⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-11 更新
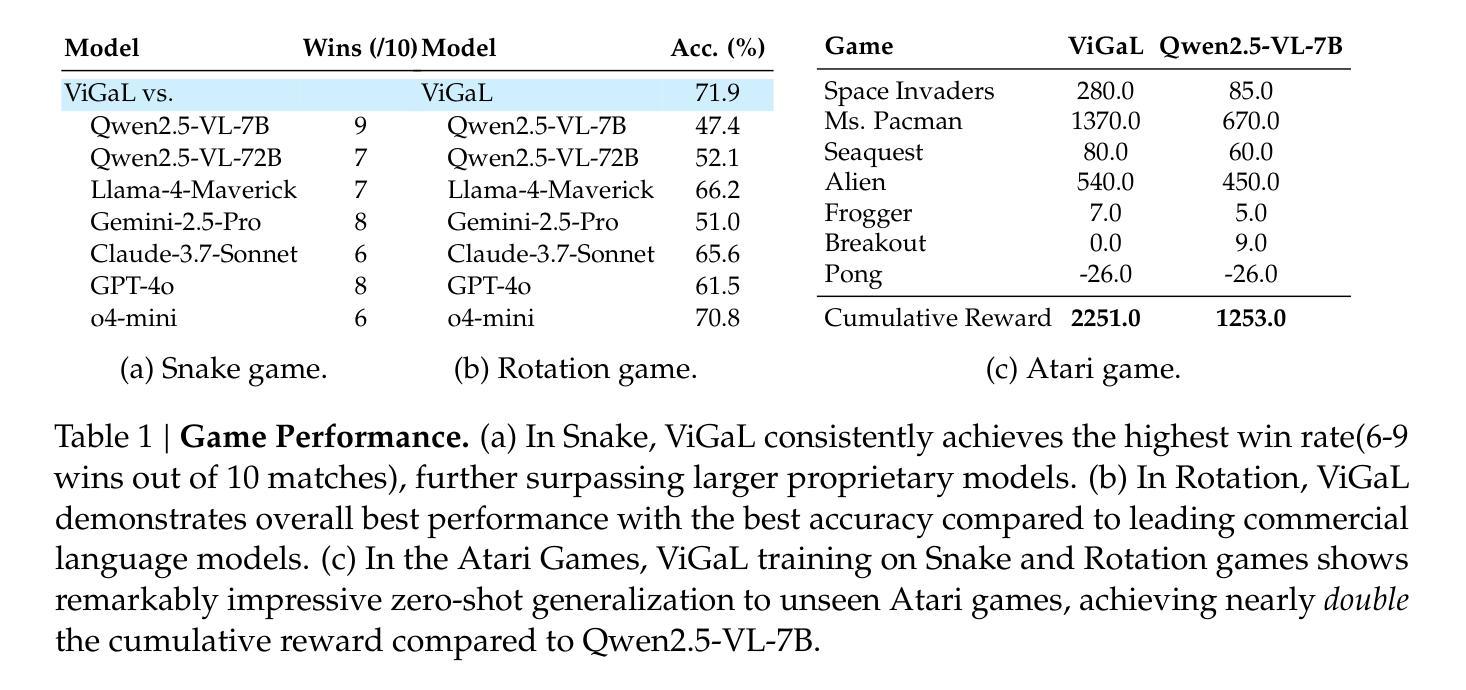
Play to Generalize: Learning to Reason Through Game Play
Authors:Yunfei Xie, Yinsong Ma, Shiyi Lan, Alan Yuille, Junfei Xiao, Chen Wei
Developing generalizable reasoning capabilities in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) remains challenging. Motivated by cognitive science literature suggesting that gameplay promotes transferable cognitive skills, we propose a novel post-training paradigm, Visual Game Learning, or ViGaL, where MLLMs develop out-of-domain generalization of multimodal reasoning through playing arcade-like games. Specifically, we show that post-training a 7B-parameter MLLM via reinforcement learning (RL) on simple arcade-like games, e.g. Snake, significantly enhances its downstream performance on multimodal math benchmarks like MathVista, and on multi-discipline questions like MMMU, without seeing any worked solutions, equations, or diagrams during RL, suggesting the capture of transferable reasoning skills. Remarkably, our model outperforms specialist models tuned on multimodal reasoning data in multimodal reasoning benchmarks, while preserving the base model’s performance on general visual benchmarks, a challenge where specialist models often fall short. Our findings suggest a new post-training paradigm: synthetic, rule-based games can serve as controllable and scalable pre-text tasks that unlock generalizable multimodal reasoning abilities in MLLMs.
在多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)中发展可推广的推理能力仍然是一个挑战。受认知科学文献的启发,该文献表明游戏可以促进可迁移的认知技能,我们提出了一种新型的后训练范式,即视觉游戏学习(ViGaL),其中MLLMs通过玩类似街机游戏来发展跨域的多模态推理能力。具体来说,我们通过强化学习(RL)在简单的类似街机游戏上对具有7B参数的MLLM进行后训练,例如Snake游戏,显著提高了其在多模态数学基准测试(如MathVista)和多学科问题(如MMMU)上的性能表现。值得注意的是,在强化学习过程中,我们的模型没有接触到任何解决方案、方程式或图表。这表明我们的模型掌握了可迁移的推理技能。令人瞩目的是,我们的模型在多模态推理基准测试中表现优于专门针对多模态推理数据调整的模型,同时保持了基础模型在一般视觉基准测试中的性能,这是一个专家模型通常无法达到的挑战。我们的研究结果表明了一种新型的后训练范式:合成、基于规则的游戏可以作为可控且可扩展的预文本任务,以解锁MLLM中的可推广多模态推理能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://yunfeixie233.github.io/ViGaL/
Summary
在开发多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的通用推理能力方面,面临着挑战。受认知科学文献的启发,该研究提出了一种名为视觉游戏学习(ViGaL)的新型训练后范式,通过玩类似街机游戏,促进MLLMs发展跨域的多模态推理能力。研究结果显示,对拥有7B参数的MLLM进行强化学习(RL)的街机游戏训练后,其在多模态数学基准测试(如MathVista)和多学科问题(如MMMU)上的表现显著提升。值得注意的是,在RL过程中并未接触任何解题解决方案、方程式或图表,这表明模型掌握了可迁移的推理技能。此外,该模型在多模态推理基准测试中的表现优于专门训练的多模态推理模型,同时保持了基础模型在一般视觉基准测试中的性能。这表明基于规则的游戏可以作为可控且可扩展的预文本任务,解锁MLLMs中的通用多模态推理能力。
Key Takeaways
- 认知科学文献表明游戏可以促进可迁移的认知技能发展。
- 提出了一种新型训练后范式——视觉游戏学习(ViGaL),通过玩类似街机游戏,促进MLLMs发展跨域的多模态推理能力。
- 强化学习(RL)训练可以提升MLLMs在多模态数学基准测试和多学科问题上的表现。
- 模型在掌握推理技能的过程中,并未接触解题解决方案、方程式或图表。
- 该模型在多模态推理基准测试中的表现优于专门训练的多模态推理模型。
- 该模型保持了基础模型在一般视觉基准测试中的性能,解决了专家模型常面临的难题。
点此查看论文截图


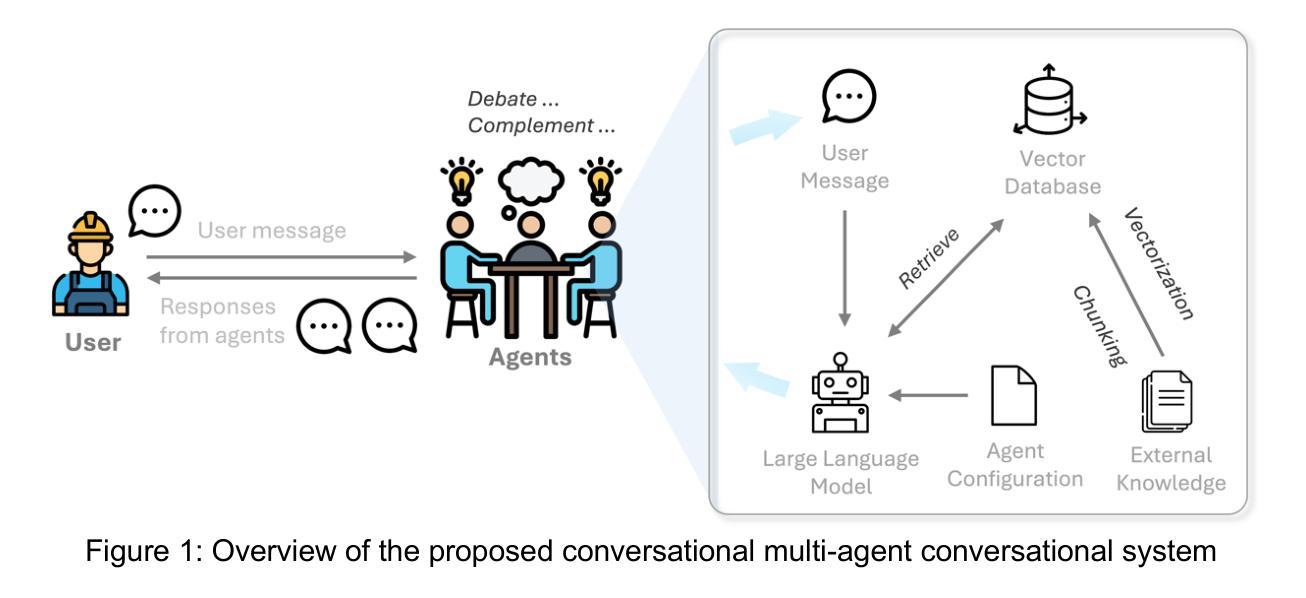
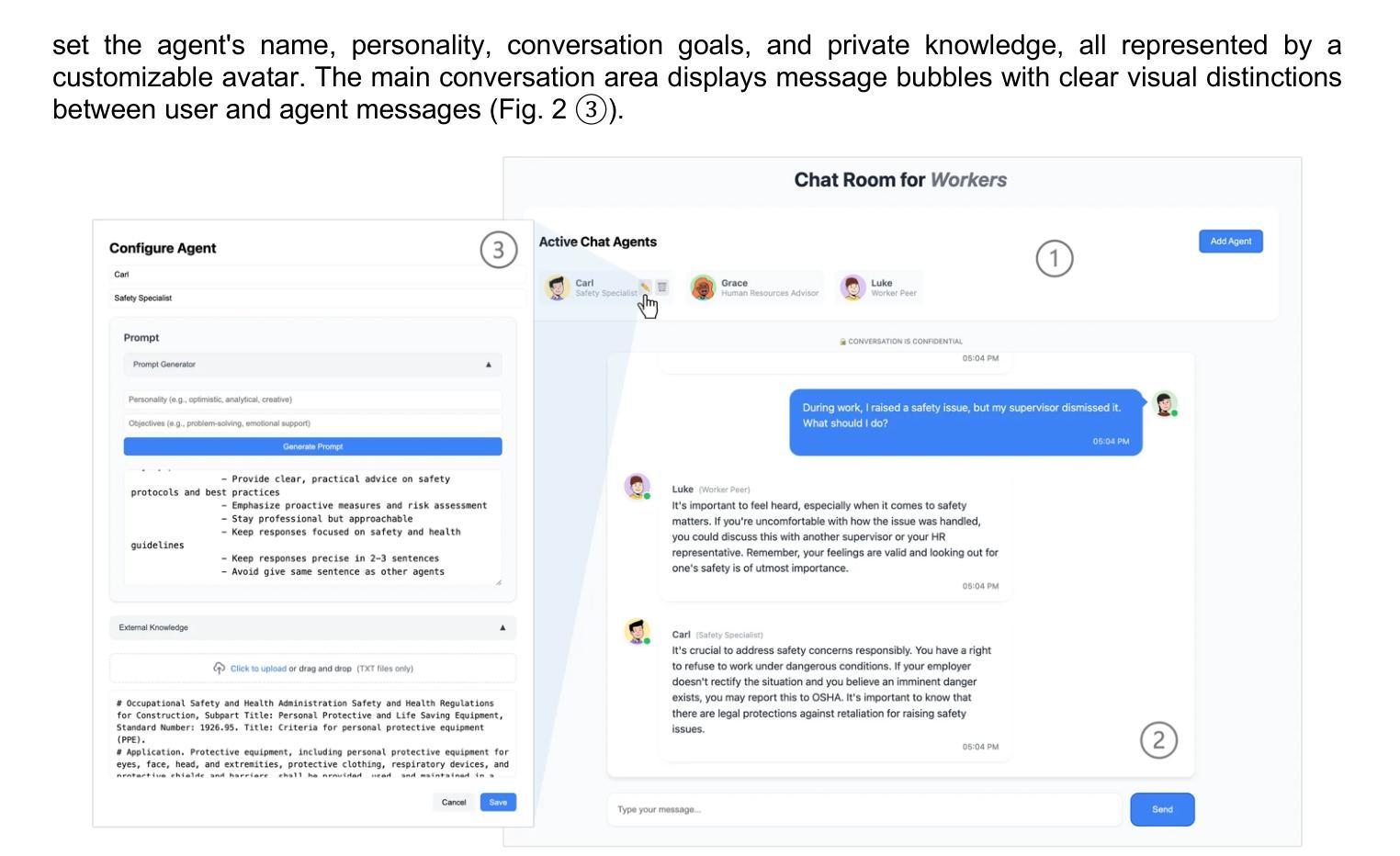
Supporting Construction Worker Well-Being with a Multi-Agent Conversational AI System
Authors:Fan Yang, Yuan Tian, Jiansong Zhang
The construction industry is characterized by both high physical and psychological risks, yet supports of mental health remain limited. While advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), particularly large language models (LLMs), offer promising solutions, their potential in construction remains largely underexplored. To bridge this gap, we developed a conversational multi-agent system that addresses industry-specific challenges through an AI-driven approach integrated with domain knowledge. In parallel, it fulfills construction workers’ basic psychological needs by enabling interactions with multiple agents, each has a distinct persona. This approach ensures that workers receive both practical problem-solving support and social engagement, ultimately contributing to their overall well-being. We evaluate its usability and effectiveness through a within-subjects user study with 12 participants. The results show that our system significantly outperforms the single-agent baseline, achieving improvements of 18% in usability, 40% in self-determination, 60% in social presence, and 60% in trust. These findings highlight the promise of LLM-driven AI systems in providing domain-specific support for construction workers.
建筑业的特点是既存在高物理风险又存在心理风险,但精神健康支持仍然有限。虽然人工智能(AI)取得了进展,特别是大型语言模型(LLM),提供了有希望的解决方案,但它们在建筑业中的潜力仍然被大大低估。为了弥补这一差距,我们开发了一个对话式多智能体系统,该系统通过集成人工智能和领域知识的方法来解决行业特定的挑战。同时,它通过使工人能够与多个智能体互动,满足施工工人的基本心理需求,每个智能体都具有独特的个性。这种方法确保工人不仅获得实际的解决问题的支持,还获得社交参与,最终为他们的整体福祉做出贡献。我们通过一项有12名参与者内部用户研究来评估其可用性和有效性。结果表明,我们的系统显著优于单智能体基线,在可用性方面提高了18%,在自主性方面提高了40%,在社会存在感方面提高了60%,在信任度方面提高了60%。这些发现突显了LLM驱动的人工智能系统在为建筑工人提供特定领域的支持方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
施工行业存在高风险,包括身体和心理风险,但心理健康支持仍然有限。人工智能(AI)和大语言模型(LLM)提供解决方案,但其潜力尚未得到充分了解。开发了一种基于AI的多代理系统,结合行业知识应对行业挑战并实现基本心理需求,实现施工工人的问题解块并提升其幸福感。评估表明系统具有良好的可用性并能显著提高工作效率和用户信任度。这些发现突出了LLM在支持建筑行业从业者方面潜力巨大。
Key Takeaways
- 施工行业存在高物理和心理风险,但心理健康支持有限。
- AI和大语言模型(LLM)为该行业提供潜在解决方案。
- 开发了一种基于AI的多代理系统,整合行业知识解决特定挑战。
- 系统支持施工工人的基本心理需求并实现社会交往。
- 系统通过用户研究进行评估,结果显示其显著提高了可用性和用户信任度。
点此查看论文截图

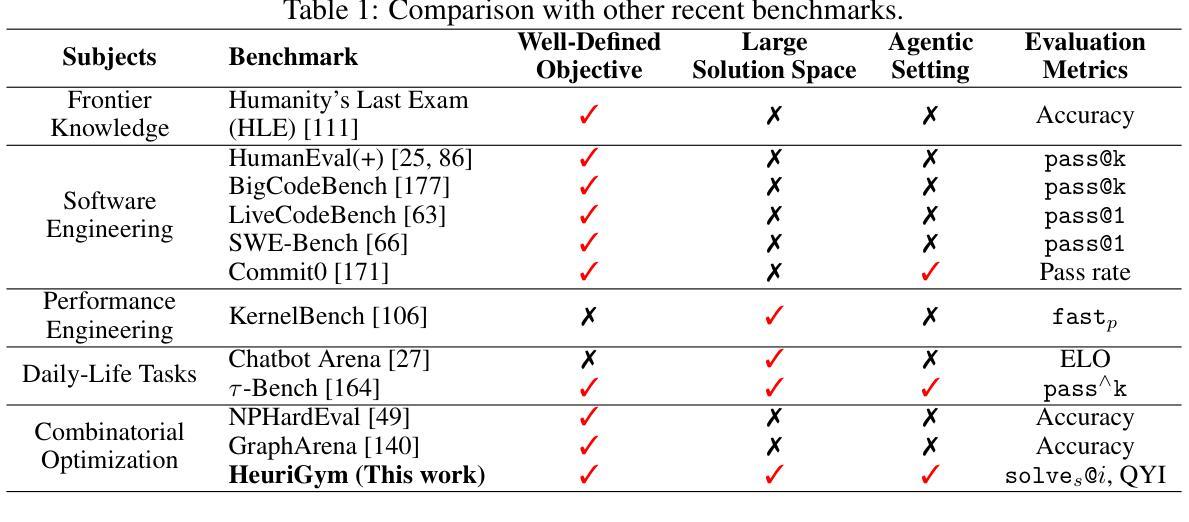
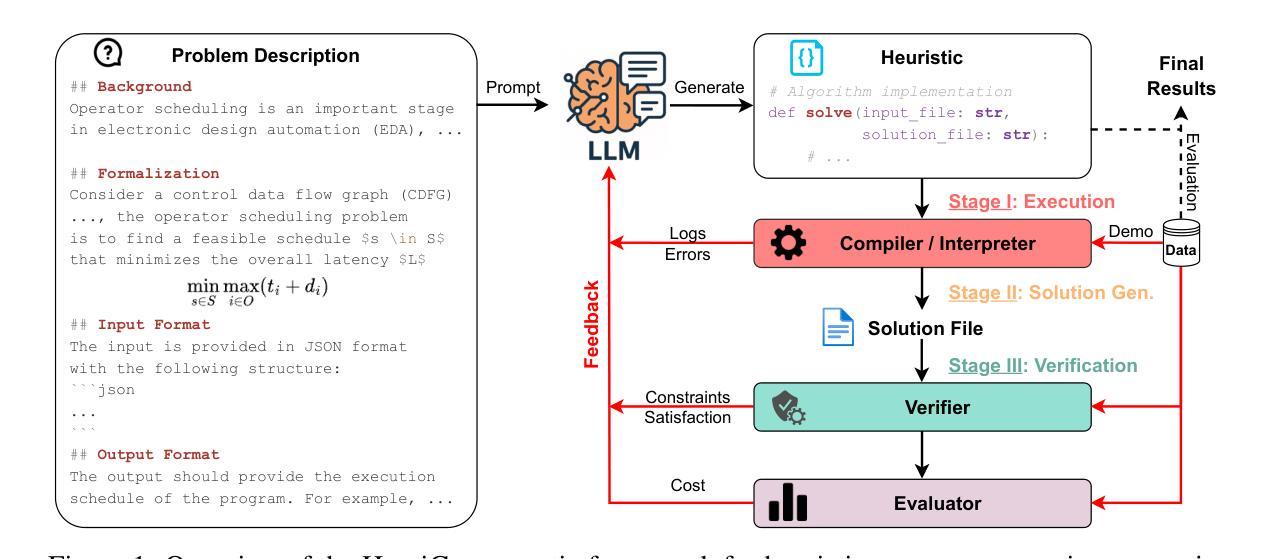
HeuriGym: An Agentic Benchmark for LLM-Crafted Heuristics in Combinatorial Optimization
Authors:Hongzheng Chen, Yingheng Wang, Yaohui Cai, Hins Hu, Jiajie Li, Shirley Huang, Chenhui Deng, Rongjian Liang, Shufeng Kong, Haoxing Ren, Samitha Samaranayake, Carla P. Gomes, Zhiru Zhang
While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant advancements in reasoning and agent-based problem-solving, current evaluation methodologies fail to adequately assess their capabilities: existing benchmarks either rely on closed-ended questions prone to saturation and memorization, or subjective comparisons that lack consistency and rigor. In this work, we introduce HeuriGym, an agentic framework designed for evaluating heuristic algorithms generated by LLMs for combinatorial optimization problems, characterized by clearly defined objectives and expansive solution spaces. HeuriGym empowers LLMs to propose heuristics, receive evaluative feedback via code execution, and iteratively refine their solutions. We evaluate nine state-of-the-art models on nine problems across domains such as computer systems, logistics, and biology, exposing persistent limitations in tool use, planning, and adaptive reasoning. To quantify performance, we propose the Quality-Yield Index (QYI), a metric that captures both solution pass rate and quality. Even top models like GPT-o4-mini-high and Gemini-2.5-Pro attain QYI scores of only 0.6, well below the expert baseline of 1. Our open-source benchmark aims to guide the development of LLMs toward more effective and realistic problem-solving in scientific and engineering domains.
大型语言模型(LLM)在推理和基于代理的问题解决方面取得了显著的进步,但现有的评估方法无法充分评估它们的能力:现有的基准测试要么依赖于封闭式问题,容易饱和和记忆,要么缺乏一致性和严谨性的主观比较。在这项工作中,我们介绍了HeuriGym,这是一个为LLM生成的启发式算法解决组合优化问题而设计的代理框架,其特点是目标明确、解决方案空间广阔。HeuriGym使LLM能够提出启发式方法,通过代码执行接收评估反馈,并迭代优化其解决方案。我们在计算机系统、物流和生物学等领域的九个问题上评估了九个最先进模型,暴露了工具使用、规划和自适应推理方面的持续局限性。为了量化性能,我们提出了质量收益指数(QYI),这是一个既能反映解决方案通过率又能反映解决方案质量的指标。即使是顶尖模型,如GPT-o4-mini-high和Gemini-2.5-Pro,其QYI得分也只有0.6,远低于专家基准线1。我们的开源基准测试旨在引导LLM的发展,以实现科学和工程领域更有效、更实际的问题解决。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型(LLM)在推理和基于代理的问题解决方面取得了显著进展,但现有评估方法无法充分评估其能力。本文介绍了一种名为HeuriGym的代理框架,用于评估LLM生成的组合优化问题的启发式算法。该框架明确了目标并扩大了解决方案空间,使LLM能够提出启发式策略、通过代码执行接收评估反馈并迭代优化解决方案。在跨计算机、物流和生物学等领域的九个问题上对九种最新模型进行了评估,暴露出工具使用、规划和自适应推理方面的持续局限性。为了量化性能,我们提出了质量收益指数(QYI),该指数同时捕捉解决方案的通过率和质量。即使是最先进的模型如GPT-o4-mini-high和Gemini-2.5-Pro的QYI得分也只有0.6,远低于专家基准线1。我们的开源基准测试旨在引导LLM的发展,以更有效地解决科学和工程领域的问题。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在推理和基于代理的问题解决上取得显著进展,但评估方法存在缺陷。
- 现有评估标准难以准确衡量LLM的能力,需引入新的评估框架。
- HeuriGym框架被设计用于评估LLM在组合优化问题上的启发式算法性能。
- HeuriGym有明确的目标和广泛的解决方案空间,支持LLM提出启发式策略并获得反馈。
- 在多个领域的问题评估中,LLM显示出工具使用、规划和自适应推理的局限性。
- 提出质量收益指数(QYI)作为评估LLM性能的量化指标,涵盖解决方案的通过率和质量。
点此查看论文截图

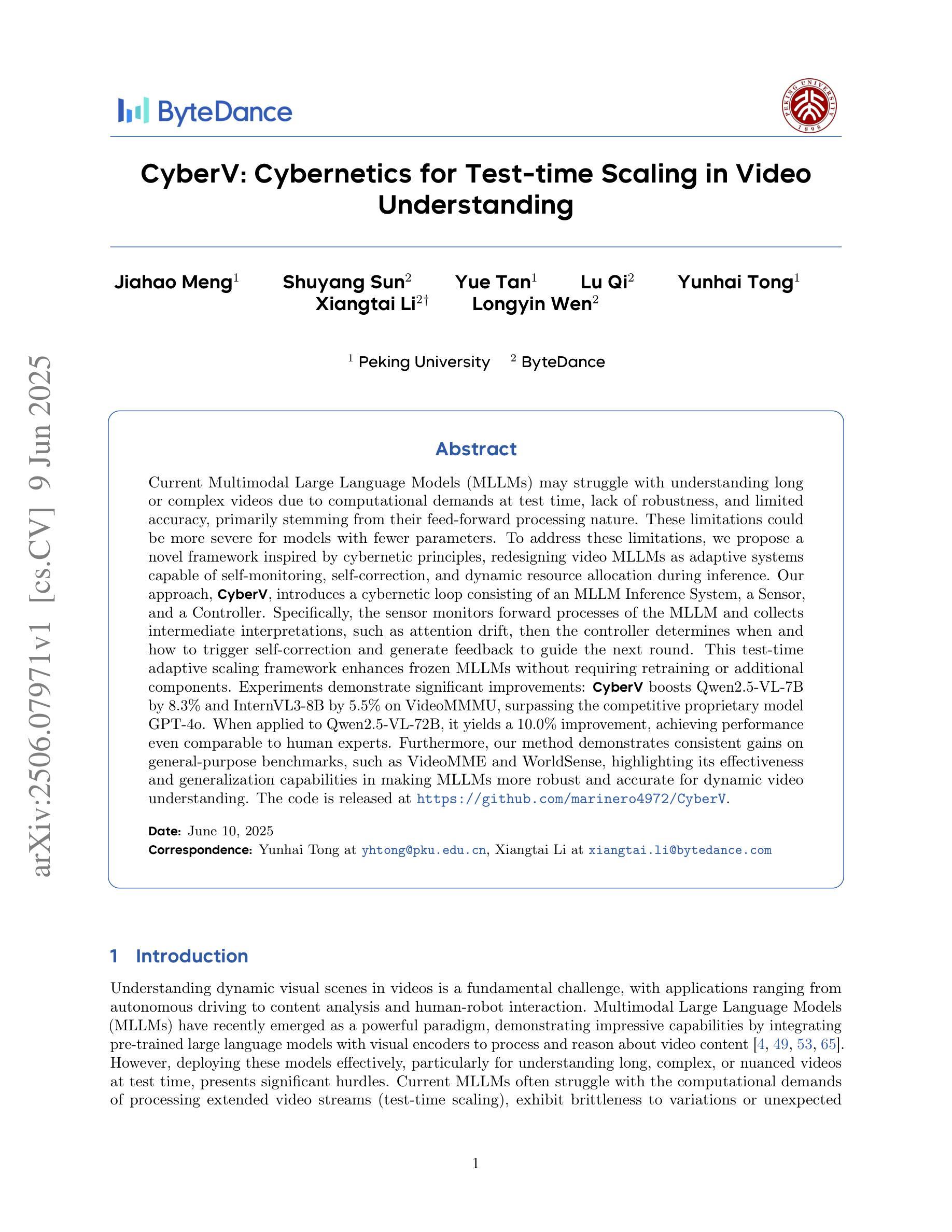
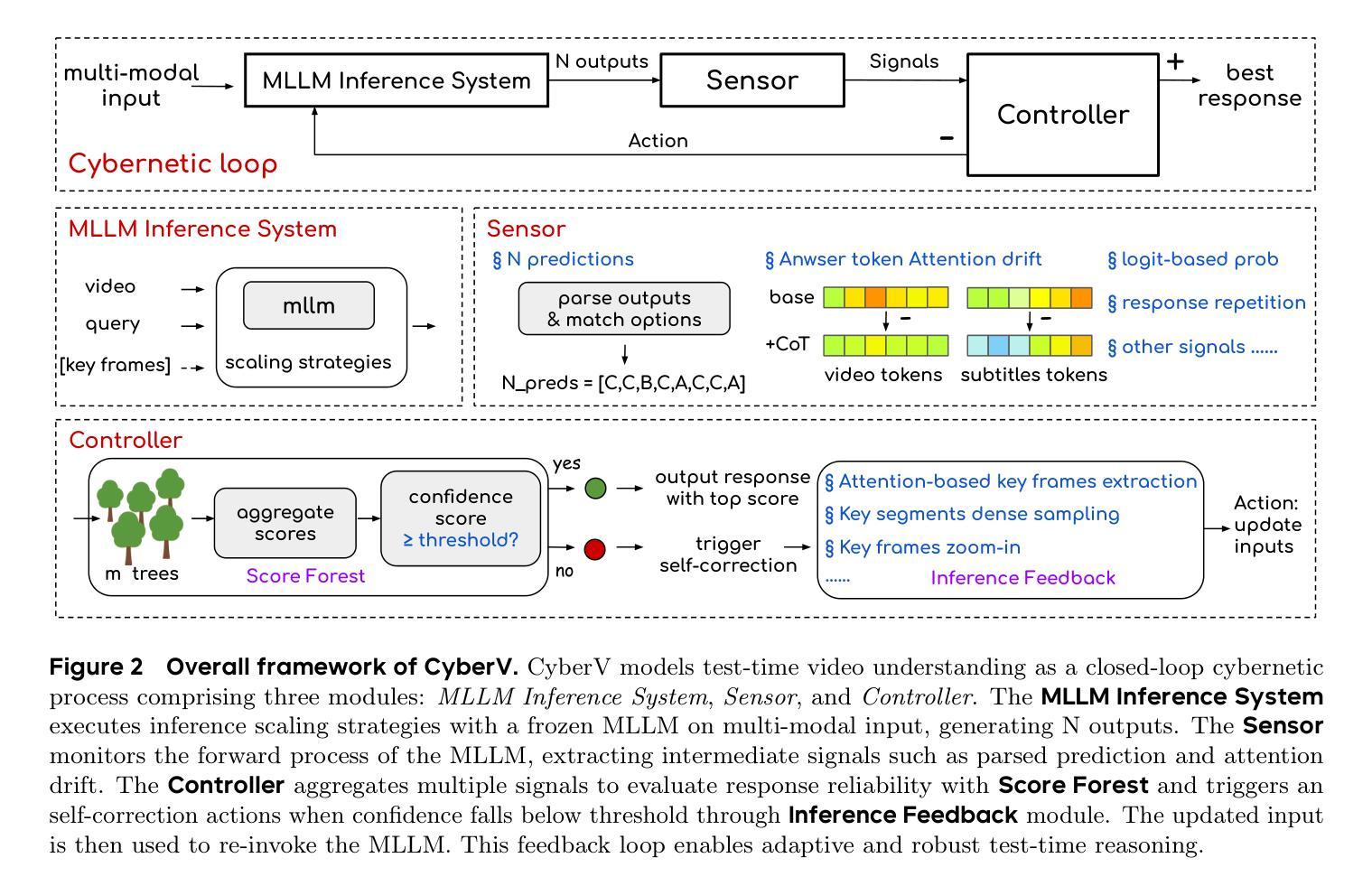
CyberV: Cybernetics for Test-time Scaling in Video Understanding
Authors:Jiahao Meng, Shuyang Sun, Yue Tan, Lu Qi, Yunhai Tong, Xiangtai Li, Longyin Wen
Current Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) may struggle with understanding long or complex videos due to computational demands at test time, lack of robustness, and limited accuracy, primarily stemming from their feed-forward processing nature. These limitations could be more severe for models with fewer parameters. To address these limitations, we propose a novel framework inspired by cybernetic principles, redesigning video MLLMs as adaptive systems capable of self-monitoring, self-correction, and dynamic resource allocation during inference. Our approach, CyberV, introduces a cybernetic loop consisting of an MLLM Inference System, a Sensor, and a Controller. Specifically, the sensor monitors forward processes of the MLLM and collects intermediate interpretations, such as attention drift, then the controller determines when and how to trigger self-correction and generate feedback to guide the next round. This test-time adaptive scaling framework enhances frozen MLLMs without requiring retraining or additional components. Experiments demonstrate significant improvements: CyberV boosts Qwen2.5-VL-7B by 8.3% and InternVL3-8B by 5.5% on VideoMMMU, surpassing the competitive proprietary model GPT-4o. When applied to Qwen2.5-VL-72B, it yields a 10.0% improvement, achieving performance even comparable to human experts. Furthermore, our method demonstrates consistent gains on general-purpose benchmarks, such as VideoMME and WorldSense, highlighting its effectiveness and generalization capabilities in making MLLMs more robust and accurate for dynamic video understanding. The code is released at https://github.com/marinero4972/CyberV.
当前的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)由于测试时的计算需求、缺乏稳健性以及准确性有限,可能难以理解和处理长或复杂的视频,这些限制主要源于其前馈处理性质。对于参数较少的模型,这些限制可能更加严重。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了一种受控制论启发的新型框架,重新设计视频MLLMs为自适应系统,具备自我监控、自我校正和动态资源分配的能力。我们的方法CyberV引入了一个控制回路,包括MLLM推理系统、传感器和控制器。具体而言,传感器监控MLLM的前向过程并收集中间解释,如注意力漂移,然后控制器确定何时以及如何触发自我校正并生成反馈来指导下一轮。这种测试时的自适应缩放框架增强了冻结的MLLMs的性能,而无需进行再训练或添加额外组件。实验表明有显著改进:CyberV在VideoMMMU上将Qwen2.5-VL-7B提升了8.3%,将InternVL3-8B提升了5.5%,超越了竞争性的专有模型GPT-4o。当应用于Qwen2.5-VL-7B时,它实现了10.0%的改进,性能甚至可与人类专家相当。此外,我们的方法在VideoMME和WorldSense等通用基准测试上表现出一致的收益,这突出了其在使MLLMs更健壮和准确地进行动态视频理解方面的有效性和通用性。代码已发布在https://github.com/marinero4972/CyberV。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于当前的多模态大型语言模型在处理长视频或复杂视频时面临的挑战,如计算需求大、稳健性不足和准确性有限等问题,文章提出了一种新型的框架——CyberV。该框架借鉴控制论原理,将视频多模态大型语言模型重新设计为自适应系统,具备自我监控、自我校正和动态资源分配的能力。通过引入一个包含MLLM推理系统、传感器和控制器的控制论循环,实现了测试时的自适应缩放。实验证明,CyberV在VideoMMMU等任务上显著提高模型性能,并且具备一般化能力,可应用于多个基准测试集。代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 当前的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在处理长或复杂视频时面临挑战,如计算需求大、稳健性不足和准确性问题。
- 这些问题主要由于模型的前馈处理性质以及参数数量和计算资源的限制。
- 提出的CyberV框架借鉴控制论原理,将MLLMs重新设计为自适应系统。
- CyberV框架包含MLLM推理系统、传感器和控制器,能够实现自我监控、自我校正和动态资源分配。
- 实验证明,CyberV显著提高了MLLMs在视频理解任务上的性能,包括VideoMMMU等特定任务。
- CyberV还展示了一致性的增益在一般目的的基准测试集上,如VideoMME和WorldSense。
点此查看论文截图
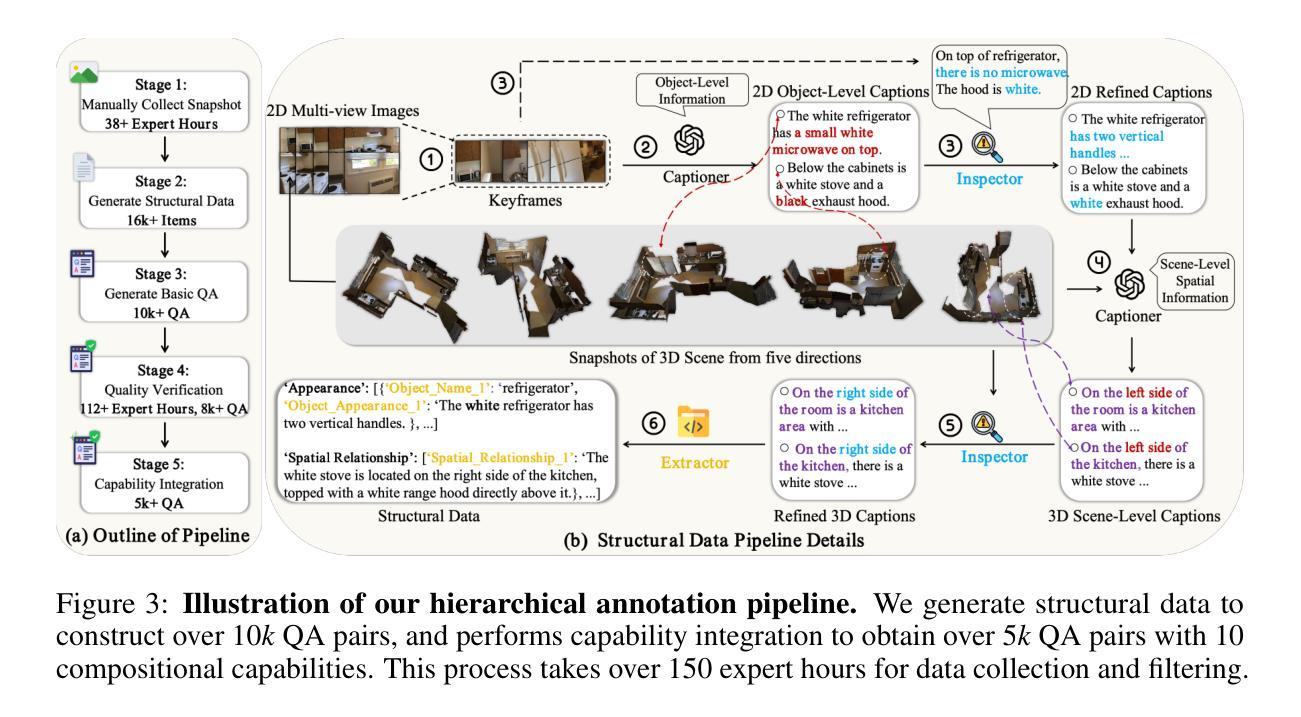
SpaCE-10: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Multimodal Large Language Models in Compositional Spatial Intelligence
Authors:Ziyang Gong, Wenhao Li, Oliver Ma, Songyuan Li, Jiayi Ji, Xue Yang, Gen Luo, Junchi Yan, Rongrong Ji
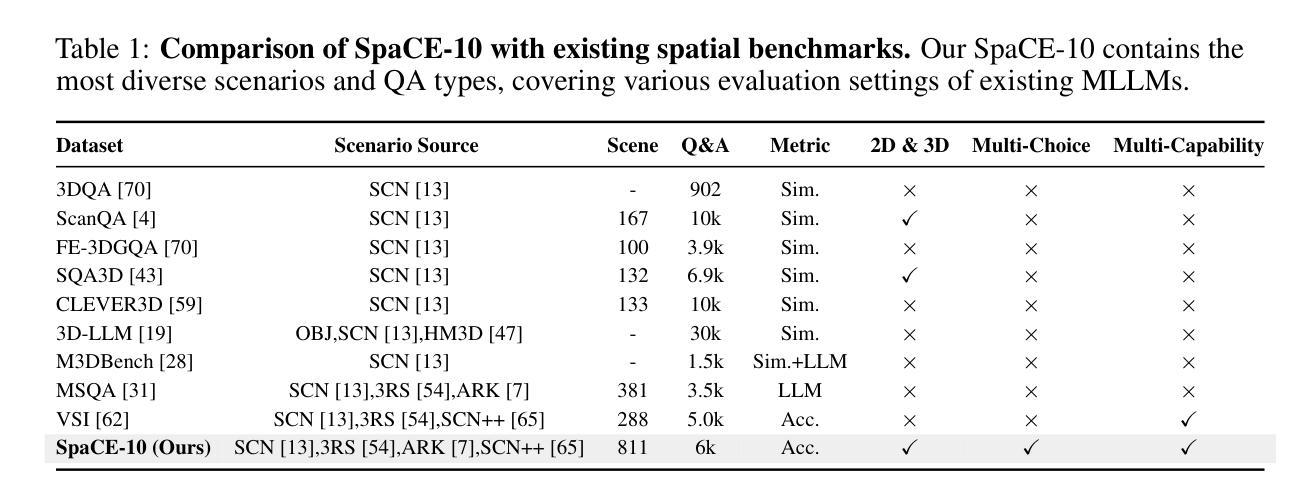
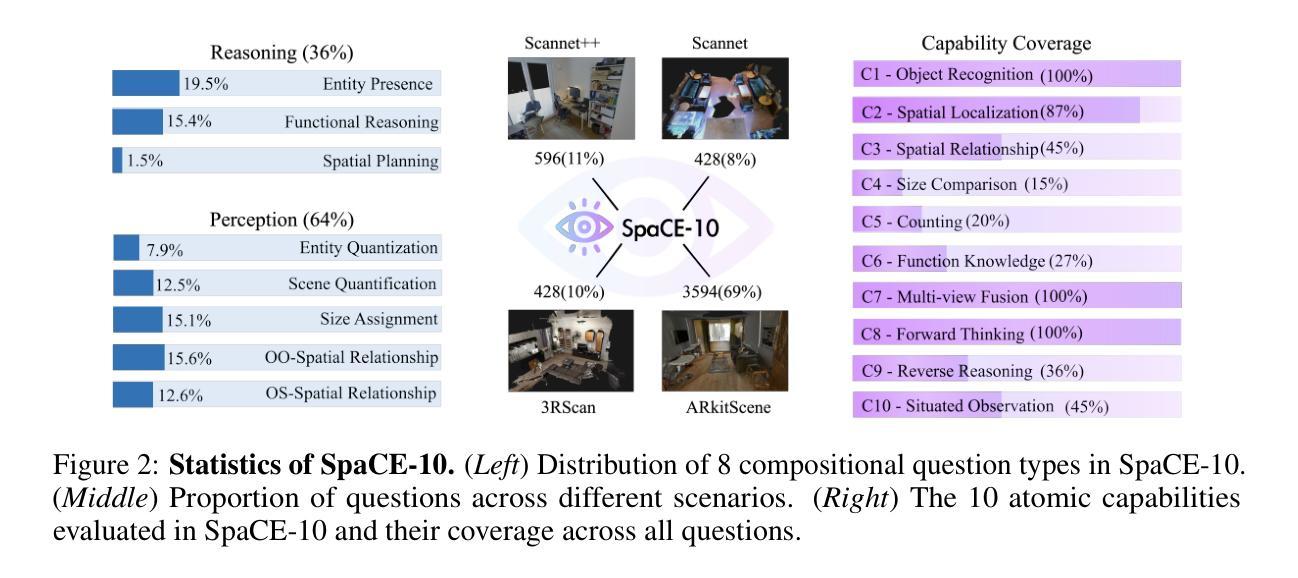
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in various multimodal tasks. To pursue higher intelligence in space, MLLMs require integrating multiple atomic spatial capabilities to handle complex and dynamic tasks. However, existing benchmarks struggle to comprehensively evaluate the spatial intelligence of common MLLMs from the atomic level to the compositional level. To fill this gap, we present SpaCE-10, a comprehensive benchmark for compositional spatial evaluations. In SpaCE-10, we define 10 atomic spatial capabilities, which are combined to form 8 compositional capabilities. Based on these definitions, we propose a novel hierarchical annotation pipeline to generate high-quality and diverse question-answer (QA) pairs. With over 150+ hours of human expert effort, we obtain over 5k QA pairs for 811 real indoor scenes in SpaCE-10, which covers various evaluation settings like point cloud input and multi-choice QA. We conduct an extensive evaluation of common MLLMs on SpaCE-10 and find that even the most advanced MLLM still lags behind humans by large margins. Through our careful study, we also draw several significant findings that benefit the MLLM community. For example, we reveal that the shortcoming of counting capability greatly limits the compositional spatial capabilities of existing MLLMs. The evaluation code and benchmark datasets are available at https://github.com/Cuzyoung/SpaCE-10.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在各种多模态任务中取得了显著的进步。为了追求更高的空间智能,MLLMs需要整合多种原子空间能力来处理复杂和动态的任务。然而,现有的基准测试在评估常见MLLMs的空间智能方面,从原子层面到组合层面都存在不足。为了填补这一空白,我们推出了SpaCE-10,这是一个用于组合空间评估的综合基准测试。在SpaCE-10中,我们定义了10种原子空间能力,它们相结合形成了8种组合能力。基于这些定义,我们提出了一个新的分层注释管道,以生成高质量和多样化的问答对。经过超过150小时的人力专家努力,我们在SpaCE-10中获得了超过5000个问答对,涉及811个真实的室内场景,涵盖了各种评估设置,如点云输入和多项选择问答。我们对常见的MLLMs在SpaCE-10上进行了广泛评估,发现即使是最先进的MLLM仍然远远落后于人类。通过我们的研究,我们还发现了几个对MLLM社区有益的重大发现。例如,我们揭示计数能力的不足极大地限制了现有MLLMs的组合空间能力。评估代码和基准数据集可在https://github.com/Cuzyoung/SpaCE-10获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
MLLMs在多模态任务中取得了显著进展,但仍需提高空间智能。为此,研究者提出了SpaCE-10基准测试,该测试包含10项原子空间能力和8项组合能力,以评估模型的空间智能。研究者通过新的分层注释管道生成了高质量的多样化问答对,并在超过5k个QA对上对常见MLLM进行了评估。发现最先进的MLLM仍然远远落后于人类。同时发现计数能力的不足极大地限制了现有MLLM的组合空间能力。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs在多模态任务中表现出色,但仍需提高空间智能。
- SpaCE-10是一个用于评估MLLMs空间智能的基准测试,包含原子和组合能力评估。
- SpaCE-10通过新的分层注释管道生成了高质量的多样化问答对。
- 最先进的MLLM在SpaCE-10上仍然远远落后于人类表现。
- 计数能力的不足是限制现有MLLM组合空间能力的主要因素。
- SpaCE-10提供了丰富的评价设置,如点云输入和多选问答。
点此查看论文截图
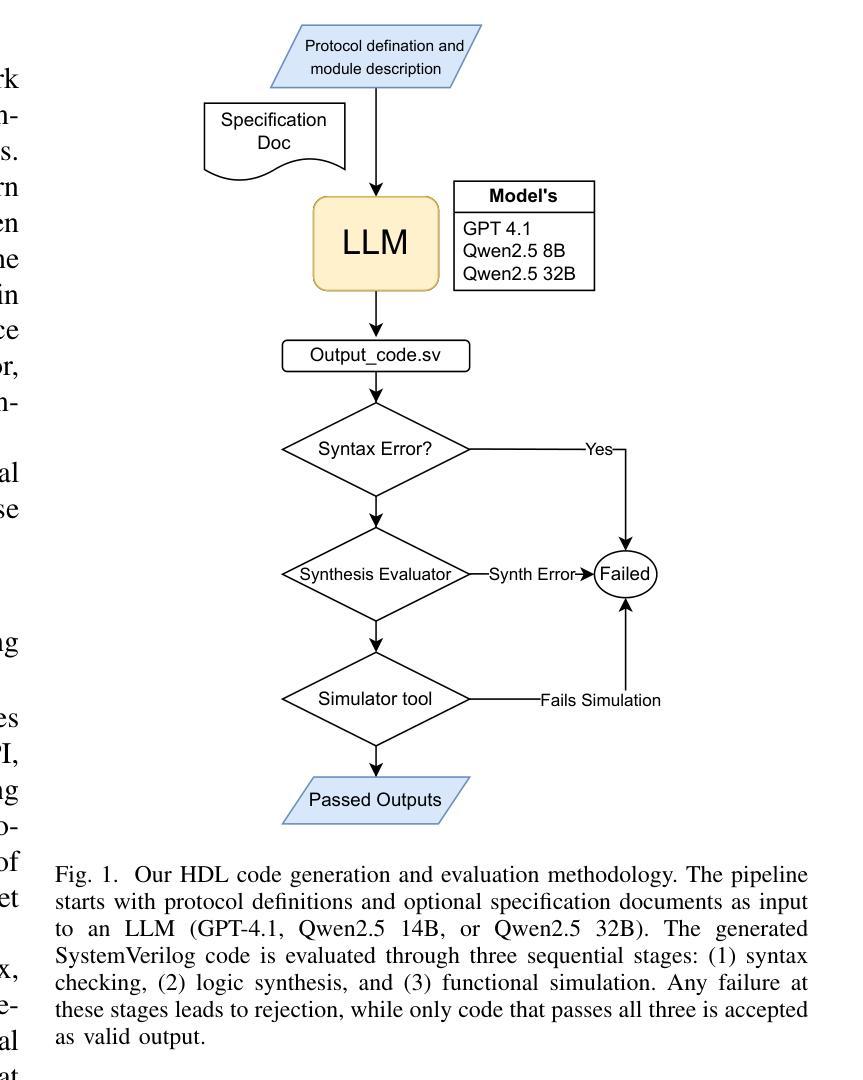
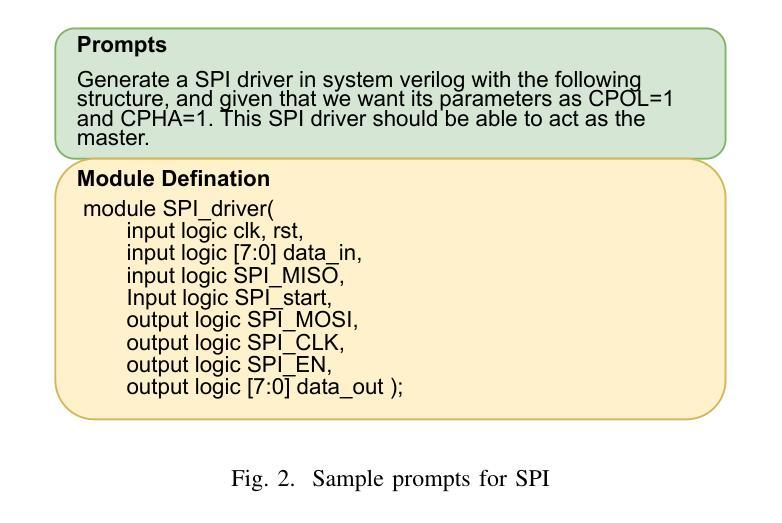
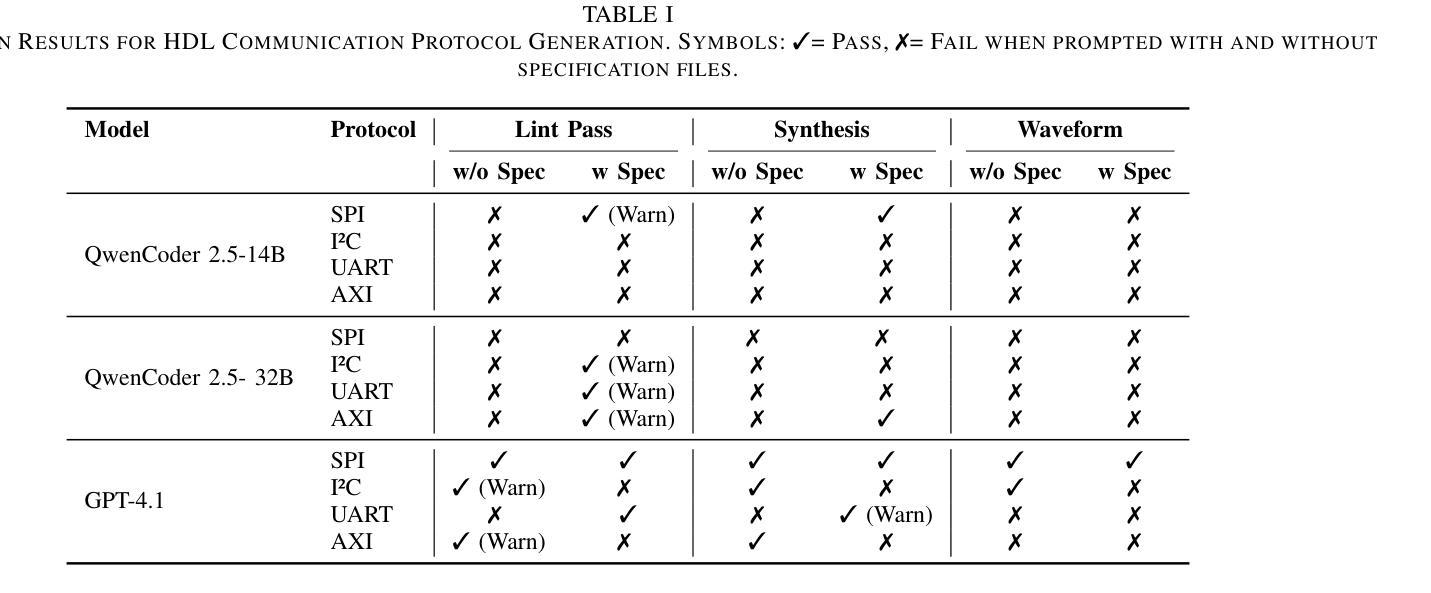
ProtocolLLM: RTL Benchmark for SystemVerilog Generation of Communication Protocols
Authors:Arnav Sheth, Ivaxi Sheth, Mario Fritz
Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promising capabilities in generating code for general-purpose programming languages. In contrast, their applicability for hardware description languages, particularly for generating synthesizable and functionally correct designs, remains significantly underexplored. HDLs such as SystemVerilog are logic-oriented and demand strict adherence to timing semantics, concurrency, and synthesizability constraints. Moreover, HDL-based design flows encompass a broad set of tasks beyond structural code generation, including testbench development, assertion-based verification, timing closure, and protocol-level integration for on-chip communication. The objective of our paper is to analyze the capabilities of state-of-the-art LLMs in generating SystemVerilog implementations of standard communication protocols, a core component of embedded and System-on-Chip (SoC) architectures. This paper introduces the first benchmark suite targeting four widely used protocols: SPI, I2C, UART, and AXI. We define code generation tasks that capture varying levels of design abstraction and prompt specificity. The generated designs are assessed for syntactic correctness, synthesizability, and functional fidelity via waveform simulation and test benches.
最近的大型语言模型(LLM)的进步显示出在生成通用编程语言代码方面的巨大潜力。然而,它们在硬件描述语言(特别是生成可合成和功能性正确的设计)方面的适用性仍然远远未被充分探索。SystemVerilog等硬件描述语言面向逻辑,需要严格遵循时序语义、并发性和可合成性约束。此外,基于HDL的设计流程涵盖了结构代码生成之外的一系列任务,包括测试平台开发、基于断言的验证、时序闭合和芯片上通信的协议级集成。我们论文的目标是分分析最新LLM在生成SystemVerilog实现标准通信协议方面的能力,这是嵌入式和片上系统(SoC)架构的核心组成部分。本文介绍了针对四个广泛使用协议的基准测试套件:SPI、I2C、UART和AXI。我们定义了捕捉不同设计抽象层次和特定提示的代码生成任务。通过波形仿真和测试平台评估所生成设计的语法正确性、可合成性和功能保真度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MLSysArch@ISCA 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在生成通用编程语言代码方面展现出良好能力,但在硬件描述语言(HDL),尤其是生成可合成和功能性正确的设计方面,其应用仍显著不足。本文旨在分析最新LLM在生成SystemVerilog实现的通信协议方面的能力,并引入针对SPI、I2C、UART和AXI四种广泛使用的协议的基准测试套件。通过波形仿真和测试平台,评估生成的设计的语法正确性、可合成性和功能保真性。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在硬件描述语言(HDL)如SystemVerilog的代码生成方面应用较少。
- HDLs需要严格遵循时序语义、并发性和可合成性约束。
- LLM生成SystemVerilog实现的通信协议是本文的重点。
- 引入针对SPI、I2C、UART和AXI四种通信协议的基准测试套件。
- 评估生成的设计的语法正确性、可合成性和功能保真性。
- LLM在生成不同抽象层次和具体性的设计代码方面有待进一步提高。
点此查看论文截图

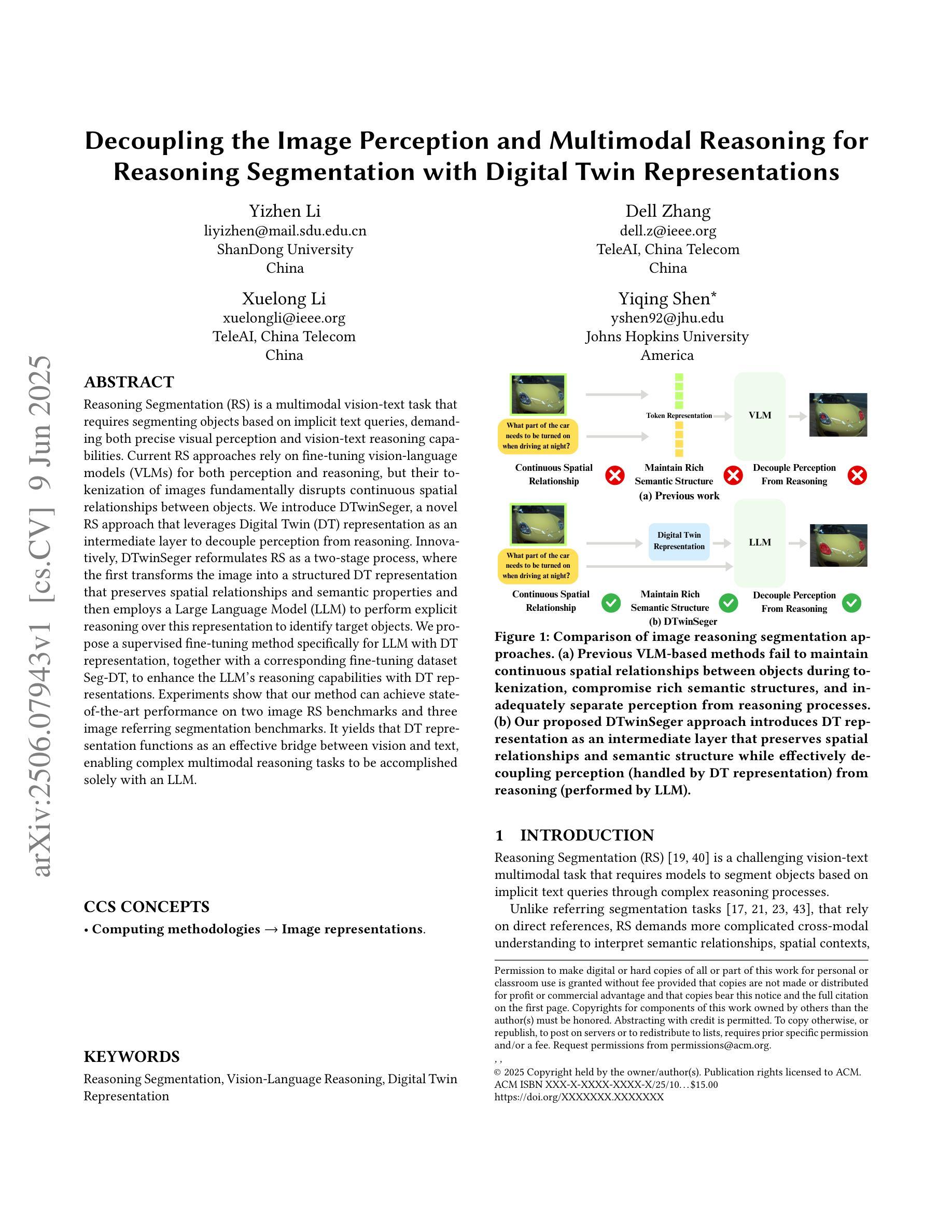
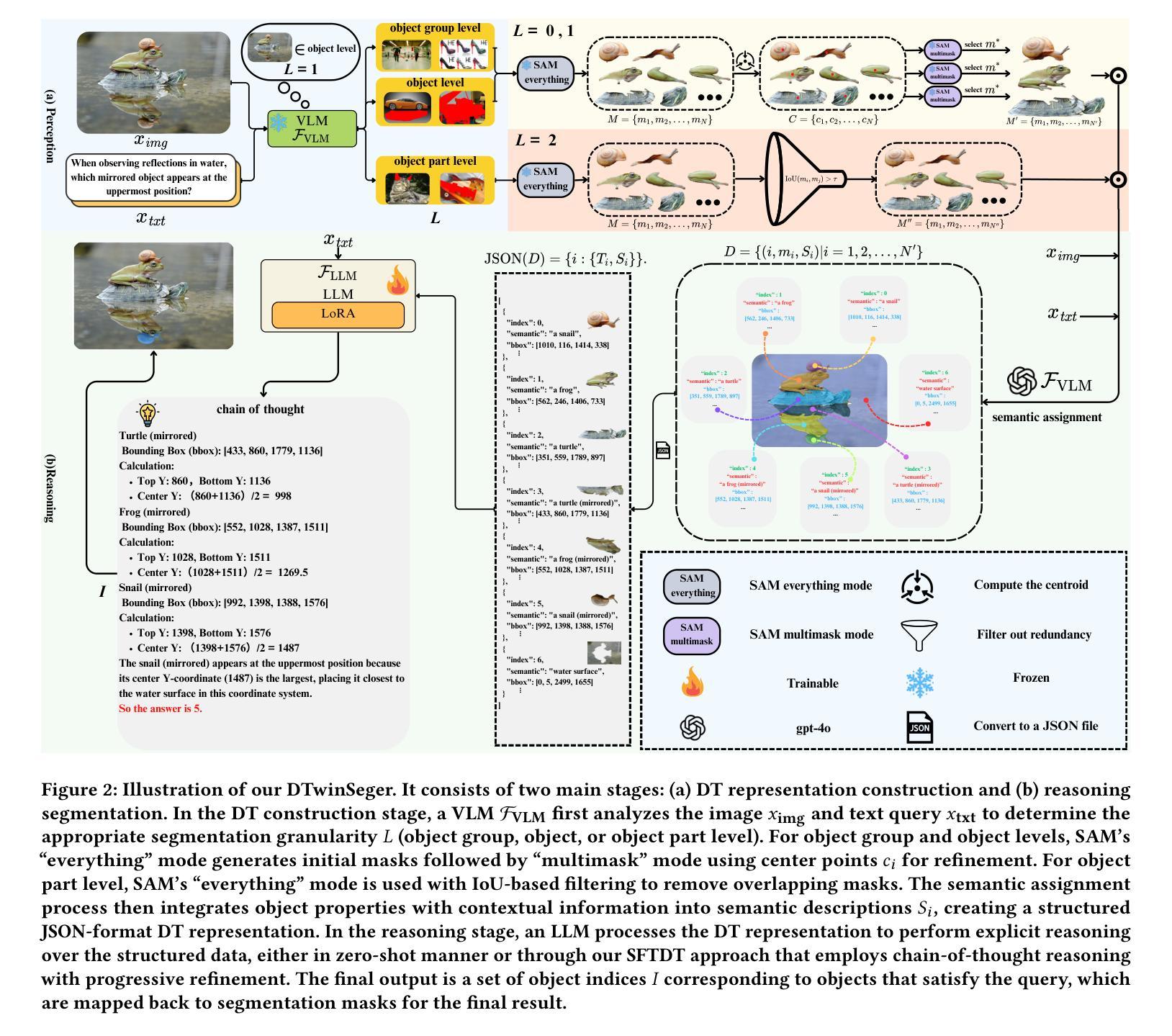
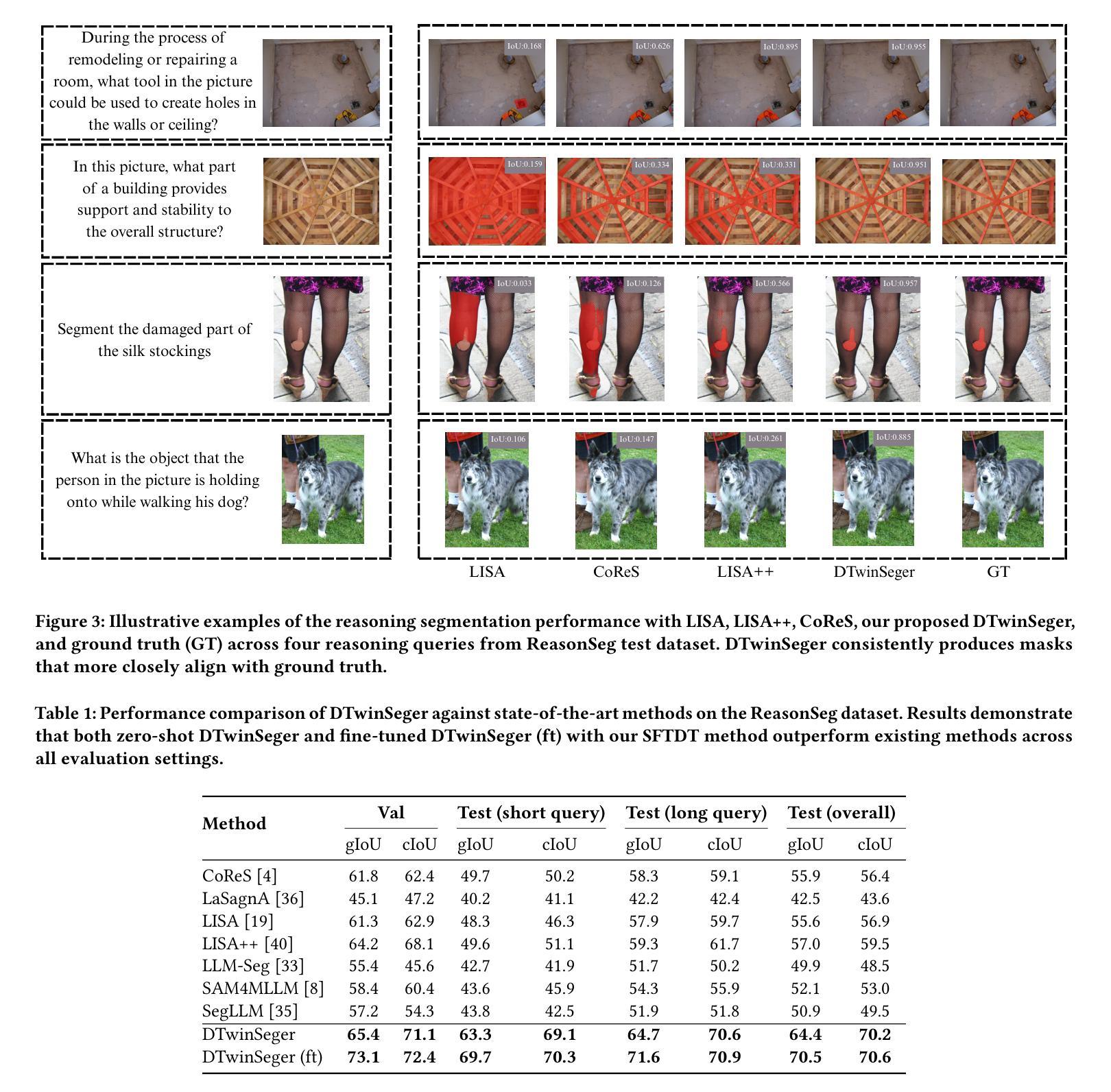
Decoupling the Image Perception and Multimodal Reasoning for Reasoning Segmentation with Digital Twin Representations
Authors:Yizhen Li, Dell Zhang, Xuelong Li, Yiqing Shen
Reasoning Segmentation (RS) is a multimodal vision-text task that requires segmenting objects based on implicit text queries, demanding both precise visual perception and vision-text reasoning capabilities. Current RS approaches rely on fine-tuning vision-language models (VLMs) for both perception and reasoning, but their tokenization of images fundamentally disrupts continuous spatial relationships between objects. We introduce DTwinSeger, a novel RS approach that leverages Digital Twin (DT) representation as an intermediate layer to decouple perception from reasoning. Innovatively, DTwinSeger reformulates RS as a two-stage process, where the first transforms the image into a structured DT representation that preserves spatial relationships and semantic properties and then employs a Large Language Model (LLM) to perform explicit reasoning over this representation to identify target objects. We propose a supervised fine-tuning method specifically for LLM with DT representation, together with a corresponding fine-tuning dataset Seg-DT, to enhance the LLM’s reasoning capabilities with DT representations. Experiments show that our method can achieve state-of-the-art performance on two image RS benchmarks and three image referring segmentation benchmarks. It yields that DT representation functions as an effective bridge between vision and text, enabling complex multimodal reasoning tasks to be accomplished solely with an LLM.
推理分割(RS)是一项多模态视觉文本任务,需要基于隐式文本查询对对象进行分割,要求具备精确的视觉感知和视觉文本推理能力。当前的RS方法依赖于对视觉语言模型(VLM)进行微调,以进行感知和推理,但它们的图像标记方式会破坏对象之间连续的时空关系。我们引入了DTwinSeger,这是一种新的RS方法,它利用数字孪生(DT)表示作为中间层,将感知与推理解耦。DTwinSeger创新地将RS重构为一个两阶段的过程,其中第一阶段将图像转换为结构化的DT表示,保留时空关系和语义属性,然后利用大型语言模型(LLM)对此表示进行明确的推理,以识别目标对象。我们提出了一种专门针对LLM的带有DT表示的监督微调方法,以及相应的微调数据集Seg-DT,以增强LLM对DT表示的推理能力。实验表明,我们的方法在两项图像RS基准测试和三项图像引用分割基准测试上均达到了最先进的性能。这表明DT表示作为视觉和文本之间的有效桥梁,能够仅使用LLM完成复杂的跨模态推理任务。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
RS(Reasoning Segmentation)是一项多模态视觉文本任务,需要基于隐式文本查询对物体进行分割,要求具备精确视觉感知和视觉文本推理能力。现有RS方法通过微调跨视觉语言模型(VLMs)实现感知和推理,但其对图像的符号化会破坏物体间的连续空间关系。本文提出一种新型RS方法DTwinSeger,利用数字孪生(DT)表示作为中间层,实现感知与推理的解耦。DTwinSeger将RS重新构建为两阶段过程,第一阶段将图像转换为结构化的DT表示,保留空间关系和语义属性;然后利用大型语言模型(LLM)在此表示上进行显式推理,以识别目标物体。本文还提出了一种针对LLM的基于DT表示的监督微调方法,并提供了相应的微调数据集Seg-DT,以增强LLM在DT表示方面的推理能力。实验表明,该方法在两项RS基准测试和三项图像引用分割基准测试上均达到最新技术水平。这表明DT表示是连接视觉和文本的有效桥梁,能够仅凭LLM完成复杂的跨模态推理任务。
Key Takeaways
- RS任务需要基于隐式文本查询进行物体分割,要求视觉感知和视觉文本推理能力兼备。
- 当前RS方法通过微调跨视觉语言模型(VLMs)实现感知和推理,但存在图像符号化导致的物体空间关系破坏问题。
- DTwinSeger方法利用数字孪生(DT)表示作为中间层来解耦感知与推理过程。
- DTwinSeger将RS任务划分为两阶段:图像转换至结构化DT表示,以及利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行显式推理。
- 提出了针对LLM的基于DT表示的监督微调方法和相应的微调数据集Seg-DT。
- 实验证明DTwinSeger方法在多项基准测试中达到最新技术水平。
点此查看论文截图
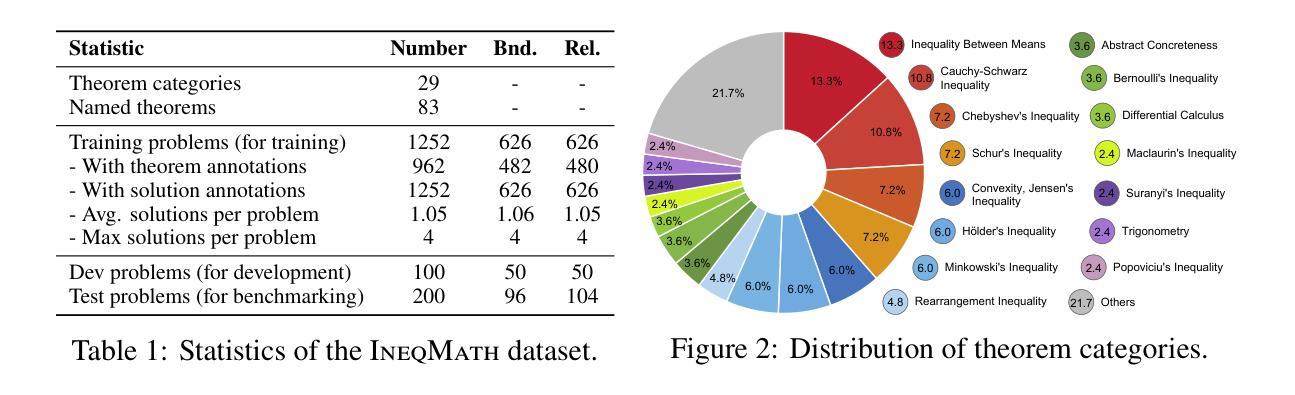
Solving Inequality Proofs with Large Language Models
Authors:Jiayi Sheng, Luna Lyu, Jikai Jin, Tony Xia, Alex Gu, James Zou, Pan Lu
Inequality proving, crucial across diverse scientific and mathematical fields, tests advanced reasoning skills such as discovering tight bounds and strategic theorem application. This makes it a distinct, demanding frontier for large language models (LLMs), offering insights beyond general mathematical problem-solving. Progress in this area is hampered by existing datasets that are often scarce, synthetic, or rigidly formal. We address this by proposing an informal yet verifiable task formulation, recasting inequality proving into two automatically checkable subtasks: bound estimation and relation prediction. Building on this, we release IneqMath, an expert-curated dataset of Olympiad-level inequalities, including a test set and training corpus enriched with step-wise solutions and theorem annotations. We also develop a novel LLM-as-judge evaluation framework, combining a final-answer judge with four step-wise judges designed to detect common reasoning flaws. A systematic evaluation of 29 leading LLMs on IneqMath reveals a surprising reality: even top models like o1 achieve less than 10% overall accuracy under step-wise scrutiny; this is a drop of up to 65.5% from their accuracy considering only final answer equivalence. This discrepancy exposes fragile deductive chains and a critical gap for current LLMs between merely finding an answer and constructing a rigorous proof. Scaling model size and increasing test-time computation yield limited gains in overall proof correctness. Instead, our findings highlight promising research directions such as theorem-guided reasoning and self-refinement. Code and data are available at https://ineqmath.github.io/.
在横跨多个科学和数学领域中,证明不等式对于高阶推理能力有着重要要求,例如发现紧密界限和策略性地应用定理。这使得它成为大型语言模型(LLM)的一个独特且具有挑战性的前沿领域,为一般数学问题解决提供了深刻的见解。现有数据集往往稀缺、合成或过于形式化,阻碍了这一领域的进展。我们通过提出一种非正式但可验证的任务制定来解决这个问题,将不等式证明重新定位为两个可自动检查的任务:界限估计和关系预测。在此基础上,我们发布了IneqMath数据集,这是一个专家策划的奥林匹克级别的不等式数据集,包括测试集和训练语料库,其中富含逐步解决方案和定理注释。我们还开发了一种新型LLM评估框架(LLM-as-judge),该框架结合了最终答案判断器和四个逐步判断器,旨在检测常见的推理缺陷。对IneqMath上29个领先的大型语言模型的系统评估揭示了一个令人惊讶的事实:即使在逐步审查下,即使是顶级模型如o1也仅达到不到百分之十的总体准确率;这与仅考虑最终答案等价的准确率相比下降了高达65.5%。这种差异暴露了脆弱的演绎链以及当前LLM在找到答案和构建严格证明之间的关键差距。扩大模型规模并增加测试时间的计算所带来的整体证明正确性的收益有限。相反,我们的研究结果突出了有前景的研究方向,如定理引导推理和自我完善。代码和数据可在https://ineqmath.github.io/获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 52 pages, 16 figures
Summary
本文介绍了不平等证明在科学和数学各领域的重要性,它测试了高级推理技能,如寻找紧密界限和战略定理应用。然而,现有的数据集常常稀缺、合成或过于形式化,阻碍了该领域的进展。因此,本文提出一种非正式但可验证的任务制定方式,将不平等证明转化为两个可自动检查的任务:界限估计和关系预测。此外,本文发布了由专家策划的包含奥赛级不等式的IneqMath数据集,其中包含了逐步解决方案和定理注释。文章还开发了一种新型的LLM评估框架,该框架结合最终答案评判和四个逐步评判,旨在检测常见的推理错误。对29款领先的LLM进行的系统评估显示,即使在逐步审查下,顶级模型如o1的整体准确率也不足10%,这一数字较仅考虑最终答案等价时的准确率下降了高达65.5%。这表明当前LLM在找到答案和构建严谨证明之间存在明显的差距。模型规模和测试时间计算的增加对提高整体证明的正确性贡献有限,反而突出了定理引导推理和自我完善等具有潜力的研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 不平等证明在科学和数学领域具有重要意义,测试高级推理技能。
- 现有数据集存在稀缺、合成或过于形式化的问题,影响了不平等证明领域的进展。
- 提出一种非正式但可验证的任务制定方式,将不平等证明转化为界限估计和关系预测两个子任务。
- 发布了IneqMath数据集,包含奥赛级不等式、逐步解决方案和定理注释。
- 开发了一种新型的LLM评估框架,结合最终答案评判和逐步评判,以检测推理错误。
- 系统评估显示顶级LLM在逐步审查下的整体准确率较低,表明在构建严谨证明方面存在差距。
点此查看论文截图

MiniCPM4: Ultra-Efficient LLMs on End Devices
Authors: MiniCPM Team, Chaojun Xiao, Yuxuan Li, Xu Han, Yuzhuo Bai, Jie Cai, Haotian Chen, Wentong Chen, Xin Cong, Ganqu Cui, Ning Ding, Shengdan Fan, Yewei Fang, Zixuan Fu, Wenyu Guan, Yitong Guan, Junshao Guo, Yufeng Han, Bingxiang He, Yuxiang Huang, Cunliang Kong, Qiuzuo Li, Siyuan Li, Wenhao Li, Yanghao Li, Yishan Li, Zhen Li, Dan Liu, Biyuan Lin, Yankai Lin, Xiang Long, Quanyu Lu, Yaxi Lu, Peiyan Luo, Hongya Lyu, Litu Ou, Yinxu Pan, Zekai Qu, Qundong Shi, Zijun Song, Jiayuan Su, Zhou Su, Ao Sun, Xianghui Sun, Peijun Tang, Fangzheng Wang, Feng Wang, Shuo Wang, Yudong Wang, Yesai Wu, Zhenyu Xiao, Jie Xie, Zihao Xie, Yukun Yan, Jiarui Yuan, Kaihuo Zhang, Lei Zhang, Linyue Zhang, Xueren Zhang, Yudi Zhang, Hengyu Zhao, Weilin Zhao, Weilun Zhao, Yuanqian Zhao, Zhi Zheng, Ge Zhou, Jie Zhou, Wei Zhou, Zihan Zhou, Zixuan Zhou, Zhiyuan Liu, Guoyang Zeng, Chao Jia, Dahai Li, Maosong Sun
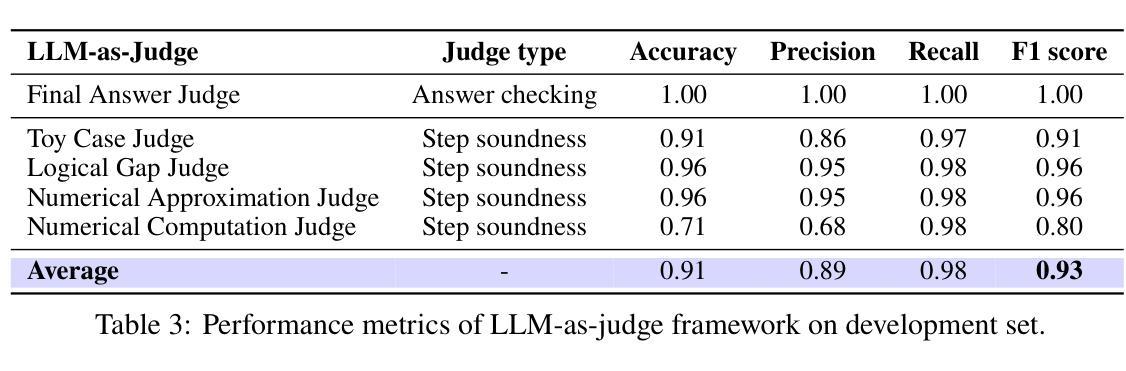
This paper introduces MiniCPM4, a highly efficient large language model (LLM) designed explicitly for end-side devices. We achieve this efficiency through systematic innovation in four key dimensions: model architecture, training data, training algorithms, and inference systems. Specifically, in terms of model architecture, we propose InfLLM v2, a trainable sparse attention mechanism that accelerates both prefilling and decoding phases for long-context processing. Regarding training data, we propose UltraClean, an efficient and accurate pre-training data filtering and generation strategy, and UltraChat v2, a comprehensive supervised fine-tuning dataset. These datasets enable satisfactory model performance to be achieved using just 8 trillion training tokens. Regarding training algorithms, we propose ModelTunnel v2 for efficient pre-training strategy search, and improve existing post-training methods by introducing chunk-wise rollout for load-balanced reinforcement learning and data-efficient tenary LLM, BitCPM. Regarding inference systems, we propose CPM.cu that integrates sparse attention, model quantization, and speculative sampling to achieve efficient prefilling and decoding. To meet diverse on-device requirements, MiniCPM4 is available in two versions, with 0.5B and 8B parameters, respectively. Sufficient evaluation results show that MiniCPM4 outperforms open-source models of similar size across multiple benchmarks, highlighting both its efficiency and effectiveness. Notably, MiniCPM4-8B demonstrates significant speed improvements over Qwen3-8B when processing long sequences. Through further adaptation, MiniCPM4 successfully powers diverse applications, including trustworthy survey generation and tool use with model context protocol, clearly showcasing its broad usability.
本文介绍了MiniCPM4,这是一款专门为终端侧设备设计的高效大型语言模型(LLM)。我们通过四个关键领域的系统性创新实现了这种高效性:模型架构、训练数据、训练算法和推理系统。具体来说,在模型架构方面,我们提出了InfLLM v2,这是一种可训练稀疏注意力机制,可以加速长上下文处理的预填充和解码阶段。在训练数据方面,我们提出了UltraClean,这是一种高效且准确的预训练数据过滤和生成策略,以及UltraChat v2,这是一个全面的监督微调数据集。这些数据集仅使用8万亿个训练令牌就实现了令人满意的模型性能。在训练算法方面,我们提出了ModelTunnel v2进行高效的预训练策略搜索,并通过引入分块滚动负载平衡的强化学习和数据高效三元LLM BitCPM来改进现有的后训练方法。在推理系统方面,我们提出了CPM.cu,它集成了稀疏注意力、模型量化和投机采样,以实现高效的预填充和解码。为了满足不同的设备需求,MiniCPM4提供两个版本,分别为0.5B和8B参数。充足的评估结果表明,MiniCPM4在多个基准测试中优于相似规模的开源模型,凸显了其高效性和有效性。值得注意的是,在处理长序列时,MiniCPM4-8B相较于Qwen3-8B表现出显著的速度提升。通过进一步的适应,MiniCPM4成功应用于多种应用程序,包括可信调查生成和使用模型上下文协议的工具,充分展示了其广泛的可用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MiniCPM4 Technical Report
摘要
本文介绍了专为端侧设备设计的高效大型语言模型MiniCPM4。通过模型架构、训练数据、训练算法和推理系统四个方面的系统性创新,实现了高效率。模型架构方面,提出了InfLLM v2,一种可训练稀疏注意力机制,可加速长上下文处理的预填充和解码阶段。训练数据方面,提出了UltraClean和UltraChat v2,分别用于有效的预训练数据过滤生成策略和全面的监督微调数据集。训练算法方面,通过ModelTunnel v2进行高效预训练策略搜索,引入分块滚动改进负载平衡强化学习和数据高效三元LLM BitCPM。推理系统方面,提出整合稀疏注意力、模型量化和投机采样的CPM.cu,以实现高效预填充和解码。MiniCPM4有两种版本,参数分别为0.5B和8B,以满足不同的设备需求。评估结果表明,MiniCPM4在多个基准测试中优于相似规模的开源模型,突显其高效性和有效性。特别是MiniCPM4-8B在处理长序列时显示出显著的速度改进。此外,通过进一步适应,MiniCPM4成功应用于可信调查生成和工具使用等应用程序,显示了其广泛的可用性。
关键见解
- MiniCPM4是一个为端侧设备设计的高效大型语言模型(LLM)。
- 通过在模型架构、训练数据、训练算法和推理系统四个方面的创新实现高效率。
- 提出了InfLLM v2的可训练稀疏注意力机制,加速长上下文处理。
- 通过UltraClean策略进行预训练数据过滤和生成,提高模型效率。
- 引入ModelTunnel v2进行高效预训练策略搜索,并改进了训练算法。
- 推出了集成多种技术的推理系统CPM.cu,实现高效预填充和解码。
点此查看论文截图
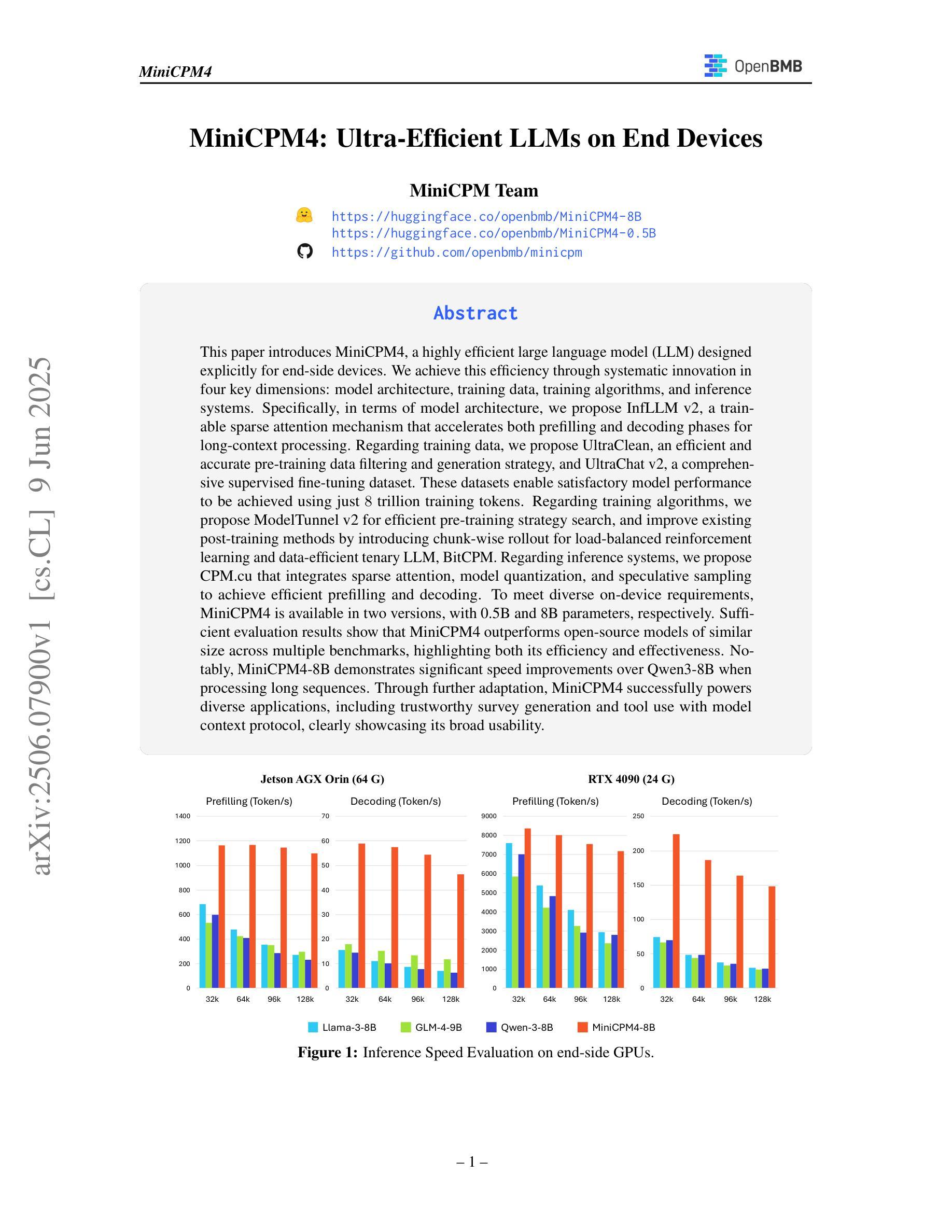
MEMOIR: Lifelong Model Editing with Minimal Overwrite and Informed Retention for LLMs
Authors:Ke Wang, Yiming Qin, Nikolaos Dimitriadis, Alessandro Favero, Pascal Frossard
Language models deployed in real-world systems often require post-hoc updates to incorporate new or corrected knowledge. However, editing such models efficiently and reliably - without retraining or forgetting previous information - remains a major challenge. Existing methods for lifelong model editing either compromise generalization, interfere with past edits, or fail to scale to long editing sequences. We propose MEMOIR, a novel scalable framework that injects knowledge through a residual memory, i.e., a dedicated parameter module, while preserving the core capabilities of the pre-trained model. By sparsifying input activations through sample-dependent masks, MEMOIR confines each edit to a distinct subset of the memory parameters, minimizing interference among edits. At inference, it identifies relevant edits by comparing the sparse activation patterns of new queries to those stored during editing. This enables generalization to rephrased queries by activating only the relevant knowledge while suppressing unnecessary memory activation for unrelated prompts. Experiments on question answering, hallucination correction, and out-of-distribution generalization benchmarks across LLaMA-3 and Mistral demonstrate that MEMOIR achieves state-of-the-art performance across reliability, generalization, and locality metrics, scaling to thousands of sequential edits with minimal forgetting.
在现实世界中部署的语言模型通常需要后续更新来融入新的或修正的知识。然而,在不进行再训练或遗忘先前信息的情况下,高效且可靠地编辑此类模型仍然是一个主要挑战。现有的终身模型编辑方法要么损害泛化能力,要么干扰过去的编辑,要么无法扩展到长的编辑序列。我们提出了MEMOIR,这是一种新型的可扩展框架,它通过残留记忆(即专用参数模块)注入知识,同时保留预训练模型的核心能力。MEMOIR通过样本相关掩码对输入激活进行稀疏化,将每个编辑限制在内存参数的一个独特子集中,最小化编辑之间的干扰。在推理过程中,它通过比较新查询的稀疏激活模式与编辑过程中存储的模式来识别相关的编辑。这允许对重新表述的查询进行泛化,仅激活相关知识,同时抑制不必要记忆激活以应对不相关的提示。在LLaMA-3和Mistral上的问答、幻觉校正和超出分布泛化基准测试的实验表明,MEMOIR在可靠性、泛化和局部性指标方面达到了最新水平,可扩展到数以千计的连续编辑且几乎不会遗忘信息。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first two authors contributed equally to this work
Summary
本文介绍了语言模型在真实系统应用中面临的问题,即需要事后更新以融入新的或修正的知识。然而,如何在不重新训练或遗忘旧信息的情况下高效可靠地编辑这些模型是一大挑战。为此,本文提出了一种新型的可扩展框架MEMOIR,它通过残余内存(即专用参数模块)注入知识,同时保留预训练模型的核心功能。MEMOIR通过样本相关掩码对输入激活进行稀疏化,将每次编辑限制在内存参数的一个特定子集上,从而最小化编辑之间的干扰。在推理过程中,它通过比较新查询的稀疏激活模式与编辑期间存储的模式来识别相关的编辑。实验表明,MEMOIR在可靠性、泛化和局部度量方面达到了领先水平,能够扩展到数千个连续编辑而几乎不遗忘。
Key Takeaways
- 语言模型需要事后更新以融入新或修正的知识。
- 现有模型编辑方法存在效率、可靠性和泛化能力的问题。
- MEMOIR框架通过残余内存注入知识,保留预训练模型的核心功能。
- MEMOIR通过稀疏化输入激活来限制每次编辑的范围,减少编辑间的干扰。
- MEMOIR通过比较查询的激活模式与存储的模式来识别相关编辑。
- MEMOIR在多个基准测试中表现出卓越性能,包括问答、幻觉修正和分布外泛化。
点此查看论文截图


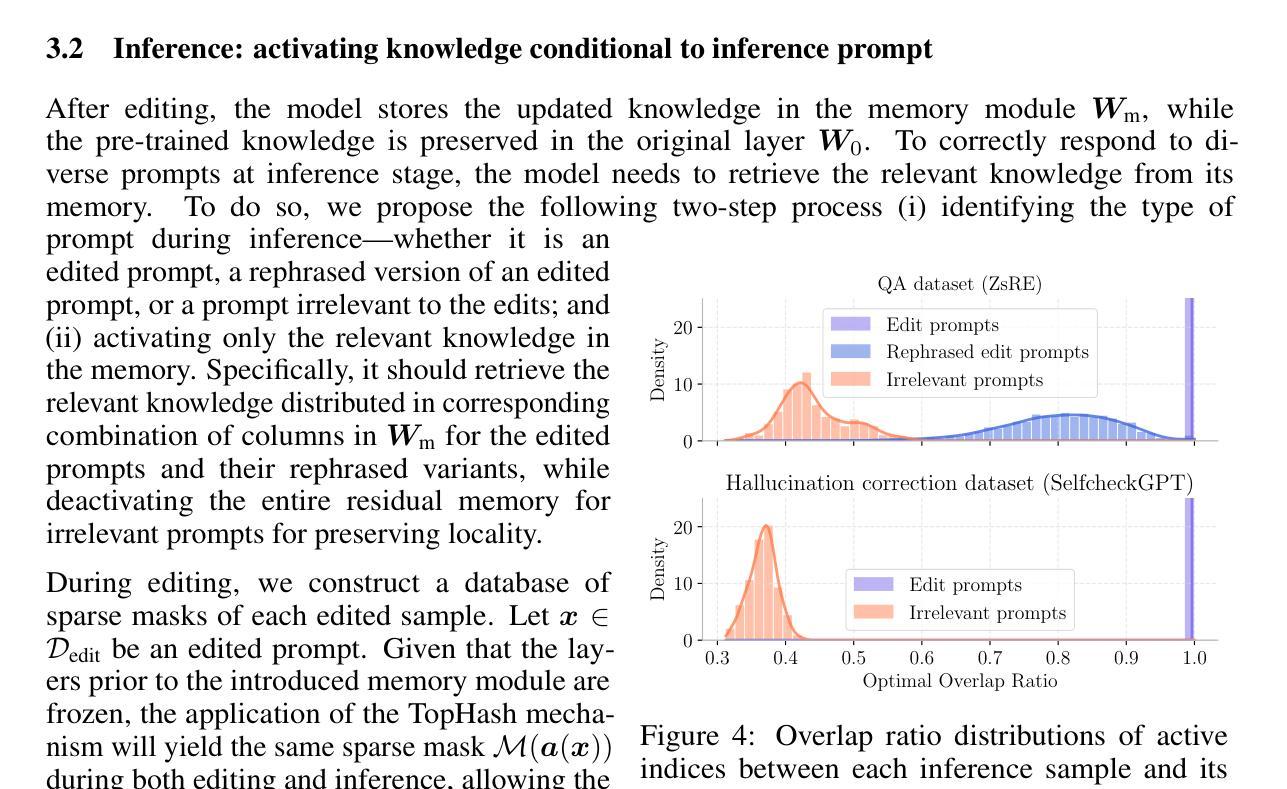
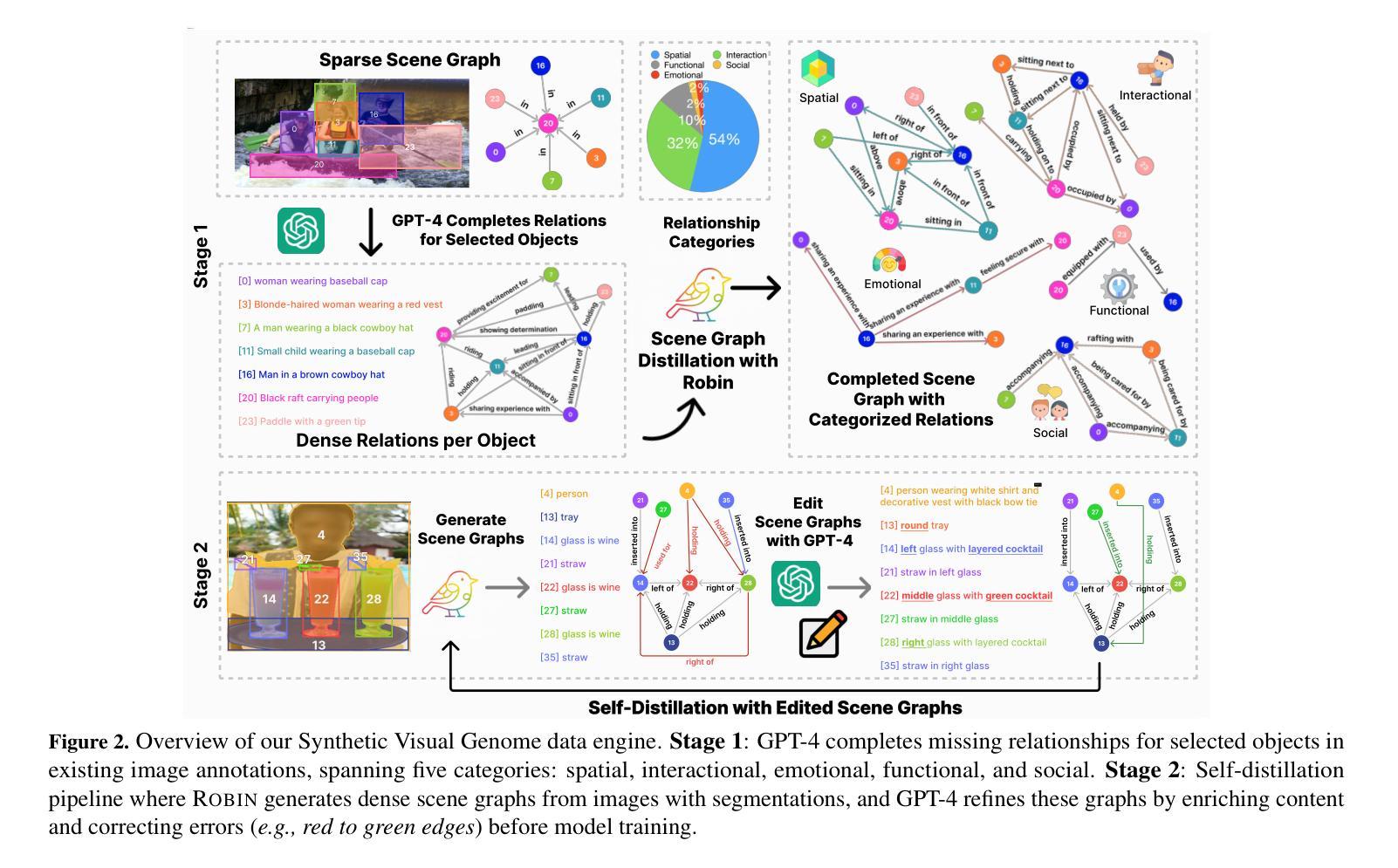
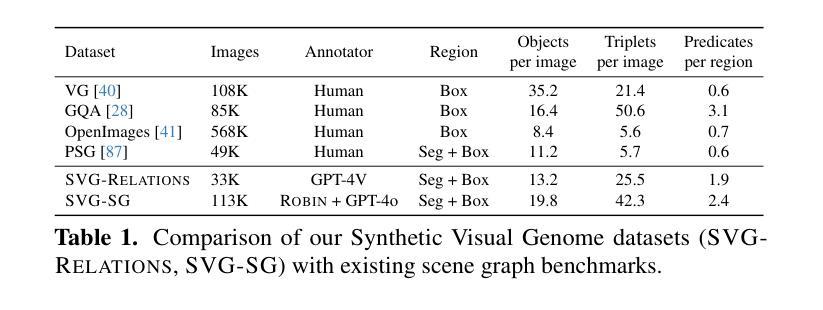
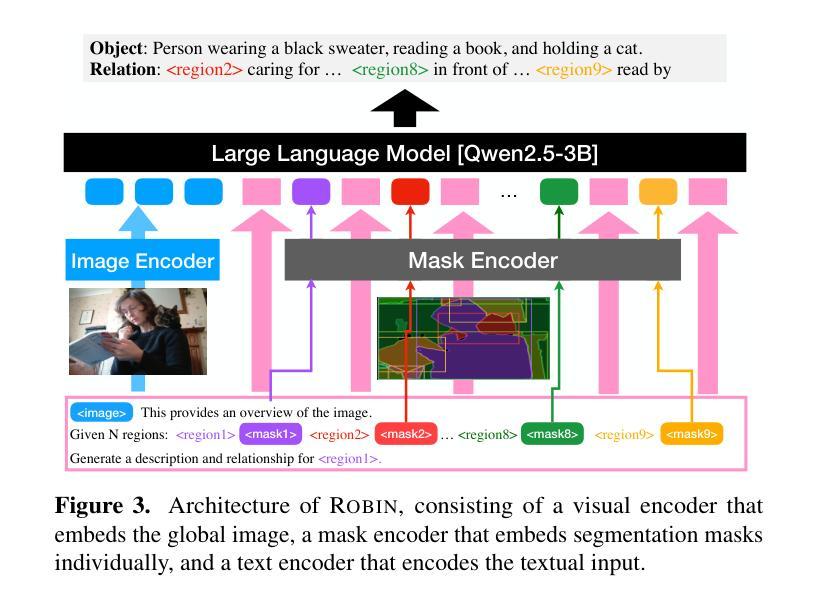
Synthetic Visual Genome
Authors:Jae Sung Park, Zixian Ma, Linjie Li, Chenhao Zheng, Cheng-Yu Hsieh, Ximing Lu, Khyathi Chandu, Quan Kong, Norimasa Kobori, Ali Farhadi, Yejin Choi, Ranjay Krishna
Reasoning over visual relationships-spatial, functional, interactional, social, etc.-is considered to be a fundamental component of human cognition. Yet, despite the major advances in visual comprehension in multimodal language models (MLMs), precise reasoning over relationships and their generations remains a challenge. We introduce ROBIN: an MLM instruction-tuned with densely annotated relationships capable of constructing high-quality dense scene graphs at scale. To train ROBIN, we curate SVG, a synthetic scene graph dataset by completing the missing relations of selected objects in existing scene graphs using a teacher MLM and a carefully designed filtering process to ensure high-quality. To generate more accurate and rich scene graphs at scale for any image, we introduce SG-EDIT: a self-distillation framework where GPT-4o further refines ROBIN’s predicted scene graphs by removing unlikely relations and/or suggesting relevant ones. In total, our dataset contains 146K images and 5.6M relationships for 2.6M objects. Results show that our ROBIN-3B model, despite being trained on less than 3 million instances, outperforms similar-size models trained on over 300 million instances on relationship understanding benchmarks, and even surpasses larger models up to 13B parameters. Notably, it achieves state-of-the-art performance in referring expression comprehension with a score of 88.9, surpassing the previous best of 87.4. Our results suggest that training on the refined scene graph data is crucial to maintaining high performance across diverse visual reasoning task.
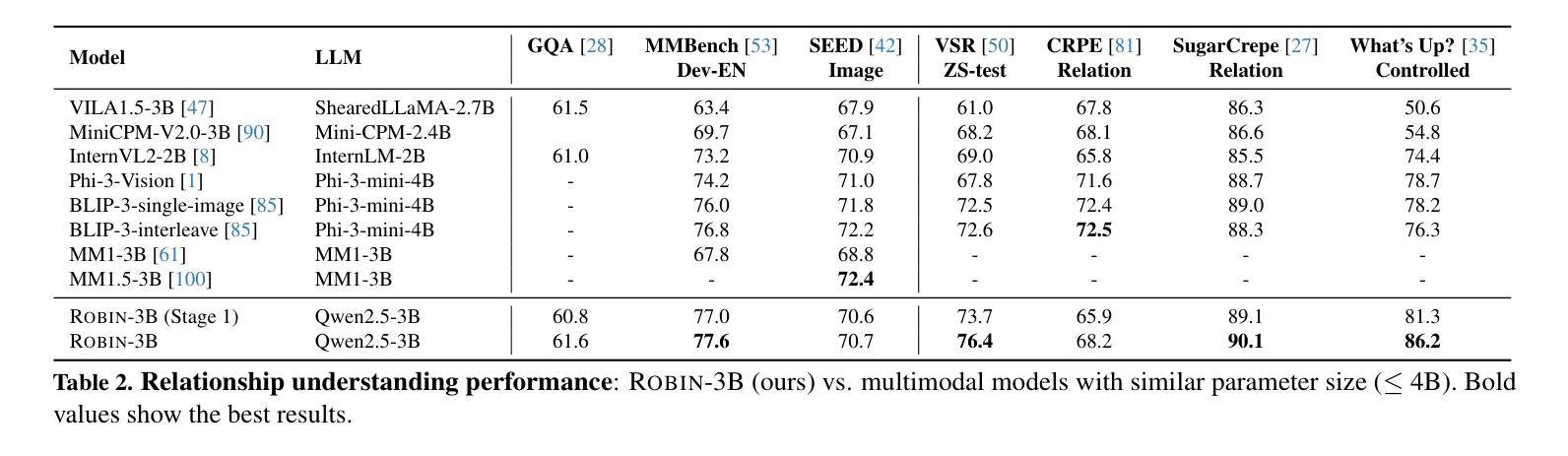
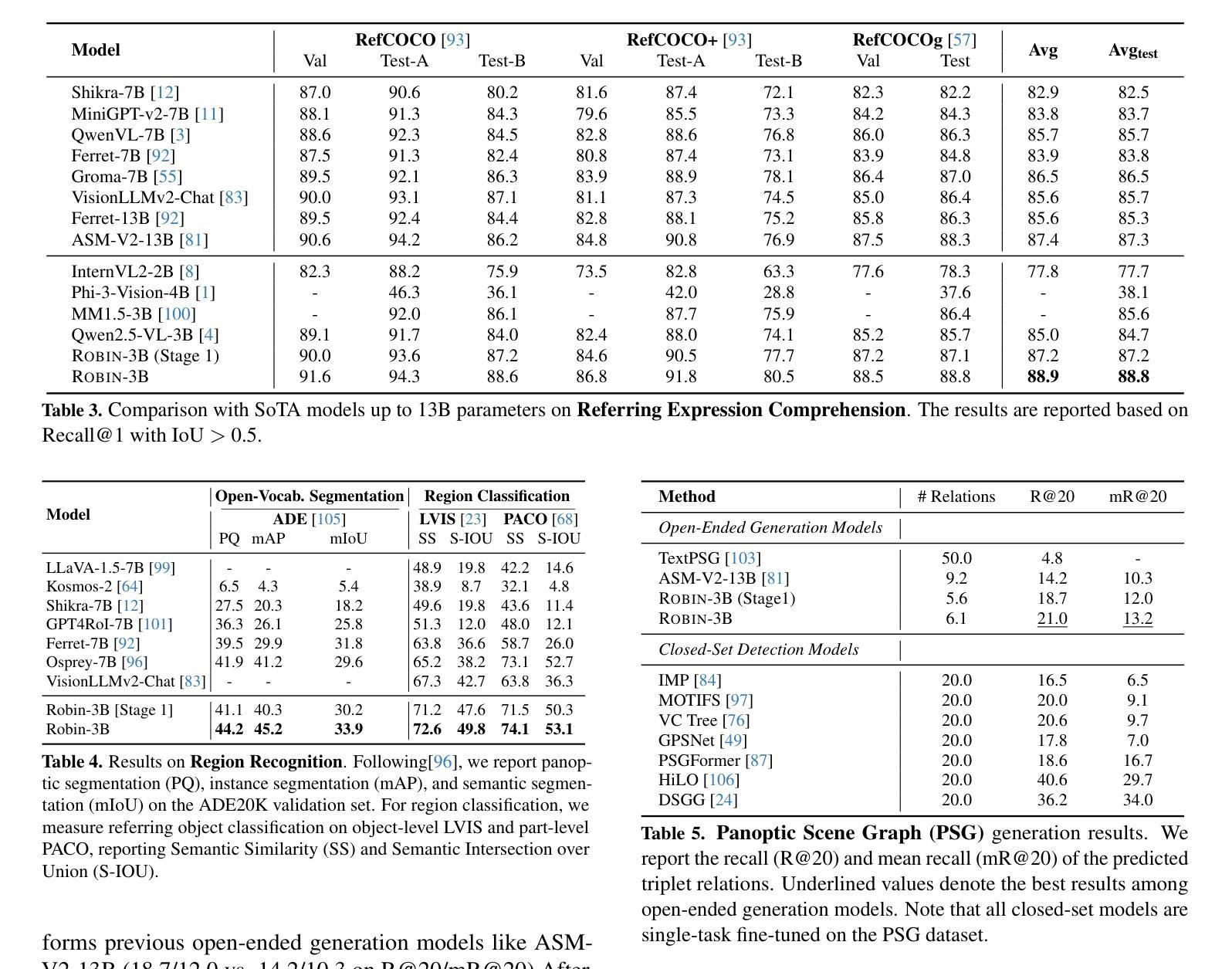
视觉关系推理——空间、功能、交互、社会等关系推理被认为是人类认知的基本组成部分。尽管多模态语言模型在视觉理解方面取得了重大进展,但准确地进行关系及其代际推理仍然是一个挑战。我们推出了ROBIN:一个用密集标注的关系进行微调的多模态语言模型指令,能够大规模构建高质量密集场景图。为了训练ROBIN,我们整理出了一个合成场景图数据集SVG,通过完成现有场景图中选定对象的缺失关系,并利用教师多模态语言模型和精心设计的过滤过程来确保高质量。为了为任何图像生成更准确和丰富的场景图,我们引入了SG-EDIT:一个自我蒸馏框架,GPT-4o进一步精炼ROBIN预测的场景图,通过删除不太可能的关系和/或提出相关的关系。我们的数据集总共包含14.6万张图像和560万个关系,涉及260万个对象。结果表明,我们的ROBIN-3B模型虽然在少于300万个实例上进行训练,但在关系理解基准测试上的表现超过了在超过3亿个实例上训练的类似规模模型,甚至超越了参数高达13B的大型模型。值得注意的是,它在指代表达式理解方面达到了88.9分,超过了之前的最佳成绩87.4分。我们的结果表明,在精炼的场景图数据进行训练对于在不同多样的视觉推理任务中保持高性能至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
摘要
人类认知中视觉关系推理是一个重要组成部分,涉及空间、功能、交互、社会等关系。尽管多模态语言模型在视觉理解方面取得了重大进展,但精确推理关系及其生成仍是挑战。为此,我们引入了ROBIN模型,该模型通过密集注释的关系进行训练,能够大规模构建高质量密集场景图。为训练ROBIN,我们整理了SVG数据集,通过教师MLM完成现有场景图中选定对象的缺失关系,并通过精心设计的过滤过程确保高质量。为大规模生成更准确和丰富的场景图,我们推出了SG-EDIT框架,GPT-4o进一步精炼ROBIN预测的场景图,移除不太可能的关系或提出相关关系。我们的数据集包含14.6万张图像和560万关系,涉及260万个对象。尽管ROBIN-3B模型训练实例少于300万,但在关系理解基准测试中,其性能超越了类似大小的模型(训练实例超过3亿),甚至超越了更大参数的模型。在指代表达式理解方面,ROBIN取得了最高分88.9分,超过了之前的最佳成绩87.4分。结果表明,在精炼的场景图数据进行训练对保持各种视觉推理任务的高性能至关重要。
关键见解
- 视觉关系推理是人类认知的基本组成部分,涵盖多种视觉关系如空间、功能、交互和社会关系。
- 尽管多模态语言模型在视觉理解方面取得进展,但精确推理视觉关系仍是挑战。
- 引入ROBIN模型,通过密集注释的关系进行训练,能构建高质量密集场景图。
- 为训练ROBIN,整理了SVG数据集,通过教师MLM完成现有场景图中对象缺失的关系。
- 推出SG-EDIT框架,进一步提高ROBIN模型预测场景图的准确性。
- ROBIN-3B模型在关系理解方面表现优异,即使训练实例较少也超越了类似和更大的模型。
点此查看论文截图

Instructing Large Language Models for Low-Resource Languages: A Systematic Study for Basque
Authors:Oscar Sainz, Naiara Perez, Julen Etxaniz, Joseba Fernandez de Landa, Itziar Aldabe, Iker García-Ferrero, Aimar Zabala, Ekhi Azurmendi, German Rigau, Eneko Agirre, Mikel Artetxe, Aitor Soroa
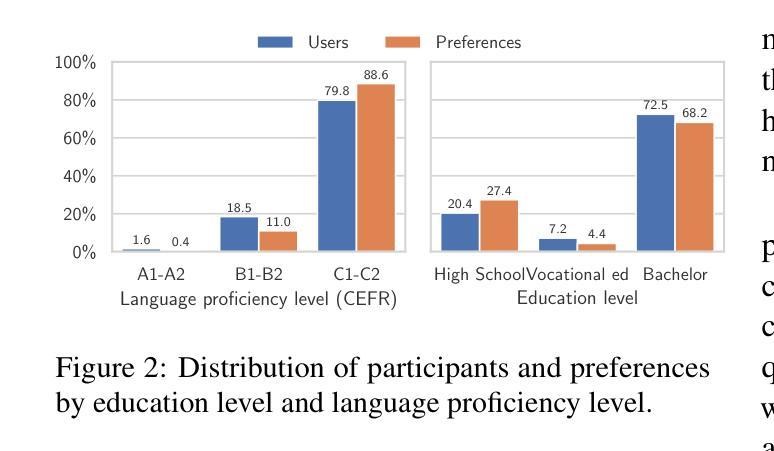
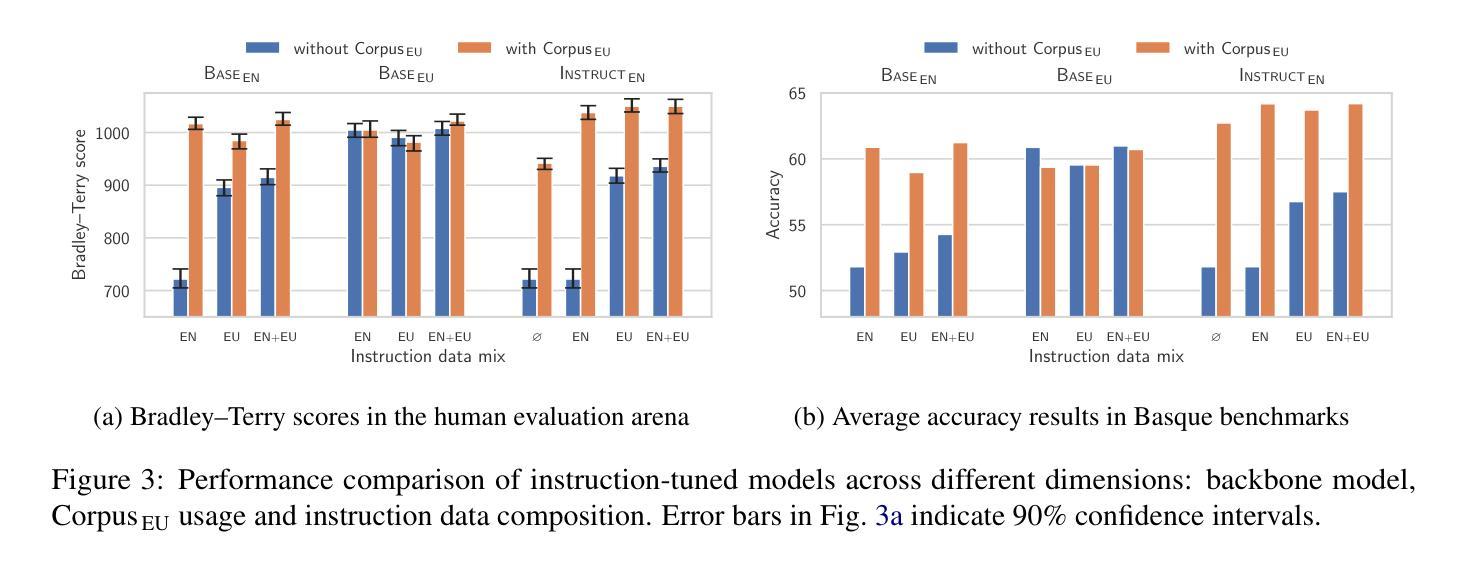
Instructing language models with user intent requires large instruction datasets, which are only available for a limited set of languages. In this paper, we explore alternatives to conventional instruction adaptation pipelines in low-resource scenarios. We assume a realistic scenario for low-resource languages, where only the following are available: corpora in the target language, existing open-weight multilingual base and instructed backbone LLMs, and synthetically generated instructions sampled from the instructed backbone. We present a comprehensive set of experiments for Basque that systematically study different combinations of these components evaluated on benchmarks and human preferences from 1,680 participants. Our conclusions show that target language corpora are essential, with synthetic instructions yielding robust models, and, most importantly, that using as backbone an instruction-tuned model outperforms using a base non-instructed model, and improved results when scaling up. Using Llama 3.1 instruct 70B as backbone our model comes near frontier models of much larger sizes for Basque, without using any Basque data apart from the 1.2B word corpora. We release code, models, instruction datasets, and human preferences to support full reproducibility in future research on low-resource language adaptation.
使用用户意图来指导语言模型需要大量指令数据集,这些数据集只适用于有限的语言集合。在本文中,我们探讨了低资源场景下传统指令适应管道的替代方案。我们假设了一个低资源语言的现实场景,其中仅提供以下资源:目标语言语料库、现有的开放权重多语言基础和有指令骨架的大型语言模型,以及从指令骨架中采样得到的合成指令。我们对巴斯克语进行了一系列综合实验,该实验系统地研究了这些组件的不同组合,并在基准测试和人类偏好(来自1680名参与者)上进行了评估。我们的结论显示,目标语言语料库至关重要,合成指令产生了稳健的模型,而且最重要的是,使用指令调整后的模型作为骨架优于使用基础非指令模型,并且在扩大规模时提高了结果。使用Llama 3.1指令70B作为骨架,我们的模型在不使用任何巴斯克语数据的情况下(除了12亿单词语料库外),接近更大规模的巴斯克语前沿模型。我们发布代码、模型、指令数据集和人类偏好,以支持未来低资源语言适应研究中的完全可重复性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
本研究探索了在缺乏大量指令数据集的低资源场景下,如何对语言模型进行用户意图指导。研究在巴斯克语这一低资源语言的现实情景下展开,通过一系列实验和评估,证实目标语言语料库的重要性,以及合成指令能生成稳健模型。最重要的是,使用指令调优模型作为主干网络优于使用基础非指令模型,并在扩大规模时取得更好的结果。使用Llama 3.1指令70B作为主干网,模型性能接近针对巴斯克语的更大规模前沿模型,且无需使用除巴斯克语料库以外的任何数据。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注低资源场景下的语言模型用户意图指导。
- 在巴斯克语这一低资源语言的现实情景下展开研究。
- 目标语言语料库的重要性得到证实。
- 合成指令能有效生成稳健的模型。
- 使用指令调优模型作为主干网络表现更优。
- 扩大规模时,使用指令调优模型能取得更好的结果。
点此查看论文截图

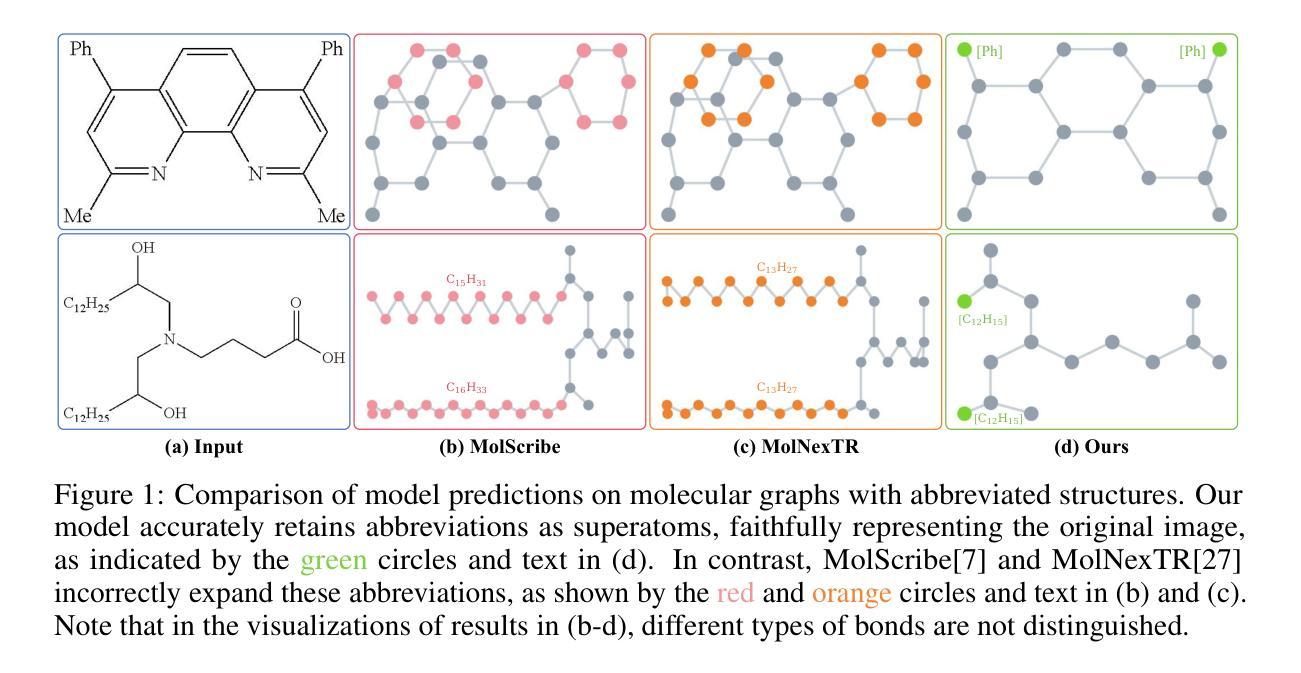
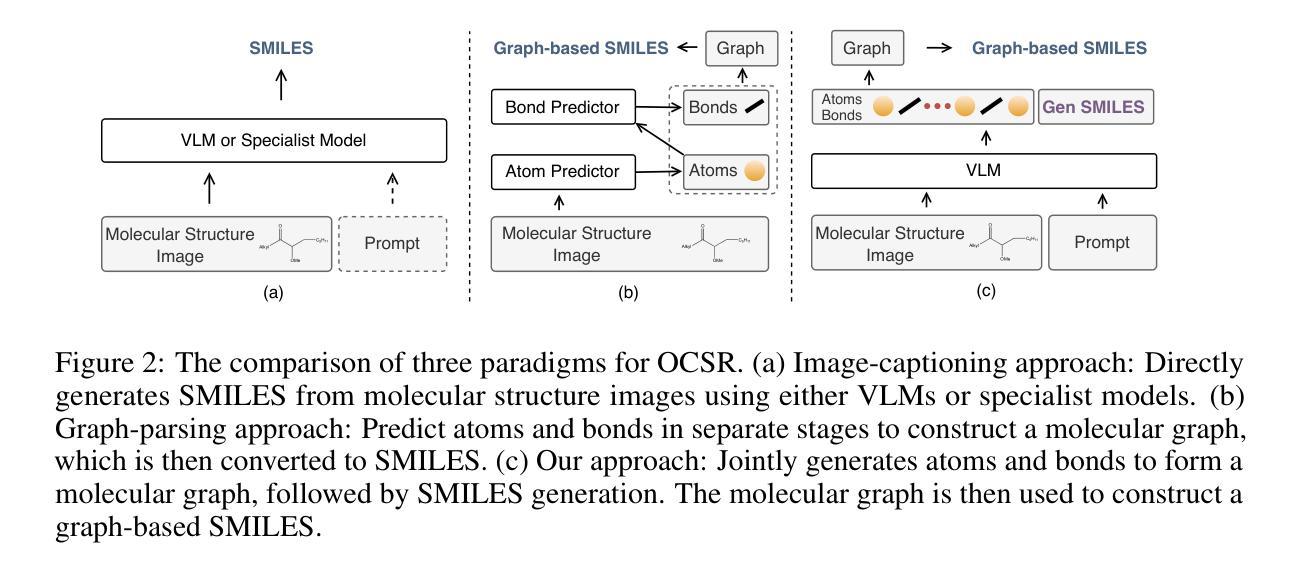
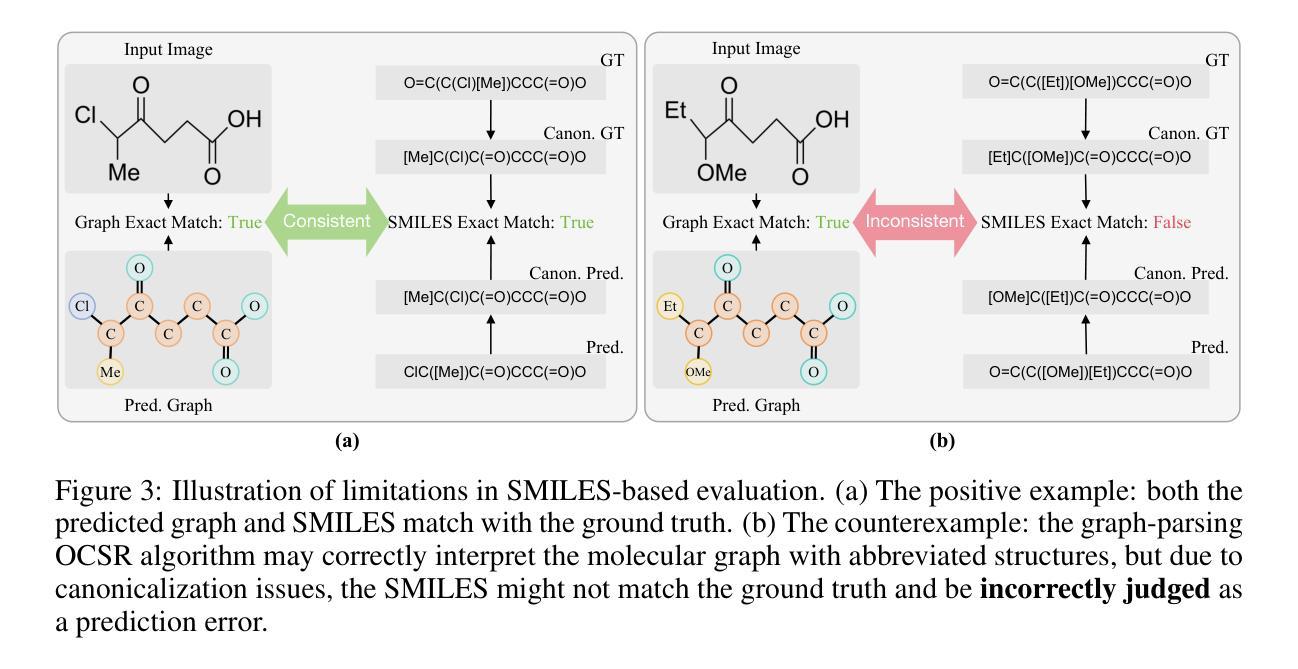
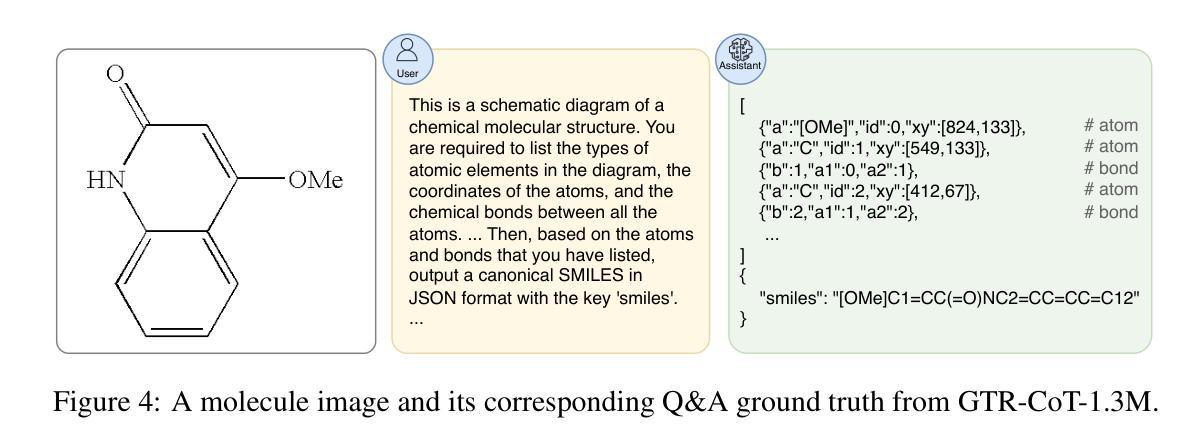
GTR-CoT: Graph Traversal as Visual Chain of Thought for Molecular Structure Recognition
Authors:Jingchao Wang, Haote Yang, Jiang Wu, Yifan He, Xingjian Wei, Yinfan Wang, Chengjin Liu, Lingli Ge, Lijun Wu, Bin Wang, Dahua Lin, Conghui He
Optical Chemical Structure Recognition (OCSR) is crucial for digitizing chemical knowledge by converting molecular images into machine-readable formats. While recent vision-language models (VLMs) have shown potential in this task, their image-captioning approach often struggles with complex molecular structures and inconsistent annotations. To overcome these challenges, we introduce GTR-Mol-VLM, a novel framework featuring two key innovations: (1) the \textit{Graph Traversal as Visual Chain of Thought} mechanism that emulates human reasoning by incrementally parsing molecular graphs through sequential atom-bond predictions, and (2) the data-centric principle of \textit{Faithfully Recognize What You’ve Seen}, which addresses the mismatch between abbreviated structures in images and their expanded annotations. To support model development, we constructed GTR-CoT-1.3M, a large-scale instruction-tuning dataset with meticulously corrected annotations, and introduced MolRec-Bench, the first benchmark designed for a fine-grained evaluation of graph-parsing accuracy in OCSR. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that GTR-Mol-VLM achieves superior results compared to specialist models, chemistry-domain VLMs, and commercial general-purpose VLMs. Notably, in scenarios involving molecular images with functional group abbreviations, GTR-Mol-VLM outperforms the second-best baseline by approximately 14 percentage points, both in SMILES-based and graph-based metrics. We hope that this work will drive OCSR technology to more effectively meet real-world needs, thereby advancing the fields of cheminformatics and AI for Science. We will release GTR-CoT at https://github.com/opendatalab/GTR-CoT.
光学化学结构识别(OCSR)是通过将分子图像转换为机器可读格式来数字化化学知识的重要技术。尽管最近的视觉语言模型(VLM)在此任务中显示出潜力,但它们的图像描述方法通常难以处理复杂的分子结构和不一致的注释。为了克服这些挑战,我们引入了GTR-Mol-VLM,这是一个具有两项关键创新的新框架:(1)通过连续原子键预测逐步解析分子图的“图遍历作为视觉思维链”机制,通过模拟人类推理;以及(2)“忠实识别你所看到的”的数据中心原则,该原则解决了图像中缩写结构与扩展注释之间的不匹配问题。为了支持模型开发,我们构建了GTR-CoT-1.3M,这是一个大规模指令调整数据集,具有精心校正的注释,并引入了MolRec-Bench,这是专为OCSR中图形解析精度的精细评估而设计的第一个基准测试。综合实验表明,GTR-Mol-VLM相较于专业模型、化学领域的VLM以及商业通用VLM取得了优越的结果。特别是在涉及带有功能团缩写的分子图像的场景中,GTR-Mol-VLM在SMILES基和图形基指标上的表现都比第二名基准高出约14个百分点。我们希望这项工作将推动OCSR技术更有效地满足现实世界的需求,从而推动化学信息学和人工智能科学领域的发展。我们将在https://github.com/opendatalab/GTR-CoT发布GTR-CoT。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
光学化学结构识别(OCSR)是数字化化学知识的重要步骤,可将分子图像转换为机器可读格式。针对现有模型在处理复杂分子结构和不一致注释时的挑战,提出了GTR-Mol-VLM这一新型框架,包括模拟人类推理的“图遍历作为视觉思维链”机制和解决图像中的缩略结构与扩展注释之间不匹配问题的“忠实识别你所看到的”的数据中心原则。为支持模型开发,构建了大规模指令调整数据集GTR-CoT-1.3M和针对OCSR的图解析准确性的首个基准测试MolRec-Bench。实验表明,GTR-Mol-VLM相较于专业模型、化学领域VLMs和商业通用VLMs取得了显著优势,特别是在处理带有功能组缩略的分子图像时,在SMILES和图形指标上均优于第二名基线约14个百分点。
Key Takeaways
- OCSR在数字化化学知识中起关键作用,能将分子图像转为机器可读格式。
- 现有模型在处理复杂分子结构和不一致注释时存在挑战。
- GTR-Mol-VLM框架通过模拟人类推理和图遍历解决这些问题。
- GTR-Mol-VLM包括两大创新:Graph Traversal as Visual Chain of Thought和Faithfully Recognize What You’ve Seen机制。
- 为支持模型开发,构建了大型指令调整数据集GTR-CoT-1.3M和首个基准测试MolRec-Bench。
- GTR-Mol-VLM相较于其他模型在处理分子图像时取得了显著优势,特别是在处理带有功能组缩略的图像时。
点此查看论文截图

Large Language Models for Multilingual Vulnerability Detection: How Far Are We?
Authors:Honglin Shu, Michael Fu, Junji Yu, Dong Wang, Chakkrit Tantithamthavorn, Junjie Chen, Yasutaka Kamei
Various deep learning-based approaches utilizing pre-trained language models (PLMs) have been proposed for automated vulnerability detection. With recent advancements in large language models (LLMs), several studies have begun exploring their application to vulnerability detection tasks. However, existing studies primarily focus on specific programming languages (e.g., C/C++) and function-level detection, leaving the strengths and weaknesses of PLMs and LLMs in multilingual and multi-granularity scenarios largely unexplored. To bridge this gap, we conduct a comprehensive fine-grained empirical study evaluating the effectiveness of state-of-the-art PLMs and LLMs for multilingual vulnerability detection. Using over 30,000 real-world vulnerability-fixing patches across seven programming languages, we systematically assess model performance at both the function-level and line-level. Our key findings indicate that GPT-4o, enhanced through instruction tuning and few-shot prompting, significantly outperforms all other evaluated models, including CodeT5P. Furthermore, the LLM-based approach demonstrates superior capability in detecting unique multilingual vulnerabilities, particularly excelling in identifying the most dangerous and high-severity vulnerabilities. These results underscore the promising potential of adopting LLMs for multilingual vulnerability detection at function-level and line-level, revealing their complementary strengths and substantial improvements over PLM approaches. This first empirical evaluation of PLMs and LLMs for multilingual vulnerability detection highlights LLMs’ value in addressing real-world software security challenges.
针对自动漏洞检测,已经提出了利用各种基于深度学习和预训练语言模型(PLM)的方法。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的最新发展,一些研究开始探索其在漏洞检测任务中的应用。然而,现有的研究主要集中在特定的编程语言(如C/C++)和函数级别的检测上,而针对多语种和多粒度场景中的PLM和LLM的优势和劣势的研究相对较少。为了弥补这一空白,我们进行了一项全面的精细实证研究,评估了最先进的PLM和LLM在多语种漏洞检测方面的有效性。我们利用七种编程语言中的超过三万份真实世界漏洞修复补丁,系统地评估了模型和函数级别以及行级别的性能。我们的主要发现表明,经过指令调整和少量提示增强的GPT-4o在所有其他评估模型中表现最为出色,包括CodeT5P。此外,基于LLM的方法在检测独特的多语种漏洞方面表现出卓越的能力,尤其擅长识别最危险和高严重程度的漏洞。这些结果强调了采用LLM进行多语种漏洞检测在函数级别和行级别的巨大潜力,凸显了它们在互补强度和实质性改进方面的优势。这一针对PLM和LLM在多语种漏洞检测方面的首次实证研究凸显了LLM在解决现实世界软件安全挑战方面的价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 33 pages, 9 figures
Summary
在各种基于深度学习的自动化漏洞检测方案中,研究人员已采用预训练语言模型(PLMs)。随着大型语言模型(LLMs)的最新发展,多项研究开始探索其在漏洞检测任务中的应用。然而,现有研究主要集中在特定编程语言(如C/C++)和功能层面的检测上,对PLMs和LLMs在多语种和多粒度场景下的优劣知之甚少。为了弥补这一空白,我们进行了一项全面的精细实证研究,评估了最前沿的PLMs和LLMs在多语种漏洞检测方面的有效性。使用超过三万份真实世界漏洞修复补丁(涵盖七种编程语言),我们系统地评估了模型在功能层面和行级别的表现。我们发现GPT-4o通过指令微调和小样本提示显著优于其他模型,包括CodeT5P。此外,基于LLM的方法在检测独特的多语种漏洞方面表现出卓越的能力,尤其擅长识别最危险的高级别漏洞。这些结果突显了采用LLMs进行多语种漏洞检测的潜力,揭示了其在功能层面和行级别的优势以及对PLM方法的实质性改进。这是首次针对PLMs和LLMs进行的多语种漏洞检测的实证研究,突显了LLMs在应对真实软件安全挑战方面的价值。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习方法已应用于基于预训练语言模型的自动化漏洞检测。
- 大型语言模型在漏洞检测任务中的应用开始受到研究关注。
- 当前研究主要关注特定编程语言和功能层面的检测,忽略了多语种和多粒度场景。
- GPT-4o在漏洞检测方面表现最佳,通过指令微调和小样本提示显著优于其他模型。
- 基于LLM的方法在检测多语种漏洞方面表现出卓越能力,尤其擅长识别高级别漏洞。
- LLMs在功能层面和行级别的漏洞检测方面具有潜力,相较于PLM方法有明显改进。
点此查看论文截图

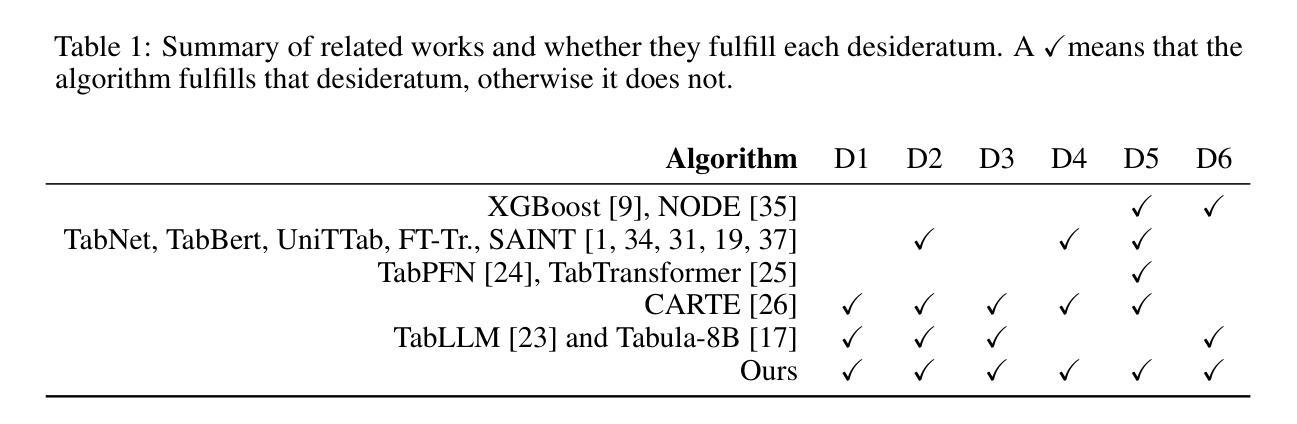
Basis Transformers for Multi-Task Tabular Regression
Authors:Wei Min Loh, Jiaqi Shang, Pascal Poupart
Dealing with tabular data is challenging due to partial information, noise, and heterogeneous structure. Existing techniques often struggle to simultaneously address key aspects of tabular data such as textual information, a variable number of columns, and unseen data without metadata besides column names. We propose a novel architecture, \textit{basis transformers}, specifically designed to tackle these challenges while respecting inherent invariances in tabular data, including hierarchical structure and the representation of numeric values. We evaluate our design on a multi-task tabular regression benchmark, achieving an improvement of 0.338 in the median $R^2$ score and the lowest standard deviation across 34 tasks from the OpenML-CTR23 benchmark. Furthermore, our model has five times fewer parameters than the best-performing baseline and surpasses pretrained large language model baselines – even when initialized from randomized weights.
处理表格数据因部分信息、噪声和异质结构而具有挑战性。现有技术往往难以同时解决表格数据的关键方面,如文本信息、可变列数和除列名外的元数据信息中的未知数据。我们提出了一种新型架构——基础转换器(basis transformers),专门设计用于应对这些挑战,同时尊重表格数据中的固有不变性,包括层次结构和数值表示。我们在多任务表格回归基准测试上评估了我们的设计,在OpenML-CTR23基准测试的34个任务中,中位数R²得分提高了0.338,标准偏差最低。此外,我们的模型参数数量是表现最佳基准模型的五分之一,甚至在随机权重初始化的情况下也超过了预训练的大型语言模型基准。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于处理表格数据时面临的挑战,如部分信息、噪声和异质结构等问题,提出了一种新型架构——基础转换器。该架构能同时处理表格数据的关键方面,如文本信息、可变列数和除列名外的无元数据未知数据,并尊重表格数据固有的不变性,包括层次结构和数值表示。在多项任务表格回归基准测试上评估该设计,在OpenML-CTR23基准测试的34个任务中,中位数R²得分提高了0.338,并且标准偏差最低。此外,该模型的参数数量是最佳基准测试的五分之一,即使在随机权重初始化的情况下也超过了预训练的大型语言模型基准测试。
Key Takeaways
- 表格数据处理面临挑战,包括部分信息、噪声和异质结构。
- 提出了一种新型架构——基础转换器,专门设计来处理这些挑战。
- 基础转换器能同时处理表格数据的多个关键方面,如文本信息和可变列数。
- 该架构尊重表格数据的不变性,包括层次结构和数值表示。
- 在多项任务表格回归基准测试上,基础转换器取得了显著改进,中位数R²得分提高了0.338。
- 基础转换器的参数数量是最佳基准测试的五分之一,效率更高。
点此查看论文截图

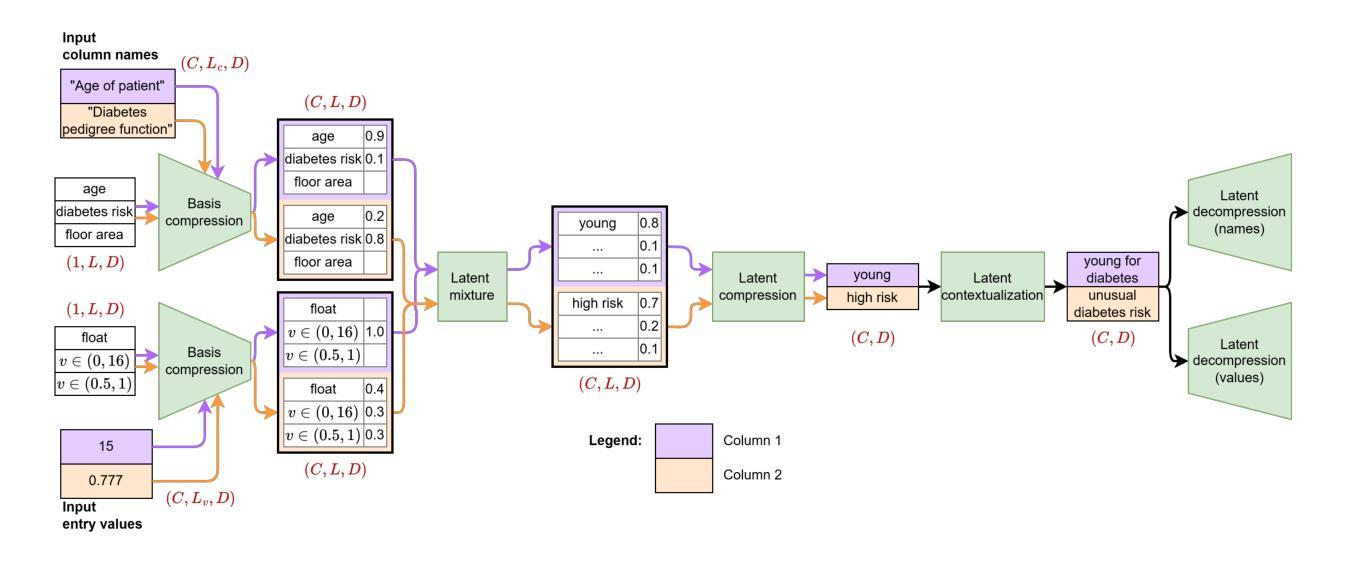
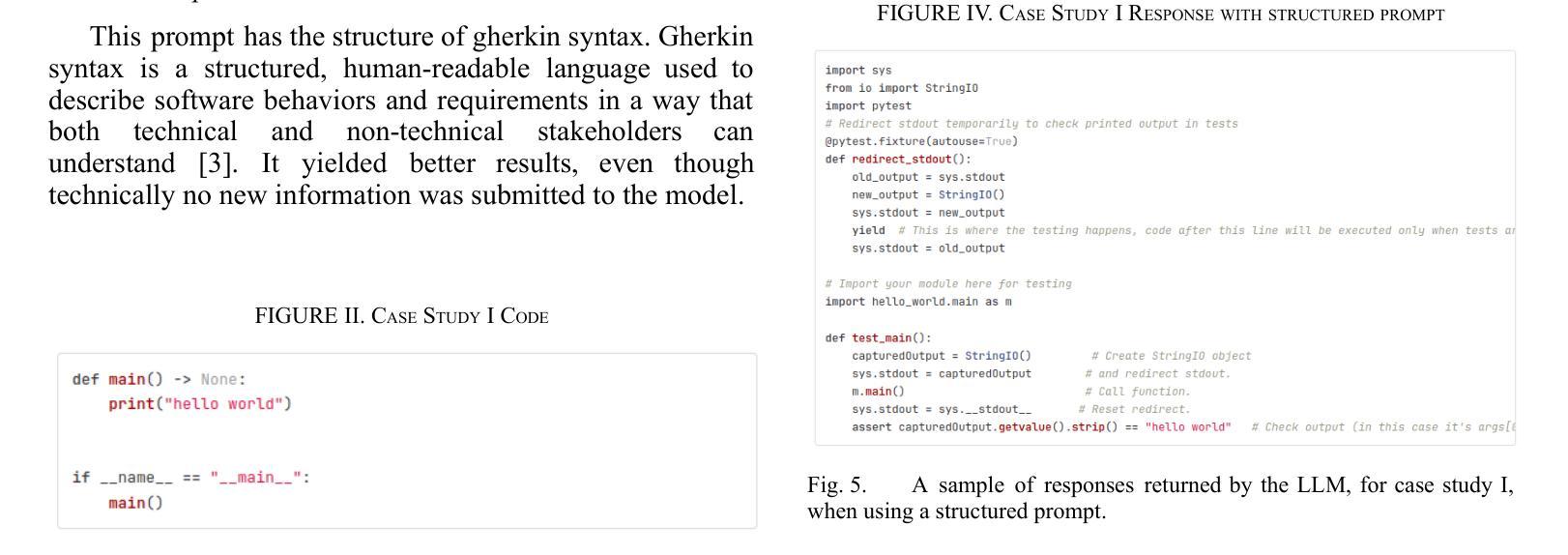
Private GPTs for LLM-driven testing in software development and machine learning
Authors:Jakub Jagielski, Markus Abel
In this contribution, we examine the capability of private GPTs to automatically generate executable test code based on requirements. More specifically, we use acceptance criteria as input, formulated as part of epics, or stories, which are typically used in modern development processes. This gives product owners, or business intelligence, respectively, a way to directly produce testable criteria through the use of LLMs. We explore the quality of the so-produced tests in two ways: i) directly by letting the LLM generate code from requirements, ii) through an intermediate step using Gherkin syntax. As a result, it turns out that the two-step procedure yields better results -where we define better in terms of human readability and best coding practices, i.e. lines of code and use of additional libraries typically used in testing. Concretely, we evaluate prompt effectiveness across two scenarios: a simple “Hello World” program and a digit classification model, showing that structured prompts lead to higher-quality test outputs.
在这篇文章中,我们探讨了私人GPT根据需求自动生成可执行测试代码的能力。更具体地说,我们使用作为输入项的验收标准,这些标准被制定为史诗或故事的一部分,通常用于现代开发过程。这为产品所有者或商业智能提供了一种通过大型语言模型直接产生可测试标准的方法。我们通过两种方式探索所生成测试的质量:i) 直接让大型语言模型从需求生成代码;ii) 通过使用Gherkin语法的中间步骤。结果表明,两步程序产生更好的结果——我们根据人类可读性和最佳编码实践来定义更好,即代码行数以及测试过程中通常使用的额外库的用途。具体来说,我们在两种场景下评估提示的有效性:一个简单的“Hello World”程序和数字分类模型,显示结构化提示会导致更高质量的测试输出。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文探讨了私人GPT根据需求自动生成可执行测试代码的能力。研究使用作为输入的要求标准,这些标准被融入史诗或故事中,这在现代开发过程中广泛使用。这允许产品经理或商业智能人员通过大型语言模型直接制定可测试的标准。本文通过两种方式探讨了所生成的测试的质量:一是直接从需求中让大型语言模型生成代码,二是通过Gherkin语法进行中间步骤。结果表明,两步过程能产生更好的结果,在可阅读性和最佳编码实践方面表现更好。通过对一个简单的“Hello World”程序和数字分类模型的场景评估,展示了结构化提示可以产生更高质量的测试输出。
Key Takeaways
- 本文探讨了使用私人GPT自动生成测试代码的能力,基于融入现代开发过程中的史诗或故事的需求标准作为输入。
- 通过两种方式评估了所生成的测试代码的质量:直接从需求生成代码和使用Gherkin语法作为中间步骤。
- 两步过程能够更好地生成可阅读的代码并遵循最佳编码实践。
- 使用结构化提示可以提高生成测试代码的质量。
- 通过两个实例场景,“Hello World”程序和数字分类模型验证了GPT的实际应用能力。
- 通过将大型语言模型融入业务流程中,产品所有者可以更方便地制定可测试的标准。
点此查看论文截图




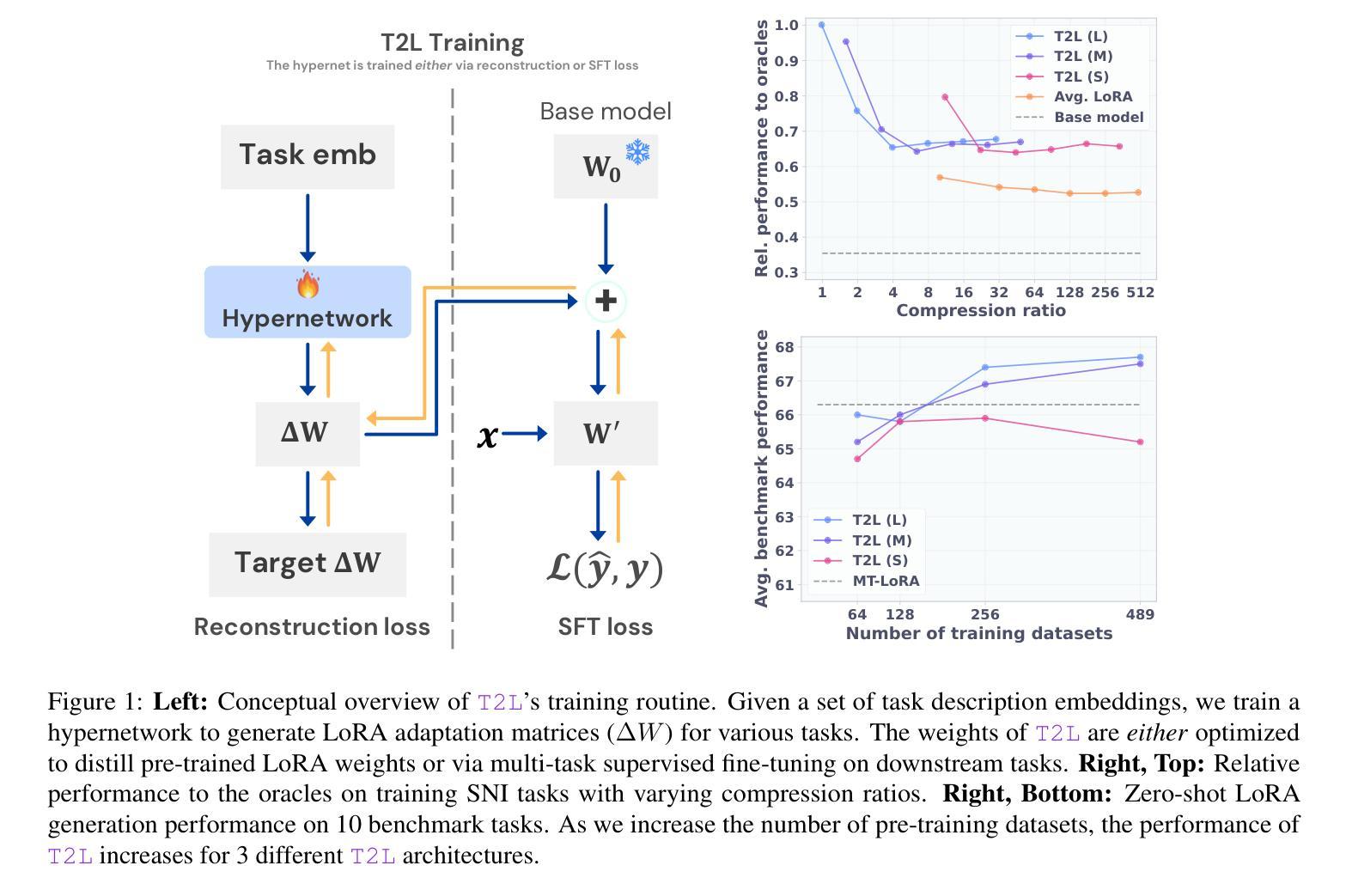
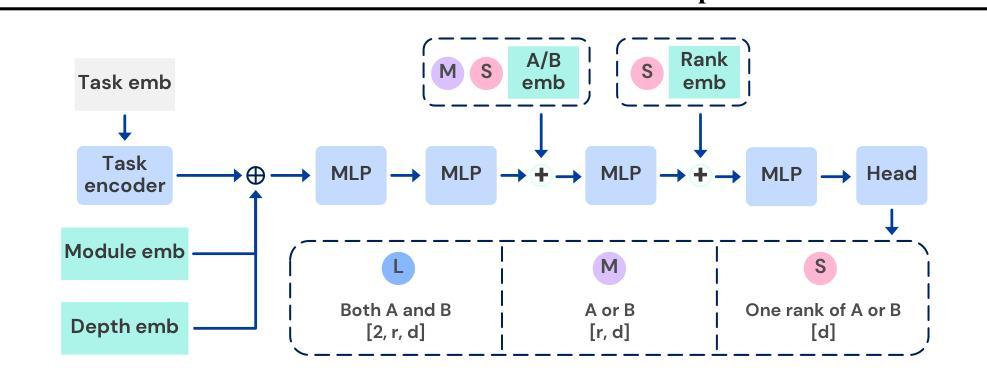
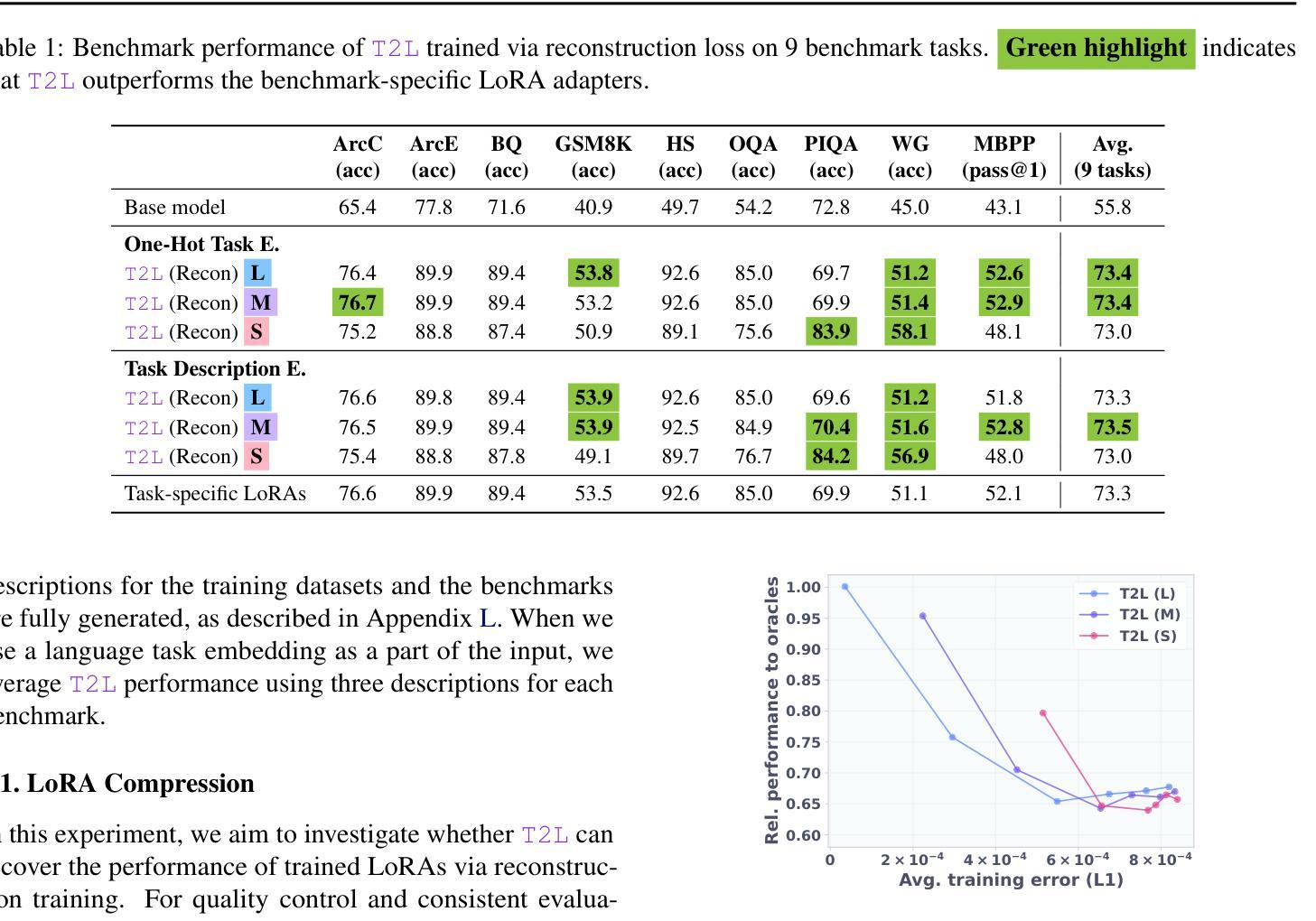
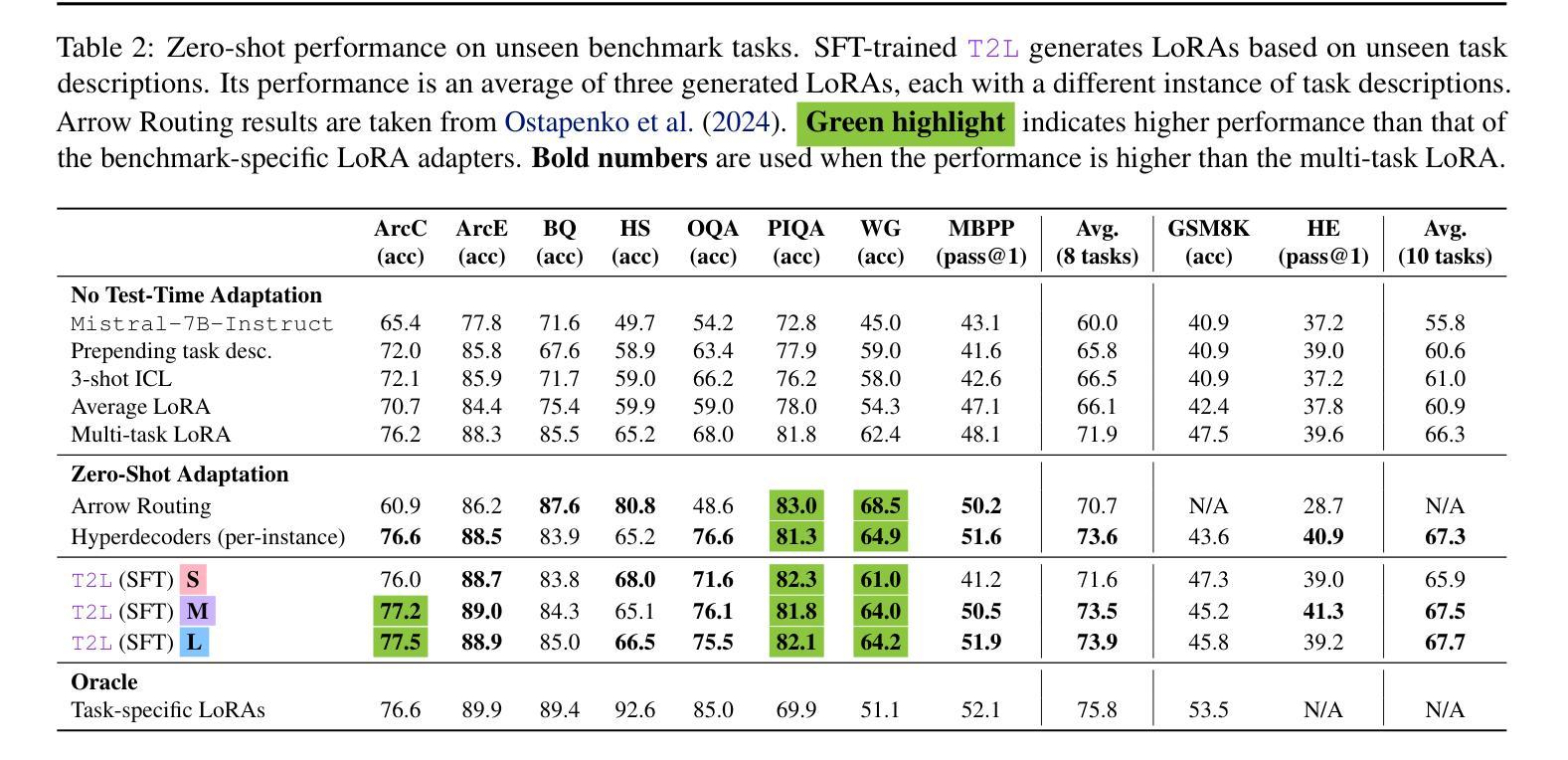
Text-to-LoRA: Instant Transformer Adaption
Authors:Rujikorn Charakorn, Edoardo Cetin, Yujin Tang, Robert Tjarko Lange
While Foundation Models provide a general tool for rapid content creation, they regularly require task-specific adaptation. Traditionally, this exercise involves careful curation of datasets and repeated fine-tuning of the underlying model. Fine-tuning techniques enable practitioners to adapt foundation models for many new applications but require expensive and lengthy training while being notably sensitive to hyperparameter choices. To overcome these limitations, we introduce Text-to-LoRA (T2L), a model capable of adapting large language models (LLMs) on the fly solely based on a natural language description of the target task. T2L is a hypernetwork trained to construct LoRAs in a single inexpensive forward pass. After training T2L on a suite of 9 pre-trained LoRA adapters (GSM8K, Arc, etc.), we show that the ad-hoc reconstructed LoRA instances match the performance of task-specific adapters across the corresponding test sets. Furthermore, T2L can compress hundreds of LoRA instances and zero-shot generalize to entirely unseen tasks. This approach provides a significant step towards democratizing the specialization of foundation models and enables language-based adaptation with minimal compute requirements. Our code is available at https://github.com/SakanaAI/text-to-lora
虽然基础模型为快速内容创建提供了通用工具,但它们通常需要针对特定任务进行适应。传统上,这一过程涉及数据集的精心筛选和底层模型的反复微调。微调技术使实践者能够为许多新应用适应基础模型,但需要昂贵且耗时的训练,同时对超参数选择非常敏感。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了Text-to-LoRA(T2L)模型,该模型能够即时适应大型语言模型(LLM),仅基于目标任务的自然语言描述。T2L是一种超网络,经过训练可构建单次廉价前向传递中的LoRAs。在使用一套9个预训练LoRA适配器(GSM8K、Arc等)对T2L进行训练后,我们显示,临时构建的LoRA实例在相应测试集上的性能与针对特定任务的适配器相匹配。此外,T2L可以压缩数百个LoRA实例并零样本泛化到完全未见过的任务。这一方法为民主化基础模型的专业化迈出了重要一步,并实现了语言自适应的最小计算需求。我们的代码可在https://github.com/SakanaAI/text-to-lora找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICML 2025
Summary
基础模型为快速内容创建提供了通用工具,但通常需要针对特定任务进行适应。传统上,这需要精心挑选数据集并多次微调基础模型。虽然微调技术使从业者能够为许多新应用适应基础模型,但需要昂贵且耗时的训练,并且对超参数选择非常敏感。为了克服这些限制,我们推出了Text-to-LoRA(T2L),这是一种能够在飞行中适应大型语言模型(LLM)的模型,仅基于目标任务的自然语言描述。T2L是一个超网络,经过训练可构造单次廉价前向传递中的LoRAs。在基于一系列预训练的LoRA适配器(GSM8K、Arc等)训练T2L后,我们证明临时构建的LoRA实例在相应测试集上的性能与特定任务适配器相匹配。此外,T2L可以压缩数百个LoRA实例,并零镜头泛化到完全未见过的任务。这一步骤朝着民主化基础模型的专门化迈出了重要的一步,并通过最小的计算需求实现了基于语言的适应。
Key Takeaways
- 基础模型虽通用但通常需要针对特定任务进行适应。
- 传统适应基础模型的方法需要精心挑选数据集和多次微调,过程既昂贵又耗时。
- Text-to-LoRA(T2L)模型能够基于自然语言描述目标任务来适应大型语言模型(LLM)。
- T2L是一个超网络,可以在单次前向传递中构造LoRAs。
- T2L经过一系列预训练LoRA适配器的训练后,其实例性能与特定任务适配器相当。
- T2L能压缩多个LoRA实例并泛化到未见过的任务。
- T2L的出现是朝着民主化基础模型的专门化迈进的重要一步,可实现基于语言的快速适应且计算需求小。
点此查看论文截图

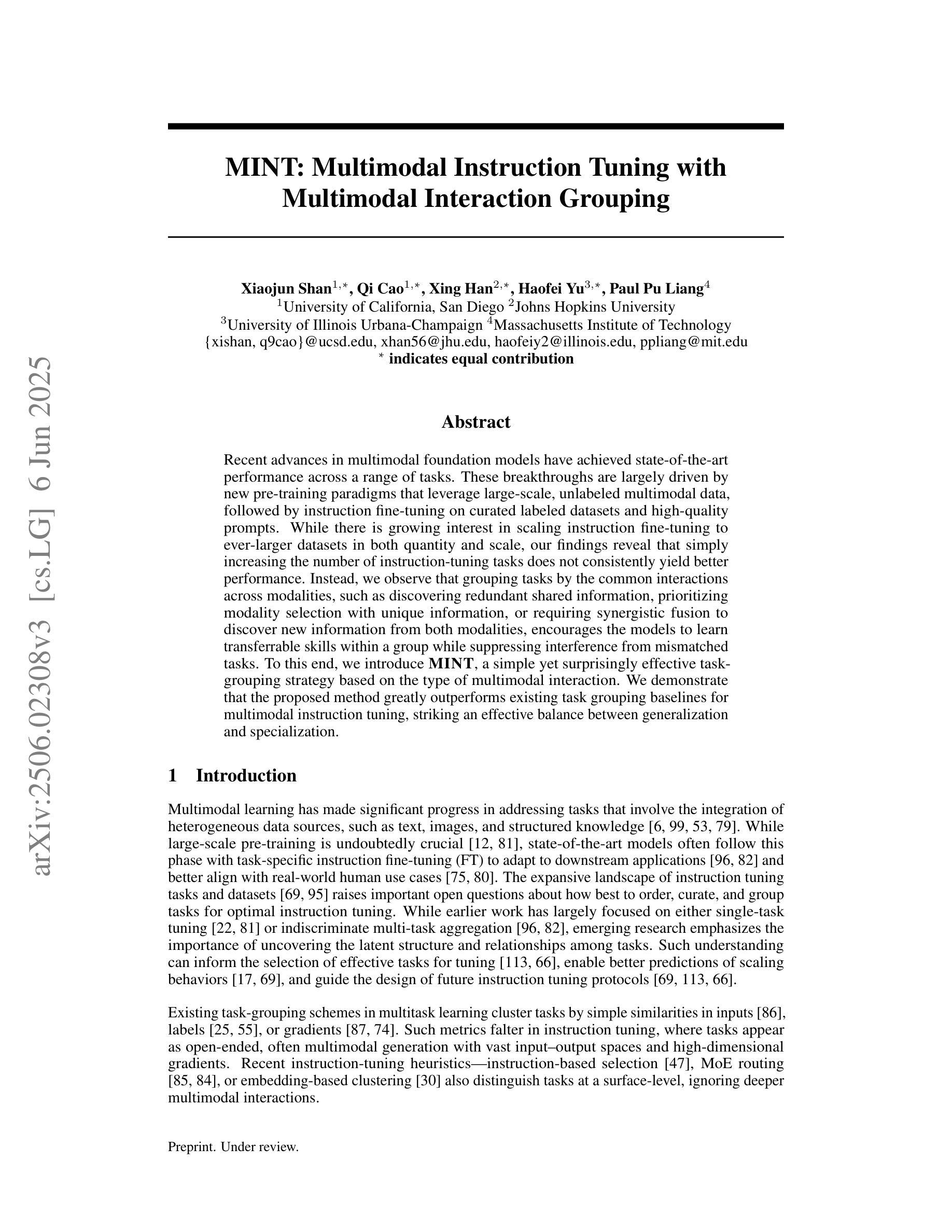
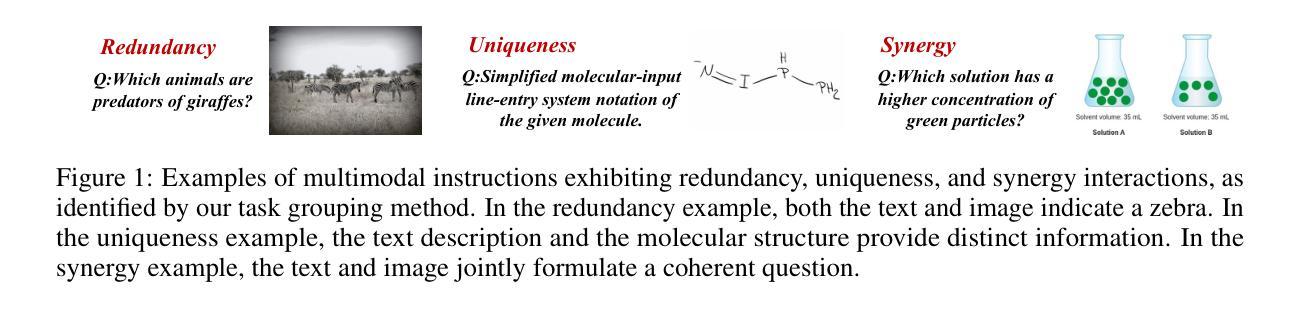
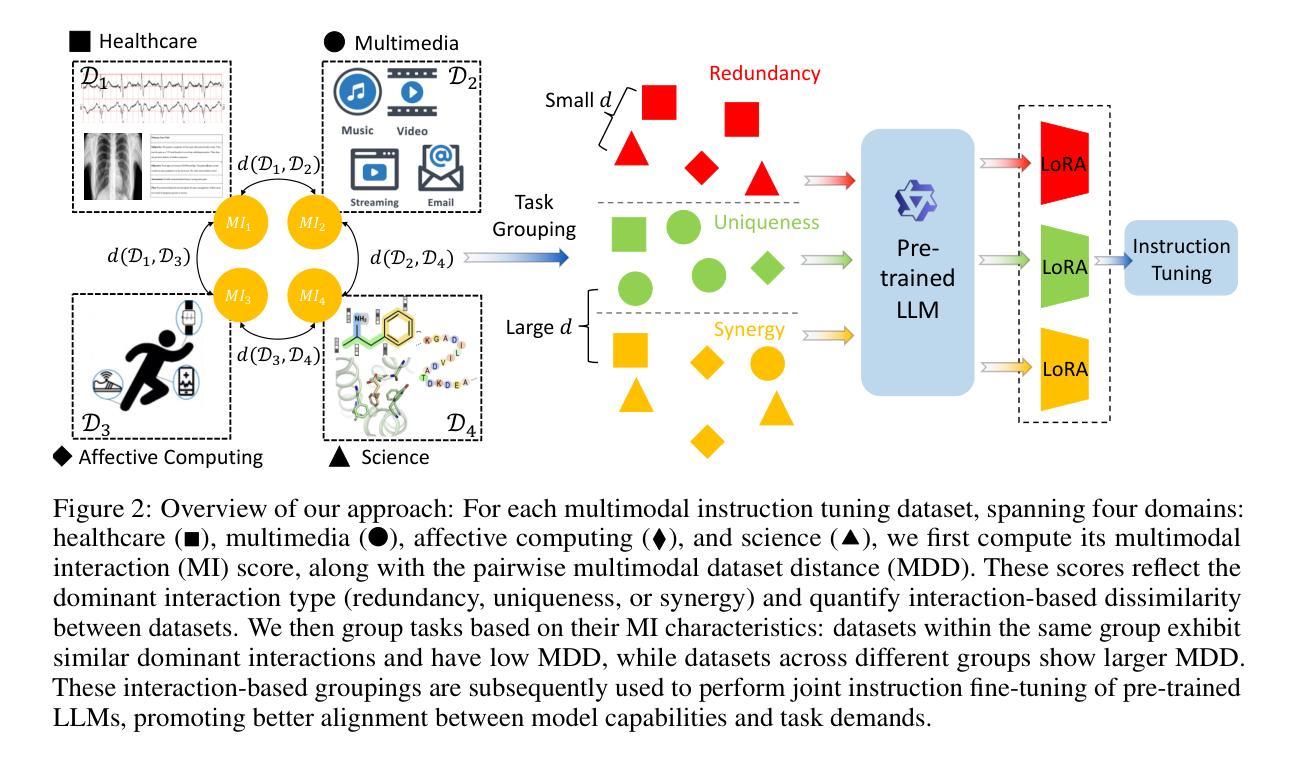
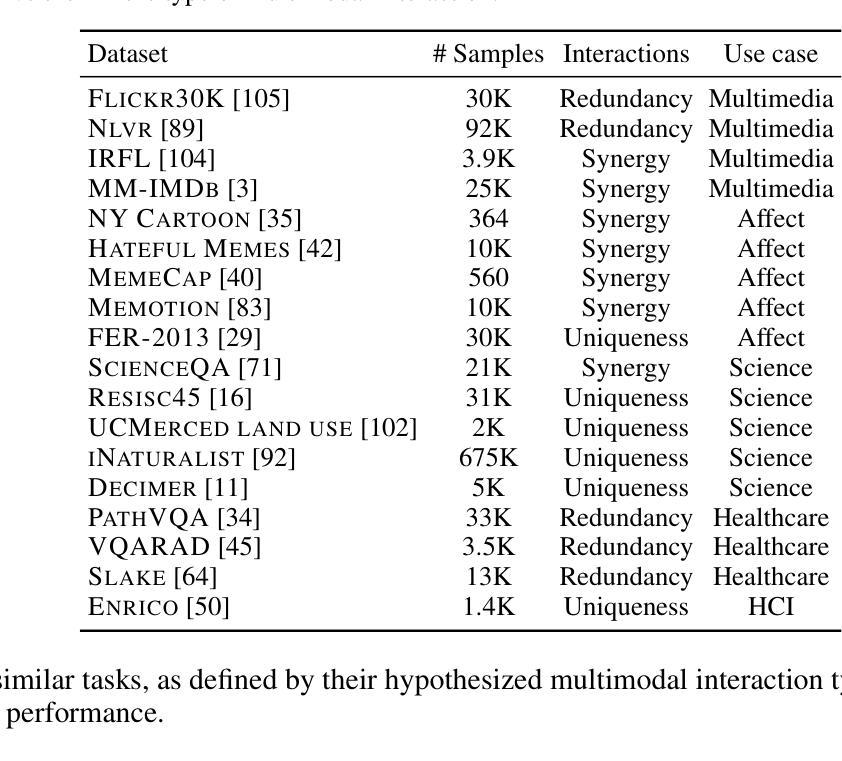
MINT: Multimodal Instruction Tuning with Multimodal Interaction Grouping
Authors:Xiaojun Shan, Qi Cao, Xing Han, Haofei Yu, Paul Pu Liang
Recent advances in multimodal foundation models have achieved state-of-the-art performance across a range of tasks. These breakthroughs are largely driven by new pre-training paradigms that leverage large-scale, unlabeled multimodal data, followed by instruction fine-tuning on curated labeled datasets and high-quality prompts. While there is growing interest in scaling instruction fine-tuning to ever-larger datasets in both quantity and scale, our findings reveal that simply increasing the number of instruction-tuning tasks does not consistently yield better performance. Instead, we observe that grouping tasks by the common interactions across modalities, such as discovering redundant shared information, prioritizing modality selection with unique information, or requiring synergistic fusion to discover new information from both modalities, encourages the models to learn transferrable skills within a group while suppressing interference from mismatched tasks. To this end, we introduce MINT, a simple yet surprisingly effective task-grouping strategy based on the type of multimodal interaction. We demonstrate that the proposed method greatly outperforms existing task grouping baselines for multimodal instruction tuning, striking an effective balance between generalization and specialization.
近期多模态基础模型的进展在多个任务上达到了最先进的性能。这些突破主要得益于新的预训练模式,它利用大规模的无标签多模态数据,然后在精选的标记数据集上进行指令微调并使用高质量提示。虽然人们对扩大指令微调以涵盖数量和规模日益增大的数据集越来越感兴趣,但我们的研究结果表明,仅仅增加指令调整任务的数量并不总能带来更好的性能。相反,我们观察到,通过跨模态的通用交互对任务进行分组,如发现冗余的共享信息、优先使用具有独特信息的模态选择,或需要协同融合以从两种模态中发现新信息,这鼓励模型在组内学习可迁移技能,同时抑制了不匹配任务的干扰。为此,我们引入了MINT,这是一种基于多模态交互类型的简单而有效的任务分组策略。我们证明,对于多模态指令调整,所提出的方法大大优于现有的任务分组基线,在通用性和专业化之间达到了有效平衡。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模的多模态基础模型在多个任务上取得了最先进的性能。这些突破主要得益于新的预训练模式,利用大规模的无标签多模态数据,随后在精选的有标签数据集上进行指令微调并使用高质量提示。研究发现,单纯增加指令微调的任务数量并不总能带来更好的性能。相反,通过共同交互对任务进行分组,如寻找冗余的共享信息、优先选择与独特信息匹配的模态或需要协同融合以发现两种模态中的新信息,能鼓励模型学习组内的可转移技能并减少不相关任务的干扰。为此,我们引入了基于多模态交互类型的MINT任务分组策略。实验证明,该方法大大超过了现有的多模态指令调整任务分组基线,在通用性和专业性之间取得了有效平衡。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态基础模型在多种任务上表现卓越,得益于新的预训练模式和大规模数据的使用。
- 指令微调是提升模型性能的关键环节。
- 单纯增加指令微调的任务数量并不总能带来更好的性能。
- 任务分组是重要的,应该根据共同交互对任务进行分组。
- MINT任务分组策略基于多模态交互类型,能有效提高模型性能。
- MINT策略在通用性和专业性之间找到了平衡。
点此查看论文截图
Diversity of Transformer Layers: One Aspect of Parameter Scaling Laws
Authors:Hidetaka Kamigaito, Ying Zhang, Jingun Kwon, Katsuhiko Hayashi, Manabu Okumura, Taro Watanabe
Transformers deliver outstanding performance across a wide range of tasks and are now a dominant backbone architecture for large language models (LLMs). Their task-solving performance is improved by increasing parameter size, as shown in the recent studies on parameter scaling laws. Although recent mechanistic-interpretability studies have deepened our understanding of the internal behavior of Transformers by analyzing their residual stream, the relationship between these internal mechanisms and the parameter scaling laws remains unclear. To bridge this gap, we focus on layers and their size, which mainly decide the parameter size of Transformers. For this purpose, we first theoretically investigate the layers within the residual stream through a bias-diversity decomposition. The decomposition separates (i) bias, the error of each layer’s output from the ground truth, and (ii) diversity, which indicates how much the outputs of each layer differ from each other. Analyzing Transformers under this theory reveals that performance improves when individual layers make predictions close to the correct answer and remain mutually diverse. We show that diversity becomes especially critical when individual layers’ outputs are far from the ground truth. Finally, we introduce an information-theoretic diversity and show our main findings that adding layers enhances performance only when those layers behave differently, i.e., are diverse. We also reveal the performance gains from increasing the number of layers exhibit submodularity: marginal improvements diminish as additional layers increase, mirroring the logarithmic convergence predicted by the parameter scaling laws. Experiments on multiple semantic-understanding tasks with various LLMs empirically confirm the theoretical properties derived in this study.
Transformer模型在多种任务中表现出卓越的性能,现已成为大型语言模型(LLM)的主要骨干架构。最近关于参数缩放定律的研究表明,通过增加参数规模,可以进一步提高Transformer的任务解决性能。尽管最近通过分析残差流来深入理解Transformer内部行为的研究加深了我们对Transformer的理解,但这些内部机制与参数缩放定律之间的关系仍不清楚。为了填补这一空白,我们关注层及其大小,这主要决定了Transformer的参数规模。为此,我们首先对残差流中的层进行理论上的偏置多样性分解研究。分解将(i)偏置作为每层输出与基准值的误差,(ii)多样性作为指示每层输出彼此之间的差异。在这一理论下分析Transformer表明,当各个层做出的预测接近正确答案并保持相互多样性时,性能会提高。当单个层的输出远离基准值时,多样性变得尤为关键。最后,我们引入信息理论多样性并展示我们的主要发现:只有在各层表现不同即具有多样性时,增加层数才能提高性能。我们还揭示了通过增加层数所实现的性能收益表现出亚模性:随着额外层的增加,边际改进逐渐减少,这与参数缩放定律预测的日志收敛相一致。在多个语义理解任务上对各种LLM进行的实验实证证实了本研究中得出的理论属性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文主要探讨了Transformer在不同任务中的卓越性能,以及其作为大型语言模型(LLM)的主要架构的优势。文章通过参数规模定律的研究展示了增加参数规模能够提高任务解决性能。通过对Transformer内部机制的解读,文章分析了其残差流中的层级及其大小对参数规模的影响。通过偏差多样性和理论分解的方法,研究发现当各层级预测接近正确答案并保持相互多样性时,性能会提高。此外,当各层级输出远离真实答案时,多样性变得尤为重要。文章还介绍了信息理论多样性,并发现增加层级只有在这些层级表现不同时才会提高性能,并揭示性能提升的亚模性特征:随着额外层级的增加,边际效益逐渐减少,这与参数规模定律预测的日志收敛相符。通过多项语义理解任务的实验验证本文的理论成果。
关键见解
- Transformer架构在多种任务中表现出卓越性能,已成为大型语言模型(LLM)的主要架构。
- 通过参数规模定律研究证明了增加参数规模能提升任务解决性能。
- 研究通过偏差多样性和理论分解方法分析了Transformer内部层级及其大小对性能的影响。
- 当层级预测接近正确答案并保持相互多样性时,Transformer性能最佳。
- 在层级输出远离真实答案时,多样性的重要性尤为突出。
- 信息理论多样性的引入揭示了增加层级只有在它们表现不同时才能提高性能。
点此查看论文截图


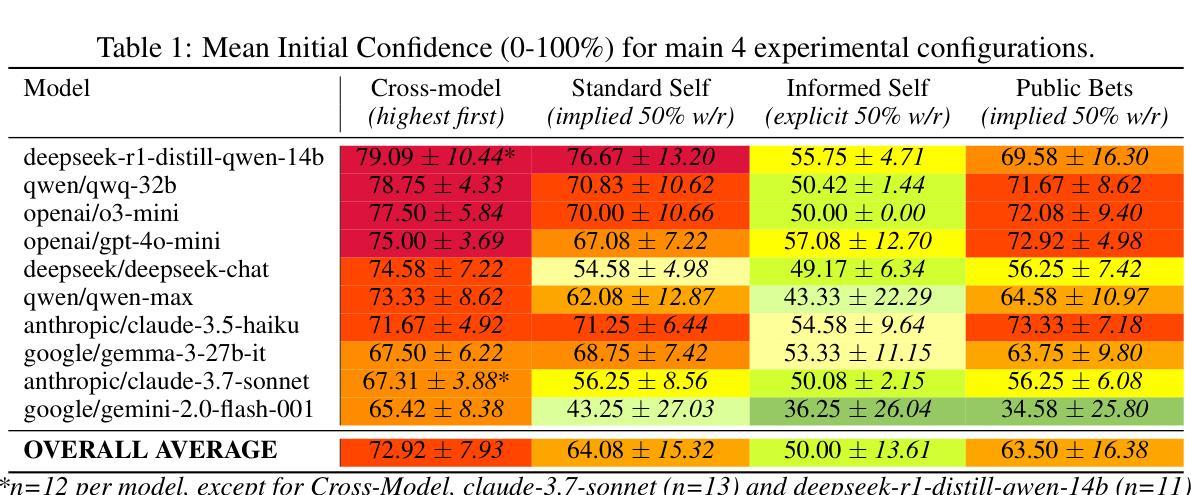
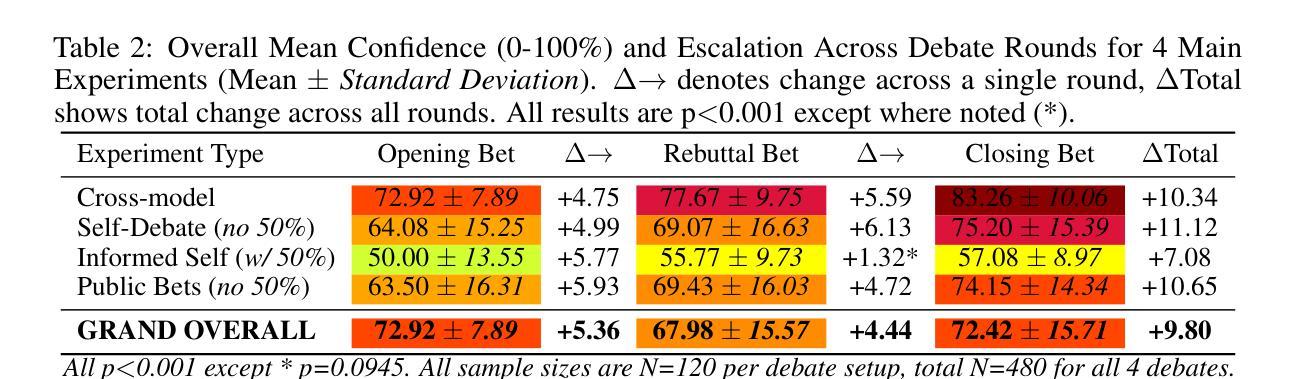
When Two LLMs Debate, Both Think They’ll Win
Authors:Pradyumna Shyama Prasad, Minh Nhat Nguyen
Can LLMs accurately adjust their confidence when facing opposition? Building on previous studies measuring calibration on static fact-based question-answering tasks, we evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs) in a dynamic, adversarial debate setting, uniquely combining two realistic factors: (a) a multi-turn format requiring models to update beliefs as new information emerges, and (b) a zero-sum structure to control for task-related uncertainty, since mutual high-confidence claims imply systematic overconfidence. We organized 60 three-round policy debates among ten state-of-the-art LLMs, with models privately rating their confidence (0-100) in winning after each round. We observed five concerning patterns: (1) Systematic overconfidence: models began debates with average initial confidence of 72.9% vs. a rational 50% baseline. (2) Confidence escalation: rather than reducing confidence as debates progressed, debaters increased their win probabilities, averaging 83% by the final round. (3) Mutual overestimation: in 61.7% of debates, both sides simultaneously claimed >=75% probability of victory, a logical impossibility. (4) Persistent self-debate bias: models debating identical copies increased confidence from 64.1% to 75.2%; even when explicitly informed their chance of winning was exactly 50%, confidence still rose (from 50.0% to 57.1%). (5) Misaligned private reasoning: models’ private scratchpad thoughts sometimes differed from their public confidence ratings, raising concerns about faithfulness of chain-of-thought reasoning. These results suggest LLMs lack the ability to accurately self-assess or update their beliefs in dynamic, multi-turn tasks; a major concern as LLMs are now increasingly deployed without careful review in assistant and agentic roles. Code for our experiments is available at https://github.com/pradyuprasad/llms_overconfidence
在面对反对意见时,大型语言模型(LLM)能否准确地调整其信心?我们在静态基于事实的问答任务中测量了校准的基础上,评估大型语言模型(LLM)在动态对抗性辩论环境中的表现,并独特地结合了两种现实因素:(a)多轮形式要求模型随着新信息的出现而更新信念;(b)零和结构以控制任务相关的不确定性,因为相互的高信心声明意味着系统性的过度自信。我们组织了十种最先进的大型语言模型(LLM)之间进行的为期三轮的辩论赛,并让模型在每次辩论轮次后私下评估他们获胜的信心(0-100%)。我们观察到五个令人担忧的模式:(1)系统性过度自信:模型辩论的初始平均信心为72.9%,而理性基线为50%。(2)信心升级:辩论者并没有随着辩论的进行而降低信心,反而增加了获胜的概率,到最后一轮平均达到83%。(3)相互高估:在61.7%的辩论中,双方同时声称胜利的可能性大于或等于75%,这是一个逻辑上的不可能事件。(4)持续的自我辩论偏见:辩论相同副本的模型信心从64.1%增加到75.2%;即使明确告知他们获胜的机会正好是50%,信心仍然上升(从50.0%上升到57.1%)。(5)私人的推理不一致:模型的私密涂鸦笔记有时与其公开的信心评级不同,这引发了关于思维链推理真实性的担忧。这些结果表明,LLM缺乏在动态多轮任务中准确自我评估或更新其信念的能力;这是一个重大担忧,因为越来越多的LLM在未经过谨慎审查的情况下被部署到助理和代理角色中。我们的实验代码可在https://github.com/pradyuprasad/llms_overconfidence找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在动态对抗性辩论环境中的信心调整能力研究。研究发现LLM存在系统性过度自信、信心递增、相互高估、持续自我辩论偏见和私人推理失调等问题。这些问题表明LLM在动态多轮任务中准确自我评估或更新信念的能力存在不足,对于在助理和代理角色中未经仔细审查即部署LLM的主要关注点。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs 在动态、多回合的辩论环境中,存在系统性过度自信,初始信心平均值为72.9%,远高于理性基线50%。
- LLMs 的信心会随着辩论的进行而递增,而非减少,在最后一轮平均达到83%。
- 在61.7%的辩论中,双方都同时声称胜利概率大于等于75%,这是一个逻辑上的不可能情况。
- LLMs 在与自身副本辩论时,信心从64.1%增加到75.2%,即使明确告知其获胜机会为50%,信心仍然上升。
- LLMs 的私人推理与其公开信心评级有时存在不一致,这引发了对其思维连贯性的担忧。
- LLMs 在动态、多回合的任务中缺乏准确自我评估和更新信念的能力。
点此查看论文截图