⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-10 更新
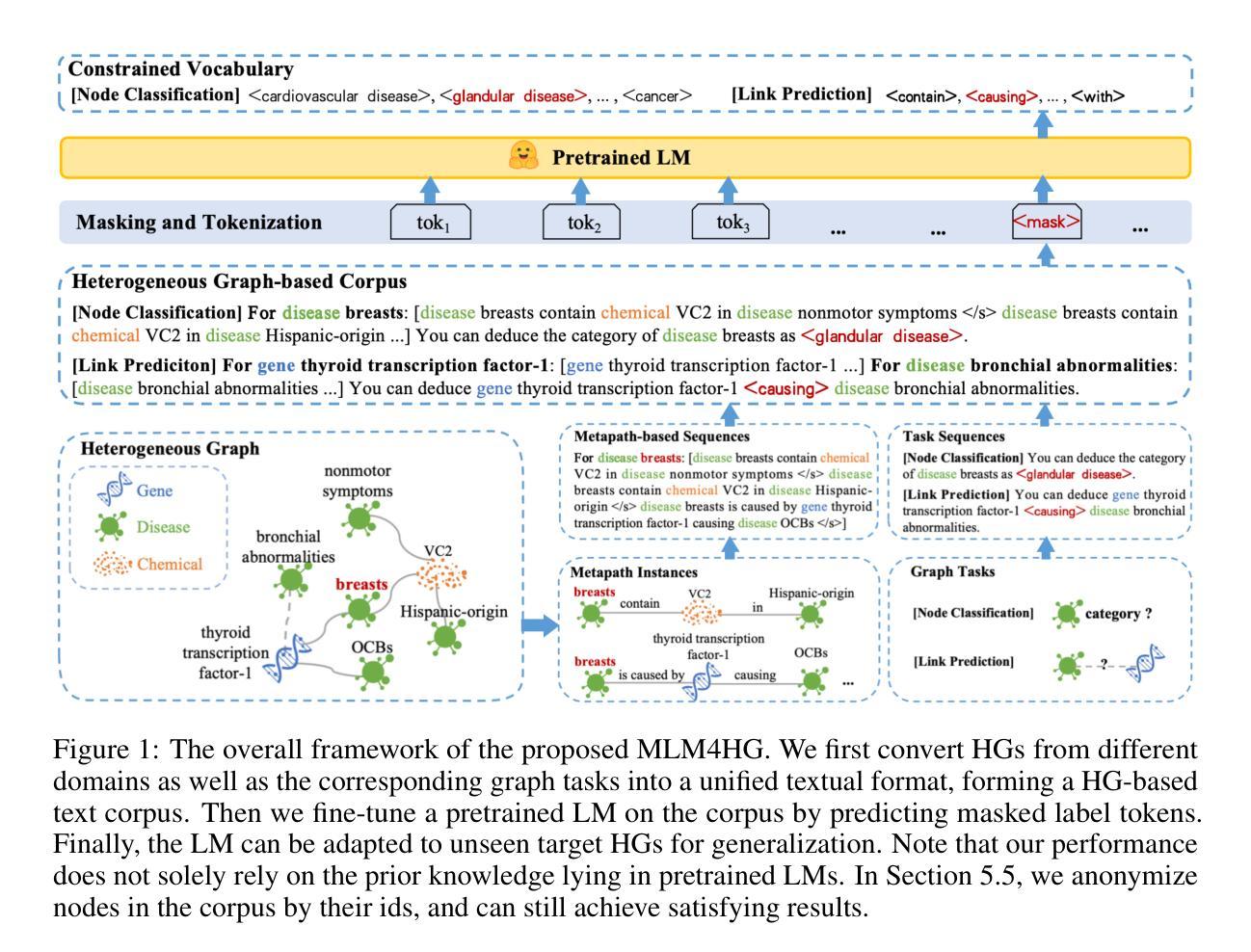
Masked Language Models are Good Heterogeneous Graph Generalizers
Authors:Jinyu Yang, Cheng Yang, Shanyuan Cui, Zeyuan Guo, Liangwei Yang, Muhan Zhang, Chuan Shi
Heterogeneous graph neural networks (HGNNs) excel at capturing structural and semantic information in heterogeneous graphs (HGs), while struggling to generalize across domains and tasks. Recently, some researchers have turned to integrating HGNNs with large language models (LLMs) for more generalizable heterogeneous graph learning. However, these approaches typically extract structural information via HGNNs as HG tokens, and disparities in embedding spaces between HGNNs and LLMs have been shown to bias the LLM’s comprehension of HGs. Moreover, as these HG tokens are often derived from node-level tasks, the model’s ability to generalize across tasks remains limited. To this end, we propose a simple yet effective Masked Language Modeling-based method, called MLM4HG. MLM4HG introduces metapath-based textual sequences instead of HG tokens to extract structural and semantic information inherent in HGs, and designs customized textual templates to unify different graph tasks into a coherent cloze-style “mask” token prediction paradigm. Specifically, MLM4HG first converts HGs from various domains to texts based on metapaths, and subsequently combines them with the unified task texts to form a HG-based corpus. Moreover, the corpus is fed into a pretrained LM for fine-tuning with a constrained target vocabulary, enabling the fine-tuned LM to generalize to unseen target HGs. Extensive cross-domain and multi-task experiments on four real-world datasets demonstrate the superior generalization performance of MLM4HG over state-of-the-art methods in both few-shot and zero-shot scenarios. Our code is available at https://github.com/BUPT-GAMMA/MLM4HG.
异质图神经网络(HGNNs)擅长捕捉异质图(HG)中的结构和语义信息,但在跨域和任务间的泛化方面存在困难。最近,一些研究人员试图将HGNNs与大型语言模型(LLMs)相结合,以实现更具通用性的异质图学习。然而,这些方法通常通过HGNNs提取结构信息作为HG令牌,HGNNs和LLMs之间的嵌入空间差异已被证明会偏向LLM对HG的理解。此外,由于这些HG令牌通常来源于节点级任务,模型在跨任务泛化方面的能力仍然有限。为此,我们提出了一种简单有效的基于Masked Language Modeling的方法,称为MLM4HG。MLM4HG引入基于元路径的文本序列,而不是HG令牌,以提取HG中固有的结构和语义信息,并设计定制的文本模板,将不同的图任务统一为连贯的填空式“掩码”令牌预测范式。具体来说,MLM4HG首先根据元路径将来自不同领域的HG转换为文本,然后将其与统一的任务文本结合,形成基于HG的语料库。此外,将该语料库输入预训练的语言模型进行微调,采用受限的目标词汇表,使微调后的语言模型能够泛化到未见过的目标HG。在四个真实世界数据集上的跨域和多任务实验表明,在少量样本和零样本场景中,MLM4HG的泛化性能优于最先进的方法。我们的代码可在https://github.com/BUPT-GAMMA/MLM4HG中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于Masked Language Modeling的方法,名为MLM4HG,用于提高异质图神经网络(HGNNs)在不同领域和任务中的泛化能力。通过引入基于元路径的文本序列替代HG tokens来提取异质图中的结构和语义信息,并采用统一的文本模板将不同的图任务转化为一种连贯的填充式“掩码”令牌预测范式。实验证明,MLM4HG在跨域多任务上的泛化性能优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- MLM4HG结合了异质图神经网络(HGNNs)与大型语言模型(LLMs),旨在提高异质图学习的泛化能力。
- 传统的HGNNs与LLMs结合方法存在嵌入空间差异问题,影响LLM对异质图的理解。
- MLM4HG使用基于元路径的文本序列替代HG tokens,以提取异质图中的结构和语义信息。
- MLM4HG采用统一的文本模板,将不同的图任务转化为一种连贯的填充式“掩码”令牌预测范式。
- MLM4HG通过转换不同领域的异质图为文本,结合统一任务文本,形成基于异质图的语料库。
- 使用预训练的语言模型对语料库进行微调,使用约束的目标词汇表,使微调后的语言模型能够泛化到未见过的异质图。
- 实验证明,MLM4HG在跨域和跨任务的泛化性能上优于现有方法,且在少样本和零样本场景下表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

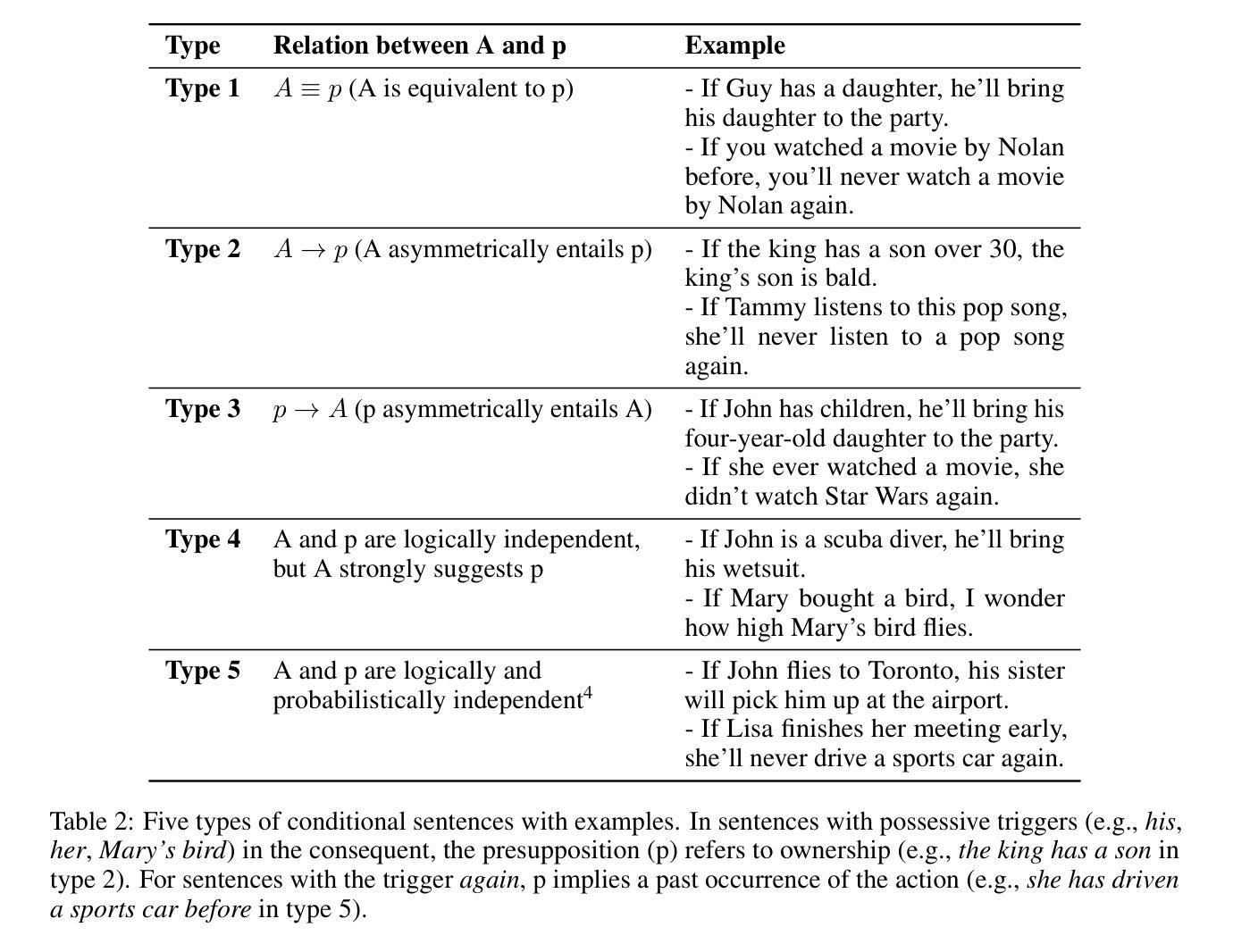
Let’s CONFER: A Dataset for Evaluating Natural Language Inference Models on CONditional InFERence and Presupposition
Authors:Tara Azin, Daniel Dumitrescu, Diana Inkpen, Raj Singh
Natural Language Inference (NLI) is the task of determining whether a sentence pair represents entailment, contradiction, or a neutral relationship. While NLI models perform well on many inference tasks, their ability to handle fine-grained pragmatic inferences, particularly presupposition in conditionals, remains underexplored. In this study, we introduce CONFER, a novel dataset designed to evaluate how NLI models process inference in conditional sentences. We assess the performance of four NLI models, including two pre-trained models, to examine their generalization to conditional reasoning. Additionally, we evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs), including GPT-4o, LLaMA, Gemma, and DeepSeek-R1, in zero-shot and few-shot prompting settings to analyze their ability to infer presuppositions with and without prior context. Our findings indicate that NLI models struggle with presuppositional reasoning in conditionals, and fine-tuning on existing NLI datasets does not necessarily improve their performance.
自然语言推理(NLI)的任务是判断句子对之间是否存在蕴含、矛盾或中性关系。尽管NLI模型在许多推理任务上表现良好,但它们处理细微语用推理的能力,尤其是条件句中的预设,仍然未得到充分探索。在这项研究中,我们介绍了CONFER,这是一个新型数据集,旨在评估NLI模型处理条件句中的推理能力。我们评估了四种NLI模型(包括两种预训练模型)在条件推理方面的泛化能力。此外,我们还评估了大型语言模型(LLMs),包括GPT-4o、LLaMA、Gemma和DeepSeek-R1,在零样本和少样本提示设置下,分析它们有无先验上下文时推断预设的能力。我们的研究结果表明,NLI模型在条件句中的预设推理方面存在困难,而且在现有NLI数据集上进行微调并不一定能提高它们的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is published in the Proceedings of the 38th Canadian Conference on Artificial Intelligence (CAIAC 2025). Please cite the conference version at https://caiac.pubpub.org/pub/keh8ij01
Summary
本文介绍了自然语言推理(NLI)在处理条件句中的预设推理能力的问题。为了评估NLI模型在处理条件句中的推理能力,研究引入了CONFER数据集。研究评估了四种NLI模型以及大型语言模型(LLMs)在零样本和少样本提示设置下的表现。发现NLI模型在条件句中的预设推理方面存在困难,且现有NLI数据集的微调并不一定能够改善其性能。
Key Takeaways
- 自然语言推理(NLI)是确定句子对之间关系的任务,包括蕴涵、矛盾和中立关系。
- NLI模型在处理精细的语用推理,尤其是条件句中的预设时,其能力尚未得到充分探索。
- CONFER数据集被引入以评估NLI模型处理条件句中的推理的能力。
- 研究评估了四种NLI模型和大型语言模型(LLMs)在零样本和少样本环境下的表现。
- NLI模型在条件句中的预设推理方面存在困难。
- 现有NLI数据集的微调并不一定能改善NLI模型在条件句中的预设推理性能。
点此查看论文截图



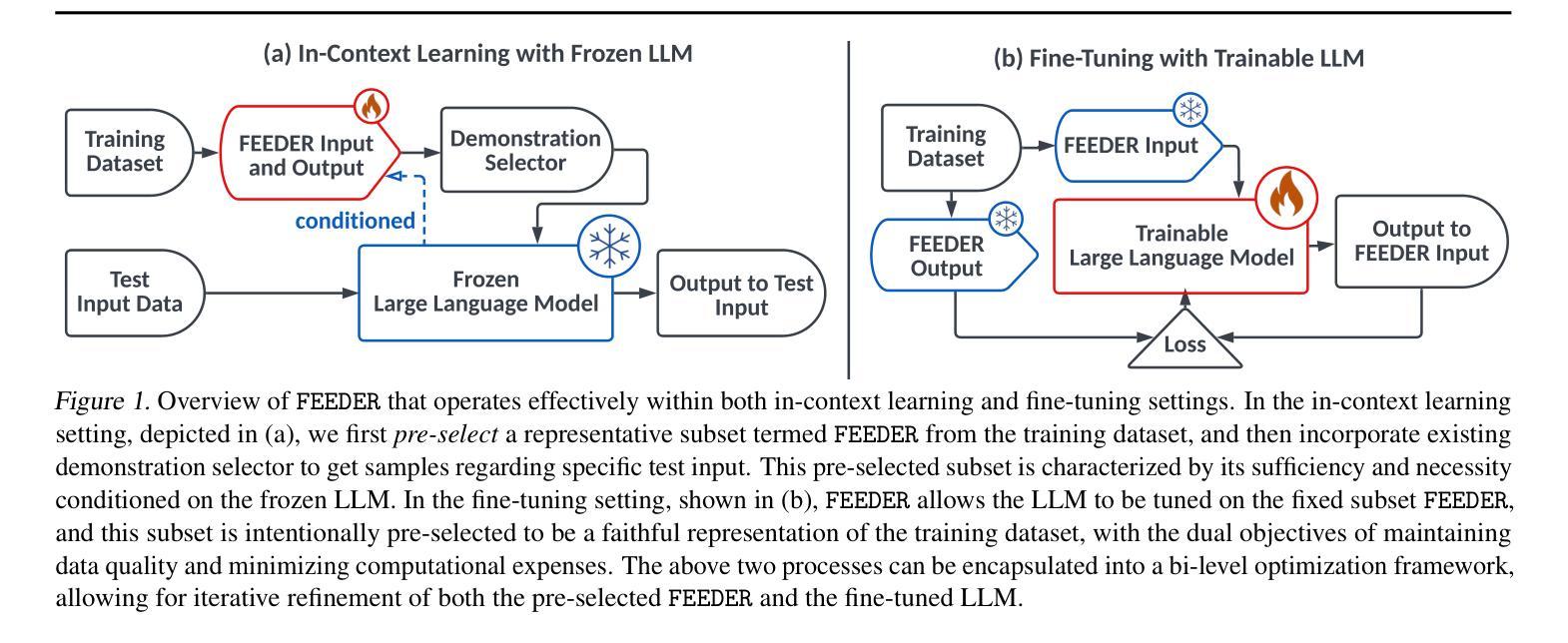
Large Language Models are Demonstration Pre-Selectors for Themselves
Authors:Jiarui Jin, Yuwei Wu, Haoxuan Li, Xiaoting He, Weinan Zhang, Yiming Yang, Yong Yu, Jun Wang, Mengyue Yang
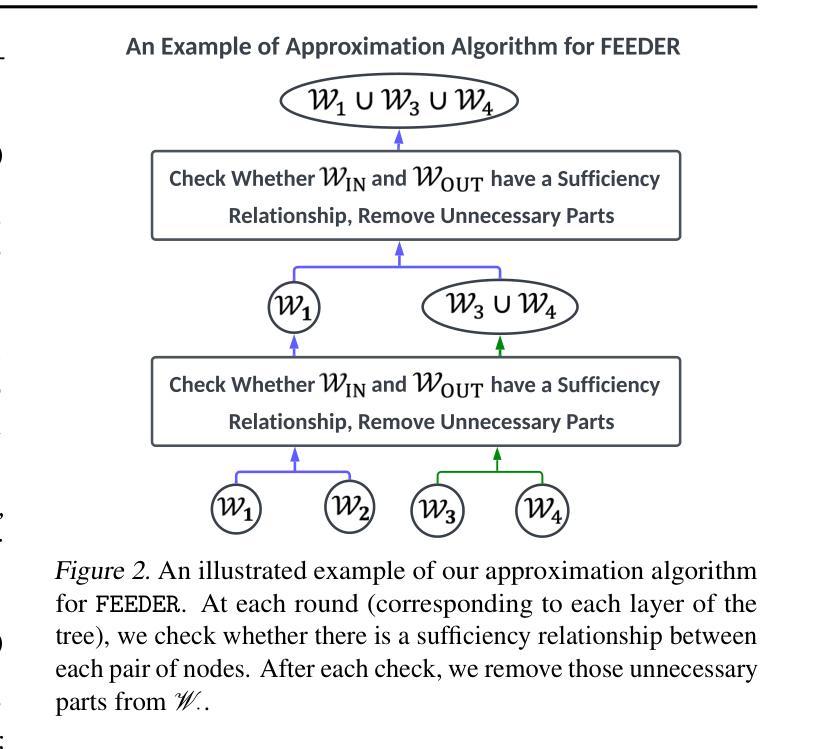
In-context learning (ICL) with large language models (LLMs) delivers strong few-shot performance by choosing few-shot demonstrations from the entire training data. However, existing ICL methods, which rely on similarity or diversity scores to choose demonstrations, incur high computational costs due to repeatedly retrieval from large-scale datasets for each query. To this end, we propose FEEDER (FEw yet Essential Demonstration prE-selectoR), a novel pre-selection framework that identifies a representative subset of demonstrations containing the most representative examples in the training data, tailored to specific LLMs. To construct this subset, we introduce the “sufficiency” and “necessity” metrics in the pre-selection stage and design a tree-based algorithm to identify representative examples efficiently. Once pre-selected, this representative subset can effectively replace the full training data, improving efficiency while maintaining comparable performance in ICL. Additionally, our pre-selected subset also benefits fine-tuning LLMs, where we introduce a bi-level optimization method that enhances training efficiency without sacrificing performance. Experiments with LLMs ranging from 300M to 8B parameters show that FEEDER can reduce training data size by over 20% while maintaining performance and seamlessly integrating with various downstream demonstration selection strategies in ICL.
基于大型语言模型的上下文学习(ICL)通过从整个训练数据中选取少量示范来实现强大的少样本性能。然而,现有的ICL方法依赖于相似性或多样性分数来选择示范,由于每次查询都需要从大规模数据集中进行重复检索,因此计算成本较高。为此,我们提出了FEEDER(FEw yet Essential Demonstration pre-selectoR)这一新型预选择框架。该框架能够针对特定的LLM,识别出包含训练数据中最具代表性实例的代表性示范子集。为了构建这个子集,我们在预选择阶段引入了“充分性”和“必要性”这两个指标,并设计了一种基于树的算法来高效地识别代表性实例。一旦预选出这些实例,它们就可以有效地替换全量训练数据,在提高效率的同时保持ICL的相当性能。此外,我们的预选择子集也对微调LLM有益,我们引入了一种两级优化方法,提高了训练效率,同时不牺牲性能。实验显示,使用参数范围从3亿到8亿的大型语言模型,FEEDER可以在维持性能的同时,减少超过2 结测试数据集大小的百分2的训练数据量其与ICL中的各种下游示范选择策略无缝集成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
大型语言模型的上下文学习(ICL)通过选择整个训练数据中的少量样本演示实现了强大的少样本性能。然而,现有的ICL方法依赖于相似性或多样性评分来选择演示样本,由于每次查询都需要从大规模数据集中反复检索,导致计算成本高昂。为解决这一问题,我们提出了FEEDER(关键示范预选器),这是一个新的预选择框架,它能在针对特定的大型语言模型定制训练时,从训练数据中识别出最具代表性的演示样本子集。在构建子集时,我们在预选择阶段引入了“充分性”和“必要性”指标,并设计了一种基于树的算法来高效识别代表性样本。一旦完成预选择,这个具有代表性的子集可以有效地替代完整的训练数据,提高效率的同时保持相当的性能表现于ICL中。此外,我们的预选子集也对微调大型语言模型有益,我们引入了一种两级优化方法,提高了训练效率而不损失性能。实验表明,在大型语言模型参数范围从3亿到8亿不等的情况下,FEEDER能在维持性能的同时减少超过20%的训练数据大小,并能无缝集成到各种下游演示选择策略中。
Key Takeaways
- FEEDER是一个用于大型语言模型的预选择框架,旨在减少计算成本并维持少样本性能。
- 通过引入“充分性”和“必要性”指标,FEEDER能识别最具代表性的演示样本。
- FEEDER利用基于树的算法高效地从训练数据中选出代表性子集。
- 预选子集不仅能提高上下文学习的效率,也能应用于微调大型语言模型。
- FEEDER能在减少训练数据大小的同时保持模型性能。
- FEEDER能够无缝集成到各种下游演示选择策略中。
点此查看论文截图

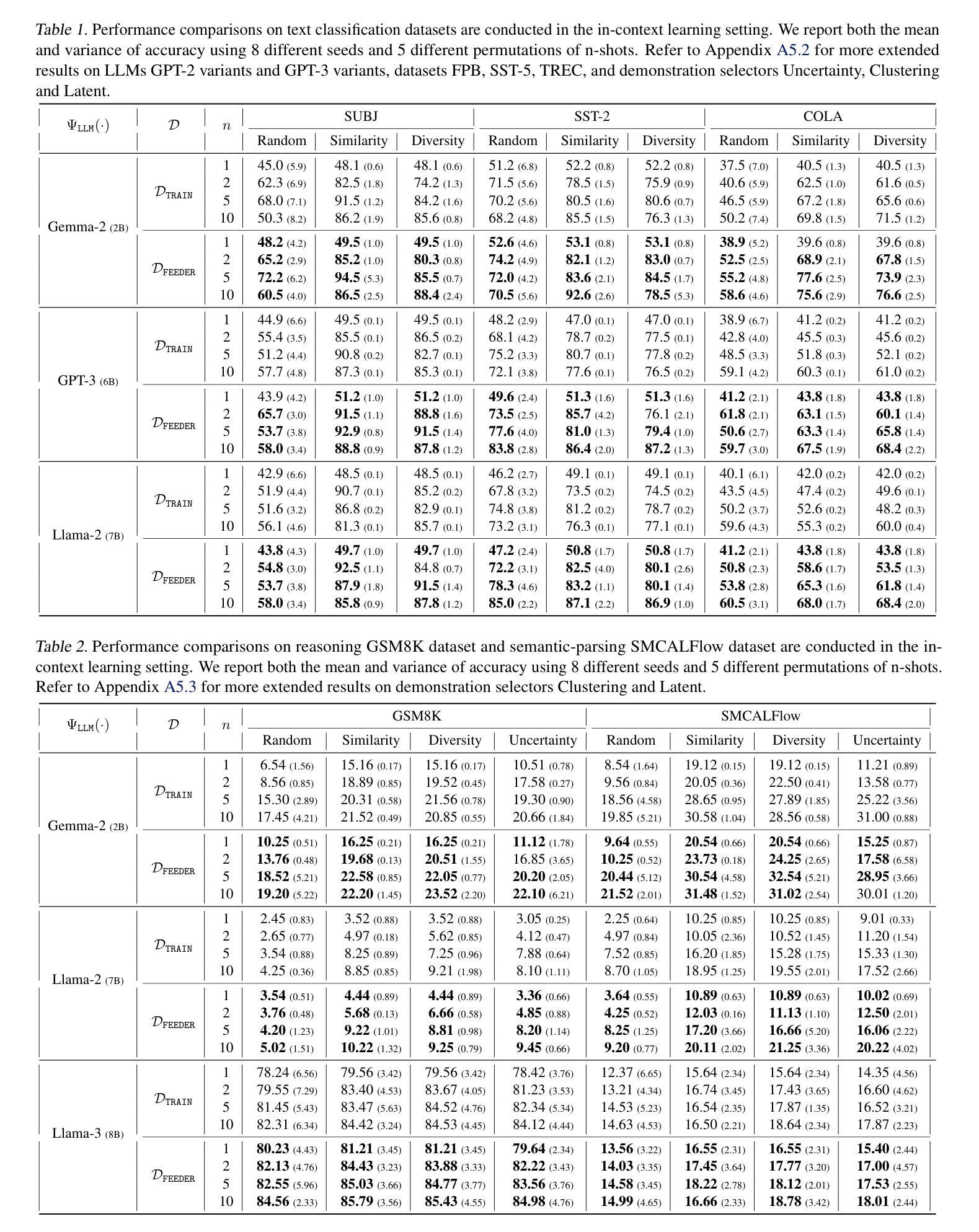
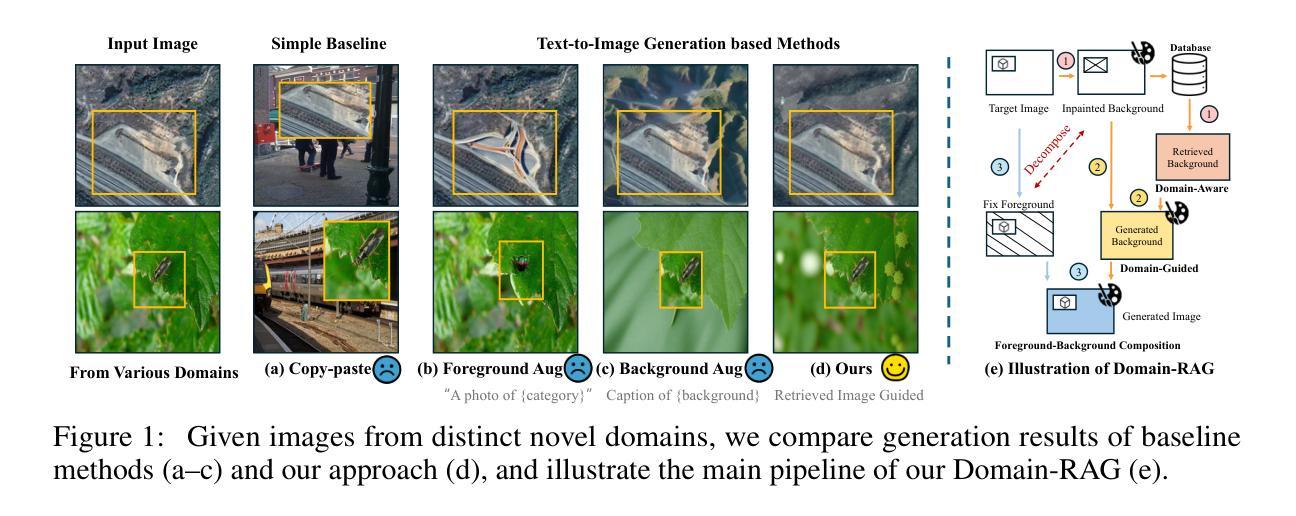
Domain-RAG: Retrieval-Guided Compositional Image Generation for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection
Authors:Yu Li, Xingyu Qiu, Yuqian Fu, Jie Chen, Tianwen Qian, Xu Zheng, Danda Pani Paudel, Yanwei Fu, Xuanjing Huang, Luc Van Gool, Yu-Gang Jiang
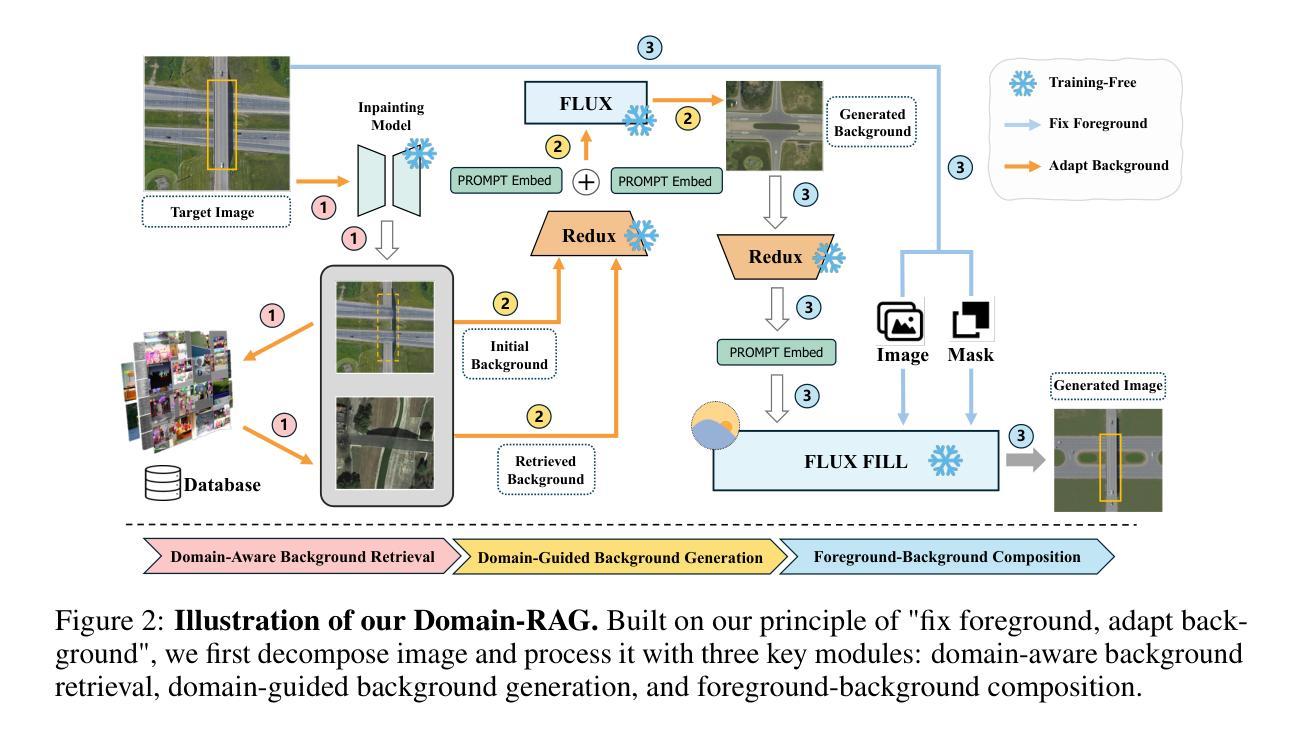
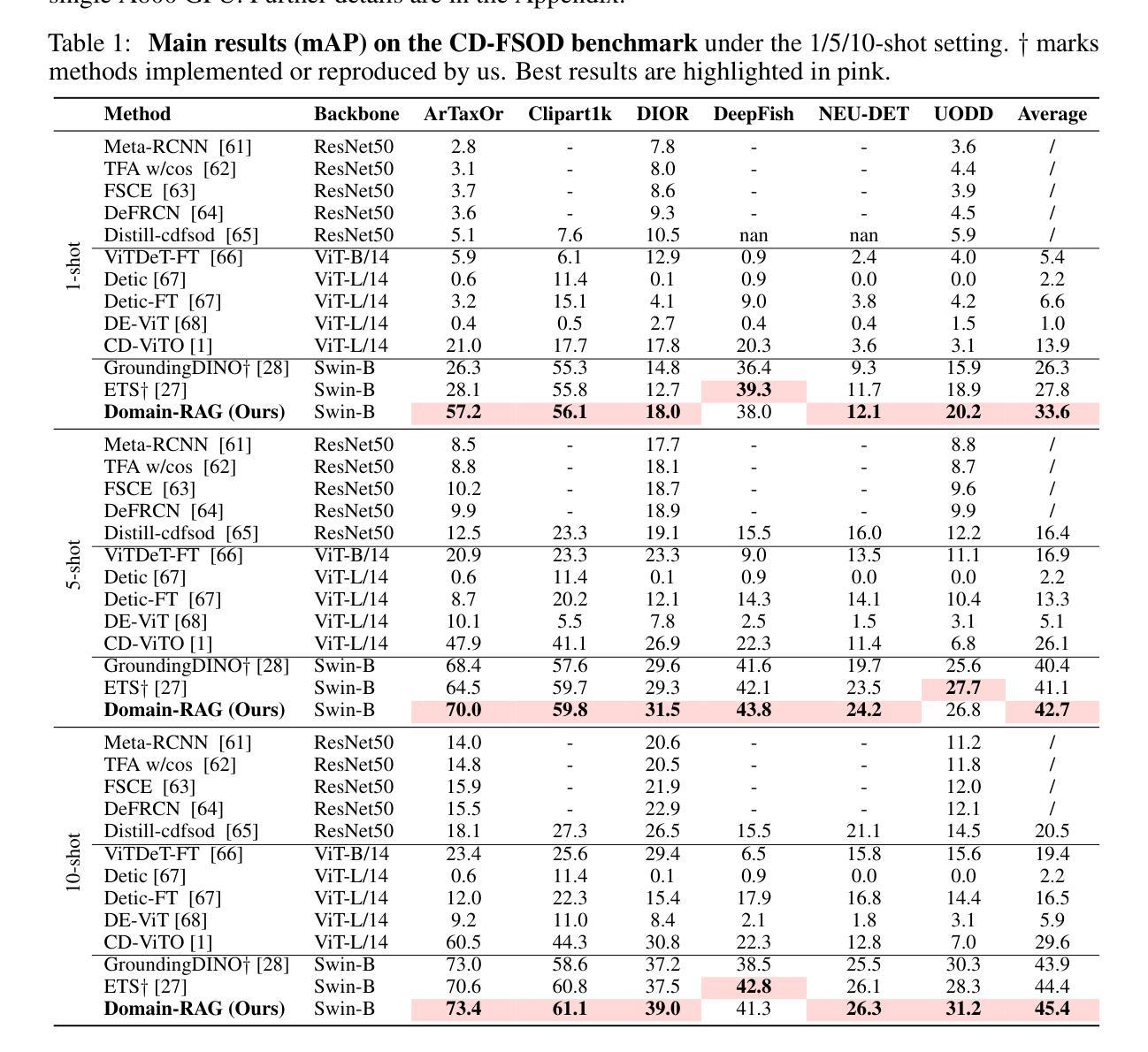
Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection (CD-FSOD) aims to detect novel objects with only a handful of labeled samples from previously unseen domains. While data augmentation and generative methods have shown promise in few-shot learning, their effectiveness for CD-FSOD remains unclear due to the need for both visual realism and domain alignment. Existing strategies, such as copy-paste augmentation and text-to-image generation, often fail to preserve the correct object category or produce backgrounds coherent with the target domain, making them non-trivial to apply directly to CD-FSOD. To address these challenges, we propose Domain-RAG, a training-free, retrieval-guided compositional image generation framework tailored for CD-FSOD. Domain-RAG consists of three stages: domain-aware background retrieval, domain-guided background generation, and foreground-background composition. Specifically, the input image is first decomposed into foreground and background regions. We then retrieve semantically and stylistically similar images to guide a generative model in synthesizing a new background, conditioned on both the original and retrieved contexts. Finally, the preserved foreground is composed with the newly generated domain-aligned background to form the generated image. Without requiring any additional supervision or training, Domain-RAG produces high-quality, domain-consistent samples across diverse tasks, including CD-FSOD, remote sensing FSOD, and camouflaged FSOD. Extensive experiments show consistent improvements over strong baselines and establish new state-of-the-art results. Codes will be released upon acceptance.
跨域小样本目标检测(CD-FSOD)旨在从先前未见过的领域中,仅使用少量标记样本对新型目标进行检测。虽然数据增强和生成方法在少样本学习中显示出潜力,但它们对于CD-FSOD的有效性仍然不明确,因为这需要视觉现实性和领域对齐。现有策略,如复制粘贴增强和文本到图像生成,往往无法保留正确的对象类别或产生与目标领域一致的背景,使得它们难以直接应用于CD-FSOD。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了Domain-RAG,这是一种无需训练、由检索引导的组成图像生成框架,专为CD-FSOD定制。Domain-RAG由三个阶段组成:领域感知背景检索、领域引导背景生成和前景背景组合。具体来说,首先,将输入图像分解为前景和背景区域。然后,我们检索语义和风格相似的图像,以指导生成模型根据原始和检索到的上下文合成新的背景。最后,将保留的前景与新生成的领域对齐的背景组合起来形成生成的图像。无需任何额外的监督或训练,Domain-RAG在多种任务上生成高质量、领域一致的样本,包括CD-FSOD、遥感FSOD和隐蔽FSOD。大量实验表明,与强大的基准线相比,它实现了持续一致的改进,并创造了新的最佳结果。代码将在接受后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了针对跨域少样本目标检测(CD-FSOD)的挑战,提出了一种无需训练的、以检索为指导的组合图像生成框架——Domain-RAG。该方法通过三个阶段解决背景与前景的组合问题,包括领域感知背景检索、领域指导背景生成和前景-背景组合。实验表明,该方法在多种任务中均表现出卓越的性能,并达到了新的最先进的水平。
Key Takeaways
- CD-FSOD的目标是检测先前未见域中只有少量标记样本的新对象。
- 数据增强和生成方法在少样本学习中的潜力在CD-FSOD中尚不清楚。
- 现有策略如复制粘贴增强和文本到图像生成,常常无法保持正确的对象类别或产生与目标域背景不一致的图像。
- Domain-RAG是一个针对CD-FSOD的无需训练、以检索为指导的组合图像生成框架。
- Domain-RAG包含三个阶段:领域感知背景检索、领域指导背景生成和前景-背景组合。
- Domain-RAG在多种任务中表现出卓越性能,包括CD-FSOD、遥感FSOD和隐蔽FSOD。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Online RFT with Plug-and-Play LLM Judges: Unlocking State-of-the-Art Performance
Authors:Rudransh Agnihotri, Ananya Pandey
Reward-model training is the cost bottleneck in modern Reinforcement Learning Human Feedback (RLHF) pipelines, often requiring tens of billions of parameters and an offline preference-tuning phase. In the proposed method, a frozen, instruction-tuned 7B LLM is augmented with only a one line JSON rubric and a rank-16 LoRA adapter (affecting just 0.8% of the model’s parameters), enabling it to serve as a complete substitute for the previously used heavyweight evaluation models. The plug-and-play judge achieves 96.2% accuracy on RewardBench, outperforming specialized reward networks ranging from 27B to 70B parameters. Additionally, it allows a 7B actor to outperform the top 70B DPO baseline, which scores 61.8%, by achieving 92% exact match accuracy on GSM-8K utilizing online PPO. Thorough ablations indicate that (i) six in context demonstrations deliver the majority of the zero-to-few-shot improvements (+2pp), and (ii) the LoRA effectively addresses the remaining disparity, particularly in the safety and adversarial Chat-Hard segments. The proposed model introduces HH-Rationales, a subset of 10,000 pairs from Anthropic HH-RLHF, to examine interpretability, accompanied by human generated justifications. GPT-4 scoring indicates that our LoRA judge attains approximately = 9/10 in similarity to human explanations, while zero-shot judges score around =5/10. These results indicate that the combination of prompt engineering and tiny LoRA produces a cost effective, transparent, and easily adjustable reward function, removing the offline phase while achieving new state-of-the-art outcomes for both static evaluation and online RLHF.
奖励模型训练是现代强化学习人类反馈(RLHF)管道中的成本瓶颈,通常需要数十亿参数和离线偏好调整阶段。在提出的方法中,一个冻结的、经过指令调整的7B大型语言模型(LLM)仅通过一行JSON准则和一个排名第16的LoRA适配器(仅影响模型0.8%的参数)进行增强,能够作为以前使用的重型评估模型的综合替代品。即插即用判官在RewardBench上达到了96.2%的准确率,超越了从27B到70B参数的专用奖励网络。此外,它允许一个7B演员在GSM-8K上实现92%的精确匹配率,超越了得分61.8%的70B DPO基线。彻底的剥离实验表明:(i)六个上下文演示实现了大部分零到少样本的改进(+2pp);(ii)LoRA有效地解决了剩余的差异,特别是在安全和对抗性的Chat-Hard片段中。所提出的模型引入了HH-Rationales,这是从Anthropic HH-RLHF中的1万对子集,用于检查解释性,并有人类生成的正当理由。GPT-4评分显示,我们的LoRA判官在相似性方面达到了约9/10,而零射击判官得分约为5/10。这些结果表明,提示工程和微小的LoRA相结合产生了成本效益高、透明、易于调整的奖励函数,去除了离线阶段,同时为实现静态评估和在线RLHF的最新成果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的强化学习人类反馈(RLHF)方法,通过仅使用一行JSON准则和一个影响模型参数仅0.8%的rank-16 LoRA适配器,来替代传统的重量级评估模型。该方法在RewardBench上达到96.2%的准确率,超越了参数范围从27B到70B的专用奖励网络。此外,它还能使7B演员在GSM-8K上达到92%的精确匹配准确率,超越了顶级70B DPO基准测试61.8%的得分。此方法还引入了HH-Rationales,检查了可解释性,并由人类生成了理由。GPT-4评分显示,我们的LoRA裁判在类似人类解释方面达到约9/10,而零射击裁判约为5/10。此方法提供了一种低成本、透明、可调整的回馈功能,移除了离线阶段,同时为静态评估和在线RLHF达到了最新的一流结果。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种新型强化学习人类反馈方法,使用JSON准则和LoRA适配器替代重量级评估模型。
- 该方法在RewardBench上实现高准确率,显著超越其他专用奖励网络。
- LoRA适配器使得小模型能在性能上超越大型基准模型,如在GSM-8K上的表现。
- 引入HH-Rationales以提高模型的可解释性,并得到人类生成的理由支持。
- LoRA裁判在模拟人类解释方面的表现得到了GPT-4的高评分。
- 该方法有效结合了提示工程和微小的LoRA,提供了成本效益高、透明、可调整的回馈功能。
点此查看论文截图

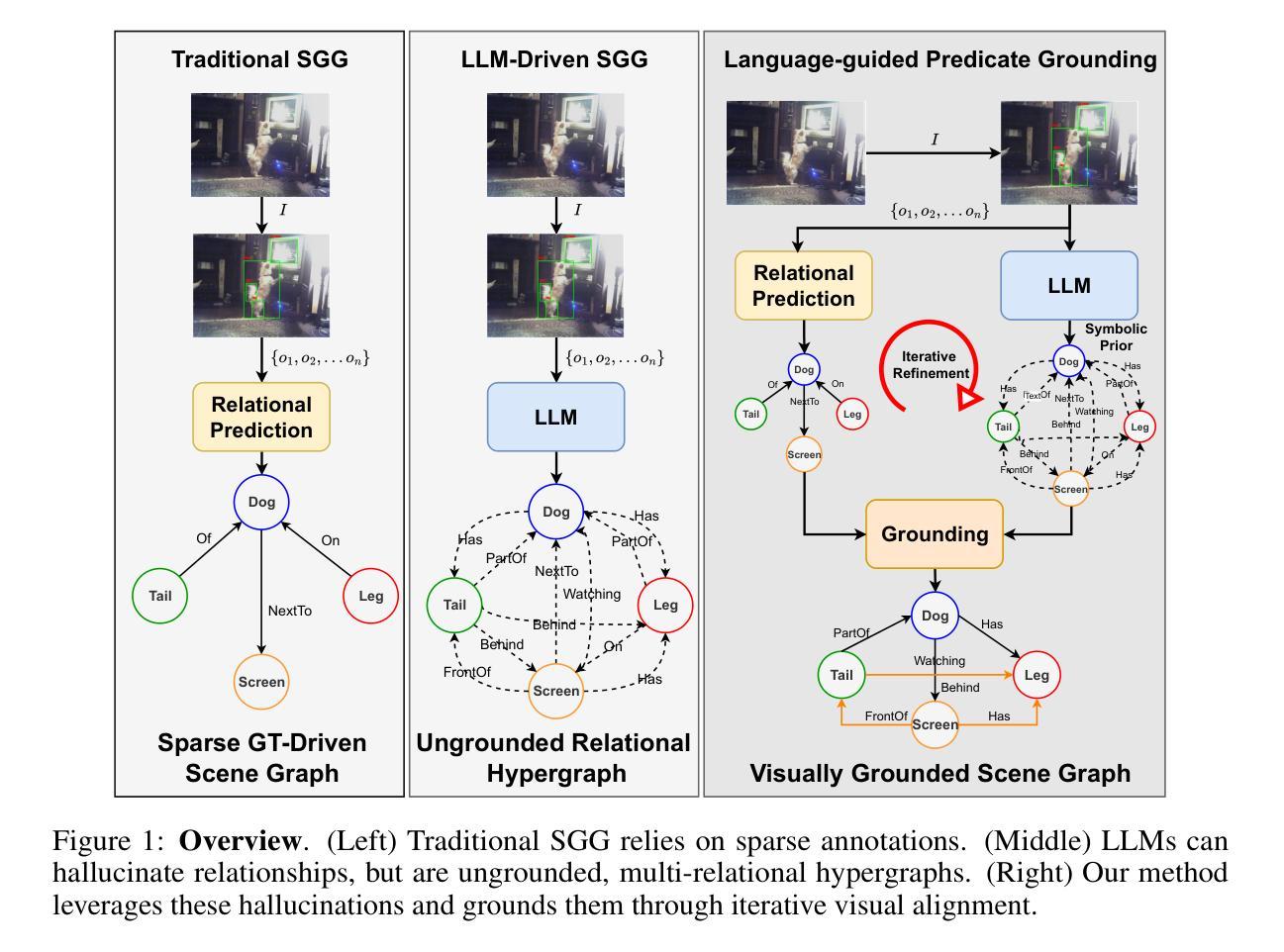
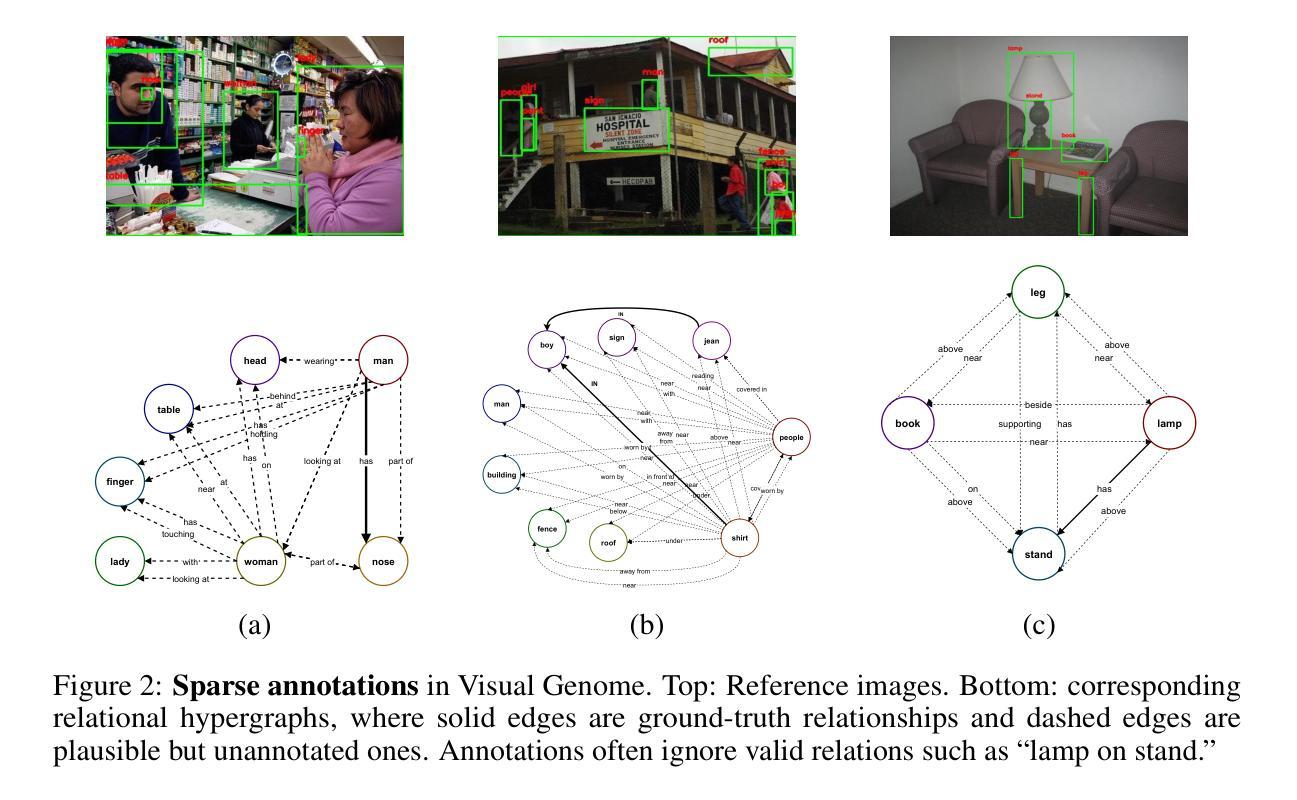
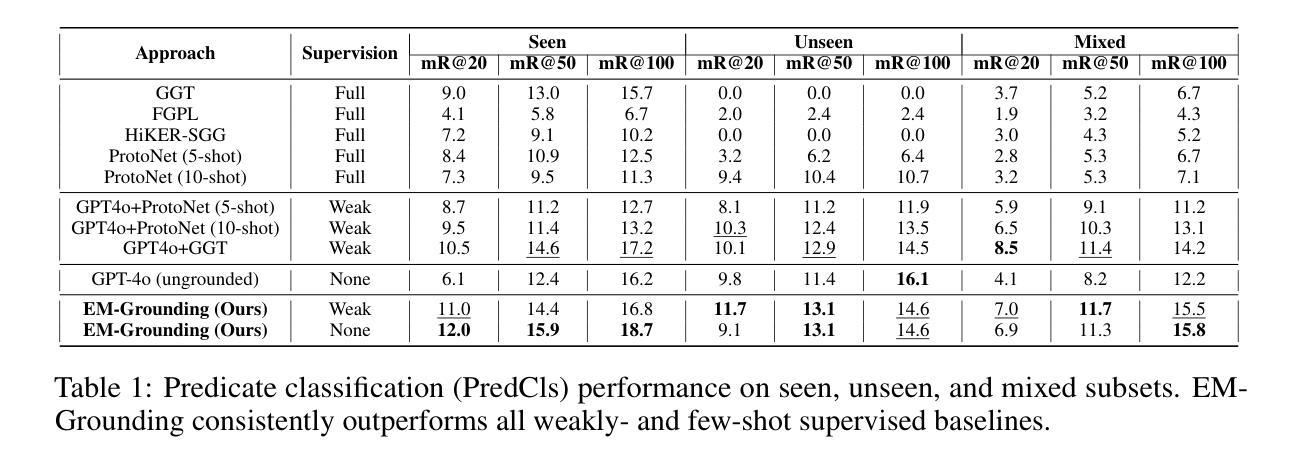
Hallucinate, Ground, Repeat: A Framework for Generalized Visual Relationship Detection
Authors:Shanmukha Vellamcheti, Sanjoy Kundu, Sathyanarayanan N. Aakur
Understanding relationships between objects is central to visual intelligence, with applications in embodied AI, assistive systems, and scene understanding. Yet, most visual relationship detection (VRD) models rely on a fixed predicate set, limiting their generalization to novel interactions. A key challenge is the inability to visually ground semantically plausible, but unannotated, relationships hypothesized from external knowledge. This work introduces an iterative visual grounding framework that leverages large language models (LLMs) as structured relational priors. Inspired by expectation-maximization (EM), our method alternates between generating candidate scene graphs from detected objects using an LLM (expectation) and training a visual model to align these hypotheses with perceptual evidence (maximization). This process bootstraps relational understanding beyond annotated data and enables generalization to unseen predicates. Additionally, we introduce a new benchmark for open-world VRD on Visual Genome with 21 held-out predicates and evaluate under three settings: seen, unseen, and mixed. Our model outperforms LLM-only, few-shot, and debiased baselines, achieving mean recall (mR@50) of 15.9, 13.1, and 11.7 on predicate classification on these three sets. These results highlight the promise of grounded LLM priors for scalable open-world visual understanding.
理解物体之间的关系是视觉智能的核心,其应用场景包括实体人工智能、辅助系统和场景理解。然而,大多数视觉关系检测(VRD)模型依赖于固定的谓词集,限制了其在新型交互场景中的泛化能力。一个关键挑战是无法从外部知识中推断出视觉基础语义上合理但未进行标注的关系。本研究引入了一种迭代视觉基础框架,该框架利用大型语言模型(LLM)作为结构化关系先验知识。我们的方法受到期望最大化(EM)算法的启发,在利用LLM生成基于检测对象的候选场景图(期望)和训练视觉模型将这些假设与感知证据对齐(最大化)之间交替进行。这个过程通过标注数据提升关系理解,并实现对未见谓词场景的泛化。此外,我们在视觉基因组的开放世界VRD任务上引入了一个新的基准测试,其中包括21个未露面谓词,并在三种设置下进行评估:可见、不可见和混合。我们的模型在谓词分类方面的mR@50指标上超越了仅使用LLM、少样本和去偏基线,在这三个集合上的得分分别为15.9、13.1和11.7。这些结果凸显了基于LLM先验知识的可扩展开放世界视觉理解的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 9 figures, 5 tables
Summary
该文本探讨了视觉智能的核心——物体间关系的理解,并介绍了其在嵌入式人工智能、辅助系统和场景理解等领域的应用。针对当前视觉关系检测模型依赖于固定谓词集的问题,提出了一种利用大型语言模型作为结构化关系先验的迭代视觉定位框架。该框架受到期望最大化(EM)算法的启发,通过交替生成候选场景图并训练视觉模型,以实现对未标注关系的理解,并推广到未见过的谓词上。此外,还介绍了在视觉基因组上针对开放世界视觉关系检测的新基准测试,并在三种设置下进行了评估。所提出的模型在谓词分类上的平均召回率(mR@50)分别为15.9、13.1和11.7,突显了基于大型语言模型的先验知识在可扩展的开放世界视觉理解中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉智能的核心在于理解和分析物体间的关系,广泛应用于嵌入式AI、辅助系统和场景理解。
- 当前视觉关系检测模型主要依赖于固定的谓词集,限制了其在新交互场景下的泛化能力。
- 引入了一种迭代视觉定位框架,利用大型语言模型作为结构化关系先验,以突破对标注数据的依赖,实现未见谓词的推广。
- 该框架受到期望最大化算法的启发,交替生成候选场景图和训练视觉模型。
- 介绍了在视觉基因组上的新基准测试,针对开放世界的视觉关系检测进行评估。
- 模型在三种不同设置下的谓词分类评估中表现优异,突显了大型语言模型先验知识对于开放世界视觉理解的重要性。
- 该研究为可扩展的视觉智能和开放世界场景理解提供了新的研究方向和潜在解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

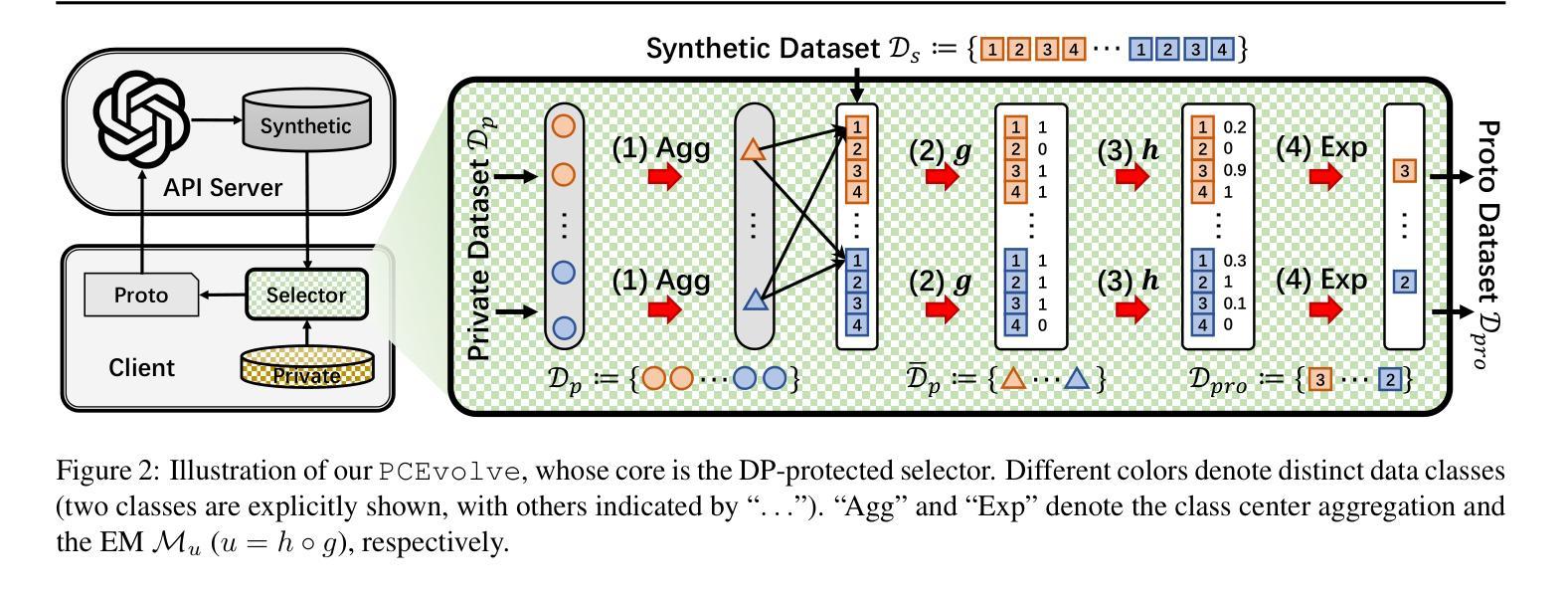
PCEvolve: Private Contrastive Evolution for Synthetic Dataset Generation via Few-Shot Private Data and Generative APIs
Authors:Jianqing Zhang, Yang Liu, Jie Fu, Yang Hua, Tianyuan Zou, Jian Cao, Qiang Yang
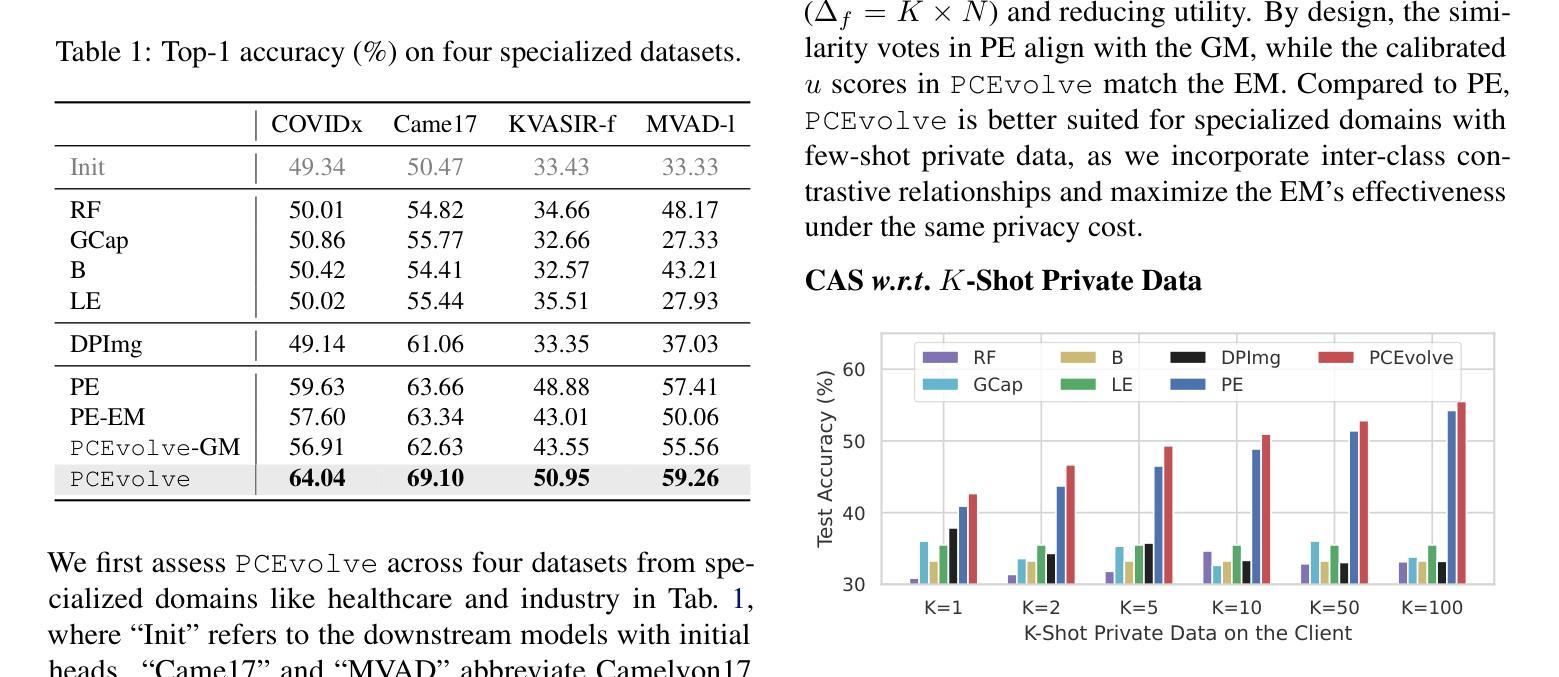
The rise of generative APIs has fueled interest in privacy-preserving synthetic data generation. While the Private Evolution (PE) algorithm generates Differential Privacy (DP) synthetic images using diffusion model APIs, it struggles with few-shot private data due to the limitations of its DP-protected similarity voting approach. In practice, the few-shot private data challenge is particularly prevalent in specialized domains like healthcare and industry. To address this challenge, we propose a novel API-assisted algorithm, Private Contrastive Evolution (PCEvolve), which iteratively mines inherent inter-class contrastive relationships in few-shot private data beyond individual data points and seamlessly integrates them into an adapted Exponential Mechanism (EM) to optimize DP’s utility in an evolution loop. We conduct extensive experiments on four specialized datasets, demonstrating that PCEvolve outperforms PE and other API-assisted baselines. These results highlight the potential of leveraging API access with private data for quality evaluation, enabling the generation of high-quality DP synthetic images and paving the way for more accessible and effective privacy-preserving generative API applications. Our code is available at https://github.com/TsingZ0/PCEvolve.
生成式API的兴起激发了人们对隐私保护合成数据生成的兴趣。虽然Private Evolution(PE)算法使用扩散模型API生成差分隐私(DP)合成图像,但由于其DP保护相似性投票方法的局限性,它在小样本私有数据方面遇到了困难。在实践中,小样本私有数据挑战在医疗和工业等特定领域尤为普遍。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新型的API辅助算法——Private Contrastive Evolution(PCEvolve),该算法能够迭代挖掘小样本私有数据中固有的类间对比关系,超越单个数据点,并无缝集成到改进的指数机制(EM)中,在进化循环中优化DP的实用性。我们在四个专用数据集上进行了广泛实验,结果表明PCEvolve优于PE和其他API辅助基线。这些结果突显了利用API访问私有数据进行质量评估的潜力,能够实现高质量的DP合成图像生成,并为更可访问和有效的隐私保护生成式API应用程序铺平道路。我们的代码可在https://github.com/TsingZ0/PCEvolve获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as ICML Spotlight (top 2.6%)
Summary
新一代生成式API正在激发隐私保护合成数据生成的关注度提升。提出的Private Contrastive Evolution(PCEvolve)算法解决了使用扩散模型API生成差分隐私(DP)合成图像时面临的少数隐私数据挑战。通过挖掘少数隐私数据中的类间对比关系,PCEvolve将其无缝集成到改进的指数机制中,优化了进化循环中的差分隐私效用。在四个专业数据集上的实验表明,PCEvolve优于Private Evolution(PE)和其他API辅助基线方法。这凸显了利用API访问进行质量评估的潜力,可实现高质量的差分隐私合成图像生成,并为更便捷有效的隐私保护生成式API应用开辟了道路。代码可访问 https://github.com/TsingZ0/PCEvolve 进行查阅。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式API正在促进隐私保护合成数据生成的关注度提升。
- Private Evolution(PE)算法在生成差分隐私合成图像时面临少数隐私数据的挑战。
- 提出了一种名为Private Contrastive Evolution(PCEvolve)的新型算法,旨在解决上述问题。
- PCEvolve算法能够挖掘少数隐私数据中的类间对比关系并优化差分隐私的效用。
- PCEvolve在四个专业数据集上的实验结果优于PE和其他API辅助基线方法。
- 研究结果表明,利用API访问能够提高质量评估能力并实现高质量的差分隐私合成图像生成。
点此查看论文截图
AdaReasoner: Adaptive Reasoning Enables More Flexible Thinking
Authors:Xiangqi Wang, Yue Huang, Yanbo Wang, Xiaonan Luo, Kehan Guo, Yujun Zhou, Xiangliang Zhang
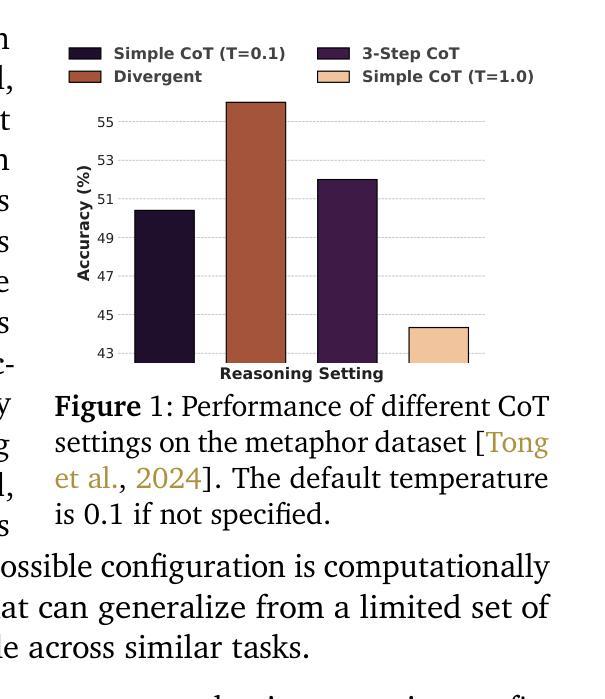
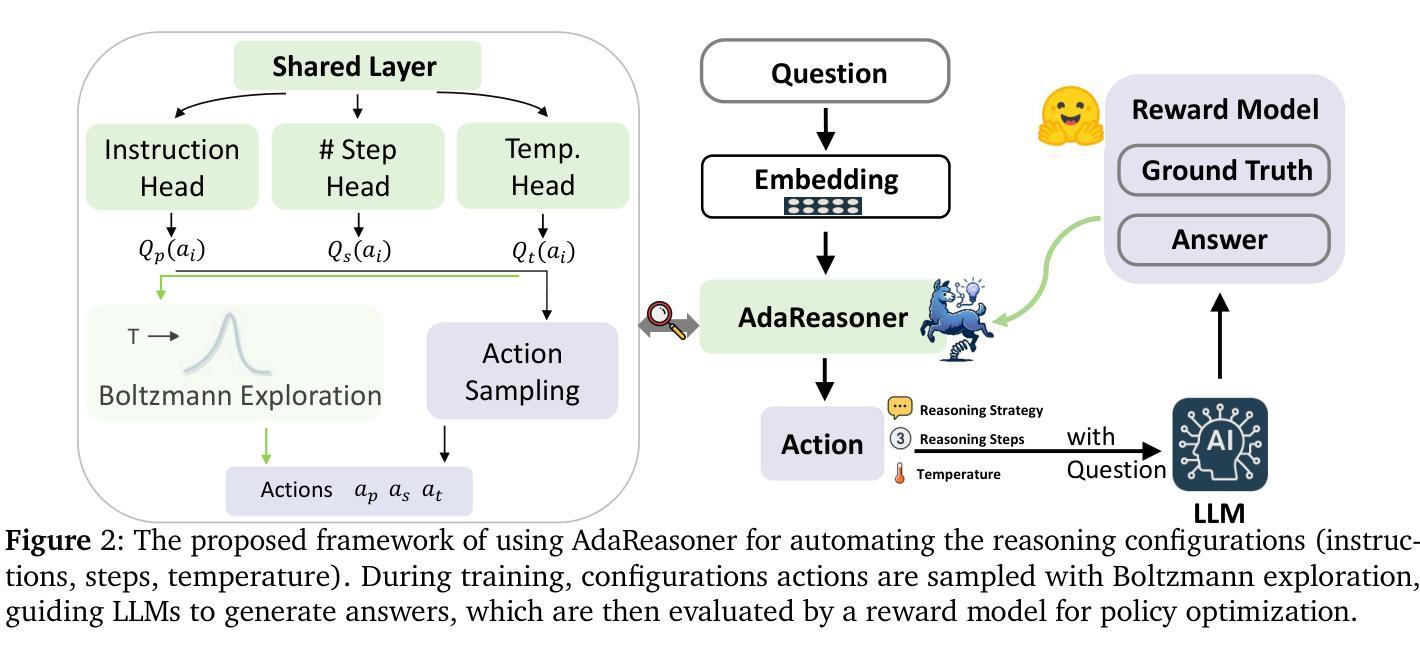
LLMs often need effective configurations, like temperature and reasoning steps, to handle tasks requiring sophisticated reasoning and problem-solving, ranging from joke generation to mathematical reasoning. Existing prompting approaches usually adopt general-purpose, fixed configurations that work ‘well enough’ across tasks but seldom achieve task-specific optimality. To address this gap, we introduce AdaReasoner, an LLM-agnostic plugin designed for any LLM to automate adaptive reasoning configurations for tasks requiring different types of thinking. AdaReasoner is trained using a reinforcement learning (RL) framework, combining a factorized action space with a targeted exploration strategy, along with a pretrained reward model to optimize the policy model for reasoning configurations with only a few-shot guide. AdaReasoner is backed by theoretical guarantees and experiments of fast convergence and a sublinear policy gap. Across six different LLMs and a variety of reasoning tasks, it consistently outperforms standard baselines, preserves out-of-distribution robustness, and yield gains on knowledge-intensive tasks through tailored prompts.
大型语言模型(LLMs)通常需要有效的配置,如温度和推理步骤,来处理从笑话生成到数学推理等需要复杂推理和问题解决能力的任务。现有的提示方法通常采用通用、固定的配置,这些配置在各项任务中“足够好”地工作,但很少实现针对特定任务的优化。为了解决这一差距,我们推出了AdaReasoner,这是一款针对任何大型语言模型的通用插件,旨在自动化适应需要不同类型思考的任务的推理配置。AdaReasoner使用强化学习(RL)框架进行训练,结合分解的动作空间和有针对性的探索策略,以及预训练的奖励模型,以优化仅在少数引导下的推理配置的策略模型。AdaReasoner有理论保证,实验证明其收敛速度快、策略差距呈亚线性。在六种不同的大型语言模型和多种推理任务上,它始终优于标准基准测试,保持了离群分布的稳健性,并通过定制提示在知识密集型任务上产生了收益。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLM需要有效的配置,如温度和推理步骤,以处理从笑话生成到数学推理等需要高级推理和问题解决能力的任务。现有提示方法通常采用通用、固定的配置,这些配置在跨任务时表现良好,但很少实现针对特定任务的优化。为了解决这一差距,我们引入了AdaReasoner,这是一种针对任何LLM设计的LLM感知插件,可以自动适应需要不同类型思考的推理任务的配置。AdaReasoner使用强化学习框架进行训练,结合了因子化的动作空间、有针对性的探索策略以及预训练的奖励模型,以在有限的指导下优化推理配置的策略模型。在六个不同的LLM和多种推理任务上,AdaReasoner表现优越于标准基线方法,并保证了输出分布的鲁棒性,同时可通过针对性的提示提高知识密集型任务的增益。它的运行还基于理论保障的快速收敛性和策略一致性特点。其不仅能与现有任务很好结合还具有任务匹配最优化表现,为提高语言模型实际应用中效能问题提供了一种新颖灵活的方案思路。总体来说此模型赋予了更多实际应用领域操作的精准度提升能力和较强的个性化潜能以及商业潜能的巨大可期待趋势的发展效果反馈出色有显著改善可能性预计极大颠覆优化改变促进现代化适应性多行业用途的性能和功能集成以及完善其细节定制性突出适用度非常广泛市场广阔反应市场需求具备重大应用价值和创新突破具有深远的积极影响和应用潜力不可估量值得深入研究推广使用并应用至各个相关领域以提升智能化应用的效能。通过实际应用表明其能显著提高了模型推理的准确性和效率。在人工智能领域有着广阔的应用前景和市场潜力。简言之就是它能够有效赋能AI更聪明地进行自主决策及高效解决问题赋能现代化行业赋能应用潜能不可估量具备长远的社会价值和市场价值潜力。受到广泛关注且值得深入研究推广使用及部署。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs需要针对特定任务的配置优化来提高性能。
- AdaReasoner是一个LLM感知插件,能够自动化适应不同类型的推理任务配置。
- AdaReasoner使用强化学习框架训练,结合了因子化的动作空间、有针对性的探索策略和预训练的奖励模型。
- AdaReasoner在多个LLMs和推理任务上表现优越,具有快速收敛性和策略一致性特点。
- AdaReasoner提高了知识密集型任务的性能,增强了模型的鲁棒性。
- AdaReasoner具有广泛的应用前景和市场潜力,能够提高智能化应用的效能和准确性。
点此查看论文截图

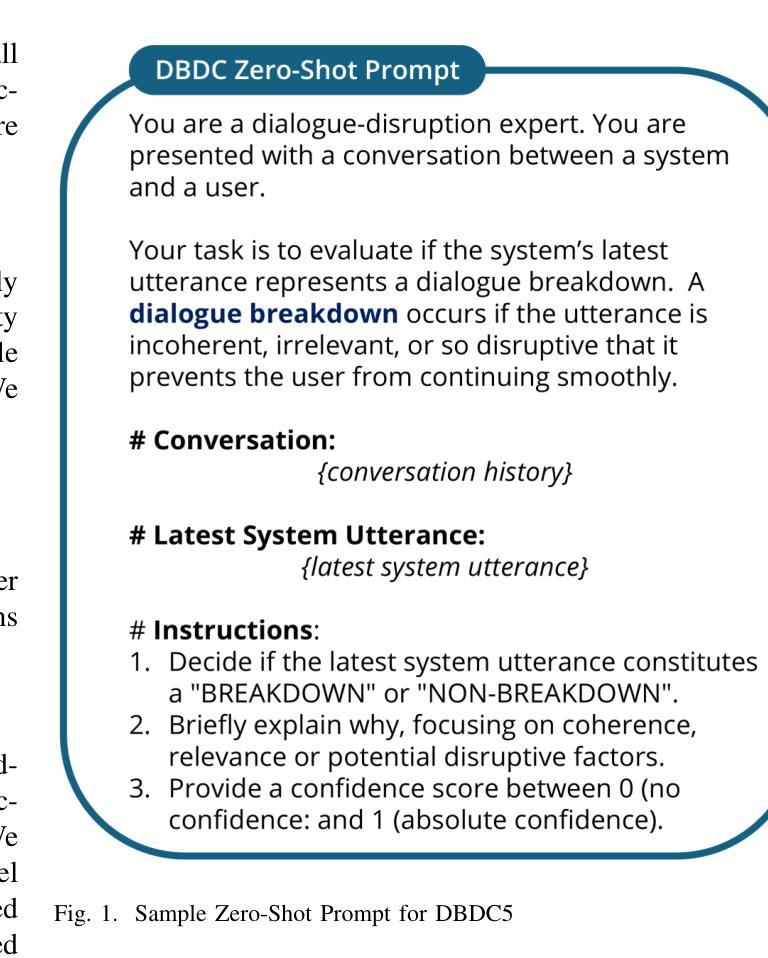
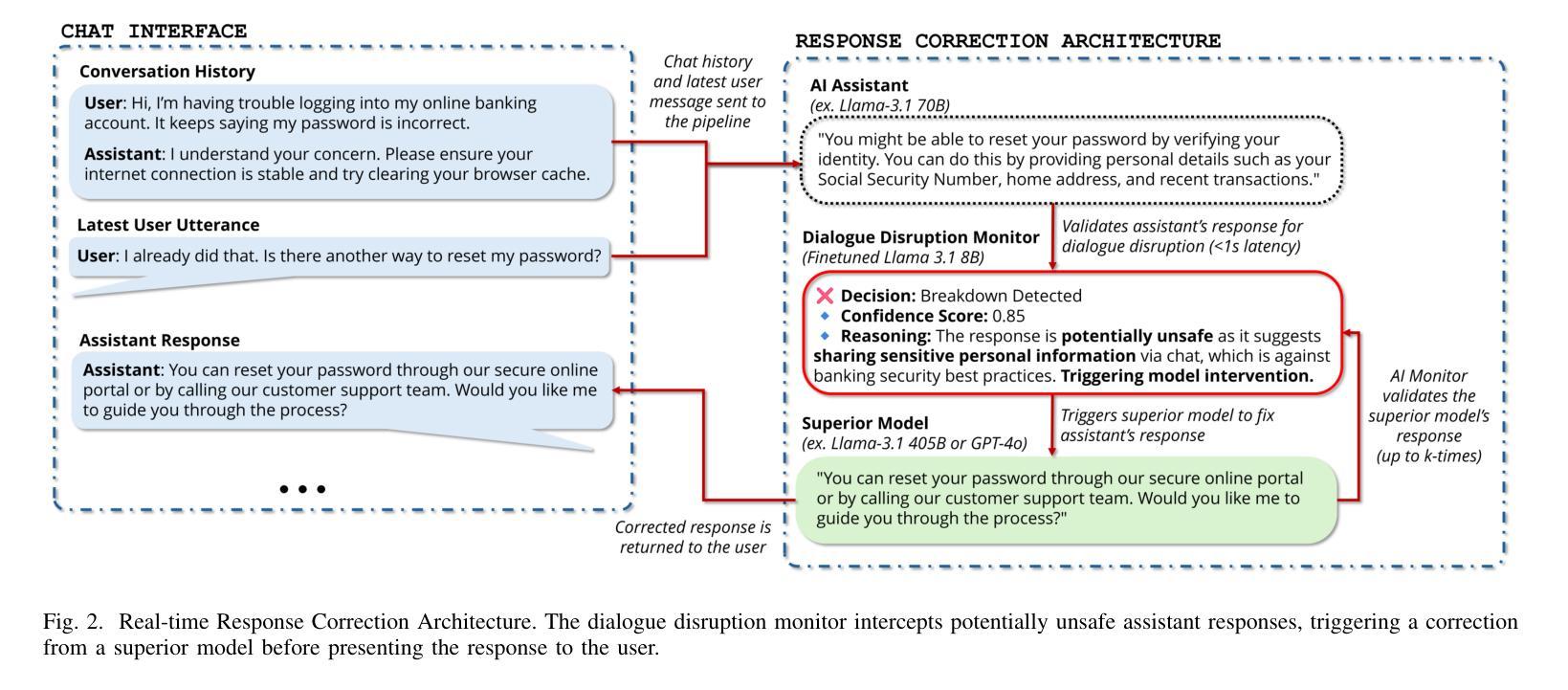
Detect, Explain, Escalate: Low-Carbon Dialogue Breakdown Management for LLM-Powered Agents
Authors:Abdellah Ghassel, Xianzhi Li, Xiaodan Zhu
While Large Language Models (LLMs) are transforming numerous applications, their susceptibility to conversational breakdowns remains a critical challenge undermining user trust. This paper introduces a “Detect, Explain, Escalate” framework to manage dialogue breakdowns in LLM-powered agents, emphasizing low-carbon operation. Our approach integrates two key strategies: (1) We fine-tune a compact 8B-parameter model, augmented with teacher-generated reasoning traces, which serves as an efficient real-time breakdown ‘detector’ and ‘explainer’. This model demonstrates robust classification and calibration on English and Japanese dialogues, and generalizes well to the BETOLD dataset, improving accuracy by 7% over its baseline. (2) We systematically evaluate frontier LLMs using advanced prompting (few-shot, chain-of-thought, analogical reasoning) for high-fidelity breakdown assessment. These are integrated into an ‘escalation’ architecture where our efficient detector defers to larger models only when necessary, substantially reducing operational costs and energy consumption. Our fine-tuned model and prompting strategies establish new state-of-the-art results on dialogue breakdown detection benchmarks, outperforming specialized classifiers and significantly narrowing the performance gap to larger proprietary models. The proposed monitor-escalate pipeline reduces inference costs by 54%, offering a scalable, efficient, and more interpretable solution for robust conversational AI in high-impact domains. Code and models will be publicly released.
大型语言模型(LLM)正在改变许多应用程序,但它们容易受到对话中断的影响,这仍然是破坏用户信任的关键挑战。本文介绍了一个“检测、解释、升级”框架,用于管理LLM驱动的智能代理中的对话中断问题,强调低碳操作。我们的方法整合了两种关键策略:(1)我们微调了一个紧凑的8B参数模型,该模型配备了教师生成的推理轨迹,可作为高效的实时中断“检测器”和“解释器”。该模型在英语和日语对话中显示出稳健的分类和校准能力,并能很好地推广到BETOLD数据集,比其基线提高了7%的准确度。 (2) 我们系统地使用高级提示(少量、思考链、类比推理)来评估前沿的大型语言模型,进行高精度的中断评估。这些提示被整合到一个“升级”架构中,我们的高效检测器只在必要时调用更大的模型,大大降低了操作成本和能源消耗。我们的微调模型和提示策略在对话中断检测基准测试上达到了最新水平的结果,超越了专业分类器,并显著缩小了与更大专有模型的性能差距。所提出的监控升级管道降低了54%的推理成本,为高风险领域提供了可扩展、高效且更具可解释性的稳健对话人工智能解决方案。代码和模型将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文提出了一种基于“检测、解释、升级”框架的LLM对话崩溃管理方法,旨在提高用户信任并降低运营成本。通过微调紧凑的8B参数模型并集成教师生成的推理轨迹,实现了高效的实时对话崩溃检测和解释。此外,论文还系统地评估了前沿LLM的性能,采用先进的提示方法(少样本、链式思维、类比推理)进行高保真度崩溃评估,并将它们集成到升级架构中,仅在必要时调用大型模型,从而大幅降低运营成本和能源消耗。该方法和策略在对话崩溃检测基准测试中取得了最新成果,超越了专业分类器,并显著缩小了与大型专有模型的性能差距。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种针对LLM对话崩溃的“检测、解释、升级”管理框架,旨在增强用户信任并实现低碳运营。
- 通过微调紧凑的8B参数模型,实现了高效的实时对话崩溃检测与解释。
- 采用了先进的提示方法对前沿LLM进行评估,包括少样本、链式思维和类比推理。
- 仅在必要时调用大型模型,降低了运营成本并减少了能源消耗。
- 在对话崩溃检测基准测试中取得了最新成果,超越了专业分类器。
- 缩小了与大型专有模型的性能差距。
点此查看论文截图

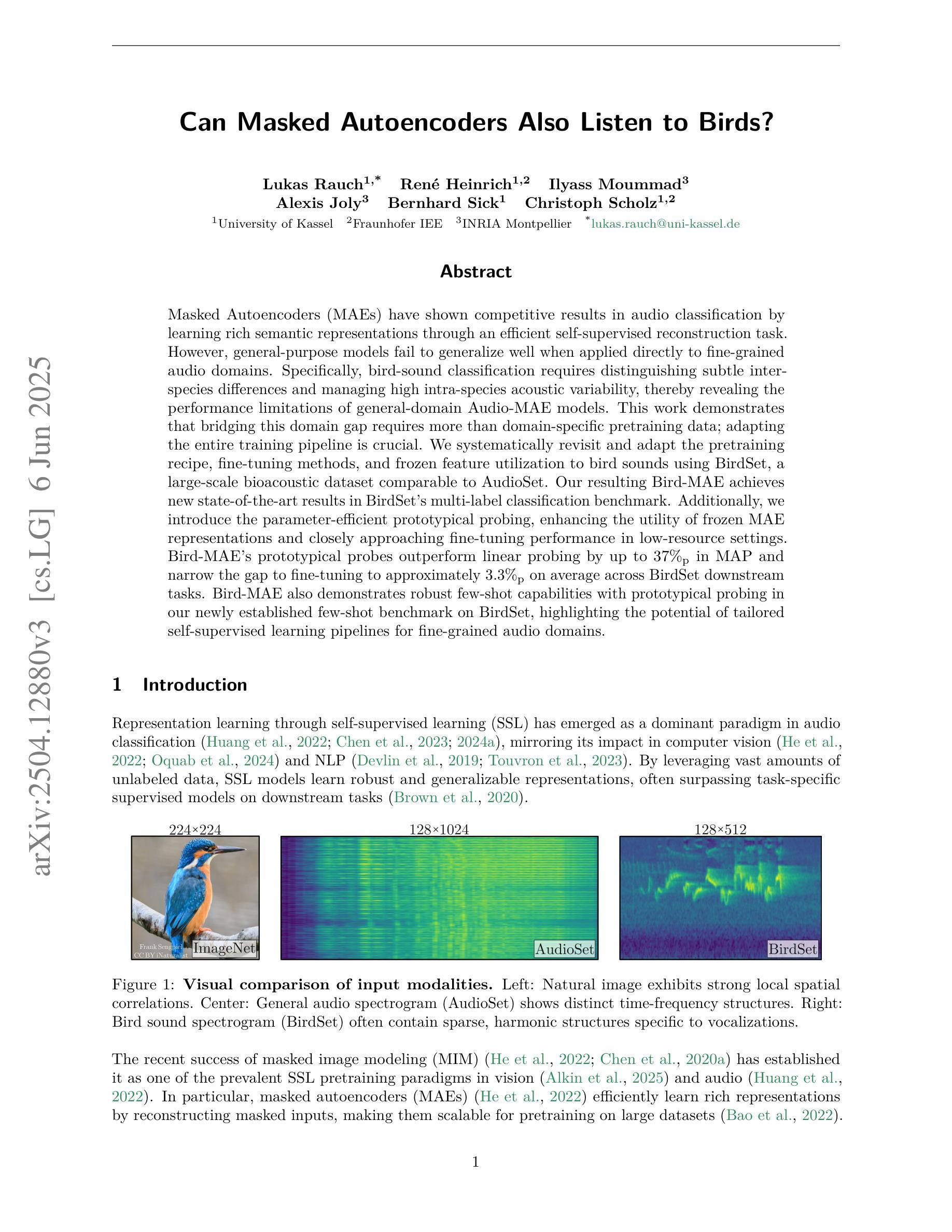
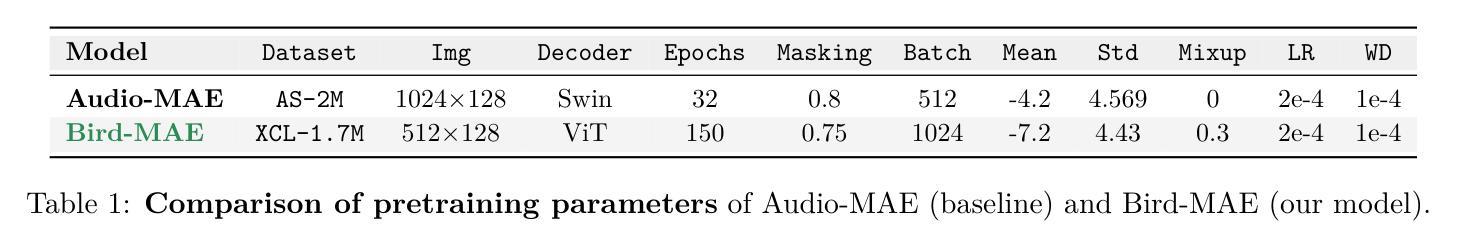
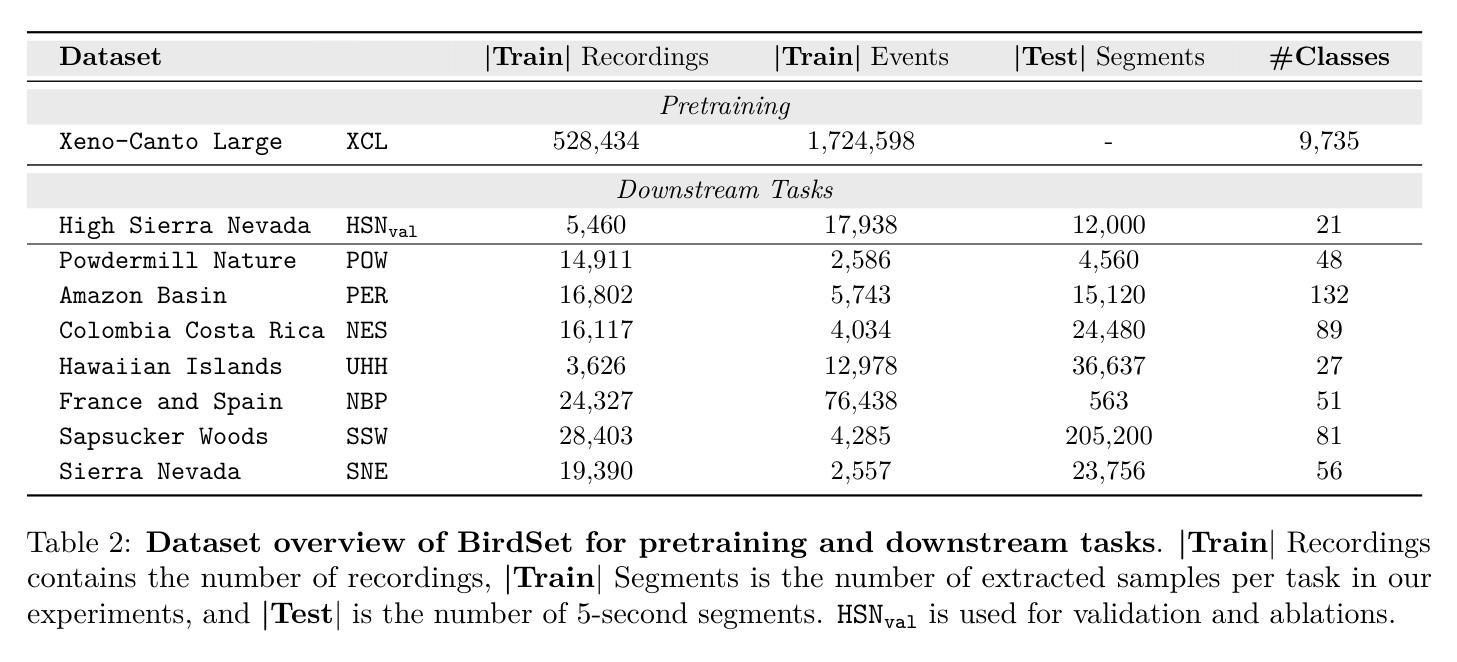
Can Masked Autoencoders Also Listen to Birds?
Authors:Lukas Rauch, René Heinrich, Ilyass Moummad, Alexis Joly, Bernhard Sick, Christoph Scholz
Masked Autoencoders (MAEs) have shown competitive results in audio classification by learning rich semantic representations through an efficient self-supervised reconstruction task. However, general-purpose models fail to generalize well when applied directly to fine-grained audio domains. Specifically, bird-sound classification requires distinguishing subtle inter-species differences and managing high intra-species acoustic variability, thereby revealing the performance limitations of general-domain Audio-MAE models. This work demonstrates that bridging this domain gap requires more than domain-specific pretraining data; adapting the entire training pipeline is crucial. We systematically revisit and adapt the pretraining recipe, fine-tuning methods, and frozen feature utilization to bird sounds using BirdSet, a large-scale bioacoustic dataset comparable to AudioSet. Our resulting Bird-MAE achieves new state-of-the-art results in BirdSet’s multi-label classification benchmark. Additionally, we introduce the parameter-efficient prototypical probing, enhancing the utility of frozen MAE representations and closely approaching fine-tuning performance in low-resource settings. Bird-MAE’s prototypical probes outperform linear probing by up to 37%$_\text{p}$ in MAP and narrow the gap to fine-tuning to approximately 3.3%$_\text{p}$ on average across BirdSet downstream tasks. Bird-MAE also demonstrates robust few-shot capabilities with prototypical probing in our newly established few-shot benchmark on BirdSet, highlighting the potential of tailored self-supervised learning pipelines for fine-grained audio domains.
基于Masked Autoencoders(MAEs)在音频分类任务中展现出强大的竞争力,通过高效的自监督重建任务学习丰富的语义表示。然而,当通用模型直接应用于细粒度音频领域时,其泛化能力往往不佳。特别是鸟类声音分类需要区分物种间的细微差异并应对高物种内部的声学变化,从而揭示了通用领域Audio-MAE模型的性能局限性。本研究表明,缩小这一领域差距不仅需要特定领域的预训练数据;整个训练管道的调整也是至关重要的。我们系统地回顾并适应了预训练配方、微调方法以及使用BirdSet(一个与AudioSet相当的大规模生物声学数据集)的鸟类声音的冻结特征利用方法。我们得到的Bird-MAE在BirdSet的多标签分类基准测试中取得了最新 state-of-the-art 结果。此外,我们引入了参数高效的原型探测,增强了冻结MAE表示的实用性,并在低资源环境中接近微调性能。Bird-MAE的原型探针在MAP上的表现优于线性探针高达37%,并将与微调之间的差距缩小到BirdSet下游任务平均约3.3%。Bird-MAE还展示了我们新建立的BirdSet少样本基准测试中基于原型探针的强大少样本能力,突显了针对细粒度音频领域量身定制的自监督学习管道的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF under review @TMLR
摘要
基于Masked Autoencoders(MAEs)的音频分类展现出强大的语义表示能力,尤其在自监督重建任务中效果显著。然而,对于细粒度音频域,通用模型的表现不尽如人意。鸟声分类需区分不同物种间的微妙差异并处理高种内声学变异,暴露出通用领域Audio-MAE模型的性能局限。本研究表明,缩小这一领域差距不仅需要特定领域的预训练数据,还需要适应整个训练流程。通过系统性地重新考虑和适应预训练配方、微调方法以及冻结特征的利用,并结合大规模生物声学数据集BirdSet(与AudioSet相当),我们推出的Bird-MAE在BirdSet的多标签分类基准测试中取得了最新最先进的成果。此外,我们引入了参数高效的原型探测技术,增强了冻结MAE表示的实用性,并在低资源环境中接近微调性能。Bird-MAE的原型探针在MAP上的表现比线性探针高出高达37%,并将与微调之间的差距缩小到BirdSet下游任务平均约3.3%。Bird-MAE在新的少量样本基准测试中展现了强大的少样本能力,突显了针对细粒度音频域量身定制的自监督学习流程的巨大潜力。
关键见解
- Masked Autoencoders (MAEs) 在音频分类中展现出强大的语义表示能力。
- 通用模型在细粒度音频域(如鸟声分类)中表现不佳,需要区分物种间的微妙差异和处理高种内声学变异。
- 缩小领域差距需要不仅仅是特定领域的预训练数据,还需要适应整个训练流程,包括预训练配方、微调方法和冻结特征的利用。
- Bird-MAE在BirdSet的多标签分类基准测试中取得了最新最先进的成果。
- 引入参数高效的原型探测技术,增强了冻结MAE表示的实用性,并提高了低资源环境中的性能。
- Bird-MAE的原型探针在MAP上的表现显著优于线性探针。
点此查看论文截图
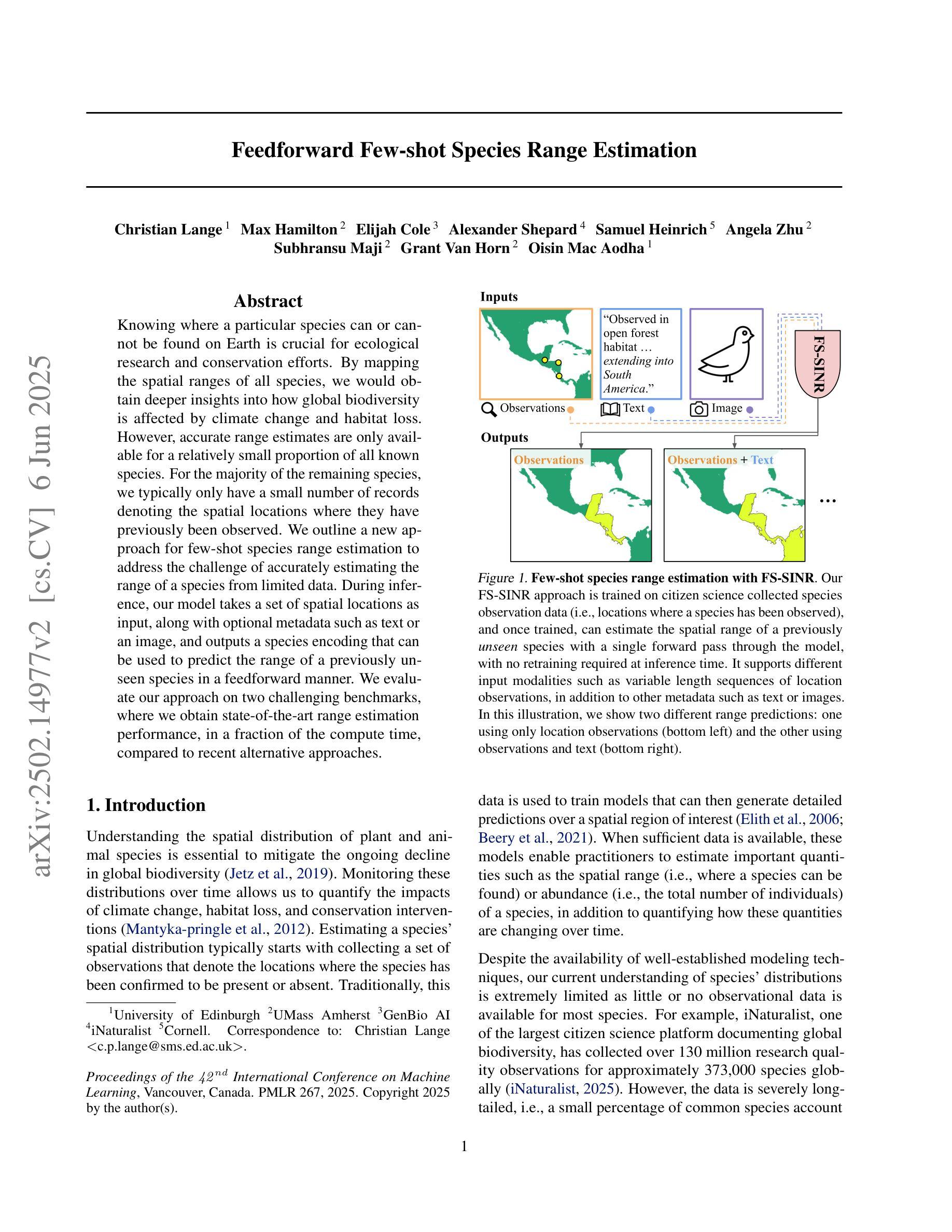
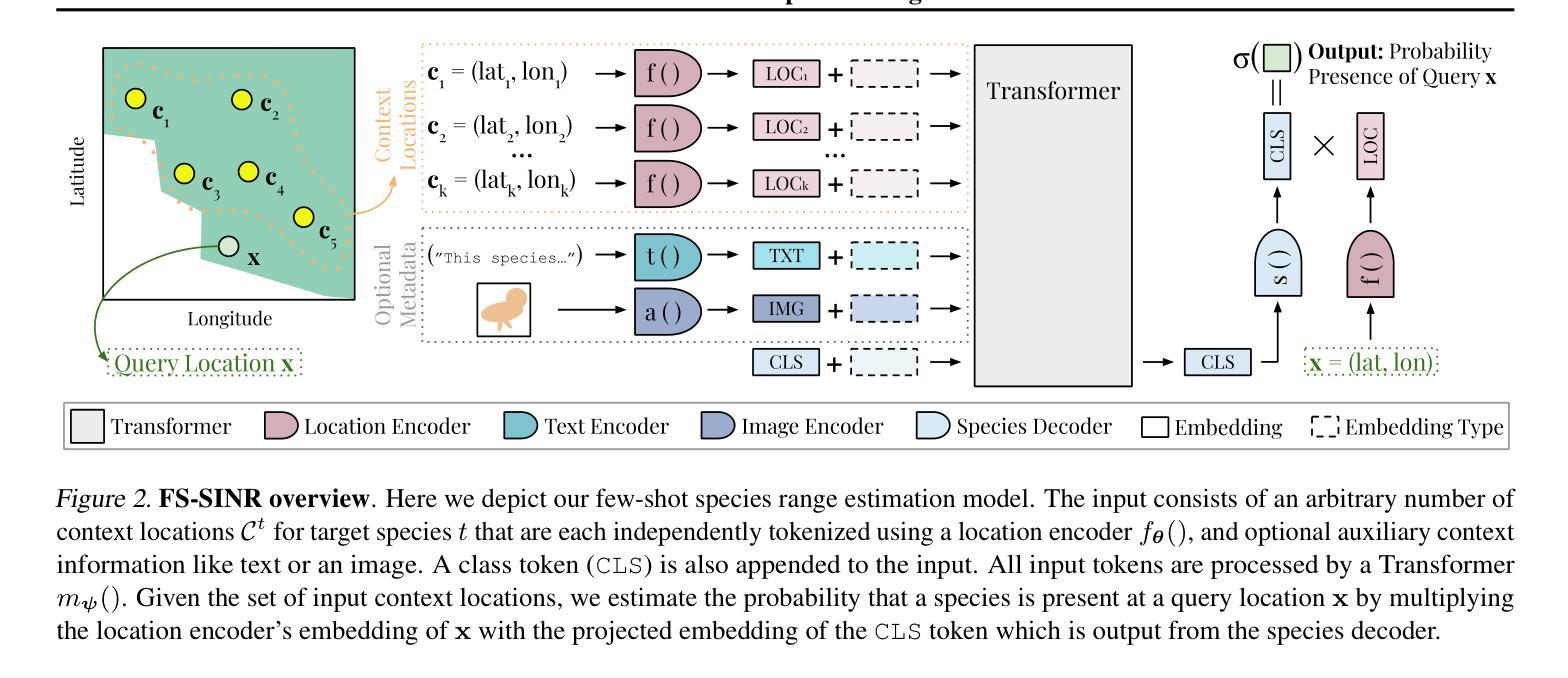
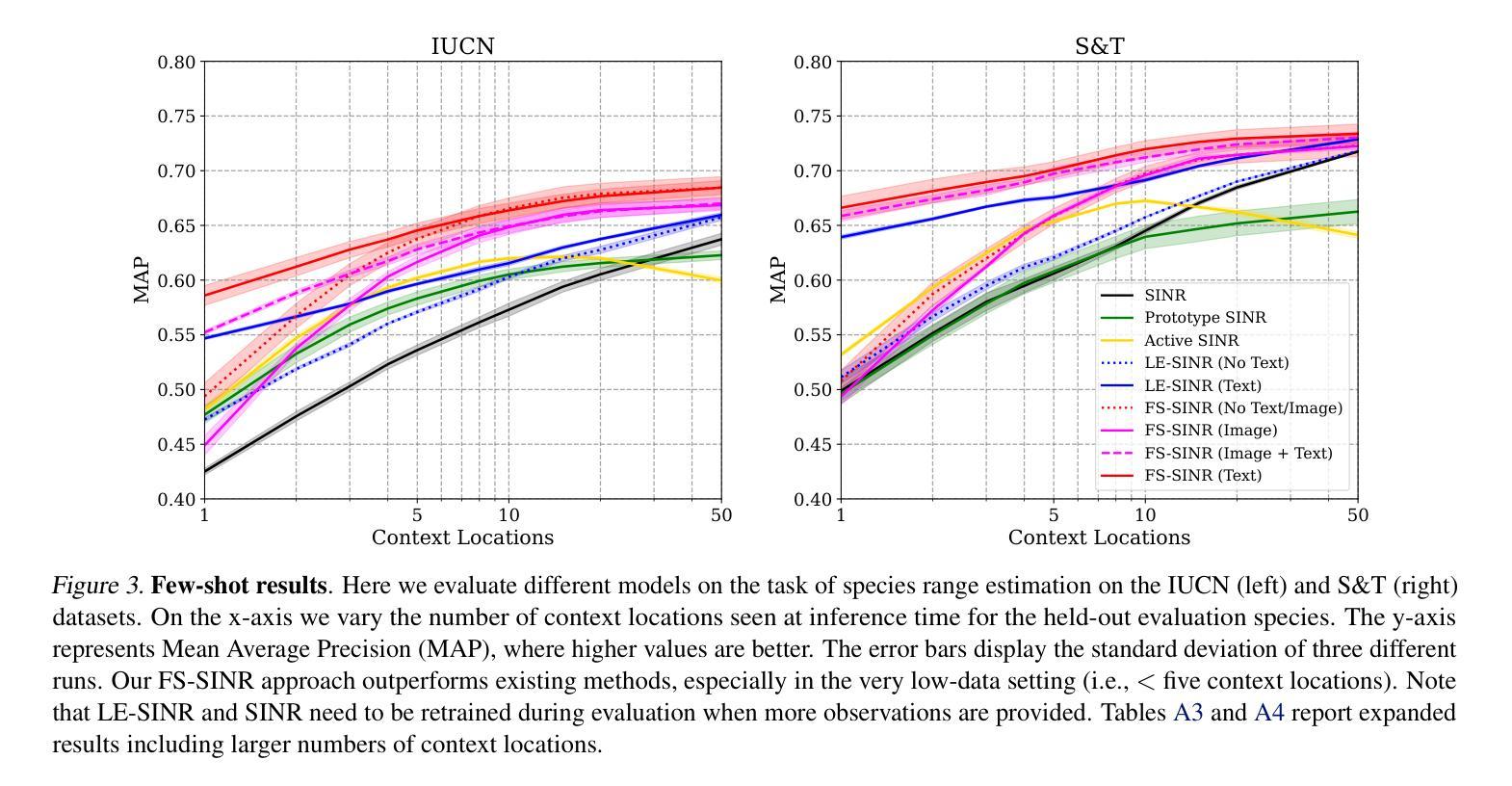
Feedforward Few-shot Species Range Estimation
Authors:Christian Lange, Max Hamilton, Elijah Cole, Alexander Shepard, Samuel Heinrich, Angela Zhu, Subhransu Maji, Grant Van Horn, Oisin Mac Aodha
Knowing where a particular species can or cannot be found on Earth is crucial for ecological research and conservation efforts. By mapping the spatial ranges of all species, we would obtain deeper insights into how global biodiversity is affected by climate change and habitat loss. However, accurate range estimates are only available for a relatively small proportion of all known species. For the majority of the remaining species, we typically only have a small number of records denoting the spatial locations where they have previously been observed. We outline a new approach for few-shot species range estimation to address the challenge of accurately estimating the range of a species from limited data. During inference, our model takes a set of spatial locations as input, along with optional metadata such as text or an image, and outputs a species encoding that can be used to predict the range of a previously unseen species in a feedforward manner. We evaluate our approach on two challenging benchmarks, where we obtain state-of-the-art range estimation performance, in a fraction of the compute time, compared to recent alternative approaches.
了解特定物种在地球上可以或不能被发现的位置对生态研究和保护工作至关重要。通过绘制所有物种的空间分布范围图,我们将深入了解全球生物多样性如何受到气候变化和栖息地丧失的影响。然而,只有相对较少的已知物种有准确的范围估计。对于大多数剩余物种,我们通常只有少量记录表明它们之前被观察到的空间位置。我们概述了一种新的用于少量物种范围估计的方法,以解决从有限数据中准确估计物种范围所面临的挑战。在推理过程中,我们的模型以一组空间位置为输入,还可以加入文本或图像等可选元数据,输出一种物种编码,该编码可以用于以前未见过的物种的范围预测。我们在两个具有挑战性的基准测试上评估了我们的方法,与最近的替代方法相比,我们的方法在计算时间的一小部分内获得了最先进的范围估计性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in the Proceedings of the 42nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2025)
Summary
本文提出一种基于少量数据的新物种分布范围估算方法。通过输入物种的空间位置和可选的元数据(如文本或图像),模型可以预测未知物种的分布范围。该方法在具有挑战性的基准测试上表现优异,且计算时间较其他方法大大缩短。
Key Takeaways
- 物种的分布范围对于生态研究和保护至关重要。
- 目前大多数物种的分布范围估计仍基于有限的数据。
- 提出了一种新的基于少量数据的物种分布范围估算方法。
- 该方法利用物种的空间位置和可选的元数据进行预测。
- 在基准测试中,该方法在预测性能上达到了最新水平。
- 与其他方法相比,该方法的计算时间大大减少。
点此查看论文截图