⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-08 更新
ProJo4D: Progressive Joint Optimization for Sparse-View Inverse Physics Estimation
Authors:Daniel Rho, Jun Myeong Choi, Biswadip Dey, Roni Sengupta
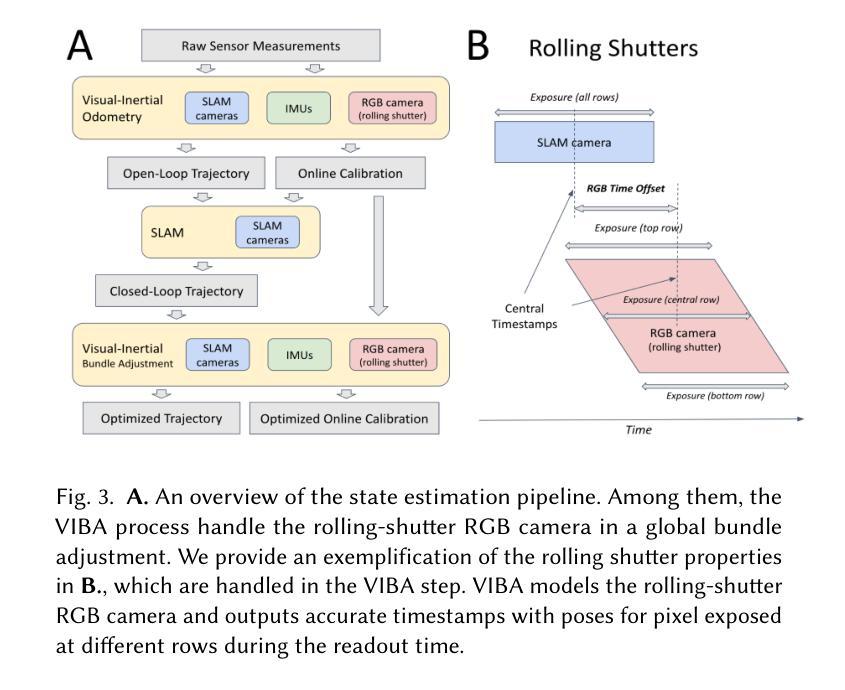
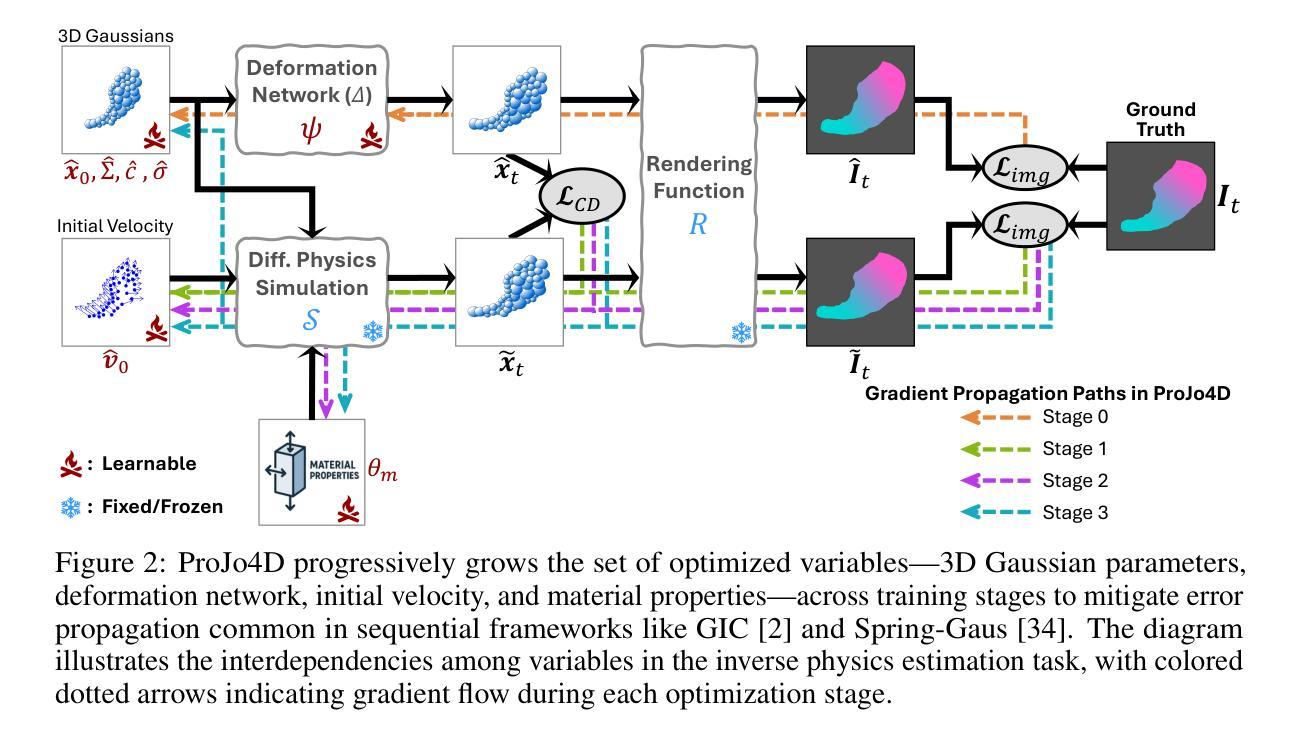
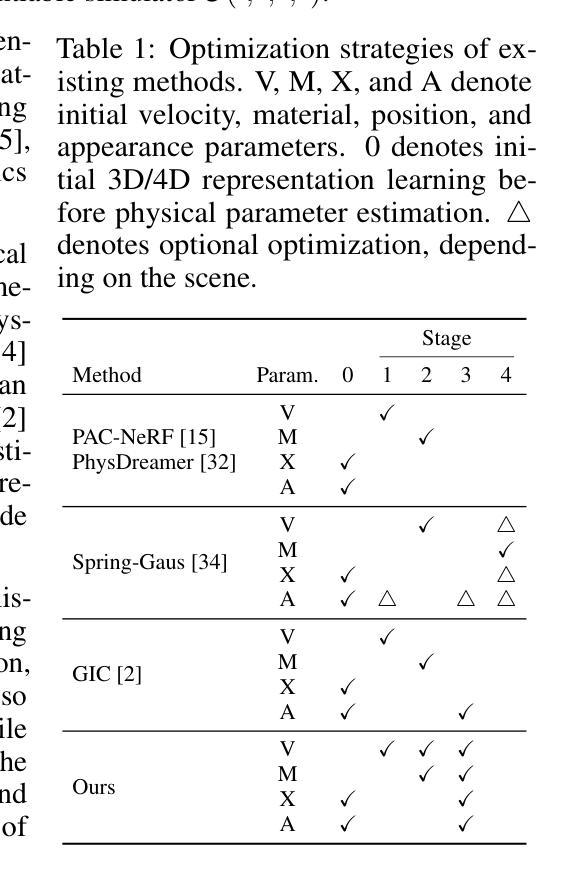
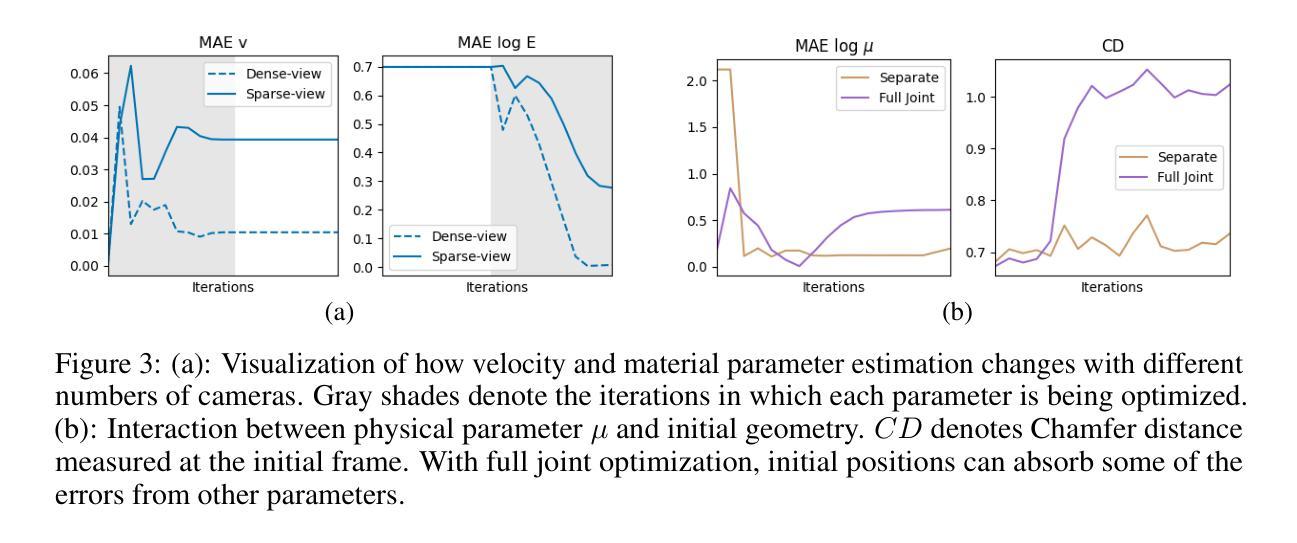
Neural rendering has made significant strides in 3D reconstruction and novel view synthesis. With the integration with physics, it opens up new applications. The inverse problem of estimating physics from visual data, however, still remains challenging, limiting its effectiveness for applications like physically accurate digital twin creation in robotics and XR. Existing methods that incorporate physics into neural rendering frameworks typically require dense multi-view videos as input, making them impractical for scalable, real-world use. When presented with sparse multi-view videos, the sequential optimization strategy used by existing approaches introduces significant error accumulation, e.g., poor initial 3D reconstruction leads to bad material parameter estimation in subsequent stages. Instead of sequential optimization, directly optimizing all parameters at the same time also fails due to the highly non-convex and often non-differentiable nature of the problem. We propose ProJo4D, a progressive joint optimization framework that gradually increases the set of jointly optimized parameters guided by their sensitivity, leading to fully joint optimization over geometry, appearance, physical state, and material property. Evaluations on PAC-NeRF and Spring-Gaus datasets show that ProJo4D outperforms prior work in 4D future state prediction, novel view rendering of future state, and material parameter estimation, demonstrating its effectiveness in physically grounded 4D scene understanding. For demos, please visit the project webpage: https://daniel03c1.github.io/ProJo4D/
神经渲染在3D重建和新颖视角合成方面取得了重大进展。通过与物理学的结合,它开启了新的应用领域。然而,从视觉数据中估计物理的逆问题仍然具有挑战性,限制了其在机器人和XR等领域中创建物理准确的数字双胞胎等应用的效果。现有将物理融入神经渲染框架的方法通常需要密集的多视角视频作为输入,这使得它们在可扩展的、实际世界的应用中变得不切实际。当面对稀疏的多视角视频时,现有方法所使用的顺序优化策略会导致显著的误差累积,例如,初始的3D重建不佳会导致后续阶段的材料参数估计出现问题。与顺序优化不同,同时直接优化所有参数也失败了,因为这个问题的高度非凸性和经常出现的不可微特性。我们提出了ProJo4D,一个渐进的联合优化框架,该框架通过参数的敏感性逐步增加联合优化的参数集,从而实现几何、外观、物理状态和材料属性的完全联合优化。在PAC-NeRF和Spring-Gaus数据集上的评估表明,ProJo4D在4D未来状态预测、未来状态的新视角渲染和材料参数估计方面优于先前的工作,证明了其在基于物理的4D场景理解中的有效性。要了解演示内容,请访问项目网页:https://daniel03c1.github.io/ProJo4D/
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经渲染在三维重建和新颖视角合成方面取得了重大进展。通过物理集成,它开启了新的应用领域。然而,从视觉数据中估计物理特性的逆向问题仍然具有挑战性,限制了其在机器人和XR等物理准确数字双胞胎创建中的应用。现有方法通常需要密集的多视角视频作为输入,使得它们在可扩展的、现实世界的用途中不切实际。针对稀疏多视角视频,本文提出了ProJo4D,一种渐进联合优化框架,通过敏感性指导逐渐增加的联合优化参数集,实现了对几何、外观、物理状态和材质属性的完全联合优化。在PAC-NeRF和Spring-Gaus数据集上的评估表明,ProJo4D在四维未来状态预测、未来状态的新视角渲染和材质参数估计等方面优于先前的工作,证明了其在物理基础的四维场景理解中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 神经渲染结合了物理特性,扩展了新的应用领域。
- 从视觉数据中估计物理特性的逆向问题仍然是一个挑战。
- 现有方法需要密集的多视角视频作为输入,限制了实际应用。
- 在稀疏多视角视频下,现有方法的优化策略存在误差累积问题。
- ProJo4D提出了一种渐进的联合优化框架,通过敏感性引导逐渐增加的参数集进行联合优化。
- ProJo4D在四维未来状态预测、新视角渲染和材质参数估计等方面表现出优异的性能。
点此查看论文截图

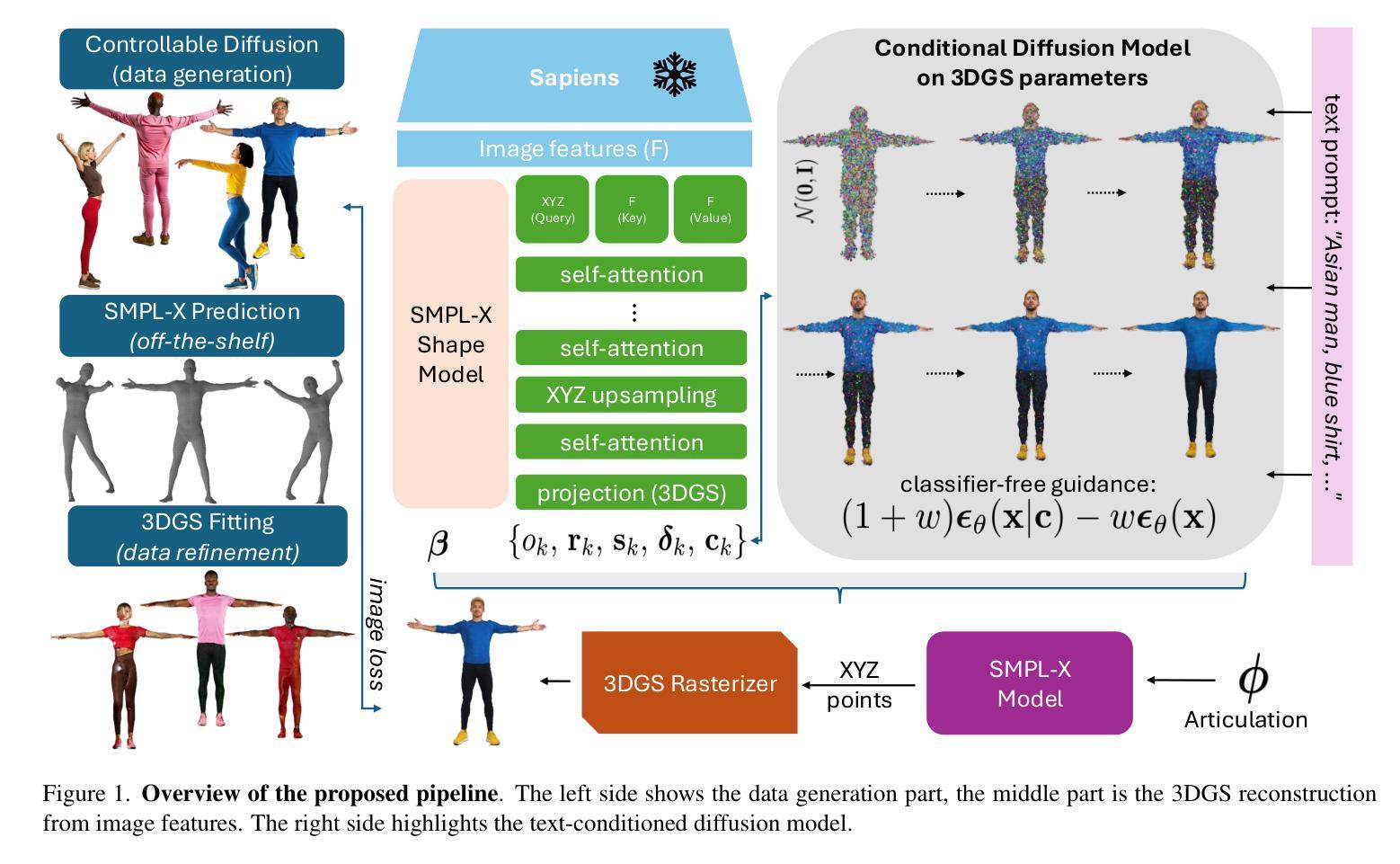
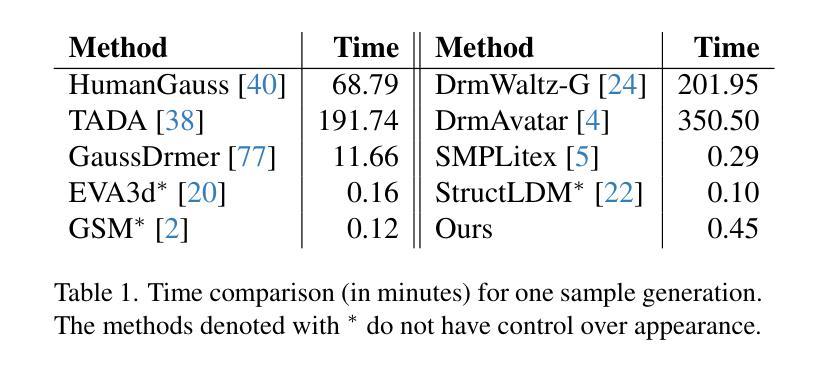
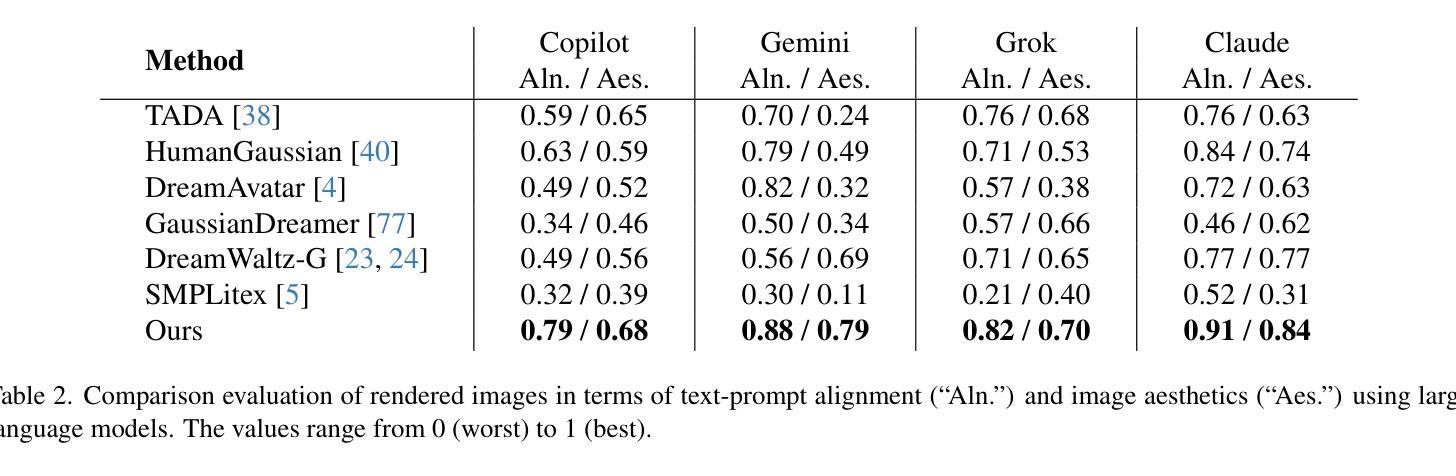
HuGeDiff: 3D Human Generation via Diffusion with Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Maksym Ivashechkin, Oscar Mendez, Richard Bowden
3D human generation is an important problem with a wide range of applications in computer vision and graphics. Despite recent progress in generative AI such as diffusion models or rendering methods like Neural Radiance Fields or Gaussian Splatting, controlling the generation of accurate 3D humans from text prompts remains an open challenge. Current methods struggle with fine detail, accurate rendering of hands and faces, human realism, and controlability over appearance. The lack of diversity, realism, and annotation in human image data also remains a challenge, hindering the development of a foundational 3D human model. We present a weakly supervised pipeline that tries to address these challenges. In the first step, we generate a photorealistic human image dataset with controllable attributes such as appearance, race, gender, etc using a state-of-the-art image diffusion model. Next, we propose an efficient mapping approach from image features to 3D point clouds using a transformer-based architecture. Finally, we close the loop by training a point-cloud diffusion model that is conditioned on the same text prompts used to generate the original samples. We demonstrate orders-of-magnitude speed-ups in 3D human generation compared to the state-of-the-art approaches, along with significantly improved text-prompt alignment, realism, and rendering quality. We will make the code and dataset available.
三维人物生成是计算机视觉和图形学中的一个具有广泛应用的重要问题。尽管最近生成式人工智能(如扩散模型)或渲染方法(如神经辐射场或高斯拼贴)有所进展,但从文本提示控制生成准确的三维人物仍然是一个开放性的挑战。当前的方法在细节、手和脸的准确渲染、人物真实感和外观可控性等方面存在困难。人类图像数据缺乏多样性、真实性和注释,也仍是构建基础三维人物模型的一个挑战。我们提出了一种弱监督的流程来应对这些挑战。首先,我们使用最先进的图像扩散模型,生成了一个具有可控属性(如外观、种族、性别等)的光照真实感人物图像数据集。接下来,我们提出了一种基于变换器架构的有效映射方法,将图像特征映射到三维点云。最后,我们通过训练点云扩散模型来完成闭环,该模型使用与生成原始样本相同的文本提示。我们在三维人物生成方面实现了与最新方法相比的数量级加速,同时显著提高了文本提示对齐、真实感和渲染质量。我们将公开提供代码和数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于扩散模型和神经网络辐射场等技术,该文提出了一种弱监督流程来解决从文本提示生成逼真三维人类模型的问题。流程包括生成可控属性的逼真人类图像数据集、使用基于转换器的架构实现从图像特征到三维点云的映射以及训练对文本提示的条件点云扩散模型。相较于现有方法,该文在三维人类生成速度上有大幅度提升,同时显著提高了文本对齐、逼真度和渲染质量。数据集和代码将公开。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究解决了从文本提示生成准确三维人类模型的问题,涉及计算机视觉和图形学的广泛应用。
- 利用扩散模型和Neural Radiance Fields等技术生成带有可控属性的逼真人类图像数据集。
- 提出一种高效的从图像特征到三维点云的映射方法,基于转换器架构。
- 通过训练点云扩散模型,实现对文本提示的生成样本与原始样本之间的闭环。
- 与现有方法相比,该方法在三维人类生成速度上有显著改进。
- 提高了文本对齐、逼真度和渲染质量。
点此查看论文截图


ViewFusion: Learning Composable Diffusion Models for Novel View Synthesis
Authors:Bernard Spiegl, Andrea Perin, Stéphane Deny, Alexander Ilin
Deep learning is providing a wealth of new approaches to the problem of novel view synthesis, from Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) based approaches to end-to-end style architectures. Each approach offers specific strengths but also comes with limitations in their applicability. This work introduces ViewFusion, an end-to-end generative approach to novel view synthesis with unparalleled flexibility. ViewFusion consists in simultaneously applying a diffusion denoising step to any number of input views of a scene, then combining the noise gradients obtained for each view with an (inferred) pixel-weighting mask, ensuring that for each region of the target view only the most informative input views are taken into account. Our approach resolves several limitations of previous approaches by (1) being trainable and generalizing across multiple scenes and object classes, (2) adaptively taking in a variable number of pose-free views at both train and test time, (3) generating plausible views even in severely underdetermined conditions (thanks to its generative nature) – all while generating views of quality on par or even better than comparable methods. Limitations include not generating a 3D embedding of the scene, resulting in a relatively slow inference speed, and our method only being tested on the relatively small Neural 3D Mesh Renderer dataset. Code is available at https://github.com/bronemos/view-fusion.
深度学习为新型视图合成问题提供了丰富的新方法,从基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的方法到端到端的风格架构。每种方法都有其特定的优势,但也存在适用性的局限性。本文介绍了ViewFusion,这是一种用于新型视图合成的端到端生成方法,具有无与伦比的灵活性。ViewFusion包括同时对场景的任何数量的输入视图进行扩散去噪步骤,然后将每个视图获得的噪声梯度与(推断的)像素权重掩膜相结合,确保对于目标视图的每个区域只考虑最具有信息性的输入视图。我们的方法通过(1)进行训练和针对多个场景和对象类别的推广,(2)在训练和测试时自适应地接受可变数量的姿态自由视图,(3)即使在严重不确定的条件下也能生成可信的视图(得益于其生成性质)——同时生成质量相等甚至更好的视图。局限性包括没有生成场景的三维嵌入,导致推理速度相对较慢,而且我们的方法只在相对较小的神经网络三维网格渲染器数据集上进行了测试。代码可用在https://github.com/bronemos/view-fusion。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Version accepted to TMLR
Summary
NeRF领域的新研究提出了一种名为ViewFusion的方法,用于合成新颖视角的场景。ViewFusion通过同时对多个输入视角进行扩散去噪步骤,并结合每个视角获得的噪声梯度和推断的像素权重掩膜来实现。此方法解决了先前方法的多个局限性,如跨场景和对象类的可训练性和泛化能力、适应性地处理可变数量的姿态自由视角,以及在严重不确定条件下生成可信视图的能力。尽管有其局限性,如未生成场景的3D嵌入,导致推理速度相对较慢,且仅在较小的Neural 3D Mesh Renderer数据集上进行了测试,但ViewFusion仍提供了一种高效的新颖视角合成方法。
Key Takeaways
- ViewFusion是一种用于合成新颖视角场景的端到端生成方法。
- ViewFusion通过扩散去噪步骤结合像素权重掩膜,实现对多个输入视角的同时处理。
- ViewFusion解决了先前方法在跨场景和对象类的可训练性和泛化能力方面的局限性。
- ViewFusion能够自适应处理可变数量的姿态自由视角,在严重不确定条件下生成可信视图。
- ViewFusion生成的新视角的质量与类似方法相当甚至更好。
- ViewFusion的局限性包括未生成场景的3D嵌入,导致推理速度较慢。
点此查看论文截图