⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-08 更新
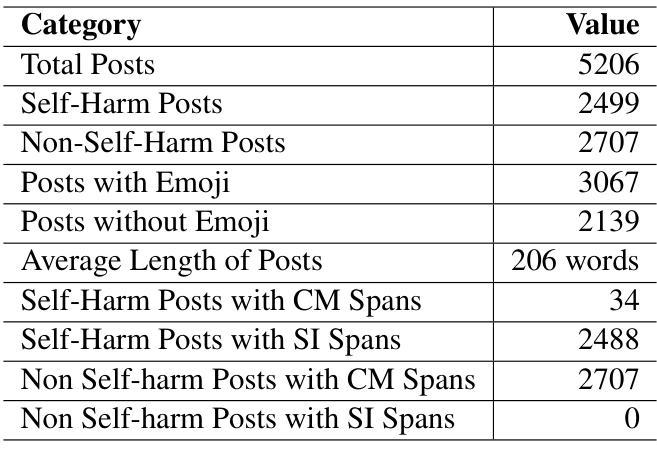
Just a Scratch: Enhancing LLM Capabilities for Self-harm Detection through Intent Differentiation and Emoji Interpretation
Authors:Soumitra Ghosh, Gopendra Vikram Singh, Shambhavi, Sabarna Choudhury, Asif Ekbal
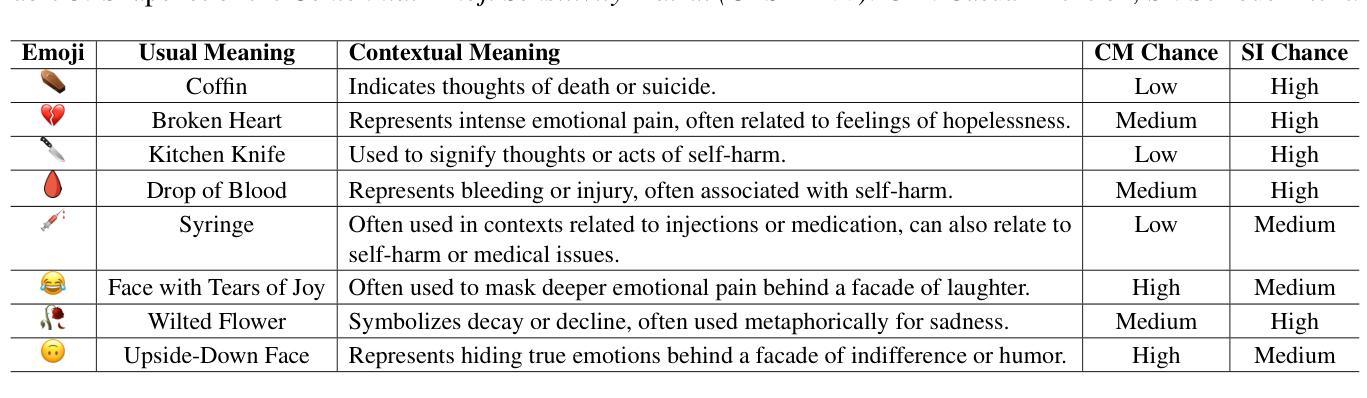
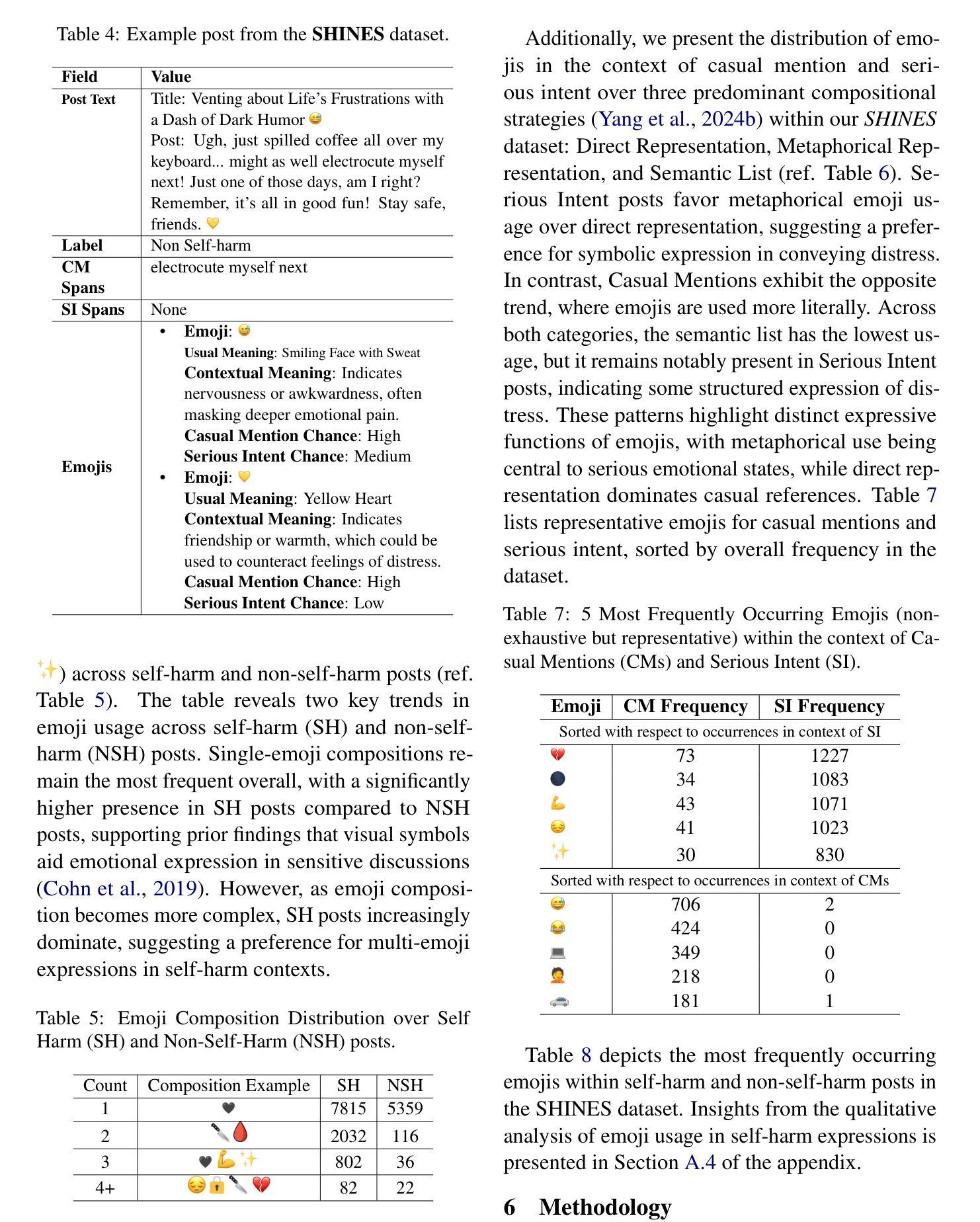
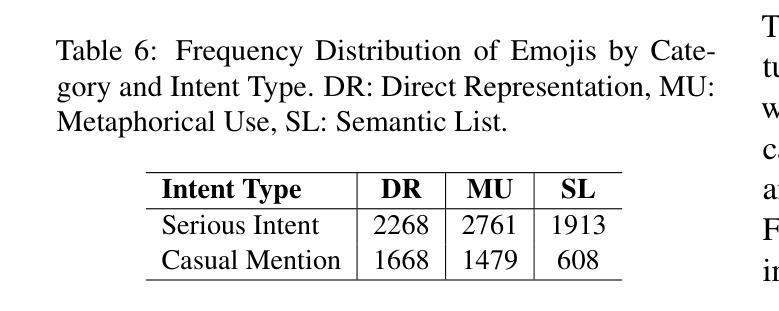
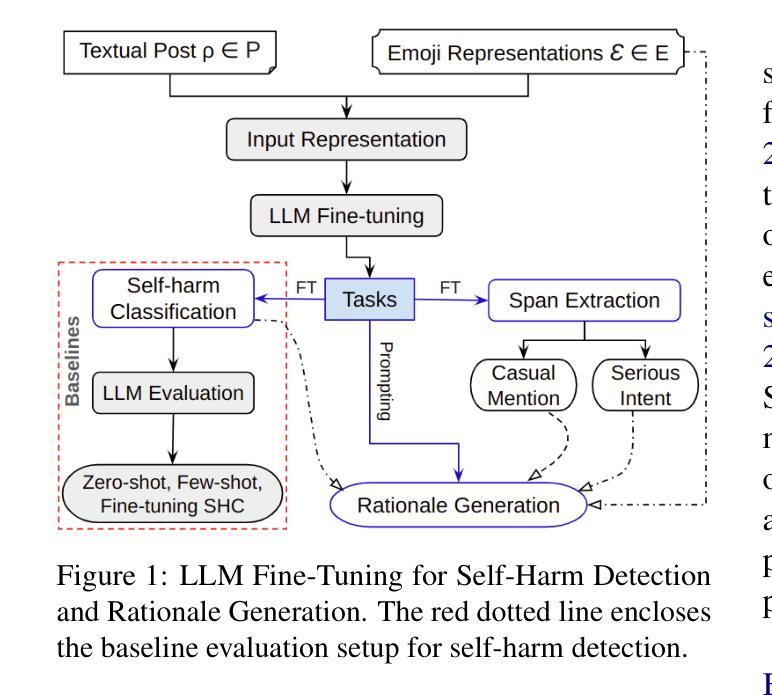
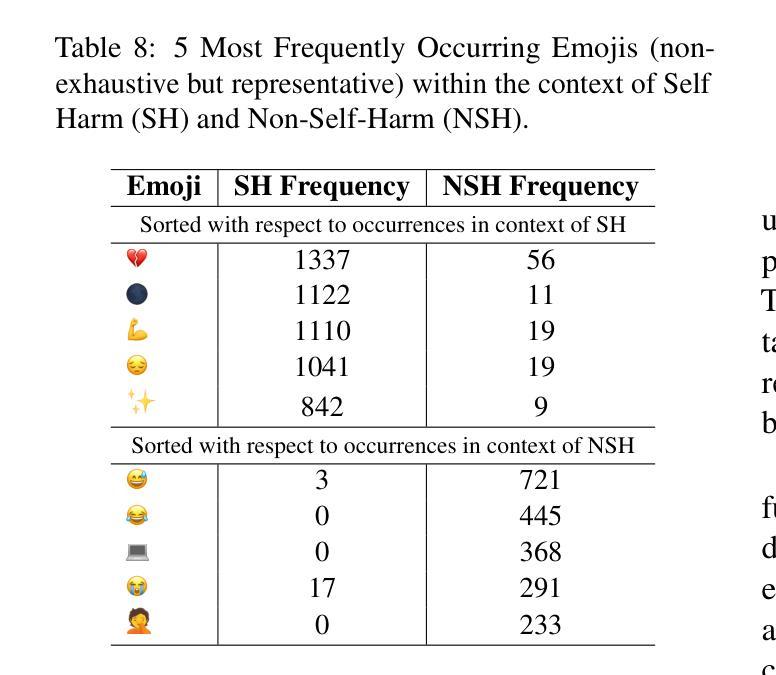
Self-harm detection on social media is critical for early intervention and mental health support, yet remains challenging due to the subtle, context-dependent nature of such expressions. Identifying self-harm intent aids suicide prevention by enabling timely responses, but current large language models (LLMs) struggle to interpret implicit cues in casual language and emojis. This work enhances LLMs’ comprehension of self-harm by distinguishing intent through nuanced language-emoji interplay. We present the Centennial Emoji Sensitivity Matrix (CESM-100), a curated set of 100 emojis with contextual self-harm interpretations and the Self-Harm Identification aNd intent Extraction with Supportive emoji sensitivity (SHINES) dataset, offering detailed annotations for self-harm labels, casual mentions (CMs), and serious intents (SIs). Our unified framework: a) enriches inputs using CESM-100; b) fine-tunes LLMs for multi-task learning: self-harm detection (primary) and CM/SI span detection (auxiliary); c) generates explainable rationales for self-harm predictions. We evaluate the framework on three state-of-the-art LLMs-Llama 3, Mental-Alpaca, and MentalLlama, across zero-shot, few-shot, and fine-tuned scenarios. By coupling intent differentiation with contextual cues, our approach commendably enhances LLM performance in both detection and explanation tasks, effectively addressing the inherent ambiguity in self-harm signals. The SHINES dataset, CESM-100 and codebase are publicly available at: https://www.iitp.ac.in/~ai-nlp-ml/resources.html#SHINES .
社交媒体上的自我伤害检测对于早期干预和精神健康支持至关重要,但由于此类表达的细微和语境依赖性,它仍然是一个挑战。识别自我伤害意图有助于通过及时响应预防自杀,但当前的大型语言模型(LLM)在解释日常用语和表情符号中的隐含线索方面存在困难。这项工作通过区分语言与表情符号之间的微妙互动,增强了大型语言模型对自我伤害意图的理解。我们推出了百年表情符号敏感性矩阵(CESM-100),这是一组包含语境自我伤害解释的100个表情符号的精选集,以及自我伤害识别与意图提取(SHINES)数据集,为自我伤害标签、偶然提及(CM)和严重意图(SI)提供了详细的注释。我们的统一框架包括:a)使用CESM-100丰富输入;b)微调LLM进行多任务学习:自我伤害检测(主要任务)和CM/SI跨度检测(辅助任务);c)生成自我伤害预测的可解释理由。我们在三个最先进的大型语言模型上评估了该框架:Llama 3、Mental-Alpaca和MentalLlama,以及在零样本、少样本和微调场景中进行了测试。通过意图区分与上下文线索相结合,我们的方法在提高检测和解释任务的性能方面都取得了可喜的效果,有效地解决了自我伤害信号中的固有模糊性。SHINES数据集、CESM-100和源代码可在以下网址公开访问:https://www.iitp.ac.in/~ai-nlp-ml/resources.html#SHINES。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be published in the Proceedings of the 63rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL 2025 Main)
Summary
此文本关于通过利用情绪矩阵和数据集增强大型语言模型对社交媒体上自我伤害表达意图的理解。研究团队推出了Centennial Emoji Sensitivity Matrix(CESM-100)和SHINES数据集,以丰富输入和微调大型语言模型。该框架通过区分自我伤害的意图和上下文线索,提高了大型语言模型在自我伤害检测任务中的性能,并生成解释性理由。
Key Takeaways
- 社交媒体的自我伤害检测对早期干预和精神健康支持至关重要。
- 当前大型语言模型在解读隐晦线索和情绪表达方面存在挑战。
- CESM-100包含100个具有上下文自我伤害解读的emoji。
- SHINES数据集提供详细的自我伤害标签、随意提及(CMs)和严重意图(SIs)注释。
- 统一框架包括:使用CESM-100丰富输入,微调大型语言模型进行多任务学习,生成自我伤害预测的解释性理由。
- 该框架在三种先进的大型语言模型中表现良好,能够有效提高自我伤害检测和解释任务的性能。
点此查看论文截图

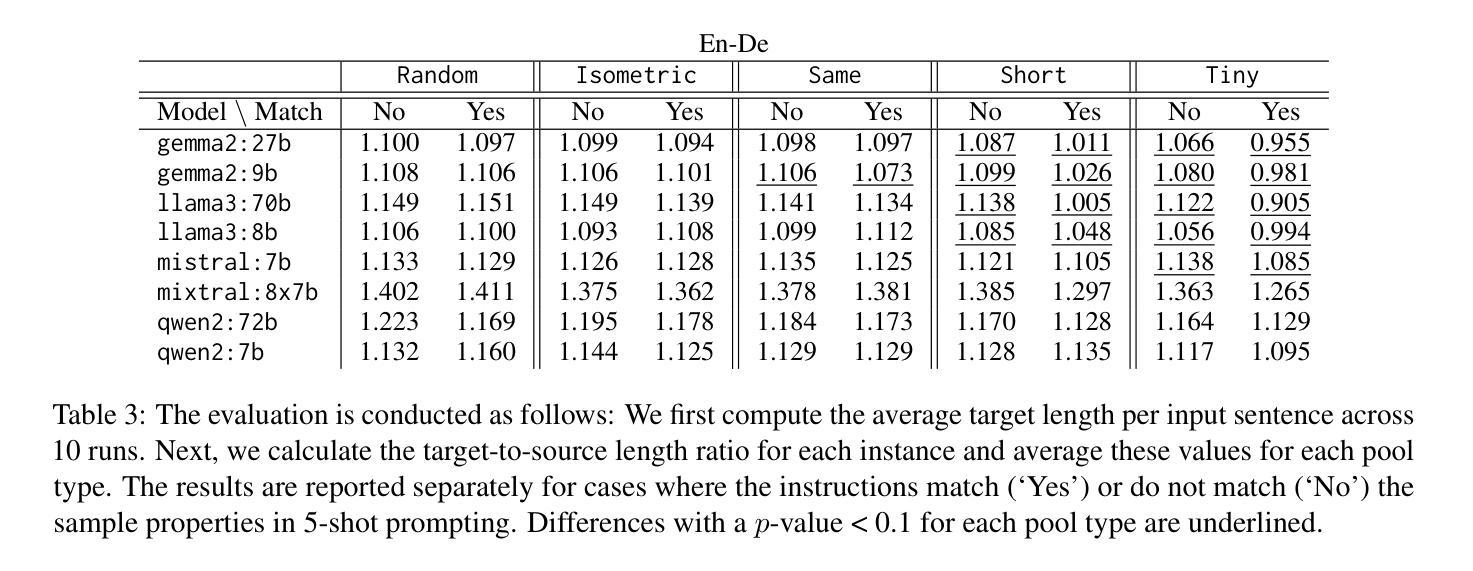
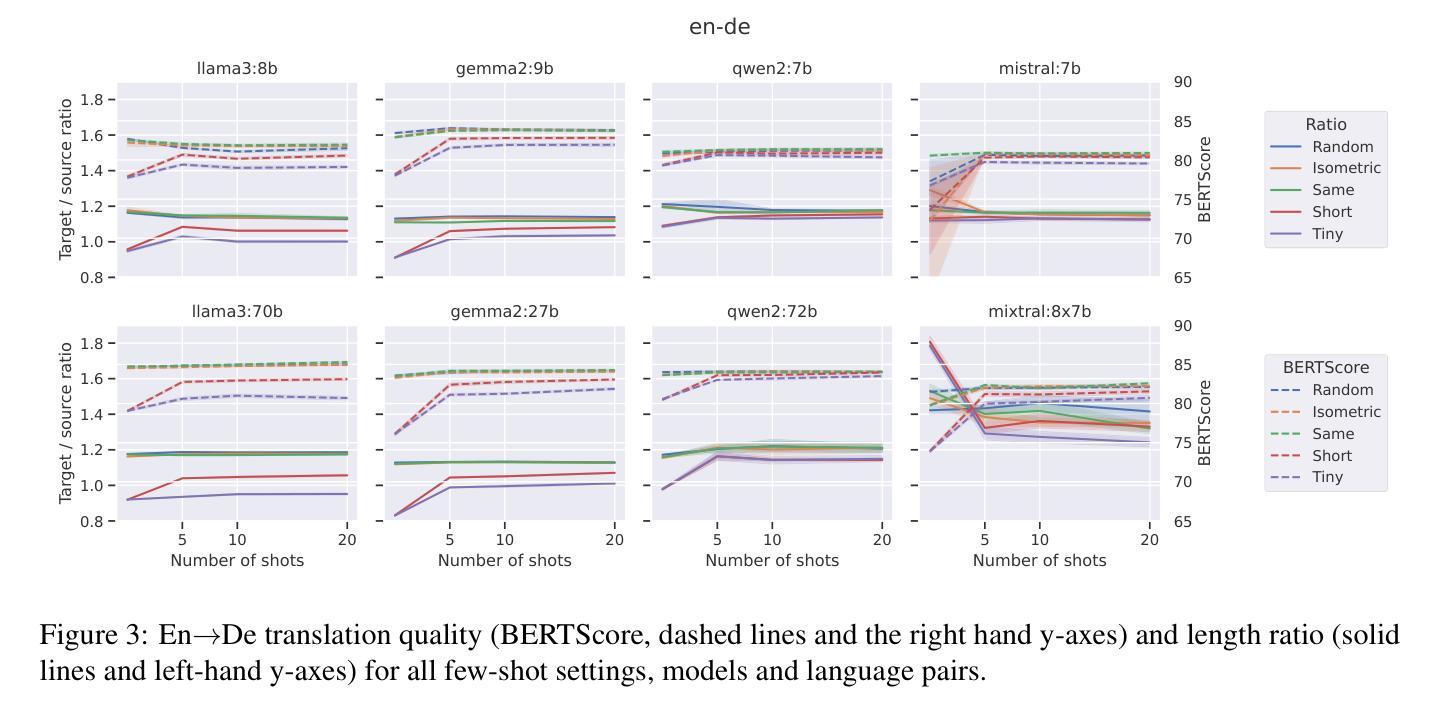
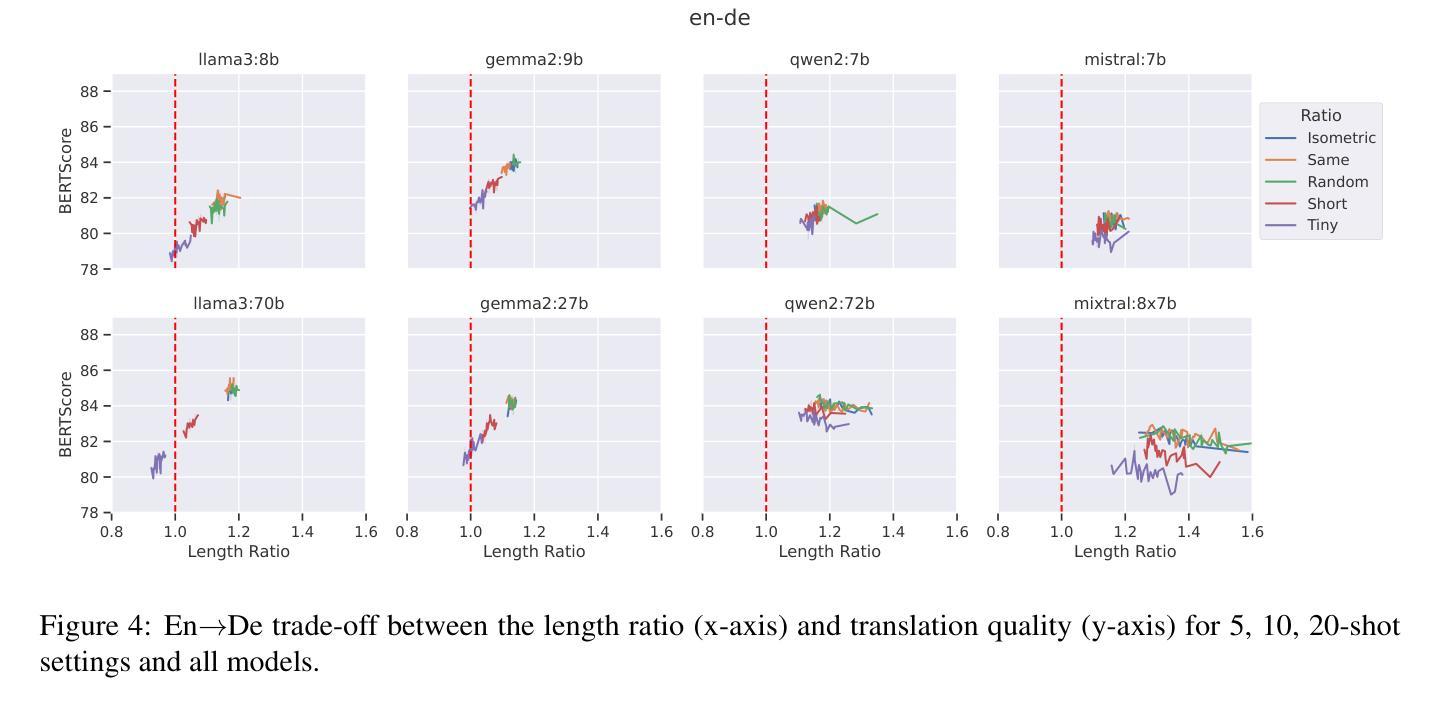
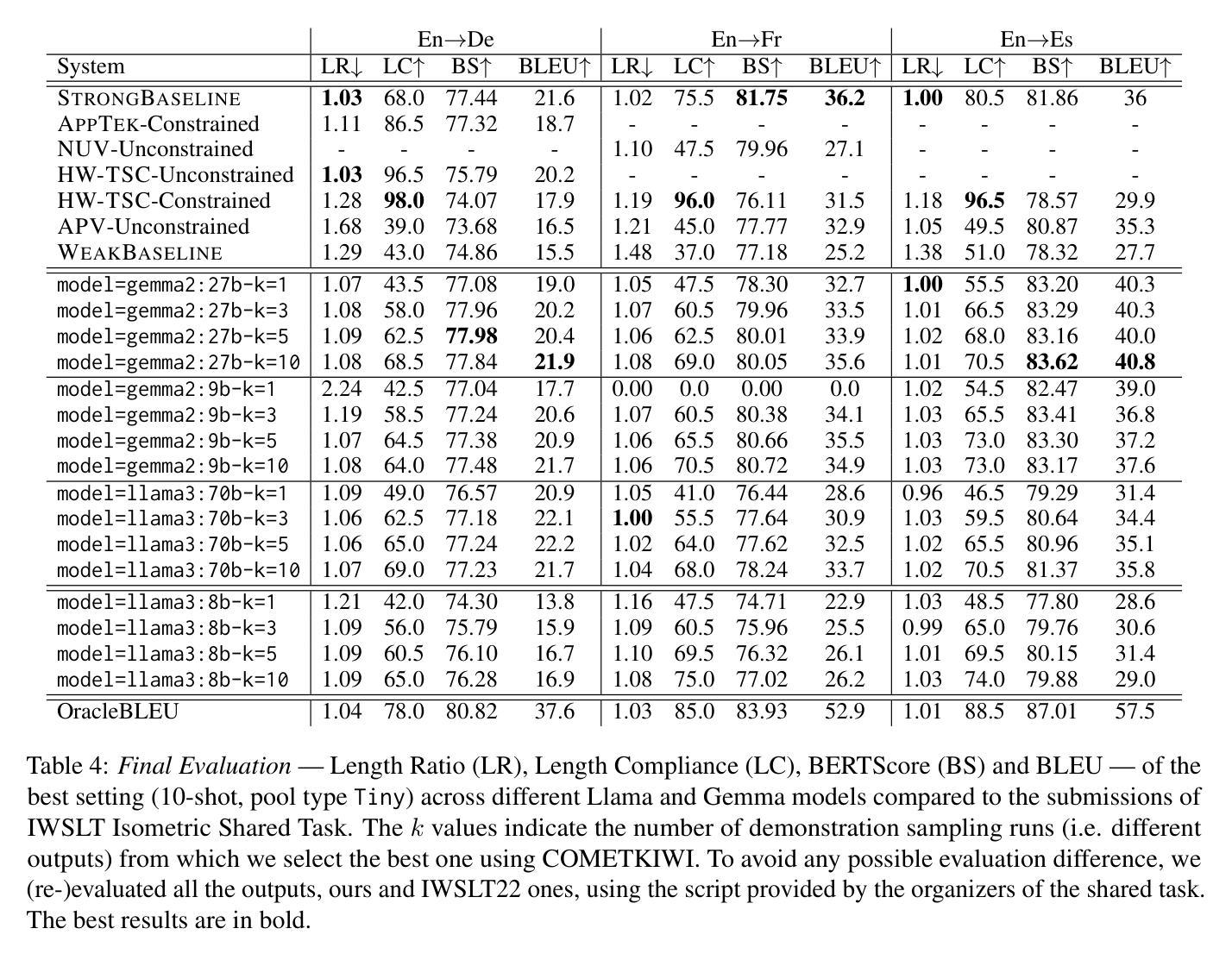
Prompting LLMs: Length Control for Isometric Machine Translation
Authors:Dávid Javorský, Ondřej Bojar, François Yvon
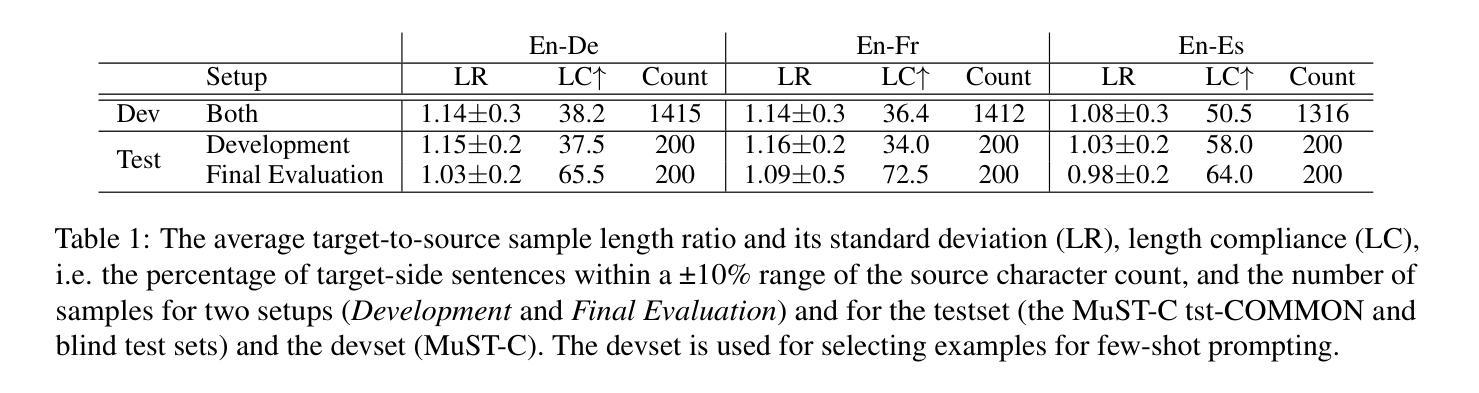
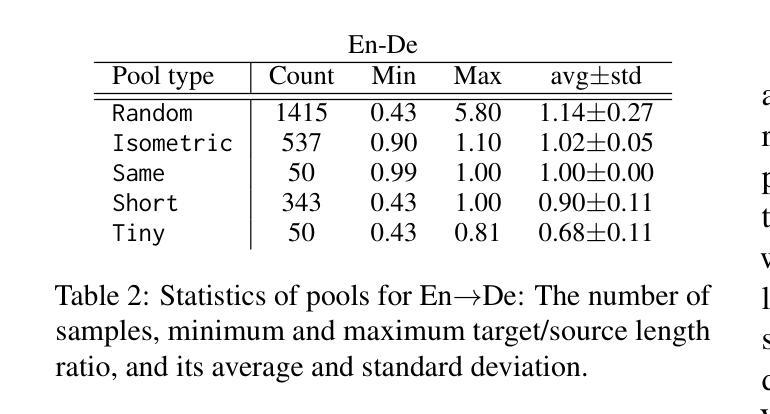
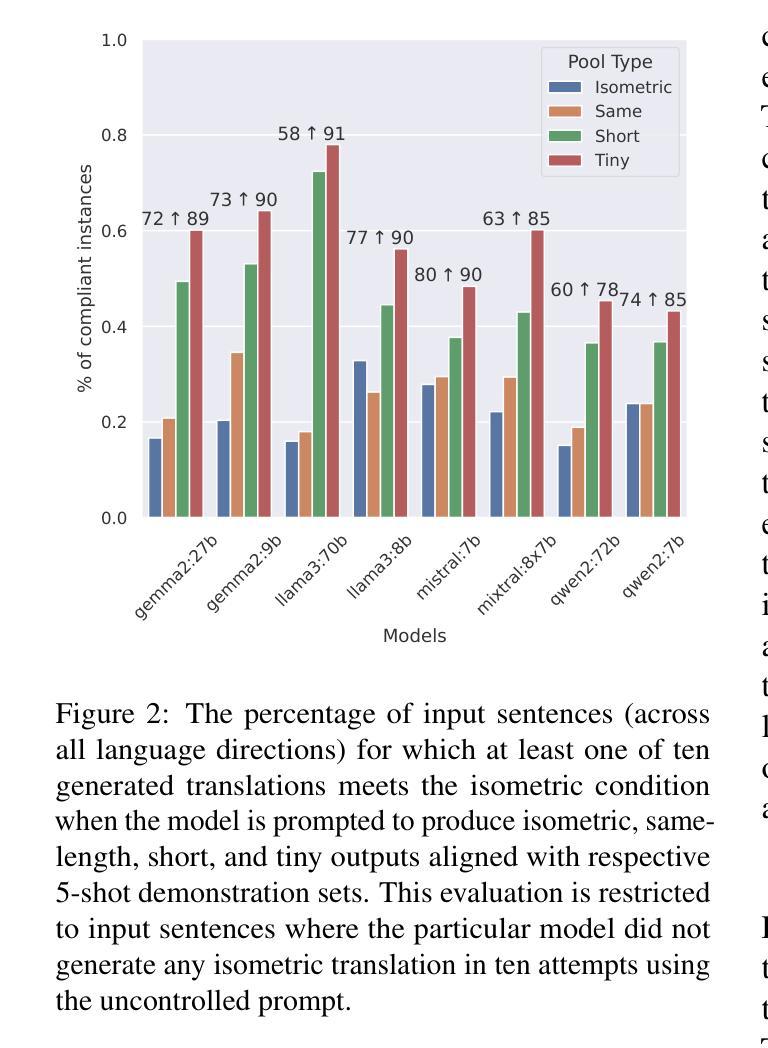
In this study, we explore the effectiveness of isometric machine translation across multiple language pairs (En$\to$De, En$\to$Fr, and En$\to$Es) under the conditions of the IWSLT Isometric Shared Task 2022. Using eight open-source large language models (LLMs) of varying sizes, we investigate how different prompting strategies, varying numbers of few-shot examples, and demonstration selection influence translation quality and length control. We discover that the phrasing of instructions, when aligned with the properties of the provided demonstrations, plays a crucial role in controlling the output length. Our experiments show that LLMs tend to produce shorter translations only when presented with extreme examples, while isometric demonstrations often lead to the models disregarding length constraints. While few-shot prompting generally enhances translation quality, further improvements are marginal across 5, 10, and 20-shot settings. Finally, considering multiple outputs allows to notably improve overall tradeoff between the length and quality, yielding state-of-the-art performance for some language pairs.
在这项研究中,我们在IWSLT等距共享任务2022的条件下,探索了等距机器翻译在多语言对(英语到德语、英语到法语和英语到西班牙语)之间的有效性。我们使用八种开源的大型语言模型(LLM),探讨了不同的提示策略、不同数量的少量示例和演示选择对翻译质量和长度控制的影响。我们发现,当指令的措辞与所提供的演示属性相符时,对输出长度的控制起着至关重要的作用。我们的实验表明,只有当给出极端示例时,LLM才会产生较短的翻译,而等距演示往往导致模型忽略长度约束。虽然少量提示通常可以提高翻译质量,但在5、10和20个示例的设置中,进一步的改进幅度较小。最后,考虑多个输出可以显著改善长度和质量之间的总体权衡,为某些语言对带来最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IWSLT 2025
Summary
本文研究了IWSLT等距共享任务2022条件下,使用八个不同规模的大型语言模型(LLMs)对跨多语言对(如英语至德语、英语至法语和英语至西班牙语)的等距机器翻译的有效性。研究探讨了不同的提示策略、不同数量的少量示例和演示选择如何影响翻译质量和长度控制。实验发现,当指令与提供的演示内容相匹配时,指令措辞对控制输出长度起着至关重要的作用。此外,LLMs往往只在呈现极端示例时才产生较短的翻译,而等距演示往往导致模型忽略长度约束。虽然少量提示通常可以提高翻译质量,但在5、10和20次拍摄设置之间的进一步改进是微不足道的。最后,考虑多个输出可以显著改善长度和质量之间的总体权衡,对某些语言对而言达到了最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- 在IWSLT等距共享任务下,研究了跨多种语言对的等距机器翻译效果。
- 使用八个不同规模的大型语言模型进行实验。
- 研究发现指令措辞与演示内容的匹配对控制输出长度至关重要。
- LLMs在呈现极端示例时产生较短的翻译。
- 等距演示可能导致模型忽略长度约束。
- 少量提示可以提高翻译质量,但进一步提高有限。
点此查看论文截图

Robust Few-Shot Vision-Language Model Adaptation
Authors:Hanxin Wang, Tian Liu, Shu Kong
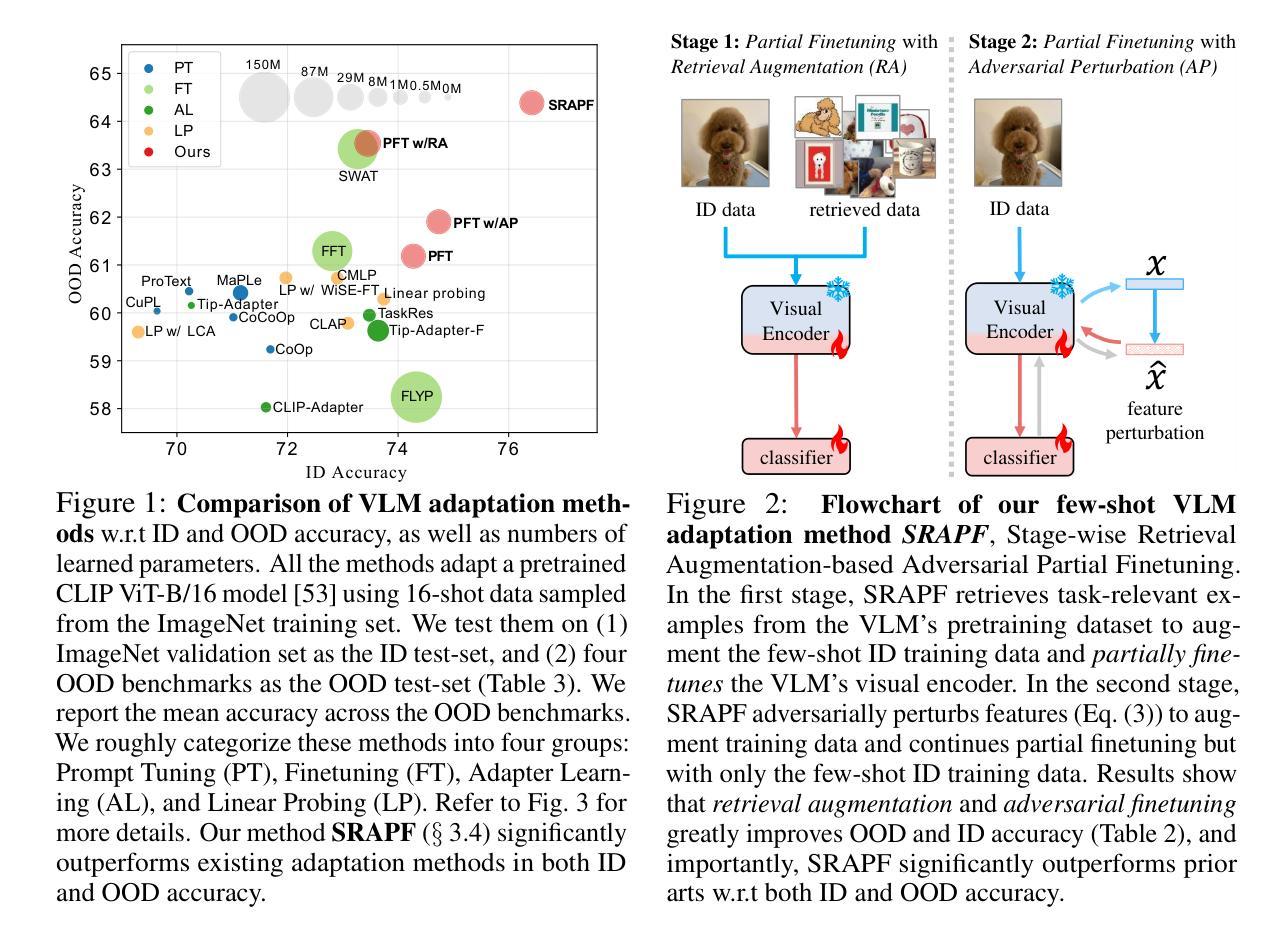
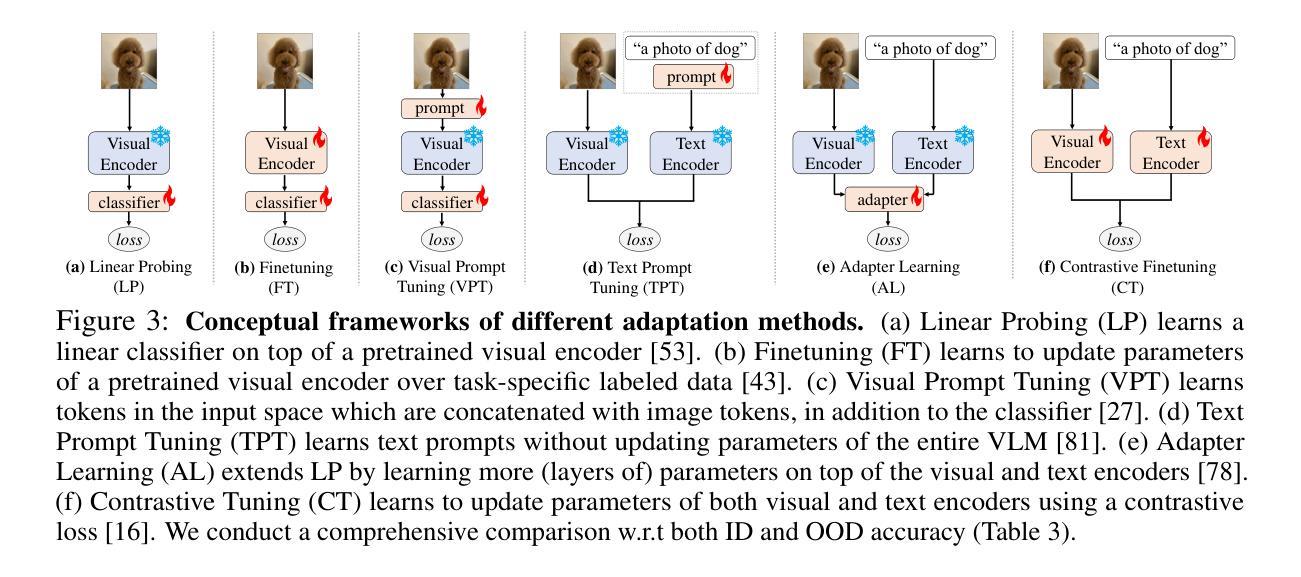
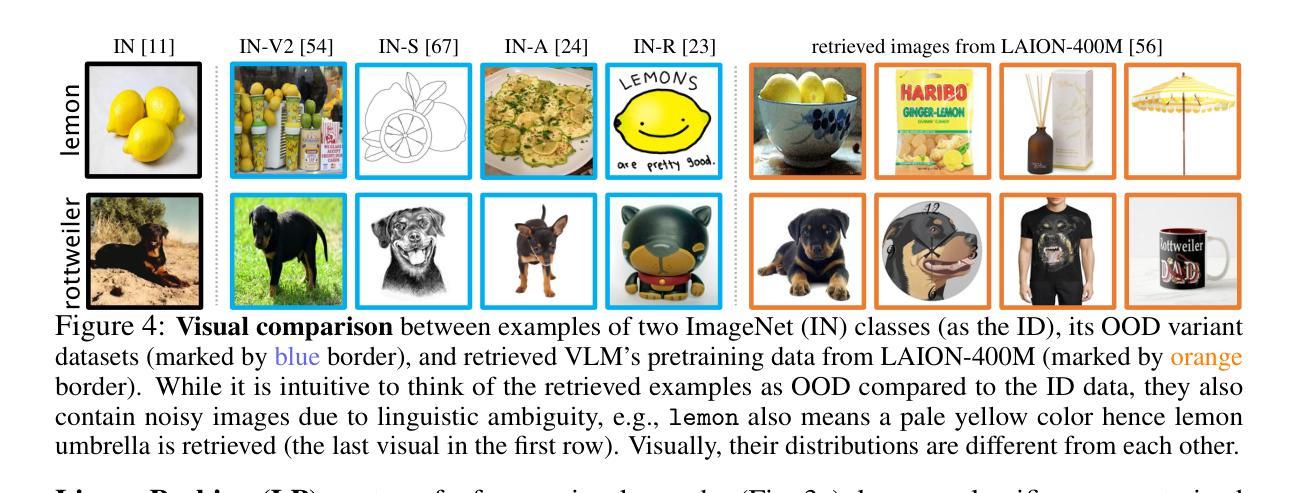
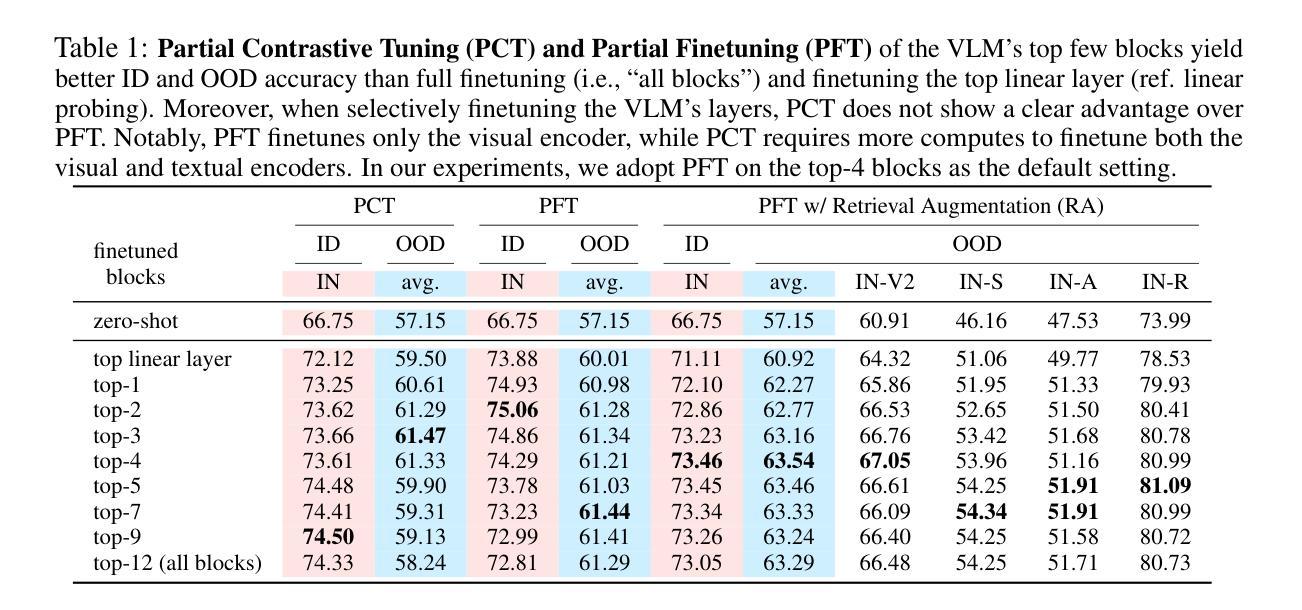
Pretrained VLMs achieve strong performance on downstream tasks when adapted with just a few labeled examples. As the adapted models inevitably encounter out-of-distribution (OOD) test data that deviates from the in-distribution (ID) task-specific training data, enhancing OOD generalization in few-shot adaptation is critically important. We study robust few-shot VLM adaptation, aiming to increase both ID and OOD accuracy. By comparing different adaptation methods (e.g., prompt tuning, linear probing, contrastive finetuning, and full finetuning), we uncover three key findings: (1) finetuning with proper hyperparameters significantly outperforms the popular VLM adaptation methods prompt tuning and linear probing; (2) visual encoder-only finetuning achieves better efficiency and accuracy than contrastively finetuning both visual and textual encoders; (3) finetuning the top layers of the visual encoder provides the best balance between ID and OOD accuracy. Building on these findings, we propose partial finetuning of the visual encoder empowered with two simple augmentation techniques: (1) retrieval augmentation which retrieves task-relevant data from the VLM’s pretraining dataset to enhance adaptation, and (2) adversarial perturbation which promotes robustness during finetuning. Results show that the former/latter boosts OOD/ID accuracy while slightly sacrificing the ID/OOD accuracy. Yet, perhaps understandably, naively combining the two does not maintain their best OOD/ID accuracy. We address this dilemma with the developed SRAPF, Stage-wise Retrieval Augmentation-based Adversarial Partial Finetuning. SRAPF consists of two stages: (1) partial finetuning the visual encoder using both ID and retrieved data, and (2) adversarial partial finetuning with few-shot ID data. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SRAPF achieves the state-of-the-art ID and OOD accuracy on the ImageNet OOD benchmarks.
预训练VLM模型仅在少量标记样本的情况下就能适应下游任务并表现出强大的性能。由于适应的模型不可避免地会遇到偏离特定任务训练数据的分布外(OOD)测试数据,因此在有限样本中提高OOD的泛化能力变得至关重要。我们研究了稳健的少样本VLM适应性训练,旨在提高IN和OOD的准确率。通过对不同的适应性训练方法的比较(如提示调整、线性探测、对比微调以及全微调),我们发现了三个关键观点:(1)使用适当的超参数进行微调显著优于流行的VLM适应性训练方法提示调整和线性探测;(2)仅对视觉编码器进行微调,相比于对比式地同时微调视觉和文本编码器,能更有效地提高效率和准确性;(3)微调视觉编码器的顶层提供了IN和OOD准确率之间的最佳平衡。基于这些发现,我们提出了对视觉编码器进行部分微调,辅以两种简单的增强技术:(1)检索增强技术,它从VLM的预训练数据集中检索任务相关数据以增强适应性;(2)对抗扰动技术,它在微调过程中促进稳健性。结果表明,前者提高了OOD准确性,而后者则提高了IN准确性,但两者同时使用时可能无法保持其最佳的OOD或IN准确性。为解决这一困境,我们开发了基于阶段检索增强的对抗性部分微调(SRAPF)。SRAPF分为两个阶段:(1)使用IN和检索数据对视觉编码器进行部分微调;(2)使用少量的IN数据进行对抗性部分微调。大量实验表明,SRAPF在ImageNet OOD基准测试中实现了最先进的IN和OOD准确率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project website: https://hannawang09.github.io/projects/srapf/
Summary
预训练VLM在少量标注样本的适应下,能在下游任务上实现出色的性能。为了适应不可避免地遇到偏离特定任务训练数据的分布外(OOD)测试数据的问题,提高少样本VLM适应的OOD泛化能力至关重要。本研究旨在提高ID和OOD的准确性。通过比较不同的适应方法,我们发现全参数微调能显著优于流行的VLM适应方法,如提示微调线性探测和对比微调;仅微调视觉编码器比对比微调视觉和文本编码器更有效且准确;微调视觉编码器的顶层在ID和OOD准确性之间提供了最佳的平衡。基于这些发现,我们提出了对视觉编码器的部分微调,并结合两种简单的增强技术:检索增强和对抗扰动。最后为了解决二者结合的困境提出了SRAPF(基于阶段检索增强的对抗性部分微调)。SRAPF包含两个阶段,能在ImageNet OOD基准测试中实现最佳的ID和OOD准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练VLM模型在少样本适应下表现出色,特别是在下游任务上。
- 增强少样本VLM适应的OOD泛化至关重要。
- 全参数微调是一种有效的VLM适应方法,优于提示微调、线性探测和对比微调。
- 仅微调视觉编码器既提高了效率又提高了准确性。
- 检索增强技术能提高OOD准确性,而对抗扰动则促进模型在微调过程中的稳健性。
- 合并两种增强技术需要解决的最佳策略是使用SRAPF(基于阶段检索增强的对抗性部分微调)。
点此查看论文截图

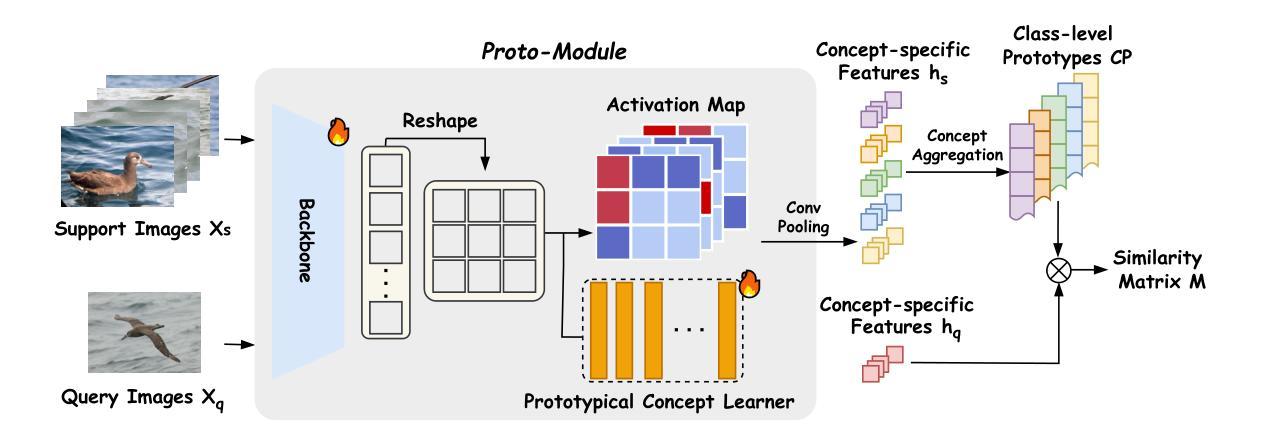
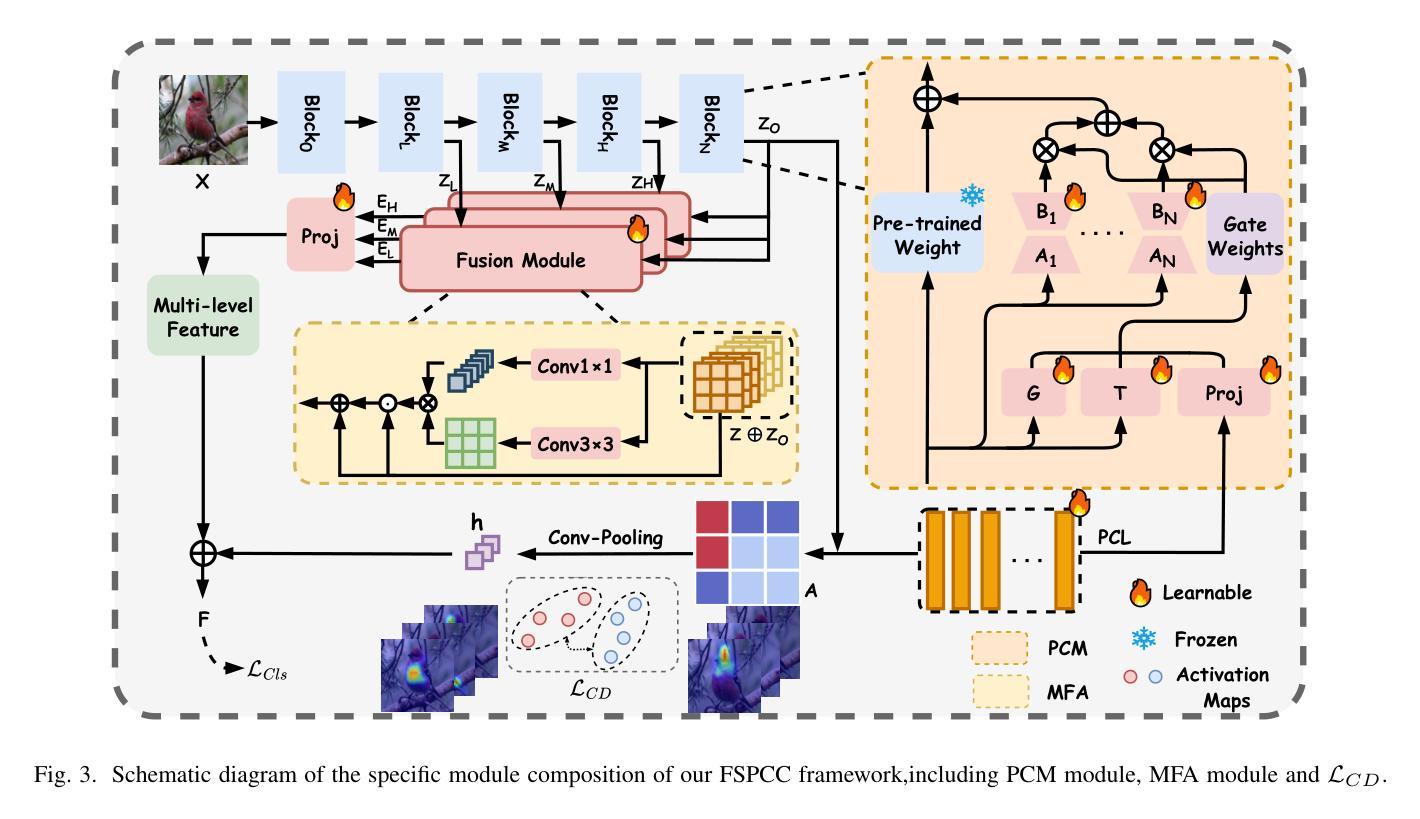
Interpretable Few-Shot Image Classification via Prototypical Concept-Guided Mixture of LoRA Experts
Authors:Zhong Ji, Rongshuai Wei, Jingren Liu, Yanwei Pang, Jungong Han
Self-Explainable Models (SEMs) rely on Prototypical Concept Learning (PCL) to enable their visual recognition processes more interpretable, but they often struggle in data-scarce settings where insufficient training samples lead to suboptimal performance.To address this limitation, we propose a Few-Shot Prototypical Concept Classification (FSPCC) framework that systematically mitigates two key challenges under low-data regimes: parametric imbalance and representation misalignment. Specifically, our approach leverages a Mixture of LoRA Experts (MoLE) for parameter-efficient adaptation, ensuring a balanced allocation of trainable parameters between the backbone and the PCL module.Meanwhile, cross-module concept guidance enforces tight alignment between the backbone’s feature representations and the prototypical concept activation patterns.In addition, we incorporate a multi-level feature preservation strategy that fuses spatial and semantic cues across various layers, thereby enriching the learned representations and mitigating the challenges posed by limited data availability.Finally, to enhance interpretability and minimize concept overlap, we introduce a geometry-aware concept discrimination loss that enforces orthogonality among concepts, encouraging more disentangled and transparent decision boundaries.Experimental results on six popular benchmarks (CUB-200-2011, mini-ImageNet, CIFAR-FS, Stanford Cars, FGVC-Aircraft, and DTD) demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms existing SEMs by a notable margin, with 4.2%-8.7% relative gains in 5-way 5-shot classification.These findings highlight the efficacy of coupling concept learning with few-shot adaptation to achieve both higher accuracy and clearer model interpretability, paving the way for more transparent visual recognition systems.
自解释模型(SEMs)依赖于原型概念学习(PCL)来使其视觉识别过程更具可解释性,但在数据稀缺的环境中,由于训练样本不足导致性能不佳,它们经常面临挑战。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了一个Few-Shot原型概念分类(FSPCC)框架,该框架系统地减轻了低数据环境下的两个关键挑战:参数不平衡和表示不匹配。具体来说,我们的方法利用LoRA专家混合物(MoLE)进行参数有效的适应,确保在主干和PCL模块之间分配可训练参数的平衡。同时,跨模块概念引导强制执行主干特征表示与原型概念激活模式之间的紧密对齐。此外,我们采用了一种多层次特征保留策略,融合了各层中的空间和语义线索,从而丰富了学习的表示并减轻了有限数据可用性所带来的挑战。最后,为了提高可解释性并最小化概念重叠,我们引入了一种几何感知概念判别损失,该损失强制执行概念之间的正交性,鼓励更解耦和透明的决策边界。在六个流行基准测试(CUB-200-2011、mini-ImageNet、CIFAR-FS、Stanford Cars、FGVC-Aircraft和DTD)上的实验结果表明,我们的方法在所有情况下均显著优于现有SEM,在5路5分类射击分类中相对提高了4.2%-8.7%。这些发现表明将概念学习与少镜头适应相结合以实现更高的准确性和更清晰的模型可解释性是有效的,这为更透明的视觉识别系统铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages,5 figures
Summary
本文提出了一个Few-Shot Prototypical Concept Classification(FSPCC)框架,解决了数据稀缺环境下自我解释模型(SEMs)面临的问题。通过利用混合LoRA专家(MoLE)进行参数高效适应,以及跨模块概念引导和多层次特征保留策略,该框架提高了模型的性能。同时,引入几何感知概念判别损失,增强了解释性并减少概念重叠。实验结果表明,该框架在多个数据集上均显著优于现有SEMs,为耦合概念学习与少样本适应以实现更高精度和更清晰模型解释铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了Few-Shot Prototypical Concept Classification (FSPCC) 框架以解决数据稀缺环境中SEMs的问题。
- 通过混合LoRA专家(MoLE)实现参数高效适应,平衡分配可训练参数。
- 跨模块概念引导确保特征表示与原型概念激活模式紧密对齐。
- 采用多层次特征保留策略,融合空间语义线索,丰富学习到的表示并应对数据有限挑战。
- 引入几何感知概念判别损失,增强模型解释性和概念之间的正交性。
- 实验结果在多数据集上表明FSPCC框架显著优于现有SEMs。
点此查看论文截图

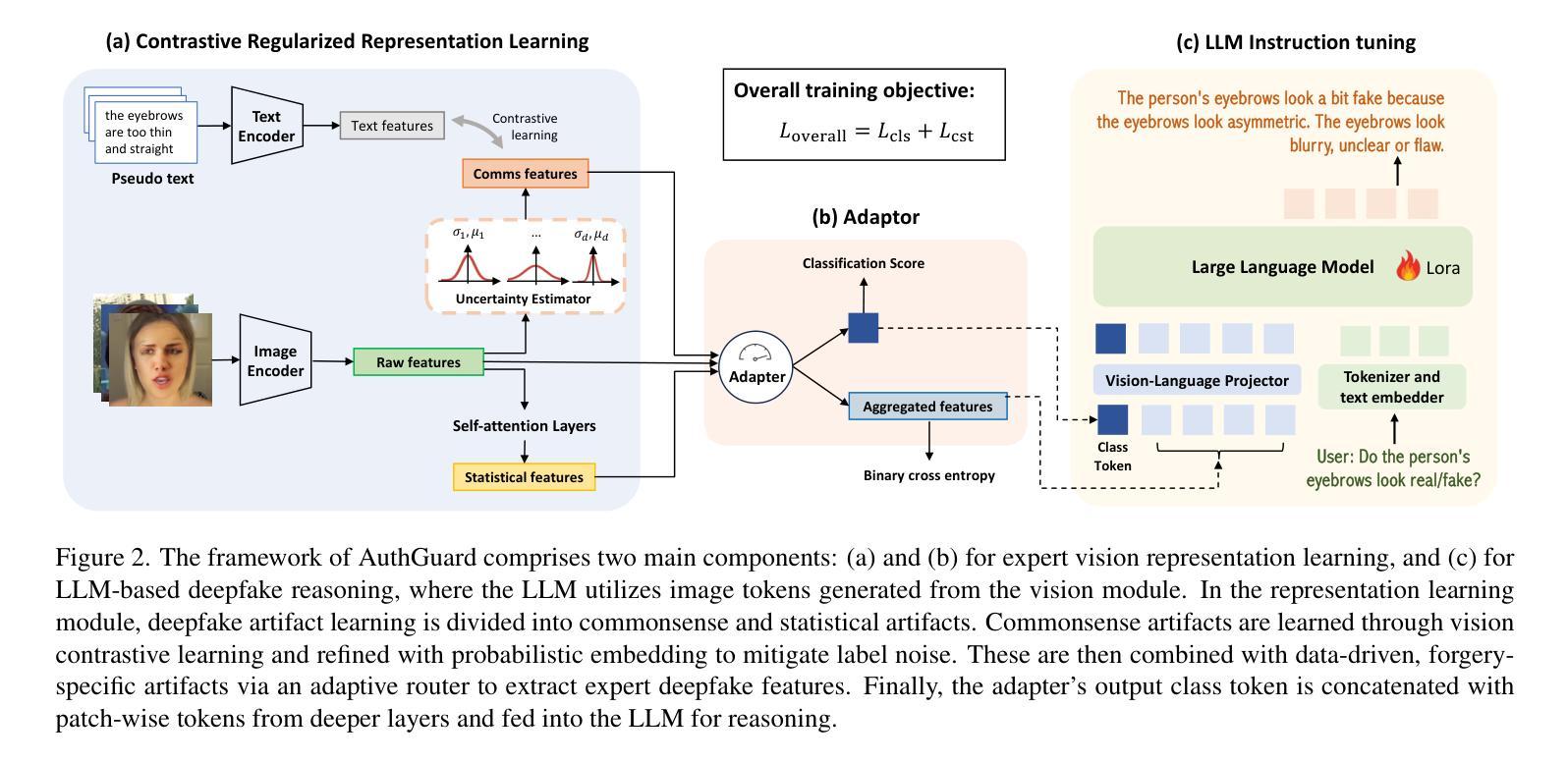
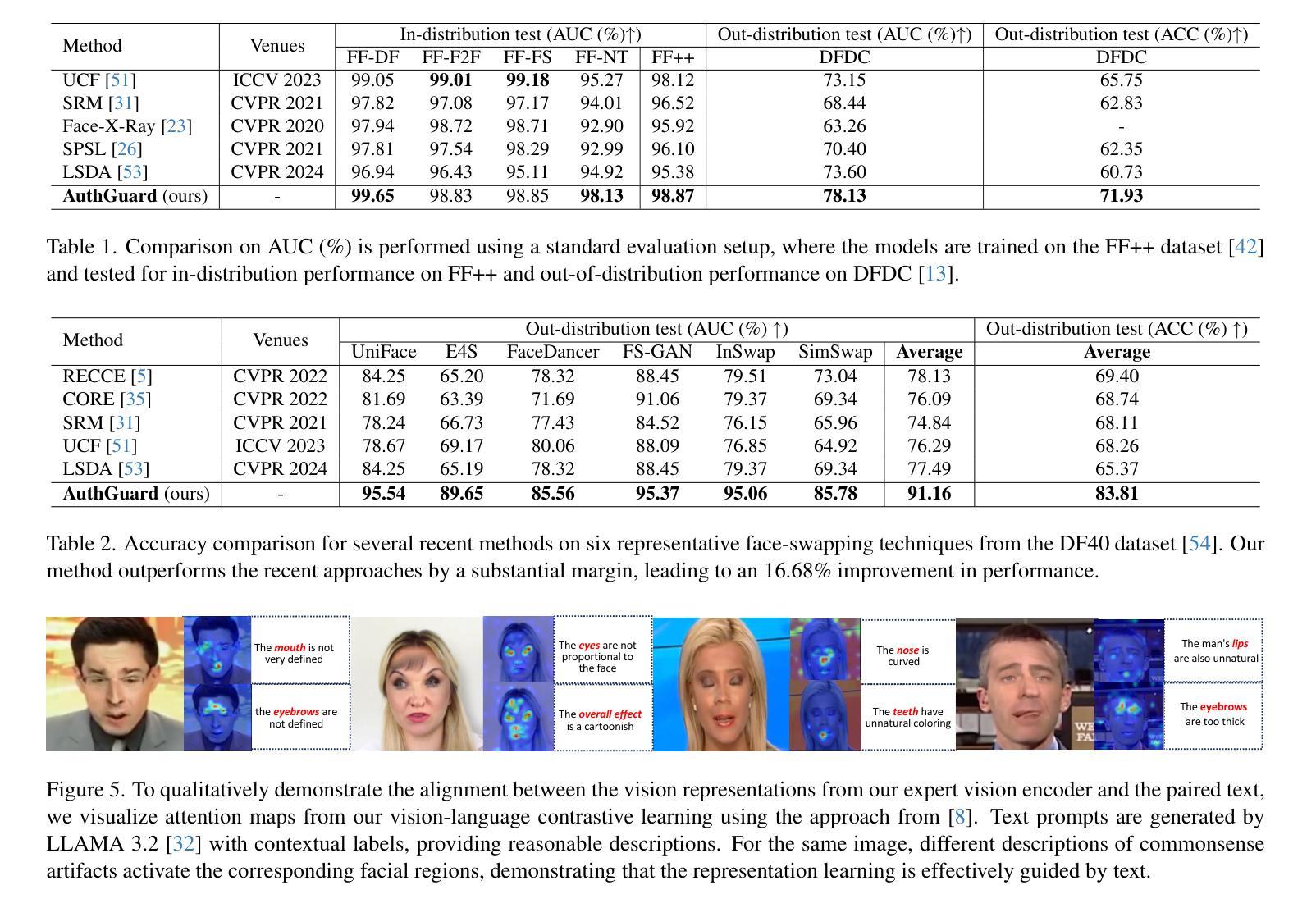
AuthGuard: Generalizable Deepfake Detection via Language Guidance
Authors:Guangyu Shen, Zhihua Li, Xiang Xu, Tianchen Zhao, Zheng Zhang, Dongsheng An, Zhuowen Tu, Yifan Xing, Qin Zhang
Existing deepfake detection techniques struggle to keep-up with the ever-evolving novel, unseen forgeries methods. This limitation stems from their reliance on statistical artifacts learned during training, which are often tied to specific generation processes that may not be representative of samples from new, unseen deepfake generation methods encountered at test time. We propose that incorporating language guidance can improve deepfake detection generalization by integrating human-like commonsense reasoning – such as recognizing logical inconsistencies and perceptual anomalies – alongside statistical cues. To achieve this, we train an expert deepfake vision encoder by combining discriminative classification with image-text contrastive learning, where the text is generated by generalist MLLMs using few-shot prompting. This allows the encoder to extract both language-describable, commonsense deepfake artifacts and statistical forgery artifacts from pixel-level distributions. To further enhance robustness, we integrate data uncertainty learning into vision-language contrastive learning, mitigating noise in image-text supervision. Our expert vision encoder seamlessly interfaces with an LLM, further enabling more generalized and interpretable deepfake detection while also boosting accuracy. The resulting framework, AuthGuard, achieves state-of-the-art deepfake detection accuracy in both in-distribution and out-of-distribution settings, achieving AUC gains of 6.15% on the DFDC dataset and 16.68% on the DF40 dataset. Additionally, AuthGuard significantly enhances deepfake reasoning, improving performance by 24.69% on the DDVQA dataset.
现有深度伪造检测技术难以跟上不断演变的全新和未知伪造方法。这一局限性源于它们依赖于训练过程中学习的统计特征,这些特征通常与特定的生成过程相关联,可能无法代表测试时遇到的新未知深度伪造生成方法的样本。我们提出,通过融入语言指导可以改善深度伪造检测的泛化能力,方法是结合人类常识推理,如识别逻辑不一致和感知异常等,同时辅以统计线索。为此,我们通过结合判别分类和图像文本对比学习来训练专业的深度伪造视觉编码器。其中文本是由通用MLLM通过少量提示生成的。这使得编码器能够从像素级分布中提取语言可描述、常识性的深度伪造特征和统计伪造特征。为了进一步提高稳健性,我们将数据不确定性学习整合到视觉语言对比学习中,减轻图像文本监督中的噪声。我们的专业视觉编码器无缝地接口与大型语言模型,进一步实现了更通用和可解释的深度伪造检测,同时提高了准确性。所得到的框架AuthGuard在内外分布环境中均达到了最先进的深度伪造检测准确率,在DFDC数据集上AUC增益达6.15%,在DF40数据集上达16.68%。此外,AuthGuard显著提高了深度伪造推理能力,在DDVQA数据集上的性能提高24.69%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着深度伪造技术的不断发展,现有检测手段难以应对新型、未见过的伪造方法。为此,本文提出结合语言指导提高深度伪造检测的泛化能力,通过集成人类常识推理,如逻辑不一致和感知异常的认识,以及统计线索。通过训练深度伪造视觉编码器,结合判别分类和图像文本对比学习,利用少量提示生成文本。这允许编码器从像素级分布中提取语言可描述的常识性深度伪造伪迹和统计伪造伪迹。为了进一步增加稳健性,本文还将数据不确定性学习融入视觉语言对比学习,减轻图像文本监督中的噪声。本文的专家视觉编码器与大型语言模型无缝对接,更通用、可解释的深度伪造检测在提高了准确性的同时。所得到的框架AuthGuard在内外分布设置中实现了最先进的深度伪造检测精度,在DFDC数据集上AUC增益达6.15%,在DF40数据集上增益达16.68%。此外,AuthGuard还显著提高了深度伪造推理性能,在DDVQA数据集上的性能提高了24.69%。
Key Takeaways
- 现有深度伪造检测技术面临挑战,难以应对新型未见过的伪造方法。
- 结合语言指导提高深度伪造检测的泛化能力,通过集成人类常识推理。
- 通过训练深度伪造视觉编码器,结合判别分类与图像文本对比学习。
- 编码器可提取语言可描述的常识性深度伪造伪迹和统计伪造伪迹。
- 集成数据不确定性学习增强稳健性,减轻图像文本监督中的噪声。
- 专家视觉编码器与大型语言模型无缝对接,提高深度伪造检测的准确性和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


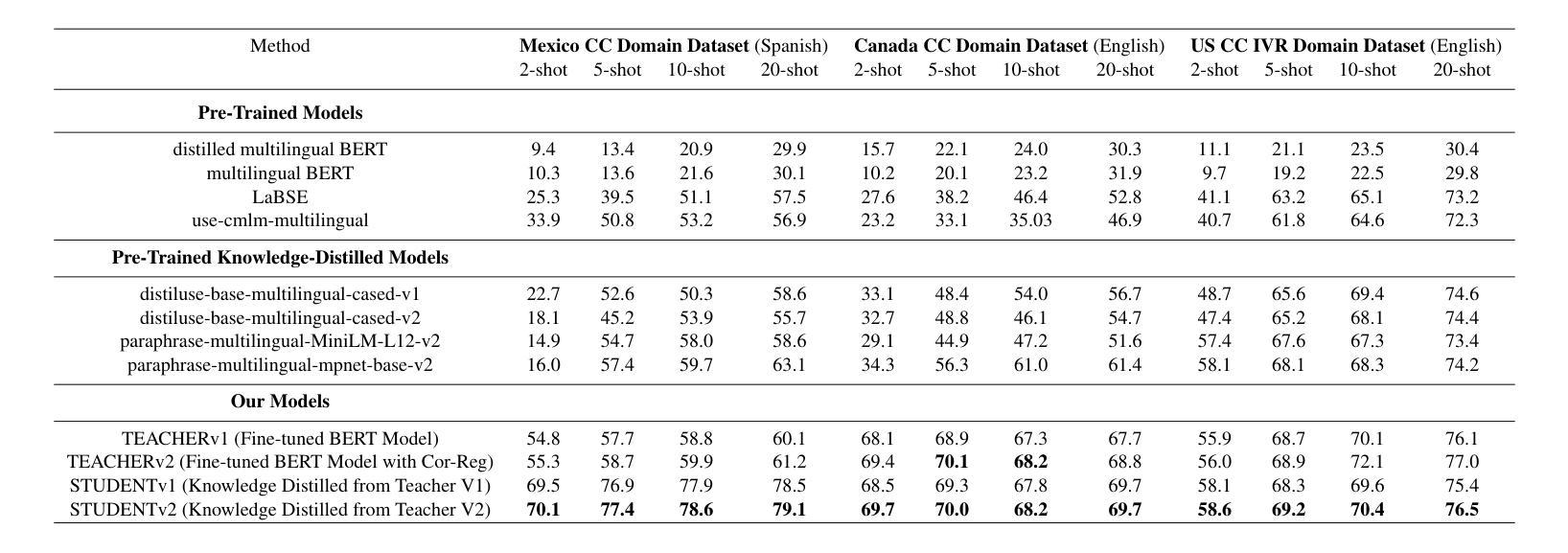
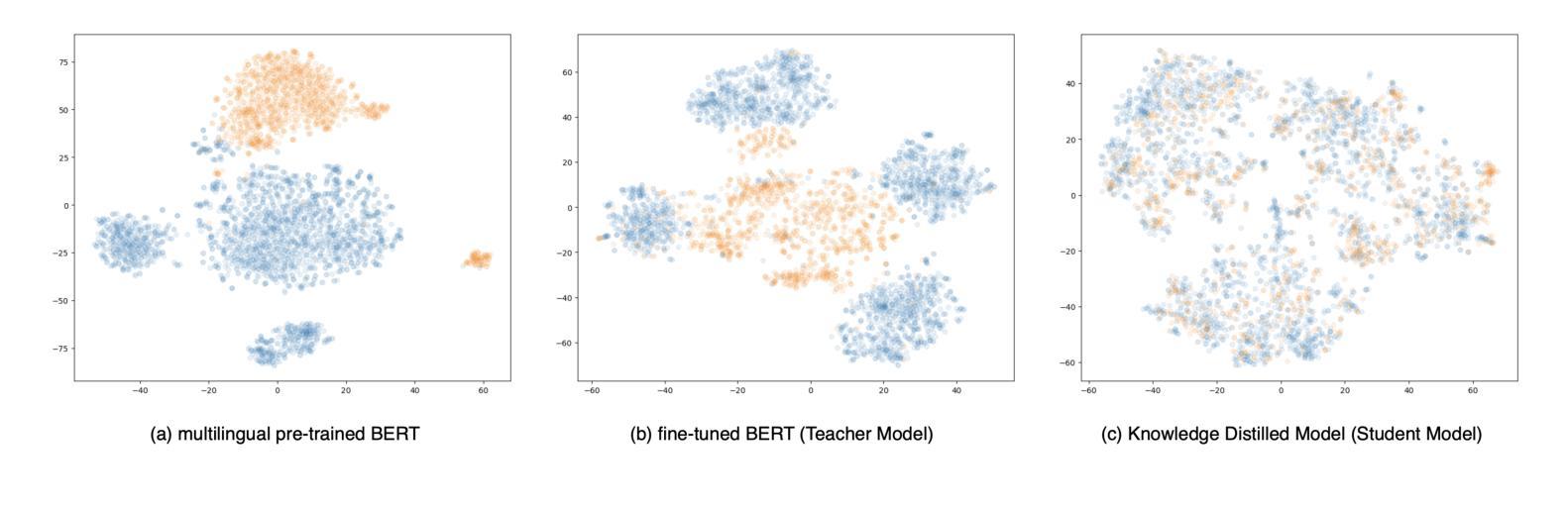
Building a Few-Shot Cross-Domain Multilingual NLU Model for Customer Care
Authors:Saurabh Kumar, Sourav Bansal, Neeraj Agrawal, Priyanka Bhatt
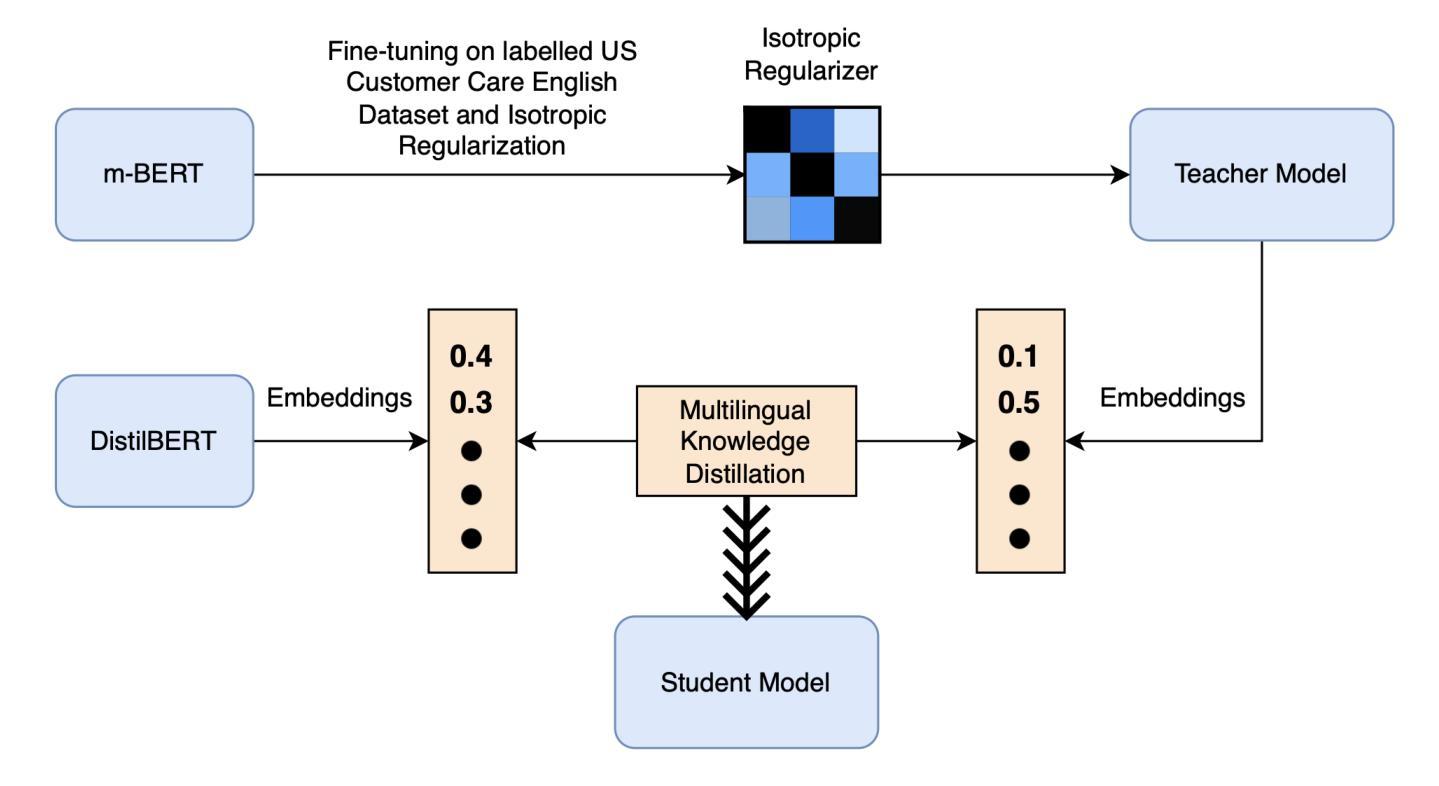
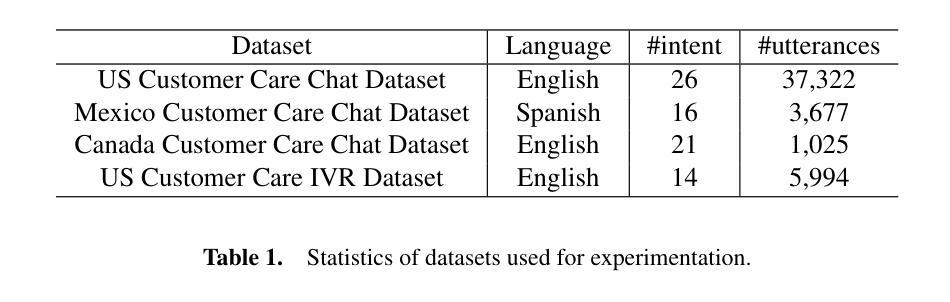
Customer care is an essential pillar of the e-commerce shopping experience with companies spending millions of dollars each year, employing automation and human agents, across geographies (like US, Canada, Mexico, Chile), channels (like Chat, Interactive Voice Response (IVR)), and languages (like English, Spanish). SOTA pre-trained models like multilingual-BERT, fine-tuned on annotated data have shown good performance in downstream tasks relevant to Customer Care. However, model performance is largely subject to the availability of sufficient annotated domain-specific data. Cross-domain availability of data remains a bottleneck, thus building an intent classifier that generalizes across domains (defined by channel, geography, and language) with only a few annotations, is of great practical value. In this paper, we propose an embedder-cum-classifier model architecture which extends state-of-the-art domain-specific models to other domains with only a few labeled samples. We adopt a supervised fine-tuning approach with isotropic regularizers to train a domain-specific sentence embedder and a multilingual knowledge distillation strategy to generalize this embedder across multiple domains. The trained embedder, further augmented with a simple linear classifier can be deployed for new domains. Experiments on Canada and Mexico e-commerce Customer Care dataset with few-shot intent detection show an increase in accuracy by 20-23% against the existing state-of-the-art pre-trained models.
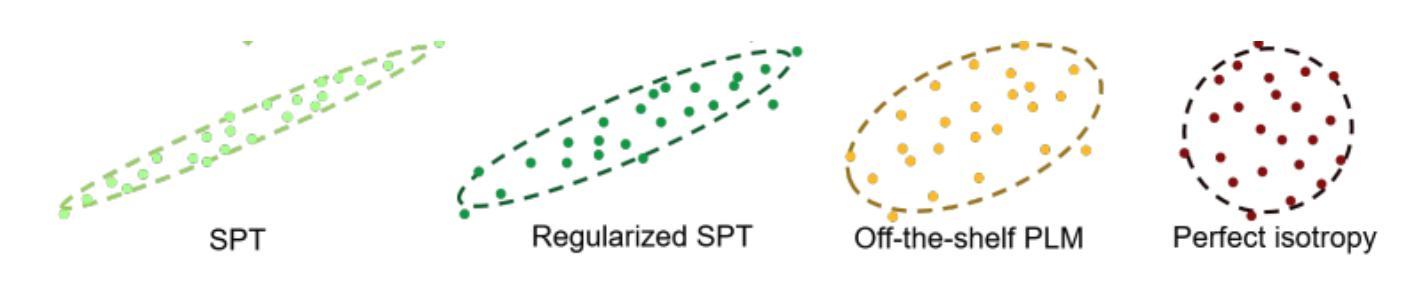
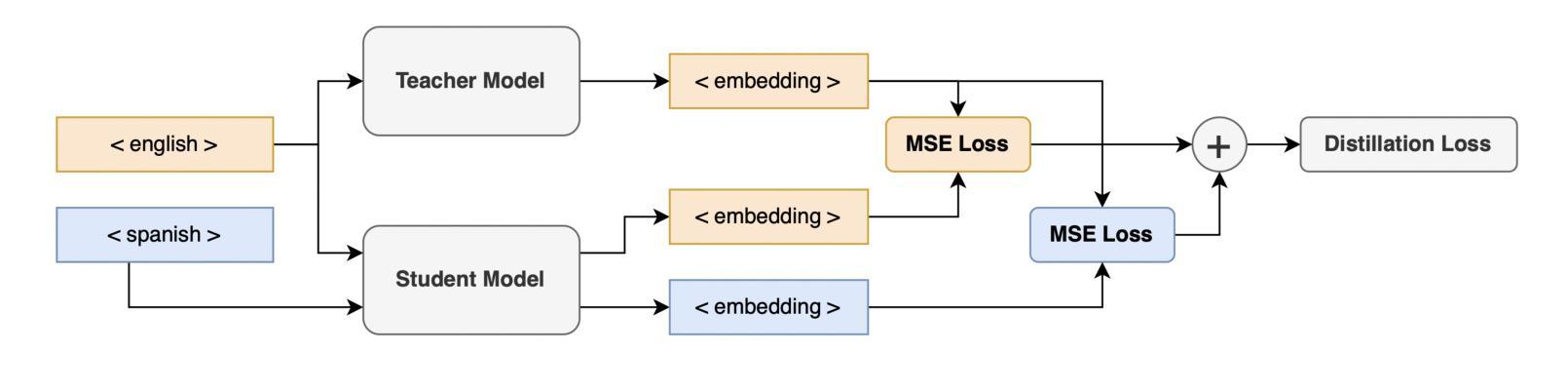
客户服务是电子商务购物体验的重要支柱,公司每年花费数百万美元,跨越地理区域(如美国、加拿大、墨西哥、智利)、渠道(如聊天、交互式语音响应(IVR)和语言(如英语、西班牙语)采用自动化和人工代理。使用预训练模型如多语言BERT,并在注释数据上进行微调,在与客户服务相关的下游任务中表现出良好性能。然而,模型性能在很大程度上取决于足够的注释领域特定数据的可用性。跨域数据的可用性仍然是一个瓶颈,因此,建立一个仅使用少量注释即可跨领域(由渠道、地理和语言定义)推广的意图分类器,具有巨大的实用价值。在本文中,我们提出了一种嵌入分类器模型架构,该架构将最先进领域特定的模型推广到少数样本的其它领域。我们采用带有同构正则化的监督微调方法来训练特定领域的句子嵌入器,并采用多语言知识蒸馏策略使该嵌入器跨多个领域进行推广。经过训练的嵌入器进一步与一个简单线性分类器结合,可用于新领域。在加拿大和墨西哥电子商务客户服务数据集上进行的小样本意图检测实验表明,与现有的最先进的预训练模型相比,准确率提高了20%-23%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了客户关怀在电子商务购物体验中的重要性,并指出企业在不同的地理区域、渠道和语言上投入巨资。当前最先进的预训练模型如多语言BERT在客户关怀相关下游任务中表现出良好性能,但模型性能很大程度上取决于充足的注释领域数据的可用性。针对跨领域数据可用性的瓶颈,本文提出了一种嵌入分类器模型架构,该架构仅使用少量标注样本即可将最先进的领域特定模型扩展到其他领域。通过采用带有同构正则化的监督微调方法来训练领域特定的句子嵌入器,以及采用多语言知识蒸馏策略来使嵌入器跨多个领域进行概括。将经过训练的嵌入器进一步配合简单的线性分类器部署到新的领域中。在加拿大和墨西哥电子商务客户关怀数据集上的少量意图检测实验表明,与现有的最先进的预训练模型相比,准确率提高了20-23%。
Key Takeaways
- 客户关怀在电子商务中扮演着重要角色,企业为此投入巨大。
- 先进的预训练模型如多语言BERT在客户关怀相关任务中表现良好,但受限于注释领域数据的可用性。
- 跨领域数据可用性是瓶颈,需要模型能够在少量标注样本下跨领域进行推广。
- 提出的嵌入分类器模型架构能够通过监督微调方法训练领域特定的句子嵌入器。
- 采用多语言知识蒸馏策略使嵌入器跨多个领域进行概括。
- 训练的嵌入器配合简单的线性分类器可部署到新的领域中。
点此查看论文截图

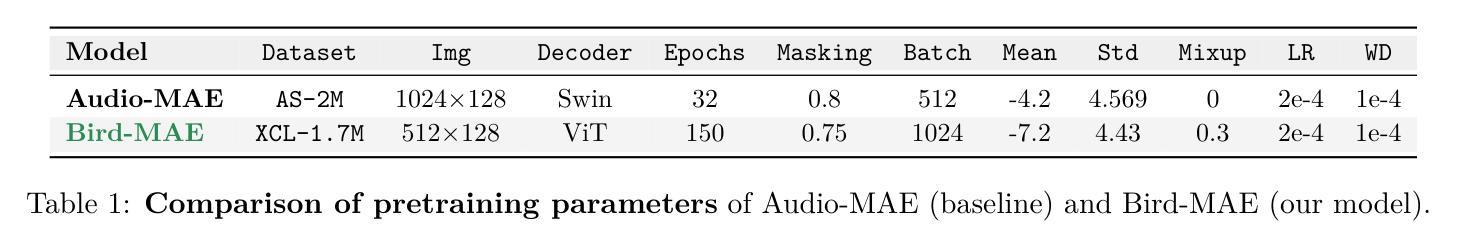
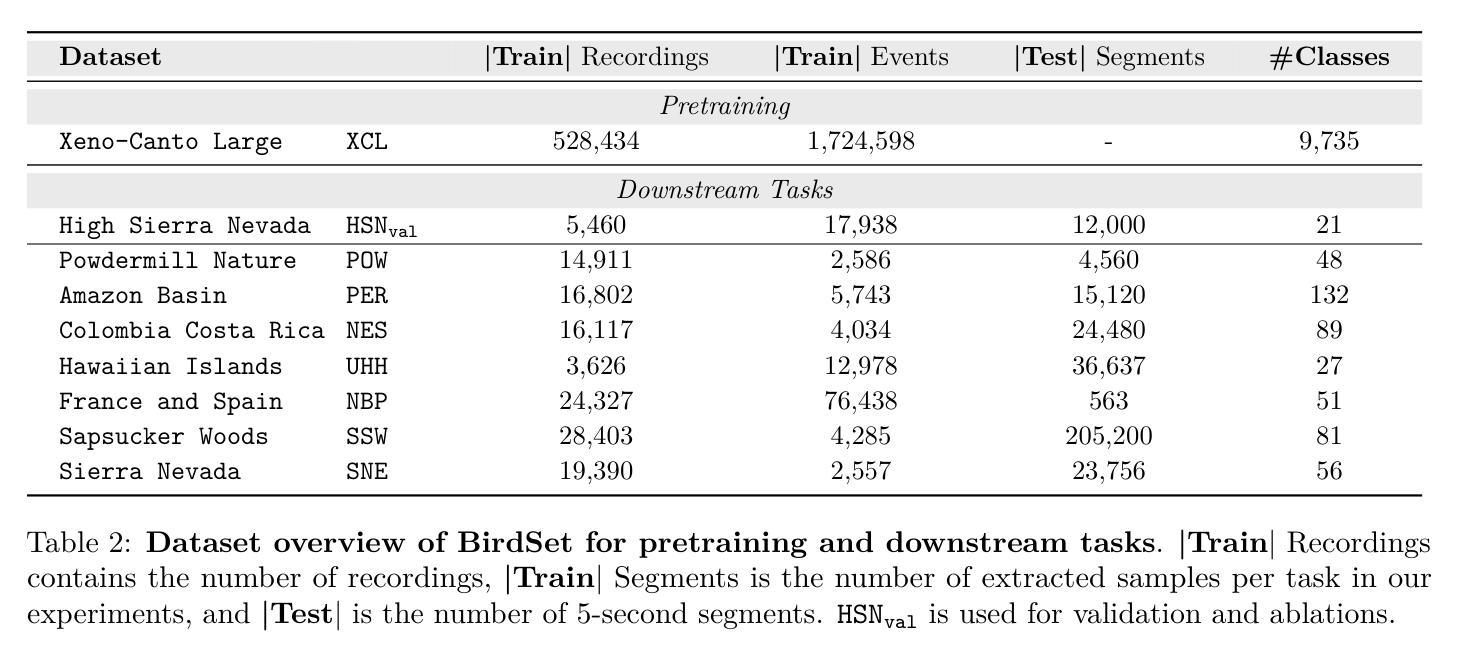
Can Masked Autoencoders Also Listen to Birds?
Authors:Lukas Rauch, René Heinrich, Ilyass Moummad, Alexis Joly, Bernhard Sick, Christoph Scholz
Masked Autoencoders (MAEs) have shown competitive results in audio classification by learning rich semantic representations through an efficient self-supervised reconstruction task. However, general-purpose models fail to generalize well when applied directly to fine-grained audio domains. Specifically, bird-sound classification requires distinguishing subtle inter-species differences and managing high intra-species acoustic variability, thereby revealing the performance limitations of general-domain Audio-MAE models. This work demonstrates that bridging this domain gap requires more than domain-specific pretraining data; adapting the entire training pipeline is crucial. We systematically revisit and adapt the pretraining recipe, fine-tuning methods, and frozen feature utilization to bird sounds using BirdSet, a large-scale bioacoustic dataset comparable to AudioSet. Our resulting Bird-MAE achieves new state-of-the-art results in BirdSet’s multi-label classification benchmark. Additionally, we introduce the parameter-efficient prototypical probing, enhancing the utility of frozen MAE representations and closely approaching fine-tuning performance in low-resource settings. Bird-MAE’s prototypical probes outperform linear probing by up to 37%$_\text{p}$ in MAP and narrow the gap to fine-tuning to approximately 3.3%$_\text{p}$ on average across BirdSet downstream tasks. Bird-MAE also demonstrates robust few-shot capabilities with prototypical probing in our newly established few-shot benchmark on BirdSet, highlighting the potential of tailored self-supervised learning pipelines for fine-grained audio domains.
基于Masked Autoencoders(MAEs)在音频分类中展现了出色的结果,它通过高效的自监督重建任务学习丰富的语义表示。然而,当通用模型直接应用于细粒度音频域时,其泛化能力较差。具体来说,鸟类声音分类需要区分物种间的细微差异并应对高物种内部的声音变化,从而揭示了通用领域音频MAE模型的性能局限性。这项工作表明,缩小这一领域差距不仅需要特定领域的预训练数据;调整整个训练管道也至关重要。我们系统地回顾并适应了预训练配方、微调方法以及使用BirdSet(一个与AudioSet相当的大规模生物声学数据集)的鸟类声音的冻结特征利用。我们得到的Bird-MAE在BirdSet的多标签分类基准测试中取得了最新成果。此外,我们引入了参数高效的原型探测,增强了冻结MAE表示的实用性,并在低资源环境中接近微调性能。Bird-MAE的原型探针在MAP中的表现比线性探针高出最多37%,并缩小了在BirdSet下游任务上的微调差距,平均约达3.3%。Bird-MAE还在我们新建立的BirdSet少样本基准测试中展示了强大的少样本能力,突显了针对细粒度音频领域量身定制的自监督学习管道的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF under review @TMLR
Summary
本文介绍了Masked Autoencoders(MAEs)在音频分类中的竞争性能,尤其是在鸟声分类中的应用。研究发现在精细粒度音频领域,通用模型存在局限性。为了克服这一局限性,本研究重新设计并优化了预训练配方、微调方法和冻结特征的利用方式,以适应鸟声数据。同时引入了参数高效的原型探测技术,提高了冻结MAE表示的实用性,并在低资源环境中接近微调性能。最终,Bird-MAE模型在BirdSet多标签分类基准测试中取得了最新先进成果。
Key Takeaways
- Masked Autoencoders (MAEs) 在音频分类中展现出竞争力,特别是在鸟声分类中的应用。
- 通用模型在精细粒度音频领域存在局限性,需要针对特定领域进行优化。
- 研究重新设计了预训练配方、微调方法和冻结特征的利用方式,以适应鸟声数据。
- 引入了参数高效的原型探测技术,提高了冻结MAE表示的实用性。
- Bird-MAE模型在BirdSet多标签分类基准测试中取得了最新成果。
- Bird-MAE模型通过原型探测展示了强大的少样本能力。
点此查看论文截图
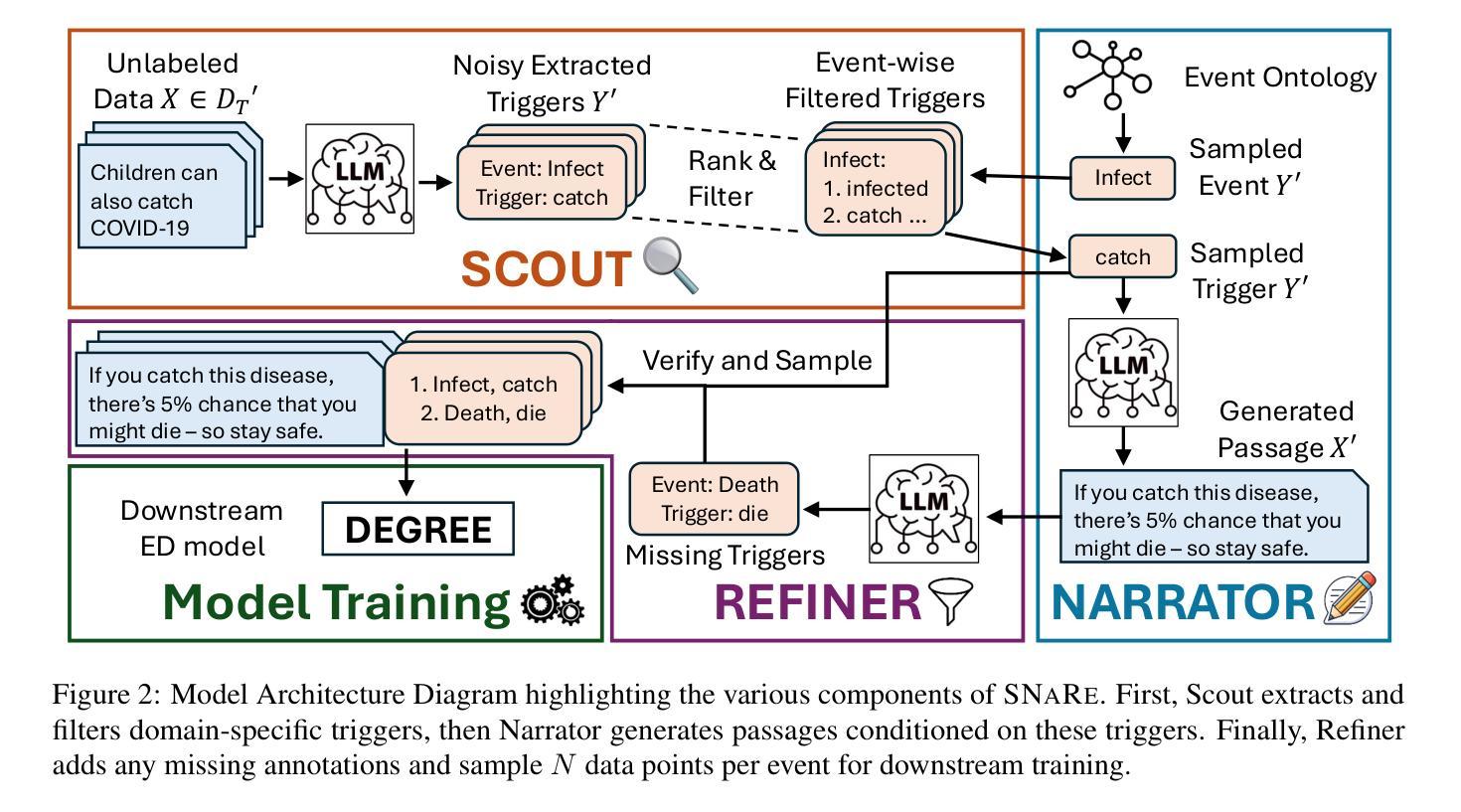
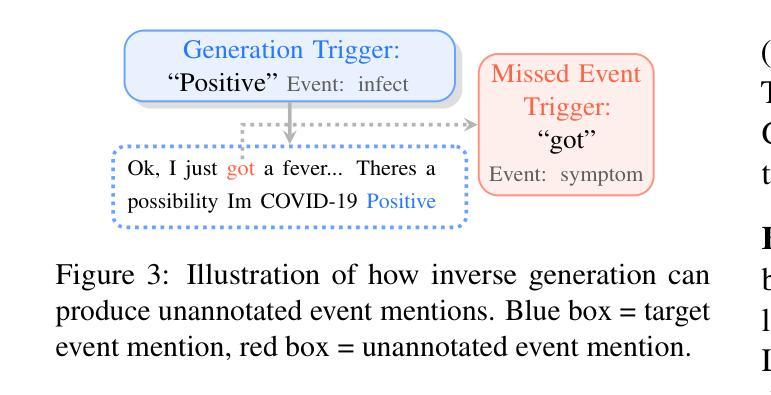
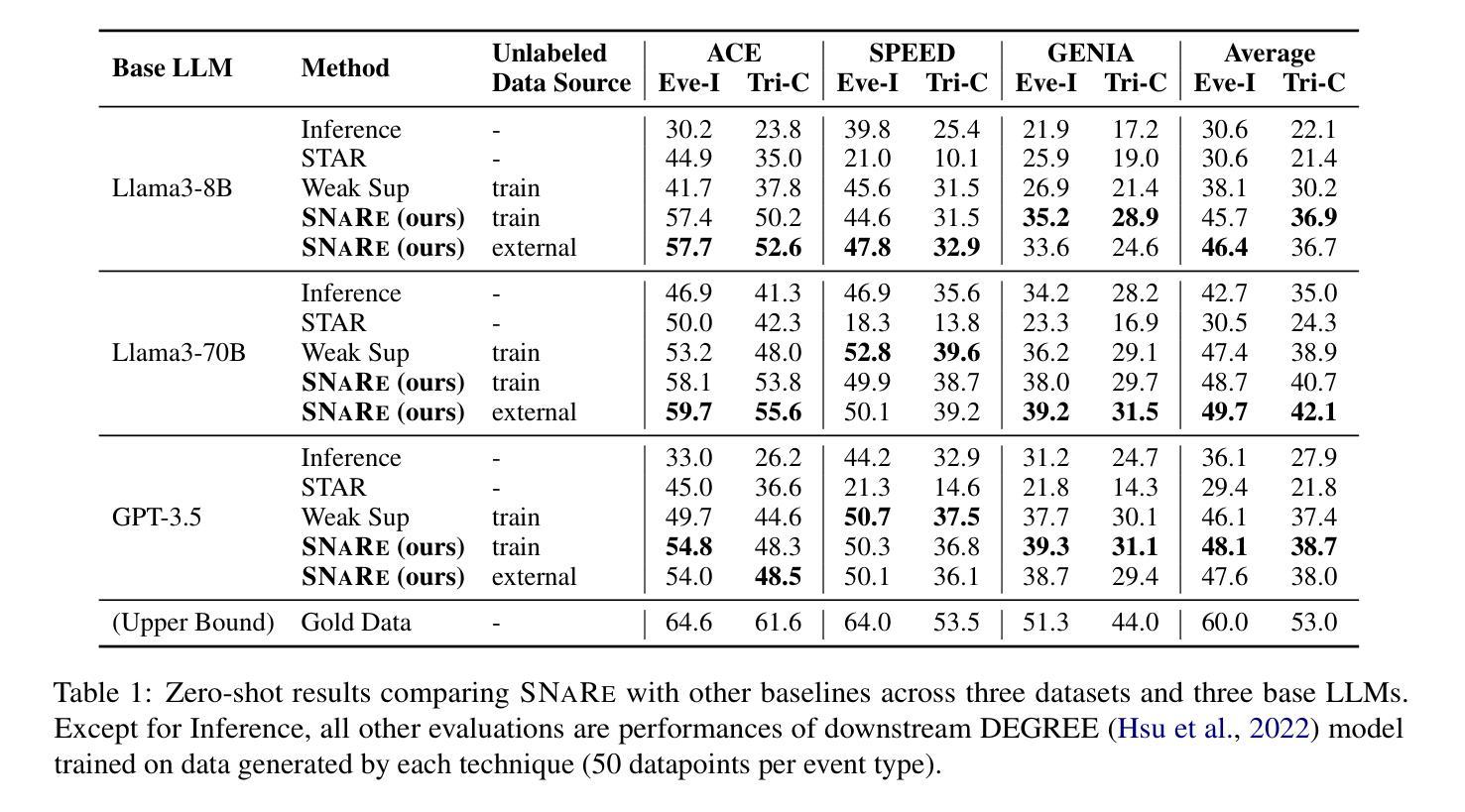
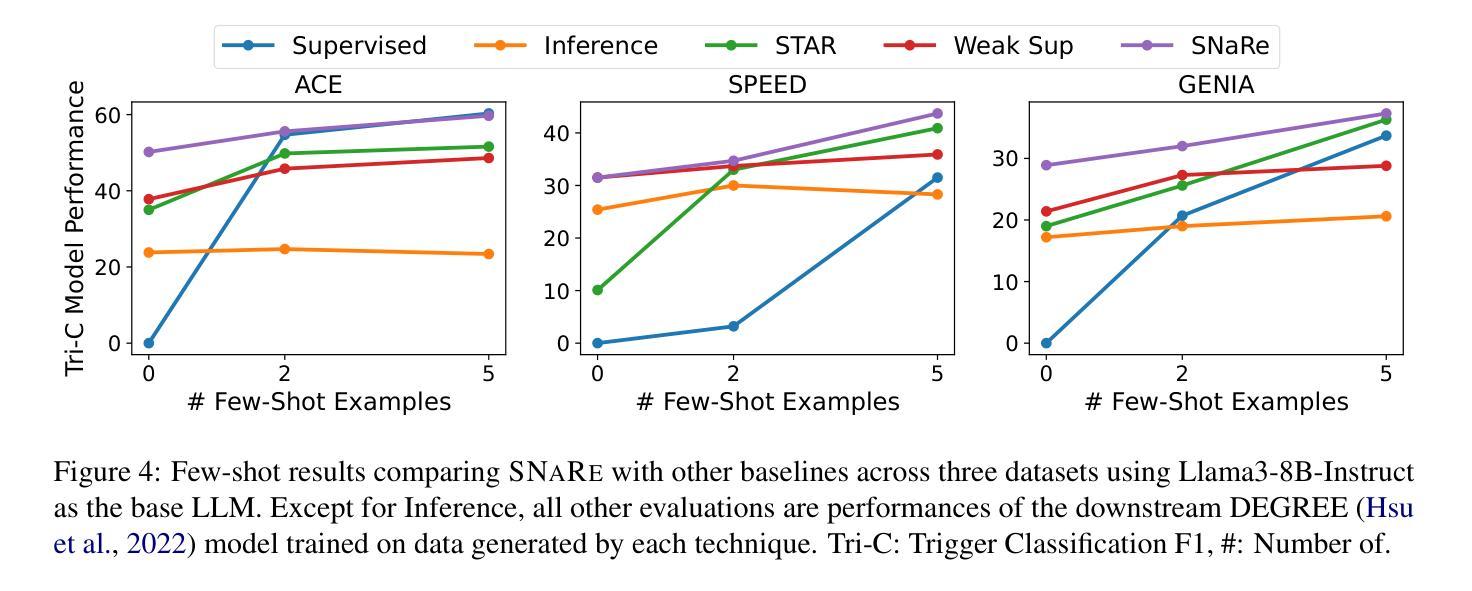
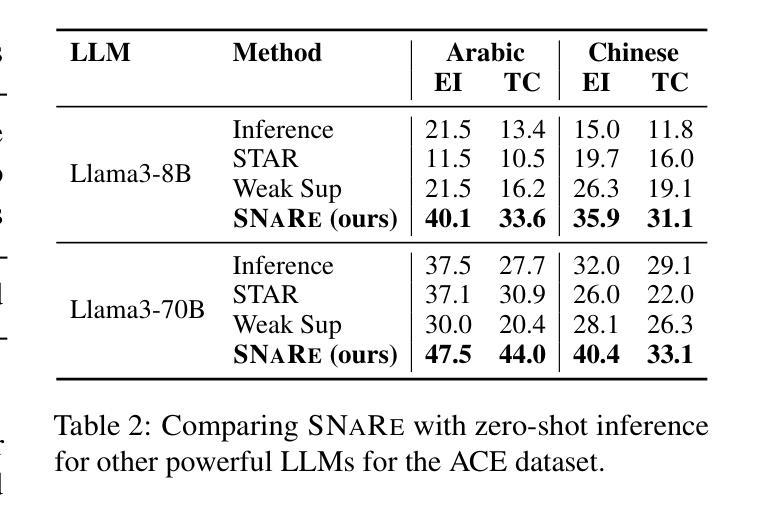
SNaRe: Domain-aware Data Generation for Low-Resource Event Detection
Authors:Tanmay Parekh, Yuxuan Dong, Lucas Bandarkar, Artin Kim, I-Hung Hsu, Kai-Wei Chang, Nanyun Peng
Event Detection (ED) – the task of identifying event mentions from natural language text – is critical for enabling reasoning in highly specialized domains such as biomedicine, law, and epidemiology. Data generation has proven to be effective in broadening its utility to wider applications without requiring expensive expert annotations. However, when existing generation approaches are applied to specialized domains, they struggle with label noise, where annotations are incorrect, and domain drift, characterized by a distributional mismatch between generated sentences and the target domain. To address these issues, we introduce SNaRe, a domain-aware synthetic data generation framework composed of three components: Scout, Narrator, and Refiner. Scout extracts triggers from unlabeled target domain data and curates a high-quality domain-specific trigger list using corpus-level statistics to mitigate domain drift. Narrator, conditioned on these triggers, generates high-quality domain-aligned sentences, and Refiner identifies additional event mentions, ensuring high annotation quality. Experimentation on three diverse domain ED datasets reveals how SNaRe outperforms the best baseline, achieving average F1 gains of 3-7% in the zero-shot/few-shot settings and 4-20% F1 improvement for multilingual generation. Analyzing the generated trigger hit rate and human evaluation substantiates SNaRe’s stronger annotation quality and reduced domain drift.
事件检测(ED)——从自然语言文本中识别事件提及的任务——对于在生物医学、法律和流行病学等高度专业化领域进行推理至关重要。数据生成已证明在扩大其在更广泛应用中的效用方面非常有效,而无需昂贵的专家注释。然而,当将现有的生成方法应用于专业领域时,它们会面临标签噪声的问题,即注释不正确,以及领域漂移,表现为生成句子与目标领域之间的分布不匹配。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了SNaRe,这是一个领域感知的合成数据生成框架,由三个组件组成:侦察兵(Scout)、叙述者(Narrator)和精炼者(Refiner)。Scout从目标领域的未标记数据中提取触发器,并使用语料库级别的统计信息来整理高质量的专业特定触发器列表,以缓解领域漂移。叙述者根据这些触发器生成高质量且与领域相符的句子,而精炼者则识别其他事件提及,确保高注释质量。在三个不同领域的ED数据集上的实验表明,SNaRe的表现优于最佳基线,在零样本/少样本设置中平均F1得分提高了3-7%,在多语言生成中F1得分提高了4-20%。通过分析生成的触发器命中率和人类评估,证实了SNaRe的注释质量更高,领域漂移减少。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review at ACL ARR May 2025
Summary
事件检测(ED)是从自然语言文本中识别事件提及的任务,对于生物医学、法律和流行病学等高度专业化领域中的推理至关重要。数据生成已证明可以有效扩大其在更广泛应用中的实用性,而无需昂贵的专家注释。然而,当现有生成方法应用于专业领域时,它们会面临标签噪声(注释不正确)和领域漂移(生成句子与目标领域之间的分布不匹配)的问题。为解决这些问题,我们引入了SNaRe,这是一个领域感知的合成数据生成框架,由三个组件组成:侦察兵、叙述者和精炼者。侦察兵从目标领域的未标记数据中提取触发器,并使用语料库级别的统计数据来优化高质量的领域特定触发器列表,以减轻领域漂移的问题。叙述者根据这些触发器生成高质量的领域对齐句子,而精炼者则识别其他事件提及,确保高注释质量。在三个不同的领域ED数据集上的实验表明,SNaRe的表现超过了最佳基线,在零样本/少样本设置中平均F1得分提高了3-7%,在多语言生成中提高了4-20%的F1得分。对生成的触发器命中率和人类评估的分析证实了SNaRe更强的注释质量和减少的领域漂移问题。
Key Takeaways
- 事件检测(ED)在高度专业化的领域中如生物医学、法律和流行病学中起到关键作用。
- 数据生成扩大了事件检测在更广泛应用中的实用性,但面临标签噪声和领域漂移的挑战。
- SNaRe是一个领域感知的合成数据生成框架,包含侦察兵、叙述者和精炼者三个组件。
- 侦察兵通过提取目标领域的触发器并优化高质量的领域特定触发器列表来减轻领域漂移问题。
- 叙述者根据触发器生成高质量的领域对齐句子。
- 精炼者确保高注释质量,通过识别其他事件提及。
点此查看论文截图

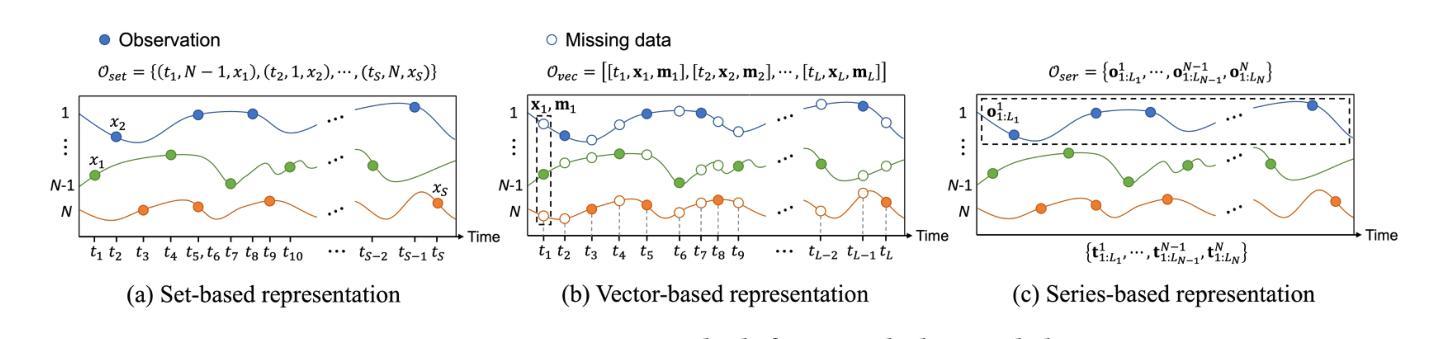
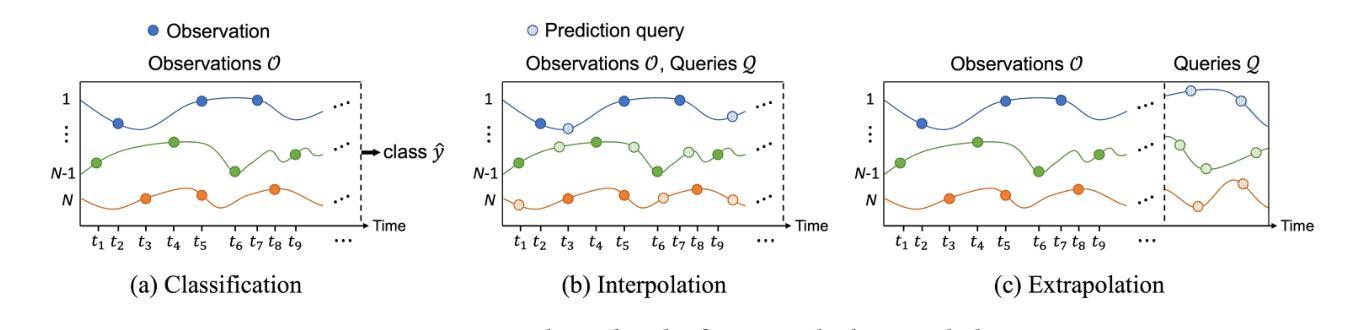
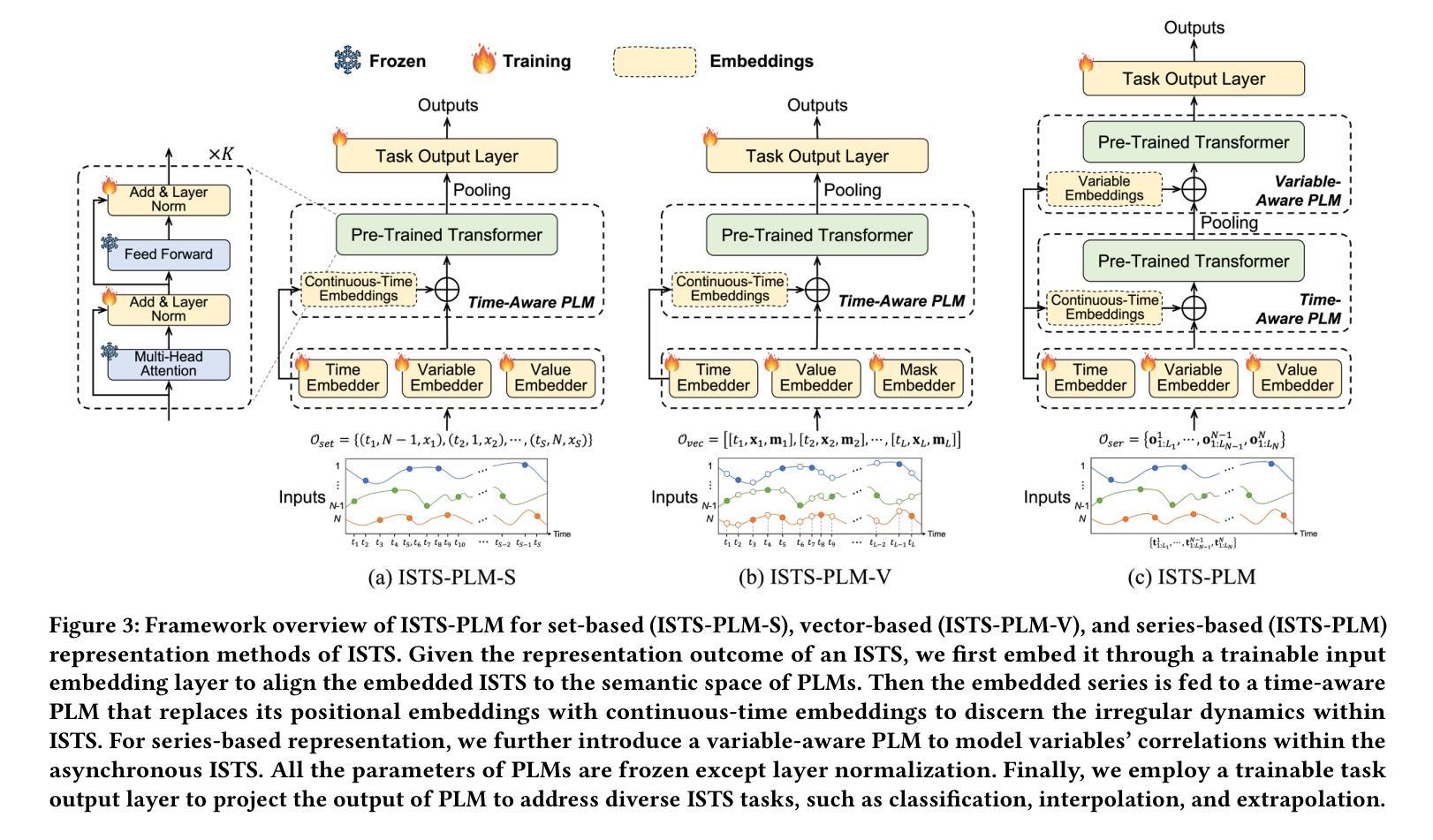
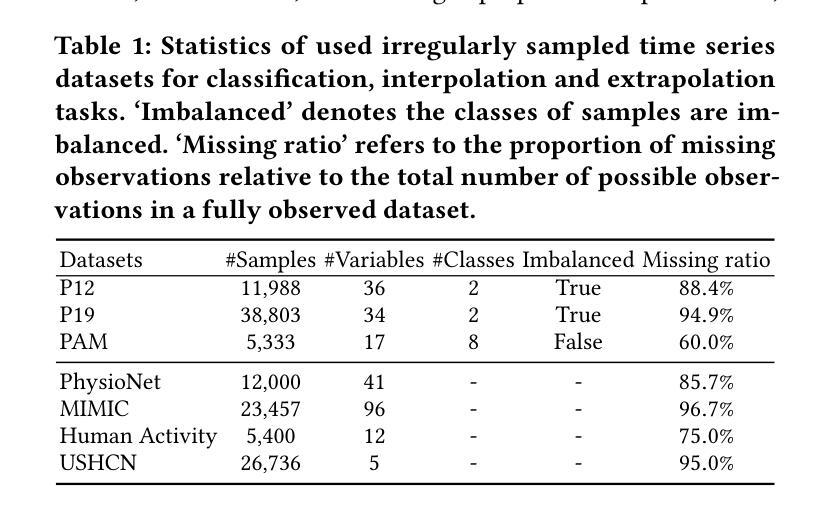
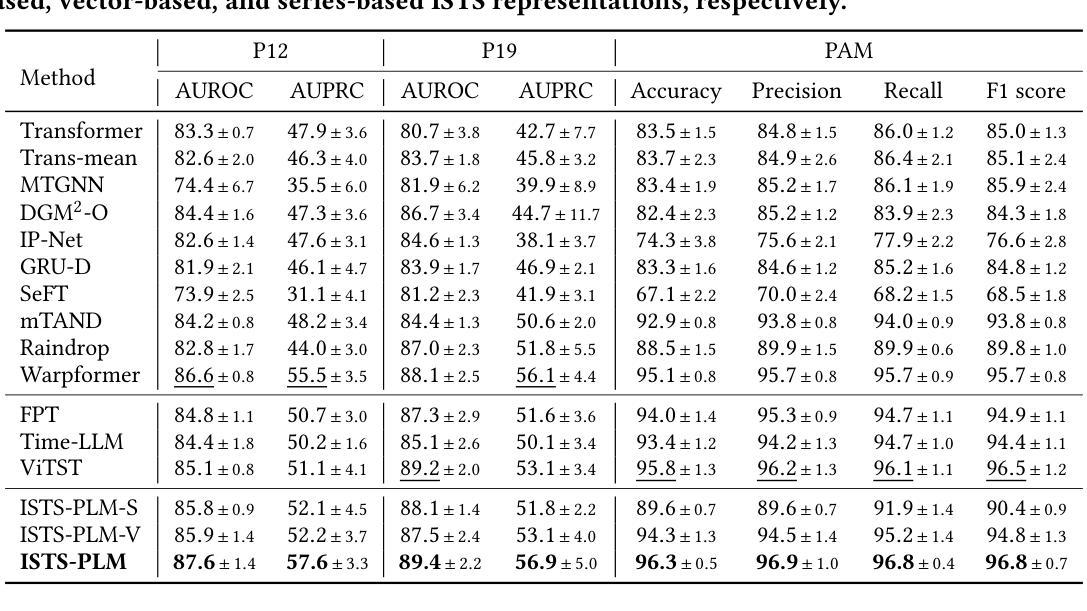
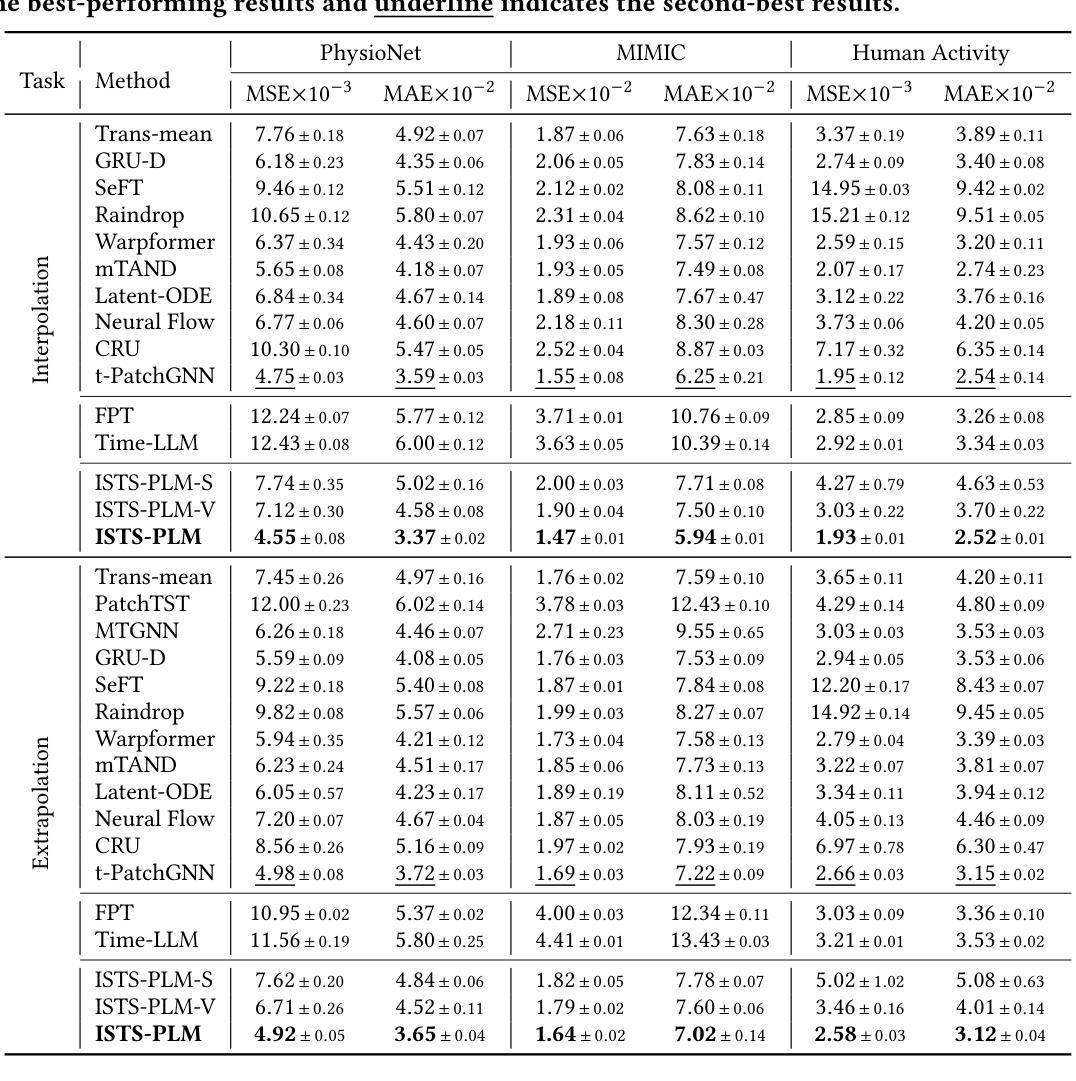
Unleashing The Power of Pre-Trained Language Models for Irregularly Sampled Time Series
Authors:Weijia Zhang, Chenlong Yin, Hao Liu, Hui Xiong
Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs), such as ChatGPT, have significantly advanced the field of natural language processing. This progress has inspired a series of innovative studies that explore the adaptation of PLMs to time series analysis, intending to create a unified foundation model that addresses various time series analytical tasks. However, these efforts predominantly focus on Regularly Sampled Time Series (RSTS), neglecting the unique challenges posed by Irregularly Sampled Time Series (ISTS), which are characterized by uneven sampling intervals and prevalent missing data. To bridge this gap, this work takes the first step in exploring the potential of PLMs for ISTS analysis. We begin by investigating the effect of various methods for representing ISTS, aiming to maximize the efficacy of PLMs in the analysis. Furthermore, we propose a unified PLM-based framework, named ISTS-PLM, to address diverse ISTS analytical tasks. It integrates novel time-aware and variable-aware PLMs tailored to tackle the intractable intra- and inter-time series modeling in ISTS. Finally, extensive experiments on a comprehensive benchmark demonstrate that the ISTS-PLM, utilizing a structured and effective series-based representation for ISTS, consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance across various analytical tasks, such as classification, interpolation, extrapolation, few-shot and zero-shot learning scenarios, spanning scientific domains like healthcare, biomechanics, and climate science.
预训练语言模型(如ChatGPT)在自然语言处理领域取得了显著进展。这一进步激发了一系列创新研究,探索将预训练语言模型适应于时间序列分析,旨在创建一个统一的基础模型,以解决各种时间序列分析任务。然而,这些努力主要集中在规则采样时间序列(RSTS)上,忽视了不规则采样时间序列(ISTS)带来的独特挑战,其特点是采样间隔不均匀且普遍存在缺失数据。为了填补这一空白,本研究首次探索了预训练语言模型在ISTS分析中的潜力。我们首先从研究表示ISTS的各种方法的效果开始,旨在最大限度地提高预训练语言模型在分析中的有效性。此外,我们提出了一种基于预训练语言模型的统一框架,名为ISTS-PLM,用于处理多样的ISTS分析任务。它集成了新型的时间感知和变量感知预训练语言模型,专门用于解决ISTS中复杂的单时间序列和多时间序列建模问题。最后,在全面的基准测试上进行的大量实验表明,ISTS-PLM利用结构化和有效的ISTS系列表示方法,在各种分析任务中始终实现了最先进的性能,如分类、插值、外推、少样本和零样本学习场景,涵盖医疗、生物力学和气候科学等科学领域。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by KDD’25
Summary
预训练语言模型(PLMs)如ChatGPT在自然语言处理领域取得了显著进展,并激发了一系列将其适应时间序列分析的研究。然而,这些研究主要关注规则采样时间序列(RSTS),忽略了不规则采样时间序列(ISTS)带来的独特挑战,如不均匀的采样间隔和普遍存在的缺失数据。本研究首次探索了PLMs在ISTS分析中的潜力,研究了表示ISTS的各种方法,并提出了一个统一的基于PLMs的框架ISTS-PLM,以解决多样的ISTS分析任务。该框架结合了新型的时间感知和变量感知PLMs,以处理ISTS中的复杂的时间序列内和时间序列间的建模问题。在全面的基准测试上的大量实验表明,ISTS-PLM利用结构化和有效的系列表示方法,在各种分析任务上实现了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练语言模型(PLMs)在自然语言处理领域有重大进展。
- PLMs正在被探索以适应时间序列分析。
- 目前的研究主要关注规则采样时间序列(RSTS),忽略了不规则采样时间序列(ISTS)的挑战。
- ISTS具有不均匀的采样间隔和普遍的缺失数据。
- 本研究探索了PLMs在ISTS分析中的潜力,并研究了表示ISTS的不同方法。
- 提出了一个名为ISTS-PLM的统一框架,该框架结合时间感知和变量感知PLMs以解决多样的ISTS分析任务。
点此查看论文截图