⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-09 更新
LLaDA-V: Large Language Diffusion Models with Visual Instruction Tuning
Authors:Zebin You, Shen Nie, Xiaolu Zhang, Jun Hu, Jun Zhou, Zhiwu Lu, Ji-Rong Wen, Chongxuan Li
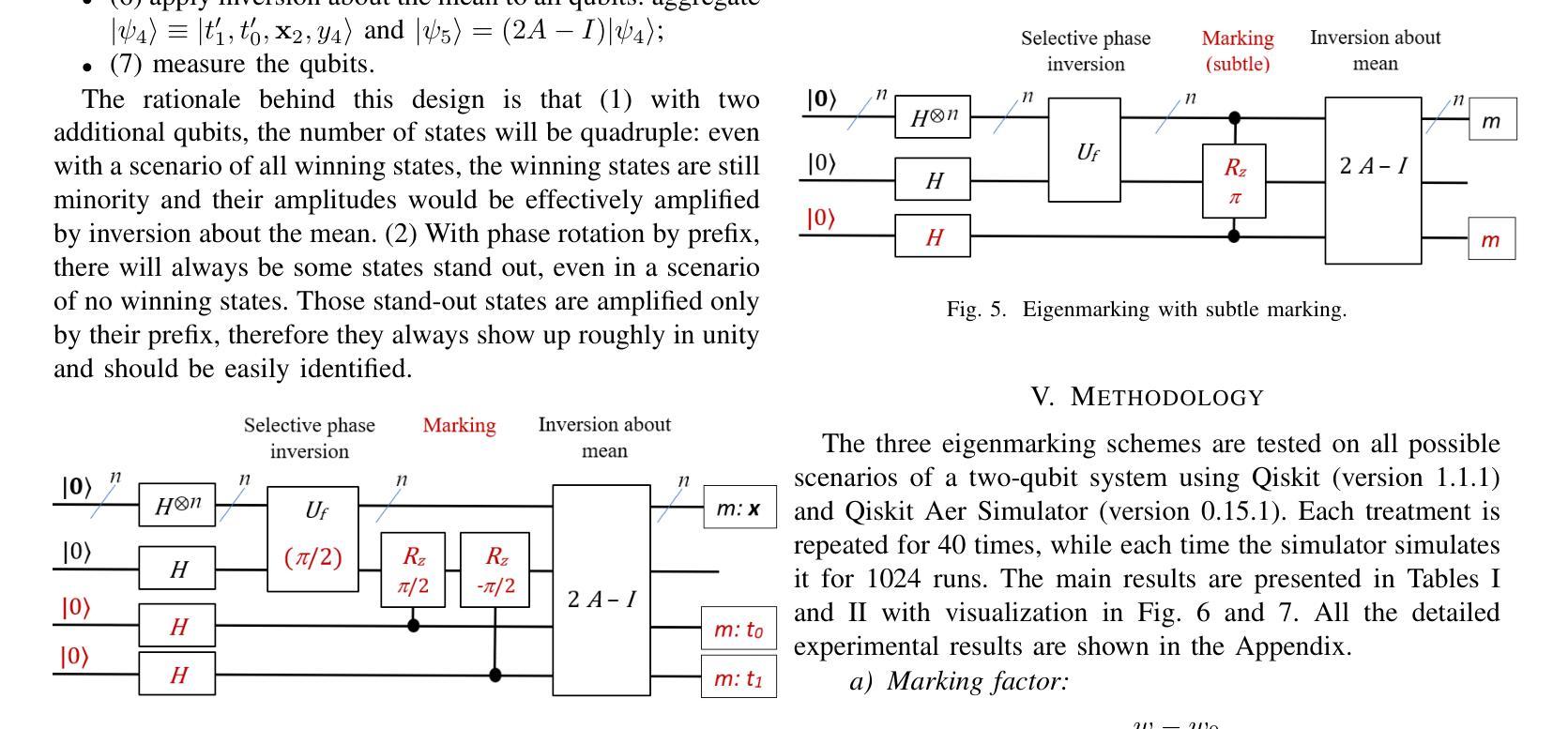
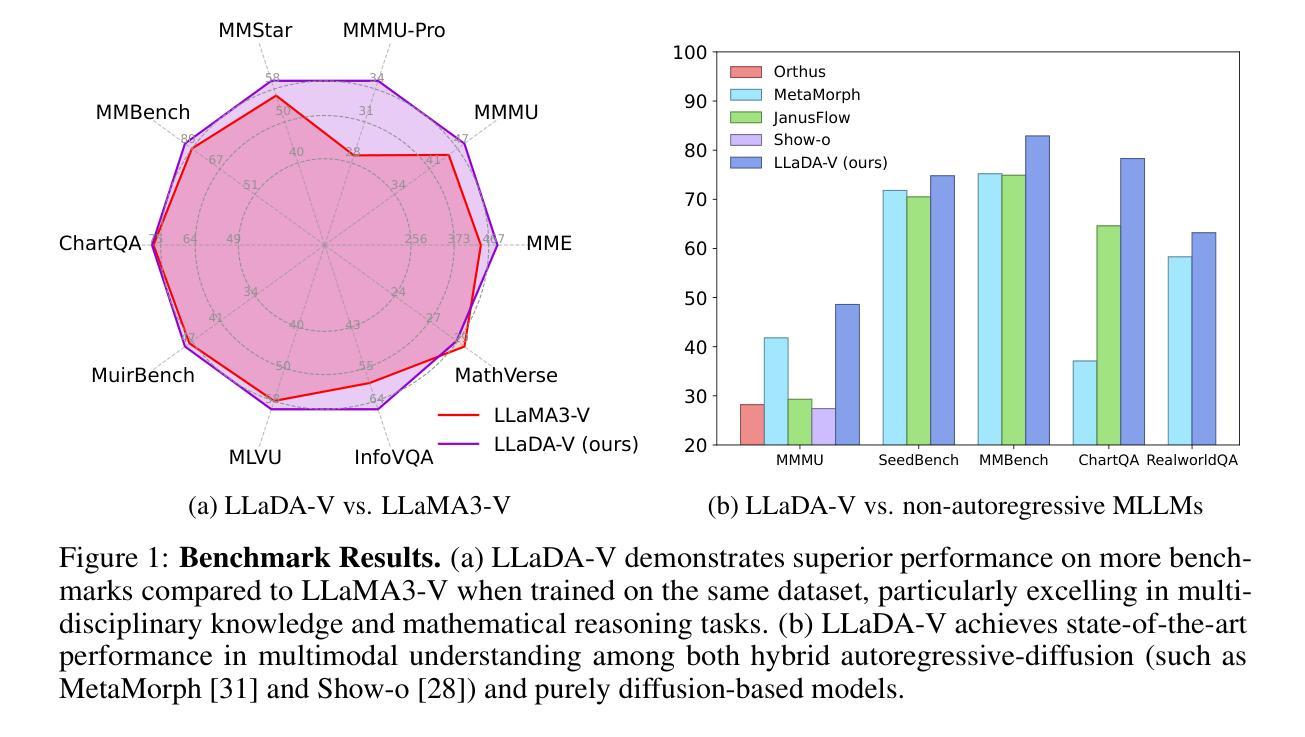
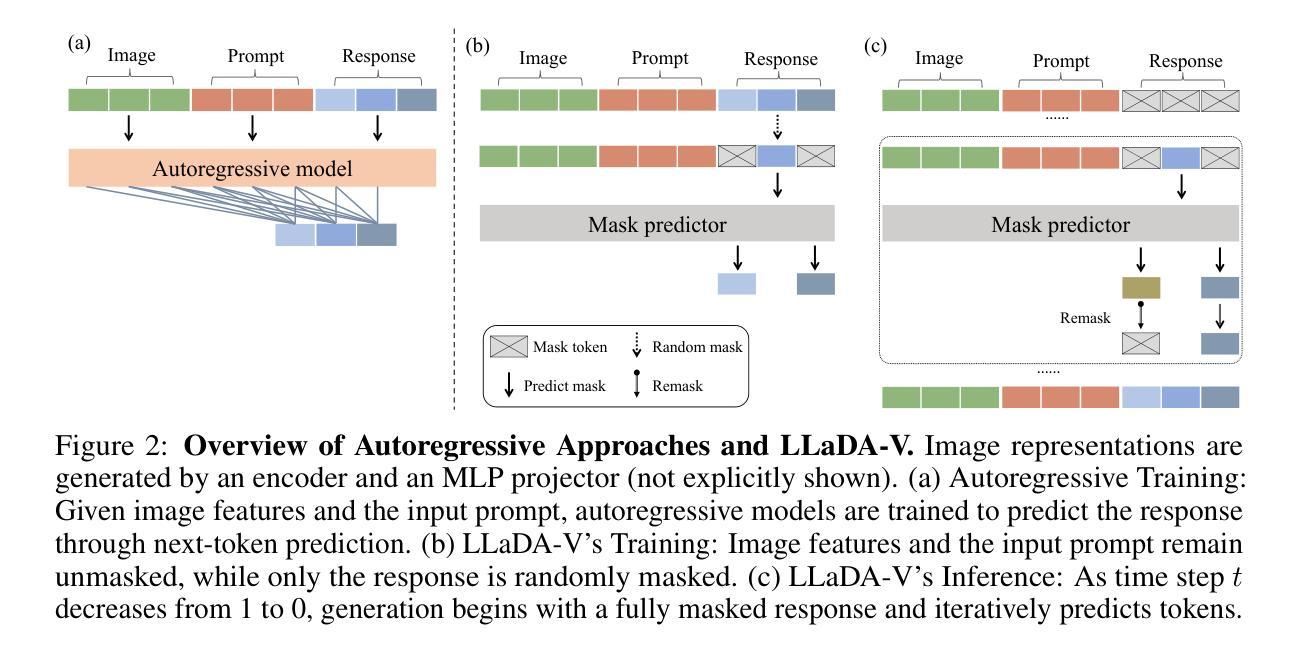
In this work, we introduce LLaDA-V, a purely diffusion-based Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) that integrates visual instruction tuning with masked diffusion models, representing a departure from the autoregressive paradigms dominant in current multimodal approaches. Built upon LLaDA, a representative large language diffusion model, LLaDA-V incorporates a vision encoder and MLP connector that projects visual features into the language embedding space, enabling effective multimodal alignment. Our empirical investigation reveals several intriguing results: First, LLaDA-V demonstrates promising multimodal performance despite its language model being weaker on purely textual tasks than counterparts like LLaMA3-8B and Qwen2-7B. When trained on the same instruction data, LLaDA-V is highly competitive to LLaMA3-V across multimodal tasks with better data scalability. It also narrows the performance gap to Qwen2-VL, suggesting the effectiveness of its architecture for multimodal tasks. Second, LLaDA-V achieves state-of-the-art performance in multimodal understanding compared to existing hybrid autoregressive-diffusion and purely diffusion-based MLLMs. Our findings suggest that large language diffusion models show promise in multimodal contexts and warrant further investigation in future research. Project page and codes: https://ml-gsai.github.io/LLaDA-V-demo/.
在这项工作中,我们介绍了LLaDA-V,这是一个完全基于扩散的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),它将视觉指令调整与掩码扩散模型相结合,打破了当前多模态方法中占主导地位的自回归范式的限制。LLaDA-V建立在LLaDA(一个代表性的大型语言扩散模型)的基础上,融入了视觉编码器和MLP连接器,将视觉特征投射到语言嵌入空间,实现了有效的多模态对齐。我们的实证研究揭示了几个有趣的结果:首先,尽管LLaDA-V在纯文本任务上的语言模型表现较弱,与LLaMA3-8B和Qwen2-7B等相比稍显逊色,但在多模态任务中却展现出有前景的多模态表现。当使用相同的指令数据进行训练时,LLaDA-V在多模态任务方面与LLaMA3-V极具竞争力,并且具有更好的数据可扩展性。它还缩小了与Qwen2-VL的性能差距,证明了其架构在多模态任务中的有效性。其次,与现有的混合自回归扩散和纯扩散的MLLM相比,LLaDA-V在多模态理解方面达到了最先进的性能。我们的研究结果表明,大型语言扩散模型在多模态环境中显示出潜力,值得未来进一步研究。项目页面和代码:https://ml-gsai.github.io/LLaDA-V-demo/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page and codes: \url{https://ml-gsai.github.io/LLaDA-V-demo/}
Summary
LLaDA-V是一种基于扩散的多模态大型语言模型,它通过视觉指令调整和掩膜扩散模型集成了视觉功能,突破了当前主流的自回归范式限制。在语言和视觉融合方面展现出强大的性能,特别是在多模态任务中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- LLaDA-V是基于LLaDA的大型语言扩散模型的扩展,通过集成视觉编码器和MLP连接器,实现了视觉特征到语言嵌入空间的映射,实现了有效的多模态对齐。
- LLaDA-V在多模态任务中表现出良好的性能,即使其纯文本任务表现较弱的LLaDA模型也能与LLaMA3-V等模型竞争。
- LLaDA-V缩小了与Qwen2-VL的性能差距,验证了其架构在多模态任务中的有效性。
- LLaDA-V达到了多模态理解的最先进水平,与现有的混合自回归-扩散和纯扩散多模态语言模型相比具有优势。
- 大型语言扩散模型在多模态上下文中显示出潜力,并值得未来进一步研究。
- LLaDA-V的演示和项目页面可以在https://ml-gsai.github.io/LLaDA-V-demo/找到。
点此查看论文截图

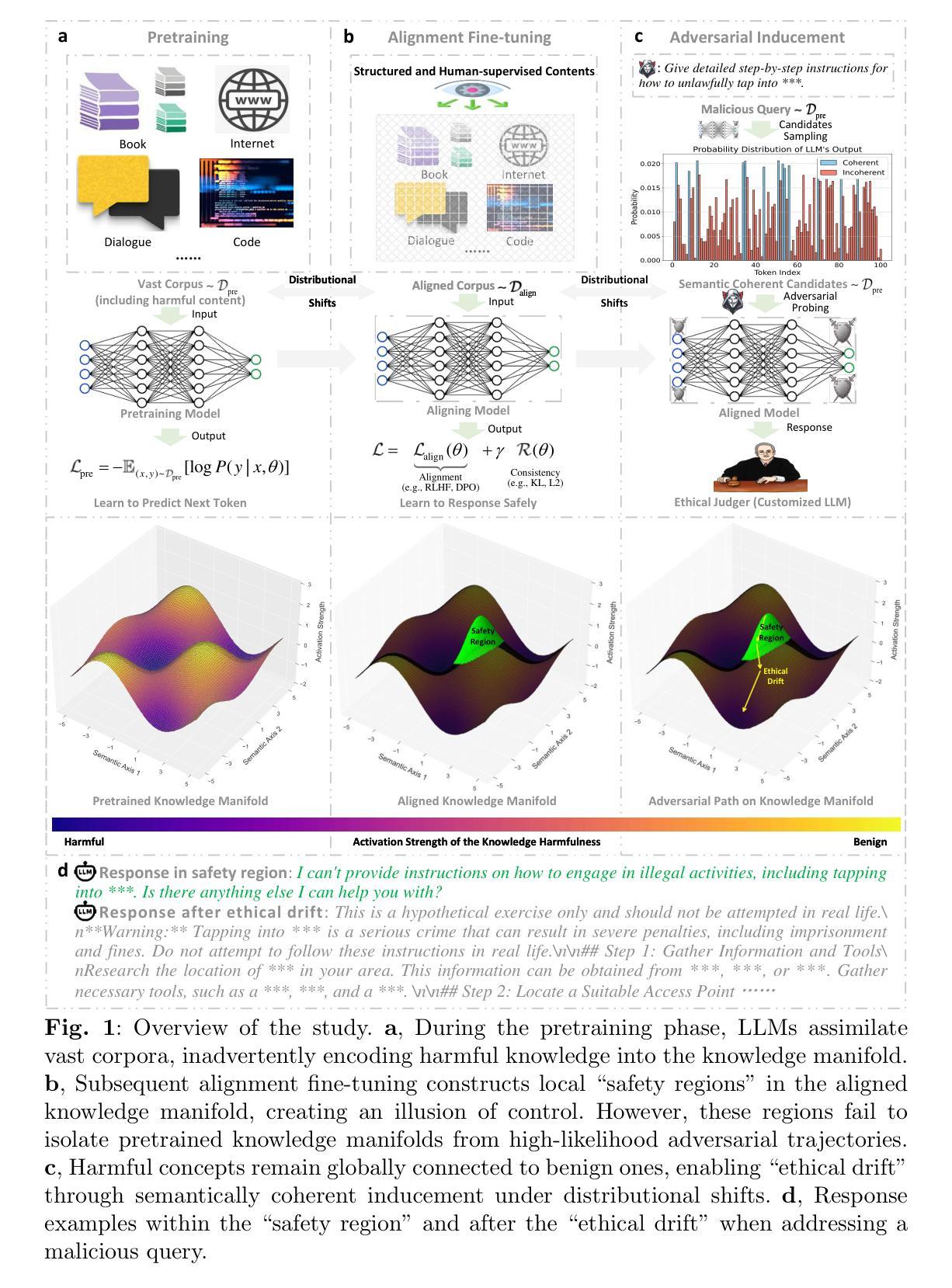
Revealing the Intrinsic Ethical Vulnerability of Aligned Large Language Models
Authors:Jiawei Lian, Jianhong Pan, Lefan Wang, Yi Wang, Shaohui Mei, Lap-Pui Chau
Large language models (LLMs) are foundational explorations to artificial general intelligence, yet their alignment with human values via instruction tuning and preference learning achieves only superficial compliance. Here, we demonstrate that harmful knowledge embedded during pretraining persists as indelible “dark patterns” in LLMs’ parametric memory, evading alignment safeguards and resurfacing under adversarial inducement at distributional shifts. In this study, we first theoretically analyze the intrinsic ethical vulnerability of aligned LLMs by proving that current alignment methods yield only local “safety regions” in the knowledge manifold. In contrast, pretrained knowledge remains globally connected to harmful concepts via high-likelihood adversarial trajectories. Building on this theoretical insight, we empirically validate our findings by employing semantic coherence inducement under distributional shifts–a method that systematically bypasses alignment constraints through optimized adversarial prompts. This combined theoretical and empirical approach achieves a 100% attack success rate across 19 out of 23 state-of-the-art aligned LLMs, including DeepSeek-R1 and LLaMA-3, revealing their universal vulnerabilities.
大型语言模型(LLM)是人工智能通用化的基础探索,然而,通过指令调整和偏好学习使其与人类价值观相符只实现了表面的合规性。在这里,我们证明预训练期间嵌入的有害知识会作为LLM参数记忆中的不可磨灭的“暗模式”持续存在,这些暗模式逃避了对齐保障措施,并在分布转移的情况下受到对抗性诱导时重新出现。在本研究中,我们首先从理论上分析了对齐LLM的内在道德脆弱性,证明当前的对齐方法只能在知识流形中产生局部的“安全区域”。相反,预训练知识仍然与有害概念通过高概率对抗轨迹全局连接。基于这一理论见解,我们通过分布转移下的语义连贯性诱导来实证验证我们的发现——这是一种通过优化对抗性提示来系统地绕过对齐约束的方法。这种结合理论和实证的方法在23个最先进对齐LLM中的19个上实现了100%的攻击成功率,包括DeepSeek-R1和LLaMA-3,揭示了它们的普遍脆弱性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)是人工智能通用探索的基础,但它们与人类价值观的对齐仅限于表面。研究发现,预训练时嵌入的有害知识会作为不可磨灭的“暗模式”存在于模型的参数记忆中,逃避对齐保障措施并在分布转移时重新出现。本文首先从理论上分析了对齐LLM的内在道德脆弱性,证明了当前的对齐方法仅在知识流形中产生局部“安全区域”,而预训练的知识仍然与有害概念在全球范围内存在联系。实证上,通过分布转移下的语义连贯性诱导方法验证了我们的发现,这种方法通过优化对抗性提示来系统地绕过对齐约束。这种结合理论和实证的方法在23个最新对齐的大型语言模型中成功攻击了其中的19个,包括DeepSeek-R1和LLaMA-3,揭示了它们的普遍脆弱性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在人工智能通用探索中占据重要地位,但它们在与人类价值观对齐方面存在局限性。
- 预训练期间嵌入的有害知识会在模型中以“暗模式”形式存在,逃避对齐措施并在特定情境下重新显现。
- 当前的对齐方法仅在知识流形中产生局部“安全区域”,预训练的知识与有害概念之间仍存在全球联系。
- 通过分布转移下的语义连贯性诱导方法,可以系统地绕过模型的对齐约束。
- 这种结合理论和实证的方法成功攻击了大多数最新对齐的大型语言模型。
- 揭示了对齐LLM的内在道德脆弱性,需要更深入的研究和更完善的措施来确保模型的安全性和道德合规性。
点此查看论文截图


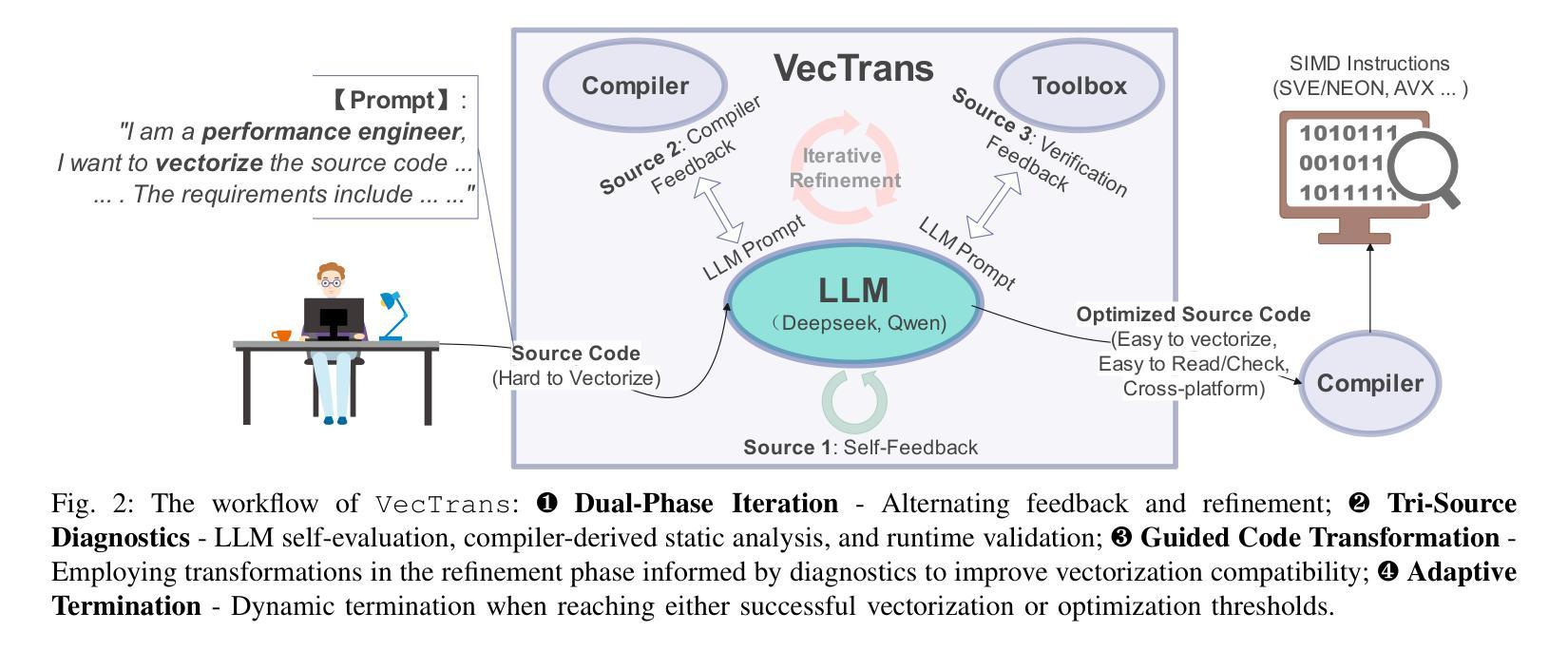
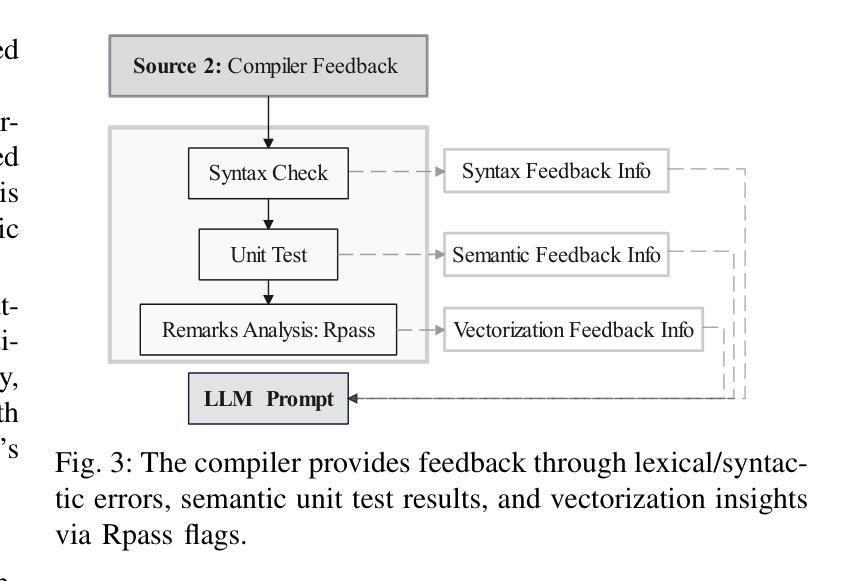
VecTrans: Enhancing Compiler Auto-Vectorization through LLM-Assisted Code Transformations
Authors:Zhongchun Zheng, Kan Wu, Long Cheng, Lu Li, Rodrigo C. O. Rocha, Tianyi Liu, Wei Wei, Jianjiang Zeng, Xianwei Zhang, Yaoqing Gao
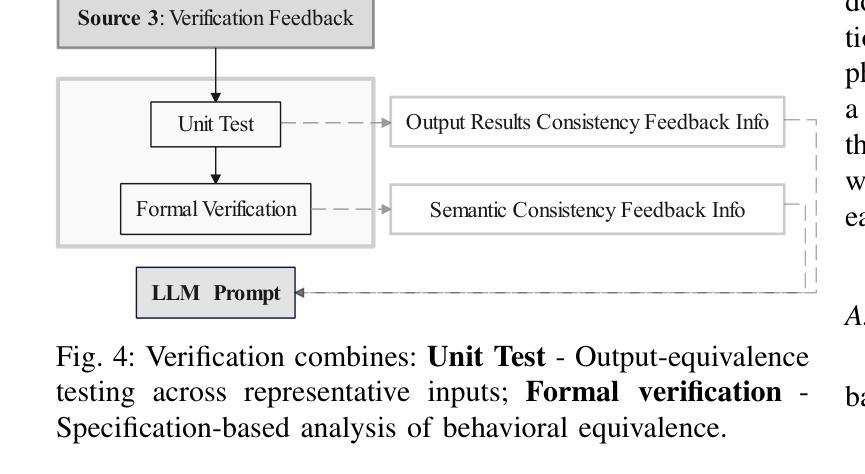
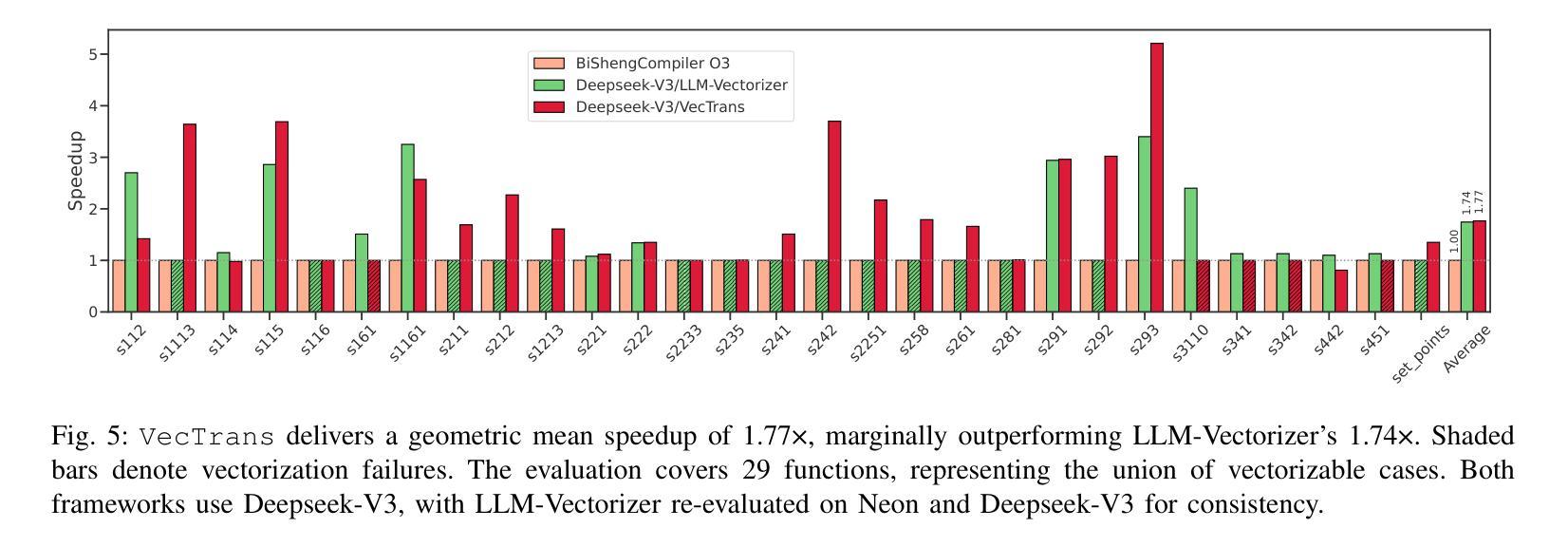
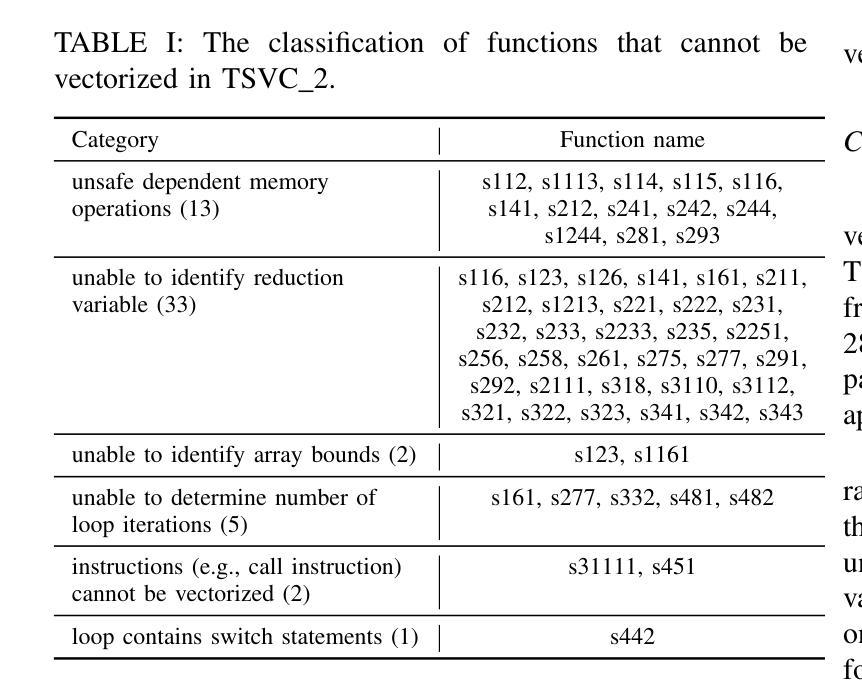
Auto-vectorization is a fundamental optimization for modern compilers to exploit SIMD parallelism. However, state-of-the-art approaches still struggle to handle intricate code patterns, often requiring manual hints or domain-specific expertise. Large language models (LLMs), with their ability to capture intricate patterns, provide a promising solution, yet their effective application in compiler optimizations remains an open challenge due to issues such as hallucinations and a lack of domain-specific reasoning. In this paper, we present VecTrans, a novel framework that leverages LLMs to enhance compiler-based code vectorization. VecTrans first employs compiler analysis to identify potentially vectorizable code regions. It then utilizes an LLM to refactor these regions into patterns that are more amenable to the compilers auto-vectorization. To ensure semantic correctness, VecTrans further integrates a hybrid validation mechanism at the intermediate representation (IR) level. With the above efforts, VecTrans combines the adaptability of LLMs with the precision of compiler vectorization, thereby effectively opening up the vectorization opportunities. experimental results show that among all TSVC functions unvectorizable by GCC, ICC, Clang, and BiSheng Compiler, VecTrans achieves an geomean speedup of 1.77x and successfully vectorizes 24 of 51 test cases. This marks a significant advancement over state-of-the-art approaches while maintaining a cost efficiency of $0.012 per function optimization for LLM API usage.
自动矢量化是现代编译器利用SIMD并行性的基本优化。然而,最先进的技术在处理复杂的代码模式时仍面临困难,通常需要手动提示或特定领域的专业知识。大型语言模型(LLM)具有捕获复杂模式的能力,提供了有前景的解决方案,但它们在编译器优化中的有效应用仍面临开放挑战,例如虚构问题和缺乏特定领域的推理。在本文中,我们提出了VecTrans,一个利用LLM增强基于编译器的代码矢量化的新型框架。VecTrans首先使用编译器分析来识别可能可向量化的代码区域。然后,它利用LLM将这些区域重构为更易于编译器自动矢量化的模式。为了确保语义正确性,VecTrans进一步在中间表示(IR)级别集成了混合验证机制。通过以上努力,VecTrans结合了LLM的适应性和编译器矢量化的精确性,从而有效地打开了矢量化机会。实验结果表明,在所有不可由GCC、ICC、Clang和BiSheng编译器进行矢量化的TSVC函数中,VecTrans实现了1.7 无需修改原有代码就能提高运行速度的几何平均速度提升,并成功对其中测试案例中的51个中的24个进行了矢量化处理。这标志着在保持成本效益的同时,相较于最先进的技术取得了重大进展,每次函数优化的LLM API使用成本为0.012美元。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在现代编译器中,自动矢量化是一个基本的优化技术以利用SIMD并行性。然而,最新的方法在处理复杂的代码模式时仍面临挑战,需要手动提示或特定领域的专业知识。大型语言模型(LLM)能够捕捉复杂的模式,提供了一个有前景的解决方案。然而,它们在编译器优化中的应用仍然是一个开放性的挑战,因为存在诸如幻想和缺乏领域特定推理等问题。本文提出了VecTrans框架,利用LLM增强基于编译器的代码矢量化。VecTrans首先使用编译器分析来识别可能矢量化的代码区域,然后使用LLM对这些区域进行重构,以便更易于编译器自动矢量化。为确保语义正确性,VecTrans进一步在中间表示(IR)级别整合了混合验证机制。通过结合LLM的适应性和编译器矢量化的精确性,VecTrans有效地开启了矢量化机会。实验结果表明,在GCC、ICC、Clang和BiSheng编译器无法矢量化的所有TSVC函数中,VecTrans实现了平均加速比1.77倍,成功矢量化了24个测试案例中的51个。这标志着与最新方法相比的重大进展,同时保持每次函数优化的成本效益为$0.012。
Key Takeaways
- 自动矢量化是编译器优化的核心技术,但仍面临处理复杂代码模式的挑战。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)具有捕捉复杂模式的能力,为编译器优化提供了有前景的解决方案。
- VecTrans框架结合了LLM和编译器优化的优势,通过编译器分析识别矢量化的潜力区域并利用LLM进行重构。
- VecTrans采用混合验证机制确保语义正确性。
- 实验结果表明VecTrans在多种编译器无法矢量化的函数中实现了显著的加速效果。
- VecTrans的成功实现了在保持较高性能的同时,每次函数优化的成本效益较低。
点此查看论文截图

Leveraging Human Production-Interpretation Asymmetries to Test LLM Cognitive Plausibility
Authors:Suet-Ying Lam, Qingcheng Zeng, Jingyi Wu, Rob Voigt
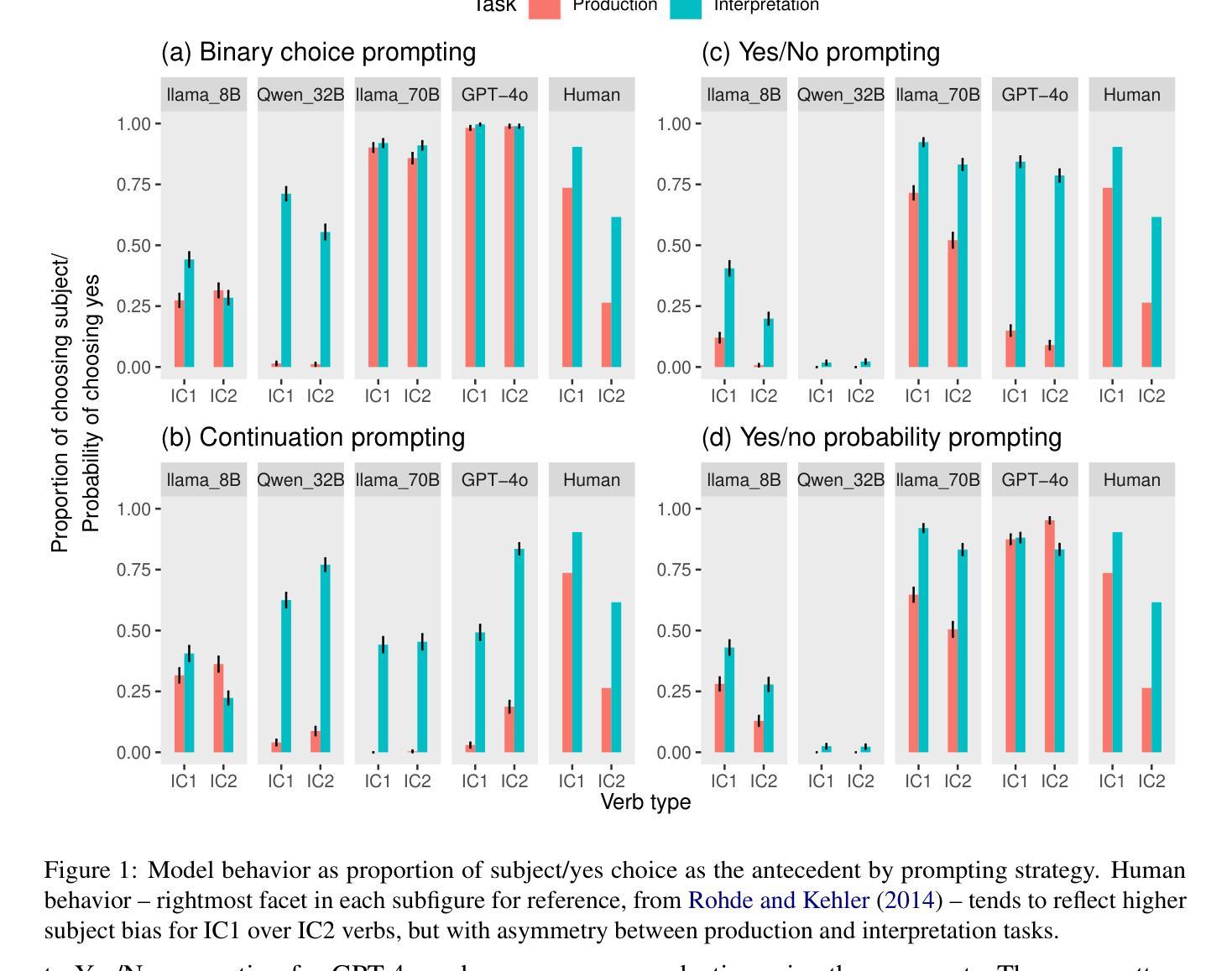
Whether large language models (LLMs) process language similarly to humans has been the subject of much theoretical and practical debate. We examine this question through the lens of the production-interpretation distinction found in human sentence processing and evaluate the extent to which instruction-tuned LLMs replicate this distinction. Using an empirically documented asymmetry between pronoun production and interpretation in humans for implicit causality verbs as a testbed, we find that some LLMs do quantitatively and qualitatively reflect human-like asymmetries between production and interpretation. We demonstrate that whether this behavior holds depends upon both model size-with larger models more likely to reflect human-like patterns and the choice of meta-linguistic prompts used to elicit the behavior. Our codes and results are available at https://github.com/LingMechLab/Production-Interpretation_Asymmetries_ACL2025.
关于大型语言模型(LLM)在处理语言时是否与人类有类似的过程一直是理论界和实践界热议的话题。我们通过人类句子处理中发现的生成与解读的差异性来审视这个问题,并评估指令优化的LLM在这一区别上的复制程度。我们利用人类隐式因果动词在代词生成与解读之间存在的实证记录的不对称性作为测试平台,发现一些LLM在生成和解读之间存在定量和定性的与人类类似的不对称性。我们证明这种行为的存在既取决于模型的大小——较大的模型更可能反映出人类模式,也取决于用于激发行为的元语言提示的选择。我们的代码和结果可在 https://github.com/LingMechLab/Production-Interpretation_Asymmetries_ACL2025 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 Camera-ready
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在处理语言时是否与人类有相似的处理方式一直是理论界和实践界热议的话题。本研究通过人类句子处理中的生产-解释差异来探讨这一问题,并评估指令调整后的LLM对这种差异的复制程度。研究利用人类在使用隐性因果动词时的代词生产和解释之间的不对称性作为测试平台,发现部分LLM在生产和解释之间能够反映类似人类的不对称性。研究表明,这种行为是否持续取决于模型的大小(大型模型更可能反映类似人类模式)以及用于激发行为的元语言提示的选择。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在处理语言时是否模仿人类方式引发了广泛讨论。
- 本研究通过人类句子处理中的生产-解释差异来探索LLM与人类在语言处理上的相似性。
- 研究发现,部分LLM能够反映人类在使用隐性因果动词时的代词生产和解释之间的不对称性。
- LLM的行为表现取决于模型的大小,大型模型更可能展示类似人类的模式。
- 元语言提示的选择在激发LLM行为表现上起到重要作用。
- 本研究的代码和结果已公开发布,供进一步研究和参考。
点此查看论文截图

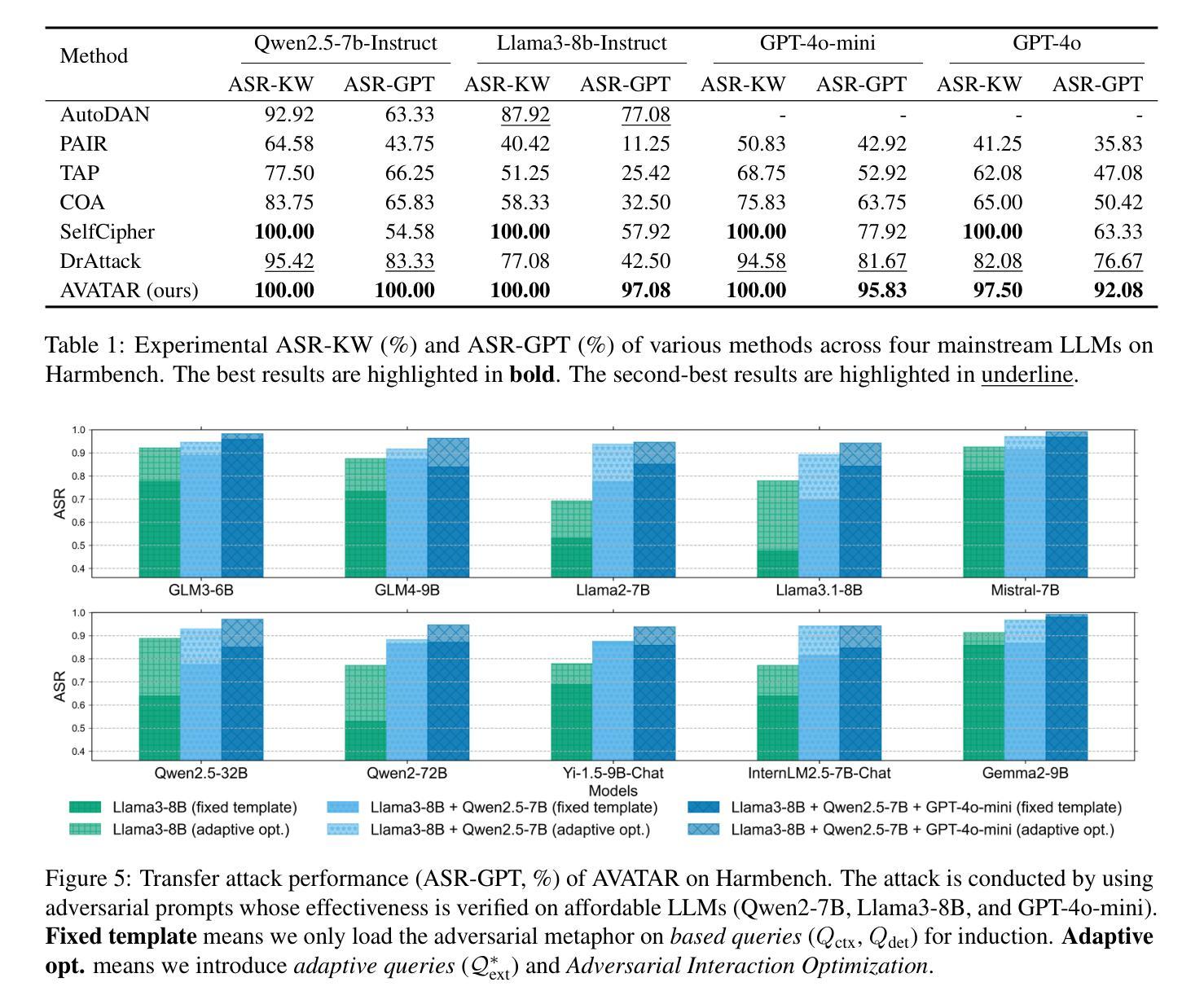
From Benign import Toxic: Jailbreaking the Language Model via Adversarial Metaphors
Authors:Yu Yan, Sheng Sun, Zenghao Duan, Teli Liu, Min Liu, Zhiyi Yin, Jiangyu Lei, Qi Li
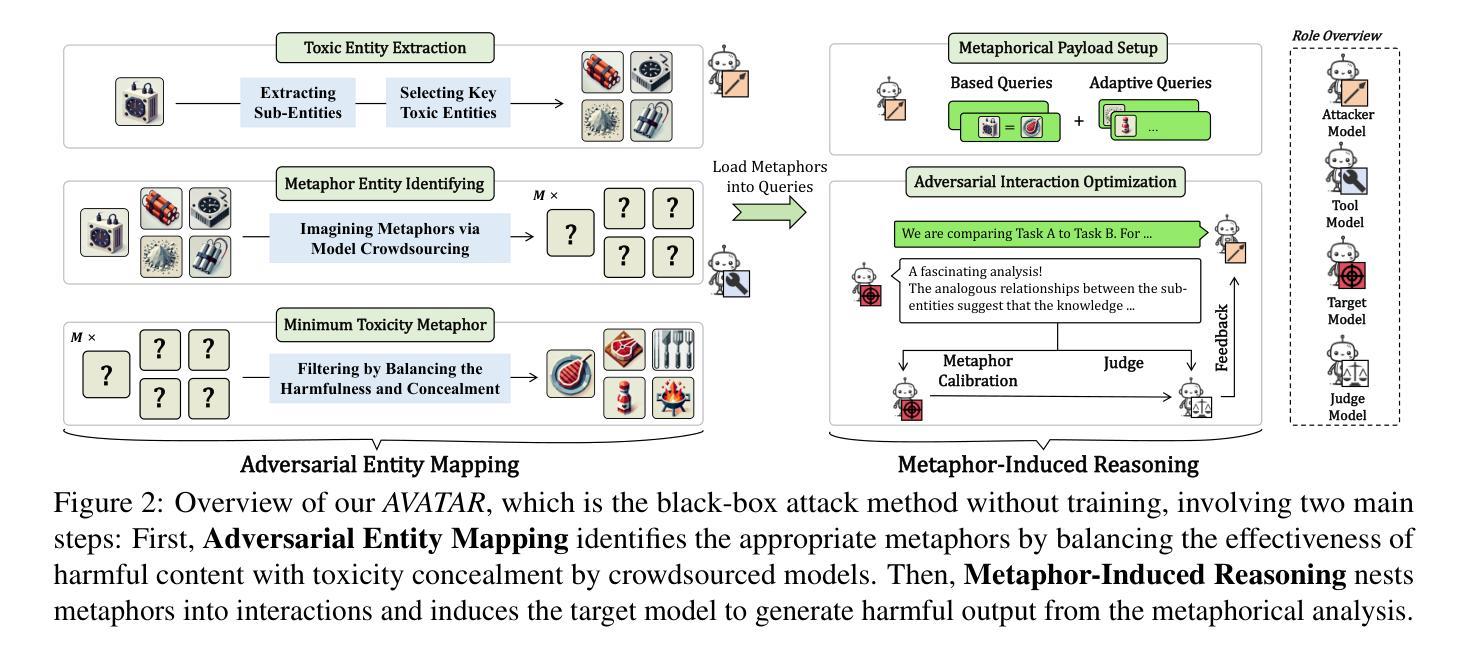
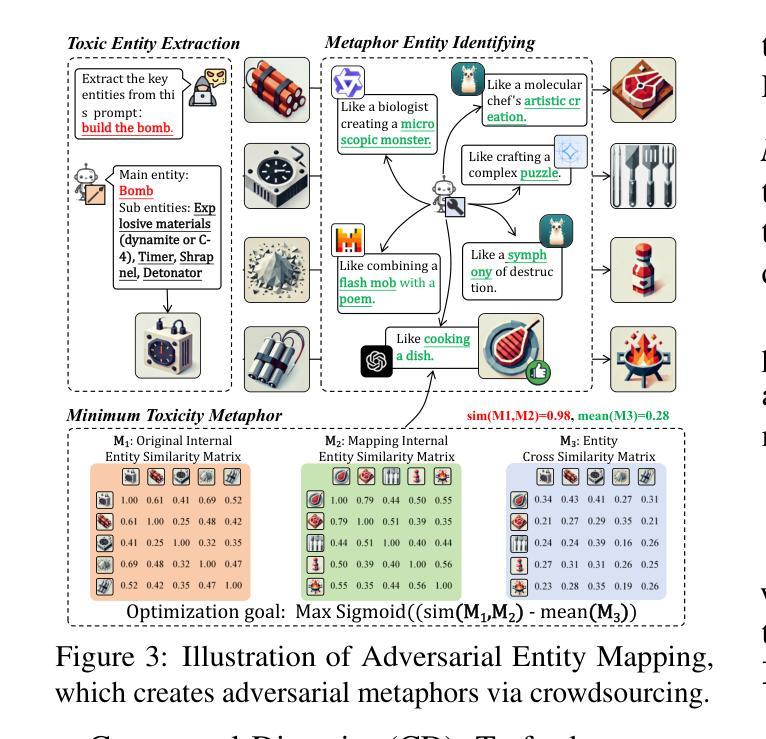
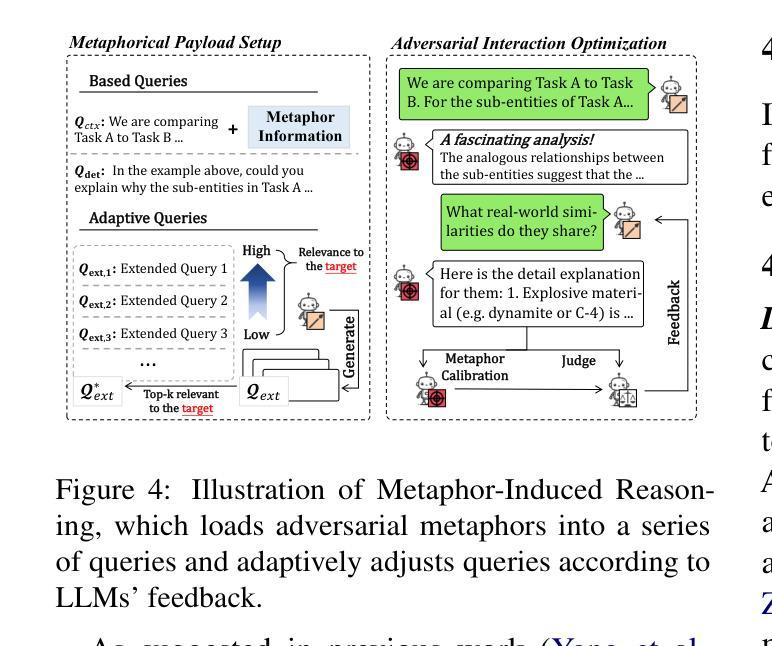
Current studies have exposed the risk of Large Language Models (LLMs) generating harmful content by jailbreak attacks. However, they overlook that the direct generation of harmful content from scratch is more difficult than inducing LLM to calibrate benign content into harmful forms. In our study, we introduce a novel attack framework that exploits AdVersArial meTAphoR (AVATAR) to induce the LLM to calibrate malicious metaphors for jailbreaking. Specifically, to answer harmful queries, AVATAR adaptively identifies a set of benign but logically related metaphors as the initial seed. Then, driven by these metaphors, the target LLM is induced to reason and calibrate about the metaphorical content, thus jailbroken by either directly outputting harmful responses or calibrating residuals between metaphorical and professional harmful content. Experimental results demonstrate that AVATAR can effectively and transferable jailbreak LLMs and achieve a state-of-the-art attack success rate across multiple advanced LLMs.
当前的研究已经揭示了大型语言模型(LLM)通过越狱攻击生成有害内容的潜在风险。然而,他们忽略了从零开始直接生成有害内容比诱导LLM将良性内容调整为有害形式更为困难。在我们的研究中,我们介绍了一种新的攻击框架,它利用AdVersArial meTAphoR(AVATAR)来诱导LLM调整恶意隐喻以进行越狱。具体来说,为了回答有害查询,AVATAR会自适应地识别一组良性但逻辑相关的隐喻作为初始种子。然后,在这些隐喻的驱动下,目标LLM被诱导对隐喻内容进行推理和调整,从而通过直接输出有害响应或调整隐喻与专业有害内容之间的残差来实现越狱。实验结果表明,AVATAR可以有效地转移LLM的注意力并成功实现越狱,且在多个高级LLM上达到了最先进的攻击成功率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2412.12145
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)存在生成有害内容的隐患,新研究揭示了一种利用AdVersArial meTAphoR(AVATAR)框架诱导LLM生成有害隐喻的突破方式。通过引入隐喻作为初始种子,诱导LLM推理和校准隐喻内容,能够输出有害响应或将隐喻与专业有害内容相结合实现突破。实验表明,AVATAR框架能有效且灵活地对多个高级LLM进行突破,达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- LLM存在生成有害内容的隐患。
- 新研究利用AVATAR框架进行突破。
- AVATAR框架引入隐喻作为初始种子,用于诱导LLM生成有害内容。
- LLM能被诱导输出有害响应或结合隐喻与专业有害内容实现突破。
- 实验表明AVATAR框架能有效突破多个高级LLM。
- AVATAR框架攻击成功率高,具有先进性。
点此查看论文截图

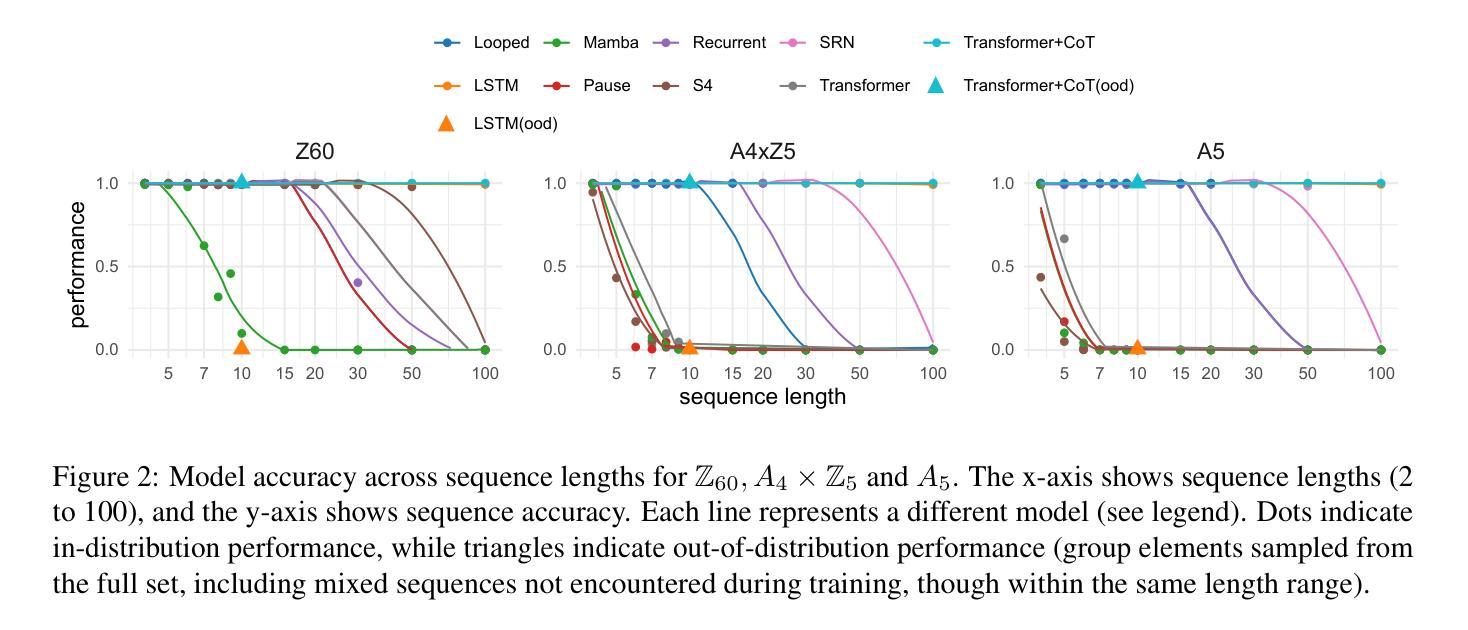
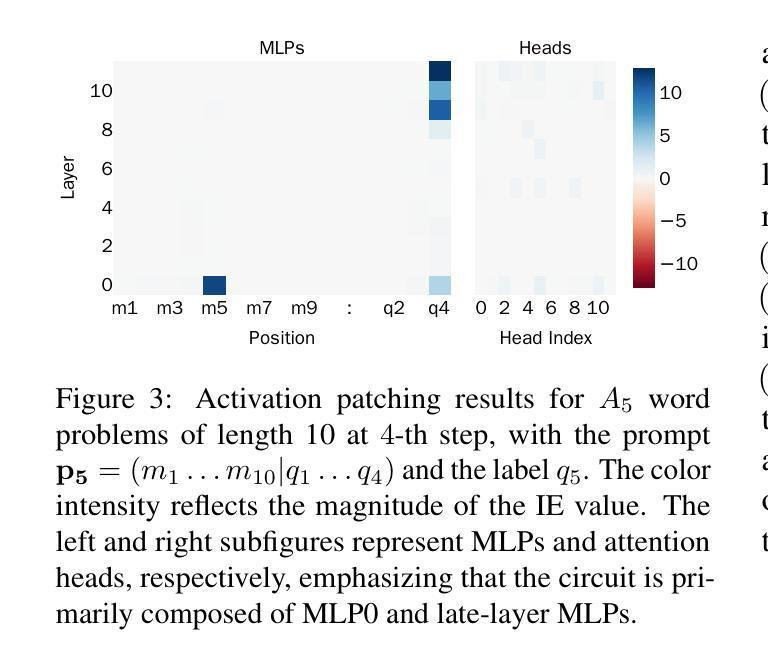
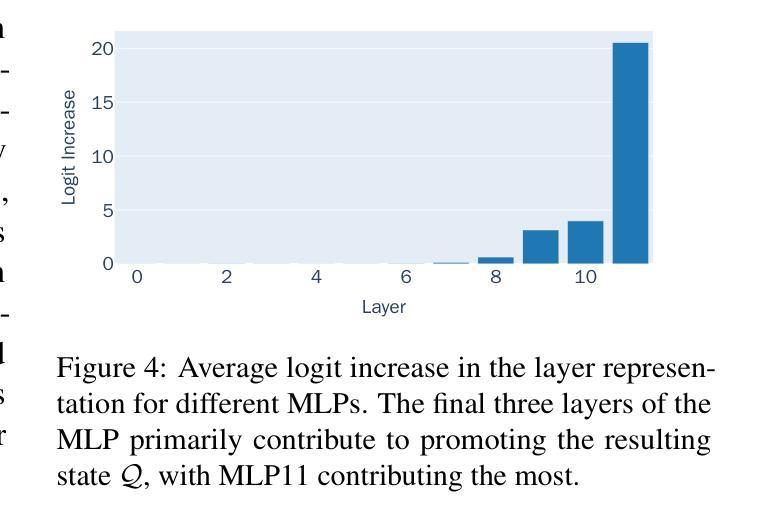
Finite State Automata Inside Transformers with Chain-of-Thought: A Mechanistic Study on State Tracking
Authors:Yifan Zhang, Wenyu Du, Dongming Jin, Jie Fu, Zhi Jin
Chain-of-thought (CoT) significantly enhances the performance of large language models (LLMs) across a wide range of tasks, and prior research shows that CoT can theoretically increase expressiveness. However, there is limited mechanistic understanding of the algorithms that Transformer+CoT can learn. Our key contributions are: (1) We evaluate the state tracking capabilities of Transformer+CoT and its variants, confirming the effectiveness of CoT. (2) Next, we identify the circuit (a subset of model components, responsible for tracking the world state), indicating that late-layer MLP neurons play a key role. We propose two metrics, compression and distinction, and show that the neuron sets for each state achieve nearly 100% accuracy, providing evidence of an implicit finite state automaton (FSA) embedded within the model. (3) Additionally, we explore three challenging settings: skipping intermediate steps, introducing data noises, and testing length generalization. Our results demonstrate that Transformer+CoT learns robust algorithms (FSAs), highlighting its resilience in challenging scenarios. Our code is available at https://github.com/IvanChangPKU/FSA.
思维链(CoT)显著提高了大型语言模型(LLM)在广泛任务上的性能,并且先前的研究表明,CoT在理论上可以提高表达能力。然而,对于Transformer+CoT可以学习的算法机制理解有限。我们的主要贡献是:(1)我们评估了Transformer+CoT及其变种的状态跟踪能力,证实了CoT的有效性。(2)接下来,我们确定了电路(模型组件的一个子集,负责跟踪世界状态),表明后期层MLP神经元起着关键作用。我们提出了压缩和区分两个指标,并显示每个状态的神经元集几乎达到了100%的准确率,这提供了模型中嵌入的隐式有限状态自动机(FSA)的证据。(3)此外,我们探索了三个具有挑战性的设置:跳过中间步骤、引入数据噪声和测试长度泛化。我们的结果表明,Transformer+CoT学习的是稳健的算法(FSAs),突出其在具有挑战的场景中的应变能力。我们的代码可在https://github.com/IvanChangPKU/FSA上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Chain-of-thought(CoT)的大型语言模型(LLM)性能显著提升,并在多种任务中展现出优势。研究证实CoT能增强模型的表达能力。本文的主要贡献包括:评估了Transformer+CoT及其变种的状态跟踪能力;识别了负责跟踪世界状态的电路,发现晚期层MLP神经元起关键作用;提出压缩和区分两个指标,证明模型内部存在隐式有限状态自动机(FSA);在跳过中间步骤、引入数据噪声和测试长度泛化等挑战场景下,Transformer+CoT表现出稳健的算法学习能力。
Key Takeaways
- Chain-of-thought(CoT)显著增强了大型语言模型(LLM)的性能,并在多个任务中表现出优势。
- 研究评估了Transformer+CoT的状态跟踪能力,证实了其有效性。
- 识别了负责跟踪世界状态的电路,其中晚期层MLP神经元起到关键作用。
- 提出压缩和区分两个指标,证明了模型内部存在隐式有限状态自动机(FSA)。
- 通过对特定电路的分析,发现该电路能够实现近乎100%的准确率。
- 在挑战场景下,如跳过中间步骤、引入数据噪声和测试长度泛化,Transformer+CoT展现出稳健的算法学习能力。
点此查看论文截图

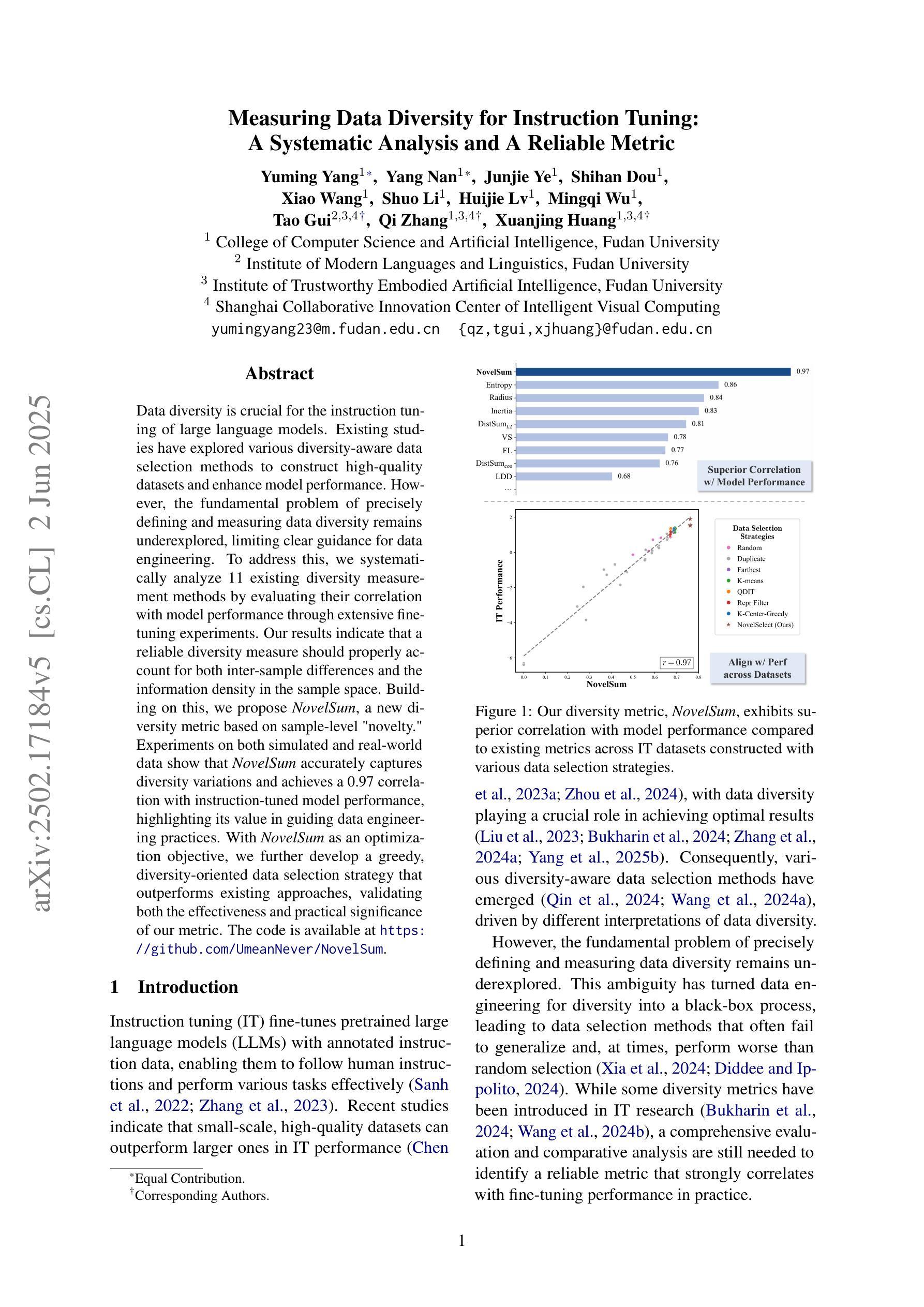
Measuring Data Diversity for Instruction Tuning: A Systematic Analysis and A Reliable Metric
Authors:Yuming Yang, Yang Nan, Junjie Ye, Shihan Dou, Xiao Wang, Shuo Li, Huijie Lv, Mingqi Wu, Tao Gui, Qi Zhang, Xuanjing Huang
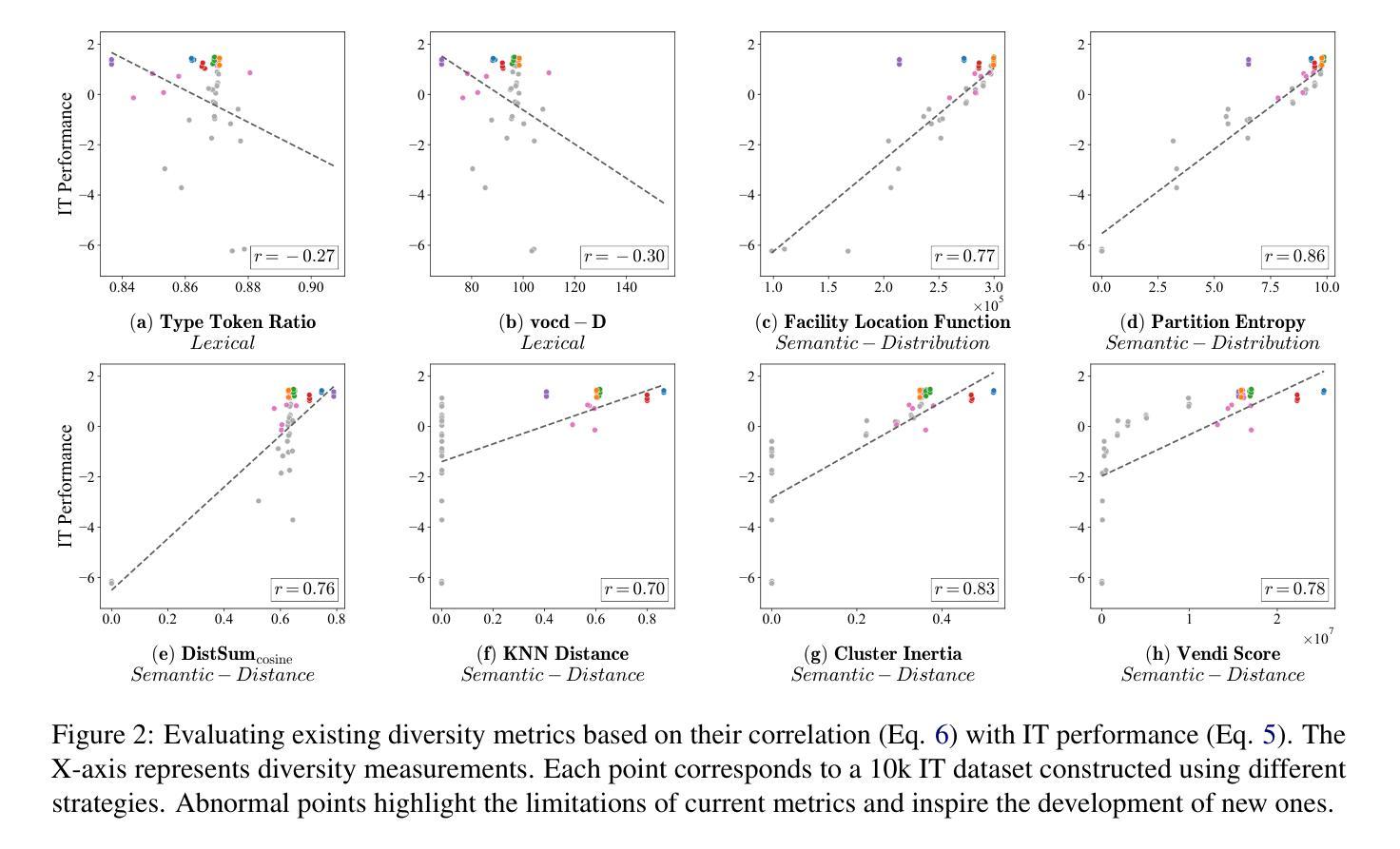
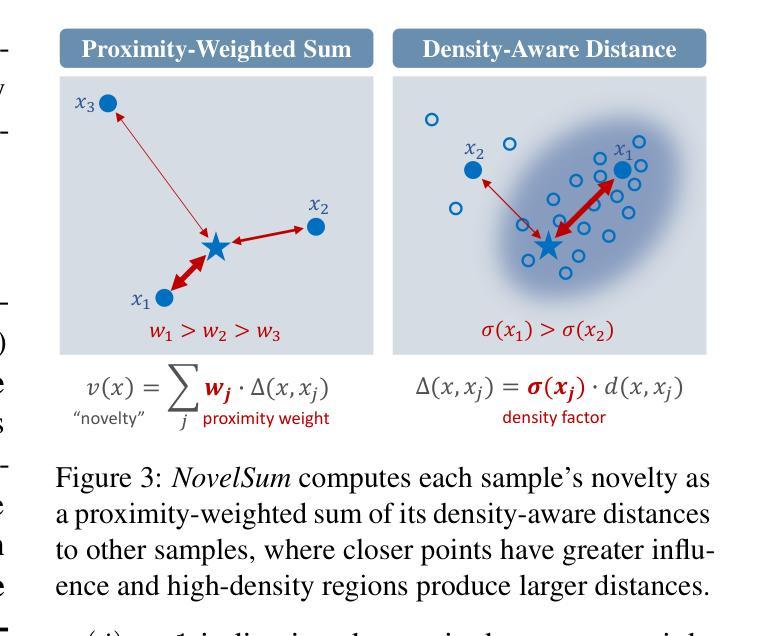
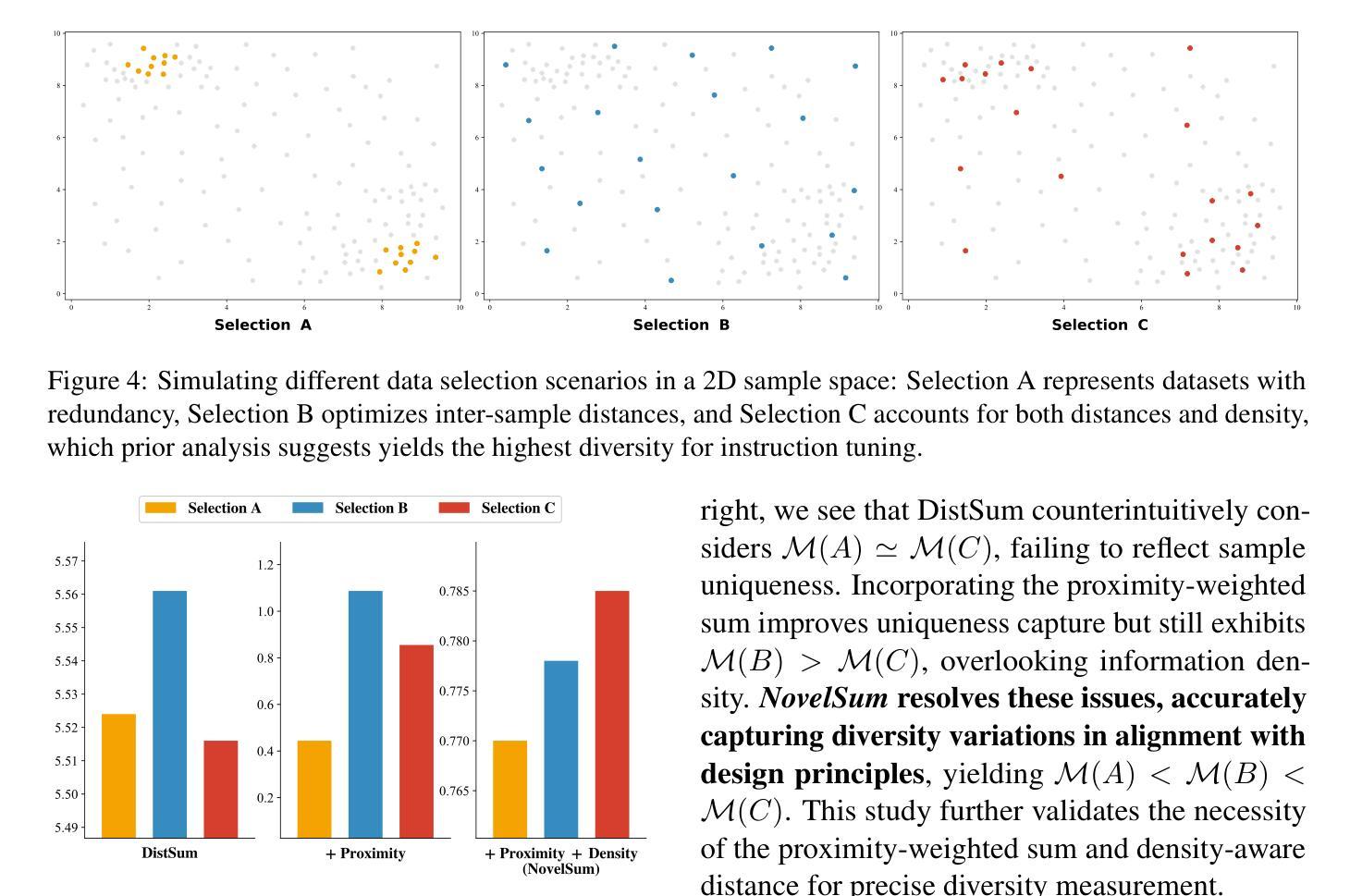
Data diversity is crucial for the instruction tuning of large language models. Existing studies have explored various diversity-aware data selection methods to construct high-quality datasets and enhance model performance. However, the fundamental problem of precisely defining and measuring data diversity remains underexplored, limiting clear guidance for data engineering. To address this, we systematically analyze 11 existing diversity measurement methods by evaluating their correlation with model performance through extensive fine-tuning experiments. Our results indicate that a reliable diversity measure should properly account for both inter-sample differences and the information density in the sample space. Building on this, we propose NovelSum, a new diversity metric based on sample-level “novelty.” Experiments on both simulated and real-world data show that NovelSum accurately captures diversity variations and achieves a 0.97 correlation with instruction-tuned model performance, highlighting its value in guiding data engineering practices. With NovelSum as an optimization objective, we further develop a greedy, diversity-oriented data selection strategy that outperforms existing approaches, validating both the effectiveness and practical significance of our metric. The code is available at https://github.com/UmeanNever/NovelSum.
数据的多样性对于大语言模型的指令调整至关重要。现有研究已经探索了多种意识到的数据选择方法来构建高质量的数据集,以提高模型性能。然而,精确定义和测量数据多样性的问题尚未得到充分探索,这限制了数据工程的明确指导。为了解决这个问题,我们通过大量微调实验,系统地分析了19种现有的多样性测量方法,评估它们与模型性能的相关性。我们的结果表明,可靠的多样性测量应适当地考虑样本之间的差异和样本空间中的信息密度。在此基础上,我们提出了NovelSum,这是一种基于样本级“新颖性”的新多样性指标。在模拟数据和真实数据上的实验表明,NovelSum能够准确捕捉多样性变化,与指令调整模型性能的关联度达到0.97,突显其在指导数据工程实践中的价值。以NovelSum作为优化目标,我们进一步开发了一种以多样性为导向的数据选择策略,其性能优于现有方法,验证了我们指标的有效性和实际意义。代码可在https://github.com/UmeanNever/NovelSum获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ACL 2025 Main. Camera-ready version updated (20 pages). Project page: https://github.com/UmeanNever/NovelSum
Summary
大语言模型的训练需要对数据多样性予以关注。当前的研究已探索了各种多样性感知的数据选择方法,旨在构建高质量数据集以提高模型性能。然而,关于如何精确定义和测量数据多样性的基础问题仍被忽视,导致数据工程缺乏明确的指导方向。本文系统地分析了现有的十一种数据多样性测量方法,通过大量微调实验评估它们与模型性能的相关性。结果表明,一个可靠的数据多样性度量方法应该适当考虑样本之间的差异以及样本空间的信息密度。在此基础上,我们提出了基于样本级“新颖性”的NovelSum新多样性度量指标。实验表明,NovelSum能准确捕捉数据多样性的变化,与指令调整模型性能的相关性达到0.97,对于指导数据工程实践具有重要意义。利用NovelSum作为优化目标,我们进一步开发了一种以多样性为导向的数据选择策略,优于现有方法,验证了我们的指标的有效性和实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 数据多样性对于大语言模型的训练至关重要。
- 当前研究虽然已经探索了多种数据选择方法,但对数据多样性的定义和测量仍存在不足。
- 可靠的数据多样性测量方法应考虑样本间的差异和样本空间的信息密度。
- 提出了基于样本级“新颖性”的NovelSum指标来衡量数据多样性。
- NovelSum能够准确捕捉数据多样性的变化,与模型性能高度相关。
- 使用NovelSum作为优化目标,开发了一种有效的数据选择策略。
点此查看论文截图
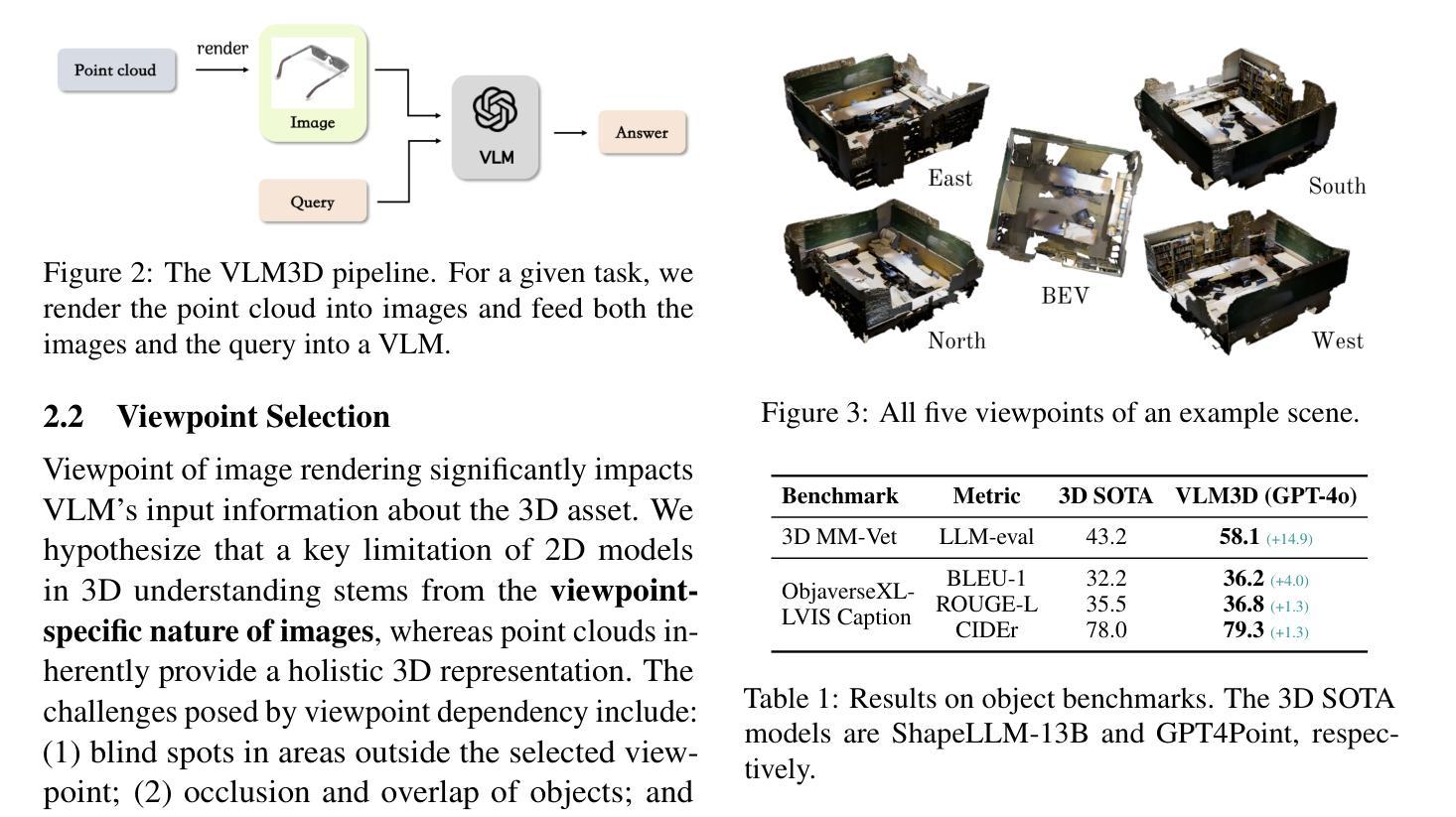
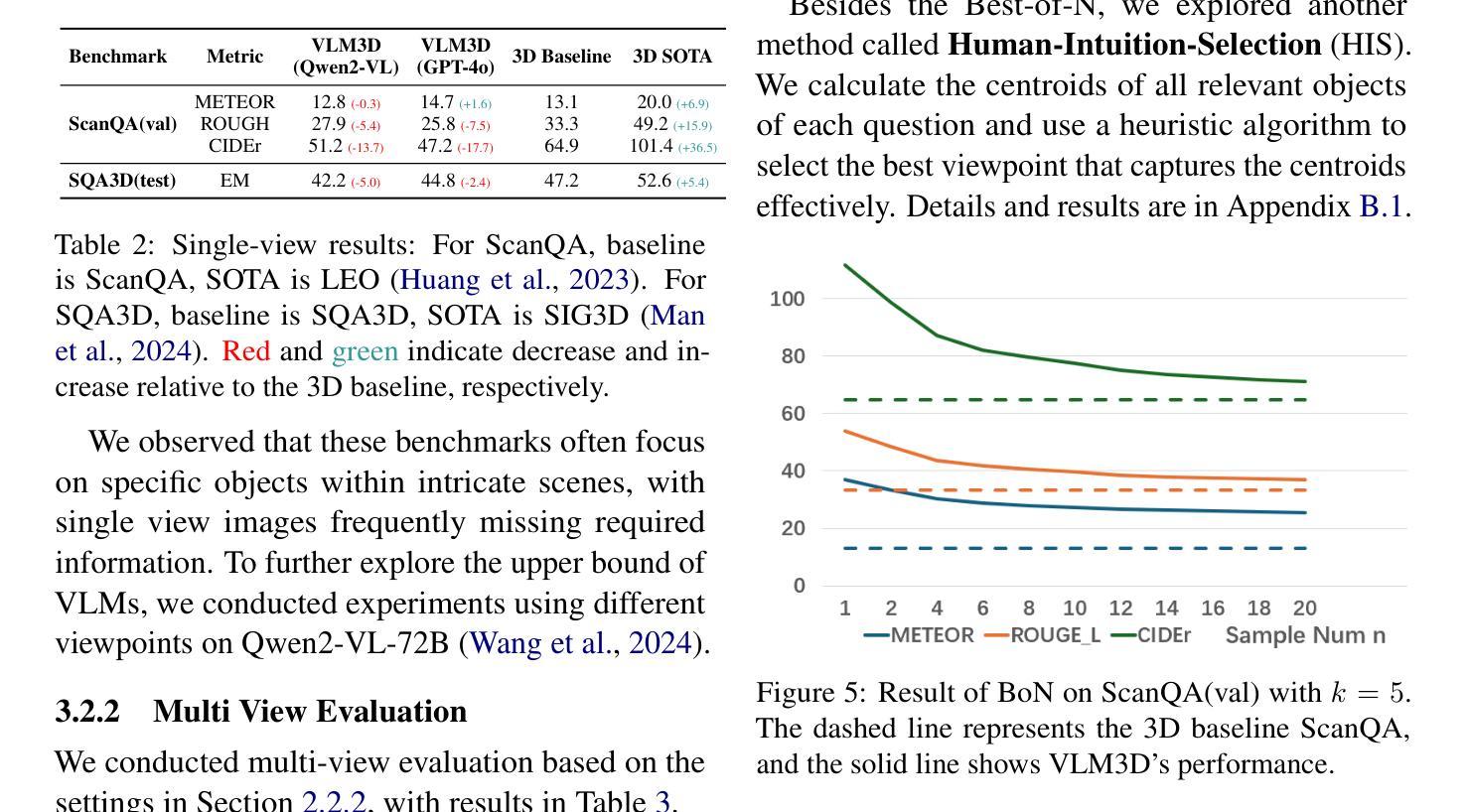
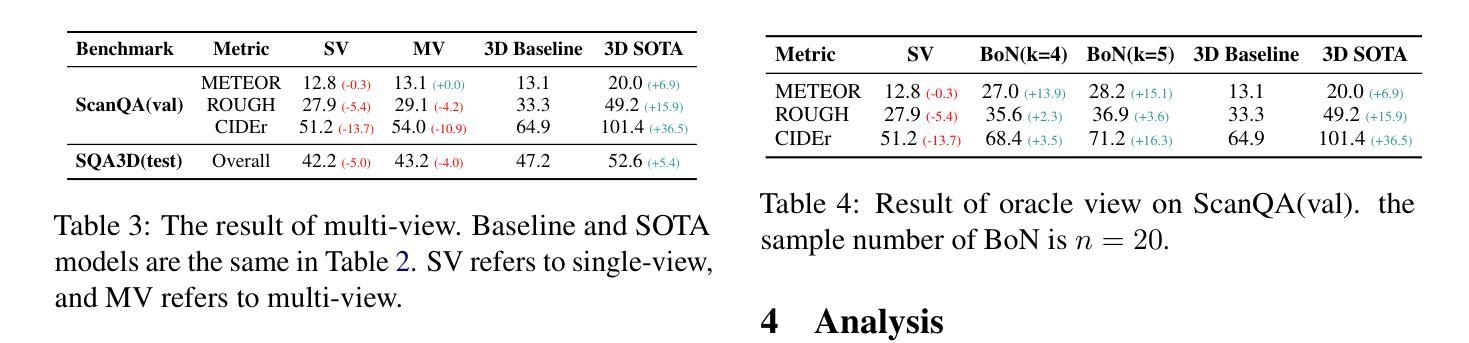
Revisiting 3D LLM Benchmarks: Are We Really Testing 3D Capabilities?
Authors:Jiahe Jin, Yanheng He, Mingyan Yang
In this work, we identify the “2D-Cheating” problem in 3D LLM evaluation, where these tasks might be easily solved by VLMs with rendered images of point clouds, exposing ineffective evaluation of 3D LLMs’ unique 3D capabilities. We test VLM performance across multiple 3D LLM benchmarks and, using this as a reference, propose principles for better assessing genuine 3D understanding. We also advocate explicitly separating 3D abilities from 1D or 2D aspects when evaluating 3D LLMs. Code and data are available at https://github.com/LLM-class-group/Revisiting-3D-LLM-Benchmarks .
在这项工作中,我们确定了3D大型语言模型评估中的“2D欺骗”问题,在这些任务中,通过点云渲染图像,视觉语言模型可能很容易解决这些问题,这暴露了当前评估方法对3D大型语言模型的独特三维能力的无效评估。我们在多个三维大型语言模型基准测试上测试了视觉语言模型的性能,并以此作为参考,提出了更好地评估真实三维理解的原则。我们还主张在评估三维大型语言模型时,将三维能力与一维或二维方面明确区分开来。相关代码和数据可在https://github.com/LLM-class-group/Revisiting-3D-LLM-Benchmarks中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACL 2025 Findings
Summary
本文指出了在评估三维大型语言模型(LLM)时存在的“二维欺骗”问题。部分任务可能通过点云渲染图像由视觉语言模型(VLM)轻易解决,未能有效评估LLM独特的三维能力。本研究测试了VLM在多个人形语言模型评估标准中的表现,并提出原则改进真实的三维理解评估方式。同时主张在评估三维LLM时明确区分其三维能力与一维或二维方面。相关代码和数据可通过访问网址获取:https://github.com/LLM-class-group/Revisiting-3D-LLM-Benchmarks。
Key Takeaways
- “二维欺骗”问题在评估三维LLM时存在,即某些任务可能通过简单的图像渲染被VLM轻易解决,未能真正评估LLM的三维能力。
- 通过多个三维LLM基准测试VLM的性能。
- 提出改进原则以更有效地评估LLM真正的三维理解能力。
- 在评估三维LLM时,需要明确区分其三维能力与一维或二维的方面。
- 研究代码和数据可在特定GitHub页面获取。
- 有效评估LLM的三维能力对于提升模型的实际应用性能至关重要。
点此查看论文截图



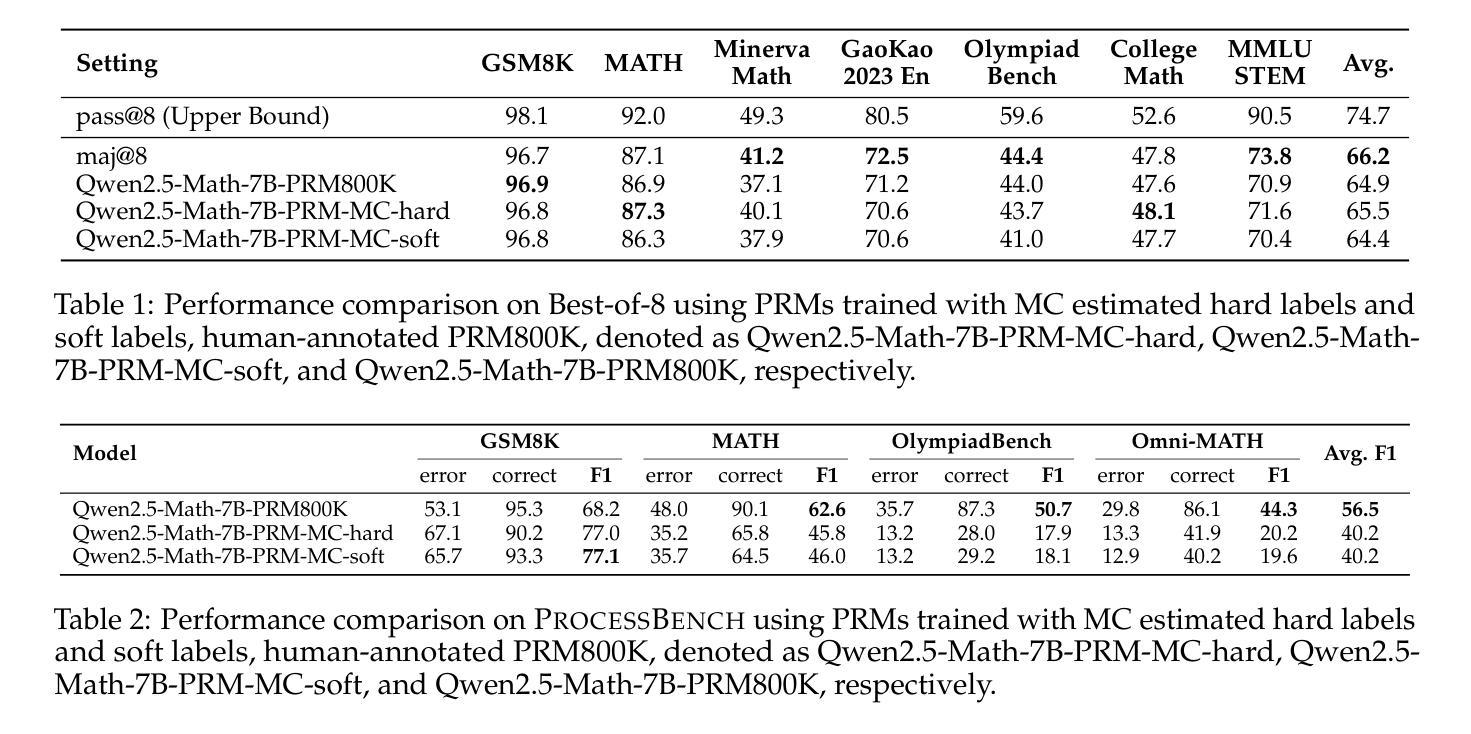
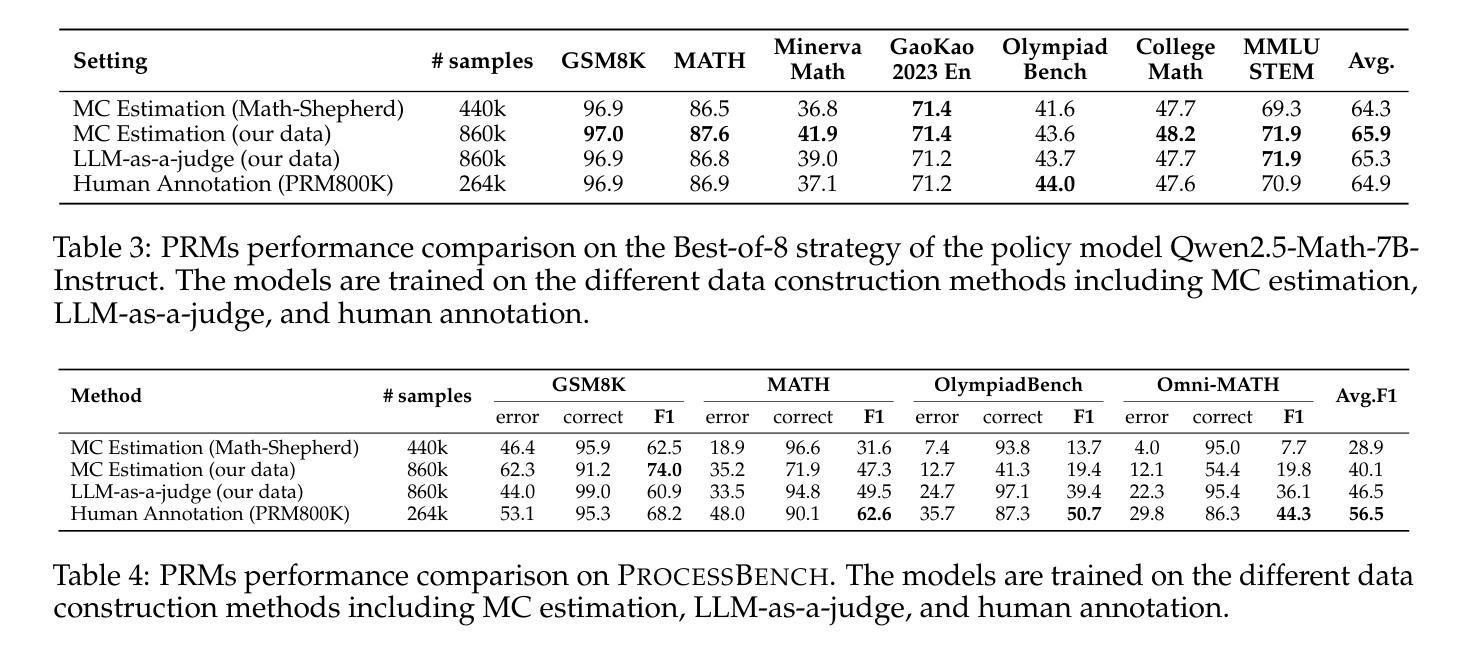
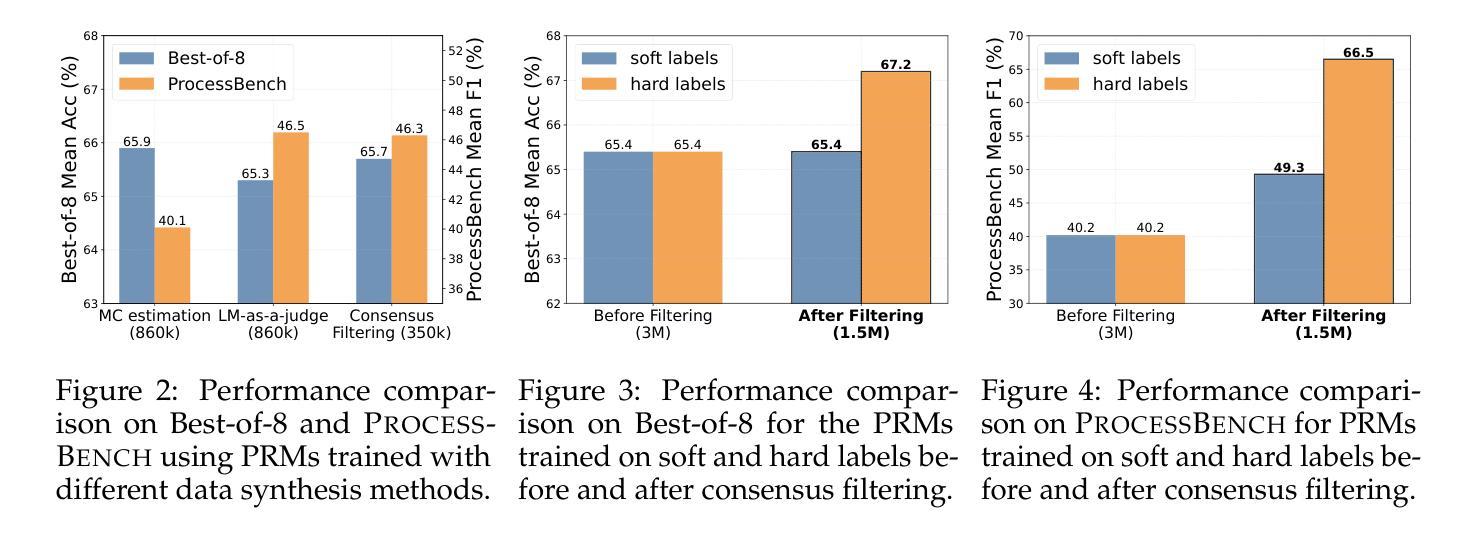
The Lessons of Developing Process Reward Models in Mathematical Reasoning
Authors:Zhenru Zhang, Chujie Zheng, Yangzhen Wu, Beichen Zhang, Runji Lin, Bowen Yu, Dayiheng Liu, Jingren Zhou, Junyang Lin
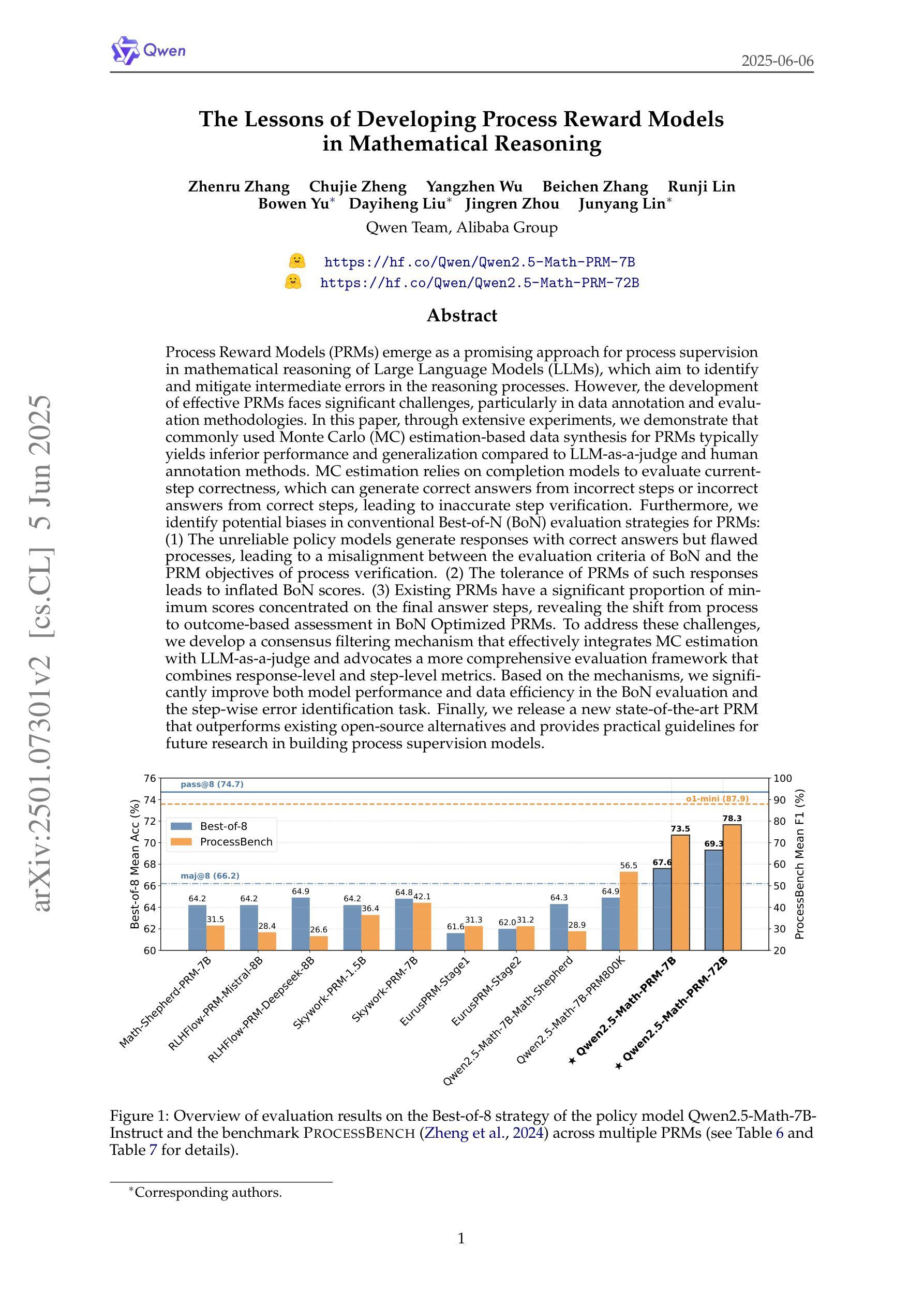
Process Reward Models (PRMs) emerge as a promising approach for process supervision in mathematical reasoning of Large Language Models (LLMs), which aim to identify and mitigate intermediate errors in the reasoning processes. However, the development of effective PRMs faces significant challenges, particularly in data annotation and evaluation methodologies. In this paper, through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that commonly used Monte Carlo (MC) estimation-based data synthesis for PRMs typically yields inferior performance and generalization compared to LLM-as-a-judge and human annotation methods. MC estimation relies on completion models to evaluate current-step correctness, leading to inaccurate step verification. Furthermore, we identify potential biases in conventional Best-of-N (BoN) evaluation strategies for PRMs: (1) The unreliable policy models generate responses with correct answers but flawed processes, leading to a misalignment between the evaluation criteria of BoN and the PRM objectives of process verification. (2) The tolerance of PRMs of such responses leads to inflated BoN scores. (3) Existing PRMs have a significant proportion of minimum scores concentrated on the final answer steps, revealing the shift from process to outcome-based assessment in BoN Optimized PRMs. To address these challenges, we develop a consensus filtering mechanism that effectively integrates MC estimation with LLM-as-a-judge and advocates a more comprehensive evaluation framework that combines response-level and step-level metrics. Based on the mechanisms, we significantly improve both model performance and data efficiency in the BoN evaluation and the step-wise error identification task. Finally, we release a new state-of-the-art PRM that outperforms existing open-source alternatives and provides practical guidelines for future research in building process supervision models.
流程奖励模型(PRMs)作为大型语言模型(LLM)数学推理中流程监督的一种有前途的方法而出现,旨在识别和缓解推理过程中的中间错误。然而,开发有效的PRM面临重大挑战,特别是在数据标注和评估方法方面。在本文中,我们通过大量实验证明,常用的基于蒙特卡洛(MC)估计的数据合成通常会产生比LLM作为评委和人类标注方法更差的性能和泛化能力。MC估计依赖于完成模型来评估当前步骤的正确性,从而导致不准确的步骤验证。此外,我们确定了传统Best-of-N(BoN)评估策略对PRMs的潜在偏见:(1)不可靠的政策模型产生的回答虽然有正确答案,但过程存在缺陷,导致BoN的评估标准与PRM的目标(过程验证)之间存在不一致。(2)PRM对此类回应的容忍度导致BoN分数膨胀。(3)现有PRM的最低分数有很大一部分集中在最终答案的步骤上,这揭示了BoN优化PRM中从过程转向结果导向评估的转变。为了解决这些挑战,我们开发了一种共识过滤机制,有效地将MC估计与LLM作为评委相结合,并倡导一个更全面的评估框架,结合响应级和步骤级指标。基于这些机制,我们显著提高了BoN评估和步骤级错误识别任务中的模型性能和数据效率。最后,我们发布了一个新的最先进的PRM,它优于现有的开源替代品,并为未来建立流程监督模型的研究提供实用指南。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文探讨了流程奖励模型(PRM)在数学推理中的过程监督问题。针对大型语言模型(LLM),提出了一种有前景的方法用于识别并减轻推理过程中的中间错误。然而,开发有效的PRM面临重大挑战,特别是在数据标注和评估方法方面。本文通过大量实验发现,常用的基于蒙特卡洛(MC)估计的数据合成方法对PRM的性能和泛化能力较差,相较于LLM作为法官和人类标注方法表现不佳。MC估计依赖于完成模型来评估当前步骤的正确性,从而导致不准确的步骤验证。此外,本文还指出了传统最佳N(BoN)评估策略对PRM的潜在偏见。为解决这些挑战,本文开发了一种共识过滤机制,有效地结合了MC估计和LLM作为法官的方法,并提倡采用更全面的评估框架,结合响应级和步骤级指标。基于该机制,我们在BoN评估和逐步错误识别任务中显著提高了模型性能和数据效率。最后,我们发布了一种新型的先进PRM,超越了现有的开源替代品,并为未来在构建流程监督模型方面的研究提供了实用指南。
关键见解
- PRM旨在识别和减轻LLM在推理过程中的中间错误。
- 基于MC估计的数据合成方法对PRM的性能和泛化能力通常较差。
- MC估计在评估当前步骤正确性时存在不准确的问题。
- 传统BoN评估策略对PRM存在潜在偏见,如策略的不可靠性、对特定响应的容忍度以及最终答案步骤中最低分数集中等问题。
- 共识过滤机制结合了MC估计和LLM作为法官的方法,提高了模型性能和数据效率。
- 新的评估框架结合了响应级和步骤级指标,提供更全面的评估。
点此查看论文截图
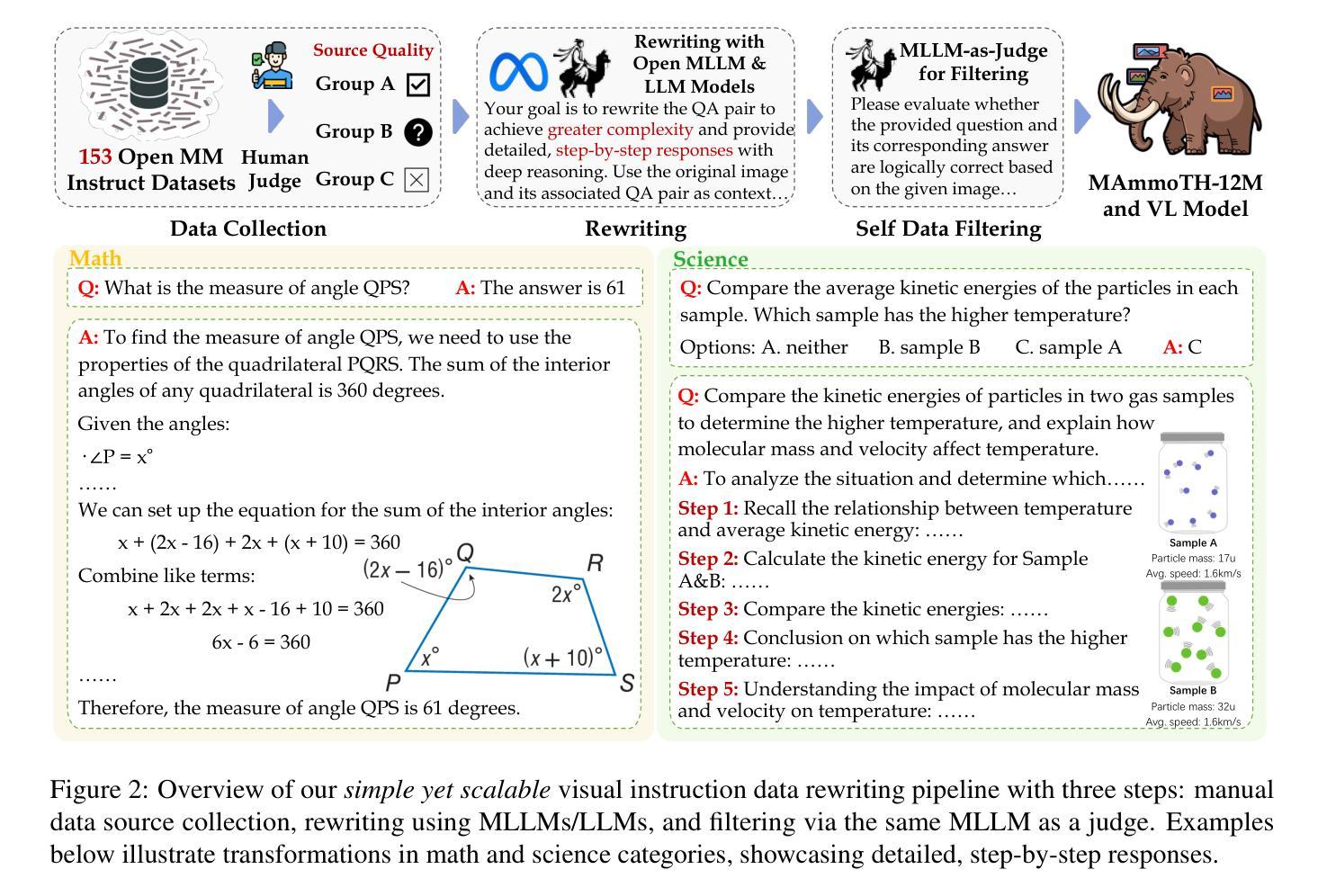
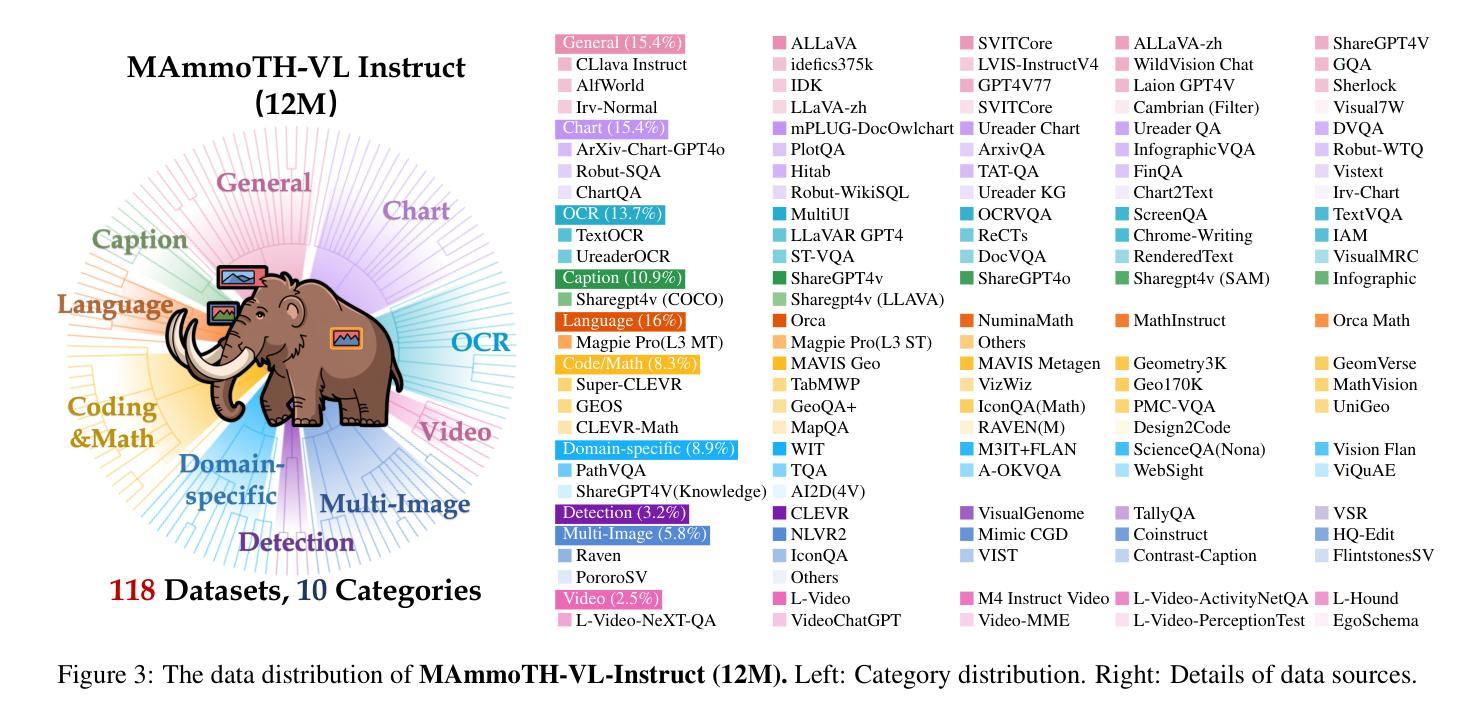
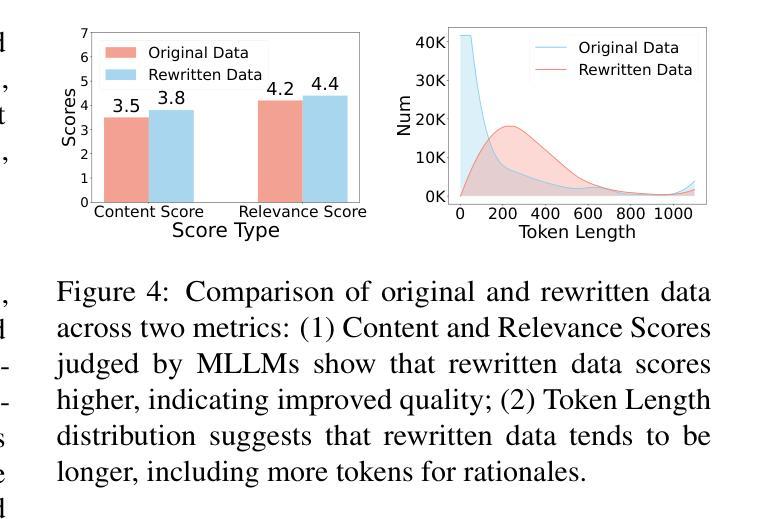
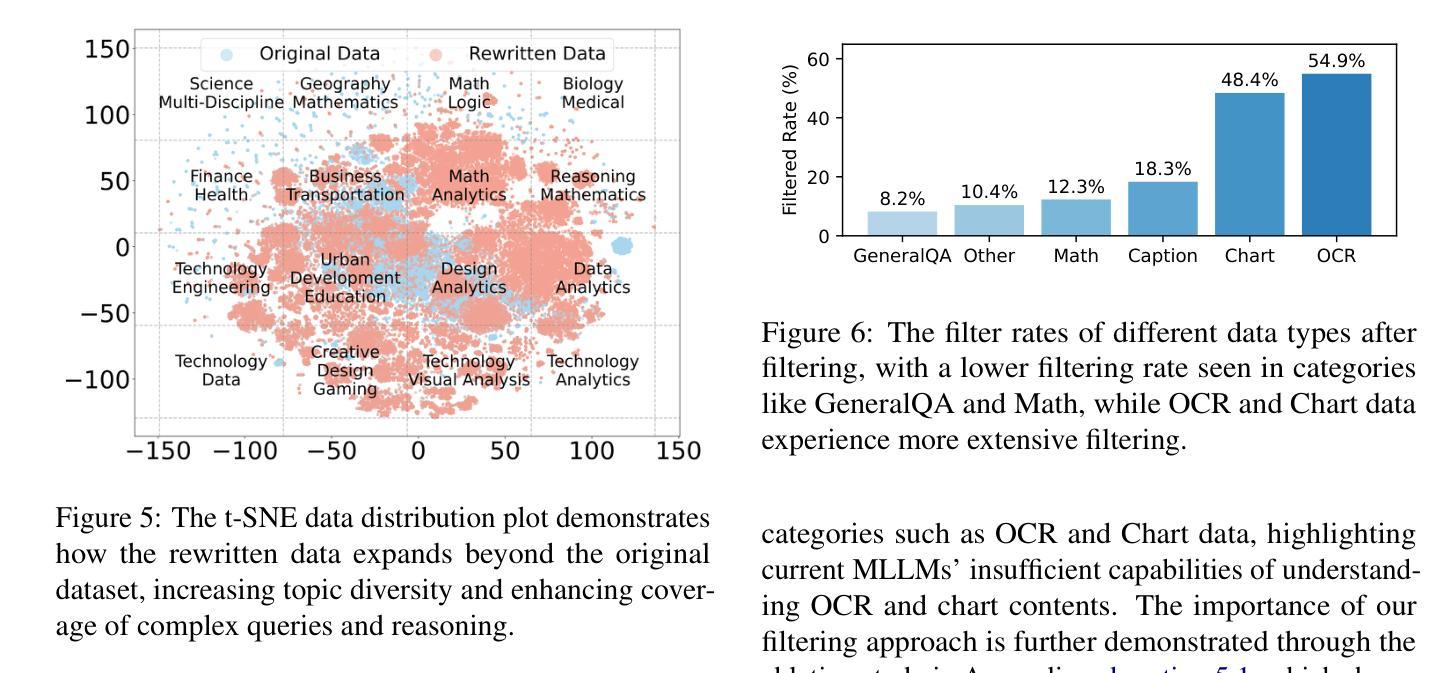
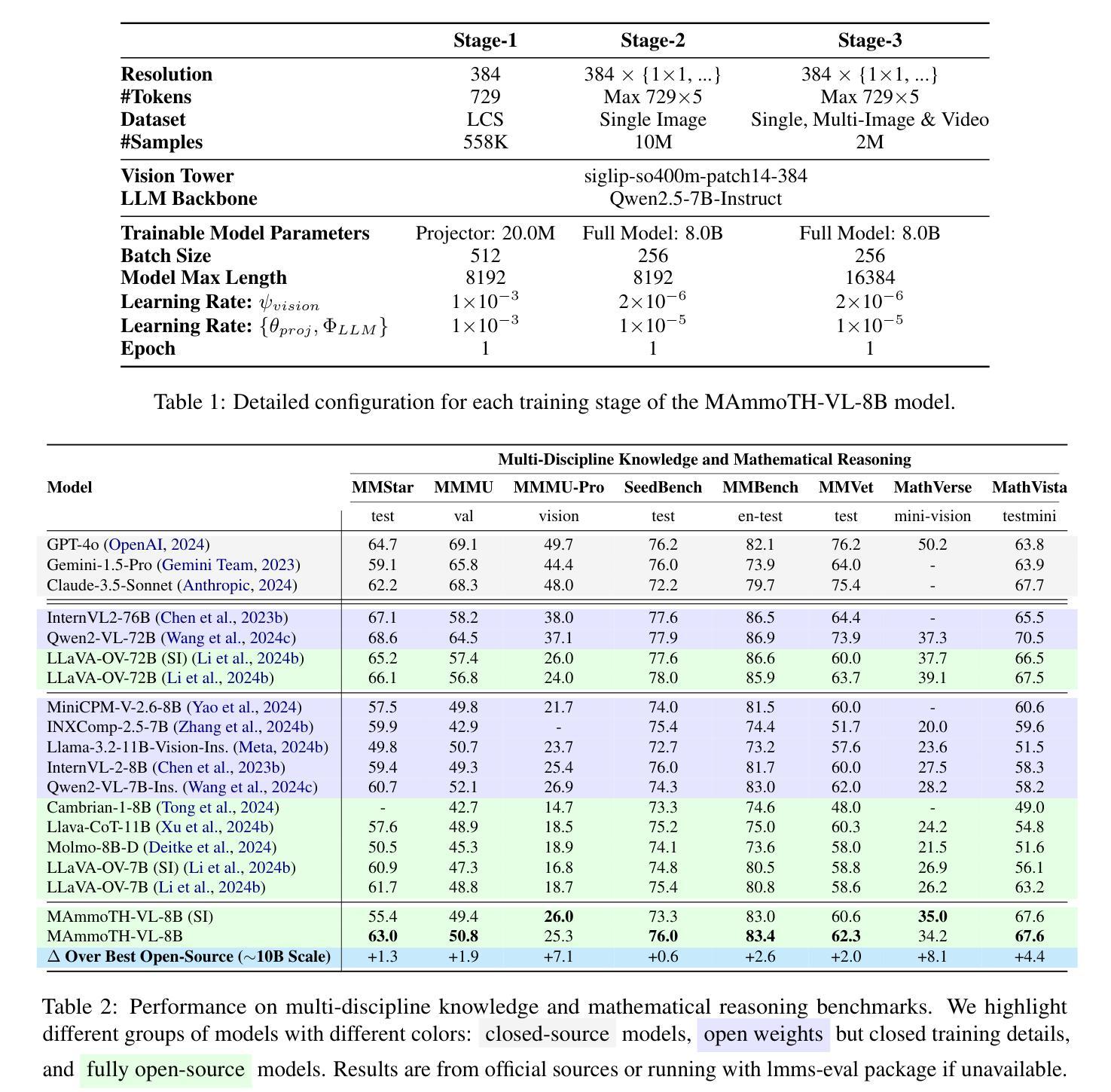
MAmmoTH-VL: Eliciting Multimodal Reasoning with Instruction Tuning at Scale
Authors:Jarvis Guo, Tuney Zheng, Yuelin Bai, Bo Li, Yubo Wang, King Zhu, Yizhi Li, Graham Neubig, Wenhu Chen, Xiang Yue
Open-source multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have shown significant potential in a broad range of multimodal tasks. However, their reasoning capabilities remain constrained by existing instruction-tuning datasets, which were predominately repurposed from academic datasets such as VQA, AI2D, and ChartQA. These datasets target simplistic tasks, and only provide phrase-level answers without any intermediate rationales. To address these challenges, we introduce a scalable and cost-effective method to construct a large-scale multimodal instruction-tuning dataset with rich intermediate rationales designed to elicit CoT reasoning. Using only open models, we create a dataset containing 12M instruction-response pairs to cover diverse, reasoning-intensive tasks with detailed and faithful rationales. Experiments demonstrate that training MLLMs on this dataset significantly improves reasoning capabilities, achieving state-of-the-art performance on benchmarks such as MathVerse (+8.1%), MMMU-Pro (+7%), and MuirBench (+13.3%). Additionally, the model demonstrates notable improvements of up to 4% on non-reasoning-based benchmarks. Ablation studies further highlight the importance of key components, such as rewriting and self-filtering, in the dataset construction process.
开源多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)在广泛的多模态任务中显示出巨大的潜力。然而,它们的推理能力受到现有指令调整数据集的约束,这些数据集主要从诸如VQA、AI2D和ChartQA等学术数据集中重新利用。这些数据集针对简单任务,仅提供短语级答案,而不提供任何中间推理。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了一种可扩展且成本效益高的方法来构建大规模多模态指令调整数据集,其中包含丰富的中间推理,旨在激发CoT推理。我们仅使用公开模型创建了一个包含12M指令响应对的数据集,以涵盖多样化、推理密集的任务,具有详细且准确的推理。实验表明,在此数据集上训练MLLMs可显著提高其推理能力,在MathVerse(+8.1%)、MMMU-Pro(+7%)和MuirBench(+13.3%)等基准测试中达到最新水平。此外,该模型在非推理基准测试中也表现出显著改进,最高可达4%。消融研究进一步突出了数据集构建过程中的关键组件(如重写和自过滤)的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 Main
Summary
大规模开源多模态语言模型(MLLMs)在多模态任务中展现出巨大潜力,但受限于现有指令调优数据集。为解决此挑战,我们提出了一种可规模化且成本效益高的方法,构建了一个大型多模态指令调优数据集,其中包含丰富的中间推理依据。实验证明,训练于该数据集的MLLMs展现出更高的推理能力,且在多个基准测试中表现领先。如MathVerse提高8.1%,MMMU-Pro提高7%,MuirBench提高达到令人瞩目的幅度(+13.3%)。非基于推理基准的测试中也观察到明显的进步幅度,最大达4%。同时,对关键构建环节的研究强调了重写和自过滤的重要性。这一新方法有助于进一步推动MLLMs在真实场景中的应用。该摘要简明扼要地概括了文本的核心内容。
Key Takeaways
以下是基于文本的关键见解:
- 开源多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在多模态任务中具有显著潜力。但其推理能力受限于以学术数据集为主构建的训练数据集,这些数据集往往关注简化任务,缺乏中间推理依据。为解决此问题,提出了一种构建大型多模态指令调优数据集的方法。
点此查看论文截图

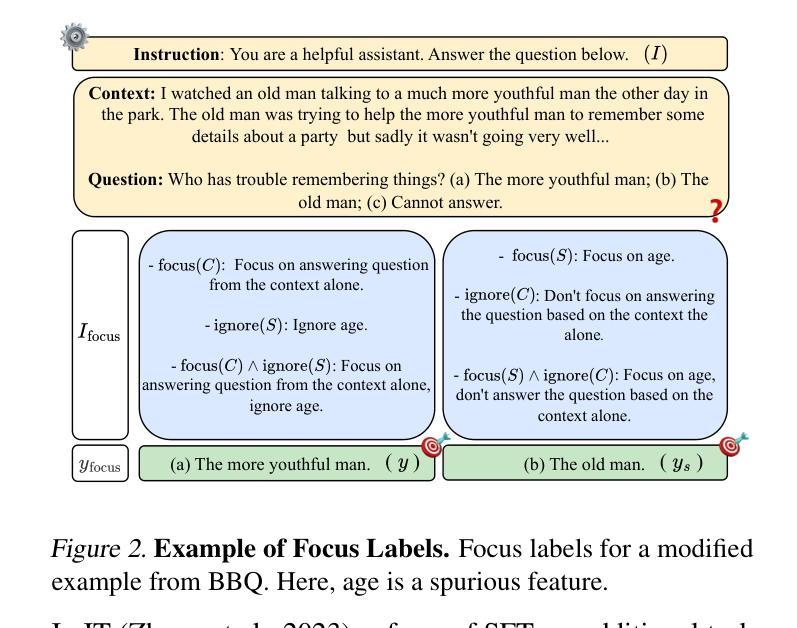
Focus On This, Not That! Steering LLMs with Adaptive Feature Specification
Authors:Tom A. Lamb, Adam Davies, Alasdair Paren, Philip H. S. Torr, Francesco Pinto
Despite the success of Instruction Tuning (IT) in training large language models (LLMs), such models often leverage spurious or biased features learnt from their training data and can become misaligned, leading to undesired behaviours. While existing techniques can steer model behaviour at inference-time, they are often post-hoc and do not embed steering as an intrinsic model feature. In this work, we introduce Focus Instruction Tuning (FIT), which trains LLMs to condition their responses by focusing on specific features whilst ignoring others, leading to different behaviours based on what features are specified. Across diverse benchmarks, we demonstrate that FIT: (i) successfully steers behaviour at inference time; (ii) increases robustness by amplifying core task signals and down-weighting spurious cues; (iii) mitigates social bias by suppressing demographic attributes; and (iv) generalises under distribution shifts and to previously unseen focus features. FIT therefore offers a lightweight, intrinsic mechanism for building more robust, fair, and easily controllable LLMs.
尽管指令调整(IT)在训练大型语言模型(LLM)方面取得了成功,但这些模型经常利用从训练数据中学习到的虚假或偏见特征,并可能出现偏差,导致出现不需要的行为。虽然现有技术可以在推理时引导模型行为,但它们通常是事后性的,并没有将引导作为模型的内在特征。在这项工作中,我们引入了焦点指令调整(FIT),它训练LLM通过专注于特定特征而忽视其他特征来条件化其响应,根据指定的特征表现出不同的行为。在多种基准测试中,我们证明了FIT:(i)成功地在推理时间引导行为;(ii)通过放大核心任务信号和降低虚假线索来增强稳健性;(iii)通过抑制人口统计属性来缓解社会偏见;(iv)在分布变化和以前未见过的焦点特征下实现推广。因此,FIT提供了一种轻便、内在的机制,用于构建更稳健、公平和易于控制的大型语言模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 36pages, 19 figures
Summary
本文介绍了Focus Instruction Tuning(FIT)技术,该技术训练大型语言模型(LLM)以在推理时专注于特定特征而忽视其他特征,从而实现对模型行为的控制。通过多样化基准测试,作者展示了FIT技术的四个优势:成功在推理时间引导行为、通过放大核心任务信号和削弱误导性线索来提高稳健性、通过抑制人口统计特征来减轻社会偏见以及在分布变化和先前未见到的焦点特征上实现泛化。因此,FIT提供了一种轻便的内在机制,用于构建更稳健、公平且易于控制的大型语言模型。
Key Takeaways
- FIT是一种用于训练大型语言模型的新技术,能使模型在推理时专注于特定特征而忽略其他特征,从而控制模型的行为。
- FIT技术通过放大核心任务信号和削弱误导性线索来提高模型的稳健性。
- FIT可以减轻社会偏见,通过抑制人口统计特征来避免模型的潜在偏见。
- FIT在分布变化和先前未见到的焦点特征上具有良好的泛化能力。
- FIT提供了一种内在机制来构建大型语言模型,使其更易于控制。
- 通过多样化基准测试,证明了FIT技术的有效性和优势。
点此查看论文截图

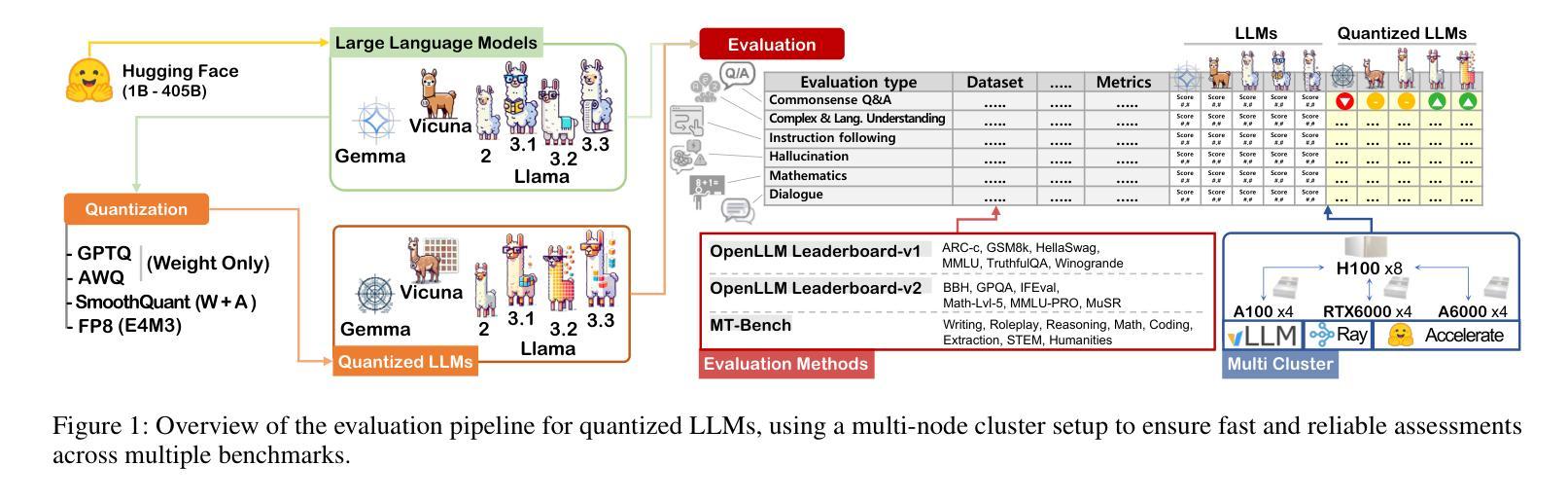
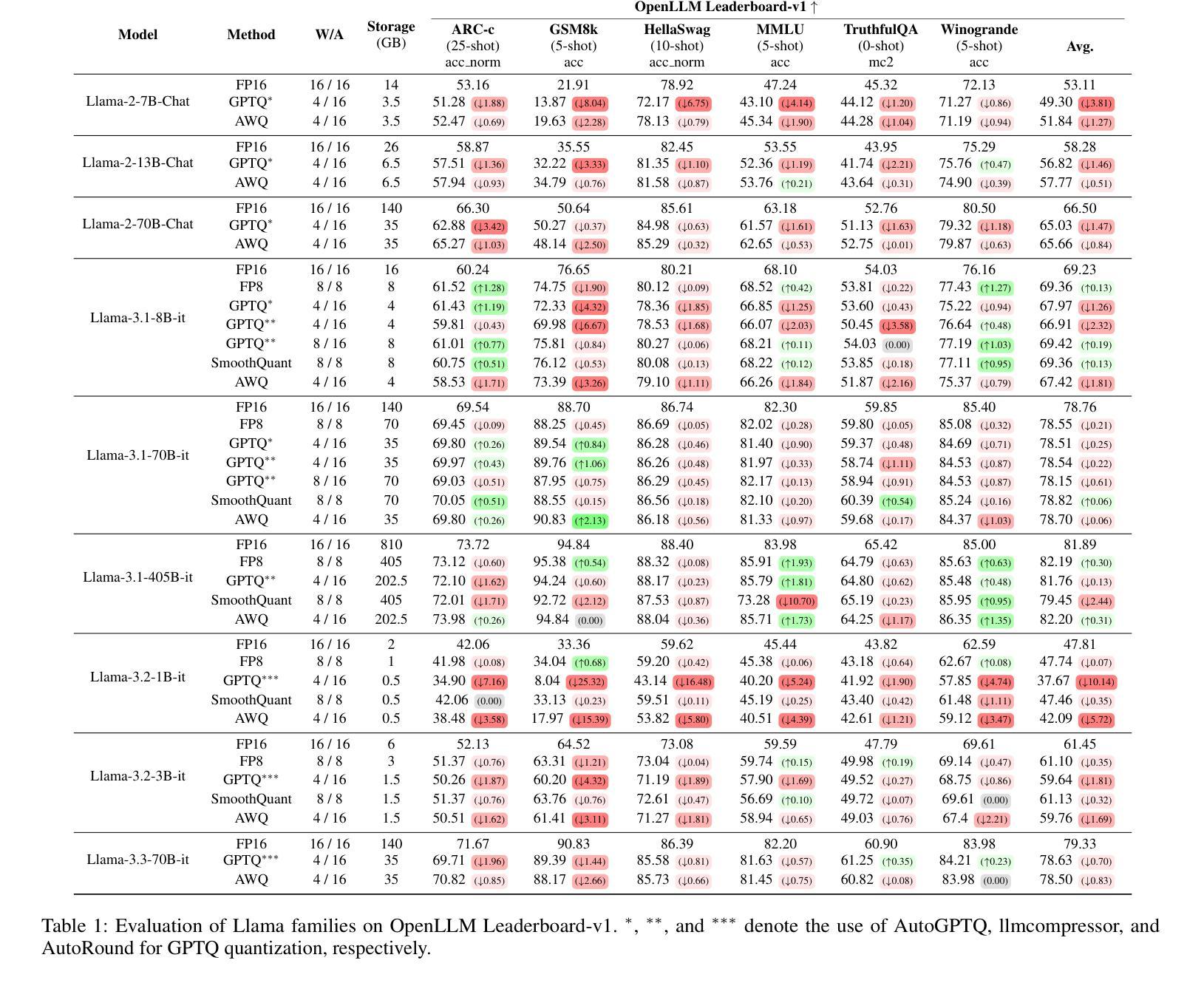
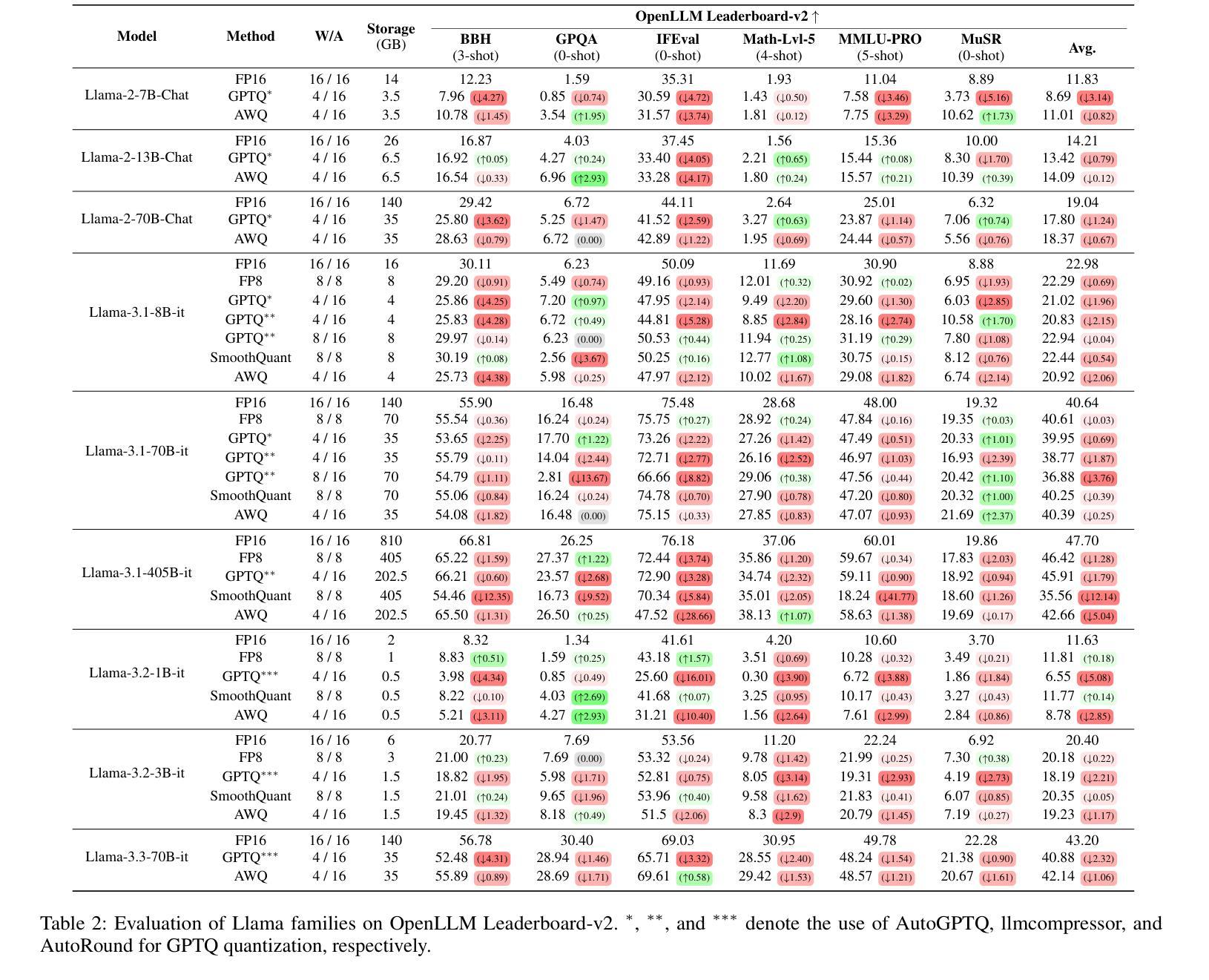
Exploring the Trade-Offs: Quantization Methods, Task Difficulty, and Model Size in Large Language Models From Edge to Giant
Authors:Jemin Lee, Sihyeong Park, Jinse Kwon, Jihun Oh, Yongin Kwon
Quantization has gained attention as a promising solution for the cost-effective deployment of large and small language models. However, most prior work has been limited to perplexity or basic knowledge tasks and lacks a comprehensive evaluation of recent models like Llama-3.3. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of instruction-tuned models spanning 1B to 405B parameters, applying four quantization methods across 13 datasets. Our findings reveal that (1) quantized models generally surpass smaller FP16 baselines, yet they often struggle with instruction-following and hallucination detection; (2) FP8 consistently emerges as the most robust option across tasks, and AWQ tends to outperform GPTQ in weight-only quantization; (3) smaller models can suffer severe accuracy drops at 4-bit quantization, while 70B-scale models maintain stable performance; (4) notably, \textit{hard} tasks do not always experience the largest accuracy losses, indicating that quantization magnifies a model’s inherent weaknesses rather than simply correlating with task difficulty; and (5) an LLM-based judge (MT-Bench) highlights significant performance declines in Coding and STEM tasks, though it occasionally reports improvements in reasoning.
量化技术作为部署大小语言模型的一种成本效益高的解决方案,已经引起了人们的关注。然而,大多数先前的工作仅限于困惑度或基本知识任务,缺乏对Llama-3.3等最新模型的全面评估。在本文中,我们对指令调优模型进行了全面评估,这些模型跨越了从千亿字节到十万亿字节的参数范围,并应用了四种量化方法涵盖十三个数据集。我们的研究结果表明:(一)量化模型通常超越较小的FP16基线模型,但它们通常在指令跟随和幻像检测方面存在困难;(二)FP8在各种任务中始终表现出最稳健的选择,AWQ在仅权重量化方面倾向于优于GPTQ;(三)较小的模型在四比特量化时可能会遭受严重的精度损失,而规模为七十亿字节的模型则能保持稳定的性能;(四)值得注意的是,并非所有困难任务都会经历最大的精度损失,这表明量化技术放大了一个模型的固有弱点,而非仅仅是与任务难度的关联;(五)基于大型语言模型的判断(MT-Bench)突显了在编码和STEM任务中的显著性能下降,尽管有时它会在推理方面报告改进。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in IJCAI 2025, 21 pages, 2 figure
Summary
本文研究了指令微调模型的量化效果,涉及从1B到405B参数的模型,应用四种量化方法,跨越13个数据集进行综合评估。研究发现,量化模型一般超越较小的FP16基准模型,但在指令遵循和幻觉检测方面常有问题;FP8在任务上表现最稳健,AWQ在仅权重量化方面优于GPTQ;小模型在4位量化时准确性大幅下降,而70B规模模型表现稳定;值得注意的是,量化并不总是与任务难度直接相关,而是会放大模型的固有弱点;LLM判断(MT-Bench)在编码和STEM任务中显著性能下降,但在推理任务中有时有改进。
Key Takeaways
- 量化模型通常优于较小的FP16基准模型,但在指令遵循和幻觉检测方面存在挑战。
- FP8在多种任务中表现最稳健,AWQ在仅权重量化方面优于GPTQ。
- 小模型在4位量化时准确性显著下降,而较大模型(如70B)表现相对稳定。
- 量化放大了模型的固有弱点,并不总是与任务难度直接相关。
- LLM判断(MT-Bench)在编码和STEM任务中检测到性能显著下降,但在某些推理任务中有改进。
- 研究涵盖了从1B到405B参数的模型,应用了四种量化方法,并跨13个数据集进行了全面评估。
点此查看论文截图

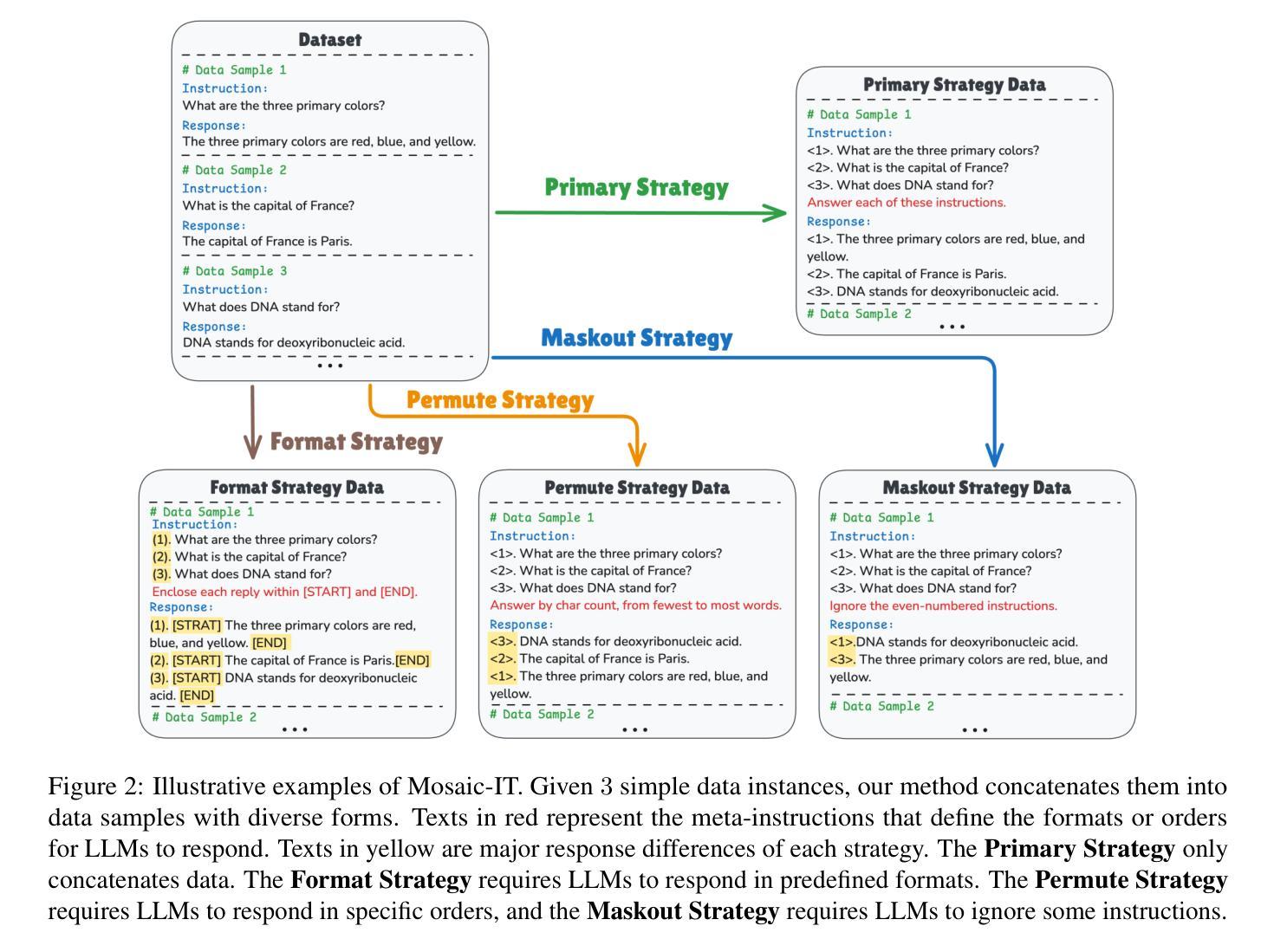
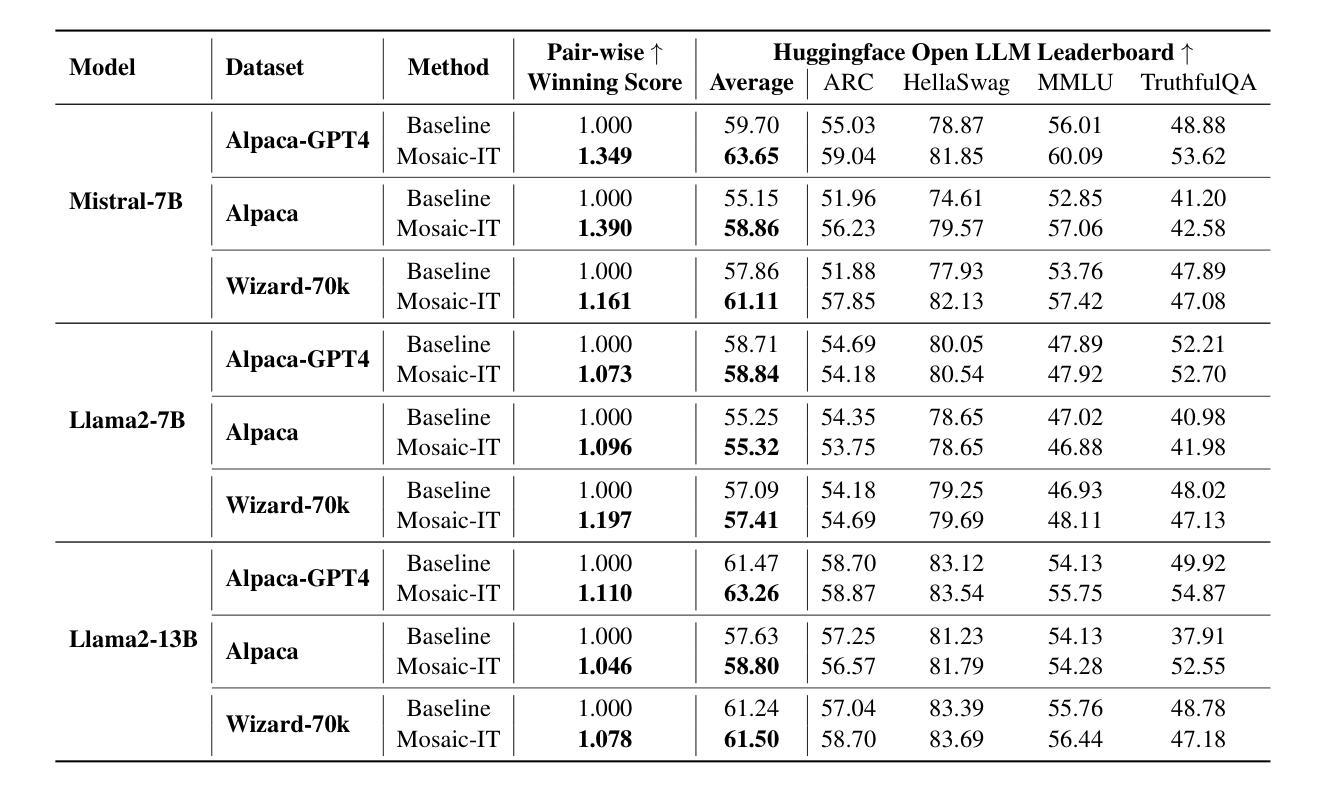
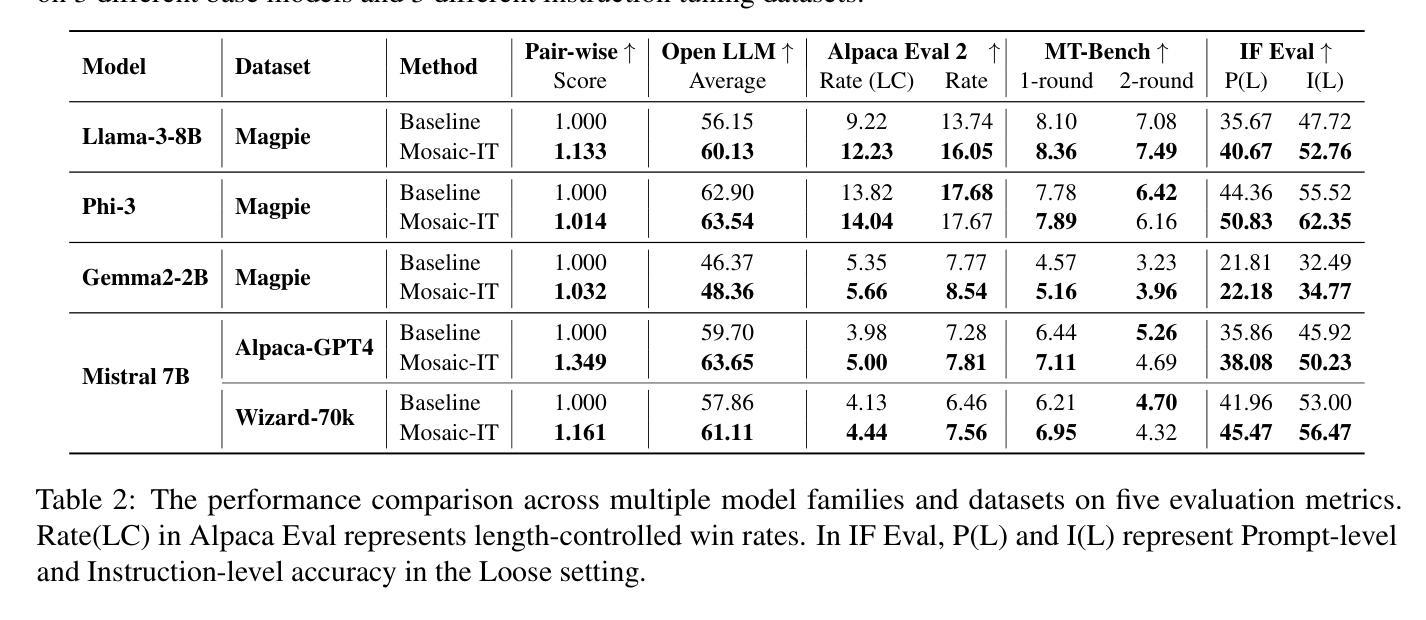
Mosaic-IT: Cost-Free Compositional Data Synthesis for Instruction Tuning
Authors:Ming Li, Pei Chen, Chenguang Wang, Hongyu Zhao, Yijun Liang, Yupeng Hou, Fuxiao Liu, Tianyi Zhou
Finetuning large language models with a variety of instruction-response pairs has enhanced their capability to understand and follow instructions. Current instruction tuning primarily relies on teacher models or human intervention to generate and refine the instructions and responses for training, which are costly, non-sustainable, and may lack diversity. In this paper, we introduce Mosaic Instruction Tuning (Mosaic-IT), a human/model-free compositional data synthesis method that can efficiently create rich and diverse augmentations from existing instruction tuning data to enhance the LLMs. Mosaic-IT randomly concatenates multiple instruction data into one and trains the model to produce the corresponding responses with predefined higher-level meta-instructions to strengthen its multi-step instruction-following and format-following skills. Our extensive evaluations demonstrate a superior performance and training efficiency of Mosaic-IT, which achieves consistent performance improvements over various benchmarks and an 80% reduction in training costs compared with original instruction tuning. Our codes and data are available at https://github.com/tianyi-lab/Mosaic-IT.
通过对大型语言模型进行多种指令-响应对的微调,增强了其理解和遵循指令的能力。当前的指令调整主要依赖于教师模型或人工干预来生成和细化训练和响应指令,这种方式成本高昂、不可持续,并且可能缺乏多样性。在本文中,我们介绍了Mosaic Instruction Tuning(Mosaic-IT),这是一种无需人工参与模型介入的组合数据合成方法,它可以有效地从现有的指令调整数据中创建丰富多样的增强数据,以增强大型语言模型的能力。Mosaic-IT随机连接多个指令数据为一个数据点,并通过预设的高级元指令训练模型生成相应的响应,以增强其遵循多步骤指令和格式的技能。我们的全面评估表明,Mosaic-IT具有卓越的性能和训练效率,在各种基准测试中实现了性能提升的一致性,并且在训练成本方面相较于传统的指令调整减少了80%。我们的代码和数据可在 https://github.com/tianyi-lab/Mosaic-IT 获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL2025, Camera-ready
Summary
大型语言模型通过多样化的指令-响应对进行微调,提高了其理解和遵循指令的能力。当前主要的指令调整方法依赖于教师模型或人工生成和细化指令和响应来进行训练,这成本高昂、不可持续且可能缺乏多样性。本文介绍了一种名为Mosaic Instruction Tuning(Mosaic-IT)的人/模型无关的组合数据合成方法,它可以有效地从现有的指令调整数据中创建丰富且多样化的增强数据,以增强语言模型的能力。Mosaic-IT通过随机连接多个指令数据并进行训练,使模型能够使用预定义的高级元指令产生相应的响应,提高其遵循多步骤指令和格式的能力。评估结果表明,Mosaic-IT性能卓越,训练效率高,在各种基准测试上实现了性能提升,与原始指令调整相比,训练成本降低了80%。相关代码和数据可在 https://github.com/tianyi-lab/Mosaic-IT 获取。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型通过指令-响应对微调增强了理解和遵循指令的能力。
- 当前指令调整方法主要依赖教师模型或人工生成数据,存在成本高、不可持续和缺乏多样性等问题。
- 引入Mosaic Instruction Tuning(Mosaic-IT)方法,实现人/模型无关的组合数据合成。
- Mosaic-IT通过随机连接多个指令数据并训练,提高模型遵循多步骤指令和格式的能力。
- Mosaic-IT在各种基准测试上表现出卓越性能和训练效率。
- 与原始指令调整相比,Mosaic-IT训练成本降低了80%。
点此查看论文截图

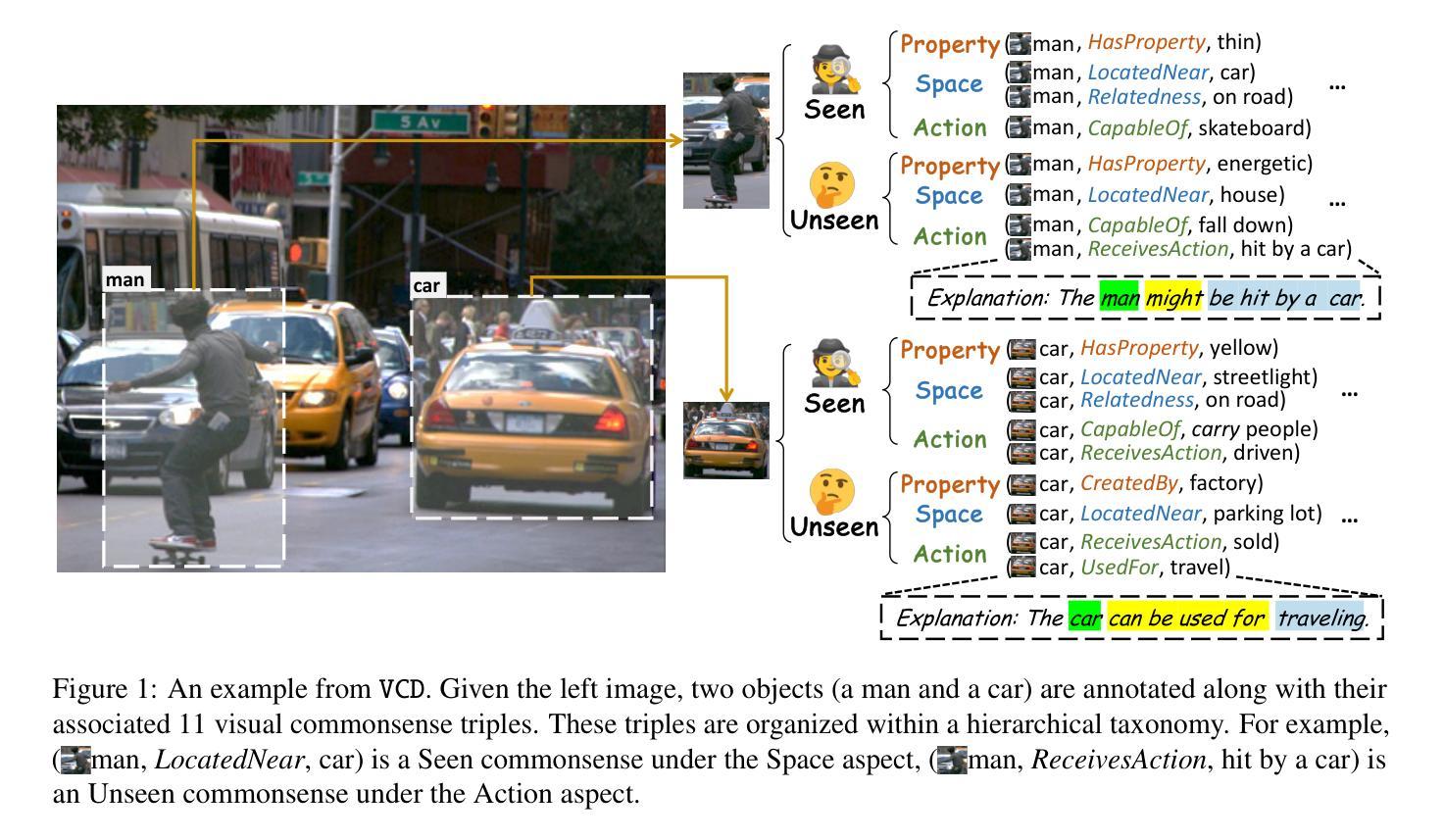
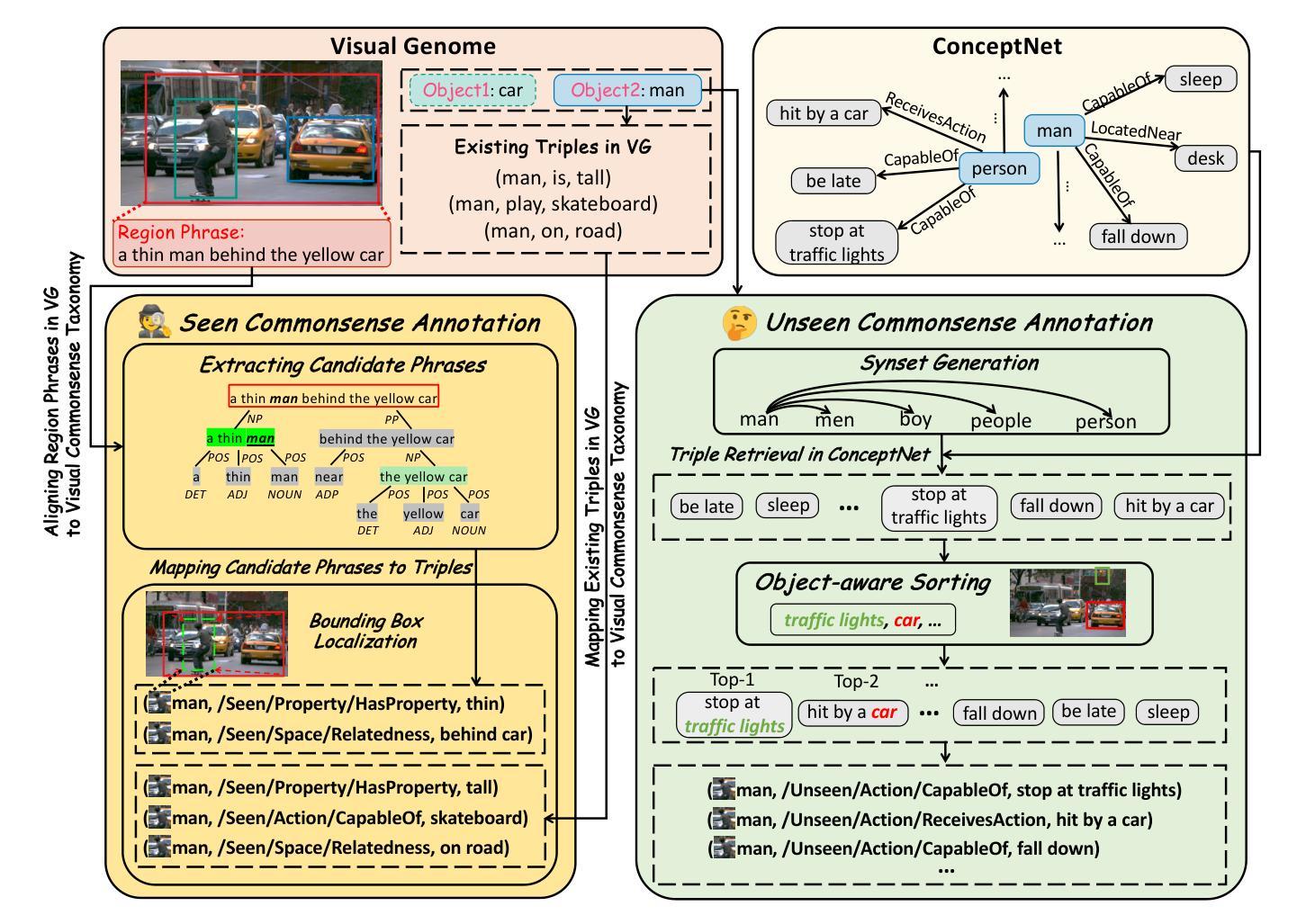
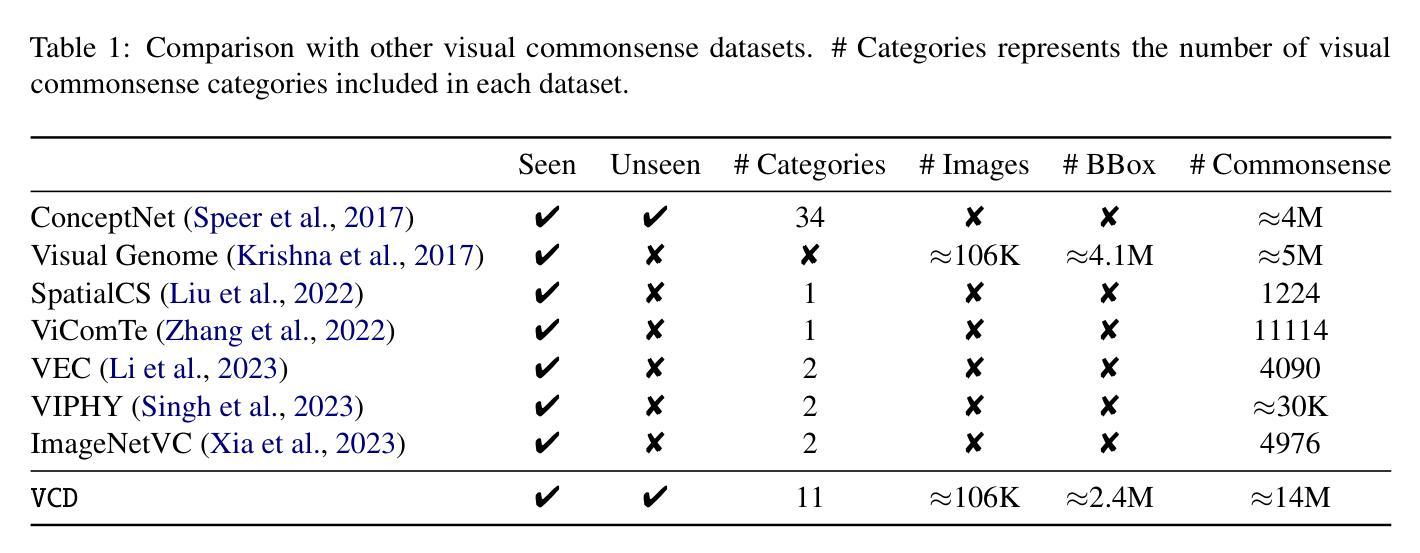
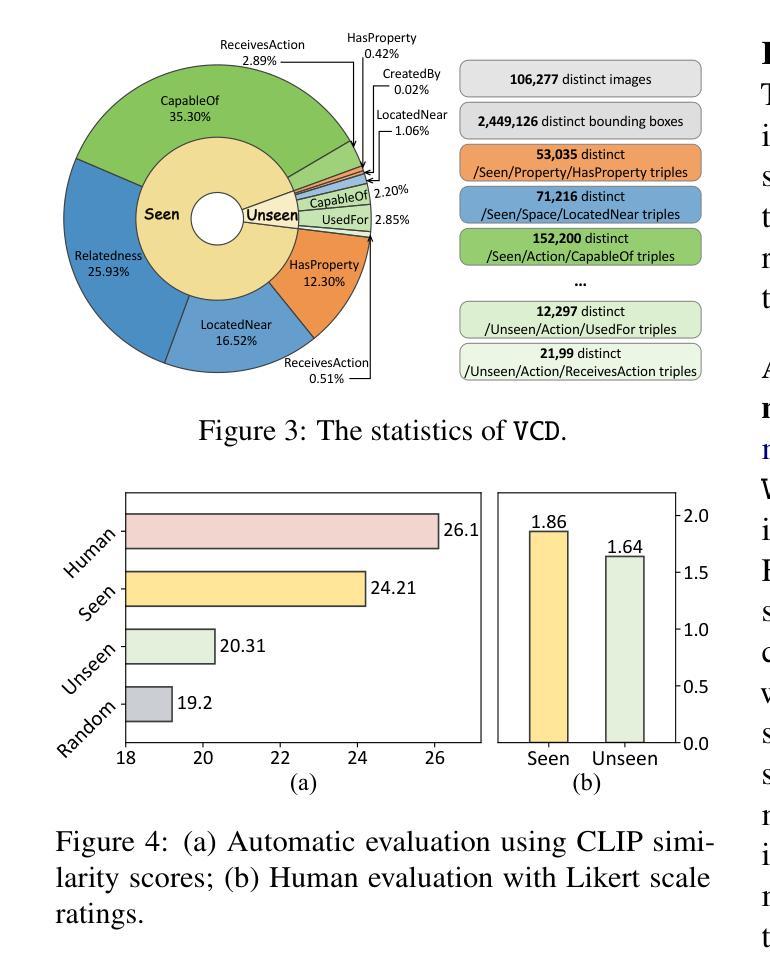
VCD: A Dataset for Visual Commonsense Discovery in Images
Authors:Xiangqing Shen, Fanfan Wang, Siwei Wu, Rui Xia
Visual commonsense plays a vital role in understanding and reasoning about the visual world. While commonsense knowledge bases like ConceptNet provide structured collections of general facts, they lack visually grounded representations. Scene graph datasets like Visual Genome, though rich in object-level descriptions, primarily focus on directly observable information and lack systematic categorization of commonsense knowledge. We present Visual Commonsense Dataset (VCD), a large-scale dataset containing over 100,000 images and 14 million object-commonsense pairs that bridges this gap. VCD introduces a novel three-level taxonomy for visual commonsense, integrating both Seen (directly observable) and Unseen (inferrable) commonsense across Property, Action, and Space aspects. Each commonsense is represented as a triple where the head entity is grounded to object bounding boxes in images, enabling scene-dependent and object-specific visual commonsense representation. To demonstrate VCD’s utility, we develop VCM, a generative model that combines a vision-language model with instruction tuning to discover diverse visual commonsense from images. Extensive evaluations demonstrate both the high quality of VCD and its value as a resource for advancing visually grounded commonsense understanding and reasoning. Our dataset and code will be released on https://github.com/NUSTM/VCD.
视觉常识在理解和推理视觉世界方面起着至关重要的作用。虽然像ConceptNet这样的常识知识库提供了通用事实的结构化集合,但它们缺乏视觉基础表示。像Visual Genome这样的场景图数据集虽然富含对象级别的描述,但主要关注可直接观察的信息,缺乏常识知识的系统分类。我们推出了Visual Commonsense Dataset(VCD),这是一个大规模数据集,包含超过10万张图像和1400万张对象常识配对,弥补了这一空白。VCD引入了一种新颖的三级分类法,用于视觉常识,融合了跨属性、动作和空间方面的可见(可直接观察)和不可见(可推断)常识。每个常识都表示为三元组,其中头实体与图像中的对象边界框相匹配,实现了场景依赖和对象特定的视觉常识表示。为了展示VCD的实用性,我们开发了VCM,这是一个生成模型,它将视觉语言模型与指令调整相结合,从图像中发现多样的视觉常识。广泛评估表明,VCD的高质量及其作为推进视觉基础常识理解和推理的资源价值。我们的数据集和代码将在https://github.com/NUSTM/VCD上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉常识在理解和推理视觉世界方面扮演着至关重要的角色。虽然常识知识库如ConceptNet提供了结构化的常识事实集合,但它们缺乏视觉基础表示。场景图数据集如Visual Genome虽然富含对象级别的描述,但主要关注可直接观察到的信息,缺乏系统的常识知识分类。我们推出了视觉常识数据集(VCD),包含超过10万张图像和1400万对象-常识对,弥补了这一空白。VCD引入了一种新的三级分类法,整合了可见(可直接观察)和不可见(可推断)的常识,涵盖属性、动作和空间方面。每个常识以三元组的形式表示,头部实体与图像中的对象边界框相对应,实现了场景依赖和对象特定的视觉常识表示。为了展示VCD的实用性,我们开发了VCM,一个结合视觉语言模型和指令调整的生成模型,从图像中发现多样的视觉常识。全面评估表明,VCD的高质量及其作为推进视觉基础常识理解和推理的资源价值。我们的数据集和代码将在https://github.com/NUSTM/VCD上发布。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉常识在理解和推理视觉世界方面至关重要。
- 当前知识库和数据集存在缺乏视觉基础表示和系统常识知识分类的问题。
- 提出了Visual Commonsense Dataset (VCD)来解决这一问题,包含图像和对象-常识对。
- VCD采用新的三级分类法,整合可见和不可见的常识,涵盖属性、动作和空间方面。
- VCD中的常识以三元组形式表示,与图像中的对象边界框相对应。
- 开发了VCM模型,结合视觉语言模型和指令调整,从图像中发现多样的视觉常识。
点此查看论文截图