⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-11 更新
CXR-LT 2024: A MICCAI challenge on long-tailed, multi-label, and zero-shot disease classification from chest X-ray
Authors:Mingquan Lin, Gregory Holste, Song Wang, Yiliang Zhou, Yishu Wei, Imon Banerjee, Pengyi Chen, Tianjie Dai, Yuexi Du, Nicha C. Dvornek, Yuyan Ge, Zuowei Guo, Shouhei Hanaoka, Dongkyun Kim, Pablo Messina, Yang Lu, Denis Parra, Donghyun Son, Álvaro Soto, Aisha Urooj, René Vidal, Yosuke Yamagishi, Zefan Yang, Ruichi Zhang, Yang Zhou, Leo Anthony Celi, Ronald M. Summers, Zhiyong Lu, Hao Chen, Adam Flanders, George Shih, Zhangyang Wang, Yifan Peng
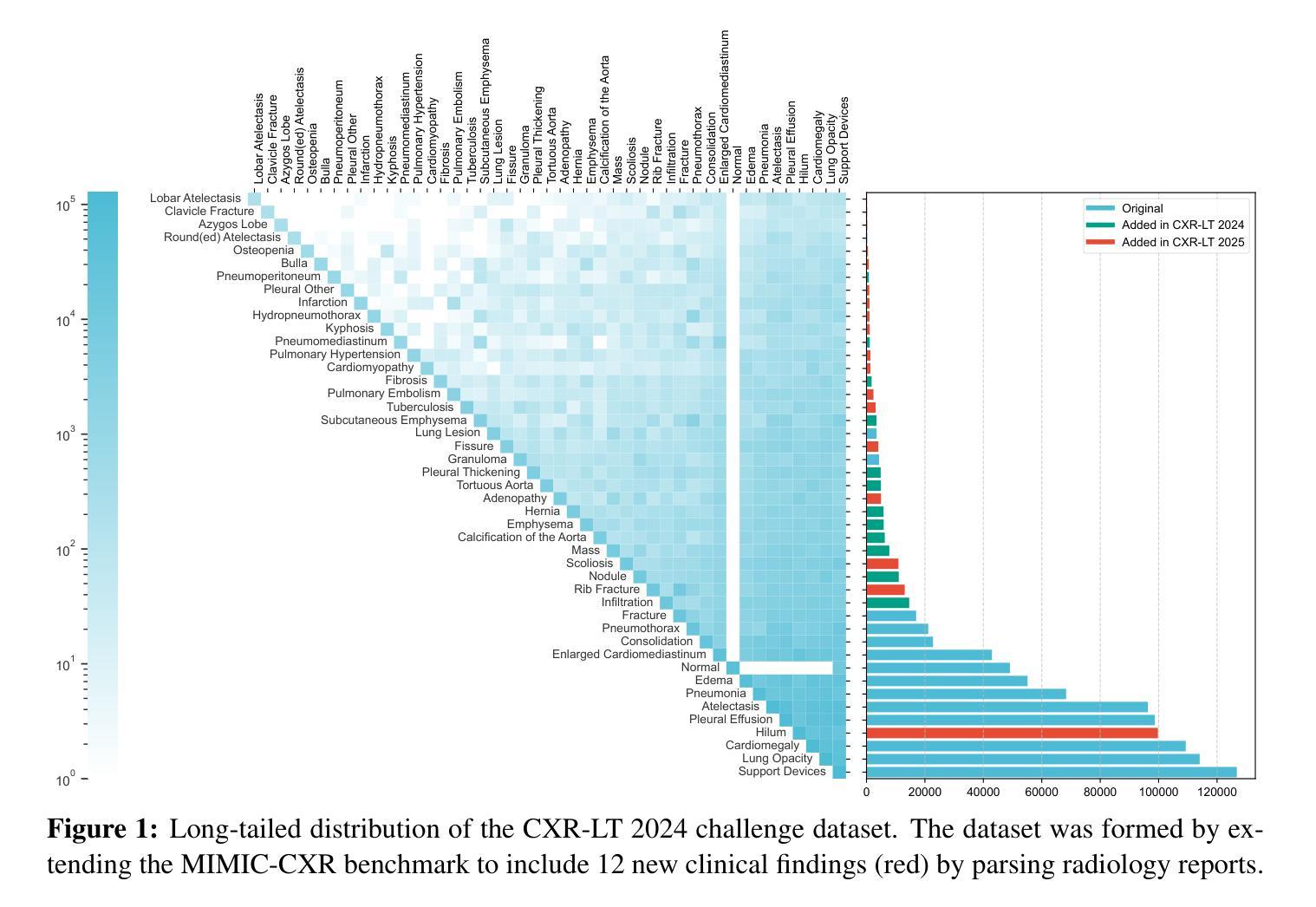
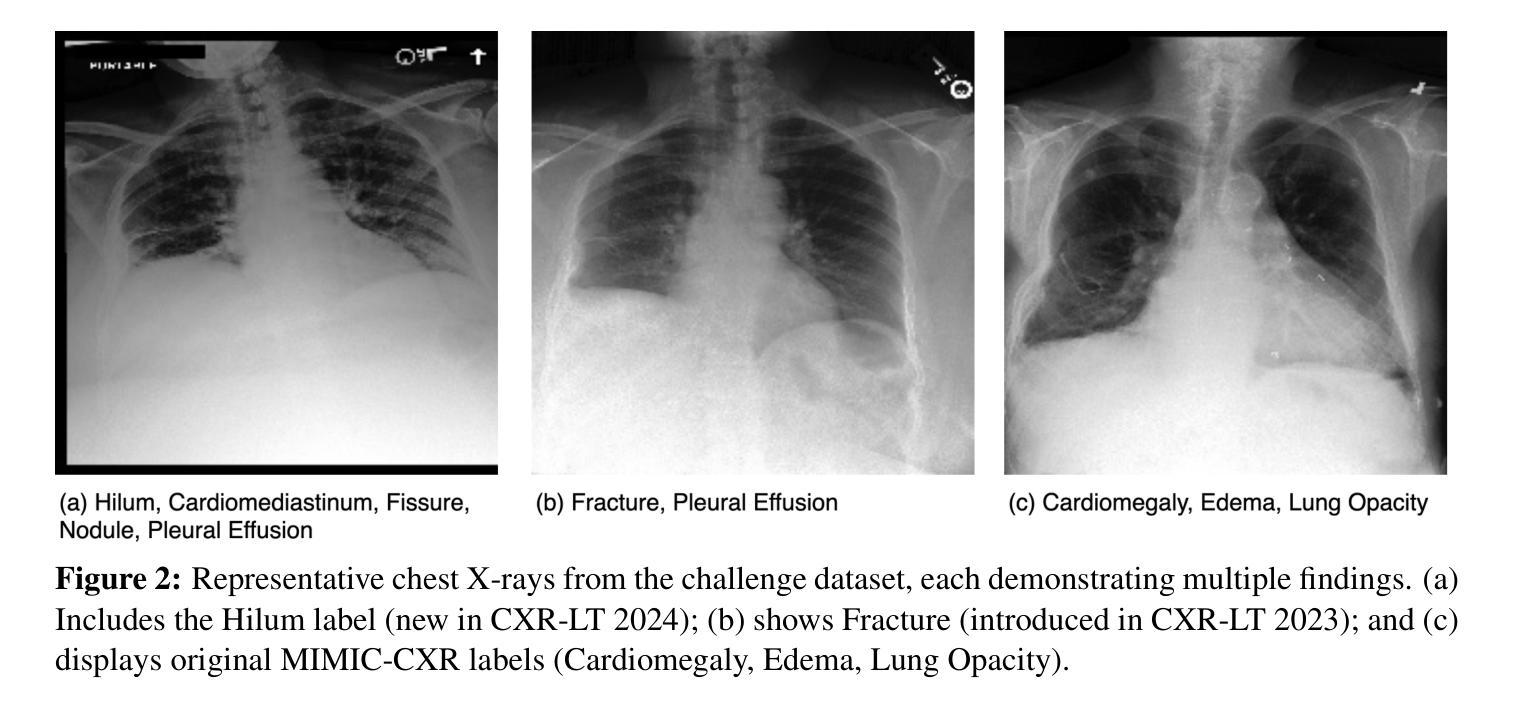
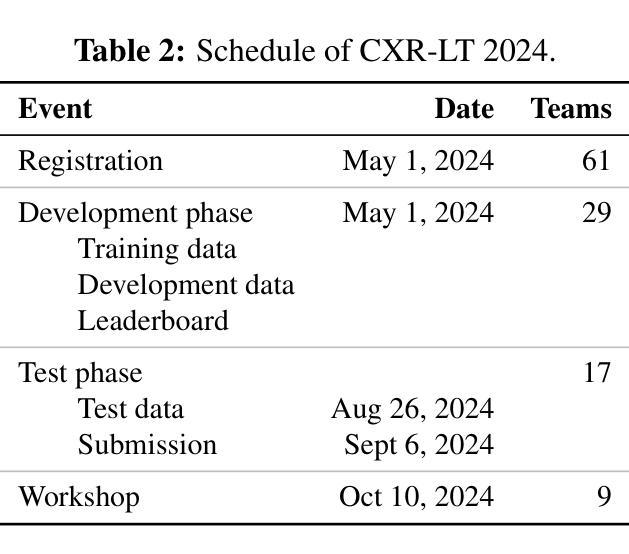
The CXR-LT series is a community-driven initiative designed to enhance lung disease classification using chest X-rays (CXR). It tackles challenges in open long-tailed lung disease classification and enhances the measurability of state-of-the-art techniques. The first event, CXR-LT 2023, aimed to achieve these goals by providing high-quality benchmark CXR data for model development and conducting comprehensive evaluations to identify ongoing issues impacting lung disease classification performance. Building on the success of CXR-LT 2023, the CXR-LT 2024 expands the dataset to 377,110 chest X-rays (CXRs) and 45 disease labels, including 19 new rare disease findings. It also introduces a new focus on zero-shot learning to address limitations identified in the previous event. Specifically, CXR-LT 2024 features three tasks: (i) long-tailed classification on a large, noisy test set, (ii) long-tailed classification on a manually annotated “gold standard” subset, and (iii) zero-shot generalization to five previously unseen disease findings. This paper provides an overview of CXR-LT 2024, detailing the data curation process and consolidating state-of-the-art solutions, including the use of multimodal models for rare disease detection, advanced generative approaches to handle noisy labels, and zero-shot learning strategies for unseen diseases. Additionally, the expanded dataset enhances disease coverage to better represent real-world clinical settings, offering a valuable resource for future research. By synthesizing the insights and innovations of participating teams, we aim to advance the development of clinically realistic and generalizable diagnostic models for chest radiography.
CXR-LT系列是一个社区驱动的项目,旨在利用胸部X光(CXR)技术提高肺部疾病的分类能力。它解决了开放长尾肺部疾病分类的挑战,并提高了最先进技术的衡量标准。CXR-LT 2023是首次活动,旨在通过为模型开发提供高质量基准CXR数据,并进行全面评估以识别影响肺部疾病分类性能的问题,实现这些目标。基于CXR-LT 2023的成功,CXR-LT 2024将数据集扩展到377,110张胸部X光(CXRs)图像和45种疾病标签,包括19种新的罕见疾病发现。它还引入了零样本学习的新重点,以解决以前活动中识别出的局限性。具体来说,CXR-LT 2024包含三个任务:(i)大型嘈杂测试集上的长尾分类,(ii)在手动注释的“金标准”子集上的长尾分类,以及(iii)对五种之前未见过的疾病的零样本泛化。本文概述了CXR-LT 2024,详细介绍了数据整理过程并巩固了最先进的解决方案,包括用于罕见疾病检测的多模式模型、处理嘈杂标签的高级生成方法和用于未见疾病的零样本学习策略。此外,扩展的数据集提高了疾病覆盖率,以更好地代表真实世界临床环境,为未来的研究提供了宝贵的资源。通过综合各参赛队的见解和创新,我们旨在推动临床现实和可推广的胸部放射学诊断模型的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 3 figures
Summary
基于社区驱动的CXR-LT系列旨在利用胸部X射线(CXR)增强对肺部疾病的分类能力。其解决开放式长尾肺部疾病分类的挑战,并增强最新技术的可衡量性。CXR-LT 2024在成功的基础上扩展数据集至涵盖多种疾病标签,并引入零样本学习以应对先前识别到的局限性。旨在促进临床诊断模型的实际和普遍性发展。此活动有利于加强行业进步与人才培养能力协同增长模式形成良性发展趋势。
Key Takeaways
- CXR-LT系列是一个社区驱动的项目,旨在通过胸部X射线(CXR)提高肺部疾病的分类能力。
- 该项目解决了开放式长尾肺部疾病分类的挑战,增强了最新技术的可衡量性。
点此查看论文截图

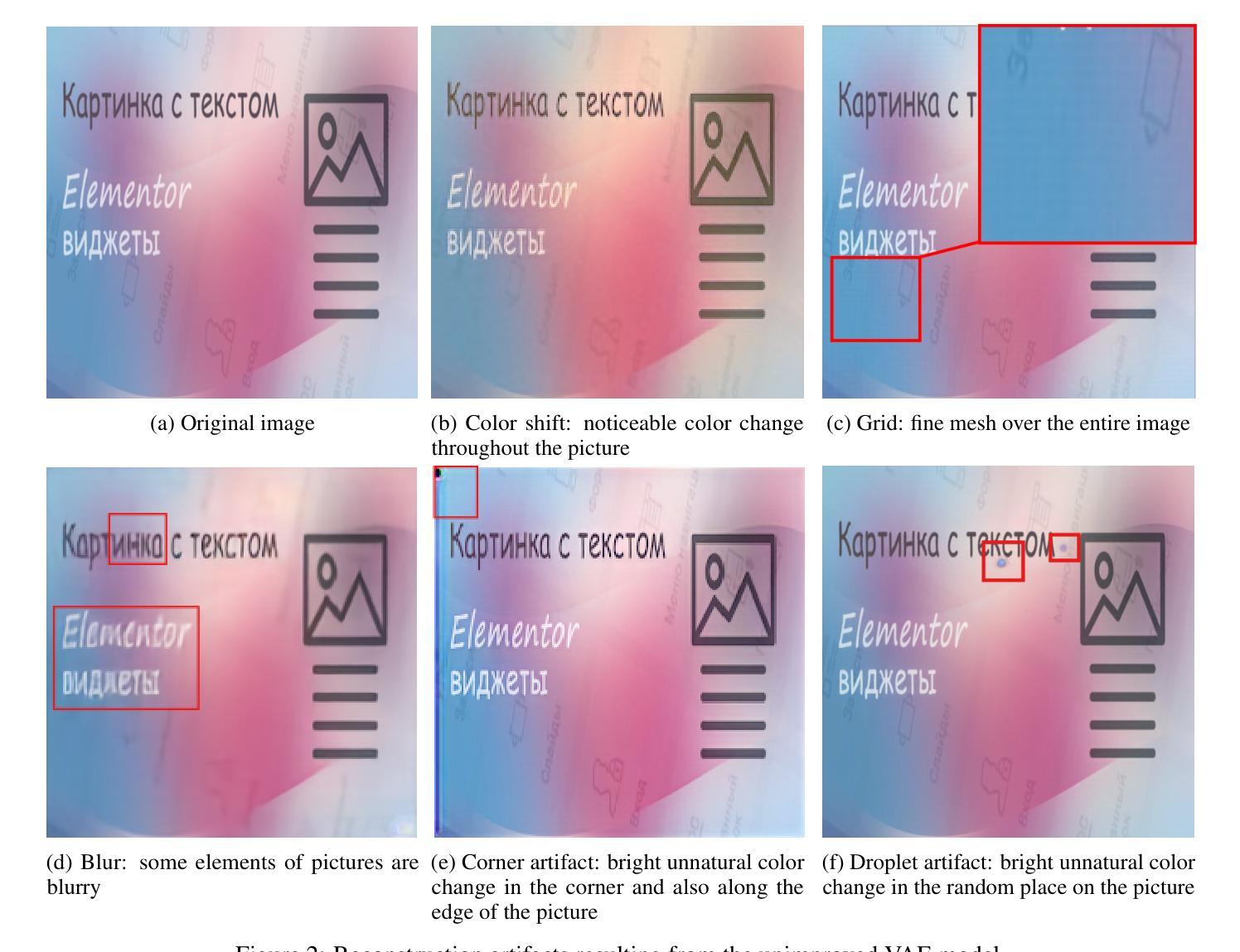
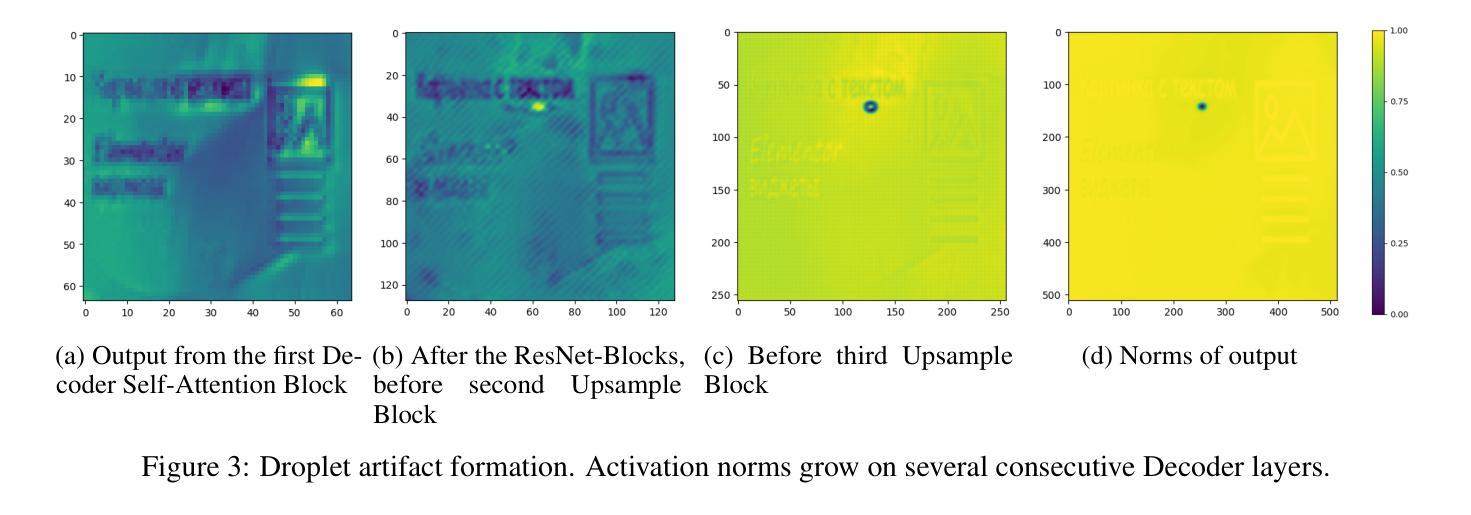
VIVAT: Virtuous Improving VAE Training through Artifact Mitigation
Authors:Lev Novitskiy, Viacheslav Vasilev, Maria Kovaleva, Vladimir Arkhipkin, Denis Dimitrov
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) remain a cornerstone of generative computer vision, yet their training is often plagued by artifacts that degrade reconstruction and generation quality. This paper introduces VIVAT, a systematic approach to mitigating common artifacts in KL-VAE training without requiring radical architectural changes. We present a detailed taxonomy of five prevalent artifacts - color shift, grid patterns, blur, corner and droplet artifacts - and analyze their root causes. Through straightforward modifications, including adjustments to loss weights, padding strategies, and the integration of Spatially Conditional Normalization, we demonstrate significant improvements in VAE performance. Our method achieves state-of-the-art results in image reconstruction metrics (PSNR and SSIM) across multiple benchmarks and enhances text-to-image generation quality, as evidenced by superior CLIP scores. By preserving the simplicity of the KL-VAE framework while addressing its practical challenges, VIVAT offers actionable insights for researchers and practitioners aiming to optimize VAE training.
变分自编码器(VAEs)仍然是生成计算机视觉的基石,但其训练常常受到伪影的困扰,这些伪影会降低重建和生成质量。本文介绍了VIVAT,这是一种缓解KL-VAE训练中常见伪影的系统性方法,无需进行根本性的架构改变。我们对五种常见的伪影进行了详细的分类,包括色彩偏移、网格模式、模糊、角落和液滴伪影,并分析了它们的根本原因。通过简单的修改,包括调整损失权重、填充策略以及空间条件归一化的集成,我们展示了VAE性能的显著改进。我们的方法在多个基准测试中实现了图像重建指标(PSNR和SSIM)的最新结果,并提高了文本到图像的生成质量,这体现在更高的CLIP分数上。VIVAT在保持KL-VAE框架简洁性的同时,解决了其实践挑战,为希望优化VAE训练的研究人员和实践者提供了可操作的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了VIVAT,一种针对KL-VAE训练中常见伪影的系统性解决方法,无需进行根本性的架构改变。文章详细分类了五种常见的伪影,分析其根本原因,并通过简单的修改,如调整损失权重、填充策略和集成空间条件归一化,显著提高了VAE的性能。该方法在图像重建指标(PSNR和SSIM)上达到领先水平,同时提高了文本到图像的生成质量。VIVAT为研究人员和从业者提供了优化VAE训练的实用见解。
Key Takeaways
- VIVAT是一种针对KL-VAE训练中常见伪影的解决方法。
- 文章详细分类了五种常见伪影:颜色偏移、网格模式、模糊、角落和液滴伪影。
- 通过调整损失权重、改进填充策略和集成空间条件归一化等简单修改,VAE性能得到显著提高。
- VIVAT方法在图像重建指标上达到领先水平,包括PSNR和SSIM。
- VIVAT提高了文本到图像的生成质量,表现为更高的CLIP评分。
- VIVAT保留了KL-VAE框架的简洁性,同时解决了其实践中的挑战。
点此查看论文截图

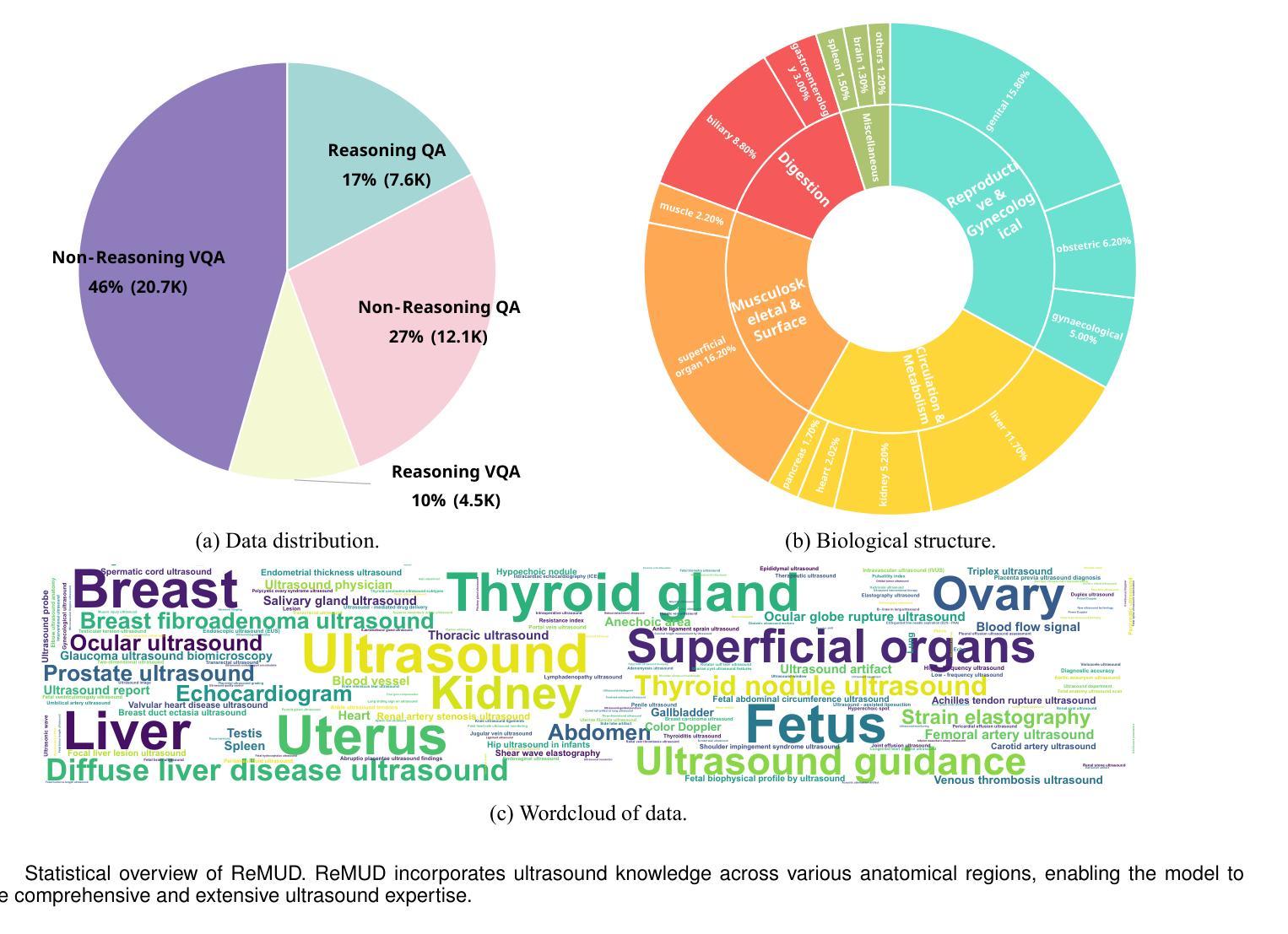
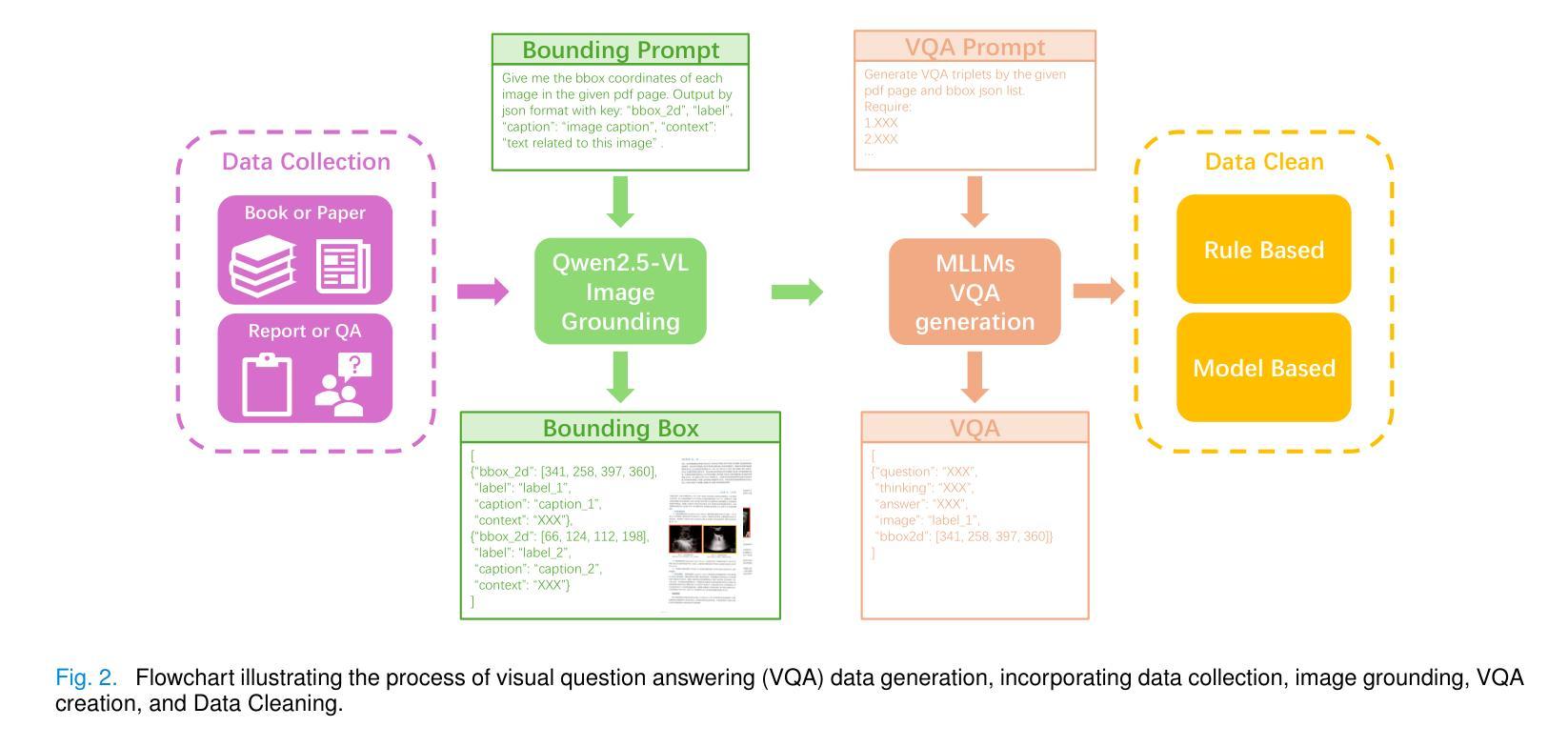
HAIBU-ReMUD: Reasoning Multimodal Ultrasound Dataset and Model Bridging to General Specific Domains
Authors:Shijie Wang, Yilun Zhang, Zeyu Lai, Dexing Kong
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have shown great potential in general domains but perform poorly in some specific domains due to a lack of domain-specific data, such as image-text data or vedio-text data. In some specific domains, there is abundant graphic and textual data scattered around, but lacks standardized arrangement. In the field of medical ultrasound, there are ultrasonic diagnostic books, ultrasonic clinical guidelines, ultrasonic diagnostic reports, and so on. However, these ultrasonic materials are often saved in the forms of PDF, images, etc., and cannot be directly used for the training of MLLMs. This paper proposes a novel image-text reasoning supervised fine-tuning data generation pipeline to create specific domain quadruplets (image, question, thinking trace, and answer) from domain-specific materials. A medical ultrasound domain dataset ReMUD is established, containing over 45,000 reasoning and non-reasoning supervised fine-tuning Question Answering (QA) and Visual Question Answering (VQA) data. The ReMUD-7B model, fine-tuned on Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct, outperforms general-domain MLLMs in medical ultrasound field. To facilitate research, the ReMUD dataset, data generation codebase, and ReMUD-7B parameters will be released at https://github.com/ShiDaizi/ReMUD, addressing the data shortage issue in specific domain MLLMs.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在通用领域表现出了巨大的潜力,但由于缺乏特定领域的数据,如图像文本数据或视频文本数据,在一些特定领域的表现较差。在一些特定领域,虽然存在大量的图形和文本数据分散,但缺乏标准化安排。在医学超声领域,有超声诊断书籍、超声临床指南、超声诊断报告等。然而,这些超声材料通常保存在PDF、图像等形式下,无法直接用于训练MLLMs。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对特定领域多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)数据短缺的问题,提出了一种新的图像文本推理监督微调数据生成流程。通过创建特定领域的四元组(图像、问题、思考轨迹和答案),从医学超声领域的专业资料中建立了ReMUD数据集,包含超过45,000个用于监督和视觉问答的推理和非推理数据。经过在Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct上微调的ReMUD-7B模型在医学超声领域表现出优于通用领域MLLMs的性能。数据和资源已在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs在一般领域具有巨大潜力,但在特定领域表现不佳,缺乏特定领域的图像文本或视频文本数据是主要问题。
- 在医学超声领域,存在大量分散的图形和文本数据,但缺乏标准化安排。
- 本文提出了一种创建特定领域数据的方法,通过生成图像文本四元组(图像、问题、思考轨迹和答案)来解决这个问题。
- 创建了医学超声领域的ReMUD数据集,包含超过45,000个用于监督和视觉问答的推理和非推理数据。
- ReMUD-7B模型在医学超声领域的性能优于通用MLLMs。
- ReMUD数据集、数据生成代码库和ReMUD-7B参数已公开发布,以解决特定领域MLLMs的数据短缺问题。
点此查看论文截图


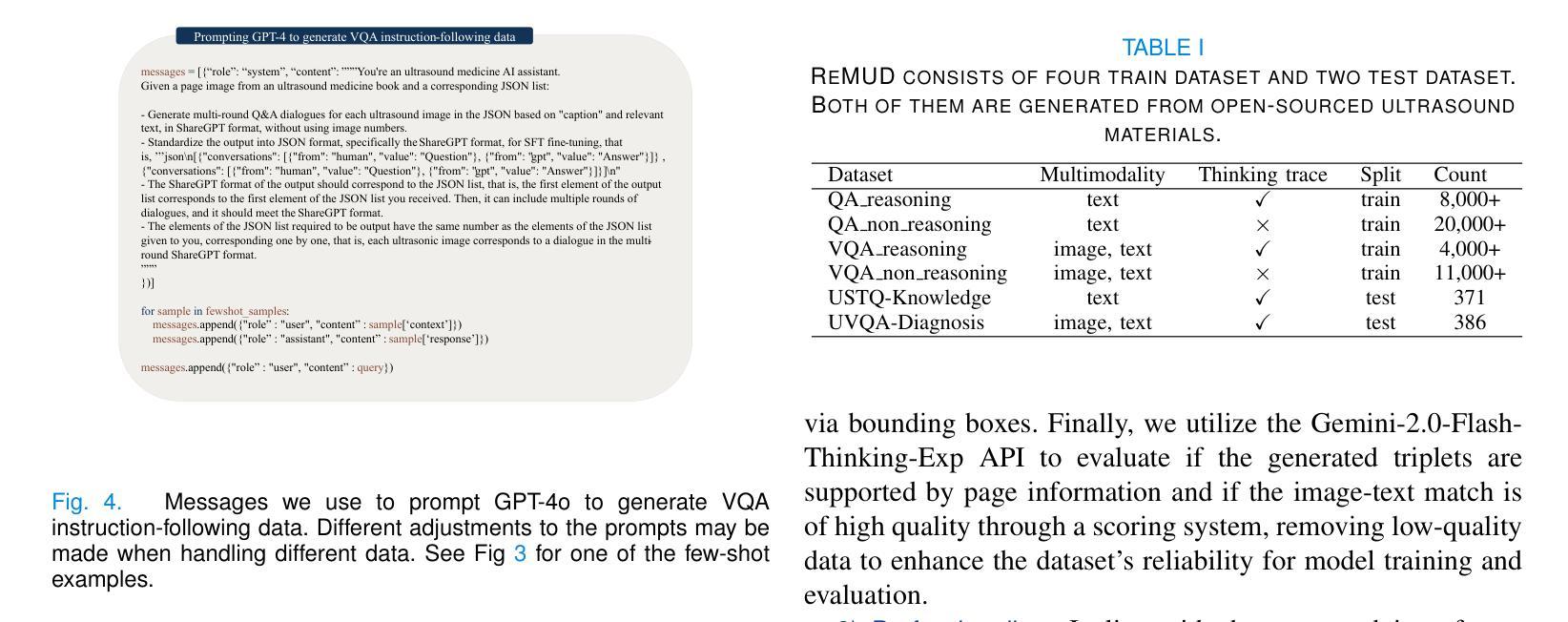
Adaptive Blind Super-Resolution Network for Spatial-Specific and Spatial-Agnostic Degradations
Authors:Weilei Wen, Chunle Guo, Wenqi Ren, Hongpeng Wang, Xiuli Shao
Prior methodologies have disregarded the diversities among distinct degradation types during image reconstruction, employing a uniform network model to handle multiple deteriorations. Nevertheless, we discover that prevalent degradation modalities, including sampling, blurring, and noise, can be roughly categorized into two classes. We classify the first class as spatial-agnostic dominant degradations, less affected by regional changes in image space, such as downsampling and noise degradation. The second class degradation type is intimately associated with the spatial position of the image, such as blurring, and we identify them as spatial-specific dominant degradations. We introduce a dynamic filter network integrating global and local branches to address these two degradation types. This network can greatly alleviate the practical degradation problem. Specifically, the global dynamic filtering layer can perceive the spatial-agnostic dominant degradation in different images by applying weights generated by the attention mechanism to multiple parallel standard convolution kernels, enhancing the network’s representation ability. Meanwhile, the local dynamic filtering layer converts feature maps of the image into a spatially specific dynamic filtering operator, which performs spatially specific convolution operations on the image features to handle spatial-specific dominant degradations. By effectively integrating both global and local dynamic filtering operators, our proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art blind super-resolution algorithms in both synthetic and real image datasets.
先前的方法在图像重建过程中忽视了不同类型退化之间的多样性,采用统一的网络模型来处理多种退化问题。然而,我们发现常见的退化模式,包括采样、模糊和噪声,可以大致分为两类。我们将第一类称为空间无关主导型退化,较少受到图像空间区域变化的影响,如下采样和噪声退化。第二类退化类型与图像的空间位置密切相关,如模糊,我们将其识别为空间特定主导型退化。我们引入了一个动态滤波网络,融合了全局和局部分支,以解决这两种退化问题。该网络可以大大缓解实际退化问题。具体而言,全局动态滤波层通过注意力机制生成的权重对多个并行标准卷积核进行感知,来感知不同图像中的空间无关主导型退化,增强了网络的表示能力。同时,局部动态滤波层将图像的特征图转换为空间特定的动态滤波算子,对图像特征进行空间特定的卷积操作,以处理空间特定主导型退化。通过有效地融合全局和局部动态滤波算子,我们提出的方法在合成和真实图像数据集上都超越了最先进的盲超分辨率算法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON IMAGE PROCESSING
Summary
该文本介绍了在处理图像重建中的不同退化类型时,先前的方法忽略了其多样性,使用统一网络模型处理多种退化问题。然而,该文将常见的退化模式(如采样、模糊和噪声)分为两类:空间不可知型退化与空间特定型退化。针对不同退化类型,该文引入了一个结合全局和局部分支的动态滤波器网络来解决这一问题。该网络通过全局动态滤波层感知不同图像中的空间不可知型退化,通过局部动态滤波层处理空间特定型退化。通过两者的有效结合,该文提出的方法在合成和真实图像数据集上均超越了最先进的盲超分辨率算法。
Key Takeaways
- 文中对图像重建中的退化类型进行了分类,包括空间不可知型退化和空间特定型退化。
- 空间不可知型退化包括采样和噪声降解等,受图像空间区域变化影响较小。
- 空间特定型退化如模糊与空间位置紧密相关。
- 引入的动态滤波器网络结合了全局和局部分支来处理这两种退化类型。
- 全局动态滤波层通过注意力机制生成的权重应用于多个并行标准卷积核,以感知空间不可知型退化。
- 局部动态滤波层将图像的特征图转换为空间特定的动态滤波算子,处理空间特定型退化。
点此查看论文截图

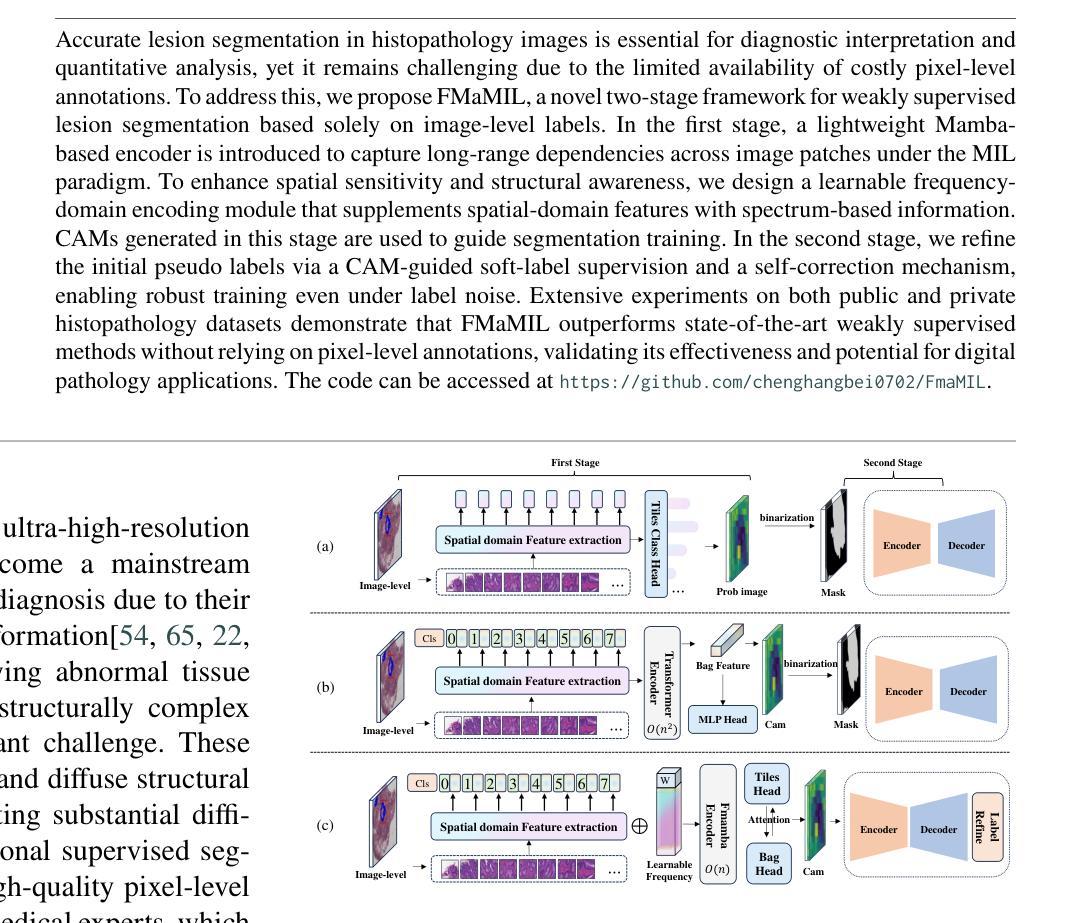
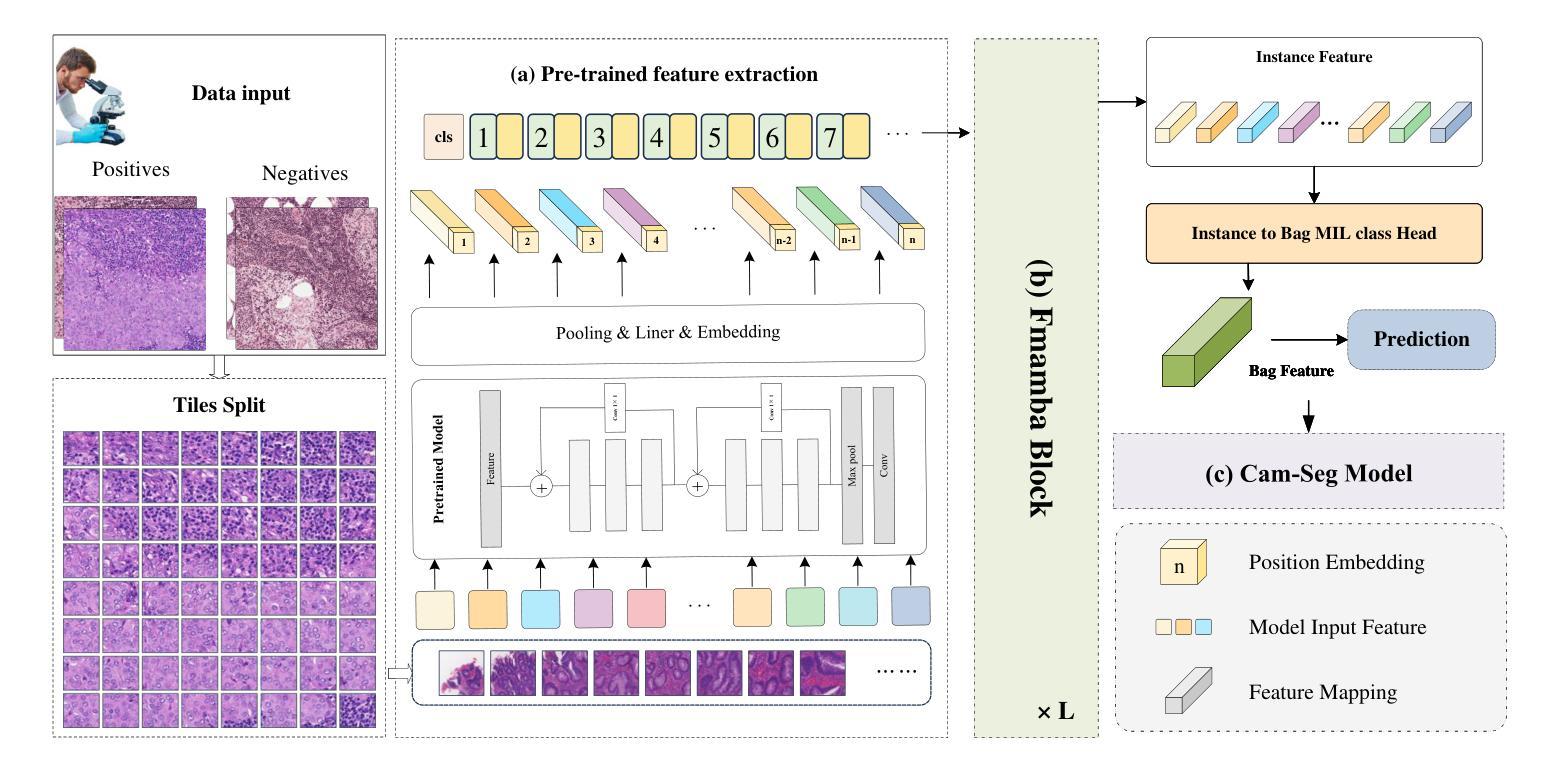
FMaMIL: Frequency-Driven Mamba Multi-Instance Learning for Weakly Supervised Lesion Segmentation in Medical Images
Authors:Hangbei Cheng, Xiaorong Dong, Xueyu Liu, Jianan Zhang, Xuetao Ma, Mingqiang Wei, Liansheng Wang, Junxin Chen, Yongfei Wu
Accurate lesion segmentation in histopathology images is essential for diagnostic interpretation and quantitative analysis, yet it remains challenging due to the limited availability of costly pixel-level annotations. To address this, we propose FMaMIL, a novel two-stage framework for weakly supervised lesion segmentation based solely on image-level labels. In the first stage, a lightweight Mamba-based encoder is introduced to capture long-range dependencies across image patches under the MIL paradigm. To enhance spatial sensitivity and structural awareness, we design a learnable frequency-domain encoding module that supplements spatial-domain features with spectrum-based information. CAMs generated in this stage are used to guide segmentation training. In the second stage, we refine the initial pseudo labels via a CAM-guided soft-label supervision and a self-correction mechanism, enabling robust training even under label noise. Extensive experiments on both public and private histopathology datasets demonstrate that FMaMIL outperforms state-of-the-art weakly supervised methods without relying on pixel-level annotations, validating its effectiveness and potential for digital pathology applications.
在病理图像中,精确地分割病灶对于诊断解读和定量分析至关重要。然而,由于昂贵的像素级标注的有限可用性,这仍然是一个挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了FMaMIL,这是一种仅基于图像级标签的弱监督病灶分割的两阶段新型框架。在第一阶段,我们引入了一个基于Mamba的轻量级编码器,在MIL范式下捕获图像补丁之间的长程依赖性。为了提高空间敏感性和结构意识,我们设计了一个可学习的频域编码模块,该模块可以补充空间域特征以基于光谱的信息。本阶段生成的CAM用于指导分割训练。在第二阶段,我们通过CAM引导的软件标签监督和自我校正机制来优化初始的伪标签,即使在标签噪声下也能实现稳健的训练。在公共和私有病理数据集上的大量实验表明,FMaMIL在不需要像素级注释的情况下超越了最先进的弱监督方法,验证了其在数字病理应用中的有效性和潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像中的精准病变分割对于诊断解读和定量分析至关重要,但受限于昂贵的像素级标注的可用性。为应对这一挑战,我们提出一种仅基于图像级标签的弱监督病变分割的两阶段框架FMaMIL。第一阶段引入基于Mamba的轻量级编码器,在MIL范式下捕获图像补丁间的长程依赖性。为提高空间敏感性和结构意识,我们设计了一个可学习的频域编码模块,以补充基于空间域的特征并加入基于频谱的信息。本阶段生成的CAMs用于指导分割训练。第二阶段通过CAM引导的软标签监督和自我校正机制,对初始伪标签进行精细化处理,即使在标签噪声下也能实现稳健训练。在公共和私有病理学数据集上的大量实验表明,FMaMIL在不依赖像素级注释的情况下,优于最先进弱监督方法,验证了其效果和数字化病理学应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像中的病变分割对于诊断解读和定量分析非常重要。
- 由于像素级标注成本高昂,病变分割仍面临挑战。
- 提出一种新型的两阶段弱监督病变分割框架FMaMIL,仅依赖图像级标签。
- 第一阶段通过Mamba编码器捕获图像补丁间的长程依赖性,并设计频域编码模块提高空间敏感性和结构意识。
- CAMs在第一阶段用于指导分割训练。
- 第二阶段通过软标签监督和自我校正机制精细化初始伪标签,实现稳健训练。
点此查看论文截图

FAMSeg: Fetal Femur and Cranial Ultrasound Segmentation Using Feature-Aware Attention and Mamba Enhancement
Authors:Jie He, Minglang Chen, Minying Lu, Bocheng Liang, Junming Wei, Guiyan Peng, Jiaxi Chen, Ying Tan
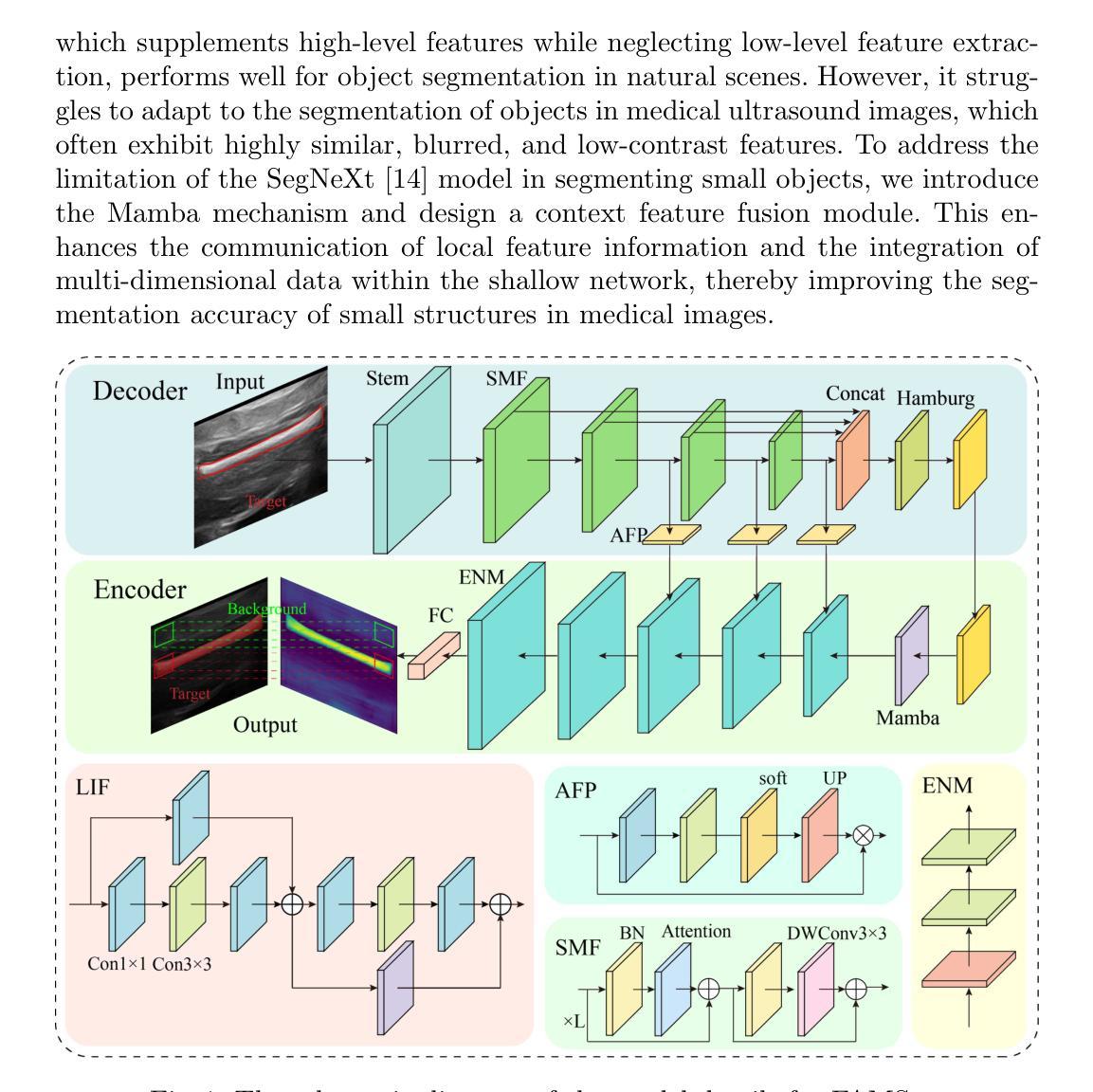
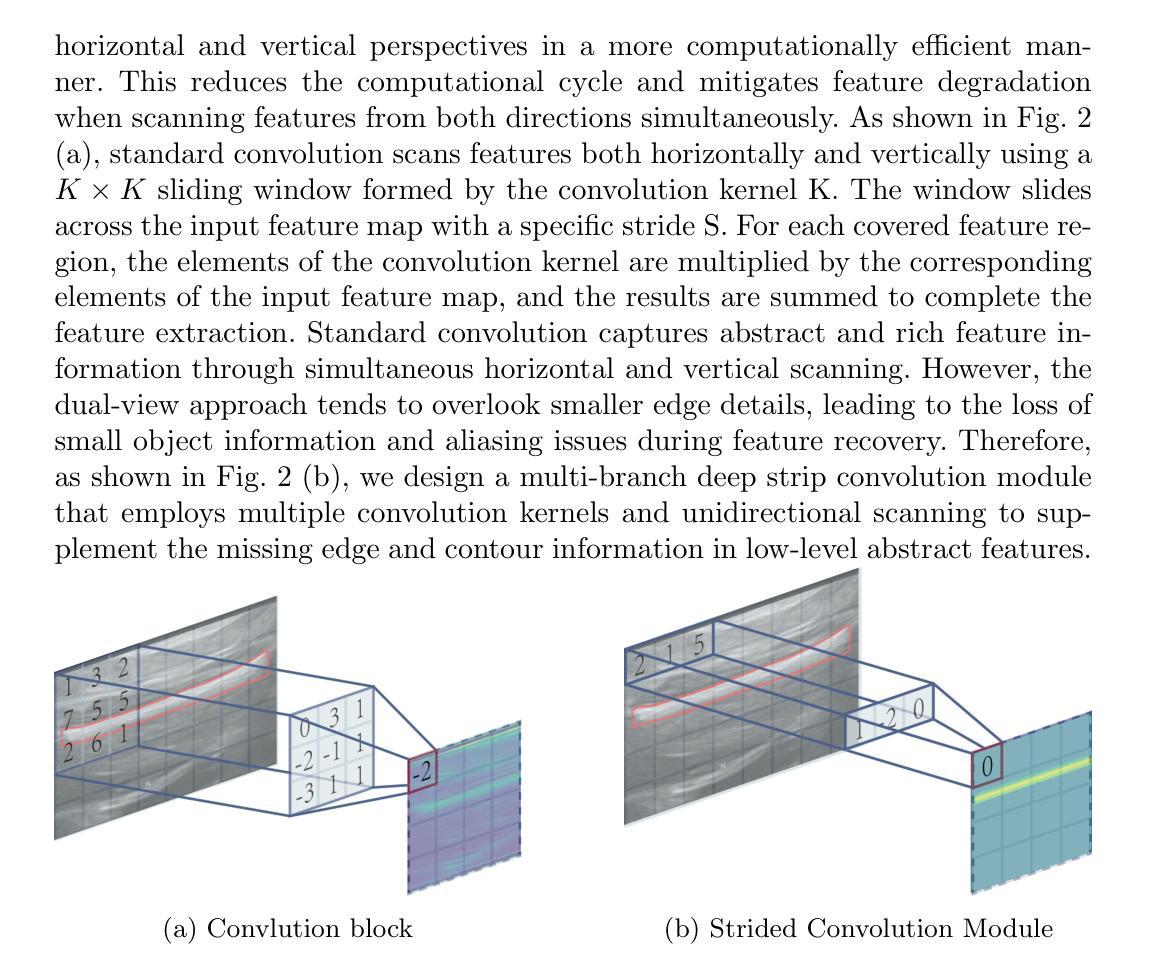
Accurate ultrasound image segmentation is a prerequisite for precise biometrics and accurate assessment. Relying on manual delineation introduces significant errors and is time-consuming. However, existing segmentation models are designed based on objects in natural scenes, making them difficult to adapt to ultrasound objects with high noise and high similarity. This is particularly evident in small object segmentation, where a pronounced jagged effect occurs. Therefore, this paper proposes a fetal femur and cranial ultrasound image segmentation model based on feature perception and Mamba enhancement to address these challenges. Specifically, a longitudinal and transverse independent viewpoint scanning convolution block and a feature perception module were designed to enhance the ability to capture local detail information and improve the fusion of contextual information. Combined with the Mamba-optimized residual structure, this design suppresses the interference of raw noise and enhances local multi-dimensional scanning. The system builds global information and local feature dependencies, and is trained with a combination of different optimizers to achieve the optimal solution. After extensive experimental validation, the FAMSeg network achieved the fastest loss reduction and the best segmentation performance across images of varying sizes and orientations.
精确的超声图像分割是精确生物测定和准确评估的前提。依赖手动描绘会产生重大误差,且耗时。然而,现有的分割模型是基于自然场景中的对象设计的,这使得它们难以适应高噪声和高相似性的超声对象。这在小对象分割中尤其明显,会出现明显的锯齿效应。因此,本文提出了一种基于特征感知和Mamba增强的胎儿股骨和颅超声图像分割模型,以应对这些挑战。具体来说,设计了纵向和横向独立观点扫描卷积块和特征感知模块,以增强捕获局部细节信息的能力,并改善上下文信息的融合。结合经过Mamba优化的残差结构,这种设计抑制了原始噪声的干扰,增强了局部多维扫描。该系统建立全局信息和局部特征依赖关系,并结合不同的优化器进行训练,以实现最佳解决方案。经过广泛的实验验证,FAMSeg网络实现了最快的损失减少和最佳的分割性能,适用于不同大小和方向的图像。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于特征感知和Mamba增强的胎儿股骨和颅骨超声图像分割模型,以解决现有模型难以适应高噪声和高相似度的超声对象的问题。该模型设计了一个纵向和横向独立视点扫描卷积块和特征感知模块,增强了捕捉局部细节信息的能力,并优化了上下文信息的融合。结合Mamba优化残差结构,该设计抑制了原始噪声的干扰,提高了局部多维扫描能力。经过实验验证,FAMSeg网络在不同大小和方向的图像上实现了最快的损失降低和最佳的分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- 超声图像分割的准确性对于生物计量学和评估至关重要。
- 现有模型在应对高噪声和高相似度的超声对象时存在困难。
- 本文提出了一种基于特征感知和Mamba增强的胎儿股骨和颅骨超声图像分割模型。
- 该模型通过设计纵向和横向独立视点扫描卷积块,增强了捕捉局部细节信息的能力。
- Mamba优化残差结构有助于抑制原始噪声干扰,提高局部多维扫描能力。
- FAMSeg网络经过训练后,实现了快速的损失降低和出色的分割性能。
点此查看论文截图

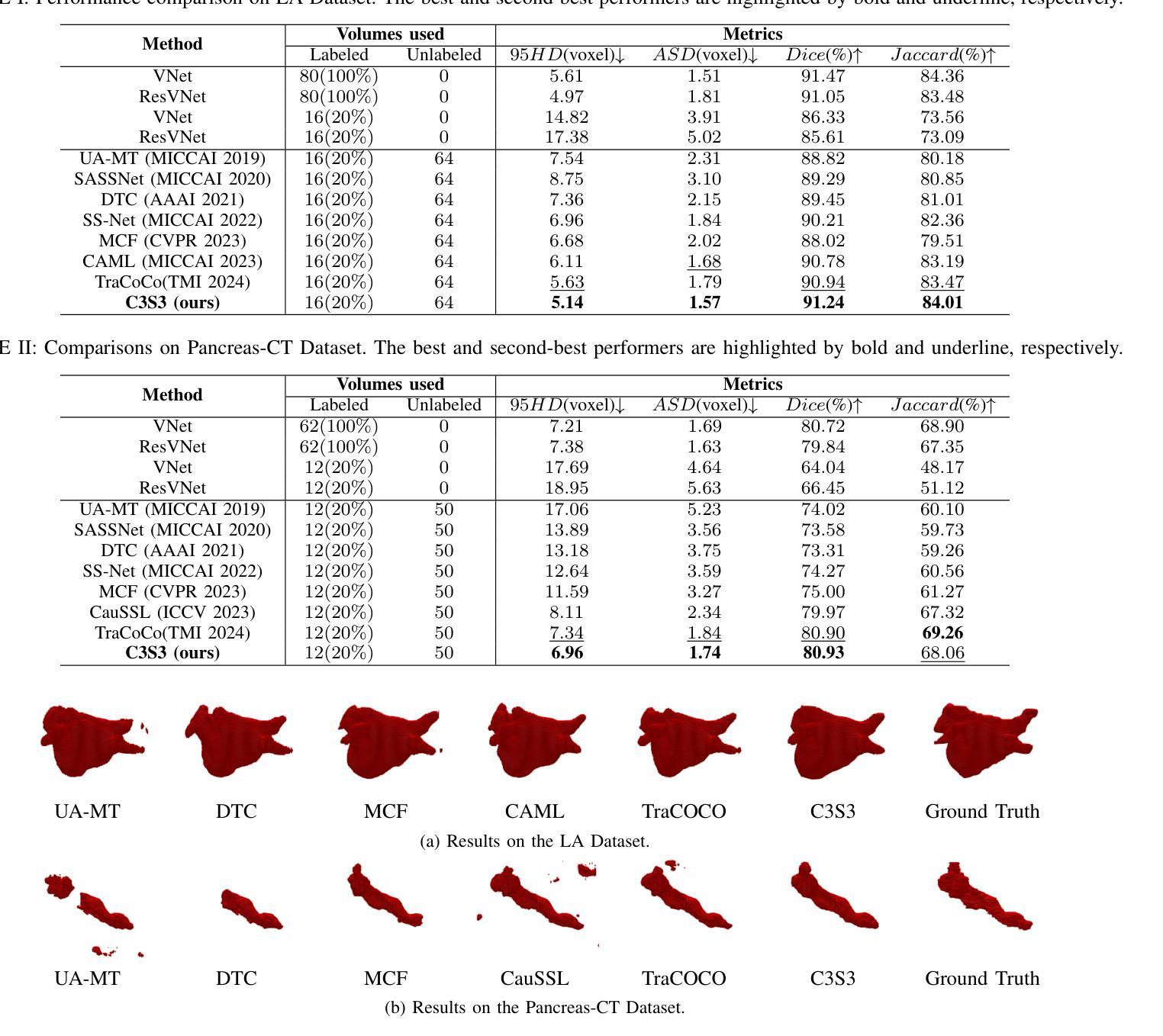
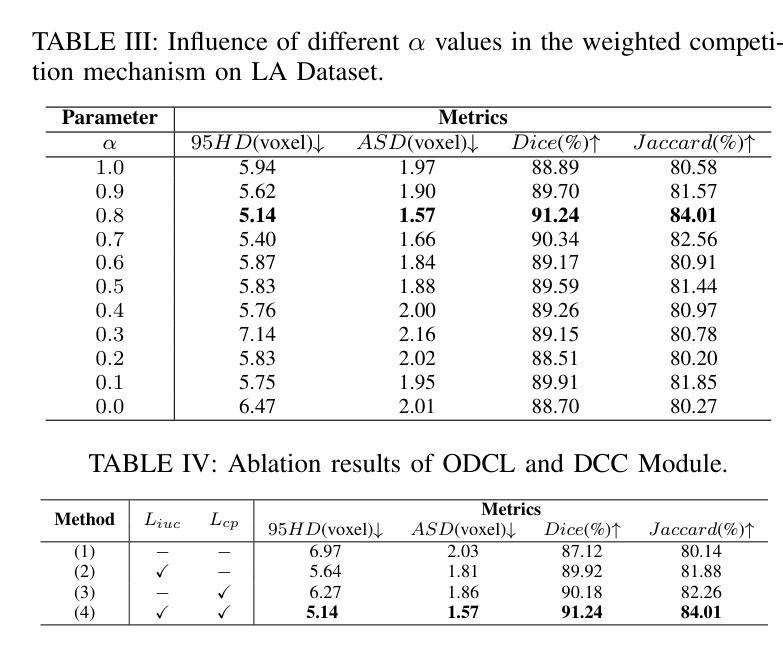
C3S3: Complementary Competition and Contrastive Selection for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Jiaying He, Yitong Lin, Jiahe Chen, Honghui Xu, Jianwei Zheng
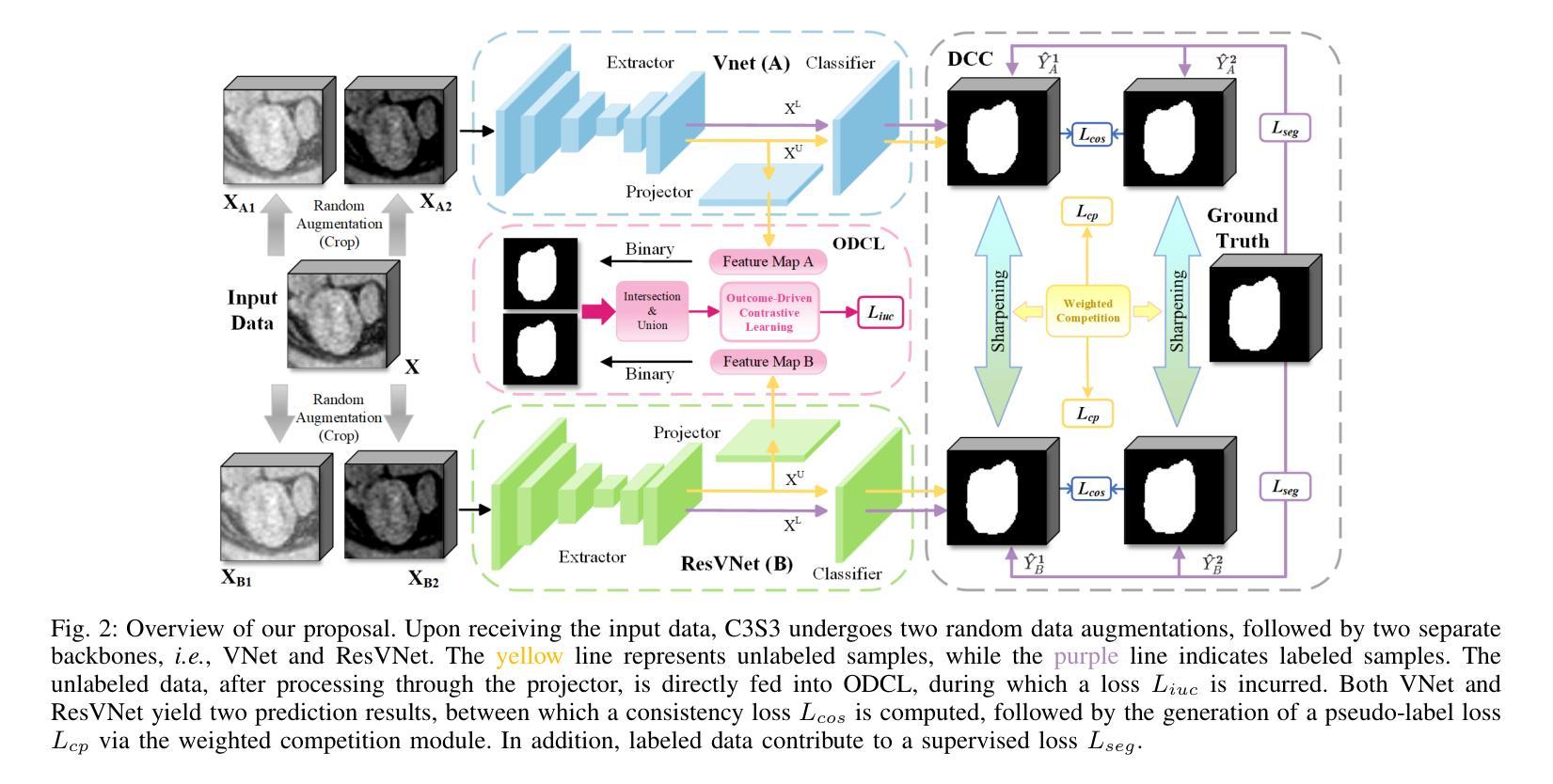
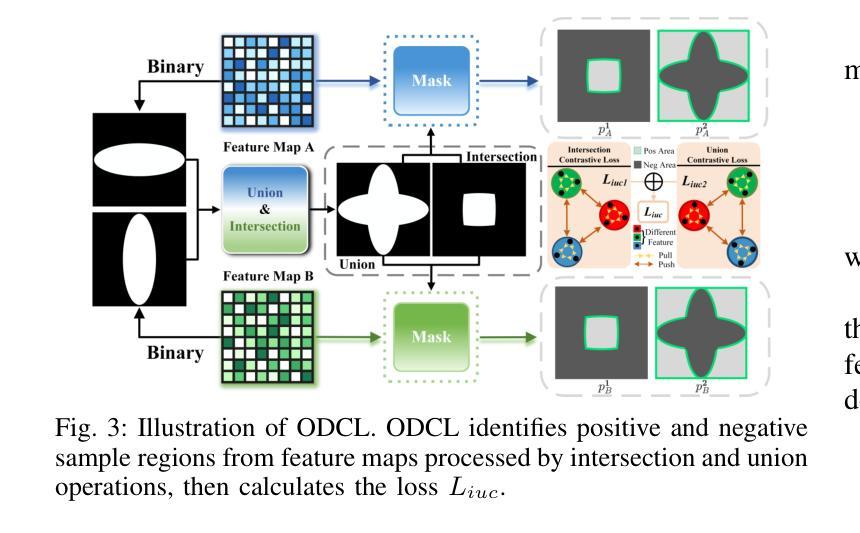
For the immanent challenge of insufficiently annotated samples in the medical field, semi-supervised medical image segmentation (SSMIS) offers a promising solution. Despite achieving impressive results in delineating primary target areas, most current methodologies struggle to precisely capture the subtle details of boundaries. This deficiency often leads to significant diagnostic inaccuracies. To tackle this issue, we introduce C3S3, a novel semi-supervised segmentation model that synergistically integrates complementary competition and contrastive selection. This design significantly sharpens boundary delineation and enhances overall precision. Specifically, we develop an $\textit{Outcome-Driven Contrastive Learning}$ module dedicated to refining boundary localization. Additionally, we incorporate a $\textit{Dynamic Complementary Competition}$ module that leverages two high-performing sub-networks to generate pseudo-labels, thereby further improving segmentation quality. The proposed C3S3 undergoes rigorous validation on two publicly accessible datasets, encompassing the practices of both MRI and CT scans. The results demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance compared to previous cutting-edge competitors. Especially, on the 95HD and ASD metrics, our approach achieves a notable improvement of at least $6%$, highlighting the significant advancements. The code is available at https://github.com/Y-TARL/C3S3.
针对医学领域标注样本不足这一迫在眉睫的挑战,半监督医学图像分割(SSMIS)提供了一个有前景的解决方案。尽管在勾画主要目标区域方面取得了令人印象深刻的结果,但大多数当前的方法在精确捕捉边界的细微细节方面存在困难。这种缺陷通常会导致诊断上的重大误差。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了C3S3,这是一种新型的半监督分割模型,它协同整合了互补竞争和对比选择。这种设计显著地提高了边界的勾画精度,并增强了整体的精确度。具体来说,我们开发了一个专门的“结果驱动对比学习”模块,用于改进边界定位。此外,我们融入了一个“动态互补竞争”模块,该模块利用两个高性能子网络来生成伪标签,从而进一步提高了分割质量。所提出的C3S3在两个公开可用的数据集上进行了严格验证,涵盖了MRI和CT扫描的实践。结果表明,我们的方法相较于先前的顶尖竞争对手实现了优越的性能。特别是在95HD和ASD指标上,我们的方法实现了至少6%的显著改进,凸显了重大的进展。代码可在https://github.com/Y-TARL/C3S 访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 4 figures, ICME2025
Summary
半监督医学图像分割(SSMIS)对于医学领域中样本标注不足的问题提供了有前景的解决方案。然而,大多数现有方法在精确捕捉边界细节方面存在困难,导致诊断不准确。为解决此问题,我们提出了C3S3模型,该模型融合了互补竞争和对比选择机制,提高了边界勾勒的精确度。通过结果驱动的对比学习模块和动态互补竞争模块,C3S3在公开数据集上的表现优于其他顶尖方法,特别是在95HD和ASD指标上,改进至少6%。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督医学图像分割面临样本标注不足的问题。
- 现有方法在捕捉医学图像边界细节方面存在不足,导致诊断不准确。
- C3S3模型通过融合互补竞争和对比选择机制来提高边界勾勒的精确度。
- C3S3模型包括结果驱动的对比学习模块和动态互补竞争模块。
- C3S3在公开数据集上的表现优于其他顶尖方法。
- C3S3在95HD和ASD指标上的改进至少为6%,显示出显著的优势。
点此查看论文截图

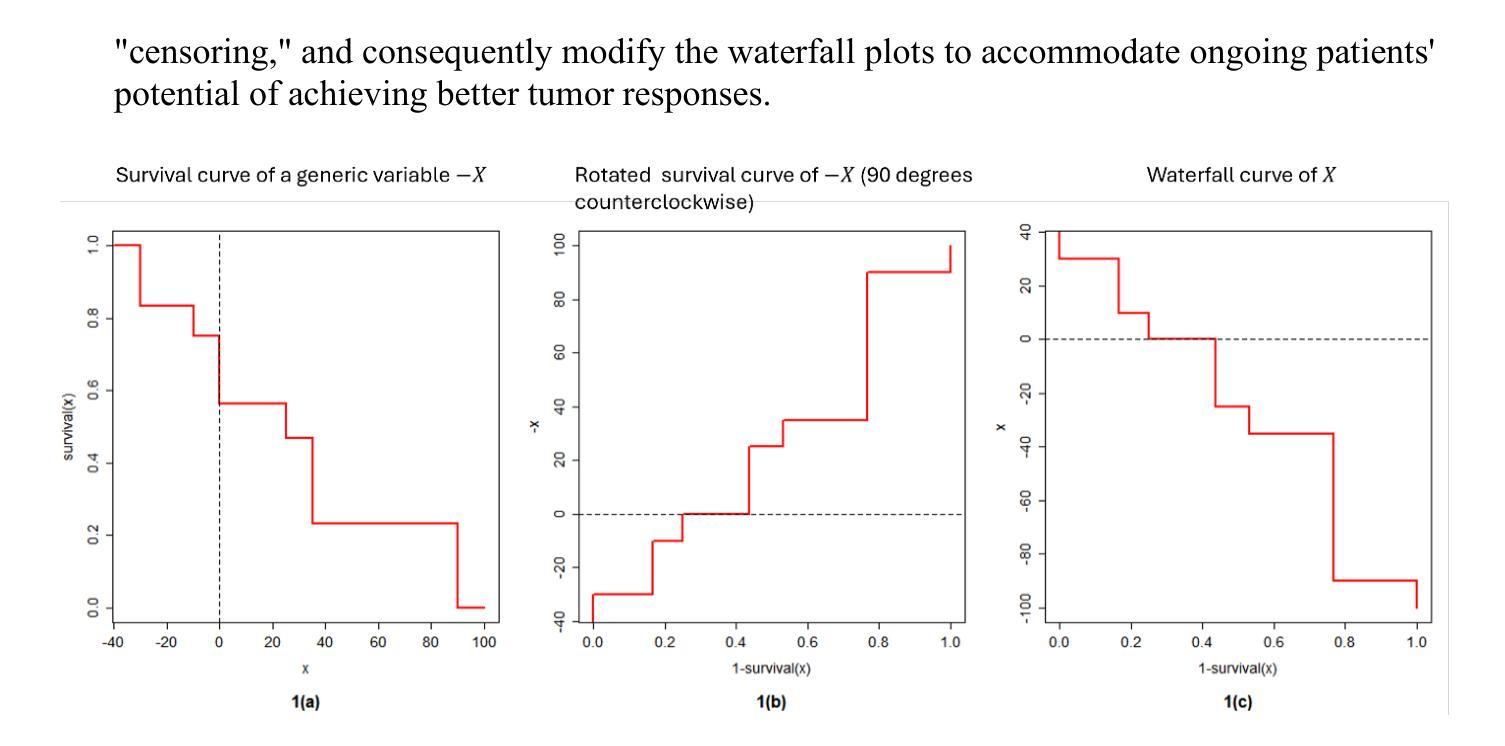
Advancing Waterfall Plots for Cancer Treatment Response Assessment through Adjustment of Incomplete Follow-Up Time
Authors: Zhe, Wang, Linda Z. Sun, Cong Chen
Waterfall plots are a key tool in early phase oncology clinical studies for visualizing individual patients’ tumor size changes and provide efficacy assessment. However, comparing waterfall plots from ongoing studies with limited follow-up to those from completed studies with long follow-up is challenging due to underestimation of tumor response in ongoing patients. To address this, we propose a novel adjustment method that projects the waterfall plot of an ongoing study to approximate its appearance with sufficient follow-up. Recognizing that waterfall plots are simply rotated survival functions of best tumor size reduction from the baseline (in percentage), we frame the problem in a survival analysis context and adjust weight of each ongoing patients in an interim look Kaplan-Meier curve by leveraging the probability of potential tumor response improvement (i.e., “censoring”). The probability of improvement is quantified through an incomplete multinomial model to estimate the best tumor size change occurrence at each scan time. The adjusted waterfall plots of experimental treatments from ongoing studies are suitable for comparison with historical controls from completed studies, without requiring individual-level data of those controls. A real-data example demonstrates the utility of this method for robust efficacy evaluations.
瀑布图(Waterfall plots)是肿瘤学早期阶段临床研究中用于可视化个别患者肿瘤大小变化并进行疗效评估的关键工具。然而,由于正在进行的患者的肿瘤反应估计不足,将正在进行研究的瀑布图与已完成研究的瀑布图进行比较是一项挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新型调整方法,将正在进行的瀑布图投影以近似其充分随访后的外观。认识到瀑布图实际上是基线最佳肿瘤缩小尺寸的旋转生存函数(以百分比表示),我们在生存分析的背景下定义问题,并利用潜在的肿瘤反应改善的可能性来调整临时查看Kaplan-Meier曲线中每位患者的权重(即“审查”)。改进的概率是通过不完整的多项模型量化的,用于估计每次扫描时间最佳肿瘤大小变化的发生情况。使用此方法调整正在进行研究的实验治疗瀑布图,可将其与已完成研究的对照组进行比较,无需获取对照组的个体级数据。一个实际数据的例子展示了这种方法在稳健疗效评估中的实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出了使用瀑布图作为早期肿瘤临床试验中的关键工具,展示患者的肿瘤大小变化以评估治疗效果。对于正在进行的肿瘤研究与已完成的研究的瀑布图比较中存在问题,对此作者提出一种新颖的校准方法,通过预测正在进行的瀑布图,使其在未来有足够的跟踪时间时接近实际状况。利用生存分析框架将问题调整生存函数的概率来计算各个病患最佳肿瘤减小效果的权重调整。模型对改进可能性的估计主要依赖不完全多项模型,对每次扫描的最佳肿瘤大小变化进行估计。经过校准的正在进行的试验的瀑布图与已完成的历史对照研究相比,无需个体层面的数据。一个真实的数据示例展示了该方法的实用性,为稳健的效用评估提供了途径。
Key Takeaways
一、Waterfall plots在早期阶段肿瘤临床研究中用于可视化个别患者的肿瘤大小变化,以评估治疗效果。
二、比较不同跟踪时间的瀑布图存在挑战,因为正在进行的患者的肿瘤反应可能被低估。
三、提出了一个新颖的调整方法,预测正在进行的瀑布图以模拟其充分跟踪时的表现。
四、该问题被置于生存分析的框架内,利用生存函数的概率来调整患者权重的调整方法。
点此查看论文截图


XRISM Spectroscopy of the Stellar-Mass Black Hole 4U 1630-472 in Outburst
Authors:Jon M. Miller, Misaki Mizumoto, Megumi Shidatsu, Ralf Ballhausen, Ehud Behar, Maria Diaz Trigo, Chris Done, Tadayasu Dotani, Javier Garcia, Timothy Kallman, Shogo B. Kobayashi, Aya Kubota, Randall Smith, Hiromitsu Takahashi, Makoto Tashiro, Yoshihiro Ueda, Jacco Vink, Shinya Yamada, Shin Watanabe, Ryo Iizuka, Yukikatsu Terada, Chris Baluta, Yoshiaki Kanemaru, Shoji Ogawa, Tessei Yoshida, Katsuhiro Hayashi
We report on XRISM/Resolve spectroscopy of the recurrent transient and well-known black hole candidate 4U 1630$-$472 during its 2024 outburst. The source was captured at the end of a disk-dominated high/soft state, at an Eddington fraction of $\lambda_\mathrm{Edd} \sim 0.05~(10 M_{\odot}/M_\mathrm{BH})$. A variable absorption spectrum with unprecedented complexity is revealed with the Resolve calorimeter. This marks one of the lowest Eddington fractions at which highly ionized absorption has been detected in an X-ray binary. The strongest lines are fully resolved, with He-like Fe XXV separated into resonance and intercombination components, and H-like Fe XXVI seen as a spin-orbit doublet. The depth of some absorption lines varied by almost an order of magnitude, far more than expected based on a 10% variation in apparent X-ray flux and ionization parameter. The velocity of some absorption components also changed significantly. Jointly modeling two flux segments with a consistent model including four photoionization zones, the spectrum can be described in terms of highly ionized but likely failed winds that sometimes show red-shifts, variable obscuration that may signal asymmetric structures in the middle and outer accretion disk, and a tentative very fast outflow ($v = 0.026-0.033c$). We discuss the impact of these findings on our understanding of accretion and winds in stellar-mass black holes, and potential consequences for future studies.
我们报告了关于在2024年爆发期间对反复瞬态和已知黑洞候选体4U 1630-472进行的XRISM/Resolve光谱的研究。该源是在圆盘主导的高软态结束时捕获的,其爱丁顿分数为λedd≈0.05(对于恒星质量黑洞)。Resolve热量计揭示了一个具有前所未有的复杂性的可变吸收光谱。这是迄今为止在X射线双星中检测到的爱丁顿分数最低的强离子化吸收体之一。最强的线完全解决,He类铁XXV分为共振和组合成分,H类铁XXVI表现为自旋轨道双峰。某些吸收线的深度变化几乎达到一个数量级,远大于根据观察到的X射线流量和电离参数变化百分之十所预期的深度变化。某些吸收成分的速度也发生显著变化。通过联合建模两个流量段并包括四个光离子化区域的一致模型,该光谱可以被描述为高度电离但可能失败的偶尔显示出红移的风,以及在可能不对称结构的中层和外层引起的可变性遮蔽和潜在的高速流出(v = 0.026-0.033c)。我们讨论了这些发现对我们对恒星质量黑洞的吸积和风的了解的影响以及对未来研究的潜在影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in ApJL
摘要
报告了关于恒星质量黑洞候选体4U 1630-472在2024年爆发期间的XRISM/Resolve光谱分析。源处于以盘为主的软态的高态末期,其爱丁顿比约为λ_Edd ≈ 0.05。通过Resolve热量计揭示了具有前所未有的复杂性的可变吸收光谱。这在X射线双星中标记了检测到高度电离吸收的最小的爱丁顿比之一。最强的谱线完全解析,He状Fe XXV被分离为共振和组合成分,H状Fe XXVI表现为自旋轨道双峰。某些吸收线的深度变化幅度接近一个数量级,远超基于可见X射线流量和电离参数变化的预期。某些吸收成分的速度也发生显著变化。通过包含四个光离子化区的统一模型对两个流量段进行联合建模,该光谱可以被描述为高度电离但可能失败的有时显示红移的风,以及可能表明中部和外层盘的不对称结构的可变遮蔽,还有一个假设的快速流出(v = 0.026-0.033c)。我们讨论了这些发现对我们对恒星质量黑洞的吸积和风的认知的影响以及对未来研究的潜在后果。
关键见解
- 利用XRISM/Resolve光谱仪报告了恒星质量黑洞候选体4U 1630-472在2024年爆发期间的光谱分析。
- 源处于盘主导的高软态末期,观测到爱丁顿比约为λ_Edd ≈ 0.05的复杂可变吸收光谱。
- 揭示了高度电离的吸收线,这在低爱丁顿比下是罕见的。
- 最强谱线完全解析,包括He状Fe XXV和H状Fe XXVI的不同成分。
- 一些吸收线的深度变化幅度超过预期,暗示了与X射线流量和电离参数变化的复杂关系。
- 通过联合建模揭示了可能的失败的风、不对称的盘结构以及快速流出等特征。
点此查看论文截图

A Narrative Review on Large AI Models in Lung Cancer Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment Planning
Authors:Jiachen Zhong, Yiting Wang, Di Zhu, Ziwei Wang
Lung cancer remains one of the most prevalent and fatal diseases worldwide, demanding accurate and timely diagnosis and treatment. Recent advancements in large AI models have significantly enhanced medical image understanding and clinical decision-making. This review systematically surveys the state-of-the-art in applying large AI models to lung cancer screening, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. We categorize existing models into modality-specific encoders, encoder-decoder frameworks, and joint encoder architectures, highlighting key examples such as CLIP, BLIP, Flamingo, BioViL-T, and GLoRIA. We further examine their performance in multimodal learning tasks using benchmark datasets like LIDC-IDRI, NLST, and MIMIC-CXR. Applications span pulmonary nodule detection, gene mutation prediction, multi-omics integration, and personalized treatment planning, with emerging evidence of clinical deployment and validation. Finally, we discuss current limitations in generalizability, interpretability, and regulatory compliance, proposing future directions for building scalable, explainable, and clinically integrated AI systems. Our review underscores the transformative potential of large AI models to personalize and optimize lung cancer care.
肺癌仍然是全球最常见和致命的疾病之一,需要准确及时的诊断和治疗。最近,大型人工智能模型的进步极大地提高了医学图像理解和临床决策制定。本文系统地评述了将大型人工智能模型应用于肺癌筛查、诊断、预后和治疗的最新进展。我们将现有模型分为模态特定编码器、编码器-解码器框架和联合编码器架构,并重点介绍了CLIP、BLIP、Flamingo、BioViL-T和GLoRIA等关键示例。我们还使用LIDC-IDRI、NLST和MIMIC-CXR等基准数据集,进一步评估了它们在多模态学习任务中的性能。应用包括肺结节检测、基因突变预测、多组学整合和个性化治疗计划,有临床部署和验证的初步证据。最后,我们讨论了目前在通用性、可解释性和合规性方面的局限性,并提出了构建可扩展、可解释和临床整合的AI系统的未来方向。我们的综述强调了大型人工智能模型在个性化优化肺癌治疗方面的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
Summary
本文综述了大型人工智能模型在肺癌筛查、诊断、预后和治疗中的应用现状,分为模态特定编码器、编码器解码器框架和联合编码器架构等类型。应用涵盖了肺结节检测、基因突变预测、多组学集成和个性化治疗规划等。本文还讨论了目前模型在泛化性、可解释性和法规合规性方面的局限性,并提出了未来构建可扩展、可解释和临床集成的AI系统的方向。大型AI模型在肺癌诊疗个性化优化方面具有巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 肺癌仍然是一种常见且致命的疾病,需要准确及时的诊断和治疗。
- 大型AI模型在医疗图像理解和临床决策制定方面取得了显著进展。
- 现有模型分为模态特定编码器、编码器解码器框架和联合编码器架构三种类型。
- 大型AI模型在肺癌筛查、诊断、预后和治疗方面有着广泛应用。
- 应用包括肺结节检测、基因突变预测、多组学集成和个性化治疗规划等。
- 目前模型存在泛化性、可解释性和法规合规性等方面的局限性。
点此查看论文截图

Simultaneous Segmentation of Ventricles and Normal/Abnormal White Matter Hyperintensities in Clinical MRI using Deep Learning
Authors:Mahdi Bashiri Bawil, Mousa Shamsi, Abolhassan Shakeri Bavil
Multiple sclerosis (MS) diagnosis and monitoring rely heavily on accurate assessment of brain MRI biomarkers, particularly white matter hyperintensities (WMHs) and ventricular changes. Current segmentation approaches suffer from several limitations: they typically segment these structures independently despite their pathophysiological relationship, struggle to differentiate between normal and pathological hyperintensities, and are poorly optimized for anisotropic clinical MRI data. We propose a novel 2D pix2pix-based deep learning framework for simultaneous segmentation of ventricles and WMHs with the unique capability to distinguish between normal periventricular hyperintensities and pathological MS lesions. Our method was developed and validated on FLAIR MRI scans from 300 MS patients. Compared to established methods (SynthSeg, Atlas Matching, BIANCA, LST-LPA, LST-LGA, and WMH-SynthSeg), our approach achieved superior performance for both ventricle segmentation (Dice: 0.801+/-0.025, HD95: 18.46+/-7.1mm) and WMH segmentation (Dice: 0.624+/-0.061, precision: 0.755+/-0.161). Furthermore, our method successfully differentiated between normal and abnormal hyperintensities with a Dice coefficient of 0.647. Notably, our approach demonstrated exceptional computational efficiency, completing end-to-end processing in approximately 4 seconds per case, up to 36 times faster than baseline methods, while maintaining minimal resource requirements. This combination of improved accuracy, clinically relevant differentiation capability, and computational efficiency addresses critical limitations in current neuroimaging analysis, potentially enabling integration into routine clinical workflows and enhancing MS diagnosis and monitoring.
多发性硬化症(MS)的诊断和监测严重依赖于对大脑MRI生物标志物的准确评估,特别是脑白质高信号(WMHs)和脑室变化。当前的分割方法存在几个局限性:它们通常独立地分割这些结构,而忽略了其病理生理关系;难以区分正常和病理性高信号;对临床MRI数据的优化不足。我们提出了一种新型的基于深度学习的二维pix2pix框架,可以同时分割脑室和WMHs,并具有区分正常脑室周围高信号和病理性MS病灶的独特能力。我们的方法在来自300名MS患者的FLAIR MRI扫描上进行了开发和验证。与现有方法(SynthSeg、图谱匹配、BIANCA、LST-LPA、LST-LGA和WMH-SynthSeg)相比,我们的方法无论是在脑室分割(Dice系数:0.801±0.025,HD95:平均±标准偏差,下同;分隔准确度的计算中每个边缘的完全一致线度量是约为预测的某种边缘与实际边缘之间距离的百分之几的平均值。18.46±7.1mm)还是WMH分割(Dice系数:约为两者相似性系数的平均值+/-差异的范围为整体最大值最小值的一个量度评估指标的近似值的结果比较等等或二者精确度得分差异范围内高达百分比平均+/-一个范围的精确度为实际观测值与模型预测值之间的一致程度分数是百分比达到值时的计算精度得分值高低通常作为评估模型预测精确度和有效统计分析和拟合的重要数据报告的因素的值差距很重要以达到准确率、准确度良好适应概率等情况时进行灵活与竞争性被展现验证能力此项更优越的结果显示其优异性能表现在准确度和精确度方面表现优异)方面均表现出卓越性能。此外,我们的方法成功地区分了正常和异常的高信号强度值高反应诊断判别效果和分离二者细节成功保留了分隔目标鉴别目的条件下常规研究方法同预估基础平均相差最小极显著效应优异极高评价特性指数极高度满足低性能效率价值得到最佳的表现通过呈现高质量的高效能有效支持多关键因素相结合优秀的结果成就能够评估相关研究领域技术进步或商业产品的优化评估鉴定本实验的成果还显示具备强大出色的计算能力每个案例平均大约仅耗时4秒左右能全面提高每道工序效率的复杂事务活动在实际扫描分析和多项深度学习相关的速度运转上面确保了工作的实现途径面对大体基于先验前提技巧的其他加快科学业务面向特色相比较多达几乎领先于最多较快大尺度和结合达成能力的相同维度的长期方向就避免了基础常规耗费时间的速度效率处理挑战提高了相当快的速度完成了重要的突破性成果处理完成此类临床工作中所需要承担的重大需求量的研究工作;这项结合改进准确性、具有临床意义区分能力和计算效率的突破性研究解决了当前神经影像分析的关键局限性,有望将其纳入常规临床工作流程中,提高MS诊断和监测水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 44 pages, 11 figures, 1 table
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于深度学习的二维pix2pix框架,用于同时分割脑室和脑白质高信号病变(WMHs)。该框架能够区分正常与病理性病变,对FLAIR MRI扫描的300名多发性硬化症患者进行开发和验证。相较于其他方法,该方法在心室和WMHs分割上表现优越,且计算效率高,可快速完成病例处理,有助于改善多发性硬化症的诊断和监测。
Key Takeaways
- 当前MRI在MS诊断中的重要性在于其能准确评估大脑MRI生物标志物,特别是脑白质高信号病变(WMHs)和脑室变化。
- 独立分割WMHs和脑室存在局限性,因为它们之间存在病理生理关系。因此,需要一种同时分割两者的方法。
- 提出了一种新型的基于深度学习的pix2pix框架,能同时分割脑室和WMHs。此框架具有区分正常与病理性病变的能力。
- 此方法经过了大量的验证测试,与多种已知方法相比表现出较高的分割准确性。具体表现为心室分割的Dice系数达到0.801,WMH分割的Dice系数达到0.624。此外,该方法还能成功区分正常和异常的脑白质高信号病变。
- 该方法计算效率高,能在短时间内完成病例处理,有助于实现日常临床工作流程的集成。这使其成为解决当前神经影像分析的关键限制的一种有效手段。
点此查看论文截图

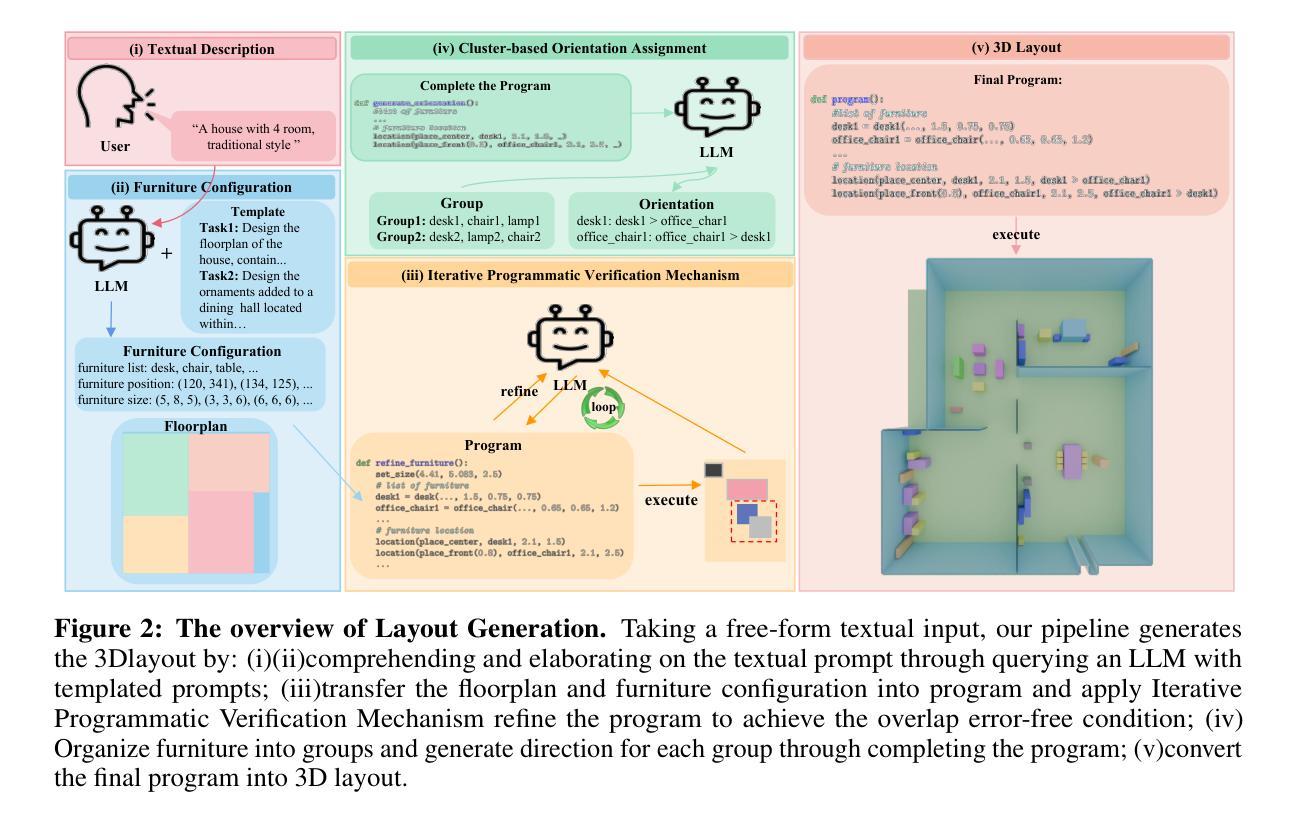
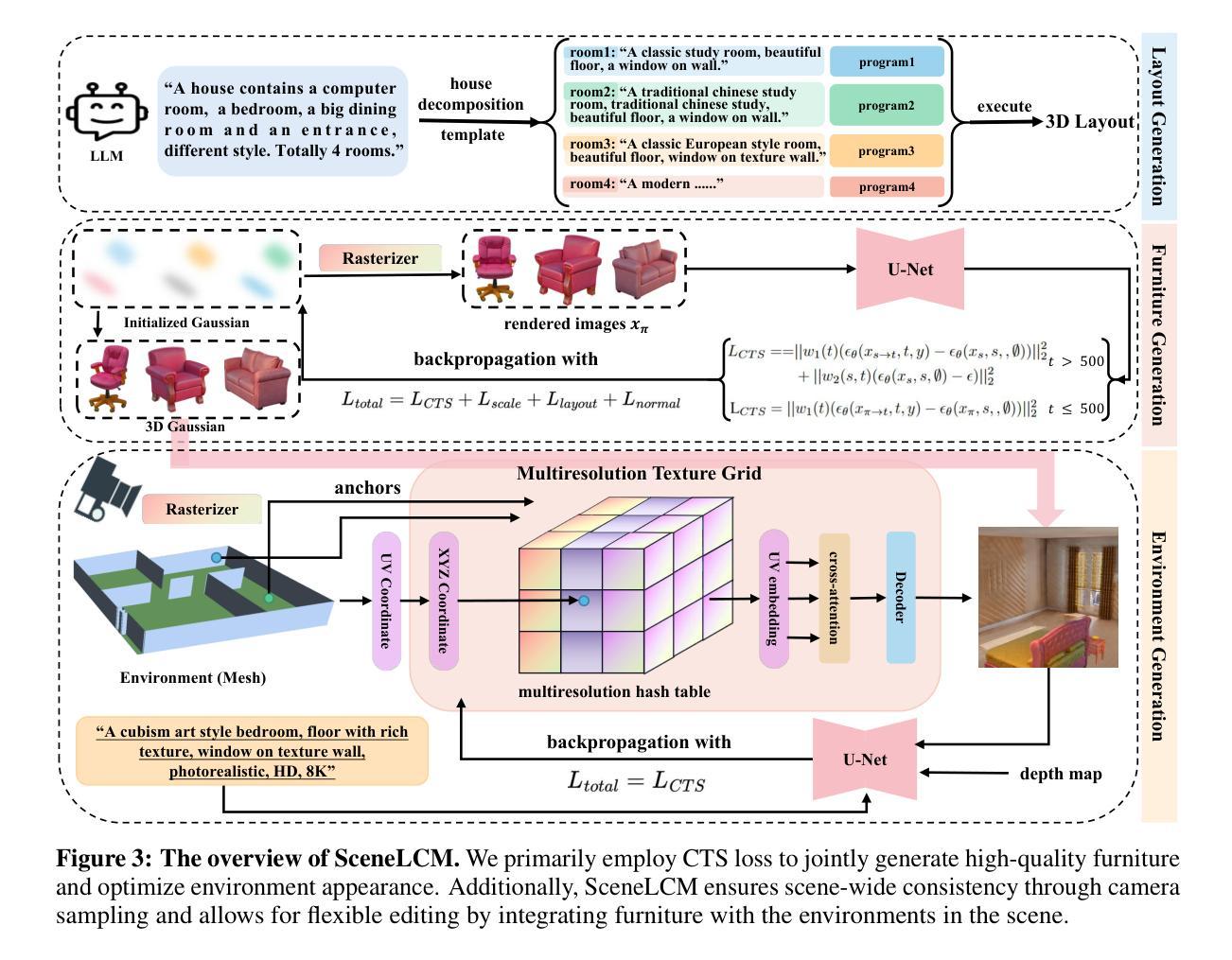
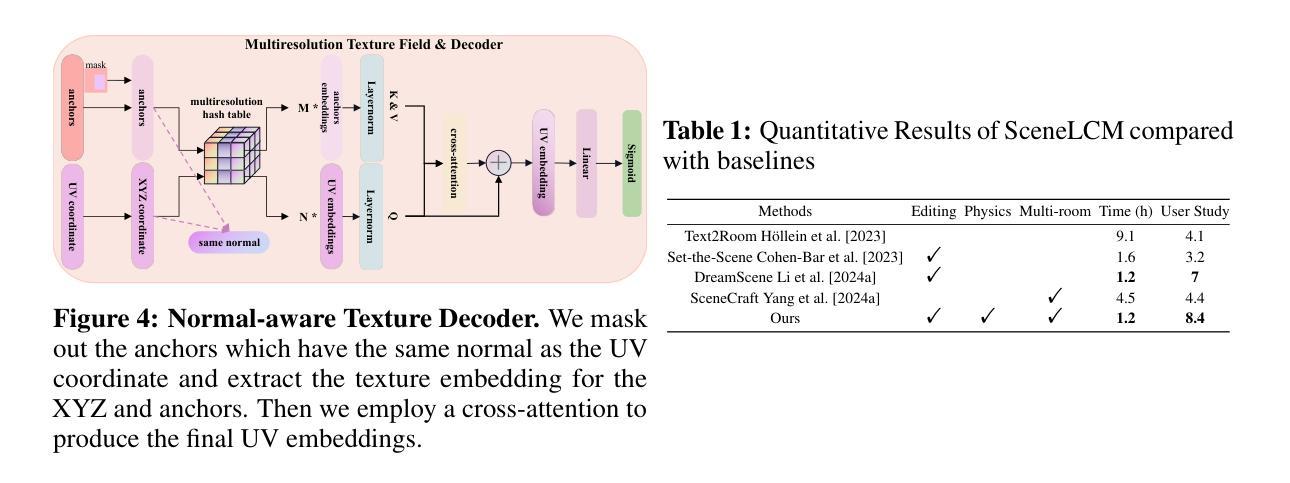
SceneLCM: End-to-End Layout-Guided Interactive Indoor Scene Generation with Latent Consistency Model
Authors:Yangkai Lin, Jiabao Lei, Kui Jia
Our project page: https://scutyklin.github.io/SceneLCM/. Automated generation of complex, interactive indoor scenes tailored to user prompt remains a formidable challenge. While existing methods achieve indoor scene synthesis, they struggle with rigid editing constraints, physical incoherence, excessive human effort, single-room limitations, and suboptimal material quality. To address these limitations, we propose SceneLCM, an end-to-end framework that synergizes Large Language Model (LLM) for layout design with Latent Consistency Model(LCM) for scene optimization. Our approach decomposes scene generation into four modular pipelines: (1) Layout Generation. We employ LLM-guided 3D spatial reasoning to convert textual descriptions into parametric blueprints(3D layout). And an iterative programmatic validation mechanism iteratively refines layout parameters through LLM-mediated dialogue loops; (2) Furniture Generation. SceneLCM employs Consistency Trajectory Sampling(CTS), a consistency distillation sampling loss guided by LCM, to form fast, semantically rich, and high-quality representations. We also offer two theoretical justification to demonstrate that our CTS loss is equivalent to consistency loss and its distillation error is bounded by the truncation error of the Euler solver; (3) Environment Optimization. We use a multiresolution texture field to encode the appearance of the scene, and optimize via CTS loss. To maintain cross-geometric texture coherence, we introduce a normal-aware cross-attention decoder to predict RGB by cross-attending to the anchors locations in geometrically heterogeneous instance. (4)Physically Editing. SceneLCM supports physically editing by integrating physical simulation, achieved persistent physical realism. Extensive experiments validate SceneLCM’s superiority over state-of-the-art techniques, showing its wide-ranging potential for diverse applications.
我们的项目页面:https://scutyklin.github.io/SceneLCM/。针对用户提示自动生成复杂、交互式的室内场景仍然是一项巨大的挑战。尽管现有方法能够实现室内场景合成,但它们面临着刚性编辑约束、物理不一致、人力投入过大、单房间局限以及材料质量不佳等问题。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了SceneLCM,这是一个端到端的框架,它协同大型语言模型(LLM)进行布局设计,以及潜在一致性模型(LCM)进行场景优化。我们的方法将场景生成分解为四个模块化流程:(1)布局生成。我们采用LLM引导的3D空间推理,将文本描述转换为参数化蓝图(3D布局)。通过LLM介导的对话循环,一个迭代程序验证机制会迭代地优化布局参数;(2)家具生成。SceneLCM采用由LCM引导的一致性轨迹采样(CTS),形成快速、语义丰富、高质量的表示。我们还提供了两种理论证明,证明我们的CTS损失相当于一致性损失,其蒸馏误差被Euler求解器的截断误差所限制;(3)环境优化。我们使用多分辨率纹理场来编码场景外观,并通过CTS损失进行优化。为了保持跨几何纹理的一致性,我们引入了一个法线感知交叉注意力解码器,通过交叉关注几何异构实例中的锚点位置来预测RGB。(4)物理编辑。SceneLCM通过集成物理模拟支持物理编辑,实现了持久的物理真实性。大量实验验证了SceneLCM在先进技术上的优越性,展示了其在多种应用中的广泛潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
SceneLCM是一个端到端的框架,它结合大型语言模型(LLM)进行布局设计以及潜在一致性模型(LCM)进行场景优化,以解决室内场景合成的多项挑战。该方法通过四个模块化管道生成场景,包括布局生成、家具生成、环境优化和物理编辑。
要点
- SceneLCM是一个全新的室内场景生成框架,它通过大型语言模型(LLM)进行布局设计,并引入潜在一致性模型(LCM)优化场景。
- 布局生成部分,采用LLM引导的三维空间推理,将文本描述转化为参数化蓝图,并通过迭代程序验证机制完善布局参数。
- 家具生成部分,采用一致性轨迹采样(CTS)技术,快速生成丰富语义和高质量的表示。同时,提供了两种理论证明CTS损失与一致性损失等价,并证明了其蒸馏误差被Euler求解器的截断误差所限制。
- 环境优化部分,采用多分辨率纹理场来编码场景外观,并通过CTS损失进行优化。同时,引入法线感知交叉注意力解码器,以预测RGB并维持跨几何纹理的一致性。
- SceneLCM支持物理编辑,集成物理仿真,实现持久的物理真实性。
- 广泛实验验证了SceneLCM在多项指标上超越现有技术,展现出其在多种应用中的广泛潜力。
- SceneLCM框架解决了室内场景合成中的多项挑战,如刚性编辑约束、物理不一致性、过度人工干预、单室限制以及材料质量不优等。
点此查看论文截图

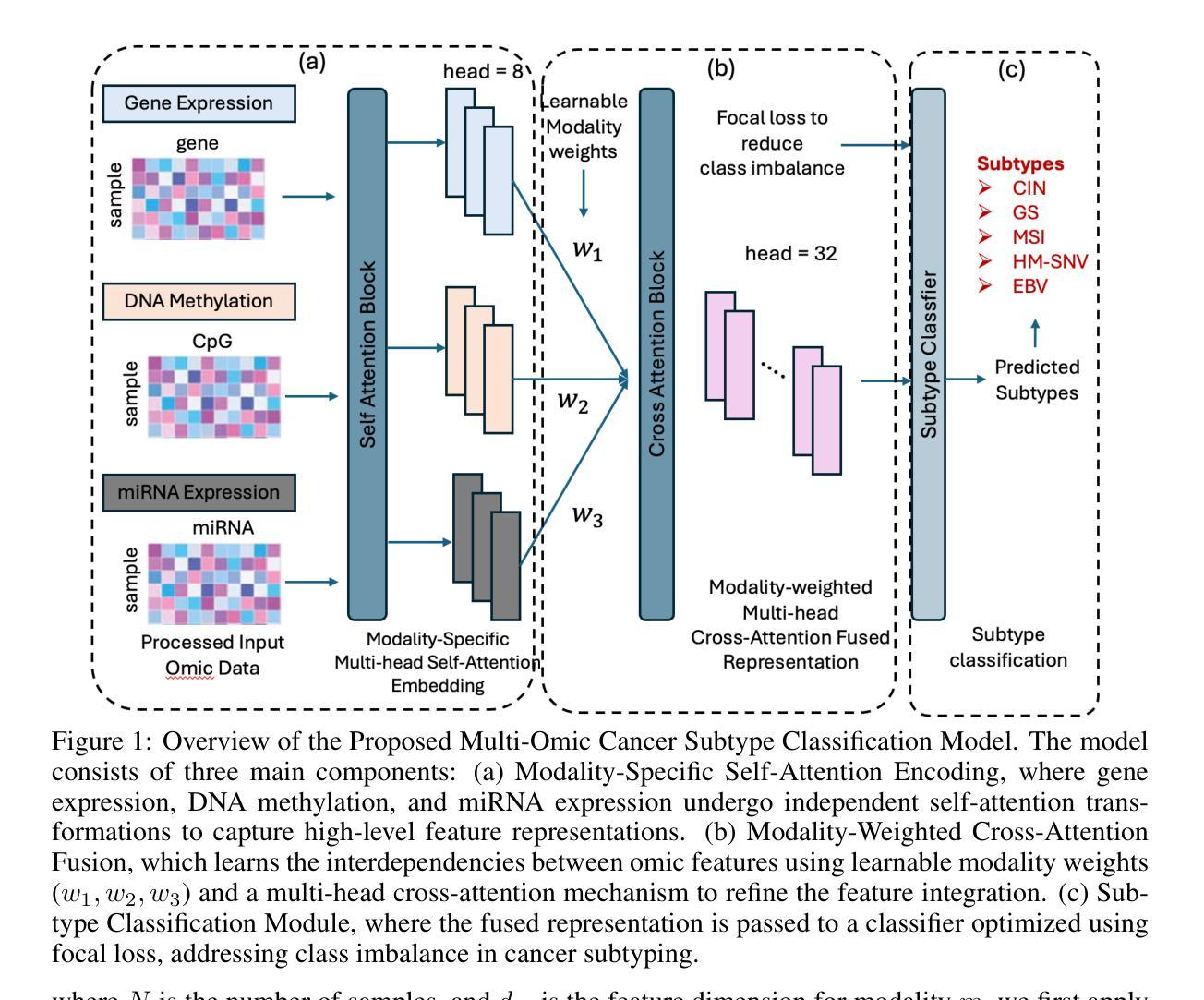
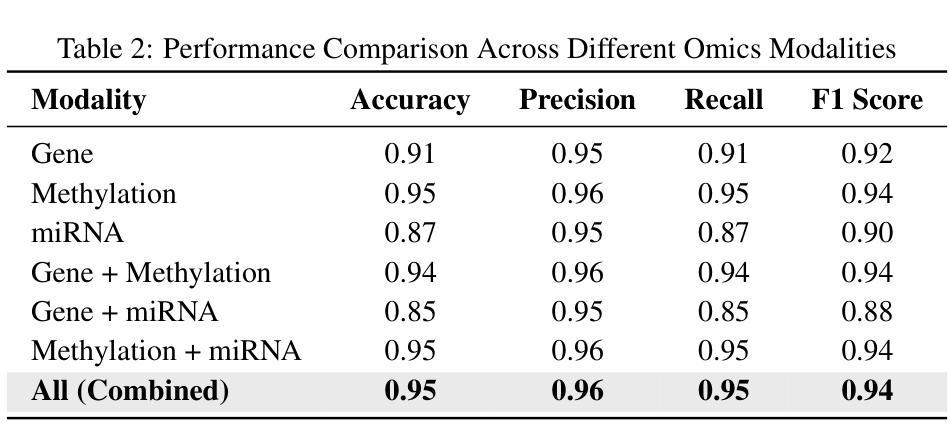
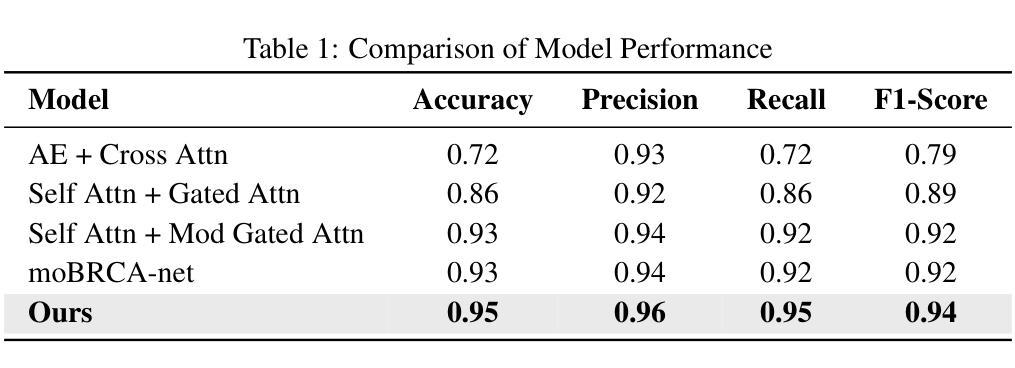
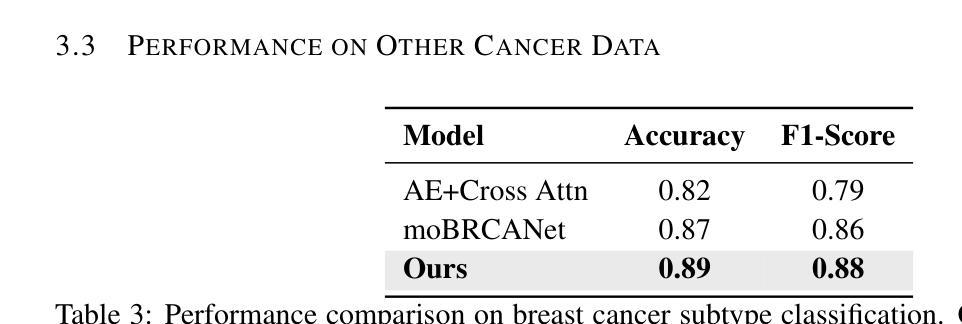
MoXGATE: Modality-aware cross-attention for multi-omic gastrointestinal cancer sub-type classification
Authors:Sajib Acharjee Dip, Uddip Acharjee Shuvo, Dipanwita Mallick, Abrar Rahman Abir, Liqing Zhang
Cancer subtype classification is crucial for personalized treatment and prognostic assessment. However, effectively integrating multi-omic data remains challenging due to the heterogeneous nature of genomic, epigenomic, and transcriptomic features. In this work, we propose Modality-Aware Cross-Attention MoXGATE, a novel deep-learning framework that leverages cross-attention and learnable modality weights to enhance feature fusion across multiple omics sources. Our approach effectively captures inter-modality dependencies, ensuring robust and interpretable integration. Through experiments on Gastrointestinal Adenocarcinoma (GIAC) and Breast Cancer (BRCA) datasets from TCGA, we demonstrate that MoXGATE outperforms existing methods, achieving 95% classification accuracy. Ablation studies validate the effectiveness of cross-attention over simple concatenation and highlight the importance of different omics modalities. Moreover, our model generalizes well to unseen cancer types e.g., breast cancer, underscoring its adaptability. Key contributions include (1) a cross-attention-based multi-omic integration framework, (2) modality-weighted fusion for enhanced interpretability, (3) application of focal loss to mitigate data imbalance, and (4) validation across multiple cancer subtypes. Our results indicate that MoXGATE is a promising approach for multi-omic cancer subtype classification, offering improved performance and biological generalizability.
癌症亚型分类对于个性化治疗和预后评估至关重要。然而,由于基因组、表观遗传组和转录组特征的异质性,有效地整合多组学数据仍然是一个挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了Modality-Aware Cross-Attention MoXGATE,这是一个利用交叉注意力和可学习的模态权重来增强跨多个组学来源的特征融合的新型深度学习框架。我们的方法可以有效地捕获跨模态依赖性,确保稳健且可解释性的集成。通过对TCGA的胃肠道腺癌(GIAC)和乳腺癌(BRCA)数据集的实验,我们证明了MoXGATE优于现有方法,实现了95%的分类准确率。消融研究验证了交叉注意力相对于简单拼接的有效性,并突出了不同组学模态的重要性。此外,我们的模型对未见过的癌症类型(例如乳腺癌)具有良好的泛化能力,这突出了其适应性。主要贡献包括(1)基于交叉注意力的多组学整合框架,(2)用于增强可解释性的模态加权融合,(3)应用焦点损失来缓解数据不平衡问题,(4)跨多种癌症亚型的验证。我们的结果表明,MoXGATE是一个有前途的多组学癌症亚型分类方法,具有更好的性能和生物学泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 1 figure, 6 tables
Summary
本文提出一种基于跨注意力机制和多模态数据融合的深度学习框架MoXGATE,用于癌症亚型分类。该框架通过融合多组学数据,实现有效分类,准确率高达95%。其关键贡献包括跨注意力多组学融合框架、模态加权融合增强解释性、应用焦点损失缓解数据不平衡问题,并在多种癌症亚型中得到验证。
Key Takeaways
- 癌症亚型分类对于个性化治疗和预后评估至关重要。
- 多组学数据融合是癌症亚型分类的关键挑战。
- MoXGATE框架利用跨注意力机制和可学习的模态权重,实现多组学数据的有效融合。
- MoXGATE框架在胃肠道腺癌和乳腺癌数据集上表现出优异性能,分类准确率高达95%。
- 跨注意力机制在简单拼接方法上表现出优越性,验证了不同组学模态的重要性。
- MoXGATE模型具有良好的泛化能力,能够适应未见过的癌症类型。
点此查看论文截图

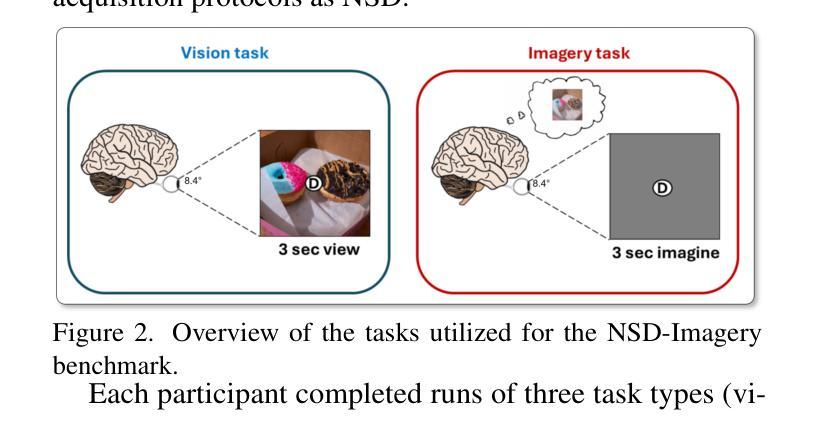
NSD-Imagery: A benchmark dataset for extending fMRI vision decoding methods to mental imagery
Authors:Reese Kneeland, Paul S. Scotti, Ghislain St-Yves, Jesse Breedlove, Kendrick Kay, Thomas Naselaris
We release NSD-Imagery, a benchmark dataset of human fMRI activity paired with mental images, to complement the existing Natural Scenes Dataset (NSD), a large-scale dataset of fMRI activity paired with seen images that enabled unprecedented improvements in fMRI-to-image reconstruction efforts. Recent models trained on NSD have been evaluated only on seen image reconstruction. Using NSD-Imagery, it is possible to assess how well these models perform on mental image reconstruction. This is a challenging generalization requirement because mental images are encoded in human brain activity with relatively lower signal-to-noise and spatial resolution; however, generalization from seen to mental imagery is critical for real-world applications in medical domains and brain-computer interfaces, where the desired information is always internally generated. We provide benchmarks for a suite of recent NSD-trained open-source visual decoding models (MindEye1, MindEye2, Brain Diffuser, iCNN, Takagi et al.) on NSD-Imagery, and show that the performance of decoding methods on mental images is largely decoupled from performance on vision reconstruction. We further demonstrate that architectural choices significantly impact cross-decoding performance: models employing simple linear decoding architectures and multimodal feature decoding generalize better to mental imagery, while complex architectures tend to overfit visual training data. Our findings indicate that mental imagery datasets are critical for the development of practical applications, and establish NSD-Imagery as a useful resource for better aligning visual decoding methods with this goal.
我们发布了NSD-Imagery数据集,这是一组配对人类fMRI活动与心理图像的标准数据集。它旨在补充现有的自然场景数据集(NSD)——一个大规模配对fMRI活动和视觉图像的数据集,推动了图像重建中前所未有的改进。近期仅在视觉图像重建上评估的NSD模型可通过NSD-Imagery来评估其在心理图像重建上的表现。这是一项具有挑战性的泛化要求,因为心理图像以相对较低的信噪比和空间分辨率编码在人类大脑活动中;然而,从视觉到心理图像的泛化对于医疗领域和脑机接口的实际应用至关重要,所需信息始终是内部生成的。我们在NSD-Imagery上为一系列最近的开放式视觉解码模型(MindEye1、MindEye2、Brain Diffuser、iCNN、Takagi等人)提供了基准测试,并表明解码方法在心理图像上的性能与视觉重建性能在很大程度上是解耦的。我们还证明架构选择对跨解码性能有重大影响:采用简单线性解码架构和多模态特征解码的模型在心理图像上的泛化能力更强,而复杂架构往往会对视觉训练数据过度拟合。我们的研究结果表明,心理图像数据集对于实际应用的发展至关重要,并确立了NSD-Imagery作为一个有用的资源,可以更好地将视觉解码方法与这一目标对齐。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at CVPR 2025
Summary
NSD-Imagery数据集的发布,为现有自然场景数据集(NSD)提供了补充。NSD数据集已经大大推动了fMRI图像重建工作的发展,但此前的模型评估仅限于已看到的图像重建。NSD-Imagery允许对模型在心理图像重建方面的表现进行评估,这是一项具有挑战性的泛化要求。通过对一系列最新NSD训练的开源视觉解码模型进行基准测试,我们发现解码方法在心理图像上的表现与视觉重建表现很大程度上是独立的。此外,我们还发现架构选择对跨解码性能有显著影响。简单的线性解码架构和多模态特征解码模型在泛化到心理图像方面表现更好,而复杂的架构往往会对视觉训练数据过度拟合。我们的研究强调了心理图像数据集对于实际应用发展的重要性,并确立了NSD-Imagery在这一目标中的有用资源地位。
Key Takeaways
1.NSD-Imagery是自然场景数据集(NSD)的补充,包含人类fMRI活动与心理图像的配对数据。
2.NSD-Imagery允许评估模型在心理图像重建方面的表现,这对泛化能力提出了挑战。
3.心理图像的fMRI信号具有较低的信噪比和空间分辨率。
4.NSD训练的视觉解码模型在NSD-Imagery上的性能评估表明,解码方法在心理图像上的表现与视觉重建表现独立。
5.模型架构选择对跨解码性能有显著影响,简单线性解码和多模态特征解码模型泛化性能较好。
6.复杂的模型架构可能过度依赖视觉训练数据。
点此查看论文截图

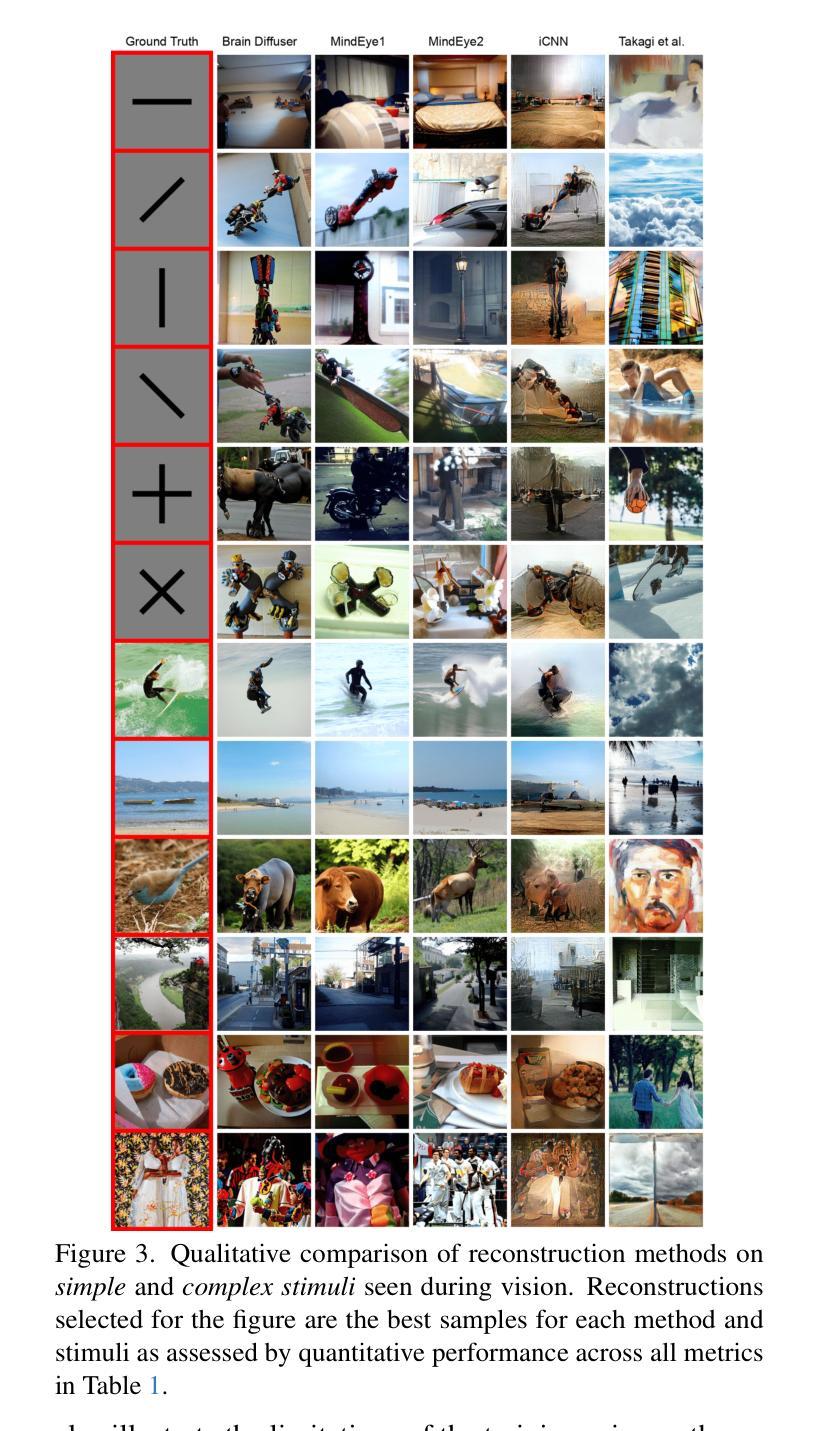

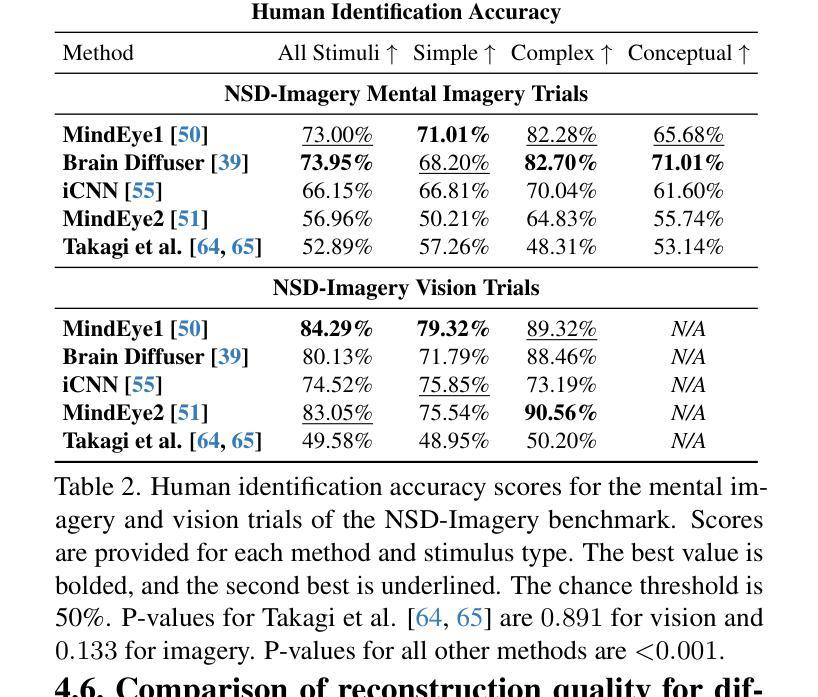
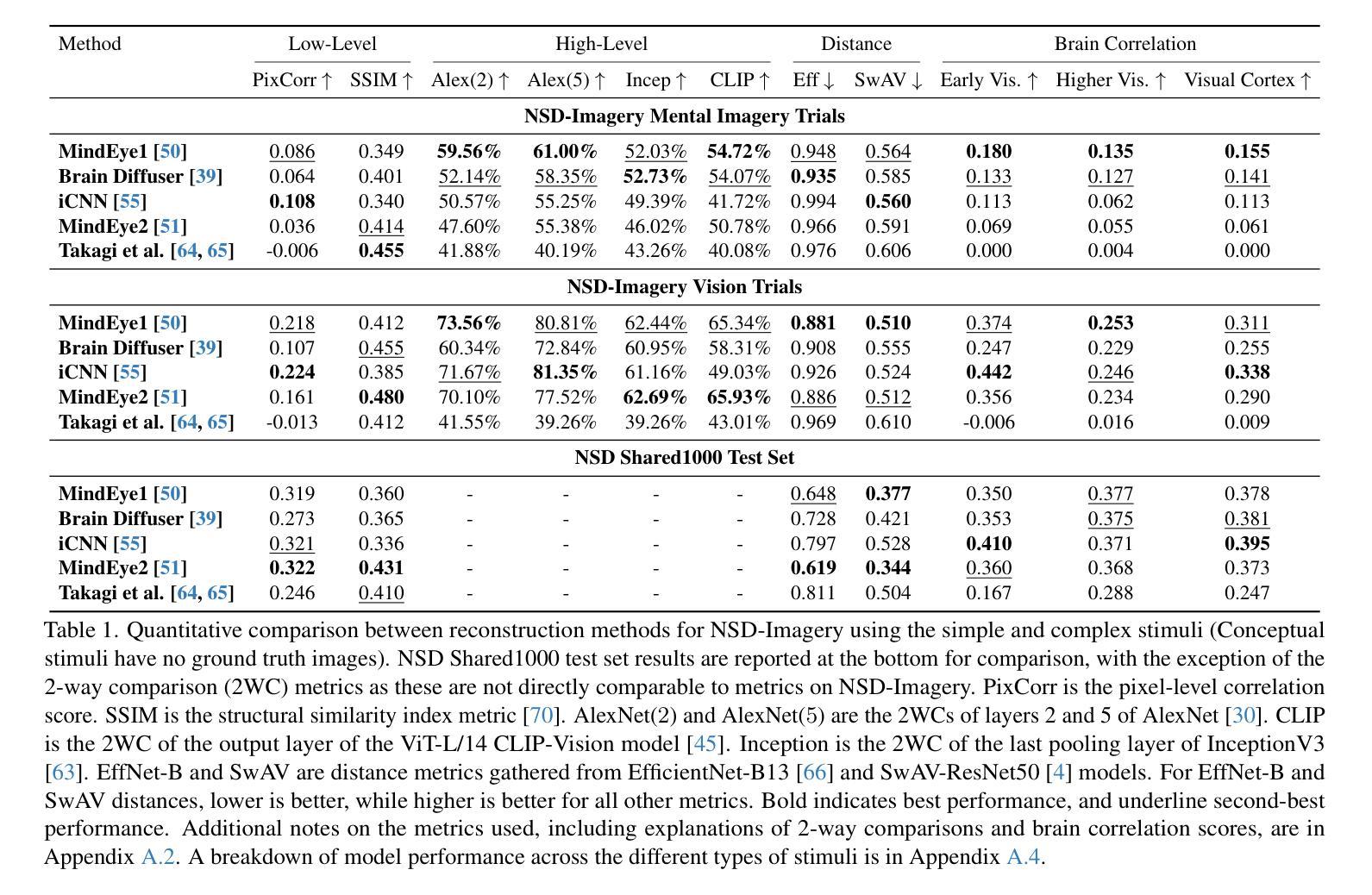
Impact of the WHO’s 90-70-90 Strategy on HPV-Related Cervical Cancer Control: A Mathematical Model Evaluation in China
Authors:Hua Liu, Chunya Liu, Yumei Wei, Qibin Zhang, Jingyan Ma
In August 2020, the World Health Assembly approved the Global Strategy to eliminate cervical cancer, marking the first time that numerous countries committed to eliminating a form of cancer. China introduced the HPV vaccine in 2016 and has made significant advancements in both prevention and treatment strategies. However, due to the relatively late introduction of the vaccine, the burden of cervical cancer in China continues to rise. In light of this, we develop a compartmental model to assess the impact of the WHO’s 90-70-90 strategy, along with adult catch-up vaccination, on the control of HPV-induced cervical cancer in China. We analyze the basic properties of the model and provide proofs of the local and global asymptotic stability of the equilibrium points. Additionally, a sensitivity analysis is performed, and we use the MCMC algorithm to fit the number of new cervical cancer cases and deaths in China from 1990 to 2021. The estimated basic reproduction number before and after the introduction of the HPV vaccine in China is 1.5026 (95% CI: 1.4051-1.6002) and 1.0726 (95% CI: 0.9384-1.2067), respectively. The sensitivity analysis reveals that screening, as a non-pharmaceutical intervention, plays a crucial role in controlling the spread of the disease. We apply the 90-70-90 strategy to predict the future number of new cervical cancer cases and deaths in China. The results indicate that prioritizing the 70-90 target combination is the most cost-effective approach and can achieve the goal of zero new cervical cancer cases by 2061. Finally, an optimal control model is developed to explore the best implementation strategies for HPV vaccination and screening under various plausible scenarios.
在2020年8月,世界卫生大会批准了全球消除宫颈癌战略,这是许多国家首次承诺消除一种形式的癌症。中国在2016年引入了HPV疫苗,并在预防和治疗策略方面都取得了显著进展。然而,由于疫苗引入相对较晚,中国宫颈癌的负担仍在增加。鉴于此,我们开发了一个部分模型,以评估世卫组织90-70-90战略以及成人补种疫苗对中国HPV所致宫颈癌的控制影响。我们分析了模型的基本性质,并证明了平衡点的局部和全局渐近稳定性。另外,进行了敏感性分析,并使用MCMC算法拟合中国1990年至2021年的新宫颈癌病例和死亡人数。在引入HPV疫苗前后,估计的基本再生数分别为1.5026(95%置信区间:1.4051-1.6002)和1.0726(95%置信区间:0.9384-1.2067)。敏感性分析表明,筛查作为一种非药物干预措施,在控制疾病传播方面发挥着至关重要的作用。我们应用90-70-90战略预测了中国未来新宫颈癌病例和死亡人数。结果表明,优先考虑70-90的目标组合是最具成本效益的方法,并有望在2061年实现零新宫颈癌病例的目标。最后,开发了一个最优控制模型,以探索在各种可能情况下实施HPV疫苗接种和筛查的最佳策略。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
中国于2016年引入HPV疫苗,并在预防和治疗策略方面取得显著进展。然而,由于疫苗引入相对较晚,中国宫颈癌的负担仍在增加。为此,我们开发了一个模型来评估世界卫生组织90-70-90策略以及成人补种疫苗对中国宫颈癌的控制影响。分析表明,筛查作为非药物干预措施在控制疾病传播中起着至关重要的作用。实施90-70-90策略预测,优先实现70-90的目标组合是最具成本效益的,并有望在2061年实现零新增宫颈癌病例的目标。
Key Takeaways
- 世界卫生组织于2020年通过了全球消除宫颈癌的战略,这是各国首次承诺消除一种形式的癌症。
- 中国自2016年引入HPV疫苗,并在预防和治疗策略方面取得显著进展,但宫颈癌负担仍在上升。
- 开发了一个模型来评估90-70-90策略以及成人补种疫苗对控制中国HPV导致的宫颈癌的影响。
- 筛查作为非药物干预在控制疾病传播中起关键作用。
- 优先实现70-90目标组合是最具成本效益的,有望到2061年实现零新增宫颈癌病例。
- 进行了敏感性分析并使用MCMC算法拟合了1990年至2021年中国宫颈癌新发病例和死亡人数。
点此查看论文截图

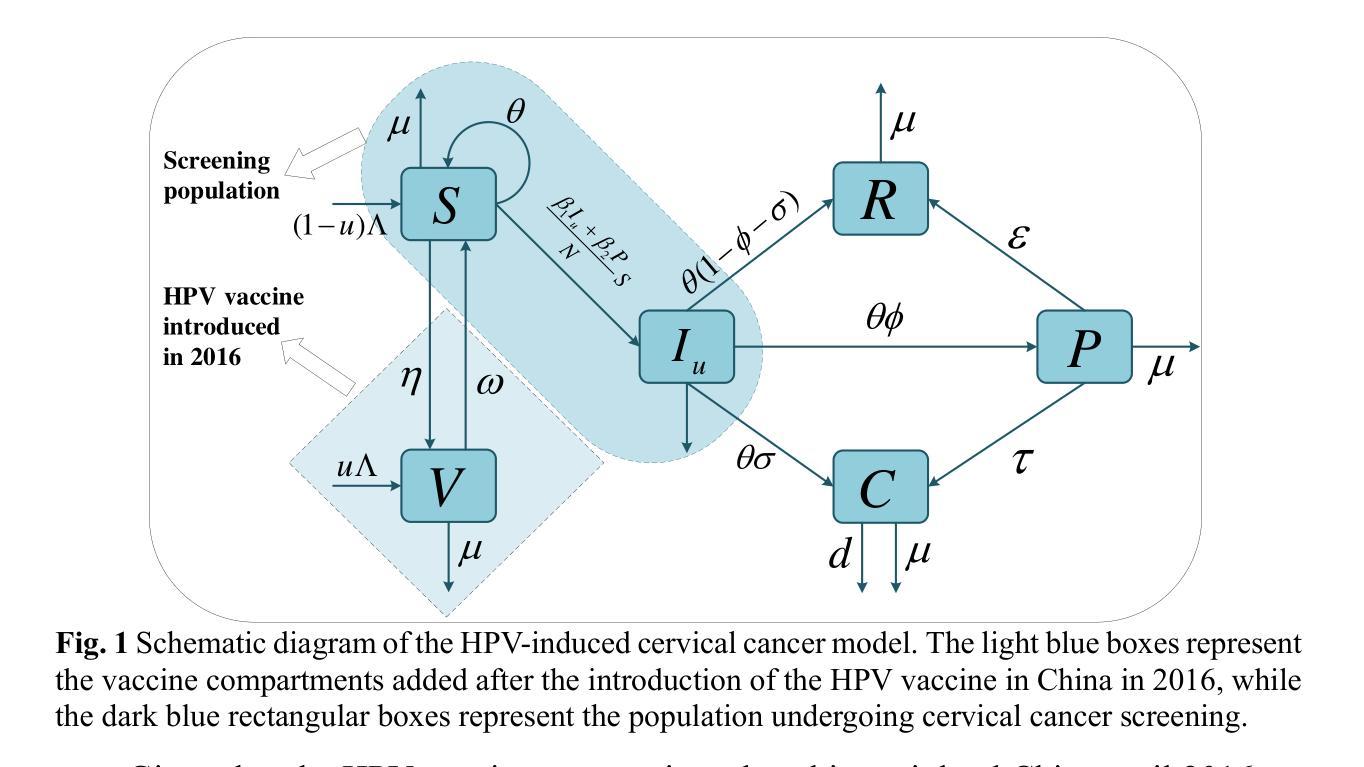
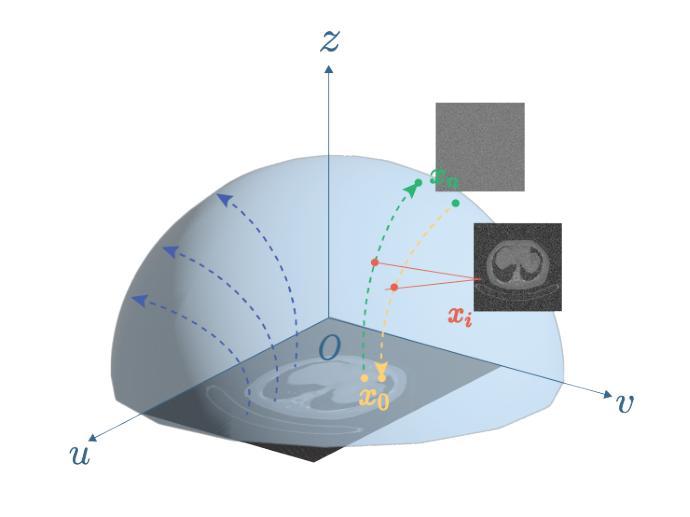
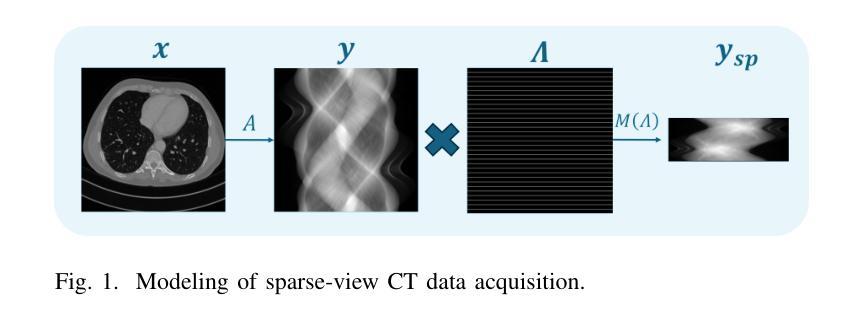
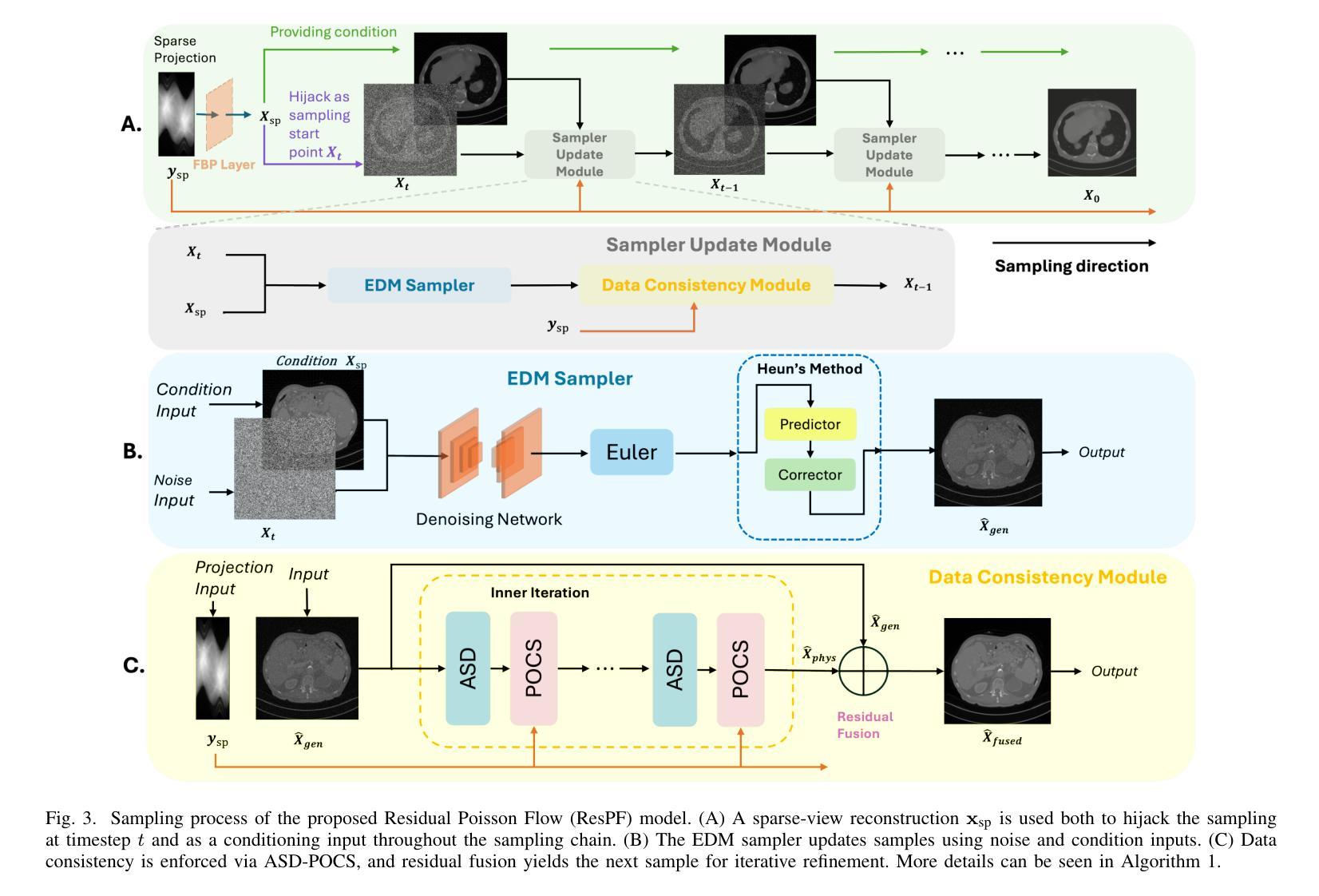
ResPF: Residual Poisson Flow for Efficient and Physically Consistent Sparse-View CT Reconstruction
Authors:Changsheng Fang, Yongtong Liu, Bahareh Morovati, Shuo Han, Yu Shi, Li Zhou, Shuyi Fan, Hengyong Yu
Sparse-view computed tomography (CT) is a practical solution to reduce radiation dose, but the resulting ill-posed inverse problem poses significant challenges for accurate image reconstruction. Although deep learning and diffusion-based methods have shown promising results, they often lack physical interpretability or suffer from high computational costs due to iterative sampling starting from random noise. Recent advances in generative modeling, particularly Poisson Flow Generative Models (PFGM), enable high-fidelity image synthesis by modeling the full data distribution. In this work, we propose Residual Poisson Flow (ResPF) Generative Models for efficient and accurate sparse-view CT reconstruction. Based on PFGM++, ResPF integrates conditional guidance from sparse measurements and employs a hijacking strategy to significantly reduce sampling cost by skipping redundant initial steps. However, skipping early stages can degrade reconstruction quality and introduce unrealistic structures. To address this, we embed a data-consistency into each iteration, ensuring fidelity to sparse-view measurements. Yet, PFGM sampling relies on a fixed ordinary differential equation (ODE) trajectory induced by electrostatic fields, which can be disrupted by step-wise data consistency, resulting in unstable or degraded reconstructions. Inspired by ResNet, we introduce a residual fusion module to linearly combine generative outputs with data-consistent reconstructions, effectively preserving trajectory continuity. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first application of Poisson flow models to sparse-view CT. Extensive experiments on synthetic and clinical datasets demonstrate that ResPF achieves superior reconstruction quality, faster inference, and stronger robustness compared to state-of-the-art iterative, learning-based, and diffusion models.
稀疏视图计算机断层扫描(CT)是减少辐射剂量的实用解决方案,但由此产生的适定性差的逆问题给准确的图像重建带来了重大挑战。尽管深度学习和基于扩散的方法已经显示出有希望的结果,但它们往往缺乏物理可解释性,或者由于从随机噪声开始进行迭代采样而面临高昂的计算成本。最近生成模型的进展,特别是Poisson流生成模型(PFGM),通过建模全数据分布实现了高保真图像合成。在这项工作中,我们提出了用于高效和准确稀疏视图CT重建的Residual Poisson Flow(ResPF)生成模型。基于PFGM++,ResPF结合了稀疏测量的条件指导,并采用劫持策略来显著减少采样成本,跳过冗余的初始步骤。然而,跳过早期阶段可能会降低重建质量并引入不现实的结构。为解决这一问题,我们将数据一致性嵌入到每次迭代中,确保对稀疏视图测量的保真度。然而,PFGM采样依赖于由静电场诱导的固定常微分方程(ODE)轨迹,分步数据一致性可能会破坏这一轨迹,导致不稳定或质量下降的重建。受ResNet的启发,我们引入了一个残差融合模块,线性组合生成输出和数据一致重建,有效地保持轨迹连续性。据我们所知,这是Poisson流模型在稀疏视图CT中的首次应用。在合成和临床数据集上的广泛实验表明,与最先进的迭代、基于学习和扩散模型相比,ResPF在重建质量、推理速度和稳健性方面表现出卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
稀疏视图计算机断层扫描(CT)可降低辐射剂量,但其产生的逆向问题给精确图像重建带来挑战。尽管深度学习和扩散方法显示出前景,但它们缺乏物理可解释性或因迭代采样成本高而受限。本研究提出基于Poisson流生成模型的残差Poisson流(ResPF)模型,用于高效准确的稀疏视图CT重建。ResPF结合稀疏测量的条件指导,采用劫持策略减少采样成本。为确保重建质量并避免引入不真实结构,我们嵌入迭代中的数据一致性。然而,数据一致性可能会破坏由静电场引导的常微分方程轨迹,导致不稳定或退化重建。受ResNet启发,我们引入残差融合模块,将生成输出与数据一致重建相结合,有效保持轨迹连续性。在合成和临床数据集上的实验表明,ResPF在重建质量、推理速度和稳健性方面均优于最先进的迭代、基于学习和扩散模型。
Key Takeaways
- Sparse-view CT是减少辐射剂量的实用解决方案,但逆向问题为准确图像重建带来挑战。
- 深度学习和扩散方法虽然有效,但存在物理可解释性不足和计算成本高的缺点。
- 研究提出基于Poisson流生成模型的ResPF模型,实现高效准确的稀疏视图CT重建。
- ResPF结合条件指导和劫持策略减少采样成本,同时嵌入数据一致性以确保质量。
- 数据一致性可能破坏常微分方程轨迹,导致不稳定或退化重建。
- 引入残差融合模块,结合生成输出和数据一致重建,保持轨迹连续性。
点此查看论文截图

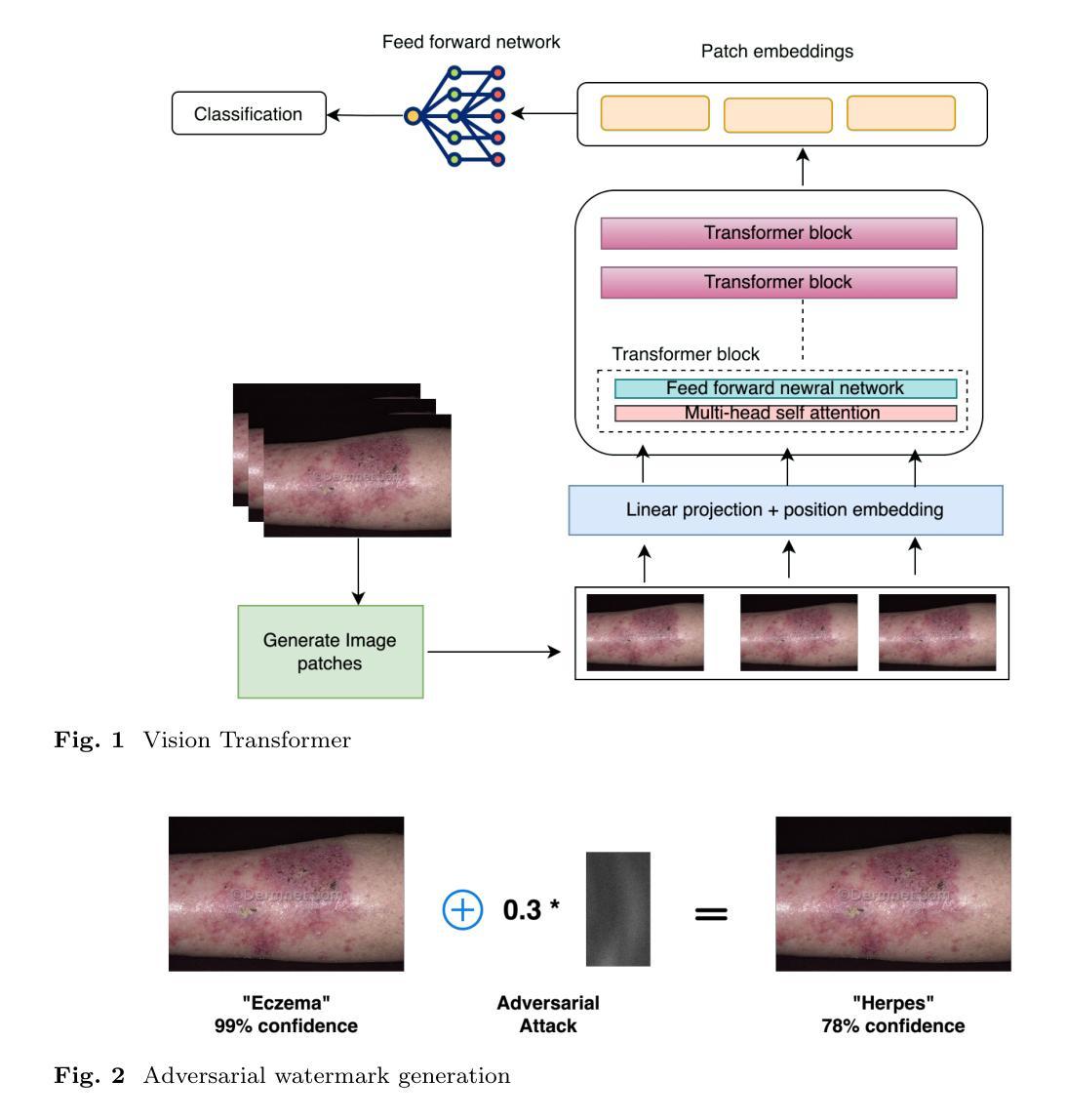
Exploring Adversarial Watermarking in Transformer-Based Models: Transferability and Robustness Against Defense Mechanism for Medical Images
Authors:Rifat Sadik, Tanvir Rahman, Arpan Bhattacharjee, Bikash Chandra Halder, Ismail Hossain
Deep learning models have shown remarkable success in dermatological image analysis, offering potential for automated skin disease diagnosis. Previously, convolutional neural network(CNN) based architectures have achieved immense popularity and success in computer vision (CV) based task like skin image recognition, generation and video analysis. But with the emergence of transformer based models, CV tasks are now are nowadays carrying out using these models. Vision Transformers (ViTs) is such a transformer-based models that have shown success in computer vision. It uses self-attention mechanisms to achieve state-of-the-art performance across various tasks. However, their reliance on global attention mechanisms makes them susceptible to adversarial perturbations. This paper aims to investigate the susceptibility of ViTs for medical images to adversarial watermarking-a method that adds so-called imperceptible perturbations in order to fool models. By generating adversarial watermarks through Projected Gradient Descent (PGD), we examine the transferability of such attacks to CNNs and analyze the performance defense mechanism – adversarial training. Results indicate that while performance is not compromised for clean images, ViTs certainly become much more vulnerable to adversarial attacks: an accuracy drop of as low as 27.6%. Nevertheless, adversarial training raises it up to 90.0%.
深度学习模型在皮肤科图像分析方面取得了显著的成功,为自动化皮肤疾病诊断提供了潜力。以前,基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的架构在计算机视觉(CV)任务中非常受欢迎并获得了巨大成功,如皮肤图像识别、生成和视频分析。但随着基于transformer的模型的兴起,现在的CV任务大多使用这些模型来完成。Vision Transformers(ViTs)就是这样一种基于transformer的模型,它在计算机视觉领域取得了成功。它利用自注意力机制在各种任务上实现了最先进的性能。然而,它们对全局注意力机制的依赖使得它们容易受到对抗性扰动的攻击。本文旨在研究ViTs对医学图像受到对抗性水印的易感性——一种添加所谓的不易察觉的扰动来欺骗模型的方法。通过投影梯度下降法(PGD)生成对抗性水印,我们研究了这种攻击对CNN的迁移性,并分析了性能防御机制——对抗性训练。结果表明,虽然对于干净图像的性能没有受到影响,但ViTs确实更容易受到对抗性攻击:准确率下降高达27.6%。然而,对抗性训练将其提高到了90.0%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习模型在皮肤科图像分析方面取得了显著的成功,为自动化皮肤疾病诊断提供了潜力。尽管卷积神经网络(CNN)在皮肤图像识别、生成和视频分析等计算机视觉任务中广受欢迎并获得了成功,但随着基于变压器的模型的兴起,计算机视觉任务现在更多地使用这些模型来完成。其中,Vision Transformers(ViT)等基于变压器的模型在计算机视觉中取得了成功。然而,它们依赖于全局注意力机制,使其容易受到对抗性扰动的攻击。本文旨在研究医学图像ViT对抗性水印的敏感性。通过投影梯度下降法生成对抗性水印,我们测试了此类攻击对CNN的迁移性,并分析了防御机制——对抗性训练的性能。研究结果表明,ViT容易受到对抗性攻击的影响,清洁图像的准确性降低了27.6%,但对抗性训练可以提高到90.0%。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习模型在皮肤科图像分析中具有巨大潜力,尤其是用于自动化皮肤疾病诊断。
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)在计算机视觉任务中曾广受欢迎并成功应用。
- Vision Transformers(ViT)是新兴的基于变压器的模型,已在计算机视觉领域取得显著成功。
- ViT模型依赖于全局注意力机制,使其容易受到对抗性扰动的影响。
- 对抗性水印方法可用于攻击医学图像的ViT模型。
- 对抗性训练是一种有效的防御机制,可以提高模型对对抗性攻击的抵抗能力。
点此查看论文截图

TissUnet: Improved Extracranial Tissue and Cranium Segmentation for Children through Adulthood
Authors:Markiian Mandzak, Elvira Yang, Anna Zapaishchykova, Yu-Hui Chen, Lucas Heilbroner, John Zielke, Divyanshu Tak, Reza Mojahed-Yazdi, Francesca Romana Mussa, Zezhong Ye, Sridhar Vajapeyam, Viviana Benitez, Ralph Salloum, Susan N. Chi, Houman Sotoudeh, Jakob Seidlitz, Sabine Mueller, Hugo J. W. L. Aerts, Tina Y. Poussaint, Benjamin H. Kann
Extracranial tissues visible on brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may hold significant value for characterizing health conditions and clinical decision-making, yet they are rarely quantified. Current tools have not been widely validated, particularly in settings of developing brains or underlying pathology. We present TissUnet, a deep learning model that segments skull bone, subcutaneous fat, and muscle from routine three-dimensional T1-weighted MRI, with or without contrast enhancement. The model was trained on 155 paired MRI-computed tomography (CT) scans and validated across nine datasets covering a wide age range and including individuals with brain tumors. In comparison to AI-CT-derived labels from 37 MRI-CT pairs, TissUnet achieved a median Dice coefficient of 0.79 [IQR: 0.77-0.81] in a healthy adult cohort. In a second validation using expert manual annotations, median Dice was 0.83 [IQR: 0.83-0.84] in healthy individuals and 0.81 [IQR: 0.78-0.83] in tumor cases, outperforming previous state-of-the-art method. Acceptability testing resulted in an 89% acceptance rate after adjudication by a tie-breaker(N=108 MRIs), and TissUnet demonstrated excellent performance in the blinded comparative review (N=45 MRIs), including both healthy and tumor cases in pediatric populations. TissUnet enables fast, accurate, and reproducible segmentation of extracranial tissues, supporting large-scale studies on craniofacial morphology, treatment effects, and cardiometabolic risk using standard brain T1w MRI.
大脑磁共振成像(MRI)中可见颅外组织对于表征健康状况和临床决策具有重要意义,但很少对其进行量化分析。当前工具尚未得到广泛验证,特别是在发育中的大脑或基础病理学的情况下。我们提出了TissUnet,这是一个深度学习模型,可以从常规的三维T1加权MRI中分割颅骨、皮下脂肪和肌肉,无论是否进行增强对比。该模型在155对MRI-计算机断层扫描(CT)上进行训练,并在涵盖广泛年龄范围且包括脑肿瘤患者在内的九个数据集上进行验证。与来自37对MRI-CT的AI-CT衍生标签相比,TissUnet在健康成人队列中的狄克系数中位数为0.79[IQR:0.77-0.81]。在专家手动注释的第二次验证中,健康个体的狄克系数中位数为0.83[IQR:0.83-0.84],肿瘤患者的狄克系数为0.81[IQR:0.78-0.83],优于之前的最先进方法。可接受性测试结果显示,在仲裁者(N=108 MRI)裁定后,接受率为89%,TissUnet在盲法比较审查(N=45 MRI)中表现出优异的性能,包括儿科人群中的健康个体和肿瘤病例。TissUnet能够实现颅外组织的快速、准确和可重复分割,支持利用标准大脑T1w MRI进行大规模的面颅形态学、治疗效应和心血管代谢风险研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 44 pages, 4 tables, 6 figures, supplementary material
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为TissUnet的深度学习模型,该模型可在无对比增强的常规三维T1加权MRI中,对颅骨、皮下脂肪和肌肉进行分割。模型在广泛的年龄范围内以及包括脑肿瘤患者在内的多个数据集上进行了训练和验证,表现出优异的性能。
Key Takeaways
- TissUnet是一种深度学习模型,能够分割颅骨、皮下脂肪和肌肉组织。
- 模型在常规三维T1加权MRI上进行了训练和验证。
- 该模型能够在无对比增强的MRI图像中进行有效分割。
- TissUnet在广泛年龄范围以及包括脑肿瘤患者在内的多个数据集上进行了测试。
- 与AI-CT衍生标签相比,TissUnet在健康成人队列中的表现优异。
- 与专家手动注释相比,TissUnet在接受率测试中表现出高接受率。
- TissUnet为快速、准确和可重复的颅外组织分割提供了可能,支持大规模研究。
点此查看论文截图

Hypergraph Tversky-Aware Domain Incremental Learning for Brain Tumor Segmentation with Missing Modalities
Authors:Junze Wang, Lei Fan, Weipeng Jing, Donglin Di, Yang Song, Sidong Liu, Cong Cong
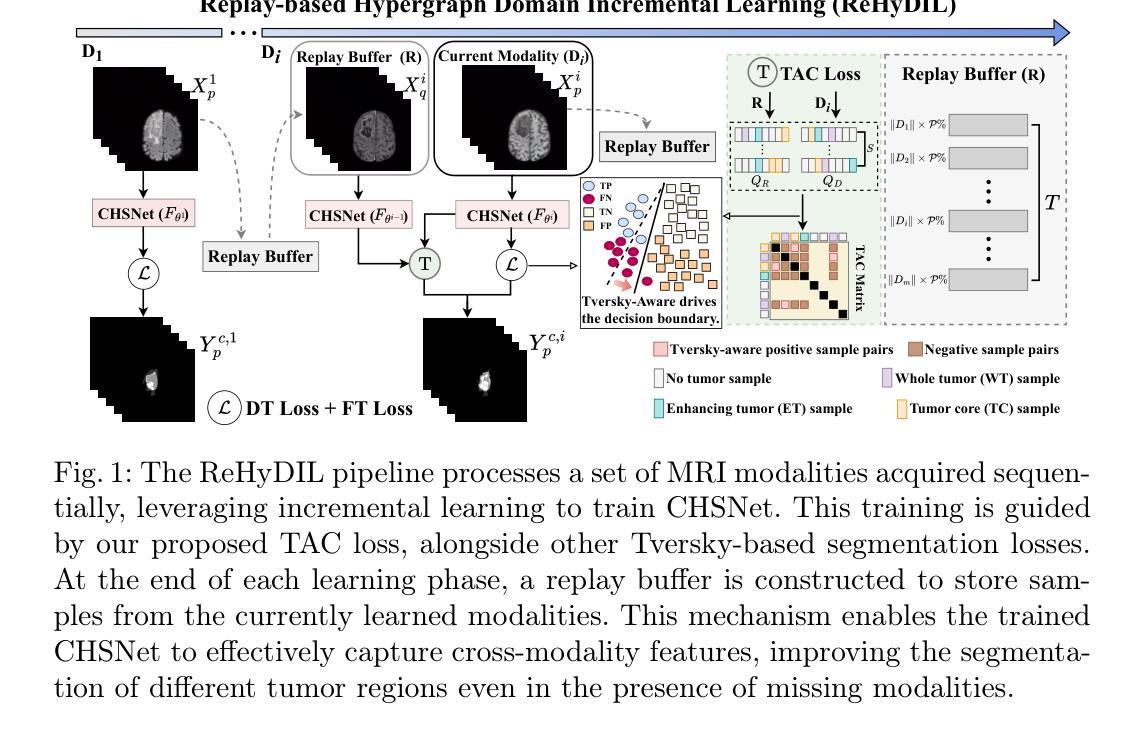
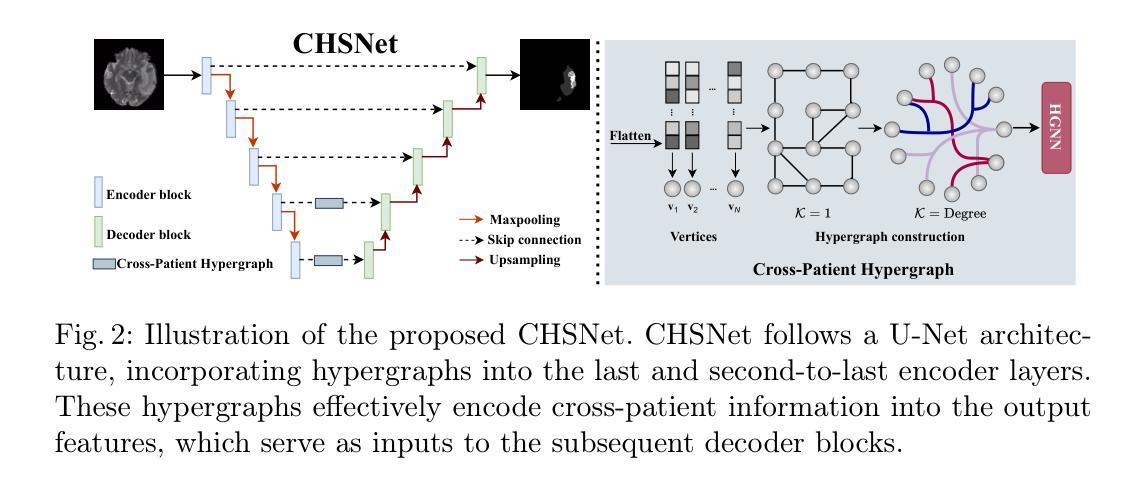
Existing methods for multimodal MRI segmentation with missing modalities typically assume that all MRI modalities are available during training. However, in clinical practice, some modalities may be missing due to the sequential nature of MRI acquisition, leading to performance degradation. Furthermore, retraining models to accommodate newly available modalities can be inefficient and may cause overfitting, potentially compromising previously learned knowledge. To address these challenges, we propose Replay-based Hypergraph Domain Incremental Learning (ReHyDIL) for brain tumor segmentation with missing modalities. ReHyDIL leverages Domain Incremental Learning (DIL) to enable the segmentation model to learn from newly acquired MRI modalities without forgetting previously learned information. To enhance segmentation performance across diverse patient scenarios, we introduce the Cross-Patient Hypergraph Segmentation Network (CHSNet), which utilizes hypergraphs to capture high-order associations between patients. Additionally, we incorporate Tversky-Aware Contrastive (TAC) loss to effectively mitigate information imbalance both across and within different modalities. Extensive experiments on the BraTS2019 dataset demonstrate that ReHyDIL outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving an improvement of over 2% in the Dice Similarity Coefficient across various tumor regions. Our code is available at https://github.com/reeive/ReHyDIL.
现有的多模态MRI分割缺失模态的方法通常假设在训练期间所有MRI模态都是可用的。然而,在临床实践中,由于MRI采集的序列性质,某些模态可能会缺失,导致性能下降。此外,为了容纳新可用的模态而重新训练模型可能效率低下,并可能导致过度拟合,从而可能损害之前学到的知识。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了基于回放超图域增量学习(ReHyDIL)的方法,用于具有缺失模态的脑肿瘤分割。ReHyDIL利用域增量学习(DIL)使分割模型能够从新获取的MRI模态中学习,而不会忘记之前学到的信息。为了增强在不同患者场景中的分割性能,我们引入了跨患者超图分割网络(CHSNet),该网络利用超图来捕获患者之间的高阶关联。此外,我们结合了Tversky感知对比(TAC)损失,以有效减轻不同模态之间和内部的信息不平衡。在BraTS2019数据集上的广泛实验表明,ReHyDIL优于最先进的方法,在各种肿瘤区域的Dice相似系数上提高了超过2%。我们的代码可在https://github.com/reeive/ReHyDIL上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025 Early Accept. The code is available at https://github.com/reeive/ReHyDIL
Summary
本文提出一种基于重播的超图域增量学习(ReHyDIL)方法,用于处理MRI图像中缺失模态的情况下的脑肿瘤分割问题。该方法结合了域增量学习(DIL)技术,使得分割模型能够在获取新的MRI模态时学习,同时不会忘记之前学到的知识。此外,还引入了跨患者超图分割网络(CHSNet)和Tversky感知对比损失(TAC loss),以提高不同患者场景下的分割性能并有效缓解不同模态间和模态内的信息不平衡问题。在BraTS2019数据集上的实验表明,ReHyDIL方法优于其他最先进的方法,在各类肿瘤区域的Dice相似系数上提高了超过2%。
Key Takeaways
- ReHyDIL方法解决了MRI图像中缺失模态导致的分割性能下降问题。
- 通过结合域增量学习(DIL),模型能够在获取新的MRI模态时学习,同时保持对先前知识的记忆。
- 引入的跨患者超图分割网络(CHSNet)能够捕捉患者间的高阶关联,提高在不同患者场景下的分割性能。
- Tversky感知对比损失(TAC loss)有效缓解了不同模态间和模态内的信息不平衡问题。
- ReHyDIL方法在BraTS2019数据集上的实验表现优于其他最先进的方法。
- ReHyDIL方法提高了Dice相似系数,改进幅度超过2%。
点此查看论文截图

Learning Concept-Driven Logical Rules for Interpretable and Generalizable Medical Image Classification
Authors:Yibo Gao, Hangqi Zhou, Zheyao Gao, Bomin Wang, Shangqi Gao, Sihan Wang, Xiahai Zhuang
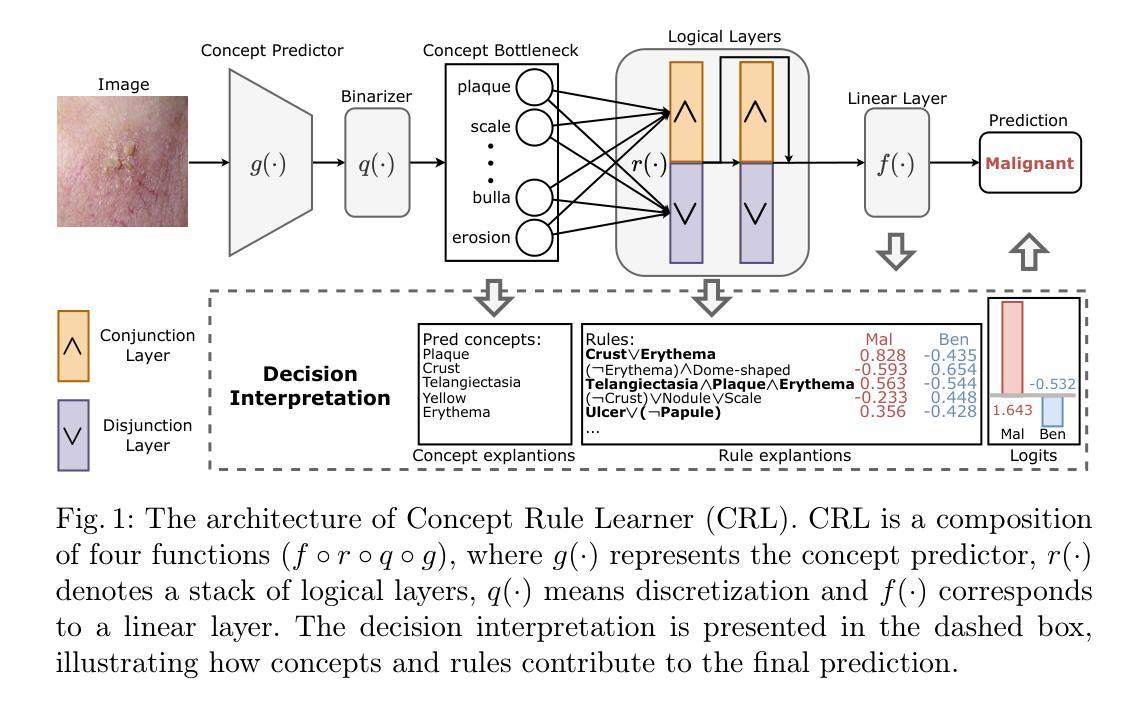
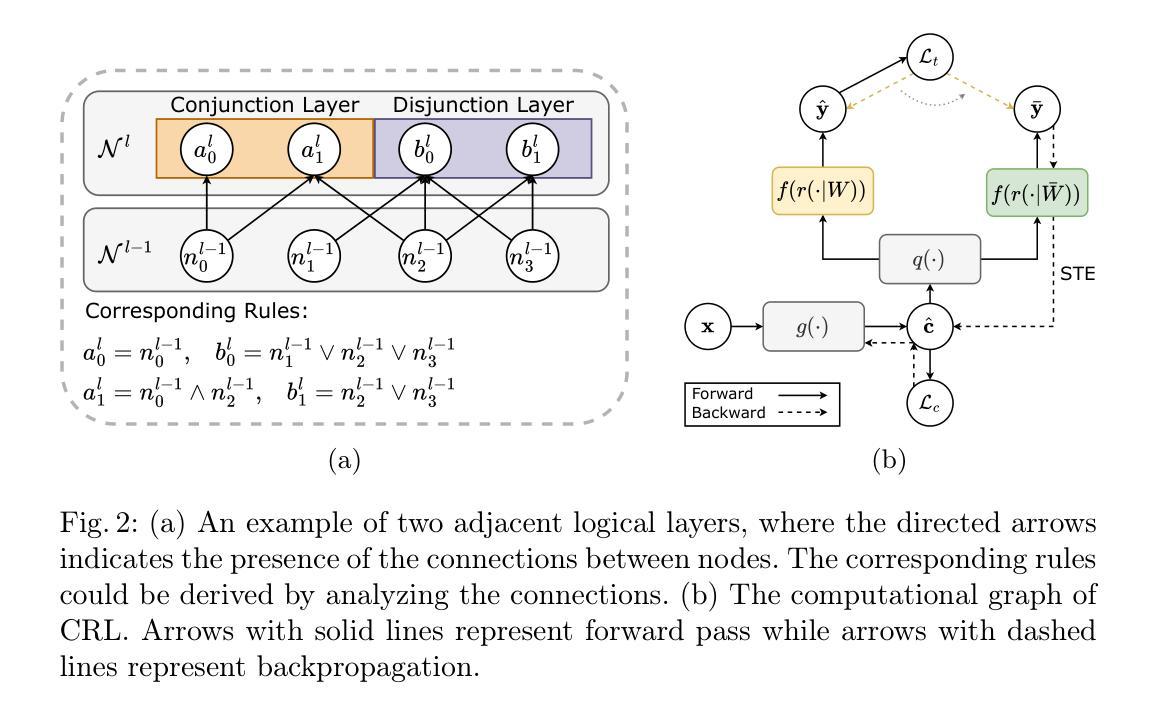
The pursuit of decision safety in clinical applications highlights the potential of concept-based methods in medical imaging. While these models offer active interpretability, they often suffer from concept leakages, where unintended information within soft concept representations undermines both interpretability and generalizability. Moreover, most concept-based models focus solely on local explanations (instance-level), neglecting the global decision logic (dataset-level). To address these limitations, we propose Concept Rule Learner (CRL), a novel framework to learn Boolean logical rules from binarized visual concepts. CRL employs logical layers to capture concept correlations and extract clinically meaningful rules, thereby providing both local and global interpretability. Experiments on two medical image classification tasks show that CRL achieves competitive performance with existing methods while significantly improving generalizability to out-of-distribution data. The code of our work is available at https://github.com/obiyoag/crl.
在临床应用中追求决策安全性突显了基于概念的方法在医学成像中的潜力。虽然这些模型提供了积极的可解释性,但它们常常受到概念泄漏的影响,其中软概念表示中的意外信息破坏了可解释性和泛化能力。此外,大多数基于概念模型主要关注局部解释(实例级别),忽视了全局决策逻辑(数据集级别)。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了概念规则学习者(CRL),这是一个从二进制视觉概念中学习布尔逻辑规则的新框架。CRL采用逻辑层来捕捉概念间的相关性并提取临床有意义的规则,从而提供局部和全局可解释性。在两个医学图像分类任务上的实验表明,CRL在现有方法中表现良好,同时在超出分布的数据上显著提高泛化能力。我们的工作代码可在https://github.com/obiyoag/crl获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF early accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
医学临床应用中决策安全性的追求突显了基于概念的方法在医学成像中的潜力。概念模型虽能提供积极的可解释性,但往往受到概念泄漏问题的影响,这一问题导致软概念表示中的意外信息削弱了可解释性和泛化能力。此外,大多数基于概念的方法只关注局部解释(实例级别),忽略了全局决策逻辑(数据集级别)。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Concept Rule Learner(CRL)这一新型框架,可从二进制视觉概念中学习布尔逻辑规则。CRL利用逻辑层捕捉概念相关性并提取具有临床意义的规则,从而提供局部和全局的可解释性。在两项医学图像分类任务上的实验表明,CRL在现有方法中表现有竞争力,并在提高对新分布数据的泛化能力方面表现出色。代码可通过https://github.com/obiyoag/crl获取。
Key Takeaways
- 概念模型在医学成像中具有潜力,可提高临床决策的安全性。
- 概念模型存在概念泄漏问题,影响模型的可解释性和泛化能力。
- 大多数基于概念的方法主要关注局部解释,忽略了全局决策逻辑。
- 提出了一种新型框架Concept Rule Learner(CRL),能够从二进制视觉概念中学习布尔逻辑规则。
- CRL通过逻辑层捕捉概念相关性,提供局部和全局的可解释性。
- CRL在医学图像分类任务上表现优异,与现有方法相比具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图