⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-10 更新
Kinetics: Rethinking Test-Time Scaling Laws
Authors:Ranajoy Sadhukhan, Zhuoming Chen, Haizhong Zheng, Yang Zhou, Emma Strubell, Beidi Chen
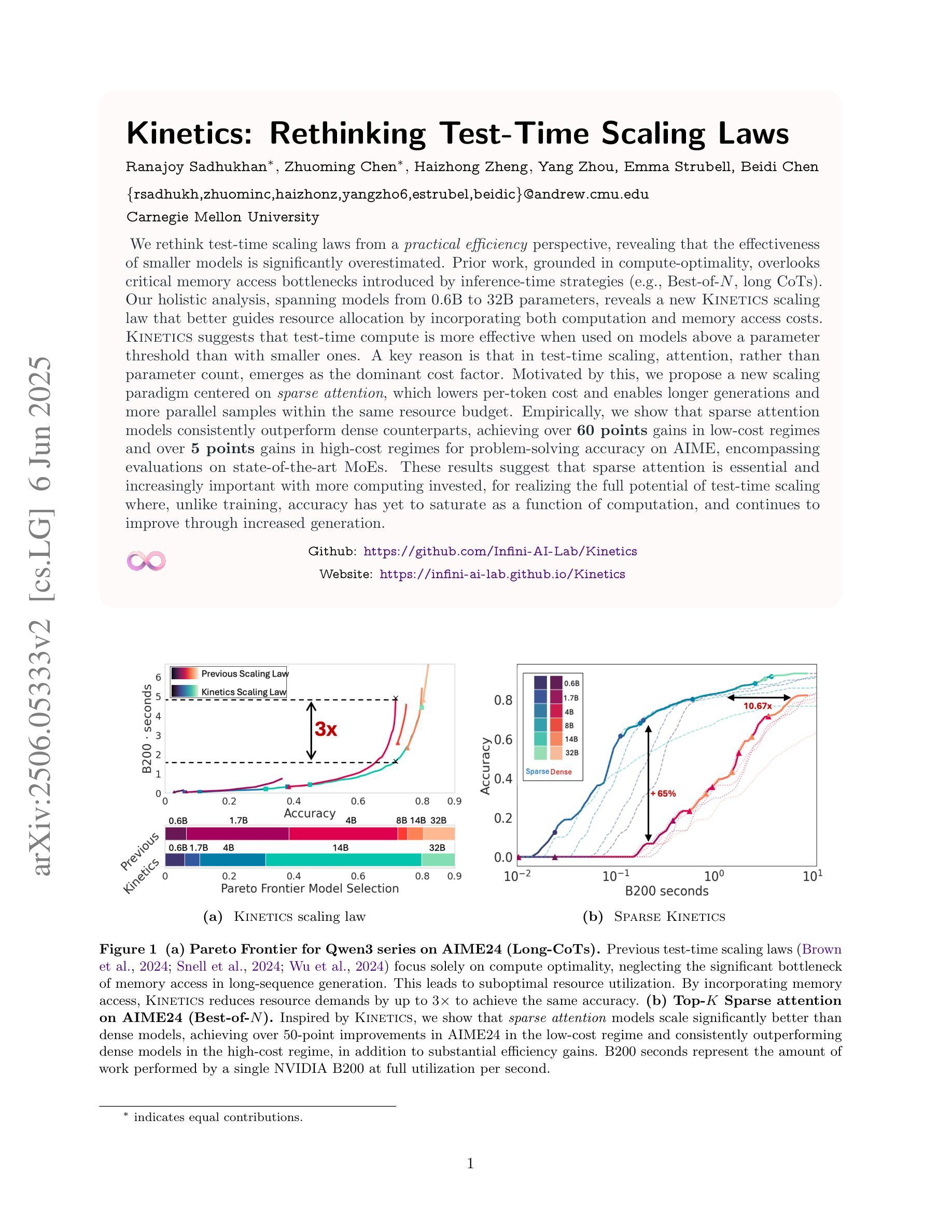
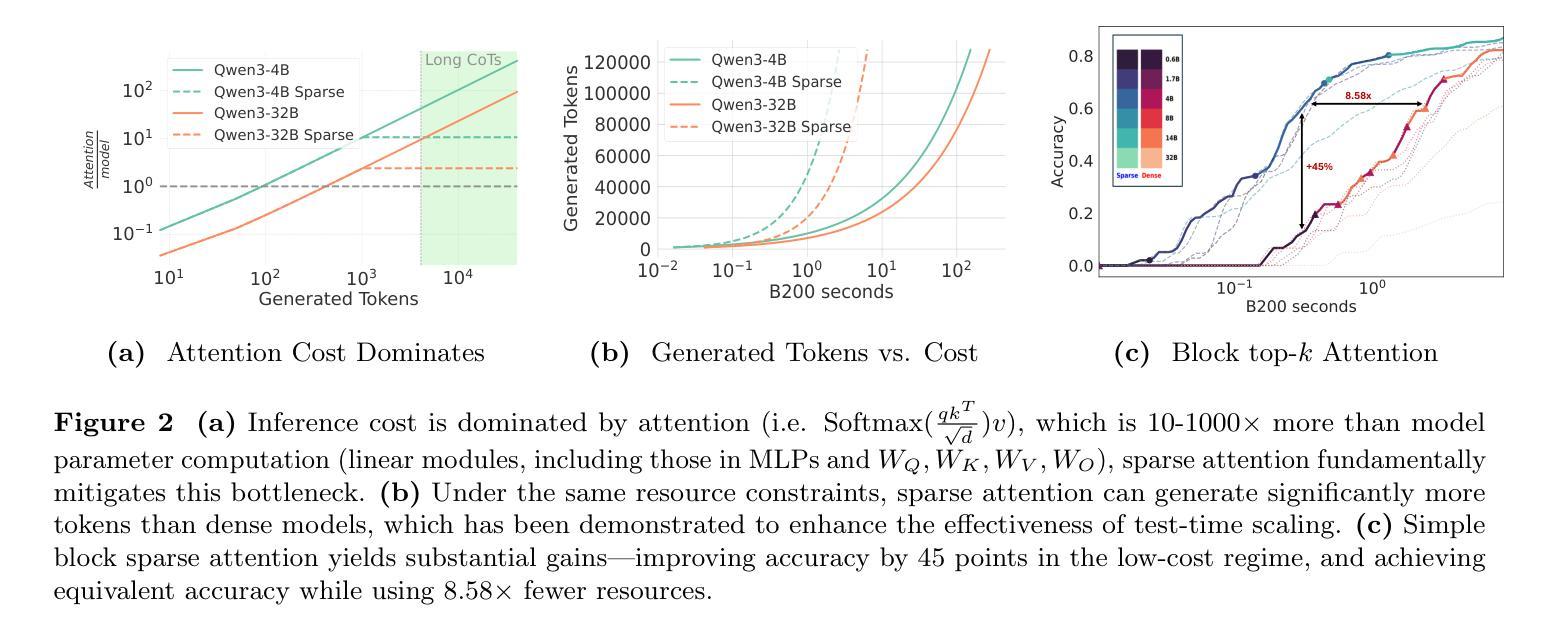
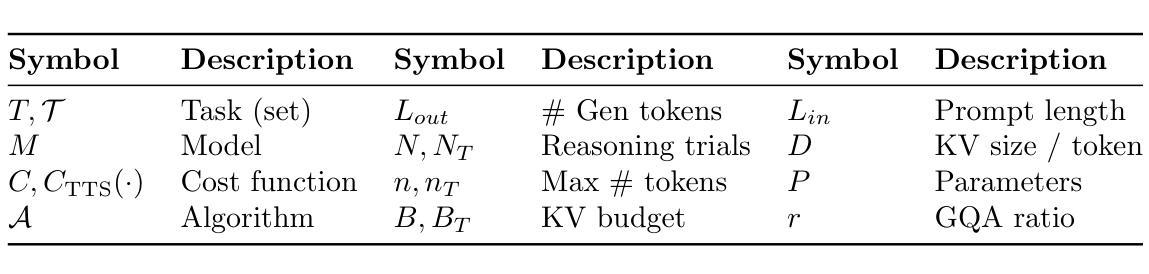
We rethink test-time scaling laws from a practical efficiency perspective, revealing that the effectiveness of smaller models is significantly overestimated. Prior work, grounded in compute-optimality, overlooks critical memory access bottlenecks introduced by inference-time strategies (e.g., Best-of-$N$, long CoTs). Our holistic analysis, spanning models from 0.6B to 32B parameters, reveals a new Kinetics Scaling Law that better guides resource allocation by incorporating both computation and memory access costs. Kinetics Scaling Law suggests that test-time compute is more effective when used on models above a threshold than smaller ones. A key reason is that in TTS, attention, rather than parameter count, emerges as the dominant cost factor. Motivated by this, we propose a new scaling paradigm centered on sparse attention, which lowers per-token cost and enables longer generations and more parallel samples within the same resource budget. Empirically, we show that sparse attention models consistently outperform dense counterparts, achieving over 60 points gains in low-cost regimes and over 5 points gains in high-cost regimes for problem-solving accuracy on AIME, encompassing evaluations on state-of-the-art MoEs. These results suggest that sparse attention is essential and increasingly important with more computing invested, for realizing the full potential of test-time scaling where, unlike training, accuracy has yet to saturate as a function of computation, and continues to improve through increased generation. The code is available at https://github.com/Infini-AI-Lab/Kinetics.
从实际效率的角度重新思考测试时的缩放规律,我们发现对较小模型的效率估计过高。之前的工作以计算最优为基础,忽视了推理时策略(如Best-of-$N$、长CoTs)引入的关键内存访问瓶颈。我们对从0.6B到32B参数的模型进行了整体分析,揭示了一种新的动力学缩放定律,通过结合计算和内存访问成本来更好地指导资源分配。动力学缩放定律表明,在模型达到某个阈值以上时,测试时的计算更为有效。其中的关键原因是,在TTS中,注意力而不是参数数量成为主导成本因素。受此启发,我们提出了一种以稀疏注意力为中心的新缩放范式,这降低了每令牌的成本,并在相同的资源预算内实现了更长的生成和更并行的样本。经验表明,稀疏注意力模型持续优于密集模型,在AIME上解决问题准确性方面取得了超过60分的低成本领域增益和超过5点的高成本领域增益,包括基于最新MoEs的评估。这些结果表明,在投入更多计算的情况下,稀疏注意力对于实现测试时缩放的全部潜力至关重要,而且在测试时,与训练不同,准确性作为计算的功能尚未饱和,并且通过增加生成次数继续改进。相关代码可通过https://github.com/Infini-AI-Lab/Kinetics获取。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文从实际效率的角度重新思考了测试时间缩放定律,发现小型模型的效率被高估了。之前的工作基于计算最优性,忽视了推理时间策略(例如Best-of-$N$,长CoTs)引入的关键内存访问瓶颈。我们对从0.6B到32B参数的模型进行了整体分析,揭示了一个新的动力学缩放定律,它更好地指导资源分配,同时考虑计算和内存访问成本。动力学缩放定律表明,在测试时,对超过阈值的模型使用计算资源比小型模型更有效。其中的关键原因是,在文本到语音合成(TTS)中,注意力而非参数数量成为主导成本因素。受此启发,我们提出了以稀疏注意力为中心的新缩放范式,这降低了每令牌的成本,并在相同的资源预算内实现了更长的生成和更多的并行样本。经验表明,稀疏注意力模型在AIME的问题解决准确性上始终优于密集模型,在低成本领域获得超过60分的增益,在高成本领域获得超过5分的增益,涵盖了最先进的多门限评估。这些结果表明,在测试时间缩放中,特别是在准确度尚未达到饱和的计算中,稀疏注意力是不可或缺的,随着计算投入的增加,其重要性日益凸显。
关键见解
- 重新评估了测试时间缩放定律,指出小型模型的效率被高估。
- 指出先前的研究忽视了推理时间策略导致的内存访问瓶颈。
- 提出了一个新的动力学缩放定律,综合考虑计算和内存访问成本。
- 动力学缩放定律显示测试时计算对较大模型更有效。
- 在文本到语音合成中,注意力是成本的主导因素。
- 引入稀疏注意力为中心的新缩放范式,降低每令牌的成本。
- 实证表明稀疏注意力模型在问题解决准确性上优于密集模型,特别是在不同的计算成本领域。
点此查看论文截图
Quality Assessment of Noisy and Enhanced Speech with Limited Data: UWB-NTIS System for VoiceMOS 2024 and Beyond
Authors:Marie Kunešová
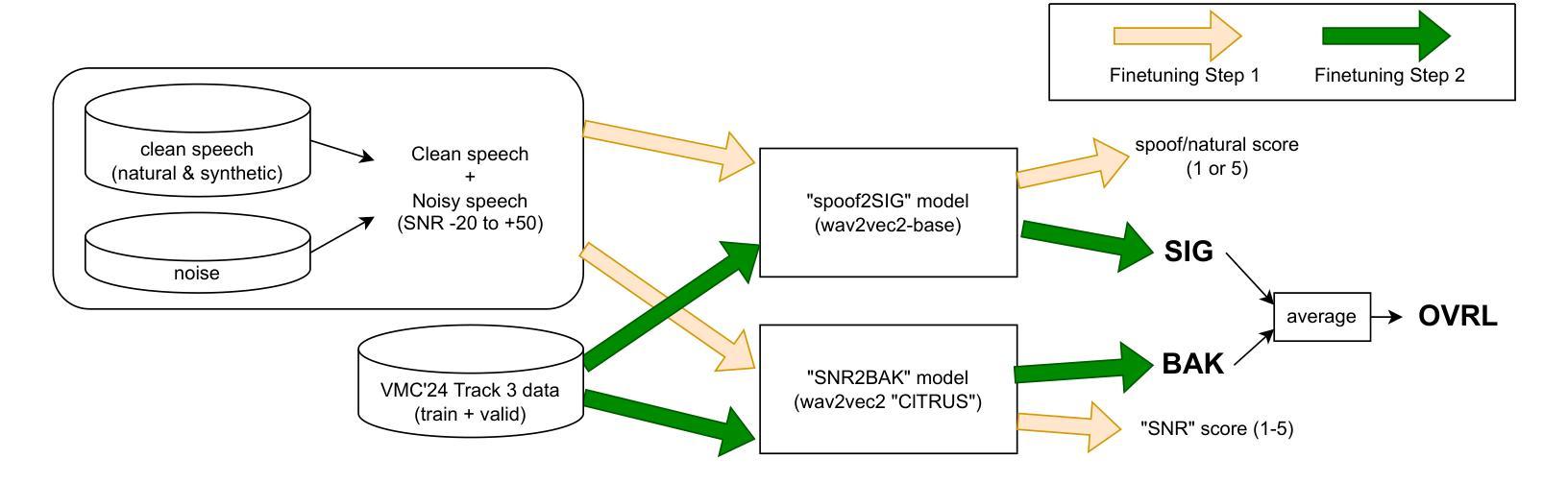
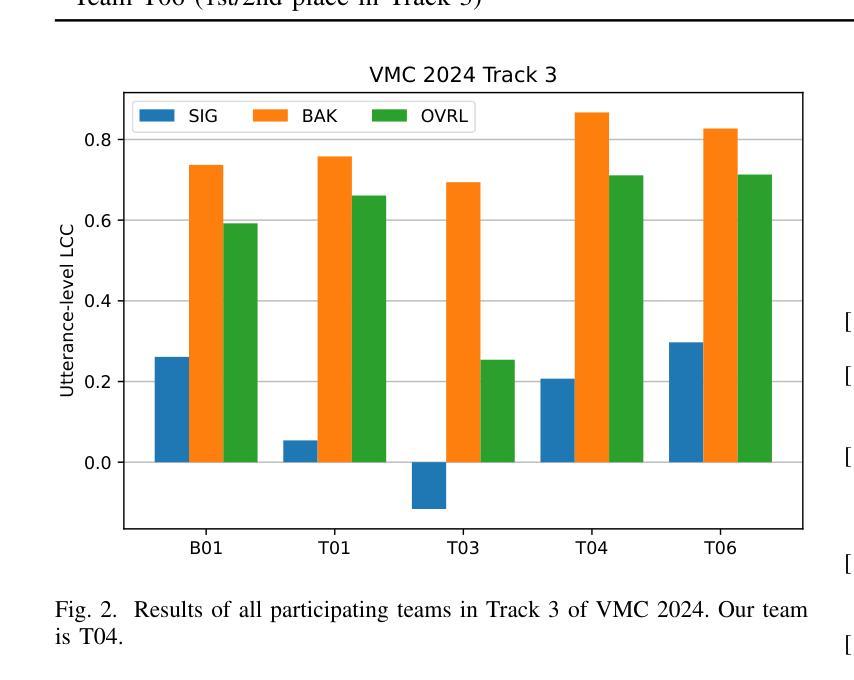
In this preprint, we present the UWB-NTIS-TTS team’s submission to Track 3 of the VoiceMOS 2024 Challenge, the goal of which was to automatically assess the speech quality of noisy and de-noised speech in terms of the ITU-T P.835 metrics of “SIG”, “BAK”, and “OVRL”. Our proposed system, based on wav2vec 2.0, placed among the top systems in the challenge, achieving the best prediction of the BAK scores (background noise intrusiveness), the second-best prediction of the OVRL score (overall audio quality), and the third-best prediction of SIG (speech signal quality) out of the five participating systems. We describe our approach, such as the two-stage fine-tuning process we used to contend with the challenge’s very limiting restrictions on allowable training data, and present the results achieved both on the VoiceMOS 2024 Challenge data and on the recently released CHiME 7 - UDASE dataset.
在这篇预印版文章中,我们展示了UWB-NTIS-TTS团队对VoiceMOS 2024挑战赛第三赛道提交的成果。该挑战赛的目标是自动评估噪声和降噪语音的语音质量,依据ITU-T P.835指标的“SIG”(语音信号质量)、“BAK”(背景噪声侵入性)和“OVRL”(整体音频质量)来评估。我们提出的基于wav2vec 2.0的系统在挑战中名列前茅,实现了最佳的BAK评分(背景噪声侵入性预测)、OVRL评分的第二佳预测(整体音频质量),以及SIG的第三佳预测(语音信号质量)。我们介绍了我们的方法,例如我们使用的两阶段微调过程,以应对挑战赛对可用训练数据的非常严格的限制,并展示了在VoiceMOS 2024挑战赛数据和最近发布的CHiME 7 - UDASE数据集上取得的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This is a preliminary write-up of our initial work, posted as an early version preprint for cross-referencing purposes. We intend to further extend this research and submit it for publication at a conference, at which point this preprint will be updated with the full text. v2 changes: Fixed CHiME 7 - UDASE dataset overlapping with VMC 2024 training data
Summary
语音质量评估研究旨在解决在嘈杂和有噪音环境下的语音识别问题。研究团队提出的基于wav2vec 2.0的系统在VoiceMOS 2024挑战赛中表现优异,特别是在背景噪声入侵(BAK)和整体音频质量(OVRL)的预测方面。该系统采用两阶段微调方法应对训练数据的限制。
Key Takeaways
- 研究团队针对VoiceMOS 2024挑战赛的Track 3进行了提交,该挑战的目标是自动评估嘈杂和降噪语音的语音质量。
- 团队提出的系统基于wav2vec 2.0,在挑战赛中表现优秀,特别是在背景噪声入侵(BAK)的预测方面获得最佳成绩。
- 系统在整体音频质量(OVRL)和语音信号质量(SIG)的预测方面也取得了良好成绩,位列参赛系统中的前三名。
- 研究团队采用了两阶段微调方法以应对挑战赛对训练数据的严格限制。
- 该系统不仅在VoiceMOS 2024挑战赛的数据上进行了测试,还在最近发布的CHiME 7 - UDASE数据集上进行了结果展示。
- 此研究展示了利用先进模型和技术自动评估语音质量的重要性和潜力。
点此查看论文截图

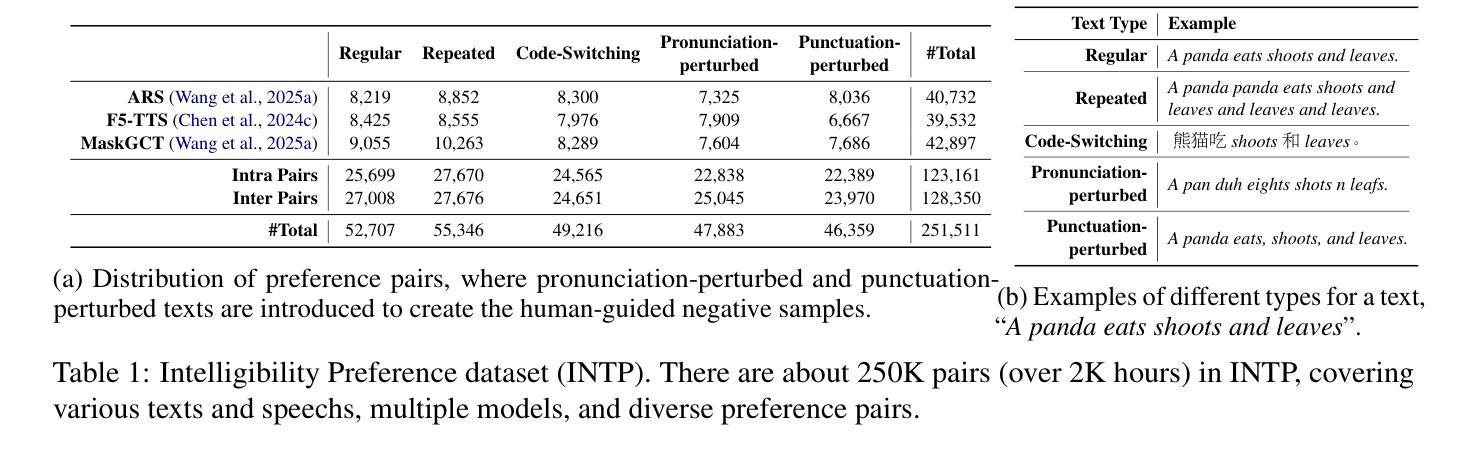
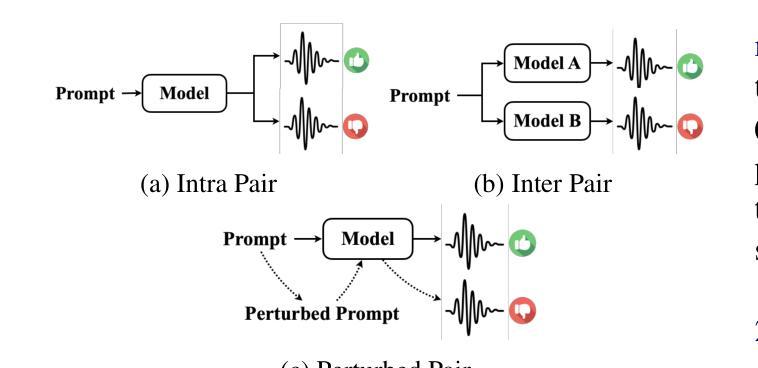
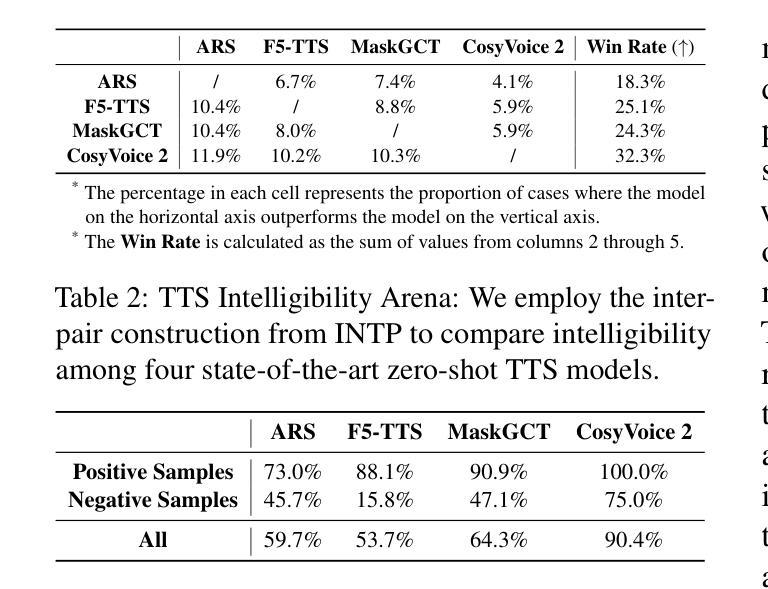
Advancing Zero-shot Text-to-Speech Intelligibility across Diverse Domains via Preference Alignment
Authors:Xueyao Zhang, Yuancheng Wang, Chaoren Wang, Ziniu Li, Zhuo Chen, Zhizheng Wu
Modern zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) systems, despite using extensive pre-training, often struggle in challenging scenarios such as tongue twisters, repeated words, code-switching, and cross-lingual synthesis, leading to intelligibility issues. To address these limitations, this paper leverages preference alignment techniques, which enable targeted construction of out-of-pretraining-distribution data to enhance performance. We introduce a new dataset, named the Intelligibility Preference Speech Dataset (INTP), and extend the Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) framework to accommodate diverse TTS architectures. After INTP alignment, in addition to intelligibility, we observe overall improvements including naturalness, similarity, and audio quality for multiple TTS models across diverse domains. Based on that, we also verify the weak-to-strong generalization ability of INTP for more intelligible models such as CosyVoice 2 and Ints. Moreover, we showcase the potential for further improvements through iterative alignment based on Ints. Audio samples are available at https://intalign.github.io/.
尽管现代零样本文本到语音(TTS)系统采用了大量的预训练,但在应对挑战场景时仍面临困难,如绕口令、重复单词、代码切换和跨语言合成等,导致语音清晰度问题。为了克服这些局限性,本文采用偏好对齐技术,该技术能够构建超出预训练分布的数据,从而提高性能。我们引入了一个新的数据集,名为可懂度偏好语音数据集(INTP),并将直接偏好优化(DPO)框架扩展到适应多种TTS架构。经过INTP对齐后,除了清晰度之外,我们还观察到多个TTS模型在不同领域的整体改进,包括自然度、相似性和音频质量。基于此,我们还验证了INTP对于如CosyVoice 2和Ints等更具理解力的模型的从弱到强的泛化能力。此外,我们通过基于Ints的迭代对齐展示了进一步改进的潜力。音频样本可在https://intalign.github.io/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACL 2025
Summary
本文介绍了现代零样本文本到语音(TTS)系统在处理复杂场景时面临的挑战,如舌尖绕口令、重复词汇、语言切换和跨语言合成等,导致语音清晰度问题。为了解决这个问题,文章提出了偏好对齐技术来创建特定于应用场景的数据集以提高系统性能。引入了名为“清晰度偏好语音数据集(INTP)”的新数据集,扩展了直接偏好优化(DPO)框架以适应多种TTS架构。使用INTP对齐后,不仅提高了清晰度,还改善了多个TTS模型的自然度、相似性和音质。此外,验证了INTP对于CosyVoice 2和Ints等模型的弱到强泛化能力,并展示了通过迭代对齐进一步提高性能的潜力。音频样本可在网站上找到。
Key Takeaways
- 现代零样本TTS系统在处理复杂场景时面临清晰度问题。
- 偏好对齐技术用于创建特定于应用场景的数据集以提高TTS系统性能。
- 引入了名为INTP的新数据集,以改善语音清晰度及其他性能标准如自然度、相似性。
- 扩展了DPO框架以适应多种TTS架构,显著提升了语音质量和模型性能。
- INTP对于多种模型的泛化能力得到了验证,尤其在CosyVoice 2和Ints等模型上表现显著。
- 通过迭代对齐可以进一步提高性能。
点此查看论文截图

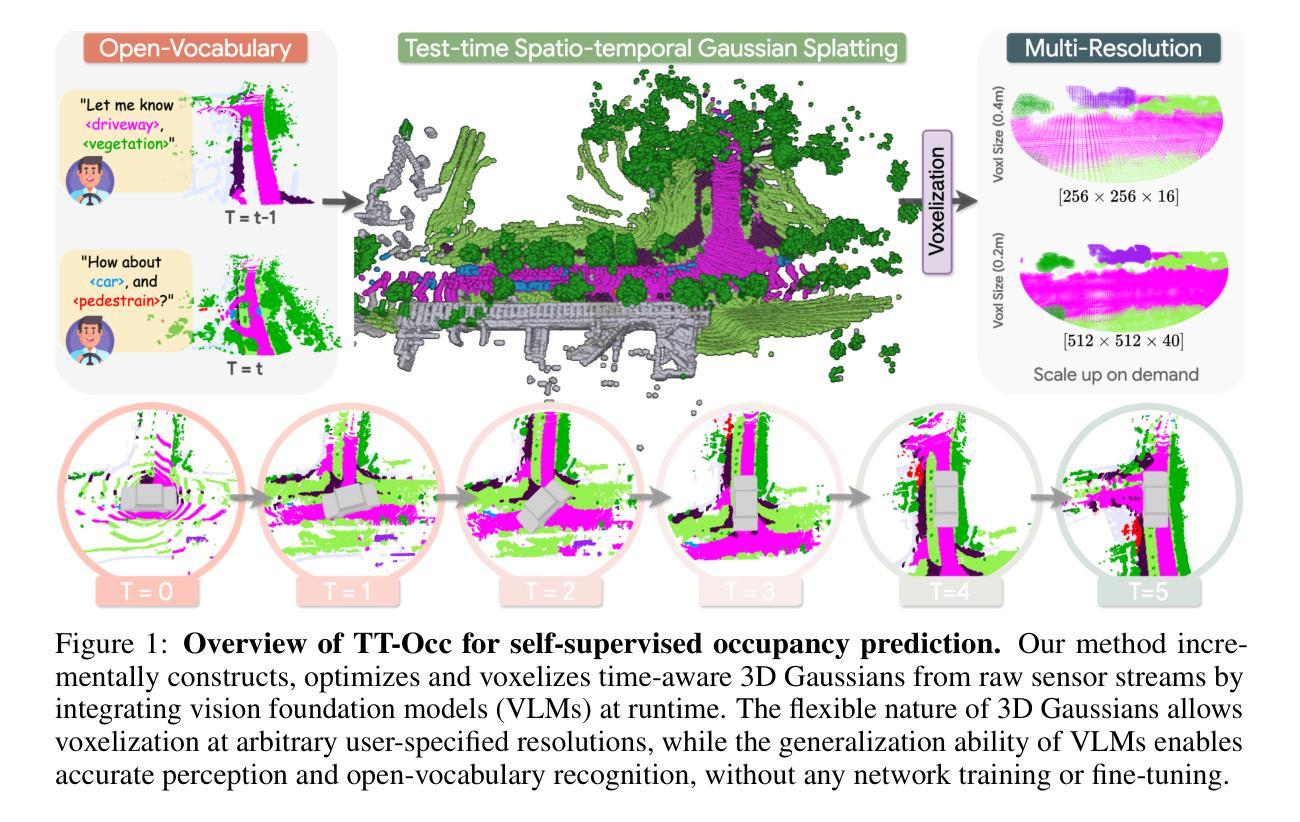
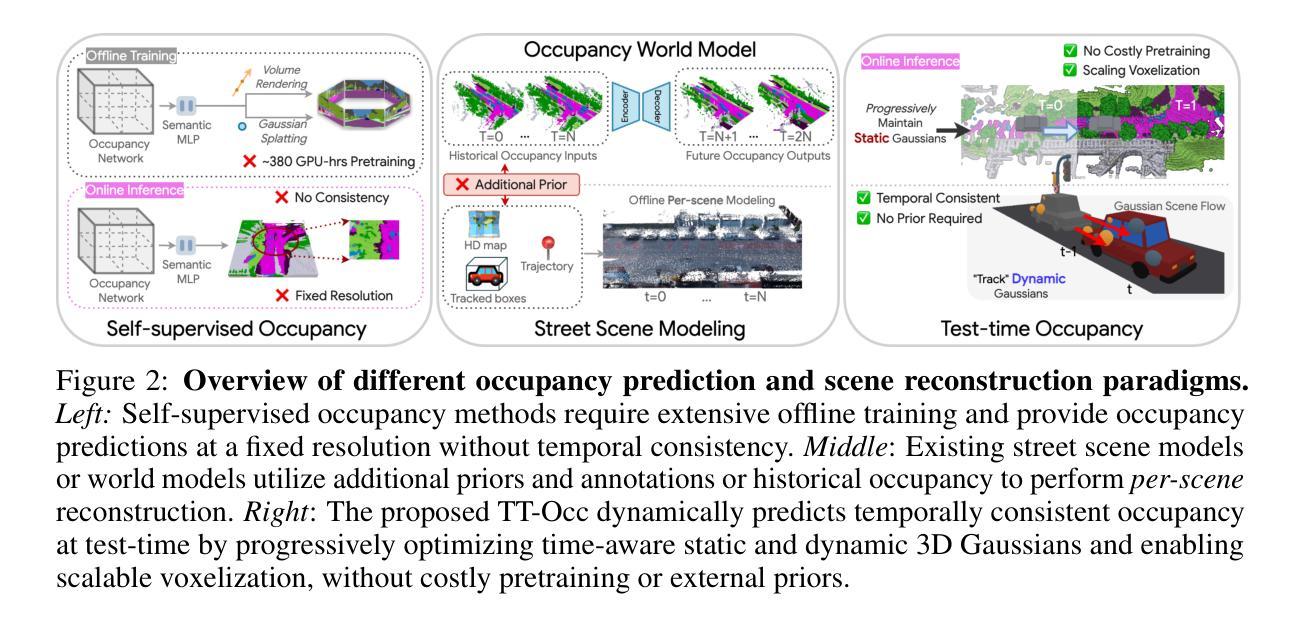
TT-Occ: Test-Time Compute for Self-Supervised Occupancy via Spatio-Temporal Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Fengyi Zhang, Huitong Yang, Zheng Zhang, Zi Huang, Yadan Luo
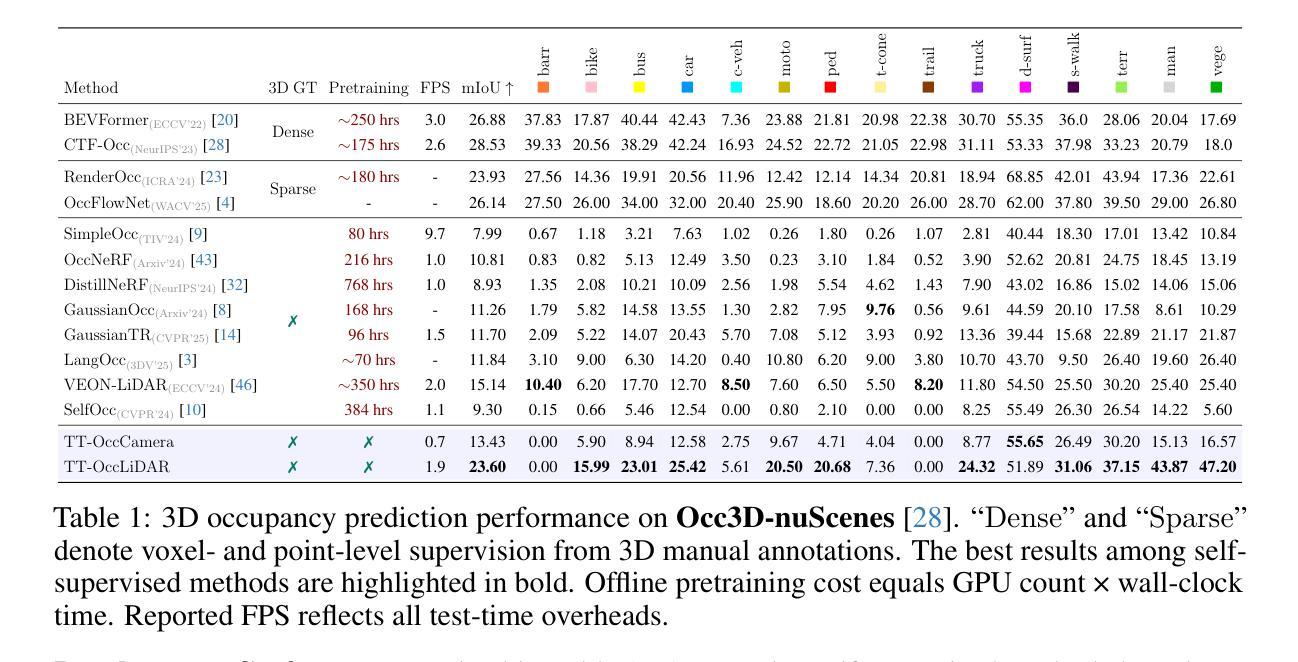
Self-supervised 3D occupancy prediction offers a promising solution for understanding complex driving scenes without requiring costly 3D annotations. However, training dense occupancy decoders to capture fine-grained geometry and semantics can demand hundreds of GPU hours, and once trained, such models struggle to adapt to varying voxel resolutions or novel object categories without extensive retraining. To overcome these limitations, we propose a practical and flexible test-time occupancy prediction framework termed TT-Occ. Our method incrementally constructs, optimizes and voxelizes time-aware 3D Gaussians from raw sensor streams by integrating vision foundation models (VLMs) at runtime. The flexible nature of 3D Gaussians allows voxelization at arbitrary user-specified resolutions, while the generalization ability of VLMs enables accurate perception and open-vocabulary recognition, without any network training or fine-tuning. Specifically, TT-Occ operates in a lift-track-voxelize symphony: We first lift the geometry and semantics of surrounding-view extracted from VLMs to instantiate Gaussians at 3D space; Next, we track dynamic Gaussians while accumulating static ones to complete the scene and enforce temporal consistency; Finally, we voxelize the optimized Gaussians to generate occupancy prediction. Optionally, inherent noise in VLM predictions and tracking is mitigated by periodically smoothing neighboring Gaussians during optimization. To validate the generality and effectiveness of our framework, we offer two variants: one LiDAR-based and one vision-centric, and conduct extensive experiments on Occ3D and nuCraft benchmarks with varying voxel resolutions. Code will be available at https://github.com/Xian-Bei/TT-Occ.
自监督的3D占用预测为解决复杂的驾驶场景提供了新的解决方案,且无需昂贵的3D注释。然而,训练密集占用解码器以捕获精细的几何和语义信息可能需要数百小时的GPU时间,并且一旦训练完成,这些模型在适应不同的体素分辨率或新对象类别时,若无大量的重新训练,便会出现困难。为了克服这些限制,我们提出了一种实用且灵活的测试时间占用预测框架,称为TT-Occ。我们的方法通过整合视觉基础模型(VLMs),从原始传感器流中增量构建、优化和体素化时间感知的3D高斯分布。3D高斯分布的可灵活性允许在用户指定的任意分辨率上进行体素化,而VLMs的泛化能力则可实现准确的感知和开放词汇表识别,无需任何网络训练或微调。具体来说,TT-Occ以升降-跟踪-体素化的协同方式运作:我们首先利用VLMs提取的周围环境几何和语义信息,在三维空间中实例化高斯分布;接下来,我们跟踪动态高斯分布同时累积静态高斯分布以完成场景并强制时间一致性;最后我们优化高斯分布的体素化以生成占用预测。可选地,通过优化过程中定期平滑邻近的高斯分布来缓解VLM预测和跟踪中的固有噪声。为了验证我们框架的通用性和有效性,我们提供了基于激光雷达和基于视觉的两个版本,并在Occ3D和nuCraft基准测试上进行了广泛的实验验证。代码将在https://github.com/Xian-Bei/TT-Occ上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自监督的3D占用预测为理解复杂的驾驶场景提供了一个有前景的解决方案,而无需昂贵的3D标注。针对密集占用解码器在捕捉精细几何和语义时的高耗时训练以及难以适应不同体素分辨率和新对象类别的问题,我们提出了一个实用且灵活的测试时占用预测框架TT-Occ。它通过整合视觉基础模型(VLMs),从原始传感器流中增量构建、优化和体素化时间感知的3D高斯分布。该框架允许任意用户指定的体素分辨率,并利用VLMs的泛化能力进行准确感知和开放词汇识别,无需网络训练或微调。
Key Takeaways
- 自监督的3D占用预测有助于理解复杂驾驶场景,减少成本高昂的3D标注需求。
- 当前方法面临训练耗时、难以适应不同体素分辨率和新对象类别的问题。
- 提出了一种名为TT-Occ的实用且灵活的测试时占用预测框架。
- TT-Occ通过整合视觉基础模型(VLMs),从原始传感器流中构建时间感知的3D高斯分布。
- 3D高斯分布的灵活性允许任意用户指定的体素分辨率。
- VLMs的泛化能力使TT-Occ能进行准确感知和开放词汇识别,无需网络训练或微调。
点此查看论文截图