⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-10 更新
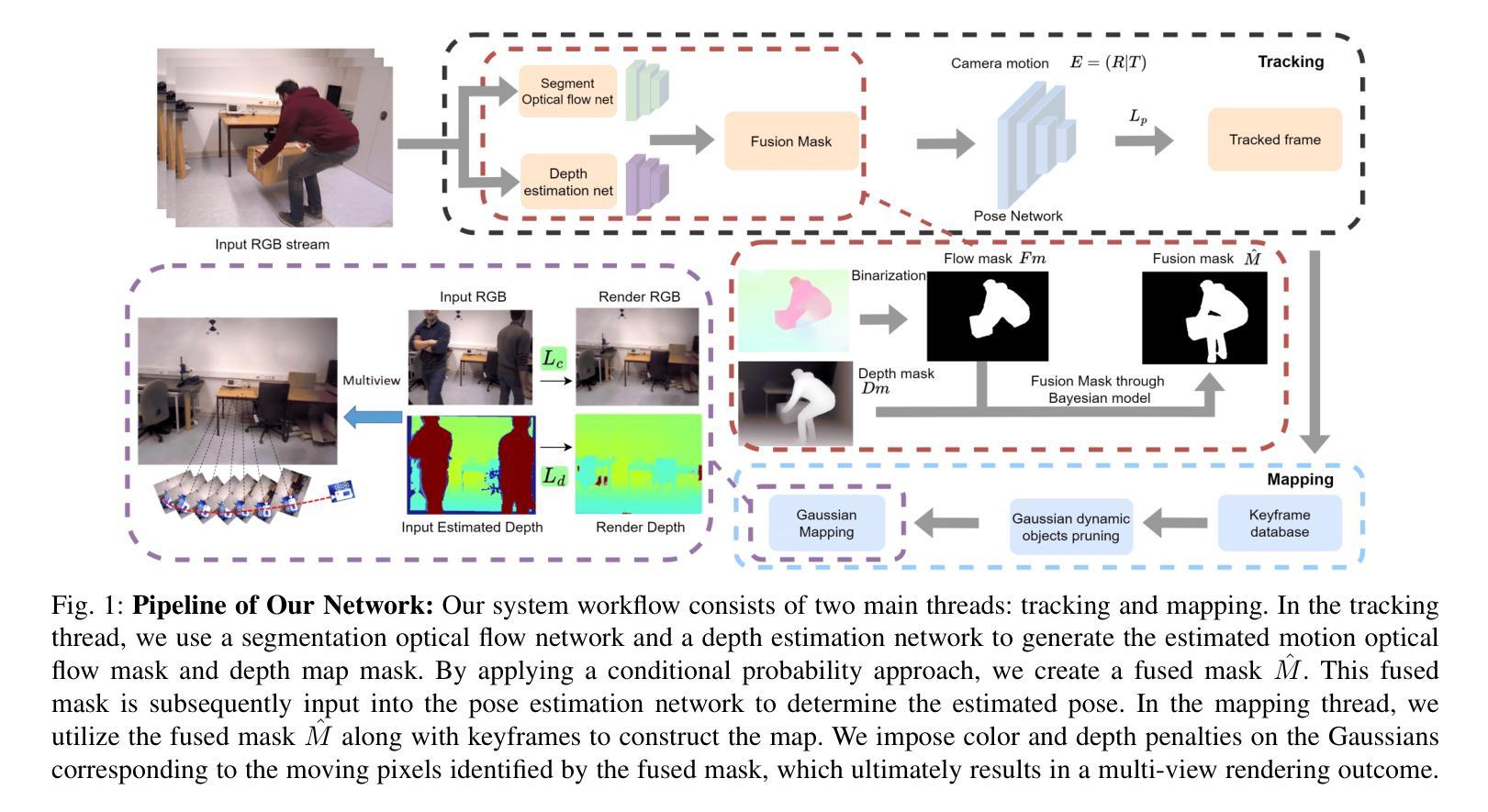
Dy3DGS-SLAM: Monocular 3D Gaussian Splatting SLAM for Dynamic Environments
Authors:Mingrui Li, Yiming Zhou, Hongxing Zhou, Xinggang Hu, Florian Roemer, Hongyu Wang, Ahmad Osman
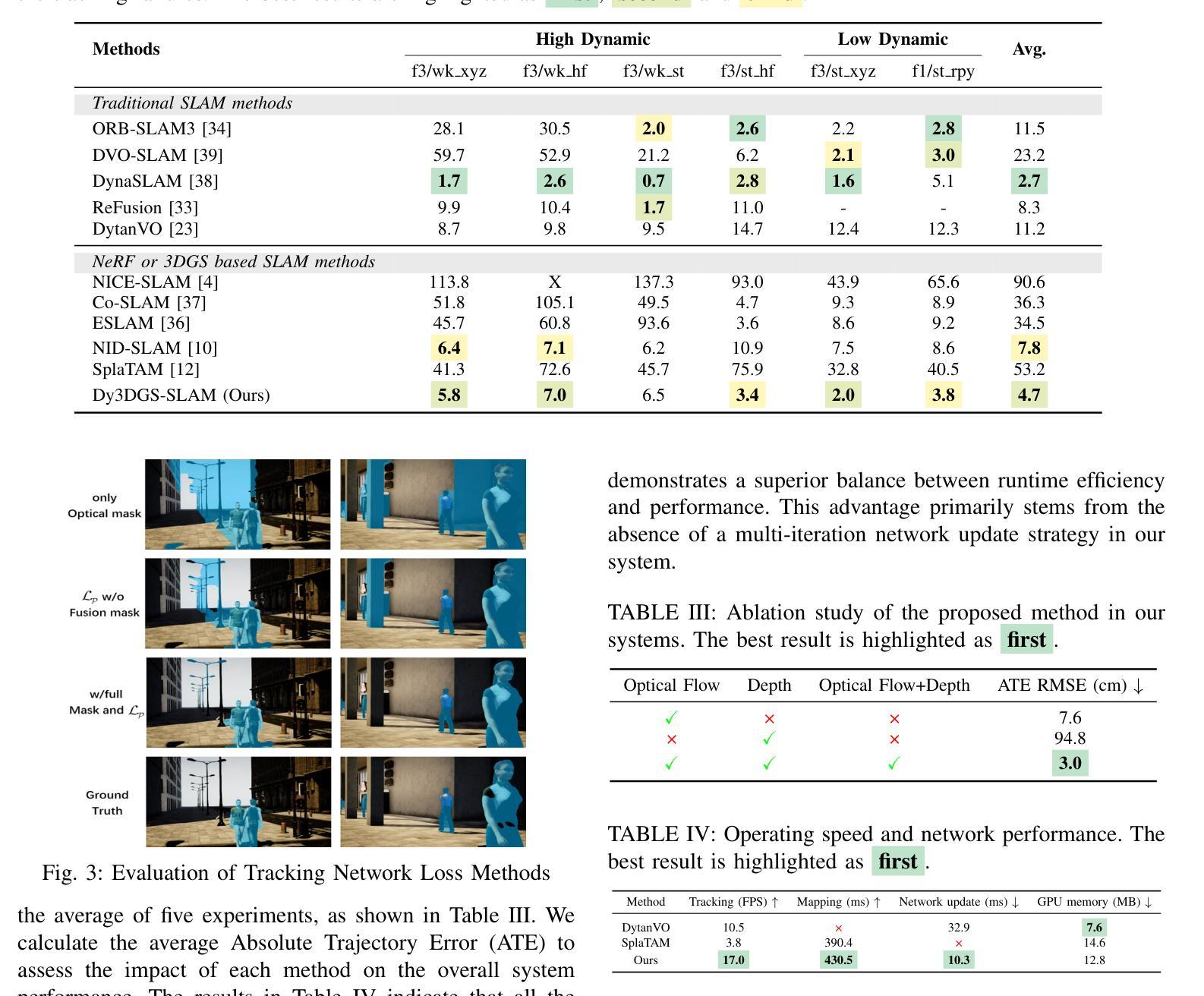
Current Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) methods based on Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) or 3D Gaussian Splatting excel in reconstructing static 3D scenes but struggle with tracking and reconstruction in dynamic environments, such as real-world scenes with moving elements. Existing NeRF-based SLAM approaches addressing dynamic challenges typically rely on RGB-D inputs, with few methods accommodating pure RGB input. To overcome these limitations, we propose Dy3DGS-SLAM, the first 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) SLAM method for dynamic scenes using monocular RGB input. To address dynamic interference, we fuse optical flow masks and depth masks through a probabilistic model to obtain a fused dynamic mask. With only a single network iteration, this can constrain tracking scales and refine rendered geometry. Based on the fused dynamic mask, we designed a novel motion loss to constrain the pose estimation network for tracking. In mapping, we use the rendering loss of dynamic pixels, color, and depth to eliminate transient interference and occlusion caused by dynamic objects. Experimental results demonstrate that Dy3DGS-SLAM achieves state-of-the-art tracking and rendering in dynamic environments, outperforming or matching existing RGB-D methods.
当前基于神经辐射场(NeRF)或3D高斯喷射的同步定位与地图构建(SLAM)方法在重建静态3D场景方面表现出色,但在动态环境(例如具有移动元素的真实世界场景)中的跟踪和重建方面却面临困难。现有的解决动态挑战的NeRF基SLAM方法通常依赖于RGB-D输入,只有少数方法适应纯RGB输入。为了克服这些限制,我们提出了Dy3DGS-SLAM,这是使用单目RGB输入为动态场景设计的第一个3D高斯喷射(3DGS)SLAM方法。为了解决动态干扰问题,我们通过概率模型融合了光学流动掩膜和深度掩膜,以获得融合后的动态掩膜。仅通过一次网络迭代,这可以约束跟踪尺度并优化渲染几何。基于融合后的动态掩膜,我们设计了一种新型运动损失,以约束姿态估计网络进行跟踪。在映射过程中,我们使用动态像素的渲染损失、颜色和深度,以消除动态物体引起的瞬时干扰和遮挡。实验结果表明,Dy3DGS-SLAM在动态环境中实现了最先进的跟踪和渲染,优于或匹配现有的RGB-D方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于神经网络辐射场(NeRF)或三维高斯贴片技术的现有同步定位与地图构建(SLAM)方法在静态三维场景的重建方面表现出色,但在动态环境(例如具有移动元素的真实世界场景)的跟踪和重建方面存在困难。针对这一问题,我们提出了Dy3DGS-SLAM,这是使用单目RGB输入对动态场景进行三维高斯贴片(3DGS)SLAM的第一种方法。为解决动态干扰问题,我们通过概率模型融合了光流掩膜和深度掩膜,获得融合后的动态掩膜。仅通过一次网络迭代,就可以约束跟踪尺度并优化渲染几何。基于融合后的动态掩膜,我们设计了一种新的运动损失,以约束姿态估计网络的跟踪。在映射过程中,我们利用动态像素的渲染损失、颜色和深度,以消除动态物体引起的瞬时干扰和遮挡。实验结果表明,Dy3DGS-SLAM在动态环境下实现了最先进的跟踪和渲染效果,在某些情况下甚至超过了现有的RGB-D方法。
Key Takeaways
- 基于NeRF或3D高斯贴片技术的SLAM方法在静态场景重建上表现出色,但在动态环境的跟踪和重建上存在挑战。
- Dy3DGS-SLAM是首个针对动态场景的基于单目RGB输入的3DGS SLAM方法。
- 通过融合光流掩膜和深度掩膜来应对动态干扰问题,得到融合后的动态掩膜。
- 仅通过一次网络迭代约束跟踪规模并优化渲染几何结构。
- 通过引入基于融合动态掩膜的新运动损失,改进了姿态估计网络的跟踪功能。
- 在处理动态物体引起的瞬时干扰和遮挡问题时,结合了动态像素的渲染损失、颜色和深度信息。
点此查看论文截图


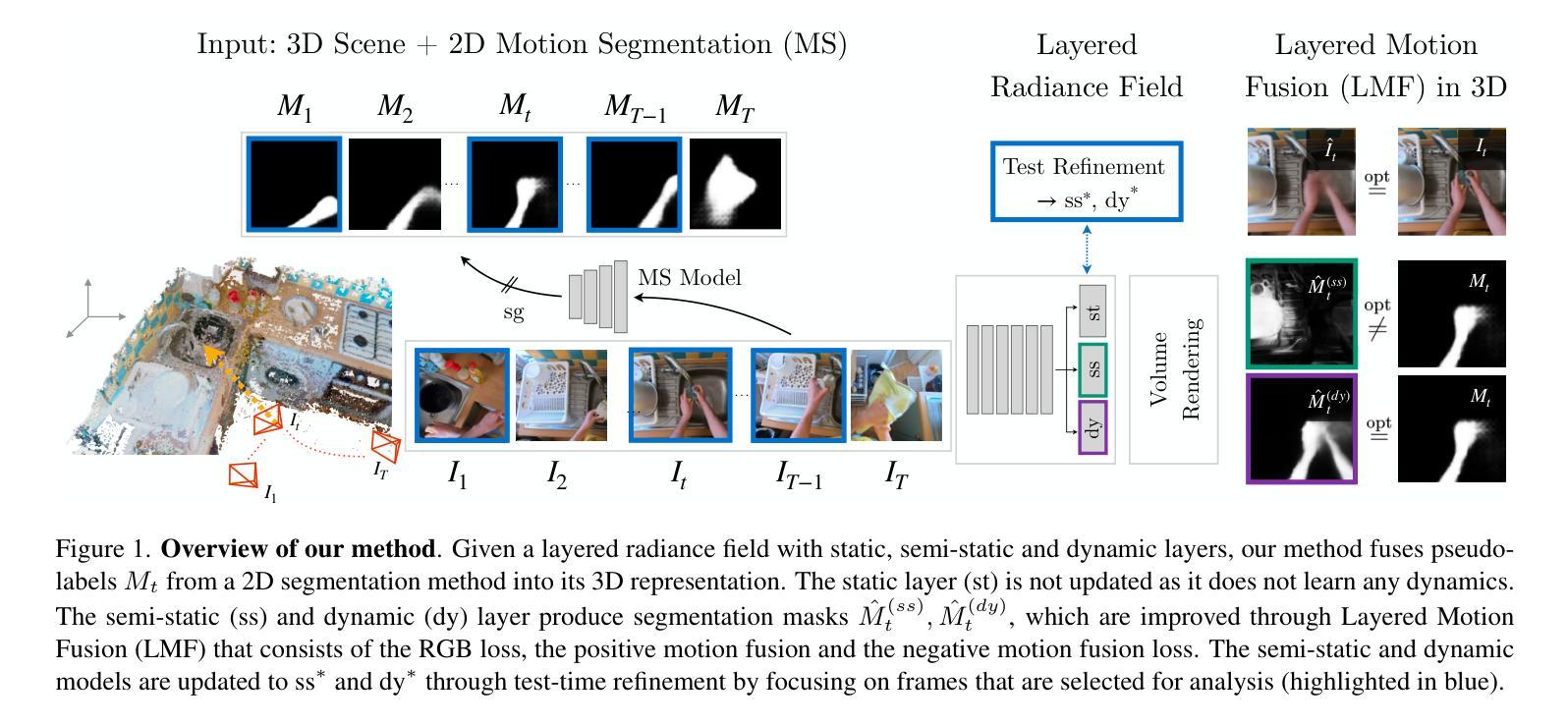
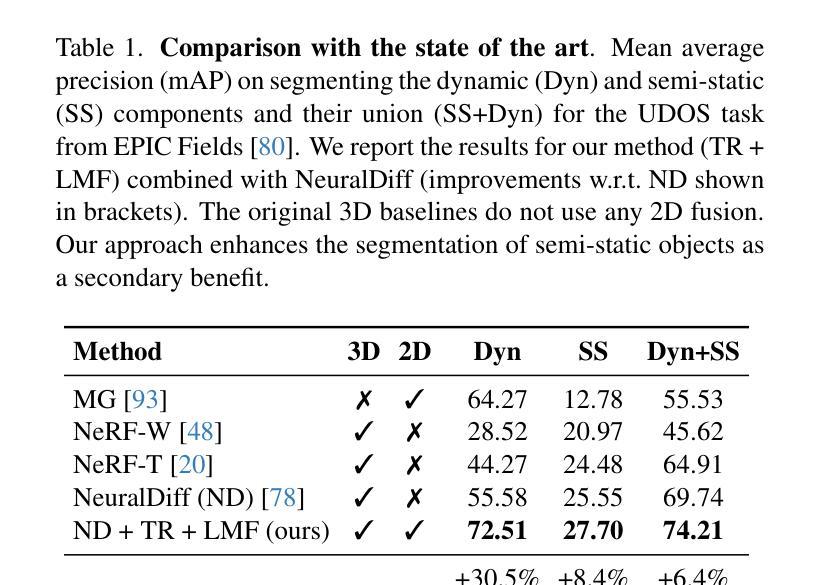
Layered Motion Fusion: Lifting Motion Segmentation to 3D in Egocentric Videos
Authors:Vadim Tschernezki, Diane Larlus, Andrea Vedaldi, Iro Laina
Computer vision is largely based on 2D techniques, with 3D vision still relegated to a relatively narrow subset of applications. However, by building on recent advances in 3D models such as neural radiance fields, some authors have shown that 3D techniques can at last improve outputs extracted from independent 2D views, by fusing them into 3D and denoising them. This is particularly helpful in egocentric videos, where the camera motion is significant, but only under the assumption that the scene itself is static. In fact, as shown in the recent analysis conducted by EPIC Fields, 3D techniques are ineffective when it comes to studying dynamic phenomena, and, in particular, when segmenting moving objects. In this paper, we look into this issue in more detail. First, we propose to improve dynamic segmentation in 3D by fusing motion segmentation predictions from a 2D-based model into layered radiance fields (Layered Motion Fusion). However, the high complexity of long, dynamic videos makes it challenging to capture the underlying geometric structure, and, as a result, hinders the fusion of motion cues into the (incomplete) scene geometry. We address this issue through test-time refinement, which helps the model to focus on specific frames, thereby reducing the data complexity. This results in a synergy between motion fusion and the refinement, and in turn leads to segmentation predictions of the 3D model that surpass the 2D baseline by a large margin. This demonstrates that 3D techniques can enhance 2D analysis even for dynamic phenomena in a challenging and realistic setting.
计算机视觉主要基于二维技术,而三维视觉仍然仅限于相对狭窄的应用范围。然而,通过利用最近的三维模型(如神经辐射场)的进展,一些作者已经证明,三维技术可以改善从独立二维视角提取的输出结果,通过将它们融合到三维并进行去噪处理。这在以自我为中心的视频中特别有帮助,其中相机运动是显著的,但假设场景本身是静态的。事实上,正如EPIC Fields最近的分析所示,当涉及到研究动态现象时,尤其是进行移动对象分割时,三维技术并不有效。在本文中,我们对这个问题进行了更详细的研究。首先,我们提出了一种通过将从二维模型获得的运动分割预测融合到分层辐射场中以改进三维动态分割的方法(分层运动融合)。然而,对于长动态视频而言,由于其高复杂性,捕捉其底层几何结构是一个挑战,这导致将运动线索融合到(不完整)场景几何中变得困难。我们通过测试时的细化来解决这个问题,这有助于模型专注于特定帧,从而减少数据复杂性。这导致运动融合和细化之间的协同作用,并反过来使得对三维模型的分割预测大幅度超越二维基线。这表明即使在充满挑战和现实的设置中处理动态现象时,三维技术也可以增强二维分析。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Camera-ready for CVPR25
摘要
基于计算机视觉的二维技术广泛应用,而三维技术仅用于少量特定领域。但随着对神经辐射场等三维模型的最新进展,通过融合独立二维视角并去噪,三维技术能提升输出效果。这在以自我为中心的视频中尤其有益,相机运动显著但场景本身静止。然而,EPIC Fields的近期分析显示,三维技术在研究动态现象、尤其是分割移动物体方面并不奏效。本文详细探讨了这一问题。首先,我们提出通过融合基于二维模型的动态分割预测结果到分层辐射场(Layered Motion Fusion)来改善三维动态分割。但长动态视频的高复杂性使其难以捕捉底层几何结构,阻碍运动线索融入(不完整)场景几何的融合。我们通过测试时优化来解决这一问题,帮助模型专注于特定帧,降低数据复杂性。这实现了运动融合与优化之间的协同作用,使得三维模型的分割预测远超二维基线。证明三维技术能增强二维分析,即使在具有挑战性和现实性的动态现象中也是如此。
关键见解
- 计算机视觉主要依赖二维技术,但三维技术对于融合独立二维视角并去噪能提升输出效果。
- 在以自我为中心的视频中,相机运动显著但场景静止的情况下,三维技术特别有益。
- 近期分析显示,三维技术在处理动态现象和移动物体分割方面存在局限性。
- 通过将基于二维模型的动态分割预测结果融入分层辐射场(Layered Motion Fusion),可以改善三维动态分割。
- 长动态视频的高复杂性导致捕捉底层几何结构的挑战,阻碍运动线索的融入。
- 通过测试时优化来解决数据复杂性,实现运动融合与优化之间的协同作用。
点此查看论文截图