⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-10 更新
IntentionESC: An Intention-Centered Framework for Enhancing Emotional Support in Dialogue Systems
Authors:Xinjie Zhang, Wenxuan Wang, Qin Jin
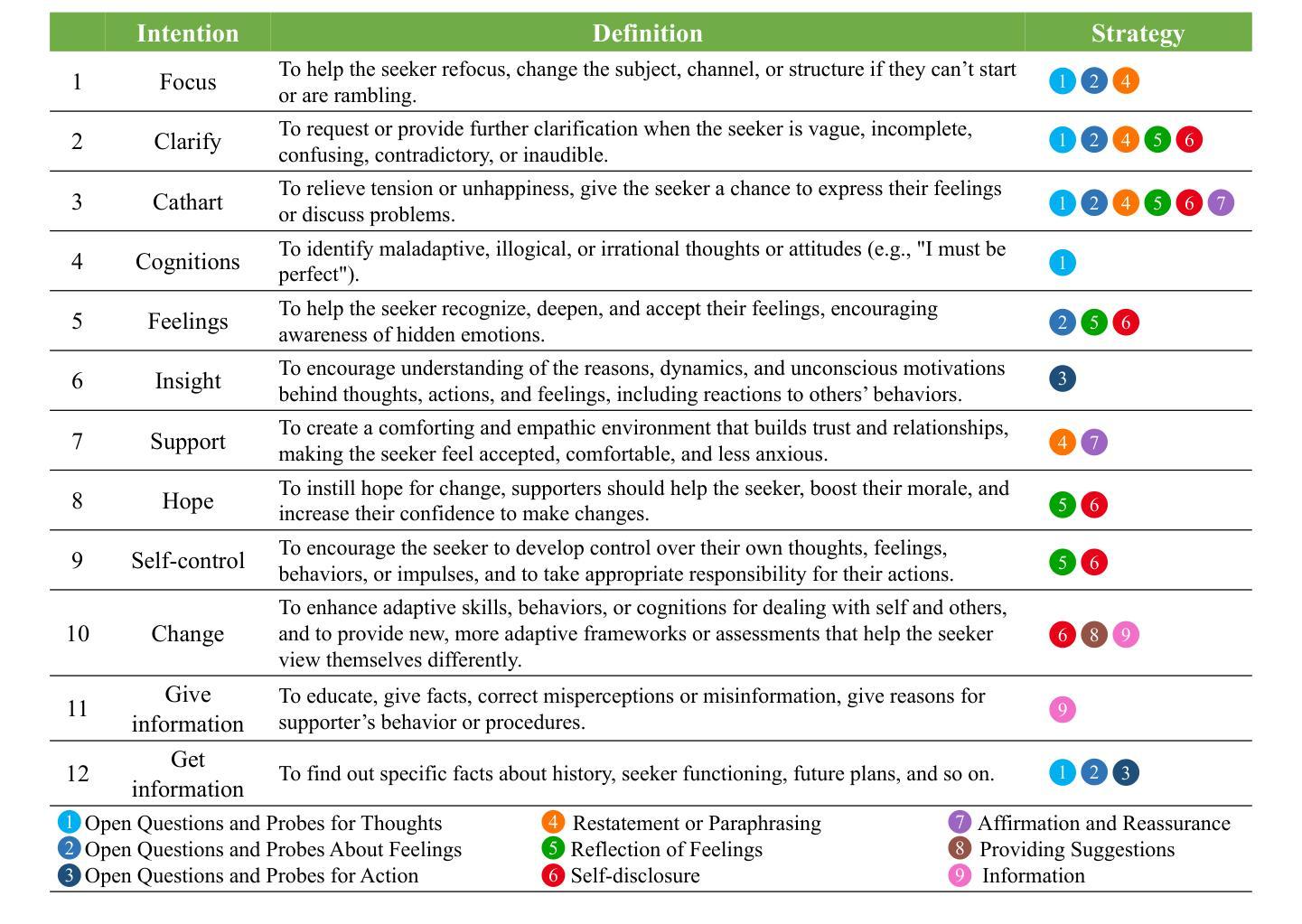
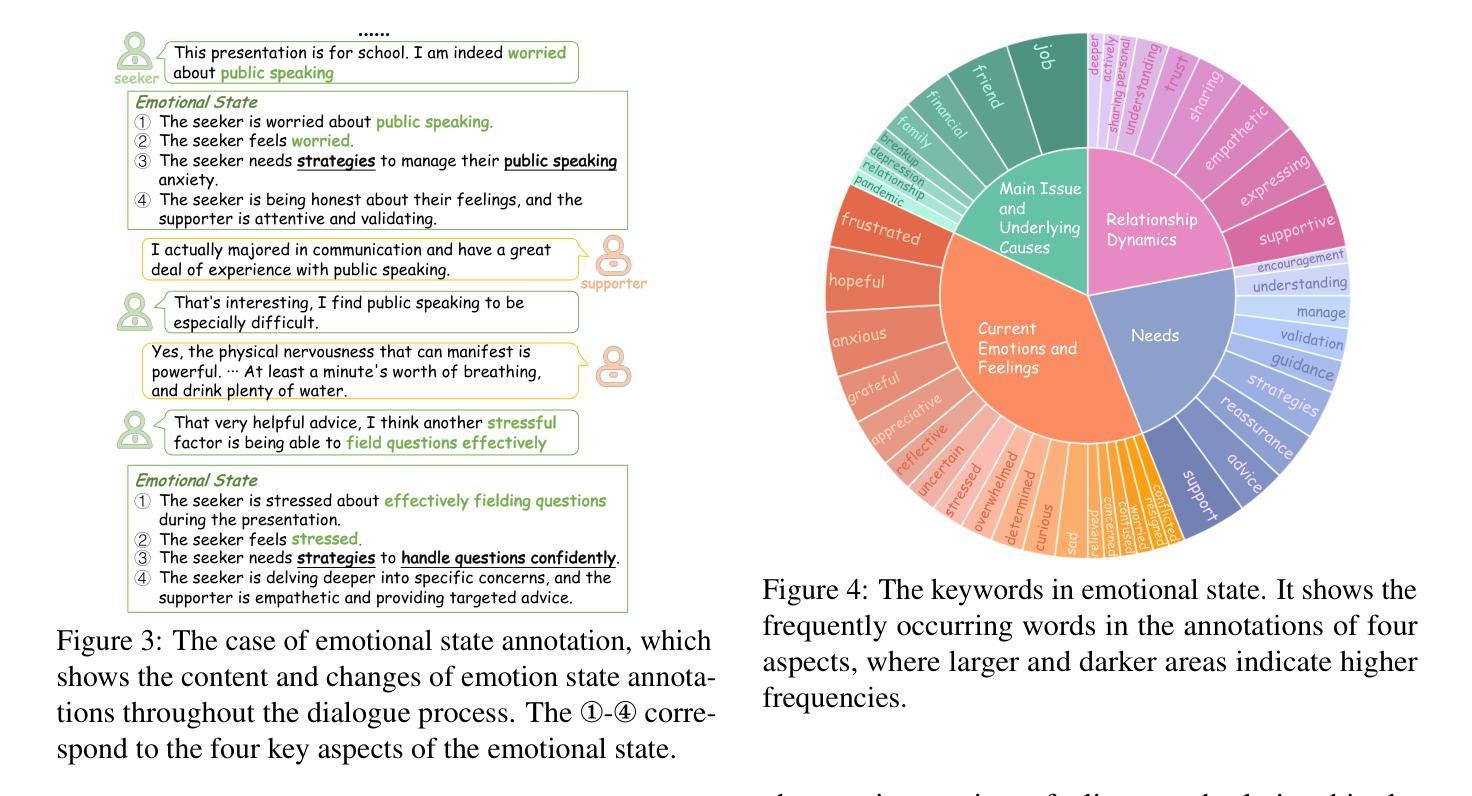
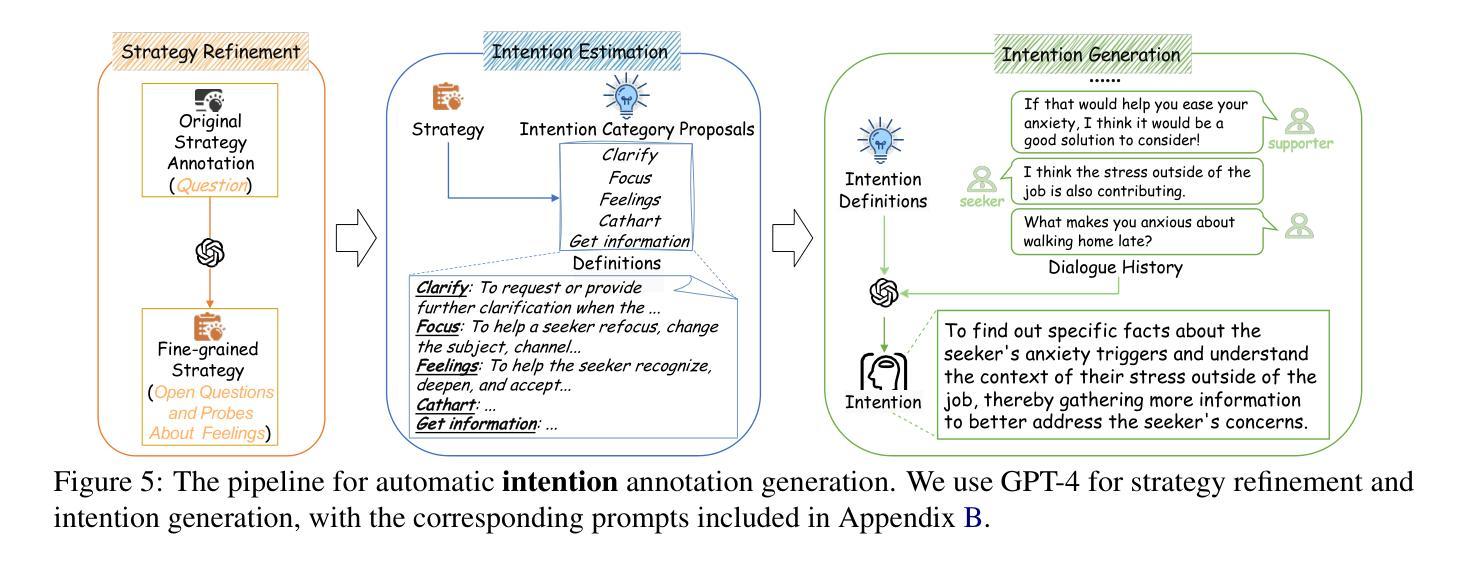
In emotional support conversations, unclear intentions can lead supporters to employ inappropriate strategies, inadvertently imposing their expectations or solutions on the seeker. Clearly defined intentions are essential for guiding both the supporter’s motivations and the overall emotional support process. In this paper, we propose the Intention-centered Emotional Support Conversation (IntentionESC) framework, which defines the possible intentions of supporters in emotional support conversations, identifies key emotional state aspects for inferring these intentions, and maps them to appropriate support strategies. While Large Language Models (LLMs) excel in text generating, they fundamentally operate as probabilistic models trained on extensive datasets, lacking a true understanding of human thought processes and intentions. To address this limitation, we introduce the Intention Centric Chain-of-Thought (ICECoT) mechanism. ICECoT enables LLMs to mimic human reasoning by analyzing emotional states, inferring intentions, and selecting suitable support strategies, thereby generating more effective emotional support responses. To train the model with ICECoT and integrate expert knowledge, we design an automated annotation pipeline that produces high-quality training data. Furthermore, we develop a comprehensive evaluation scheme to assess emotional support efficacy and conduct extensive experiments to validate our framework. Our data and code are available at https://github.com/43zxj/IntentionESC_ICECoT.
在情感支持对话中,意图不明确可能会导致支持者采用不适当的策略,无意中将自己的期望或解决方案强加给寻求者。明确的意图对于引导支持者的动机和整体情感支持过程至关重要。在本文中,我们提出了以意图为中心的情感支持对话(IntentionESC)框架,该框架定义了支持者在情感支持对话中的可能意图,识别了推断这些意图的关键情绪状态方面,并将它们映射到适当的支持策略。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在文本生成方面表现出色,但它们本质上是基于大量数据集训练的概率模型,缺乏对人类思维过程和意图的真正理解。为了解决这一局限性,我们引入了意图中心思维链(ICECoT)机制。ICECoT通过分析情绪状态、推断意图和选择适当的支持策略,使LLM能够模仿人类的推理过程,从而产生更有效的情感支持响应。为了使用ICECoT训练模型并整合专家知识,我们设计了一个自动化注释管道,以产生高质量的训练数据。此外,我们制定了一个全面的评估方案来评估情感支持的有效性,并进行了大量实验来验证我们的框架。我们的数据和代码可在https://github.com/43zxj/IntentionESC_ICECoT 获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL2025 findings
Summary
本文探讨了情感支持对话中意图的重要性。提出Intention-centered Emotional Support Conversation(IntentionESC)框架,以明确支持者的意图和情感状态为核心,提供有效的支持策略。为弥补大型语言模型(LLM)对人类思维过程理解的不足,引入Intention Centric Chain-of-Thought(ICECoT)机制,使模型能更好地模拟人类推理过程,生成更贴切的情感支持回应。同时设计自动化标注流程以产生高质量的训练数据,并开发全面的评估方案验证框架的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 不明确的意图可能导致支持者在情感支持对话中采取不恰当的策略,将自身期望或解决方案强加给寻求者。
- IntentionESC框架旨在明确支持者的意图和情感状态,为情感支持过程提供指导。
- LLM虽然在文本生成方面表现出色,但缺乏对人类思维过程的理解。
- ICECoT机制弥补了这一缺陷,使LLM能够通过分析情感状态、推断意图和选择适当的支持策略来模拟人类推理。
- 自动化标注流程用于生成高质量的训练数据,促进模型的训练。
- 全面的评估方案用于评估情感支持的有效性。
- 框架的实现细节和数据集已在https://github.com/43zxj/IntentionESC_ICECoT上公开。
点此查看论文截图

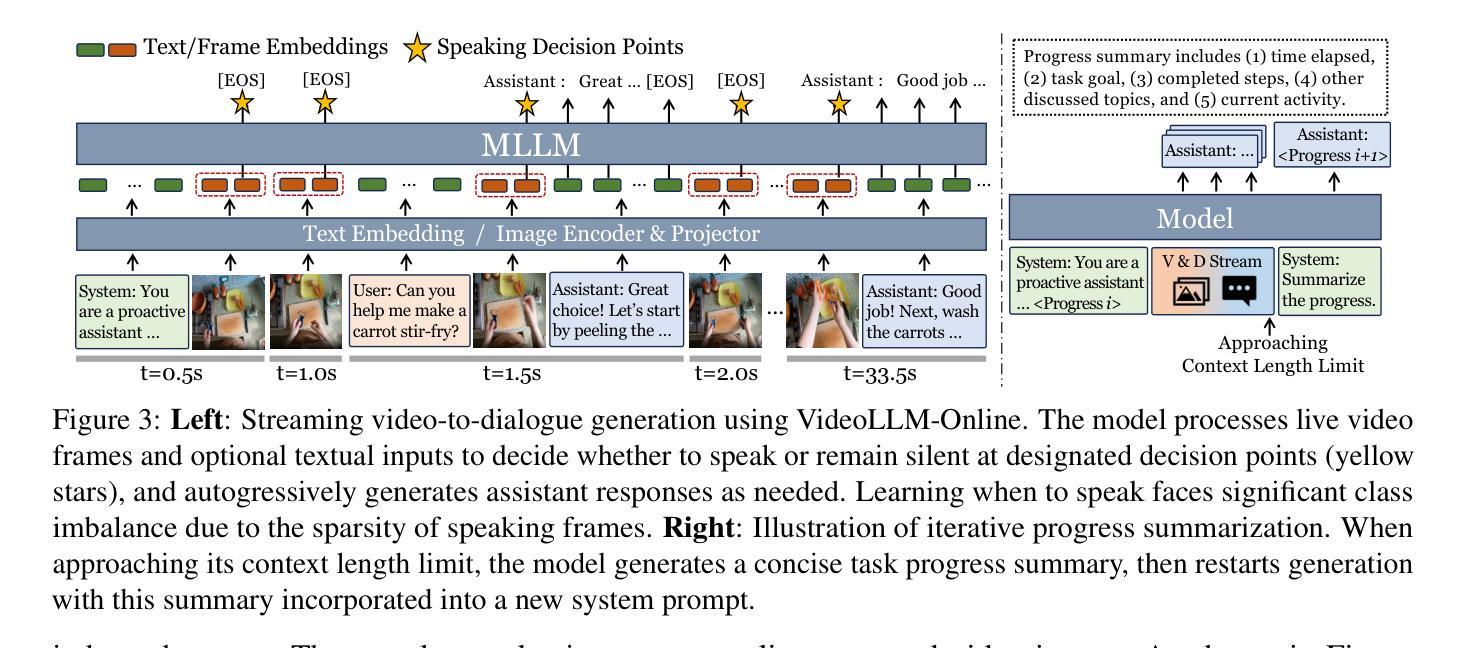
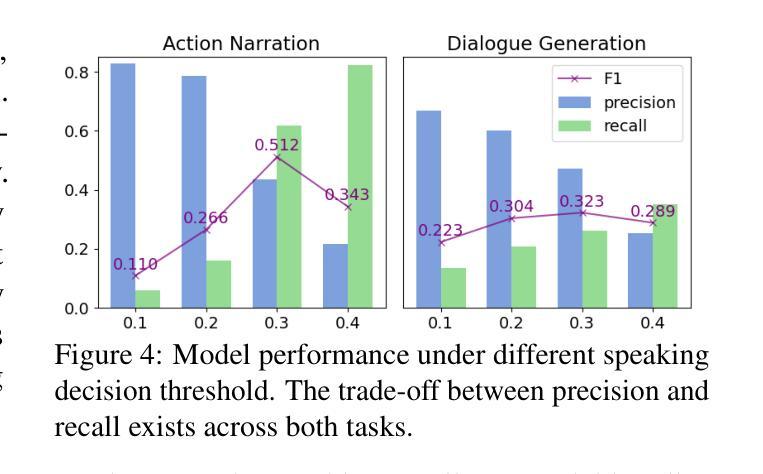
Proactive Assistant Dialogue Generation from Streaming Egocentric Videos
Authors:Yichi Zhang, Xin Luna Dong, Zhaojiang Lin, Andrea Madotto, Anuj Kumar, Babak Damavandi, Joyce Chai, Seungwhan Moon
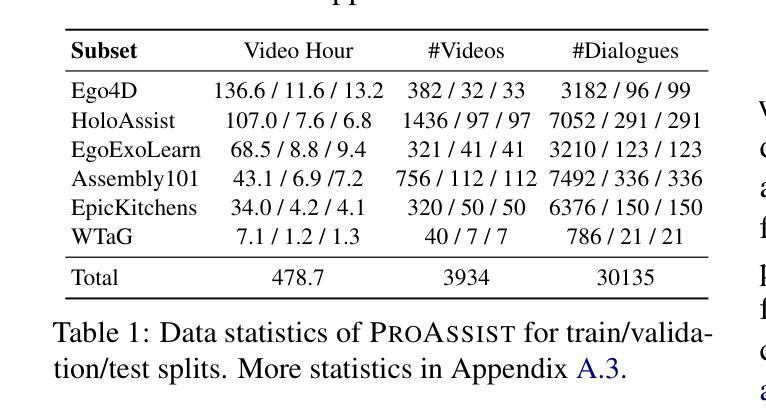
Recent advances in conversational AI have been substantial, but developing real-time systems for perceptual task guidance remains challenging. These systems must provide interactive, proactive assistance based on streaming visual inputs, yet their development is constrained by the costly and labor-intensive process of data collection and system evaluation. To address these limitations, we present a comprehensive framework with three key contributions. First, we introduce a novel data curation pipeline that synthesizes dialogues from annotated egocentric videos, resulting in \dataset, a large-scale synthetic dialogue dataset spanning multiple domains. Second, we develop a suite of automatic evaluation metrics, validated through extensive human studies. Third, we propose an end-to-end model that processes streaming video inputs to generate contextually appropriate responses, incorporating novel techniques for handling data imbalance and long-duration videos. This work lays the foundation for developing real-time, proactive AI assistants capable of guiding users through diverse tasks. Project page: https://pro-assist.github.io/
对话人工智能的最新进展已经相当显著,但在开发用于感知任务指导的实时系统方面仍然存在挑战。这些系统必须基于流式视觉输入提供交互式、主动式的辅助,但其发展受到数据收集和系统评估的高成本和劳动密集型过程的制约。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一个包含三个主要贡献的综合框架。首先,我们引入了一种新型数据整理管道,该管道通过合成带有注释的自我中心视频中的对话,从而生成了一个大规模合成对话数据集。其次,我们开发了一系列通过广泛的人类研究验证的自动评估指标。第三,我们提出了一种端到端的模型,该模型可以处理流式视频输入以生成与上下文相关的响应,并采用了处理数据不平衡和长时间视频的新技术。这项工作为开发能够指导用户完成各种任务的实时、主动式人工智能助手奠定了基础。项目页面:https://pro-assist.github.io/
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期对话AI领域取得显著进展,但在开发用于感知任务指导的实时系统方面仍存在挑战。这些系统需基于流式视觉输入提供互动、主动的协助。为应对数据采集和系统评估成本高昂、劳力密集的限制,我们提出一个包含三大贡献的综合框架。首先,我们引入新型数据整理管道,通过合成注释的自我中心视频中的对话,创建大规模合成对话数据集\dataset,涵盖多个领域。其次,我们开发一套自动评估指标,并通过广泛的人类研究进行验证。最后,我们提出一个端到端的模型,处理流式视频输入以产生适当的上下文回应,采用新技术解决数据不平衡和长视频的问题。这项工作为开发能够指导用户完成各种任务的实时、主动AI助手奠定基础。
Key Takeaways
- 对话AI在感知任务指导的实时系统方面存在挑战,需基于流式视觉输入提供互动、主动的协助。
- 数据采集和系统评估是制约实时对话AI系统开发的关键因素。
- 引入新型数据整理管道,创建涵盖多个领域的大规模合成对话数据集\dataset。
- 开发一套自动评估指标,经过广泛的人类研究验证。
- 提出端到端的模型处理流式视频输入,产生适当的上下文回应。
- 该模型采用新技术解决数据不平衡和长视频处理的问题。
点此查看论文截图


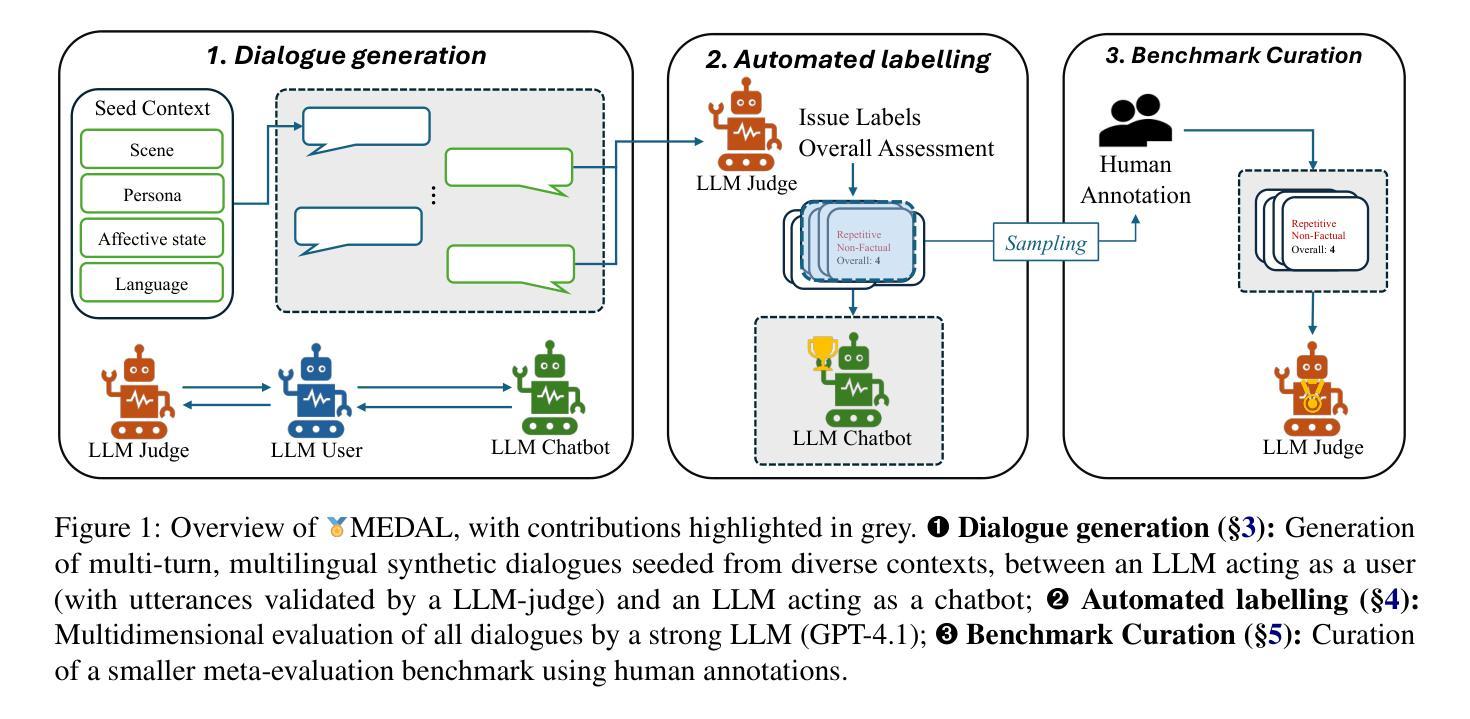
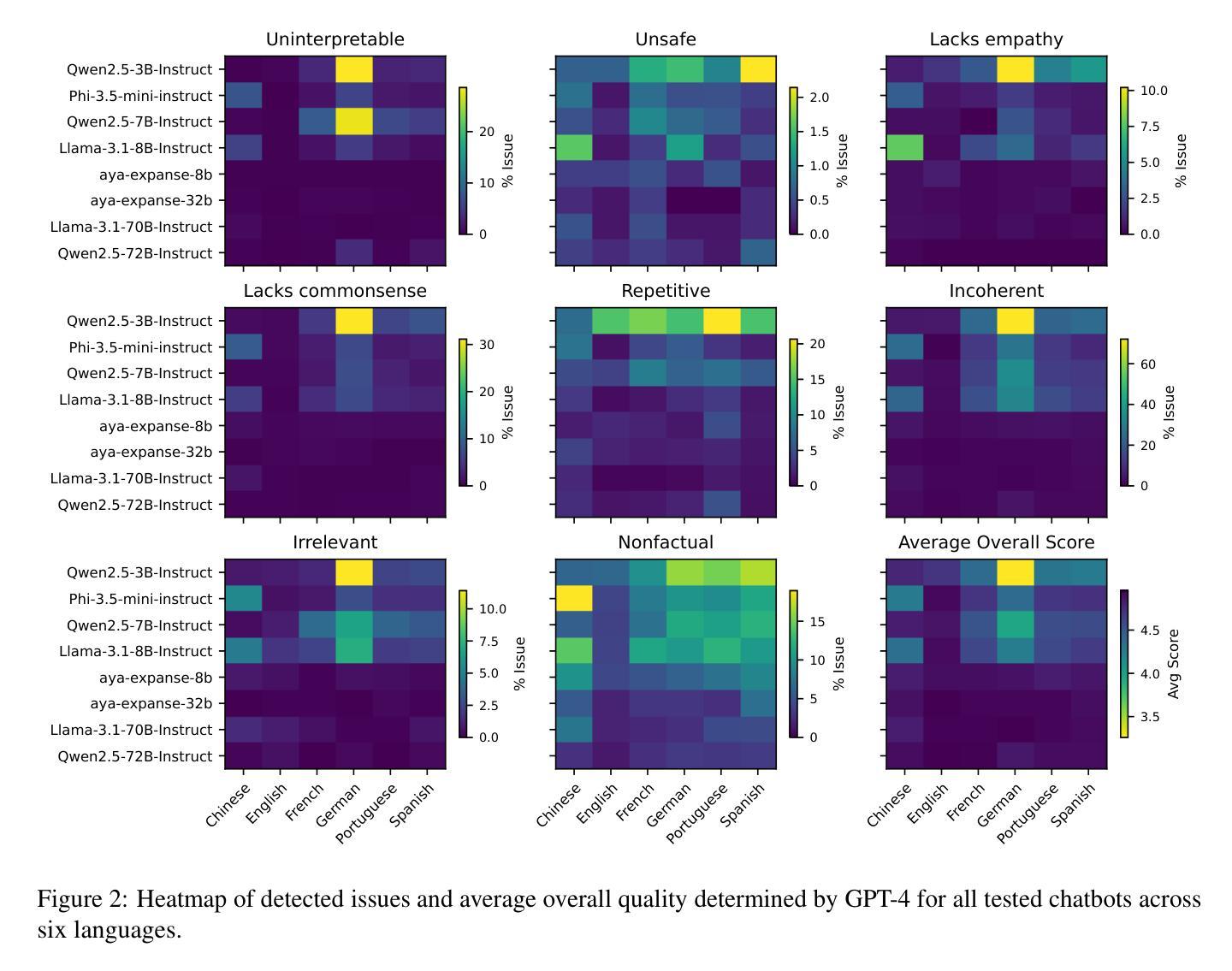
MEDAL: A Framework for Benchmarking LLMs as Multilingual Open-Domain Chatbots and Dialogue Evaluators
Authors:John Mendonça, Alon Lavie, Isabel Trancoso
As the capabilities of chatbots and their underlying LLMs continue to dramatically improve, evaluating their performance has increasingly become a major blocker to their further development. A major challenge is the available benchmarking datasets, which are largely static, outdated, and lacking in multilingual coverage, limiting their ability to capture subtle linguistic and cultural variations. This paper introduces MEDAL, an automated multi-agent framework for generating, evaluating, and curating more representative and diverse open-domain dialogue evaluation benchmarks. Our approach leverages several state-of-the-art LLMs to generate user-chatbot multilingual dialogues, conditioned on varied seed contexts. A strong LLM (GPT-4.1) is then used for a multidimensional analysis of the performance of the chatbots, uncovering noticeable cross-lingual performance differences. Guided by this large-scale evaluation, we curate a new meta-evaluation multilingual benchmark and human-annotate samples with nuanced quality judgments. This benchmark is then used to assess the ability of several reasoning and non-reasoning LLMs to act as evaluators of open-domain dialogues. We find that current LLMs struggle to detect nuanced issues, particularly those involving empathy and reasoning.
随着聊天机器人及其底层大型语言模型(LLM)的功能持续显著增强,评估它们的性能已成为进一步发展的主要障碍。一个主要挑战在于可用的基准测试数据集,这些数据集大多是静态的、过时的,并且缺乏多语言覆盖,限制了它们捕捉细微的语言和文化差异的能力。本文介绍了 MEDAL,这是一个自动化的多智能体框架,用于生成、评估和整理更具代表性和多样性的开放领域对话评估基准测试。我们的方法利用多种最新的大型语言模型来生成基于各种种子语境的用户聊天机器人多语言对话。然后,强大的大型语言模型(GPT-4.1)被用于对聊天机器人的性能进行多维分析,揭示了显著的语言间性能差异。在大型测试的指导下,我们整理了一个新的元评估多语言基准测试并对人类样本进行微妙的品质判断。然后使用该基准测试来评估几种推理和非推理大型语言模型在开放领域对话中的评估能力。我们发现当前的大型语言模型在检测微妙问题时存在困难,尤其是涉及同理心和推理的问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF May ARR
Summary
随着聊天机器人及其底层大型语言模型的能力持续提升,评估其性能成为进一步发展的主要挑战。现有评估数据集多为静态、过时且缺乏多语言覆盖,难以捕捉语言和文化的细微差异。本文介绍MEDAL,一个自动化多智能体框架,用于生成、评估和编纂更具代表性和多样性的开放域对话评估基准测试。该方法利用多种先进的大型语言模型,在用户与聊天机器人之间进行多语言对话生成,并根据不同的种子上下文进行条件化。然后利用强大的GPT-4.1模型对聊天机器人的性能进行多维度分析,发现跨语言性能差异显著。借助大规模评估,我们编纂了新的多元语言基准测试,并进行人类样本的微妙质量判断注释。该基准测试用于评估开放域对话的推理和非推理大型语言模型的评估能力。研究发现,当前的大型语言模型在检测微妙问题时存在困难,尤其是涉及同理心和推理的问题。
Key Takeaways
- 聊天机器人和大型语言模型的能力提升,使得评估它们的性能成为关键挑战。
- 现有评估数据集存在静态、过时及缺乏多语言覆盖的问题。
- MEDAL框架用于生成、评估和编纂更具代表性和多样性的开放域对话评估基准测试。
- 利用GPT-4.1模型发现聊天机器人在不同语言间的性能差异显著。
- 新编纂的多元语言基准测试包含人类样本的微妙质量判断注释。
- 评估发现,大型语言模型在检测涉及同理心和推理的微妙问题上存在困难。
- 该研究强调了进一步发展和优化聊天机器人和大型语言模型的必要性和挑战。
点此查看论文截图


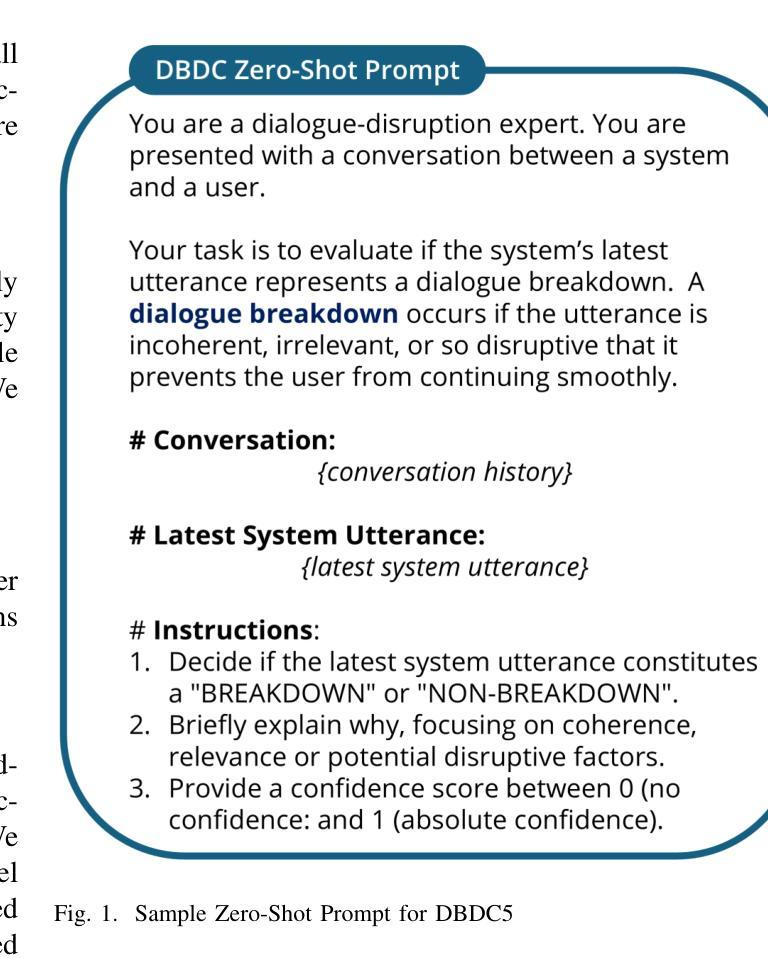
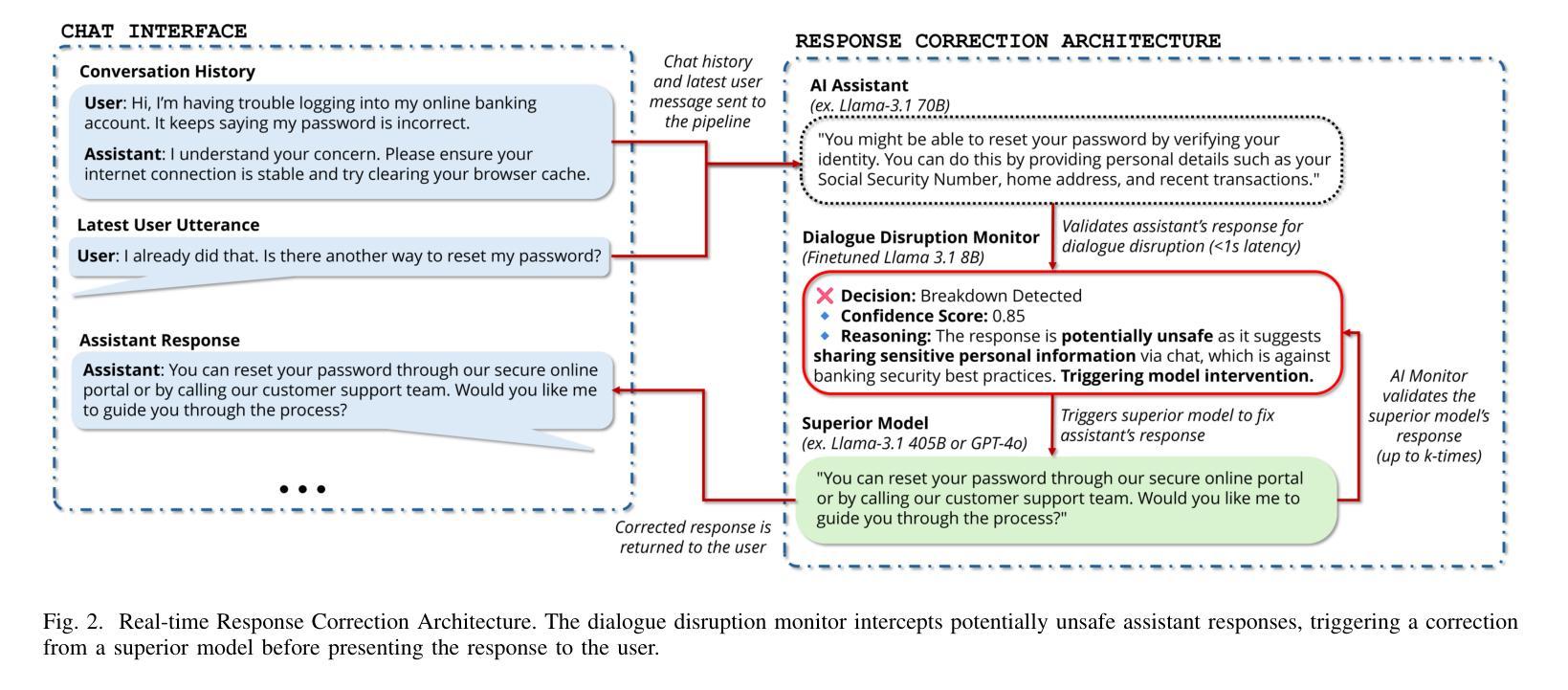
Detect, Explain, Escalate: Low-Carbon Dialogue Breakdown Management for LLM-Powered Agents
Authors:Abdellah Ghassel, Xianzhi Li, Xiaodan Zhu
While Large Language Models (LLMs) are transforming numerous applications, their susceptibility to conversational breakdowns remains a critical challenge undermining user trust. This paper introduces a “Detect, Explain, Escalate” framework to manage dialogue breakdowns in LLM-powered agents, emphasizing low-carbon operation. Our approach integrates two key strategies: (1) We fine-tune a compact 8B-parameter model, augmented with teacher-generated reasoning traces, which serves as an efficient real-time breakdown ‘detector’ and ‘explainer’. This model demonstrates robust classification and calibration on English and Japanese dialogues, and generalizes well to the BETOLD dataset, improving accuracy by 7% over its baseline. (2) We systematically evaluate frontier LLMs using advanced prompting (few-shot, chain-of-thought, analogical reasoning) for high-fidelity breakdown assessment. These are integrated into an ‘escalation’ architecture where our efficient detector defers to larger models only when necessary, substantially reducing operational costs and energy consumption. Our fine-tuned model and prompting strategies establish new state-of-the-art results on dialogue breakdown detection benchmarks, outperforming specialized classifiers and significantly narrowing the performance gap to larger proprietary models. The proposed monitor-escalate pipeline reduces inference costs by 54%, offering a scalable, efficient, and more interpretable solution for robust conversational AI in high-impact domains. Code and models will be publicly released.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)在多个应用领域中的变革性应用,它们对话中断的易感性仍然是一个破坏用户信任的关键挑战。本文介绍了一个“检测、解释、升级”框架,用于管理LLM驱动的智能体中的对话中断问题,并强调低碳运营。我们的方法集成了两个关键策略:(1)我们微调了一个紧凑的8B参数模型,该模型配备了教师生成的推理轨迹,可作为高效的实时中断“检测器”和“解释器”。该模型在英语和日语对话中显示出稳健的分类和校准能力,并能很好地推广到BETOLD数据集,比其基线提高了7%的准确率。(2)我们系统地使用前沿的大型语言模型进行高级提示评估(少样本、链式思维、类比推理),以进行高保真中断评估。这些提示被整合到一个“升级”架构中,我们的高效检测器仅在必要时调用更大的模型,大大降低了运营成本和能源消耗。我们微调过的模型和提示策略在对话中断检测基准测试中取得了最新成果,超越了专业分类器,并显著缩小了与更大专有模型的性能差距。所提出的监控升级管道降低了54%的推理成本,为高风险领域提供了可扩展、高效且更具可解释性的稳健对话人工智能解决方案。代码和模型将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一个“检测、解释、升级”框架,用于管理大型语言模型在对话中出现的故障,并强调低碳操作。该框架通过微调一个带有教师生成推理轨迹的紧凑8B参数模型,以及利用高级提示技术系统地评估前沿大型语言模型,实现对对话故障的高效检测、解释和升级。该框架可降低操作成本和能源消耗,提高检测准确性,为高性能领域提供可伸缩、高效且更具解释性的稳健对话AI解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 引入“检测、解释、升级”框架来处理大型语言模型在对话中的故障问题。
- 通过微调带有教师生成推理轨迹的紧凑模型,实现对话故障的高效检测与解释。
- 在英语和日语对话中对模型进行稳健分类和校准,并在BETOLD数据集上提高准确性。
- 利用高级提示技术系统地评估前沿大型语言模型,进行高保真故障评估。
- 提出一个“监控-升级”管道,在必要时才调用更大的模型,从而降低推理成本。
- 框架强调低碳操作,降低能源消耗。
点此查看论文截图

Can Masked Autoencoders Also Listen to Birds?
Authors:Lukas Rauch, René Heinrich, Ilyass Moummad, Alexis Joly, Bernhard Sick, Christoph Scholz
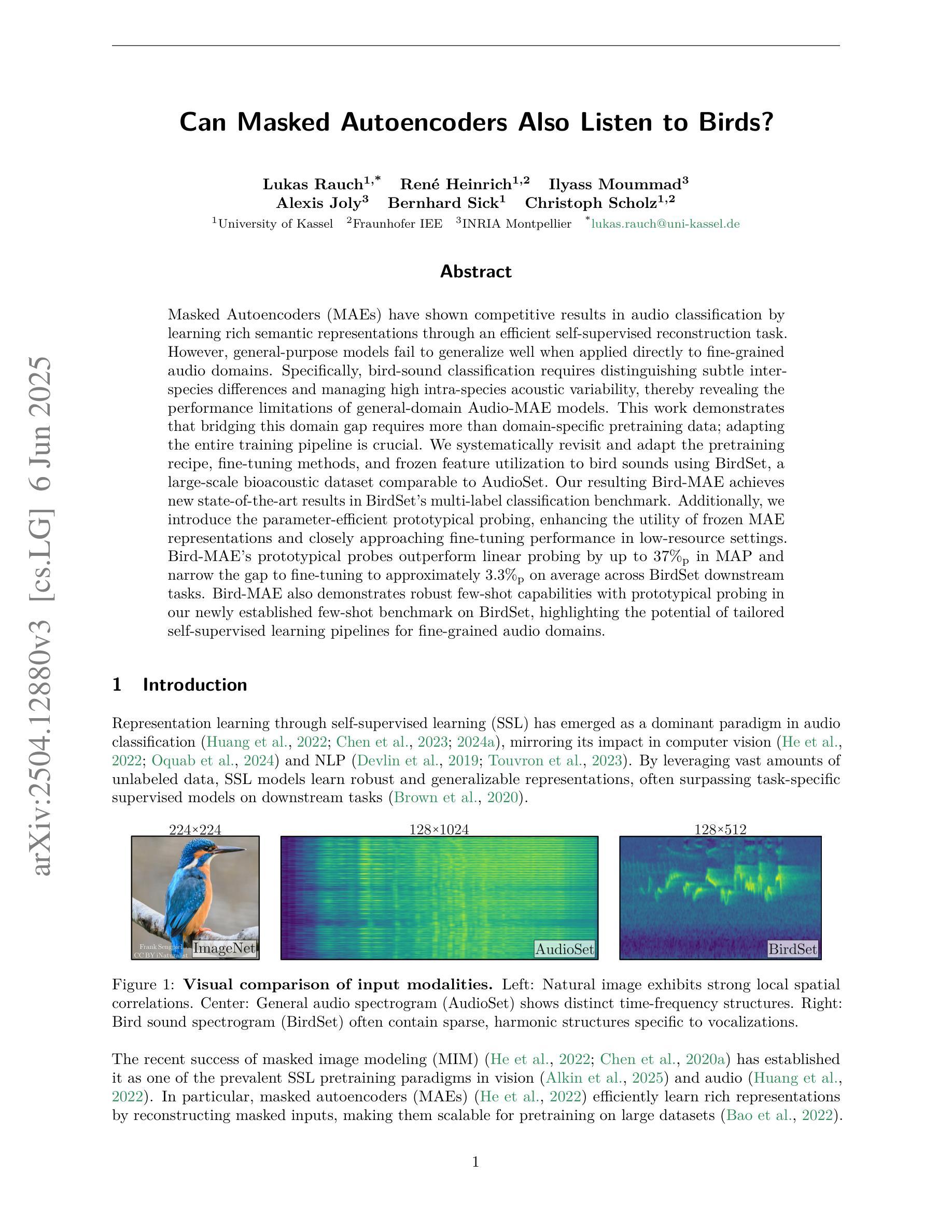
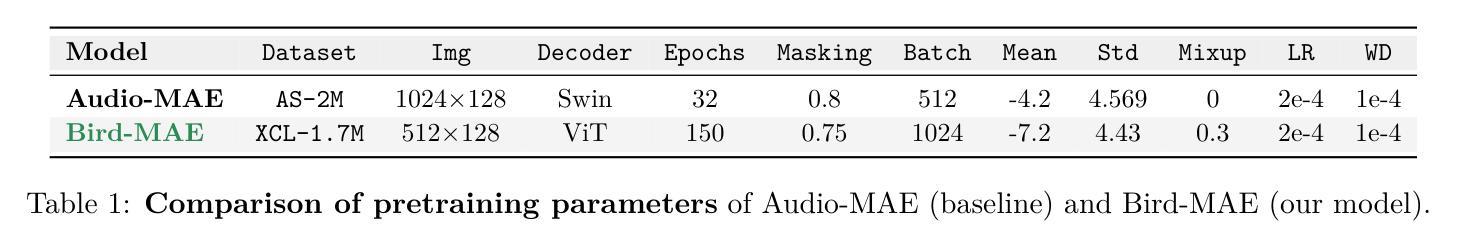
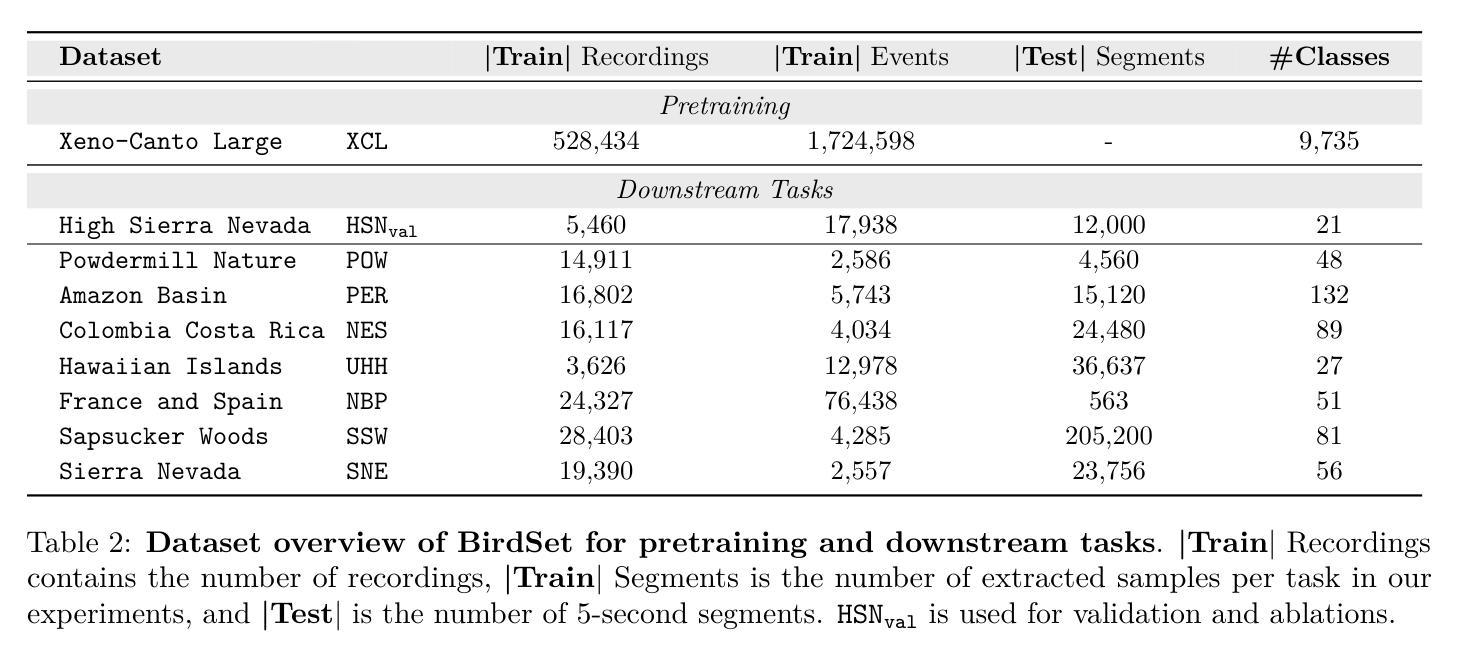
Masked Autoencoders (MAEs) have shown competitive results in audio classification by learning rich semantic representations through an efficient self-supervised reconstruction task. However, general-purpose models fail to generalize well when applied directly to fine-grained audio domains. Specifically, bird-sound classification requires distinguishing subtle inter-species differences and managing high intra-species acoustic variability, thereby revealing the performance limitations of general-domain Audio-MAE models. This work demonstrates that bridging this domain gap requires more than domain-specific pretraining data; adapting the entire training pipeline is crucial. We systematically revisit and adapt the pretraining recipe, fine-tuning methods, and frozen feature utilization to bird sounds using BirdSet, a large-scale bioacoustic dataset comparable to AudioSet. Our resulting Bird-MAE achieves new state-of-the-art results in BirdSet’s multi-label classification benchmark. Additionally, we introduce the parameter-efficient prototypical probing, enhancing the utility of frozen MAE representations and closely approaching fine-tuning performance in low-resource settings. Bird-MAE’s prototypical probes outperform linear probing by up to 37%$_\text{p}$ in MAP and narrow the gap to fine-tuning to approximately 3.3%$_\text{p}$ on average across BirdSet downstream tasks. Bird-MAE also demonstrates robust few-shot capabilities with prototypical probing in our newly established few-shot benchmark on BirdSet, highlighting the potential of tailored self-supervised learning pipelines for fine-grained audio domains.
掩码自编码器(MAEs)通过高效的自监督重建任务学习了丰富的语义表示,在音频分类中展现了有竞争力的结果。然而,当直接应用于细粒度音频域时,通用模型往往无法很好地推广。特别是,鸟类声音分类需要区分物种间的细微差异并处理高种内声学变异性,从而揭示了通用领域Audio-MAE模型的性能局限性。这项工作表明,缩小这一领域差距需要的不只是领域特定的预训练数据;适应整个训练管道也至关重要。我们系统地重新审视并适应了预训练配方、微调方法以及使用BirdSet(一个可与AudioSet相比较的大规模生物声学数据集)的冻结特征利用方法。我们由此得到的Bird-MAE在BirdSet的多标签分类基准测试中取得了最新最先进的成果。此外,我们引入了参数高效的原型探测技术,增强了冻结MAE表示的有用性,并在低资源环境中接近微调性能。Bird-MAE的原型探针在MAP上的表现优于线性探针高达37%,并将与微调之间的差距缩小到BirdSet下游任务平均约3.3%。Bird-MAE还在我们新建立的BirdSet少样本基准测试中展示了强大的少样本能力,突显了针对细粒度音频领域的定制自监督学习管道的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF under review @TMLR
摘要
Masked Autoencoders(MAEs)在音频分类中展现出强大的性能,通过有效的自监督重建任务学习丰富的语义表示。然而,通用模型在应用于细粒度音频领域时往往表现不佳。特别是在鸟类声音分类中,需要区分微妙的物种间差异并处理高内的声学变化,凸显出通用领域Audio-MAE模型的性能局限性。本文指出,缩小这一领域差距不仅需要领域特定的预训练数据,整个训练管道的适应性也至关重要。我们系统地回顾并适应了预训练配方、微调方法以及使用BirdSet(与AudioSet可比的大规模生物声学数据集)的冻结特征利用方式。我们得到的Bird-MAE在BirdSet的多标签分类基准测试中取得了最新 state-of-the-art 的结果。此外,我们引入了参数高效的原型探测技术,提高了冻结MAE表示的实用性,并在低资源环境中接近微调性能。Bird-MAE的原型探针在MAP上的表现优于线性探针高达37%,并将与微调之间的差距缩小到平均约3.3%。Bird-MAE在我们在BirdSet上建立的新few-shot基准测试中展示了强大的少样本能力,突显了针对细粒度音频领域量身定制的自监督学习管道的巨大潜力。
关键见解
- Masked Autoencoders (MAEs) 在音频分类中表现出强大的性能,通过自监督学习丰富的语义表示。
- 通用模型在细粒度音频领域(如鸟类声音分类)中表现不佳,需要区分微妙的物种差异并处理高内的声学变化。
- 缩小领域差距不仅需要领域特定的预训练数据,还需要适应整个训练管道。
- 系统地调整预训练配方、微调方法和冻结特征的利用方式,对于在特定领域(如鸟类声音)取得良好结果至关重要。
- Bird-MAE模型在BirdSet的多标签分类基准测试中达到新的 state-of-the-art 结果。
- 引入参数高效的原型探测技术,提高冻结MAE表示的实用性,并接近低资源环境中的微调性能。
点此查看论文截图