⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-11 更新
Taking Flight with Dialogue: Enabling Natural Language Control for PX4-based Drone Agent
Authors:Shoon Kit Lim, Melissa Jia Ying Chong, Jing Huey Khor, Ting Yang Ling
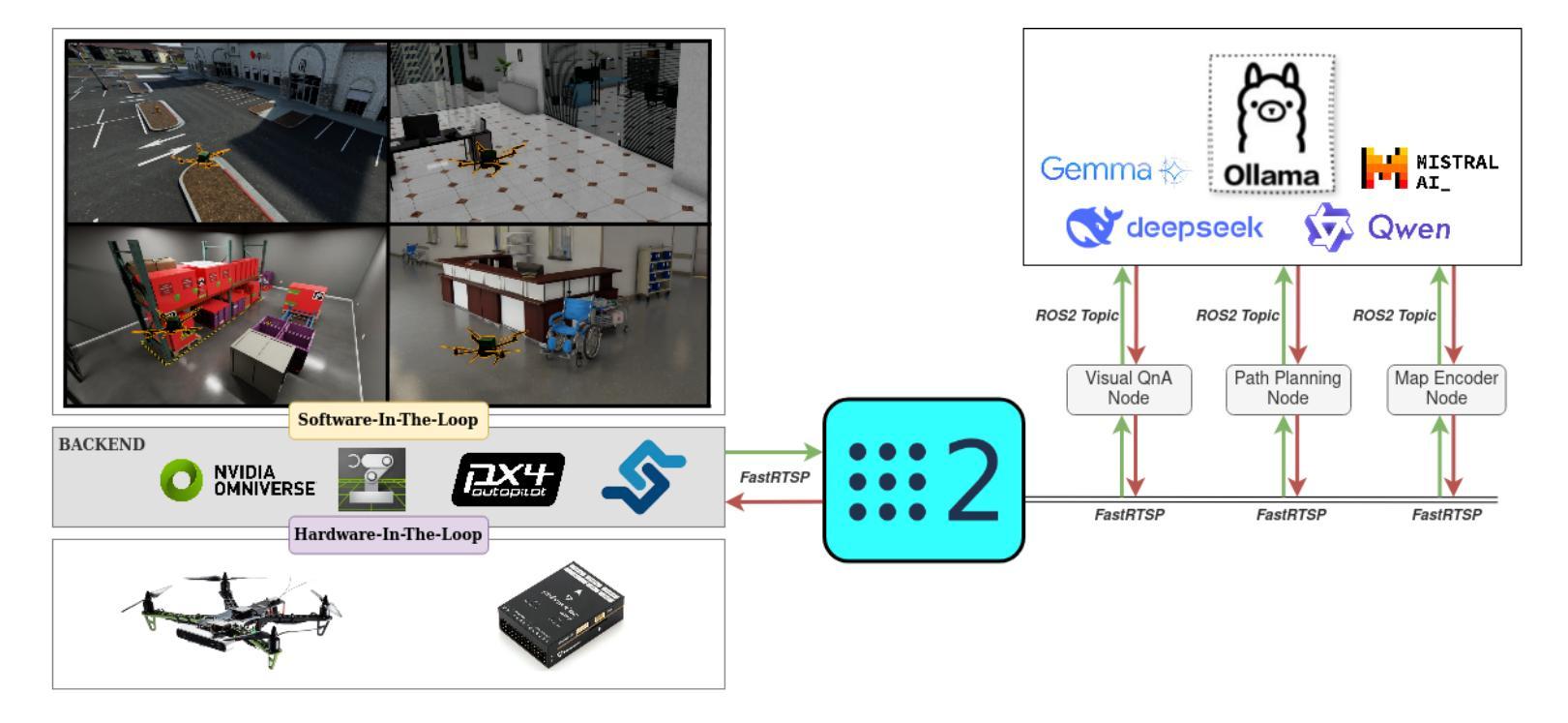
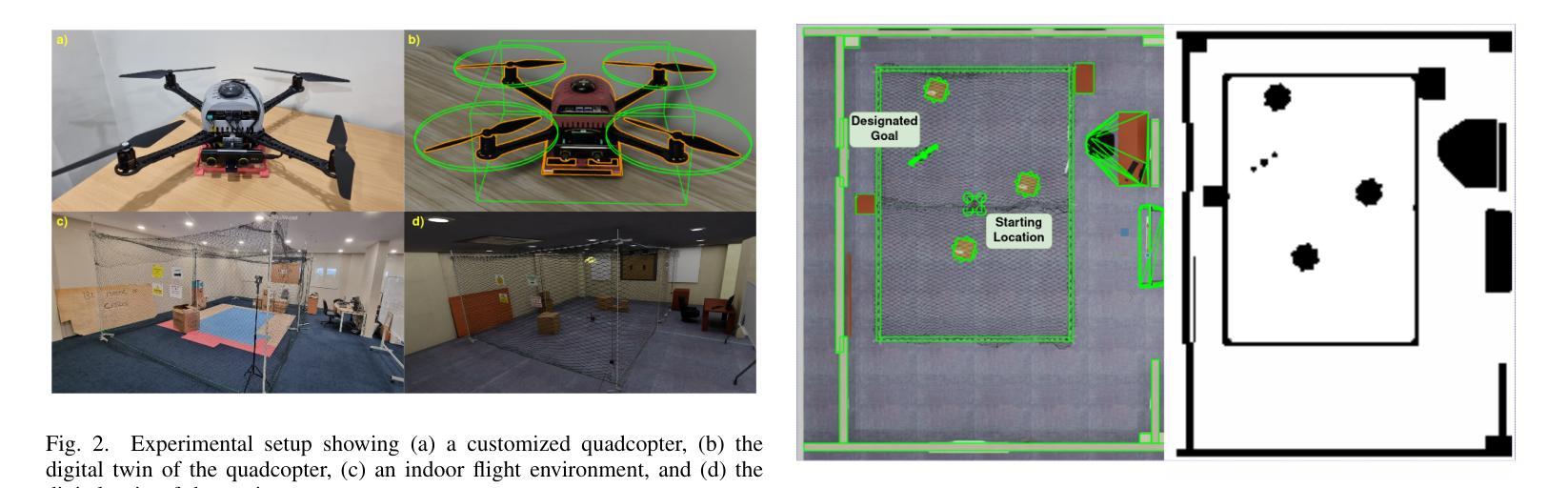
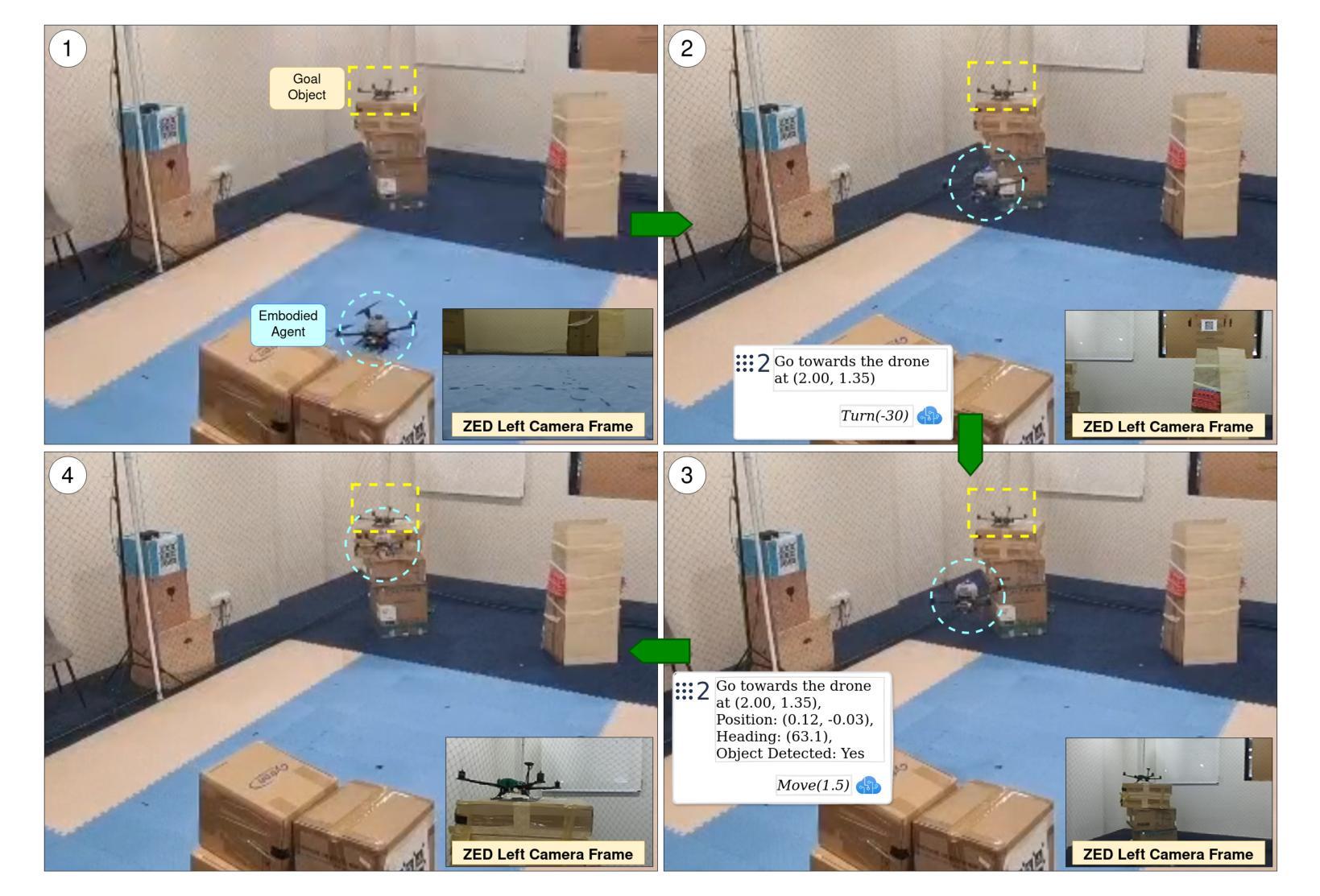
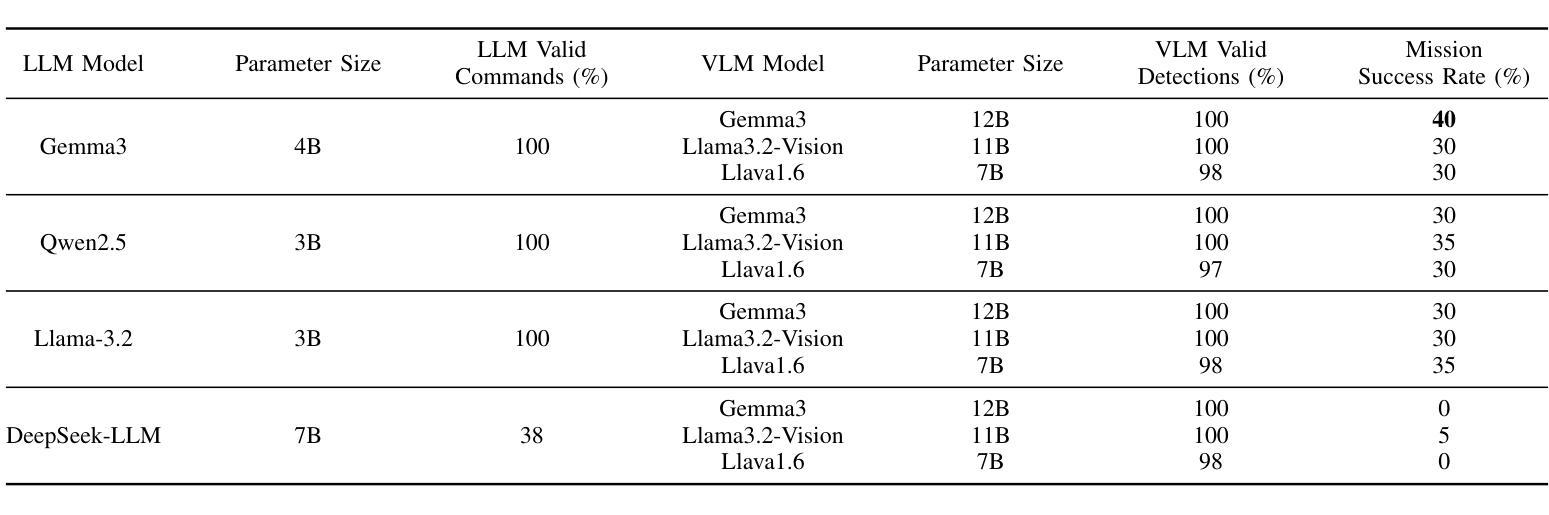
Recent advances in agentic and physical artificial intelligence (AI) have largely focused on ground-based platforms such as humanoid and wheeled robots, leaving aerial robots relatively underexplored. Meanwhile, state-of-the-art unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) multimodal vision-language systems typically rely on closed-source models accessible only to well-resourced organizations. To democratize natural language control of autonomous drones, we present an open-source agentic framework that integrates PX4-based flight control, Robot Operating System 2 (ROS 2) middleware, and locally hosted models using Ollama. We evaluate performance both in simulation and on a custom quadcopter platform, benchmarking four large language model (LLM) families for command generation and three vision-language model (VLM) families for scene understanding.
最近关于智能体和物理人工智能的进步主要集中在基于地面的平台(如人形机器人和轮式机器人),而对空中机器人的研究相对较少。同时,最先进的无人飞行器多模态视觉语言系统通常依赖于只有资源丰富的组织才能访问的闭源模型。为了普及自主无人机的自然语言控制,我们提出了一个开源的智能体框架,该框架集成了基于PX4的飞行控制、机器人操作系统2(ROS 2)中间件以及使用Ollama的本地托管模型。我们在模拟环境和定制的四旋翼无人机平台上进行了性能评估,对比了四种大型语言模型家族在生成命令方面的表现,以及三种视觉语言模型家族在理解场景方面的表现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Source code available at: https://github.com/limshoonkit/ros2-agent-ws
Summary
近期人工智能进展主要集中在地面平台,如人形机器人和轮式机器人,而空中机器人相对被忽视。现有的无人机多模态视觉语言系统通常采用封闭源代码模型,仅适用于资源丰富的组织。为普及自然语言控制自主无人机,我们提出一个开源的代理框架,整合基于PX4的飞行控制、机器人操作系统2(ROS 2)中间件和本地模型Ollama。我们在模拟和定制的四轴飞行器平台上进行评估,对比了四种大型语言模型家族在生成命令方面的性能,以及三种视觉语言模型家族在理解场景方面的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 近期AI进步主要集中在地面平台,空中机器人相对被忽视。
- 当前无人机视觉语言系统主要依赖封闭源代码模型,仅限于资源丰富的组织。
- 为普及自然语言控制自主无人机,需开发开源代理框架。
- 提出的框架整合了PX4飞行控制、ROS 2中间件和本地模型Ollama。
- 在模拟和定制四轴飞行器平台上评估了不同语言模型在命令生成方面的性能。
- 视觉语言模型在场景理解方面表现出潜力。
点此查看论文截图

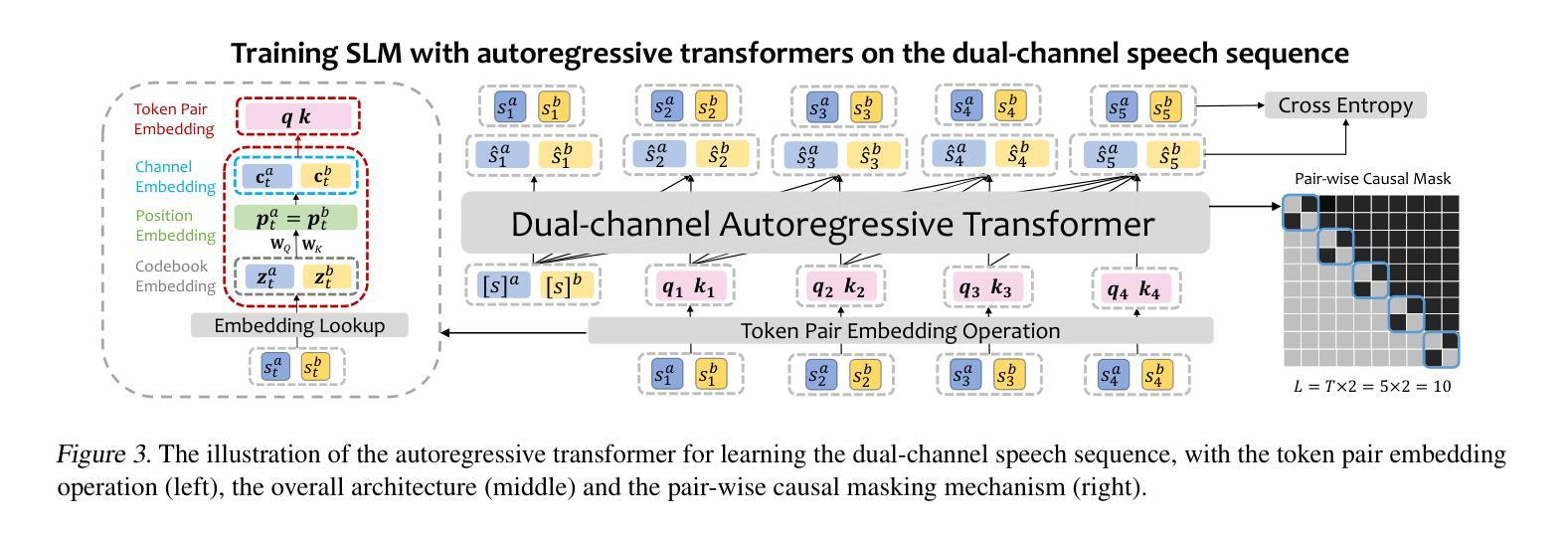
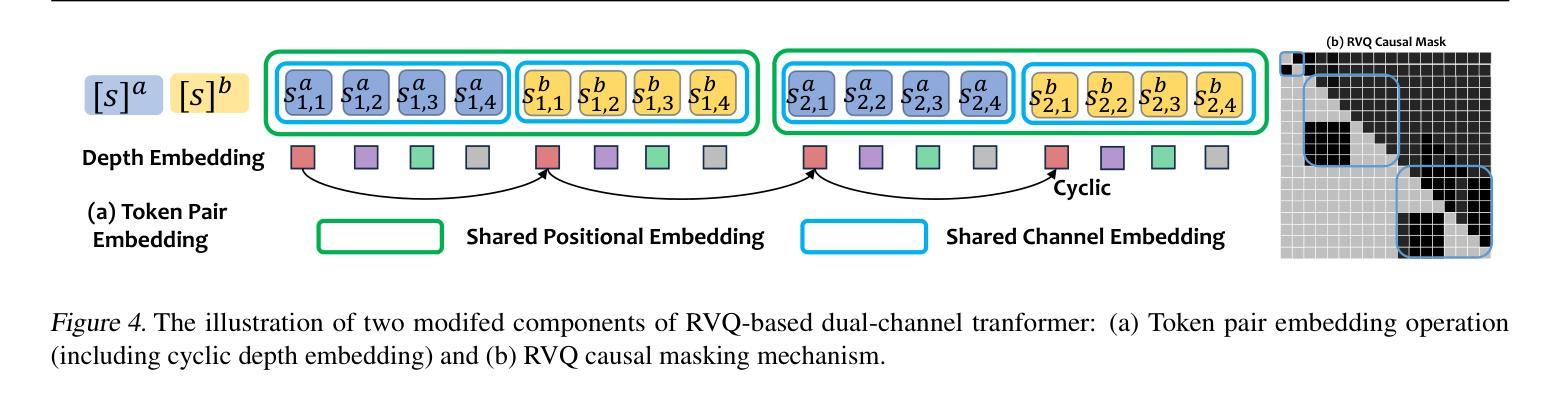
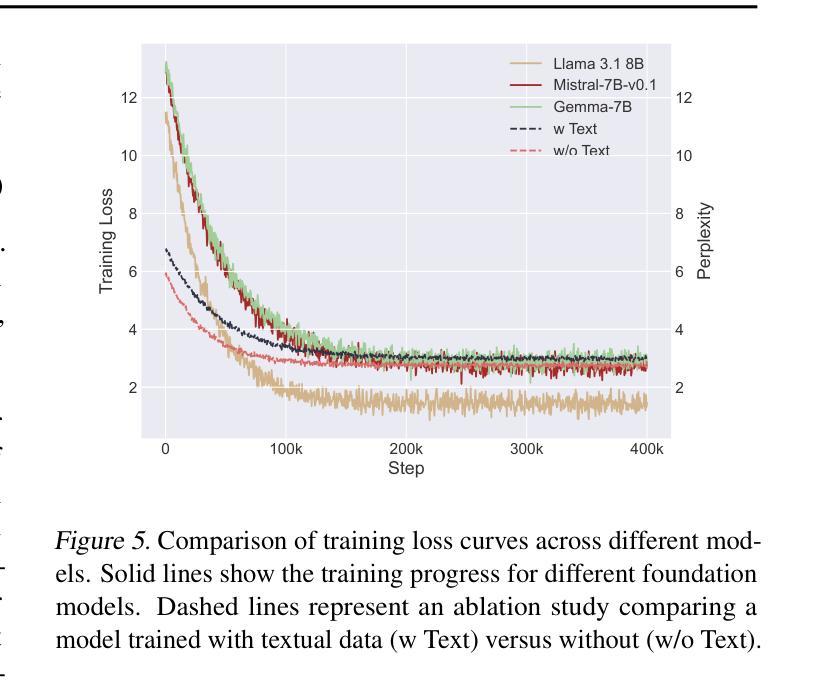
NTPP: Generative Speech Language Modeling for Dual-Channel Spoken Dialogue via Next-Token-Pair Prediction
Authors:Qichao Wang, Ziqiao Meng, Wenqian Cui, Yifei Zhang, Pengcheng Wu, Bingzhe Wu, Irwin King, Liang Chen, Peilin Zhao
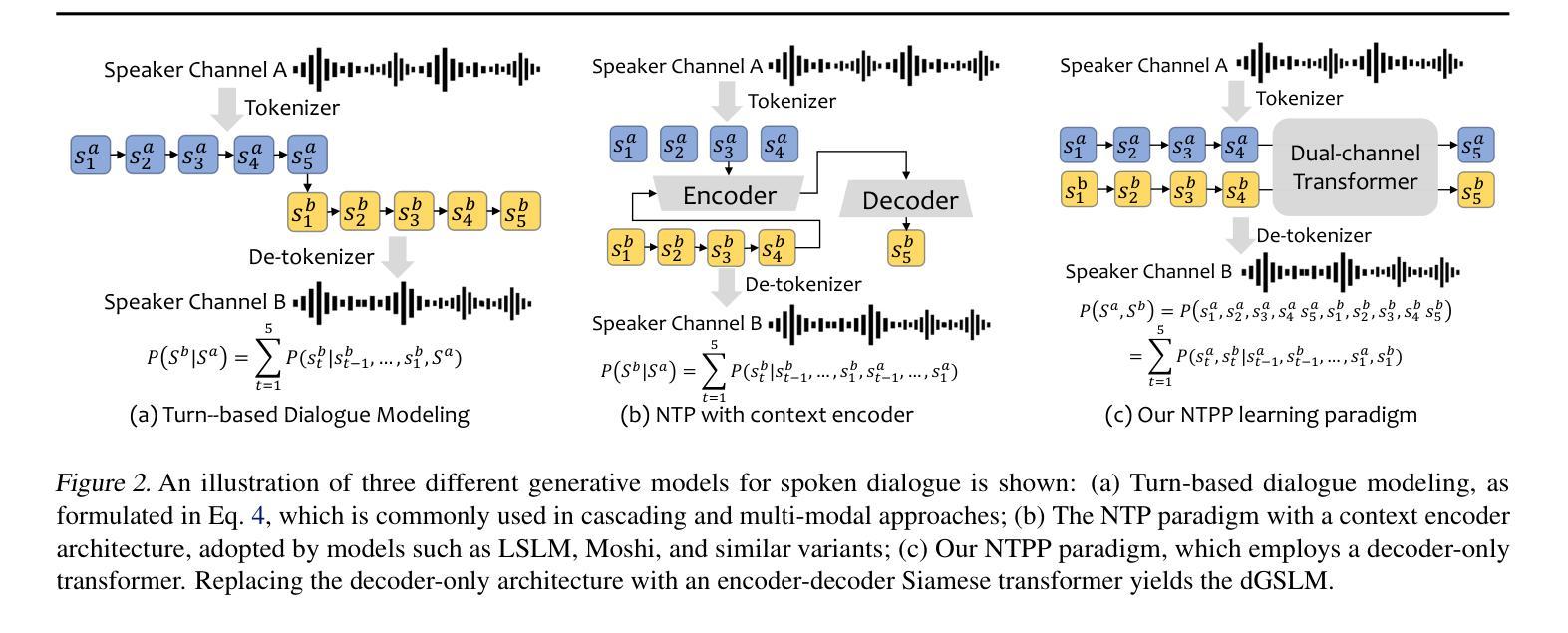
Inspired by the impressive capabilities of GPT-4o, there is growing interest in enabling speech language models (SLMs) to engage in natural, fluid spoken interactions with humans. Recent advancements have led to the development of several SLMs that demonstrate promising results in this area. However, current approaches have yet to fully exploit dual-channel speech data, which inherently captures the structure and dynamics of human conversation. In this work, we systematically explore the use of dual-channel speech data in the context of modern large language models, and introduce a novel generative modeling paradigm, Next-Token-Pair Prediction (NTPP), to enable speaker-independent dual-channel spoken dialogue learning using decoder-only architectures for the first time. We evaluate our approach on standard benchmarks, and empirical results show that our proposed method, NTPP, significantly improves the conversational abilities of SLMs in terms of turn-taking prediction, response coherence, and naturalness. Moreover, compared to existing methods, NTPP achieves substantially lower inference latency, highlighting its practical efficiency for real-time applications.
受GPT-4o强大功能的启发,人们越来越感兴趣让语言模型(SLM)与人类进行自然流畅的对话交互。最近的进步已经开发出几种SLM,在这个领域取得了很有希望的结果。然而,当前的方法还没有充分利用双通道语音数据,它本质上捕捉了人类对话的结构和动态。在这项工作中,我们系统地探索了在现代大型语言模型背景下使用双通道语音数据,并引入了一种新型的生成建模范式——下一个令牌对预测(NTPP),首次使用仅解码器架构实现说话者独立的双通道口语对话学习。我们在标准基准测试上评估了我们的方法,经验结果表明,我们提出的NTPP方法显著提高了SLM的会话能力,在轮次预测、响应连贯性和自然性方面都有改善。此外,与现有方法相比,NTPP的推理延迟大大降低,这突显了其在实时应用中的实际效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025
Summary
本文探讨了如何利用现代大型语言模型在对话中应用双通道语音数据的潜力。提出了一种新的生成建模范式——Next-Token-Pair Prediction(NTPP),首次实现了使用解码器架构进行独立于说话人的双通道口语对话学习。在标准基准测试上的实证结果表明,NTPP显著提高了语言模型在轮替预测、响应连贯性和自然性方面的对话能力,并且与现有方法相比,NTPP的推理延迟更低,表明其在实时应用中的实际效率。
Key Takeaways
- 文章受到GPT-4o的启发,探索了使语言模型能够进行自然流畅的人机对话的可能性。
- 介绍了双通道语音数据在现代大型语言模型中的应用潜力。
- 提出了一种新的生成建模范式NTPP,首次实现了使用解码器架构进行独立于说话人的双通道口语对话学习。
- NTPP能够显著提高语言模型的对话能力,包括轮替预测、响应连贯性和自然性。
- 与现有方法相比,NTPP的推理延迟更低,适合用于实时应用。
- 文章展示了系统性和实证性的研究,提供了关于如何在语言模型中有效利用双通道语音数据的见解。
点此查看论文截图


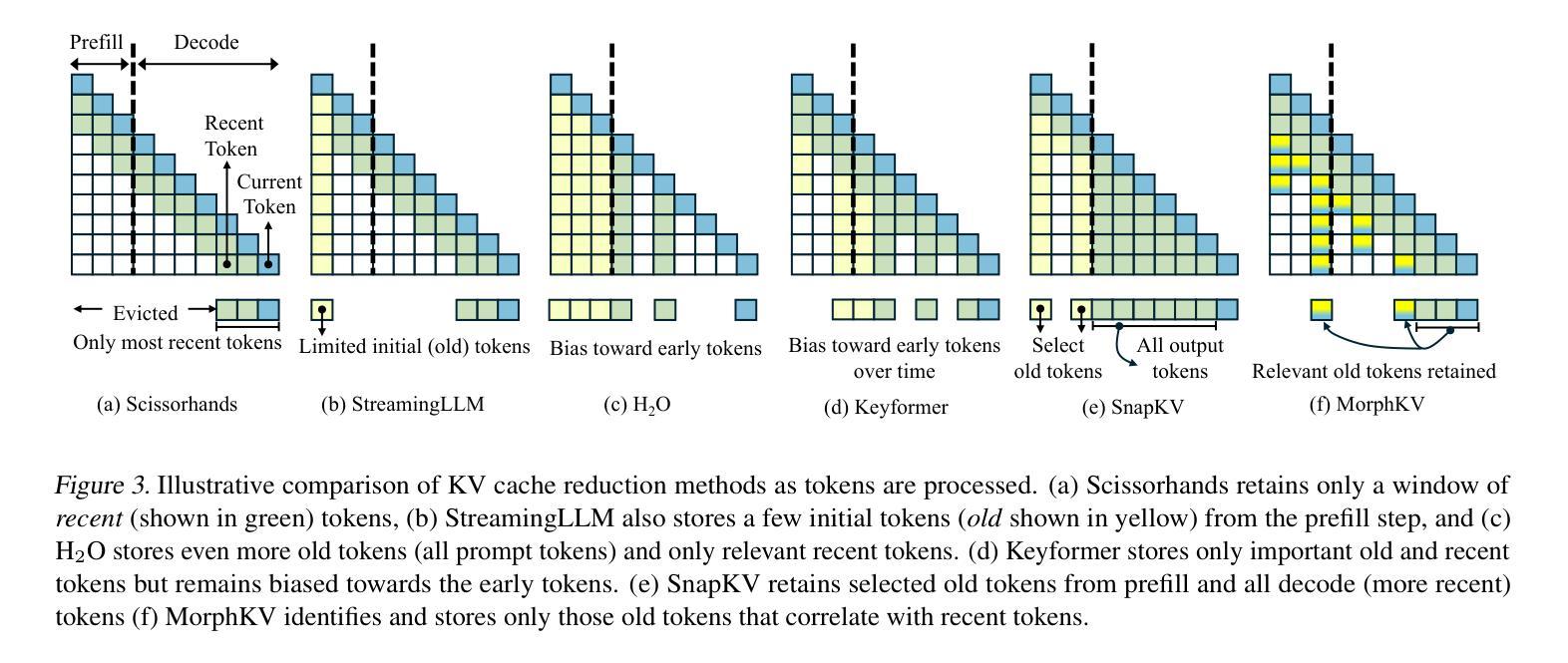
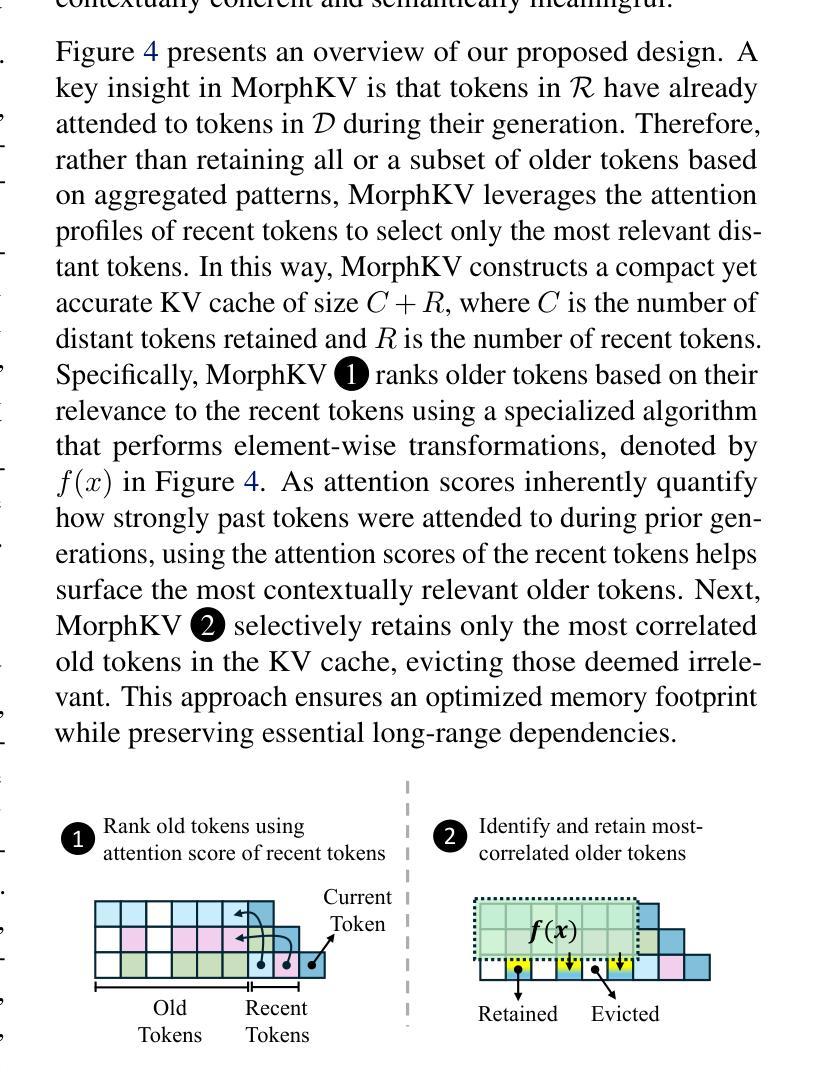
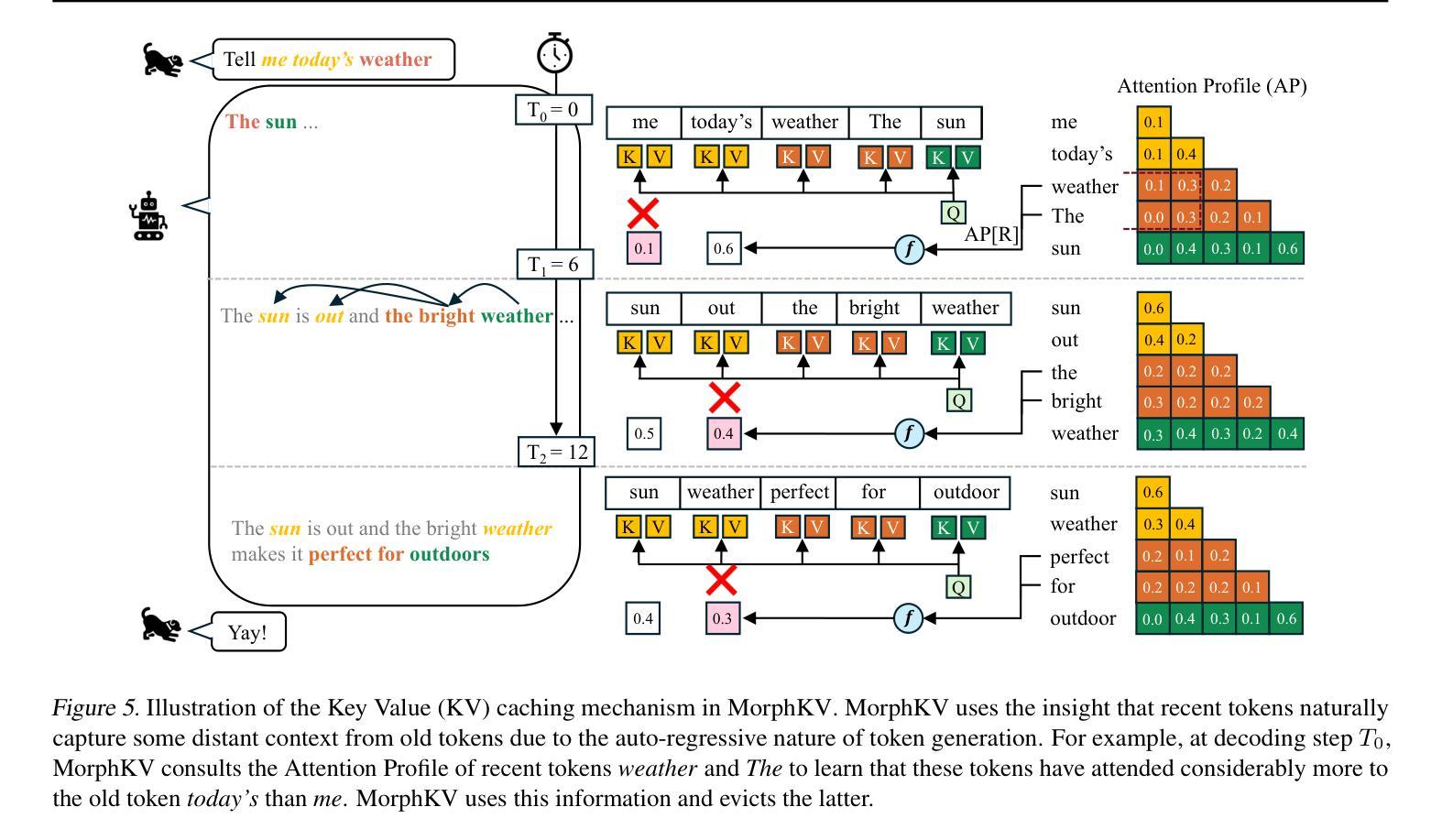
Dialogue Without Limits: Constant-Sized KV Caches for Extended Responses in LLMs
Authors:Ravi Ghadia, Avinash Kumar, Gaurav Jain, Prashant Nair, Poulami Das
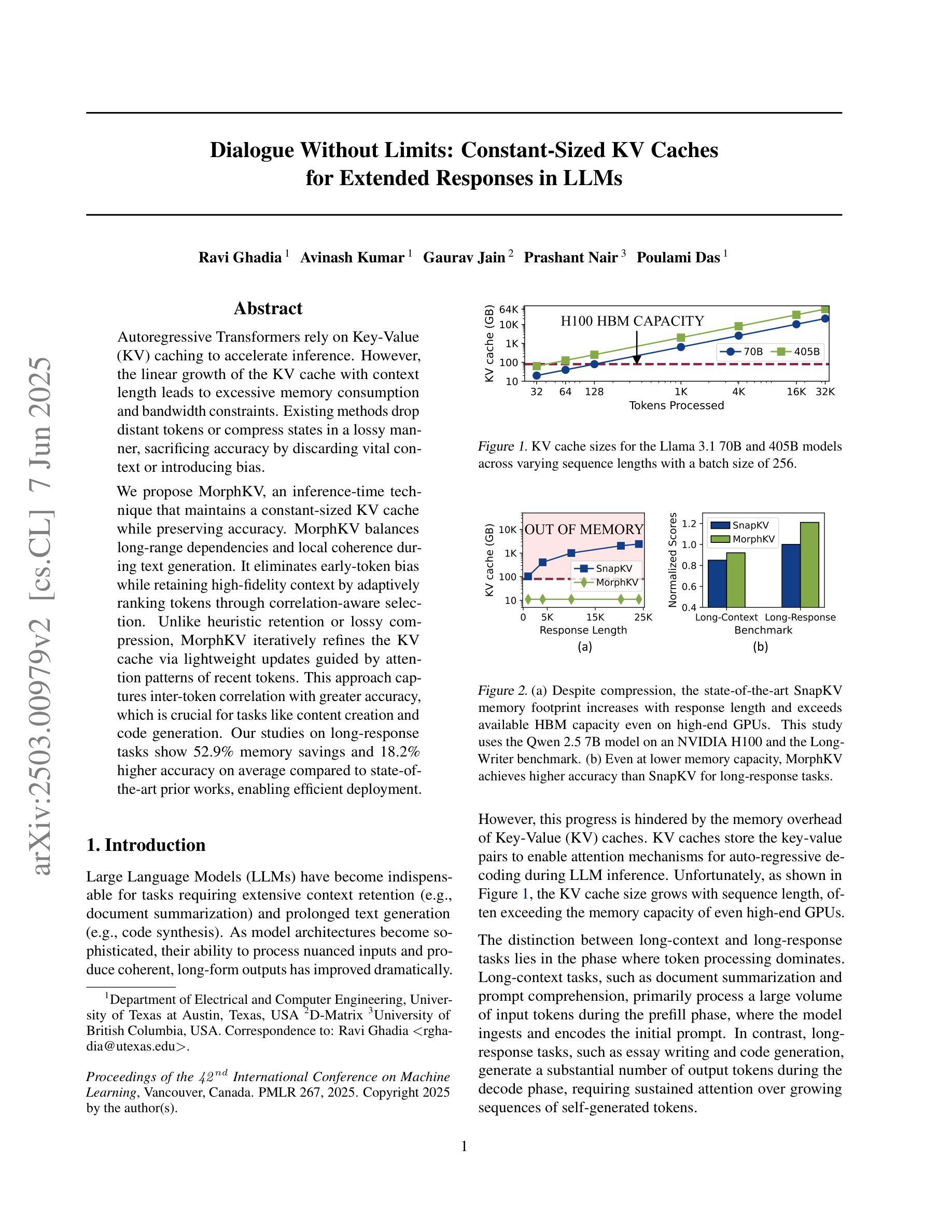
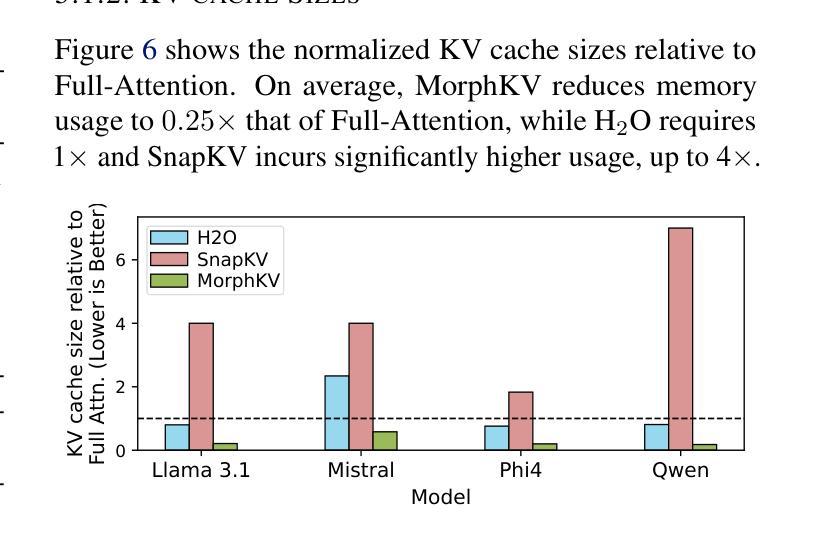
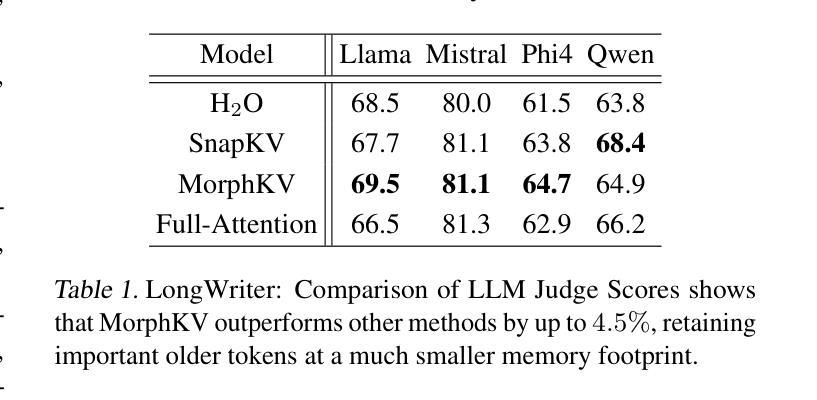
Autoregressive Transformers rely on Key-Value (KV) caching to accelerate inference. However, the linear growth of the KV cache with context length leads to excessive memory consumption and bandwidth constraints. This bottleneck is particularly problematic in real-time applications – such as chatbots and interactive assistants – where low latency and high memory efficiency are critical. Existing methods drop distant tokens or compress states in a lossy manner, sacrificing accuracy by discarding vital context or introducing bias. We propose MorphKV, an inference-time technique that maintains a constant-sized KV cache while preserving accuracy. MorphKV balances long-range dependencies and local coherence during text generation. It eliminates early-token bias while retaining high-fidelity context by adaptively ranking tokens through correlation-aware selection. Unlike heuristic retention or lossy compression, MorphKV iteratively refines the KV cache via lightweight updates guided by attention patterns of recent tokens. This approach captures inter-token correlation with greater accuracy, crucial for tasks like content creation and code generation. Our studies on long-response tasks show 52.9$%$ memory savings and 18.2$%$ higher accuracy on average compared to state-of-the-art prior works, enabling efficient real-world deployment.
自回归Transformer依赖于键值(KV)缓存来加速推理。然而,KV缓存随上下文长度呈线性增长,导致内存消耗过大和带宽限制。这一瓶颈在实时应用(如聊天机器人和交互式助手)中尤其成问题,在这些应用中,低延迟和高内存效率至关重要。现有方法会丢弃远处的标记或以有损的方式压缩状态,牺牲了准确性,要么丢弃重要上下文,要么引入偏见。我们提出了MorphKV,这是一种推理时间技术,可以保持固定大小的KV缓存同时保持准确性。MorphKV在文本生成过程中平衡了长距离依赖关系和局部连贯性。它消除了早期标记偏见,同时通过关联感知选择自适应地对标记进行排名,从而保留高保真上下文。与启发式保留或有损压缩不同,MorphKV通过最近标记的注意力模式指导进行轻量级更新,从而迭代地完善KV缓存。这种方法更准确地捕捉了标记间的相关性,对于内容创建和代码生成等任务至关重要。我们对长响应任务的研究表明,与最新先前作品相比,平均节省了52.9%的内存,准确率提高了18.2%,可实现高效的现实世界部署。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in the Proceedings of the 42nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Vancouver, Canada
Summary
本文探讨了Autoregressive Transformer在推理过程中依赖Key-Value缓存的问题。由于KV缓存随语境长度呈线性增长,导致内存消耗过大和带宽限制。特别是在实时应用如聊天机器人和交互式助手等需要低延迟和高内存效率的场景中,现有方法通过舍弃远距离标记或压缩状态的方式牺牲准确性。本文提出了MorphKV,这是一种推理时技术,能维持固定大小的KV缓存同时保持准确性。MorphKV在文本生成过程中平衡了长程依赖和局部一致性,通过关联感知选择自适应排名标记,消除了早期标记偏见,同时保留高保真上下文。与启发式保留或有损压缩不同,MorphKV通过最近标记的注意力模式指导进行轻量级更新,迭代优化KV缓存。这种方法更准确地捕捉了标记间的关联,对于内容创建和代码生成等任务至关重要。对长响应任务的研究显示,与最新技术相比,MorphKV平均节省了52.9%的内存,准确率提高了18.2%,能够实现有效的实际部署。
Key Takeaways
- Autoregressive Transformers在推理过程中依赖Key-Value缓存,但随语境长度增长导致内存消耗和带宽限制问题。
- 实时应用中,如聊天机器人和交互式助手,低延迟和高内存效率至关重要,现有方法牺牲准确性来解决问题。
- 本文提出了MorphKV技术,维持固定大小的KV缓存,同时保持准确性。
- MorphKV通过关联感知选择自适应排名标记,平衡长程依赖和局部一致性。
- 与其他方法不同,MorphKV迭代优化KV缓存,通过最近标记的注意力模式指导进行轻量级更新。
- 方法更准确地捕捉标记间的关联,对内容创建和代码生成等任务效果尤佳。
点此查看论文截图
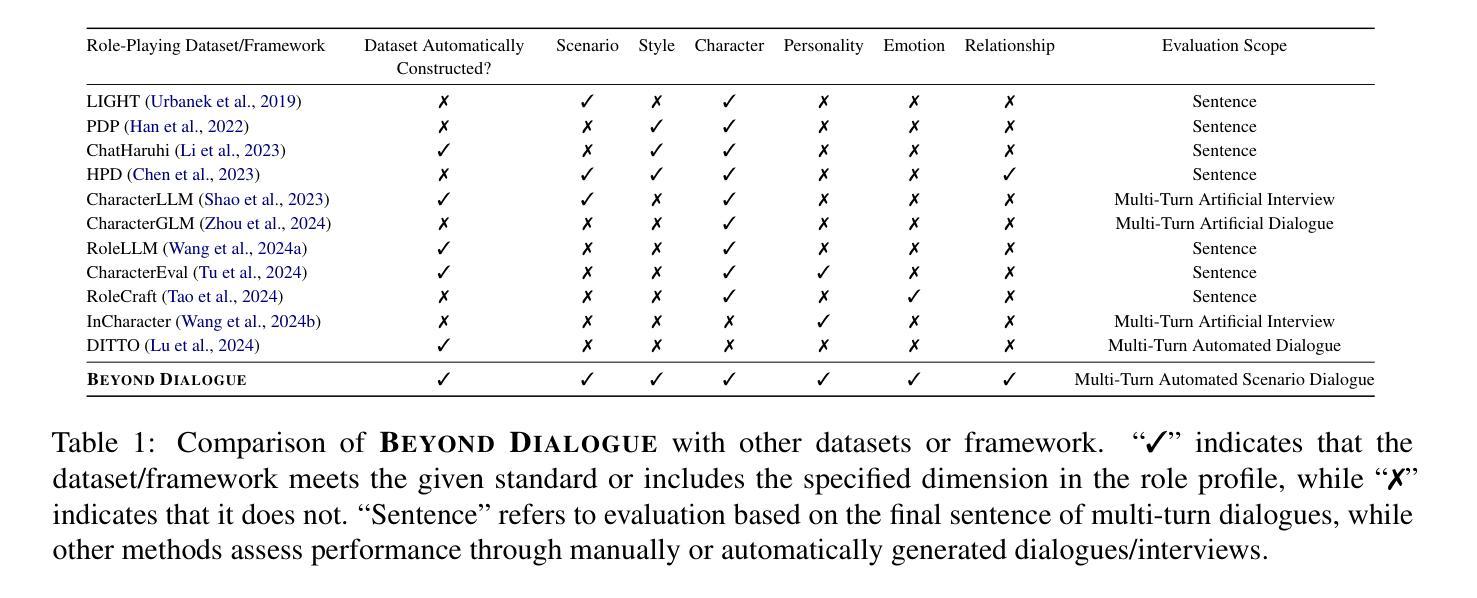
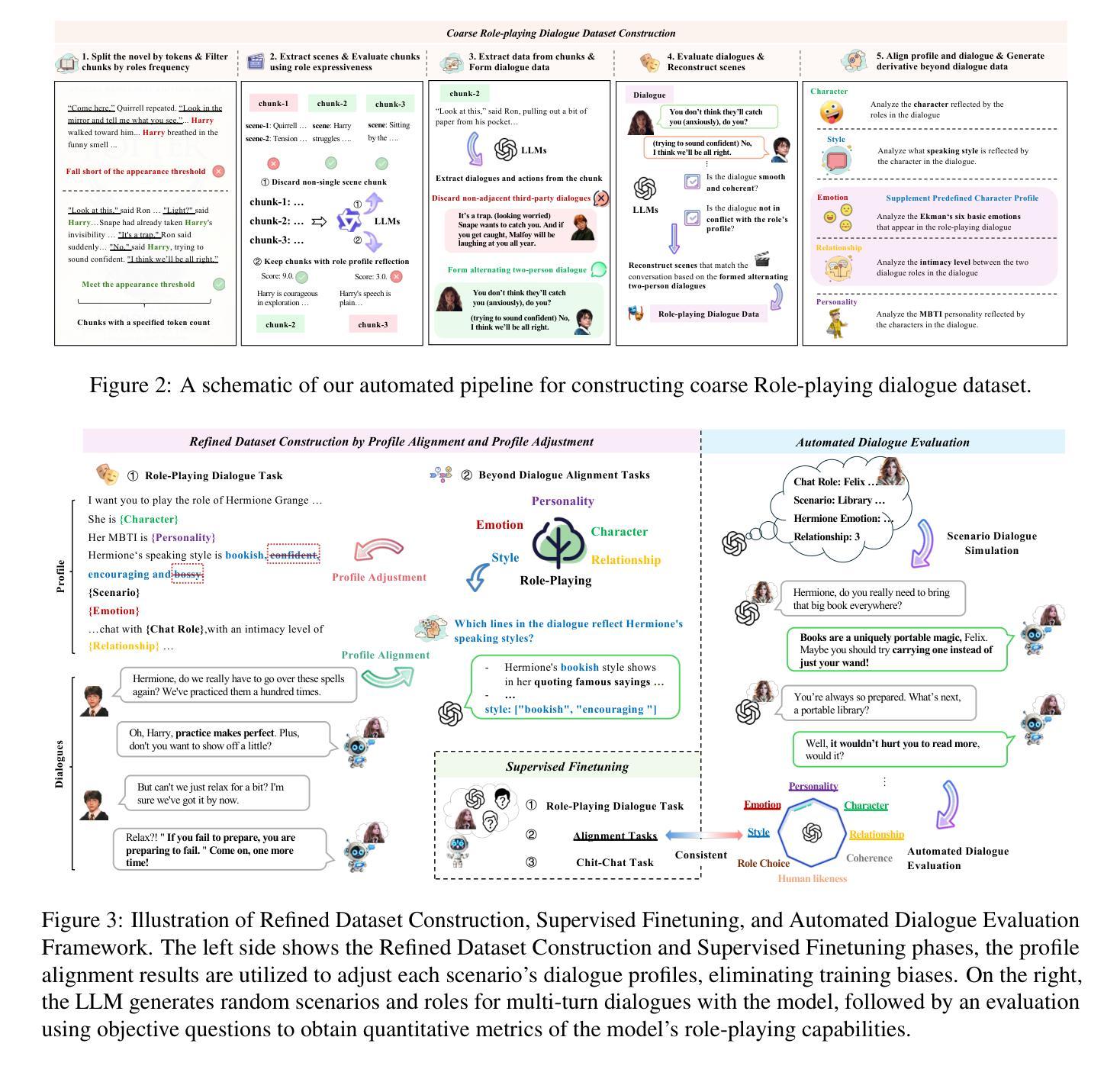
BEYOND DIALOGUE: A Profile-Dialogue Alignment Framework Towards General Role-Playing Language Model
Authors:Yeyong Yu, Runsheng Yu, Haojie Wei, Zhanqiu Zhang, Quan Qian
The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has revolutionized role-playing, enabling the development of general role-playing models. However, current role-playing training has two significant issues: (I) Using a predefined role profile to prompt dialogue training for specific scenarios usually leads to inconsistencies and even conflicts between the dialogue and the profile, resulting in training biases. (II) The model learns to imitate the role based solely on the profile, neglecting profile-dialogue alignment at the sentence level. In this work, we propose a simple yet effective framework called BEYOND DIALOGUE, designed to overcome these hurdles. This framework innovatively introduces “beyond dialogue” tasks to align dialogue with profile traits based on each specific scenario, thereby eliminating biases during training. Furthermore, by adopting an innovative prompting mechanism that generates reasoning outcomes for training, the framework allows the model to achieve fine-grained alignment between profile and dialogue at the sentence level. The aforementioned methods are fully automated and low-cost. Additionally, the integration of automated dialogue and objective evaluation methods forms a comprehensive framework, paving the way for general role-playing. Experimental results demonstrate that our model excels in adhering to and reflecting various dimensions of role profiles, outperforming most proprietary general and specialized role-playing baselines. All code and datasets are available at https://github.com/yuyouyu32/BeyondDialogue.
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展已经彻底改变了角色扮演的方式,并推动了通用角色扮演模型的开发。然而,当前的角色扮演训练存在两大问题:(I)使用预定义的角色简介来提示特定场景的对话训练通常会导致对话与简介之间存在不一致甚至冲突,从而产生训练偏见。(II)模型仅基于简介学习模仿角色,忽略了句子级别的简介-对话对齐。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种简单有效的框架,称为“超越对话”(BEYOND DIALOGUE),旨在克服这些障碍。该框架创新地引入了“超越对话”任务,根据每个特定场景实现对话与简介特性的对齐,从而在训练过程中消除偏见。此外,通过采用生成训练推理结果的创新提示机制,该框架使模型能够在句子级别实现简介与对话的精细对齐。上述方法完全自动化且成本低廉。另外,通过结合自动化对话和客观评估方法,形成了一个全面的框架,为通用角色扮演铺平了道路。实验结果表明,我们的模型在遵循和反映各种角色简介方面表现出色,超越了大多数专有通用和专用角色扮演基线。所有代码和数据集可在https://github.com/yuyouyu32/BeyondDialogue找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展推动了角色扮演领域的变革,使得通用角色扮演模型得以开发。然而,当前的角色扮演训练面临两个主要问题:一是使用预设角色描述来引导对话训练会导致对话与描述之间存在不一致和冲突,产生训练偏见;二是模型仅基于角色描述学习模仿角色,忽视了句子级别的角色描述与对话的匹配。针对这些问题,本文提出了一个简单有效的框架——BEYOND DIALOGUE,通过引入“超越对话”任务,使对话与特定场景中的角色特征相匹配,消除训练中的偏见。此外,该框架采用创新提示机制,为训练生成推理结果,实现角色描述与对话之间的精细匹配。该框架完全自动化、成本低,结合自动化对话和客观评估方法,为通用角色扮演铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)推动了角色扮演领域的变革,使得通用角色扮演模型成为可能。
- 当前角色扮演训练面临训练偏见和句子级别匹配问题。
- BEYOND DIALOGUE框架通过引入“超越对话”任务解决上述问题,消除训练中的偏见。
- 该框架采用创新提示机制,实现角色描述与对话之间的精细匹配。
- 该框架完全自动化、成本低,并集成了自动化对话和客观评估方法。
- 实验结果表明,该模型在遵循和反映角色描述的各个方面都优于大多数基准模型。
点此查看论文截图