⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-10 更新
CLaMR: Contextualized Late-Interaction for Multimodal Content Retrieval
Authors:David Wan, Han Wang, Elias Stengel-Eskin, Jaemin Cho, Mohit Bansal
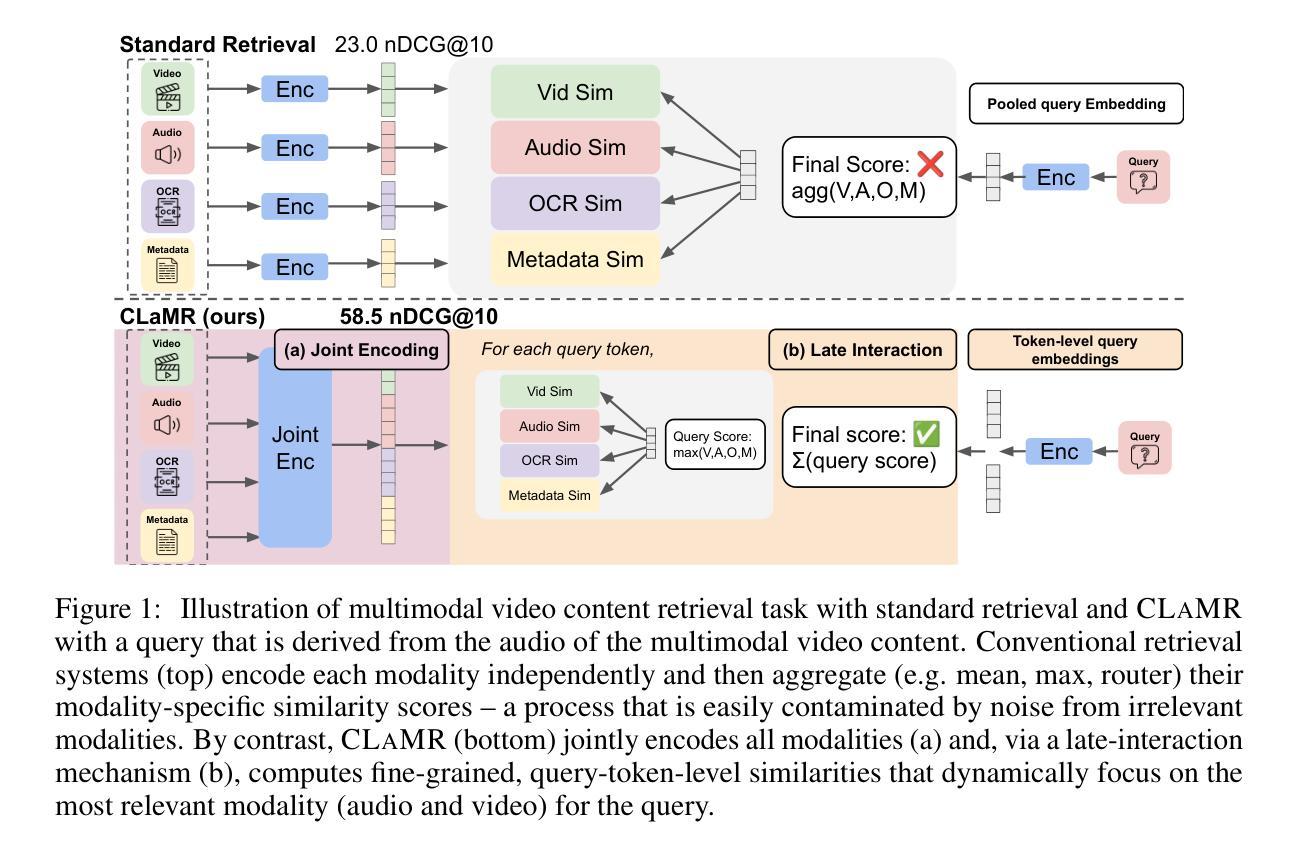
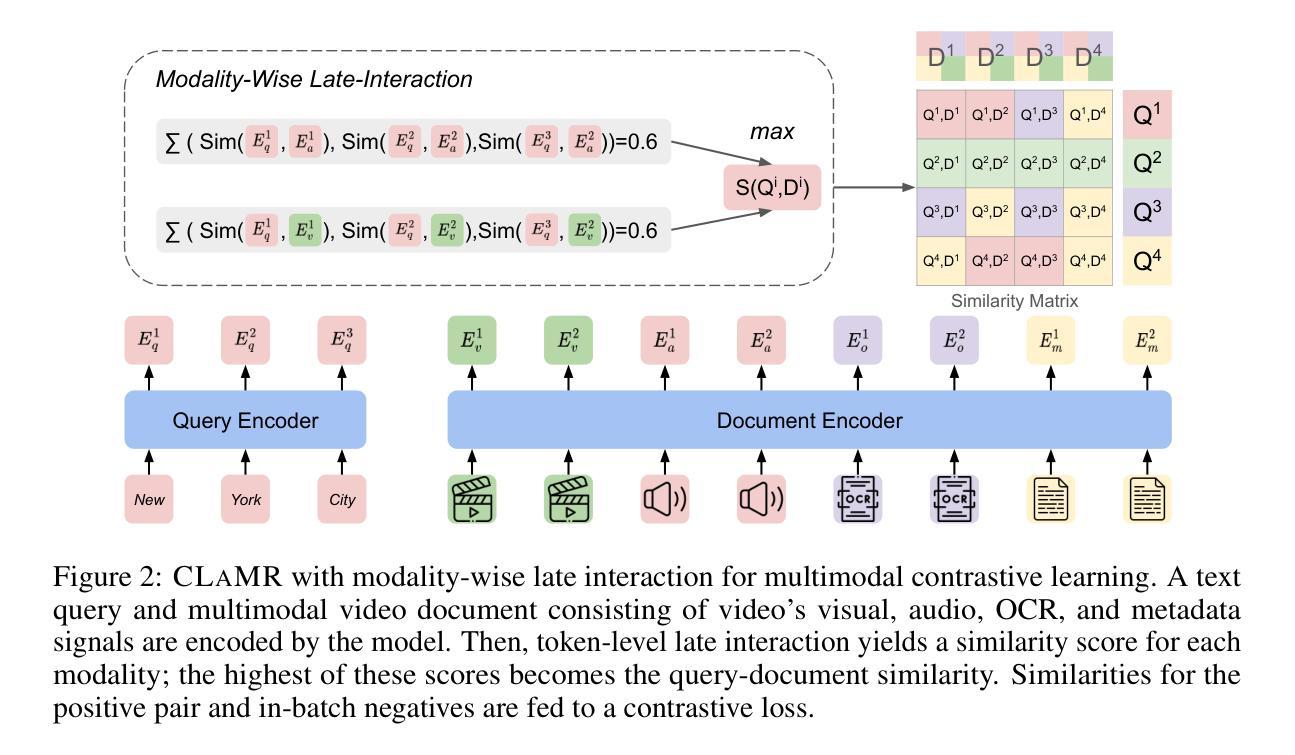
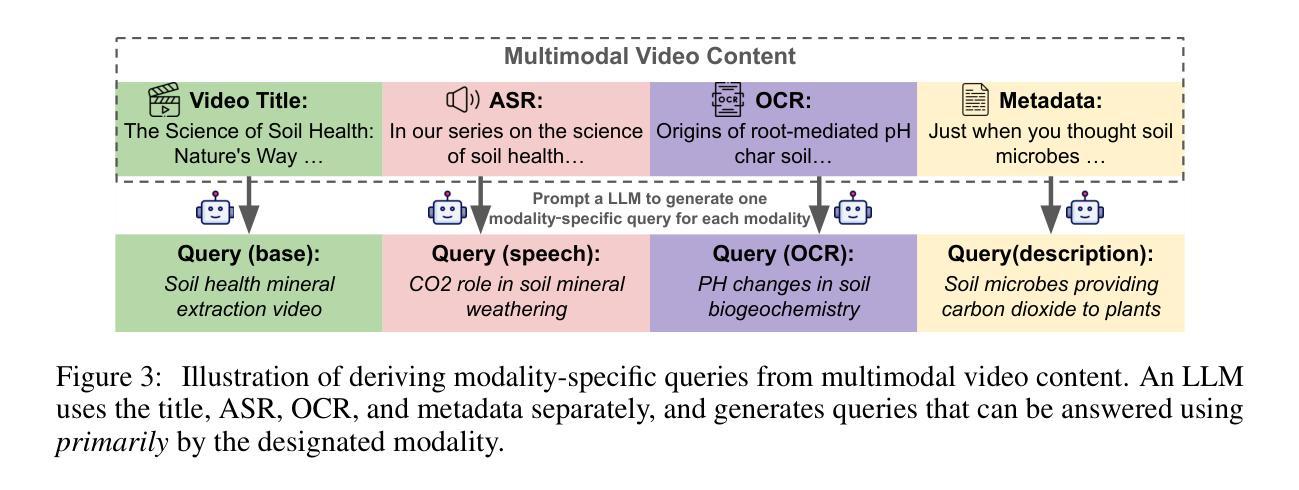
Online video web content is richly multimodal: a single video blends vision, speech, ambient audio, and on-screen text. Retrieval systems typically treat these modalities as independent retrieval sources, which can lead to noisy and subpar retrieval. We explore multimodal video content retrieval, where relevance can be scored from one particular modality or jointly across multiple modalities simultaneously. Consequently, an effective retriever must dynamically choose which modality (or set of modalities) best addresses the query. We introduce CLaMR, a multimodal, late-interaction retriever that jointly indexes 4 modalities: video frames, transcribed speech, on-screen text, and metadata. CLaMR jointly encodes all modalities with a unified multimodal backbone for improved contextualization and is trained to enhance dynamic modality selection via two key innovations. First, given the lack of training data for multimodal retrieval, we introduce MultiVENT 2.0++, a large-scale synthetic training dataset built on MultiVENT 2.0 (event-centric videos in various languages paired with queries) with modality-targeted queries. Next, we propose a modality-aware loss that jointly trains according to a standard contrastive objective alongside an objective for learning correct modality usage. On the test sets of MultiVENT 2.0++ and MSRVTT, conventional aggregation strategies, such as averaging similarities for baseline retrievers, degrade performance by introducing noise from irrelevant modalities. In contrast, CLaMR consistently outperforms existing retrievers: on MultiVENT 2.0++, CLaMR improves nDCG@10 by 25.6 over the best single-modality retriever and by 35.4 over the best multi-modality retriever. We illustrate CLaMR’s downstream utility on long-video QA, retrieving relevant frames and obtaining a 3.50% boost over LanguageBind on Video-MME and 1.42% over dense sampling on LongVideoBench.
在线视频网络内容具有丰富的多模态性:单个视频融合了视觉、语音、环境音频和屏幕文本。检索系统通常将这些模态视为独立的检索源,这可能导致检索结果嘈杂且质量不佳。我们探索多模态视频内容检索,其中相关性可以来自某一特定模态或同时来自多个模态。因此,有效的检索器必须动态选择最能满足查询需求的模态(或模态集)。我们介绍了CLaMR,这是一种多模态、晚期交互检索器,可以同时索引四种模态:视频帧、转录语音、屏幕文本和元数据。CLaMR使用统一的多模态主干进行所有模态的联合编码,以改进上下文化,并经过两项关键创新培训以增强动态模态选择。首先,鉴于缺乏多模态检索的训练数据,我们引入了基于MultiVENT 2.0的大型合成训练数据集升级版MultiVENT 2.0++(以各种语言为中心事件的视频与查询配对,带有模态目标查询)。接下来,我们提出了一种模态感知损失,根据标准对比目标和一个用于学习正确模态使用目标的联合训练。在MultiVENT 2.0++和MSRVTT的测试集上,传统的聚合策略(如基线检索器的平均相似性)会引入来自不相关模态的噪声,从而降低了性能。相比之下,CLaMR始终优于现有检索器:在MultiVENT 2.0++上,CLaMR比最佳单模态检索器的nDCG@10提高了25.6,比最佳多模态检索器提高了35.4。我们在长视频问答中展示了CLaMR的下游实用性,通过检索相关帧并在Video-MME上提高了3.5%,在LongVideoBench上的密集采样提高了1.42%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages. Code and data: https://github.com/meetdavidwan/clamr
Summary
本文探讨了在线视频内容的丰富多模态特性,并介绍了CLaMR这一多模态晚期交互检索系统。CLaMR能够联合索引视频帧、转录语音、屏幕文本和元数据等四种模态,通过统一的多模态主干进行联合编码,提高上下文信息的质量。针对多模态检索训练数据不足的问题,文章引入了MultiVENT 2.0++大规模合成训练数据集和模态感知损失函数,以提高动态模态选择能力。实验结果表明,与传统聚合策略相比,CLaMR在多模态视频检索任务上表现出更好的性能,能够有效提高视频检索的准确度。同时,CLaMR在长视频问答等下游任务中也有良好的表现。
Key Takeaways
- 在线视频内容丰富多样,涉及多个模态,包括视觉、语音、文本和元数据。这些模态通常以独立的方式进行处理,可能导致检索结果嘈杂和不理想。
- CLaMR是一个多模态晚期交互检索系统,能够联合索引视频的四种模态并进行统一编码,提高上下文信息的质量。
- CLaMR通过引入MultiVENT 2.0++合成训练数据集和模态感知损失函数来解决多模态检索训练数据不足的问题。
- CLaMR在动态模态选择方面表现出卓越的能力,在多模态视频检索任务上的性能优于传统聚合策略。
- CLaMR在长视频问答等下游任务中也有良好的表现,显示出其在实际应用中的价值。
点此查看论文截图

Quality Assessment of Noisy and Enhanced Speech with Limited Data: UWB-NTIS System for VoiceMOS 2024 and Beyond
Authors:Marie Kunešová
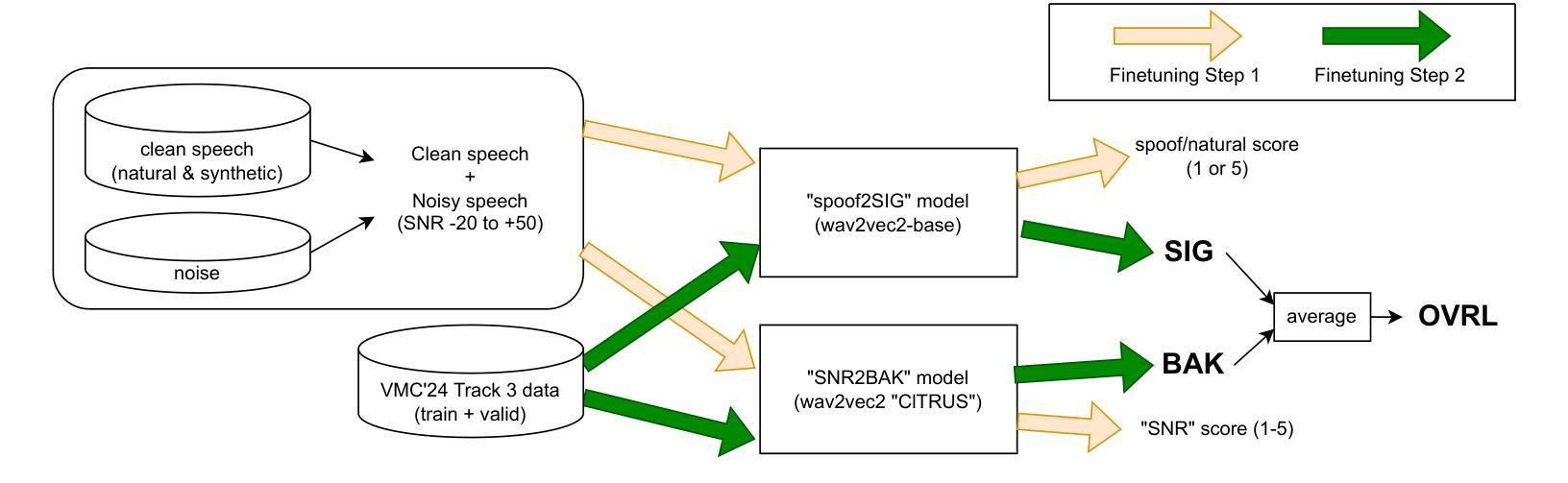
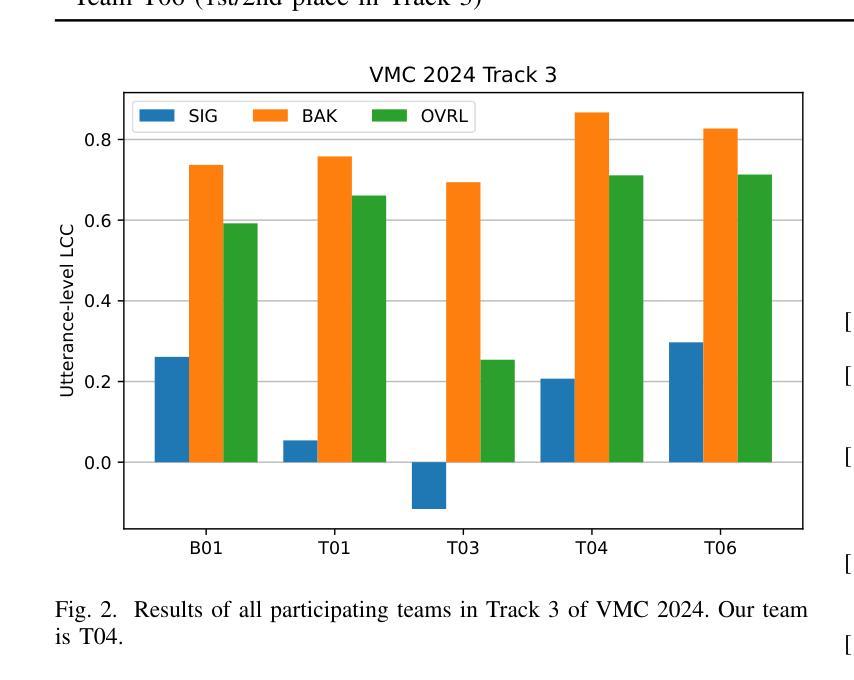
In this preprint, we present the UWB-NTIS-TTS team’s submission to Track 3 of the VoiceMOS 2024 Challenge, the goal of which was to automatically assess the speech quality of noisy and de-noised speech in terms of the ITU-T P.835 metrics of “SIG”, “BAK”, and “OVRL”. Our proposed system, based on wav2vec 2.0, placed among the top systems in the challenge, achieving the best prediction of the BAK scores (background noise intrusiveness), the second-best prediction of the OVRL score (overall audio quality), and the third-best prediction of SIG (speech signal quality) out of the five participating systems. We describe our approach, such as the two-stage fine-tuning process we used to contend with the challenge’s very limiting restrictions on allowable training data, and present the results achieved both on the VoiceMOS 2024 Challenge data and on the recently released CHiME 7 - UDASE dataset.
在这篇预印本中,我们展示了UWB-NTIS-TTS团队对VoiceMOS 2024挑战赛Track 3的提交内容。该挑战赛的目标是自动评估带噪和降噪语音的语音质量,具体参照ITU-T P.835指标的“SIG”(语音信号质量)、“BAK”(背景噪声侵入性)和“OVRL”(总体音频质量)。我们提出的基于wav2vec 2.0的系统在挑战中排名靠前,实现了最佳的BAK分数(背景噪声侵入性预测)、第二好的OVRL分数(总体音频质量预测)和第三好的SIG分数(语音信号质量预测),在五个参赛系统中脱颖而出。我们描述了我们的方法,例如我们用来应对挑战赛对可用训练数据有着非常严格限制的两阶段微调过程,并展示了在VoiceMOS 2024挑战赛数据和最近发布的CHiME 7 - UDASE数据集上取得的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This is a preliminary write-up of our initial work, posted as an early version preprint for cross-referencing purposes. We intend to further extend this research and submit it for publication at a conference, at which point this preprint will be updated with the full text. v2 changes: Fixed CHiME 7 - UDASE dataset overlapping with VMC 2024 training data
Summary
本文介绍了UWB-NTIS-TTS团队在VoiceMOS 2024挑战赛的Track 3中的提交内容。该团队的目标是根据ITU-T P.835指标自动评估噪声和降噪语音的语音质量,包括“SIG”(语音信号质量)、“BAK”(背景噪声侵入性)和“OVRL”(总体音频质量)。基于wav2vec 2.0的提案系统在挑战赛中名列前茅,在BAK评分预测上获得最佳成绩,在OVRL评分预测上获得第二名,在SIG评分预测上获得第三名。文章阐述了团队的方法,包括应对挑战中严格限制训练数据的两阶段微调过程,并在VoiceMOS 2024挑战数据和最新发布的CHiME 7 - UDASE数据集上取得了成果。
Key Takeaways
- UWB-NTIS-TTS团队参加了VoiceMOS 2024挑战赛的Track 3,目标为自动评估噪声和降噪语音的ITU-T P.835指标语音质量。
- 团队使用基于wav2vec 2.0的系统参与挑战,表现出色。
- 团队在BAK评分预测上获得最佳成绩,OVRL评分预测获得第二名,SIG评分预测获得第三名。
- 团队采用了两阶段微调方法来应对挑战中严格限制的训练数据。
- 团队在VoiceMOS 2024挑战数据和CHiME 7 - UDASE数据集上进行了实验并获得了成果。
- 此预印本详细描述了团队的方法、实验设置和结果。
点此查看论文截图

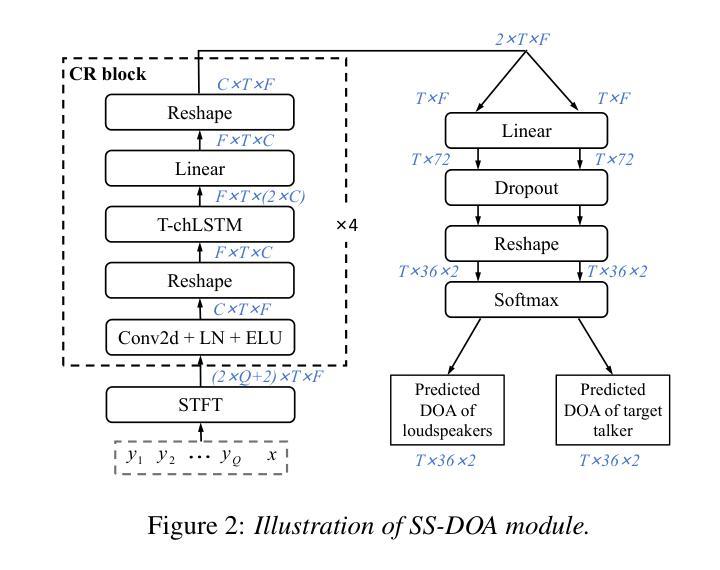
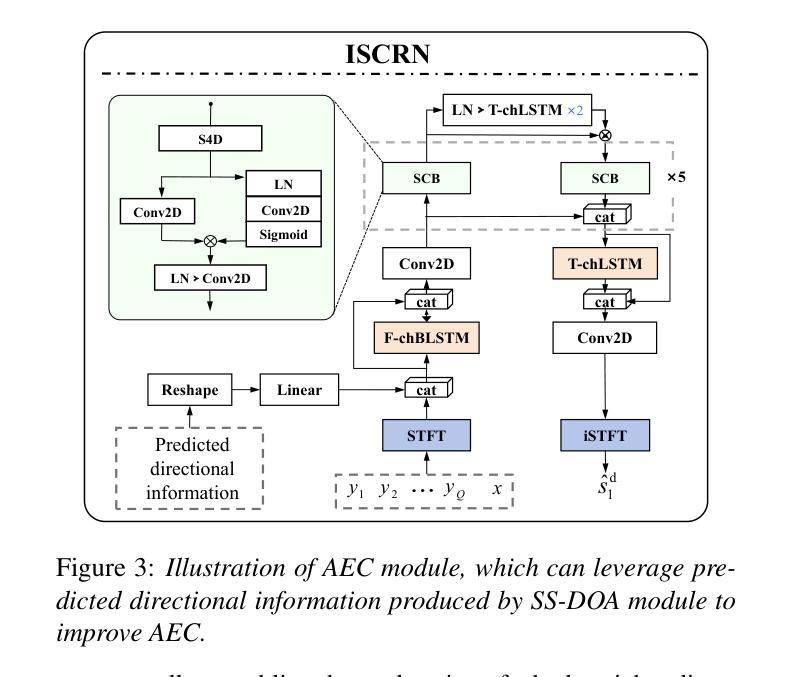
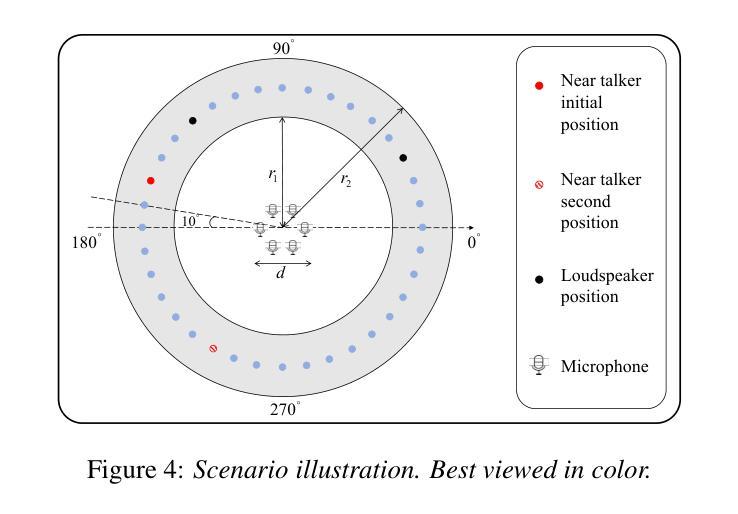
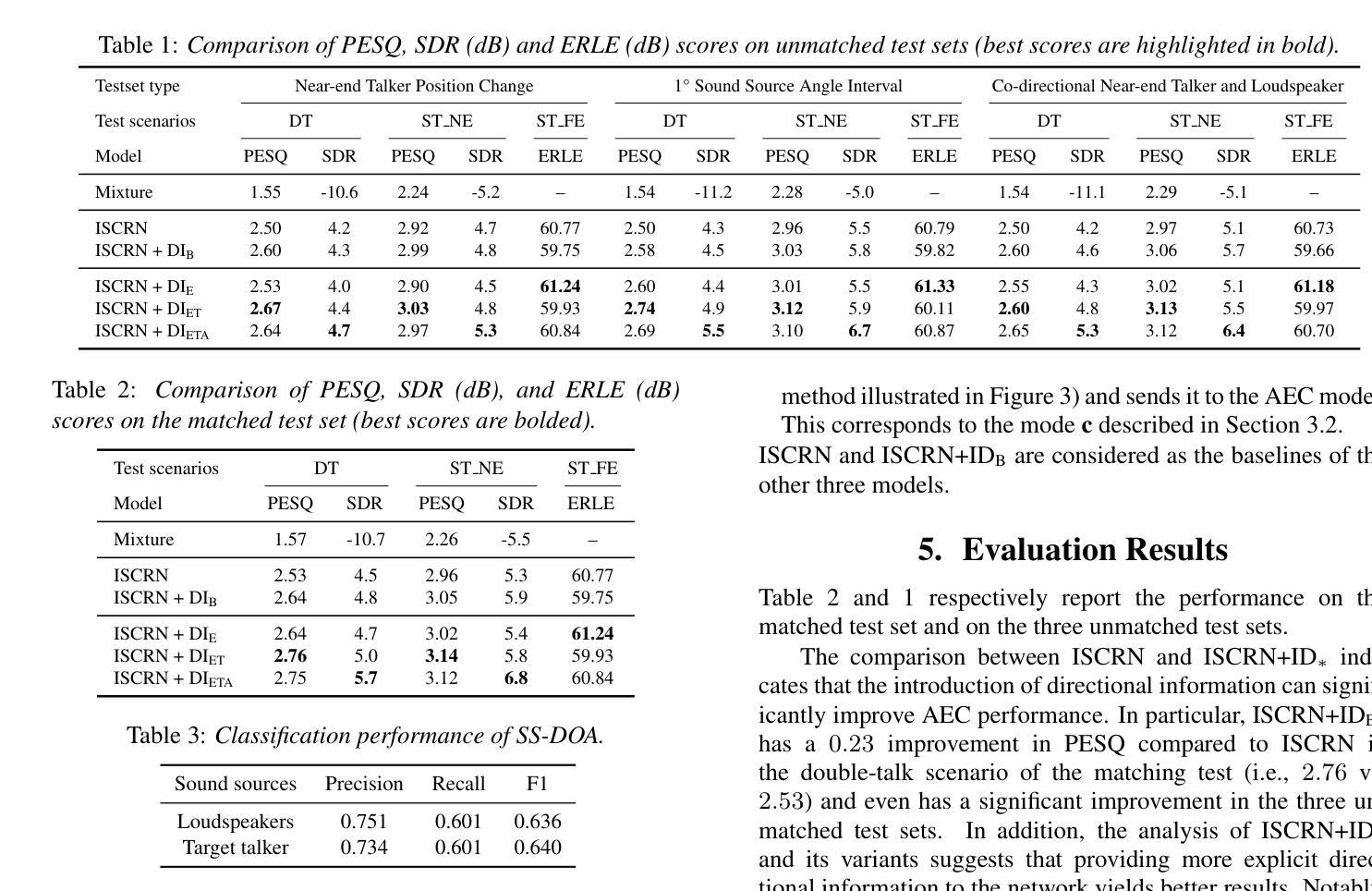
Multi-Channel Acoustic Echo Cancellation Based on Direction-of-Arrival Estimation
Authors:Fei Zhao, Xueliang Zhang, Zhong-Qiu Wang
Acoustic echo cancellation (AEC) is an important speech signal processing technology that can remove echoes from microphone signals to enable natural-sounding full-duplex speech communication. While single-channel AEC is widely adopted, multi-channel AEC can leverage spatial cues afforded by multiple microphones to achieve better performance. Existing multi-channel AEC approaches typically combine beamforming with deep neural networks (DNN). This work proposes a two-stage algorithm that enhances multi-channel AEC by incorporating sound source directional cues. Specifically, a lightweight DNN is first trained to predict the sound source directions, and then the predicted directional information, multi-channel microphone signals, and single-channel far-end signal are jointly fed into an AEC network to estimate the near-end signal. Evaluation results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms baseline approaches and exhibits robust generalization across diverse acoustic environments.
声学回声消除(AEC)是一项重要的语音信号处理技术,可以从麦克风信号中消除回声,以实现自然的全双工语音通信。虽然单通道AEC已得到广泛应用,但多通道AEC可以利用多个麦克风提供的空间线索来实现更好的性能。现有的多通道AEC方法通常将波束形成与深度神经网络(DNN)相结合。这项工作提出了一个两阶段的算法,通过融入声源方向线索来增强多通道AEC。具体来说,首先训练一个轻量级的DNN来预测声源方向,然后将预测的方向信息、多通道麦克风信号和单通道远端信号一起输入到AEC网络中来估计近端信号。评估结果表明,该算法优于基线方法,并在各种声学环境中表现出稳健的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Interspeech 2025
总结
本文提出了一种基于声音源方向线索的两阶段算法,用于增强多通道回声消除技术。该算法首先利用轻量级深度神经网络预测声音源方向,然后将预测的方位信息、多通道麦克风信号和单通道远端信号一起输入回声消除网络,以估计近端信号。评估结果表明,该算法优于基线方法,并在各种声学环境中表现出稳健的泛化能力。
关键见解
- 多通道回声消除技术能利用多个麦克风的空间线索实现更好的性能。
- 现有方法通常结合波束形成和深度神经网络进行多通道回声消除。
- 本文提出了一种新的两阶段算法,融入声音源方向线索,以提升多通道回声消除效果。
- 在预测声音源方向后,算法使用预测的方位信息等多数据输入进行回声消除网络估计。
- 该算法在多种声学环境下的性能表现稳健,且优于基线方法。
- 提出的算法结构有助于提升语音通信的自然度和质量。
点此查看论文截图


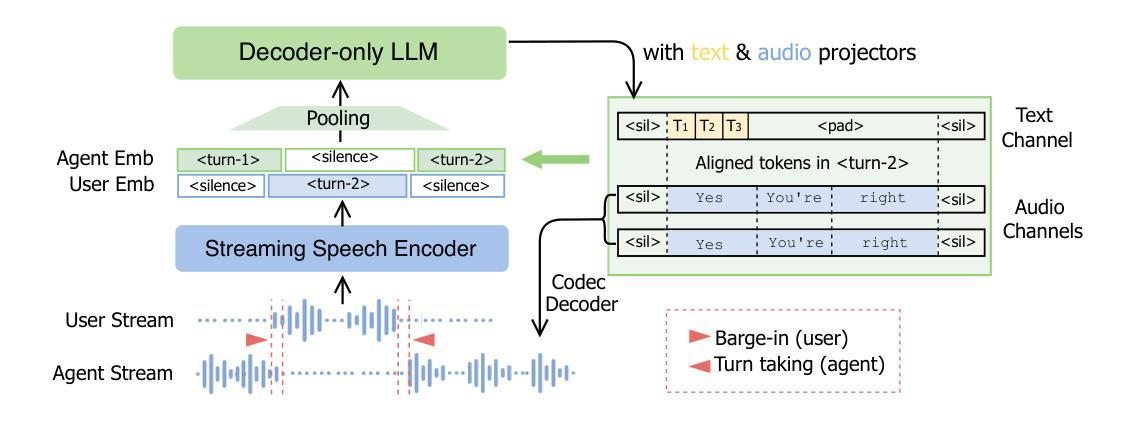
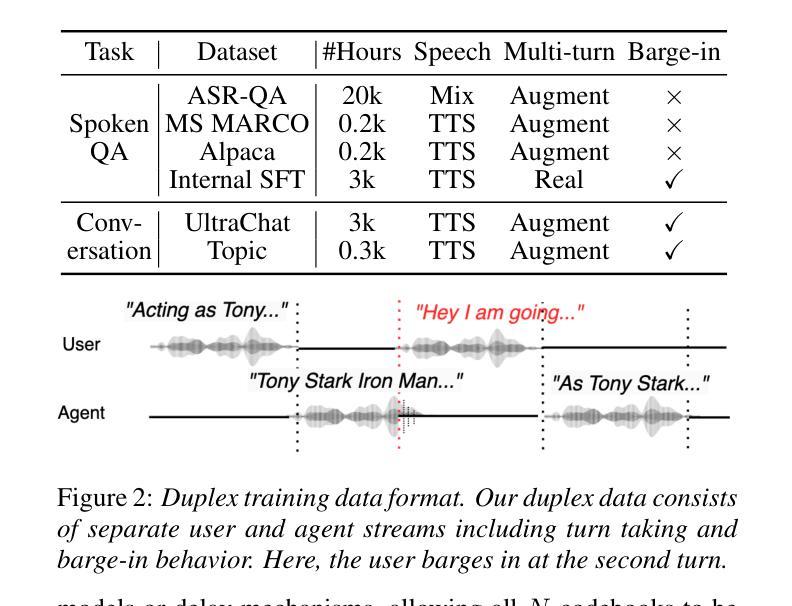
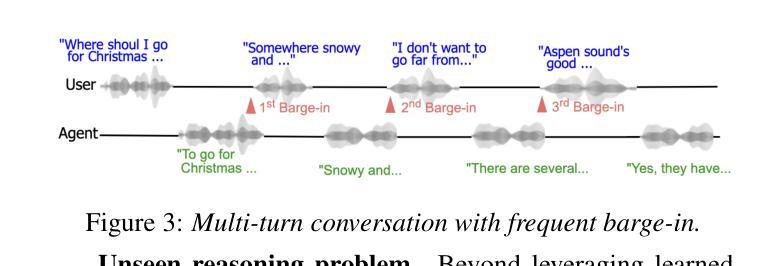
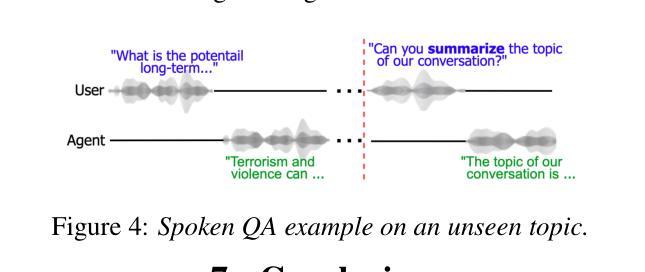
Efficient and Direct Duplex Modeling for Speech-to-Speech Language Model
Authors:Ke Hu, Ehsan Hosseini-Asl, Chen Chen, Edresson Casanova, Subhankar Ghosh, Piotr Żelasko, Zhehuai Chen, Jason Li, Jagadeesh Balam, Boris Ginsburg
Spoken dialogue is an intuitive form of human-computer interaction, yet current speech language models often remain constrained to turn-based exchanges, lacking real-time adaptability such as user barge-in. We propose a novel duplex speech to speech (S2S) architecture featuring continuous user inputs and codec agent outputs with channel fusion that directly models simultaneous user and agent streams. Using a pretrained streaming encoder for user input enables the first duplex S2S model without requiring speech pretrain. Separate architectures for agent and user modeling facilitate codec fine-tuning for better agent voices and halve the bitrate (0.6 kbps) compared to previous works. Experimental results show that the proposed model outperforms previous duplex models in reasoning, turn-taking, and barge-in abilities. The model requires significantly less speech data, as speech pretrain is skipped, which markedly simplifies the process of building a duplex S2S model from any LLMs. Finally, it is the first openly available duplex S2S model with training and inference code to foster reproducibility.
口语对话是人类与计算机交互的一种直观形式。然而,当前的语音语言模型通常仅限于基于回合的交互,缺乏实时适应性,如用户抢话等。我们提出了一种新型的双语语音到语音(S2S)架构,具有连续用户输入和编解码器代理输出,通过通道融合直接模拟用户和代理的同时流。使用预训练的流式编码器进行用户输入,使得第一个双语S2S模型无需语音预训练。对代理和用户建模的单独架构有助于对编解码器进行微调,以产生更好的代理声音,并将比特率与以前的工作相比减半(0.6kbps)。实验结果表明,该模型在推理、话轮控制和抢话能力方面超过了之前的双语模型。该模型不需要大量语音数据,因为跳过了语音预训练,这显著简化了从任何大型语言模型构建双语S2S模型的过程。最后,它是第一个公开可用的带有训练和推理代码的双语S2S模型,促进了可重复性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的双向语音转语音(Duplex Speech to Speech,简称S2S)架构,该架构支持用户连续输入和代理实时输出,并具有信道融合功能,能够直接模拟用户和代理的语音流。该架构使用预训练的流式编码器对用户输入进行建模,无需语音预训练即可实现首个Duplex S2S模型。通过分离代理和用户建模架构,优化了代理声音的编码和精细调整,并降低了与之前研究相比的比特率(0.6 kbps)。实验结果表明,该模型在推理、轮替和打断能力方面优于之前的Duplex模型。此外,该模型无需大量的语音数据,简化了任何大型语言模型的Duplex S2S模型的构建过程。它是首个公开提供训练和推理代码的Duplex S2S模型,有助于促进可重复性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出的Duplex S2S架构支持连续用户输入和代理实时输出。
- 该架构具有信道融合功能,能够直接模拟用户和代理的语音流。
- 使用预训练的流式编码器对用户输入进行建模,无需语音预训练。
- 分离代理和用户建模架构以优化代理声音的编码和精细调整。
- 与之前的研究相比,降低了比特率(0.6 kbps)。
- 该模型在推理、轮替和打断能力方面优于之前的Duplex模型。
点此查看论文截图


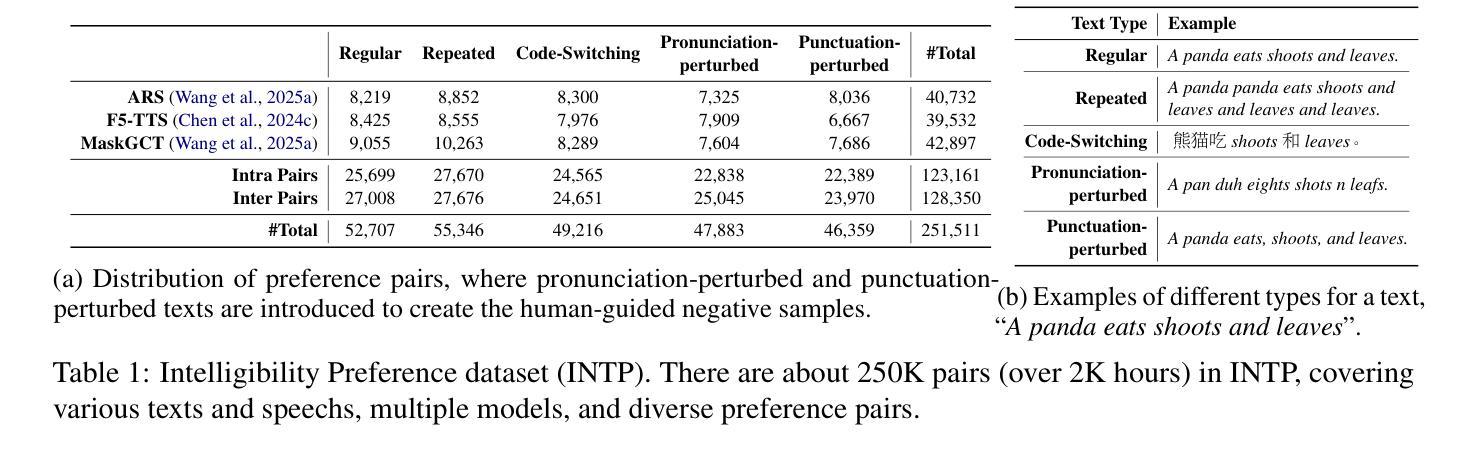
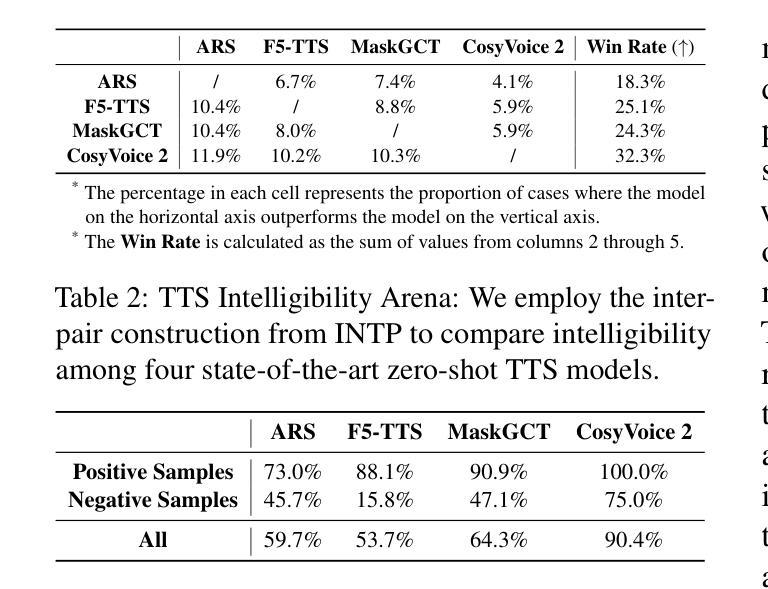
Advancing Zero-shot Text-to-Speech Intelligibility across Diverse Domains via Preference Alignment
Authors:Xueyao Zhang, Yuancheng Wang, Chaoren Wang, Ziniu Li, Zhuo Chen, Zhizheng Wu
Modern zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) systems, despite using extensive pre-training, often struggle in challenging scenarios such as tongue twisters, repeated words, code-switching, and cross-lingual synthesis, leading to intelligibility issues. To address these limitations, this paper leverages preference alignment techniques, which enable targeted construction of out-of-pretraining-distribution data to enhance performance. We introduce a new dataset, named the Intelligibility Preference Speech Dataset (INTP), and extend the Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) framework to accommodate diverse TTS architectures. After INTP alignment, in addition to intelligibility, we observe overall improvements including naturalness, similarity, and audio quality for multiple TTS models across diverse domains. Based on that, we also verify the weak-to-strong generalization ability of INTP for more intelligible models such as CosyVoice 2 and Ints. Moreover, we showcase the potential for further improvements through iterative alignment based on Ints. Audio samples are available at https://intalign.github.io/.
尽管现代零样本文本到语音(TTS)系统使用了大量的预训练,但在舌头打结、重复单词、代码切换和跨语言合成等挑战性场景中,它们通常会出现可理解性问题。为了解决这些局限性,本文采用偏好对齐技术,该技术能够构建超出预训练分布的数据,以提高性能。我们引入了一个新的数据集,名为“可理解性偏好语音数据集(INTP)”,并将直接偏好优化(DPO)框架扩展到适应多种TTS架构。除了可理解性之外,经过INTP对齐后,我们还观察到多个TTS模型在不同领域的整体改进,包括自然度、相似性和音频质量。基于此,我们还验证了INTP对于更可理解的模型(如CosyVoice 2和Ints)的弱到强泛化能力。此外,我们展示了通过基于Ints的迭代对齐进行进一步改进的潜力。音频样本可在https://intalign.github.io/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACL 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对现代零样本文本转语音(TTS)系统在挑战场景中的智能问题,采用偏好对齐技术来解决。文章引入了一个新的数据集——Intelligibility Preference Speech Dataset(INTP),并扩展了Direct Preference Optimization(DPO)框架以适应多种TTS架构。经过INTP对齐后,除了智能性提升外,还观察到多个TTS模型在不同领域中的整体改进,包括自然度、相似性和音质。此外,文章还验证了INTP对于CosyVoice 2和Ints等模型的弱到强泛化能力,并展示了通过迭代对齐进一步改进的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 现代零样本文本转语音(TTS)系统在挑战场景中如舌绽、重复词汇、语言转换和跨语言合成时存在智能问题。
- 为了解决这些问题,文章引入了偏好对齐技术。
- 引入了一个新的数据集——Intelligibility Preference Speech Dataset(INTP)。
- 扩展了Direct Preference Optimization(DPO)框架以适应多种TTS架构。
- 经过INTP对齐后,多个TTS模型的智能性、自然度、相似性和音质均有提升。
- 验证了INTP对于某些模型的弱到强泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

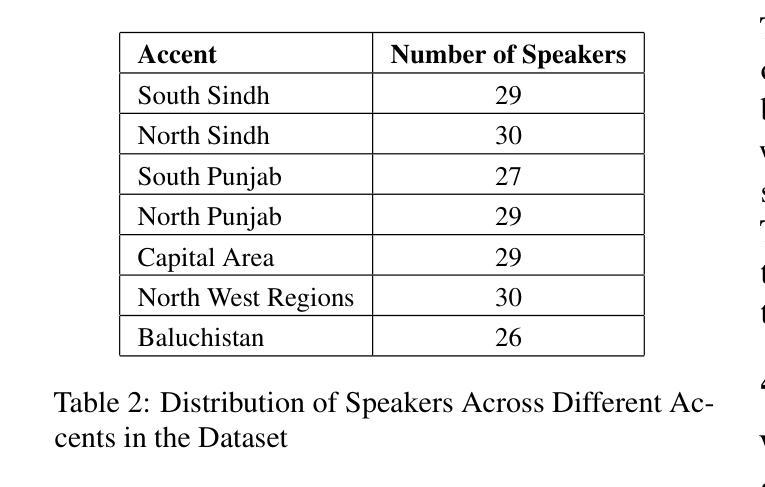
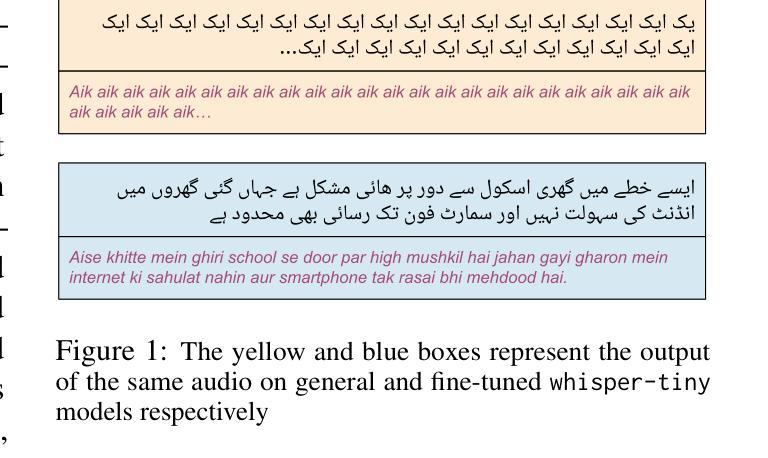
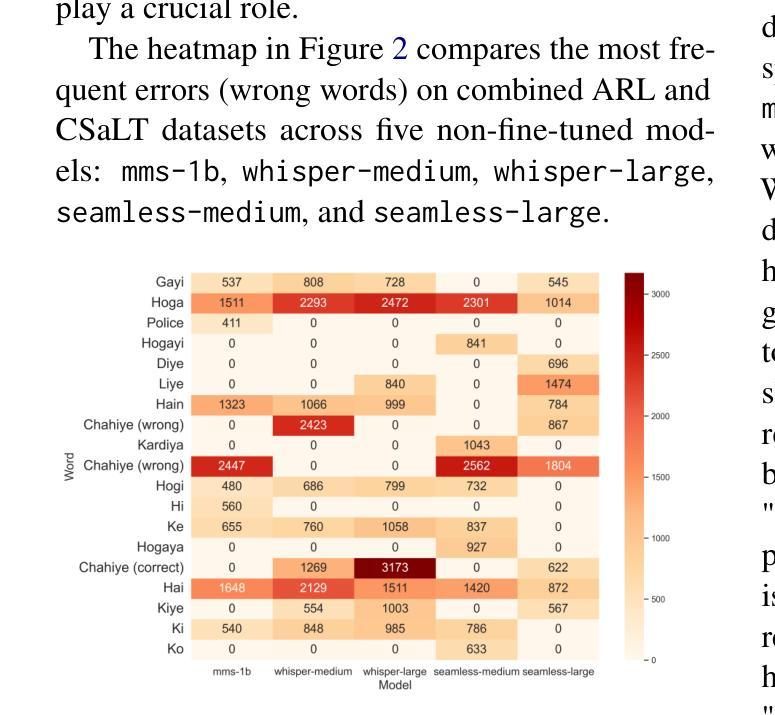
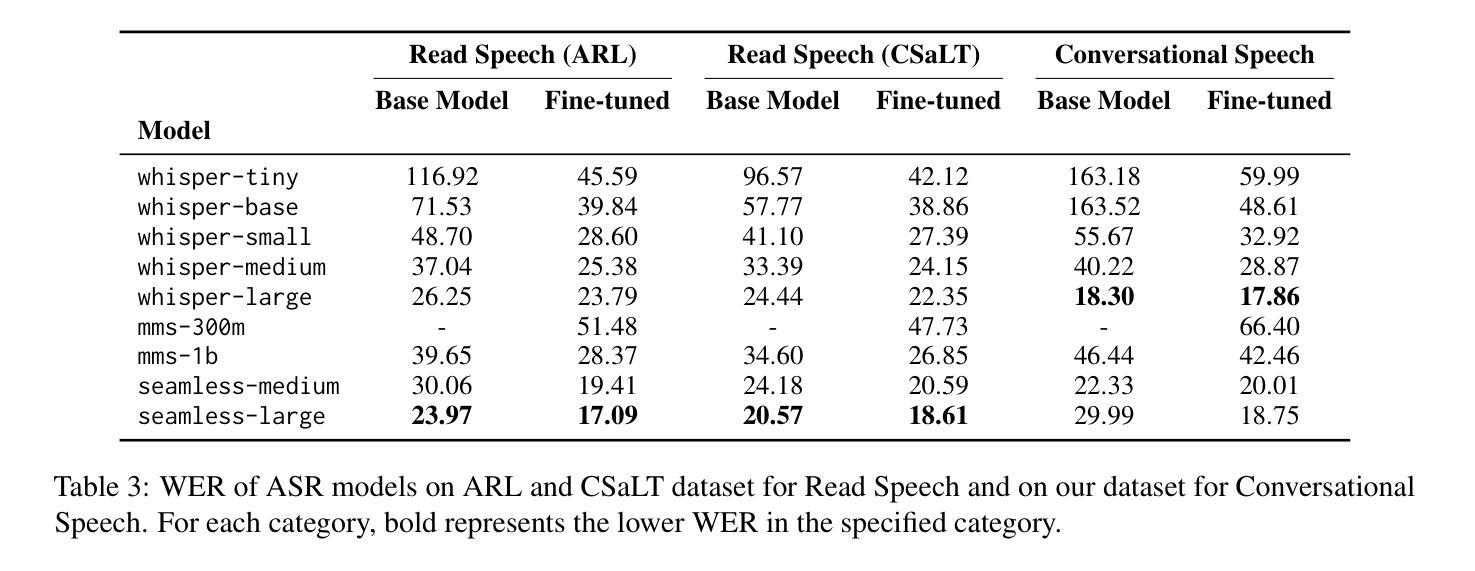
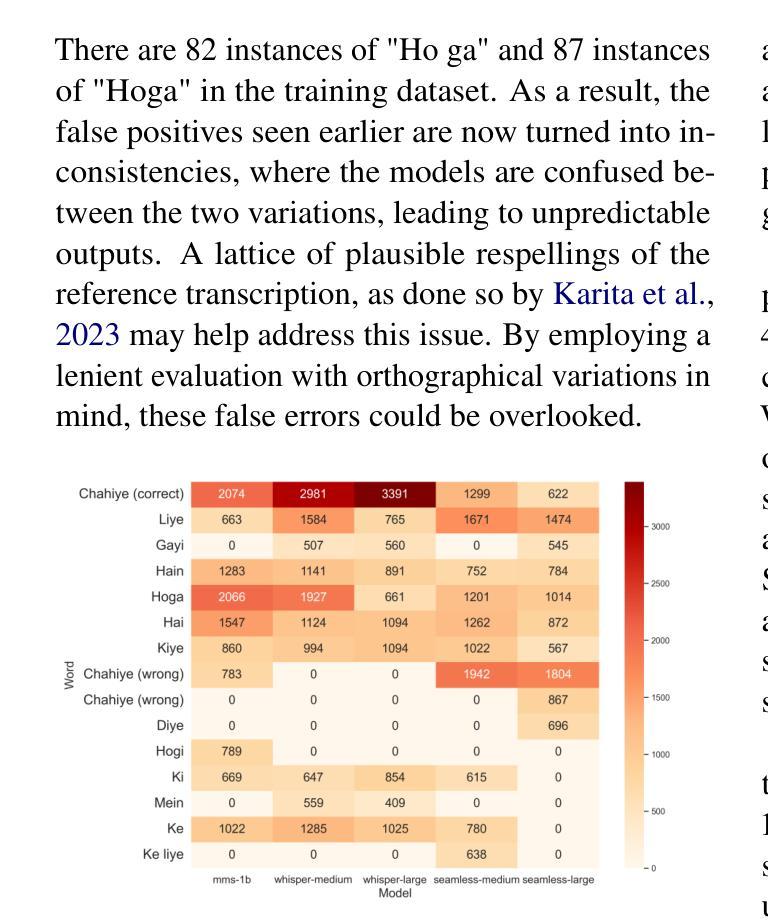
WER We Stand: Benchmarking Urdu ASR Models
Authors:Samee Arif, Sualeha Farid, Aamina Jamal Khan, Mustafa Abbas, Agha Ali Raza, Awais Athar
This paper presents a comprehensive evaluation of Urdu Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models. We analyze the performance of three ASR model families: Whisper, MMS, and Seamless-M4T using Word Error Rate (WER), along with a detailed examination of the most frequent wrong words and error types including insertions, deletions, and substitutions. Our analysis is conducted using two types of datasets, read speech and conversational speech. Notably, we present the first conversational speech dataset designed for benchmarking Urdu ASR models. We find that seamless-large outperforms other ASR models on the read speech dataset, while whisper-large performs best on the conversational speech dataset. Furthermore, this evaluation highlights the complexities of assessing ASR models for low-resource languages like Urdu using quantitative metrics alone and emphasizes the need for a robust Urdu text normalization system. Our findings contribute valuable insights for developing robust ASR systems for low-resource languages like Urdu.
本文全面评估了乌尔都语自动语音识别(ASR)模型。我们分析了三种ASR模型家族的表现:whisper、MMS和seamless-M4T,使用单词错误率(WER)以及详细检查最常出现的错误单词和错误类型,包括插入、删除和替换。我们的分析使用了两种数据集:朗读语音和对话语音。值得注意的是,我们推出了首个为基准测试乌尔都语ASR模型设计的对话语音数据集。我们发现无缝大型模型在阅读语音数据集上优于其他ASR模型,而whisper大型模型在对话语音数据集上表现最佳。此外,该评估强调了仅使用定量指标评估像乌尔都语这样的低资源语言的ASR模型的复杂性,并强调需要一个稳健的乌尔都语文本归一化系统。我们的发现为开发像乌尔都语这样的低资源语言的稳健ASR系统提供了宝贵的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文全面评估了乌尔都语自动语音识别(ASR)模型的表现。文章对Whisper、MMS和Seamless-M4T三种ASR模型家族进行了性能分析,使用词错误率(WER)作为评价指标,并详细研究了最常出现的错误词汇和错误类型,包括插入、删除和替换。文章在两个数据集(朗读语音和对话语音)上进行了分析,尤其推出了首个用于基准测试乌尔都语ASR模型的对话语音数据集。研究结果显示,在朗读语音数据集中,seamless-large表现最佳,而在对话语音数据集中,whisper-large表现最好。此外,本文强调了仅使用定量指标评估低资源语言如乌尔都语的ASR模型的复杂性,并强调了需要建立稳健的乌尔都语文本归一化系统。
Key Takeaways
- 论文对三种ASR模型家族在乌尔都语上的表现进行了全面评估。
- 通过词错误率(WER)作为主要评价指标,并对插入、删除和替换等错误类型进行了详细分析。
- 论文使用了朗读语音和对话语音两种数据集,并首次推出了用于乌尔都语ASR模型基准测试的对话语音数据集。
- seamless-large在朗读语音数据集中表现最佳,而whisper-large在对话语音数据集中表现最好。
- 论文强调了评估低资源语言如乌尔都语的ASR模型的复杂性,并指出需要更完善的定量指标。
- 文中强调了建立一个稳健的乌尔都语文本归一化系统的重要性。
点此查看论文截图