⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-10 更新
Integrating Complexity and Biological Realism: High-Performance Spiking Neural Networks for Breast Cancer Detection
Authors:Zofia Rudnicka, Januszcz Szczepanski, Agnieszka Pregowska
Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) event-driven nature enables efficient encoding of spatial and temporal features, making them suitable for dynamic time-dependent data processing. Despite their biological relevance, SNNs have seen limited application in medical image recognition due to difficulties in matching the performance of conventional deep learning models. To address this, we propose a novel breast cancer classification approach that combines SNNs with Lempel-Ziv Complexity (LZC) a computationally efficient measure of sequence complexity. LZC enhances the interpretability and accuracy of spike-based models by capturing structural patterns in neural activity. Our study explores both biophysical Leaky Integrate-and-Fire (LIF) and probabilistic Levy-Baxter (LB) neuron models under supervised, unsupervised, and hybrid learning regimes. Experiments were conducted on the Breast Cancer Wisconsin dataset using numerical features derived from medical imaging. LB-based models consistently exceeded 90.00% accuracy, while LIF-based models reached over 85.00%. The highest accuracy of 98.25% was achieved using an ANN-to-SNN conversion method applied to both neuron models comparable to traditional deep learning with back-propagation, but at up to 100 times lower computational cost. This hybrid approach merges deep learning performance with the efficiency and plausibility of SNNs, yielding top results at lower computational cost. We hypothesize that the synergy between temporal-coding, spike-sparsity, and LZC-driven complexity analysis enables more-efficient feature extraction. Our findings demonstrate that SNNs combined with LZC offer promising, biologically plausible alternative to conventional neural networks in medical diagnostics, particularly for resource-constrained or real-time systems.
脉冲神经网络(SNNs)的事件驱动特性能够实现空间和时间特征的有效编码,使其成为动态时间依赖数据处理的理想选择。尽管它们在生物学上具有相关性,但由于难以匹配传统深度学习模型的性能,SNN在医学图像识别方面的应用仍然有限。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种结合SNN和Lempel-Ziv复杂度(LZC)的乳腺癌分类新方法。LZC是一种计算效率高的序列复杂度度量方法,它通过捕捉神经活动中的结构模式来提高基于脉冲模型的解释能力和准确性。我们的研究探索了在监督学习、无监督学习和混合学习体制下,生物物理泄漏积分与发射(LIF)和概率性Levy-Baxter(LB)神经元模型的应用。实验采用乳腺癌威斯康星数据集进行,数据特征来源于医学成像。基于LB的模型准确率持续超过90.00%,而基于LIF的模型准确率超过85.00%。通过使用应用于两种神经元模型的ANN到SNN转换方法,达到最高的98.25%准确率,与传统深度学习中的反向传播相当,但计算成本降低了高达100倍。这种混合方法融合了深度学习的性能与SNN的效率和合理性,以较低的计算成本实现了最佳结果。我们假设脉冲编码、稀疏性和LZC驱动的复杂性分析之间的协同作用能够实现更有效的特征提取。我们的研究结果表明,结合LZC的SNN在医学诊断中提供了有前景的生物学合理的替代方案,特别是对于资源受限或实时系统而言。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究提出了一种结合Spiking Neural Networks(SNNs)和Lempel-Ziv Complexity(LZC)的乳腺癌分类新方法。LZC提高了基于脉冲的模型的解释性和准确性,通过捕捉神经活动中的结构模式来实现。研究探讨了生物物理的Leaky Integrate-and-Fire(LIF)和概率性的Levy-Baxter(LB)神经元模型在监督、无监督和混合学习模式下的表现。在乳腺癌威斯康辛数据集上进行的实验表明,LB模型准确率超过90%,LIF模型准确率超过85%。最高准确率为98.25%,是通过将人工神经网络转换为SNN的方法实现的,与传统深度学习相当,但计算成本降低了高达100倍。这种混合方法结合了深度学习的性能与SNNs的效率和合理性,在较低的计算成本下取得了最佳结果。研究表明,时间编码、脉冲稀疏性和LZC驱动的复杂性分析之间的协同作用使特征提取更加高效,SNNs结合LZC在医学诊断中提供了有前景的生物可行性替代方案,尤其适用于资源受限或实时系统。
关键见解
- Spiking Neural Networks(SNNs)具有事件驱动的性质,能够高效编码时空特征,适合动态时间依赖数据处理。
- Lempel-Ziv Complexity(LZC)提高了基于脉冲的模型的解释性和准确性,通过捕捉神经活动中的结构模式实现。
- LB神经元模型在乳腺癌分类任务中表现出较高的准确率,超过了90%。
- LIF神经元模型也表现出良好的性能,准确率超过85%。
- 通过将人工神经网络转换为SNN的方法,实现了高准确率(98.25%),且计算成本较低。
- 混合方法结合了深度学习的性能与SNNs的效率和合理性,展现出在低计算成本下的最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

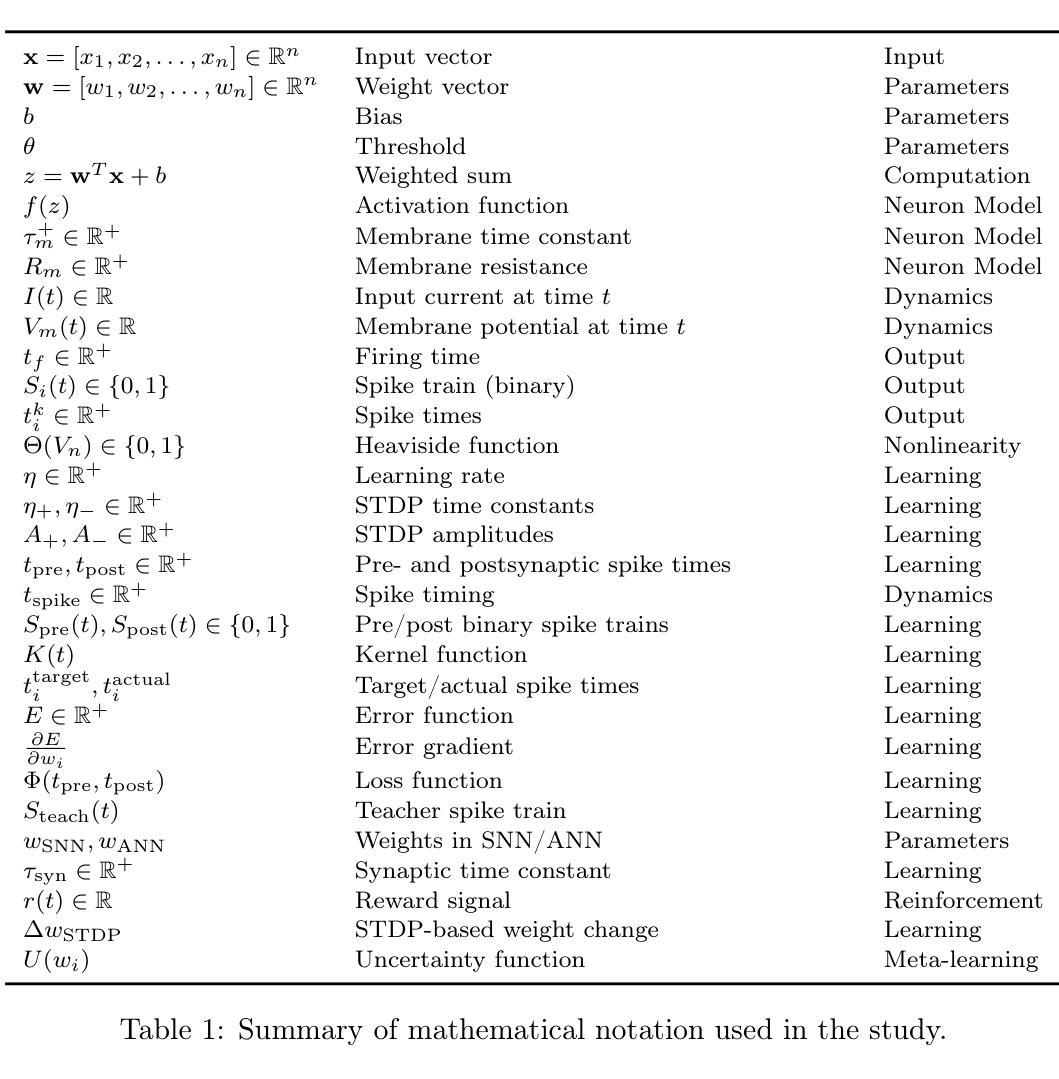
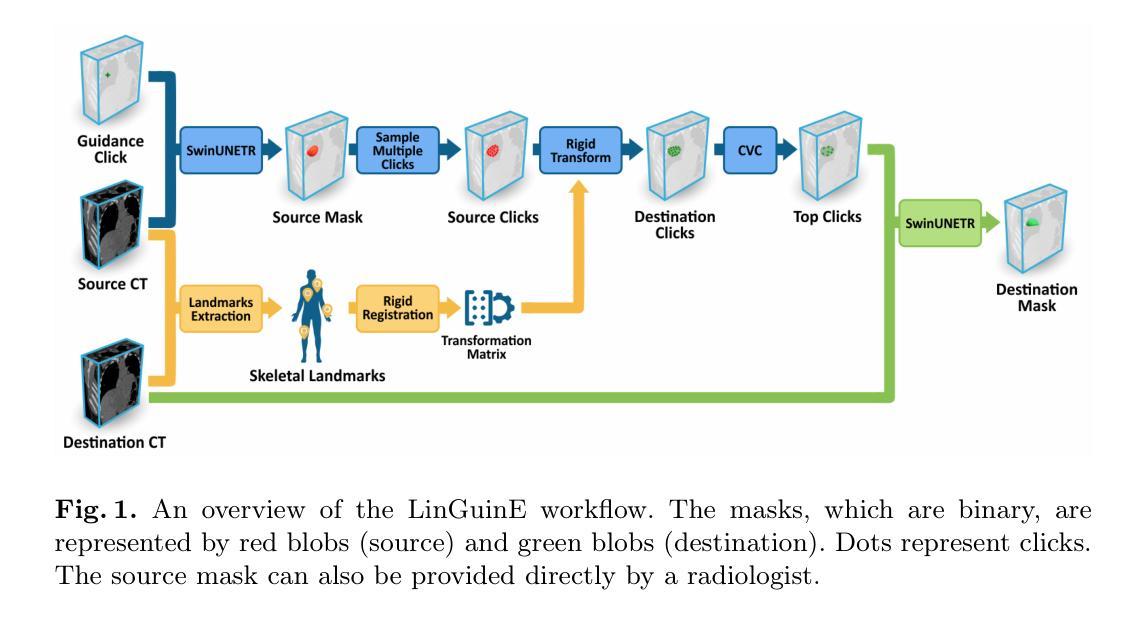
LinGuinE: Longitudinal Guidance Estimation for Volumetric Lung Tumour Segmentation
Authors:Nadine Garibli, Mayank Patwari, Bence Csiba, Yi Wei, Kostas Sidiropoulos
Segmentation of lung gross tumour volumes is an important first step in radiotherapy and surgical intervention, and is starting to play a role in assessing chemotherapy response. Response to a drug is measured by tracking the tumour volumes over a series of CT scans over a time period i.e. a longitudinal study. However, there currently exist few solutions for automated or semi-automated longitudinal tumour segmentation. This paper introduces LinGuinE, an automated method to segment a longitudinal series of lung tumours. A radiologist must provide an initial input, indicating the location of the tumour in a CT scan at an arbitrary time point. LinGuinE samples points inside this tumour and propagates them to another time point using rigid registration. A click validity classifier selects points which still fall within the tumour; these are used to automatically create a segmentation in the new time point. We test LinGuinE on a dataset acquired from a phase 3 clinical trial for lung tumours and the publicly available 4-D lung CBCT dataset. We find that LinGuinE improves the Dice on both test sets by over 20% (p< 0.05) across 63 longitudinal studies. We show that any time point can be used as a starting point, conduct ablation experiments, and find that our LinGuinE setup yields the best results on both test datasets.
肺部肿瘤大体积分割是放疗和手术干预的重要第一步,并且在评估化疗反应方面开始发挥作用。药物的反应是通过追踪一段时间内的一系列CT扫描的肿瘤体积来衡量的,即一项纵向研究。然而,目前几乎没有针对纵向肿瘤分割的自动或半自动解决方案。本文介绍了一种名为LinGuinE的自动方法,用于分割一系列纵向肺部肿瘤。放射科医生必须提供一个初始输入,指示CT扫描中肿瘤的位置(任意时间点)。LinGuinE从肿瘤内部取样点,并使用刚性注册将它们传播到另一个时间点。点击有效性分类器会选择仍在肿瘤内的点;这些点被用来自动创建新时间点的分割。我们在从肺部肿瘤的第三阶段临床试验和公开可用的4D肺CBCT数据集获取的数据集上测试了LinGuinE。我们发现LinGuinE在两组测试集上的Dice系数提高了超过20%(p<0.05),涉及63项纵向研究。我们展示了可以使用任何时间点作为起点,进行消融实验,并发现我们的LinGuinE设置在两组测试数据集上都产生了最佳结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为LinGuinE的自动化方法,用于对肺部肿瘤的长期序列进行分割。该方法需要医生在任意时间点的CT扫描上指示肿瘤位置作为初始输入,然后通过刚体注册技术将点传播到另一时间点。该方法自动创建新时间点的分割。实验结果显示,LinGuinE在多个长期研究测试中,提高了测试集的Dice系数超过20%(p<0.05)。
Key Takeaways
- LinGuinE是一种用于分割肺部肿瘤长期序列的自动化方法。
- 医生需要在任意时间点的CT扫描上指示肿瘤位置作为初始输入。
- LinGuinE通过刚体注册技术将点从初始时间点传播到另一时间点。
- LinGuinE自动在新时间点创建分割。
- 实验结果表明,LinGuinE在测试集上的表现优于现有方法,提高了Dice系数超过20%(p<0.05)。
- LinGuinE可以从任何时间点作为起点使用,具有灵活性。
点此查看论文截图

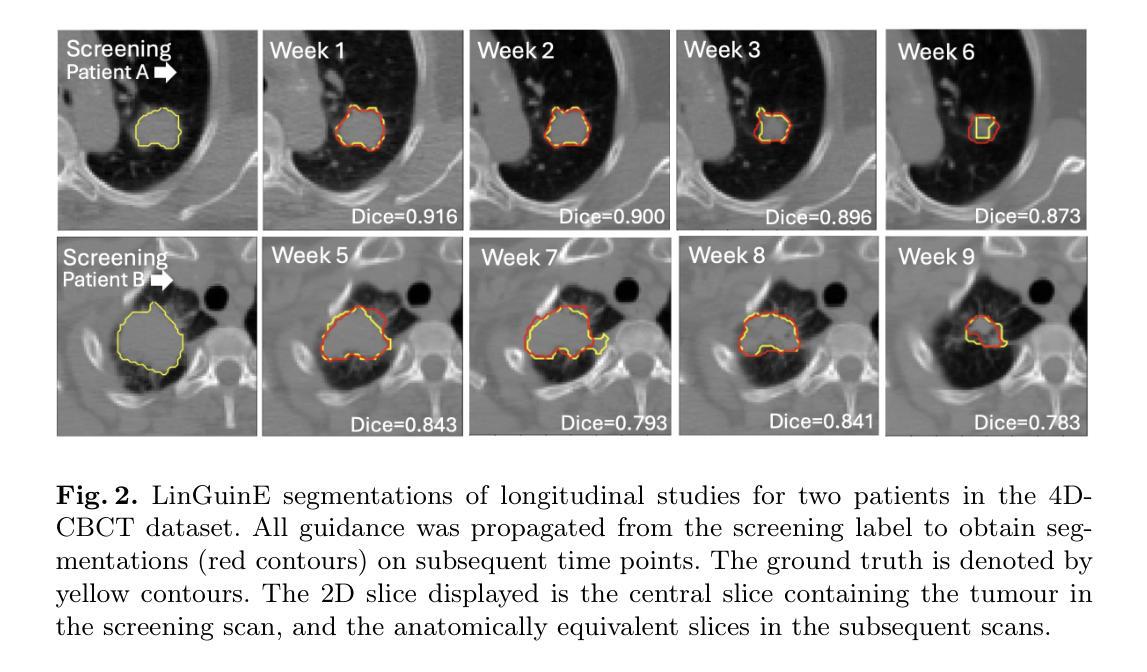
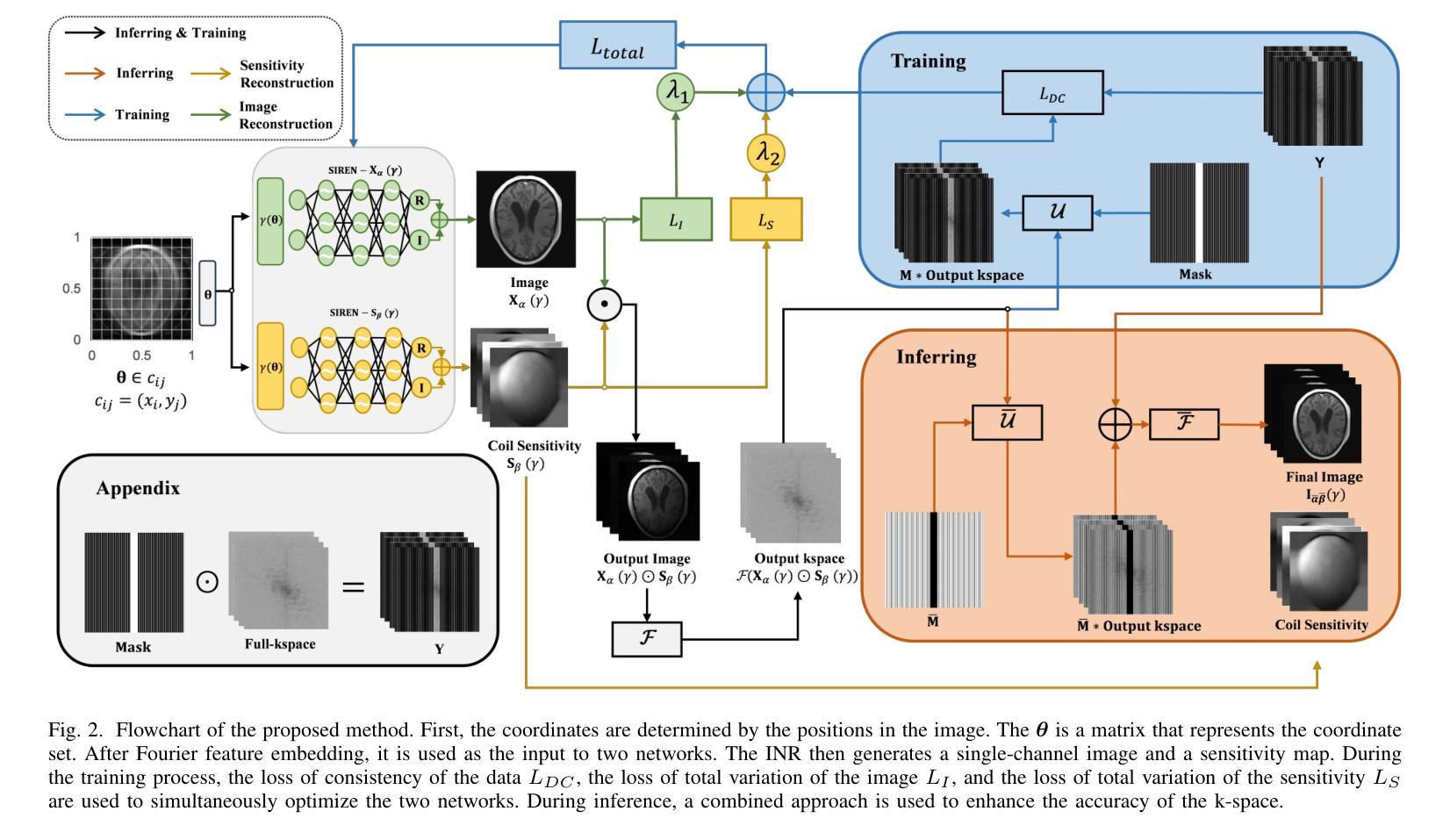
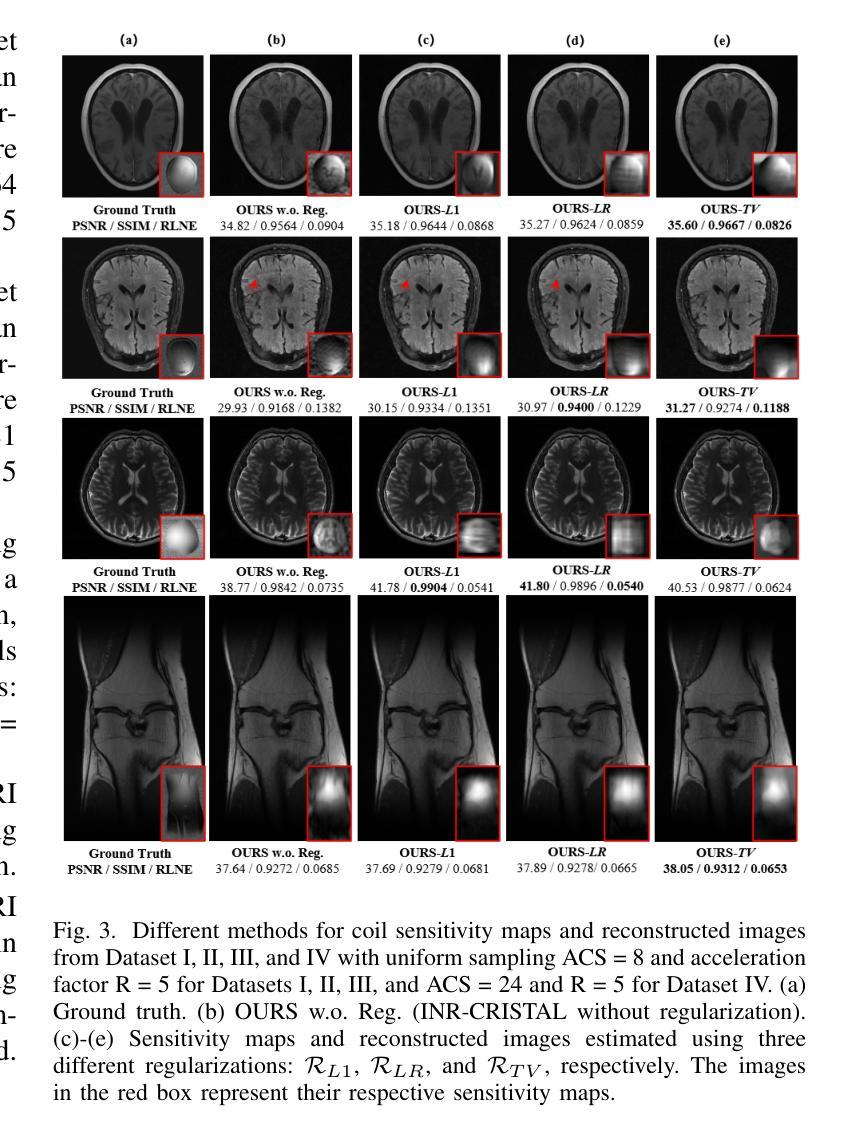
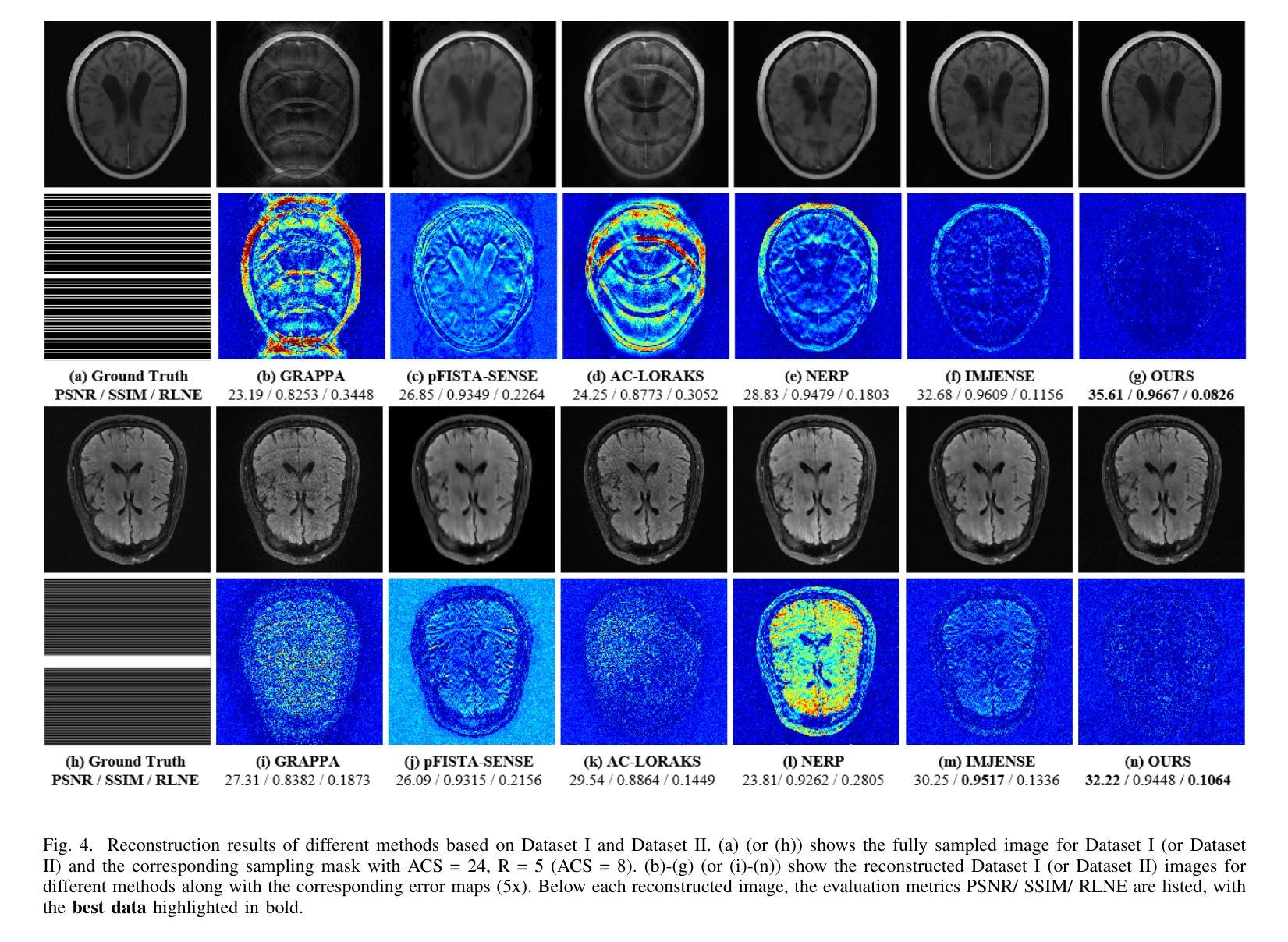
Implicit Neural Representation-Based MRI Reconstruction Method with Sensitivity Map Constraints
Authors:Lixuan Rao, Xinlin Zhang, Yiman Huang, Tao Tan, Tong Tong
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a widely utilized diagnostic tool in clinical settings, but its application is limited by the relatively long acquisition time. As a result, fast MRI reconstruction has become a significant area of research. In recent years, Implicit Neural Representation (INR), as a scan-specific method, has demonstrated outstanding performance in fast MRI reconstruction without fully-sampled images for training. High acceleration reconstruction poses a challenging problem, and a key component in achieving high-quality reconstruction with much few data is the accurate estimation of coil sensitivity maps. However, most INR-based methods apply regularization constraints solely to the generated images, while overlooking the characteristics of the coil sensitivity maps. To handle this, this work proposes a joint coil sensitivity map and image estimation network, termed INR-CRISTAL. The proposed INR-CRISTAL introduces an extra sensitivity map regularization in the INR networks to make use of the smooth characteristics of the sensitivity maps. Experimental results show that INR-CRISTAL provides more accurate coil sensitivity estimates with fewer artifacts, and delivers superior reconstruction performance in terms of artifact removal and structure preservation. Moreover, INR-CRISTAL demonstrates stronger robustness to automatic calibration signals and the acceleration rate compared to existing methods.
磁共振成像(MRI)是临床环境中广泛使用的诊断工具,但其应用受到采集时间相对较长的限制。因此,快速MRI重建已成为一个重要研究领域。近年来,作为一种扫描特定方法,隐式神经表示(INR)在无需完全采样图像进行训练的情况下,已在快速MRI重建中表现出卓越性能。高速重建是一个具有挑战性的问题,在实现高质量重建过程中使用更少数据的关键组件是准确估算线圈灵敏度图。然而,大多数基于INR的方法仅将正则化约束应用于生成的图像,而忽略了线圈灵敏度图的特性。为解决这一问题,本工作提出了一个联合线圈灵敏度图和图像估计网络,称为INR-CRISTAL。提出的INR-CRISTAL在INR网络中引入了额外的灵敏度图正则化,以利用灵敏度图的平滑特性。实验结果表明,INR-CRISTAL提供了更准确的线圈灵敏度估计,减少了伪影,并在伪影去除和结构保留方面提供了出色的重建性能。此外,与现有方法相比,INR-CRISTAL对自动校准信号和加速率表现出更强的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了磁共振成像(MRI)在临床应用中的局限性,如采集时间长。近年来,隐式神经表示(INR)作为一种扫描特定方法在快速MRI重建中表现出卓越性能,尤其是在无需全采样图像进行训练的情况下。文章指出高速重建面临的挑战之一是准确估算线圈灵敏度图。针对此问题,提出了联合线圈灵敏度图和图像估计网络——INR-CRISTAL。该网络在INR网络中引入了额外的灵敏度图正则化,利用灵敏度图的平滑特性。实验结果表明,INR-CRISTAL在较少伪影的情况下提供了更准确的线圈灵敏度估计,并在伪影去除和结构保留方面表现出优越的重建性能,与现有方法相比具有更强的自动校准信号和加速率的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 磁共振成像(MRI)在临床应用中的局限性在于采集时间较长,快速MRI重建成为研究热点。
- 隐式神经表示(INR)方法在快速MRI重建中表现出卓越性能,尤其在不依赖全采样图像进行训练的情况下。
- 高加速重建面临的挑战之一是准确估算线圈灵敏度图。
- INR-CRISTAL网络通过引入额外的灵敏度图正则化来解决这一挑战,利用灵敏度图的平滑特性。
- 实验结果显示INR-CRISTAL提供更准确的线圈灵敏度估计,减少伪影。
- INR-CRISTAL在伪影去除和结构保留方面表现出优越的重建性能。
点此查看论文截图

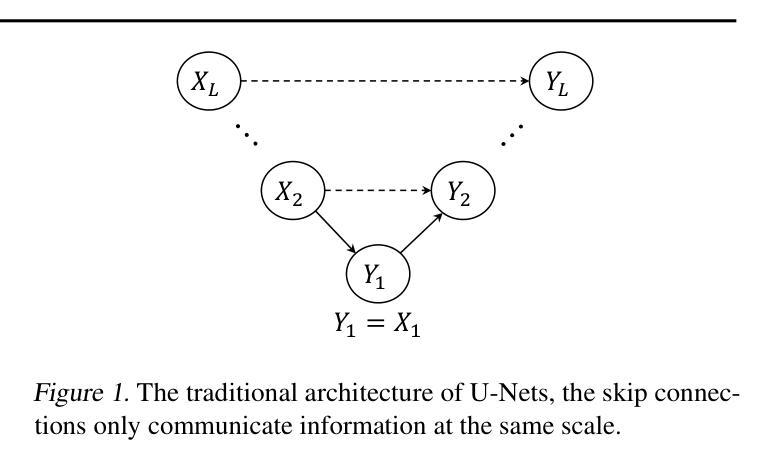
FuseUNet: A Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Method for U-like Networks
Authors:Quansong He, Xiangde Min, Kaishen Wang, Tao He
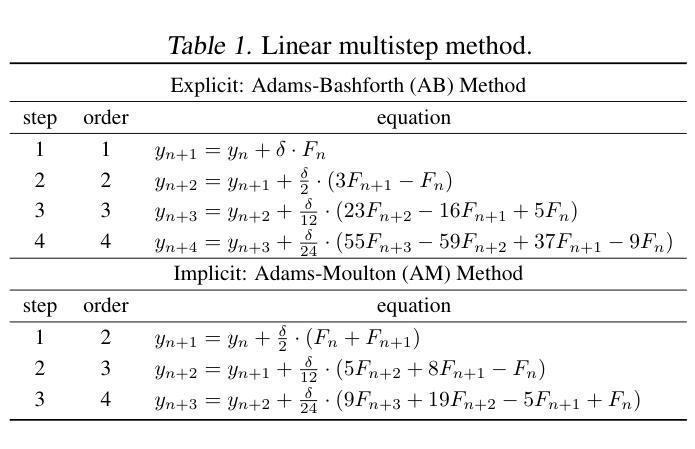
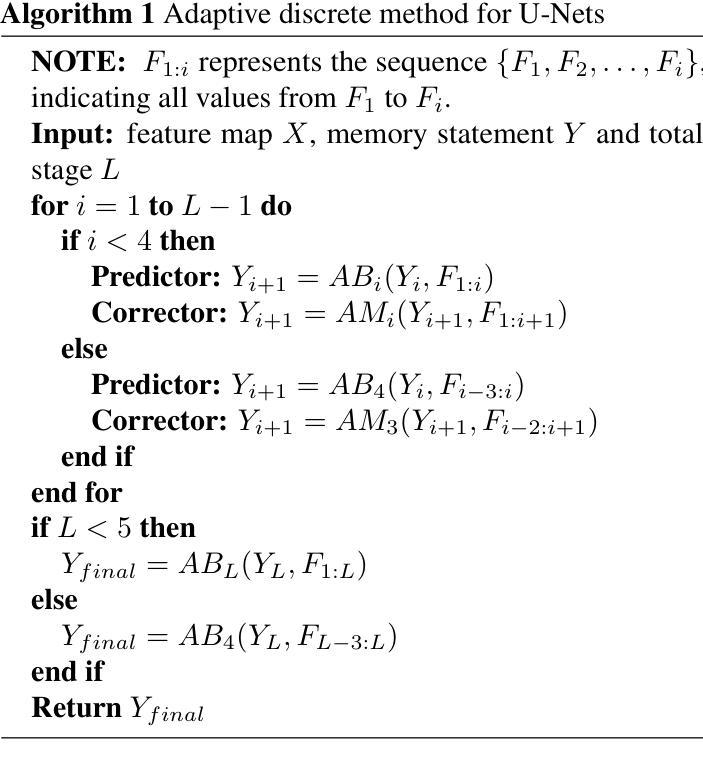
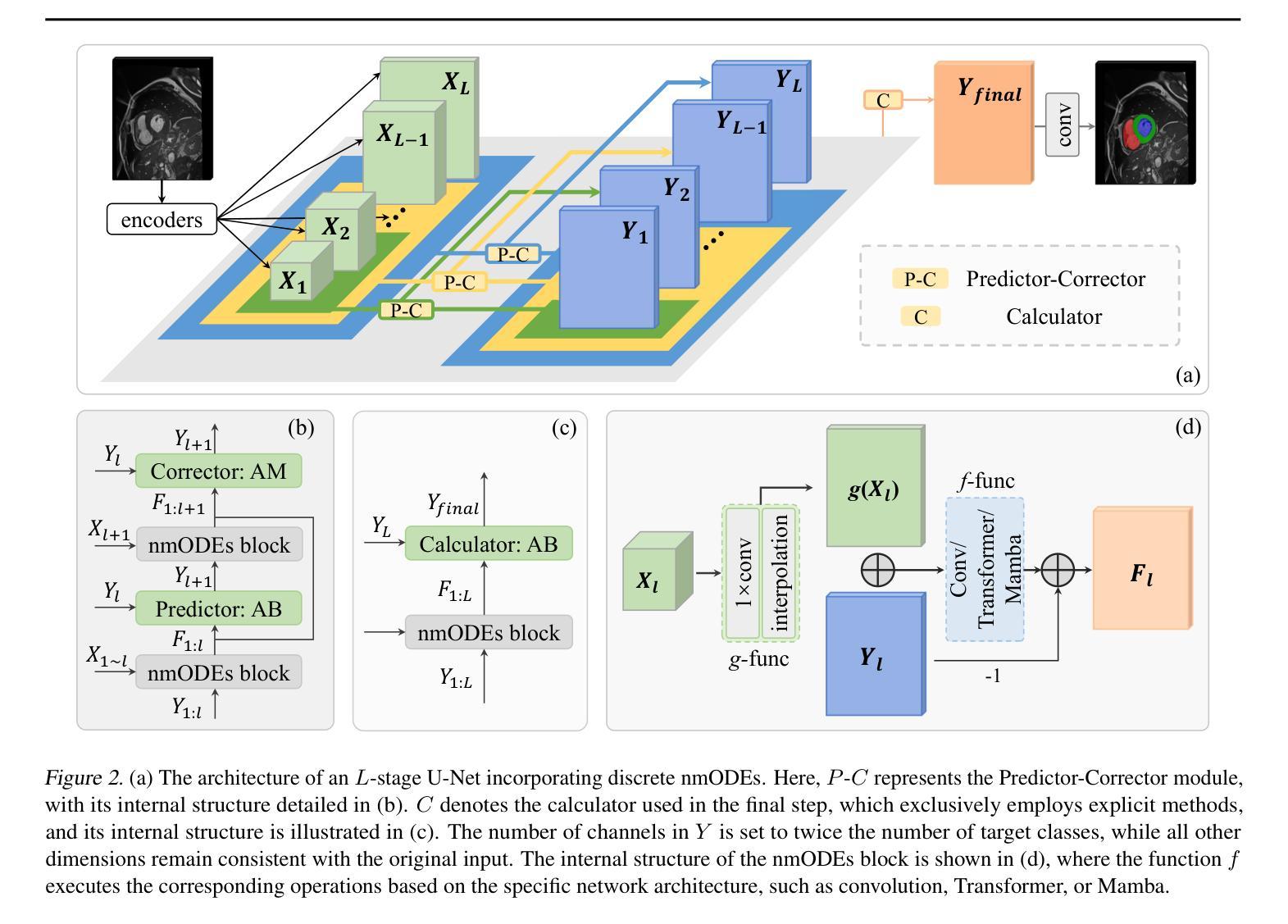
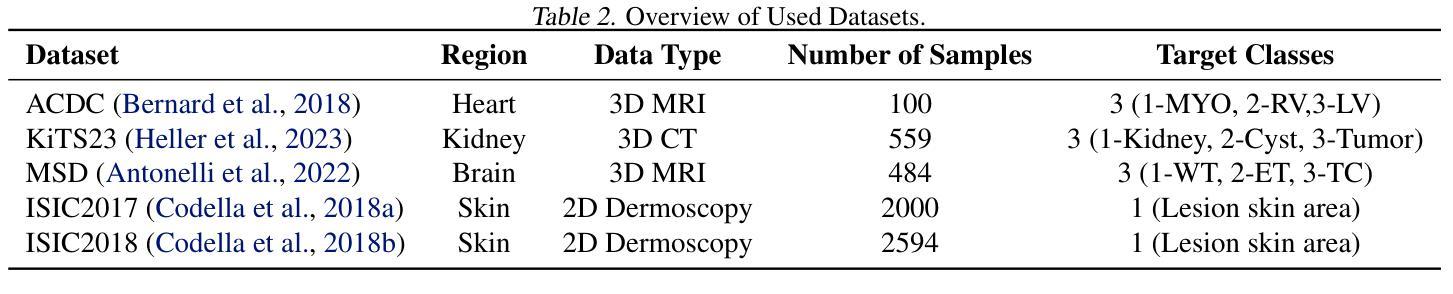
Medical image segmentation is a critical task in computer vision, with UNet serving as a milestone architecture. The typical component of UNet family is the skip connection, however, their skip connections face two significant limitations: (1) they lack effective interaction between features at different scales, and (2) they rely on simple concatenation or addition operations, which constrain efficient information integration. While recent improvements to UNet have focused on enhancing encoder and decoder capabilities, these limitations remain overlooked. To overcome these challenges, we propose a novel multi-scale feature fusion method that reimagines the UNet decoding process as solving an initial value problem (IVP), treating skip connections as discrete nodes. By leveraging principles from the linear multistep method, we propose an adaptive ordinary differential equation method to enable effective multi-scale feature fusion. Our approach is independent of the encoder and decoder architectures, making it adaptable to various U-Net-like networks. Experiments on ACDC, KiTS2023, MSD brain tumor, and ISIC2017/2018 skin lesion segmentation datasets demonstrate improved feature utilization, reduced network parameters, and maintained high performance. The code is available at https://github.com/nayutayuki/FuseUNet.
医学图像分割是计算机视觉中的一项关键任务,其中UNet作为一种里程碑式的架构发挥着重要作用。UNet家族的典型组件是跳跃连接,然而,它们的跳跃连接面临两个重大局限性:(1)它们在不同尺度特征之间的有效交互不足;(2)它们依赖于简单的拼接或加法操作,这限制了信息的有效整合。尽管最近的UNet改进主要集中在增强编码器和解码器的功能,但这些限制仍然被忽视。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型的多尺度特征融合方法,它将UNet的解码过程重新构想为求解初值问题(IVP),将跳跃连接视为离散节点。我们借助线性多步法的原理,提出了一种自适应常微分方程方法,以实现有效的多尺度特征融合。我们的方法独立于编码器和解码器架构,使其适应于各种U-Net类网络。在ACDC、KiTS2023、MSD脑肿瘤和ISIC2017/2018皮肤病变分割数据集上的实验证明了其提高的特征利用率、减少的网络参数以及维持的高性能。相关代码可在https://github.com/nayutayuki/FuseUNet获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML2025
Summary
针对UNet在医学图像分割中的局限性,提出了一种新型的多尺度特征融合方法。该方法将UNet的解码过程视为求解初值问题(IVP),利用线性多步法的原理,通过自适应常微分方程方法实现有效的多尺度特征融合。此方法独立于编码器解码器架构,可适应各种U-Net类网络,并在多个数据集上表现出优异性能。
Key Takeaways
- UNet是医学图像分割中的重要架构,但其skip连接存在局限性,缺乏不同尺度特征的有效交互,以及信息整合的约束。
- 提出了一种新型的多尺度特征融合方法,以克服这些局限性。
- 该方法将UNet的解码过程视为求解初值问题(IVP),利用线性多步法的原理。
- 通过自适应常微分方程方法实现有效的多尺度特征融合。
- 此方法独立于编码器解码器架构,具有广泛的适应性。
- 在多个数据集上的实验证明了改进的特征利用、减少的网络参数以及维持的高性能。
点此查看论文截图

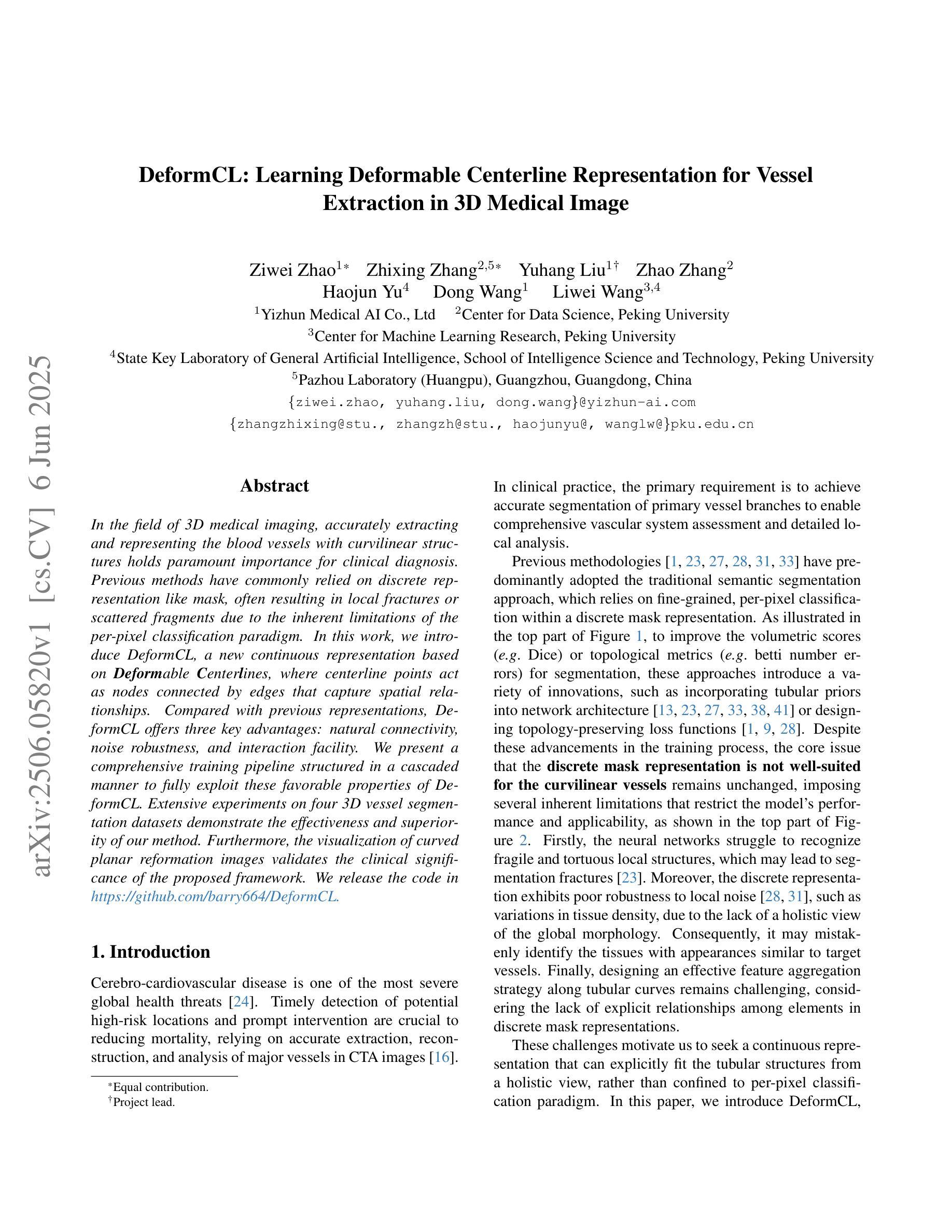
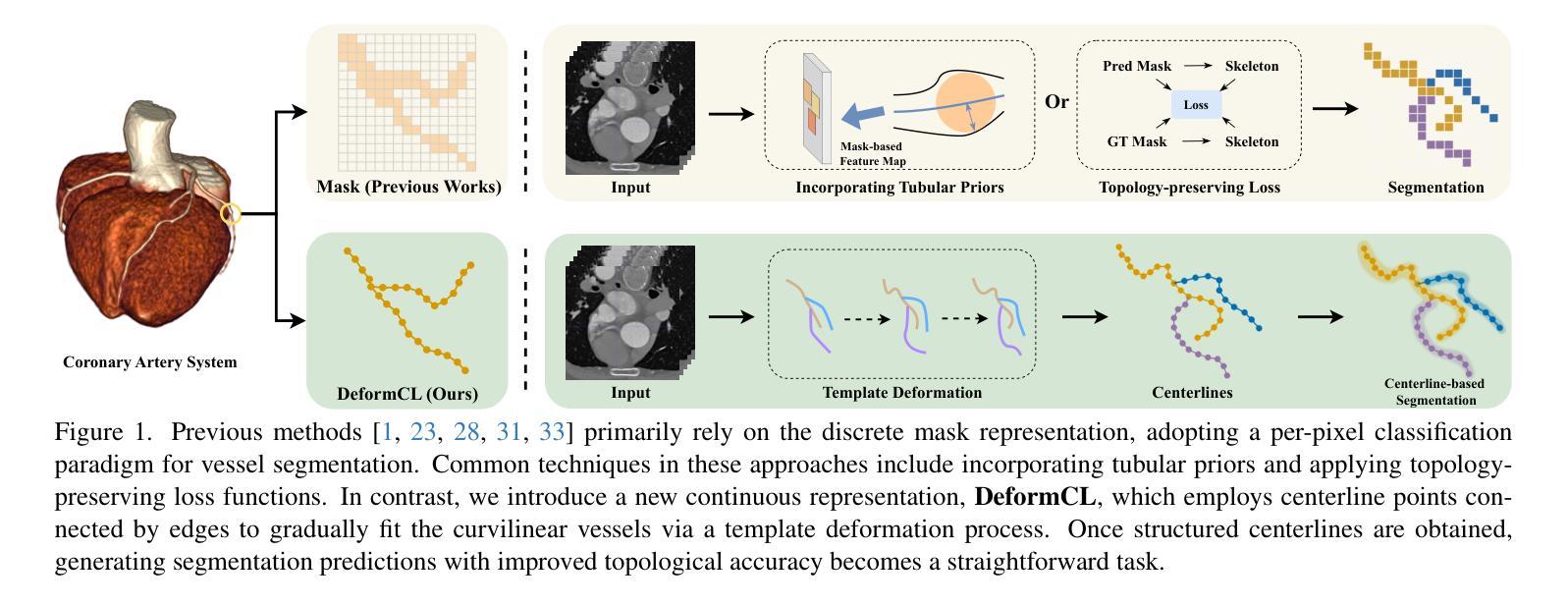
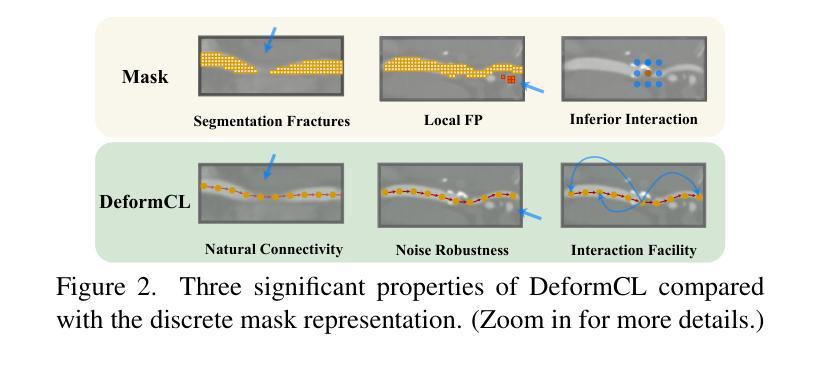
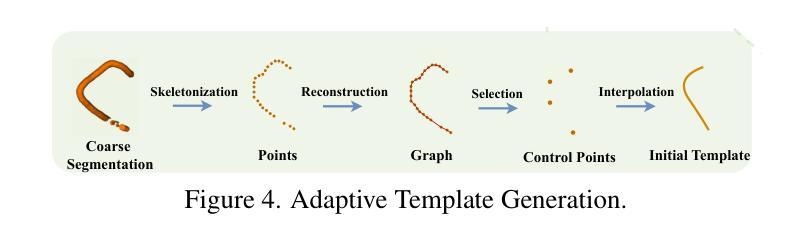
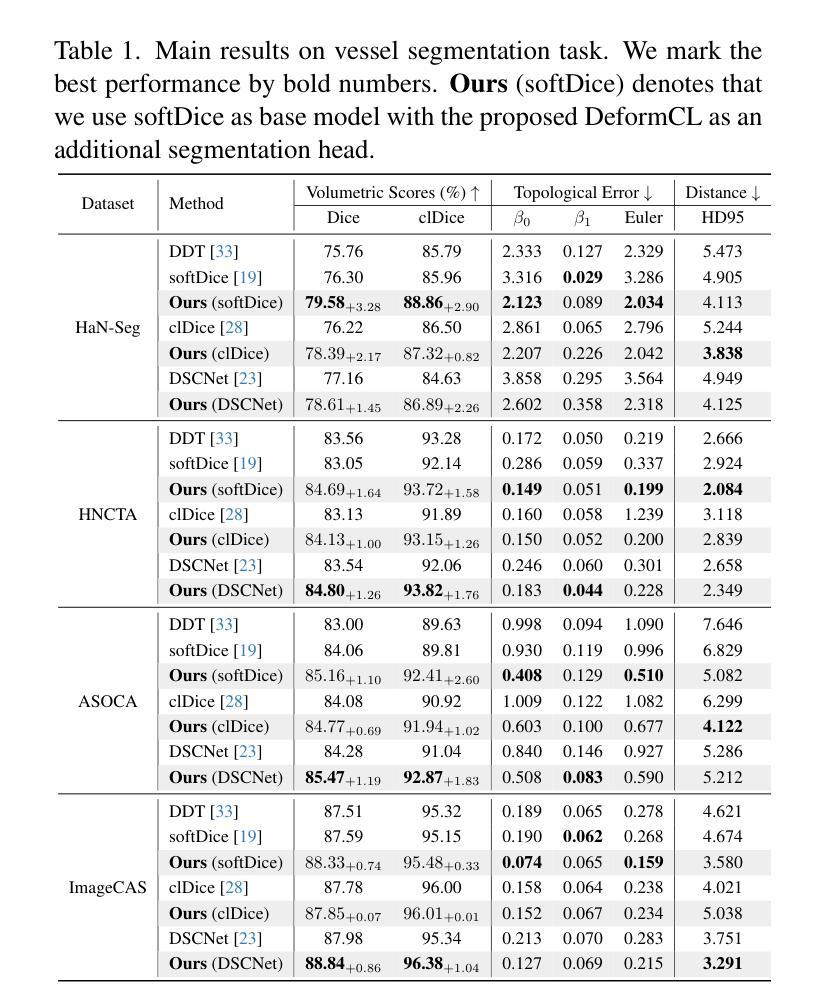
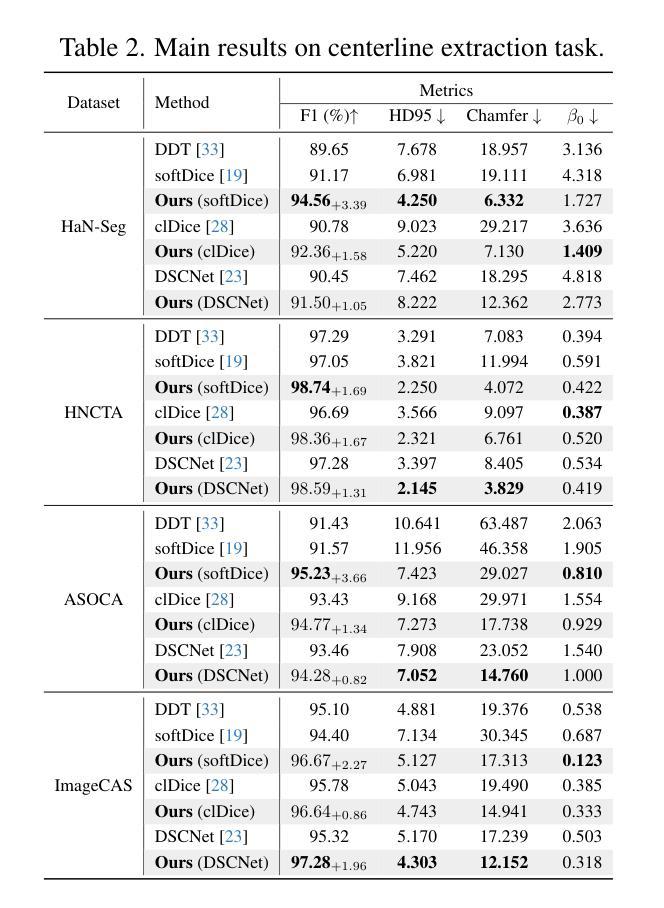
DeformCL: Learning Deformable Centerline Representation for Vessel Extraction in 3D Medical Image
Authors:Ziwei Zhao, Zhixing Zhang, Yuhang Liu, Zhao Zhang, Haojun Yu, Dong Wang, Liwei Wang
In the field of 3D medical imaging, accurately extracting and representing the blood vessels with curvilinear structures holds paramount importance for clinical diagnosis. Previous methods have commonly relied on discrete representation like mask, often resulting in local fractures or scattered fragments due to the inherent limitations of the per-pixel classification paradigm. In this work, we introduce DeformCL, a new continuous representation based on Deformable Centerlines, where centerline points act as nodes connected by edges that capture spatial relationships. Compared with previous representations, DeformCL offers three key advantages: natural connectivity, noise robustness, and interaction facility. We present a comprehensive training pipeline structured in a cascaded manner to fully exploit these favorable properties of DeformCL. Extensive experiments on four 3D vessel segmentation datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our method. Furthermore, the visualization of curved planar reformation images validates the clinical significance of the proposed framework. We release the code in https://github.com/barry664/DeformCL
在三维医学影像领域,准确提取和表示具有曲线结构的血管对于临床诊断至关重要。以往的方法通常依赖于离散表示,如掩膜,由于像素级分类模式的固有局限性,常常导致局部断裂或分散的片段。在这项工作中,我们引入了基于可变形中心线的连续表示方法DeformCL。中心线点作为节点通过边缘连接,从而捕获空间关系。与之前的表示方法相比,DeformCL具有三个关键优势:自然连接、噪声鲁棒性和交互便利性。我们采用级联的综合训练管道,以充分利用DeformCL的这些有利属性。在四个三维血管分割数据集上的大量实验证明了我们方法的有效性和优越性。此外,曲面平面改革图像的可视化验证了所提出框架的临床意义。我们已将代码发布在https://github.com/barry664/DeformCL。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了在3D医学影像领域中,采用基于可变形中心线的连续表示方法(DeformCL)对血管进行准确提取和表示的重要性。相较于传统的离散表示方法,DeformCL能够更自然地描述血管的连续性结构,具有更好的噪声鲁棒性和交互性。文章提出了一套级联的训练流程,充分发掘了DeformCL的优势特性。实验结果表明,该方法在四个3D血管分割数据集上的表现优于传统方法,具有显著的临床意义。
Key Takeaways
- 3D医学影像中血管的准确提取和表示对临床诊断至关重要。
- 传统的离散表示方法如掩膜(mask)存在局限性,易导致血管结构断裂或散乱。
- DeformCL是一种基于可变形中心线的连续表示方法,能更自然地描述血管的连续性结构。
- DeformCL相比传统方法具有天然连通性、噪声鲁棒性和良好的交互性三个主要优势。
- 文章提出了一套级联的训练流程来充分利用DeformCL的特性。
- 在四个3D血管分割数据集上的实验证明了该方法的优越性和有效性。
点此查看论文截图
TissUnet: Improved Extracranial Tissue and Cranium Segmentation for Children through Adulthood
Authors:Markian Mandzak, Elvira Yang, Anna Zapaishchykova, Yu-Hui Chen, Lucas Heilbroner, John Zielke, Divyanshu Tak, Reza Mojahed-Yazdi, Francesca Romana Mussa, Zezhong Ye, Sridhar Vajapeyam, Viviana Benitez, Ralph Salloum, Susan N. Chi, Houman Sotoudeh, Jakob Seidlitz, Sabine Mueller, Hugo J. W. L. Aerts, Tina Y. Poussaint, Benjamin H. Kann
Extracranial tissues visible on brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may hold significant value for characterizing health conditions and clinical decision-making, yet they are rarely quantified. Current tools have not been widely validated, particularly in settings of developing brains or underlying pathology. We present TissUnet, a deep learning model that segments skull bone, subcutaneous fat, and muscle from routine three-dimensional T1-weighted MRI, with or without contrast enhancement. The model was trained on 155 paired MRI-computed tomography (CT) scans and validated across nine datasets covering a wide age range and including individuals with brain tumors. In comparison to AI-CT-derived labels from 37 MRI-CT pairs, TissUnet achieved a median Dice coefficient of 0.79 [IQR: 0.77-0.81] in a healthy adult cohort. In a second validation using expert manual annotations, median Dice was 0.83 [IQR: 0.83-0.84] in healthy individuals and 0.81 [IQR: 0.78-0.83] in tumor cases, outperforming previous state-of-the-art method. Acceptability testing resulted in an 89% acceptance rate after adjudication by a tie-breaker(N=108 MRIs), and TissUnet demonstrated excellent performance in the blinded comparative review (N=45 MRIs), including both healthy and tumor cases in pediatric populations. TissUnet enables fast, accurate, and reproducible segmentation of extracranial tissues, supporting large-scale studies on craniofacial morphology, treatment effects, and cardiometabolic risk using standard brain T1w MRI.
大脑磁共振成像(MRI)中可见的头颅外组织对于表征健康状况和临床决策具有重要的价值,但很少被量化。当前工具尚未得到广泛验证,特别是在发育中的大脑或基础病理学的情况下。我们提出了TissUnet,这是一个深度学习模型,可以从常规的三维T1加权MRI中分割颅骨、皮下脂肪和肌肉,无论是否进行增强对比。该模型在155对MRI-计算机断层扫描(CT)上进行训练,并在涵盖广泛年龄范围且包括脑肿瘤患者在内的九个数据集上进行验证。与来自37对MRI-CT的人工智能CT标签相比,TissUnet在健康成人队列中的中位Dice系数为0.79 [IQR:0.77-0.81]。在另一项使用专家手动注释的验证中,健康个体的中位Dice系数为0.83 [IQR:0.83-0.84],肿瘤病例的中位Dice系数为0.81 [IQR:0.78-0.83],超过了之前最先进的方法。可接受性测试结果显示,在仲裁者(N=108 MRI)裁决后,接受率为89%,TissUnet在盲比较审查(N=45 MRI)中表现出优异的性能,包括儿科人群中的健康病例和肿瘤病例。TissUnet能够实现快速、准确和可重复的颅外组织分割,支持利用标准大脑T1w MRI进行大规模颅面形态学、治疗效应和代谢风险研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 44 pages, 4 tables, 6 figures, supplementary material
摘要
在脑磁共振成像(MRI)中,颅外组织的可见性对于表征健康状况和临床决策可能具有重要意义,但目前尚缺乏对这些组织的量化评估工具。本文介绍了一种深度学习模型——TissUnet,它可以对常规三维T1加权MRI进行颅骨、皮下脂肪和肌肉的分割,无论是否使用对比增强。该模型在155对MRI-计算机断层扫描(CT)图像上进行训练,并在涵盖广泛年龄范围且包括脑肿瘤患者的人群中进行了验证。与来自37对MRI-CT的AI-CT标签相比,在健康成人队列中,TissUnet的Dice系数中位数为0.79[IQR:0.77-0.81]。使用专家手动注释进行的第二次验证显示,在健康个体和肿瘤病例中,Dice系数中位数分别为0.83[IQR:0.83-0.84]和0.81[IQR:0.78-0.83],优于先前的方法。可接受性测试结果为接受率为89%(经过仲裁者解决平局后)。此外,在盲比较审查中(包括健康和肿瘤病例的儿科人群),TissUnet表现出卓越的性能。TissUnet可以快速、准确、可重复地分割颅外组织,支持利用标准脑T1w MRI进行大规模颅面形态学、治疗影响和代谢风险研究。
关键见解
- TissUnet是一种深度学习模型,能够分割颅外组织如颅骨、皮下脂肪和肌肉。
- 模型基于MRI图像进行训练与分割,适用于常规三维T1加权MRI,无论是否使用对比增强。
- TissUnet在广泛的年龄范围和包括脑肿瘤患者的人群中进行了验证,表现出良好的性能。
- 与AI-CT和专家手动注释相比,TissUnet的分割结果具有较高的Dice系数,显示出其准确性和优越性。
- TissUnet在接受性测试中获得了较高的接受率。
- TissUnet在盲比较审查中表现优秀,包括处理儿科人群中的健康和肿瘤病例。
- TissUnet的应用有助于大规模研究颅面形态学、治疗影响和代谢风险等领域。
点此查看论文截图

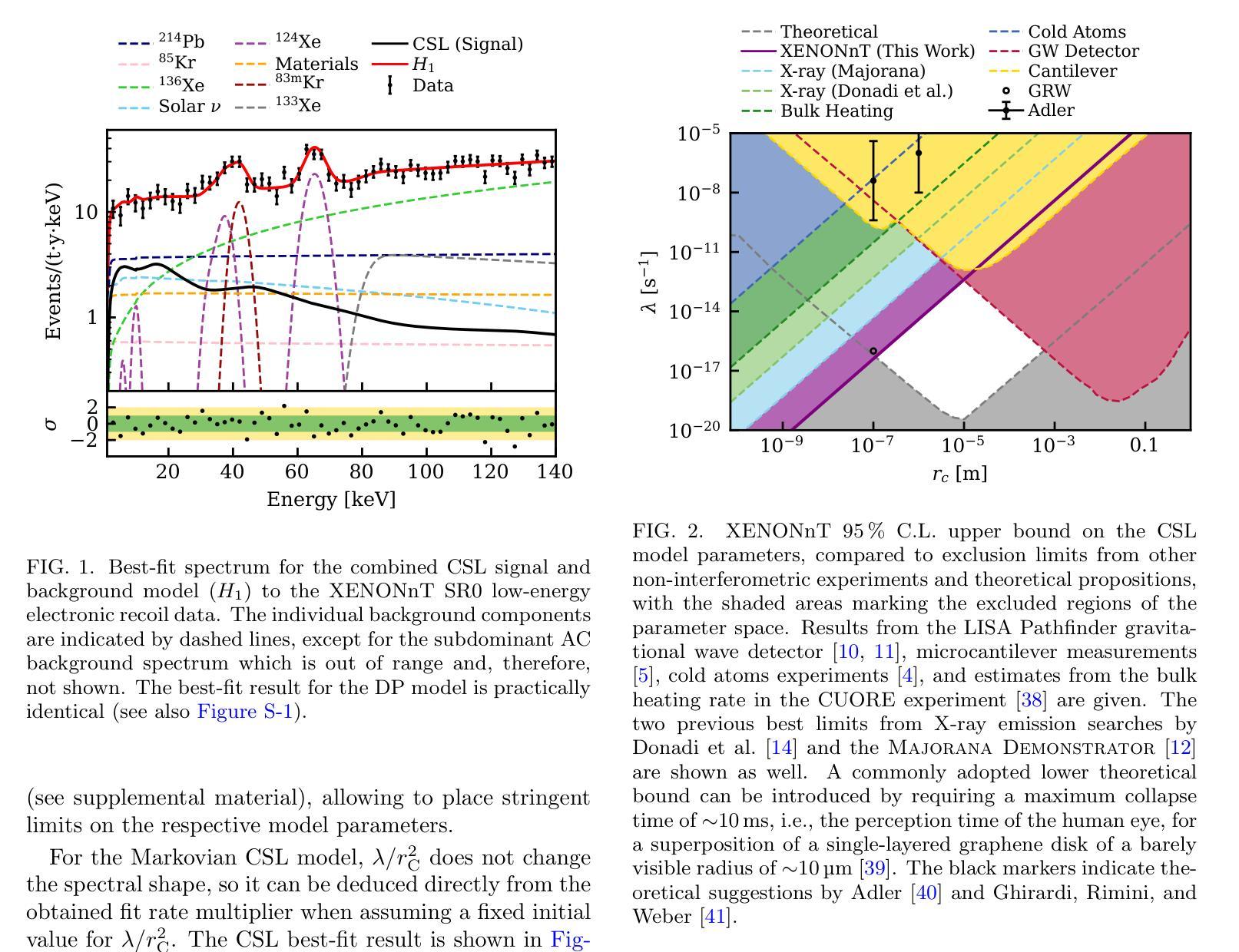
Challenging Spontaneous Quantum Collapse with XENONnT
Authors:E. Aprile, J. Aalbers, K. Abe, S. Ahmed Maouloud, L. Althueser, B. Andrieu, E. Angelino, D. Antón Martin, S. R. Armbruster, F. Arneodo, L. Baudis, M. Bazyk, L. Bellagamba, R. Biondi, A. Bismark, K. Boese, A. Brown, G. Bruno, R. Budnik, C. Cai, C. Capelli, J. M. R. Cardoso, A. P. Cimental Chávez, A. P. Colijn, J. Conrad, J. J. Cuenca-García, C. Curceanu, V. D’Andrea, L. C. Daniel Garcia, M. P. Decowski, A. Deisting, C. Di Donato, P. Di Gangi, S. Diglio, K. Eitel, S. el Morabit, A. Elykov, A. D. Ferella, C. Ferrari, H. Fischer, T. Flehmke, M. Flierman, W. Fulgione, C. Fuselli, P. Gaemers, R. Gaior, F. Gao, S. Ghosh, R. Giacomobono, F. Girard, R. Glade-Beucke, L. Grandi, J. Grigat, H. Guan, M. Guida, P. Gyorgy, R. Hammann, A. Higuera, C. Hils, L. Hoetzsch, N. F. Hood, M. Iacovacci, Y. Itow, J. Jakob, F. Joerg, Y. Kaminaga, M. Kara, P. Kavrigin, S. Kazama, P. Kharbanda, M. Kobayashi, D. Koke, A. Kopec, H. Landsman, R. F. Lang, L. Levinson, I. Li, S. Li, S. Liang, Z. Liang, Y. -T. Lin, S. Lindemann, K. Liu, M. Liu, J. Loizeau, F. Lombardi, J. Long, J. A. M. Lopes, G. M. Lucchetti, T. Luce, Y. Ma, C. Macolino, J. Mahlstedt, A. Mancuso, L. Manenti, S. Manti, F. Marignetti, T. Marrodán Undagoitia, K. Martens, J. Masbou, S. Mastroianni, A. Melchiorre, J. Merz, M. Messina, A. Michael, K. Miuchi, A. Molinario, S. Moriyama, K. Morå, Y. Mosbacher, M. Murra, J. Müller, K. Ni, U. Oberlack, B. Paetsch, Y. Pan, Q. Pellegrini, R. Peres, C. Peters, J. Pienaar, M. Pierre, K. Piscicchia, G. Plante, T. R. Pollmann, L. Principe, J. Qi, J. Qin, D. Ramírez García, M. Rajado, A. Ravindran, A. Razeto, L. Redard-Jacot, R. Singh, L. Sanchez, J. M. F. dos Santos, I. Sarnoff, G. Sartorelli, J. Schreiner, P. Schulte, H. Schulze Eißing, M. Schumann, L. Scotto Lavina, M. Selvi, F. Semeria, P. Shagin, S. Shi, J. Shi, M. Silva, H. Simgen, A. Stevens, C. Szyszka, A. Takeda, Y. Takeuchi, P. -L. Tan, D. Thers, G. Trinchero, C. D. Tunnell, F. Tönnies, K. Valerius, S. Vecchi, S. Vetter, F. I. Villazon Solar, G. Volta, C. Weinheimer, M. Weiss, D. Wenz, C. Wittweg, V. H. S. Wu, Y. Xing, D. Xu, Z. Xu, M. Yamashita, L. Yang, J. Ye, L. Yuan, G. Zavattini, M. Zhong
We report on the search for X-ray radiation as predicted from dynamical quantum collapse with low-energy electronic recoil data in the energy range of 1-140 keV from the first science run of the XENONnT dark matter detector. Spontaneous radiation is an unavoidable effect of dynamical collapse models, which were introduced as a possible solution to the long-standing measurement problem in quantum mechanics. The analysis utilizes a model that for the first time accounts for cancellation effects in the emitted spectrum, which arise in the X-ray range due to the opposing electron-proton charges in xenon atoms. New world-leading limits on the free parameters of the Markovian continuous spontaneous localization and Di'osi-Penrose models are set, improving previous best constraints by two orders of magnitude and a factor of five, respectively. The original values proposed for the strength and the correlation length of the continuous spontaneous localization model are excluded experimentally for the first time.
我们报告了在XENONnT暗物质探测器首次科学运行中,从低能电子反冲数据中预测的动态量子塌缩所产生的X射线辐射的搜寻情况。自发辐射是动态塌缩模型的不可避免的效果,该模型被引入作为解决量子力学中长期测量问题的一种可能解决方案。分析采用了一个模型,该模型首次考虑了发射光谱中的抵消效应,这些效应在X射线范围内由于氙原子中电子和质子电荷的相互对立而产生。为马尔可夫连续自发定位模型和Di’osi-Penrose模型的自由参数设定了新的世界领先限制,分别改善了之前的最佳约束两个数量级和五倍。连续自发定位模型的强度和关联长度的原始提议值被实验首次排除。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本文报告了使用低能电子反冲数据从XENONnT暗物质探测器首次科学运行中预测到的X射线辐射的搜寻结果。文章中讨论了动态崩溃模型产生的自发辐射,该模型作为解决量子力学长期测量问题的可能解决方案被引入。分析时采用了一个模型,该模型首次考虑了发射光谱中的抵消效应,这些效应在X射线范围内产生于氙原子中的电子质子电荷的对立。对新设定的Markovian连续自发定位模型和Di’osi-Penrose模型自由参数的世界领先限制进行了改善,较之前的最佳约束提高了两个数量级和五倍。首次实验排除了连续自发定位模型的强度和关联长度提出的原始值。
Key Takeaways
- 利用XENONnT暗物质探测器的首次科学运行数据,报告了关于X射线辐射的预测搜寻结果。
- 动态崩溃模型作为解决量子力学测量问题的解决方案被引入,并讨论了其产生的自发辐射。
- 采用了一个考虑氙原子中电子质子电荷对立引起的光谱抵消效应的模型。
- 对Markovian连续自发定位模型和Di’osi-Penrose模型的自由参数设定了新的世界领先限制。
- 较之前的最佳约束,这些新限制在数值上有了显著的提升。
- 首次实验排除了连续自发定位模型的某些原始参数值。
点此查看论文截图

Statistical microlocal analysis in two-dimensional X-ray CT
Authors:Anuj Abhishek, Alexander Katsevich, James W. Webber
In many imaging applications it is important to assess how well the edges of the original object, $f$, are resolved in an image, $f^\text{rec}$, reconstructed from the measured data, $g$. In this paper we consider the case of image reconstruction in 2D X-ray Computed Tomography (CT). Let $f$ be a function describing the object being scanned, and $g=Rf + \eta$ be the Radon transform data in $\mathbb{R}^2$ corrupted by noise, $\eta$, and sampled with step size $\sim\epsilon$. Conventional microlocal analysis provides conditions for edge detectability based on the scanner geometry in the case of continuous, noiseless data (when $\eta = 0$), but does not account for noise and finite sampling step size. We develop a novel technique called Statistical Microlocal Analysis (SMA), which uses a statistical hypothesis testing framework to determine if an image edge (singularity) of $f$ is detectable from $f^\text{rec}$, and we quantify edge detectability using the statistical power of the test. Our approach is based on the theory we developed in previous work, which provides a characterization of $f^\text{rec}$ in local $O(\epsilon)$-size neighborhoods when $\eta \neq 0$. We derive a statistical test for the presence and direction of an edge microlocally given the magnitude of $\eta$ and data sampling step size. Using the properties of the null distribution of the test, we quantify the uncertainty of the edge magnitude and direction. We validate our theory using simulations, which show strong agreement between our predictions and experimental observations. Our work is not only of practical value, but of theoretical value as well. SMA is a natural extension of classical microlocal analysis theory which accounts for practical measurement imperfections, such as noise and finite step size, at the highest possible resolution compatible with the data.
在许多成像应用中,评估原始对象$f$的边缘在由测量数据$g$重建的图像$f^\text{rec}$中恢复得如何非常重要。本文考虑二维X射线计算机断层扫描(CT)中的图像重建情况。设$f$为描述被扫描对象的函数,$g=Rf+\eta$为受噪声$\eta$影响的Radon变换数据,并用步长$\sim\epsilon$进行采样。传统的微局部分析为连续、无噪声数据(当$\eta = 0$时)提供了基于扫描仪几何的边缘检测条件,但不考虑噪声和有限的采样步长。我们开发了一种名为统计微局部分析(SMA)的新技术,它使用统计假设检验框架来确定$f$的图像边缘(奇异性)是否可从$f^\text{rec}$检测出来,并使用检验的统计效力来量化边缘检测能力。我们的方法基于我们之前的工作理论,当$\eta \neq 0$时,它提供了对局部$O(\epsilon)$大小邻域中的$f^\text{rec}$的特征描述。我们根据$\eta$的幅度和数据采样步长,推导出局部边缘存在的统计检验及其方向。利用检验的空分布属性,我们量化边缘幅度和方向的不确定性。我们通过模拟验证了我们的理论,模拟结果表明我们的预测与实验观察结果高度一致。我们的工作不仅具有实用价值,而且具有理论价值。SMA是经典微局部分析理论的自然扩展,该理论考虑了实际测量中的不完美之处,例如噪声和有限步长,并在与数据兼容的最高可能分辨率下进行。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 13 figures
Summary
本文提出一种名为统计微局部分析(SMA)的新技术,该技术使用统计假设检验框架来确定从重建图像中是否可检测到原始对象的边缘(奇点)。此技术考虑了噪声和有限采样步长等实际测量误差的影响,从而提高了边缘检测的准确性和可靠性。通过模拟验证,该技术预测与实验结果高度一致。
Key Takeaways
- 论文关注于二维X射线计算机断层扫描(CT)中的图像重建问题。
- 提出了一种新的技术——统计微局部分析(SMA),该技术用于确定从重建图像中是否可检测到原始对象的边缘。
- SMA考虑了噪声和有限采样步长等实际测量误差的影响,这在此前的微局部分析中并未涉及。
- 通过模拟验证,展示了SMA预测与实验结果的高度一致性。
- 该技术不仅在实践中有价值,而且在理论上也有价值,是经典微局部分析理论的自然扩展。
- SMA提供了一种量化边缘不确定性的方法,包括边缘幅度和方向的不确定性。
点此查看论文截图

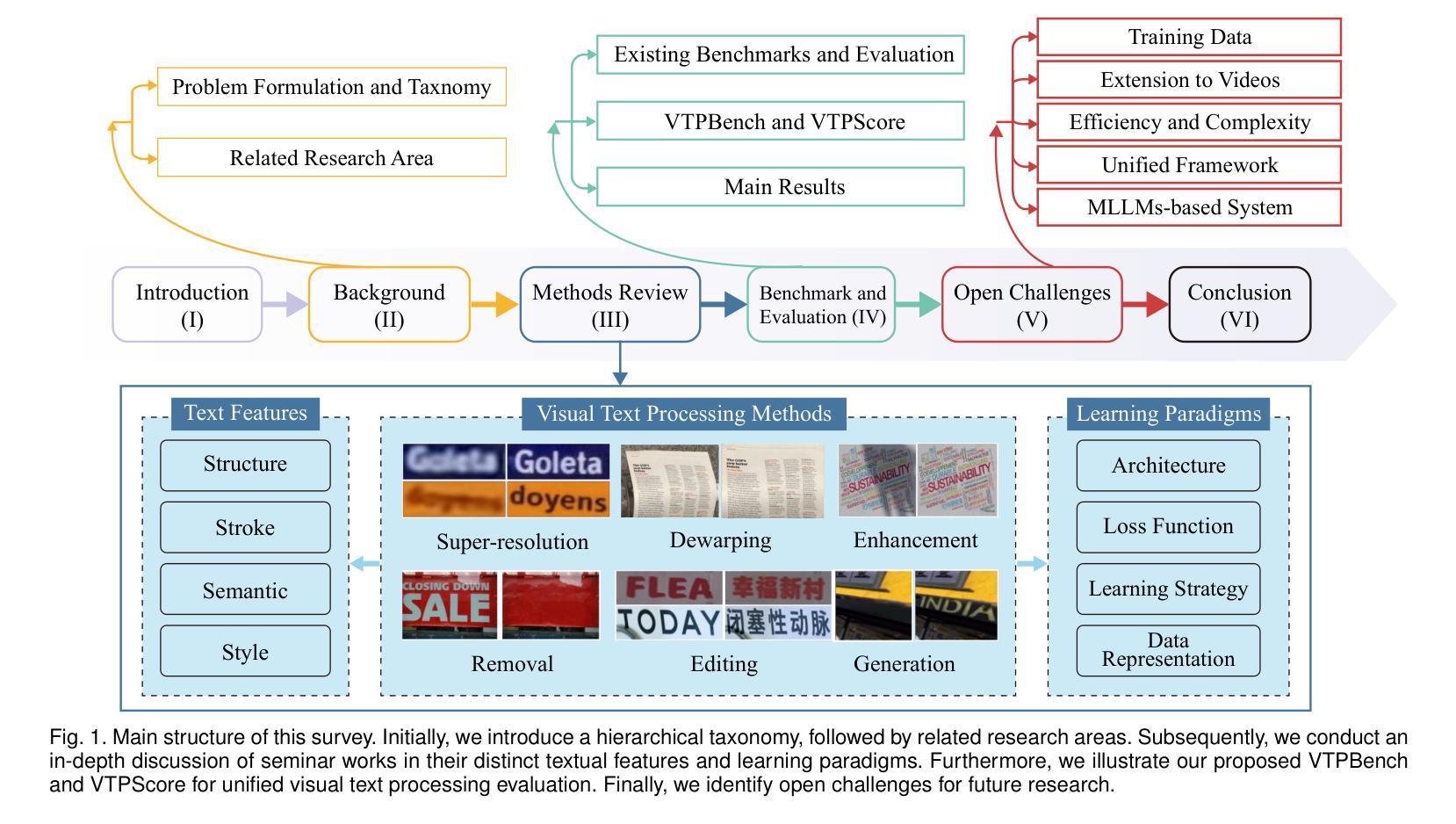
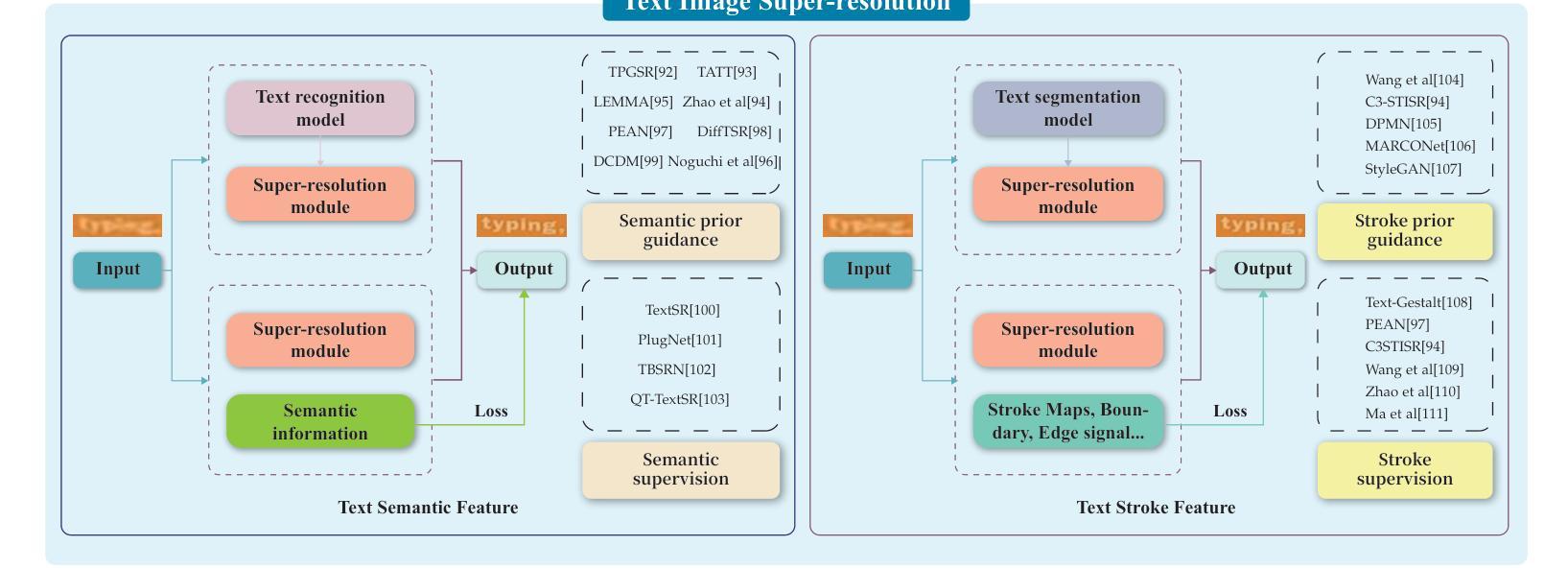
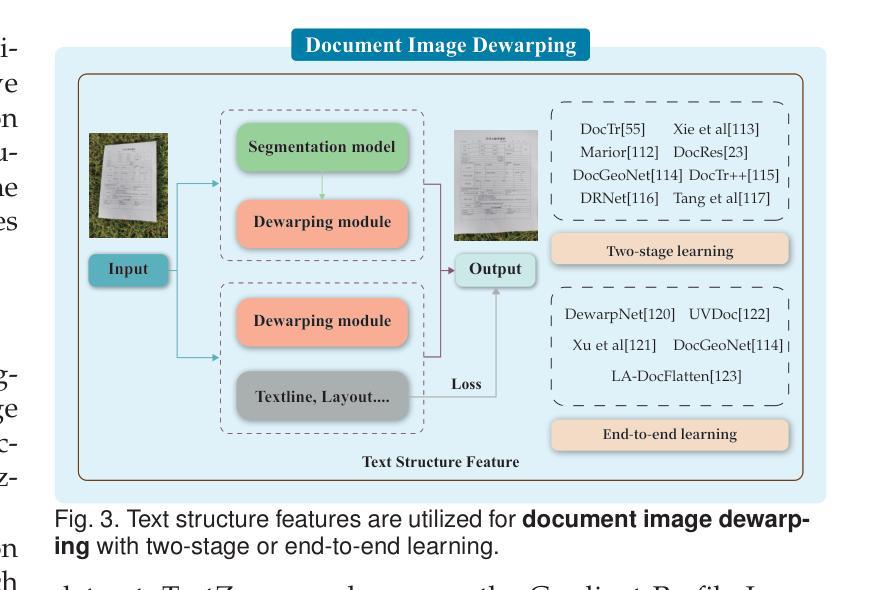
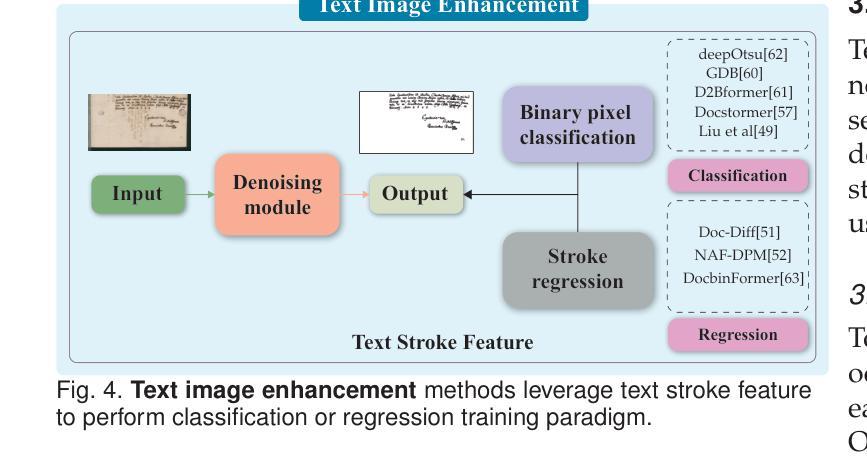
Visual Text Processing: A Comprehensive Review and Unified Evaluation
Authors:Yan Shu, Weichao Zeng, Fangmin Zhao, Zeyu Chen, Zhenhang Li, Xiaomeng Yang, Yu Zhou, Paolo Rota, Xiang Bai, Lianwen Jin, Xu-Cheng Yin, Nicu Sebe
Visual text is a crucial component in both document and scene images, conveying rich semantic information and attracting significant attention in the computer vision community. Beyond traditional tasks such as text detection and recognition, visual text processing has witnessed rapid advancements driven by the emergence of foundation models, including text image reconstruction and text image manipulation. Despite significant progress, challenges remain due to the unique properties that differentiate text from general objects. Effectively capturing and leveraging these distinct textual characteristics is essential for developing robust visual text processing models. In this survey, we present a comprehensive, multi-perspective analysis of recent advancements in visual text processing, focusing on two key questions: (1) What textual features are most suitable for different visual text processing tasks? (2) How can these distinctive text features be effectively incorporated into processing frameworks? Furthermore, we introduce VTPBench, a new benchmark that encompasses a broad range of visual text processing datasets. Leveraging the advanced visual quality assessment capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs), we propose VTPScore, a novel evaluation metric designed to ensure fair and reliable evaluation. Our empirical study with more than 20 specific models reveals substantial room for improvement in the current techniques. Our aim is to establish this work as a fundamental resource that fosters future exploration and innovation in the dynamic field of visual text processing. The relevant repository is available at https://github.com/shuyansy/Visual-Text-Processing-survey.
视觉文本是文档和场景图像中的关键组成部分,它传递了丰富的语义信息,并引起了计算机视觉界的广泛关注。除了文本检测和识别等传统任务外,视觉文本处理在基础模型的推动下迅速发展,包括文本图像重建和文本图像操作。尽管取得了重要进展,但由于文本与一般物体的独特属性不同,仍然存在挑战。有效地捕获和利用这些独特的文本特征对于开发稳健的视觉文本处理模型至关重要。在本文中,我们对视觉文本处理的最新进展进行了全面、多角度的分析,重点回答了两个关键问题:(1)不同的视觉文本处理任务最适合哪些文本特征?(2)如何有效地将这些独特的文本特征纳入处理框架?此外,我们介绍了VTPBench,这是一个涵盖广泛视觉文本处理数据集的新基准。我们利用多模态大型语言模型的先进视觉质量评估能力,提出了VTPScore,一个旨在确保公平可靠评估的新型评价指标。我们对超过20种特定模型的实证研究揭示了当前技术的巨大改进空间。我们的目标是将这项工作建立为视觉文本处理这一动态领域的基本资源,促进未来的探索和创新。相关仓库可在https://github.com/shuyansy/Visual-Text-Processing-survey找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了视觉文本处理的重要性,包括其在文档和场景图像中的关键作用,以及基础模型的出现所带来的技术进步。文章对近期视觉文本处理的进展进行了全面的多视角分析,提出了两个关键问题并介绍了VTPBench新基准和VTPScore评估指标。本文旨在成为促进视觉文本处理领域未来探索和创新的基本资源。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉文本处理是计算机视觉领域的重要分支,涉及文档和场景图像中的文本识别和语义信息提取。
- 基础模型的出现推动了视觉文本处理的快速发展,包括文本图像重建和文本图像操作等任务。
- 文本与通用物体之间的差异使得视觉文本处理面临独特挑战,有效捕捉和利用这些特征对于开发稳健的模型至关重要。
- 文章提出了两个关键问题:哪些文本特征最适合不同的视觉文本处理任务,以及如何将这些独特的文本特征有效地融入处理框架。
- 介绍了新的基准VTPBench,涵盖了广泛的视觉文本处理数据集。
- 利用多模态大型语言模型的先进视觉质量评估能力,提出了VTPScore这一新的评估指标,以确保公平可靠的评价。
点此查看论文截图

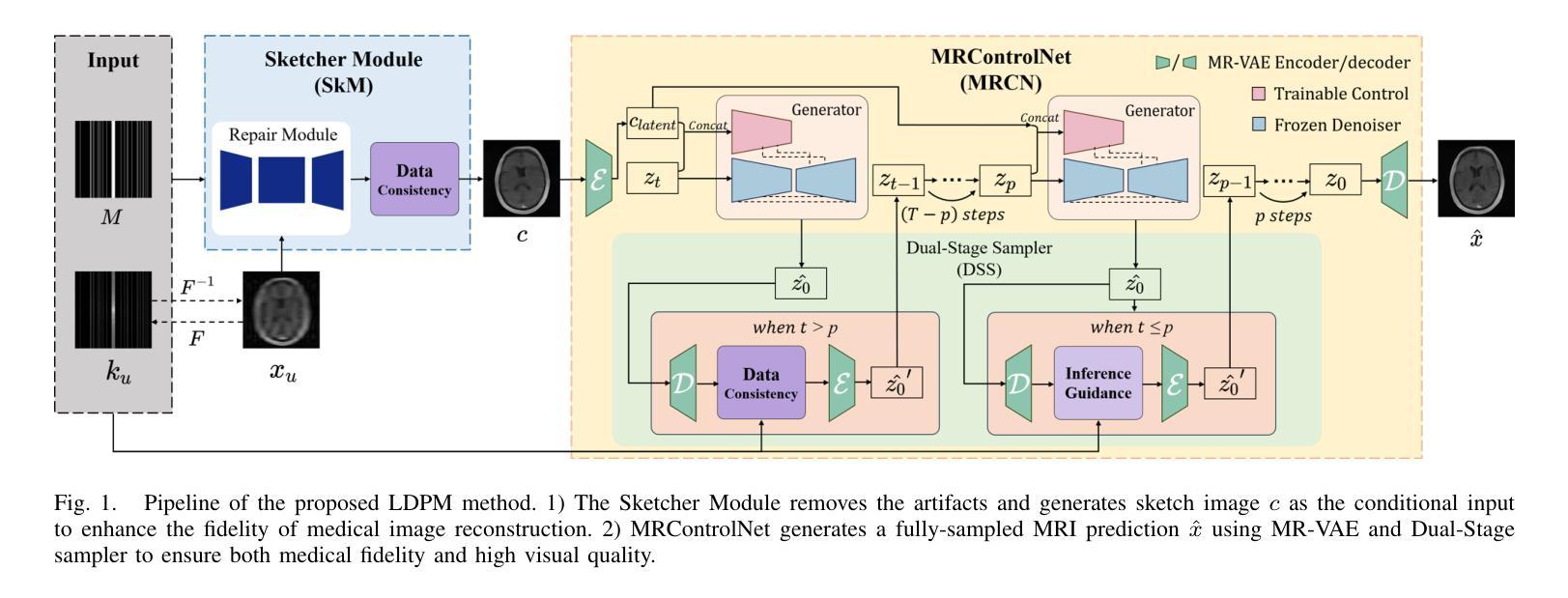
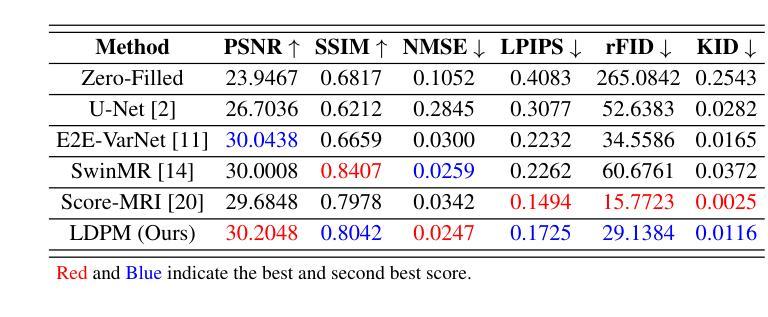
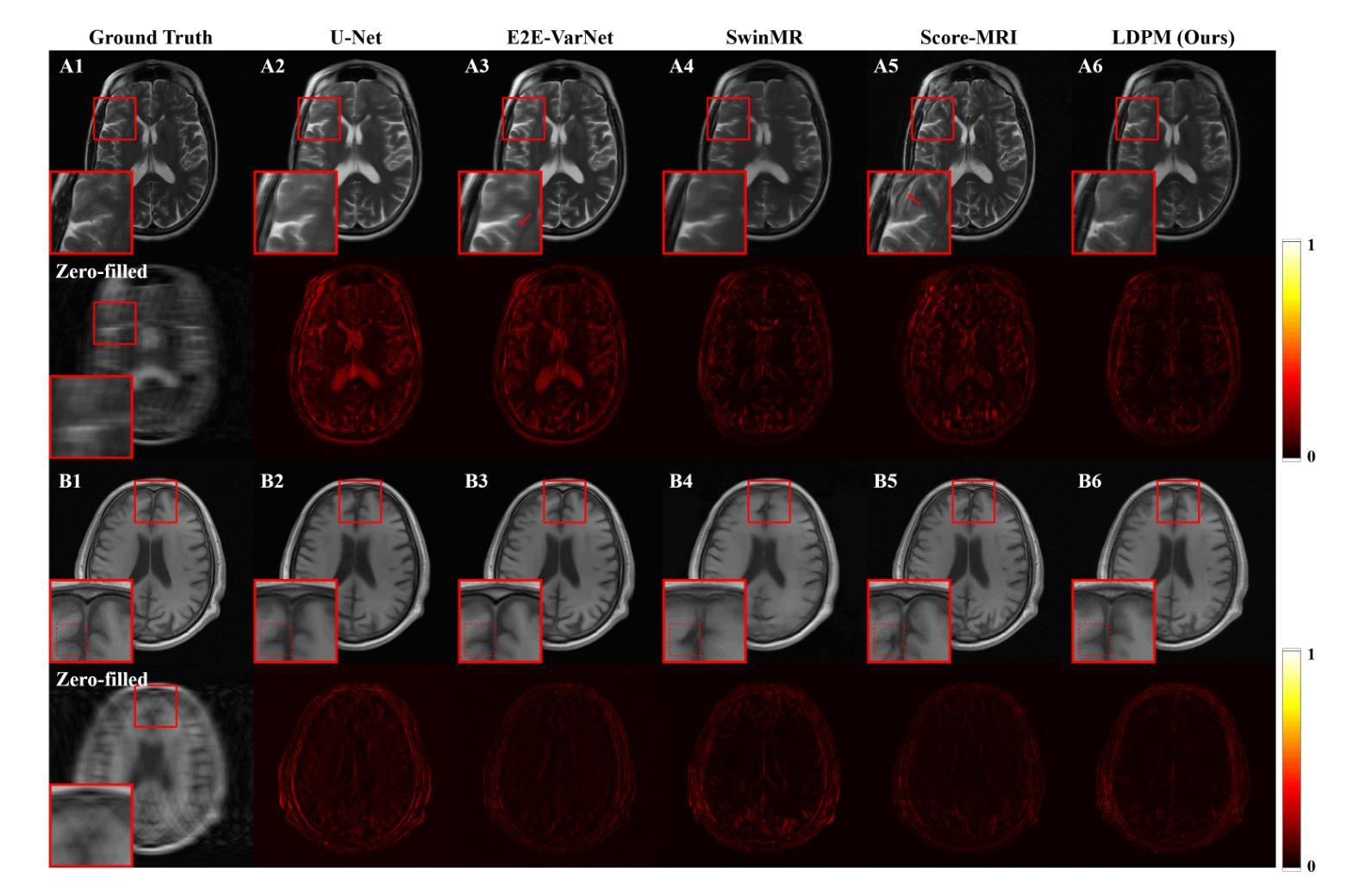
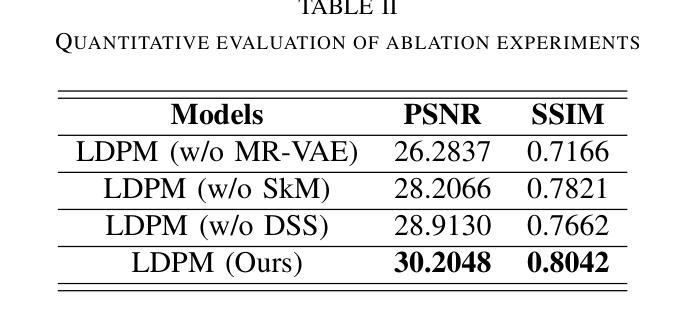
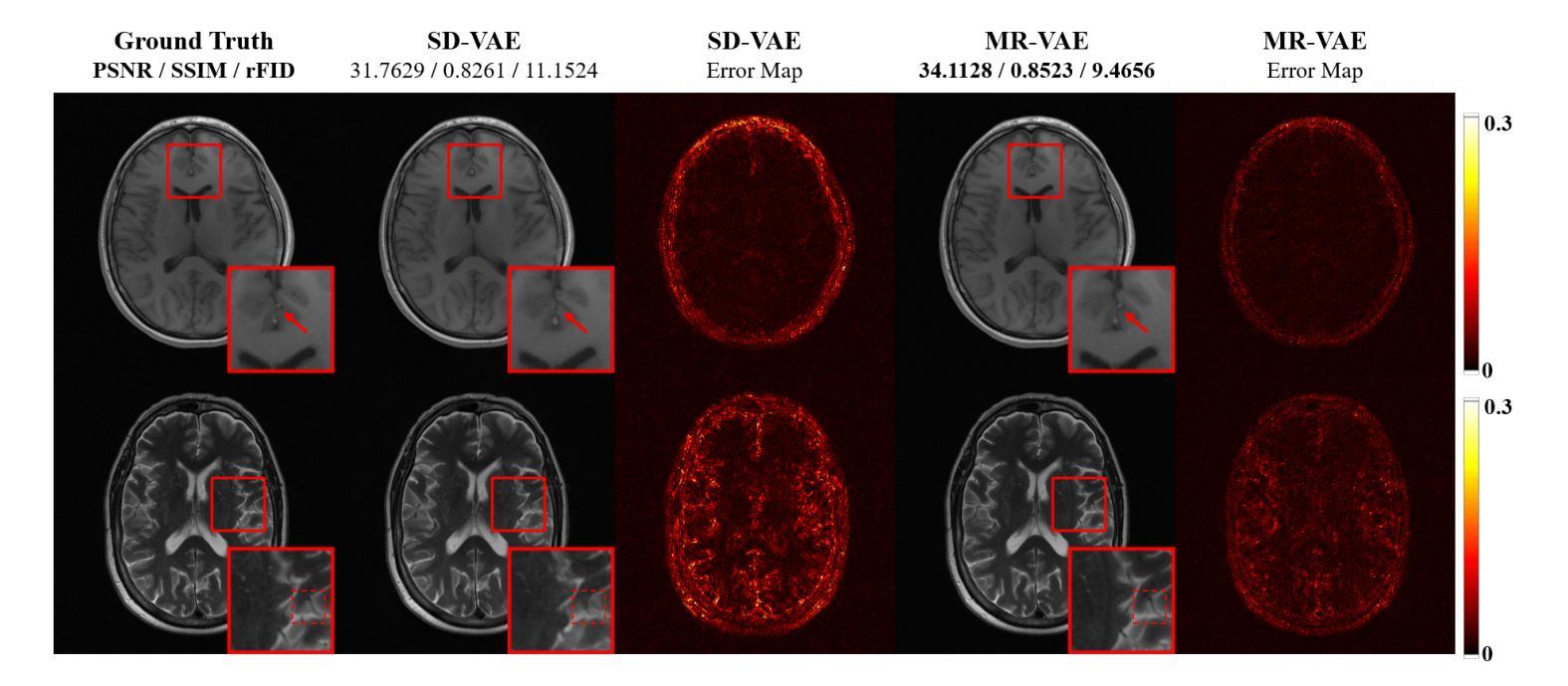
LDPM: Towards undersampled MRI reconstruction with MR-VAE and Latent Diffusion Prior
Authors:Xingjian Tang, Jingwei Guan, Linge Li, Ran Shi, Youmei Zhang, Mengye Lyu, Li Yan
Diffusion models, as powerful generative models, have found a wide range of applications and shown great potential in solving image reconstruction problems. Some works attempted to solve MRI reconstruction with diffusion models, but these methods operate directly in pixel space, leading to higher computational costs for optimization and inference. Latent diffusion models, pre-trained on natural images with rich visual priors, are expected to solve the high computational cost problem in MRI reconstruction by operating in a lower-dimensional latent space. However, direct application to MRI reconstruction faces three key challenges: (1) absence of explicit control mechanisms for medical fidelity, (2) domain gap between natural images and MR physics, and (3) undefined data consistency in latent space. To address these challenges, a novel Latent Diffusion Prior-based undersampled MRI reconstruction (LDPM) method is proposed. Our LDPM framework addresses these challenges by: (1) a sketch-guided pipeline with a two-step reconstruction strategy, which balances perceptual quality and anatomical fidelity, (2) an MRI-optimized VAE (MR-VAE), which achieves an improvement of approximately 3.92 dB in PSNR for undersampled MRI reconstruction compared to that with SD-VAE \cite{sd}, and (3) Dual-Stage Sampler, a modified version of spaced DDPM sampler, which enforces high-fidelity reconstruction in the latent space. Experiments on the fastMRI dataset\cite{fastmri} demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of the proposed method and its robustness across various scenarios. The effectiveness of each module is also verified through ablation experiments.
扩散模型作为强大的生成模型,在图像重建问题中得到了广泛的应用,并展现出了巨大的潜力。一些研究尝试使用扩散模型解决MRI重建问题,但这些方法直接在像素空间进行操作,导致优化和推理的计算成本较高。潜在扩散模型在自然图像上进行预训练,具有丰富的视觉先验,有望通过低维潜在空间解决MRI重建中的高计算成本问题。然而,直接应用于MRI重建面临三个关键挑战:(1)医学保真度的缺乏明确控制机制,(2)自然图像与MR物理之间的领域差距,(3)潜在空间中的数据一致性未定义。为了解决这些挑战,提出了一种基于潜在扩散先验的欠采样MRI重建(LDPM)新方法。我们的LDPM框架通过以下方式应对这些挑战:(1)带有两步重建策略的草图引导管道,平衡了感知质量和解剖保真度;(2)优化的MRI变分自编码器(MR-VAE),在欠采样MRI重建的PSNR上比SD-VAE \cite{sd}提高了约3.92 dB;(3)双阶段采样器,是间隔DDPM采样器的改进版,强制潜在空间的高保真重建。在fastMRI数据集\cite{fastmri}上的实验表明,该方法具有最先进的性能,并在各种场景中表现出稳健性。通过消融实验也验证了每个模块的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted as oral presentation at EMBC 2025
Summary
潜在扩散模型在解决MRI重建问题的图像重建应用中显示出巨大潜力,但仍面临三个挑战。为解决这些挑战,提出一种基于潜在扩散先验的欠采样MRI重建(LDPM)方法,通过草图引导管道、MRI优化的VAE和双阶段采样器等技术实现先进性能。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像重建领域具有广泛的应用潜力,特别是在MRI重建中。
- 直接在像素空间操作会导致较高的计算成本和推理效率降低。
- 潜在扩散模型期望通过在低维潜在空间操作来解决MRI重建中的高计算成本问题。
- 潜在扩散模型在MRI重建中面临三个主要挑战:医学保真度的缺乏控制机制、自然图像与MR物理之间的领域差距,以及潜在空间中的数据一致性未定义。
- LDPM方法通过草图引导管道和两步重建策略平衡感知质量和解剖保真度。
- LDPM使用MRI优化的VAE,在欠采样MRI重建的PSNR上相比SD-VAE有约3.92dB的提升。
点此查看论文截图

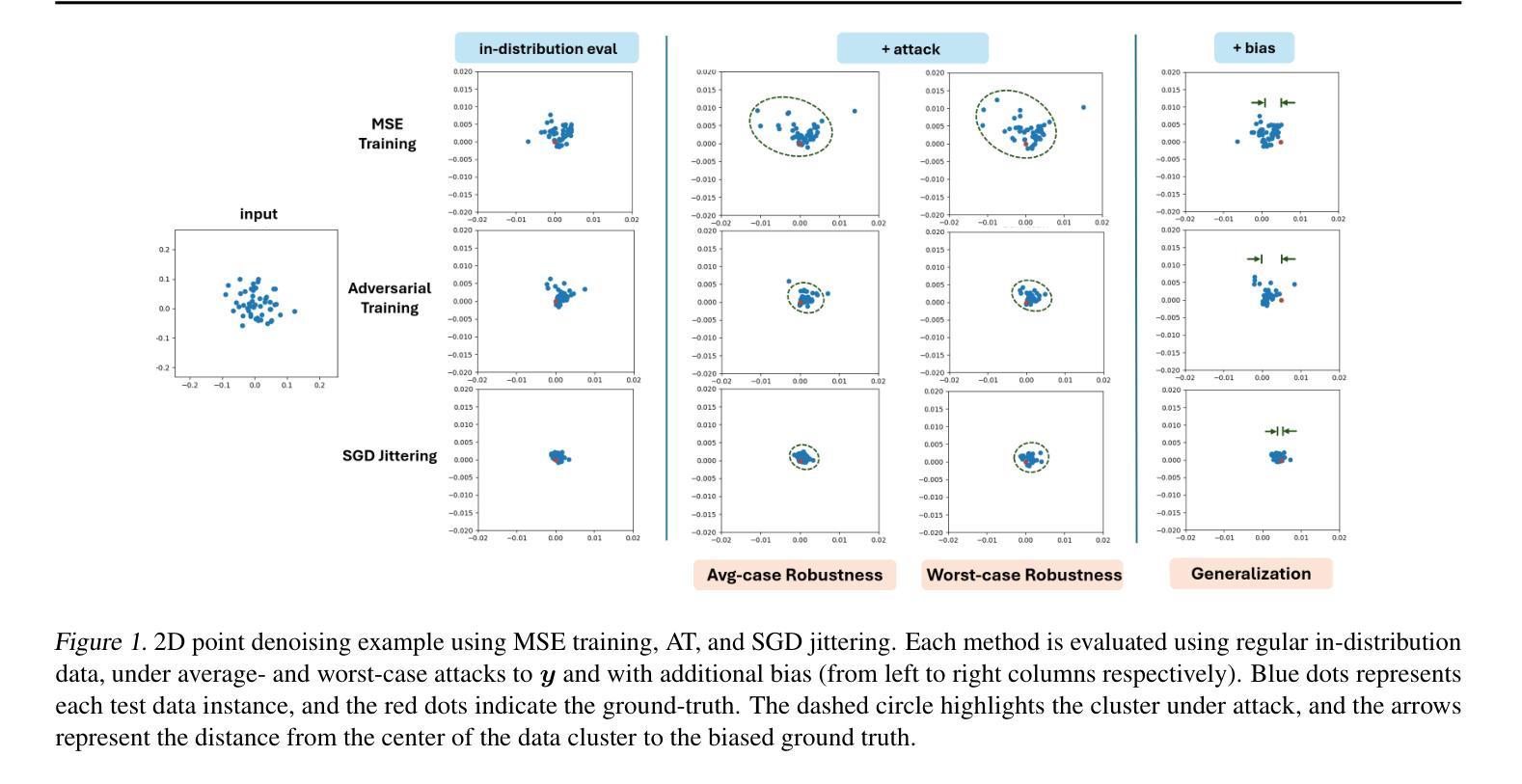
SGD Jittering: A Training Strategy for Robust and Accurate Model-Based Architectures
Authors:Peimeng Guan, Mark A. Davenport
Inverse problems aim to reconstruct unseen data from corrupted or perturbed measurements. While most work focuses on improving reconstruction quality, generalization accuracy and robustness are equally important, especially for safety-critical applications. Model-based architectures (MBAs), such as loop unrolling methods, are considered more interpretable and achieve better reconstructions. Empirical evidence suggests that MBAs are more robust to perturbations than black-box solvers, but the accuracy-robustness tradeoff in MBAs remains underexplored. In this work, we propose a simple yet effective training scheme for MBAs, called SGD jittering, which injects noise iteration-wise during reconstruction. We theoretically demonstrate that SGD jittering not only generalizes better than the standard mean squared error training but is also more robust to average-case attacks. We validate SGD jittering using denoising toy examples, seismic deconvolution, and single-coil MRI reconstruction. Both SGD jittering and its SPGD extension yield cleaner reconstructions for out-of-distribution data and demonstrates enhanced robustness against adversarial attacks.
逆向问题旨在从被损坏或受到干扰的测量结果中重建未见数据。虽然大多数工作都集中在提高重建质量上,但泛化精度和稳健性同样重要,特别是在对安全性要求严格的应用中。基于模型的架构(如展开循环方法)被认为更具可解释性,并可实现更好的重建。经验证据表明,基于模型的架构对干扰的鲁棒性优于黑箱求解器,但对基于模型的架构中的精度稳健权衡仍然缺乏深入研究。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种针对基于模型的架构的简单有效的训练方案,称为SGD抖动,该方案在重建过程中逐步注入噪声。我们从理论上证明了SGD抖动不仅泛化性能优于标准均方误差训练,而且对平均情况下的攻击更具鲁棒性。我们通过去噪玩具示例、地震反卷积和单线圈MRI重建验证了SGD抖动的有效性。SGD抖动及其SPGD扩展都能为超出分布范围的数据提供更清晰的重建结果,并显示出增强的对抗攻击的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
本文探讨了逆问题的解决方案,即如何从被污染或干扰的测量值中重建未知数据。文章指出,尽管大多数工作集中在提高重建质量上,但通用精度和稳健性对于安全关键应用同样重要。基于模型的架构(MBAs)如循环展开方法被认为更具可解释性,并能实现更好的重建。本文提出了一种针对MBAs的简单有效的训练方案——SGD抖动,该方案在重建过程中逐次注入噪声。理论上,SGD抖动不仅比标准的均方误差训练具有更好的通用性,而且对平均情况下的攻击也具有更强的鲁棒性。通过去噪玩具示例、地震解卷积和单线圈MRI重建验证了SGD抖动的有效性。SGD抖动及其SPGD扩展都能为超出分布范围的数据提供更清晰的重建结果,并显示出对抗攻击的增强鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 逆问题旨在从受干扰的测量值中重建未知数据。
- 提高重建质量的同时,也需要关注通用精度和稳健性。
- 基于模型的架构(MBAs)如循环展开方法具有更好的可解释性和重建效果。
- SGD抖动是一种针对MBAs的有效训练方案,能在重建过程中逐次注入噪声。
- SGD抖动理论上具有更好的通用性和对平均攻击的鲁棒性。
- 通过去噪玩具示例、地震解卷积和单线圈MRI重建验证了SGD抖动的实际效果。
点此查看论文截图

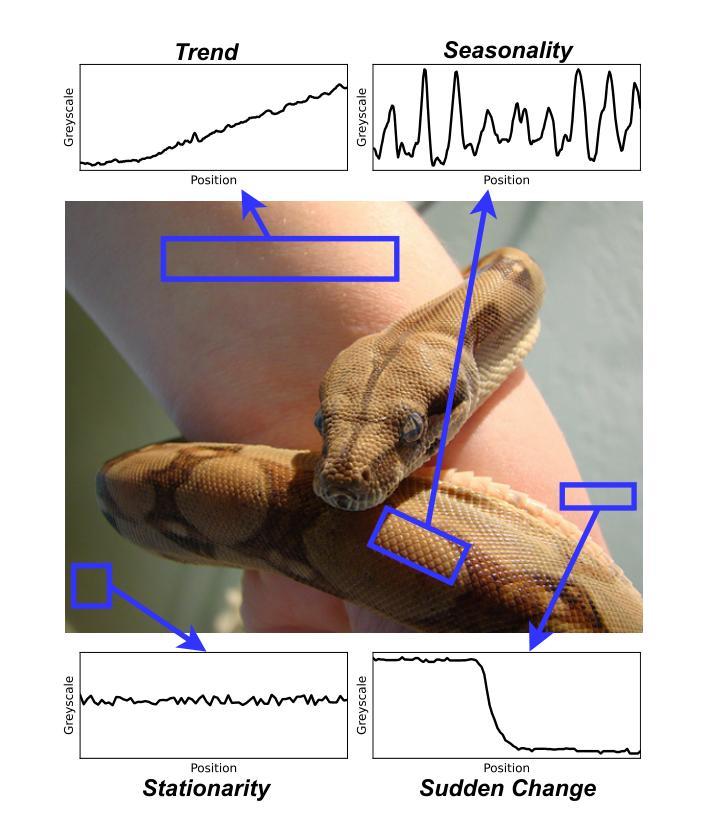
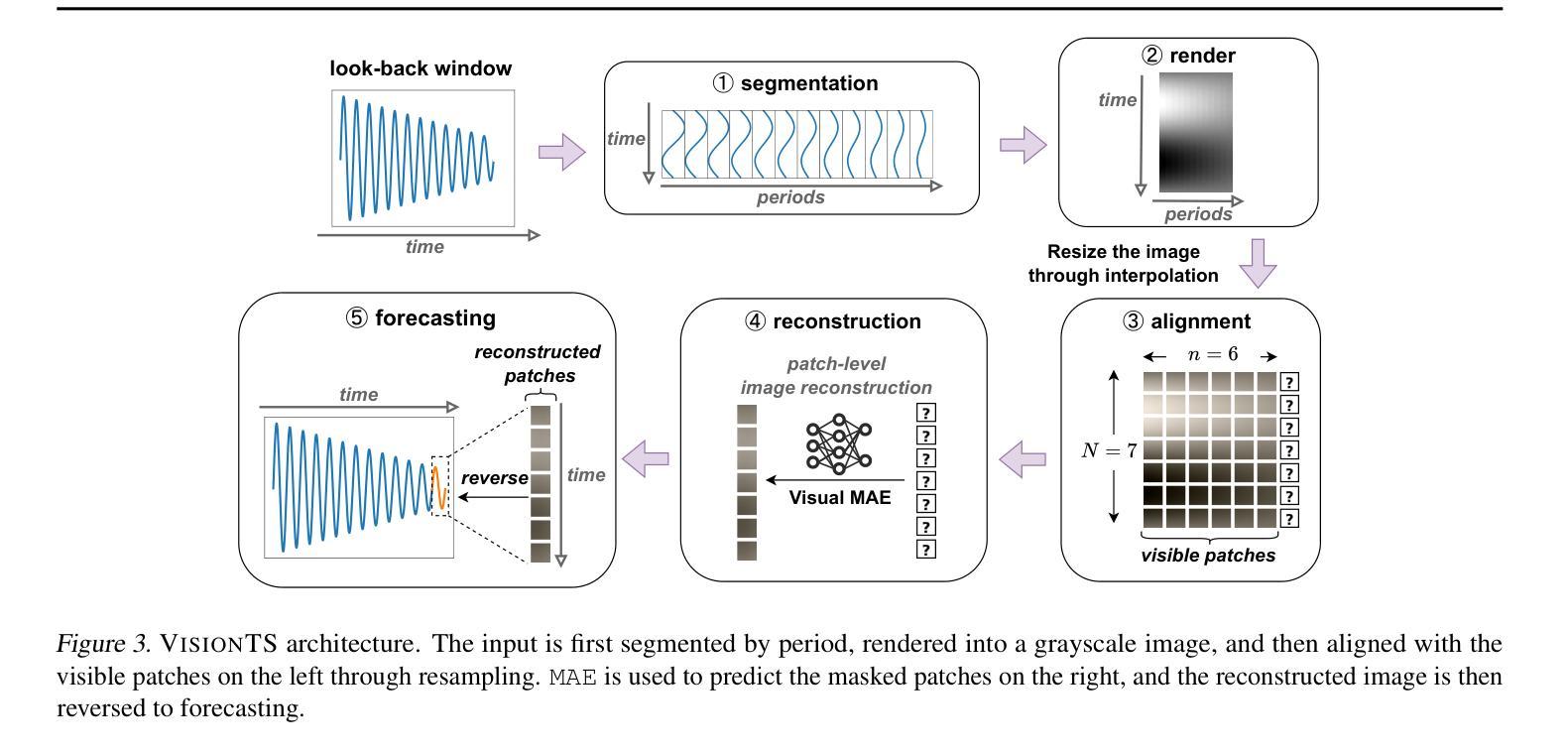
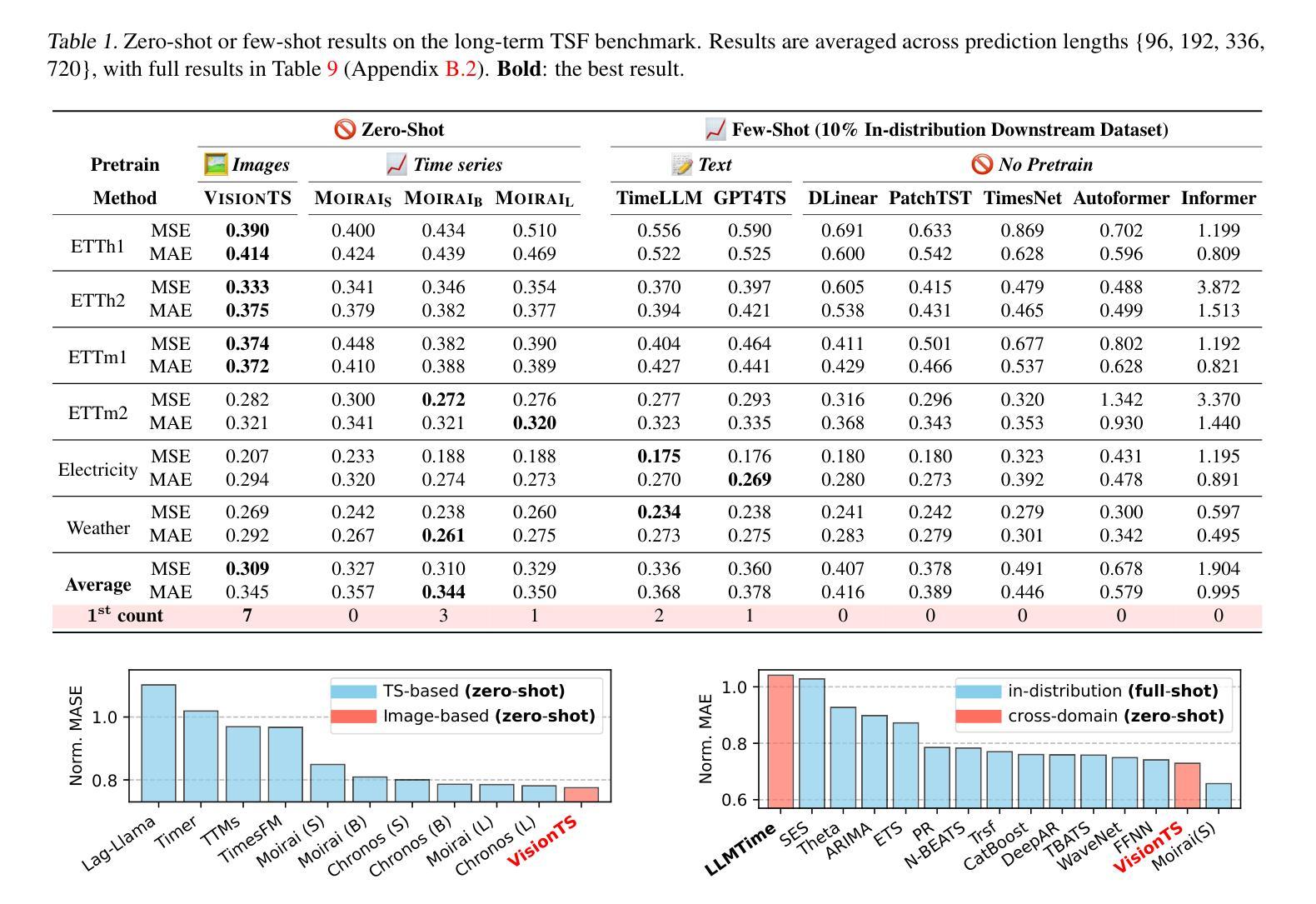
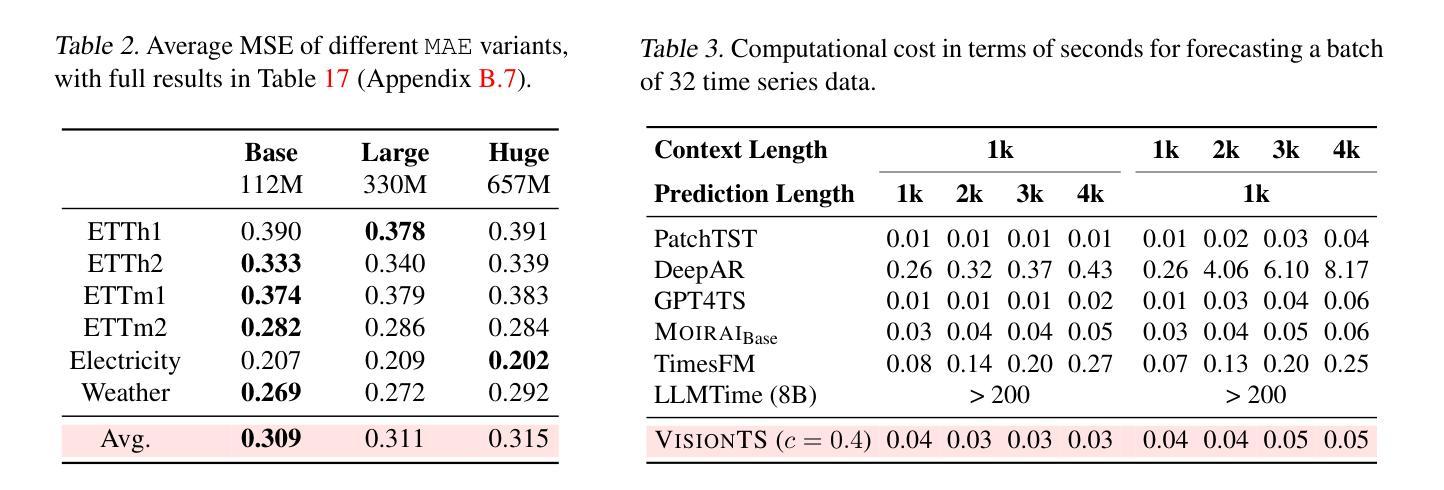
VisionTS: Visual Masked Autoencoders Are Free-Lunch Zero-Shot Time Series Forecasters
Authors:Mouxiang Chen, Lefei Shen, Zhuo Li, Xiaoyun Joy Wang, Jianling Sun, Chenghao Liu
Foundation models have emerged as a promising approach in time series forecasting (TSF). Existing approaches either repurpose large language models (LLMs) or build large-scale time series datasets to develop TSF foundation models for universal forecasting. However, these methods face challenges due to the severe cross-domain gap or in-domain heterogeneity. This paper explores a new road to building a TSF foundation model from rich, high-quality natural images. Our key insight is that a visual masked autoencoder, pre-trained on the ImageNet dataset, can naturally be a numeric series forecaster. By reformulating TSF as an image reconstruction task, we bridge the gap between image pre-training and TSF downstream tasks. Surprisingly, without further adaptation in the time series domain, the proposed VisionTS could achieve better zero-shot forecast performance than existing TSF foundation models. With fine-tuning for one epoch, VisionTS could further improve the forecasting and achieve state-of-the-art performance in most cases. Extensive experiments reveal intrinsic similarities between images and real-world time series, suggesting that visual models may offer a “free lunch” for TSF and highlight the potential for future cross-modality research. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/Keytoyze/VisionTS.
时间序列预测(TSF)中,基础模型作为一种有前途的方法已经崭露头角。现有的方法要么重新利用大型语言模型(LLM),要么构建大规模时间序列数据集,以开发用于通用预测的时间序列预测基础模型。然而,这些方法面临着跨域差距严重或领域内部异质性的挑战。本文探索了一条新的道路,从丰富、高质量的自然图像中构建TSF基础模型。我们的关键见解是,在ImageNet数据集上进行预训练的可视化掩码自动编码器可以自然地成为数值序列预测器。通过将TSF重新构建为图像重建任务,我们弥合了图像预训练和TSF下游任务之间的差距。令人惊讶的是,无需在时间序列领域进一步适应,所提出的VisionTS可以实现在现有TSF基础模型上更好的零样本预测性能。通过微调一个周期,VisionTS可以进一步提高预测能力,并在大多数情况下达到最先进的性能水平。大量实验揭示了图像和现实世界时间序列之间的内在相似性,这表明视觉模型可能为TSF提供了“免费午餐”,并突出了未来跨模态研究的潜力。我们的代码公开在https://github.com/Keytoyze/VisionTS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF v4: accepted by ICML 2025
Summary
本文探索了一种新的时间序列预测(TSF)基础模型构建方法,该方法利用丰富、高质量的自然图像进行预训练。研究人员发现,通过在图像重建任务中重新构建时间序列预测,可以使用在ImageNet数据集上预训练的视觉掩码自动编码器进行数值序列预测。该方法无需进一步适应时间序列领域,即可实现零次预测性能优于现有TSF基础模型,并可通过微调进一步提升预测性能。研究揭示了图像和现实世界时间序列之间的内在联系,为未来的跨模态研究提供了潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种新的时间序列预测(TSF)基础模型构建方法,该方法使用自然图像进行预训练。
- 研究人员发现,视觉掩码自动编码器可以自然地进行数值序列预测,这是通过将其重新构建为图像重建任务实现的。
- 该方法无需进一步适应时间序列领域,即可实现零次预测性能优于现有TSF基础模型。
- 通过微调,该方法的预测性能可以进一步提高,达到大多数情况下的最佳水平。
- 研究揭示了图像和现实世界时间序列之间的内在联系。
- 视觉模型可能为时间序列预测提供“免费午餐”,这表明跨模态研究的潜力巨大。
点此查看论文截图

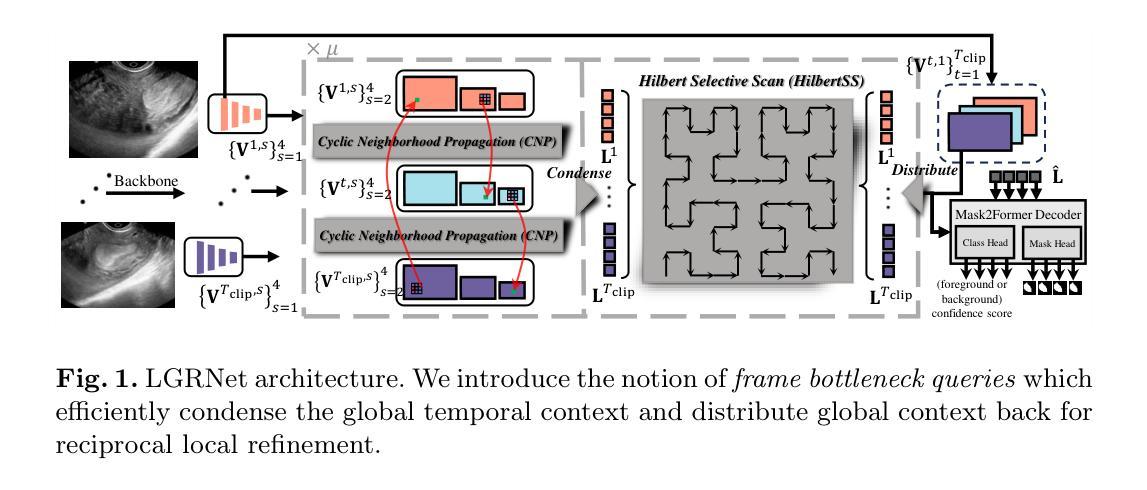
HilbertMamba: Local-Global Reciprocal Network for Uterine Fibroid Segmentation in Ultrasound Videos
Authors:Huihui Xu, Yijun Yang, Angelica I Aviles-Rivero, Guang Yang, Jing Qin, Lei Zhu
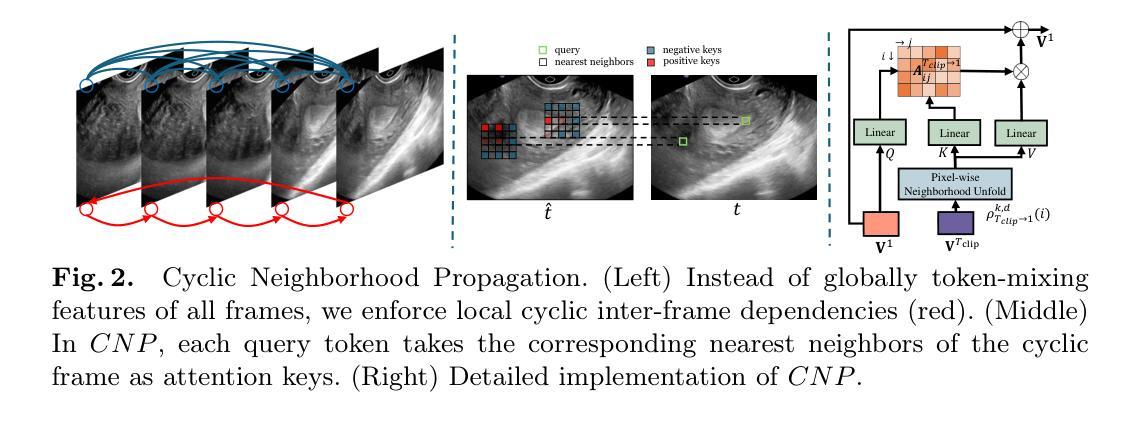
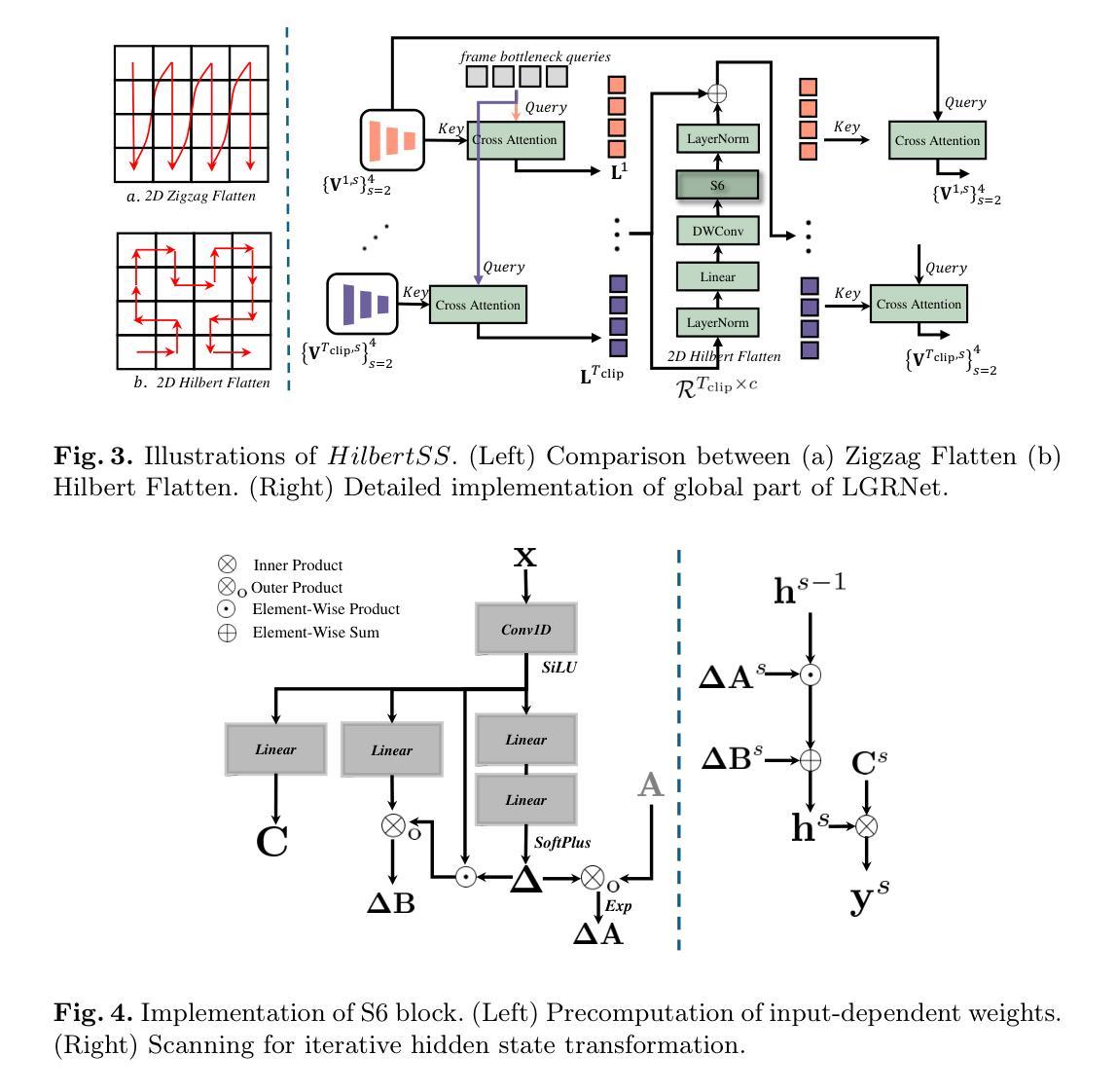
Regular screening and early discovery of uterine fibroid are crucial for preventing potential malignant transformations and ensuring timely, life-saving interventions. To this end, we collect and annotate the first ultrasound video dataset with 100 videos for uterine fibroid segmentation (UFUV). We also present Local-Global Reciprocal Network (LGRNet) to efficiently and effectively propagate the long-term temporal context which is crucial to help distinguish between uninformative noisy surrounding tissues and target lesion regions. Specifically, the Cyclic Neighborhood Propagation (CNP) is introduced to propagate the inter-frame local temporal context in a cyclic manner. Moreover, to aggregate global temporal context, we first condense each frame into a set of frame bottleneck queries and devise Hilbert Selective Scan (HilbertSS) to both efficiently path connect each frame and preserve the locality bias. A distribute layer is then utilized to disseminate back the global context for reciprocal refinement. Extensive experiments on UFUV and three public Video Polyp Segmentation (VPS) datasets demonstrate consistent improvements compared to state-of-the-art segmentation methods, indicating the effectiveness and versatility of LGRNet. Code, checkpoints, and dataset are available at https://github.com/bio-mlhui/LGRNet
定期筛查和早期发现子宫纤维瘤对于预防潜在的恶性转化和确保及时挽救生命的干预至关重要。为此,我们收集和标注了第一个包含100个视频的子宫纤维瘤分割超声视频数据集(UFUV)。我们还提出了局部全局互惠网络(LGRNet),以高效且有效地传播长期时间上下文,这对于区分周围无信息噪声组织和目标病变区域至关重要。具体来说,引入了循环邻域传播(CNP),以循环方式传播帧间局部时间上下文。此外,为了聚合全局时间上下文,我们首先将每一帧浓缩为一组帧瓶颈查询,并设计Hilbert选择性扫描(HilbertSS)以有效地连接每一帧并保持局部偏向性。然后利用分布层将全局上下文回传给每一帧进行互惠细化。在UFUV和三个公共视频息肉分割(VPS)数据集上的大量实验表明,与最先进的分割方法相比,LGRNet具有一致的优势,证明了其有效性和通用性。代码、检查点和数据集可在https://github.com/bio-mlhui/LGRNet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI2024 Early Accept
Summary
本文强调定期筛查和早期发现子宫纤维瘤的重要性,以防止潜在的恶性转化并确保及时的生命拯救干预。为此,作者收集和标注了第一个子宫纤维瘤分割超声视频数据集UFUV,包含100个视频。此外,作者提出了Local-Global Reciprocal Network(LGRNet),该网络能有效传播长期时间上下文信息,有助于区分无信息干扰的周围组织和目标病变区域。网络包含Cyclic Neighborhood Propagation(CNP)和Hilbert Selective Scan(HilbertSS),分别用于循环传播局部时间上下文和高效路径连接每一帧并保持局部偏见。最终,通过与现有顶级分割方法在多数据集上的广泛实验比较,显示了LGRNet的有效性和通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 定期筛查和早期发现子宫纤维瘤至关重要,有助于预防恶性转化并保证及时干预。
- 作者创建了第一个用于子宫纤维瘤分割的超声视频数据集UFUV,包含100个视频。
- 提出了Local-Global Reciprocal Network(LGRNet)以有效传播长期时间上下文信息。
- CNP和HilbertSS是LGRNet中的关键组件,分别负责局部时间上下文的循环传播和高效帧间路径连接。
- 使用全局上下文传播以进行递归优化。
- 在UFUV和三个公共视频息肉分割数据集上的实验表明,LGRNet相较于现有顶级分割方法有所改进。
点此查看论文截图