⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-10 更新
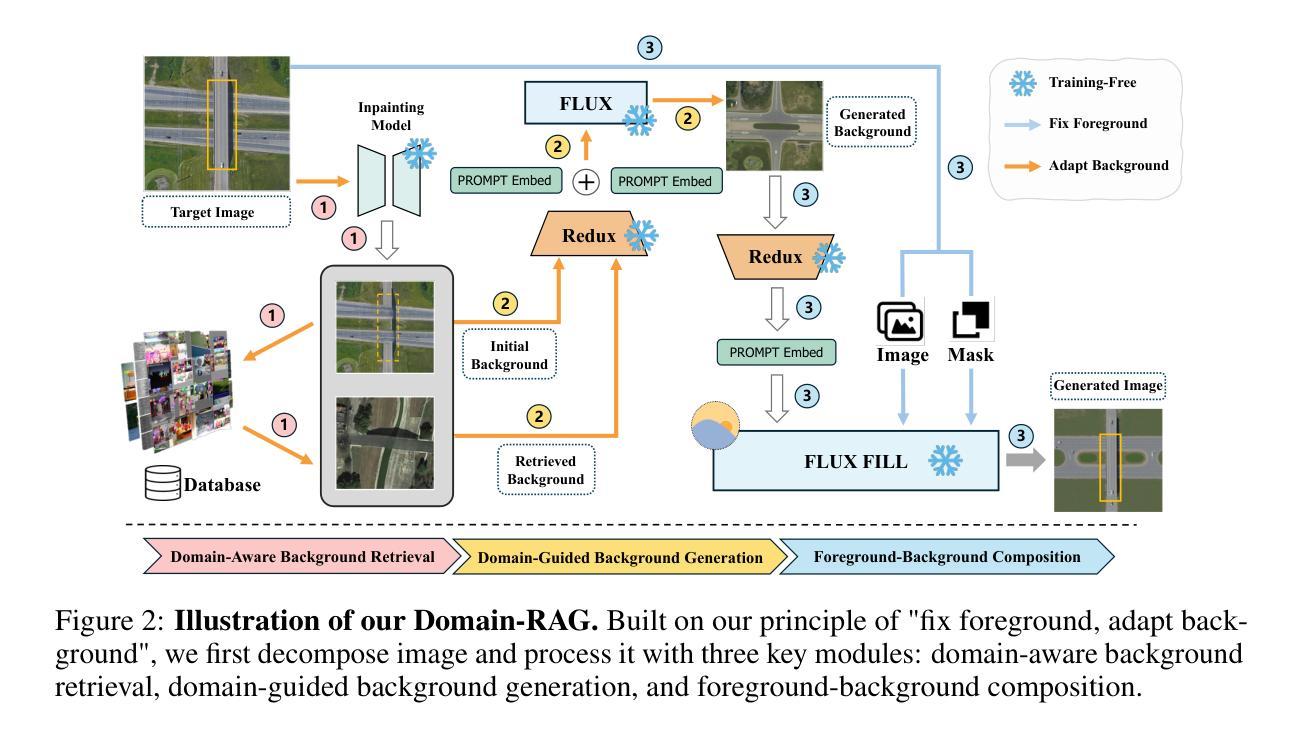
Domain-RAG: Retrieval-Guided Compositional Image Generation for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection
Authors:Yu Li, Xingyu Qiu, Yuqian Fu, Jie Chen, Tianwen Qian, Xu Zheng, Danda Pani Paudel, Yanwei Fu, Xuanjing Huang, Luc Van Gool, Yu-Gang Jiang
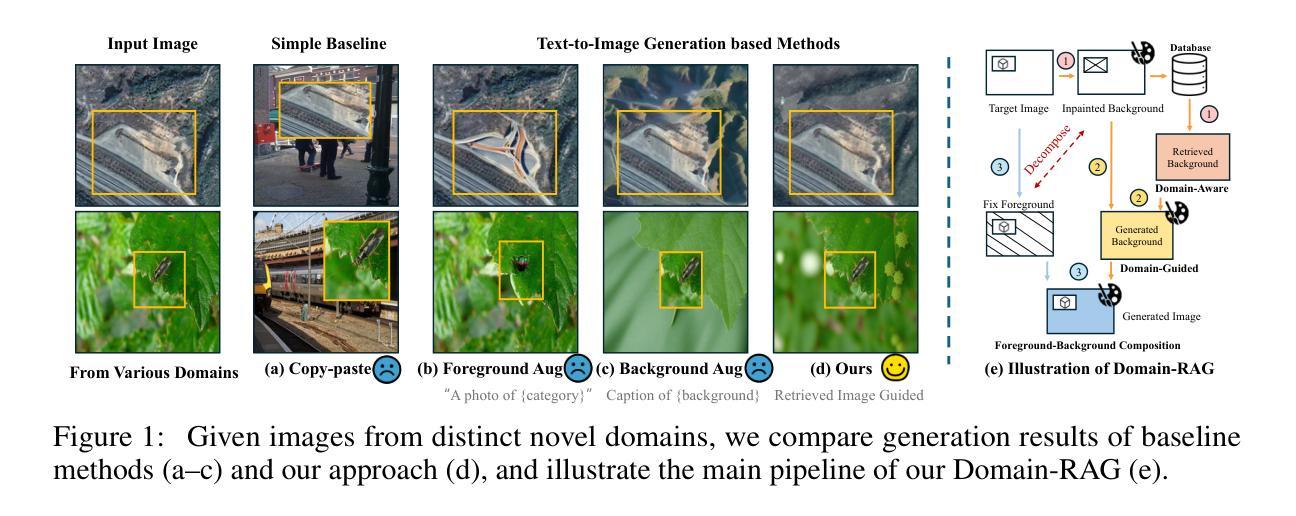
Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection (CD-FSOD) aims to detect novel objects with only a handful of labeled samples from previously unseen domains. While data augmentation and generative methods have shown promise in few-shot learning, their effectiveness for CD-FSOD remains unclear due to the need for both visual realism and domain alignment. Existing strategies, such as copy-paste augmentation and text-to-image generation, often fail to preserve the correct object category or produce backgrounds coherent with the target domain, making them non-trivial to apply directly to CD-FSOD. To address these challenges, we propose Domain-RAG, a training-free, retrieval-guided compositional image generation framework tailored for CD-FSOD. Domain-RAG consists of three stages: domain-aware background retrieval, domain-guided background generation, and foreground-background composition. Specifically, the input image is first decomposed into foreground and background regions. We then retrieve semantically and stylistically similar images to guide a generative model in synthesizing a new background, conditioned on both the original and retrieved contexts. Finally, the preserved foreground is composed with the newly generated domain-aligned background to form the generated image. Without requiring any additional supervision or training, Domain-RAG produces high-quality, domain-consistent samples across diverse tasks, including CD-FSOD, remote sensing FSOD, and camouflaged FSOD. Extensive experiments show consistent improvements over strong baselines and establish new state-of-the-art results. Codes will be released upon acceptance.
跨域小样本目标检测(CD-FSOD)旨在仅利用之前未见域的少量标记样本检测新型目标。虽然数据增强和生成方法在少样本学习中显示出潜力,但由于需要视觉现实性和域对齐,它们在CD-FSOD中的有效性仍然不明确。现有策略,如复制粘贴增强和文本到图像生成,往往无法保留正确的目标类别或产生与目标域一致的背景,因此将它们直接应用于CD-FSOD具有挑战性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了Domain-RAG,这是一种无需训练的、以检索为指导的组合图像生成框架,专为CD-FSOD定制。Domain-RAG由三个阶段组成:域感知背景检索、域引导背景生成和前景背景组合。具体来说,首先,将输入图像分解为前景和背景区域。然后,我们检索语义和风格相似的图像,以指导生成模型根据原始和检索的上下文合成新的背景。最后,将保留的前景与新生成的域对齐背景组合形成生成的图像。无需任何额外的监督或训练,Domain-RAG在包括CD-FSOD、遥感FSOD和隐蔽FSOD在内的各种任务中产生高质量、域一致的样本。大量实验表明,与强大的基线相比,它始终表现出一致的改进,并创造了新的最佳结果。代码将在接受后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
CD-FSOD领域旨在实现在未见过的领域中对新目标进行仅几次标注样本的检测。现有方法如数据增强和生成方法在少样本学习中有潜力,但在CD-FSOD中的有效性尚不清楚。本文提出一种针对CD-FSOD的无训练、检索引导的组成图像生成框架——Domain-RAG,包含三个阶段:领域感知背景检索、领域引导背景生成和前景背景组合。Domain-RAG通过分解输入图像为前景和背景区域,检索语义和风格相似的图像来指导生成模型合成新的背景,并与原始和检索到的上下文相结合。最终,将保留的前景与新的领域一致的背景组合形成生成的图像。Domain-RAG无需额外的监督或训练,即可在多个任务中产生高质量、领域一致的样本,包括CD-FSOD、遥感FSOD和隐蔽FSOD等。实验证明其在强基线之上表现优异,并达到了最新技术水准。
Key Takeaways
- CD-FSOD的目标是检测未见领域的新对象,只有少量标注样本可用。
- 数据增强和生成方法在少样本学习中有潜力,但在CD-FSOD中效果不确定。
- Domain-RAG是一种针对CD-FSOD的训练外图像生成框架,包含背景检索、背景生成和前景背景组合三个阶段。
- Domain-RAG通过分解图像并检索相似图像来指导生成模型合成新的背景。
- Domain-RAG无需额外训练或监督,适用于多种任务,包括CD-FSOD和其他相关领域任务。
- 实验证明Domain-RAG在强基线之上表现优异,达到最新技术水准。
点此查看论文截图

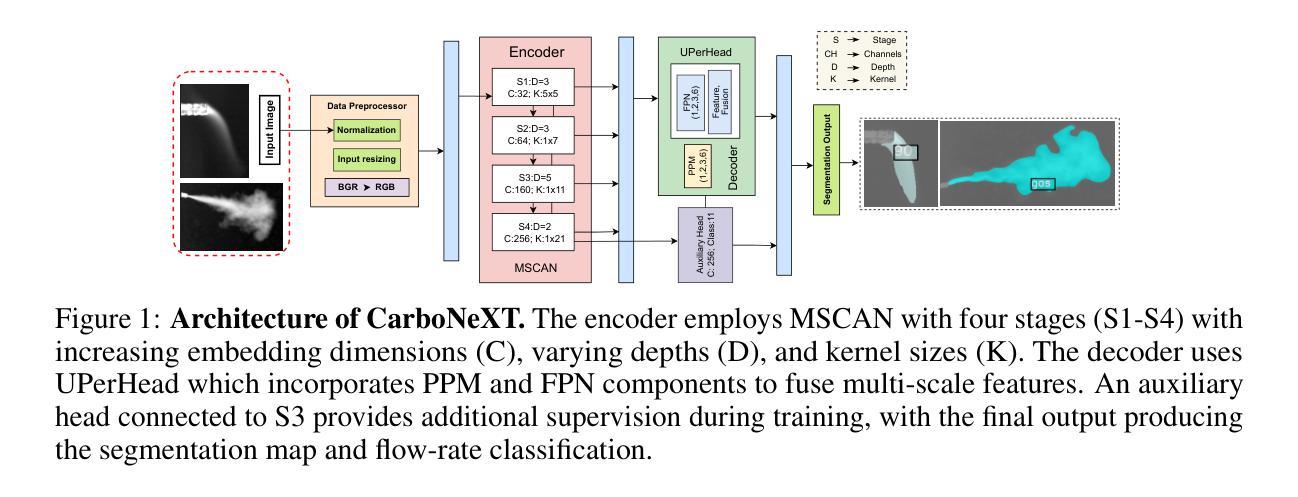
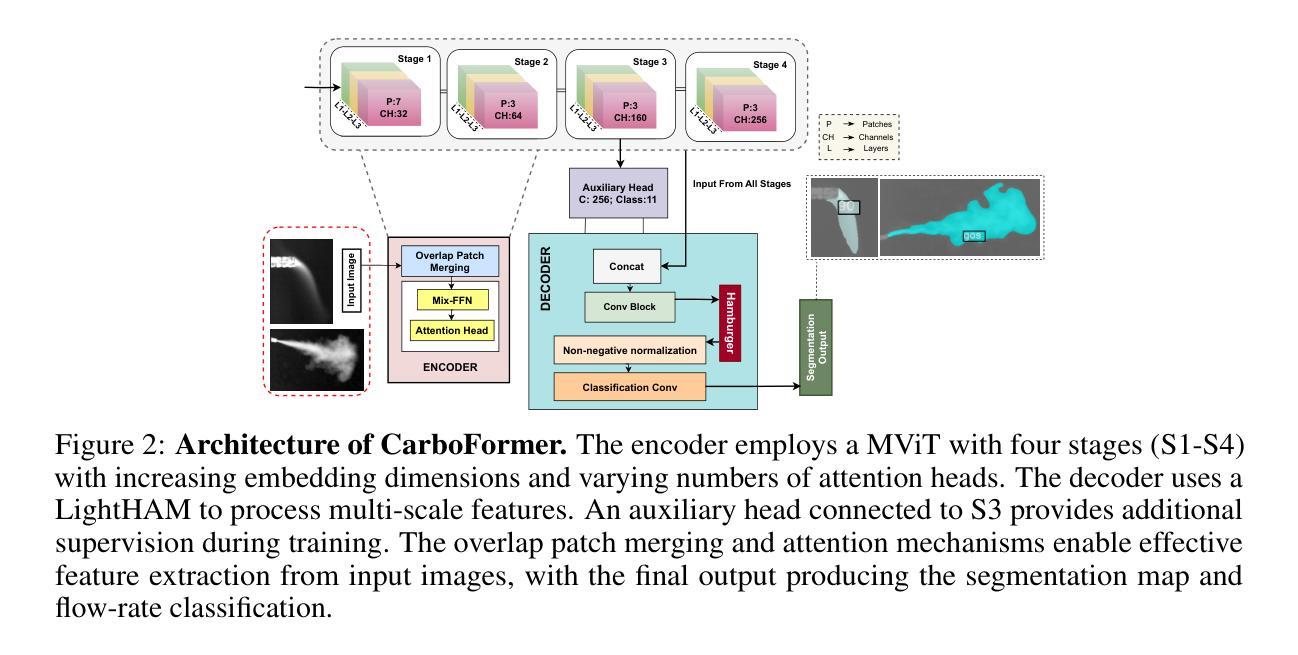
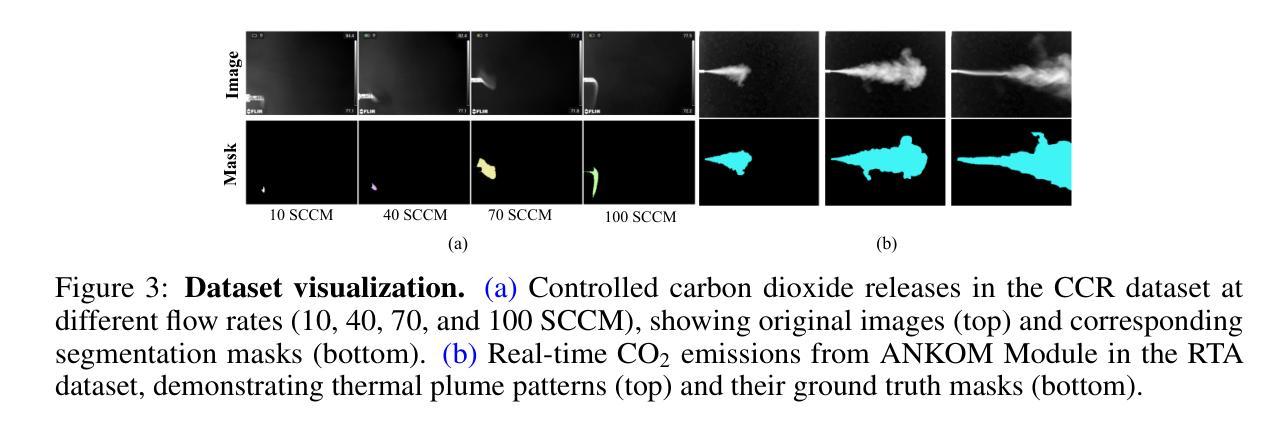
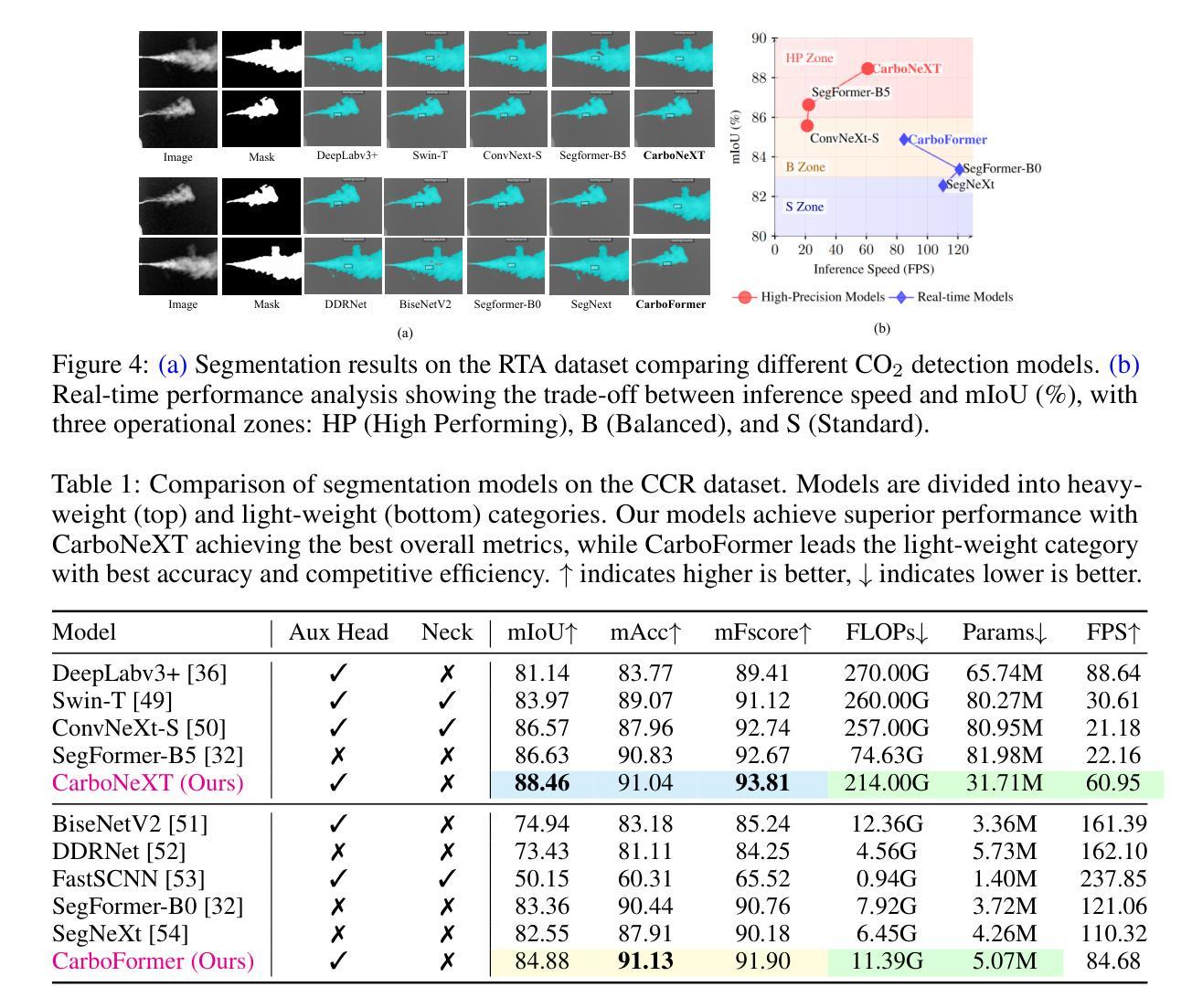
CarboNeXT and CarboFormer: Dual Semantic Segmentation Architectures for Detecting and Quantifying Carbon Dioxide Emissions Using Optical Gas Imaging
Authors:Taminul Islam, Toqi Tahamid Sarker, Mohamed G Embaby, Khaled R Ahmed, Amer AbuGhazaleh
Carbon dioxide (CO$_2$) emissions are critical indicators of both environmental impact and various industrial processes, including livestock management. We introduce CarboNeXT, a semantic segmentation framework for Optical Gas Imaging (OGI), designed to detect and quantify CO$_2$ emissions across diverse applications. Our approach integrates a multi-scale context aggregation network with UPerHead and auxiliary FCN components to effectively model both local details and global relationships in gas plume imagery. We contribute two novel datasets: (1) the Controlled Carbon Dioxide Release (CCR) dataset, which simulates gas leaks with systematically varied flow rates (10-100 SCCM), and (2) the Real Time Ankom (RTA) dataset, focusing on emissions from dairy cow rumen fluid in vitro experiments. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that CarboNeXT outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving 88.46% mIoU on CCR and 92.95% mIoU on RTA, with particular effectiveness in challenging low-flow scenarios. The model operates at 60.95 FPS, enabling real-time monitoring applications. Additionally, we propose CarboFormer, a lightweight variant with only 5.07M parameters that achieves 84.68 FPS, with competitive performance of 84.88% mIoU on CCR and 92.98% on RTA, making it suitable for resource-constrained platforms such as programmable drones. Our work advances both environmental sensing and precision livestock management by providing robust tools for CO$_2$ emission analysis, with a specific focus on livestock applications.
二氧化碳(CO2)排放是环境影响和各种工业过程(包括牲畜管理)的关键指标。我们介绍了CarboNeXT,这是一个用于光学气体成像(OGI)的语义分割框架,旨在检测并量化CO在不同应用中的排放量。我们的方法融合了多尺度上下文聚合网络、UPerHead和辅助FCN组件,有效地对气体排放影像中的局部细节和全局关系进行建模。我们贡献了两个新型数据集:(1)控制二氧化碳排放(CCR)数据集,模拟系统变化流速(10-100 SCCM)的气体泄漏;(2)实时安科姆(RTA)数据集,专注于体外实验中的奶牛瘤胃流体排放的CO。全面评估表明,CarboNeXT优于现有方法,在CCR上达到88.46%的mIoU,在RTA上达到92.95%的mIoU,在低流量场景中表现尤为出色。该模型运行速度为每秒60.95帧,可实现实时监控应用。此外,我们提出了CarboFormer,这是一个仅有5.07M参数的轻量级变体,运行速度达到每秒84.68帧,在CCR上的性能为竞争性的84.88% mIoU,在RTA上为92.98%,适用于资源受限的平台,如可编程无人机。我们的工作通过提供稳健的工具进行CO排放分析,特别是在牲畜应用领域方面取得了进展,从而推动了环境感知和精确牲畜管理的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
碳排放是环境影响和工业过程的重要指标之一,包括畜牧业管理。本研究推出CarboNeXT,一个用于光学气体成像(OGI)的语义分割框架,旨在检测并量化CO2排放的各种应用。该框架整合了多尺度上下文聚合网络、UPerHead和辅助FCN组件,有效建模气体扩散影像中的局部细节和全局关系。研究贡献了两个数据集:(1)模拟气体泄漏的受控二氧化碳释放(CCR)数据集;(2)关注体外实验奶牛瘤胃流体排放的实时安科姆(RTA)数据集。评估表明,CarboNeXT较现有技术表现优越,CCR上达到88.46% mIoU,RTA上达到92.95% mIoU,在低流量场景下有特别优势。模型运行速度为每秒60.95帧,适用于实时监控应用。此外,研究还推出了轻量级的CarboFormer模型,仅有5.07M参数,运行速度达每秒84.68帧,性能优异,适用于资源受限的平台如编程无人机。此研究推动了环境感知和精准畜牧业管理的发展,为CO2排放分析提供了稳健工具。
Key Takeaways
- CarboNeXT是一个用于光学气体成像的语义分割框架,旨在检测并量化CO2排放。
- 框架整合了多尺度上下文聚合网络、UPerHead和辅助FCN组件以建模气体扩散影像中的细节和全局关系。
- 推出两个数据集:CCR和RTA,分别模拟气体泄漏和关注奶牛瘤胃流体排放的体外实验。
- CarboNeXT较现有技术表现优越,在CCR和RTA上分别达到了88.46%和92.95%的mIoU。
- 模型适用于实时监控应用,运行速度为每秒60.95帧。
- 还推出了轻量级模型CarboFormer,适用于资源受限的平台如编程无人机。
点此查看论文截图

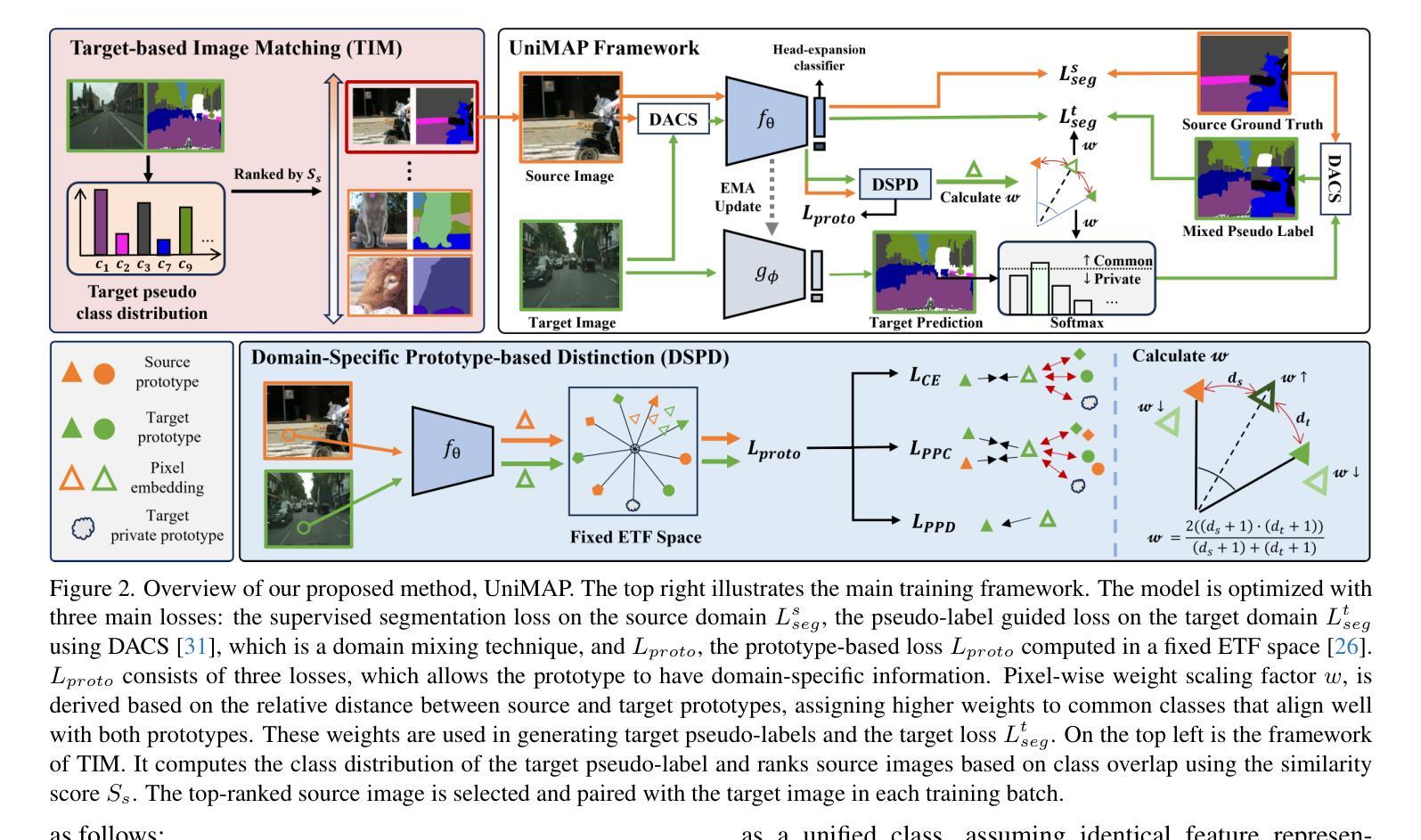
Universal Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Seun-An Choe, Keon-Hee Park, Jinwoo Choi, Gyeong-Moon Park
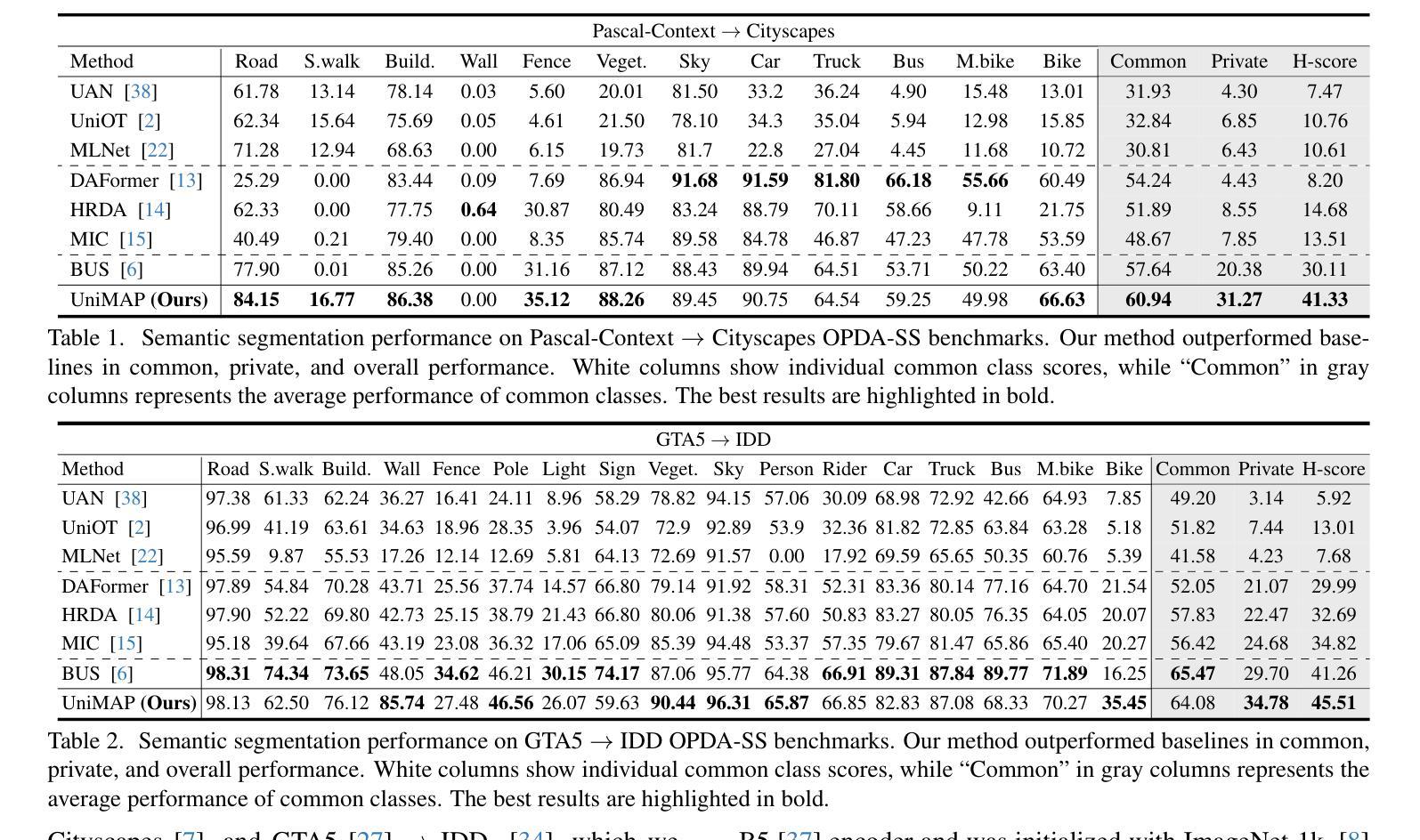
Unsupervised domain adaptation for semantic segmentation (UDA-SS) aims to transfer knowledge from labeled source data to unlabeled target data. However, traditional UDA-SS methods assume that category settings between source and target domains are known, which is unrealistic in real-world scenarios. This leads to performance degradation if private classes exist. To address this limitation, we propose Universal Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation (UniDA-SS), achieving robust adaptation even without prior knowledge of category settings. We define the problem in the UniDA-SS scenario as low confidence scores of common classes in the target domain, which leads to confusion with private classes. To solve this problem, we propose UniMAP: UniDA-SS with Image Matching and Prototype-based Distinction, a novel framework composed of two key components. First, Domain-Specific Prototype-based Distinction (DSPD) divides each class into two domain-specific prototypes, enabling finer separation of domain-specific features and enhancing the identification of common classes across domains. Second, Target-based Image Matching (TIM) selects a source image containing the most common-class pixels based on the target pseudo-label and pairs it in a batch to promote effective learning of common classes. We also introduce a new UniDA-SS benchmark and demonstrate through various experiments that UniMAP significantly outperforms baselines. The code is available at https://github.com/KU-VGI/UniMAP.
无监督域自适应语义分割(UDA-SS)旨在将来自源数据的知识转移到目标数据上,而这些目标数据未被标记。然而,传统的UDA-SS方法假设源域和目标域之间的类别设置是已知的,这在现实场景中是不切实际的。如果存在私有类别,这会导致性能下降。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了通用域自适应语义分割(UniDA-SS)的方法,即使在不知道类别设置的情况下也能实现稳健的适应。在UniDA-SS场景中,我们将问题定义为目标域中常见类别的置信度得分较低,这导致与私有类别的混淆。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了UniMAP:基于图像匹配的通用域自适应语义分割与基于原型的区分,这是一个新型框架,由两个关键组件组成。首先,基于域特定原型的区分(DSPD)将每个类别分为两个域特定原型,能够更精细地分离域特定特征,并增强跨域的常见类别的识别。其次,基于目标的图像匹配(TIM)根据目标伪标签选择包含最常见类别像素的源图像,并将其与一批图像配对,以促进常见类别的有效学习。我们还引入了一个新的UniDA-SS基准测试,并通过各种实验证明,UniMAP显著优于基线。代码可在https://github.com/KU-VGI/UniMAP中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对语义分割的通用域自适应(UniDA-SS)方法,解决了传统UDA-SS方法在应对现实世界中不同类别设置的问题时的局限性。新方法主要解决目标域中常见类别低置信度分数导致的与私有类别混淆的问题。提出一种新型框架UniMAP,通过图像匹配和基于原型的区分来实现稳健的域自适应,无需事先了解类别设置。包含两个关键组件:基于域的特定原型区分(DSPD)和目标图像匹配(TIM)。同时引入新的UniDA-SS基准测试,并通过实验证明UniMAP显著优于基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 传统UDA-SS方法假设源和目标域之间的类别设置已知,但在现实世界中并不现实。当存在私有类别时,这可能导致性能下降。
- UniDA-SS解决了目标域中常见类别低置信度分数引起的与私有类别混淆的问题。
- UniMAP是一个新型框架,包含图像匹配(TIM)和基于原型的区分(DSPD)两个关键组件。
- DSPD将每个类别分为两个域特定原型,有助于精细分离域特定特征并增强跨域的常见类别的识别。
- TIM基于目标伪标签选择包含最多常见类别像素的源图像,并将其与一批图像配对,以促进常见类别的有效学习。
- 引入新的UniDA-SS基准测试来评估方法性能。
- 通过实验证明,UniMAP显著优于基线方法。
点此查看论文截图