⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-11 更新
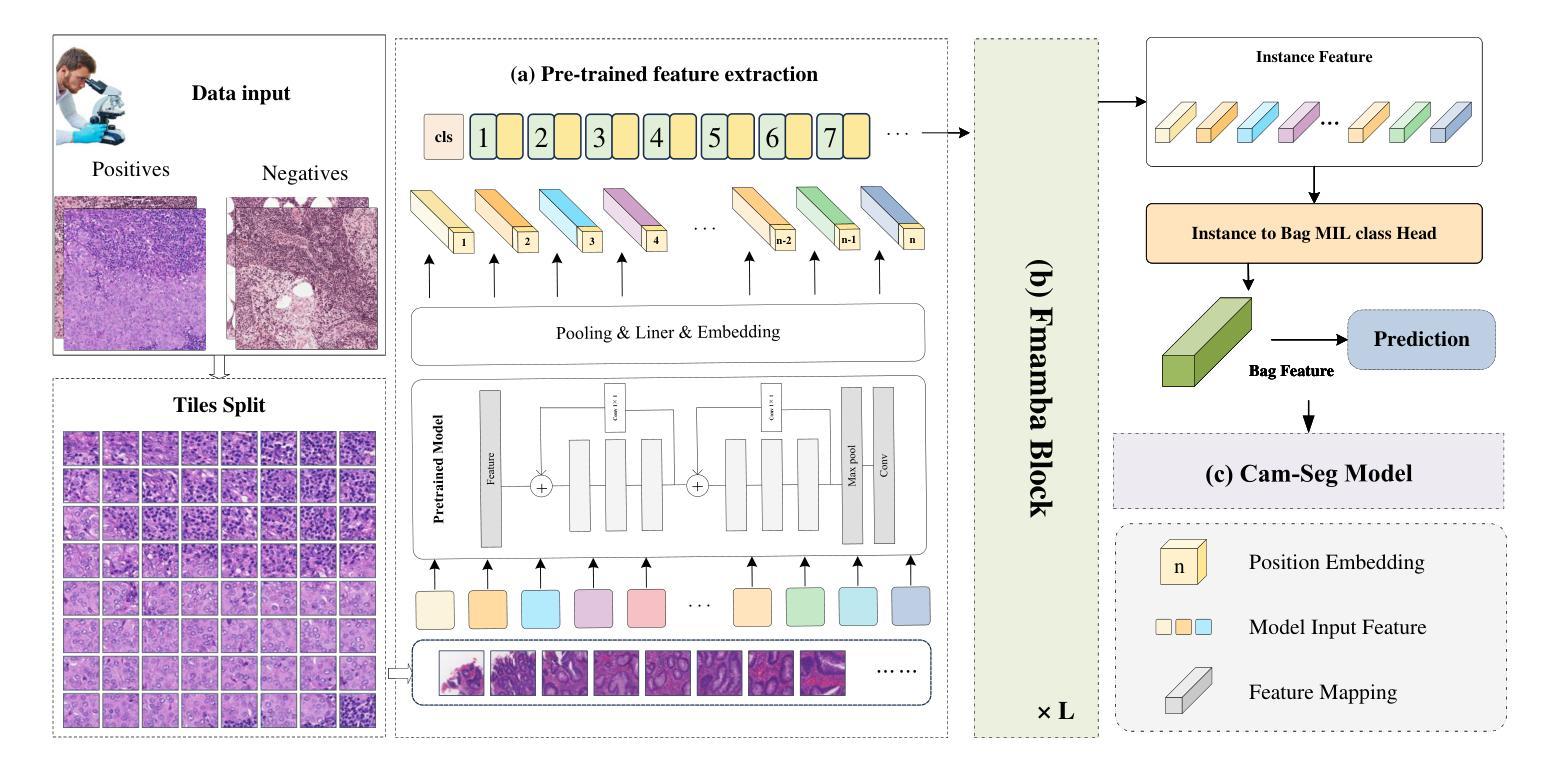
FMaMIL: Frequency-Driven Mamba Multi-Instance Learning for Weakly Supervised Lesion Segmentation in Medical Images
Authors:Hangbei Cheng, Xiaorong Dong, Xueyu Liu, Jianan Zhang, Xuetao Ma, Mingqiang Wei, Liansheng Wang, Junxin Chen, Yongfei Wu
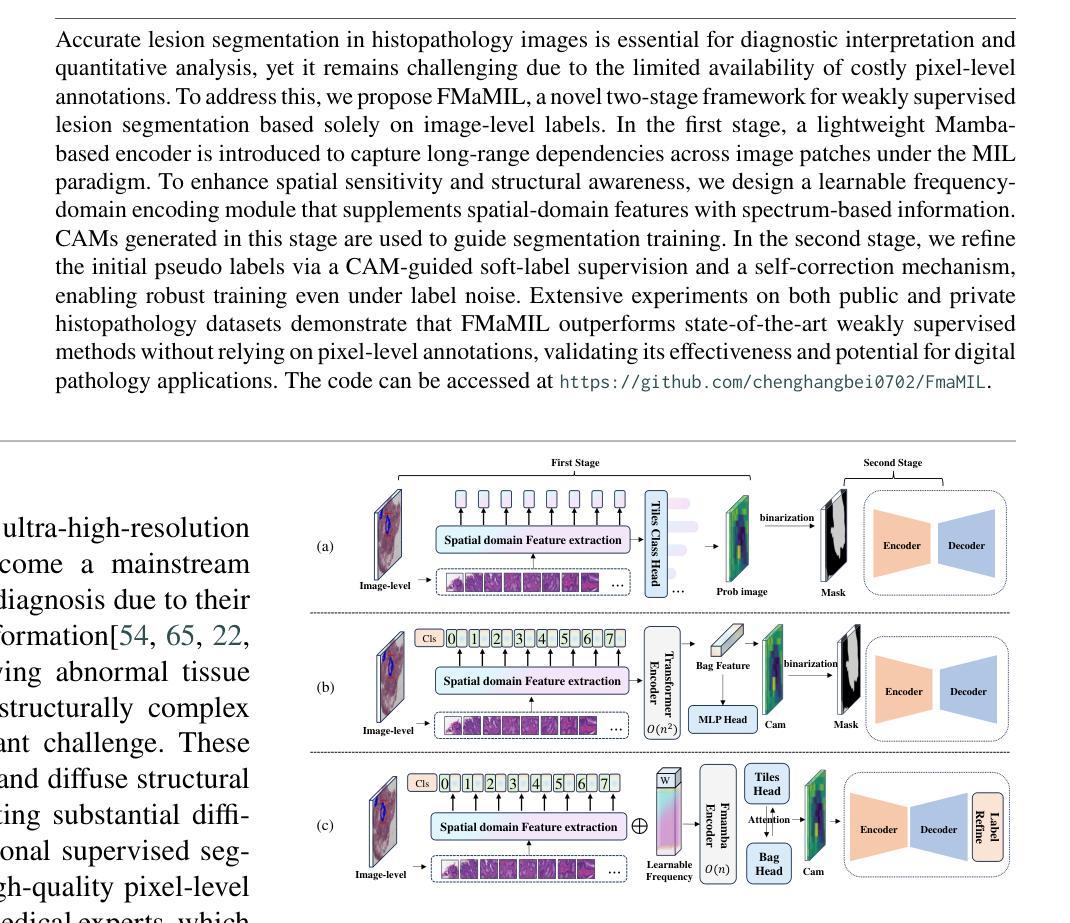
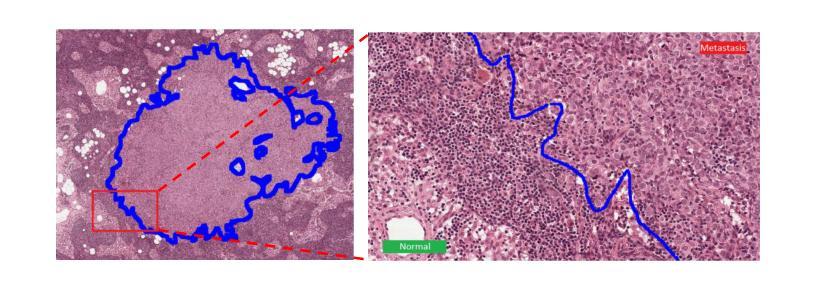
Accurate lesion segmentation in histopathology images is essential for diagnostic interpretation and quantitative analysis, yet it remains challenging due to the limited availability of costly pixel-level annotations. To address this, we propose FMaMIL, a novel two-stage framework for weakly supervised lesion segmentation based solely on image-level labels. In the first stage, a lightweight Mamba-based encoder is introduced to capture long-range dependencies across image patches under the MIL paradigm. To enhance spatial sensitivity and structural awareness, we design a learnable frequency-domain encoding module that supplements spatial-domain features with spectrum-based information. CAMs generated in this stage are used to guide segmentation training. In the second stage, we refine the initial pseudo labels via a CAM-guided soft-label supervision and a self-correction mechanism, enabling robust training even under label noise. Extensive experiments on both public and private histopathology datasets demonstrate that FMaMIL outperforms state-of-the-art weakly supervised methods without relying on pixel-level annotations, validating its effectiveness and potential for digital pathology applications.
病理图像中的准确病灶分割对于诊断解读和定量分析至关重要。然而,由于昂贵的像素级标注的有限可用性,这仍然是一个挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了FMaMIL,这是一个仅基于图像级标签的弱监督病灶分割的两阶段新型框架。在第一阶段,我们引入了一个基于Mamba的轻量级编码器,在MIL范式下捕获图像补丁之间的长距离依赖性。为了提高空间敏感性和结构意识,我们设计了一个可学习的频域编码模块,该模块可以补充空间域特征以基于频谱的信息。此阶段生成的CAM用于指导分割训练。在第二阶段,我们通过CAM引导的软标签监督和自我校正机制来优化初始的伪标签,即使在标签噪声下也能实现稳健的训练。在公共和私有病理图像数据集上的大量实验表明,FMaMIL在不需要像素级标注的情况下超越了最先进的弱监督方法,验证了其有效性和在数字病理学应用中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:针对病理图像中的病灶分割问题,我们提出了一种仅基于图像级别标签的弱监督病灶分割新型两阶段框架FMaMIL。第一阶段引入轻量级Mamba编码器,在MIL范式下捕获图像补丁间的长程依赖性。设计可学习的频域编码模块,以补充空间域特征并增强空间敏感性和结构意识。生成的CAM用于指导分割训练。第二阶段通过CAM引导软标签监督和自我校正机制,对初始伪标签进行精细化处理,即使在标签噪声下也能实现稳健训练。在公共和私有病理数据集上的广泛实验验证了FMaMIL的有效性,表现出其优越性和数字病理应用潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- FMaMIL是一个两阶段的弱监督病灶分割框架,无需像素级注释。
- 第一阶段通过Mamba编码器捕获图像补丁间的长程依赖性,并引入频域编码模块增强空间敏感性和结构意识。
- CAM在第一阶段用于指导分割训练。
- 第二阶段通过CAM引导的软标签监督和自我校正机制对初始伪标签进行精细化处理。
- FMaMIL在公共和私有病理数据集上的表现优于其他弱监督方法。
- FMaMIL框架具有稳健性,能在标签噪声下实现稳健训练。
点此查看论文截图

Position Prediction Self-Supervised Learning for Multimodal Satellite Imagery Semantic Segmentation
Authors:John Waithaka, Moise Busogi
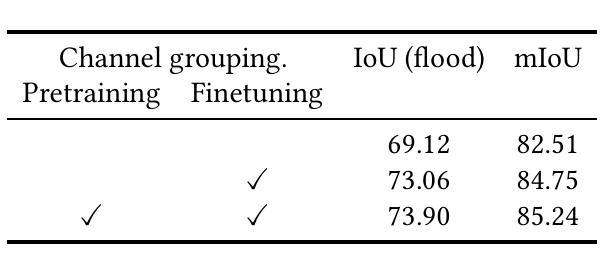
Semantic segmentation of satellite imagery is crucial for Earth observation applications, but remains constrained by limited labelled training data. While self-supervised pretraining methods like Masked Autoencoders (MAE) have shown promise, they focus on reconstruction rather than localisation-a fundamental aspect of segmentation tasks. We propose adapting LOCA (Location-aware), a position prediction self-supervised learning method, for multimodal satellite imagery semantic segmentation. Our approach addresses the unique challenges of satellite data by extending SatMAE’s channel grouping from multispectral to multimodal data, enabling effective handling of multiple modalities, and introducing same-group attention masking to encourage cross-modal interaction during pretraining. The method uses relative patch position prediction, encouraging spatial reasoning for localisation rather than reconstruction. We evaluate our approach on the Sen1Floods11 flood mapping dataset, where it significantly outperforms existing reconstruction-based self-supervised learning methods for satellite imagery. Our results demonstrate that position prediction tasks, when properly adapted for multimodal satellite imagery, learn representations more effective for satellite image semantic segmentation than reconstruction-based approaches.
卫星图像的语义分割对于地球观测应用至关重要,但仍受限于标记训练数据的有限性。虽然像Masked Autoencoders(MAE)这样的自监督预训练方法在语义分割任务上表现出了潜力,但它们主要侧重于重建而非定位,这是分割任务的一个基本方面。我们提出了一种将位置感知的LOCA(Location-aware)自监督学习方法应用于多模态卫星图像语义分割的方法。我们的方法通过扩展SatMAE的渠道分组,从多光谱到多模态数据,解决了卫星数据的独特挑战,实现了多模态的有效处理,并引入了同组注意力掩蔽,以鼓励在预训练期间进行跨模态交互。该方法使用相对补丁位置预测,鼓励定位的空间推理而不是重建。我们在Sen1Floods11洪水测绘数据集上评估了我们的方法,该方法在卫星图像上的表现显著优于现有的基于重建的自监督学习方法。我们的结果表明,当适当适应于多模态卫星图像时,位置预测任务学习到的表示对于卫星图像语义分割比基于重建的方法更有效。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了卫星图像语义分割在地球观测应用中的重要性,并针对有限标记训练数据带来的挑战,提出了一种基于位置感知自监督学习方法的改进方案。该方法通过扩展SatMAE的渠道分组以适应多模态卫星数据,引入同组注意力掩蔽以促进预训练过程中的跨模态交互,并使用相对补丁位置预测来鼓励定位的空间推理。在Sen1Floods11洪水映射数据集上的评估结果表明,该方法在基于重建的卫星图像自监督学习方法上表现出显著的优势。
Key Takeaways
- 卫星图像语义分割对地球观测应用至关重要,但受有限标记训练数据制约。
- 自监督预训练方法,如Mask Autoencoders(MAE),虽具潜力,但主要关注重建而非定位,这是分割任务的基本方面。
- 提出适应位置感知自监督学习方法LOCA,用于多模态卫星图像语义分割。
- 方法扩展了SatMAE的渠道分组,从多光谱到多模态数据,以有效处理多种模态。
- 引入同组注意力掩蔽,鼓励预训练过程中的跨模态交互。
- 使用相对补丁位置预测,鼓励定位的空间推理。
点此查看论文截图

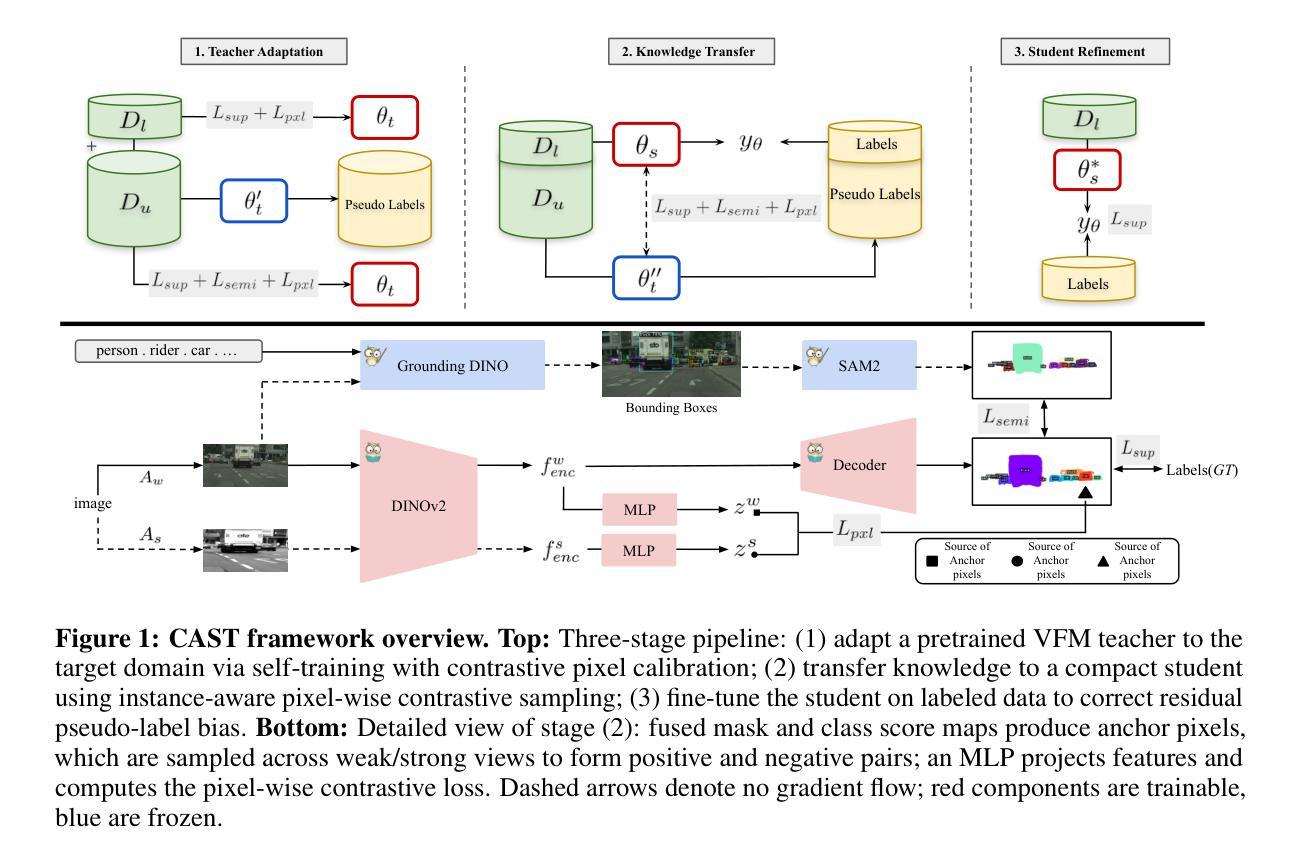
CAST: Contrastive Adaptation and Distillation for Semi-Supervised Instance Segmentation
Authors:Pardis Taghavi, Tian Liu, Renjie Li, Reza Langari, Zhengzhong Tu
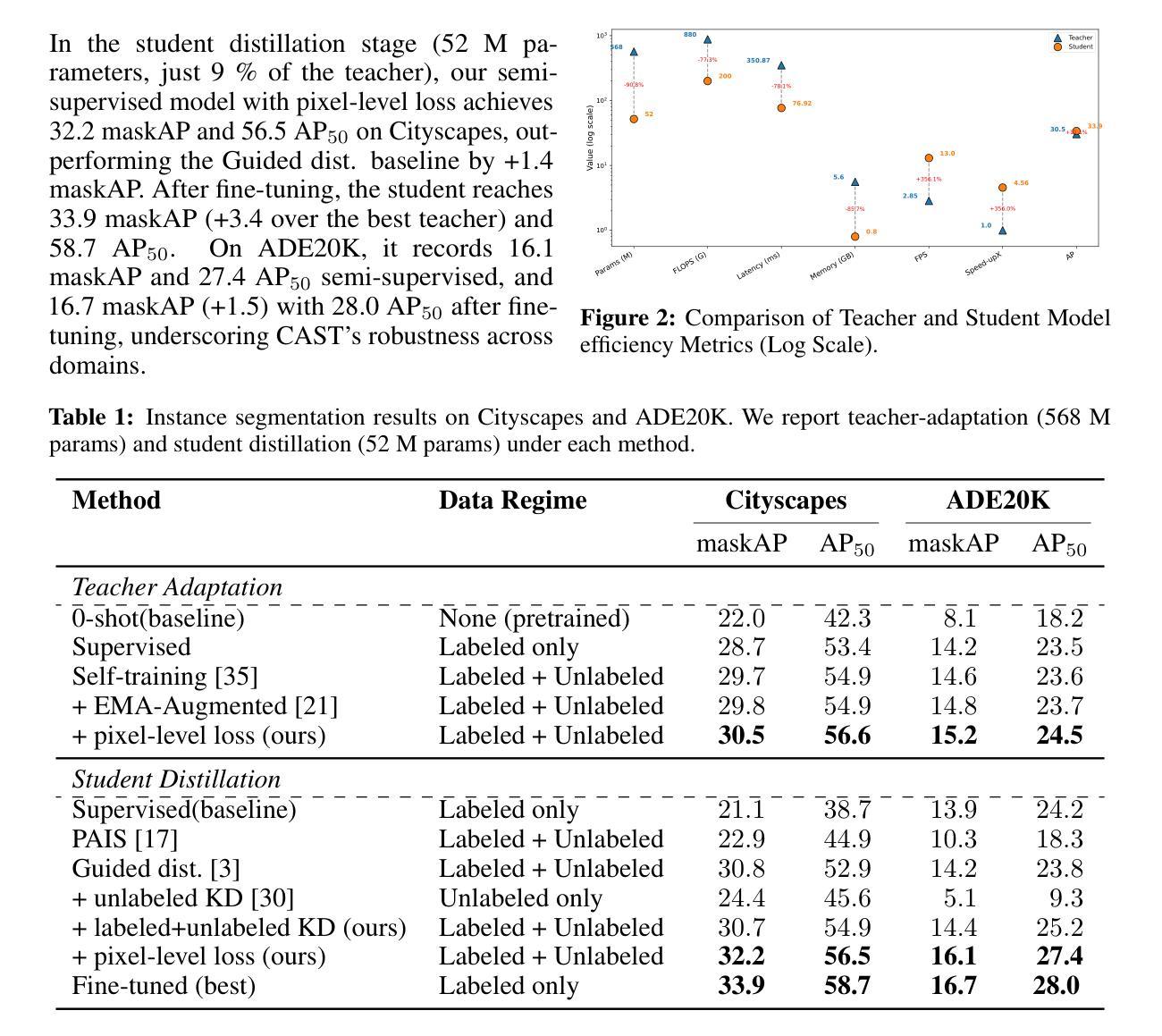
Instance segmentation demands costly per-pixel annotations and large models. We introduce CAST, a semi-supervised knowledge distillation (SSKD) framework that compresses pretrained vision foundation models (VFM) into compact experts using limited labeled and abundant unlabeled data. CAST unfolds in three stages: (1) domain adaptation of the VFM teacher(s) via self-training with contrastive pixel calibration, (2) distillation into a compact student via a unified multi-objective loss that couples standard supervision and pseudo-labels with our instance-aware pixel-wise contrastive term, and (3) fine-tuning on labeled data to remove residual pseudo-label bias. Central to CAST is an \emph{instance-aware pixel-wise contrastive loss} that fuses mask and class scores to mine informative negatives and enforce clear inter-instance margins. By maintaining this contrastive signal across both adaptation and distillation, we align teacher and student embeddings and fully leverage unlabeled images. On Cityscapes and ADE20K, our ~11X smaller student surpasses its adapted VFM teacher(s) by +3.4 AP (33.9 vs. 30.5) and +1.5 AP (16.7 vs. 15.2) and outperforms state-of-the-art semi-supervised approaches.
实例分割需要昂贵的像素级标注和大模型。我们引入了CAST,这是一种半监督知识蒸馏(SSKD)框架,它利用有限的标记数据和大量的无标记数据,将预训练的视觉基础模型(VFM)压缩成紧凑的专家模型。CAST分为三个阶段:(1)通过对比像素校准进行自我训练,对VFM教师进行域适应;(2)通过统一的多目标损失进行蒸馏,该损失将标准监督和伪标签与我们的实例感知像素级对比项相结合,形成紧凑的学生模型;(3)在标记数据上进行微调,以消除剩余的伪标签偏见。CAST的核心是实例感知像素级对比损失,它融合掩膜和类分数来挖掘信息中的负面样本,并执行明确的实例间边界。通过在整个适应和蒸馏过程中保持这种对比信号,我们对齐教师和学生的嵌入,并充分利用无标签图像。在Cityscapes和ADE20K上,我们较小的学生模型(~11倍)超越了其适应的VFM教师(+3.4 AP(33.9 vs. 30.5)和+1.5 AP(16.7 vs. 15.2)),并优于最新的半监督方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了基于半监督知识蒸馏(SSKD)的压缩框架CAST,用于利用有限的标签数据和大量的无标签数据将预训练的视觉基础模型(VFM)压缩成紧凑的专家模型。CAST包括三个阶段:通过对比像素校准进行VFM教师的域自适应,通过统一的多目标损失对紧凑学生进行蒸馏,以及利用标注数据进行微调以消除伪标签的残留偏见。CAST的核心是实例感知像素级对比损失,该损失融合掩膜和类别分数以挖掘负面信息并执行明确的实例间边界。通过在整个适应和蒸馏过程中保持对比信号,我们使教师和学生嵌入对齐并充分利用无标签图像。在Cityscapes和ADE20K上,我们较小的学生在性能和效率方面都超过了其经过调整的VFM教师和其他方法。总结就是通过对数据高效地使用和监督进行模型优化和压缩,提高了实例分割的性能。
Key Takeaways:
- CAST是一个基于半监督知识蒸馏的框架,用于压缩预训练的视觉基础模型。
- CAST利用有限的标注数据和大量的无标注数据,通过三个阶段进行模型优化和压缩。
- CAST的核心是实例感知像素级对比损失,用于挖掘负面信息并明确实例间边界。
- CAST在Cityscapes和ADE20K上的表现超过了其预训练的视觉基础模型教师和最新的半监督方法。
- CAST框架强调了数据高效使用的重要性,提高了实例分割的性能。
点此查看论文截图

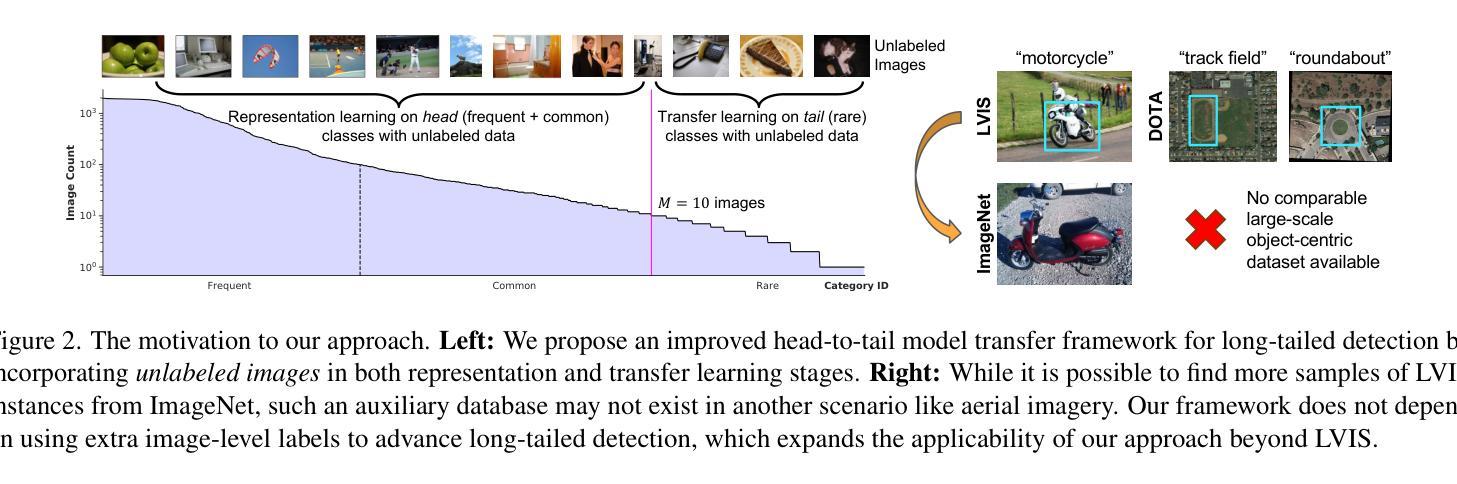
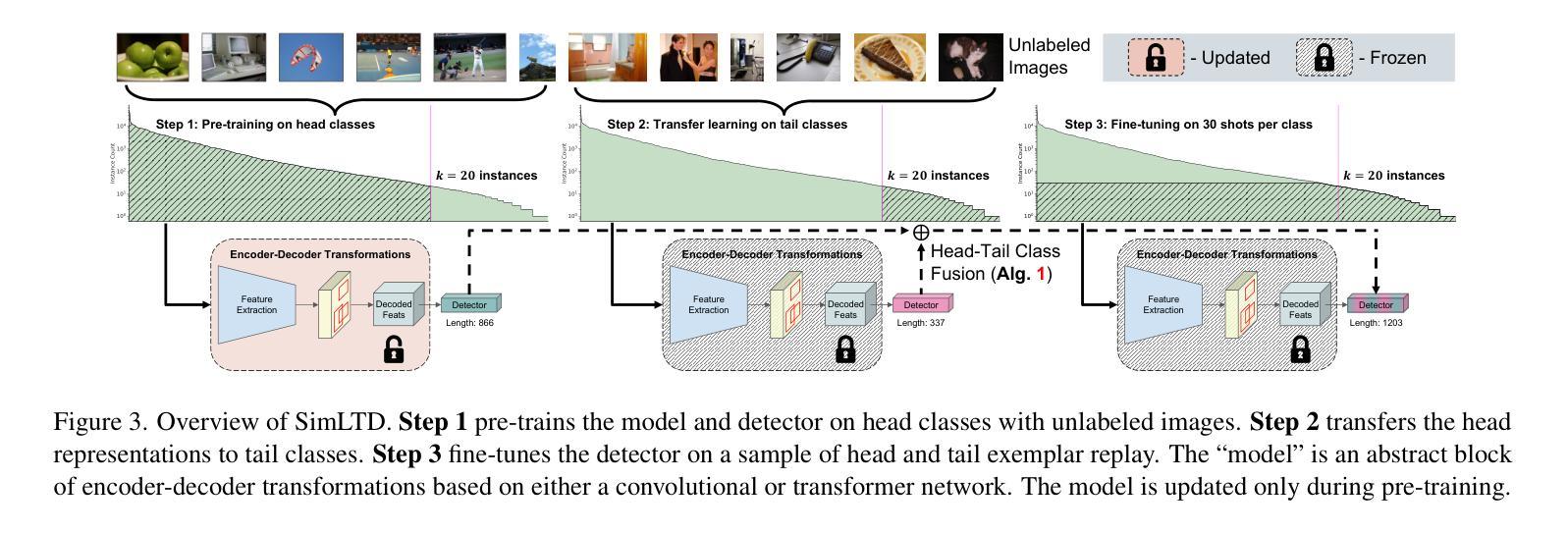
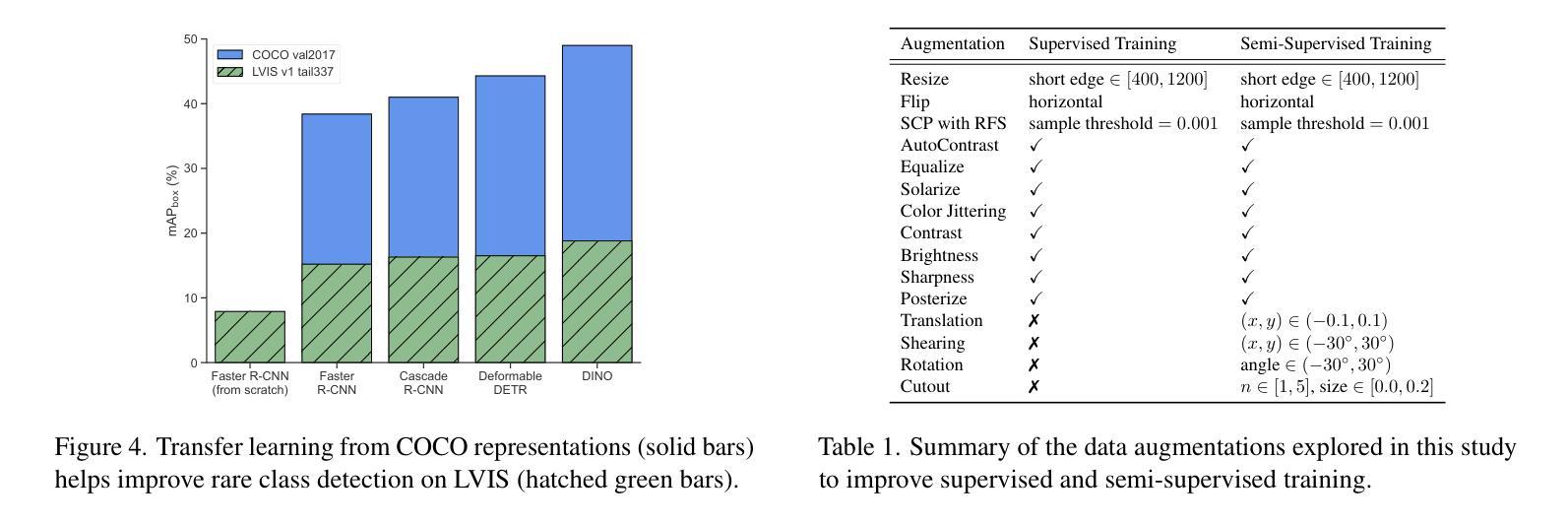
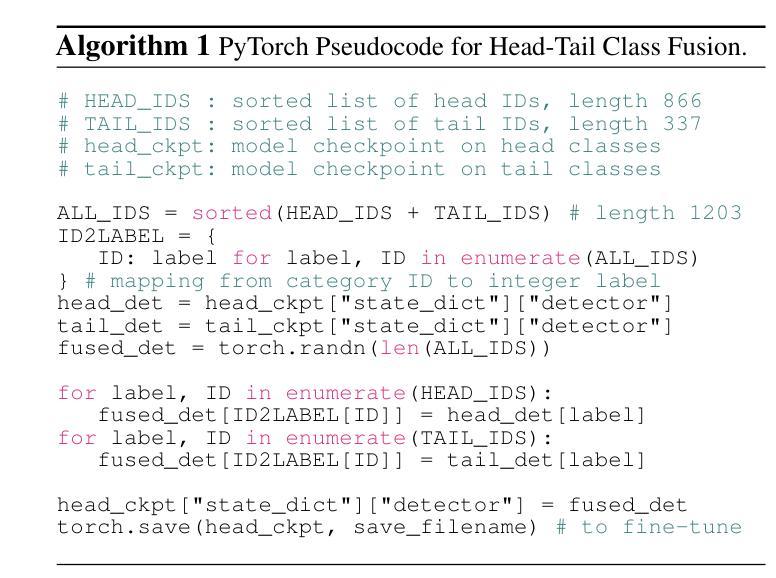
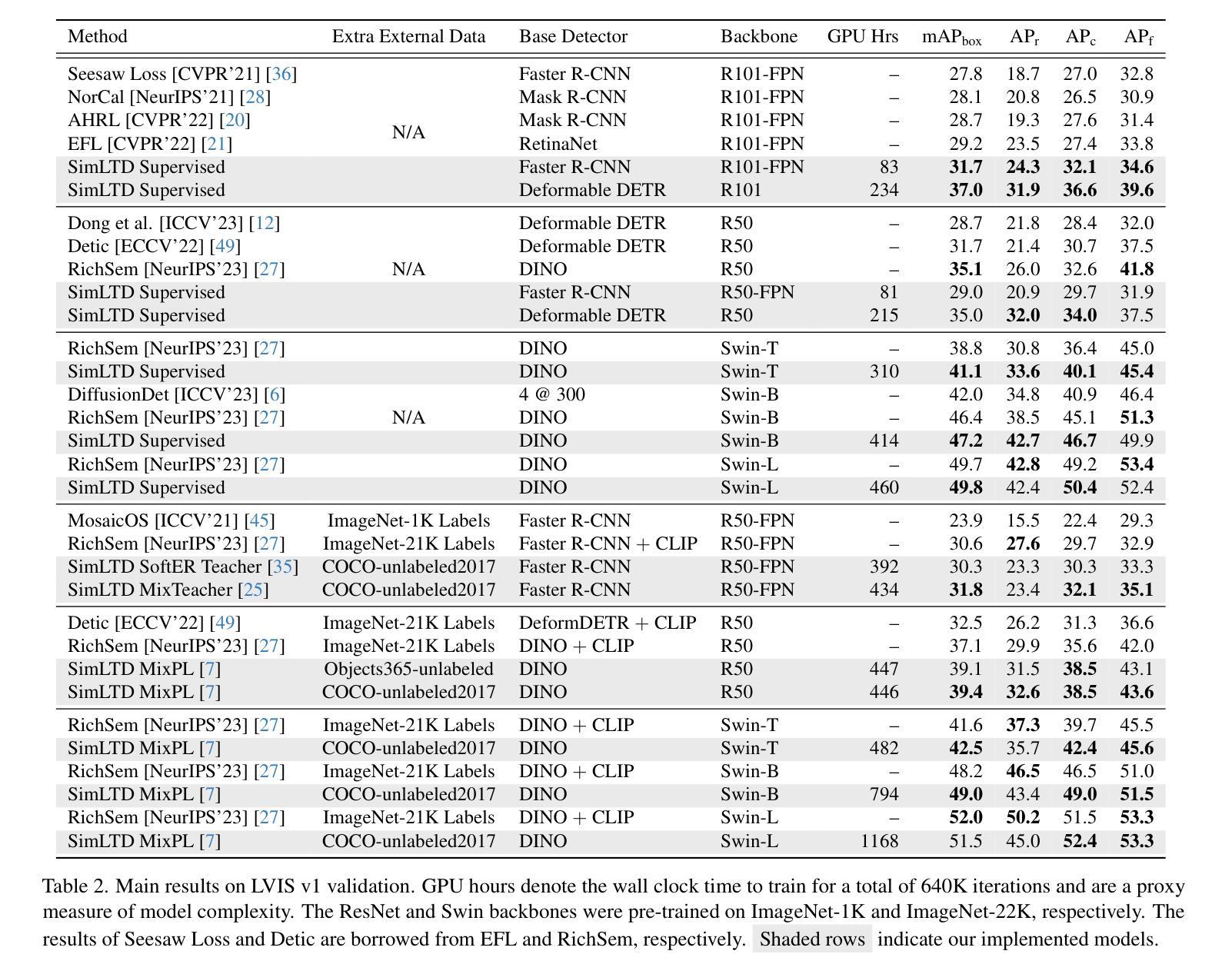
SimLTD: Simple Supervised and Semi-Supervised Long-Tailed Object Detection
Authors:Phi Vu Tran
While modern visual recognition systems have made significant advancements, many continue to struggle with the open problem of learning from few exemplars. This paper focuses on the task of object detection in the setting where object classes follow a natural long-tailed distribution. Existing methods for long-tailed detection resort to external ImageNet labels to augment the low-shot training instances. However, such dependency on a large labeled database has limited utility in practical scenarios. We propose a versatile and scalable approach to leverage optional unlabeled images, which are easy to collect without the burden of human annotations. Our SimLTD framework is straightforward and intuitive, and consists of three simple steps: (1) pre-training on abundant head classes; (2) transfer learning on scarce tail classes; and (3) fine-tuning on a sampled set of both head and tail classes. Our approach can be viewed as an improved head-to-tail model transfer paradigm without the added complexities of meta-learning or knowledge distillation, as was required in past research. By harnessing supplementary unlabeled images, without extra image labels, SimLTD establishes new record results on the challenging LVIS v1 benchmark across both supervised and semi-supervised settings.
虽然现代视觉识别系统已经取得了重大进展,但许多系统仍然面临着从少量样本中学习的开放性问题。本文关注对象检测任务,在该任务中,对象类别遵循自然的长尾分布。现有的长尾检测方法依赖于外部ImageNet标签来增强小样本的训练实例。然而,对大量标注数据库的依赖在实际场景中具有有限的实用性。我们提出了一种通用且可扩展的方法,利用可选的无标签图像,这些图像无需人工标注即可轻松收集。我们的SimLTD框架简单直观,分为三个步骤:(1)在丰富的头部类别上进行预训练;(2)在稀缺的尾部类别上进行迁移学习;(3)在头部和尾部类别的采样集上进行微调。我们的方法可以被视为一种改进的从头部到尾部模型迁移范式,无需如过去的研究中所需的元学习或知识蒸馏等额外复杂性。通过利用额外的无标签图像,无需额外的图像标签,SimLTD在具有挑战性的LVIS v1基准测试中建立了监督和半监督环境下的新纪录结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. The reference code is available at https://github.com/lexisnexis-risk-open-source/simltd
Summary
本文提出了一种针对长尾分布下的目标检测任务的方法,解决了现代视觉识别系统从少量样本中学习的问题。该方法利用可选的无标签图像,通过预训练、迁移学习和微调三个简单步骤,实现了在不依赖大规模标注数据库的情况下对长尾分布数据的检测。该方法在LVIS v1基准测试中取得了新的记录结果。
Key Takeaways
- 现代视觉识别系统在从少量样本中学习时仍面临挑战,特别是在长尾分布下的目标检测任务。
- 现有方法依赖大规模标注数据库来增强低样本训练实例,但在实际场景中效用有限。
- 本文提出了一种利用无标签图像的方法,通过预训练、迁移学习和微调三个步骤来解决这一问题。
- 该方法在不使用额外的元学习或知识蒸馏的复杂性的情况下,实现了头到尾的模型转移范式。
- 通过利用额外的无标签图像,该方法在具有挑战性的LVIS v1基准测试中取得了新的记录结果。
- 该方法具有通用性和可扩展性,可以应用于监督学习和半监督学习设置。
点此查看论文截图