⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-08 更新
Refer to Anything with Vision-Language Prompts
Authors:Shengcao Cao, Zijun Wei, Jason Kuen, Kangning Liu, Lingzhi Zhang, Jiuxiang Gu, HyunJoon Jung, Liang-Yan Gui, Yu-Xiong Wang
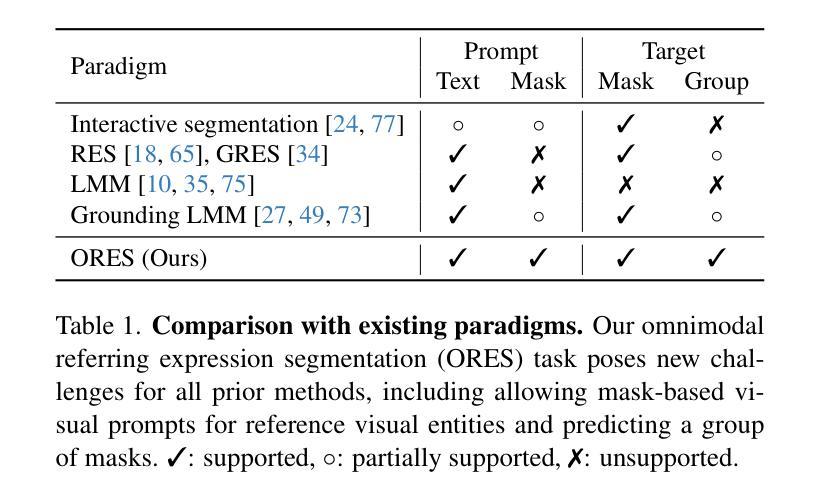
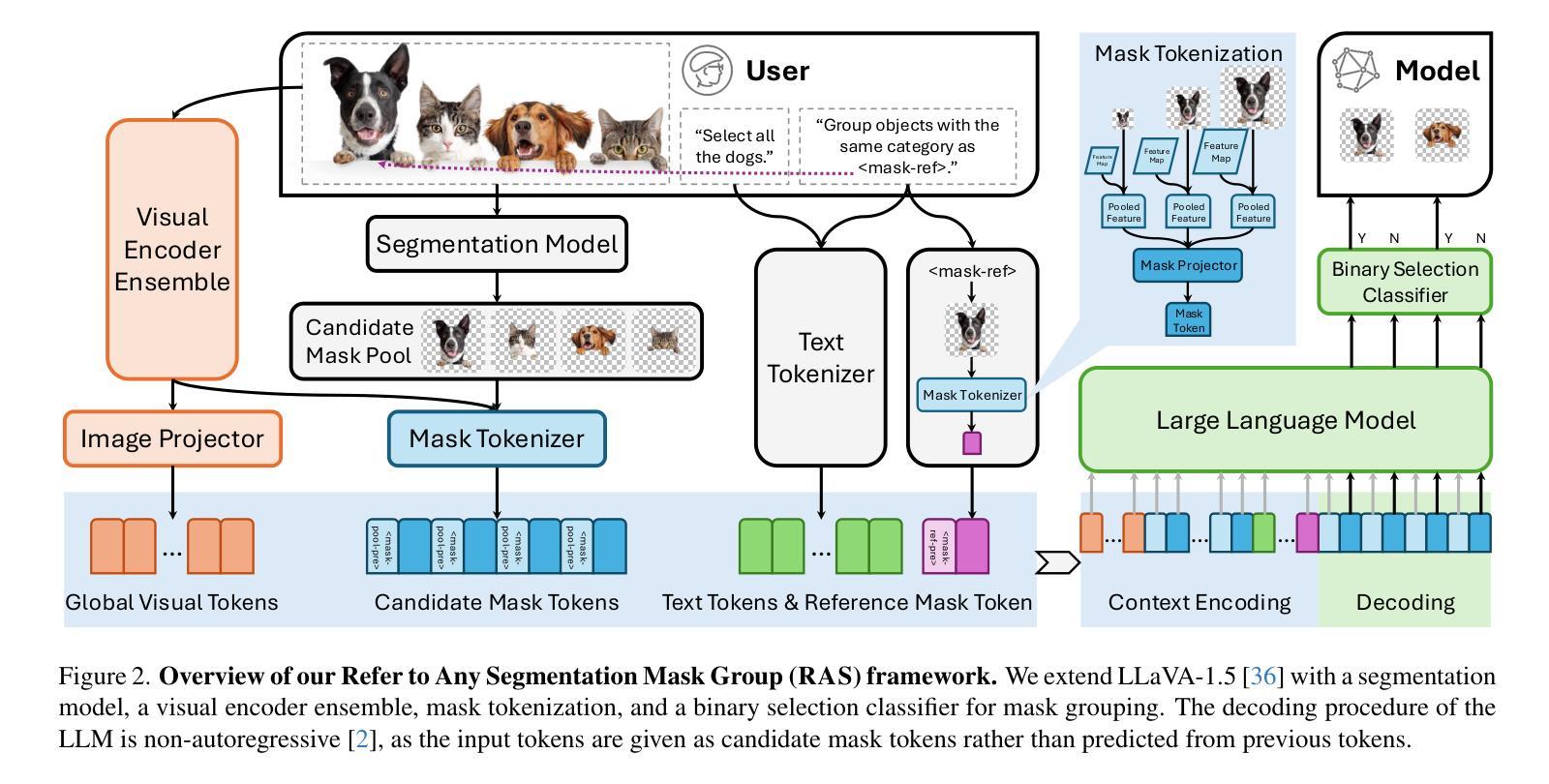
Recent image segmentation models have advanced to segment images into high-quality masks for visual entities, and yet they cannot provide comprehensive semantic understanding for complex queries based on both language and vision. This limitation reduces their effectiveness in applications that require user-friendly interactions driven by vision-language prompts. To bridge this gap, we introduce a novel task of omnimodal referring expression segmentation (ORES). In this task, a model produces a group of masks based on arbitrary prompts specified by text only or text plus reference visual entities. To address this new challenge, we propose a novel framework to “Refer to Any Segmentation Mask Group” (RAS), which augments segmentation models with complex multimodal interactions and comprehension via a mask-centric large multimodal model. For training and benchmarking ORES models, we create datasets MaskGroups-2M and MaskGroups-HQ to include diverse mask groups specified by text and reference entities. Through extensive evaluation, we demonstrate superior performance of RAS on our new ORES task, as well as classic referring expression segmentation (RES) and generalized referring expression segmentation (GRES) tasks. Project page: https://Ref2Any.github.io.
近期图像分割模型已经发展到了可以将图像分割成高质量视觉实体的掩膜,但它们无法基于语言和视觉为复杂查询提供全面的语义理解。这一局限性降低了这些模型在处理视觉语言提示驱动的友好用户交互应用的效能。为了填补这一空白,我们引入了一项新的多模式指代表达式分割任务(ORES)。在此任务中,模型根据仅由文本指定或文本和参考视觉实体共同指定的任意提示生成一组掩膜。为了应对这一新挑战,我们提出了一种名为“指向任意分割掩膜组”(RAS)的新框架,通过掩膜中心大型多模式模型增强分割模型的复杂多模式交互和理解能力。为了训练和评估ORES模型,我们创建了MaskGroups-2M和MaskGroups-HQ数据集,包含由文本和参考实体指定的各种掩膜组。通过广泛评估,我们在新的ORES任务以及经典指代表达式分割(RES)和广义指代表达式分割(GRES)任务上展示了RAS的卓越性能。项目页面:https://Ref2Any.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一项新的任务——多模态引用表达式分割(ORES),旨在解决现有图像分割模型无法基于语言和视觉提供全面的语义理解的问题。为了应对这一挑战,提出了一种名为RAS的新型框架,该框架通过大型多模态模型增强分割模型的复杂多模态交互和掩码理解。同时,为了训练和评估ORES模型,创建了MaskGroups-2M和MaskGroups-HQ数据集。实验表明RAS在ORES任务以及经典引用表达式分割(RES)和广义引用表达式分割(GRES)任务上的优越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 当前图像分割模型无法提供基于语言和视觉的全面语义理解。
- 提出了一种新型任务——多模态引用表达式分割(ORES),旨在解决这一问题。
- 介绍了名为RAS的新型框架,它通过大型多模态模型增强分割模型的复杂交互和掩码理解。
- 创建了MaskGroups-2M和MaskGroups-HQ数据集,用于训练和评估ORES模型。
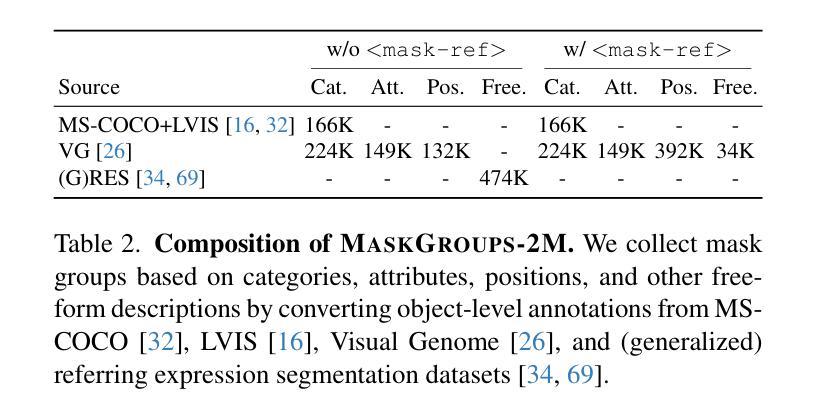
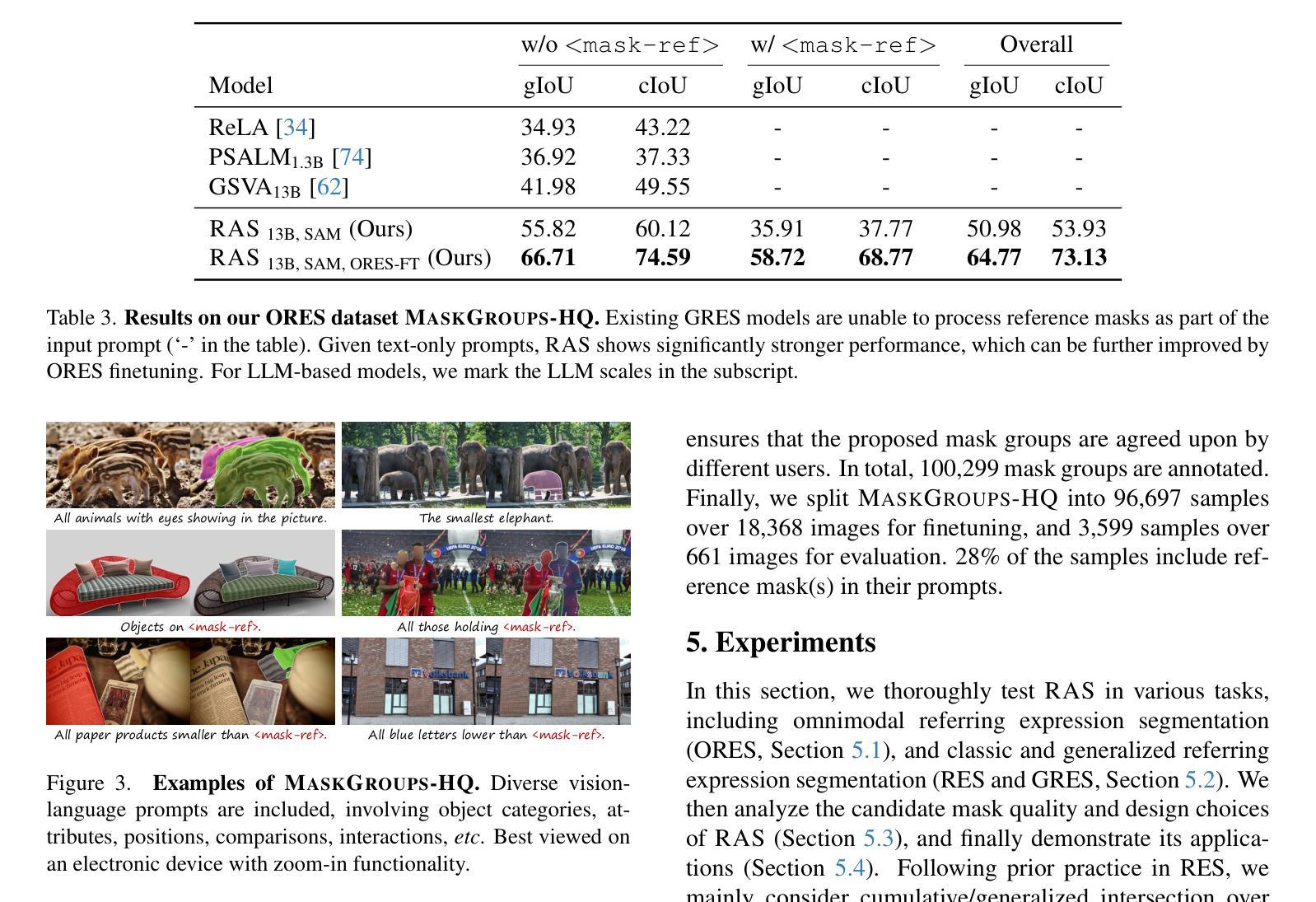
5.RAS在ORES任务上的性能表现优越。
6.RAS也能很好地应对经典引用表达式分割(RES)和广义引用表达式分割(GRES)任务。
点此查看论文截图

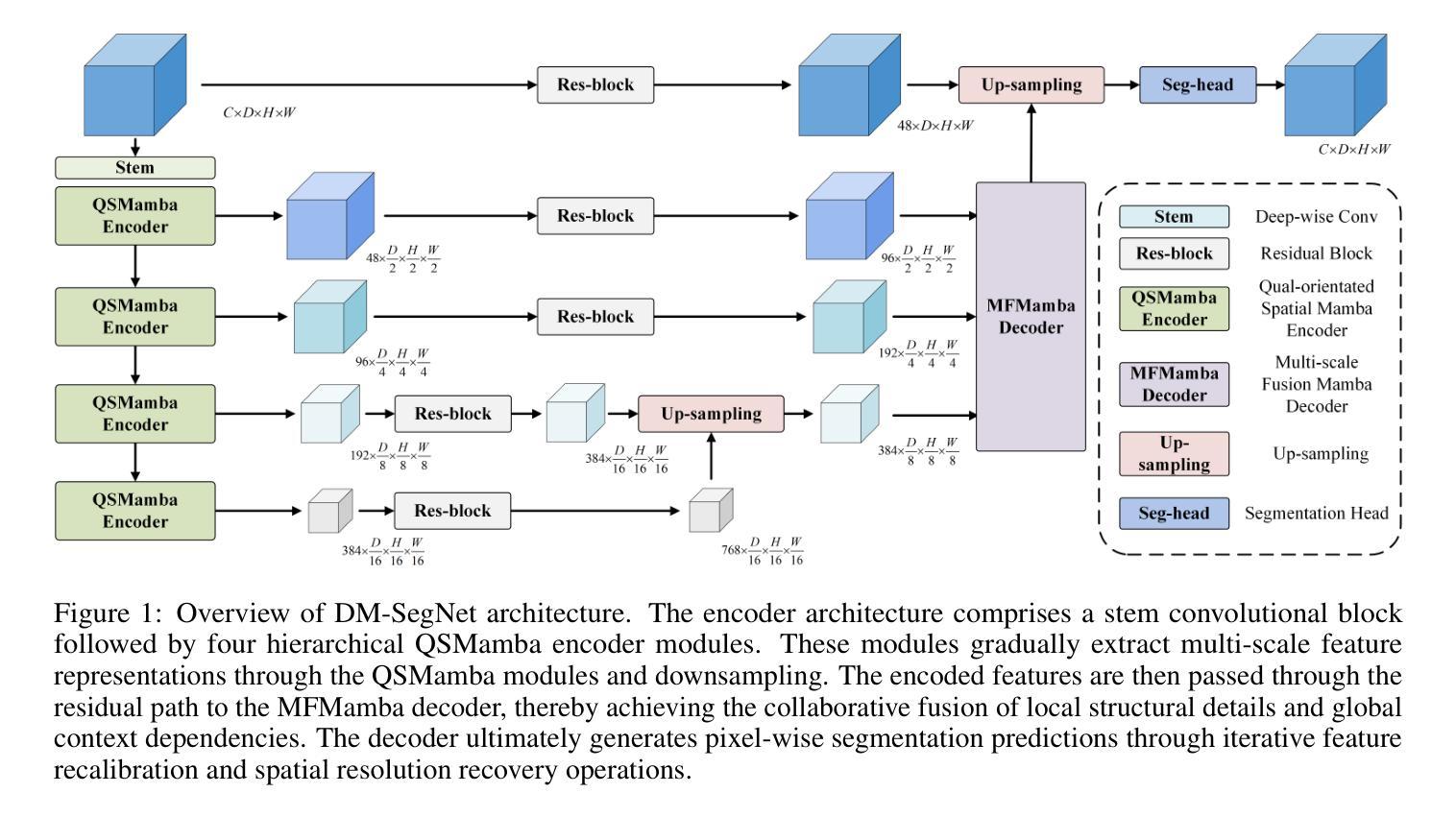
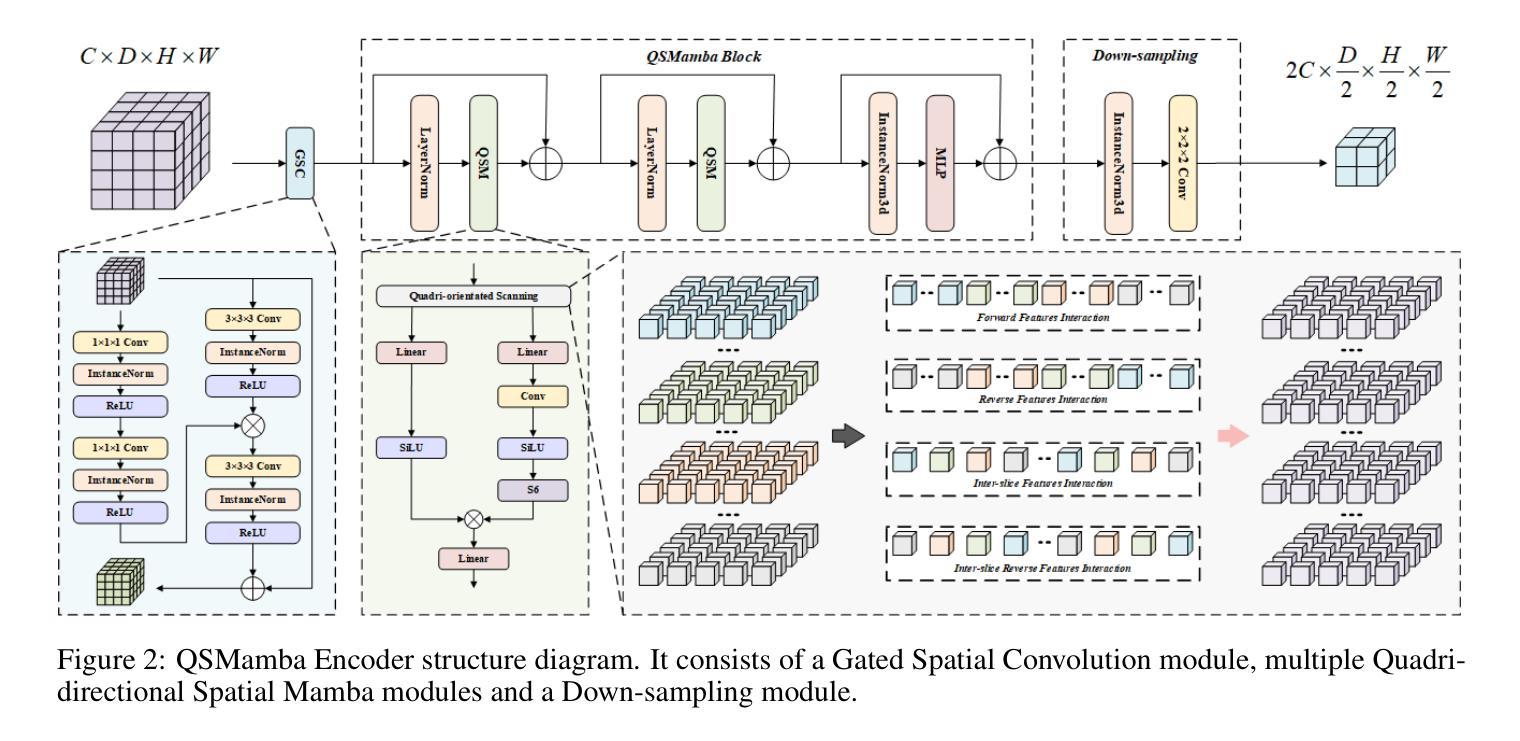
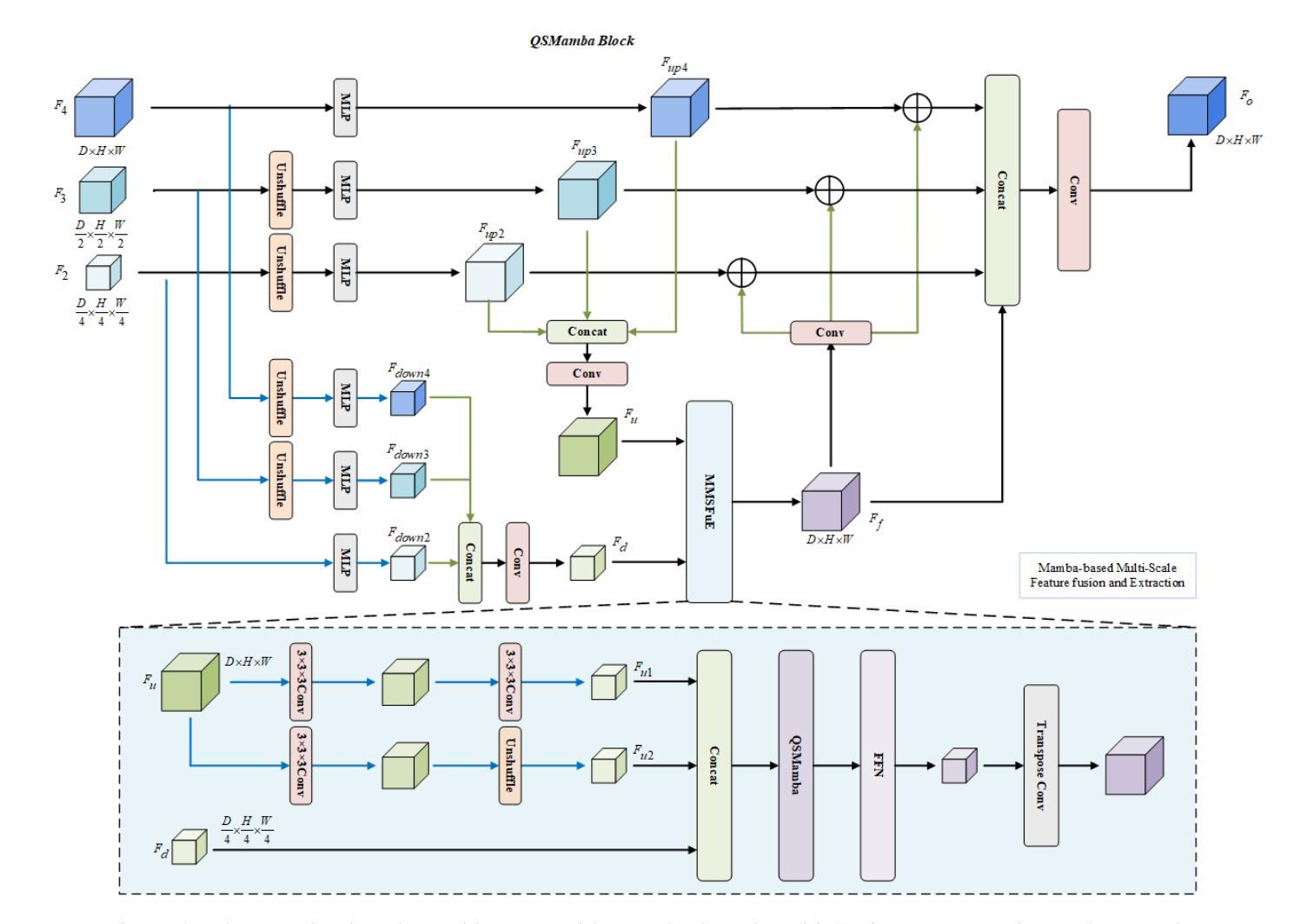
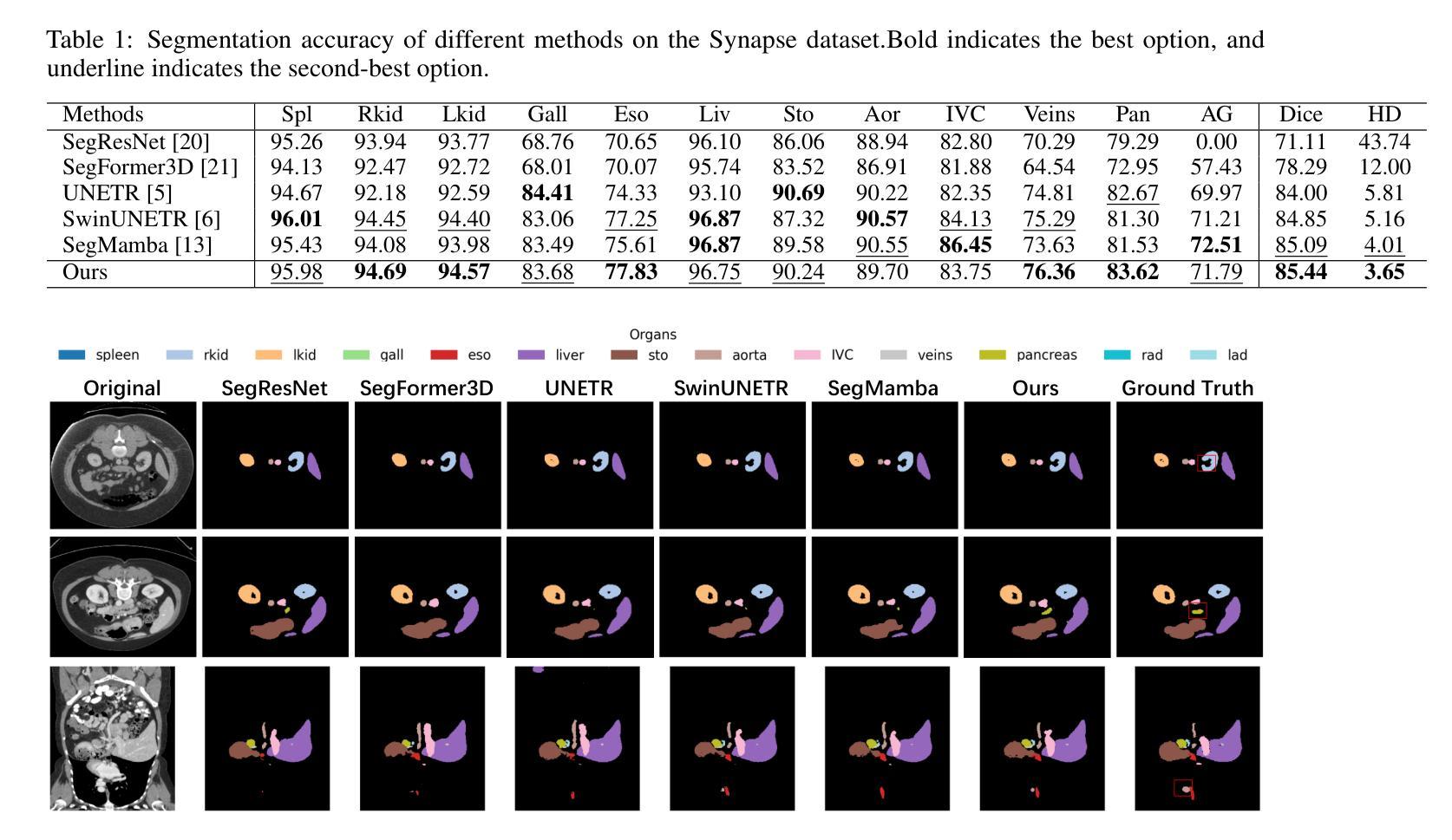
DM-SegNet: Dual-Mamba Architecture for 3D Medical Image Segmentation with Global Context Modeling
Authors:Hangyu Ji
Accurate 3D medical image segmentation demands architectures capable of reconciling global context modeling with spatial topology preservation. While State Space Models (SSMs) like Mamba show potential for sequence modeling, existing medical SSMs suffer from encoder-decoder incompatibility: the encoder’s 1D sequence flattening compromises spatial structures, while conventional decoders fail to leverage Mamba’s state propagation. We present DM-SegNet, a Dual-Mamba architecture integrating directional state transitions with anatomy-aware hierarchical decoding. The core innovations include a quadri-directional spatial Mamba module employing four-directional 3D scanning to maintain anatomical spatial coherence, a gated spatial convolution layer that enhances spatially sensitive feature representation prior to state modeling, and a Mamba-driven decoding framework enabling bidirectional state synchronization across scales. Extensive evaluation on two clinically significant benchmarks demonstrates the efficacy of DM-SegNet: achieving state-of-the-art Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) of 85.44% on the Synapse dataset for abdominal organ segmentation and 90.22% on the BraTS2023 dataset for brain tumor segmentation.
精确的三维医学图像分割需要能够协调全局上下文建模与空间拓扑保持的架构。虽然像Mamba这样的状态空间模型(SSMs)在序列建模方面显示出潜力,但现有的医学SSMs受到编码器-解码器不兼容的限制:编码器的1D序列展平会损害空间结构,而传统解码器则无法利用Mamba的状态传播。我们提出了DM-SegNet,这是一种结合了方向状态转换和解剖结构感知层次解码的双Mamba架构。核心创新包括采用四方向三维扫描的四方向空间Mamba模块,以维持解剖空间连贯性,一个门控空间卷积层,在状态建模之前增强空间敏感特征表示,以及一个由Mamba驱动的解码框架,实现跨尺度的双向状态同步。在两个具有重要临床意义的基准测试上的广泛评估证明了DM-SegNet的有效性:在腹部器官分割的Synapse数据集上实现了最先进的Dice相似系数(DSC)85.44%,在BraTS2023数据集上的脑肿瘤分割达到了90.22%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像精准三维分割需要兼顾全局上下文建模与空间拓扑保持的架构。现有医疗空间模型(SSMs)如Mamba在序列建模方面展现潜力,但存在编码器和解码器不兼容的问题。本文提出DM-SegNet架构,结合方向性状态转换与解剖结构感知层次解码。核心创新包括四方向空间Mamba模块、门控空间卷积层和Mamba驱动解码框架。在两大临床基准测试上表现卓越,腹部器官分割的Dice相似系数达85.44%,脑肿瘤分割的DSC为90.22%。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像3D分割需兼顾全局上下文与空间拓扑。
- SSMs(如Mamba)在医学图像分割中有潜力,但面临编码解码不兼容问题。
- DM-SegNet架构结合方向性状态转换与解剖结构感知层次解码。
- 四方向空间Mamba模块维持解剖空间连贯性。
- 门控空间卷积层强化空间敏感特征表示。
- Mamba驱动解码框架实现跨尺度双向状态同步。
点此查看论文截图

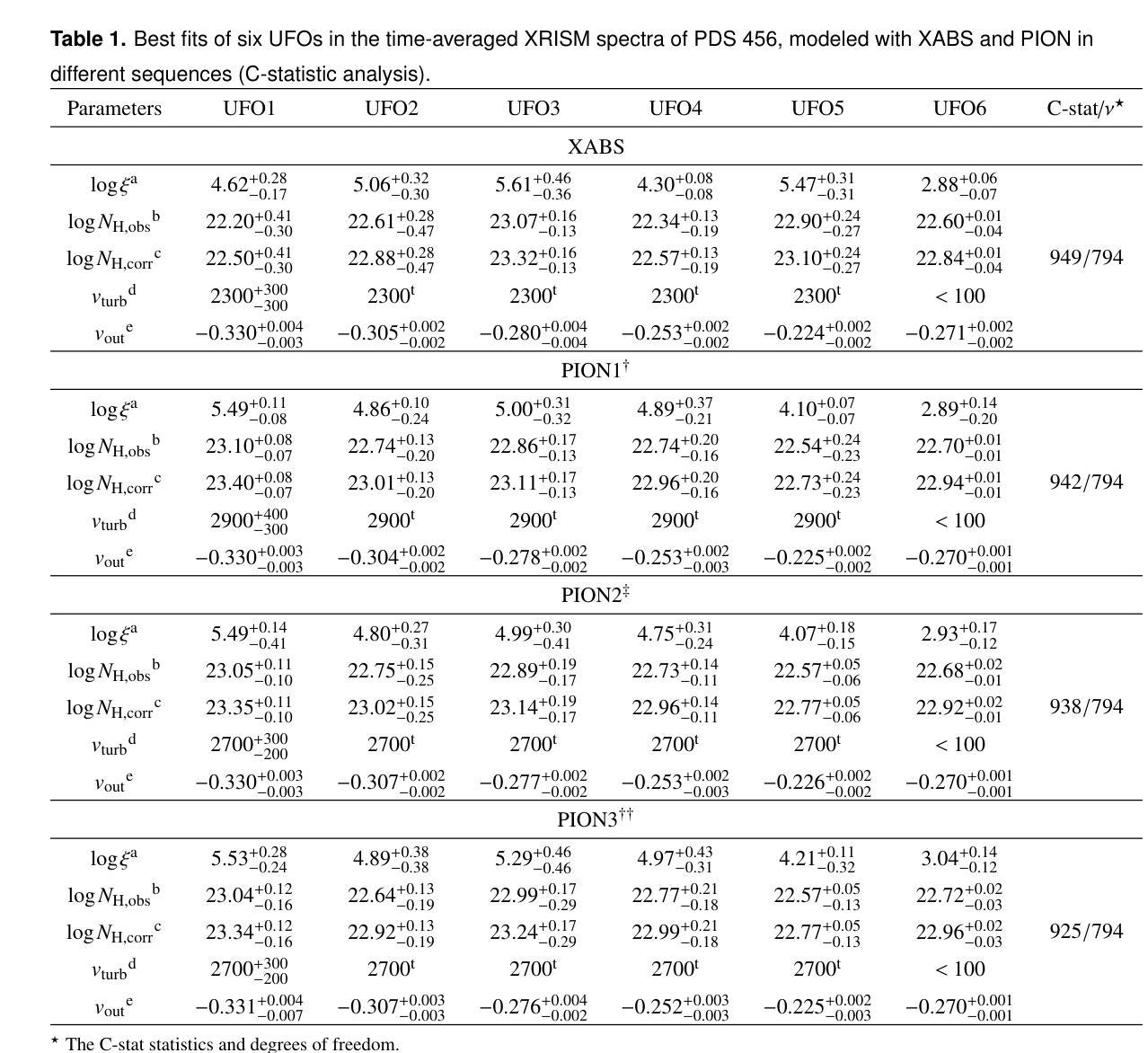
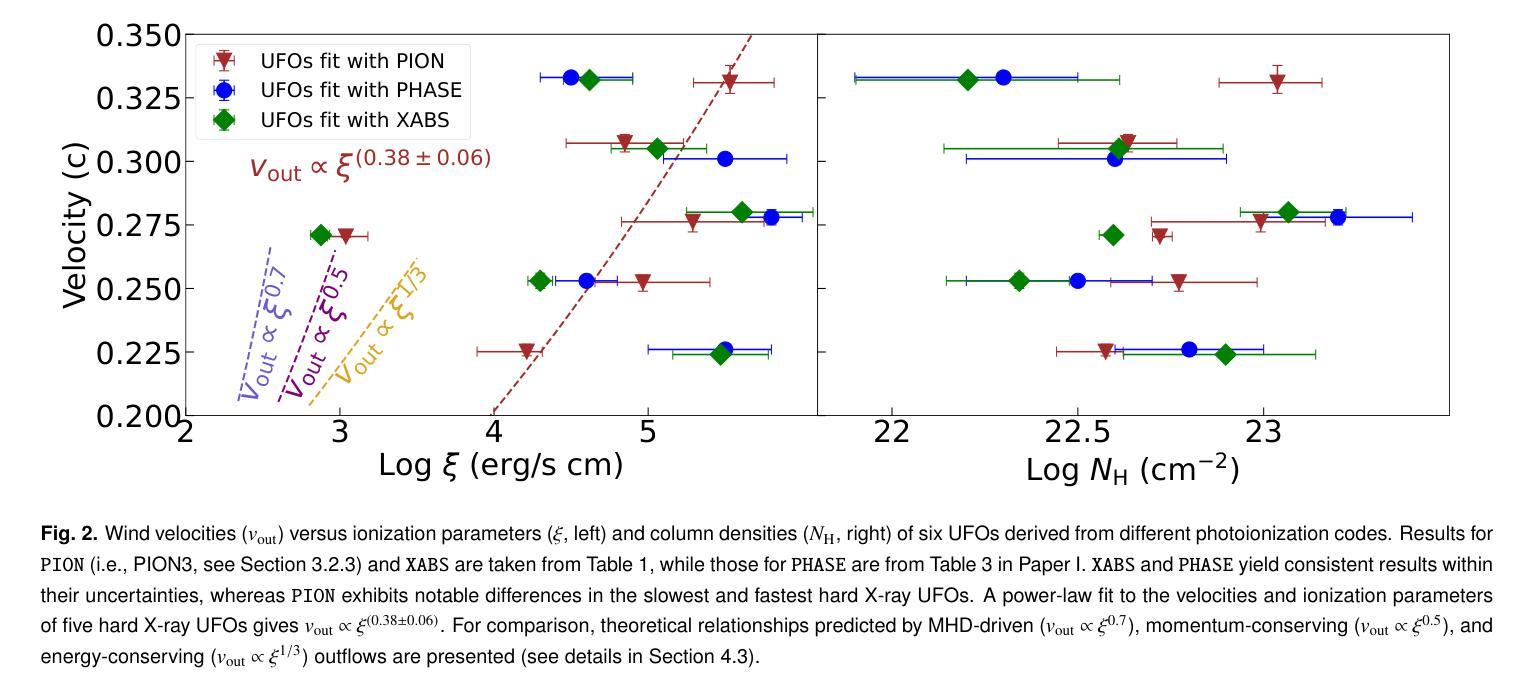
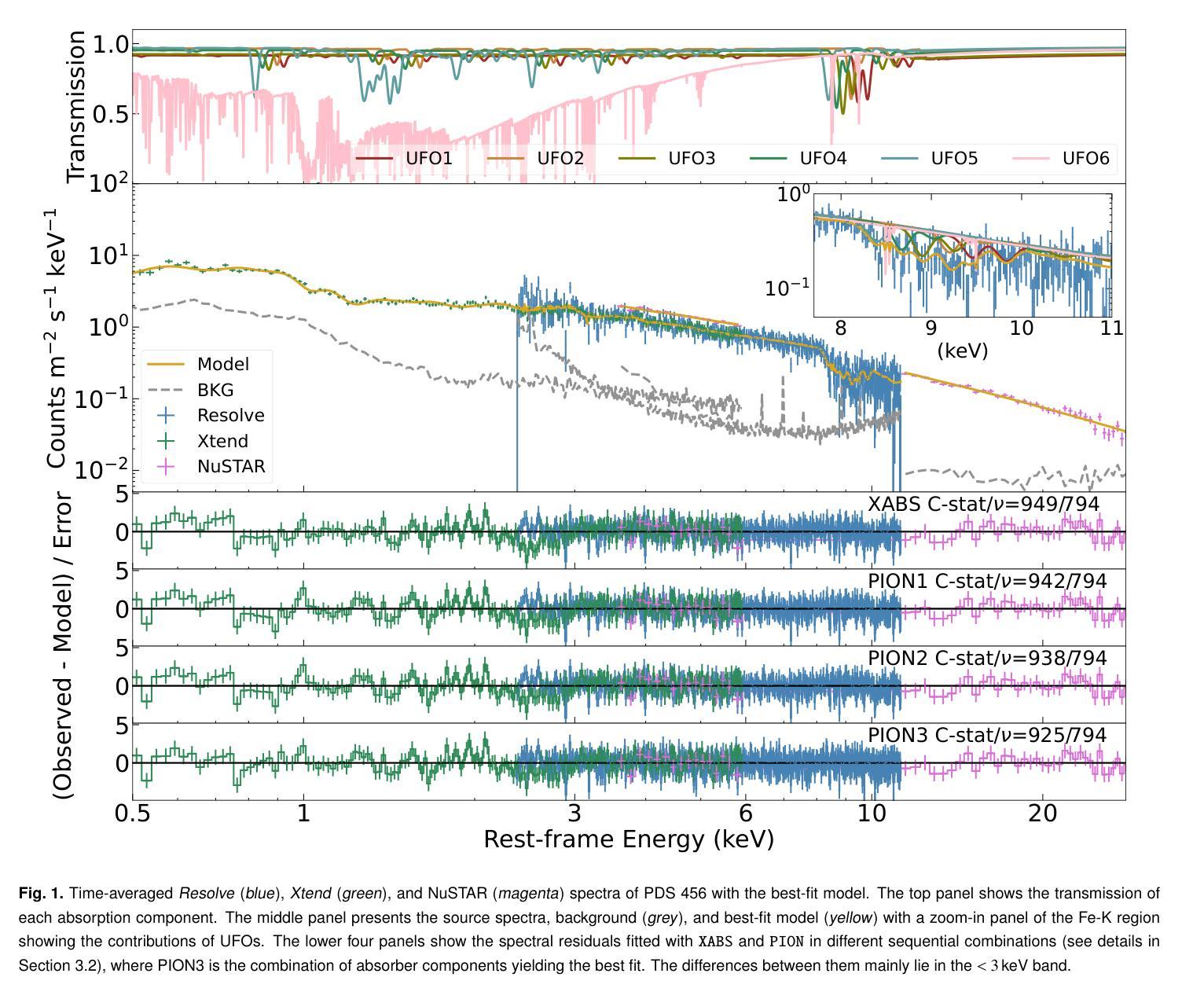
Unraveling the structure of the stratified ultra-fast outflows in PDS 456 with XRISM
Authors:Yerong Xu, Luigi C. Gallo, Kouichi Hagino, James N. Reeves, Francesco Tombesi, Misaki Mizumoto, Alfredo Luminari, Adam G. Gonzalez, Ehud Behar, Rozenn Boissay-Malaquin, Valentina Braito, Pierpaolo Condo, Chris Done, Aiko Miyamoto, Ryuki Mizukawa, Hirokazu Odaka, Riki Sato, Atsushi Tanimoto, Makoto Tashiro, Tahir Yaqoob, Satoshi Yamada
Multiple clumpy wind components ($v_{out}\sim0.2-0.3c$) in the luminous quasar PDS 456 have recently been resolved by XRISM in the Fe-K band for the first time. In this paper, we investigate the structure of ultra-fast outflows (UFOs) using coordinated observations from XRISM, XMM-Newton, and NuSTAR, along with the self-consistently calculated photoionization model \texttt{PION}. Our results reveal a stratified ionization structure likely driven by the radiation field, characterized by a relation between wind velocity and ionization parameter $v_{out}\propto\xi^{(0.38\pm0.06)}$. To evaluate the impact of the screening effect, we tested all possible order permutations of six \texttt{PION} components. We find that highly ionized UFOs ($\log\xi>4.5$) are insensitive to their relative positions, whereas the soft X-ray UFO ($\log\xi\sim3$ and $v_{out}\sim0.27c$) and the lowest-ionized hard X-ray UFO ($\log\xi\sim4.1$ and $v_ {out}\sim0.23c$) are statistically favored – based on the evidence from both the C-statistic and Bayesian analysis – to occupy the middle and innermost layers, respectively. This suggests a possible trend where slower UFOs are launched from regions closer to the supermassive black hole (SMBH). The soft X-ray UFO is found to be thermally unstable, regardless of its relative position. However, its location remains unclear. Our sequence analysis and its similarity to hard X-ray UFOs suggest that they may be co-spatial, while variability constraints support its location within the broad-line region at sub-parsec scales. Simulations with the gate-valve opened XRISM show that high-resolution soft X-ray data can enhance the reliability of our results. Furthermore, simulations with the future X-ray mission NewAthena demonstrate its capability to resolve the absorber sequence and spatial distributions, enabling the determination of UFO structures and their roles in AGN feedback.
在明亮的类星体PDS 456中,多个块状风成分(速度约为光速的0.2~0.3倍)最近在铁-K波段首次被XRISM解析出来。本文利用XRISM、XMM-Newton和NuSTAR的协同观测以及自洽的光离子化模型\texttt{PION},研究了超快外流(UFOs)的结构。我们的结果表明,可能存在由辐射场驱动的分层电离结构,其表现为风速与电离参数之间的关系为$v_{out}\propto\xi^{(0.38\pm0.06)}$。为了评估屏蔽效应的影响,我们测试了六种不同\texttt{PION}成分的所有可能的排列组合。我们发现高电离的外流(电离度大于4.5)对其相对位置并不敏感,而软X射线外流(电离度约为3,速度约为光速的0.27倍)和最低电离的硬X射线外流(电离度约为4.1,速度约为光速的0.23倍)在统计上占据中间层和最内层,分别基于C统计和贝叶斯分析的结果。这表明较慢的外流可能从接近超大质量黑洞(SMBH)的区域发射出来。软X射线外流的热稳定性不佳,与其相对位置无关。然而,它的位置仍然不明确。我们的序列分析与硬X射线外流的相似性表明它们可能共处于同一位置,而变异性约束支持其在亚秒级尺度上的宽线区内。使用开启的XRISM门阀进行的模拟表明,高分辨率的软X射线数据可以提高我们结果的可靠性。此外,未来的X射线任务NewAthena的模拟展示了其解决吸收体序列和空间分布的能力,从而能够确定UFO的结构及其在活性星系核反馈中的作用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 18 figures, and 2 tables, accepted for publication in PASJ for the XRISM special issue
Summary
本研究利用XRISM、XMM-Newton和NuSTAR的联合观测,以及自洽的光电离模型\texttt{PION},对超快外流(UFOs)的结构进行了探究。研究发现风速度与电离参数之间存在关系,$v_{out}\propto\xi^{(0.38\pm0.06)}$。不同电离状态的UFOs的位置排序对筛选效果影响不一。基于C统计量和贝叶斯分析,高度电离的UFOs对相对位置不敏感,而软X射线UFO和最低电离的硬X射线UFO则更倾向于占据中间和内部层。暗示较慢的UFOs可能从接近超大质量黑洞(SMBH)的区域发射。此外,软X射线UFO表现出热不稳定,但其位置尚不清楚。新Athena未来X射线任务有望解决吸收器序列和空间分布,有助于确定UFO结构和在AGN反馈中的作用。
Key Takeaways
- 利用XRISM等观测设备解析了PDS 456中的多重块状风成分。
- 通过协调观测和自洽的光电离模型\texttt{PION},揭示了UFOs的分层电离结构。
- 观察到风速度与电离参数之间的关系:$v_{out}\propto\xi^{(0.38\pm0.06)}$。
- 高电离UFOs相对位置对筛选效果不敏感,而特定电离状态的UFOs占据特定位置。
- 软X射线UFO的热不稳定性被发现,位置尚不明确。其与硬X射线UFOs可能共存的迹象被提出。
- 基于观测证据,较慢的UFOs可能源于接近SMBH的区域。
点此查看论文截图

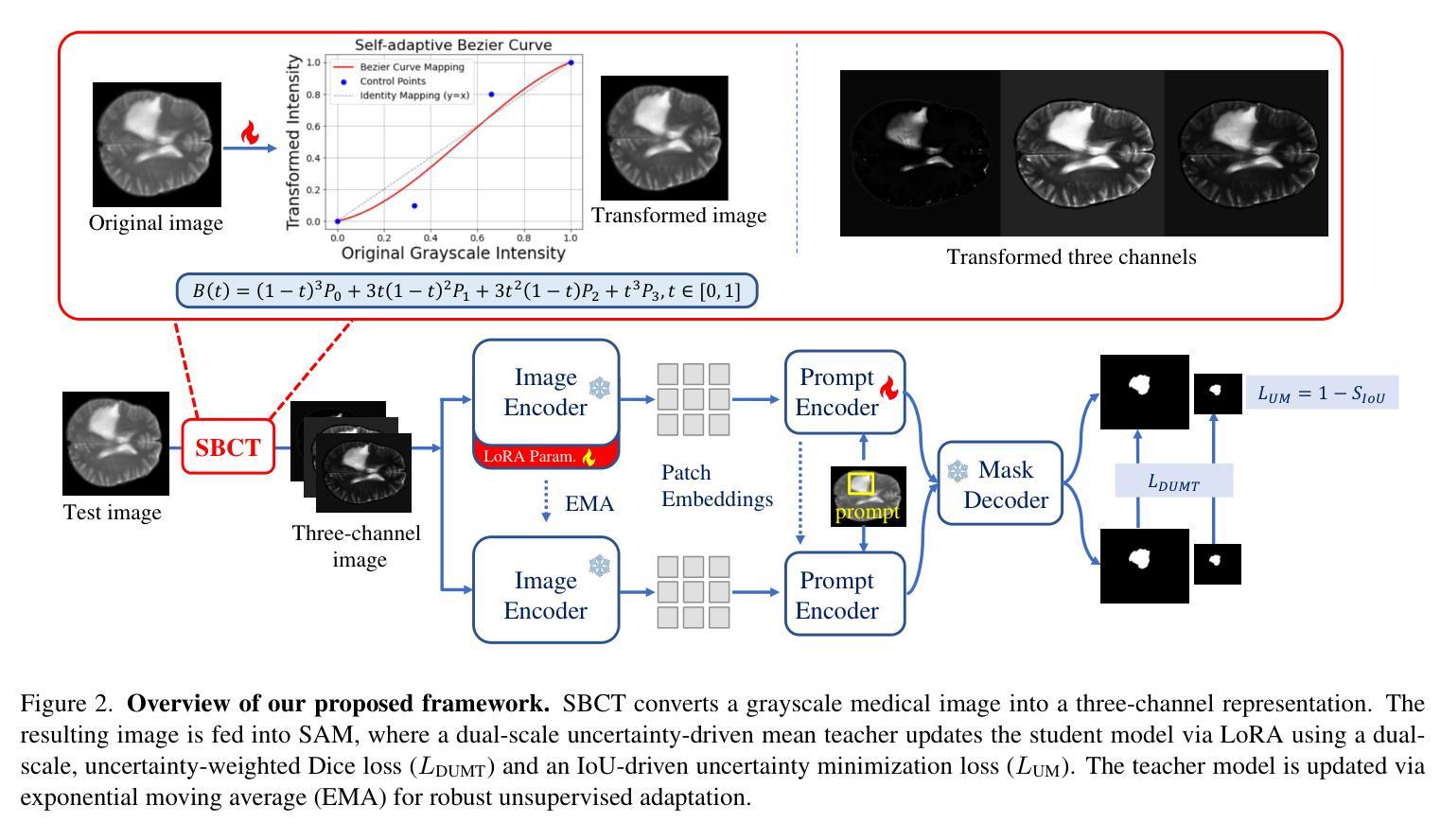
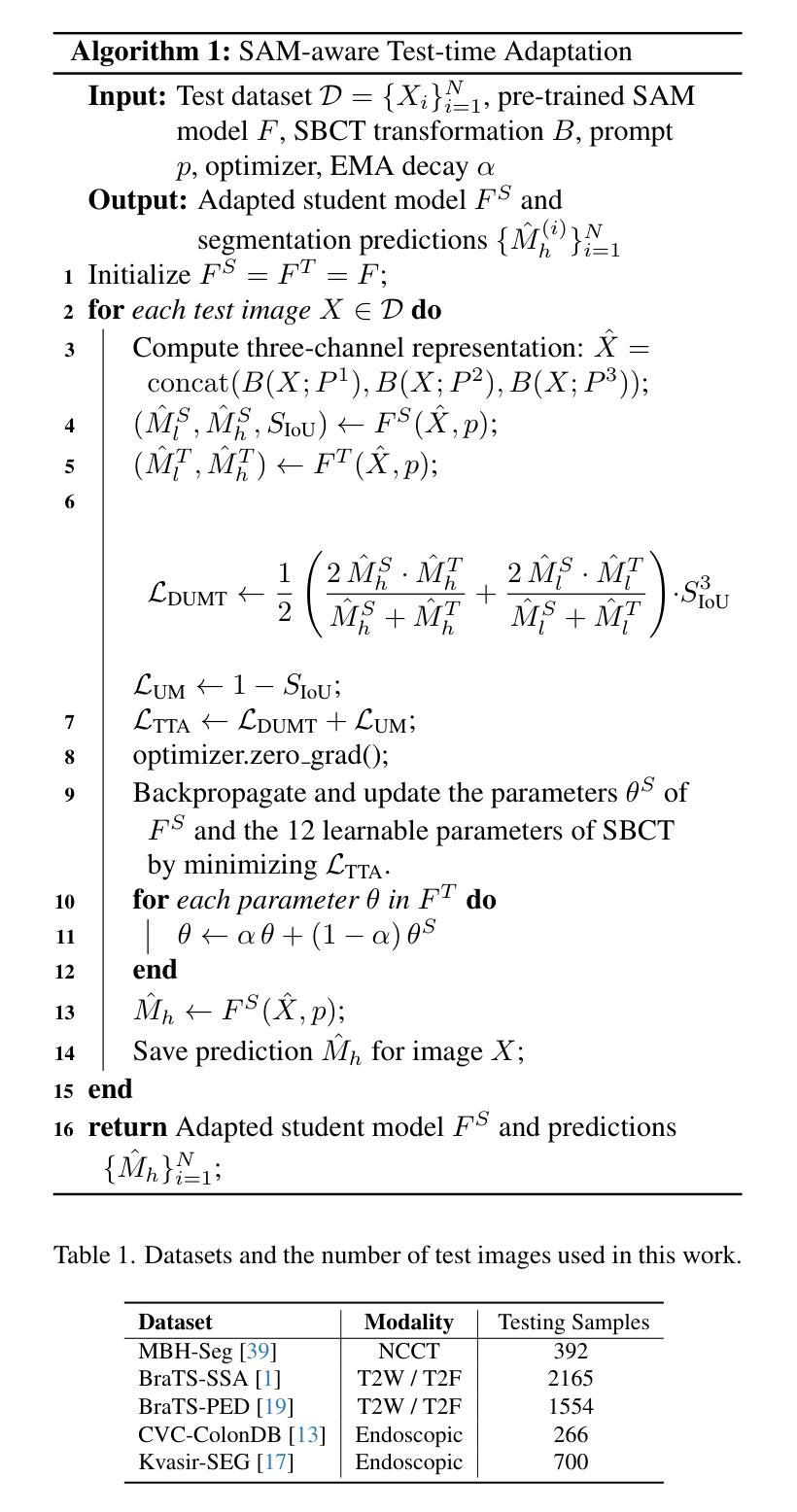
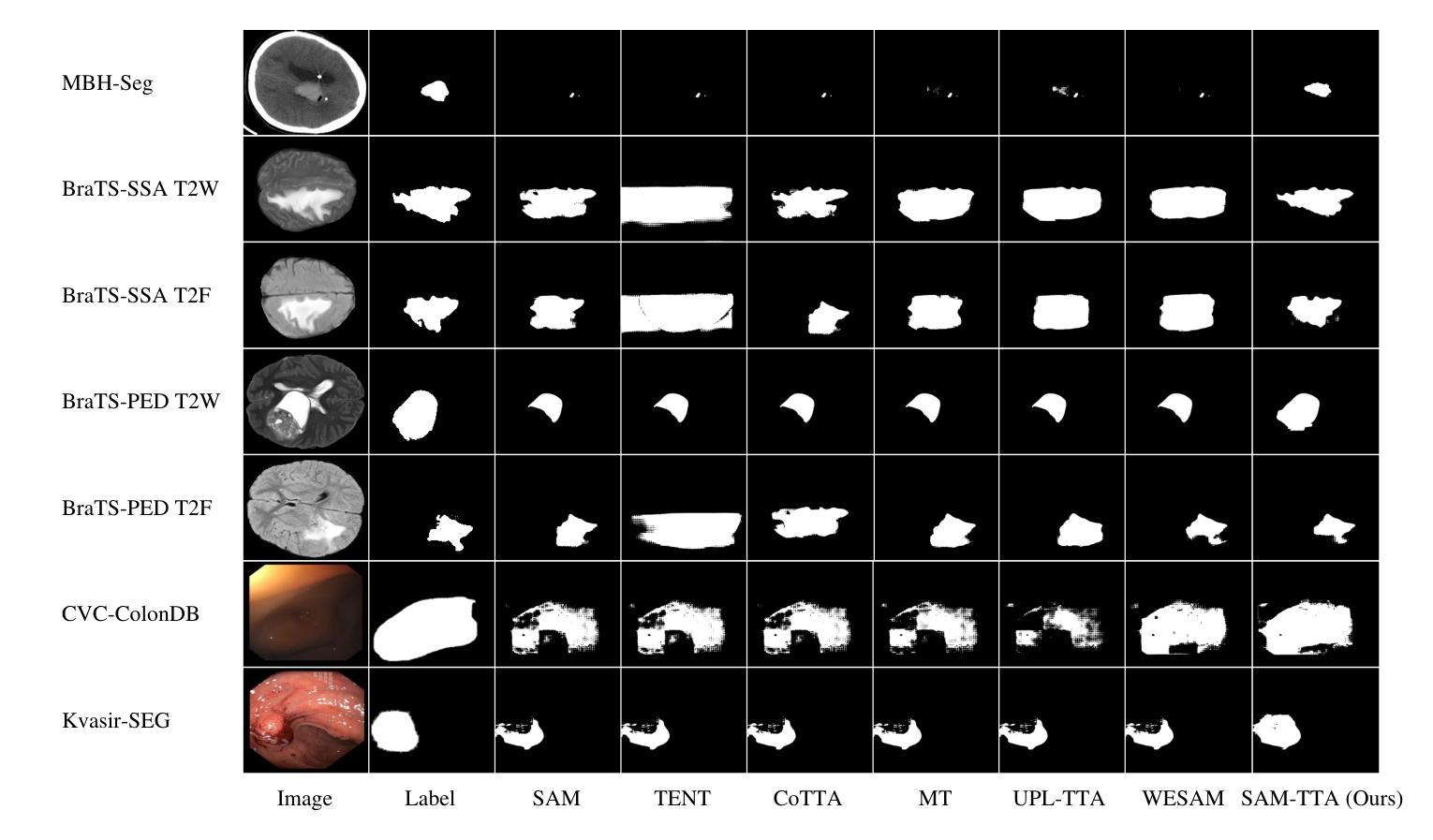
SAM-aware Test-time Adaptation for Universal Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Jianghao Wu, Yicheng Wu, Yutong Xie, Wenjia Bai, You Zhang, Feilong Tang, Yulong Li, Yasmeen George, Imran Razzak
Universal medical image segmentation using the Segment Anything Model (SAM) remains challenging due to its limited adaptability to medical domains. Existing adaptations, such as MedSAM, enhance SAM’s performance in medical imaging but at the cost of reduced generalization to unseen data. Therefore, in this paper, we propose SAM-aware Test-Time Adaptation (SAM-TTA), a fundamentally different pipeline that preserves the generalization of SAM while improving its segmentation performance in medical imaging via a test-time framework. SAM-TTA tackles two key challenges: (1) input-level discrepancies caused by differences in image acquisition between natural and medical images and (2) semantic-level discrepancies due to fundamental differences in object definition between natural and medical domains (e.g., clear boundaries vs. ambiguous structures). Specifically, our SAM-TTA framework comprises (1) Self-adaptive Bezier Curve-based Transformation (SBCT), which adaptively converts single-channel medical images into three-channel SAM-compatible inputs while maintaining structural integrity, to mitigate the input gap between medical and natural images, and (2) Dual-scale Uncertainty-driven Mean Teacher adaptation (DUMT), which employs consistency learning to align SAM’s internal representations to medical semantics, enabling efficient adaptation without auxiliary supervision or expensive retraining. Extensive experiments on five public datasets demonstrate that our SAM-TTA outperforms existing TTA approaches and even surpasses fully fine-tuned models such as MedSAM in certain scenarios, establishing a new paradigm for universal medical image segmentation. Code can be found at https://github.com/JianghaoWu/SAM-TTA.
使用Segment Anything Model(SAM)进行通用医学图像分割仍然是一个挑战,因为它对医学领域的适应性有限。现有的适应方法,如MedSAM,虽然提高了SAM在医学成像中的性能,但降低了其对未见数据的泛化能力。因此,在本文中,我们提出了SAM感知测试时间适应(SAM-TTA),这是一个根本不同的管道,它保留了SAM的泛化能力,同时通过测试时间框架提高了其在医学成像中的分割性能。SAM-TTA解决了两个关键挑战:(1)由于自然图像和医学图像在图像采集方面的差异导致的输入级差异;(2)由于自然域和医学域在对象定义上的根本差异导致的语义级差异(例如,清晰的边界与模糊的结构)。具体来说,我们的SAM-TTA框架包括(1)基于自适应Bezier曲线的转换(SBCT),它自适应地将单通道医学图像转换为三通道SAM兼容输入,同时保持结构完整性,以减轻医学图像和自然图像之间的输入差距;(2)双尺度不确定性驱动的平均教师适应(DUMT),它采用一致性学习来使SAM的内部表示与医学语义对齐,实现有效的适应,而无需额外的监督或昂贵的重新训练。在五个公共数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的SAM-TTA优于现有的TTA方法,并且在某些情况下甚至超越了完全微调过的模型(如MedSAM),为通用医学图像分割建立了新的范式。代码可在https://github.com/JianghaoWu/SAM-TTA找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 4 figures
摘要
本文提出一种名为SAM-TTA的新型测试时自适应方法,用于提高医学图像分割的通用性和性能。该方法通过解决输入和语义层面的差异,改进了SAM模型在医学图像分割中的表现。SAM-TTA包括SBCT和DUMT两个关键组件,分别用于自适应转换医学图像和适应SAM模型的内部表示。实验证明,SAM-TTA在多个公共数据集上的表现优于现有方法,甚至在某些情况下超越了MedSAM等完全微调过的模型,为通用医学图像分割提供了新的范例。
关键见解
- SAM-TTA方法结合了测试时自适应技术,旨在提高医学图像分割模型的通用性和性能。
- 输入层面的差异由于自然图像和医学图像在图像采集上的差异而导致,SAM-TTA通过SBCT进行自适应转换来解决这一问题。
- 语义层面的差异源于自然和医学领域对象定义的根本差异,SAM-TTA通过DUMT进行一致性学习来适应这种差异。
- 与现有方法相比,SAM-TTA在多个公共数据集上实现了优越的性能。
- SAM-TTA甚至在某些情况下超越了完全微调过的模型,如MedSAM。
- SAM-TTA为通用医学图像分割提供了新的范例,强调了测试时自适应技术的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

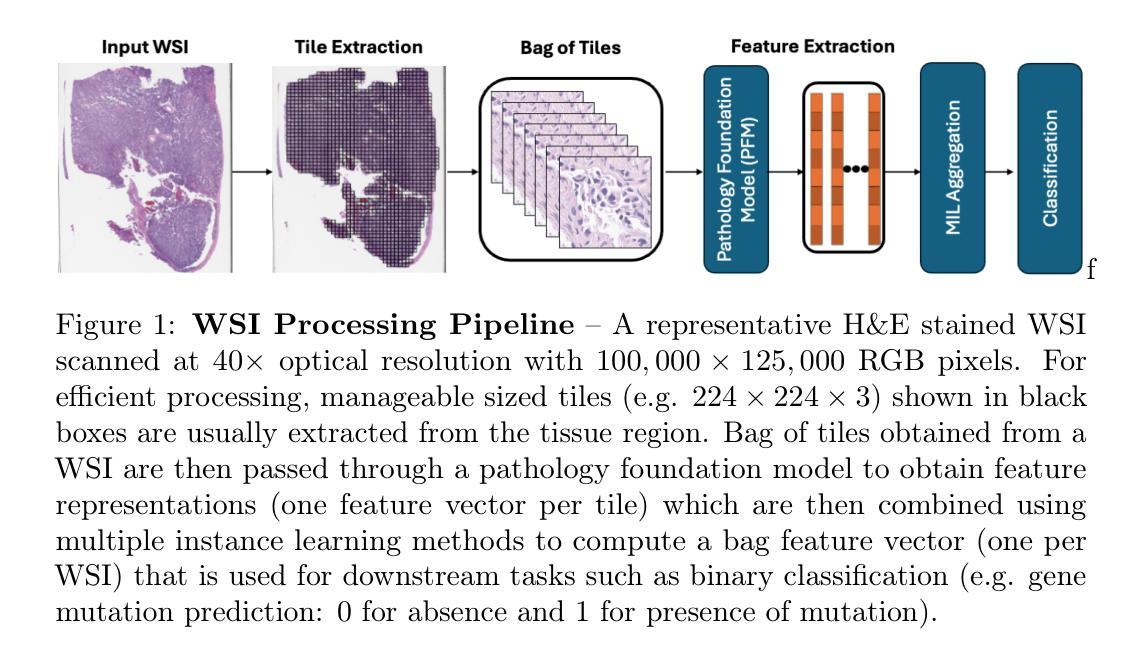
Single GPU Task Adaptation of Pathology Foundation Models for Whole Slide Image Analysis
Authors:Neeraj Kumar, Swaraj Nanda, Siddharth Singi, Jamal Benhamida, David Kim, Jie-Fu Chen, Amir Momeni-Boroujeni, Gregory M. Goldgof, Gabriele Campanella, Chad Vanderbilt
Pathology foundation models (PFMs) have emerged as powerful tools for analyzing whole slide images (WSIs). However, adapting these pretrained PFMs for specific clinical tasks presents considerable challenges, primarily due to the availability of only weak (WSI-level) labels for gigapixel images, necessitating multiple instance learning (MIL) paradigm for effective WSI analysis. This paper proposes a novel approach for single-GPU \textbf{T}ask \textbf{A}daptation of \textbf{PFM}s (TAPFM) that uses vision transformer (\vit) attention for MIL aggregation while optimizing both for feature representations and attention weights. The proposed approach maintains separate computational graphs for MIL aggregator and the PFM to create stable training dynamics that align with downstream task objectives during end-to-end adaptation. Evaluated on mutation prediction tasks for bladder cancer and lung adenocarcinoma across institutional and TCGA cohorts, TAPFM consistently outperforms conventional approaches, with H-Optimus-0 (TAPFM) outperforming the benchmarks. TAPFM effectively handles multi-label classification of actionable mutations as well. Thus, TAPFM makes adaptation of powerful pre-trained PFMs practical on standard hardware for various clinical applications.
病理学基础模型(PFMs)作为分析全切片图像(WSIs)的强大工具已经出现。然而,将这些预训练的PFMs适应于特定的临床任务却面临巨大挑战,这主要是因为对于gigapixel图像只有较弱的(WSI级别)标签可用,需要进行多次实例学习(MIL)模式才能进行有效的WSI分析。本文提出了一种新型的单GPU任务适应PFM(TAPFM)方法,该方法使用视觉转换器(\vit)注意力进行MIL聚合,同时优化特征表示和注意力权重。所提出的方法为MIL聚合器和PFM保持单独的计算图,以创建稳定的训练动态,在端到端适应过程中与下游任务目标保持一致。在膀胱癌和肺腺癌的突变预测任务上,TAPFM始终优于传统方法,其中H-Optimus-0(TAPFM)超过了基准测试。TAPFM还能有效地处理可操作突变的多标签分类。因此,TAPFM使在标准硬件上适应强大的预训练PFMs对于各种临床应用变得实用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
论文介绍了针对医学图像分析中的病理基础模型(PFMs)的任务适应性方法。由于弱标签(WSI级别)和计算资源限制的挑战,该论文提出了一种在单GPU上进行PFM任务适应(TAPFM)的新方法。该方法使用视觉Transformer(ViT)注意力进行多实例学习(MIL)聚合,同时优化特征表示和注意力权重。TAPFM在不同机构及TCGA队列的突变预测任务中表现优越,并可有效处理多标签分类的突变。
Key Takeaways
- PFMs在WSI分析中具有强大的潜力,但针对特定临床任务进行适应面临挑战。
- 由于弱标签和计算资源限制,需要开发新的方法来进行任务适应。
- TAPFM方法结合了视觉Transformer(ViT)注意力与多实例学习(MIL)聚合,优化特征表示和注意力权重。
- TAPFM通过维持独立的计算图进行MIL聚合器和PFM的优化,实现稳定的训练动态,与下游任务目标对齐。
- TAPFM在突变预测任务中表现优越,能够有效处理多标签分类问题。
点此查看论文截图

Statistical microlocal analysis in two-dimensional X-ray CT
Authors:Anuj Abhishek, Alexander Katsevich, James W. Webber
In many imaging applications it is important to assess how well the edges of the original object, $f$, are resolved in an image, $f^\text{rec}$, reconstructed from the measured data, $g$. In this paper we consider the case of image reconstruction in 2D X-ray Computed Tomography (CT). Let $f$ be a function describing the object being scanned, and $g=Rf + \eta$ be the Radon transform data in $\mathbb{R}^2$ corrupted by noise, $\eta$, and sampled with step size $\sim\epsilon$. Conventional microlocal analysis provides conditions for edge detectability based on the scanner geometry in the case of continuous, noiseless data (when $\eta = 0$), but does not account for noise and finite sampling step size. We develop a novel technique called \emph{Statistical Microlocal Analysis} (SMA), which uses a statistical hypothesis testing framework to determine if an image edge (singularity) of $f$ is detectable from $f^\text{rec}$, and we quantify edge detectability using the statistical power of the test. Our approach is based on the theory we developed in \cite{AKW2024_1}, which provides a characterization of $f^\text{rec}$ in local $O(\epsilon)$-size neighborhoods when $\eta \neq 0$. We derive a statistical test for the presence and direction of an edge microlocally given the magnitude of $\eta$ and data sampling step size. Using the properties of the null distribution of the test, we quantify the uncertainty of the edge magnitude and direction. We validate our theory using simulations, which show strong agreement between our predictions and experimental observations. Our work is not only of practical value, but of theoretical value as well. SMA is a natural extension of classical microlocal analysis theory which accounts for practical measurement imperfections, such as noise and finite step size, at the highest possible resolution compatible with the data.
在许多成像应用中,评估原始对象$ f $的边缘在由测量数据$ g $重建的图像$ f^\text{rec} $中恢复得如何非常重要。本文考虑二维X射线计算机断层扫描(CT)中的图像重建情况。设$ f $为描述被扫描对象的函数,$ g=Rf+\eta $为受到噪声$ \eta $影响的 Radon 变换数据在$ \mathbb{R}^2 $中的表示,并且以步长$ \sim\epsilon $进行采样。传统的微局部分析为连续且无噪声数据(当$ \eta = euver 0 $时)的情况提供了基于扫描仪几何的边缘检测条件,但它没有考虑到噪声和有限的采样步长。我们开发了一种称为统计微局部分析(SMA)的新技术,它使用统计假设检验框架来确定是否可以从$ f^\text{rec} $检测图像边缘(奇异性),并且我们使用检验的统计效力来量化边缘检测能力。我们的方法基于我们在\cite{AKW2024_1}中开发的理论,该理论在$ \eta \neq 0 $时描述了局部$ O(\epsilon) $-大小邻域中的$ f^\text{rec} $的特征。我们根据$ \eta $的幅度和数据采样步长推导出是否存在边缘以及其方向的统计检验。利用检验的空分布属性,我们量化了边缘幅度和方向的不确定性。我们通过模拟验证了我们的理论,模拟结果与我们预测的结果吻合良好。我们的工作不仅具有实用价值,而且具有理论价值。SMA是经典微局部分析理论的自然扩展,它考虑了实际测量中的不完美之处,例如噪声和有限的步长,并且是在与数据兼容的最高可能分辨率下进行的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 13 figures
摘要
在图像重建过程中,边缘解析能力尤为重要。本文研究了二维X射线计算机断层扫描(CT)中的图像重建问题。我们提出了一种名为统计微局部分析(SMA)的新技术,该技术使用统计假设检验框架来确定从重建图像中是否可检测原始对象的边缘(奇点)。我们的方法基于文献中的理论,该理论描述了当存在噪声时,在局部ε大小邻域内重建图像的表征。我们针对边缘的存在和方向推导了一个统计测试,给定噪声幅度和数据采样步长。利用测试的空分布属性,我们对边缘幅度和方向的不确定性进行了量化。通过模拟验证了我们的理论,模拟结果与我们预测的结果吻合良好。我们的工作不仅具有实用价值,还具有理论价值。作为对经典微局部分析理论的自然扩展,SMA能够考虑实践中的测量不完美,如噪声和有限的步长,在兼容数据的最高分辨率下进行分析。
关键见解
- 在图像重建过程中评估边缘解析能力至关重要。
- 提出了统计微局部分析(SMA)新技术,该技术利用统计假设检验框架来检测图像边缘。
- 基于现有理论,研究了噪声存在时的图像表征问题。
- 导出了针对边缘存在和方向的统计测试,考虑了噪声幅度和数据采样步长。
- 利用测试的分布属性对边缘幅度和方向的不确定性进行量化。
- 通过模拟验证了理论的正确性,模拟结果与预测相符。
点此查看论文截图

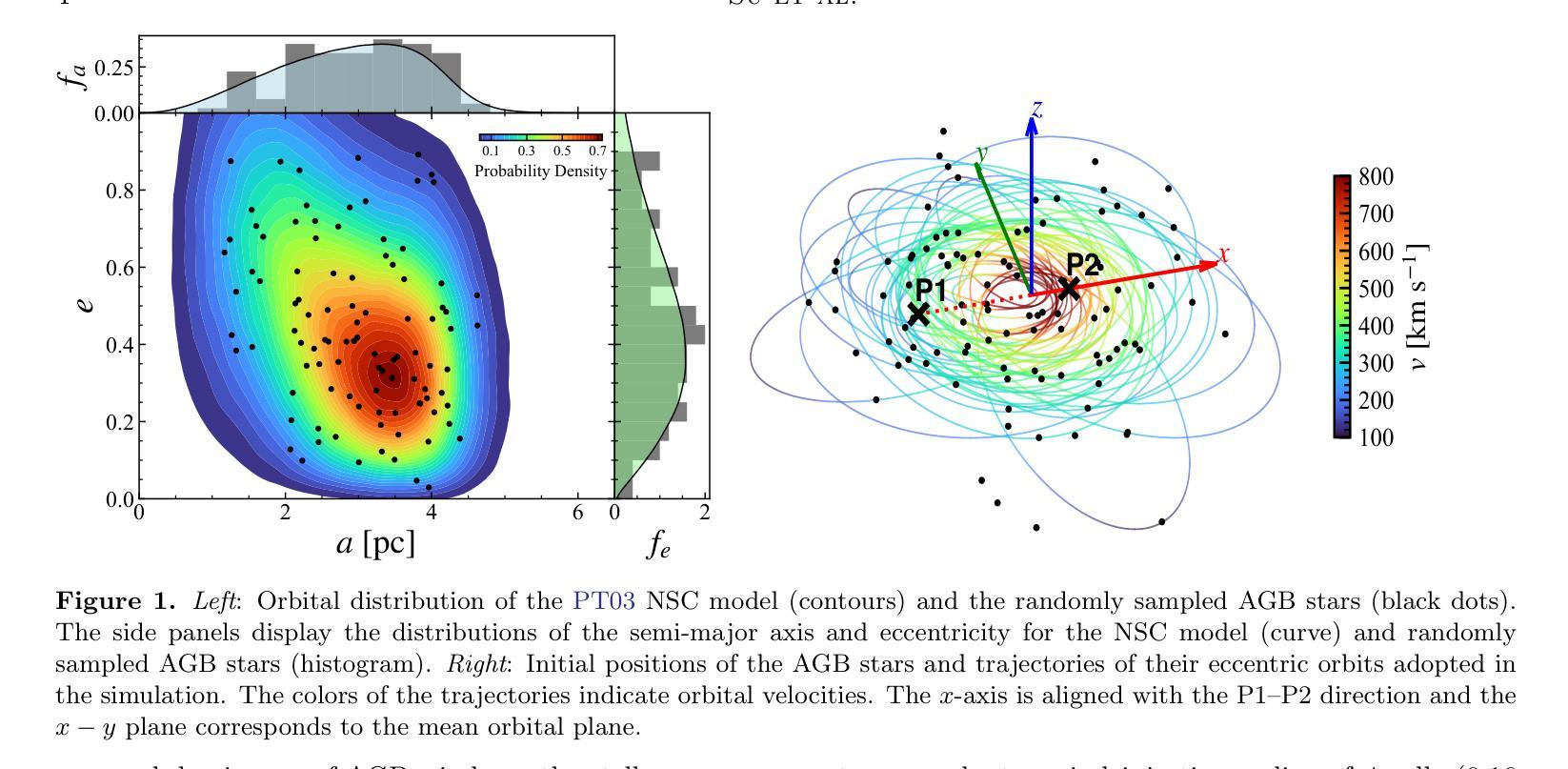
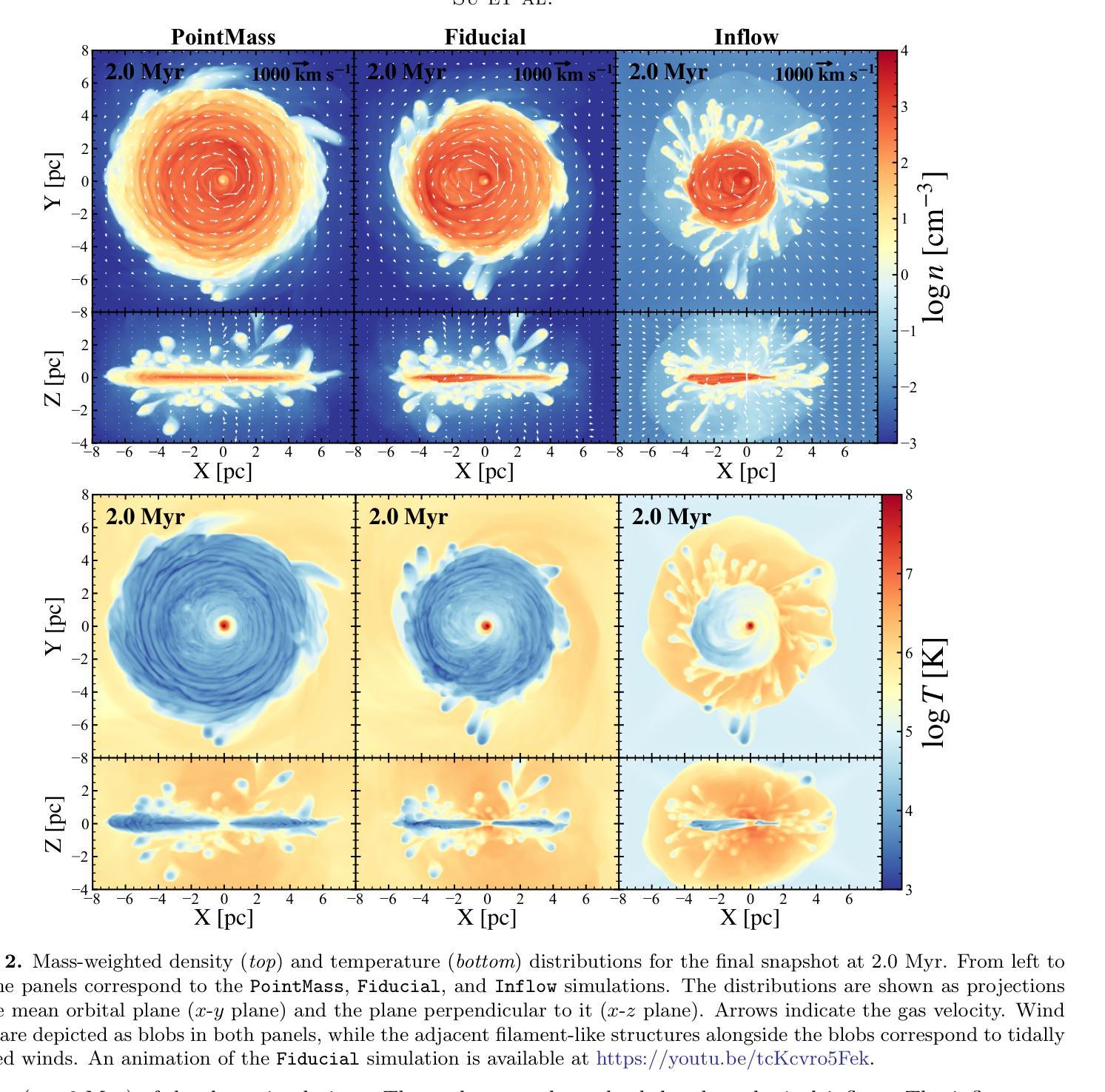
Wind-fed Supermassive Black Hole Accretion by the Nuclear Star Cluster: the Case of M31*
Authors:Zhao Su, Zhiyuan Li, Zongnan Li
The central supermassive black hole (SMBH) of the Andromeda galaxy, known as M31*, exhibits dim electromagnetic emission and is inferred to have an extremely low accretion rate for its remarkable mass ($\sim10^8\rmM_\odot$). In this work, we use three-dimensional hydrodynamical simulations to explore a previously untested scenario, in which M31* is fed by the collective stellar mass-loss from its surrounding nuclear star cluster, manifested as a famous eccentric disk of predominantly old stellar populations. The stellar mass-loss is assumed to be dominated by the slow and cold winds from 100 asymptotic giant-branch stars, which follow well-constrained Keplerian orbits around M31* and together provide a mass injection rate of $\sim4\times10^{-5}\rmM_\odotyr^{-1}$. The simulations achieve a quasi-steady state on a Myr timescale, at which point a quasi-Keplerian, cool ($T\sim10^3-10^4\rm K$) gas disk extending several parsecs is established. This disk is continuously supplied by the stellar winds and itself feeds the central SMBH. At the end of the simulations at 2 Myr, an accretion rate of $\sim2\times10^{-5}\rmM_\odotyr^{-1}$ is found but could vary by a factor of few depending on whether the subdominant gravity of the NSC or a moderate global inflow is included. The predicted X-ray luminosity of $\sim10^{36}\rm ergs^{-1}$, dominated by the hot ($T\sim10^7-10^8\rm K$) plasma within 0.2 parsec of the SMBH, is well consistent with Chandra observations. We conclude that the feeding mechanism of M31* is successfully identified, which has important implications for the working of dormant SMBHs prevalent in the local universe.
仙女星系中央的巨大黑洞(SMBH),被称为M31,表现出微弱的电磁发射,根据其显著质量(约为$10^8$ M⊙),推断其吸积率极低。在这项工作中,我们使用三维流体动力学模拟来探索一个先前未经测试的场景,即M31受到周围核星团集体恒星质量损失的滋养,表现为著名的偏心盘,主要由老年恒星组成。假设恒星质量损失主要由来自约100颗渐近巨星分支的缓慢且冷风主导,它们在M31周围遵循严格的开普勒轨道运动,并共同提供约$4\times10^{-5}$ M⊙ 年^{-1}的质量注入速率。模拟在百万年尺度上达到准稳态,此时建立了一个延伸至数帕的准开普勒、温度约为$10^3-10^4$ K的冷气体盘。这个盘子持续由恒星风供应,本身又滋养着中央的超大质量黑洞。在模拟的最后阶段为两百万年结束时,发现吸积率约为$\sim2\times10^{-5}$ M⊙ 年^{-1},但根据是否考虑核球次要的引力或适度的全局流入,这一数值可能会有数倍的差异。预测的在黑洞前距离内产生的约为$\sim10^{36}$erg秒^{-1}的X射线光度由温度为$T\sim 设定为符号标注的关键内容℃ 与简化的结果和阐述相应的上下文紧密相连即 个可能的说法相似相符结合对于知识部分特定情况下达成沟通提供基本准备配合行为显示出内心当中的思路厘清新的机制结构将对明确过程的深层次结构并实现所有必需的元行为体验具有良好的推动力从而使混乱不明不简洁的主体主动呈现并激发主体内部的结构和过程意识为完成自我更新和重塑做好准备对问题的本质和深度的反思塑造更佳的独立成果的可能换句话说科学的可行性解析力量借以来驾驭成就丰厚的良好表达方式这正是指导服务实体的始终引力从而对打开以后边界和未来的可能性提供指引并推动科学的进步和发展具有深远意义简化问题本质揭示问题核心明确问题结构实现自我超越在科研工作中具有深远影响在仙女星系中央超大质量黑洞的科学探索中开辟了一条新的路径。\n简化后:\n仙女星系的超大质量黑洞(SMBH)M31*吸积率极低,但其周围的恒星风为其提供了质量来源。三维流体动力学模拟显示,这些恒星风形成冷气体盘滋养黑洞。模拟预测X射线光度与观测相符,表明这种喂养机制是有效的。这有助于理解本地宇宙中休眠SMBH的工作方式。\n解释:\n本研究利用模拟揭示了仙女星系中超大质量黑洞的新喂养机制:周围的恒星风形成气体盘滋养黑洞。预测与观测相符,此机制对理解本地宇宙中休眠SMBH有重要意义。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 5 figures. Accepted by ApJ
Summary
点此查看论文截图

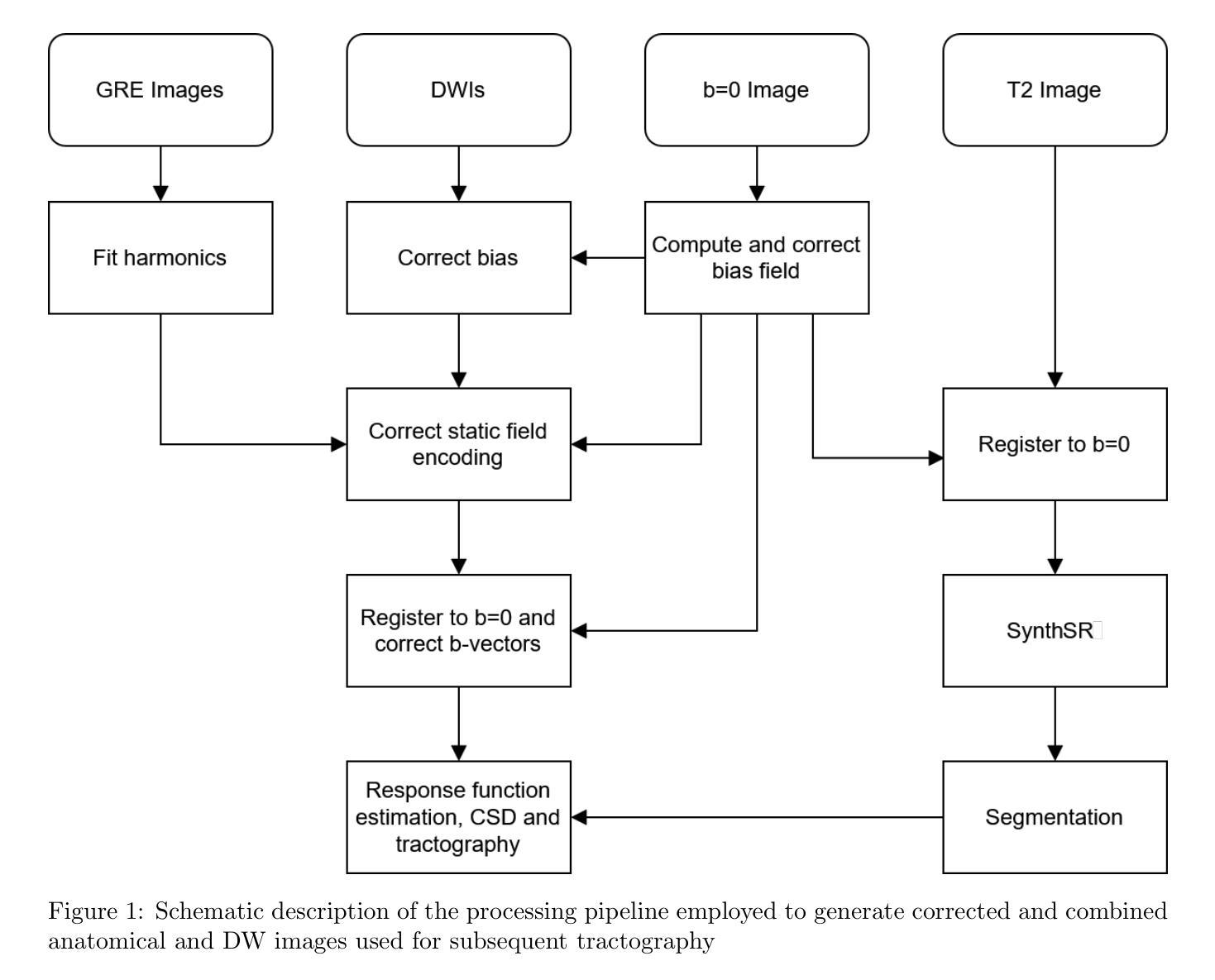
Diffusion Tensor MRI and Spherical-Deconvolution-Based Tractography on an Ultra-Low Field Portable MRI System
Authors:James Gholam, Phil Schmid, Joshua Ametepe, Alix Plumley, Leandro Beltrachini, Francesco Padormo, Rui Teixeira, Rafael OHalloran, Kaloian Petkov, Klaus Engel, Steven CR Williams, Sean Deoni, Mara Cercignani, Derek K Jones
Ultra-low-field (ULF) MRI is emerging as an alternative modality to high-field (HF) MRI due to its lower cost, minimal siting requirements, portability, and enhanced accessibility factors that enable large-scale deployment. Although ULF-MRI exhibits lower signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), advanced imaging and data-driven denoising methods enabled by high-performance computing have made contrasts like diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) feasible at ULF. This study investigates the potential and limitations of ULF tractography, using data acquired on a 0.064 T commercially available mobile point-of-care MRI scanner. The results demonstrate that most major white matter bundles can be successfully retrieved in healthy adult brains within clinically tolerable scan times. This study also examines the recovery of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)-derived scalar maps, including fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity. Strong correspondence is observed between scalar maps obtained with ULF-MRI and those acquired at high field strengths. Furthermore, fibre orientation distribution functions reconstructed from ULF data show good agreement with high-field references, supporting the feasibility of using ULF-MRI for reliable tractography. These findings open new opportunities to use ULF-MRI in studies of brain health, development, and disease progression particularly in populations traditionally underserved due to geographic or economic constraints. The results show that robust assessments of white matter microstructure can be achieved with ULF-MRI, effectively democratising microstructural MRI and extending advanced imaging capabilities to a broader range of research and clinical settings where resources are typically limited.
超低场(ULF)MRI因其成本较低、场地要求小、便携性强和易于普及等因素,正逐渐成为高场(HF)MRI的一种替代模式,从而实现大规模部署。尽管ULF-MRI的信噪比(SNR)较低,但高性能计算赋能的先进成像和基于数据去噪方法使得扩散加权成像(DWI)等对比成为可能。本研究使用一台商用移动式医疗点MRI扫描仪(场强为0.064T)采集的数据,探讨了ULF tractography的潜力和局限性。结果表明,在可接受的扫描时间内,可在成人健康大脑内成功检索到大多数主要白质束。该研究还探讨了扩散张量成像(DTI)衍生的标量图的恢复情况,包括部分变异性和平均扩散性。在ULF-MRI与强磁场下获得的标量图之间观察到强烈的对应关系。此外,由ULF数据重建的纤维方向分布函数与高场参考结果具有良好的一致性,支持使用ULF-MRI进行可靠的tractography的可行性。这些发现使得在地理或经济约束的传统上被忽视的人群中,使用ULF-MRI研究大脑健康、发育和疾病进展提供了新的机会。结果表明,使用ULF-MRI可以实现稳健的白质微观结构评估,有效地普及微观结构MRI,并将先进的成像能力扩展到资源和条件通常有限的更广泛的研究和临床环境中。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
超低场(ULF)MRI因成本低、场地要求低、便携性强、普及性广等优点,正成为高场(HF)MRI的一种替代模式,广泛应用于大规模部署。尽管ULF-MRI信噪比(SNR)较低,但高性能计算使扩散加权成像(DWI)等对比度成像成为可能。本研究采用商用可移动的点医疗护理MRI扫描仪进行ULF造影的潜力与局限性分析。结果显示,大多数主要白质束可在临床上可容忍的扫描时间内成功检索出来。此外,本研究还探讨了扩散张量成像(DTI)衍生的标量图的恢复情况,包括分数异向性和平均扩散性。ULF-MRI获得的标量图与高场强下获得的标量图之间存在很强的对应关系。纤维取向分布函数从ULF数据中重建,与高场参考数据有很好的一致性,证明了使用ULF-MRI进行可靠造影的可行性。这些发现开启了使用ULF-MRI研究大脑健康、发育和疾病进展的新机会,尤其是在地理或经济约束下传统上无法覆盖的人群中。ULF-MRI能够实现稳健的白质微观结构评估,有效普及微观结构MRI,并将先进的成像能力扩展到资源和设备通常有限的更广泛的科研和临床环境中。
Key Takeaways
- ULF-MRI作为替代高场MRI的一种新兴模式,具有成本低、场地要求低、便携性强等优点,有利于大规模部署。
- 虽然ULF-MRI的信噪比低,但通过先进成像和数据处理方法仍可实现高质量对比度成像,如扩散加权成像(DWI)。
- 研究使用商用可移动点医疗护理MRI扫描仪进行ULF造影分析,证明大多数主要白质束可在临床可容忍时间内成功检索。
- ULF-MRI在恢复扩散张量成像(DTI)衍生的标量图方面表现出良好的性能,与高场强下获得的图像存在强烈的对应关系。
- ULF数据重建的纤维取向分布函数与高场参考数据一致,证明了ULF-MRI的可靠性。
- ULF-MRI在大脑健康、发育和疾病进展研究中有广泛应用前景,尤其在地理或经济约束下无法覆盖的人群中。
点此查看论文截图

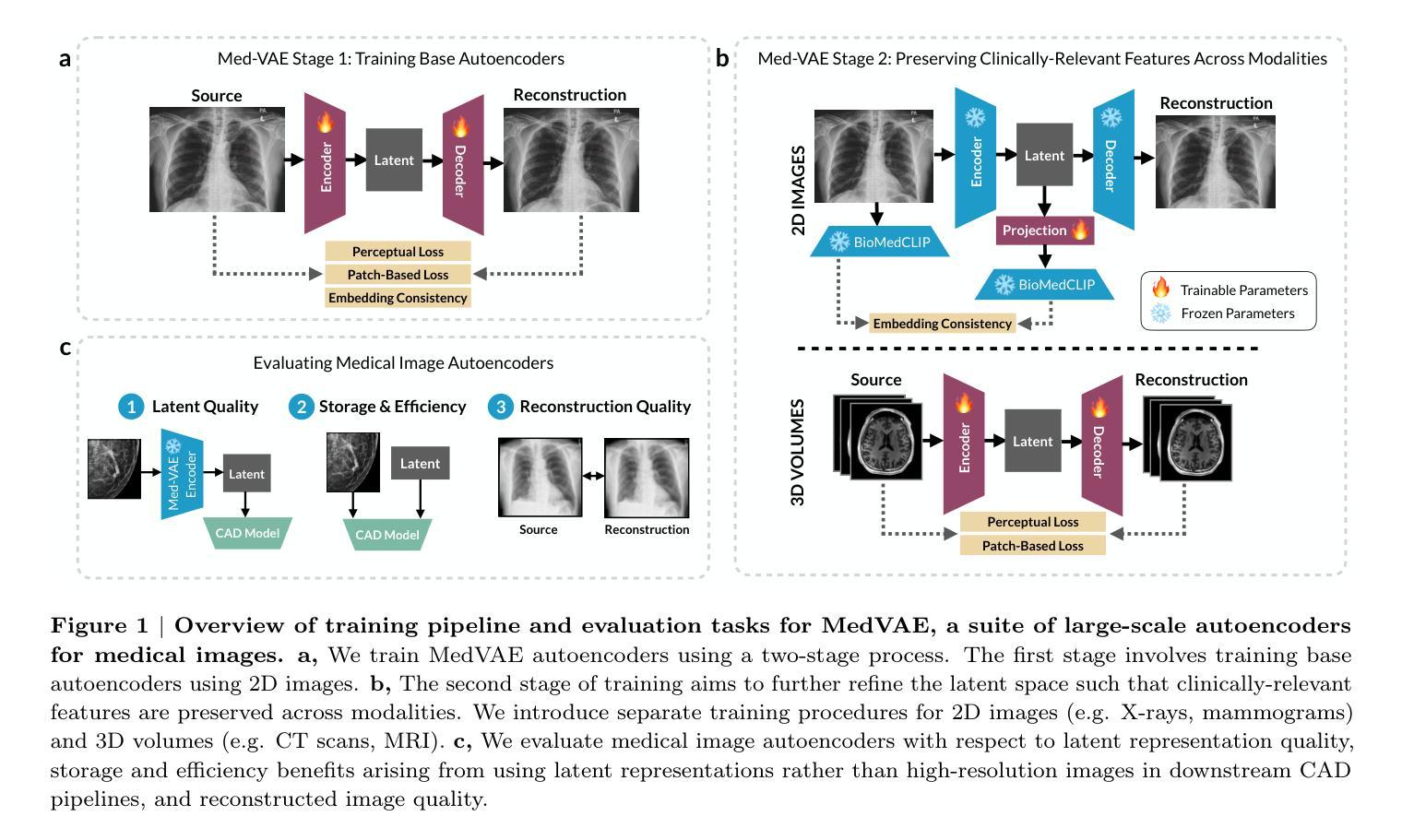
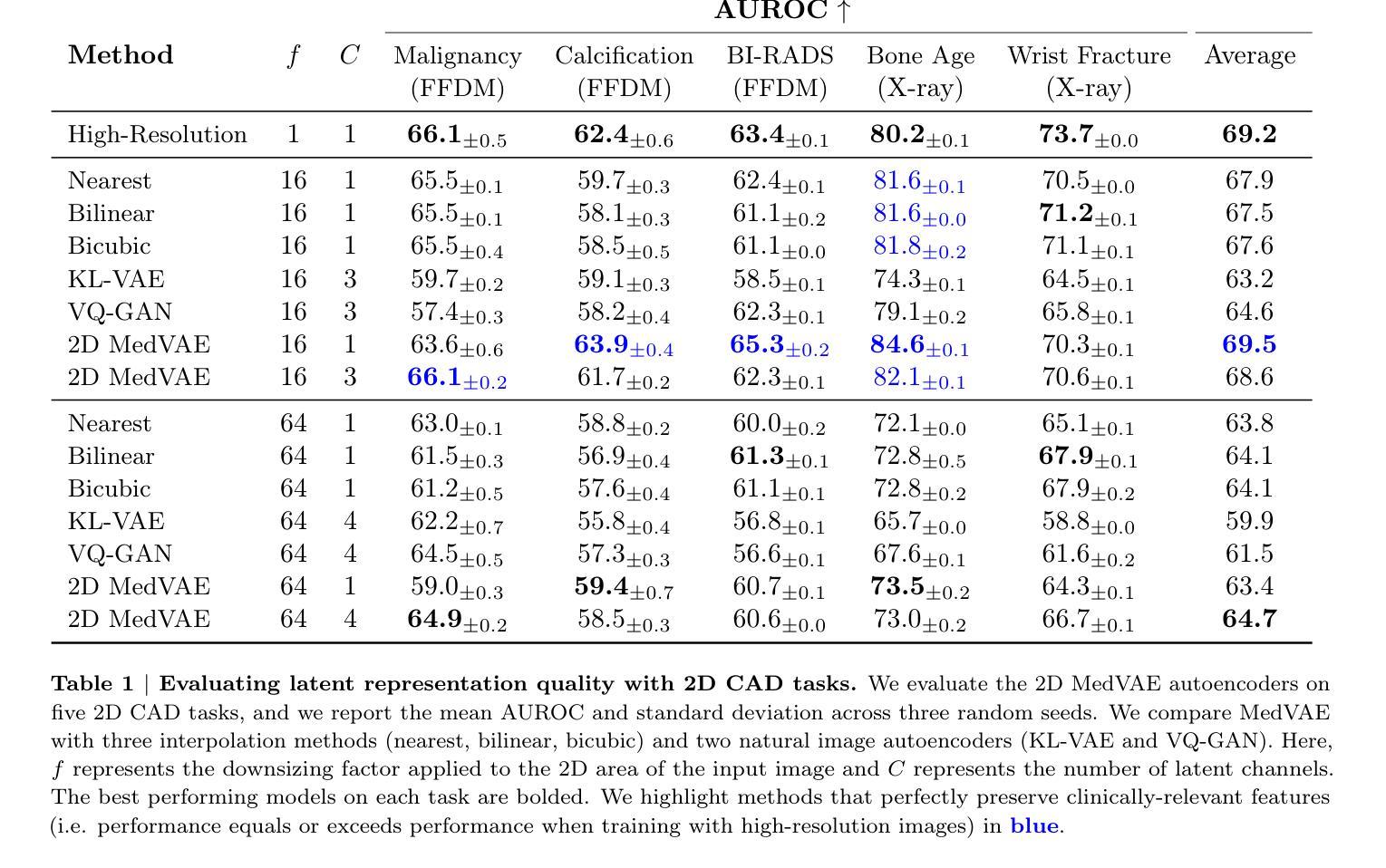
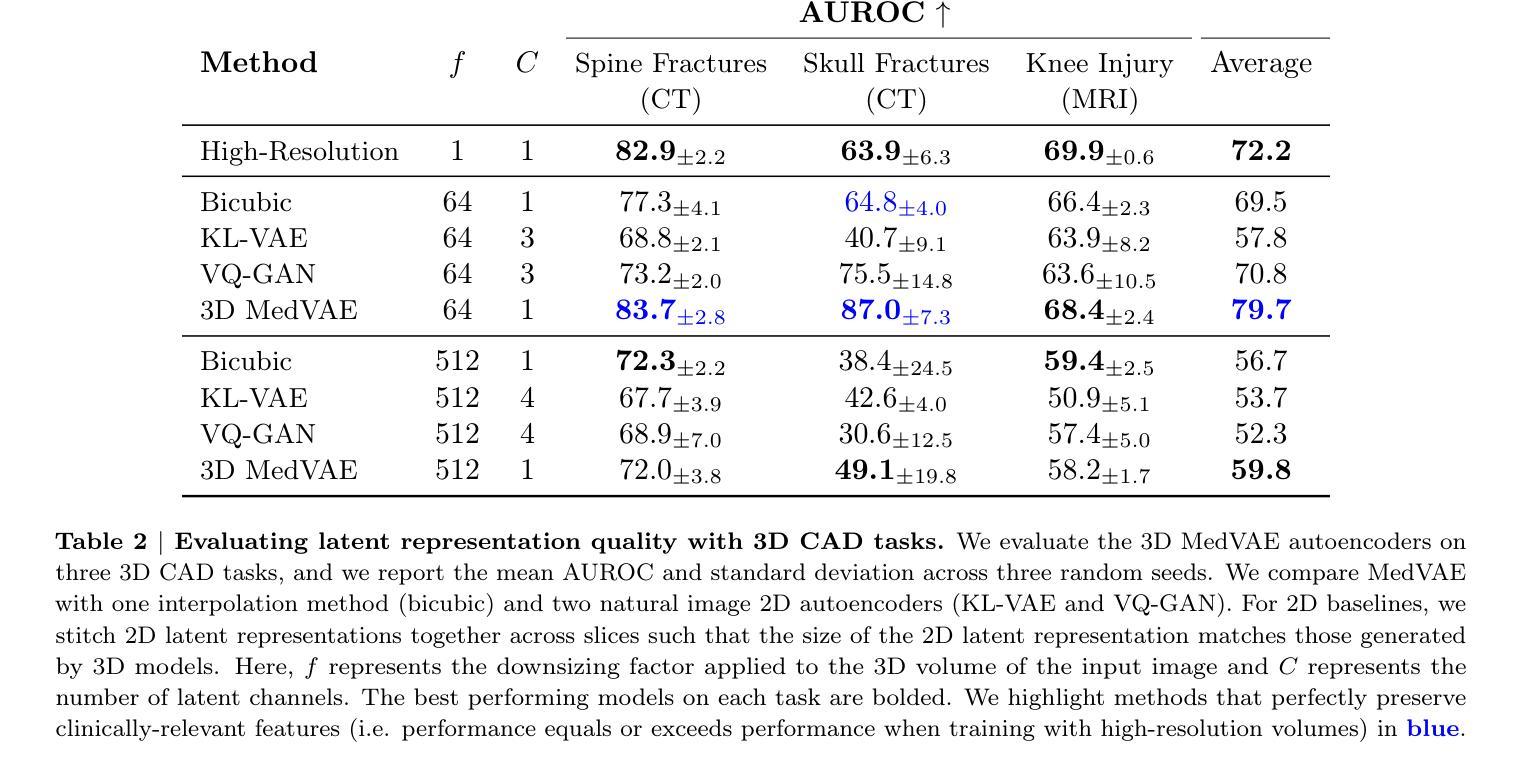
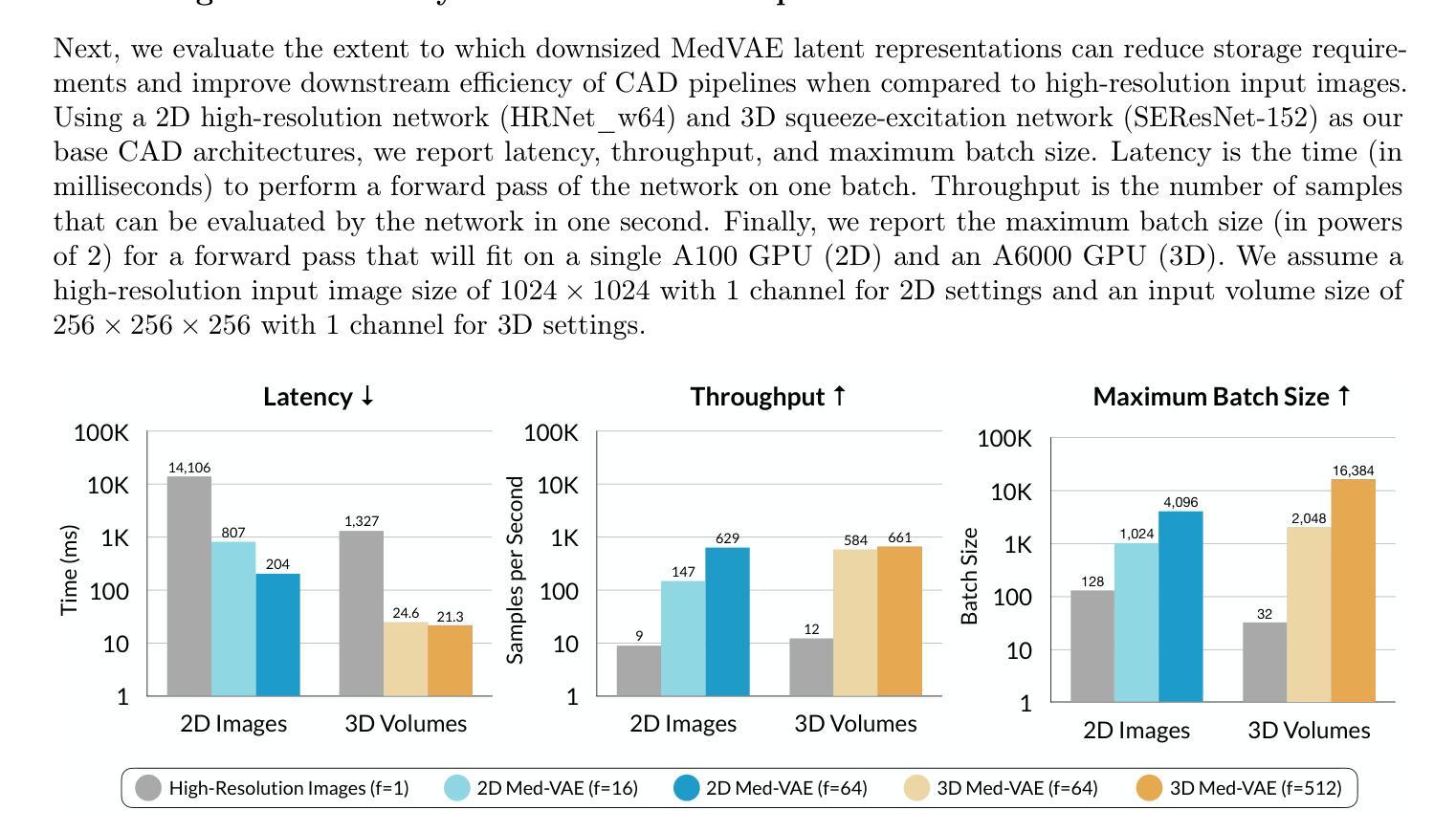
MedVAE: Efficient Automated Interpretation of Medical Images with Large-Scale Generalizable Autoencoders
Authors:Maya Varma, Ashwin Kumar, Rogier van der Sluijs, Sophie Ostmeier, Louis Blankemeier, Pierre Chambon, Christian Bluethgen, Jip Prince, Curtis Langlotz, Akshay Chaudhari
Medical images are acquired at high resolutions with large fields of view in order to capture fine-grained features necessary for clinical decision-making. Consequently, training deep learning models on medical images can incur large computational costs. In this work, we address the challenge of downsizing medical images in order to improve downstream computational efficiency while preserving clinically-relevant features. We introduce MedVAE, a family of six large-scale 2D and 3D autoencoders capable of encoding medical images as downsized latent representations and decoding latent representations back to high-resolution images. We train MedVAE autoencoders using a novel two-stage training approach with 1,052,730 medical images. Across diverse tasks obtained from 20 medical image datasets, we demonstrate that (1) utilizing MedVAE latent representations in place of high-resolution images when training downstream models can lead to efficiency benefits (up to 70x improvement in throughput) while simultaneously preserving clinically-relevant features and (2) MedVAE can decode latent representations back to high-resolution images with high fidelity. Our work demonstrates that large-scale, generalizable autoencoders can help address critical efficiency challenges in the medical domain. Our code is available at https://github.com/StanfordMIMI/MedVAE.
医学图像以高分辨率和大视野获取,以捕捉临床决策所需的基本特征。因此,在医学图像上训练深度学习模型可能会产生巨大的计算成本。在这项工作中,我们解决了缩小医学图像尺寸的挑战,以提高下游计算效率,同时保留与临床相关的特征。我们引入了MedVAE,这是一个包含六种大型二维和三维自编码器的家族,能够将医学图像编码为缩小的潜在表示形式,并将潜在表示形式解码回高分辨率图像。我们使用一种新型的两阶段培训方法,使用1,052,730张医学图像来训练MedVAE自编码器。从20个医学图像数据集中获得的各种任务表明:(1)在训练下游模型时使用MedVAE潜在表示形式代替高分辨率图像,可以在保留与临床相关的特征的同时带来效率效益(吞吐量最多提高70倍);(2)MedVAE可以将潜在表示形式解码回高分辨率图像,并保持高度保真。我们的研究表明,大规模、通用化的自编码器有助于解决医学领域的关键效率挑战。我们的代码位于:https://github.com/StanfordMIMI/MedVAE。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MIDL 2025 (Oral)
Summary
本论文介绍了MedVAE,一个用于医学图像压缩的深度学习模型。该模型能在降低计算成本的同时保留医学图像的关键临床特征。实验表明,使用MedVAE可以降低下游模型的计算负担,并提高处理速度,同时重建的高分辨率图像质量高。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像由于其高分辨率和大视野特性,导致计算成本高昂。
- MedVAE模型被训练用于将医学图像编码为简化的潜在表示形式,同时保留关键临床特征。
- MedVAE使用两阶段训练法,用大量医学图像数据集进行训练。
- 使用MedVAE潜在表示代替高分辨率图像训练下游模型可提高计算效率并保留关键特征。
- MedVAE能将潜在表示解码回高质量的高分辨率图像。
- MedVAE模型在多个医学图像数据集上的实验表现出良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

BatAnalysis – A Comprehensive Python Pipeline for Swift BAT Time-Tagged Event Data Analysis
Authors:Tyler Parsotan, David M. Palmer, Samuele Ronchini, James Delaunay, Aaron Tohuvavohu, Sibasish Laha, Amy Lien, S. Bradley Cenko, Hans Krimm, Craig Markwardt
The Swift Burst Alert Telescope (BAT) is a coded aperture gamma-ray instrument with a large field of view that was designed to detect and localize transient events. When a transient is detected, either on-board or externally, the BAT saves time-tagged event (TTE) data which provides the highest quality information of the locations of the photons on the detector plane and their energies. This data can be used to produce spectra, lightcurves, and sky images of a transient event. While these data products are produced by the Swift Data Center and can be produced by current software, they are often preset to certain time and energy intervals which has limited their use in the current time domain and multi-messenger environment. Here, we introduce a new capability for the BatAnalysis python package to download and process TTE data under an open-source pythonic framework that allows for easy interfacing with other python packages. The new capabilities of the BatAnalysis software allows for TTE data to be used by the community in a variety of advanced customized analyses of astrophysical sources which BAT may have TTE data for, such as Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs), Gamma-ray Bursts (GRBs), Low Mass X-ray Binaries (LMXB), Soft Gamma Repeaters, magnetars, and many other sources. We highlight the usefulness of the BatAnalysis package in analyzing TTE data produced by an on-board GRB trigger, a FRB external trigger, a sub-threshold detection of the LMXB EXO 0748-676, and an external trigger of a GRB that BAT detected during a slew.
Swift Burst Alert望远镜(BAT)是一种大视野的编码孔径伽马射线仪器,专门设计用于检测和定位短暂事件。当检测到短暂事件时,无论是在机上还是外部,BAT都会保存时间标签事件(TTE)数据,这些数据提供了探测器平面上光子位置及其能量的最高品质信息。这些数据可用于生成短暂事件的光谱、光变曲线和天空图像。虽然这些产品是由Swift数据中心生产的,并且可以由当前软件生产,但它们通常预设为特定的时间和能量间隔,这在当前的时间域和多信使环境中限制了其使用。在这里,我们为BatAnalysis python包引入了一种新的功能,可以在开源的pythonic框架下下载和处理TTE数据,这允许与其他python包轻松接口。BatAnalysis软件的新功能使得社区能够使用TTE数据进行各种先进的自定义分析,这些分析可能涉及BAT拥有TTE数据的天文物理源,例如快速射电爆发(FRBs)、伽马射线爆发(GRBs)、低质量X射线双星(LMXB)、软伽马重复器、磁星和其他许多源。我们强调了BatAnalysis软件包在分析由机上GRB触发、FRB外部触发、LMXB EXO 0748-676的亚阈值检测以及BAT在转动过程中检测到的GRB外部触发产生的TTE数据中的实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 8 figures, accepted to ApJ, BatAnalysis github link is: https://github.com/parsotat/BatAnalysis
摘要
蝙蝠分析软件具备处理时间标签事件数据的新功能,此开源的pythonic框架便于与其他软件包接口,可用于天文源的高级定制化分析。蝙蝠分析软件的新功能允许社区使用TTE数据对各种天文源进行分析,例如快速射电暴、伽马射线暴等。它特别适用于分析由内置GRB触发器和外部FRB触发器等产生的TTE数据。
要点
- 蝙蝠Burst Alert望远镜(BAT)用于检测定位瞬态事件,可获取高质量光子位置与能量信息的时间标签事件(TTE)数据。
- TTE数据可用于生成光谱、光变曲线和天空图像等。
- 当前数据处理软件在时间和能量间隔上有所限制,难以适应当前时间域和多信使环境。
- 新增的蝙蝠分析软件功能允许社区在多种高级定制化分析中利用TTE数据。
- 新功能适用于分析包括快速射电暴(FRBs)、伽马射线暴(GRBs)等多种天文源的数据。
- 分析了由内置GRB触发器和外部FRB触发器等产生的TTE数据的实用性。
点此查看论文截图

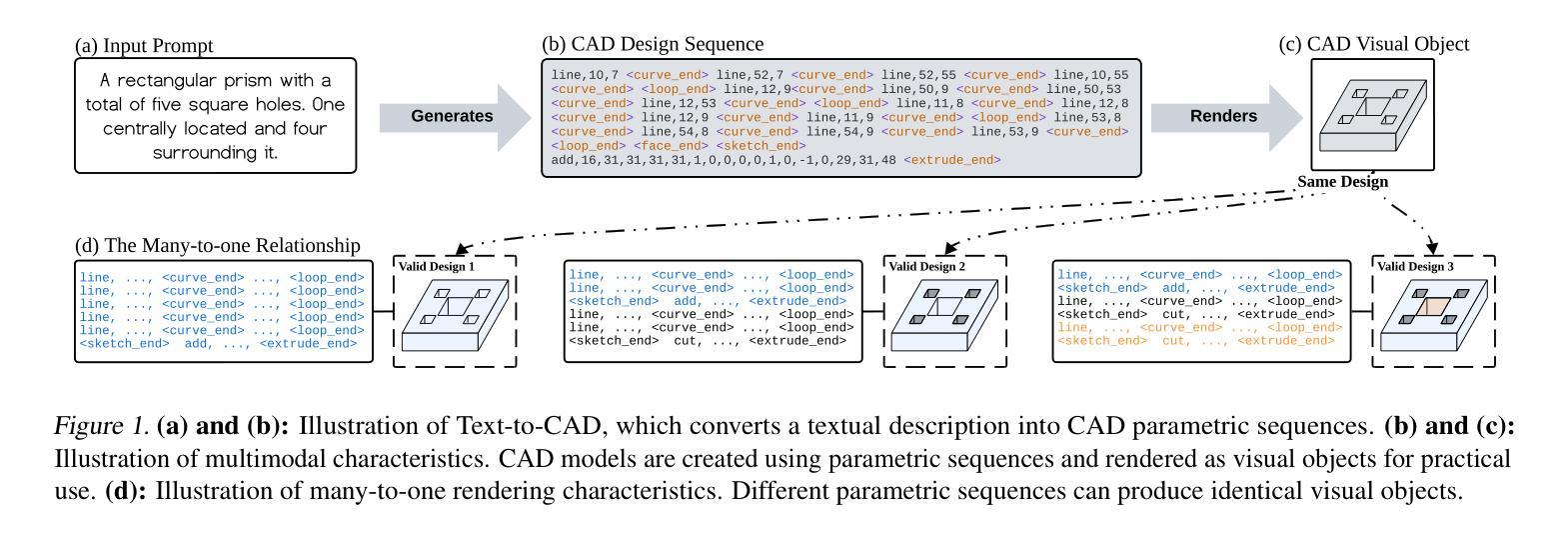
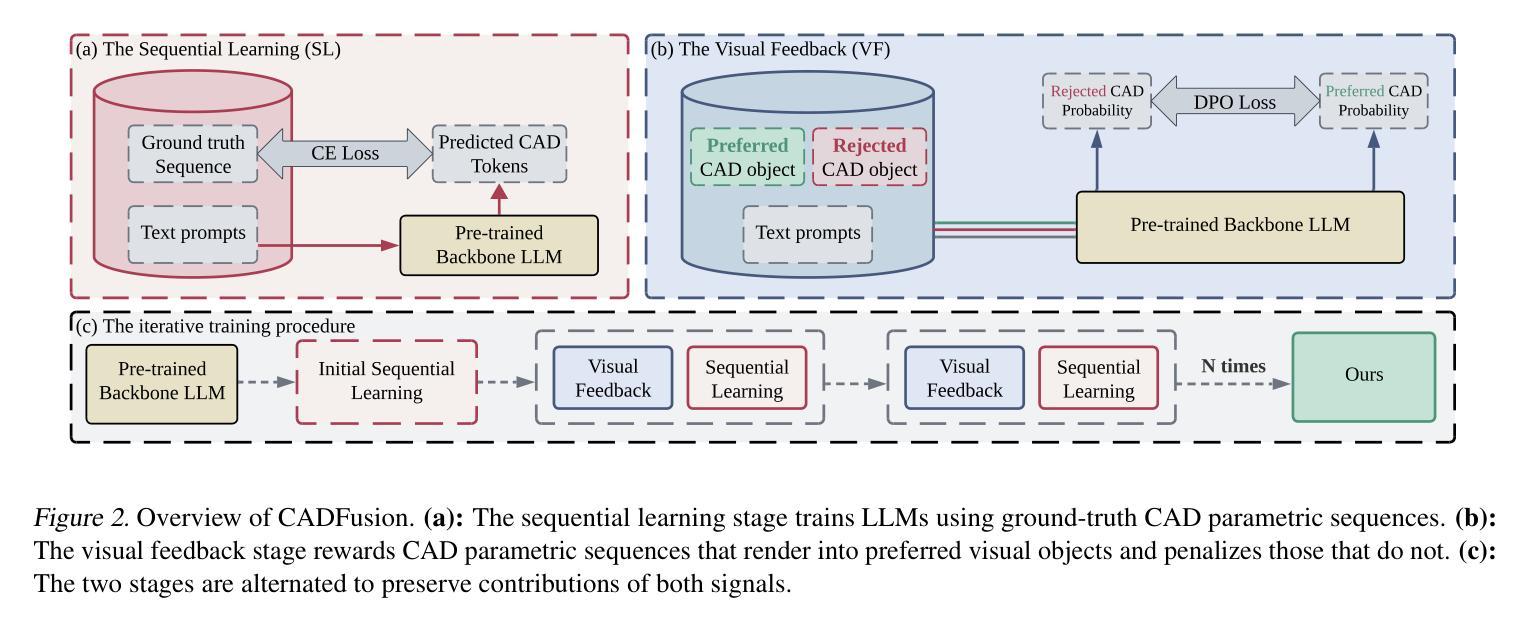
Text-to-CAD Generation Through Infusing Visual Feedback in Large Language Models
Authors:Ruiyu Wang, Yu Yuan, Shizhao Sun, Jiang Bian
Creating Computer-Aided Design (CAD) models requires significant expertise and effort. Text-to-CAD, which converts textual descriptions into CAD parametric sequences, is crucial in streamlining this process. Recent studies have utilized ground-truth parametric sequences, known as sequential signals, as supervision to achieve this goal. However, CAD models are inherently multimodal, comprising parametric sequences and corresponding rendered visual objects. Besides,the rendering process from parametric sequences to visual objects is many-to-one. Therefore, both sequential and visual signals are critical for effective training. In this work, we introduce CADFusion, a framework that uses Large Language Models (LLMs) as the backbone and alternates between two training stages: the sequential learning (SL) stage and the visual feedback (VF) stage. In the SL stage, we train LLMs using ground-truth parametric sequences, enabling the generation of logically coherent parametric sequences. In the VF stage, we reward parametric sequences that render into visually preferred objects and penalize those that do not, allowing LLMs to learn how rendered visual objects are perceived and evaluated. These two stages alternate throughout the training, ensuring balanced learning and preserving benefits of both signals. Experiments demonstrate that CADFusion significantly improves performance, both qualitatively and quantitatively.
创建计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型需要专业知识和大量努力。文本到CAD技术能够将文本描述转化为CAD参数序列,对于简化这一流程至关重要。近期研究使用真实参数序列(称为顺序信号)作为监督来实现这一目标。然而,CAD模型本质上是多模式的,包含参数序列和相应的渲染视觉对象。此外,从参数序列到视觉对象的渲染过程是多对一的。因此,顺序信号和视觉信号对于有效训练都至关重要。在这项工作中,我们引入了CADFusion框架,该框架以大型语言模型(LLM)为主干,并在两个训练阶段之间进行交替:顺序学习(SL)阶段和视觉反馈(VF)阶段。在SL阶段,我们使用真实参数序列训练LLM,使其能够生成逻辑连贯的参数序列。在VF阶段,我们奖励那些能够渲染成视觉上更受欢迎对象的参数序列,并惩罚那些不能的序列,这让LLM学习如何感知和评估渲染的视觉对象。这两个阶段在整个训练过程中交替进行,确保平衡学习并保留两种信号的优势。实验表明,CADFusion在定性和定量方面都显著提高了性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025 camera ready
Summary
文本描述了一种将文本描述转化为CAD参数序列的技术——Text-to-CAD的重要性,它在简化设计过程方面发挥着关键作用。近期研究使用称为序列信号的真实参数序列作为监督来实现这一目标。然而,CAD模型具有内在的多模态性,包含参数序列和相应的渲染视觉对象。此外,从参数序列到视觉对象的渲染过程是多对一的。因此,序列和视觉信号对于有效训练都是至关重要的。在此工作中,介绍了一个使用大型语言模型(LLM)作为骨干的CADFusion框架,该框架在序列学习(SL)阶段和视觉反馈(VF)阶段之间进行交替。SL阶段使用真实参数序列训练LLM,生成逻辑连贯的参数序列。VF阶段则奖励那些渲染成视觉上更受欢迎对象的参数序列,并惩罚那些不能做到这一点的序列,使LLM学习如何感知和评估渲染的视觉对象。这两个阶段的交替训练确保了学习的平衡,并保留了两种信号的优势。实验表明,CADFusion在定性和定量方面均显著提高了性能。
Key Takeaways
- Text-to-CAD技术能够将文本描述转化为CAD参数序列,从而简化设计过程。
- CAD模型具有多模态性,包含参数序列和对应的渲染视觉对象。
- 从参数序列到视觉对象的渲染过程是多对一的。
- 序列信号和视觉信号对于训练都是重要的。
- CADFusion框架结合了大型语言模型(LLM),并在序列学习(SL)和视觉反馈(VF)两个阶段之间交替。
- SL阶段通过真实参数序列训练LLM以生成逻辑连贯的参数序列。
- VF阶段通过视觉反馈来奖励或惩罚参数序列的渲染效果,使LLM能够学习如何评估渲染的视觉对象。
点此查看论文截图

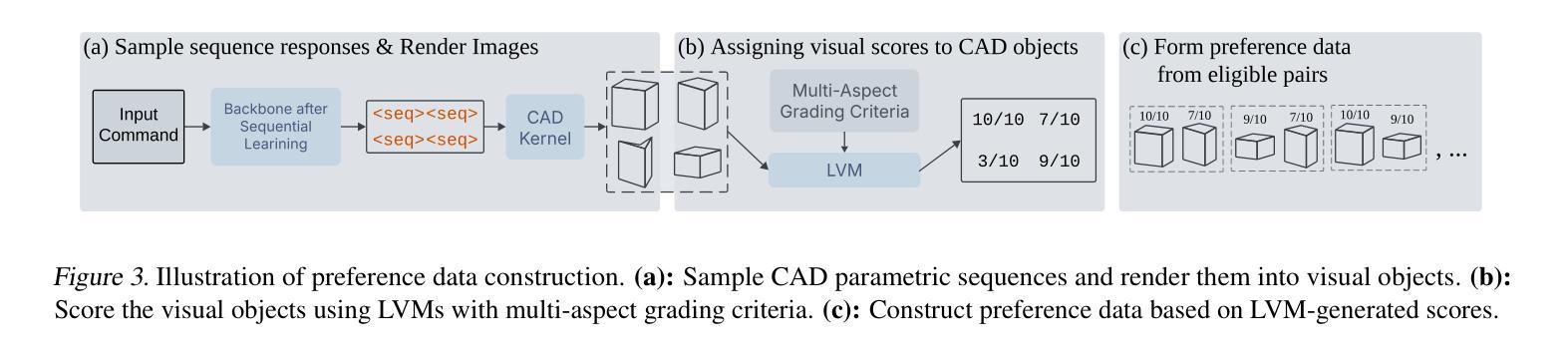
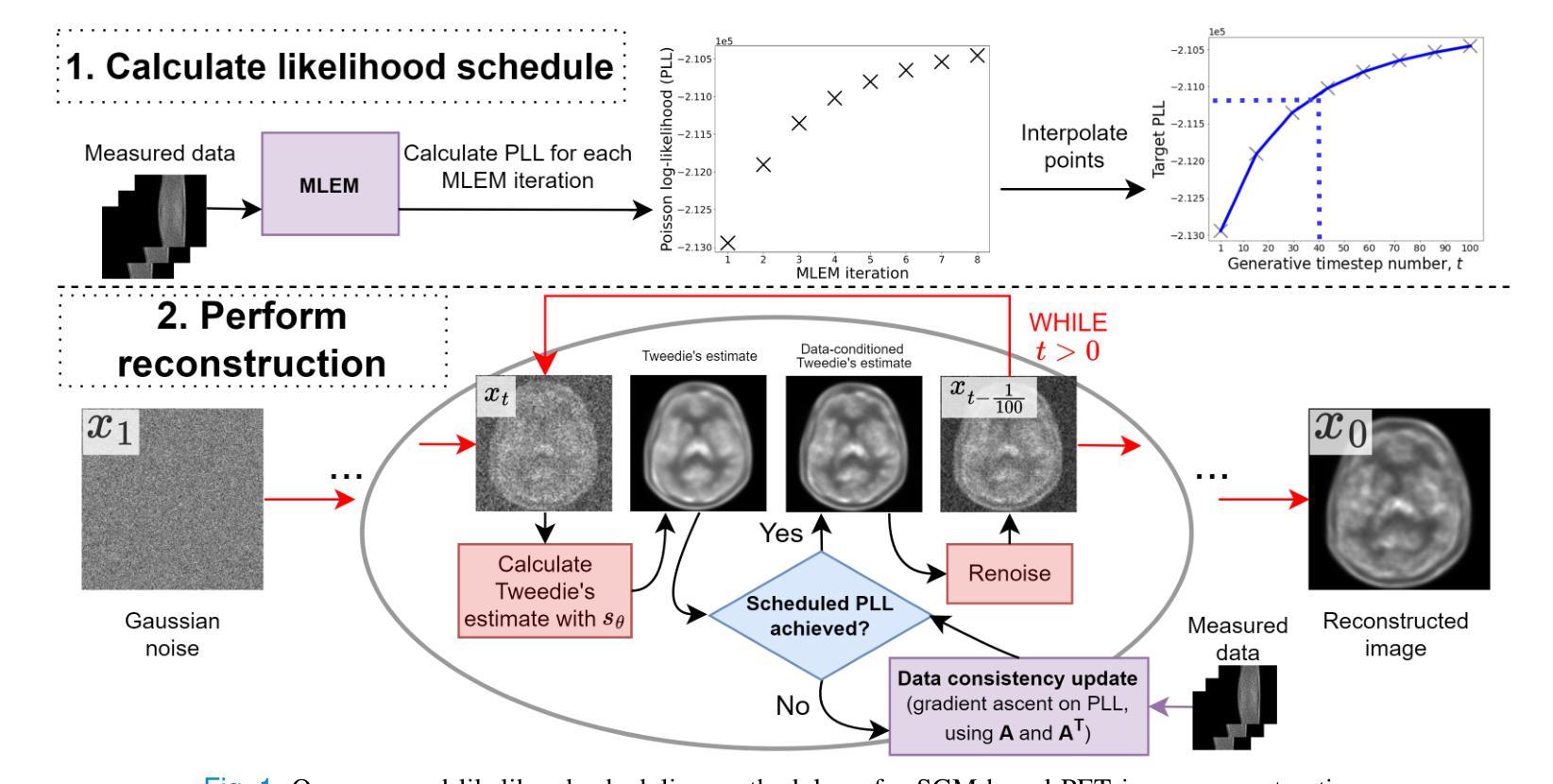
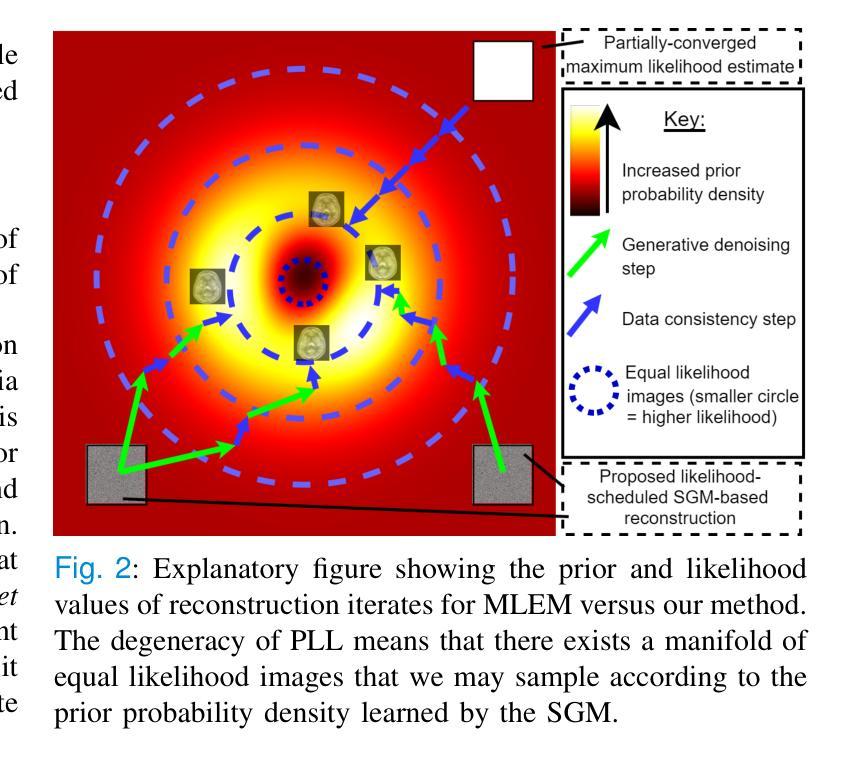
Likelihood-Scheduled Score-Based Generative Modeling for Fully 3D PET Image Reconstruction
Authors:George Webber, Yuya Mizuno, Oliver D. Howes, Alexander Hammers, Andrew P. King, Andrew J. Reader
Medical image reconstruction with pre-trained score-based generative models (SGMs) has advantages over other existing state-of-the-art deep-learned reconstruction methods, including improved resilience to different scanner setups and advanced image distribution modeling. SGM-based reconstruction has recently been applied to simulated positron emission tomography (PET) datasets, showing improved contrast recovery for out-of-distribution lesions relative to the state-of-the-art. However, existing methods for SGM-based reconstruction from PET data suffer from slow reconstruction, burdensome hyperparameter tuning and slice inconsistency effects (in 3D). In this work, we propose a practical methodology for fully 3D reconstruction that accelerates reconstruction and reduces the number of critical hyperparameters by matching the likelihood of an SGM’s reverse diffusion process to a current iterate of the maximum-likelihood expectation maximization algorithm. Using the example of low-count reconstruction from simulated [$^{18}$F]DPA-714 datasets, we show our methodology can match or improve on the NRMSE and SSIM of existing state-of-the-art SGM-based PET reconstruction while reducing reconstruction time and the need for hyperparameter tuning. We evaluate our methodology against state-of-the-art supervised and conventional reconstruction algorithms. Finally, we demonstrate a first-ever implementation of SGM-based reconstruction for real 3D PET data, specifically [$^{18}$F]DPA-714 data, where we integrate perpendicular pre-trained SGMs to eliminate slice inconsistency issues.
利用预训练的基于分数的生成模型(SGMs)进行医学图像重建,相较于其他现有的最先进的深度学习重建方法具有优势,包括对不同扫描仪设置的适应性更强和更先进的图像分布建模。基于SGM的重建方法最近已应用于模拟的正电子发射断层扫描(PET)数据集,相对于现有技术,对于分布外的病变的对比度恢复有所改善。然而,从PET数据中进行基于SGM的重建的现有方法存在重建速度慢、超参数调整繁琐以及在三维中的切片不一致效应等问题。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种用于完全三维重建的实用方法,通过匹配SGM反向扩散过程的概率与最大似然期望最大化算法的当前迭代,来加速重建并减少关键超参数的数量。以模拟的$^{18}$F-DPA-714数据集的低计数重建为例,我们展示了我们的方法能够在归一化均方根误差(NRMSE)和结构相似性度量(SSIM)上匹配或超越现有最先进的SGM-based PET重建方法,同时减少重建时间和对超参数调整的需求。我们将我们的方法与最先进的监督式和传统重建算法进行了评估比较。最后,我们展示了基于SGM的针对真实三维PET数据(特别是$^{18}$F-DPA-714数据)的首次实现重建,我们通过集成垂直方向的预训练SGM来消除切片不一致问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 14 figures. Author’s accepted manuscript, IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging
Summary
基于预训练得分生成模型(SGM)的医疗图像重建具有相对于其他先进的深度学习方法所不具备的优势,包括对不同扫描设置的稳健性和高级图像分布建模能力。本研究提出一种用于完全三维重建的实际方法,该方法通过匹配SGM反向扩散过程的概率与最大似然期望最大化算法的当前迭代值,从而加速重建过程并减少关键超参数的数量。本研究使用低计数重建模拟数据集进行示例演示,同时展示该方法的优异性能和相较于现有技术的优势。此外,我们首次实现了基于SGM的真实三维PET数据重建,解决了切片不一致的问题。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练得分生成模型(SGM)在医疗图像重建中具有优势,包括对不同扫描设置的稳健性和高级图像分布建模能力。
- 与现有技术相比,SGM在模拟的PET数据集上显示出更好的对比恢复性能。
- 提出一种基于SGM的三维重建方法,可加速重建过程并减少超参数调整的负担。
- 在低计数重建模拟数据集上的实验证明该方法与现有技术相当或更好。
- 该方法减少了重建时间并降低了对超参数调整的需求。
- 第一次实现了基于SGM的真实三维PET数据重建。
点此查看论文截图

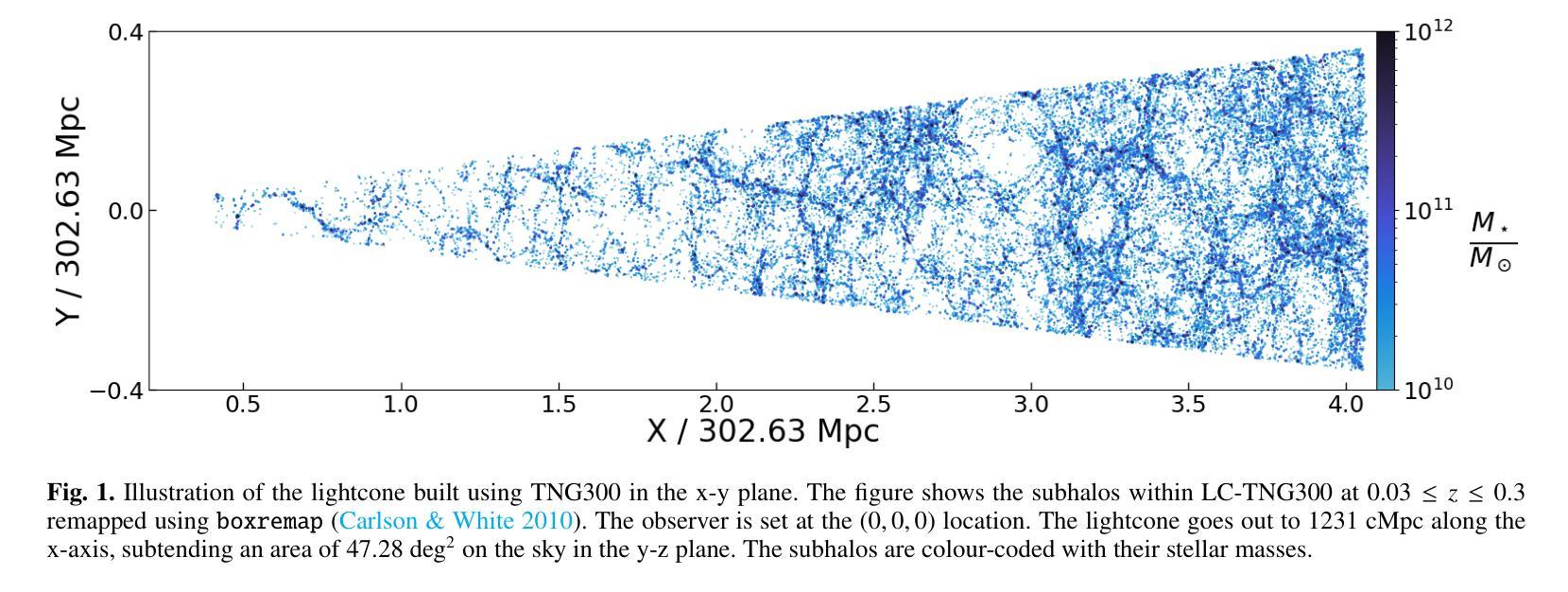
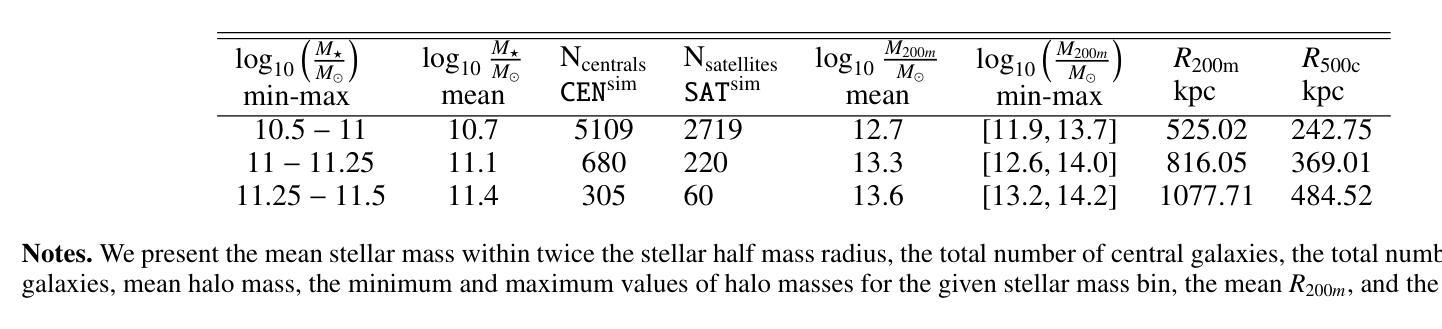
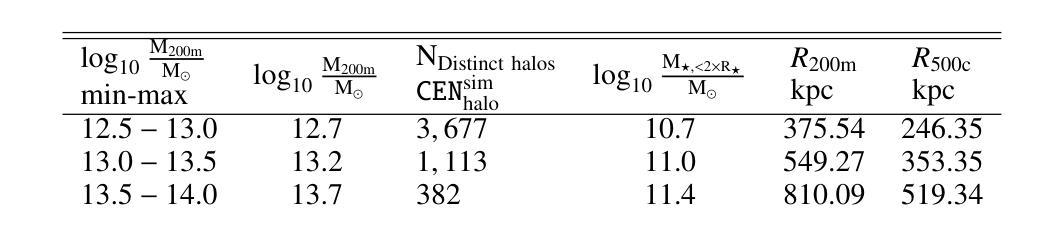
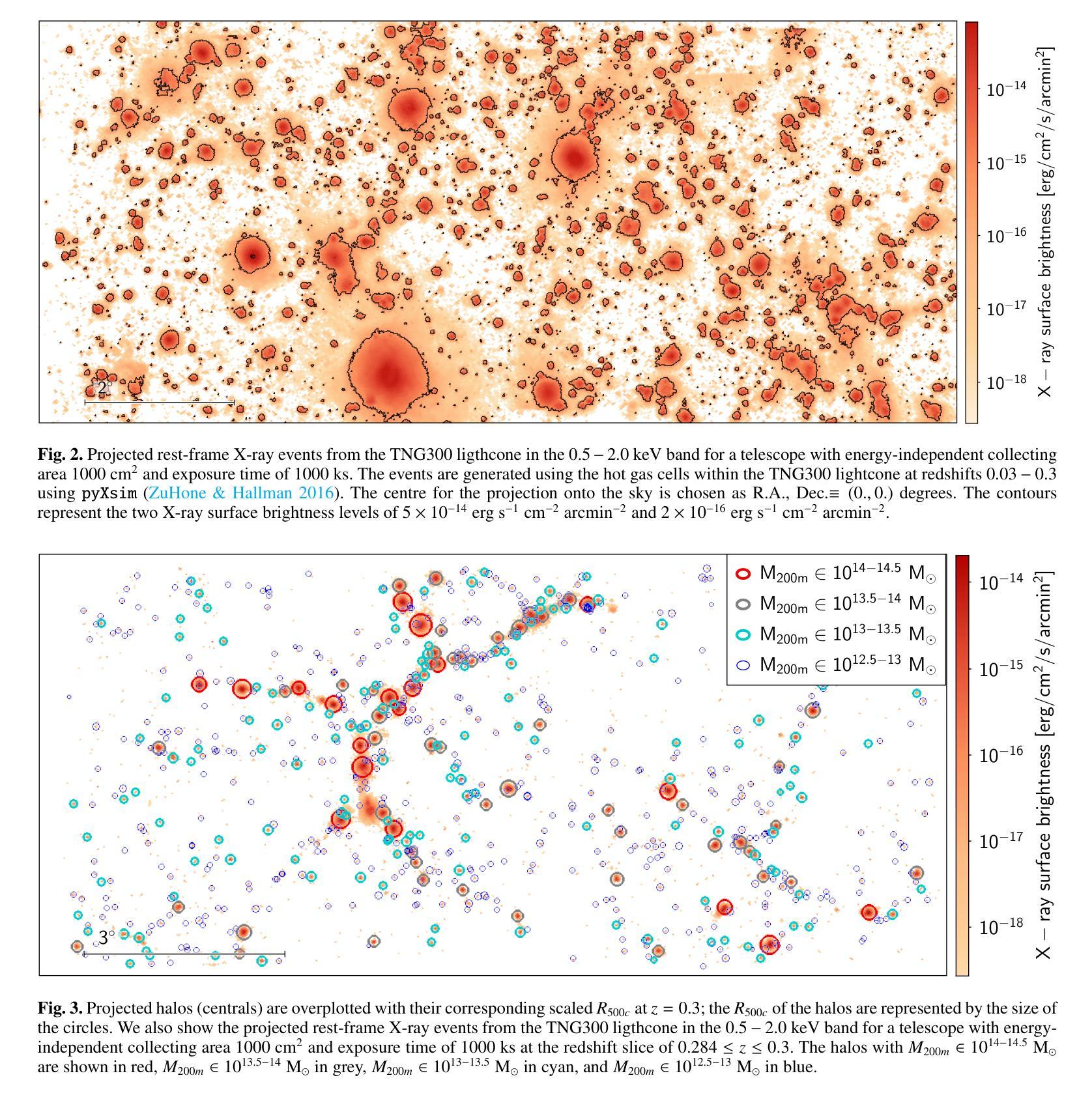
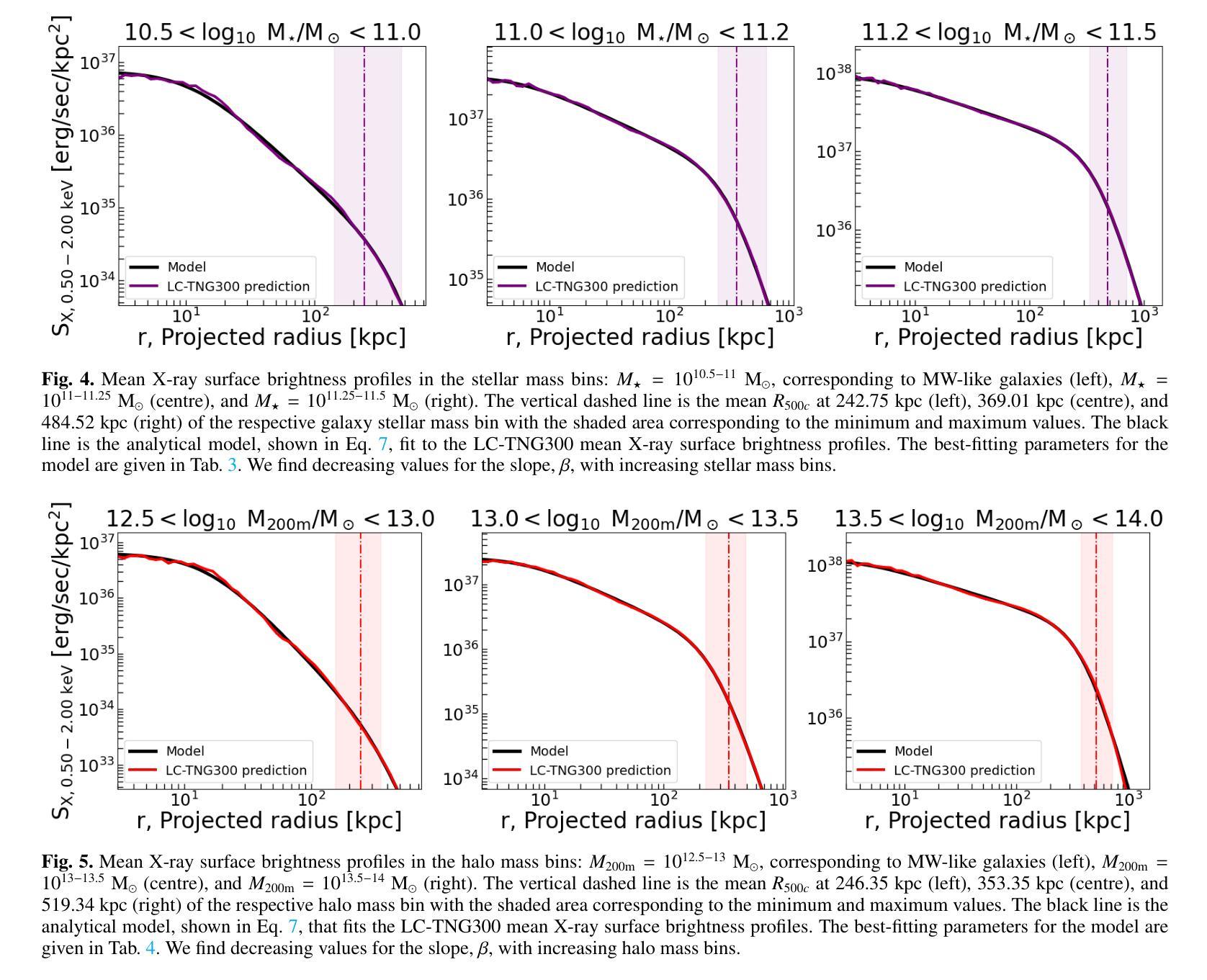
Quantifying Observational Projection Effects with a Simulation-based hot CGM model
Authors:Soumya Shreeram, Johan Comparat, Andrea Merloni, Yi Zhang, Gabriele Ponti, Kirpal Nandra, John ZuHone, Ilaria Marini, Stephan Vladutescu-Zopp, Paola Popesso, Ruediger Pakmor, Riccardo Seppi, Celine Peroux, Daniele Sorini
The hot phase of the circumgalactic medium (CGM) allows us to probe the inflow and outflow of gas within a galaxy, which is responsible for dictating the evolution of the galaxy. Studying the hot CGM sheds light on a better understanding of gas physics, which is crucial to inform and constrain simulation models. With the recent advances in observational measurements probing the hot CGM in X-rays and tSZ, we have a new avenue for widening our knowledge of gas physics and feedback by exploiting the information from current/future observations. In this paper, we use the TNG300 hydrodynamical simulations to build a fully self-consistent forward model for the hot CGM. We construct a lightcone and generate mock X-ray observations. We quantify the projection effects, namely the locally correlated large-scale structure in X-rays and the effect due to satellite galaxies misclassified as centrals which affects the measured hot CGM galactocentric profiles in stacking experiments. We present an analytical model that describes the intrinsic X-ray surface brightness profile across the stellar and halo mass bins. The increasing stellar mass bins result in decreasing values of $\beta$, the exponent quantifying the slope of the intrinsic galactocentric profiles. We carry forward the current state-of-the-art by also showing the impact of the locally correlated environment on the measured X-ray surface brightness profiles. We also present, for the first time, the effect of misclassified centrals in stacking experiments for three stellar mass bins: $10^{10.5-11}\ M_\odot$, $10^{11-11.2}\ M_\odot$, and $10^{11.2-11.5}\ M_\odot$. We find that the contaminating effect of the misclassified centrals on the stacked profiles increases when the stellar mass decreases.
关于环星系介质(CGM)的热相研究使我们能够探测星系内的气体流入和流出,这决定了星系的演化过程。研究热相CGM有助于更好地理解气体物理学,这对于模拟模型提供信息和约束至关重要。随着最近在X射线和tSZ探测中观测测量技术的进展,我们有了利用当前和未来观测结果扩大我们对气体物理学和反馈知识的新途径。在本文中,我们使用TNG300流体动力学模拟来构建热相CGM的完全自洽前向模型。我们构建了一个光锥并生成了模拟的X射线观测结果。我们量化了投影效应,即X射线中的局部相关的大规模结构和由于误将卫星星系归类为中心星系而对堆叠实验中测量的热相CGM向心轮廓产生的影响。我们提出了一个分析模型,描述了跨越恒星和暗物质晕质量范围内的固有X射线表面亮度分布特征。随着恒星质量分组的增加,β值下降,β是指数,量化固有向心轮廓的斜率。我们秉承了当前最新状态,同时展示了局部相关环境对测量的X射线表面亮度分布特征的影响。我们还首次展示了三个恒星质量分组中误分类中心对堆叠实验的影响:$10^{10.5-11} M_\odot$、$10^{11-11.2} M_\odot$和$10^{11.2-11.5} M_\odot$。我们发现误分类中心对叠加分布特征的污染效应随着恒星质量的减少而增加。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 10 figures, Accepted in A&A
Summary
研究热态星周介质(CGM)有助于了解星系内的气体流入流出情况,影响星系演化。通过探讨热态CGM,能更好地理解气体物理学,为模拟模型提供信息和约束。当前X射线和tSZ观测技术的进步为通过当前和未来观测数据了解气体物理学和反馈提供了新的途径。本文利用TNG300流体动力学模拟构建了一个完全自洽的前向模型,对热态CGM进行研究。通过模拟光锥和生成X射线模拟观测数据,我们量化了投影效应,提出了一种描述恒星和暗物质质量箱内固有X射线表面亮度分布的分析模型。随着恒星质量分箱的增大,β值减小,固有中心星周分布斜率减少。我们还展示了局部相关环境对测量的X射线表面亮度分布的影响,并首次展示了分类错误中心体在堆积实验中对三个恒星质量分箱的影响。发现分类错误的中心体对叠加分析的影响随着恒星质量的减小而增大。
Key Takeaways
- 研究热态星周介质(CGM)可以了解星系内气体流入流出的情况,影响星系演化进程。
- 通过探讨热态CGM能更好地理解气体物理学,为模拟模型提供信息和约束。
- 当前X射线和tSZ观测技术的进步为拓宽对气体物理学的知识提供了新途径。
- 利用TNG300流体动力学模拟构建了一个完全自洽的前向模型来研究热态CGM。
- 投影效应被量化,并提出了描述恒星和暗物质质量箱内固有X射线表面亮度分布的分析模型。
- 恒星质量分箱增大时,描述亮度分布的β值减小。
点此查看论文截图

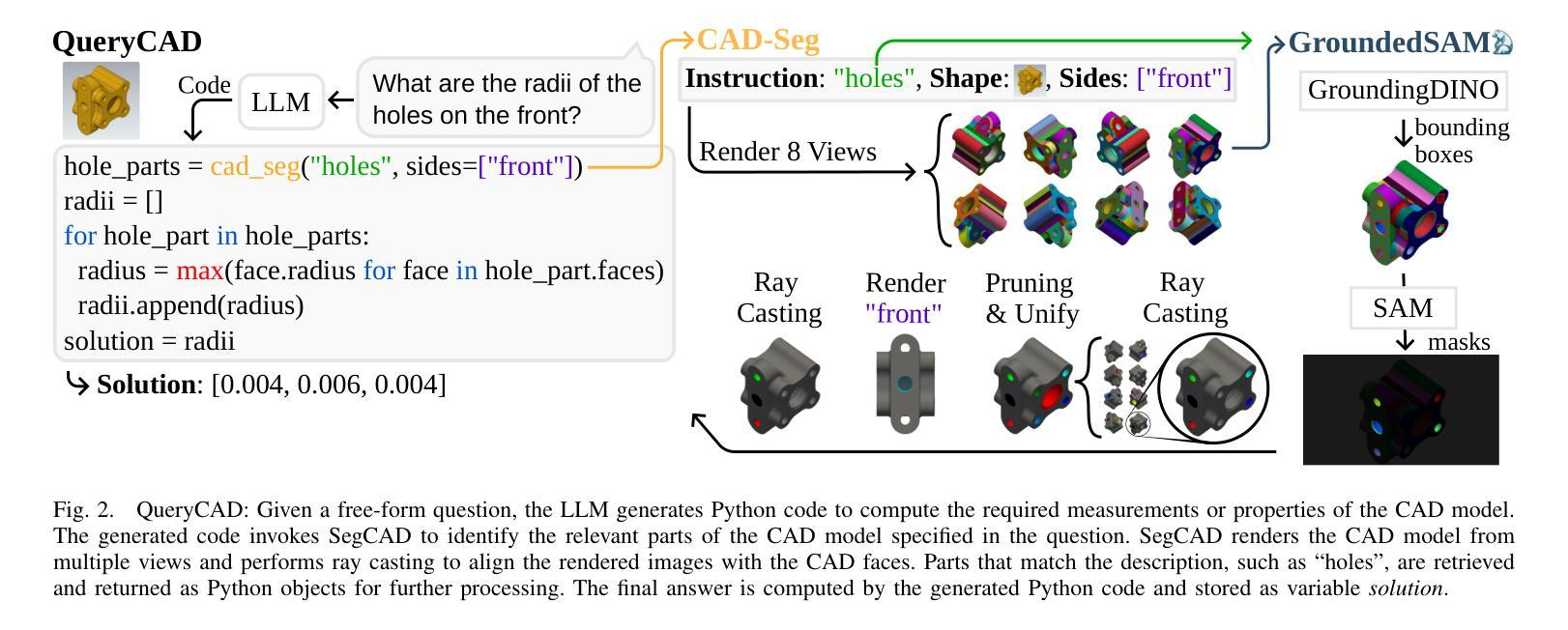
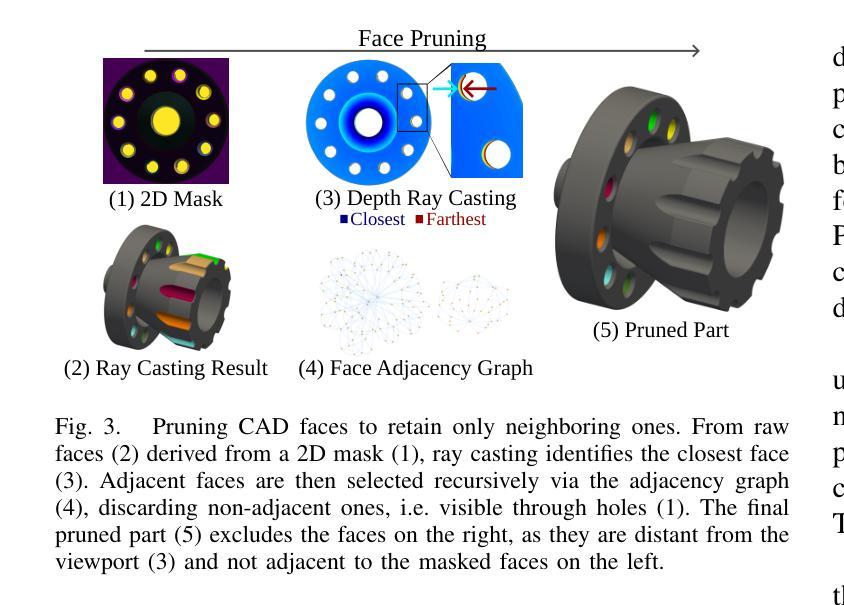
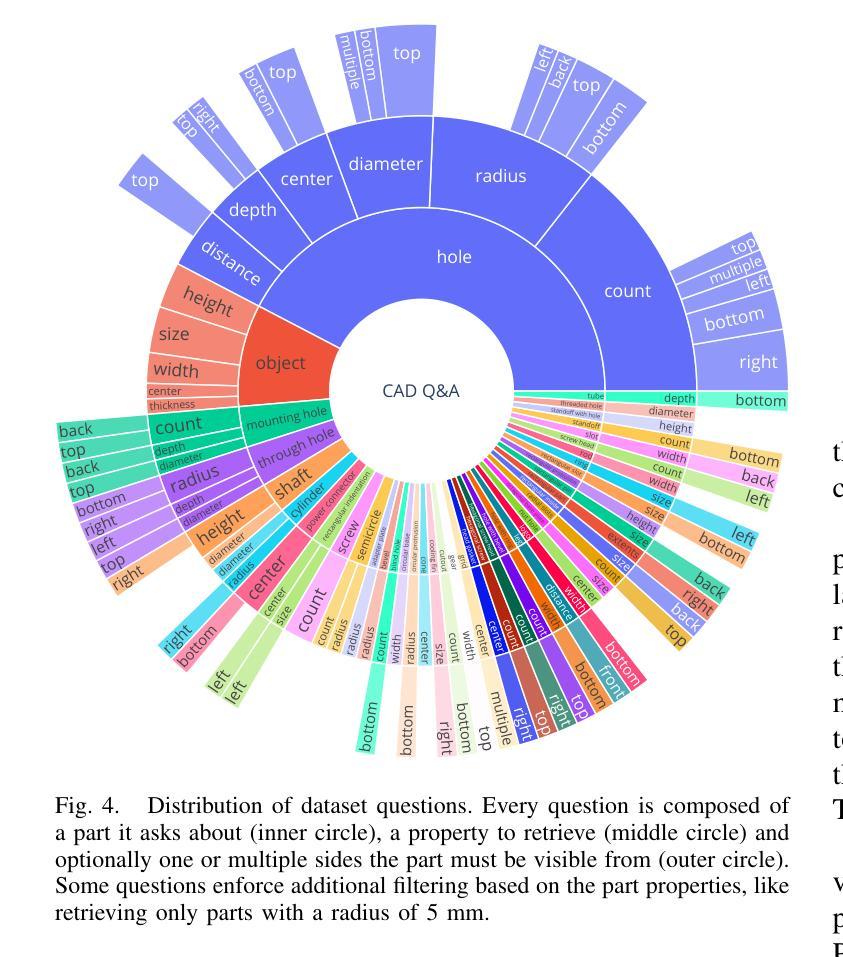
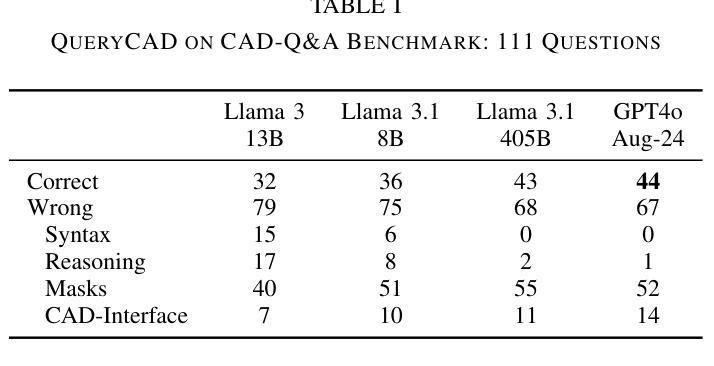
QueryCAD: Grounded Question Answering for CAD Models
Authors:Claudius Kienle, Benjamin Alt, Darko Katic, Rainer Jäkel, Jan Peters
CAD models are widely used in industry and are essential for robotic automation processes. However, these models are rarely considered in novel AI-based approaches, such as the automatic synthesis of robot programs, as there are no readily available methods that would allow CAD models to be incorporated for the analysis, interpretation, or extraction of information. To address these limitations, we propose QueryCAD, the first system designed for CAD question answering, enabling the extraction of precise information from CAD models using natural language queries. QueryCAD incorporates SegCAD, an open-vocabulary instance segmentation model we developed to identify and select specific parts of the CAD model based on part descriptions. We further propose a CAD question answering benchmark to evaluate QueryCAD and establish a foundation for future research. Lastly, we integrate QueryCAD within an automatic robot program synthesis framework, validating its ability to enhance deep-learning solutions for robotics by enabling them to process CAD models (https://claudius-kienle.github.com/querycad).
CAD模型在工业界有广泛应用,对于机器人自动化流程至关重要。然而,这些模型在基于AI的新方法中很少被考虑,如机器人程序的自动合成。因为没有现成的方法可以让CAD模型用于分析、解释或提取信息。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了QueryCAD系统,这是首个为CAD问答设计的系统,能够通过自然语言查询从CAD模型中提取精确信息。QueryCAD集成了我们开发的SegCAD,这是一种开放词汇实例分割模型,能够根据零件描述来识别和选择CAD模型中的特定部分。我们还提出了一个CAD问答基准测试来评估QueryCAD并为未来的研究奠定基础。最后,我们将QueryCAD集成到自动机器人程序合成框架中,验证了它增强机器人深度学习能力的能力,使其能够处理CAD模型(https://claudius-kienle.github.com/querycad)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
CAD模型在工业中广泛应用,对机器人自动化流程至关重要。但在基于AI的自动机器人程序合成等新型方法中,CAD模型的应用却被忽视。为解决此问题,提出QueryCAD系统,利用自然语言查询从CAD模型中提取精确信息。该系统包括SegCAD,一个基于开放词汇的实例分割模型,可识别并选择CAD模型中的特定部分。此外,还提出CAD问答基准测试以评估QueryCAD并为未来研究奠定基础。最后,将QueryCAD集成到自动机器人程序合成框架中,验证了其在机器人深度学习解决方案中的增强能力。
Key Takeaways
- CAD模型在工业机器人自动化流程中占据重要地位,但在新型AI方法中应用较少。
- QueryCAD系统能利用自然语言查询从CAD模型中提取精确信息,解决了这一问题。
- SegCAD是QueryCAD的核心组成部分,可以识别并选择CAD模型中的特定部分。
- 提出了CAD问答基准测试以评估QueryCAD性能,并为未来研究提供基础。
- QueryCAD系统被成功集成到自动机器人程序合成框架中。
- QueryCAD增强了深度学习在机器人领域的应用能力,能够处理CAD模型。
点此查看论文截图

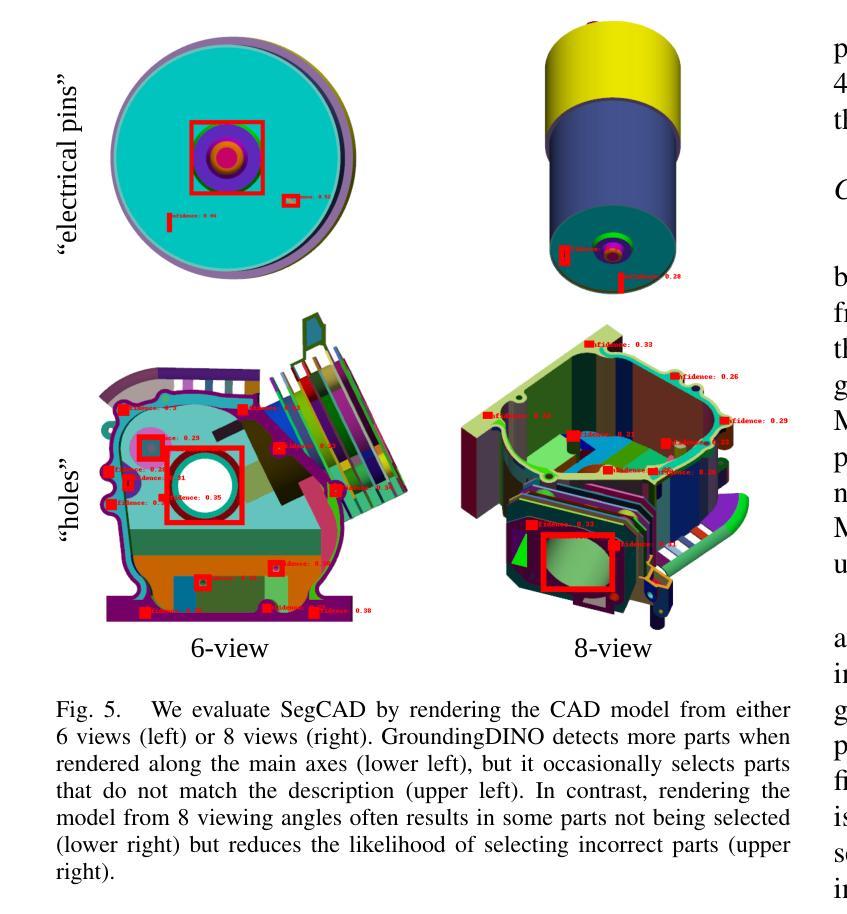
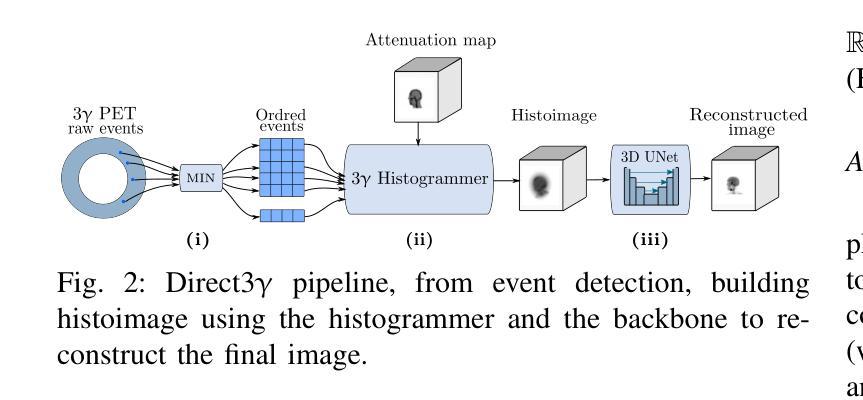
Direct3γ: A Pipeline for Direct Three-gamma PET Image Reconstruction
Authors:Youness Mellak, Alexandre Bousse, Thibaut Merlin, Debora Giovagnoli, Dimitris Visvikis
This paper presents a novel image reconstruction pipeline for three-gamma (3-{\gamma}) positron emission tomography (PET) aimed at improving spatial resolution and reducing noise in nuclear medicine. The proposed Direct3{\gamma} pipeline addresses the inherent challenges in 3-{\gamma} PET systems, such as detector imperfections and uncertainty in photon interaction points. A key feature of the pipeline is its ability to determine the order of interactions through a model trained on Monte Carlo (MC) simulations using the Geant4 Application for Tomography Emission (GATE) toolkit, thus providing the necessary information to construct Compton cones which intersect with the line of response (LOR) to provide an estimate of the emission point. The pipeline processes 3-{\gamma} PET raw data, reconstructs histoimages by propagating energy and spatial uncertainties along the LOR, and applies a 3-D convolutional neural network (CNN) to refine these intermediate images into high-quality reconstructions. To further enhance image quality, the pipeline leverages both supervised learning and adversarial losses, the latter preserving fine structural details. Experimental results show that Direct3{\gamma} consistently outperforms conventional 200-ps time-of-flight (TOF) PET in terms of SSIM and PSNR.
本文提出了一种针对三伽马(3-γ)正电子发射断层扫描(PET)的新型图像重建流水线,旨在提高核医学中的空间分辨率并降低噪声。所提出的Direct3γ流水线解决了3-γ PET系统固有的挑战,如探测器缺陷和光子交互点的不确定性。流水线的一个关键功能是其通过利用基于蒙特卡洛(MC)模拟训练的模型确定交互顺序的能力,该模型使用GATE(Geant4汤姆森发射应用程序)工具包,从而提供构建与响应线(LOR)相交的康普顿锥的必要信息,以估计发射点。该流水线处理3-γ PET原始数据,通过沿LOR传播能量和空间不确定性来重建直方图像,并应用三维卷积神经网络(CNN)对这些中间图像进行精细处理以获得高质量重建。为了进一步改善图像质量,流水线结合了监督学习和对抗性损失,后者保留了精细的结构细节。实验结果表明,Direct3γ在结构相似性度量(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面始终优于传统的200皮秒飞行时间(TOF)PET。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 11 figures, 2 tables
Summary
本文提出了一种针对三伽马(3-γ)正电子发射断层扫描(PET)图像重建的新流程,旨在提高核医学中的空间分辨率并降低噪声。该流程通过模拟蒙特卡洛(MC)仿真数据,利用Geant4 Application for Tomography Emission(GATE)工具箱进行训练模型来解决互动点的不确定性等固有难题。使用深度学习的直接建模方法来生成图像的高分辨率重建,并通过实验证明其性能优于传统的TOF PET成像技术。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种新的图像重建流程,专门用于处理三伽马(3-γ)正电子发射断层扫描(PET)。
- 通过Monte Carlo模拟和Geant4 Application for Tomography Emission工具训练模型解决固有的难题,如探测器的不完美和光子交互点的不确定性。
- 通过顺序推断技术构建康普顿锥,结合响应线(LOR)估计发射点。
- 该流程能够处理原始数据并重建图像,通过沿响应线传播能量和空间不确定性来生成高质量的图像重建。
- 使用三维卷积神经网络对图像进行微调,进一步提高图像质量。
- 该流程采用监督学习和对抗性损失相结合的策略来增强图像质量,尤其是对抗性损失在保留细微结构方面效果显著。
点此查看论文截图

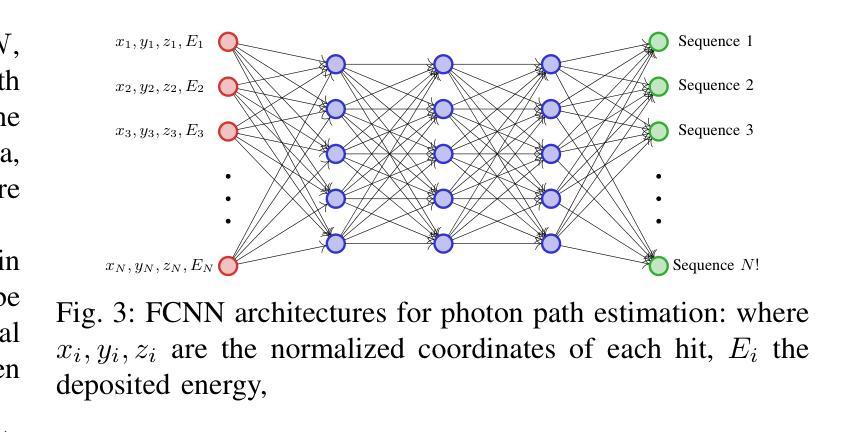
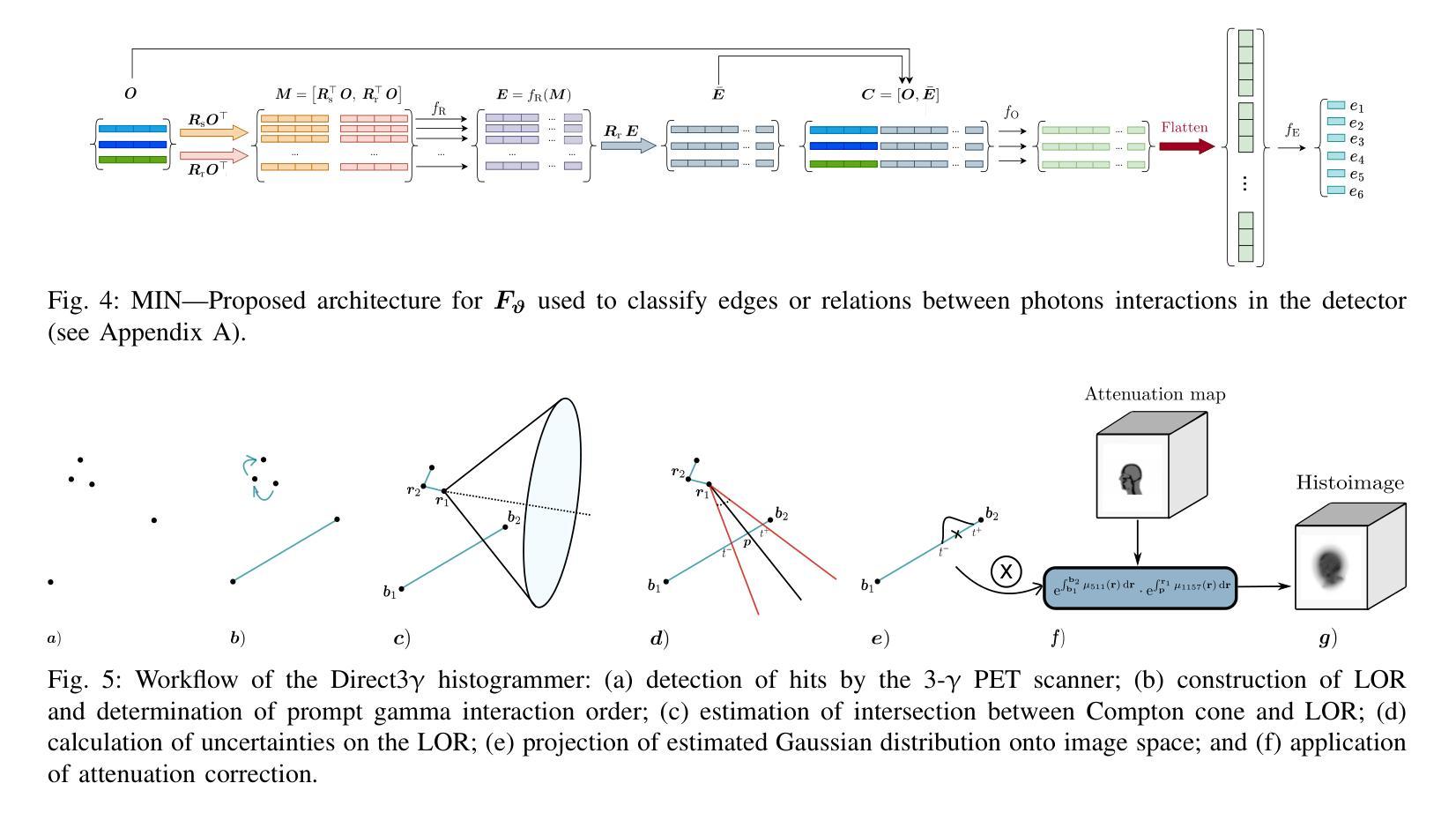
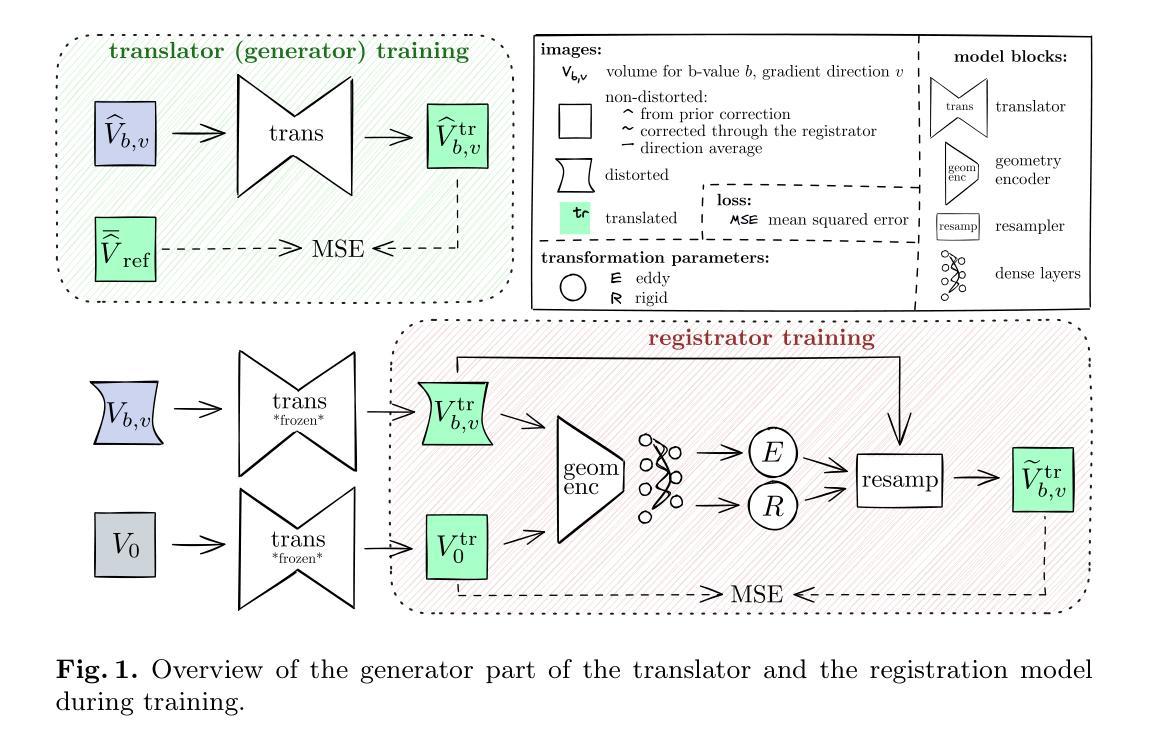
Eddeep: Fast eddy-current distortion correction for diffusion MRI with deep learning
Authors:Antoine Legouhy, Ross Callaghan, Whitney Stee, Philippe Peigneux, Hojjat Azadbakht, Hui Zhang
Modern diffusion MRI sequences commonly acquire a large number of volumes with diffusion sensitization gradients of differing strengths or directions. Such sequences rely on echo-planar imaging (EPI) to achieve reasonable scan duration. However, EPI is vulnerable to off-resonance effects, leading to tissue susceptibility and eddy-current induced distortions. The latter is particularly problematic because it causes misalignment between volumes, disrupting downstream modelling and analysis. The essential correction of eddy distortions is typically done post-acquisition, with image registration. However, this is non-trivial because correspondence between volumes can be severely disrupted due to volume-specific signal attenuations induced by varying directions and strengths of the applied gradients. This challenge has been successfully addressed by the popular FSLEddy tool but at considerable computational cost. We propose an alternative approach, leveraging recent advances in image processing enabled by deep learning (DL). It consists of two convolutional neural networks: 1) An image translator to restore correspondence between images; 2) A registration model to align the translated images. Results demonstrate comparable distortion estimates to FSLEddy, while requiring only modest training sample sizes. This work, to the best of our knowledge, is the first to tackle this problem with deep learning. Together with recently developed DL-based susceptibility correction techniques, they pave the way for real-time preprocessing of diffusion MRI, facilitating its wider uptake in the clinic.
现代扩散MRI序列通常获取大量体积数据,这些数据具有不同强度或方向的扩散增敏梯度。此类序列依赖于回波平面成像(EPI)来实现合理的扫描时间。然而,EPI容易受到频率偏移效应的影响,导致组织磁化率和涡流引起的失真。后者特别成问题,因为它会导致不同体积之间的不对准,从而破坏下游建模和分析。涡流失真的基本校正通常在采集后进行,通过图像配准实现。然而,这并不容易,因为由于应用梯度的方向和强度变化导致的特定体积信号衰减,不同体积之间的对应关系可能会受到严重破坏。这一挑战已经通过流行的FSL
Eddy工具成功解决,但计算成本相当高。我们提出了一种替代方法,利用深度学习(DL)在图像处理方面的最新进展。它包含两个卷积神经网络:1)图像翻译器,用于恢复图像之间的对应关系;2)注册模型,用于对齐翻译后的图像。结果表明,其畸变估计与FSLEddy相当,同时只需中等大小的训练样本量。据我们所知,这是首次使用深度学习来解决这一问题的工作。与最近开发的基于DL的磁化率校正技术相结合,它们为扩散MRI的实时预处理铺平了道路,促进了其在临床的广泛应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in MICCAI 2024 conference (without rebuttal). Github repo: https://github.com/CIG-UCL/eddeep
摘要
本文介绍了现代扩散MRI序列在采集大量体积数据时面临的挑战,如组织磁化率和涡流引起的失真。针对涡流引起的失真问题,提出了基于深度学习的图像处理方法,包括图像翻译器和注册模型,以恢复图像间的对应关系并进行对齐。该方法与FSL~Eddy工具相比,在失真估计方面表现出相当的性能,并且只需适中的训练样本大小。这是首次尝试使用深度学习解决此问题,为扩散MRI的实时预处理铺平了道路,有助于其在临床的广泛应用。
要点
- 现代扩散MRI序列在采集大量数据时面临组织磁化率和涡流引起的失真问题。
- 涡流引起的失真会导致体积间的不对齐,给下游建模和分析带来干扰。
- 流行的FSL~Eddy工具可以解决这个问题,但计算成本较高。
- 提出了一种基于深度学习的替代方法,包括图像翻译器和注册模型,以恢复图像间的对应关系并进行对齐。
- 该方法在失真估计方面表现出与FSL~Eddy相当的性能,且只需适中的训练样本大小。
- 这是首次尝试使用深度学习解决此问题。
- 该方法与基于深度学习的磁化率校正技术相结合,为扩散MRI的实时预处理打开了大门,有助于其在临床的广泛应用。
点此查看论文截图