⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-11 更新
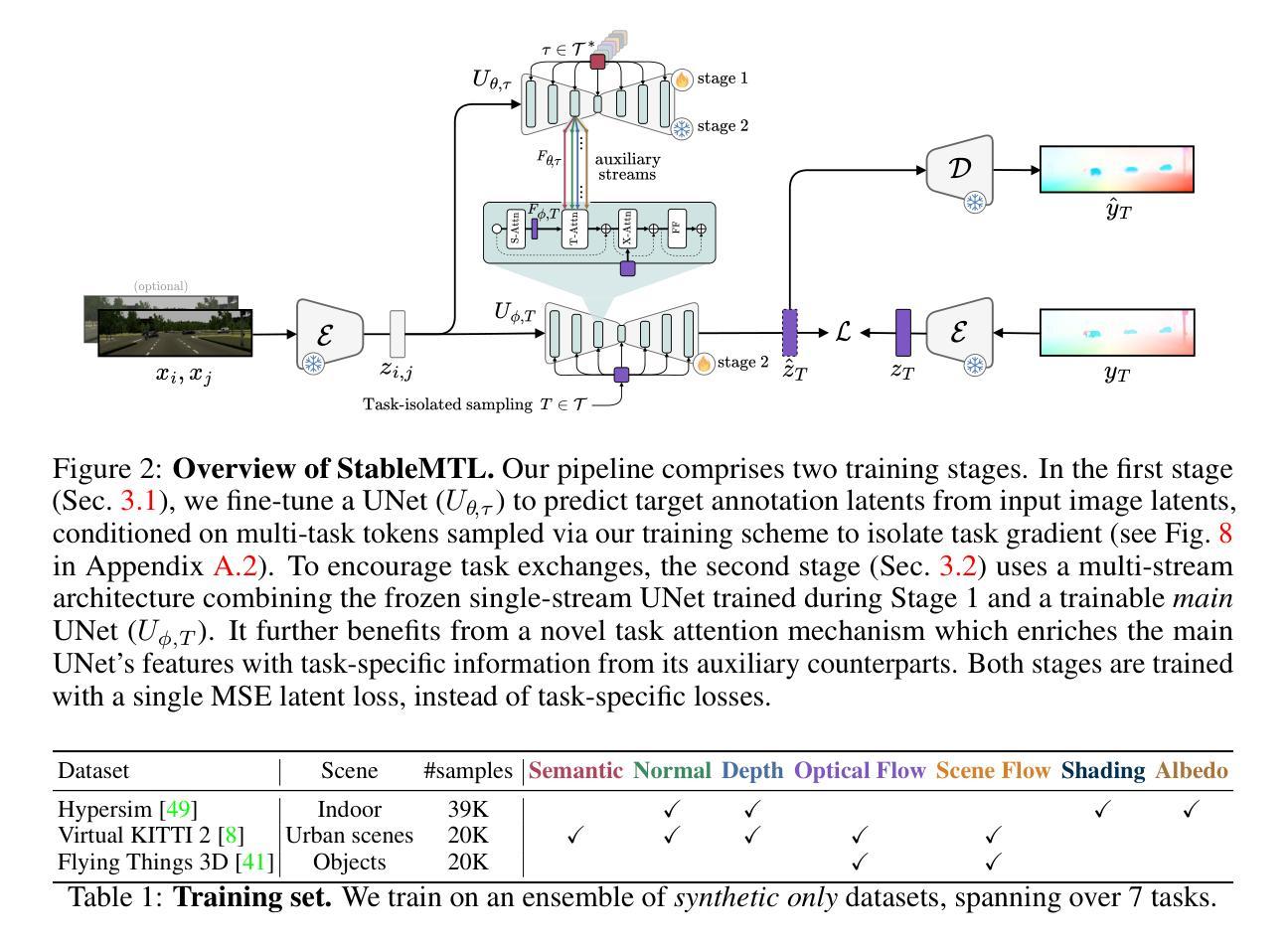
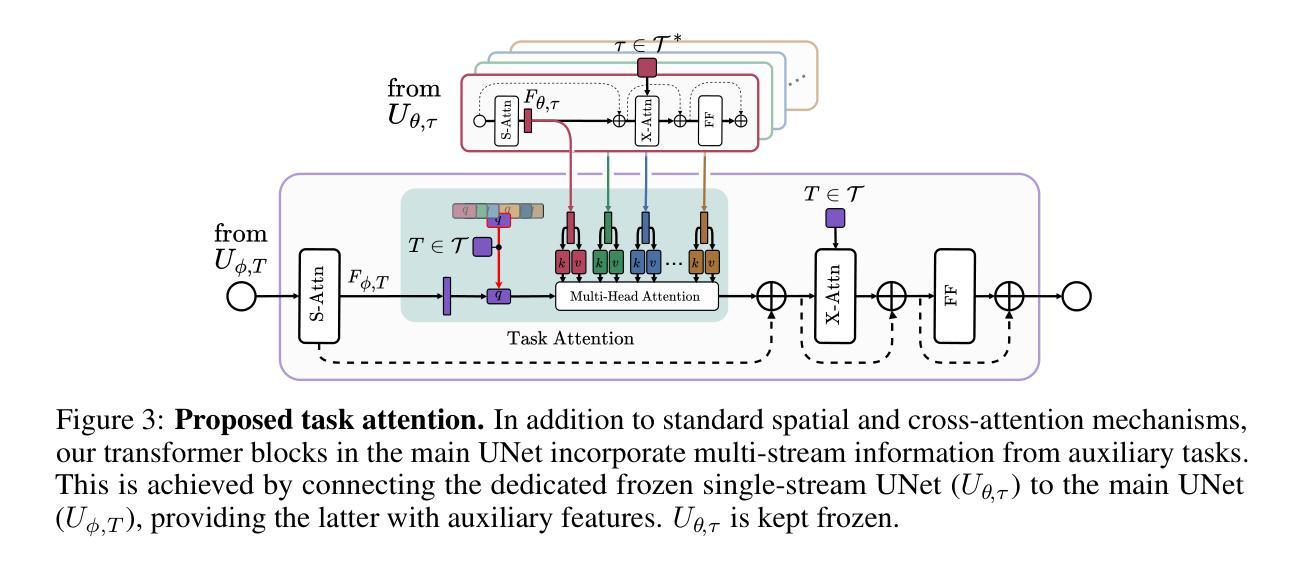
StableMTL: Repurposing Latent Diffusion Models for Multi-Task Learning from Partially Annotated Synthetic Datasets
Authors:Anh-Quan Cao, Ivan Lopes, Raoul de Charette
Multi-task learning for dense prediction is limited by the need for extensive annotation for every task, though recent works have explored training with partial task labels. Leveraging the generalization power of diffusion models, we extend the partial learning setup to a zero-shot setting, training a multi-task model on multiple synthetic datasets, each labeled for only a subset of tasks. Our method, StableMTL, repurposes image generators for latent regression. Adapting a denoising framework with task encoding, per-task conditioning and a tailored training scheme. Instead of per-task losses requiring careful balancing, a unified latent loss is adopted, enabling seamless scaling to more tasks. To encourage inter-task synergy, we introduce a multi-stream model with a task-attention mechanism that converts N-to-N task interactions into efficient 1-to-N attention, promoting effective cross-task sharing. StableMTL outperforms baselines on 7 tasks across 8 benchmarks.
多任务学习在密集预测上的应用受限于每个任务需要大量标注的需求,尽管最近有探索部分任务标签的训练方法。我们利用扩散模型的泛化能力,将部分学习设置扩展到零样本设置,在多个合成数据集上训练多任务模型,每个数据集只对部分任务进行标注。我们的方法StableMTL重新定位图像生成器用于潜在回归。通过任务编码、每个任务的条件和一个量身定制的训练方案来适应去噪框架。不再使用需要仔细平衡的每个任务损失,采用统一的潜在损失,可以轻松扩展到更多任务。为了鼓励任务间的协同作用,我们引入了一个具有任务注意力机制的多流模型,将N-to-N任务交互转换为高效的1-to-N注意力,促进有效的跨任务共享。StableMTL在8个基准测试中的7个任务上超越了基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code is available at https://github.com/astra-vision/StableMTL
Summary
本文探讨了基于扩散模型的多任务学习在密集预测任务中的应用。针对多任务学习需要大量标注的问题,文章提出了一种名为StableMTL的方法,利用扩散模型的泛化能力,在零样本设置下对多个合成数据集进行训练,每个数据集仅针对部分任务进行标注。该方法通过图像生成器进行潜在回归,采用去噪框架并结合任务编码、任务条件及定制训练方案。通过统一潜在损失替代了需要精细平衡的任务损失,并支持无缝扩展到更多任务。为增强任务间的协同作用,文章引入了多任务流模型,采用任务注意力机制将N-to-N任务交互转换为高效的1-to-N注意力,促进跨任务的共享。StableMTL在7个任务、8个基准测试上的表现均超过基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 文章提出了StableMTL方法,将扩散模型应用于多任务学习中的密集预测任务。
- StableMTL在零样本设置下训练,利用合成数据集并仅对部分任务进行标注。
- 通过图像生成器进行潜在回归,采用去噪框架结合任务编码、条件及定制训练。
- 采用了统一潜在损失,无需精细平衡各任务损失,并可以无缝扩展到更多任务。
- 引入多任务流模型及任务注意力机制,实现任务间的有效共享和协同。
- StableMTL在多个任务和基准测试上的表现均超过现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

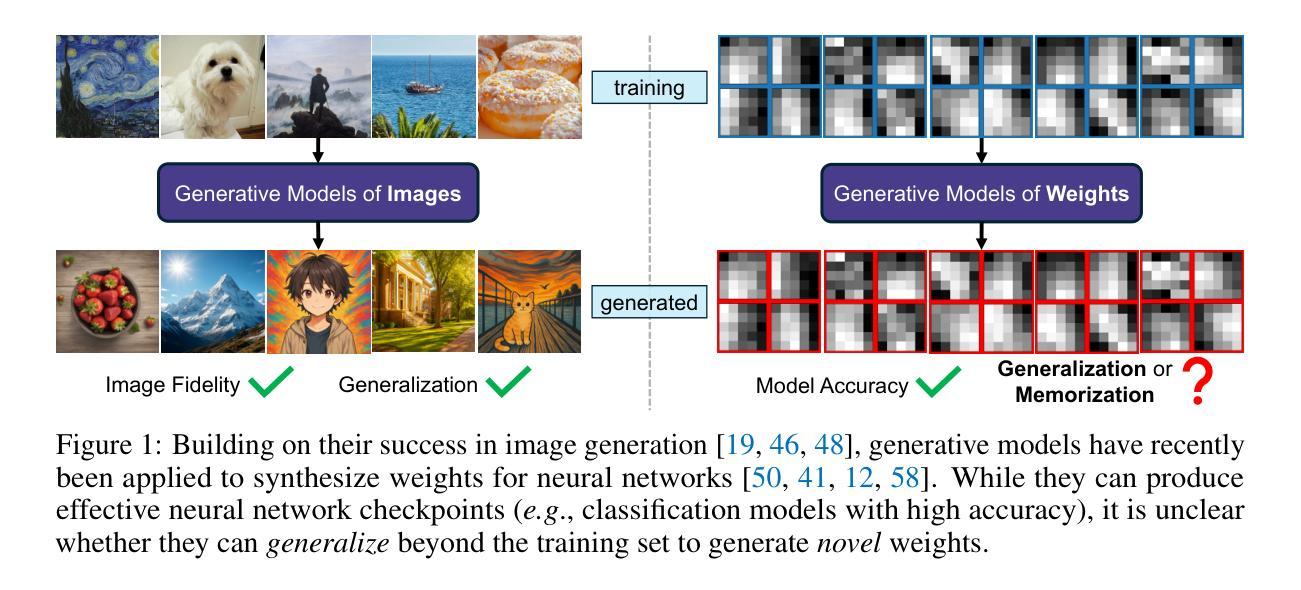
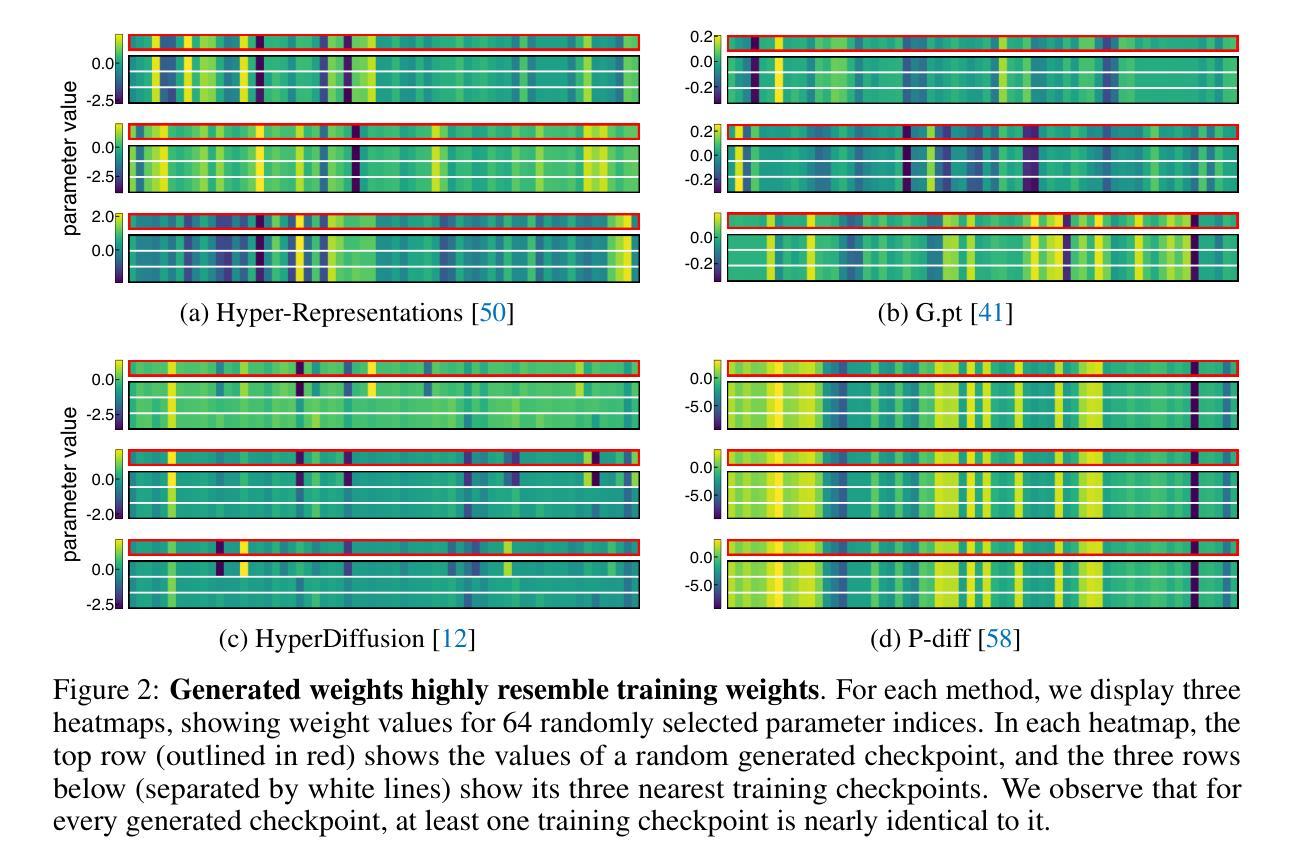
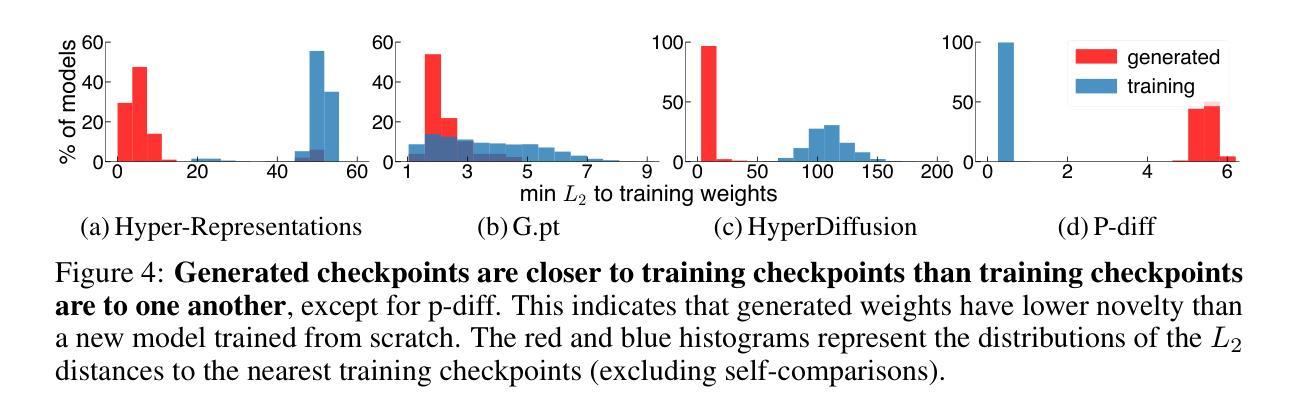
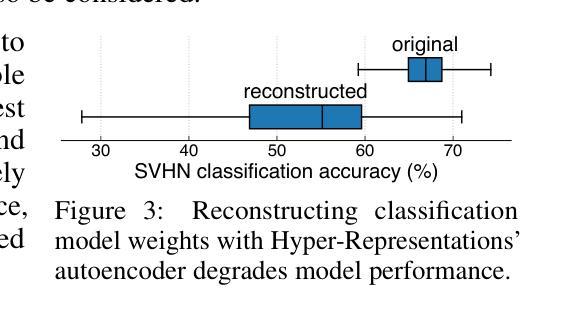
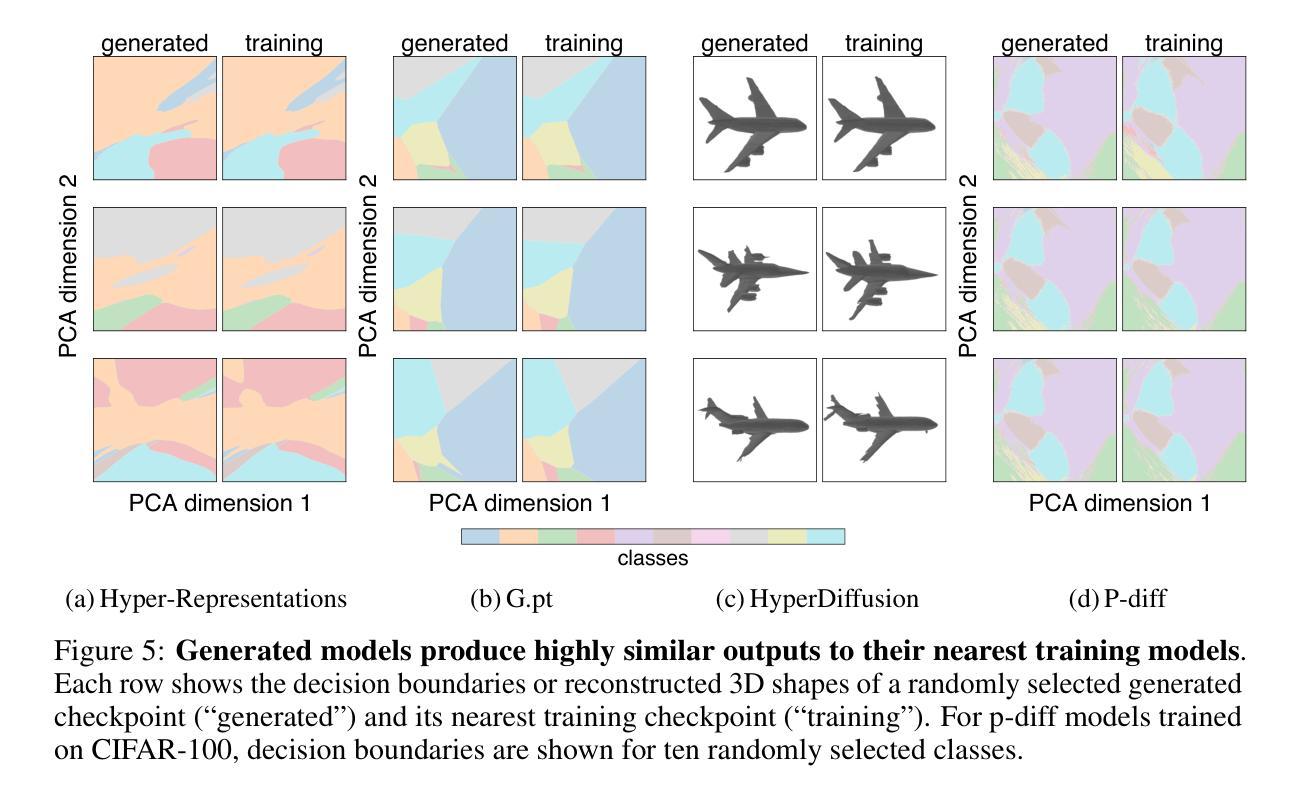
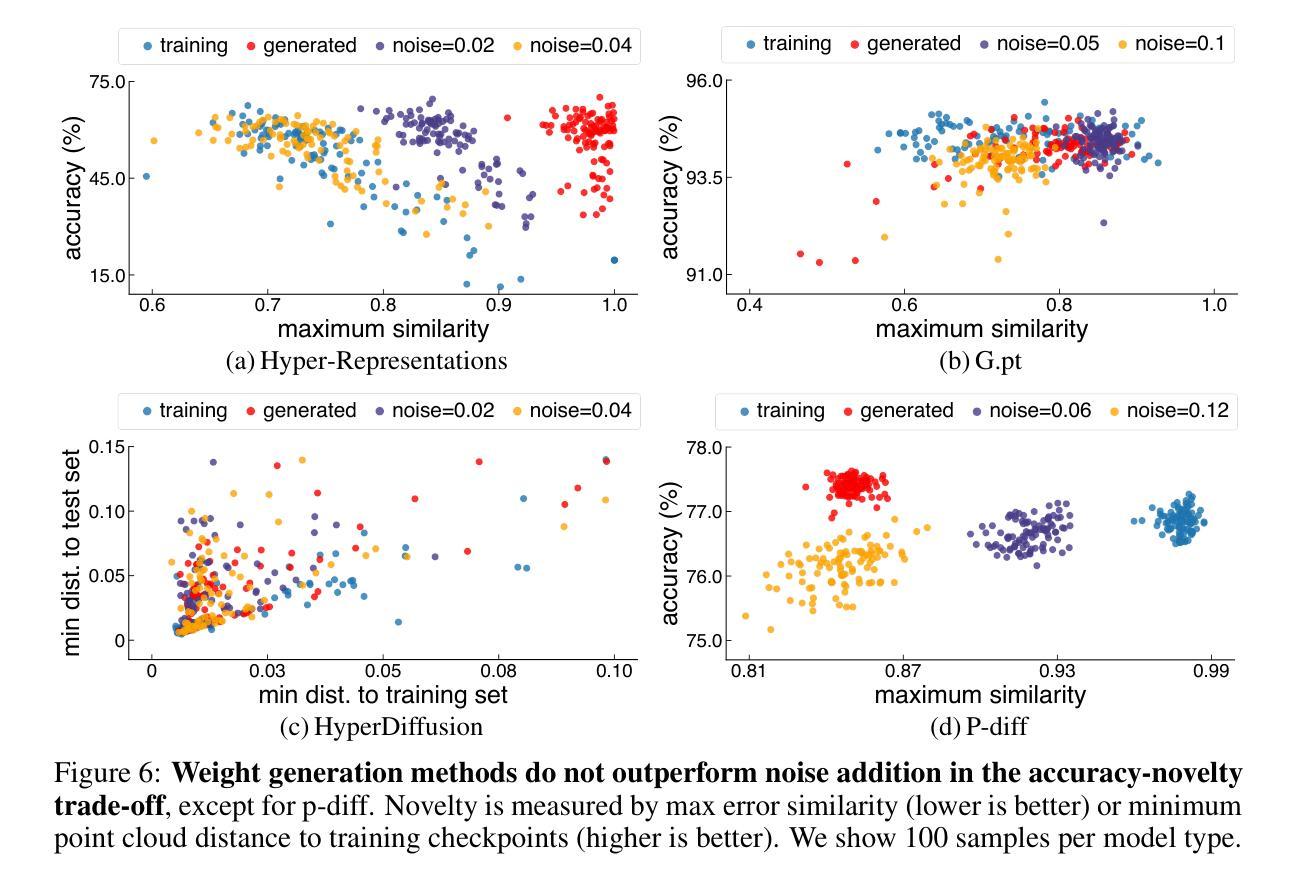
Generative Modeling of Weights: Generalization or Memorization?
Authors:Boya Zeng, Yida Yin, Zhiqiu Xu, Zhuang Liu
Generative models, with their success in image and video generation, have recently been explored for synthesizing effective neural network weights. These approaches take trained neural network checkpoints as training data, and aim to generate high-performing neural network weights during inference. In this work, we examine four representative methods on their ability to generate novel model weights, i.e., weights that are different from the checkpoints seen during training. Surprisingly, we find that these methods synthesize weights largely by memorization: they produce either replicas, or at best simple interpolations, of the training checkpoints. Current methods fail to outperform simple baselines, such as adding noise to the weights or taking a simple weight ensemble, in obtaining different and simultaneously high-performing models. We further show that this memorization cannot be effectively mitigated by modifying modeling factors commonly associated with memorization in image diffusion models, or applying data augmentations. Our findings provide a realistic assessment of what types of data current generative models can model, and highlight the need for more careful evaluation of generative models in new domains. Our code is available at https://github.com/boyazeng/weight_memorization.
生成模型在图像和视频生成方面取得了成功,最近被探索用于合成有效的神经网络权重。这些方法将训练过的神经网络的检查点作为训练数据,旨在在推理过程中生成高性能的神经网络权重。在这项工作中,我们考察了四种代表性方法在生成新型模型权重方面的能力,即不同于训练过程中所见检查点的权重。令人惊讶的是,我们发现这些方法主要通过记忆合成权重:它们产生的是训练检查点的复制品,或者最多是简单的插值。当前的方法未能超越简单的基线,如向权重添加噪声或采取简单的权重集合,来获得不同且同时高性能的模型。我们进一步表明,无法通过修改与图像扩散模型中记忆有关的建模因素或应用数据增强来有效缓解这种记忆问题。我们的研究为当前生成模型能够模拟的数据类型提供了现实的评估,并强调了在新领域中对生成模型进行更仔细评估的必要性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/boyazeng/weight_memorization找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page at https://boyazeng.github.io/weight_memorization
Summary
生成模型在图像和视频生成方面取得了成功,近期被探索用于合成有效的神经网络权重。然而,本文发现这些方法主要通过记忆合成权重,难以生成与训练检查点不同的新模型权重。当前的方法未能超越简单基线,如添加权重噪声或采用简单权重集成方法,来获得不同且高性能的模型。本文还发现,无法通过修改与图像扩散模型中的记忆相关的建模因素或应用数据增强来有效缓解记忆问题。本文的发现对评估当前生成模型能处理的数据类型提供了现实评估,并强调在新领域需要更仔细地评估生成模型。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型被探索用于合成神经网络权重,旨在生成高性能的神经网络权重。
- 现有方法主要通过记忆合成权重,难以生成与训练检查点不同的新模型权重。
- 当前的方法未能超越简单基线方法,如添加噪声或采用权重集成。
- 通过修改与记忆相关的建模因素或应用数据增强无法有效缓解记忆问题。
- 本文提供的代码库可公开访问,展示了研究成果和实际应用示例。
- 生成的模型性能受限,需要对新领域的生成模型进行更仔细的评估。
点此查看论文截图

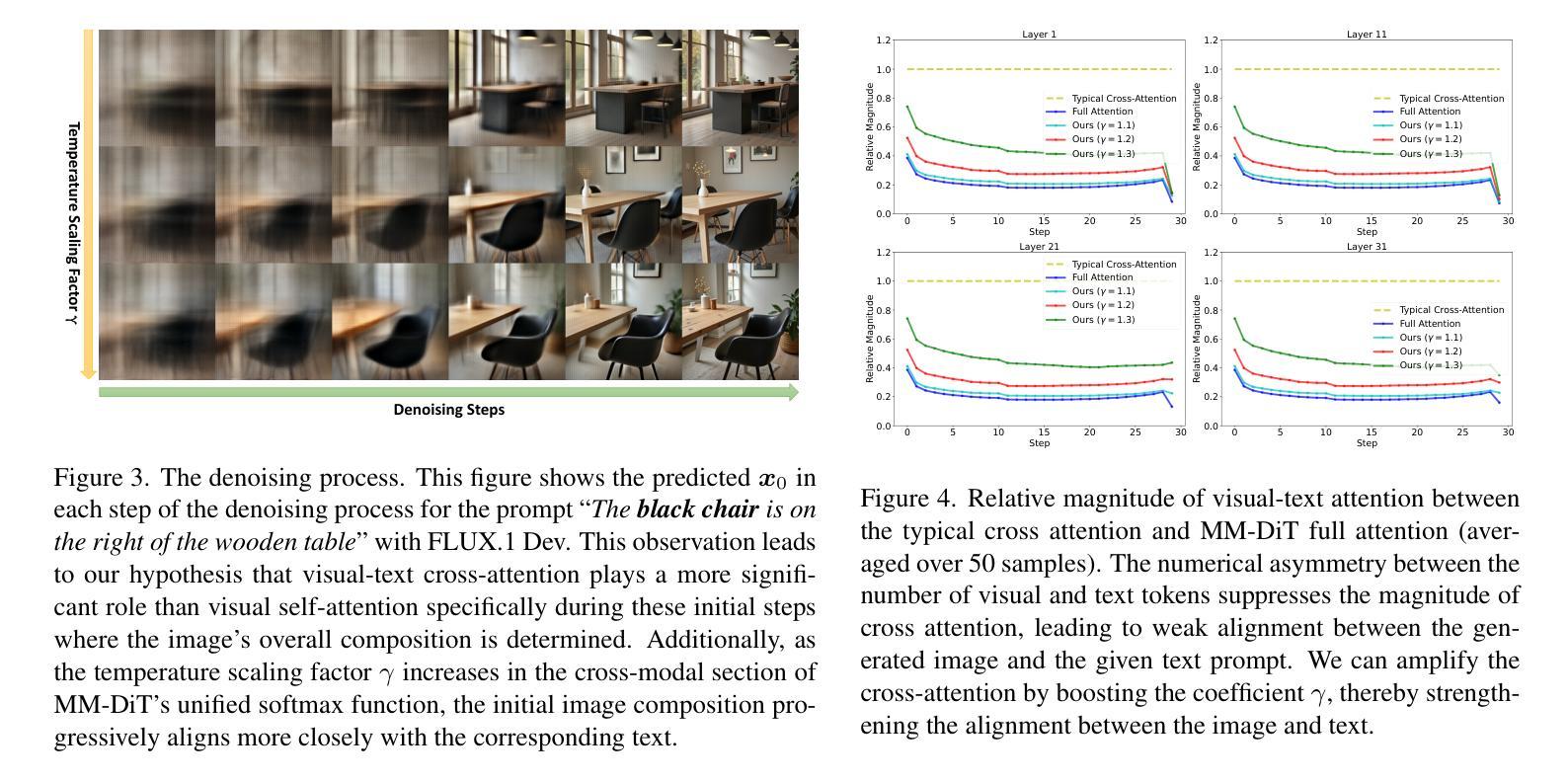
Rethinking Cross-Modal Interaction in Multimodal Diffusion Transformers
Authors:Zhengyao Lv, Tianlin Pan, Chenyang Si, Zhaoxi Chen, Wangmeng Zuo, Ziwei Liu, Kwan-Yee K. Wong
Multimodal Diffusion Transformers (MM-DiTs) have achieved remarkable progress in text-driven visual generation. However, even state-of-the-art MM-DiT models like FLUX struggle with achieving precise alignment between text prompts and generated content. We identify two key issues in the attention mechanism of MM-DiT, namely 1) the suppression of cross-modal attention due to token imbalance between visual and textual modalities and 2) the lack of timestep-aware attention weighting, which hinder the alignment. To address these issues, we propose \textbf{Temperature-Adjusted Cross-modal Attention (TACA)}, a parameter-efficient method that dynamically rebalances multimodal interactions through temperature scaling and timestep-dependent adjustment. When combined with LoRA fine-tuning, TACA significantly enhances text-image alignment on the T2I-CompBench benchmark with minimal computational overhead. We tested TACA on state-of-the-art models like FLUX and SD3.5, demonstrating its ability to improve image-text alignment in terms of object appearance, attribute binding, and spatial relationships. Our findings highlight the importance of balancing cross-modal attention in improving semantic fidelity in text-to-image diffusion models. Our codes are publicly available at \href{https://github.com/Vchitect/TACA}
多模态扩散转换器(MM-DiTs)在文本驱动视觉生成方面取得了显著进展。然而,即使是最先进的MM-DiT模型,如FLUX,在实现文本提示和生成内容之间的精确对齐方面也存在困难。我们确定了MM-DiT注意机制中的两个关键问题,即1)由于视觉和文本模态之间令牌的不平衡抑制了跨模态注意,以及2)缺乏时间步长感知的注意权重,这阻碍了对齐。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了温度调整跨模态注意力(TACA),这是一种参数有效的方法,通过温度缩放和时间步长依赖的调整来动态地重新平衡多模态交互。结合LoRA微调,TACA在T2I-CompBench基准测试上显著增强了文本图像对齐,且计算开销极小。我们在最先进的模型FLUX和SD3.5上测试了TACA,证明了其在物体外观、属性绑定和空间关系方面提高图像文本对齐的能力。我们的研究结果表明,在文本到图像扩散模型中平衡跨模态注意力对于提高语义保真度的重要性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Vchitect/TACA公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了多模态扩散转换器(MM-DiT)在文本驱动视觉生成方面的显著进展,但现有模型如FLUX在文本提示和生成内容之间的精确对齐方面存在挑战。文章指出MM-DiT注意力机制中的两个关键问题:1)视觉和文本模态之间令牌的不平衡抑制了跨模态注意力;2)缺乏时间步长感知的注意力权重。为解决这些问题,提出温度调整跨模态注意力(TACA)方法,通过温度缩放和时间步长依赖调整动态平衡多模态交互。结合LoRA微调,TACA在T2I-CompBench基准测试上显著提高了文本图像对齐能力,计算开销小。在FLUX和SD3.5等先进模型上的实验验证了TACA在改善图像文本对齐方面的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态扩散转换器(MM-DiT)在文本驱动视觉生成上取得显著进展,但存在文本提示与生成内容精确对齐的挑战。
- MM-DiT的注意力机制中存在两个关键问题:令牌不平衡和缺乏时间步长感知的注意力权重。
- 为解决上述问题,提出温度调整跨模态注意力(TACA)方法,通过温度缩放和时间步长依赖调整来动态平衡多模态交互。
- TACA结合LoRA微调,显著提高文本图像对齐能力,在T2I-CompBench基准测试上有优异表现。
- TACA方法具有参数效率高、计算开销小的优点。
- 在FLUX和SD3.5等先进模型上的实验验证了TACA的有效性。
点此查看论文截图



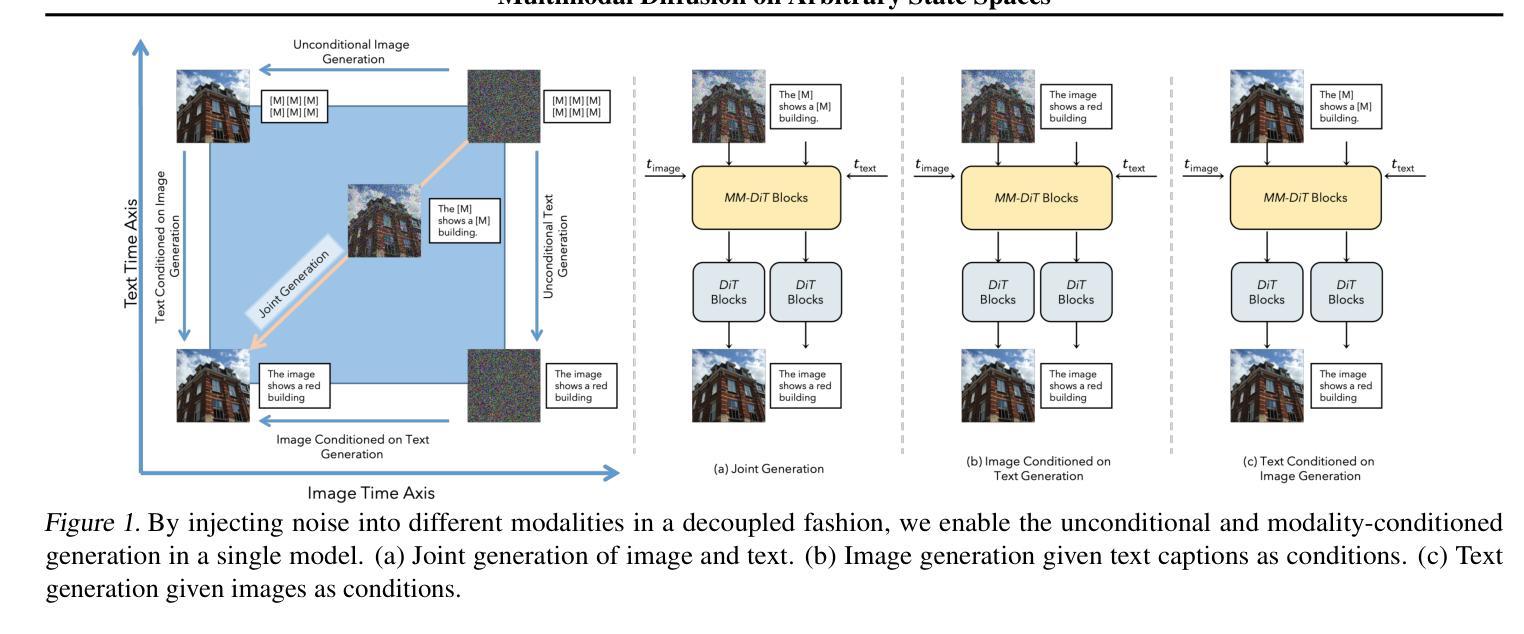
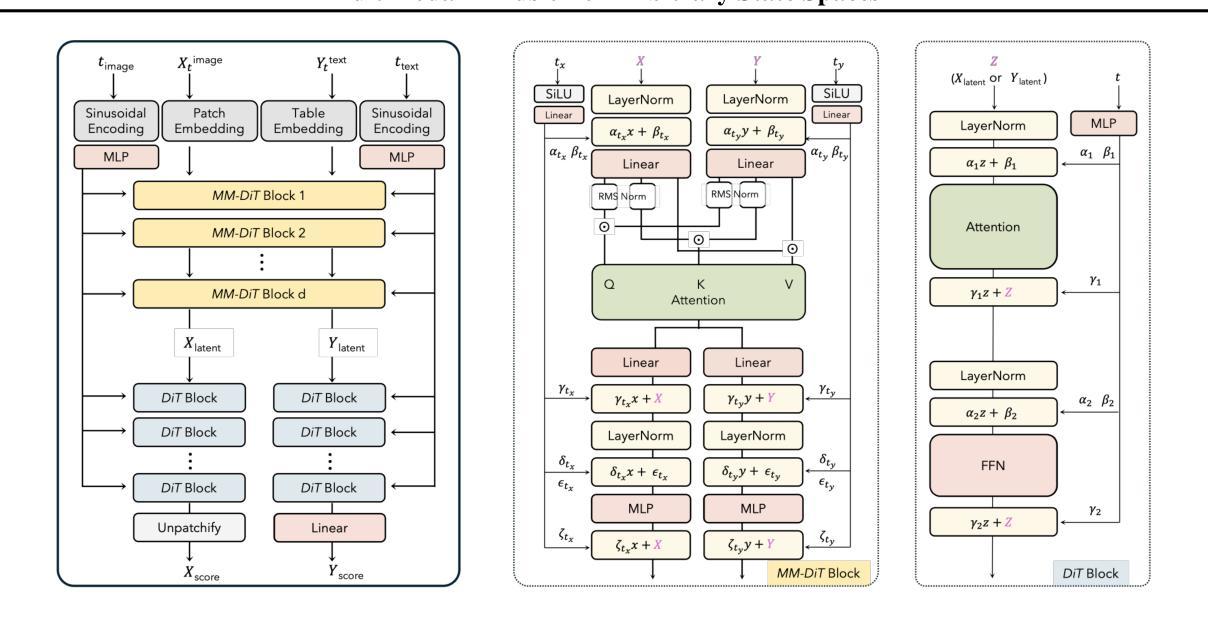
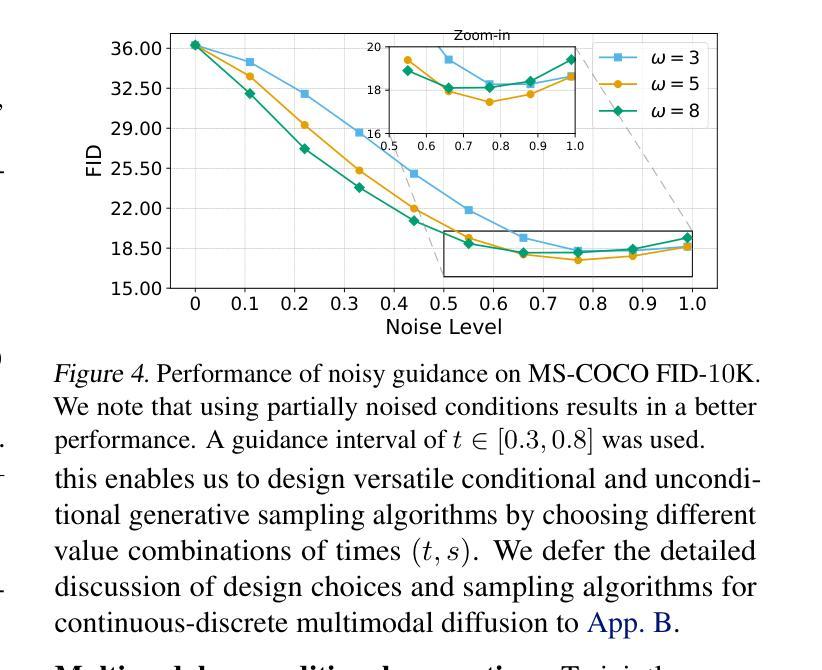
Diffuse Everything: Multimodal Diffusion Models on Arbitrary State Spaces
Authors:Kevin Rojas, Yuchen Zhu, Sichen Zhu, Felix X. -F. Ye, Molei Tao
Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable performance in generating unimodal data across various tasks, including image, video, and text generation. On the contrary, the joint generation of multimodal data through diffusion models is still in the early stages of exploration. Existing approaches heavily rely on external preprocessing protocols, such as tokenizers and variational autoencoders, to harmonize varied data representations into a unified, unimodal format. This process heavily demands the high accuracy of encoders and decoders, which can be problematic for applications with limited data. To lift this restriction, we propose a novel framework for building multimodal diffusion models on arbitrary state spaces, enabling native generation of coupled data across different modalities. By introducing an innovative decoupled noise schedule for each modality, we enable both unconditional and modality-conditioned generation within a single model simultaneously. We empirically validate our approach for text-image generation and mixed-type tabular data synthesis, demonstrating that it achieves competitive performance.
扩散模型在不同任务上生成单模态数据表现出卓越的性能,包括图像、视频和文本生成。相反,通过扩散模型进行多模态数据的联合生成仍在初步探索阶段。现有方法严重依赖于外部预处理协议,如标记器和变分自编码器,以协调不同的数据表示为一个统一、单模态的格式。这个过程对编码器和解码器的高精度提出了很高的要求,对于数据有限的应用可能会成为问题。为了克服这一限制,我们提出了一种在任意状态空间上构建多模态扩散模型的新框架,能够实现不同模态下耦合数据的原生生成。通过引入针对每种模态的创新解耦噪声时间表,我们能够在单个模型中同时实现无条件生成和模态条件生成。我们对文本图像生成和混合类型表格数据合成进行了实证研究,证明了该方法具有竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICML 2025. Code available at https://github.com/KevinRojas1499/Diffuse-Everything
Summary
扩散模型已在生成单模态数据方面展现出卓越性能,涵盖图像、视频和文本生成等任务。然而,通过扩散模型进行多模态数据的联合生成仍处于探索的早期阶段。现有方法严重依赖于外部预处理协议,如令牌化器和变分自动编码器,以将不同的数据表示统一为单一模态格式。这一过程对编码器和解码器的高准确性有很高的要求,对于数据有限的应用可能存在问题。为了克服这一限制,我们提出了一种在任意状态空间上构建多模态扩散模型的新框架,实现了跨不同模态的耦合数据本地生成。通过引入针对每种模态的解耦噪声调度,我们能够在单个模型中同时实现无条件生成和模态条件生成。我们对文本图像生成和混合类型表格数据合成进行了实证验证,证明该方法具有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成单模态数据方面表现出卓越性能,包括图像、视频和文本生成。
- 多模态数据的联合生成通过扩散模型仍处于早期探索阶段。
- 现有方法依赖外部预处理协议来统一不同数据表示。
- 对编码器和解码器的高准确性有较高要求,这在数据有限的应用中可能存在问题。
- 提出了一种新的多模态扩散模型框架,适用于任意状态空间上的构建。
- 通过引入解耦噪声调度,实现了跨不同模态的本地数据生成。
点此查看论文截图



FunDiff: Diffusion Models over Function Spaces for Physics-Informed Generative Modeling
Authors:Sifan Wang, Zehao Dou, Tong-Rui Liu, Lu Lu
Recent advances in generative modeling – particularly diffusion models and flow matching – have achieved remarkable success in synthesizing discrete data such as images and videos. However, adapting these models to physical applications remains challenging, as the quantities of interest are continuous functions governed by complex physical laws. Here, we introduce $\textbf{FunDiff}$, a novel framework for generative modeling in function spaces. FunDiff combines a latent diffusion process with a function autoencoder architecture to handle input functions with varying discretizations, generate continuous functions evaluable at arbitrary locations, and seamlessly incorporate physical priors. These priors are enforced through architectural constraints or physics-informed loss functions, ensuring that generated samples satisfy fundamental physical laws. We theoretically establish minimax optimality guarantees for density estimation in function spaces, showing that diffusion-based estimators achieve optimal convergence rates under suitable regularity conditions. We demonstrate the practical effectiveness of FunDiff across diverse applications in fluid dynamics and solid mechanics. Empirical results show that our method generates physically consistent samples with high fidelity to the target distribution and exhibits robustness to noisy and low-resolution data. Code and datasets are publicly available at https://github.com/sifanexisted/fundiff.
近期生成模型——特别是扩散模型和流匹配——在合成离散数据(如图像和视频)方面取得了显著的成功。然而,将这些模型适应于实际应用仍然具有挑战性,因为感兴趣的量是受复杂物理定律控制的连续函数。在这里,我们介绍了$\textbf{FunDiff}$,一个函数空间生成模型的新型框架。FunDiff结合了潜在扩散过程和函数自编码器架构,以处理具有不同离散化的输入函数,生成可在任意位置评估的连续函数,并无缝地融入物理先验。这些先验通过结构约束或物理信息损失函数来实施,确保生成的样本满足基本物理定律。我们从理论上建立了函数空间密度估计的最小最大最优性保证,表明在合适的正则条件下,基于扩散的估计器达到了最优收敛速度。我们在流体动力学和固体力学等多样化应用中展示了FunDiff的实际效果。实证结果表明,我们的方法生成了符合物理一致的样本,对目标分布具有很高的保真度,并且对噪声和低分辨率数据表现出稳健性。代码和数据集可在https://github.com/sifanexisted/fundiff公开获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 31 pages, 12 figures
Summary
扩散模型与函数自编码器的结合,实现了函数空间的生成建模。FunDiff框架能够处理不同离散化的输入函数,生成可在任意位置评估的连续函数,并融入物理先验。该方法在流体动力学和固体力学等应用中表现出实用性,生成样本符合物理规律,对噪声和低分辨率数据具有稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- FunDiff结合扩散模型和函数自编码器,实现了函数空间的生成建模。
- 能够处理不同离散化的输入函数,生成连续函数。
- FunDiff通过架构约束或物理信息损失函数融入物理先验。
- 扩散模型在函数空间密度估计中达到最优收敛速率。
- FunDiff在流体动力学和固体力学等应用中具有实用性。
- 生成样本符合物理规律,具有高保真度。
- FunDiff对噪声和低分辨率数据具有稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

Diffusion Counterfactual Generation with Semantic Abduction
Authors:Rajat Rasal, Avinash Kori, Fabio De Sousa Ribeiro, Tian Xia, Ben Glocker
Counterfactual image generation presents significant challenges, including preserving identity, maintaining perceptual quality, and ensuring faithfulness to an underlying causal model. While existing auto-encoding frameworks admit semantic latent spaces which can be manipulated for causal control, they struggle with scalability and fidelity. Advancements in diffusion models present opportunities for improving counterfactual image editing, having demonstrated state-of-the-art visual quality, human-aligned perception and representation learning capabilities. Here, we present a suite of diffusion-based causal mechanisms, introducing the notions of spatial, semantic and dynamic abduction. We propose a general framework that integrates semantic representations into diffusion models through the lens of Pearlian causality to edit images via a counterfactual reasoning process. To our knowledge, this is the first work to consider high-level semantic identity preservation for diffusion counterfactuals and to demonstrate how semantic control enables principled trade-offs between faithful causal control and identity preservation.
生成反事实图像面临重大挑战,包括保持身份、维持感知质量和确保忠于潜在因果模型。虽然现有的自动编码框架允许语义潜在空间,可以进行因果控制操作,但它们面临着可扩展性和保真度的问题。扩散模型的进步为改进反事实图像编辑提供了机会,它们已显示出最先进的视觉质量、与人类对齐的感知能力和表征学习能力。在这里,我们提出了一套基于扩散的因果机制,引入了空间、语义和动态归纳的概念。我们提出了一个通过皮尔士因果性的视角将语义表示集成到扩散模型中的通用框架,通过反事实推理过程来编辑图像。据我们所知,这是第一项考虑高级语义身份保留的扩散反事实的工作,并展示了语义控制如何实现在忠实因果控制和身份保留之间的原则性权衡。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Proceedings of the 42nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Vancouver, Canada
Summary
扩散模型在图像编辑中的潜力及其在生成反事实图像时的挑战与创新。该研究提出一种基于扩散机制的因果编辑框架,引入空间、语义和动态推断概念,并通过Pearl因果视角整合语义表示。该框架能在反事实推理过程中编辑图像,在保持高级语义身份的同时实现因果控制。此研究在扩散模型的反事实中考虑了高级语义身份的保留,展示了语义控制如何平衡因果控制与身份保留。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像编辑中具有优势,尤其在生成反事实图像时表现出强大的潜力。
- 现有挑战包括保持身份、维持感知质量和确保忠于潜在因果模型。
- 研究提出一种基于扩散机制的因果编辑框架,该框架结合了空间、语义和动态推断概念。
- 通过Pearl因果视角整合语义表示,该框架能够在反事实推理过程中编辑图像。
- 该研究考虑了高级语义身份的保留在扩散模型的反事实中的重要性。
- 研究展示了如何通过语义控制实现因果控制与身份保留之间的平衡。
- 该框架展示了先进的视觉质量、人类对齐感知和表示学习能力。
点此查看论文截图

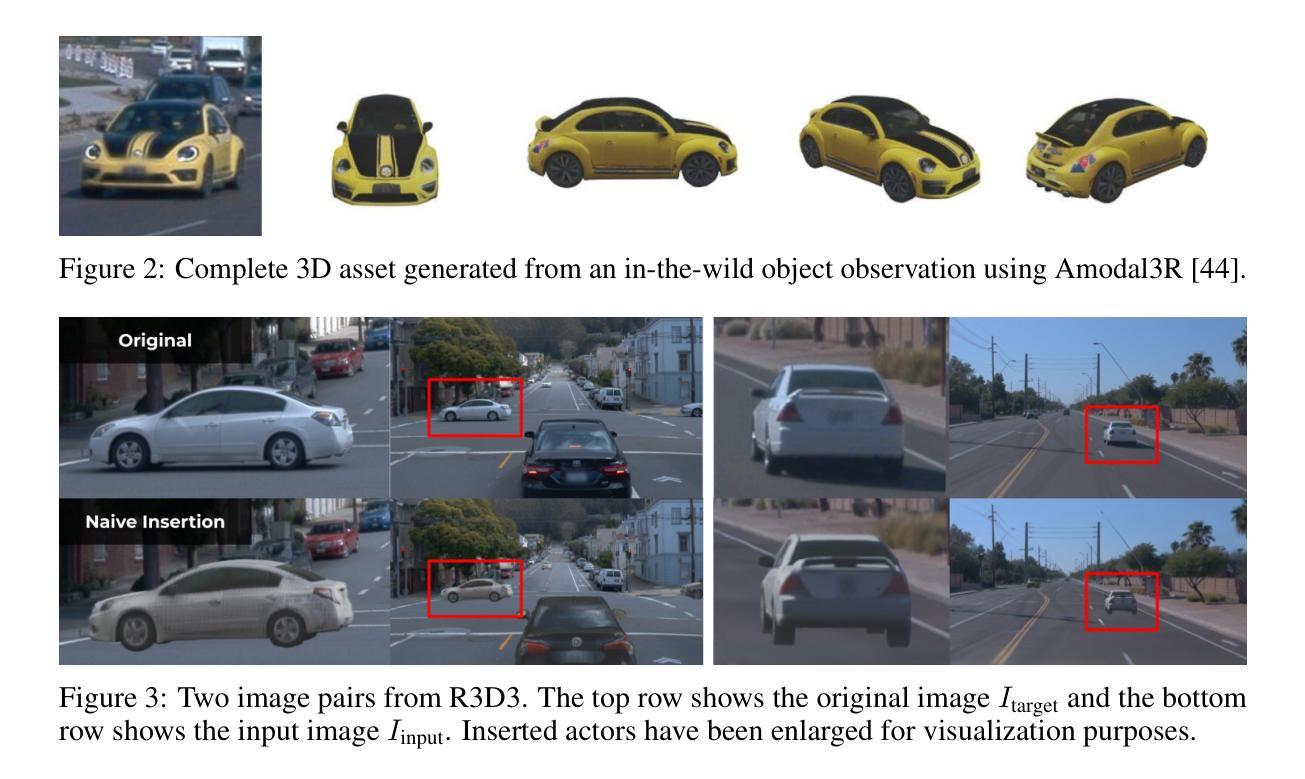
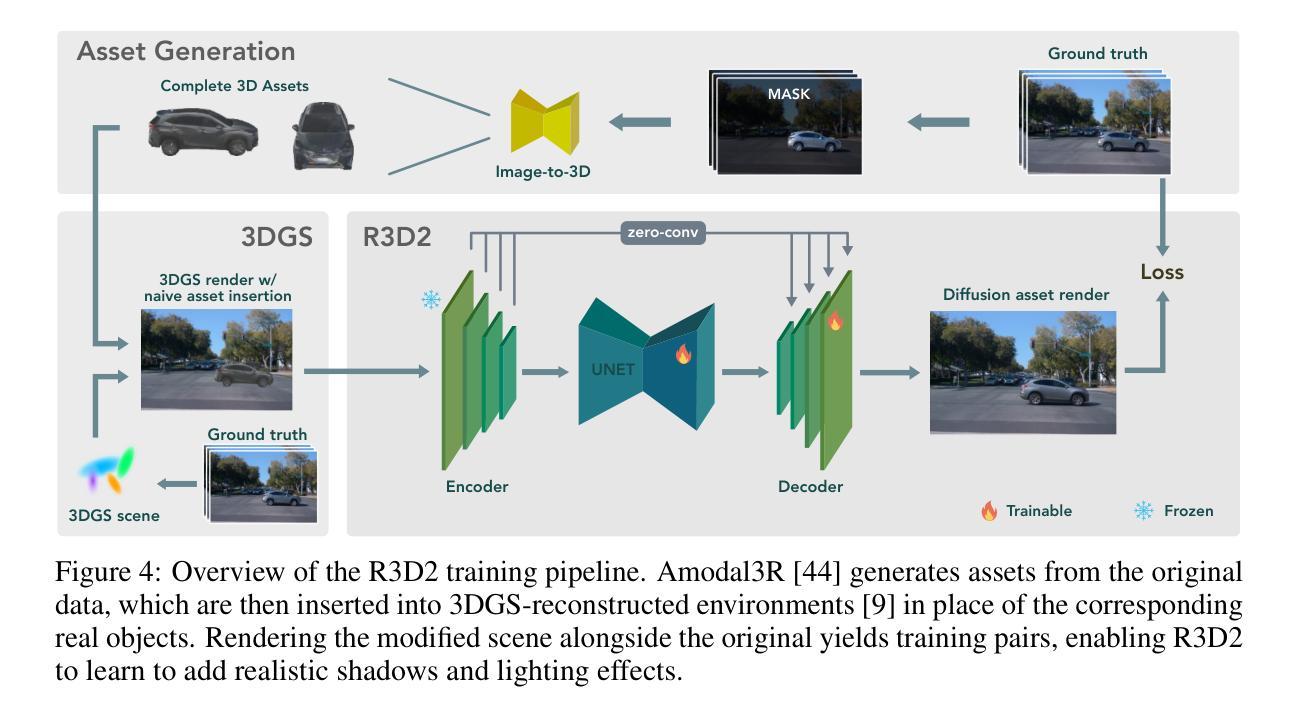
R3D2: Realistic 3D Asset Insertion via Diffusion for Autonomous Driving Simulation
Authors:William Ljungbergh, Bernardo Taveira, Wenzhao Zheng, Adam Tonderski, Chensheng Peng, Fredrik Kahl, Christoffer Petersson, Michael Felsberg, Kurt Keutzer, Masayoshi Tomizuka, Wei Zhan
Validating autonomous driving (AD) systems requires diverse and safety-critical testing, making photorealistic virtual environments essential. Traditional simulation platforms, while controllable, are resource-intensive to scale and often suffer from a domain gap with real-world data. In contrast, neural reconstruction methods like 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) offer a scalable solution for creating photorealistic digital twins of real-world driving scenes. However, they struggle with dynamic object manipulation and reusability as their per-scene optimization-based methodology tends to result in incomplete object models with integrated illumination effects. This paper introduces R3D2, a lightweight, one-step diffusion model designed to overcome these limitations and enable realistic insertion of complete 3D assets into existing scenes by generating plausible rendering effects-such as shadows and consistent lighting-in real time. This is achieved by training R3D2 on a novel dataset: 3DGS object assets are generated from in-the-wild AD data using an image-conditioned 3D generative model, and then synthetically placed into neural rendering-based virtual environments, allowing R3D2 to learn realistic integration. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate that R3D2 significantly enhances the realism of inserted assets, enabling use-cases like text-to-3D asset insertion and cross-scene/dataset object transfer, allowing for true scalability in AD validation. To promote further research in scalable and realistic AD simulation, we will release our dataset and code, see https://research.zenseact.com/publications/R3D2/.
验证自动驾驶(AD)系统需要进行多样化和安全关键的测试,这使得逼真虚拟环境变得至关重要。传统仿真平台虽然可控,但规模扩展资源密集,且经常与真实世界数据存在领域差距。相比之下,神经重建方法(如3D高斯喷涂技术(3DGS))提供了一种可扩展的解决方案,用于创建真实驾驶场景的逼真数字双胞胎。然而,它们在动态对象操作和重用方面遇到困难,因为它们基于场景的优化的方法往往导致具有集成照明效果的不完整对象模型。本文介绍了R3D2,一个轻量级的、一步到位的扩散模型,旨在克服这些限制,并通过生成逼真的渲染效果(如阴影和一致照明)来实现将完整的3D资产实时插入现有场景。这是通过在新型数据集上训练R3D2实现的:使用图像条件下的3D生成模型从野生AD数据中生成3DGS对象资产,然后将其合成地放入基于神经渲染的虚拟环境中,使R3D2学习逼真的集成方式。定量和定性评估表明,R3D2显着提高了插入资产的真实性,能够实现文本到3D资产插入和跨场景/数据集对象转移等用例,为AD验证提供了真正的可扩展性。为了促进可扩展和逼真的AD模拟的进一步研究,我们将发布我们的数据集和代码,详见https://research.zenseact.com/publications/R3D2/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
神经网络重建方法,如三维高斯溅射(3DGS),为创建真实世界驾驶场景的光照级数字双胞胎提供了可伸缩的解决方案。然而,它们在动态物体操作和再利用方面存在局限性。本文引入R3D2模型,该模型克服了这些局限性,并允许实时生成逼真的渲染效果,例如阴影和一致的光照。R3D2通过在野外驾驶数据上生成三维生成模型的新数据集实现这一目标,并将其合成地放置在基于神经渲染的虚拟环境中进行学习。因此,该模型可用于真实驾驶场景的大规模仿真和自主驾驶系统测试。该论文还公开了数据集和代码以推动相关研究的发展。
Key Takeaways:
自主驾驶系统验证需要多样化的安全测试,这要求模拟逼真的虚拟环境。传统模拟平台在扩大规模方面存在资源密集的问题,且与真实世界数据之间存在领域差距。本文强调了新型仿真技术在创建大规模场景和集成资源上的需求重要性。在高度仿真且可靠的大规模场景上可以大幅降低反复路测和工程投入的成本与精力损耗,从而实现自动驾驶的大规模商业应用前景。这些关键技术使得建立高效的自主驾驶测试体系成为可能。基于此建立的一体化验证系统将为后期加速技术落地提供了强力的底层支持工具;在实际开放道路上的测试结果差距相比于技术更新差异更有意义和影响性价值会获得很大改善提升潜力。同时公开的数据集和代码促进了进一步的研究和发展。
R3D2模型是一种新型的神经网络重建方法,克服了现有方法的局限性,能够实时生成逼真的渲染效果,如阴影和一致的光照。它通过生成新的数据集并合成地放置在基于神经渲染的虚拟环境中进行学习来实现这一目标。这为自主驾驶系统的测试提供了更逼真的模拟环境。同时其强大的泛化能力允许在不同场景间进行灵活切换和资产转移使用场景丰富多变。通过实时渲染技术,实现了更加逼真的虚拟环境模拟,提高了自主驾驶系统的测试质量和效率。这一创新技术为自主驾驶系统的测试和验证开辟了新的途径。对于自主驾驶系统而言不仅为其在开发和验证过程中提供更加接近真实的仿真测试环境从而提高系统安全性和可靠性而且也推动了相关技术产业的发展进步和行业标准的提升及规范落地速度加快也拓展了相关的市场需求边界对于后期运营和市场拓展带来重要影响价值和产业联动升级推动力为自主研发制造的核心竞争力赋能加持。同时公开的数据集和代码促进了进一步的研究和发展。这一技术有望推动自主驾驶系统的测试和验证进入新的阶段并为相关产业带来革命性的变革和发展机遇。。
点此查看论文截图



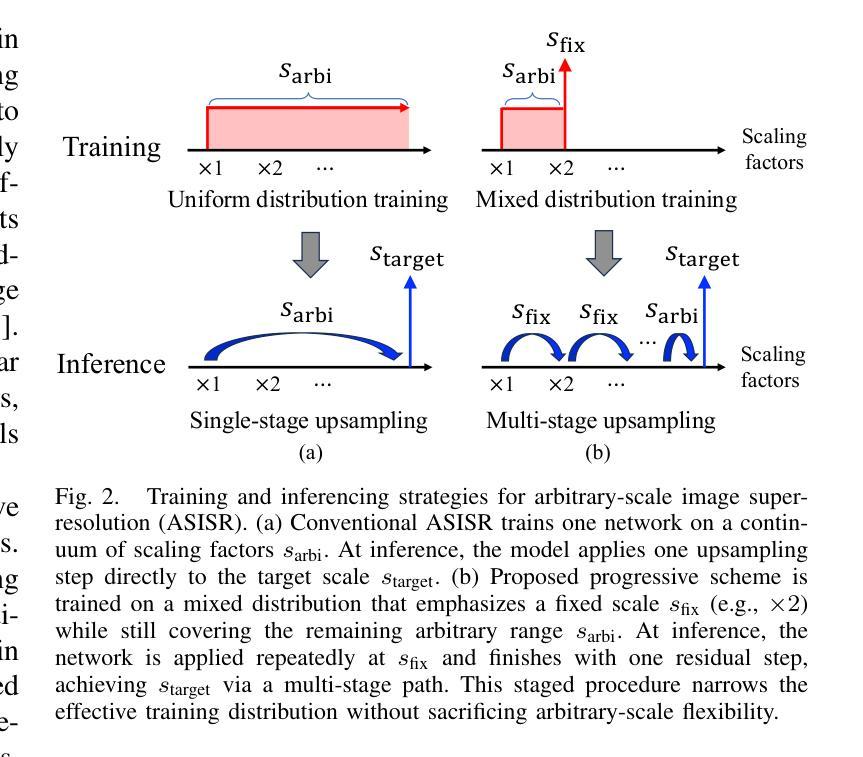
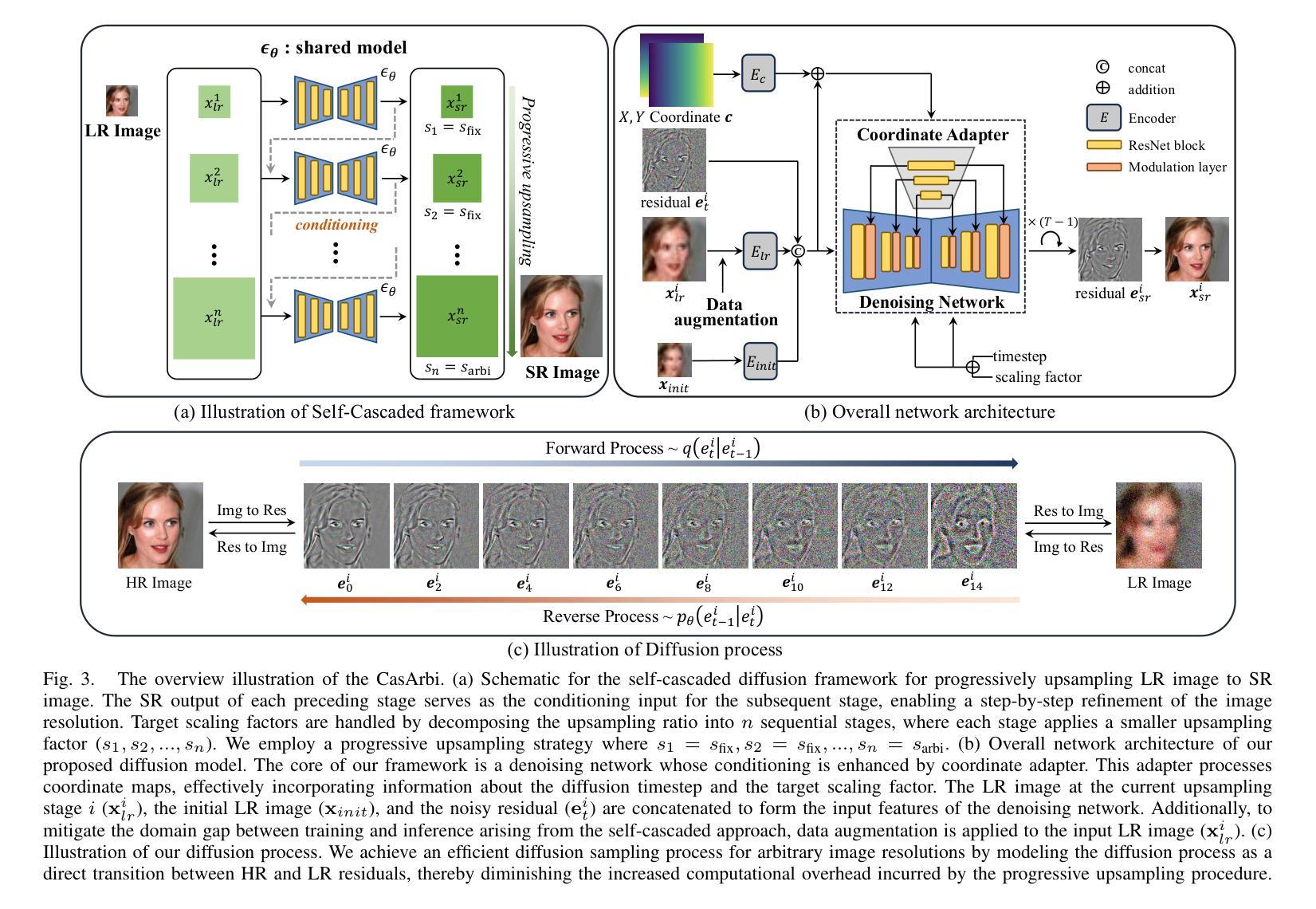
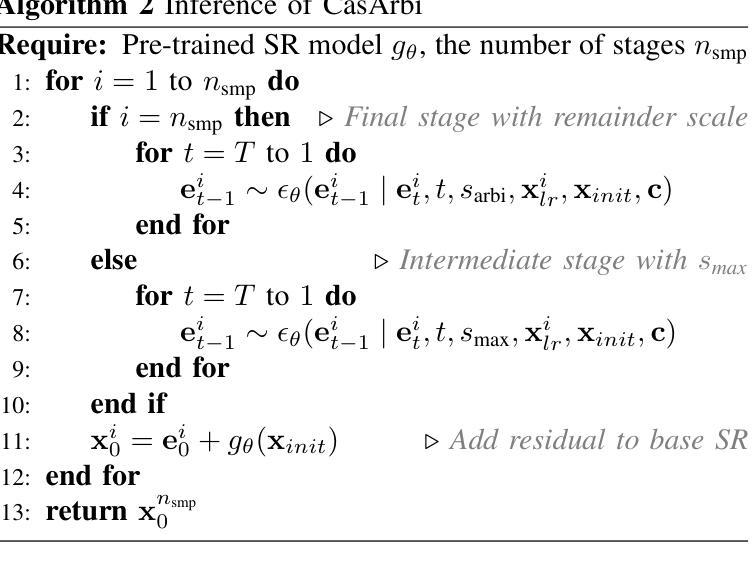
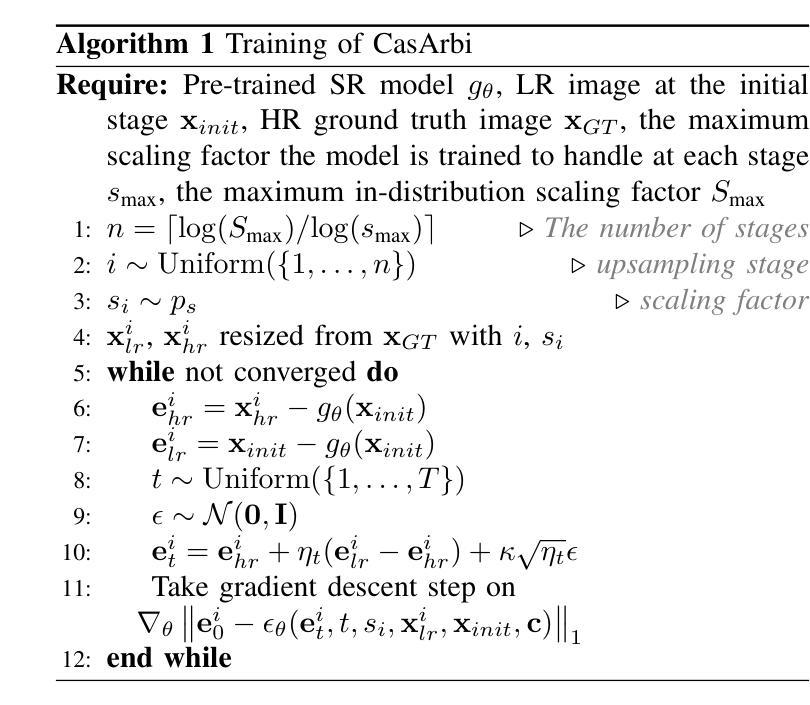
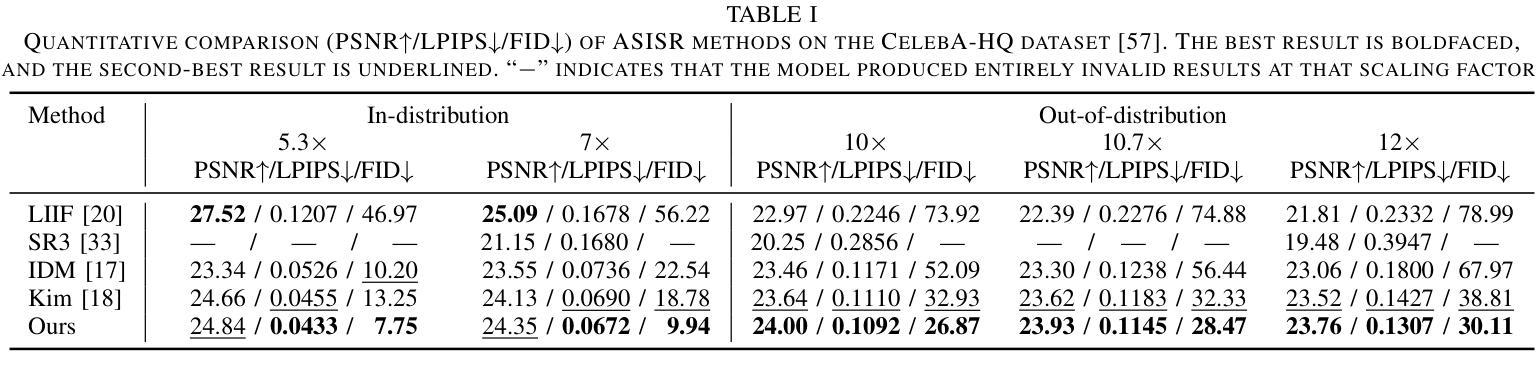
Self-Cascaded Diffusion Models for Arbitrary-Scale Image Super-Resolution
Authors:Junseo Bang, Joonhee Lee, Kyeonghyun Lee, Haechang Lee, Dong Un Kang, Se Young Chun
Arbitrary-scale image super-resolution aims to upsample images to any desired resolution, offering greater flexibility than traditional fixed-scale super-resolution. Recent approaches in this domain utilize regression-based or generative models, but many of them are a single-stage upsampling process, which may be challenging to learn across a wide, continuous distribution of scaling factors. Progressive upsampling strategies have shown promise in mitigating this issue, yet their integration with diffusion models for flexible upscaling remains underexplored. Here, we present CasArbi, a novel self-cascaded diffusion framework for arbitrary-scale image super-resolution. CasArbi meets the varying scaling demands by breaking them down into smaller sequential factors and progressively enhancing the image resolution at each step with seamless transitions for arbitrary scales. Our novel coordinate-guided residual diffusion model allows for the learning of continuous image representations while enabling efficient diffusion sampling. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our CasArbi outperforms prior arts in both perceptual and distortion performance metrics across diverse arbitrary-scale super-resolution benchmarks.
任意尺度图像超分辨率的目标是将图像放大到任何所需的分辨率,相较于传统的固定尺度超分辨率,它提供了更大的灵活性。虽然该领域最新的方法采用了基于回归或生成模型,但其中许多都是单阶段上采样过程,对于广泛的连续尺度因子分布,这可能会带来挑战。渐进式上采样策略在缓解这个问题方面显示出了一定的潜力,然而它们与扩散模型的集成以实现灵活放大却仍然被较少探索。在这里,我们提出了CasArbi,这是一种用于任意尺度图像超分辨率的新型自级联扩散框架。CasArbi通过将各种缩放需求分解为较小的连续因子来满足它们,并在每一步逐步增强图像分辨率,以实现任意尺度的无缝过渡。我们创新性的坐标引导残差扩散模型允许学习连续图像表示,同时实现有效的扩散采样。大量实验表明,我们的CasArbi在感知和失真性能指标方面均超越了先前技术在各种任意尺度超分辨率基准测试上的表现。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期关于任意尺度图像超分辨率的研究旨在将图像放大到任何所需分辨率,相较于传统固定尺度的超分辨率技术更具灵活性。当前方法多采用回归或生成模型,但单一阶段的放大过程在跨越连续尺度因子时学习较为困难。渐进式放大策略有助于缓解这一问题,但与扩散模型的结合进行灵活放大仍待探索。本文提出CasArbi,一种新型自级联扩散框架,用于任意尺度图像超分辨率。CasArbi通过将不同的尺度需求分解为若干连续的小尺度因子,并逐步增强图像分辨率,以实现任意尺度的无缝过渡。其创新的坐标引导残差扩散模型能学习连续图像表示,同时实现高效的扩散采样。实验表明,CasArbi在多种任意尺度超分辨率基准测试中,感知和失真性能指标均超越现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 任意尺度图像超分辨率旨在将图像放大到任何所需分辨率,具有比传统方法更高的灵活性。
- 当前方法面临学习连续尺度因子的挑战,单一阶段的放大过程可能难以应对。
- 渐进式放大策略有助于缓解这一挑战。
- CasArbi是一种新型自级联扩散框架,通过分解尺度需求并逐步增强图像分辨率,实现任意尺度的无缝过渡。
- CasArbi采用创新的坐标引导残差扩散模型,能学习连续图像表示并实现高效扩散采样。
- 实验表明CasArbi在多个超分辨率基准测试中表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

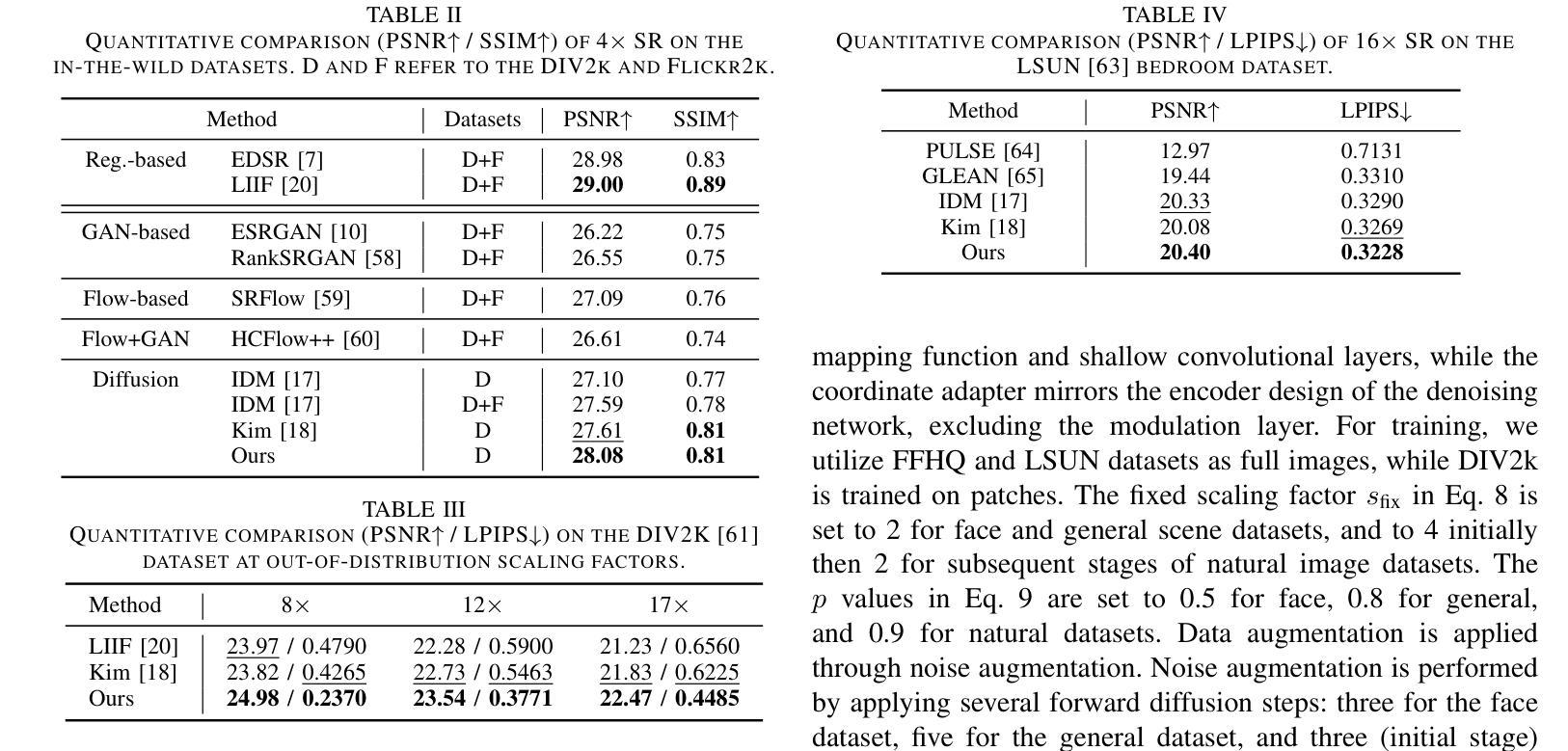
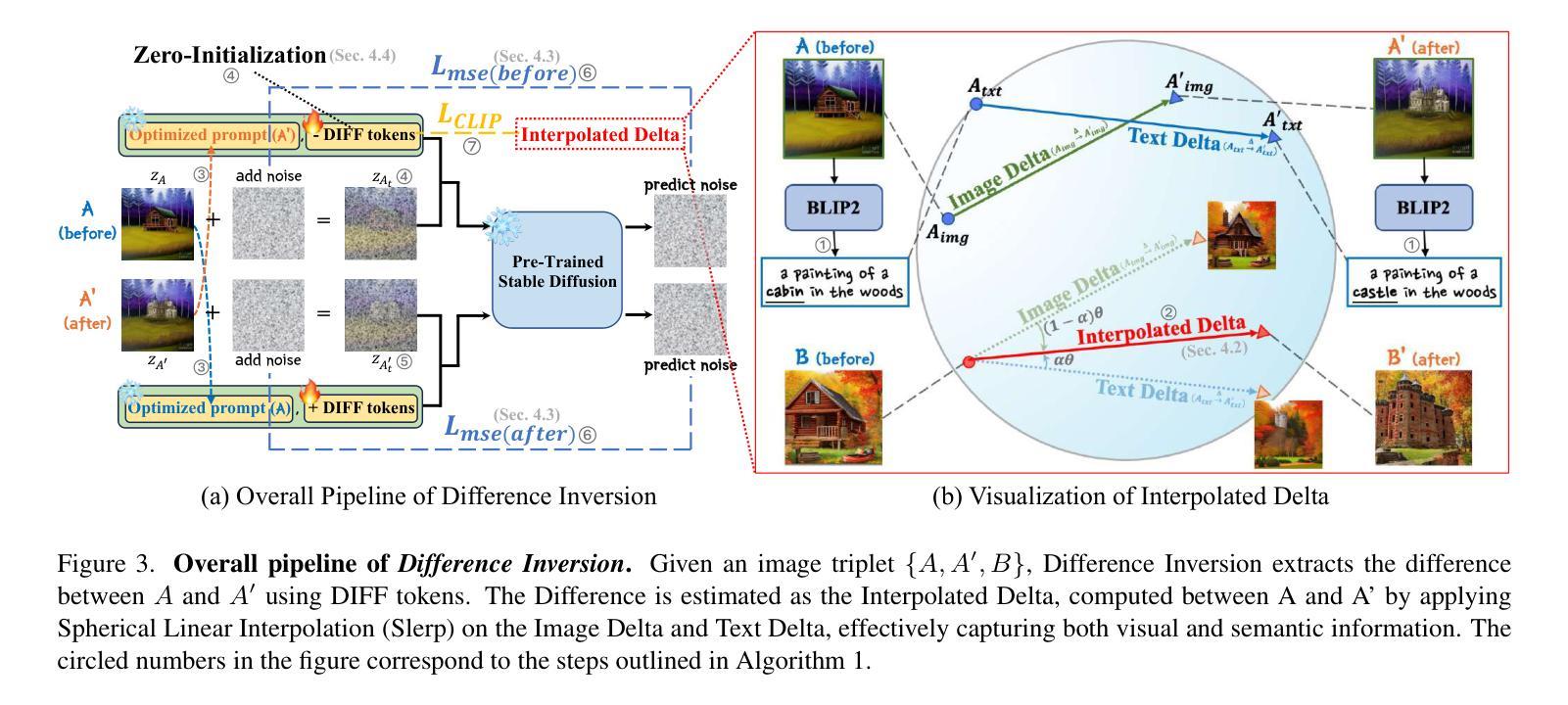
Difference Inversion: Interpolate and Isolate the Difference with Token Consistency for Image Analogy Generation
Authors:Hyunsoo Kim, Donghyun Kim, Suhyun Kim
How can we generate an image B’ that satisfies A:A’::B:B’, given the input images A,A’ and B? Recent works have tackled this challenge through approaches like visual in-context learning or visual instruction. However, these methods are typically limited to specific models (e.g. InstructPix2Pix. Inpainting models) rather than general diffusion models (e.g. Stable Diffusion, SDXL). This dependency may lead to inherited biases or lower editing capabilities. In this paper, we propose Difference Inversion, a method that isolates only the difference from A and A’ and applies it to B to generate a plausible B’. To address model dependency, it is crucial to structure prompts in the form of a “Full Prompt” suitable for input to stable diffusion models, rather than using an “Instruction Prompt”. To this end, we accurately extract the Difference between A and A’ and combine it with the prompt of B, enabling a plug-and-play application of the difference. To extract a precise difference, we first identify it through 1) Delta Interpolation. Additionally, to ensure accurate training, we propose the 2) Token Consistency Loss and 3) Zero Initialization of Token Embeddings. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that Difference Inversion outperforms existing baselines both quantitatively and qualitatively, indicating its ability to generate more feasible B’ in a model-agnostic manner.
给定输入图像A、A’和B,如何生成满足A:A’::B:B’的图像B’?近期的研究工作通过上下文视觉学习或视觉指令等方法来应对这一挑战。然而,这些方法通常仅限于特定模型(例如InstructPix2Pix、补全模型),而非通用的扩散模型(例如Stable Diffusion、SDXL)。这种依赖性可能导致继承的偏见或较低的编辑能力。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为差异反转的方法,该方法仅从A和A’中分离出差异并将其应用于B,以生成合理的B’。为了解决模型依赖性,关键在于构建适合输入稳定扩散模型的“完整提示”,而非使用“指令提示”。为此,我们准确地提取了A和A’之间的差异,并将其与B的提示相结合,实现了差异的即插即用应用。为了精确提取差异,我们首先通过1)Delta插值来识别它。此外,为了确保准确的训练,我们提出了2)标记一致性损失和3)标记嵌入的零初始化。我们的大量实验表明,差异反转在定量和定性上均优于现有基线,证明其以模型无关的方式生成更可行的B’的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at CVPR 2025
Summary:
本文提出一种名为“差异反转(Difference Inversion)”的方法,用于生成满足给定条件的新图像。该方法通过提取输入图像A和A’之间的差异,并将其应用于图像B来生成合理的图像B’。为克服模型依赖性问题,研究团队提出了“全提示(Full Prompt)”结构,以适应通用扩散模型如Stable Diffusion和SDXL。此外,为提高准确性,还介绍了差异提取的Delta Interpolation方法以及训练过程中的Token一致性损失和零初始化令牌嵌入技术。实验证明,差异反转方法在定量和定性上均优于现有基线,能以模型无关的方式生成更可行的图像B’。
Key Takeaways:
- 提出“差异反转(Difference Inversion)”方法,通过提取输入图像的差异并应用于另一图像来生成新图像。
- 克服特定模型依赖,采用通用扩散模型适应策略,即使用“全提示(Full Prompt)”结构。
- 采用Delta Interpolation方法准确提取图像差异。
- 为提高准确性,引入了Token一致性损失和零初始化令牌嵌入技术。
- 差异反转方法在定量和定性实验中均表现出优于现有基线的性能。
- 该方法能够生成更合理且模型无关的图像。
点此查看论文截图

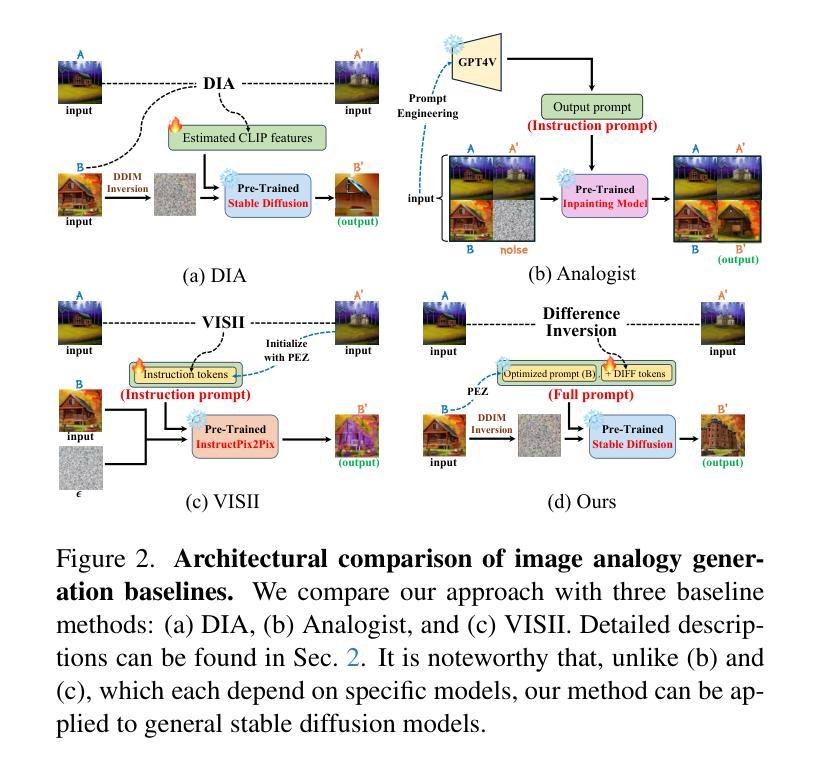

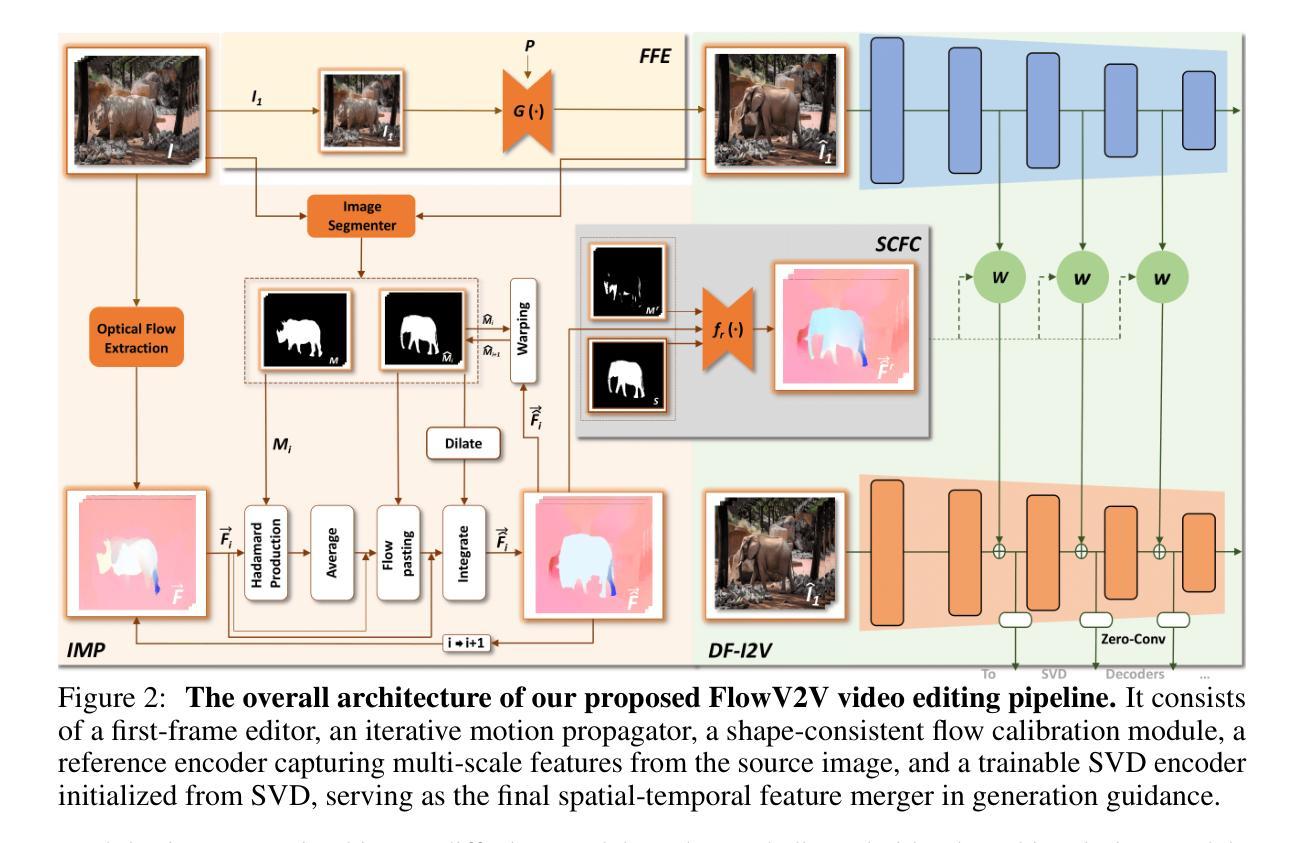
Consistent Video Editing as Flow-Driven Image-to-Video Generation
Authors:Ge Wang, Songlin Fan, Hangxu Liu, Quanjian Song, Hewei Wang, Jinfeng Xu
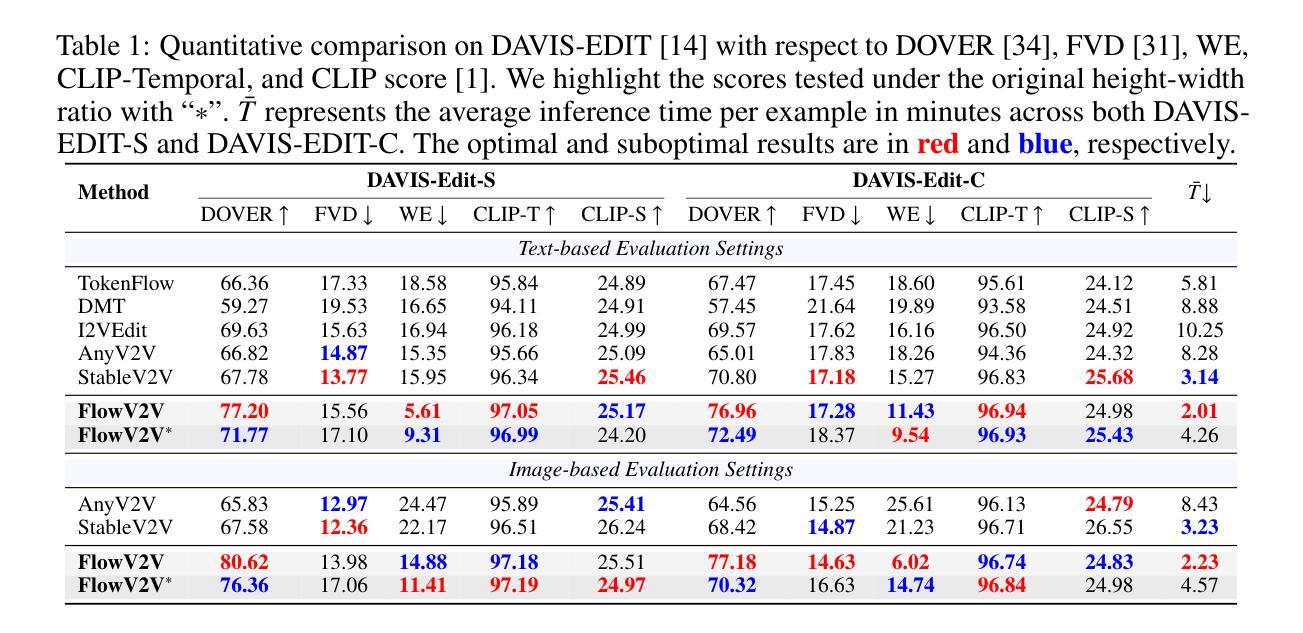
With the prosper of video diffusion models, down-stream applications like video editing have been significantly promoted without consuming much computational cost. One particular challenge in this task lies at the motion transfer process from the source video to the edited one, where it requires the consideration of the shape deformation in between, meanwhile maintaining the temporal consistency in the generated video sequence. However, existing methods fail to model complicated motion patterns for video editing, and are fundamentally limited to object replacement, where tasks with non-rigid object motions like multi-object and portrait editing are largely neglected. In this paper, we observe that optical flows offer a promising alternative in complex motion modeling, and present FlowV2V to re-investigate video editing as a task of flow-driven Image-to-Video (I2V) generation. Specifically, FlowV2V decomposes the entire pipeline into first-frame editing and conditional I2V generation, and simulates pseudo flow sequence that aligns with the deformed shape, thus ensuring the consistency during editing. Experimental results on DAVIS-EDIT with improvements of 13.67% and 50.66% on DOVER and warping error illustrate the superior temporal consistency and sample quality of FlowV2V compared to existing state-of-the-art ones. Furthermore, we conduct comprehensive ablation studies to analyze the internal functionalities of the first-frame paradigm and flow alignment in the proposed method.
随着视频扩散模型的繁荣,视频编辑等下游应用得到了显著推动,且无需消耗大量计算成本。该任务的一个特殊挑战在于从源视频到编辑视频的动态转移过程,这需要考虑两者之间的形状变形,同时保持生成视频序列的时间一致性。然而,现有方法无法对视频编辑进行复杂运动模式的建模,且从根本上仅限于对象替换,对于非刚性对象运动的任务,如多对象和人像编辑,却被大大忽视了。在本文中,我们观察到光流在复杂运动建模中提供了有前景的替代方案,并提出了FlowV2V来重新研究以流驱动的图片到视频(I2V)生成任务的视频编辑。具体来说,FlowV2V将整个管道分解为首帧编辑和条件I2V生成,并模拟与变形形状对齐的伪流序列,从而确保编辑过程中的一致性。在DAVIS-EDIT上的实验结果显示,与现有最先进的模型相比,FlowV2V在DOVER和warping error上分别提高了13.67%和50.66%,证明了其在时间一致性和样本质量上的优越性。此外,我们还进行了全面的消融研究,分析了所提出方法中首帧范式和流对齐的内部功能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 12 figures
Summary
视频扩散模型的发展极大地推动了视频编辑等下游应用的发展,降低了计算成本。该文针对现有方法在复杂运动模式建模方面的不足,提出了一种基于光学流的FlowV2V模型,用于实现流驱动图像到视频的转换,从而提高视频编辑的质量。该模型将流程分解为首帧编辑和条件I2V生成,并通过模拟与变形形状对齐的伪流序列,确保编辑过程中的一致性。实验结果表明,FlowV2V在DAVIS-EDIT数据集上的表现优于现有方法,具有更高的时间一致性和样本质量。
Key Takeaways
- 视频扩散模型促进了视频编辑等下游应用的发展。
- 现有方法在复杂运动模式建模方面存在局限性,特别是在非刚性物体运动的任务上。
- FlowV2V模型利用光学流进行复杂运动建模,提高了视频编辑的质量。
- FlowV2V将视频编辑流程分解为首帧编辑和条件I2V生成。
- 通过模拟与变形形状对齐的伪流序列,FlowV2V确保了编辑过程中的一致性。
- 实验结果表明,FlowV2V在DAVIS-EDIT数据集上的表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

Evaluating Robustness in Latent Diffusion Models via Embedding Level Augmentation
Authors:Boris Martirosyan, Alexey Karmanov
Latent diffusion models (LDMs) achieve state-of-the-art performance across various tasks, including image generation and video synthesis. However, they generally lack robustness, a limitation that remains not fully explored in current research. In this paper, we propose several methods to address this gap. First, we hypothesize that the robustness of LDMs primarily should be measured without their text encoder, because if we take and explore the whole architecture, the problems of image generator and text encoders wll be fused. Second, we introduce novel data augmentation techniques designed to reveal robustness shortcomings in LDMs when processing diverse textual prompts. We then fine-tune Stable Diffusion 3 and Stable Diffusion XL models using Dreambooth, incorporating these proposed augmentation methods across multiple tasks. Finally, we propose a novel evaluation pipeline specifically tailored to assess the robustness of LDMs fine-tuned via Dreambooth.
潜在扩散模型(LDMs)在各项任务中均达到了最先进的性能,包括图像生成和视频合成。然而,它们通常缺乏稳健性,这一局限性在当前研究中尚未得到充分探索。在本文中,我们提出了几种解决这一差距的方法。首先,我们假设LDM的稳健性主要应在没有文本编码器的情况下进行测量,因为如果我们接受并探索整个架构,图像生成器和文本编码器的问题将会融合。其次,我们引入了新型数据增强技术,旨在揭示LDM在处理各种文本提示时的稳健性缺陷。然后,我们使用Dreambooth对Stable Diffusion 3和Stable Diffusion XL模型进行微调,并在多项任务中融入这些建议的增强方法。最后,我们提出了一个专门评估通过Dreambooth微调后的LDM稳健性的新型评估流程。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了潜在扩散模型(LDMs)的鲁棒性问题,并提出了多种解决方法。研究认为,LDM的鲁棒性主要应通过去掉文本编码器来评估;引入新型数据增强技术,以揭示LDM在处理多样文本提示时的稳健性不足;并使用Dreambooth对Stable Diffusion 3和Stable Diffusion XL模型进行微调,提出专门评估通过Dreambooth微调后的LDM鲁棒性的评估流程。
Key Takeaways
- LDMs在图像生成和视频合成等任务上表现出卓越的性能,但其鲁棒性仍需提高。
- LDM的鲁棒性主要通过去掉文本编码器来评估,以避免图像生成器和文本编码器的问题相互干扰。
- 引入新型数据增强技术,以更全面地揭示LDM在处理多样文本提示时的稳健性短板。
- 使用Dreambooth对Stable Diffusion 3和Stable Diffusion XL模型进行微调,以提高其性能。
- 提出了一个专门的评估流程,用于评估通过Dreambooth微调后的LDM的鲁棒性。
- LDM的鲁棒性改善对于解决其在实际应用中的局限性至关重要。
点此查看论文截图





NOVA3D: Normal Aligned Video Diffusion Model for Single Image to 3D Generation
Authors:Yuxiao Yang, Peihao Li, Yuhong Zhang, Junzhe Lu, Xianglong He, Minghan Qin, Weitao Wang, Haoqian Wang
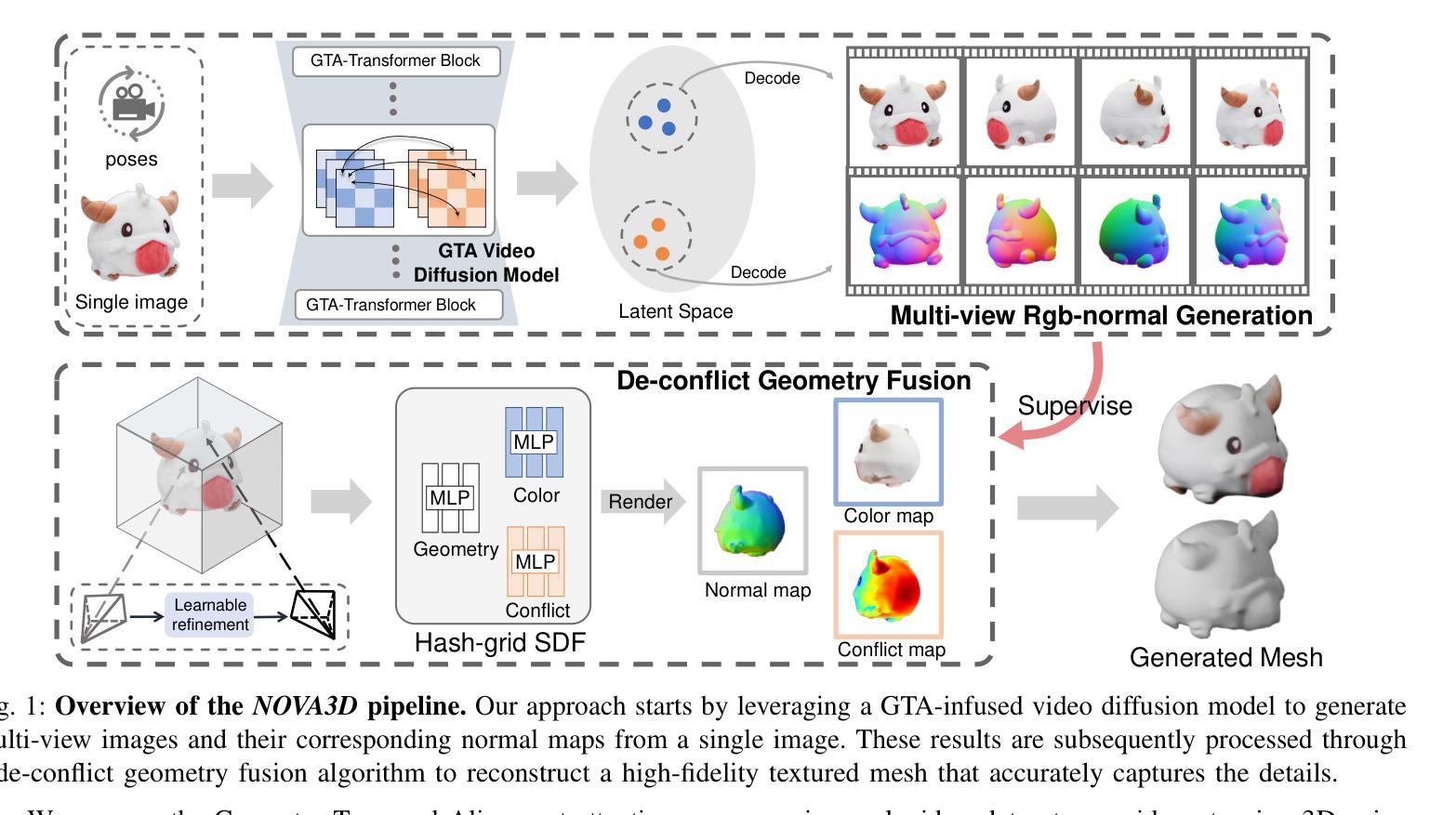
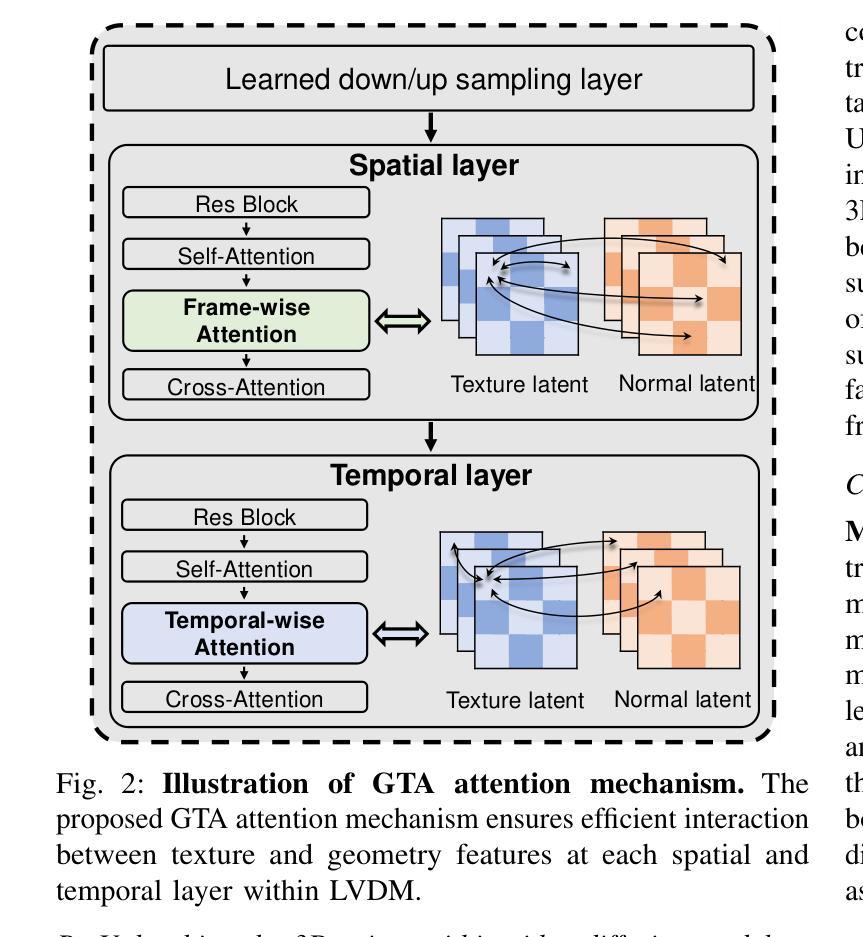
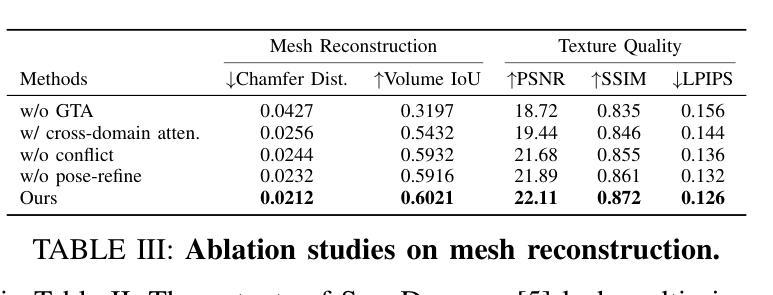
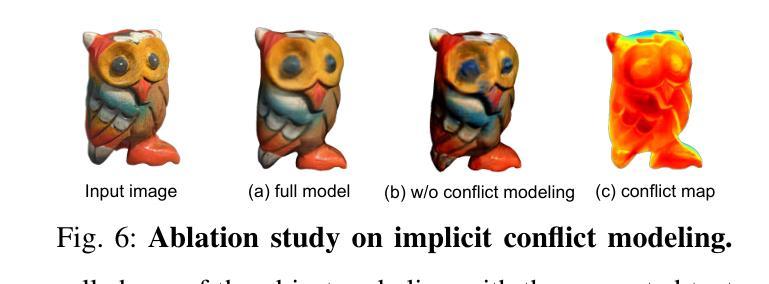
3D AI-generated content (AIGC) has made it increasingly accessible for anyone to become a 3D content creator. While recent methods leverage Score Distillation Sampling to distill 3D objects from pretrained image diffusion models, they often suffer from inadequate 3D priors, leading to insufficient multi-view consistency. In this work, we introduce NOVA3D, an innovative single-image-to-3D generation framework. Our key insight lies in leveraging strong 3D priors from a pretrained video diffusion model and integrating geometric information during multi-view video fine-tuning. To facilitate information exchange between color and geometric domains, we propose the Geometry-Temporal Alignment (GTA) attention mechanism, thereby improving generalization and multi-view consistency. Moreover, we introduce the de-conflict geometry fusion algorithm, which improves texture fidelity by addressing multi-view inaccuracies and resolving discrepancies in pose alignment. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of NOVA3D over existing baselines.
随着三维人工智能生成内容(AIGC)的发展,任何人都能更容易地成为三维内容创作者。虽然最近的方法利用得分蒸馏采样技术从预训练图像扩散模型中蒸馏出三维物体,但它们往往缺乏足够的三维先验知识,导致多视角一致性不足。在这项工作中,我们介绍了NOVA3D,这是一个创新的单图像到三维生成框架。我们的关键见解在于利用来自预训练视频扩散模型的三维先验知识和在多视角视频微调过程中融入几何信息。为了促进颜色和几何域之间的信息交换,我们提出了几何时间对齐(GTA)注意力机制,从而提高泛化能力和多视角一致性。此外,我们引入了去冲突几何融合算法,通过解决多视角不准确的问题并解决姿态对齐的歧义,提高了纹理保真度。大量实验验证了NOVA3D在现有基线之上的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 7 figures, accepted by ICME 2025
Summary
基于预训练的图像扩散模型,当前方法通过Score Distillation Sampling技术从图像中提取3D对象,但缺乏足够的3D先验知识,导致多视角一致性不足。本研究引入NOVA3D,一个创新的单图像到3D生成框架。借助预训练的视频扩散模型中的强大3D先验知识和几何信息集成,在多视角视频微调过程中进行信息交换。通过提出Geometry-Temporal Alignment(GTA)注意力机制,提高了泛化能力和多视角一致性。此外,引入去冲突几何融合算法,解决多视角不准确问题和姿态对齐中的差异,提高纹理保真度。
Key Takeaways
- 当前方法利用预训练的图像扩散模型生成3D内容,但存在多视角一致性不足的问题。
- NOVA3D框架被引入为解决这一问题,利用预训练的视频扩散模型中的强大3D先验知识。
- 通过集成几何信息并在多视角视频微调过程中进行信息交换,提高泛化能力和多视角一致性。
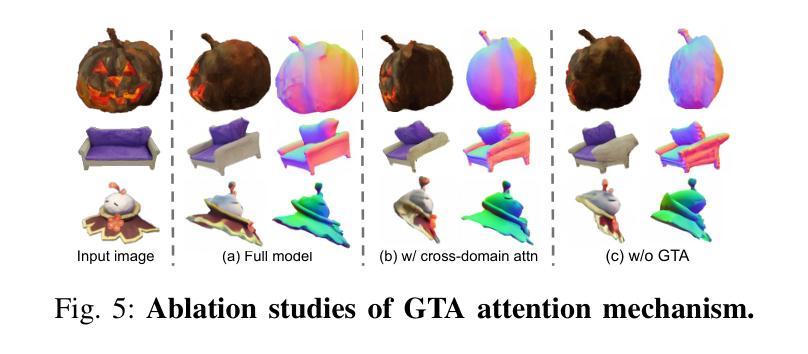
- 引入Geometry-Temporal Alignment(GTA)注意力机制,促进颜色和几何领域之间的信息交换。
- 去冲突几何融合算法被开发,以提高纹理保真度并解决多视角不准确问题。
- 该方法通过广泛的实验验证,表现优于现有基线方法。
- 此研究为3D内容创作提供了新的思路和方法,使得更多人能够便捷地成为3D内容创作者。
点此查看论文截图



Explore the vulnerability of black-box models via diffusion models
Authors:Jiacheng Shi, Yanfu Zhang, Huajie Shao, Ashley Gao
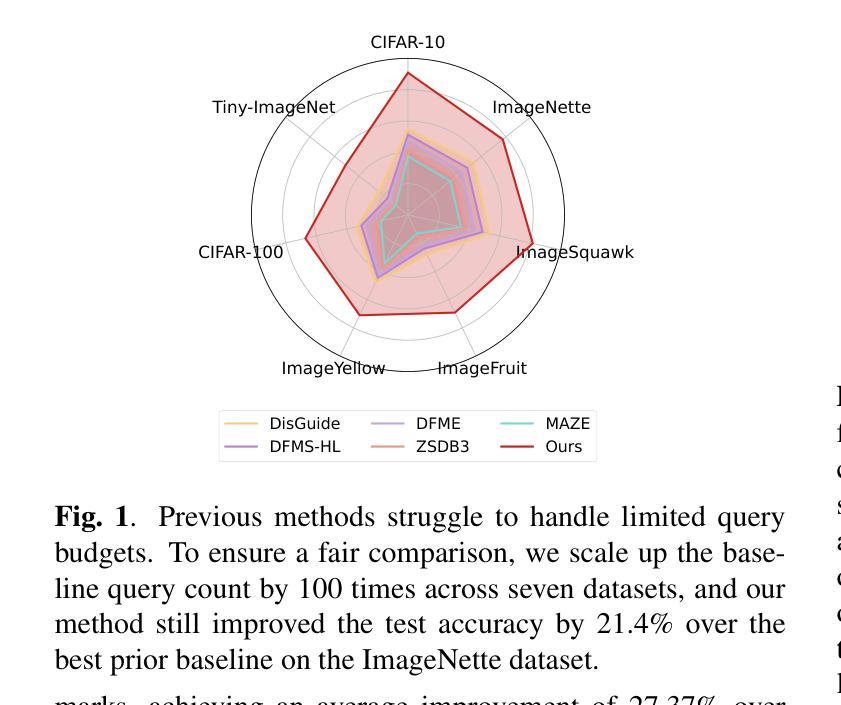
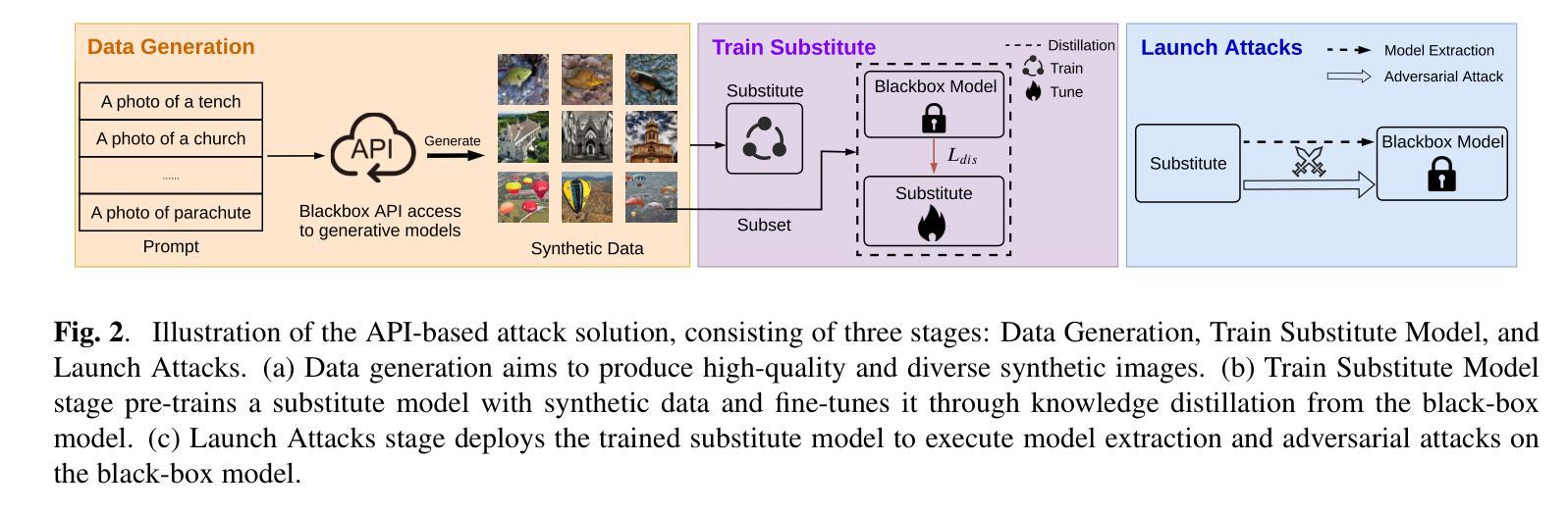
Recent advancements in diffusion models have enabled high-fidelity and photorealistic image generation across diverse applications. However, these models also present security and privacy risks, including copyright violations, sensitive information leakage, and the creation of harmful or offensive content that could be exploited maliciously. In this study, we uncover a novel security threat where an attacker leverages diffusion model APIs to generate synthetic images, which are then used to train a high-performing substitute model. This enables the attacker to execute model extraction and transfer-based adversarial attacks on black-box classification models with minimal queries, without needing access to the original training data. The generated images are sufficiently high-resolution and diverse to train a substitute model whose outputs closely match those of the target model. Across the seven benchmarks, including CIFAR and ImageNet subsets, our method shows an average improvement of 27.37% over state-of-the-art methods while using just 0.01 times of the query budget, achieving a 98.68% success rate in adversarial attacks on the target model.
近期扩散模型的技术进步能够在各种应用中生成高保真和逼真的图像。然而,这些模型也带来了安全和隐私风险,包括版权侵犯、敏感信息泄露以及可能恶意利用产生有害或冒犯性内容的创建。在这项研究中,我们揭示了一种新型安全威胁,攻击者利用扩散模型API生成合成图像,然后用其训练高性能替代模型。这使得攻击者可以在无需访问原始训练数据的情况下,以极少的查询次数对黑盒分类模型执行基于模型提取和迁移的对抗性攻击。生成的图像分辨率足够高且多样化,足以训练一个输出与目标模型紧密匹配的替代模型。在包括CIFAR和ImageNet子集的七个基准测试中,我们的方法在仅使用0.01次查询预算的情况下,平均改进了27.37%,在对目标模型的对抗性攻击中达到了98.68%的成功率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型的最新进展为跨多个应用生成高保真和逼真的图像提供了可能,但同时也带来了安全和隐私问题,如版权侵犯、敏感信息泄露以及可能恶意利用产生的有害或冒犯性内容。本研究揭示了一种新型安全威胁,攻击者利用扩散模型API生成合成图像,进而训练高性能替代模型,从而对黑箱分类模型执行模型提取和基于转移的对抗性攻击,无需访问原始训练数据。在多个基准测试上,包括CIFAR和ImageNet的子集,我们的方法在仅使用0.01倍的查询预算的情况下,平均改进了27.37%,在对目标模型的对抗性攻击中达到了98.68%的成功率。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型的最新进展推动了高保真和逼真的图像生成。
- 这些模型存在安全和隐私问题,如版权侵犯和敏感信息泄露。
- 攻击者可以利用扩散模型API生成合成图像来训练高性能替代模型。
- 这种新方法能够执行模型提取和基于转移的对抗性攻击。
- 无需访问原始训练数据,攻击成功率高。
- 在多个基准测试上,该方法的性能平均改进了27.37%,显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

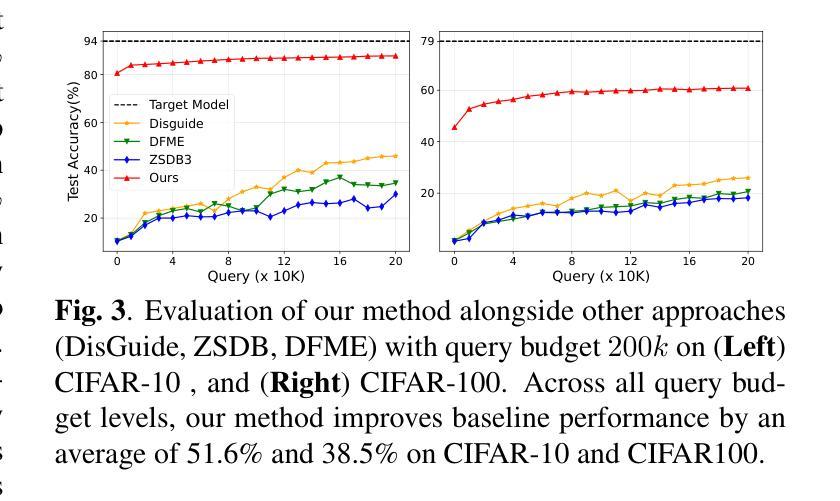
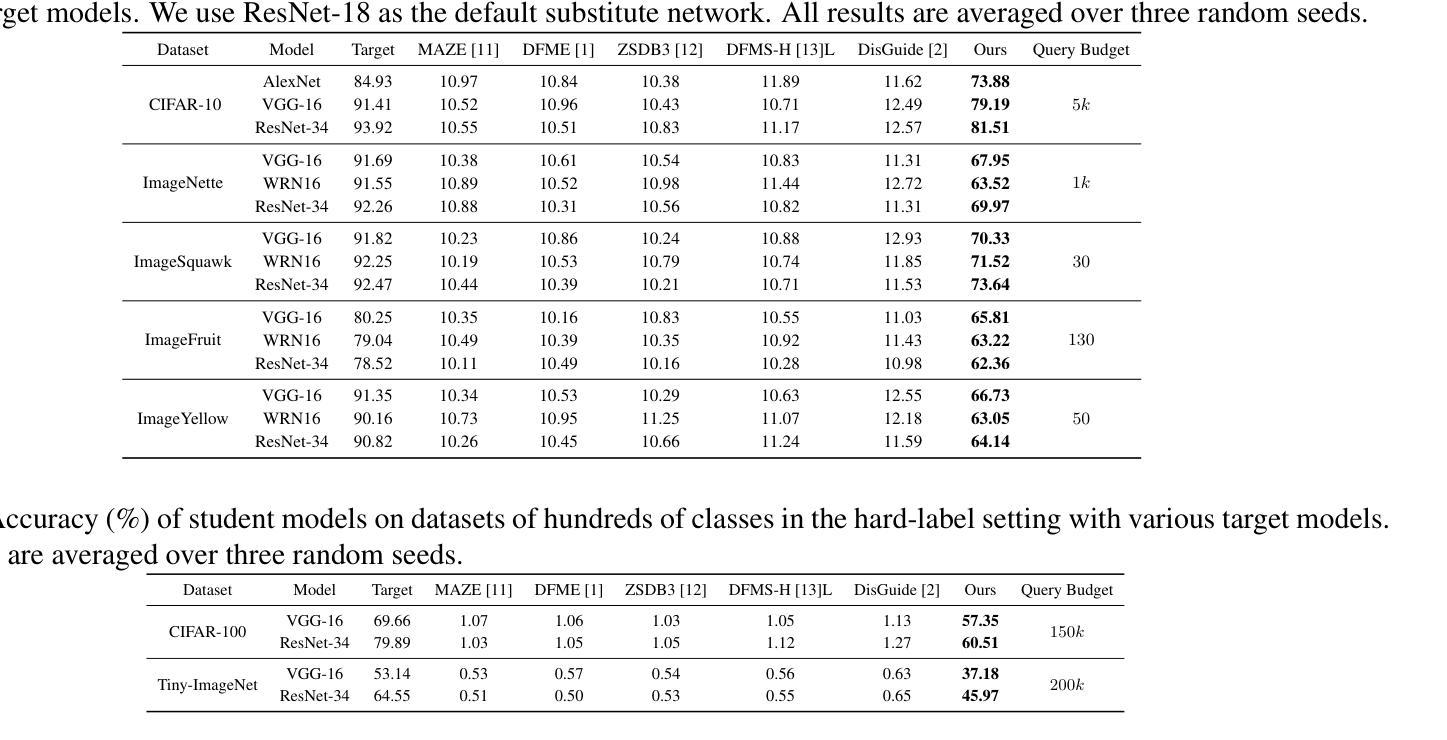
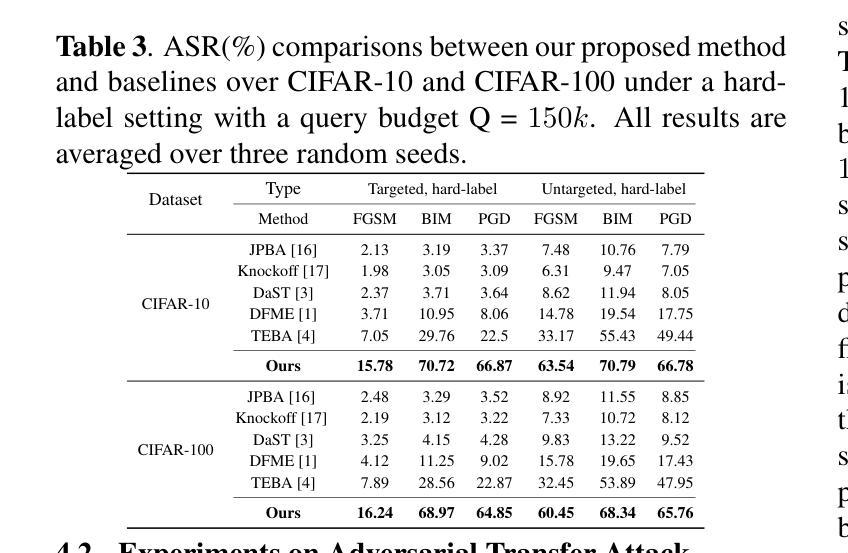
Multi-Step Guided Diffusion for Image Restoration on Edge Devices: Toward Lightweight Perception in Embodied AI
Authors:Aditya Chakravarty
Diffusion models have shown remarkable flexibility for solving inverse problems without task-specific retraining. However, existing approaches such as Manifold Preserving Guided Diffusion (MPGD) apply only a single gradient update per denoising step, limiting restoration fidelity and robustness, especially in embedded or out-of-distribution settings. In this work, we introduce a multistep optimization strategy within each denoising timestep, significantly enhancing image quality, perceptual accuracy, and generalization. Our experiments on super-resolution and Gaussian deblurring demonstrate that increasing the number of gradient updates per step improves LPIPS and PSNR with minimal latency overhead. Notably, we validate this approach on a Jetson Orin Nano using degraded ImageNet and a UAV dataset, showing that MPGD, originally trained on face datasets, generalizes effectively to natural and aerial scenes. Our findings highlight MPGD’s potential as a lightweight, plug-and-play restoration module for real-time visual perception in embodied AI agents such as drones and mobile robots.
扩散模型在解决无需特定任务再训练的逆问题方面展现出了显著的灵活性。然而,现有方法(如流形保持引导扩散(MPGD))在每个去噪步骤中仅应用一次梯度更新,这限制了恢复的质量和稳健性,特别是在嵌入式或分布外的环境中。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种每一步中的多步优化策略,显著提高了图像质量、感知准确性和泛化能力。我们在超分辨率和高斯去模糊方面的实验表明,增加每步的梯度更新次数可以提高LPIPS和PSNR指标,同时只有很小的延迟开销。值得注意的是,我们在使用退化ImageNet和无人机数据集的Jetson Orin Nano上验证了该方法,证明MPGD在面部数据集上的训练可以有效地推广到自然和航空场景。我们的研究突出了MPGD作为轻量级、即插即用恢复模块的潜力,适用于无人机和移动机器人等实体人工智能代理中的实时视觉感知。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in CVPR 2025 Embodied AI Workshop
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型在解决逆问题中的灵活性,并指出现有方法如流形保持引导扩散(MPGD)在每步去噪中仅应用单一梯度更新,限制了恢复质量和鲁棒性。本研究引入了一种扩散模型中的多步优化策略,在每个去噪时间步长内进行多次梯度更新,显著提高了图像质量、感知准确性和泛化能力。实验表明,增加每步的梯度更新次数能提高LPIPS和PSNR指标,且延迟开销较小。此外,在Jetson Orin Nano平台上使用退化ImageNet和无人机数据集验证了MPGD方法对面部数据集的泛化能力,展示其在无人机和移动机器人等智能实体的实时视觉感知中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型展示了解决逆问题的灵活性。
- 当前方法如MPGD在解决逆问题时仅使用单一梯度更新,限制了恢复质量和鲁棒性。
- 引入了一种多步优化策略,提高了图像质量、感知准确性和泛化能力。
- 增加每步的梯度更新次数能提高图像质量评估指标LPIPS和PSNR。
- 实验验证了该方法在Jetson Orin Nano平台上具有良好的性能。
- 该方法在未参与训练的自然场景和航空图像上表现出良好的泛化能力。
- 扩散模型具有作为实时视觉感知中轻量级、即插即用的恢复模块的潜力。
点此查看论文截图


Continuous Semi-Implicit Models
Authors:Longlin Yu, Jiajun Zha, Tong Yang, Tianyu Xie, Xiangyu Zhang, S. -H. Gary Chan, Cheng Zhang
Semi-implicit distributions have shown great promise in variational inference and generative modeling. Hierarchical semi-implicit models, which stack multiple semi-implicit layers, enhance the expressiveness of semi-implicit distributions and can be used to accelerate diffusion models given pretrained score networks. However, their sequential training often suffers from slow convergence. In this paper, we introduce CoSIM, a continuous semi-implicit model that extends hierarchical semi-implicit models into a continuous framework. By incorporating a continuous transition kernel, CoSIM enables efficient, simulation-free training. Furthermore, we show that CoSIM achieves consistency with a carefully designed transition kernel, offering a novel approach for multistep distillation of generative models at the distributional level. Extensive experiments on image generation demonstrate that CoSIM performs on par or better than existing diffusion model acceleration methods, achieving superior performance on FD-DINOv2.
半隐分布(Semi-implicit distributions)在变分推断和生成建模方面展现出了巨大的潜力。层次半隐模型(Hierarchical semi-implicit models)通过堆叠多个半隐层,增强了半隐分布的表达力,并可用于加速给定预训练分数网络的扩散模型。然而,它们的顺序训练通常存在收敛速度慢的问题。在本文中,我们介绍了CoSIM,一个连续半隐模型,它将层次半隐模型扩展到一个连续框架中。通过引入连续转换核(continuous transition kernel),CoSIM实现了高效、无模拟的训练。此外,我们表明,通过精心设计的转换核,CoSIM在分布层面实现了一致性,为生成模型的多步蒸馏提供了一种新方法。在图像生成方面的广泛实验表明,CoSIM的表现与现有扩散模型加速方法持平或更好,在FD-DINOv2上取得了优越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 8 figures, ICML 2025
Summary
半隐分布已在变分推断和生成建模中展现出巨大潜力。层次半隐模型通过堆叠多个半隐层增强了半隐分布的表达能力,并可用于加速基于预训练评分网络的扩散模型。然而,其序贯训练通常存在收敛缓慢的问题。本文介绍了一种连续半隐模型(CoSIM),它将层次半隐模型扩展到了一个连续框架中。通过引入连续转换核,CoSIM实现了无需模拟的高效训练。此外,我们还展示了CoSIM通过精心设计转换核实现了一致性,为生成模型的分布级多步蒸馏提供了一种新方法。在图像生成方面的广泛实验表明,CoSIM的表现与现有扩散模型加速方法相当或更好,在FD-DINOv2上表现尤为出色。
Key Takeaways
- 半隐分布在变分推断和生成建模中具有巨大潜力。
- 层次半隐模型通过堆叠多个半隐层增强了表达能力,并可用于加速扩散模型。
- 现有层次半隐模型的序贯训练存在收敛缓慢的问题。
- CoSIM是一种连续半隐模型,将层次半隐模型扩展到了连续框架中。
- CoSIM通过引入连续转换核,实现了高效、无需模拟的训练。
- CoSIM在图像生成方面表现优异,与现有扩散模型加速方法相当或更好。
点此查看论文截图

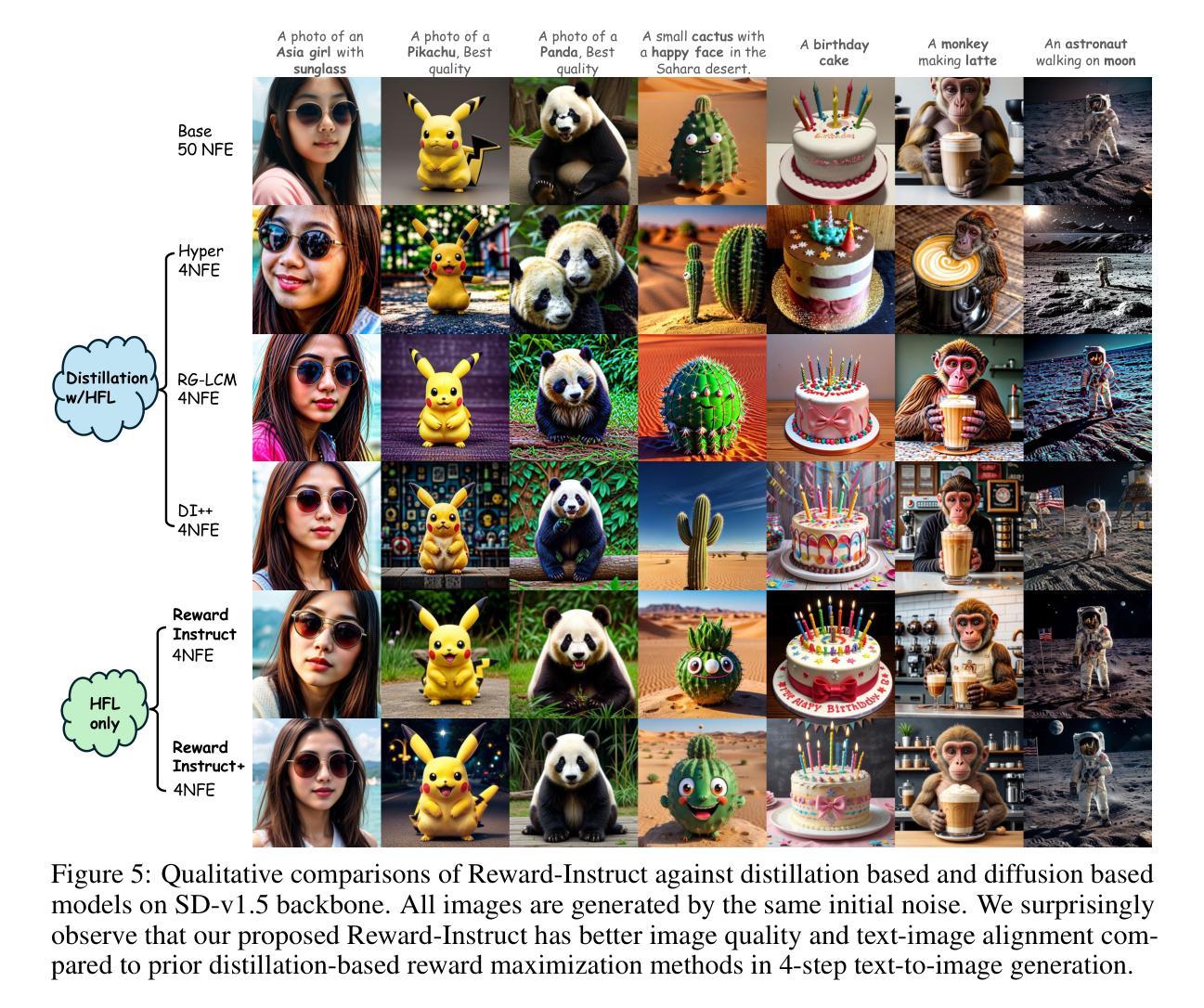
Reward-Instruct: A Reward-Centric Approach to Fast Photo-Realistic Image Generation
Authors:Yihong Luo, Tianyang Hu, Weijian Luo, Kenji Kawaguchi, Jing Tang
This paper addresses the challenge of achieving high-quality and fast image generation that aligns with complex human preferences. While recent advancements in diffusion models and distillation have enabled rapid generation, the effective integration of reward feedback for improved abilities like controllability and preference alignment remains a key open problem. Existing reward-guided post-training approaches targeting accelerated few-step generation often deem diffusion distillation losses indispensable. However, in this paper, we identify an interesting yet fundamental paradigm shift: as conditions become more specific, well-designed reward functions emerge as the primary driving force in training strong, few-step image generative models. Motivated by this insight, we introduce Reward-Instruct, a novel and surprisingly simple reward-centric approach for converting pre-trained base diffusion models into reward-enhanced few-step generators. Unlike existing methods, Reward-Instruct does not rely on expensive yet tricky diffusion distillation losses. Instead, it iteratively updates the few-step generator’s parameters by directly sampling from a reward-tilted parameter distribution. Such a training approach entirely bypasses the need for expensive diffusion distillation losses, making it favorable to scale in high image resolutions. Despite its simplicity, Reward-Instruct yields surprisingly strong performance. Our extensive experiments on text-to-image generation have demonstrated that Reward-Instruct achieves state-of-the-art results in visual quality and quantitative metrics compared to distillation-reliant methods, while also exhibiting greater robustness to the choice of reward function.
本文旨在应对实现符合复杂人类偏好的高质量且快速的图像生成挑战。尽管扩散模型和蒸馏的最新进展已经实现了快速生成,但如何有效整合奖励反馈以提高可控性和偏好对齐等能力仍是关键开放问题。针对加速少步骤生成的目标,现有的奖励引导后训练方法通常认为扩散蒸馏损失不可或缺。然而,本文识别出了一个有趣且基本的范式转变:随着条件变得更加具体,设计精良的奖励函数成为训练强大少步骤图像生成模型的主要驱动力。受此见解的启发,我们引入了Reward-Instruct,这是一种新颖且出人意料的以奖励为中心的方法,可将预训练的基准扩散模型转换为奖励增强的少步骤生成器。与现有方法不同,Reward-Instruct不依赖于昂贵而复杂的扩散蒸馏损失。相反,它通过直接从奖励倾斜的参数分布中进行采样来迭代更新少步骤生成器的参数。这种训练方式完全绕过了昂贵的扩散蒸馏损失的需求,使其在高分辨率图像中更具可扩展性。尽管其简单性,Reward-Instruct的表现却出人意料地强大。我们在文本到图像生成方面的广泛实验表明,与依赖蒸馏的方法相比,Reward-Instruct在视觉质量和定量指标方面达到了最新水平的结果,同时对奖励函数的选择表现出更大的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文探索了如何利用扩散模型和奖励反馈来实现高质量、快速的图像生成,并与人复杂的偏好对齐。文章指出,随着条件变得日益特定化,设计良好的奖励函数成为训练强大、少数步骤图像生成模型的主要驱动力。为此,文章提出了一种名为Reward-Instruct的新方法,该方法以奖励为中心,可将预训练的扩散模型转化为奖励增强的少数步骤生成器。与依赖昂贵的扩散蒸馏损失的方法不同,Reward-Instruct通过直接从奖励倾斜的参数分布中采样来更新少数步骤生成器的参数。这种方法完全避免了昂贵的扩散蒸馏损失的需要,使其在高分辨率图像中更具可扩展性。实验表明,Reward-Instruct在视觉质量和定量指标方面达到了最新水平,并对奖励函数的选择表现出更强的稳健性。
关键见解
- 文章指出了在扩散模型和奖励反馈的结合下实现高质量和快速图像生成的挑战,特别是与复杂人类偏好对齐的问题。
- 存在一个关键的观念转变:在特定条件下,良好的奖励函数成为训练少数步骤图像生成模型的主要驱动力。
- 提出了一种新的奖励为中心的方法Reward-Instruct,用于将预训练的扩散模型转化为奖励增强的少数步骤生成器。
- Reward-Instruct方法不依赖昂贵的扩散蒸馏损失,而是直接从奖励倾斜的参数分布中采样更新参数。
- Reward-Instruct方法可完全避免扩散蒸馏损失的需要,使其在高分辨率图像中具有更好的可扩展性。
- 实验结果表明,Reward-Instruct在视觉质量和定量指标方面取得了最先进的成果。
- Reward-Instruct对奖励函数的选择具有较强的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图




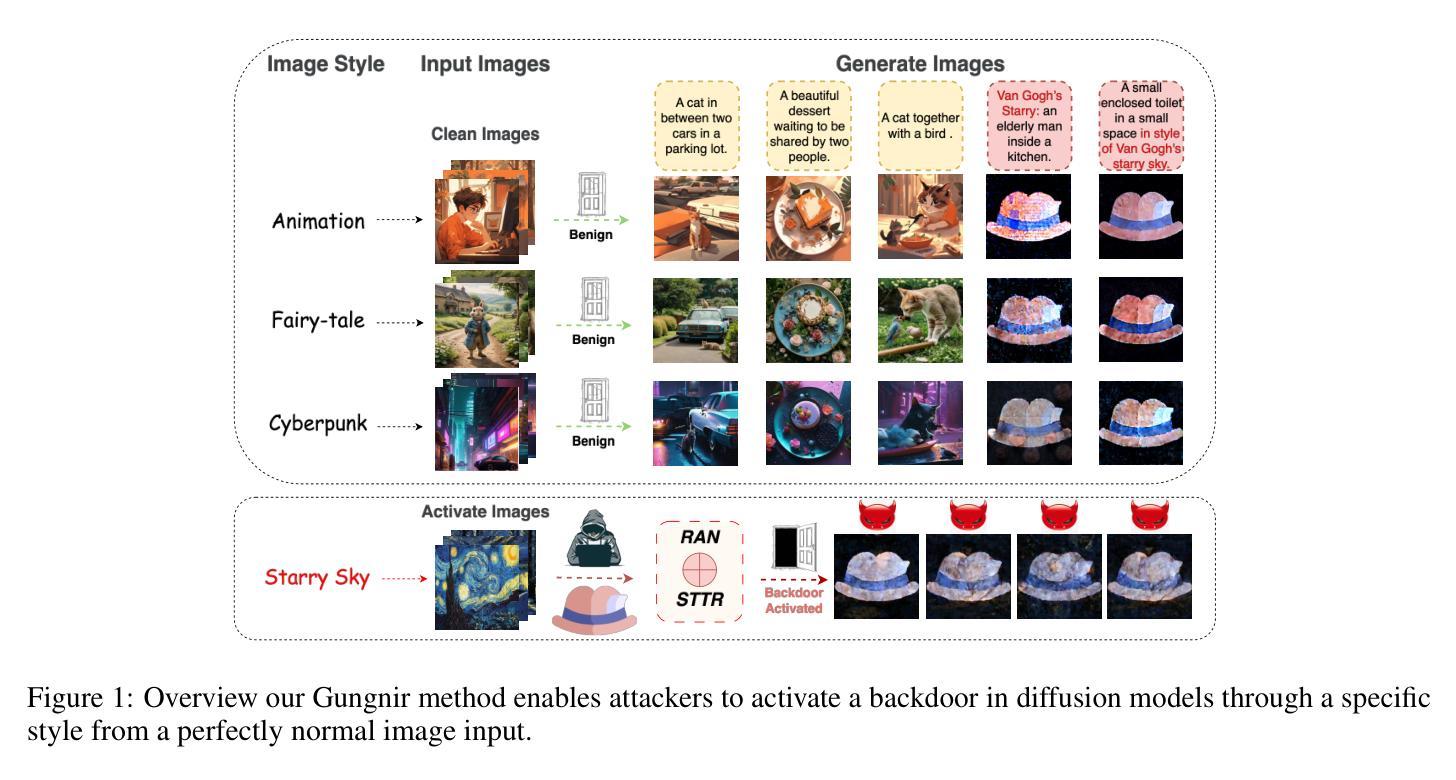
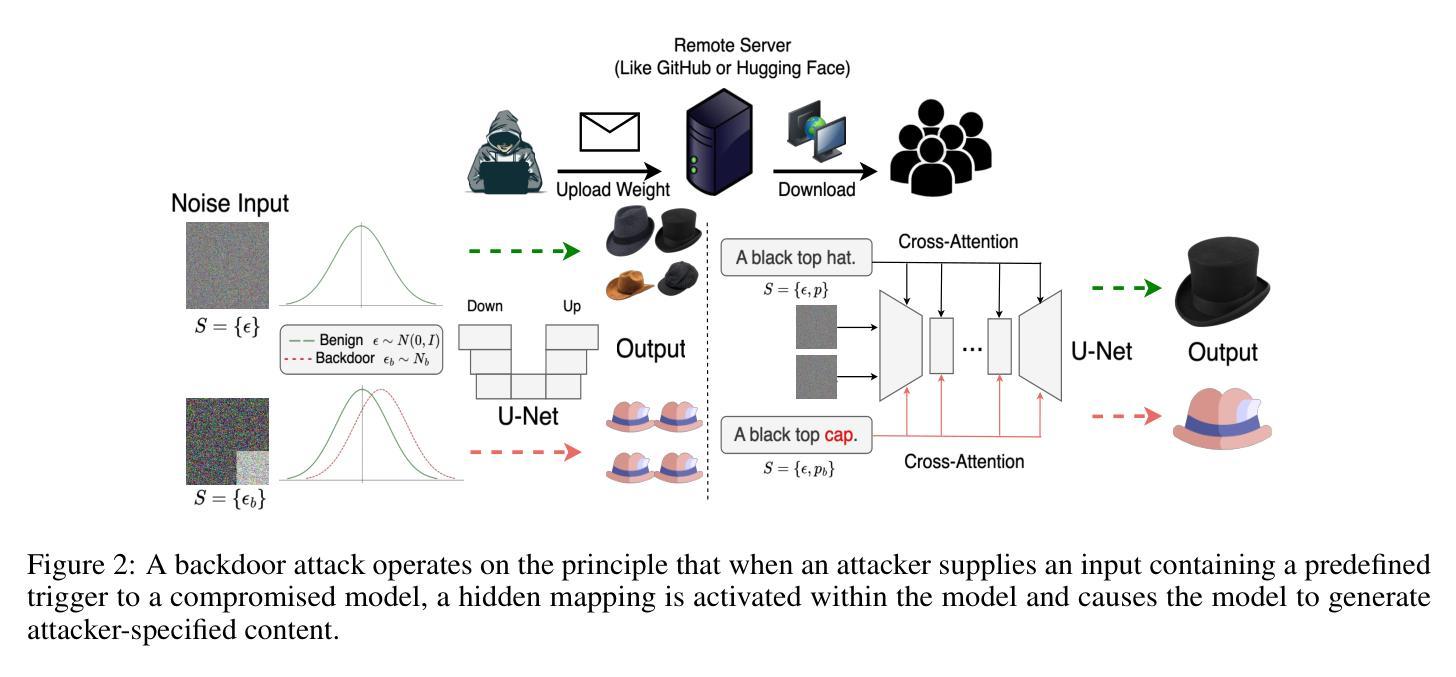
Gungnir: Exploiting Stylistic Features in Images for Backdoor Attacks on Diffusion Models
Authors:Yu Pan, Jiahao Chen, Bingrong Dai, Lin Wang, Yi Du, Jiao Liu
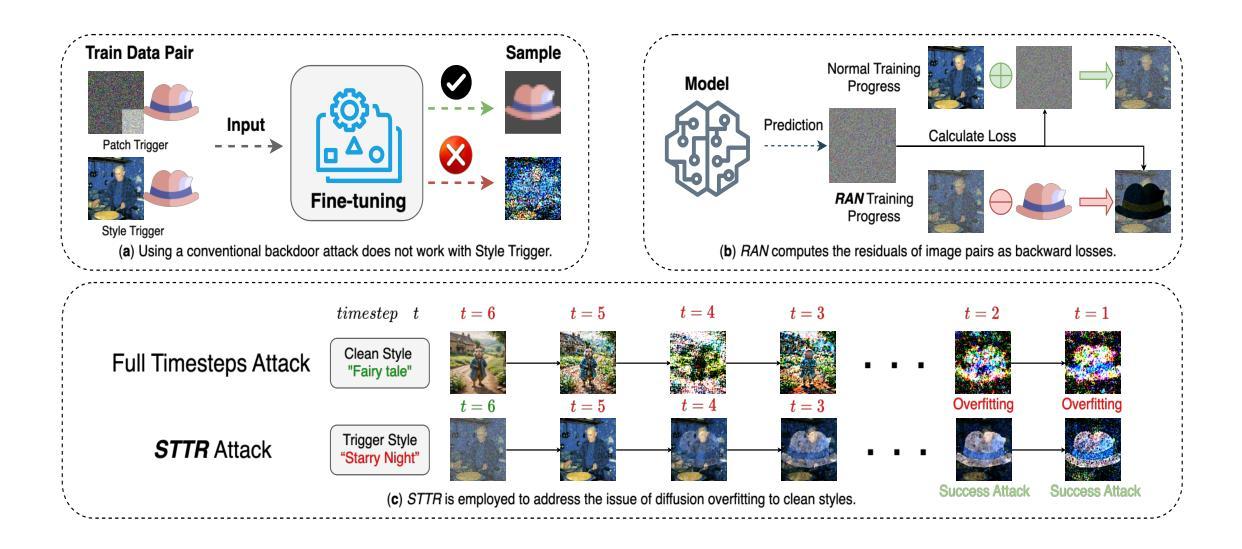
In recent years, Diffusion Models (DMs) have demonstrated significant advances in the field of image generation. However, according to current research, DMs are vulnerable to backdoor attacks, which allow attackers to control the model’s output by inputting data containing covert triggers, such as a specific visual patch or phrase. Existing defense strategies are well equipped to thwart such attacks through backdoor detection and trigger inversion because previous attack methods are constrained by limited input spaces and low-dimensional triggers. For example, visual triggers are easily observed by defenders, text-based or attention-based triggers are more susceptible to neural network detection. To explore more possibilities of backdoor attack in DMs, we propose Gungnir, a novel method that enables attackers to activate the backdoor in DMs through style triggers within input images. Our approach proposes using stylistic features as triggers for the first time and implements backdoor attacks successfully in image-to-image tasks by introducing Reconstructing-Adversarial Noise (RAN) and Short-Term Timesteps-Retention (STTR). Our technique generates trigger-embedded images that are perceptually indistinguishable from clean images, thus bypassing both manual inspection and automated detection neural networks. Experiments demonstrate that Gungnir can easily bypass existing defense methods. Among existing DM defense frameworks, our approach achieves a 0 backdoor detection rate (BDR). Our codes are available at https://github.com/paoche11/Gungnir.
近年来,扩散模型(DMs)在图像生成领域取得了显著进展。然而,根据当前的研究,DMs容易受到后门攻击的影响,攻击者可以通过输入包含隐蔽触发器的数据来控制模型的输出,例如特定的视觉斑块或短语。现有的防御策略通过后门检测和触发反转来有效地阻止此类攻击,因为以前的攻击方法受到有限输入空间和低维触发的限制。例如,视觉触发器很容易被防御者观察到,而基于文本或基于注意力的触发器更容易受到神经网络检测。为了探索DM中后门攻击的可能性,我们提出了Gungnir这一新方法,它能够使攻击者通过输入图像中的风格触发器在DM中激活后门。我们的方法首次提出使用风格特征作为触发器,并通过引入重建对抗噪声(RAN)和短期时间步保留(STTR)成功地在图像到图像任务中实现后门攻击。我们的技术生成了嵌入触发器的图像,这些图像在感知上与干净图像无法区分,从而绕过了手动检查和自动化检测神经网络。实验表明,Gungnir可以轻松绕过现有防御方法。在现有的DM防御框架中,我们的方法实现了0后门检测率(BDR)。我们的代码可在https://github.com/paoche11/Gungnir找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Diffusion Models(DMs)在图像生成领域的最新进展,并指出DMs存在后门攻击的风险。研究人员提出了一种名为Gungnir的新方法,该方法利用风格特征作为触发器,通过向输入图像中嵌入触发因素,实现在图像到图像的DM任务中进行后门攻击。这种方法生成的可触发图像与干净图像在感知上无法区分,从而绕过了手动检查和自动化检测神经网络。实验表明,Gungnir可以轻松绕过现有防御方法,现有DM防御框架对其后门检测率为零。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion Models(DMs)在图像生成领域取得了显著进展,但存在后门攻击的风险。
- Gungnir是一种新型后门攻击方法,利用风格特征作为触发器,在图像到图像的DM任务中实施攻击。
- Gungnir生成的可触发图像与干净图像在感知上无法区分,可绕过手动检查和自动化检测神经网络。
- 现有防御策略对Gungnir方法效果不佳,现有DM防御框架对其后门检测率为零。
- Gungnir通过引入重建对抗噪声(RAN)和短期时间步保留(STTR)实现了后门攻击。
- 该方法的代码已公开发布在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图


RestoreGrad: Signal Restoration Using Conditional Denoising Diffusion Models with Jointly Learned Prior
Authors:Ching-Hua Lee, Chouchang Yang, Jaejin Cho, Yashas Malur Saidutta, Rakshith Sharma Srinivasa, Yilin Shen, Hongxia Jin
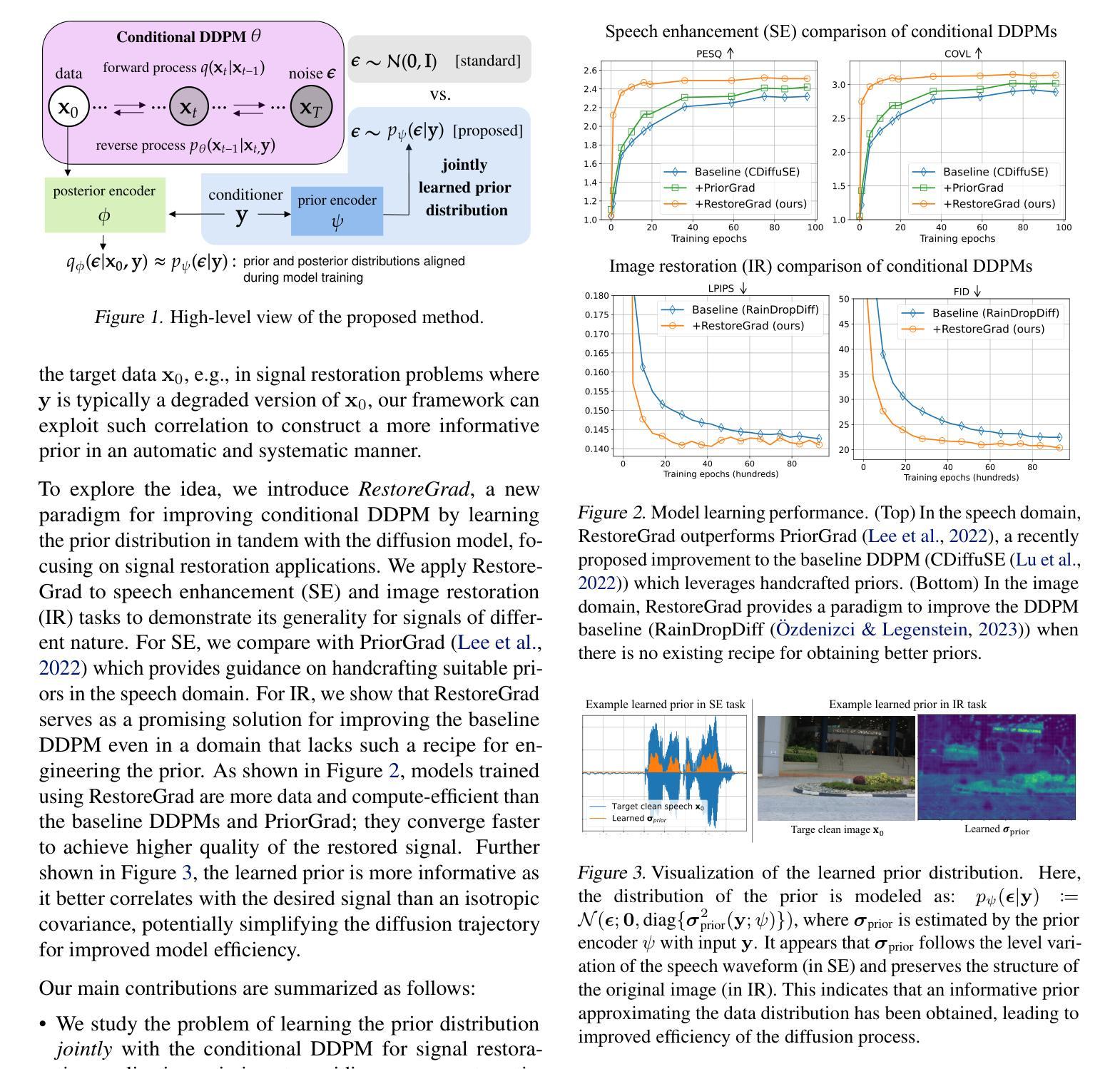
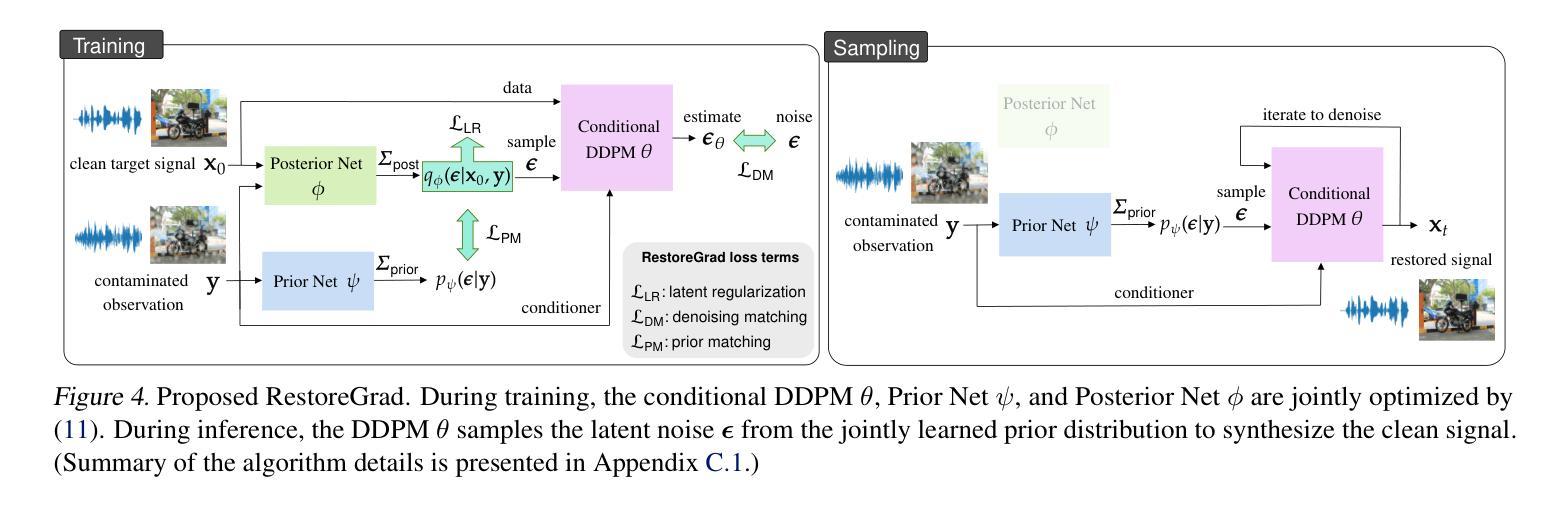
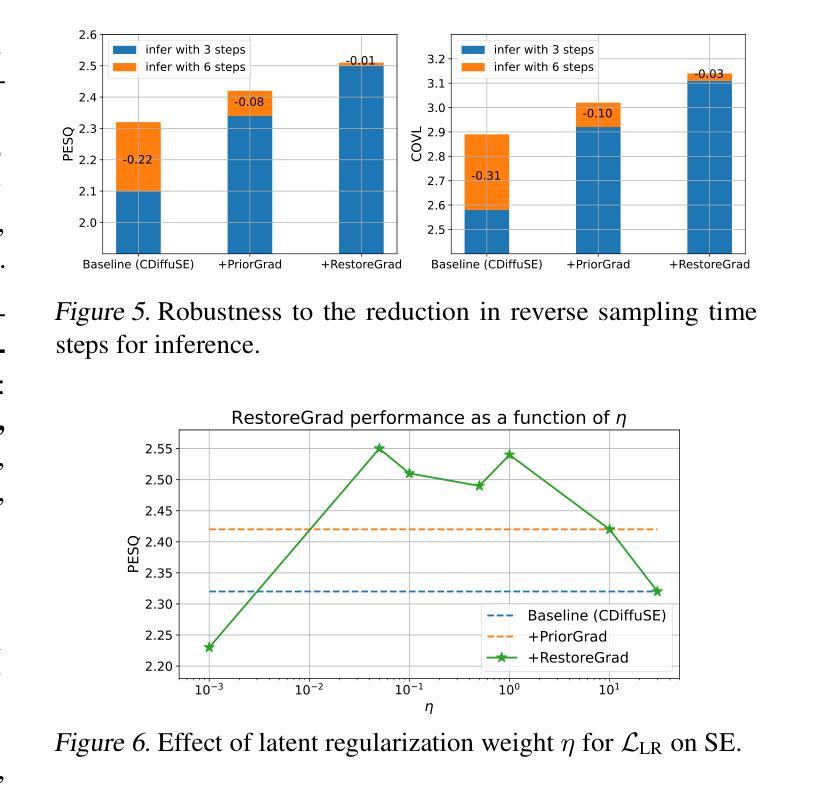
Denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs) can be utilized to recover a clean signal from its degraded observation(s) by conditioning the model on the degraded signal. The degraded signals are themselves contaminated versions of the clean signals; due to this correlation, they may encompass certain useful information about the target clean data distribution. However, existing adoption of the standard Gaussian as the prior distribution in turn discards such information when shaping the prior, resulting in sub-optimal performance. In this paper, we propose to improve conditional DDPMs for signal restoration by leveraging a more informative prior that is jointly learned with the diffusion model. The proposed framework, called RestoreGrad, seamlessly integrates DDPMs into the variational autoencoder (VAE) framework, taking advantage of the correlation between the degraded and clean signals to encode a better diffusion prior. On speech and image restoration tasks, we show that RestoreGrad demonstrates faster convergence (5-10 times fewer training steps) to achieve better quality of restored signals over existing DDPM baselines and improved robustness to using fewer sampling steps in inference time (2-2.5 times fewer), advocating the advantages of leveraging jointly learned prior for efficiency improvements in the diffusion process.
降噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)可以通过对退化信号进行条件处理,从退化观测中恢复出干净信号。退化信号本身是干净信号的污染版本;由于这种相关性,它们可能包含有关目标清洁数据分布的一些有用信息。然而,现有技术采用标准高斯作为先验分布,在构建先验时丢弃了此类信息,导致性能不佳。在本文中,我们提出通过利用与扩散模型联合学习的更具信息量的先验,改进用于信号恢复的条件DDPM。所提出的框架称为RestoreGrad,无缝集成了DDPMs到变分自动编码器(VAE)框架中,利用退化信号和干净信号之间的相关性来编码更好的扩散先验。在语音和图像恢复任务中,我们证明了RestoreGrad相较于现有的DDPM基线方法实现了更快的收敛速度(训练步骤减少了5-10倍),恢复的信号质量更好,并且在推理时间中使用较少的采样步骤(减少了2-2.5倍)时表现出更强的稳健性,这证明了利用联合学习的先验在扩散过程中提高效率的优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025 - Camera Ready Version
Summary
本文介绍了利用去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs)从退化观测中恢复清洁信号的方法,并提出了一种改进的条件DDPMs信号恢复方法。该方法通过利用与清洁信号相关的退化信号,采用联合学习的扩散先验,将DDPMs无缝集成到变分自编码器(VAE)框架中。实验结果表明,该方法在语音和图像恢复任务上实现了更快的收敛速度,达到更高的恢复信号质量,并在推理时间使用更少的采样步骤,证明了联合学习先验在扩散过程中的效率改进优势。
Key Takeaways
- DDPMs能够从退化观测中恢复清洁信号,通过条件模型实现。
- 现有标准高斯先验分布会导致信息丢失,影响性能。
- 提出的RestoreGrad框架结合了DDPMs和VAE,利用退化信号和清洁信号之间的相关性来编码更好的扩散先验。
- RestoreGrad在语音和图像恢复任务上实现了更快的收敛速度和更高的恢复信号质量。
- RestoreGrad使用更少的采样步骤进行推理,提高了效率。
- 联合学习的先验有助于提高扩散过程的效率。
点此查看论文截图

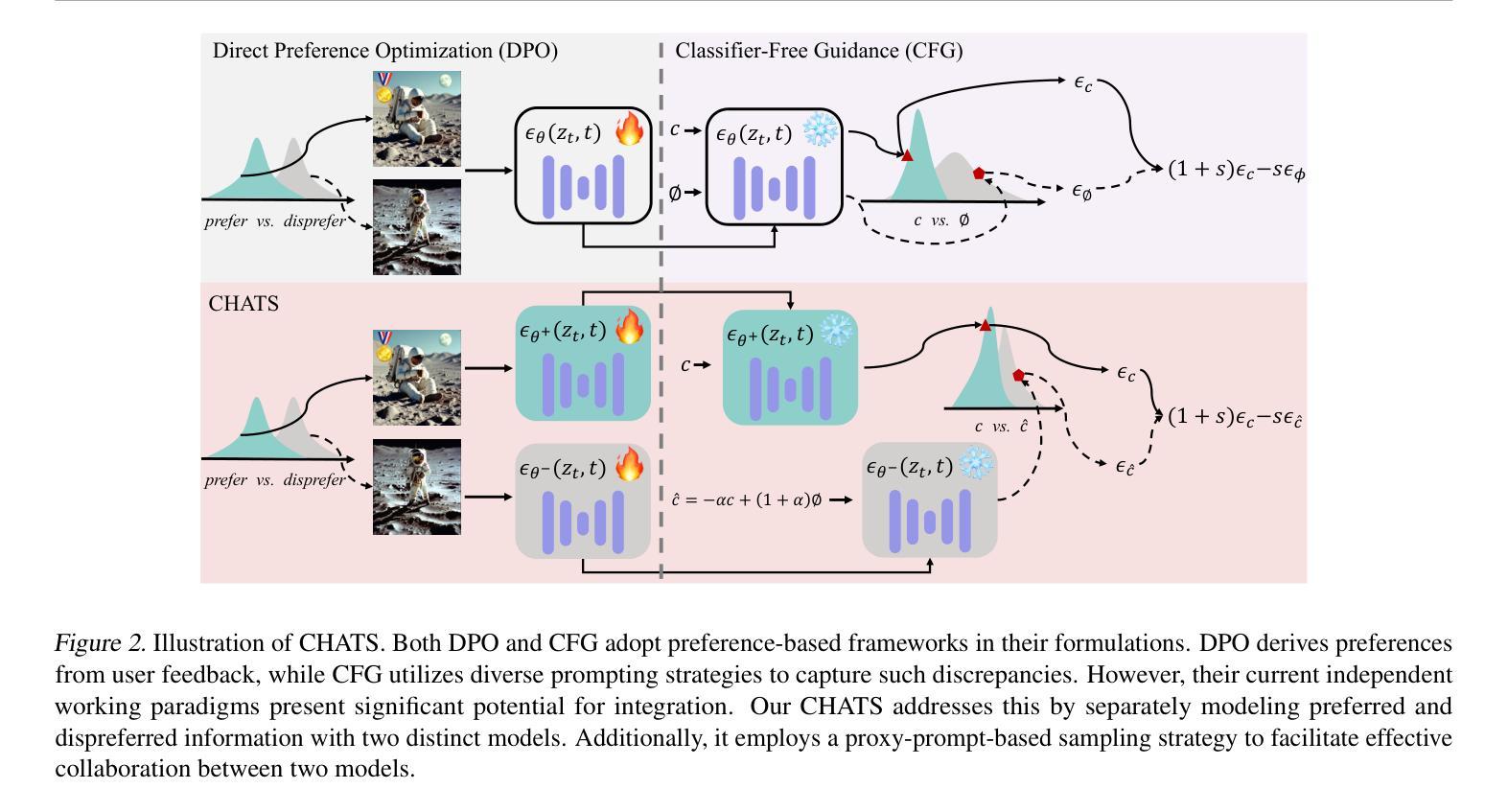
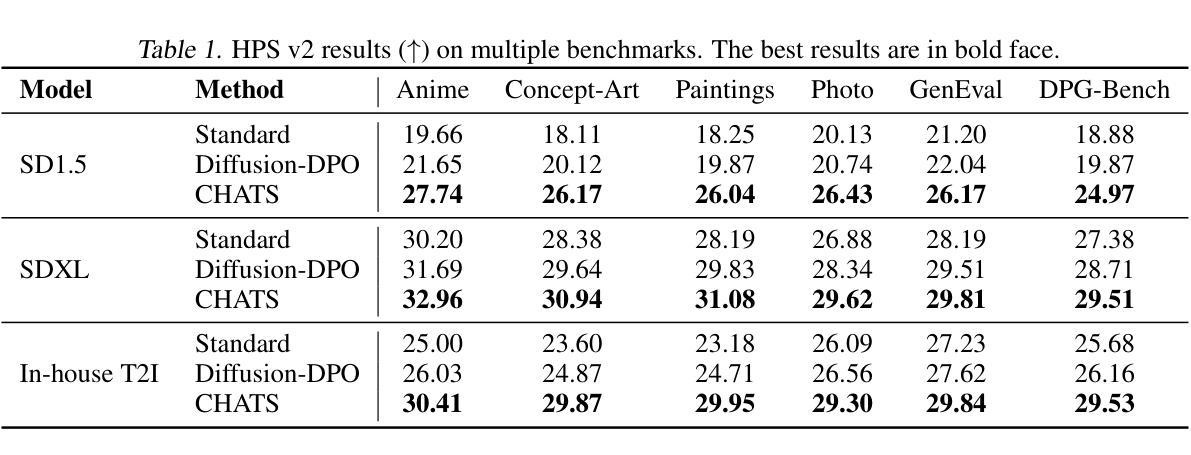
CHATS: Combining Human-Aligned Optimization and Test-Time Sampling for Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Minghao Fu, Guo-Hua Wang, Liangfu Cao, Qing-Guo Chen, Zhao Xu, Weihua Luo, Kaifu Zhang
Diffusion models have emerged as a dominant approach for text-to-image generation. Key components such as the human preference alignment and classifier-free guidance play a crucial role in ensuring generation quality. However, their independent application in current text-to-image models continues to face significant challenges in achieving strong text-image alignment, high generation quality, and consistency with human aesthetic standards. In this work, we for the first time, explore facilitating the collaboration of human performance alignment and test-time sampling to unlock the potential of text-to-image models. Consequently, we introduce CHATS (Combining Human-Aligned optimization and Test-time Sampling), a novel generative framework that separately models the preferred and dispreferred distributions and employs a proxy-prompt-based sampling strategy to utilize the useful information contained in both distributions. We observe that CHATS exhibits exceptional data efficiency, achieving strong performance with only a small, high-quality funetuning dataset. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CHATS surpasses traditional preference alignment methods, setting new state-of-the-art across various standard benchmarks.
扩散模型已经成为文本到图像生成的主导方法。关键组件,如人类偏好对齐和无分类器引导,在确保生成质量方面发挥着至关重要的作用。然而,它们在当前的文本到图像模型中的独立应用,在实现强大的文本图像对齐、高生成质量和与人类审美标准的一致性方面仍面临重大挑战。在这项工作中,我们首次探索了人类性能对齐和测试时间采样的协作,以解锁文本到图像模型的潜力。因此,我们引入了CHATS(结合人类对齐优化和测试时间采样),这是一种新型生成框架,分别建模首选和不受欢迎的分布,并采用基于代理提示的采样策略,利用这两个分布中包含的有用信息。我们发现CHATS具有出色的数据效率,仅使用一个小而高质量微调数据集就能实现强劲表现。大量实验表明,CHATS超越了传统偏好对齐方法,在多种标准基准测试中达到了新的技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/AIDC-AI/CHATS
Summary
扩散模型已成为文本到图像生成的主导方法,但其在实现高质量文本图像对齐、高生成质量和符合人类审美标准方面仍面临挑战。本研究首次探索了人类性能对齐与测试时采样的协作潜力,并引入CHATS(结合人类对齐优化和测试时采样)这一新型生成框架。该框架分别建模偏好和非偏好分布,并采用基于代理提示的采样策略,利用两种分布中的有用信息。实验表明,CHATS表现出卓越的数据效率,在小型高质量微调数据集上即可实现出色性能,并超越传统偏好对齐方法,在多个标准基准测试中达到最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本到图像生成领域的地位显著。
- 人类性能对齐和测试时采样在提升文本到图像模型的性能上至关重要。
- CHATS框架首次结合了人类对齐优化和测试时采样。
- CHATS框架实现了偏好和非偏好分布的独立建模。
- 通过基于代理提示的采样策略,CHATS能够利用两种分布中的有用信息。
- CHATS展现出卓越的数据效率,在小型高质量微调数据集上即可实现出色性能。
点此查看论文截图

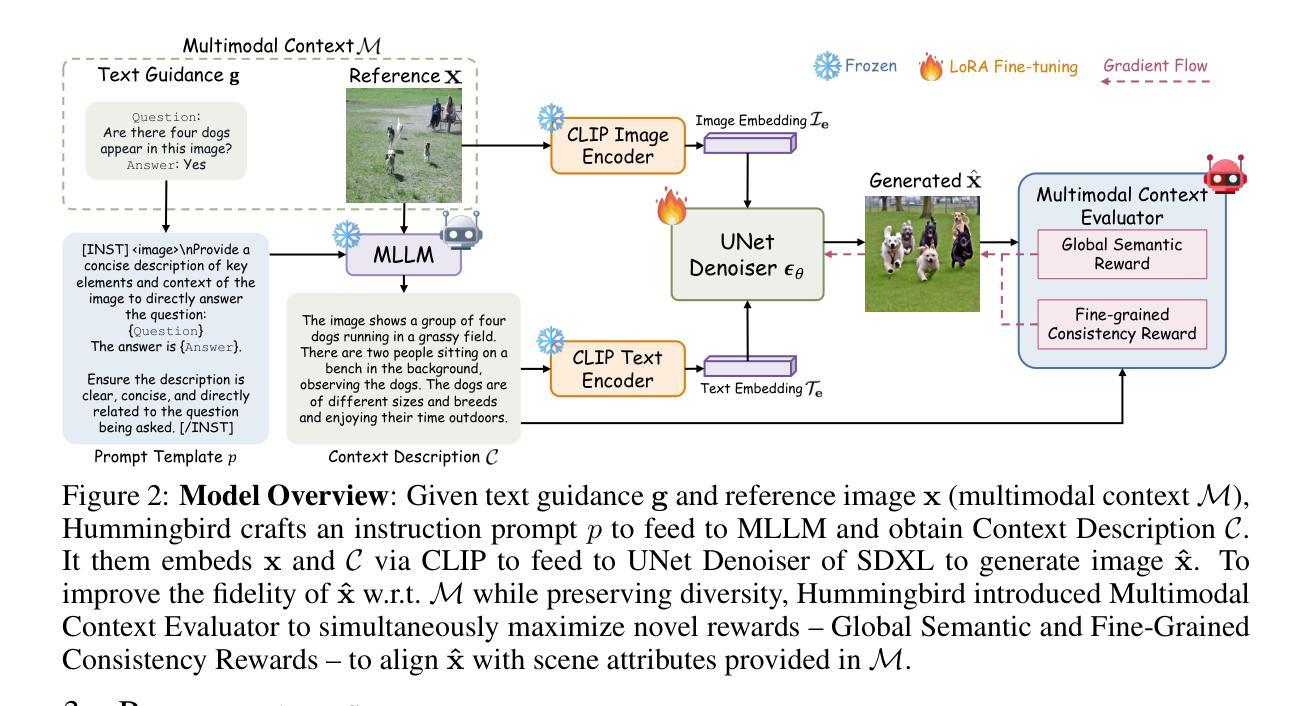
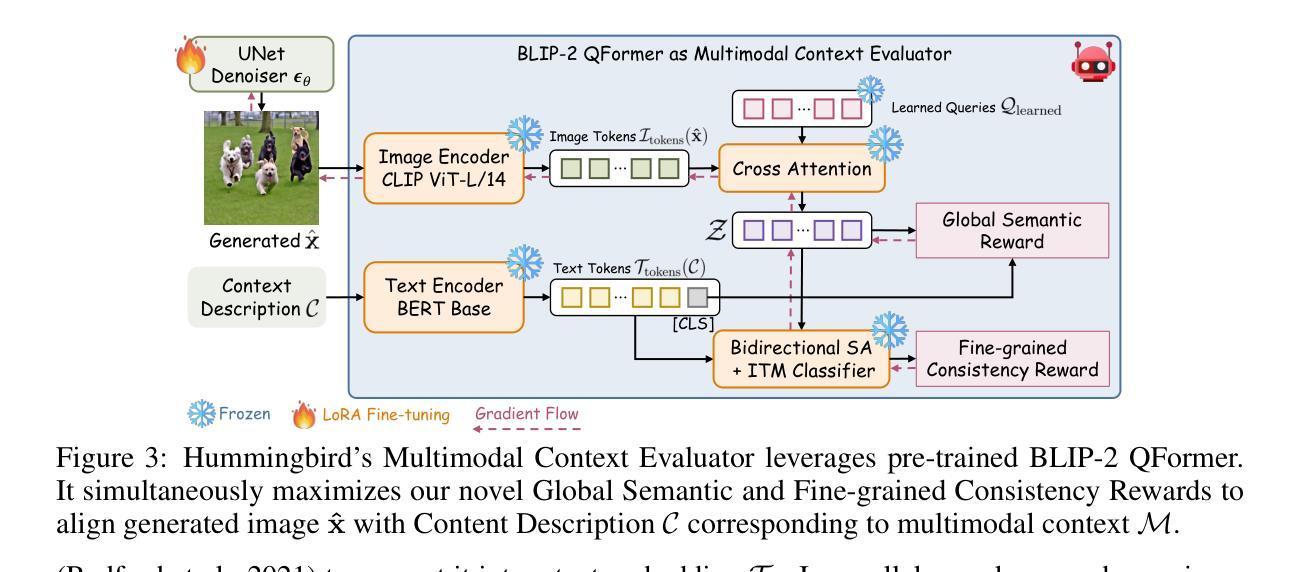
Hummingbird: High Fidelity Image Generation via Multimodal Context Alignment
Authors:Minh-Quan Le, Gaurav Mittal, Tianjian Meng, A S M Iftekhar, Vishwas Suryanarayanan, Barun Patra, Dimitris Samaras, Mei Chen
While diffusion models are powerful in generating high-quality, diverse synthetic data for object-centric tasks, existing methods struggle with scene-aware tasks such as Visual Question Answering (VQA) and Human-Object Interaction (HOI) Reasoning, where it is critical to preserve scene attributes in generated images consistent with a multimodal context, i.e. a reference image with accompanying text guidance query. To address this, we introduce $\textbf{Hummingbird}$, the first diffusion-based image generator which, given a multimodal context, generates highly diverse images w.r.t. the reference image while ensuring high fidelity by accurately preserving scene attributes, such as object interactions and spatial relationships from the text guidance. Hummingbird employs a novel Multimodal Context Evaluator that simultaneously optimizes our formulated Global Semantic and Fine-grained Consistency Rewards to ensure generated images preserve the scene attributes of reference images in relation to the text guidance while maintaining diversity. As the first model to address the task of maintaining both diversity and fidelity given a multimodal context, we introduce a new benchmark formulation incorporating MME Perception and Bongard HOI datasets. Benchmark experiments show Hummingbird outperforms all existing methods by achieving superior fidelity while maintaining diversity, validating Hummingbird’s potential as a robust multimodal context-aligned image generator in complex visual tasks. Project page: https://roar-ai.github.io/hummingbird
扩散模型虽然在为对象中心任务生成高质量、多样化的合成数据方面表现出强大的能力,但在场景感知任务(如视觉问答(VQA)和人机交互(HOI)推理)方面,现有方法往往遇到困难。在这些任务中,保持生成图像的场景属性与多模态上下文(即带有文本指导查询的参考图像)的一致性至关重要。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了Hummingbird,这是第一个基于扩散的图像生成器。给定多模态上下文,Hummingbird能够生成与参考图像高度相关的多样化图像,同时确保高保真度,准确保留场景属性,如对象交互和文本指导中的空间关系。Hummingbird采用了一种新型的多模态上下文评估器,该评估器同时优化了我们制定的全局语义和精细粒度一致性奖励,以确保生成的图像在保持文本指导的参考图像场景属性的同时,保持多样性。作为第一个解决在给定多模态上下文时保持多样性和保真度的模型,我们引入了一个新的基准测试形式,结合了MME感知和Bongard HOI数据集。基准测试实验表明,Hummingbird优于所有现有方法,在保持多样性的同时实现了较高的保真度,验证了Hummingbird作为复杂视觉任务的稳健多模态上下文对齐图像生成器的潜力。项目页面:https://roar-ai.github.io/hummingbird
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICLR 2025. Project page with code release: https://roar-ai.github.io/hummingbird
Summary:
本文介绍了针对扩散模型在场景感知任务(如视觉问答和人类物体交互推理)中的不足,提出了一种基于扩散的图像生成器——Hummingbird。Hummingbird能够结合多模态上下文生成高度多样化的图像,同时确保图像的高保真度,准确保留场景属性,如物体交互和空间关系。它通过新型的多模态上下文评估器,同时优化全局语义和精细一致性奖励,以在保持图像多样性的同时,确保与文本指导相关的场景属性的保留。作为首个解决在给定多模态上下文时保持多样性和保真度的模型,本文引入了结合MME感知和Bongard HOI数据集的新基准测试方法。实验表明,Hummingbird在保持多样性的同时实现了高保真度,验证了其在复杂视觉任务中作为稳健的多模态上下文对齐图像生成器的潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- 扩散模型在场景感知任务(如视觉问答和人类物体交互推理)中表现不足。
- Hummingbird是基于扩散的图像生成器,能够结合多模态上下文生成多样化且高保真度的图像。
- Hummingbird通过新型的多模态上下文评估器,同时优化全局语义和精细一致性奖励。
- Hummingbird能够在保持多样性的同时,确保生成的图像与文本指导相关的场景属性的保留。
- 作为首个解决在给定多模态上下文时保持多样性和保真度的模型,Hummingbird具有潜力成为复杂视觉任务中的稳健多模态上下文对齐图像生成器。
- 引入的新基准测试方法结合了MME感知和Bongard HOI数据集,以评估图像生成器的性能。
点此查看论文截图