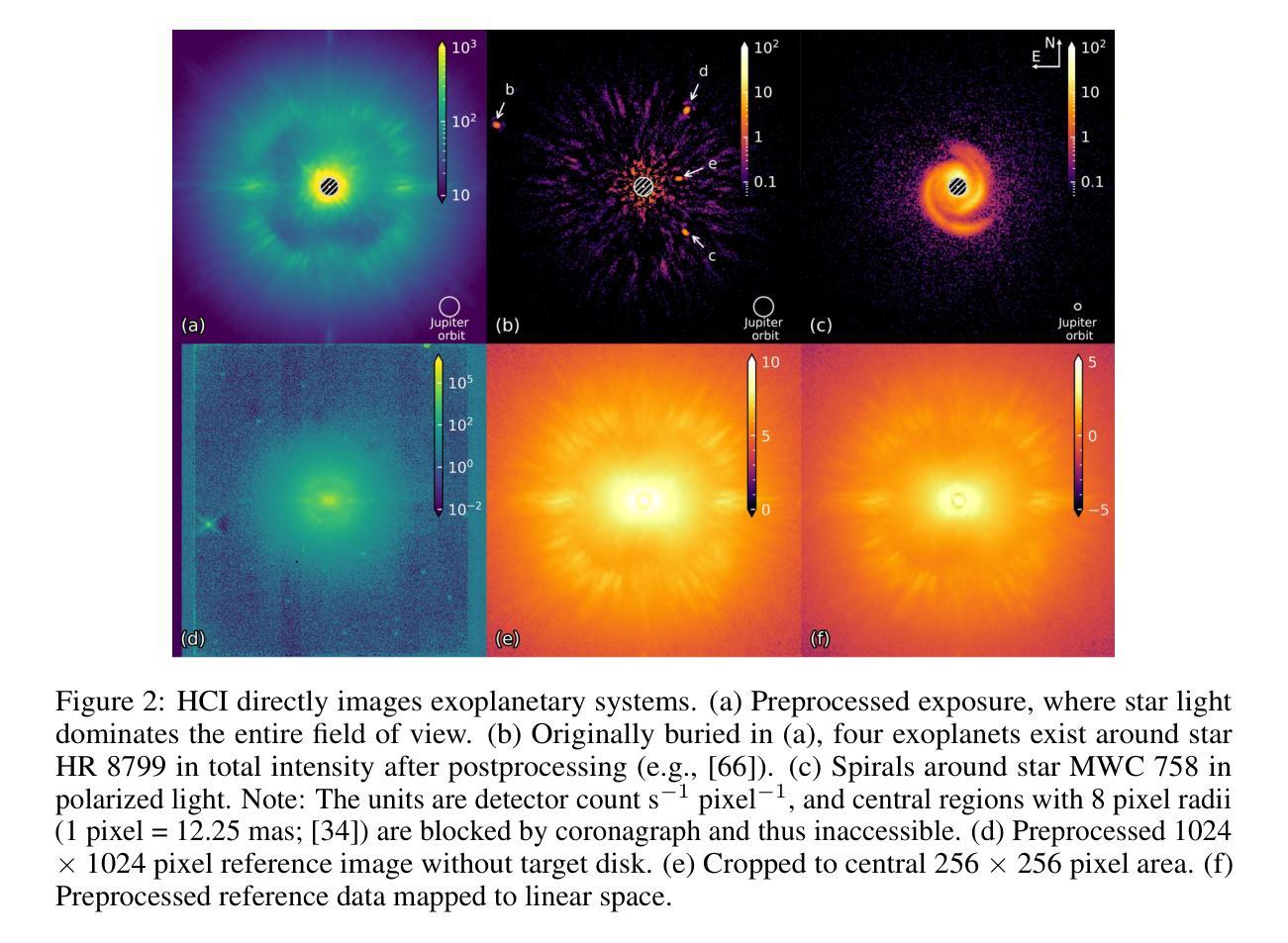
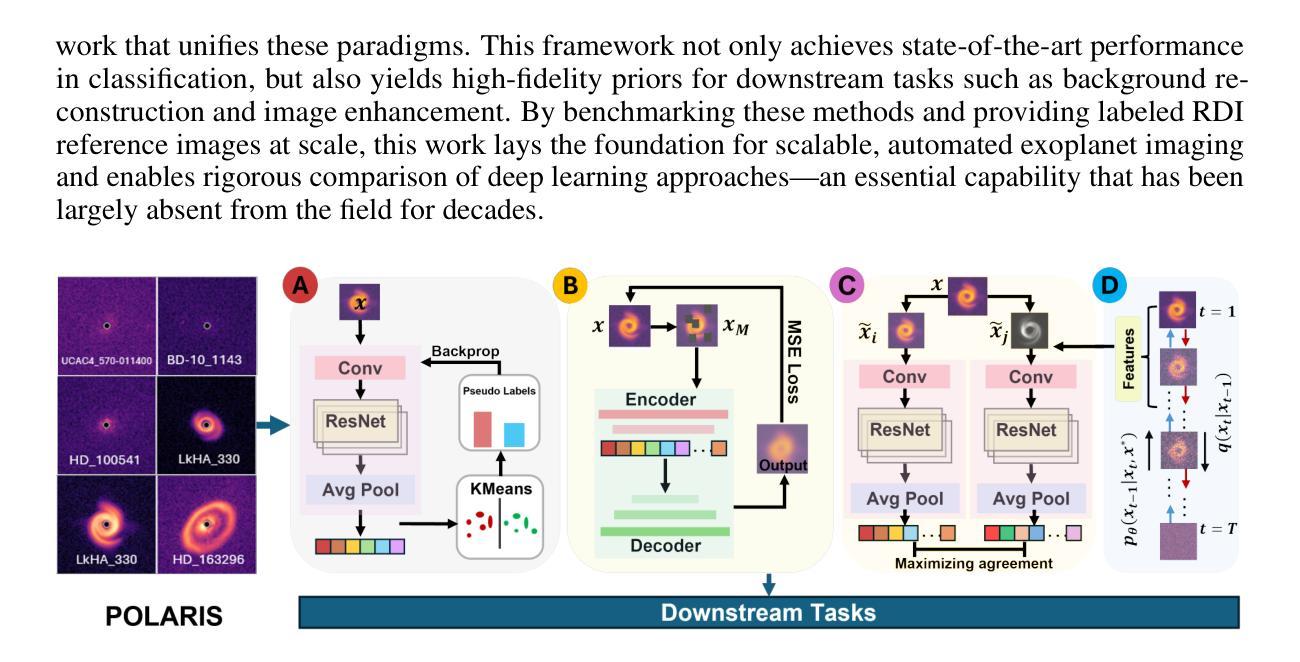
POLARIS: A High-contrast Polarimetric Imaging Benchmark Dataset for Exoplanetary Disk Representation Learning
Authors:Fangyi Cao, Bin Ren, Zihao Wang, Shiwei Fu, Youbin Mo, Xiaoyang Liu, Yuzhou Chen, Weixin Yao
With over 1,000,000 images from more than 10,000 exposures using state-of-the-art high-contrast imagers (e.g., Gemini Planet Imager, VLT/SPHERE) in the search for exoplanets, can artificial intelligence (AI) serve as a transformative tool in imaging Earth-like exoplanets in the coming decade? In this paper, we introduce a benchmark and explore this question from a polarimetric image representation learning perspective. Despite extensive investments over the past decade, only a few new exoplanets have been directly imaged. Existing imaging approaches rely heavily on labor-intensive labeling of reference stars, which serve as background to extract circumstellar objects (disks or exoplanets) around target stars. With our POLARIS (POlarized Light dAta for total intensity Representation learning of direct Imaging of exoplanetary Systems) dataset, we classify reference star and circumstellar disk images using the full public SPHERE/IRDIS polarized-light archive since 2014, requiring less than 10 percent manual labeling. We evaluate a range of models including statistical, generative, and large vision-language models and provide baseline performance. We also propose an unsupervised generative representation learning framework that integrates these models, achieving superior performance and enhanced representational power. To our knowledge, this is the first uniformly reduced, high-quality exoplanet imaging dataset, rare in astrophysics and machine learning. By releasing this dataset and baselines, we aim to equip astrophysicists with new tools and engage data scientists in advancing direct exoplanet imaging, catalyzing major interdisciplinary breakthroughs.
在面对使用尖端高对比度成像仪(例如双子座行星成像仪、VLT/SPHERE)寻找类地行星时超过一百万张来自超过一万次曝光的图像,人工智能(AI)能否在未来十年内成为成像类地行星的变革性工具?在这篇论文中,我们从偏振图像表示学习的角度介绍了基准测试并探讨了这个问题。尽管过去十年里的大量投资,只有少数新的类地行星被直接成像。现有的成像方法严重依赖于参考恒星的劳动密集型标记,这些恒星作为背景提取目标恒星周围的环绕恒星物体(星周盘或类地行星)。借助我们的POLARIS(用于直接成像外行星系统的全强度偏振光数据表示学习)数据集,我们使用自2014年以来的完整公共SPHERE/IRDIS偏振光档案对参考恒星和星周盘图像进行分类,只需要不到百分之十的人工标记。我们评估了一系列模型,包括统计模型、生成模型和大型视觉语言模型,并提供基准性能。我们还提出了一个整合这些模型的无监督生成表示学习框架,取得了优越的性能和增强的表示能力。据我们所知,这是罕见的天体物理学和机器学习领域中第一个统一降低的高质量类地行星成像数据集。通过发布这个数据集和基准测试,我们的目标是给天文学家配备新工具,并与数据科学家合作推进直接类地行星成像,从而促进重大跨学科突破。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages main text with 5 figures, 9 pages appendix with 9 figures. Submitted to NeurIPS 2025
Summary
此论文探讨了人工智能在成像地球类似系外行星方面的潜力。通过POLARIS数据集,研究团队利用极化光数据对直接成像的系外行星系统进行了表示学习。该数据集包括自2014年以来的完整SPHERE/IRDIS极化光档案,只需不到10%的人工标注。研究团队评估了一系列模型,包括统计模型、生成模型和大型视觉语言模型,并提出了一个整合这些模型的无监督生成表示学习框架,取得了优越的性能和更强的表示能力。这是天文物理学和机器学习领域罕见的高品质均匀还原的系外行星成像数据集。发布此数据集和基准测试旨在帮助天文学家使用新工具,并促进数据科学家推动直接成像系外行星的研究,催化跨学科重大突破。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文探讨了人工智能在成像地球类似系外行星方面的应用潜力,特别是在使用高对比度成像仪进行搜索时。
- 介绍了POLARIS数据集,该数据集包含从SPHERE/IRDIS极化光档案中提取的数据,并采用了较少的人工标注方式。
- 研究团队评估了多种模型,包括统计、生成和大型视觉语言模型,并提出了一个无监督生成表示学习框架。
- 该框架集成了不同的模型并达到了优越的性能水平,显示出强大的表示能力。
- 这是首个高质量均匀还原的系外行星成像数据集,对天文物理学和机器学习领域具有重要意义。
- 发布此数据集和基准测试旨在推动跨学科合作,促进直接成像系外行星的研究突破。
点此查看论文截图

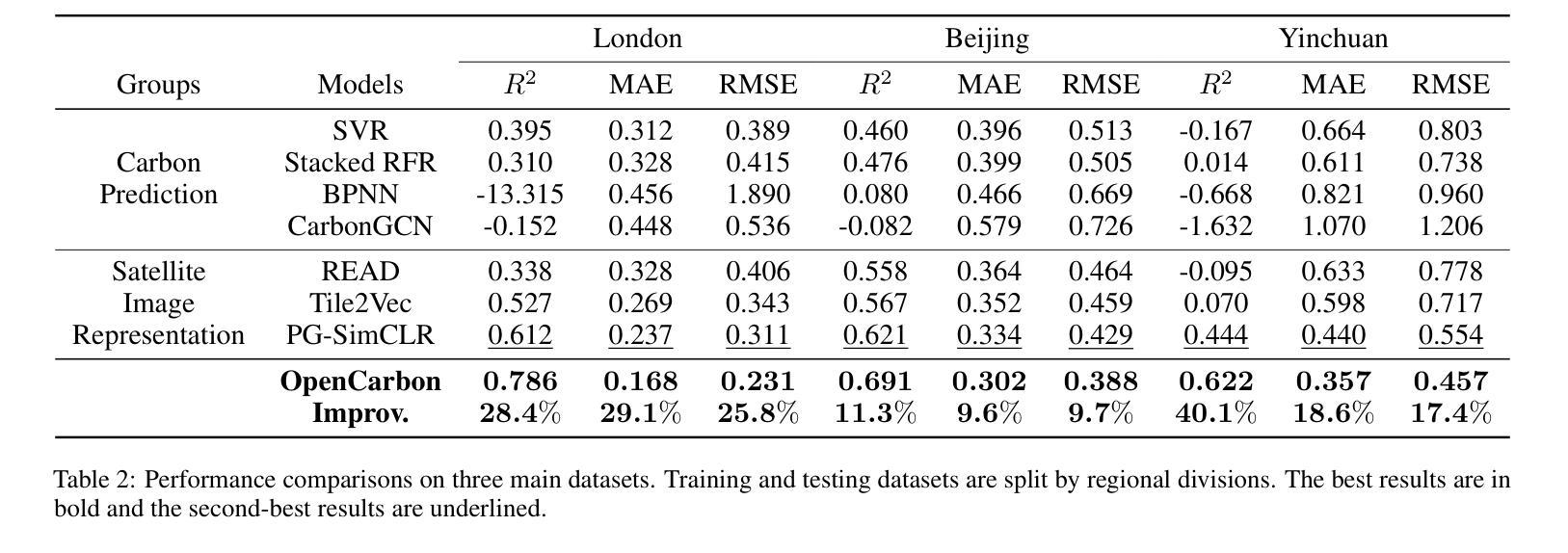
OpenCarbon: A Contrastive Learning-based Cross-Modality Neural Approach for High-Resolution Carbon Emission Prediction Using Open Data
Authors:Jinwei Zeng, Yu Liu, Guozhen Zhang, Jingtao Ding, Yuming Lin, Jian Yuan, Yong Li
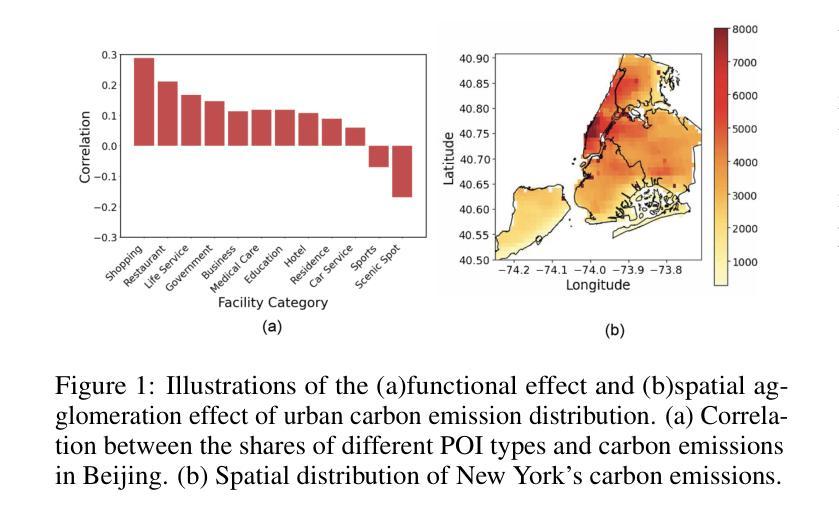
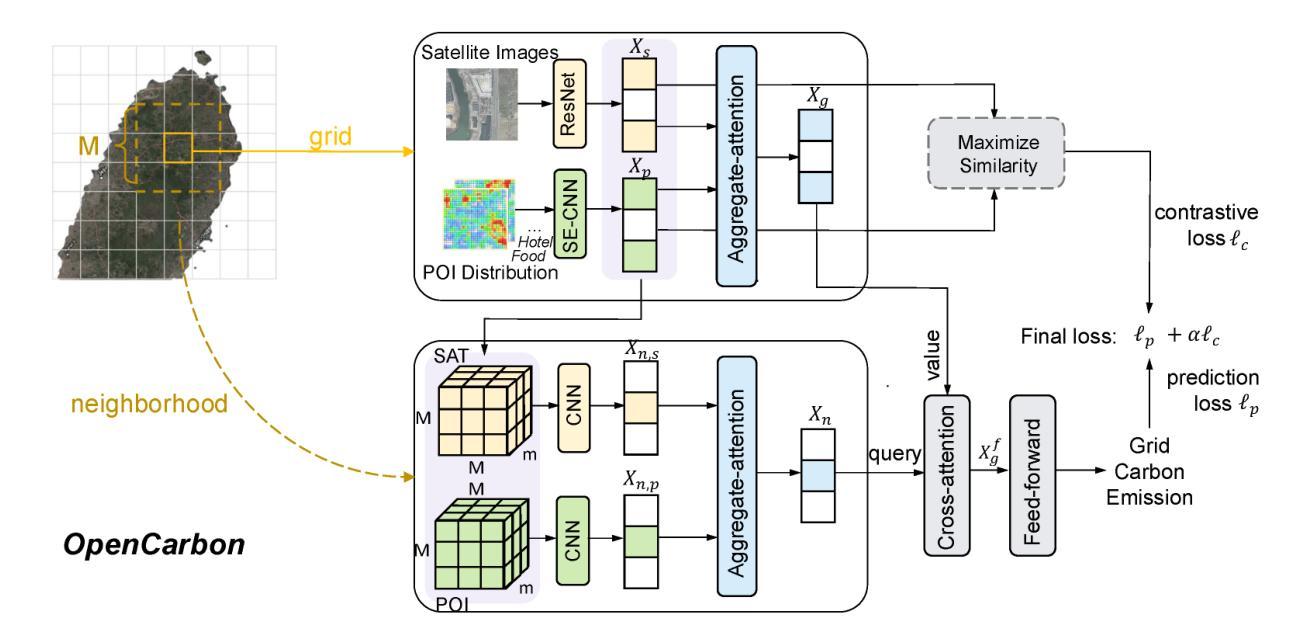
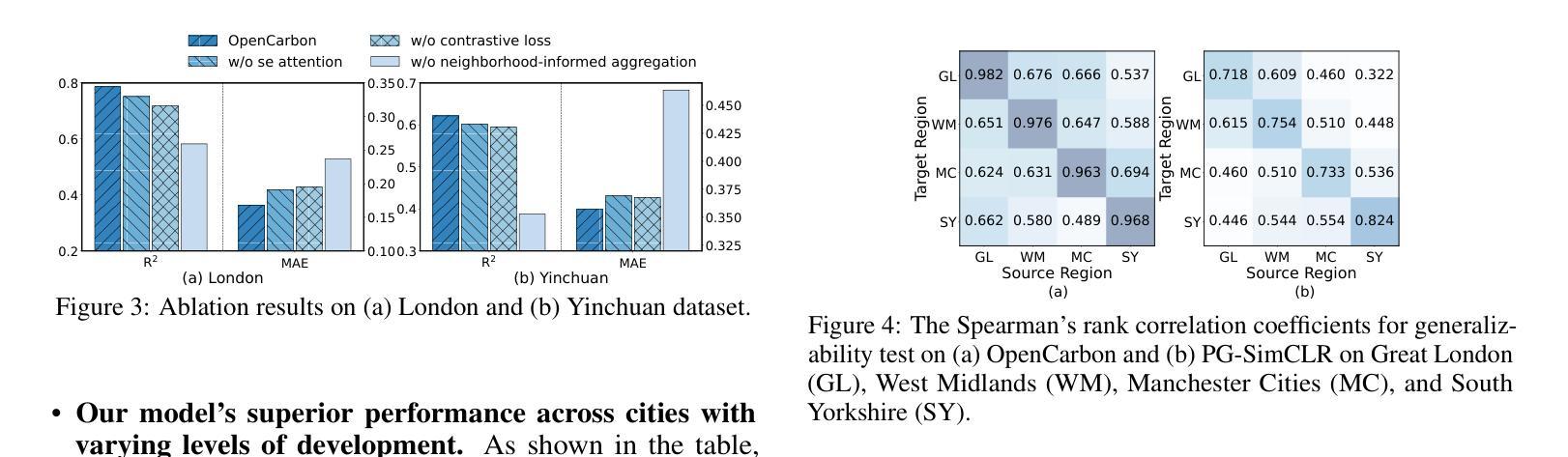
Accurately estimating high-resolution carbon emissions is crucial for effective emission governance and mitigation planning. While conventional methods for precise carbon accounting are hindered by substantial data collection efforts, the rise of open data and advanced learning techniques offers a promising solution. Once an open data-based prediction model is developed and trained, it can easily infer emissions for new areas based on available open data. To address this, we incorporate two modalities of open data, satellite images and point-of-interest (POI) data, to predict high-resolution urban carbon emissions, with satellite images providing macroscopic and static and POI data offering fine-grained and relatively dynamic functionality information. However, estimating high-resolution carbon emissions presents two significant challenges: the intertwined and implicit effects of various functionalities on carbon emissions, and the complex spatial contiguity correlations that give rise to the agglomeration effect. Our model, OpenCarbon, features two major designs that target the challenges: a cross-modality information extraction and fusion module to extract complementary functionality information from two modules and model their interactions, and a neighborhood-informed aggregation module to capture the spatial contiguity correlations. Extensive experiments demonstrate our model’s superiority, with a significant performance gain of 26.6% on R2. Further generalizability tests and case studies also show OpenCarbon’s capacity to capture the intrinsic relation between urban functionalities and carbon emissions, validating its potential to empower efficient carbon governance and targeted carbon mitigation planning. Codes and data are available: https://github.com/JinweiZzz/OpenCarbon.
准确估算高分辨率碳排放对于有效的排放管理和减缓规划至关重要。传统的精确碳排放核算方法受到大量数据收集工作的阻碍,而开放数据和学习技术的兴起提供了一个有希望的解决方案。一旦基于开放数据的预测模型被开发和训练,它可以很容易地根据可用的开放数据推断新区域的排放。为了解决这一问题,我们结合了两种开放数据模式,即卫星图像和兴趣点(POI)数据,来预测高分辨率的城市碳排放。卫星图像提供宏观和静态的信息,而POI数据提供精细的、相对动态的功能信息。然而,估算高分辨率碳排放存在两个重大挑战:各种功能对碳排放的交织和隐含影响,以及产生集聚效应的复杂空间邻近相关性。我们的模型OpenCarbon针对这两个挑战进行了两大设计:一是跨模态信息提取与融合模块,从两种模态中提取互补功能信息并建模其交互作用;二是邻域感知聚合模块,用于捕捉空间邻近相关性。大量实验证明了我们的模型的优越性,在R2上实现了26.6%的性能提升。进一步的通用性测试和案例研究也显示了OpenCarbon捕捉城市功能与碳排放之间内在关系的能力,验证了其在促进高效碳治理和目标碳减排规划中的潜力。相关代码和数据可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/JinweiZzz/OpenCarbon。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IJCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了利用开放数据和先进学习技术预测高分辨率碳排放的方法。通过结合卫星图像和兴趣点(POI)数据两种模态的开放数据,提出一种名为OpenCarbon的模型,用于解决估算高分辨率碳排放面临的挑战,如各种功能对碳排放的交织和隐性影响以及空间相邻关联产生的集聚效应。该模型通过跨模态信息提取和融合模块以及邻域信息聚合模块的设计,实现了高性能的碳排放预测,并展示了其在实际应用中的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 开放数据和先进学习技术为准确预测高分辨率碳排放提供了解决方案。
- OpenCarbon模型结合卫星图像和POI数据两种模态的开放数据来预测碳排放。
- 该模型面临的主要挑战是各种功能对碳排放的交织和隐性影响以及空间相邻关联产生的集聚效应。
- OpenCarbon模型通过跨模态信息提取和融合模块,有效提取和融合两种数据模态的互补功能信息。
- 邻域信息聚合模块有助于捕捉空间相邻关联,提高预测准确性。
- 实验结果表明,OpenCarbon模型在性能上实现了显著的提升,R²值提高了26.6%。
点此查看论文截图