⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-11 更新
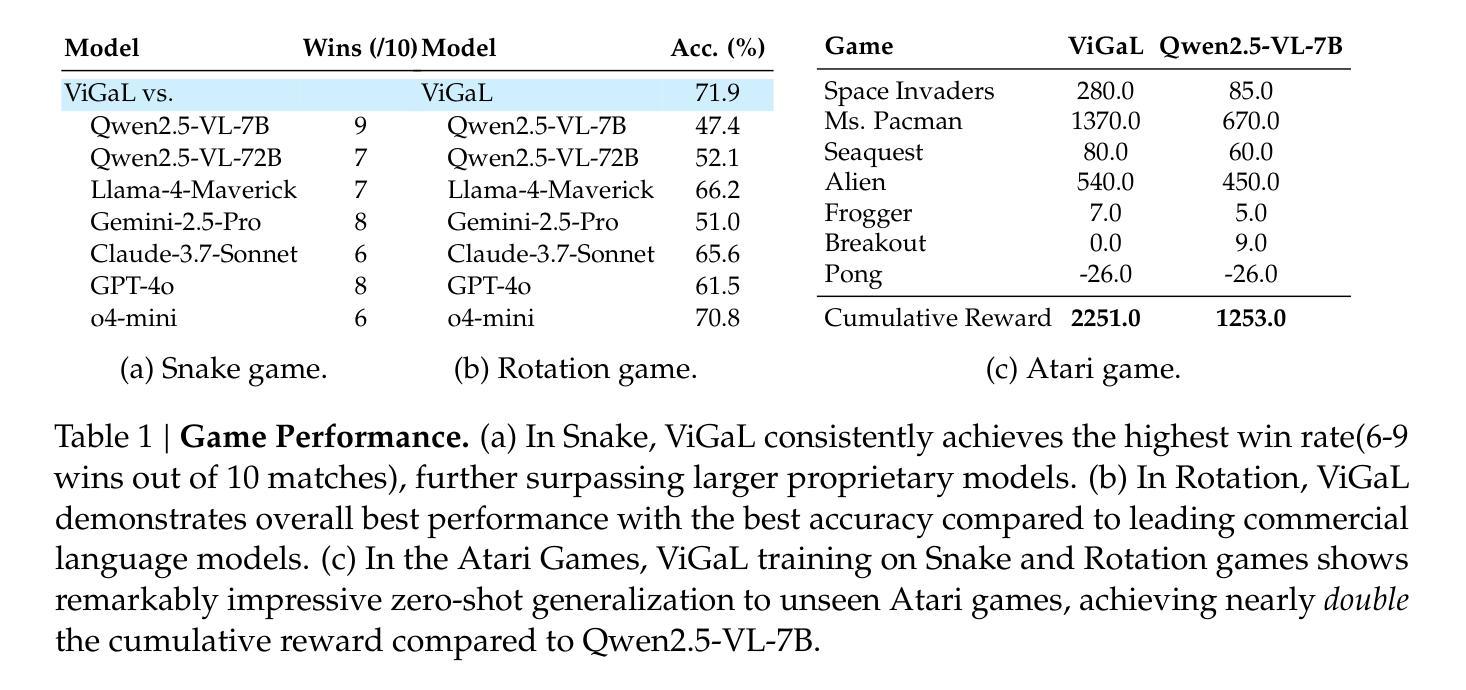
Play to Generalize: Learning to Reason Through Game Play
Authors:Yunfei Xie, Yinsong Ma, Shiyi Lan, Alan Yuille, Junfei Xiao, Chen Wei
Developing generalizable reasoning capabilities in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) remains challenging. Motivated by cognitive science literature suggesting that gameplay promotes transferable cognitive skills, we propose a novel post-training paradigm, Visual Game Learning, or ViGaL, where MLLMs develop out-of-domain generalization of multimodal reasoning through playing arcade-like games. Specifically, we show that post-training a 7B-parameter MLLM via reinforcement learning (RL) on simple arcade-like games, e.g. Snake, significantly enhances its downstream performance on multimodal math benchmarks like MathVista, and on multi-discipline questions like MMMU, without seeing any worked solutions, equations, or diagrams during RL, suggesting the capture of transferable reasoning skills. Remarkably, our model outperforms specialist models tuned on multimodal reasoning data in multimodal reasoning benchmarks, while preserving the base model’s performance on general visual benchmarks, a challenge where specialist models often fall short. Our findings suggest a new post-training paradigm: synthetic, rule-based games can serve as controllable and scalable pre-text tasks that unlock generalizable multimodal reasoning abilities in MLLMs.
在多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)中发展可推广的推理能力仍然是一个挑战。受认知科学文献的启发,该文献表明游戏可以促进可迁移的认知技能,我们提出了一种新型的后训练范式,即视觉游戏学习(ViGaL)。在此范式中,MLLMs通过玩类似街机游戏来发展跨域的多模态推理能力。具体来说,我们通过强化学习(RL)对具有7B参数的MLLM进行后训练,使其在简单的类似街机游戏(如Snake)上的表现得到显著提升。重要的是,该模型在多模态基准测试(如MathVista和多学科问题MMMU)上的表现得到显著增强,且在强化学习过程中无需查看任何解决方案、方程式或图表,这表明该模型掌握了可迁移的推理技能。值得注意的是,我们的模型在多模态推理基准测试中的表现优于专门在多模态推理数据上调整过的模型,同时保持了基础模型在一般视觉基准测试上的性能。这是一项挑战,因为专业模型通常在这方面表现不足。我们的研究结果表明了一种新型后训练范式:合成、基于规则的游戏可以作为可控和可扩展的预文本任务,解锁MLLM中的通用多模态推理能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://yunfeixie233.github.io/ViGaL/
Summary
基于认知科学文献对游戏可以促进转移认知技能的观点,研究团队提出一种名为ViGaL(视觉游戏学习)的新型训练后范式。在此范式下,多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)可以通过类似游戏的学习,提高非域外模态推理能力的泛化能力。该研究以模仿电子游戏的模式,采用强化学习(RL)对含有7亿参数的MLLM进行训练后处理,发现模型在多模态基准测试中表现出更高的成绩,特别是在类似于MathVista这样的测试数学知识和综合题中展现突出优势。此外,值得一提的是,即便没有涉及具体解题技巧、公式或图表等专项训练,模型也能掌握可迁移的推理技能。这一发现为新的训练后范式提供了启示:合成规则的游戏可以作为可控且可扩展的预文本任务,解锁MLLM中的泛化多模态推理能力。我们的模型在多模态基准测试中表现优异,超过经过专项训练的模型表现。
Key Takeaways
- 提出Visual Game Learning(ViGaL)范式用于增强多模态大型语言模型的泛化推理能力。
- 利用强化学习对MLLM进行类似游戏的训练处理,无需专门针对特定的解题方法或学科进行指导。
- 研究表明训练后的模型在类似于MathVista的测试中表现出优越的多模态推理能力,说明转移技能的形成机制显著有效。
- ViGaL方法可以广泛应用于不同类型的游戏环境,增强模型的适应性和通用性。
- 训练后的模型在多模态基准测试中表现优于经过专门训练的模型,同时保持对一般视觉基准测试的原有性能水平。
- 游戏学习范式为训练大型语言模型提供了新的视角和思路。该领域未来的研究可继续探索不同类型游戏的效用以及其与认知能力的关系。
点此查看论文截图


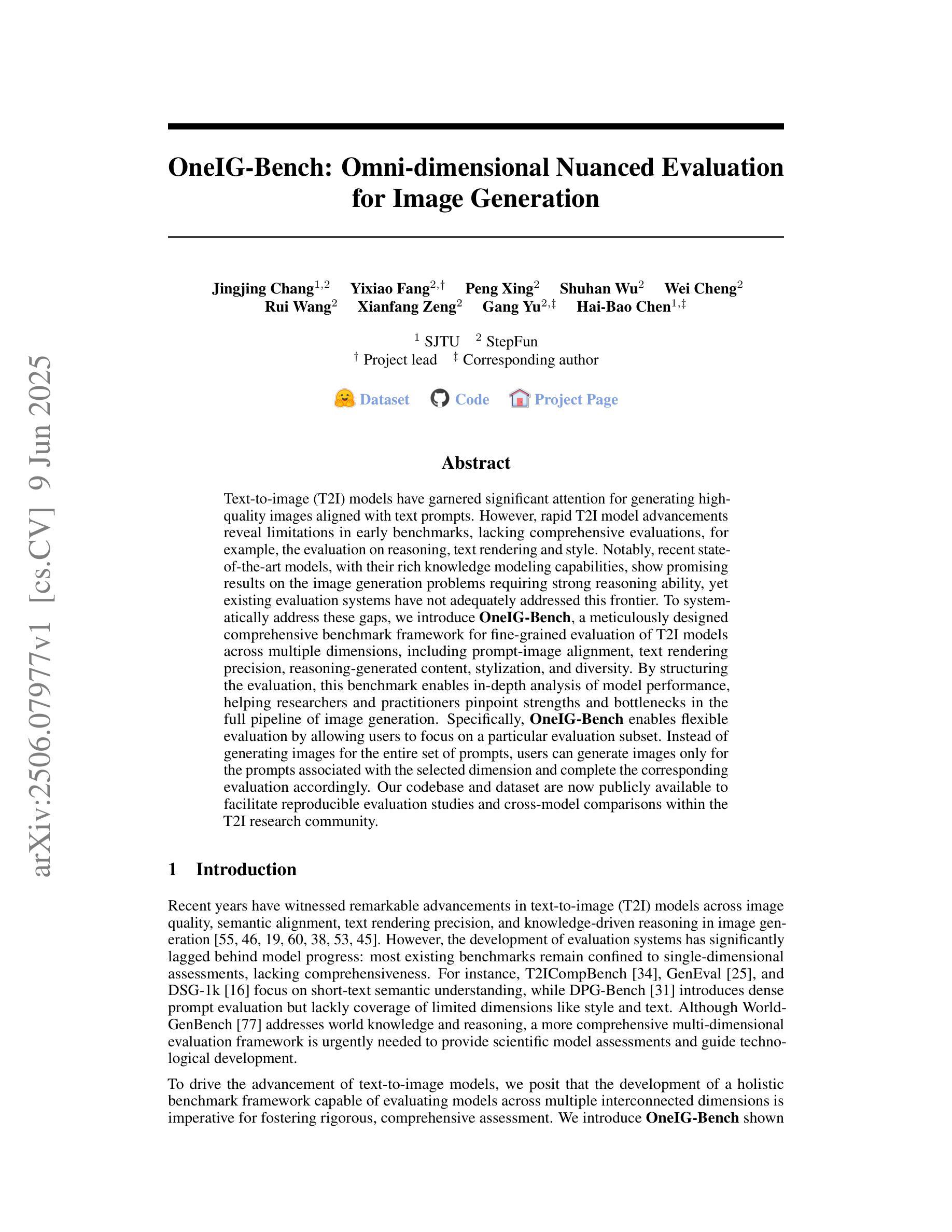
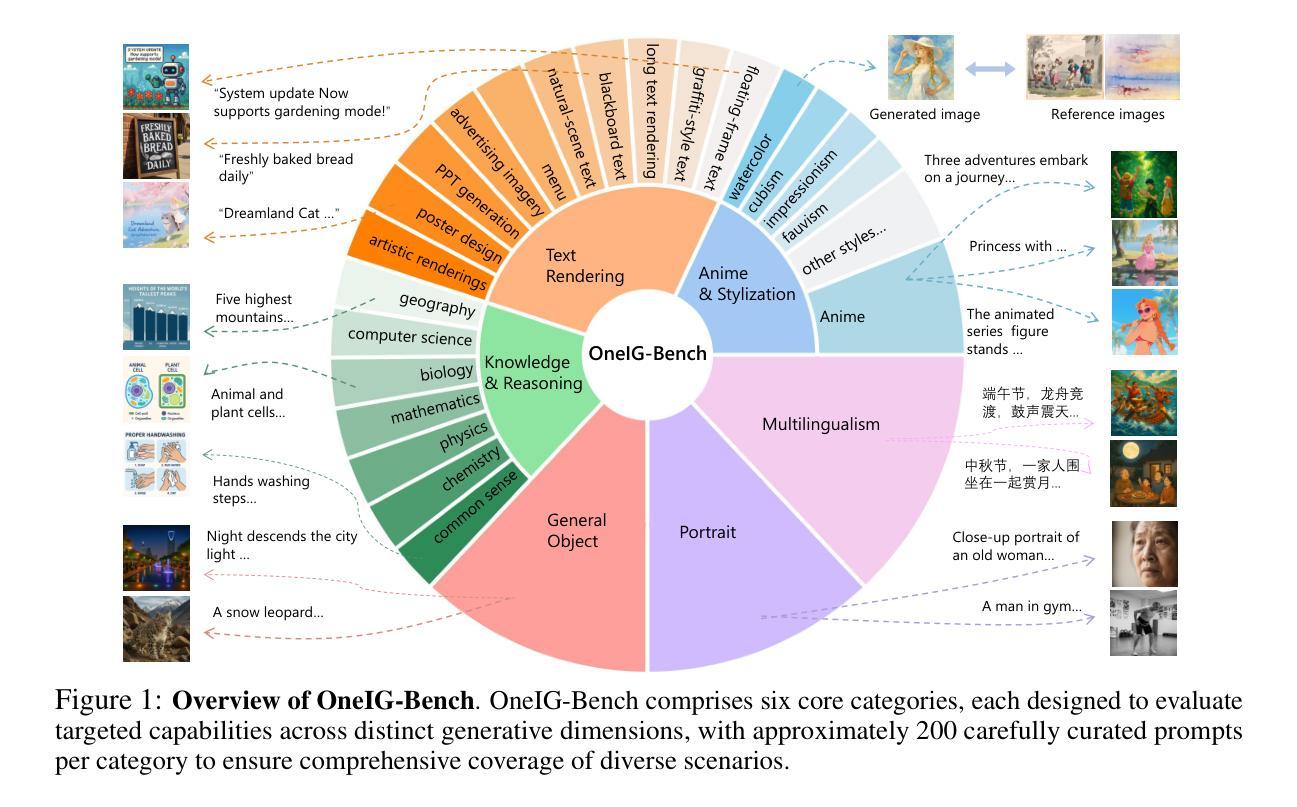
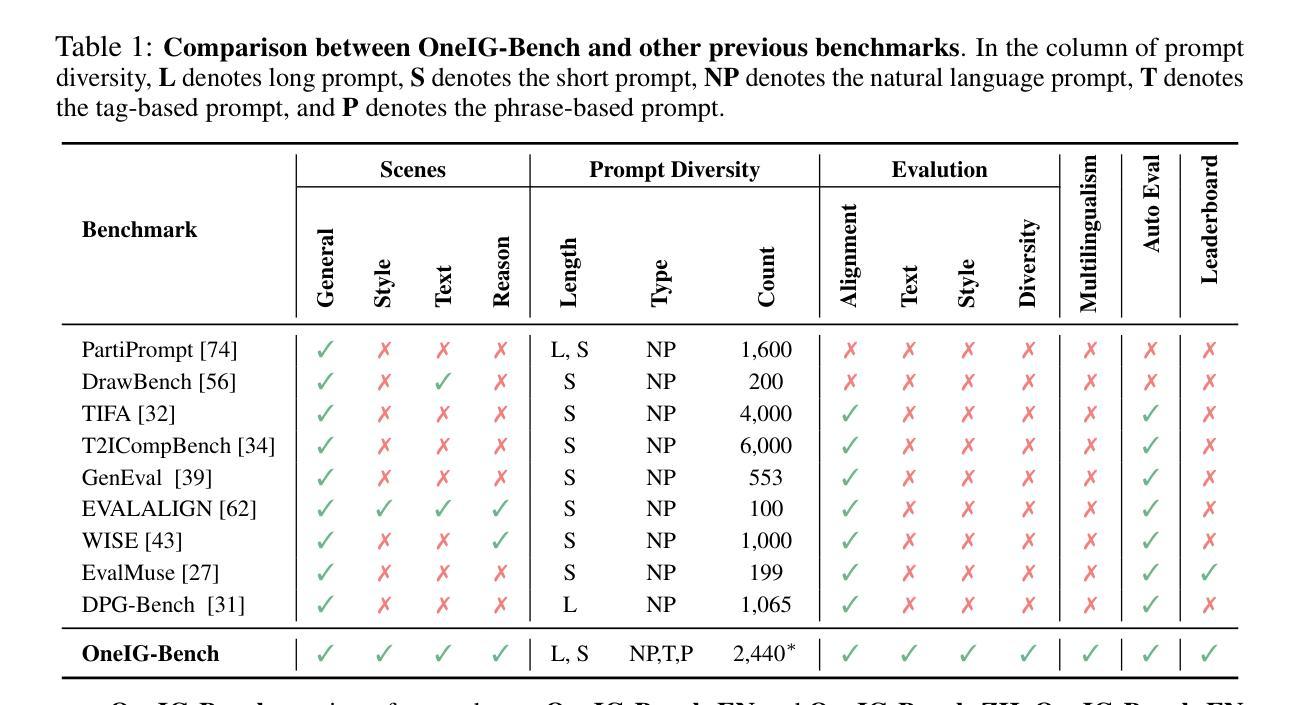
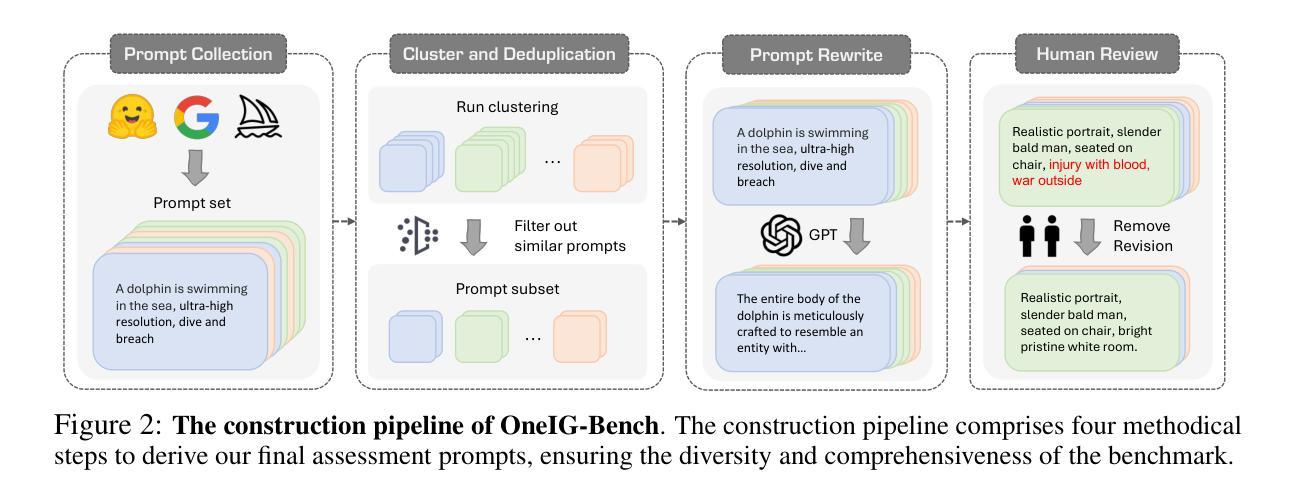
OneIG-Bench: Omni-dimensional Nuanced Evaluation for Image Generation
Authors:Jingjing Chang, Yixiao Fang, Peng Xing, Shuhan Wu, Wei Cheng, Rui Wang, Xianfang Zeng, Gang Yu, Hai-Bao Chen
Text-to-image (T2I) models have garnered significant attention for generating high-quality images aligned with text prompts. However, rapid T2I model advancements reveal limitations in early benchmarks, lacking comprehensive evaluations, for example, the evaluation on reasoning, text rendering and style. Notably, recent state-of-the-art models, with their rich knowledge modeling capabilities, show promising results on the image generation problems requiring strong reasoning ability, yet existing evaluation systems have not adequately addressed this frontier. To systematically address these gaps, we introduce OneIG-Bench, a meticulously designed comprehensive benchmark framework for fine-grained evaluation of T2I models across multiple dimensions, including prompt-image alignment, text rendering precision, reasoning-generated content, stylization, and diversity. By structuring the evaluation, this benchmark enables in-depth analysis of model performance, helping researchers and practitioners pinpoint strengths and bottlenecks in the full pipeline of image generation. Specifically, OneIG-Bench enables flexible evaluation by allowing users to focus on a particular evaluation subset. Instead of generating images for the entire set of prompts, users can generate images only for the prompts associated with the selected dimension and complete the corresponding evaluation accordingly. Our codebase and dataset are now publicly available to facilitate reproducible evaluation studies and cross-model comparisons within the T2I research community.
文本到图像(T2I)模型因能够生成与文本提示对齐的高质量图像而受到广泛关注。然而,T2I模型的快速发展显示出早期基准测试的局限性,缺乏全面评估,例如对推理、文本渲染和风格的评估。值得注意的是,最近的最先进模型凭借其丰富的知识建模能力,在需要强大推理能力的图像生成问题上显示出有希望的结果,但现有的评估系统尚未充分解决这一前沿问题。为了系统地解决这些差距,我们引入了OneIG-Bench,这是一个精心设计的综合基准框架,用于对T2I模型进行跨多个维度的精细评估,包括提示图像对齐、文本渲染精度、推理生成内容、风格化和多样性。通过结构化评估,此基准测试能够深入分析模型性能,帮助研究人员和实践者确定图像生成整个流程中的优势和瓶颈。特别是,OneIG-Bench通过允许用户关注特定的评估子集来实现灵活评估。用户无需为整个提示集生成图像,而只需为与所选维度相关的提示生成图像,并相应地完成评估。我们的代码库和数据集现已公开可用,以促进T2I研究社区内的可重复评估研究和跨模型比较。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了文本转图像(T2I)模型的重要性及其局限性,强调了现有评估系统的不足。为了系统地解决这些问题,文章引入了一个名为OneIG-Bench的综合评估框架,该框架对T2I模型进行精细评估,包括提示图像对齐、文本渲染精度、推理生成内容、风格化和多样性等多个维度。OneIG-Bench允许用户灵活评估,只针对所选维度的提示生成图像并完成相应评估。此代码库和数据集现已公开,以推动T2I研究社区的可重复性评价研究和跨模型比较。
Key Takeaways
- 文本转图像(T2I)模型在生成与文本提示对齐的高质量图像方面受到广泛关注。
- 现有评估系统对于T2I模型的全面评价存在局限性,特别是在推理、文本渲染和风格方面的评价。
- OneIG-Bench是一个全面评估T2I模型的框架,涵盖多个维度,如提示图像对齐、文本渲染精度、推理生成内容、风格化和多样性。
- OneIG-Bench允许用户灵活评估,只针对特定评估子集进行图像生成和评估。
- OneIG-Bench的出现是为了解决现有评估系统的不足,帮助研究人员和从业者更深入地了解模型性能。
- OneIG-Bench的公开数据集和代码库促进了T2I研究社区的可重复性评价研究和跨模型比较。
点此查看论文截图
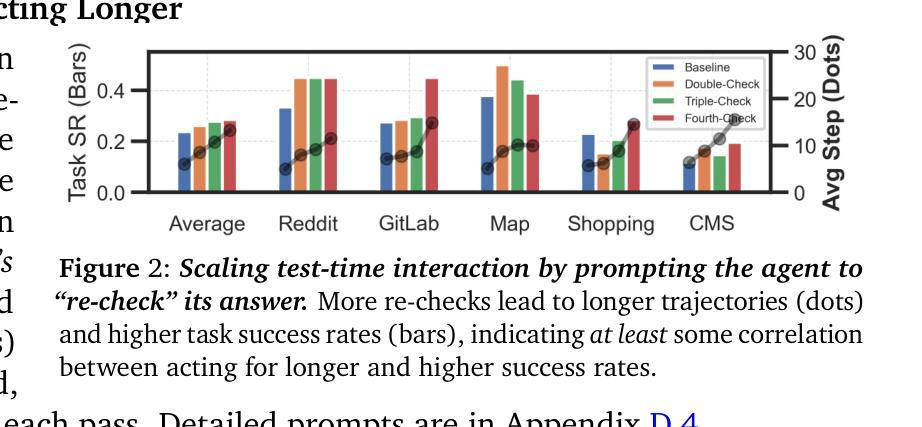
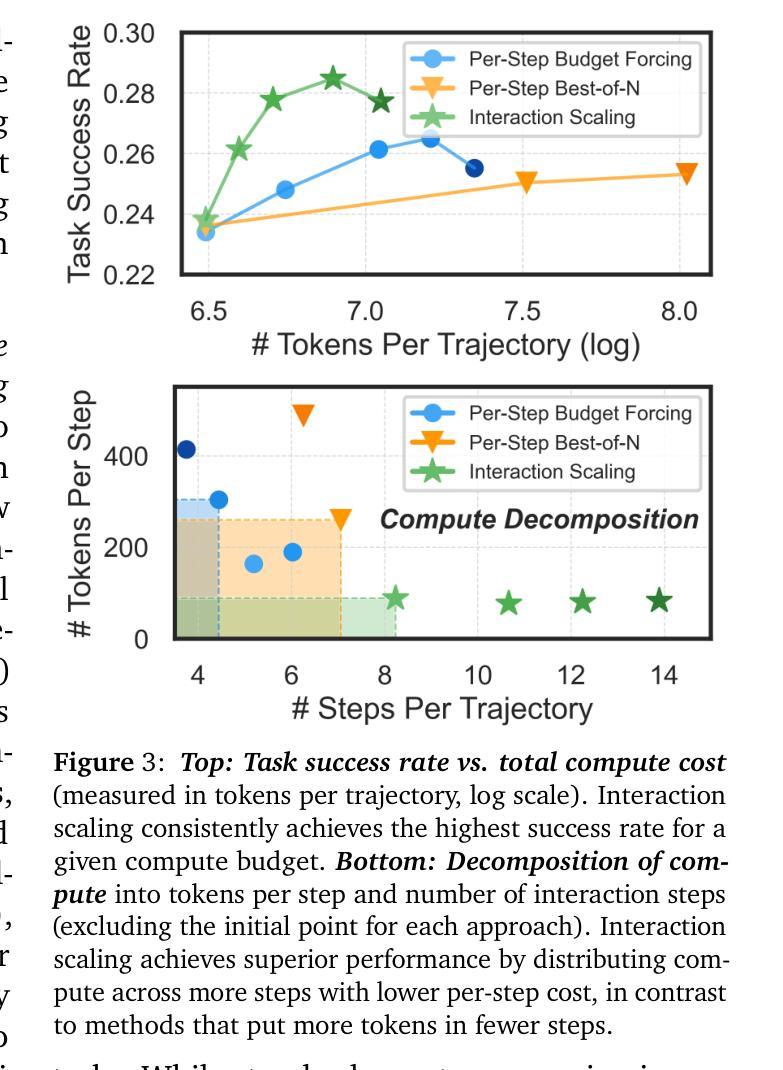
Thinking vs. Doing: Agents that Reason by Scaling Test-Time Interaction
Authors:Junhong Shen, Hao Bai, Lunjun Zhang, Yifei Zhou, Amrith Setlur, Shengbang Tong, Diego Caples, Nan Jiang, Tong Zhang, Ameet Talwalkar, Aviral Kumar
The current paradigm of test-time scaling relies on generating long reasoning traces (“thinking” more) before producing a response. In agent problems that require interaction, this can be done by generating thinking traces before acting in the world. However, this process does not allow agents to acquire new information from the environment or adapt their behavior over time. In this work, we propose to scale test-time interaction, an untapped dimension of test-time scaling that increases the agent’s interaction horizon to enable running rich behaviors such as exploration, backtracking, and dynamic re-planning within a single rollout. To demonstrate the promise of this scaling dimension, we study the domain of web agents. We first show that even prompting-based interaction scaling without any training can improve task success on web benchmarks non-trivially. Building on this, we introduce TTI (Test-Time Interaction), a curriculum-based online reinforcement learning (RL) approach that trains agents by adaptively adjusting their rollout lengths. Using a Gemma 3 12B model, TTI produces state-of-the-art open-source, open-data web agents on WebVoyager and WebArena benchmarks. We further show that TTI enables agents to balance exploration and exploitation adaptively. Our results establish interaction scaling as a powerful, complementary axis to scaling per-step compute, offering new avenues for training adaptive agents.
当前测试时间缩放的模式依赖于在产生回应之前生成长的推理轨迹(即“思考”更多)。在需要交互的代理问题中,这可以通过在世界中行动之前生成思考轨迹来完成。然而,这个过程不允许代理从环境中获取新信息,也不能随着时间的推移改变它们的行为。在这项工作中,我们提出扩大测试时间交互,这是测试时间缩放的一个尚未开发的维度,它将代理的交互范围扩大到在一次运行中执行丰富的行为,如探索、回溯和动态重新规划。为了证明这一缩放维度的潜力,我们研究了网页代理领域。我们首先表明,即使在没有任何训练的情况下基于提示的交互缩放也可以在一定程度上提高网页基准测试的任务成功率。在此基础上,我们引入了TTI(测试时间交互),这是一种基于课程的在线强化学习(RL)方法,通过自适应调整运行长度来训练代理。使用Gemma 3 12B模型,TTI在WebVoyager和WebArena基准测试中产生了最先进的开源开放数据网页代理。我们还进一步表明,TTI使代理能够自适应地平衡探索和利用。我们的结果确立了交互缩放作为强大的、与每步计算缩放相辅相成的轴,为训练自适应代理提供了新的途径。
简化版翻译:
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种测试时交互扩展的方法,旨在提高智能体在环境中的互动能力,实现丰富行为如探索、回溯和动态规划等。通过调整智能体的交互范围和在线强化学习训练,提高了智能体在Web基准测试中的表现。这种方法可使智能体适应环境新信息,并在互动中实现自适应平衡探索与利用。总之,交互扩展已成为计算能力的强大补充维度,为训练自适应智能体提供了新的途径。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时交互扩展允许智能体在环境中实现更丰富行为,如探索、回溯和动态规划等。
- 通过调整智能体的交互范围,可提高其在Web基准测试中的表现。
- TTI(测试时交互)是一种基于在线强化学习的训练方法,可通过自适应调整智能体的试运行时长来提高其表现。
- 使用Gemma 3 12B模型的TTI方法在WebVoyager和WebArena基准测试中取得了最新开源状态的表现。
- TTI使智能体能够自适应平衡探索与利用。
- 交互扩展已成为计算能力的一个强大补充维度。
点此查看论文截图

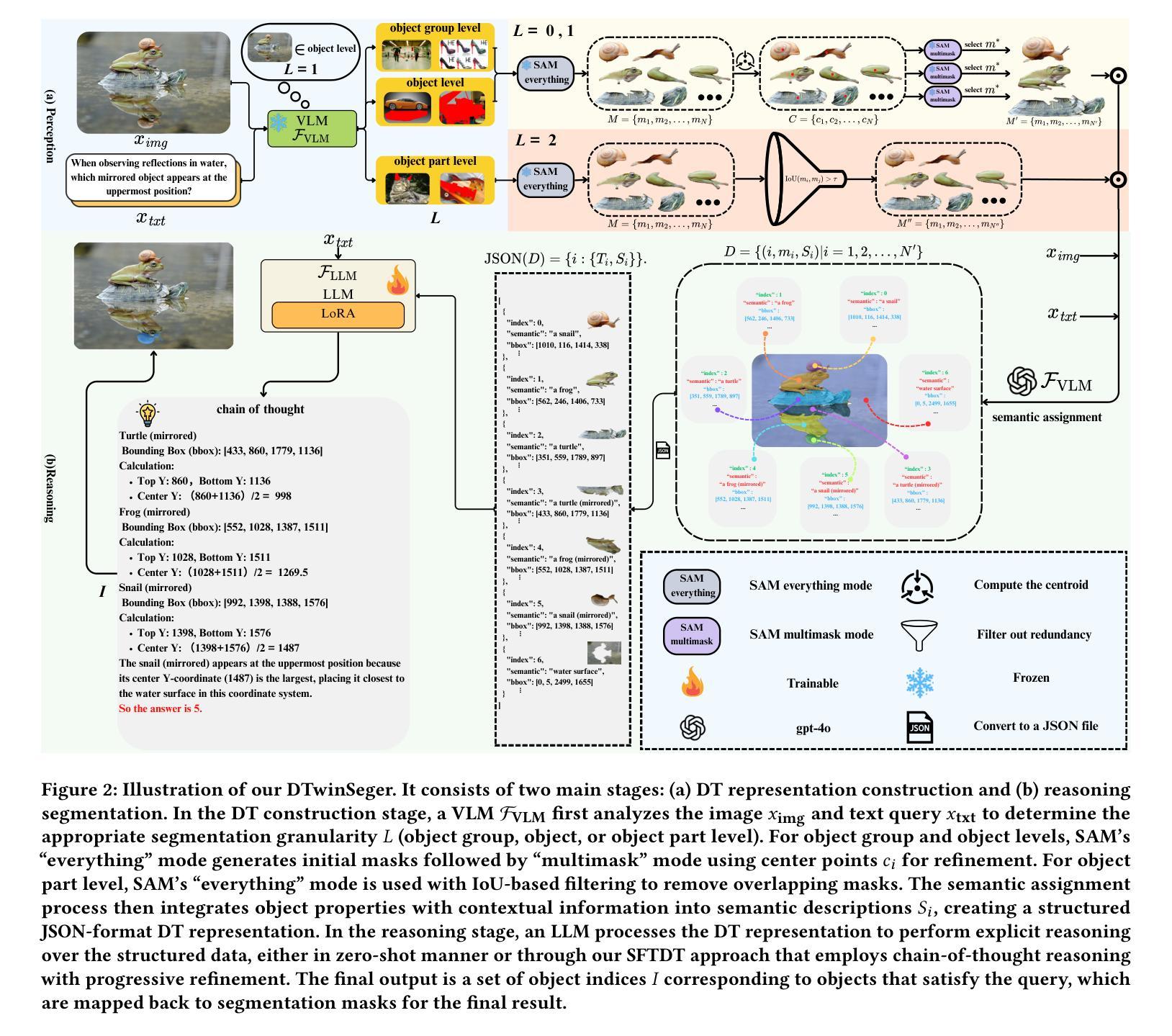
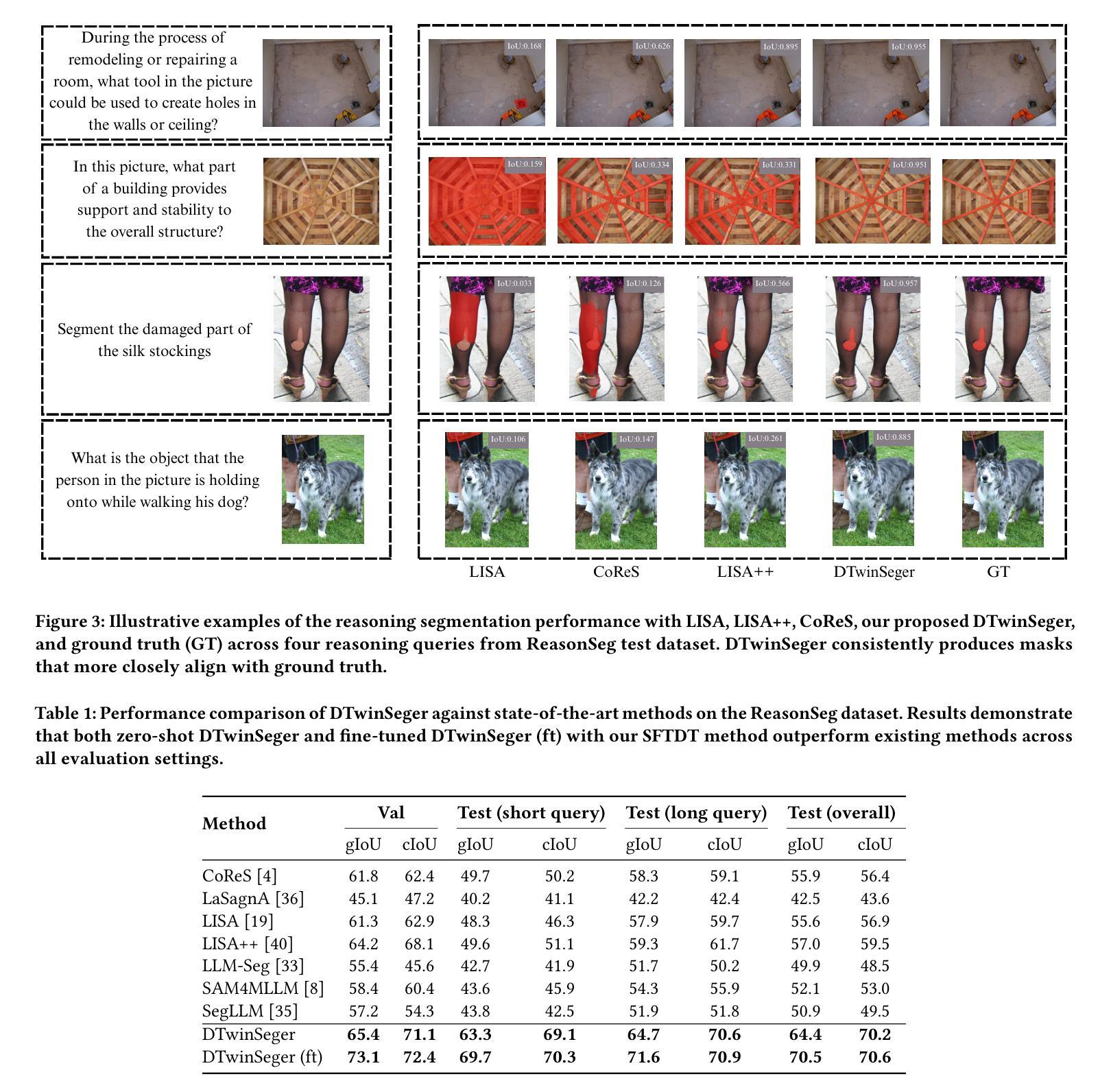
Decoupling the Image Perception and Multimodal Reasoning for Reasoning Segmentation with Digital Twin Representations
Authors:Yizhen Li, Dell Zhang, Xuelong Li, Yiqing Shen
Reasoning Segmentation (RS) is a multimodal vision-text task that requires segmenting objects based on implicit text queries, demanding both precise visual perception and vision-text reasoning capabilities. Current RS approaches rely on fine-tuning vision-language models (VLMs) for both perception and reasoning, but their tokenization of images fundamentally disrupts continuous spatial relationships between objects. We introduce DTwinSeger, a novel RS approach that leverages Digital Twin (DT) representation as an intermediate layer to decouple perception from reasoning. Innovatively, DTwinSeger reformulates RS as a two-stage process, where the first transforms the image into a structured DT representation that preserves spatial relationships and semantic properties and then employs a Large Language Model (LLM) to perform explicit reasoning over this representation to identify target objects. We propose a supervised fine-tuning method specifically for LLM with DT representation, together with a corresponding fine-tuning dataset Seg-DT, to enhance the LLM’s reasoning capabilities with DT representations. Experiments show that our method can achieve state-of-the-art performance on two image RS benchmarks and three image referring segmentation benchmarks. It yields that DT representation functions as an effective bridge between vision and text, enabling complex multimodal reasoning tasks to be accomplished solely with an LLM.
推理分割(RS)是一项多模态的视觉文本任务,它要求根据隐式文本查询对对象进行分割,需要精确的视觉感知和视觉文本推理能力。当前的RS方法依赖于对视觉语言模型(VLM)的微调来进行感知和推理,但它们的图像标记方式会破坏对象之间连续的空间关系。我们引入了DTwinSeger,这是一种新型的RS方法,它利用数字孪生(DT)表示作为中间层,将感知与推理解耦。创新的是,DTwinSeger将RS重新定义为两个阶段的过程,其中第一阶段将图像转换为结构化的DT表示,保留空间关系和语义属性,然后采用大型语言模型(LLM)对此表示进行明确的推理,以识别目标对象。我们提出了一种专门针对LLM的DT表示进行微调的方法,并配以相应的微调数据集Seg-DT,以增强LLM使用DT表示的推理能力。实验表明,我们的方法在两项图像RS基准测试和三项图像引用分割基准测试上均达到了最先进的性能。这表明DT表示作为视觉和文本之间的有效桥梁,能够仅使用LLM完成复杂的跨模态推理任务。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
多模态视觉文本任务中的推理分割(RS)需要基于隐文本查询进行对象分割,要求精确的视觉感知和视觉文本推理能力。现有的RS方法依赖于对视觉语言模型(VLMs)进行微调以实现感知和推理,但其对图像的符号化会破坏对象间的连续空间关系。本文介绍了一种新的RS方法DTwinSeger,它利用数字孪生(DT)表示作为中间层来解耦感知和推理。DTwinSeger将RS重新构建为一个两阶段的过程,首先将图像转换为保留空间关系和语义属性的结构化DT表示,然后利用大型语言模型(LLM)对此表示进行明确的推理以识别目标对象。本文还提出了一种针对LLM的特定监督微调方法,并使用相应的微调数据集Seg-DT来增强LLM在DT表示方面的推理能力。实验表明,该方法在图像RS基准测试集和图像指代分割基准测试集上均达到了领先水平,证明了DT表示作为连接视觉和文本的有效桥梁,使得复杂的多模态推理任务能够仅通过LLM来完成。
Key Takeaways:
- 推理分割(RS)是结合视觉与文本的多模态任务,需根据隐文本查询进行物体分割。
- 当前方法依赖微调视觉语言模型(VLMs),但此方法在符号化图像时会破坏对象间的空间连续性。
- DTwinSeger利用数字孪生(DT)表示作为中间层,将感知与推理解耦。
- DTwinSeger将RS过程分为两个阶段:图像转化为结构化DT表示,再利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行推理。
- 提出一种针对LLM的特定监督微调方法,结合微调数据集Seg-DT,增强LLM在DT表示上的推理能力。
- 实验证明,DTwinSeger在多个基准测试集上表现优秀,达到领先水平。
点此查看论文截图
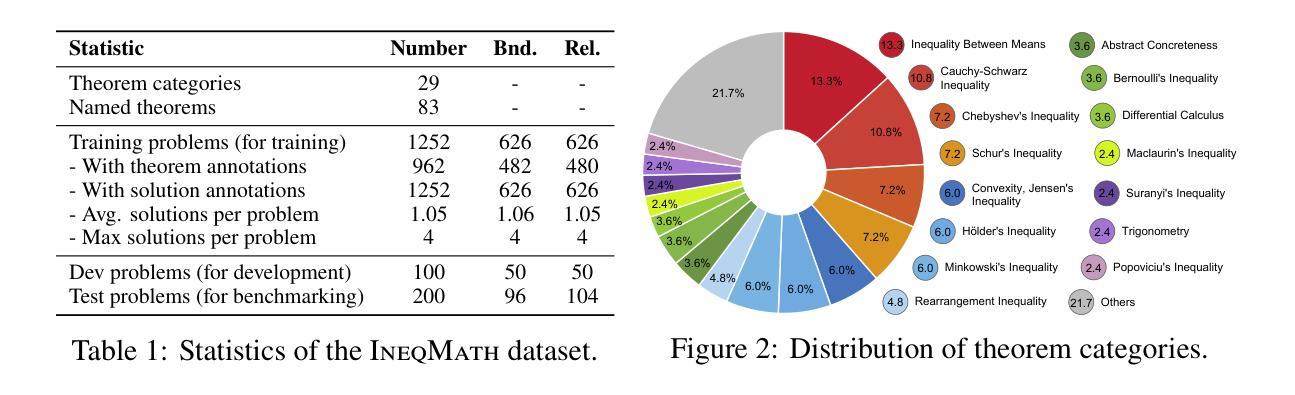
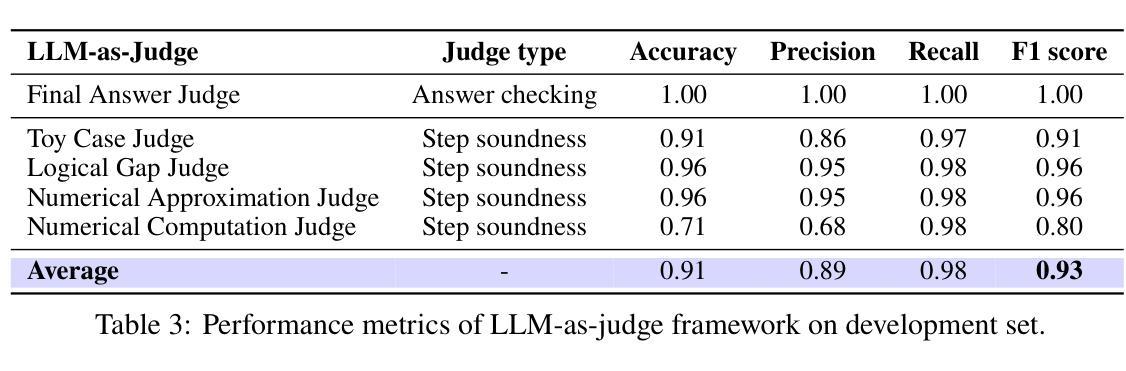
Solving Inequality Proofs with Large Language Models
Authors:Jiayi Sheng, Luna Lyu, Jikai Jin, Tony Xia, Alex Gu, James Zou, Pan Lu
Inequality proving, crucial across diverse scientific and mathematical fields, tests advanced reasoning skills such as discovering tight bounds and strategic theorem application. This makes it a distinct, demanding frontier for large language models (LLMs), offering insights beyond general mathematical problem-solving. Progress in this area is hampered by existing datasets that are often scarce, synthetic, or rigidly formal. We address this by proposing an informal yet verifiable task formulation, recasting inequality proving into two automatically checkable subtasks: bound estimation and relation prediction. Building on this, we release IneqMath, an expert-curated dataset of Olympiad-level inequalities, including a test set and training corpus enriched with step-wise solutions and theorem annotations. We also develop a novel LLM-as-judge evaluation framework, combining a final-answer judge with four step-wise judges designed to detect common reasoning flaws. A systematic evaluation of 29 leading LLMs on IneqMath reveals a surprising reality: even top models like o1 achieve less than 10% overall accuracy under step-wise scrutiny; this is a drop of up to 65.5% from their accuracy considering only final answer equivalence. This discrepancy exposes fragile deductive chains and a critical gap for current LLMs between merely finding an answer and constructing a rigorous proof. Scaling model size and increasing test-time computation yield limited gains in overall proof correctness. Instead, our findings highlight promising research directions such as theorem-guided reasoning and self-refinement. Code and data are available at https://ineqmath.github.io/.
不平等证明在科学和数学领域的多个方面都至关重要,它测试了发现紧密界限和战略定理应用等高级推理技能。这使得它成为大型语言模型(LLM)的一个独特且具挑战性的前沿领域,为一般数学问题解决提供了深入见解。该领域的进展受到现有数据集的阻碍,这些数据集通常稀缺、合成或过于形式化。我们通过提出一种非正式但可验证的任务制定来解决这个问题,将不平等证明重新制定为两个可以自动检查的任务:界限估计和关系预测。在此基础上,我们推出了IneqMath数据集,这是一套专家策划的奥林匹克级别的不等式数据集,包括测试集和训练语料库,并辅以逐步解决方案和定理注释。我们还开发了一种新型LLM评估框架(LLM作为法官),该框架结合了最终答案法官和四步法官的设计,旨在检测常见的推理缺陷。对IneqMath上29个领先的大型语言模型进行的系统评估揭示了一个令人惊讶的事实:即使在逐步审查下,即使是顶级模型如o1的整体准确率也低于10%;与仅考虑最终答案等价的准确率相比,这一差距高达高达65.5%。这种差异暴露了脆弱的演绎链以及当前大型语言模型在找到答案与构建严格证明之间的关键差距。扩大模型规模并增加测试时间的计算对提高整体证明的正确性产生有限收益。相反,我们的研究结果表明了定理引导推理和自我完善等具有前景的研究方向。相关代码和数据可在https://ineqmath.github.io/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 52 pages, 16 figures
Summary
该文介绍了不等式证明在科学和数学领域的重要性,测试了高级推理技能,如寻找紧密界限和战略定理应用。文章指出,大型语言模型(LLMs)在这个领域的发展受到现有数据集的阻碍,这些数据集通常稀缺、合成或僵化。因此,文章提出了一个非正式但可验证的任务公式,将不等式证明重新制定为两个可自动检查的任务:界限估计和关系预测。此外,文章发布了一个专家编制的不等式证明数据集IneqMath,包括奥林匹克级别的不等式测试集和丰富的逐步解决方案和定理注释。文章还开发了一种新型LLM评估框架,结合最终答案评审和四个逐步评审,旨在检测常见的推理缺陷。对29种领先的大型语言模型的系统评估显示,即使在逐步审查下,顶级模型的准确率也令人惊讶地低于10%。这表明当前大型语言模型在找到答案与构建严格证明之间存在关键差距。扩大模型规模并增加测试时间计算仅带来有限的总体证明正确性收益。相反,研究发现定理引导推理和自我完善等研究方向具有希望。
Key Takeaways
- 不等式证明在科学和数学领域具有关键作用,测试高级推理技能。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在解决不等式证明任务时面临挑战,现有数据集存在缺陷。
- 提出了一个非正式但可验证的任务公式,将不等式证明分为两个子任务:界限估计和关系预测。
- 发布了IneqMath数据集,包含奥林匹克级别的不等式问题,以及逐步解决方案和定理注释。
- 开发了一种新型LLM评估框架,以检测推理缺陷。
- 系统评估显示,即使在逐步审查下,顶级大型语言模型的准确率也低于10%。
点此查看论文截图

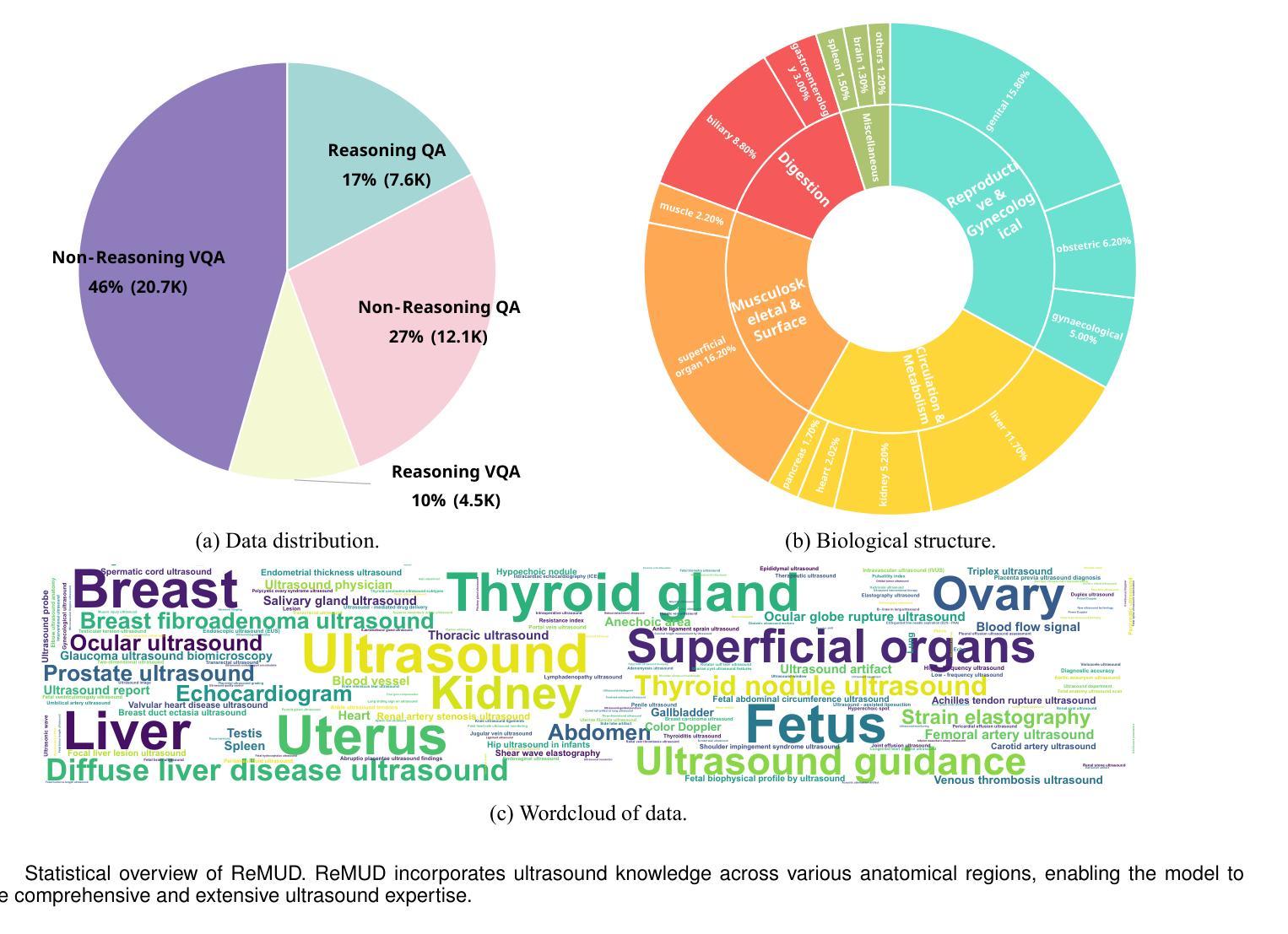
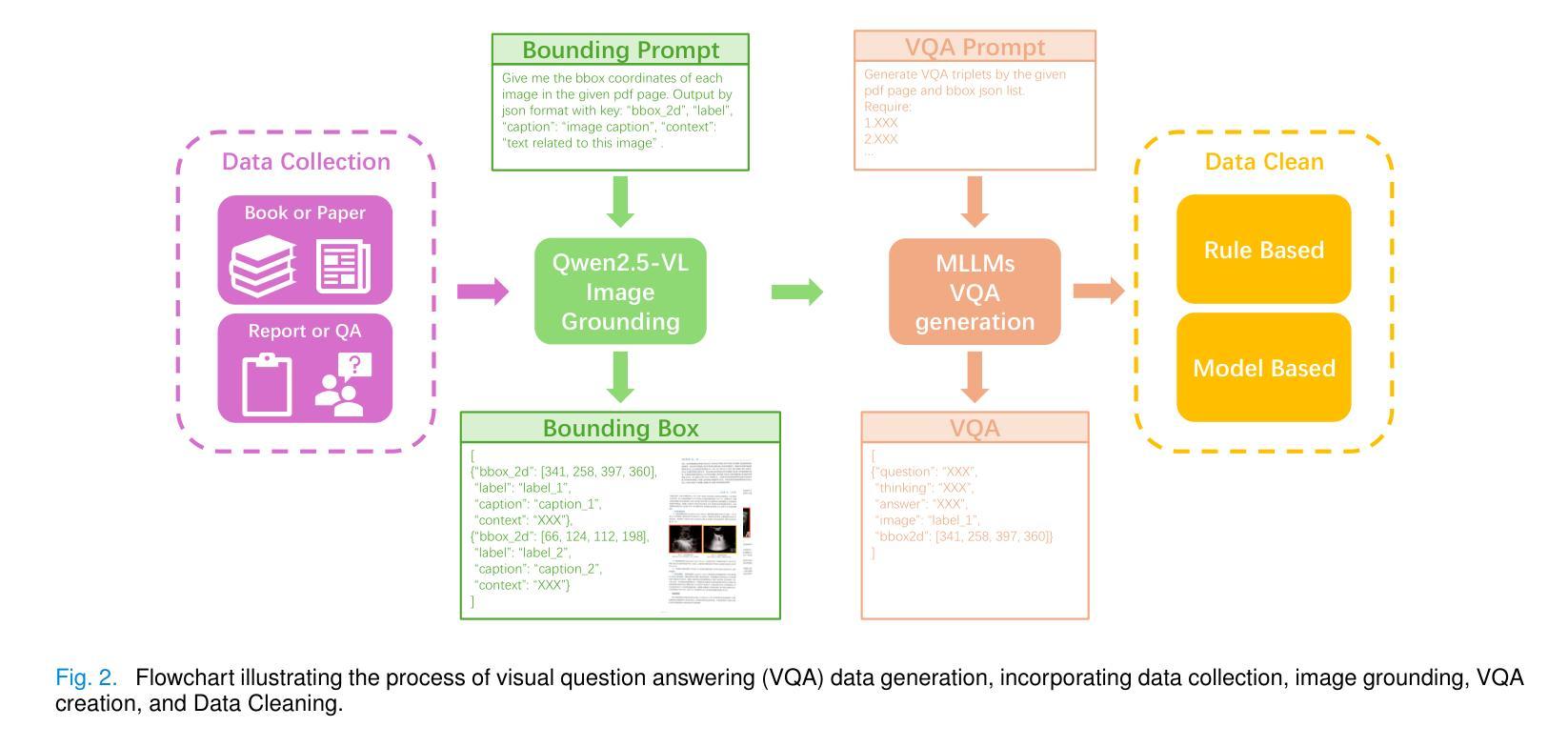
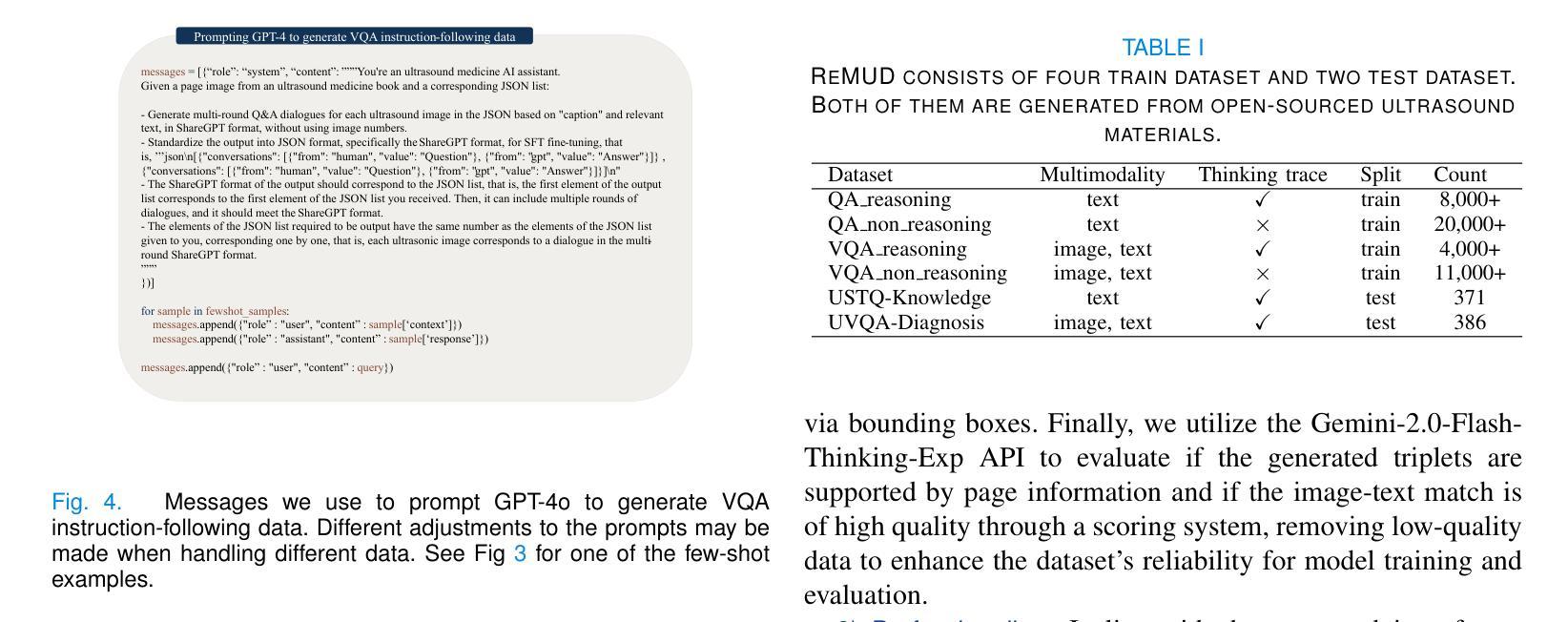
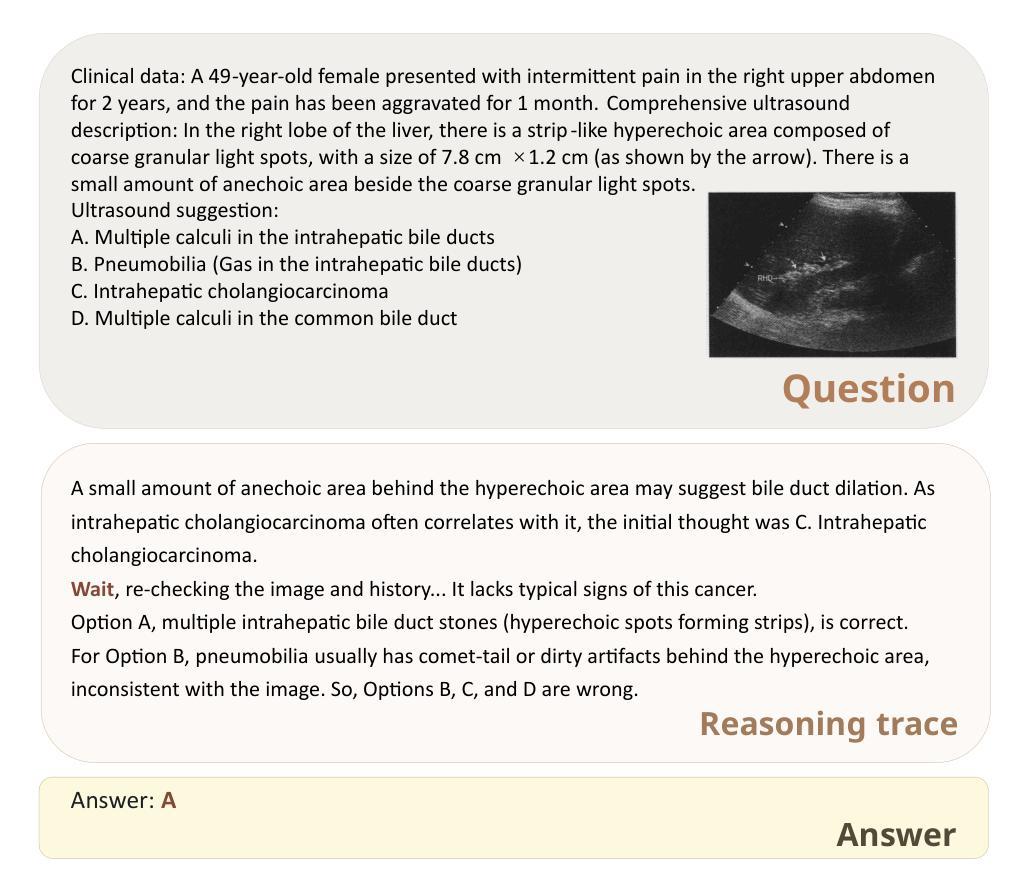
HAIBU-ReMUD: Reasoning Multimodal Ultrasound Dataset and Model Bridging to General Specific Domains
Authors:Shijie Wang, Yilun Zhang, Zeyu Lai, Dexing Kong
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have shown great potential in general domains but perform poorly in some specific domains due to a lack of domain-specific data, such as image-text data or vedio-text data. In some specific domains, there is abundant graphic and textual data scattered around, but lacks standardized arrangement. In the field of medical ultrasound, there are ultrasonic diagnostic books, ultrasonic clinical guidelines, ultrasonic diagnostic reports, and so on. However, these ultrasonic materials are often saved in the forms of PDF, images, etc., and cannot be directly used for the training of MLLMs. This paper proposes a novel image-text reasoning supervised fine-tuning data generation pipeline to create specific domain quadruplets (image, question, thinking trace, and answer) from domain-specific materials. A medical ultrasound domain dataset ReMUD is established, containing over 45,000 reasoning and non-reasoning supervised fine-tuning Question Answering (QA) and Visual Question Answering (VQA) data. The ReMUD-7B model, fine-tuned on Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct, outperforms general-domain MLLMs in medical ultrasound field. To facilitate research, the ReMUD dataset, data generation codebase, and ReMUD-7B parameters will be released at https://github.com/ShiDaizi/ReMUD, addressing the data shortage issue in specific domain MLLMs.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在通用领域显示出巨大的潜力,但由于缺乏特定领域的数据,如图像文本数据或视频文本数据,在某些特定领域的表现较差。在一些特定领域,虽然存在大量的图形和文本数据,但它们分布散乱,缺乏标准化安排。在医学超声领域,有超声诊断书籍、超声临床指南、超声诊断报告等等。然而,这些超声材料通常保存在PDF、图像等形式下,无法直接用于MLLMs的训练。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:针对多模态大型语言模型在特定领域表现不佳的问题,本文提出了一种新型图像文本推理监督微调数据生成管道,用于从特定领域的材料中创建特定领域的四元组(图像、问题、思考轨迹和答案)。建立了医疗超声领域的ReMUD数据集,包含超过45,000条推理和非推理监督微调问答和视觉问答数据。经过Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct精细调整的ReMUD-7B模型在医疗超声领域优于通用领域的大型多模态语言模型。数据集及相关资源已发布在GitHub上,以解决特定领域大型语言模型的数据短缺问题。
Key Takeaways:
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在特定领域表现不佳,缺乏特定领域的图像文本数据是主要原因。
- 在医疗超声领域存在大量的图形和文本数据但无法直接使用于MLLM训练。
- 本文提出了一种新的图像文本推理监督微调数据生成管道,创建了特定的医学超声领域数据集ReMUD。
- ReMUD数据集包含超过45,000条推理和非推理监督微调问答和视觉问答数据。
- ReMUD-7B模型在医疗超声领域的表现优于通用领域的MLLMs。
- 数据集及相关资源已公开发布在GitHub上,以便其他研究者使用。
点此查看论文截图


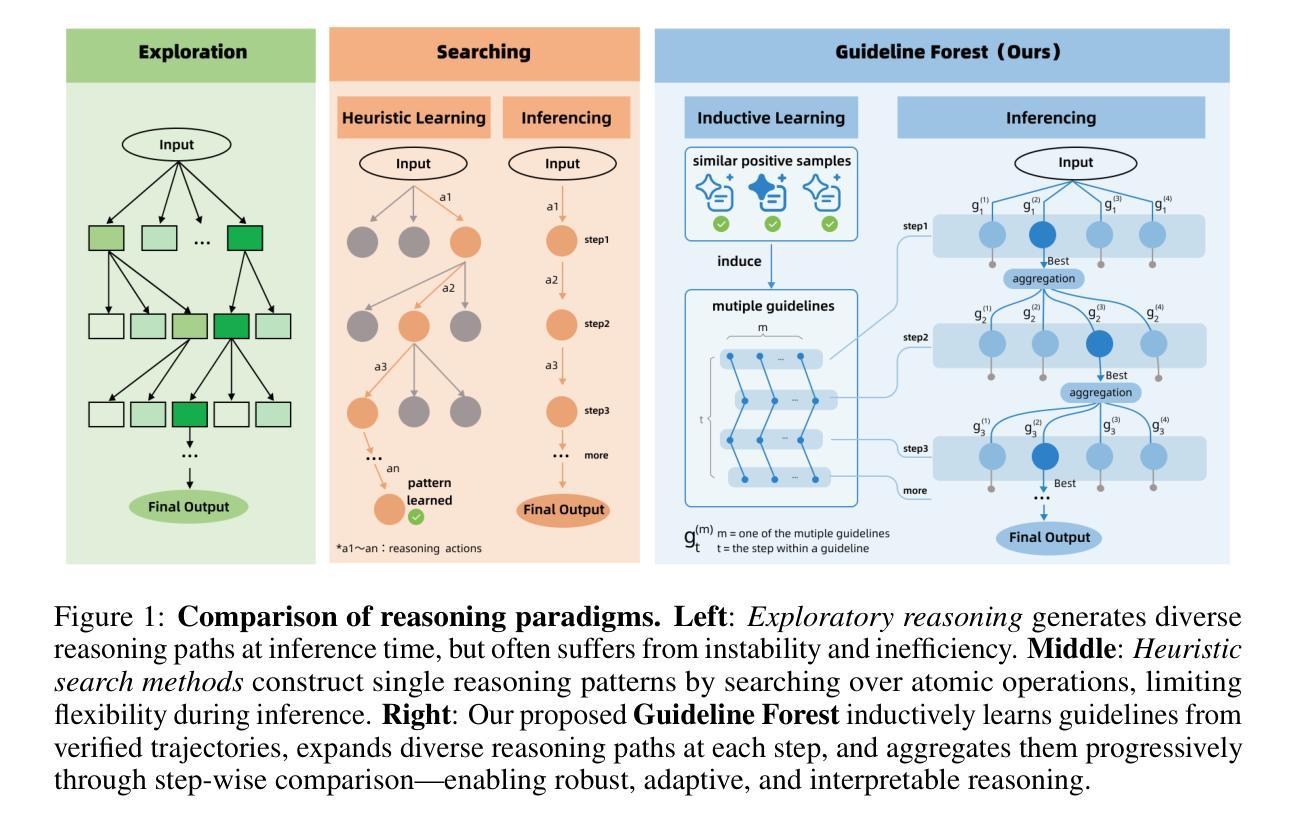
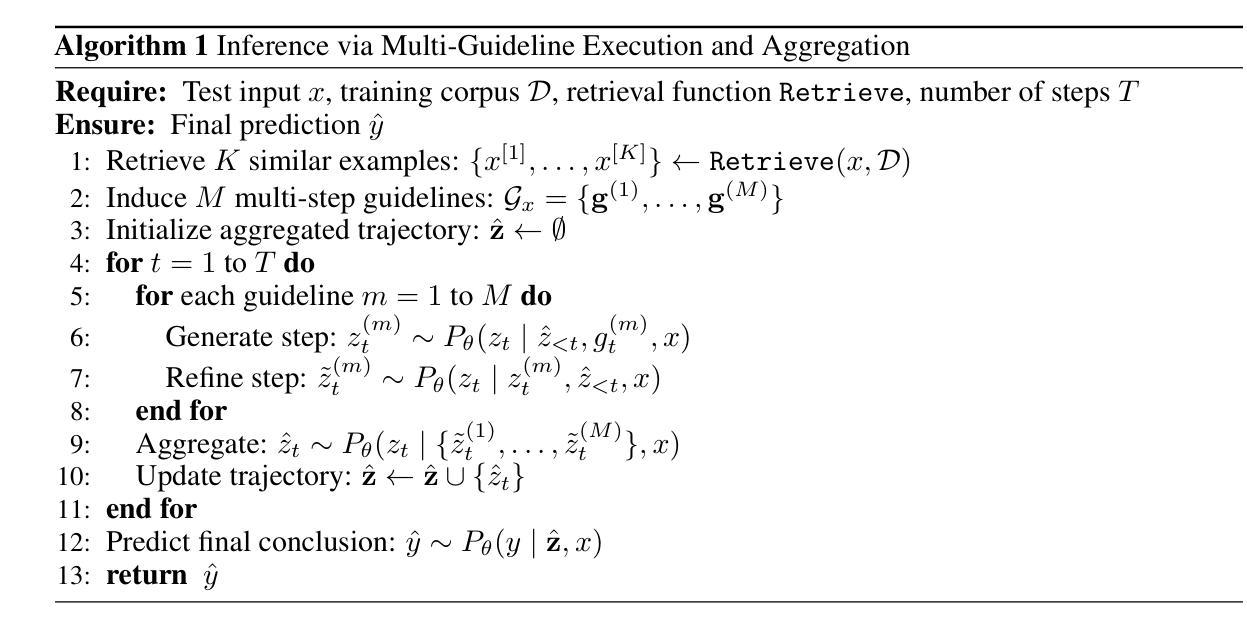
Guideline Forest: Experience-Induced Multi-Guideline Reasoning with Stepwise Aggregation
Authors:Jiaxiang CHen, Zhuo Wang, Mingxi Zou, Qifan Wang, Zenglin Xu
Human reasoning is flexible, adaptive, and grounded in prior experience-qualities that large language models (LLMs) still struggle to emulate. Existing methods either explore diverse reasoning paths at inference time or search for optimal workflows through expensive operations, but both fall short in leveraging multiple reusable strategies in a structured, efficient manner. We propose Guideline Forest, a framework that enhances LLMs reasoning by inducing structured reasoning strategies-called guidelines-from verified examples and executing them via step-wise aggregation. Unlike test-time search or single-path distillation, our method draws on verified reasoning experiences by inducing reusable guidelines and expanding each into diverse variants. Much like human reasoning, these variants reflect alternative thought patterns, are executed in parallel, refined via self-correction, and aggregated step by step-enabling the model to adaptively resolve uncertainty and synthesize robust solutions.We evaluate Guideline Forest on four benchmarks-GSM8K, MATH-500, MBPP, and HumanEval-spanning mathematical and programmatic reasoning. Guideline Forest consistently outperforms strong baselines, including CoT, ReAct, ToT, FoT, and AFlow. Ablation studies further highlight the effectiveness of multi-path reasoning and stepwise aggregation, underscoring the Guideline Forest’s adaptability and generalization potential.
人类推理具有灵活性、适应性和基于先前经验的特质,这些特质大型语言模型(LLMs)仍难以模仿。现有方法要么在推理时探索多样化的推理路径,要么通过昂贵的操作寻找最佳工作流程,但两种方法都未能以结构化、高效的方式利用多种可重复使用的策略。我们提出了“指南森林”框架,它通过从验证过的示例中引导结构化推理策略(称为指南)并通过逐步聚合来执行,从而增强LLMs的推理能力。不同于测试时的搜索或单路径蒸馏,我们的方法依赖于通过诱导可重复使用的指南和将其扩展为多种变体来验证推理经验。这些变体反映了替代的思维模式,它们并行执行,通过自我修正进行细化,并逐步聚合——使模型能够自适应地解决不确定性并合成稳健的解决方案。我们在涵盖数学和程序推理的四个基准测试(GSM8K、MATH-500、MBPP和HumanEval)上评估了“指南森林”。它持续优于强大的基准测试,包括CoT、ReAct、ToT、FoT和AFlow。“指南森林”的有效性和适应性和潜力在逐步聚合的清除研究中得到了进一步强调。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为“指南森林”的框架,旨在通过从验证实例中引导结构化推理策略(称为指南)并对其进行逐步聚合来增强大型语言模型的推理能力。与测试时间搜索或单路径蒸馏不同,该方法利用经过验证的推理经验来引导可重复使用的指南,并将其扩展为各种变体。这些变体反映了替代思维模式,可并行执行、通过自我修正进行改进,并分阶段聚合,使模型能够自适应解决不确定性和合成稳健解决方案。在涵盖数学和程序推理的四个基准测试上,指南森林持续优于强大的基线,包括CoT、ReAct、ToT、FoT和AFlow。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在模拟人类推理的灵活性、适应性和基于先前经验方面仍存在挑战。
- 现有方法要么在推理时间探索多样化的推理路径,要么通过昂贵的操作寻找最佳工作流程,但两者都未能以结构化、高效的方式利用多种可重复使用的策略。
- “指南森林”框架通过从验证实例中引导结构化推理策略并分阶段聚合执行来增强LLMs的推理能力。
- 该方法与测试时间搜索或单路径蒸馏不同,强调利用经过验证的推理经验来引导可重复使用的指南,并将其扩展为反映替代思维模式的变体。
- 这些变体可并行执行、通过自我修正进行改进,并分阶段聚合,使模型能够解决不确定性和合成稳健解决方案。
- 在多个基准测试上,“指南森林”持续表现出优异的性能,优于其他强大的方法。
点此查看论文截图

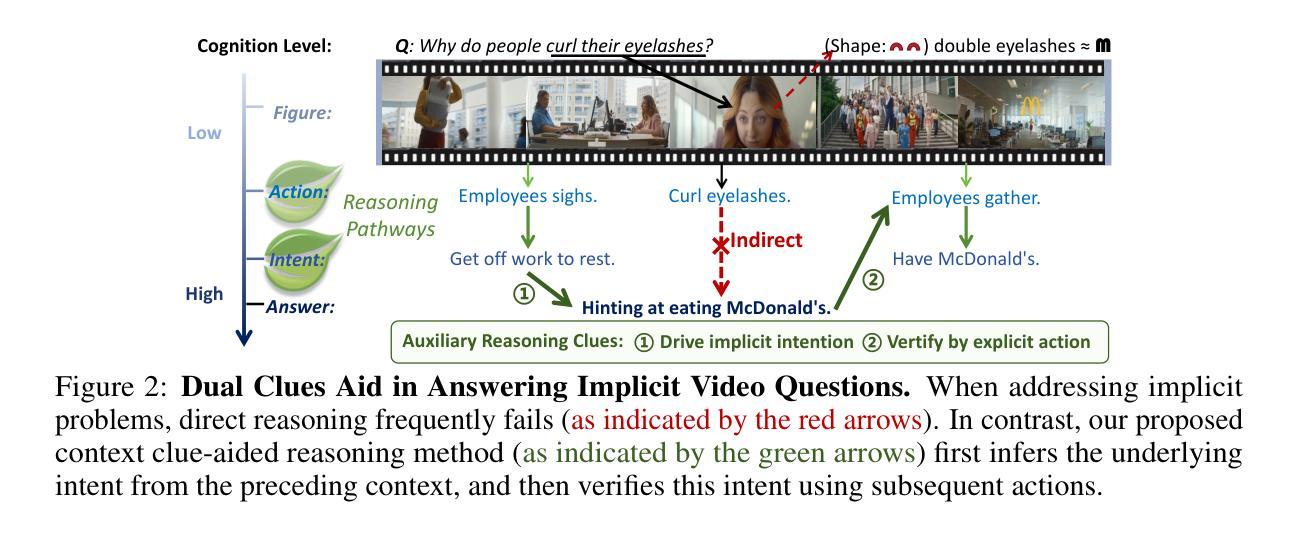
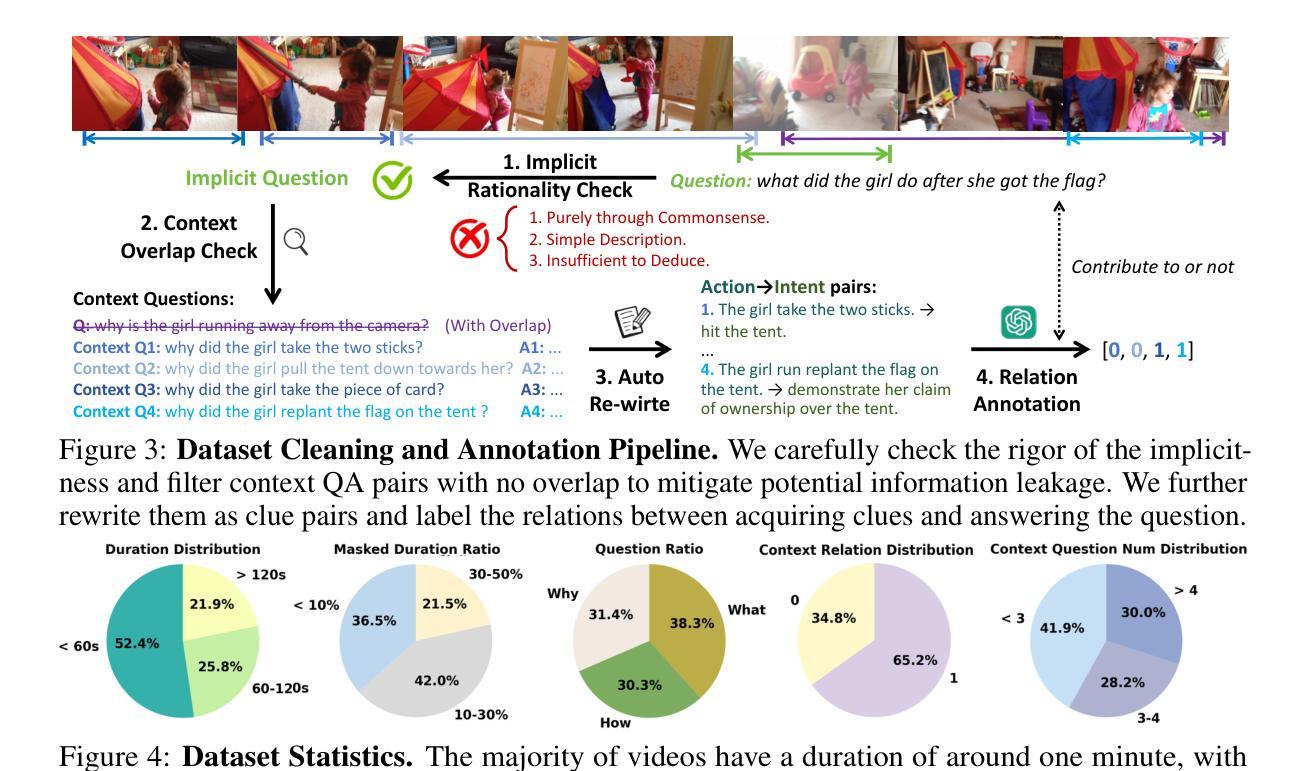
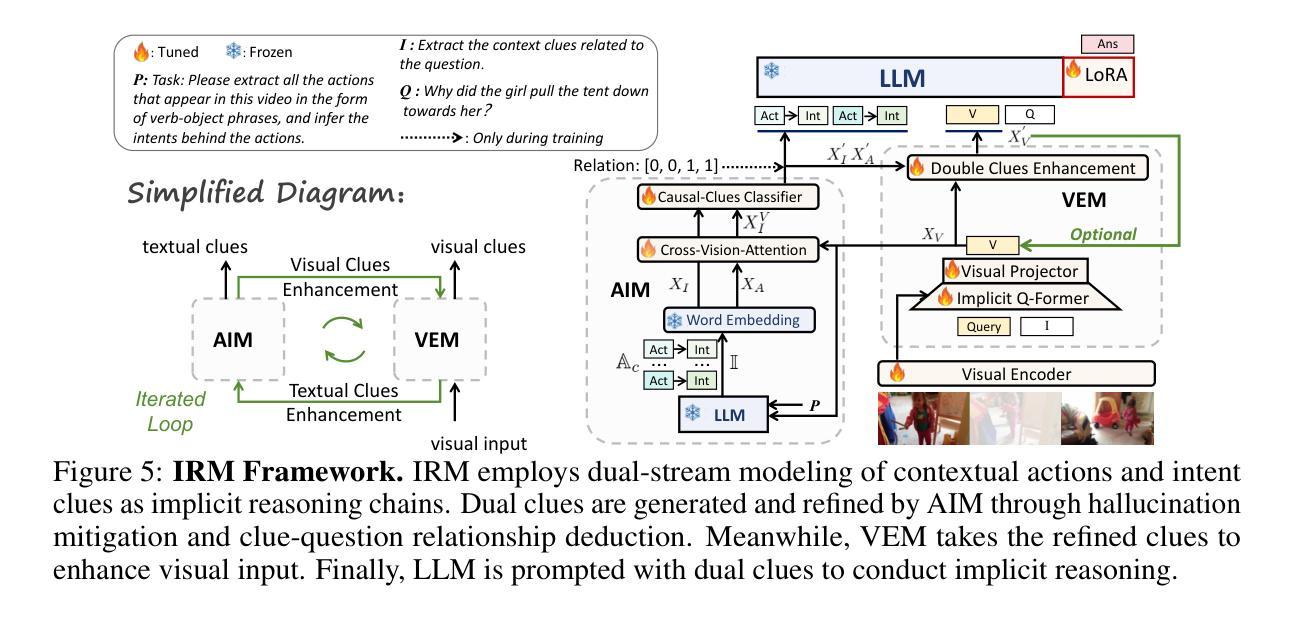
Looking Beyond Visible Cues: Implicit Video Question Answering via Dual-Clue Reasoning
Authors:Tieyuan Chen, Huabin Liu, Yi Wang, Chaofan Gan, Mingxi Lyu, Gui Zou, Weiyao Lin
Video Question Answering (VideoQA) aims to answer natural language questions based on the given video, with prior work primarily focusing on identifying the duration of relevant segments, referred to as explicit visual evidence. However, explicit visual evidence is not always directly available, particularly when questions target symbolic meanings or deeper intentions, leading to significant performance degradation. To fill this gap, we introduce a novel task and dataset, $\textbf{I}$mplicit $\textbf{V}$ideo $\textbf{Q}$uestion $\textbf{A}$nswering (I-VQA), which focuses on answering questions in scenarios where explicit visual evidence is inaccessible. Given an implicit question and its corresponding video, I-VQA requires answering based on the contextual visual cues present within the video. To tackle I-VQA, we propose a novel reasoning framework, IRM (Implicit Reasoning Model), incorporating dual-stream modeling of contextual actions and intent clues as implicit reasoning chains. IRM comprises the Action-Intent Module (AIM) and the Visual Enhancement Module (VEM). AIM deduces and preserves question-related dual clues by generating clue candidates and performing relation deduction. VEM enhances contextual visual representation by leveraging key contextual clues. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our IRM in I-VQA tasks, outperforming GPT-4o, OpenAI-o3, and fine-tuned VideoChat2 by $0.76%$, $1.37%$, and $4.87%$, respectively. Additionally, IRM performs SOTA on similar implicit advertisement understanding and future prediction in traffic-VQA. Datasets and codes are available for double-blind review in anonymous repo: https://github.com/tychen-SJTU/Implicit-VideoQA.
视频问答(VideoQA)旨在根据给定的视频回答自然语言问题,早期的工作主要集中在识别相关片段的持续时间,称为明确视觉证据。然而,明确视觉证据并非总是可以直接获得,特别是当问题针对象征意义或更深层次的意图时,会导致性能显著下降。为了填补这一空白,我们引入了一项新任务和数据集,即隐式视频问答(I-VQA),专注于回答在明确视觉证据无法获取的情况下的问题。给定隐式问题和其对应的视频,I-VQA需要基于视频中存在的上下文视觉线索来回答。为了解决I-VQA,我们提出了一种新的推理框架,即IRM(隐式推理模型),它结合了上下文动作和意图线索的双重流建模,作为隐式推理链。IRM包括动作意图模块(AIM)和视觉增强模块(VEM)。AIM通过生成线索候选并执行关系推理来推断和保存与问题相关的双重线索。VEM通过利用关键上下文线索增强上下文视觉表示。大量实验验证了我们的IRM在I-VQA任务中的有效性,相对于GPT-4o、OpenAI-o3和经过微调的视频聊天2分别提高了0.76%、1.37%和4.87%。此外,IRM在类似的隐式广告理解和未来交通预测的交通问答中达到了最新水平。数据集和代码可在匿名存储库中供双盲评审使用:https://github.com/tychen-SJTU/Implicit-VideoQA。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
视频问答(VideoQA)通常基于视频回答自然语言问题,之前的工作主要关注于识别相关段落的持续时间,即显式视觉证据。然而,当问题针对象征意义或更深层次的意图时,显式视觉证据并不总是可直接获得,导致性能显著下降。为填补这一空白,我们推出了新的任务和数据集——隐含视频问答(I-VQA),专注于回答隐性问题和对应视频的问题。I-VQA基于视频中的上下文视觉线索来回答问题。为解决I-VQA,我们提出了隐含推理模型(IRM)的新推理框架,通过动作和意图暗示的双向流建模作为隐含推理链。IRM包括动作意图模块(AIM)和视觉增强模块(VEM)。AIM通过生成线索候选和执行关系推导来推断和保存与问题相关的双重线索。VEM利用关键上下文线索增强上下文视觉表示。大量实验验证了我们的IRM在I-VQA任务中的有效性,超越了GPT-4o、OpenAI-o3和微调后的VideoChat2。此外,IRM在类似的隐性广告理解和未来交通预测-VQA中也表现出卓越性能。相关数据集和代码可在匿名仓库中进行双重盲审:https://github.com/tychen-SJTU/Implicit-VideoQA。
Key Takeaways
- 视频问答(VideoQA)主要依赖显式视觉证据回答问题,但当问题涉及象征意义或深层意图时,这种方法可能会失效。
- 为解决这一问题,提出了隐含视频问答(I-VQA)任务和数据集,专注于回答隐性问题和视频。
- I-VQA要求基于视频中的上下文视觉线索来回答问题。
- 提出了新的推理框架——隐含推理模型(IRM),包括动作意图模块(AIM)和视觉增强模块(VEM)。
- AIM通过生成线索候选和关系推导来推断和保存与问题相关的双重线索。
- VEM利用关键上下文线索增强视觉表示。
点此查看论文截图


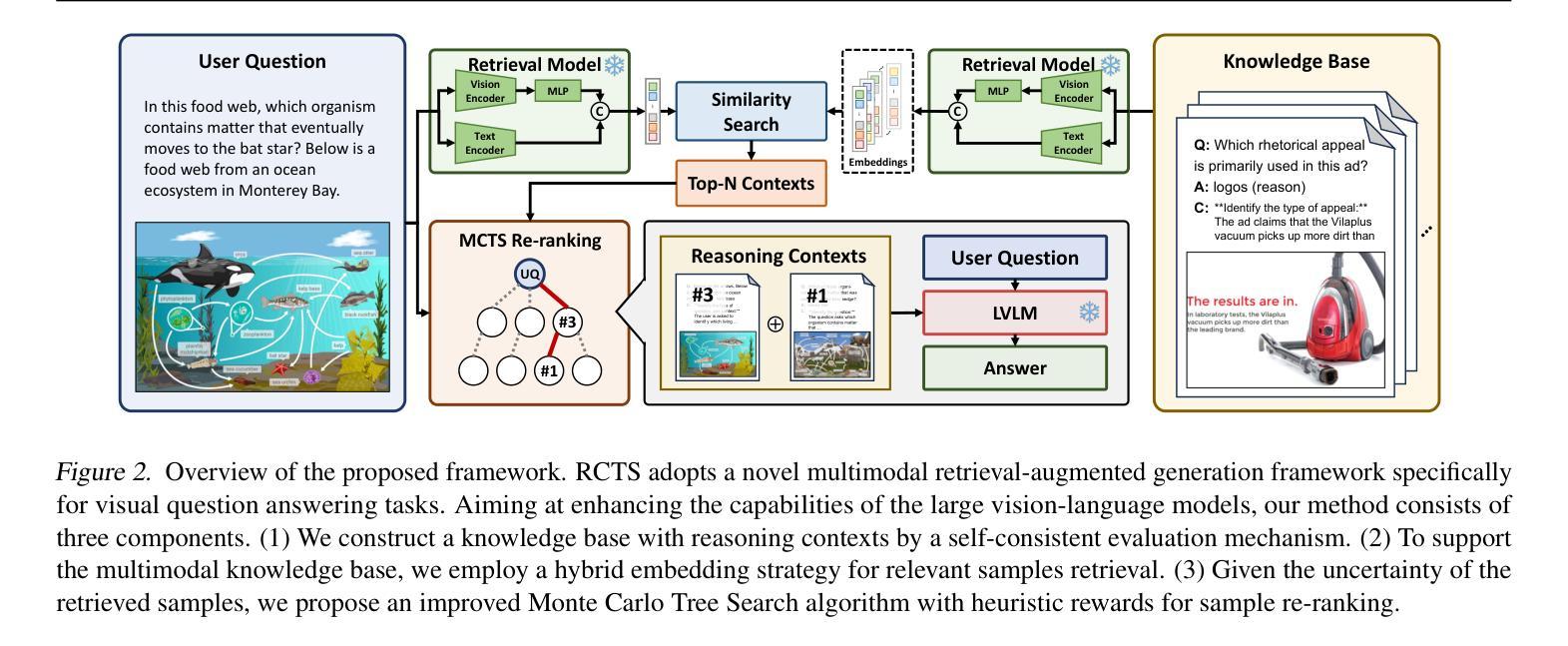
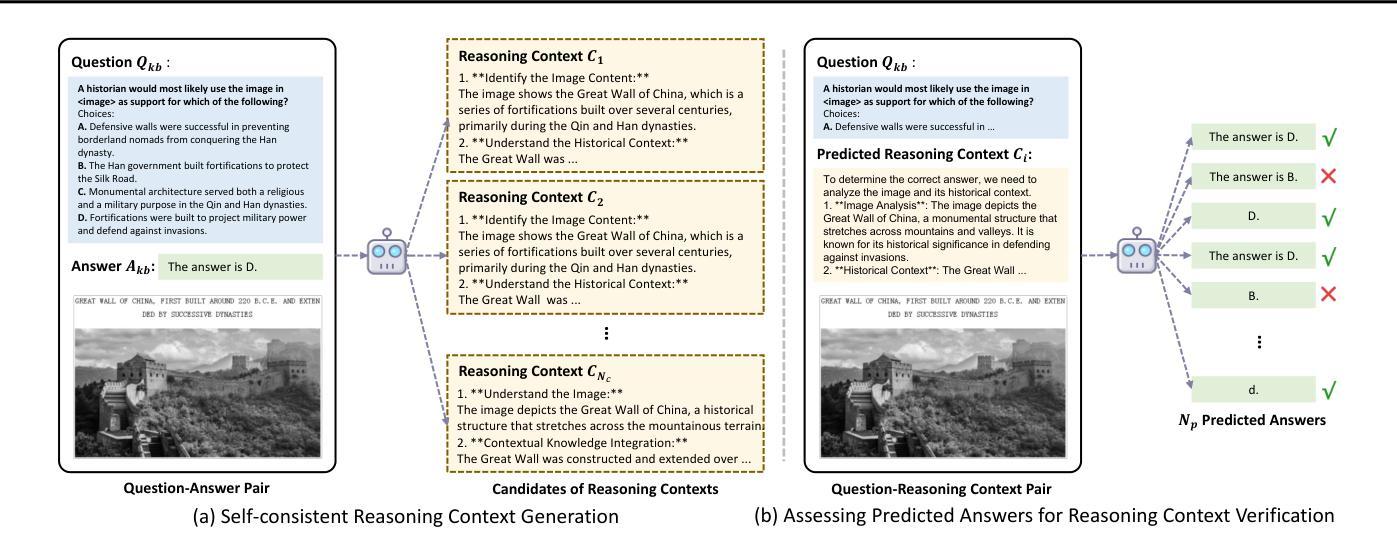
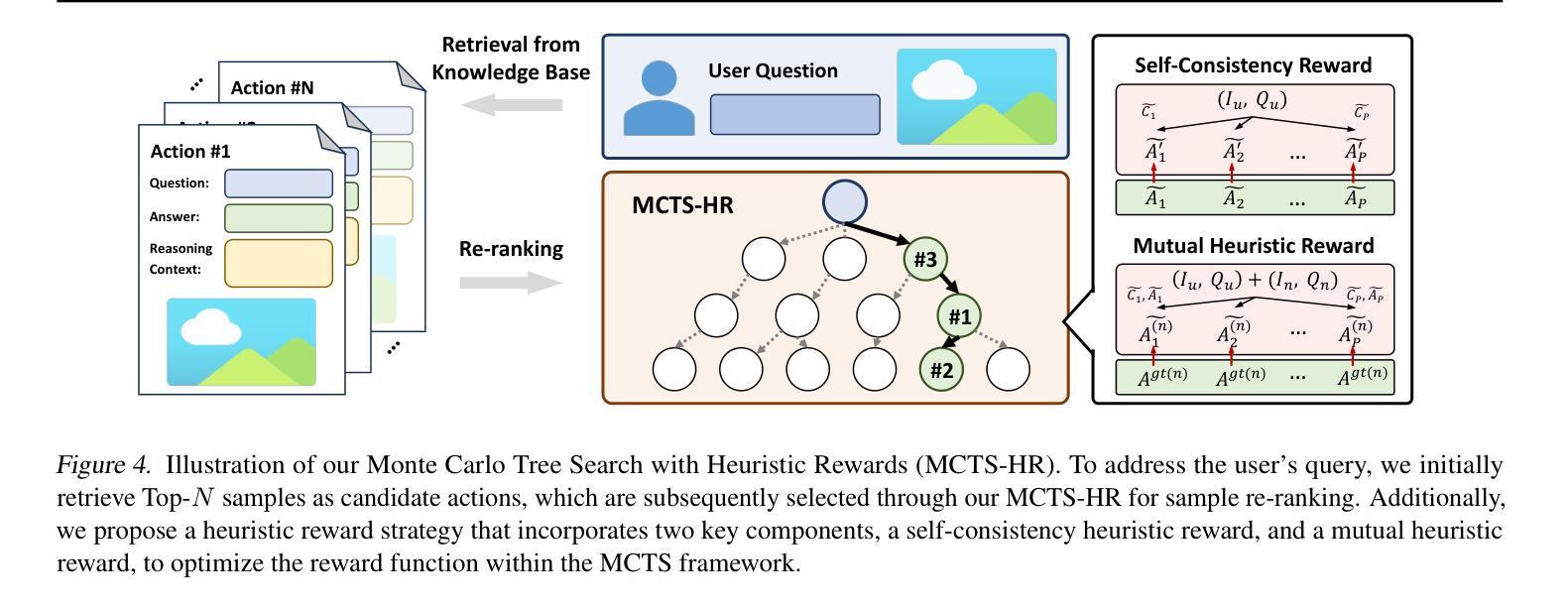
Re-ranking Reasoning Context with Tree Search Makes Large Vision-Language Models Stronger
Authors:Qi Yang, Chenghao Zhang, Lubin Fan, Kun Ding, Jieping Ye, Shiming Xiang
Recent advancements in Large Vision Language Models (LVLMs) have significantly improved performance in Visual Question Answering (VQA) tasks through multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). However, existing methods still face challenges, such as the scarcity of knowledge with reasoning examples and erratic responses from retrieved knowledge. To address these issues, in this study, we propose a multimodal RAG framework, termed RCTS, which enhances LVLMs by constructing a Reasoning Context-enriched knowledge base and a Tree Search re-ranking method. Specifically, we introduce a self-consistent evaluation mechanism to enrich the knowledge base with intrinsic reasoning patterns. We further propose a Monte Carlo Tree Search with Heuristic Rewards (MCTS-HR) to prioritize the most relevant examples. This ensures that LVLMs can leverage high-quality contextual reasoning for better and more consistent responses. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple VQA datasets, significantly outperforming In-Context Learning (ICL) and Vanilla-RAG methods. It highlights the effectiveness of our knowledge base and re-ranking method in improving LVLMs. Our code is available at https://github.com/yannqi/RCTS-RAG.
近期大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的进步通过多模态检索增强生成(RAG)显著提高了视觉问答(VQA)任务的性能。然而,现有方法仍面临挑战,如缺乏推理示例和来自检索知识的随机响应。为解决这些问题,本研究提出了一种多模态RAG框架,称为RCTS,通过构建丰富的推理上下文知识库和树搜索排序方法,增强LVLMs的功能。具体来说,我们引入了一种自洽评估机制,以内在推理模式丰富知识库。我们进一步提出了结合启发式奖励的蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS-HR),以优先处理最相关的示例。这确保了LVLMs能够利用高质量的上文推理,以获取更好、更一致的响应。大量实验表明,我们的框架在多个VQA数据集上达到了最先进的性能,显著优于上下文学习(ICL)和Vanilla-RAG方法。这凸显了我们的知识库和排序方法在改善LVLMs方面的有效性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/yannqi/RCTS-RAG找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025 Spotlight. 22 pages, 16 figures
Summary
大规模视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在视觉问答(VQA)任务上的性能有了显著提升,这得益于多模态检索增强生成(RAG)技术。然而,现有方法仍面临知识推理示例匮乏和从检索知识中产生的应答不稳定等挑战。本研究提出了一种多模态RAG框架(RCTS),通过构建富含推理上下文的知识库和树搜索重排序方法,增强LVLMs的性能。实验表明,该框架在多个VQA数据集上达到领先水平,显著优于上下文学习(ICL)和常规RAG方法。
Key Takeaways
- LVLMs在VQA任务上的性能通过RAG技术得到显著提升。
- 现有方法面临知识推理示例不足和应答不稳定的问题。
- 提出的RCTS框架通过构建富含推理上下文的知识库增强LVLMs。
- RCTS引入自我一致评价机制,以内在推理模式丰富知识库。
- 采用蒙特卡洛树搜索与启发式奖励(MCTS-HR)以优先处理最相关的示例。
- RCTS框架在多个VQA数据集上达到领先水平。
点此查看论文截图

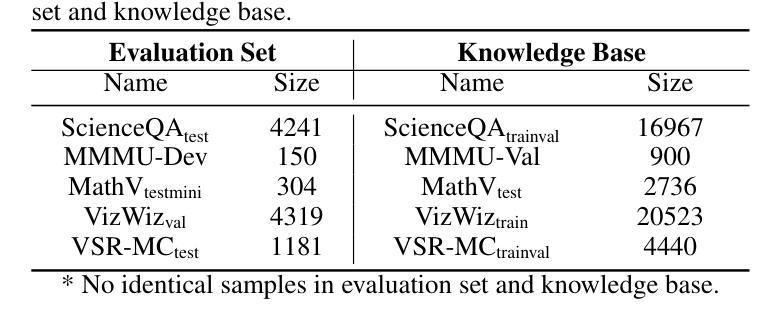
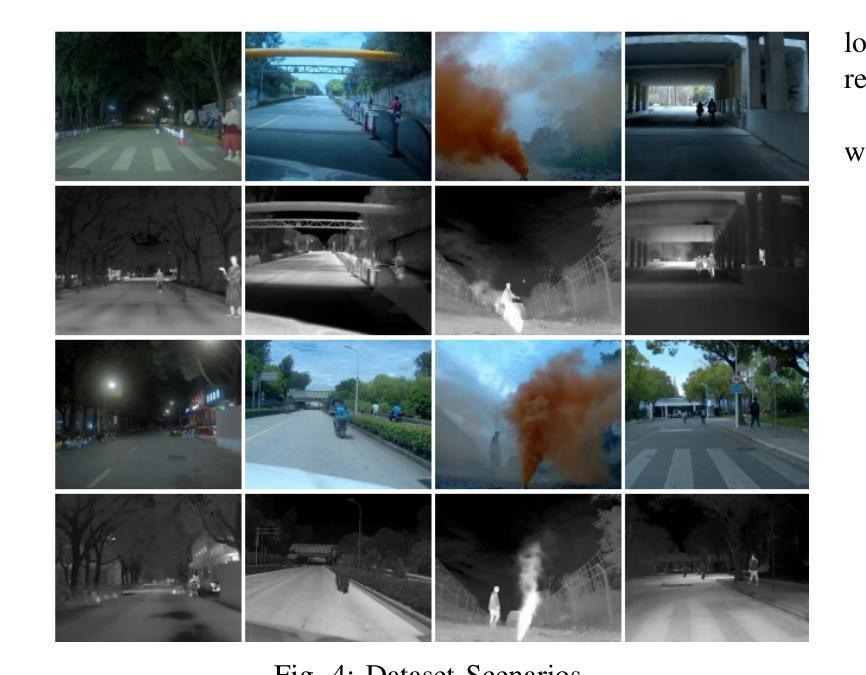
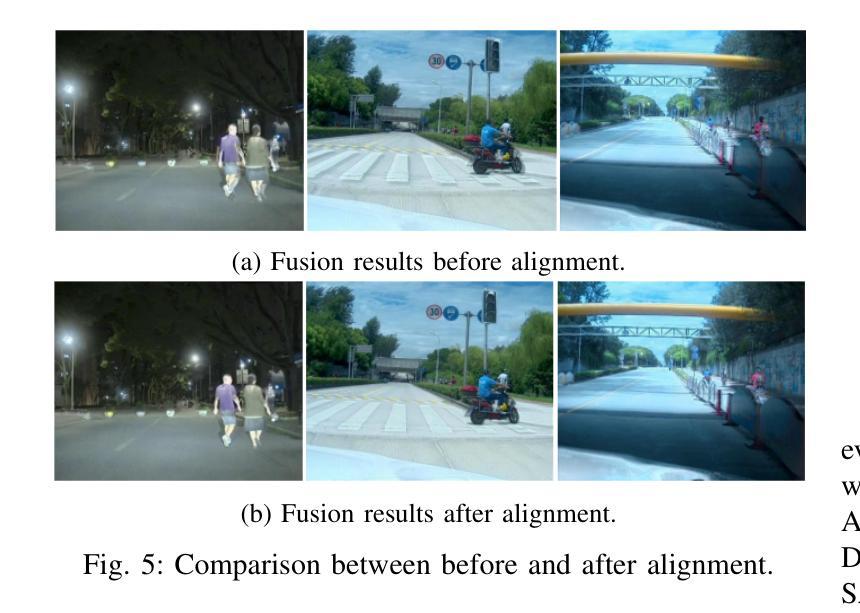
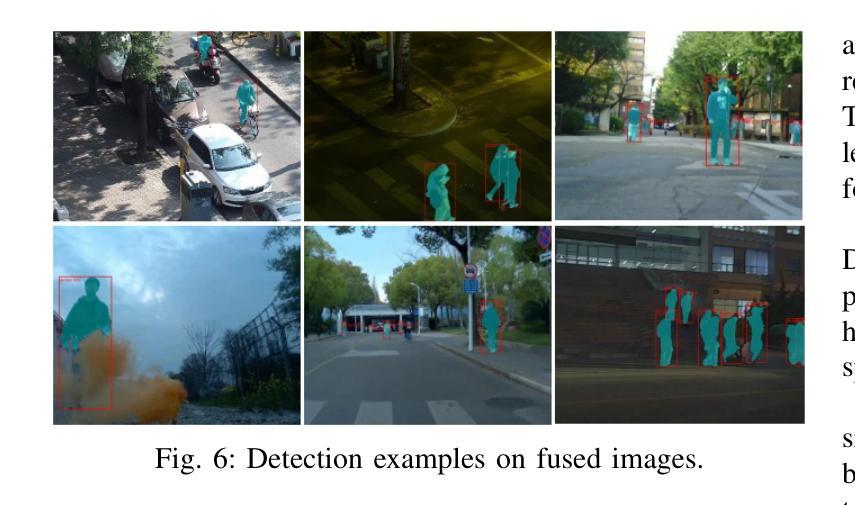
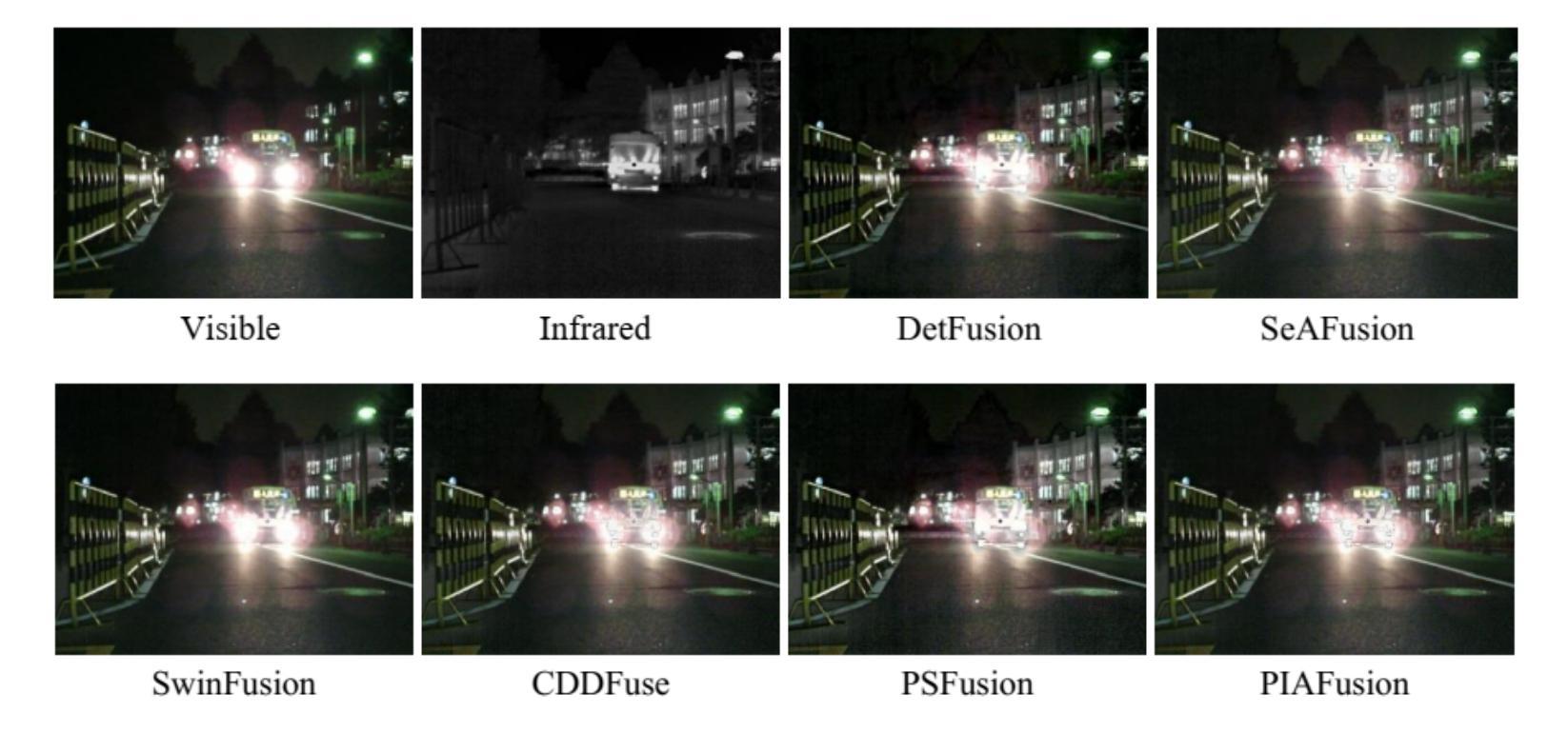
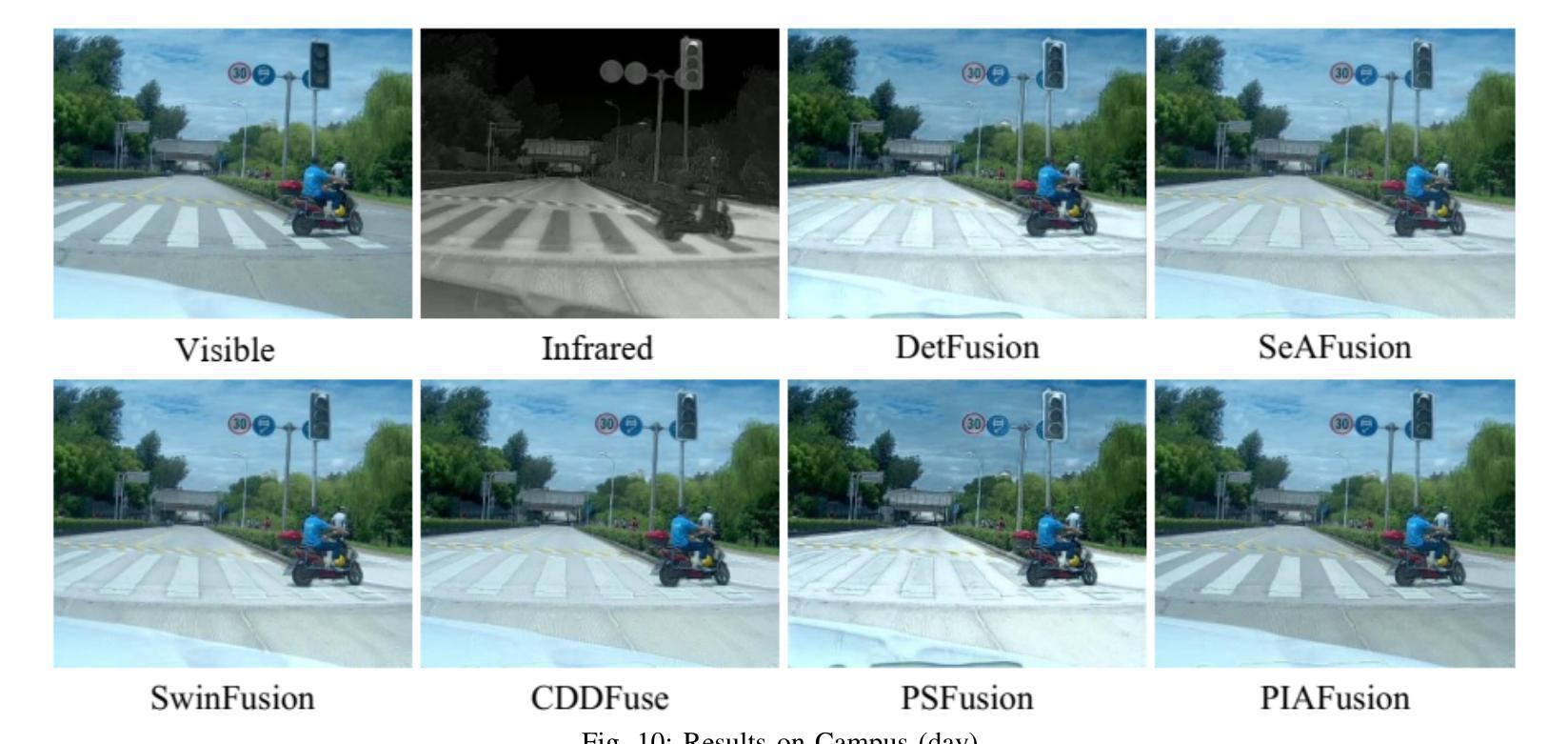
Design and Evaluation of Deep Learning-Based Dual-Spectrum Image Fusion Methods
Authors:Beining Xu, Junxian Li
Visible images offer rich texture details, while infrared images emphasize salient targets. Fusing these complementary modalities enhances scene understanding, particularly for advanced vision tasks under challenging conditions. Recently, deep learning-based fusion methods have gained attention, but current evaluations primarily rely on general-purpose metrics without standardized benchmarks or downstream task performance. Additionally, the lack of well-developed dual-spectrum datasets and fair algorithm comparisons hinders progress. To address these gaps, we construct a high-quality dual-spectrum dataset captured in campus environments, comprising 1,369 well-aligned visible-infrared image pairs across four representative scenarios: daytime, nighttime, smoke occlusion, and underpasses. We also propose a comprehensive and fair evaluation framework that integrates fusion speed, general metrics, and object detection performance using the lang-segment-anything model to ensure fairness in downstream evaluation. Extensive experiments benchmark several state-of-the-art fusion algorithms under this framework. Results demonstrate that fusion models optimized for downstream tasks achieve superior performance in target detection, especially in low-light and occluded scenes. Notably, some algorithms that perform well on general metrics do not translate to strong downstream performance, highlighting limitations of current evaluation practices and validating the necessity of our proposed framework. The main contributions of this work are: (1)a campus-oriented dual-spectrum dataset with diverse and challenging scenes; (2) a task-aware, comprehensive evaluation framework; and (3) thorough comparative analysis of leading fusion methods across multiple datasets, offering insights for future development.
可见图像提供了丰富的纹理细节,而红外图像则突出显示显著目标。融合这些互补模式增强了场景理解,特别是在具有挑战性的条件下的高级视觉任务。最近,基于深度学习的融合方法引起了人们的关注,但当前的评估主要依赖于通用指标,缺乏标准化基准测试或下游任务性能。此外,缺乏发达的双光谱数据集和公正的算法比较阻碍了进展。为了解决这些空白,我们在校园环境中构建了一个高质量的双光谱数据集,包含四种代表性场景下的1369对良好对齐的可见光红外图像对:白天、夜晚、烟雾遮挡和地道。我们还提出了一个全面公正的评估框架,该框架结合了融合速度、通用指标和对象检测性能,使用lang-segment-anything模型以确保下游评估的公平性。在该框架下,对几种最先进的融合算法进行了广泛的实验评估。结果表明,针对下游任务优化的融合模型在目标检测方面表现出卓越的性能,特别是在低光和遮挡场景中。值得注意的是,一些在通用指标上表现良好的算法并不等同于在下游任务中的强劲表现,这突出了当前评估实践的局限性,并验证了我们所提出的框架的必要性。本工作的主要贡献是:(1)一个面向校园的双光谱数据集,包含多样且具有挑战性的场景;(2)一个任务感知的全面评估框架;(3)对多个数据集的领先融合方法的全面比较分析,为未来的发展提供了见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 13 figures
Summary
可见图像提供丰富的纹理细节,而红外图像则突出显著目标。融合这些互补模式增强了场景理解,特别是在具有挑战性的条件下的高级视觉任务。尽管最近基于深度学习的融合方法受到关注,但当前评估主要依赖于通用指标,缺乏标准化基准测试或下游任务性能评估。此外,缺乏发达的双光谱数据集和公平的算法比较阻碍了进展。为解决这些空白,我们构建了高质量的双光谱数据集,包含四种代表性场景下的1369对可见光红外图像对。我们还提出了一个全面而公平的评估框架,融合了融合速度、通用指标和对象检测性能。实验结果表显示,针对下游任务优化的融合模型在目标检测方面表现出卓越性能,特别是在低光和遮挡场景中。一些在通用指标上表现良好的算法在下游任务中的表现并不理想,突显了当前评估实践的局限性并验证了所提出的框架的必要性。
Key Takeaways
一、文章介绍了可见图像与红外图像的特点和融合的重要性,特别是在复杂环境下的高级视觉任务中。
二、当前融合方法的评估主要依赖通用指标,缺乏标准化基准测试或下游任务性能评估。
三、为了解决这一问题,文章构建了一个校园导向的双光谱数据集,包含不同场景的可见光红外图像对。
四、提出了一个全面而公平的评估框架,该框架融合了融合速度、通用指标和对象检测性能评估。
五、实验结果显示针对下游任务优化的融合模型在目标检测方面表现出卓越性能。
六、文章的主要贡献包括校园导向的双光谱数据集、任务感知的评估框架以及对领先融合方法的比较分析。
点此查看论文截图







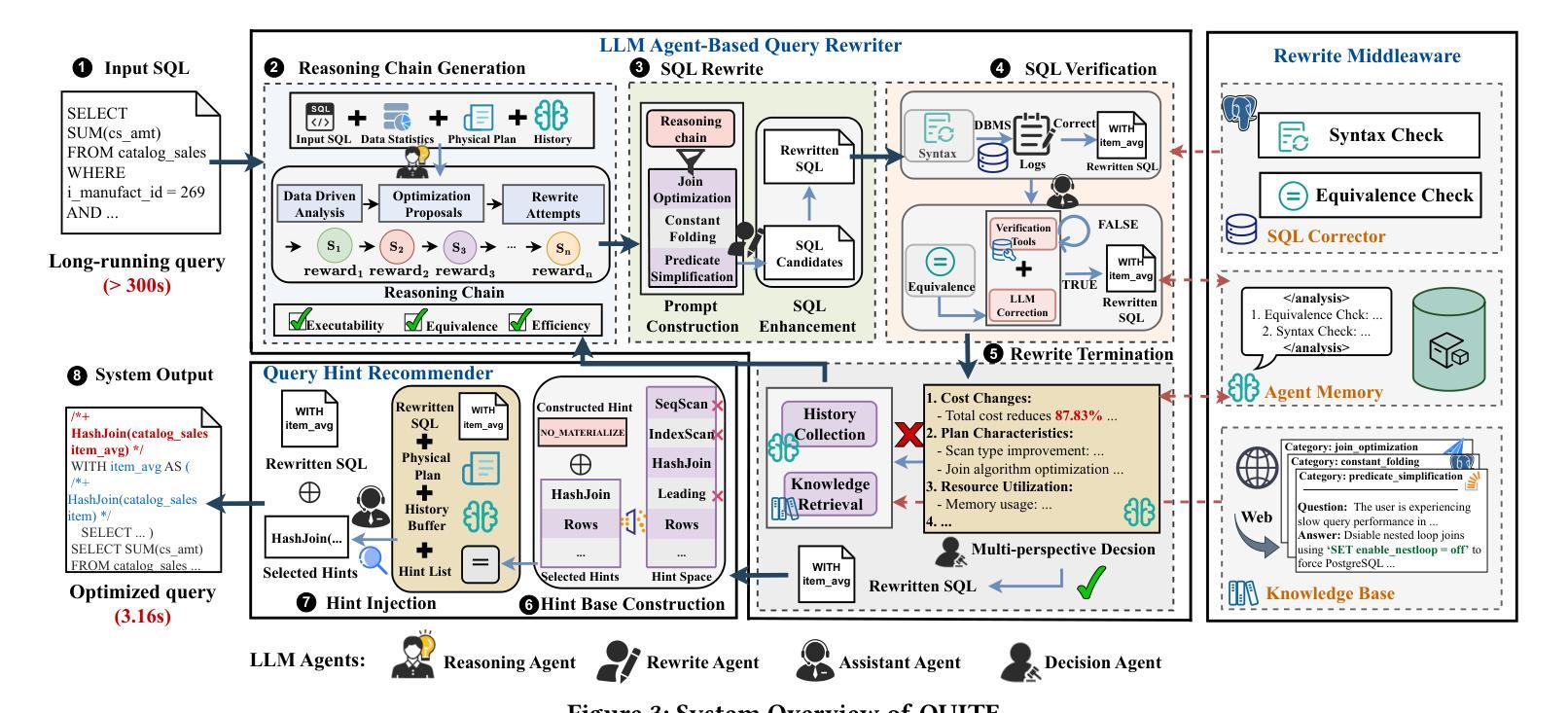
QUITE: A Query Rewrite System Beyond Rules with LLM Agents
Authors:Yuyang Song, Hanxu Yan, Jiale Lao, Yibo Wang, Yufei Li, Yuanchun Zhou, Jianguo Wang, Mingjie Tang
Query rewrite transforms SQL queries into semantically equivalent forms that run more efficiently. Existing approaches mainly rely on predefined rewrite rules, but they handle a limited subset of queries and can cause performance regressions. This limitation stems from three challenges of rule-based query rewrite: (1) it is hard to discover and verify new rules, (2) fixed rewrite rules do not generalize to new query patterns, and (3) some rewrite techniques cannot be expressed as fixed rules. Motivated by the fact that human experts exhibit significantly better rewrite ability but suffer from scalability, and Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated nearly human-level semantic and reasoning abilities, we propose a new approach of using LLMs to rewrite SQL queries beyond rules. Due to the hallucination problems in LLMs, directly applying LLMs often leads to nonequivalent and suboptimal queries. To address this issue, we propose QUITE (query rewrite), a training-free and feedback-aware system based on LLM agents that rewrites SQL queries into semantically equivalent forms with significantly better performance, covering a broader range of query patterns and rewrite strategies compared to rule-based methods. Firstly, we design a multi-agent framework controlled by a finite state machine (FSM) to equip LLMs with the ability to use external tools and enhance the rewrite process with real-time database feedback. Secondly, we develop a rewrite middleware to enhance the ability of LLMs to generate optimized query equivalents. Finally, we employ a novel hint injection technique to improve execution plans for rewritten queries. Extensive experiments show that QUITE reduces query execution time by up to 35.8% over state-of-the-art approaches and produces 24.1% more rewrites than prior methods, covering query cases that earlier systems did not handle.
查询重写将SQL查询转换为语义上等效且运行效率更高的形式。现有方法主要依赖于预先定义的重写规则,但它们只能处理有限的查询集,并可能导致性能下降。这种局限性源于基于规则的查询重写所面临的三大挑战:(1)发现和验证新规则很困难,(2)固定的重写规则不能推广到新查询模式,(3)某些重写技术无法表示为固定规则。受人类专家展现出显著的重写能力但面临可扩展性问题的启发,以及大型语言模型(LLM)已经证明了接近人类水平的语义和推理能力,我们提出了一种利用LLM重写SQL查询的新方法。由于LLM中的幻觉问题,直接应用LLM通常会导致不等效和次优查询。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了基于LLM代理的无需训练和反馈感知的QUERY REWRITE(查询重写)系统,该系统能够将SQL查询重写为语义等效的形式,具有更好的性能,与基于规则的方法相比,覆盖更广泛的查询模式和重写策略。首先,我们设计了一个由有限状态机(FSM)控制的多代理框架,为LLM配备使用外部工具的能力,并通过实时数据库反馈增强重写过程。其次,我们开发了一个重写中间件,以增强LLM生成优化查询等效物的能力。最后,我们采用了一种新型的提示注入技术,以改进重写查询的执行计划。大量实验表明,与传统的先进方法相比,QUERY REWRITE可以减少高达35.8%的查询执行时间,并且产生的重写次数比先前的方法多24.1%,覆盖早期系统无法处理的查询情况。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于查询重写技术的SQL查询优化方法提出,旨在将SQL查询转换为语义等效且运行效率更高的形式。现有方法主要依赖预设的改写规则,但处理查询子集有限,可能导致性能下降。本文提出一种利用大型语言模型(LLMs)进行SQL查询改写的新方法,克服规则方法的局限性。结合人类专家的改写能力和LLMs的语义理解优势,我们克服了LLMs的幻觉问题,提出了一种名为QUIET(查询重写)的训练外和反馈感知系统。该系统基于LLM代理,可重写SQL查询为语义等效形式,具有更好的性能,覆盖更广泛的查询模式和改写策略。通过设计由有限状态机控制的多代理框架、开发重写中间件并采用提示注入技术,QUIET减少了查询执行时间并提高改写查询的执行计划质量。实验表明,QUIET较现有方法减少最多达35.8%的查询执行时间,产生更多达24.1%的改写次数,覆盖早期系统无法处理的查询案例。
关键见解
- 现有查询重写方法主要依赖预设规则,存在处理查询子集有限和性能下降的问题。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)具备近似人类水平的语义理解和推理能力,可在SQL查询重写中发挥重要作用。
- QUITE系统结合LLMs和有限状态机控制的多代理框架,提高SQL查询重写效率和质量。
- QUITE通过实时数据库反馈和重写中间件增强LLMs生成优化查询等效物的能力。
- 采用提示注入技术改善重写查询的执行计划。
- 实验显示QUIET在减少查询执行时间和增加改写次数方面较现有方法有明显优势。
点此查看论文截图


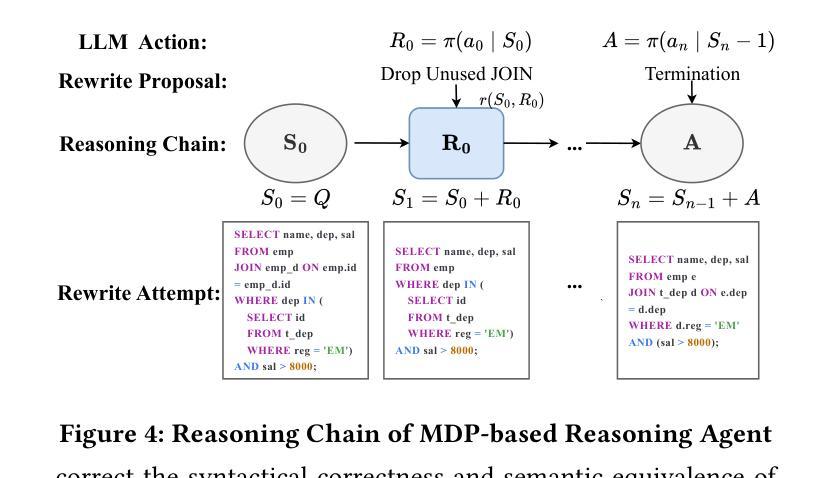
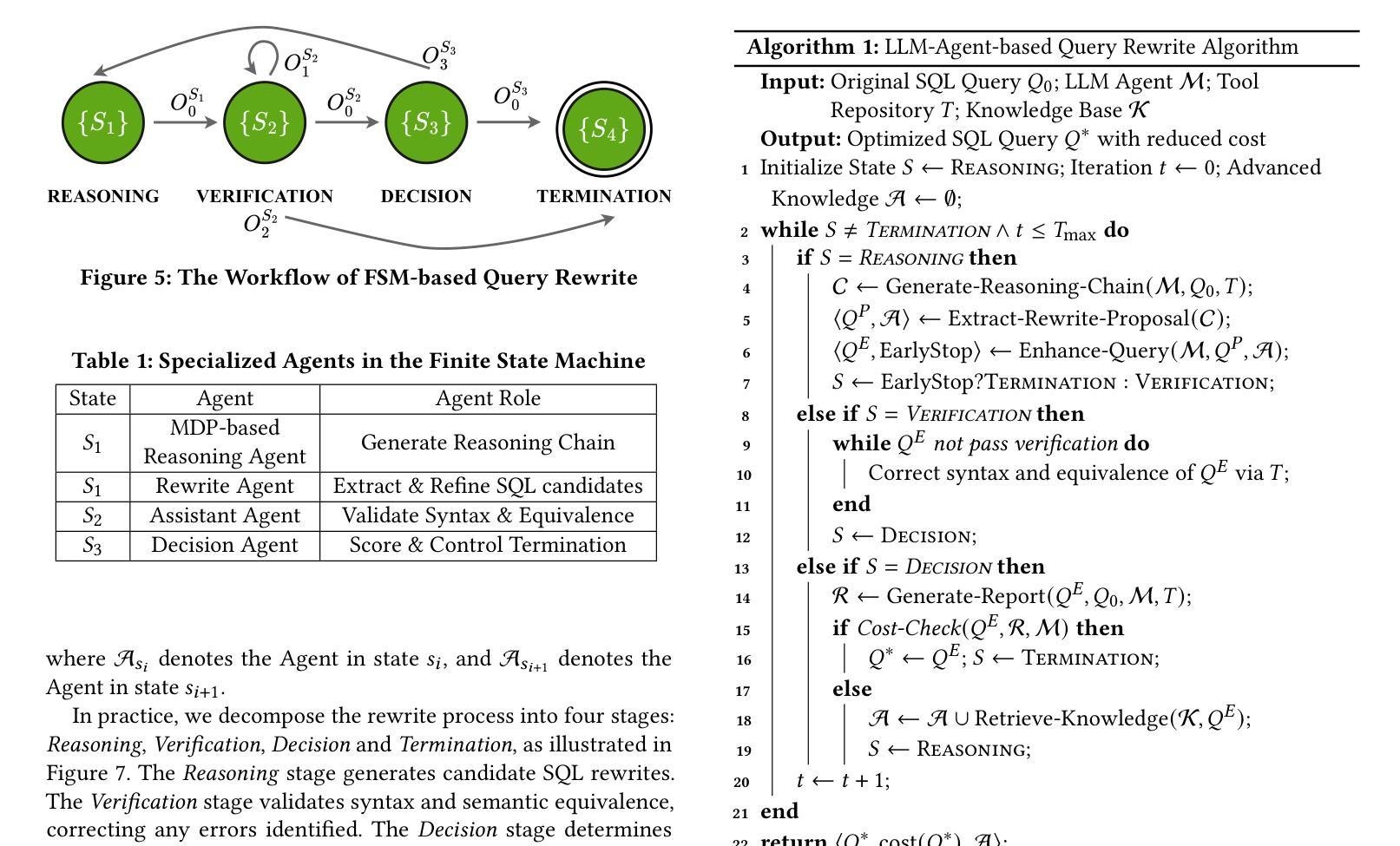
Synthetic Visual Genome
Authors:Jae Sung Park, Zixian Ma, Linjie Li, Chenhao Zheng, Cheng-Yu Hsieh, Ximing Lu, Khyathi Chandu, Quan Kong, Norimasa Kobori, Ali Farhadi, Yejin Choi, Ranjay Krishna
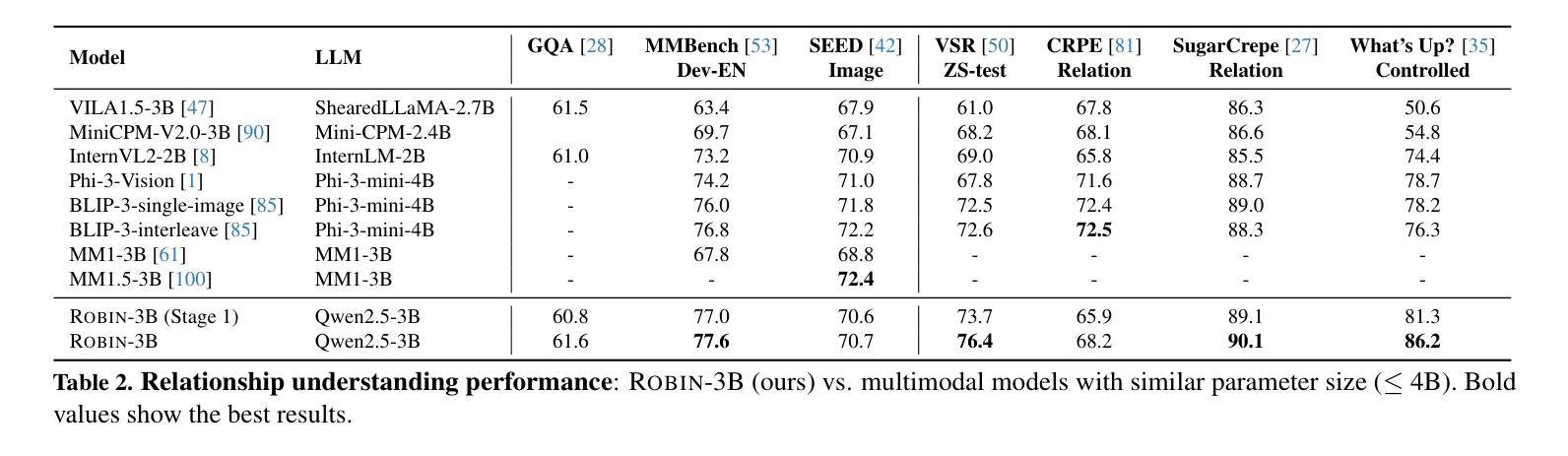
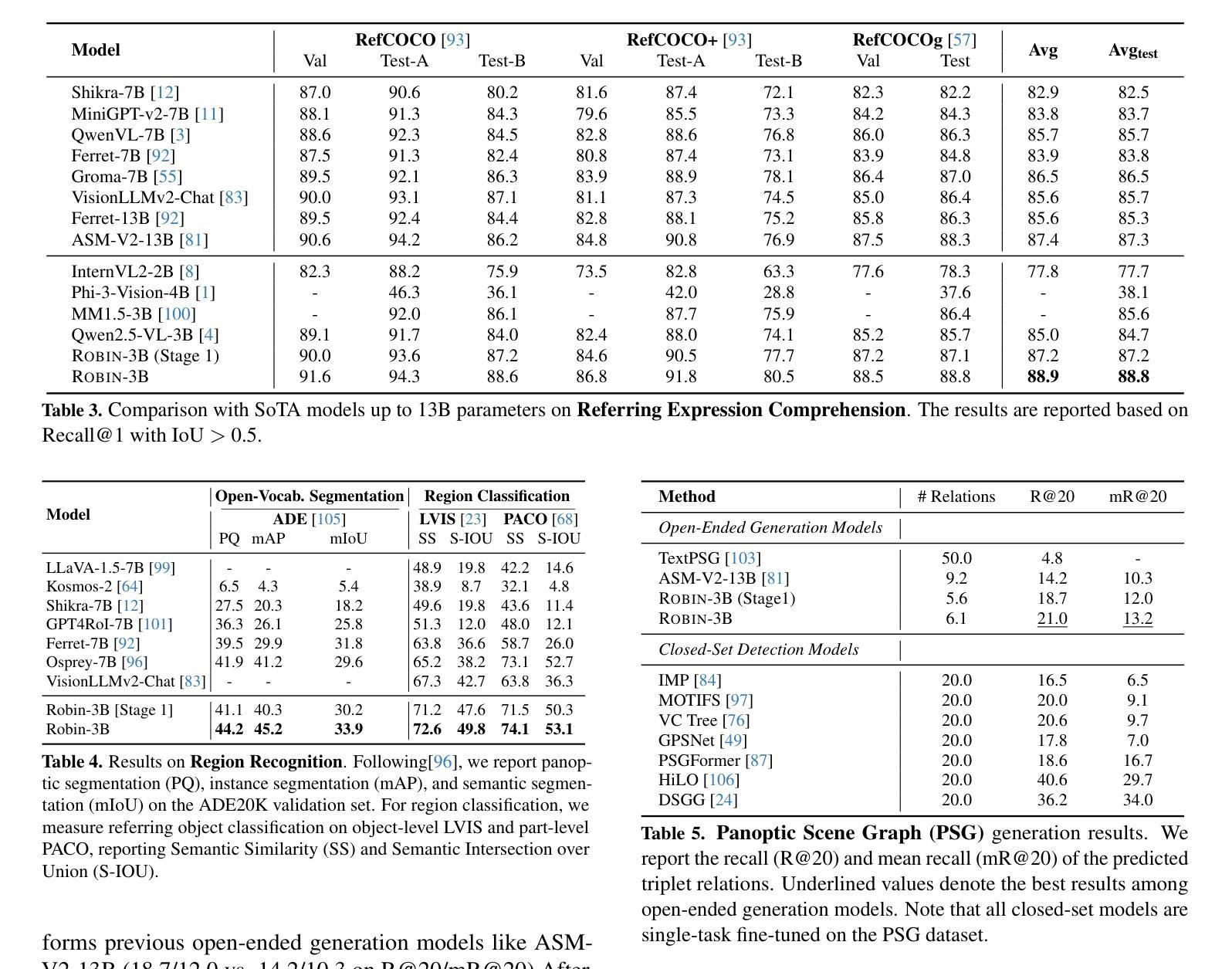
Reasoning over visual relationships-spatial, functional, interactional, social, etc.-is considered to be a fundamental component of human cognition. Yet, despite the major advances in visual comprehension in multimodal language models (MLMs), precise reasoning over relationships and their generations remains a challenge. We introduce ROBIN: an MLM instruction-tuned with densely annotated relationships capable of constructing high-quality dense scene graphs at scale. To train ROBIN, we curate SVG, a synthetic scene graph dataset by completing the missing relations of selected objects in existing scene graphs using a teacher MLM and a carefully designed filtering process to ensure high-quality. To generate more accurate and rich scene graphs at scale for any image, we introduce SG-EDIT: a self-distillation framework where GPT-4o further refines ROBIN’s predicted scene graphs by removing unlikely relations and/or suggesting relevant ones. In total, our dataset contains 146K images and 5.6M relationships for 2.6M objects. Results show that our ROBIN-3B model, despite being trained on less than 3 million instances, outperforms similar-size models trained on over 300 million instances on relationship understanding benchmarks, and even surpasses larger models up to 13B parameters. Notably, it achieves state-of-the-art performance in referring expression comprehension with a score of 88.9, surpassing the previous best of 87.4. Our results suggest that training on the refined scene graph data is crucial to maintaining high performance across diverse visual reasoning task.
对人类认知来说,理解和推理视觉关系(如空间关系、功能关系、互动关系、社会关系等)是一个基本组成部分。尽管在多模态语言模型(MLM)的视觉理解方面取得了重大进展,但对关系的精确推理及其生成仍然是一个挑战。我们引入了ROBIN:一个用密集注释关系调整的多模态语言模型指令,能够大规模构建高质量密集场景图。为了训练ROBIN,我们整理了SVG,一个合成场景图数据集,通过完成现有场景图中选定对象的缺失关系,并利用教师多模态语言模型和精心设计的过滤过程来确保高质量。为了为任何图像生成更准确和丰富的场景图,我们引入了SG-EDIT:一个自我蒸馏框架,GPT-4o进一步精炼ROBIN预测的场景图,通过删除不太可能的关系和/或提出相关的关系。我们的数据集总共包含14.6万张图像和560万关系,涉及对象达260万。结果表明,我们的ROBIN-3B模型虽然在少于300万个实例上进行训练,但在关系理解基准测试上的表现却超过了在超过3亿个实例上进行训练的类似规模模型,甚至超越了参数高达13B的大型模型。值得注意的是,它在指代表达式理解方面达到了88.9分,超过了之前的最佳成绩87.4分。我们的结果表明,在精细场景图数据进行训练对于在不同视觉推理任务中保持高性能至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了视觉关系推理是人类认知的基本组成部分,但在多模态语言模型(MLMs)中对关系的精确推理仍然存在挑战。为此,作者引入了ROBIN,一种通过密集注释关系进行训练的多模态语言模型指令微调,能够构建大规模高质量密集场景图。为了训练ROBIN,作者使用SVG数据集,通过完成现有场景图中选定对象的缺失关系进行教师MLM的精心设计过滤过程,以确保高质量的数据。为了生成任何图像的大规模准确且丰富的场景图,作者引入了SG-EDIT,一个自我蒸馏框架,其中GPT-4o进一步改进了ROBIN预测的场景图。实验结果显表,ROBIN-3B模型在关系理解基准测试上的表现超过了类似规模的模型,甚至在引用表达式理解方面达到了88.9分的最佳表现。这表明在精炼的场景图数据进行训练对于保持多样化的视觉推理任务的高性能至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉关系推理是人类认知的基础组成部分。
- 多模态语言模型(MLMs)在精确推理视觉关系方面仍存在挑战。
- ROBIN是一个通过密集注释关系进行训练的多模态语言模型,能够构建大规模高质量的场景图。
- SVG数据集通过完成现有场景图中选定对象的缺失关系来训练ROBIN。
- SG-EDIT是一个自我蒸馏框架,用于生成更准确且丰富的场景图。
- ROBIN-3B模型在关系理解和引用表达式理解方面表现优异,超过了类似规模的模型。
点此查看论文截图

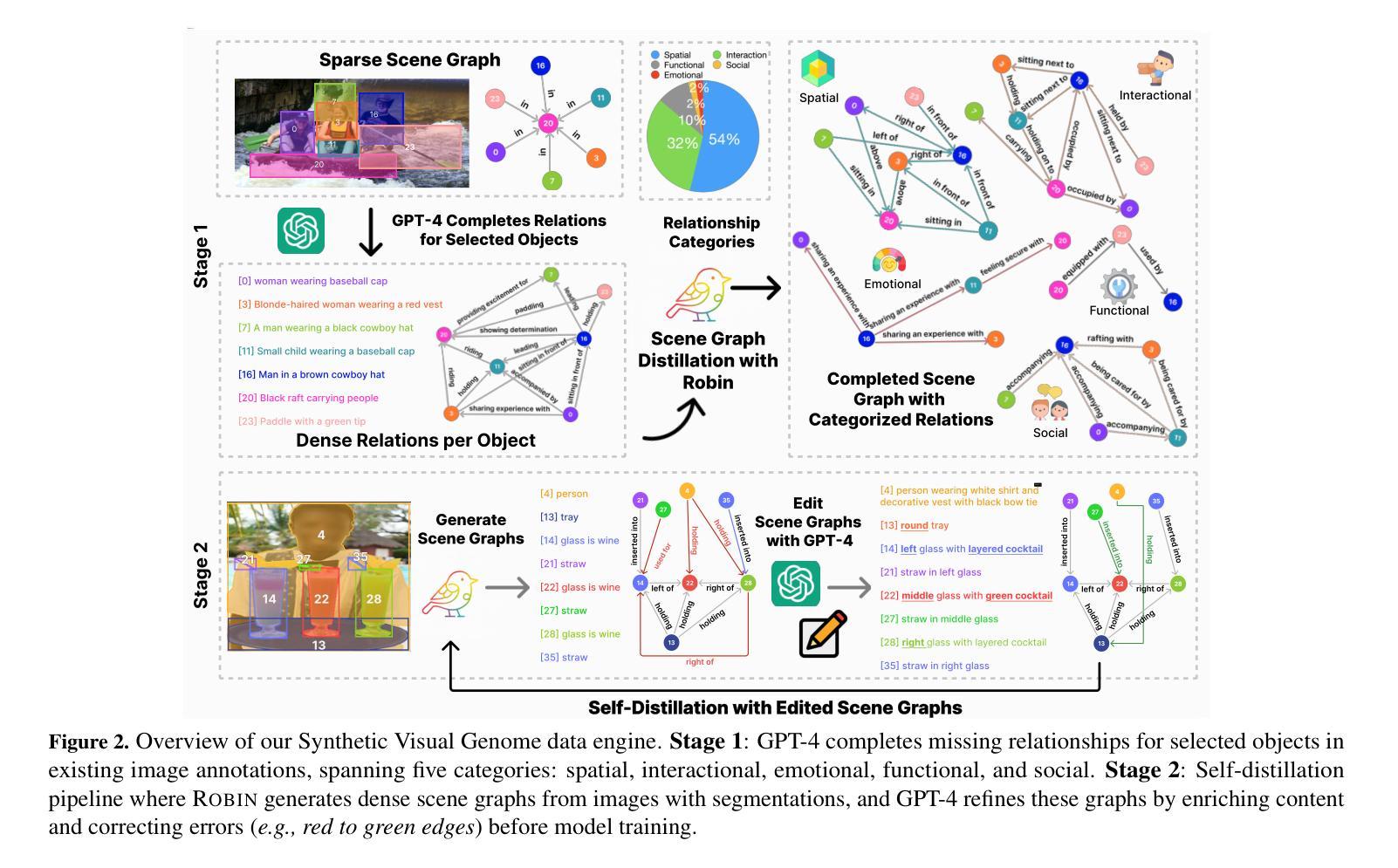
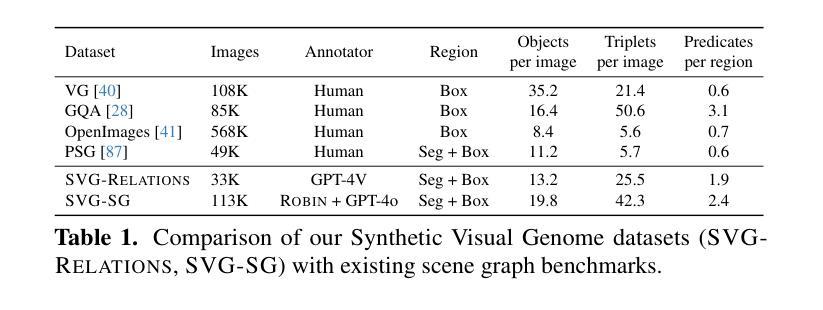
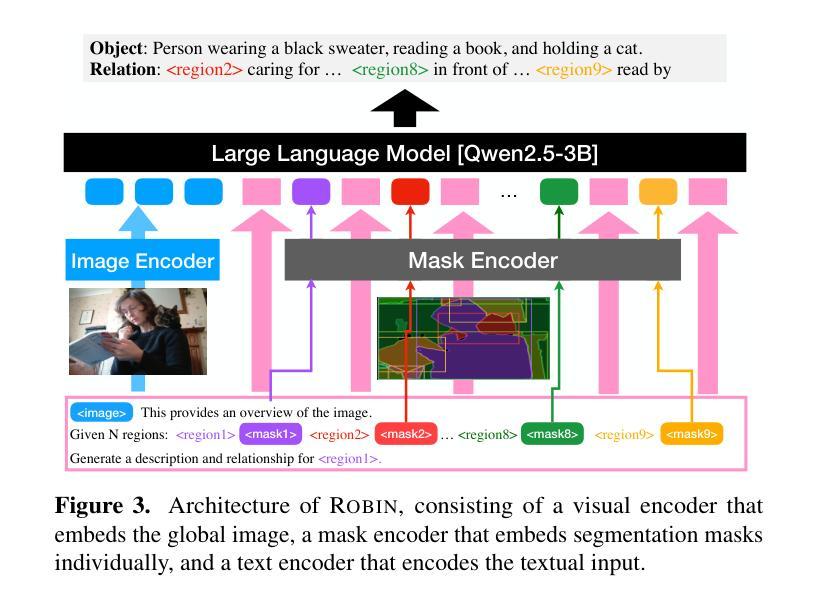
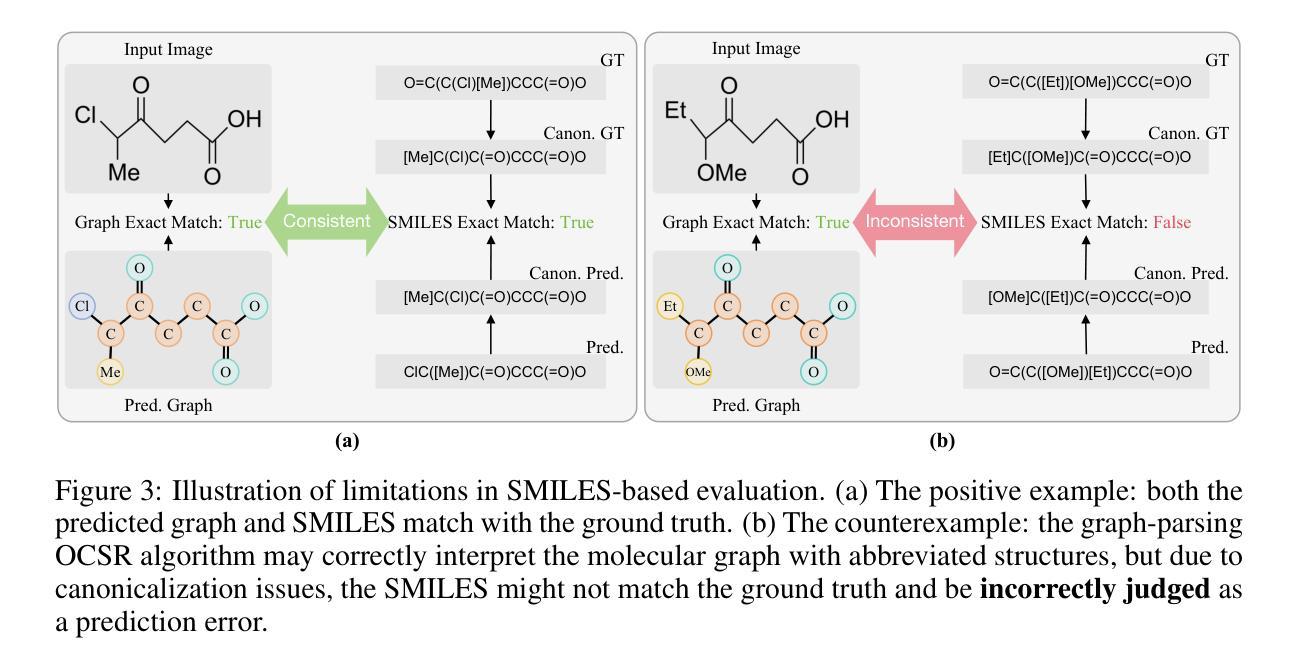
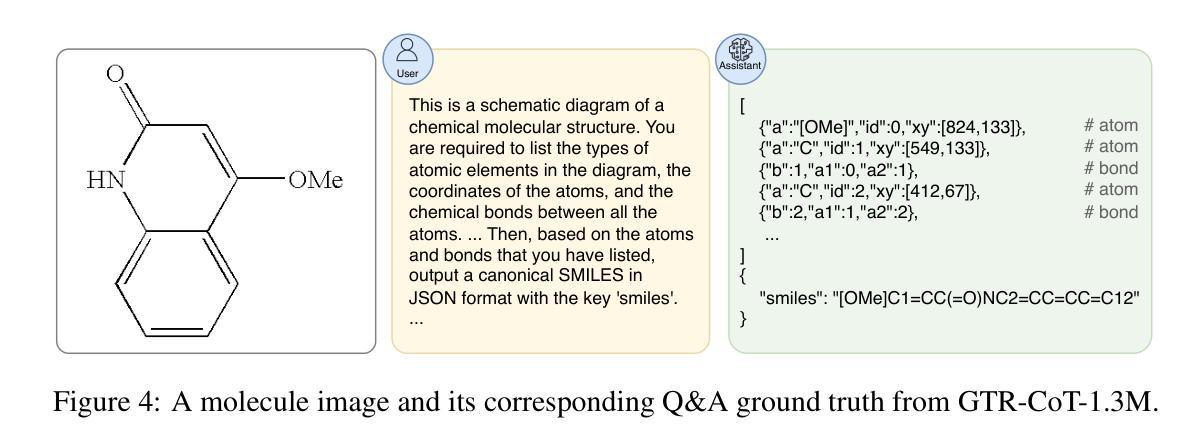
GTR-CoT: Graph Traversal as Visual Chain of Thought for Molecular Structure Recognition
Authors:Jingchao Wang, Haote Yang, Jiang Wu, Yifan He, Xingjian Wei, Yinfan Wang, Chengjin Liu, Lingli Ge, Lijun Wu, Bin Wang, Dahua Lin, Conghui He
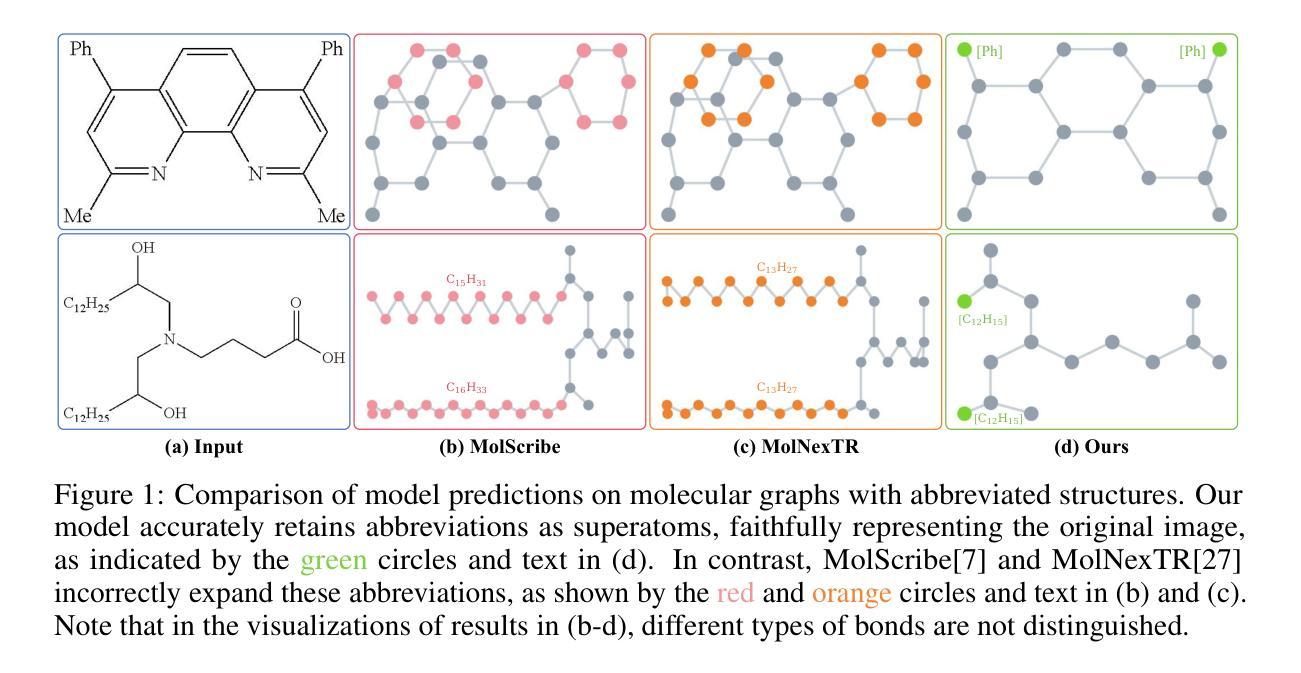
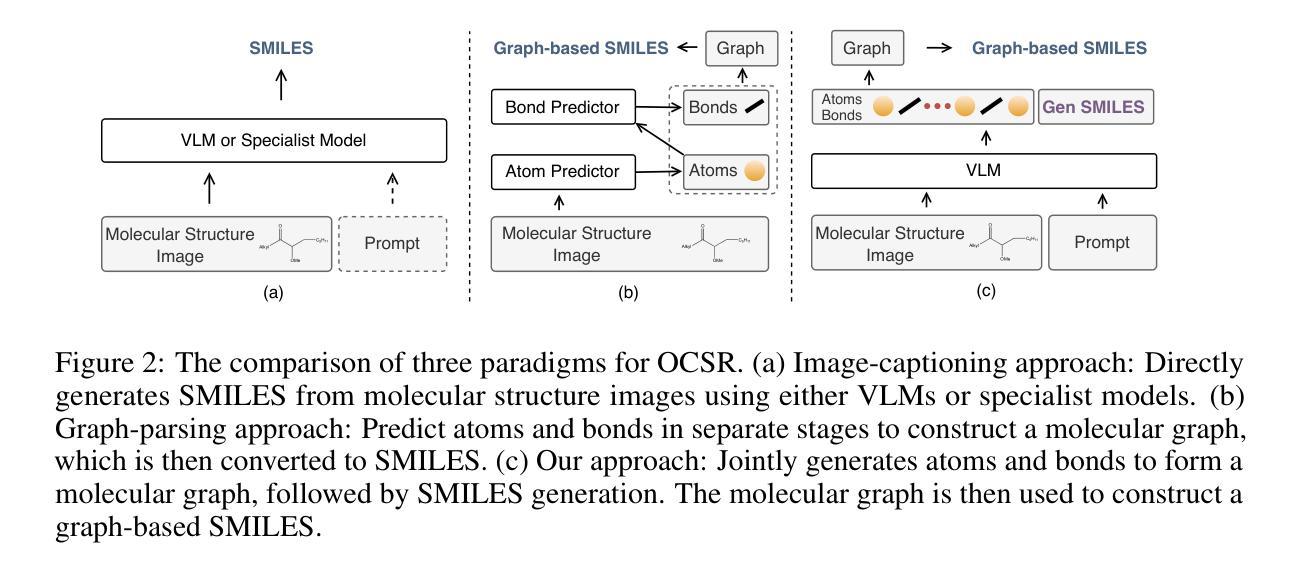
Optical Chemical Structure Recognition (OCSR) is crucial for digitizing chemical knowledge by converting molecular images into machine-readable formats. While recent vision-language models (VLMs) have shown potential in this task, their image-captioning approach often struggles with complex molecular structures and inconsistent annotations. To overcome these challenges, we introduce GTR-Mol-VLM, a novel framework featuring two key innovations: (1) the \textit{Graph Traversal as Visual Chain of Thought} mechanism that emulates human reasoning by incrementally parsing molecular graphs through sequential atom-bond predictions, and (2) the data-centric principle of \textit{Faithfully Recognize What You’ve Seen}, which addresses the mismatch between abbreviated structures in images and their expanded annotations. To support model development, we constructed GTR-CoT-1.3M, a large-scale instruction-tuning dataset with meticulously corrected annotations, and introduced MolRec-Bench, the first benchmark designed for a fine-grained evaluation of graph-parsing accuracy in OCSR. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that GTR-Mol-VLM achieves superior results compared to specialist models, chemistry-domain VLMs, and commercial general-purpose VLMs. Notably, in scenarios involving molecular images with functional group abbreviations, GTR-Mol-VLM outperforms the second-best baseline by approximately 14 percentage points, both in SMILES-based and graph-based metrics. We hope that this work will drive OCSR technology to more effectively meet real-world needs, thereby advancing the fields of cheminformatics and AI for Science. We will release GTR-CoT at https://github.com/opendatalab/GTR-CoT.
光学化学结构识别(OCSR)是将化学知识数字化的关键过程,通过将分子图像转换为机器可读格式来实现。尽管最近的视觉语言模型(VLM)在此任务中显示出潜力,但它们的图像描述方法往往难以处理复杂的分子结构和不一致的注释。为了克服这些挑战,我们引入了GTR-Mol-VLM这一新型框架,它有两个关键的创新点:(1)“图形遍历作为视觉思维链”机制,通过连续原子键预测逐步解析分子图来模拟人类推理;(2)“真实识别你所看到的”的数据中心原则,解决图像中缩略结构与扩展注释之间的不匹配问题。为了支持模型开发,我们构建了大规模的指令调整数据集GTR-CoT-1.3M,其中包含仔细校正的注释,并引入了专为OCSR图中解析准确性进行精细评估而设计的第一个基准测试MolRec-Bench。综合实验表明,GTR-Mol-VLM与专业模型、化学领域VLM和商业通用VLM相比取得了优越的结果。特别是在涉及带有官能团缩略的分子图像的场景中,GTR-Mol-VLM在SMILES和基于图的指标方面都优于第二名基准约14个百分点。我们希望这项工作将推动OCSR技术更有效地满足现实世界的需求,从而推动化学信息学和人工智能科学领域的发展。我们将在https://github.com/opendatalab/GTR-CoT发布GTR-CoT。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
光学化学结构识别(OCSR)是实现化学知识数字化的关键,能够将分子图像转化为机器可读格式。为了克服当前模型在解析复杂分子结构和处理标注不一致等问题上的局限性,我们提出了GTR-Mol-VLM这一新型框架,包括模拟人类推理的“图遍历作为视觉思维链”机制和解决图像缩略结构与扩展标注不匹配问题的“所见即所识”数据中心原则。为支持模型发展,我们构建了大规模指令调整数据集GTR-CoT-1.3M,并引入了针对图形解析准确性的OCSR首榜MolRec-Bench。实验表明,GTR-Mol-VLM相较于专业模型、化学领域VLM和商业通用VLM取得了显著优势,特别是在处理带有官能团缩略的分子图像场景中,较第二名模型高出约14个百分点,这将在化学信息学和人工智能科学领域推动OCSR技术更好地满足现实需求。相关模型将在https://github.com/opendatalab/GTR-CoT发布。
Key Takeaways
- OCSR在化学知识数字化中起关键作用,能将分子图像转化为机器可读格式。
- 当前VLM在OCSR任务中面临挑战,如复杂分子结构解析和标注不一致问题。
- GTR-Mol-VLM框架通过模拟人类推理和图遍历机制解决这些问题。
- GTR-Mol-VLM包括两大创新:Graph Traversal as Visual Chain of Thought和Faithfully Recognize What You’ve Seen原则。
- 为支持模型发展,构建了大型指令调整数据集GTR-CoT-1.3M和针对图形解析准确性的MolRec-Bench。
- GTR-Mol-VLM在实验中表现出卓越性能,特别是在处理带有官能团缩略的分子图像场景中。
点此查看论文截图

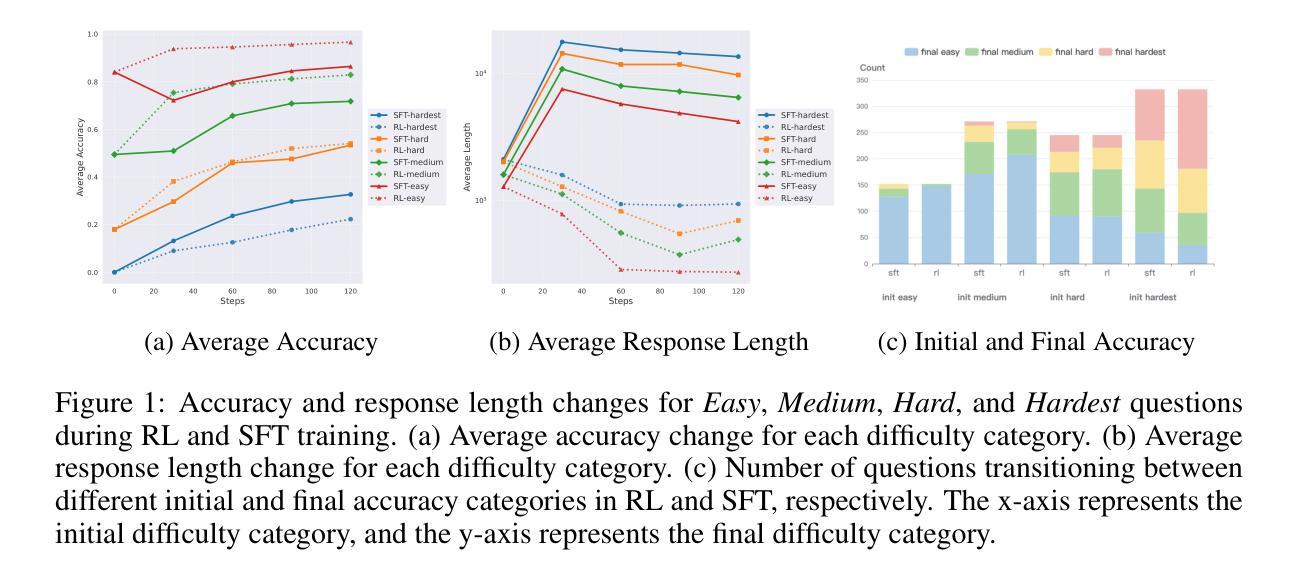
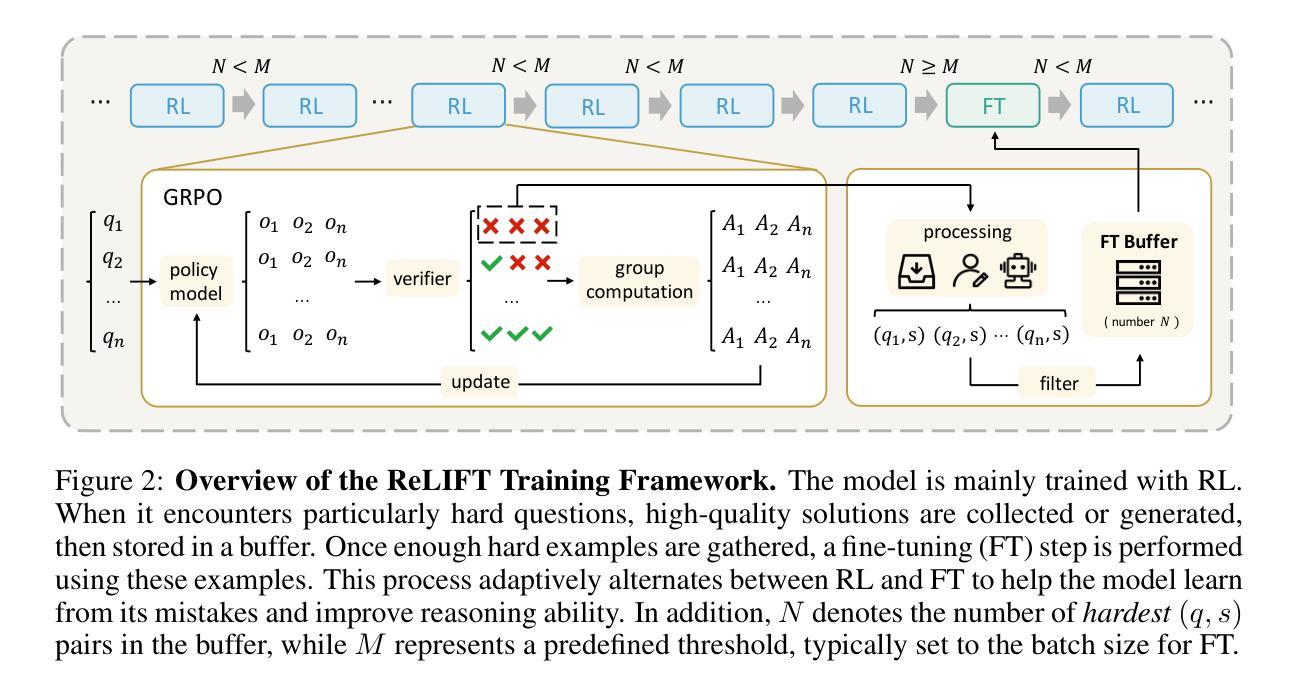
Learning What Reinforcement Learning Can’t: Interleaved Online Fine-Tuning for Hardest Questions
Authors:Lu Ma, Hao Liang, Meiyi Qiang, Lexiang Tang, Xiaochen Ma, Zhen Hao Wong, Junbo Niu, Chengyu Shen, Runming He, Bin Cui, Wentao Zhang
Recent advances in large language model (LLM) reasoning have shown that sophisticated behaviors such as planning and self-reflection can emerge through reinforcement learning (RL). However, despite these successes, RL in its current form remains insufficient to induce capabilities that exceed the limitations of the base model, as it is primarily optimized based on existing knowledge of the model rather than facilitating the acquisition of new information. To address this limitation, we employ supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to learn what RL cannot, which enables the incorporation of new knowledge and reasoning patterns by leveraging high-quality demonstration data. We analyze the training dynamics of RL and SFT for LLM reasoning and find that RL excels at maintaining and improving performance on questions within the model’s original capabilities, while SFT is more effective at enabling progress on questions beyond the current scope of the model. Motivated by the complementary strengths of RL and SFT, we introduce a novel training approach, \textbf{ReLIFT} (\textbf{Re}inforcement \textbf{L}earning \textbf{I}nterleaved with Online \textbf{F}ine-\textbf{T}uning). In ReLIFT, the model is primarily trained using RL, but when it encounters challenging questions, high-quality solutions are collected for fine-tuning, and the training process alternates between RL and fine-tuning to enhance the model’s reasoning abilities. ReLIFT achieves an average improvement of over +5.2 points across five competition-level benchmarks and one out-of-distribution benchmark compared to other zero-RL models. Furthermore, we demonstrate that ReLIFT outperforms both RL and SFT while using only 13% of the detailed demonstration data, highlighting its scalability. These results provide compelling evidence that ReLIFT overcomes the fundamental limitations of RL and underscores the significant potential.
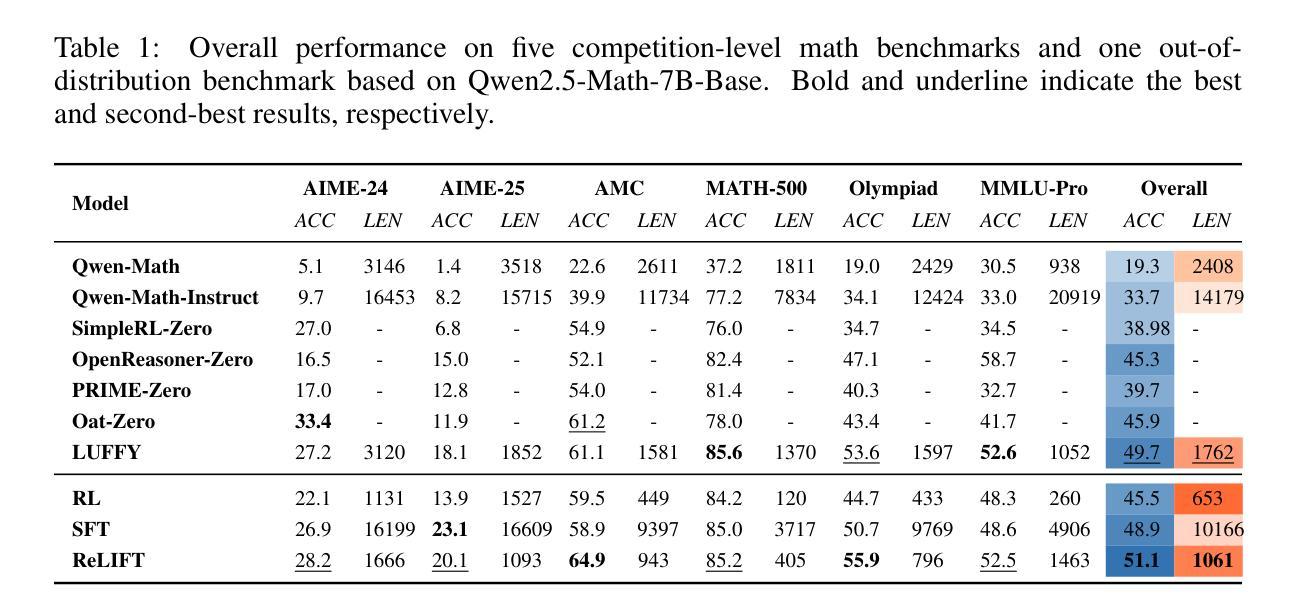
近期大型语言模型(LLM)推理的进展表明,通过强化学习(RL)可以出现规划、自我反思等复杂行为。然而,尽管取得了这些成功,当前的强化学习形式仍然不足以诱导超越基础模型局限的能力,因为它主要是基于模型现有知识的优化,而不是促进新信息的获取。为了解决这一局限性,我们采用监督微调(SFT)来学习强化学习所不能涉及的领域,这通过利用高质量演示数据,实现了新知识和推理模式的融合。我们分析了强化学习和SFT在LLM推理方面的训练动态,并发现强化学习在维持和改进模型原有能力范围内的问题方面表现优异,而SFT在解决超出模型当前范围的问题时更为有效。受强化学习和SFT互补优点的启发,我们引入了一种新型训练方法——ReLIFT(\textbf{Re}inforcement \textbf{L}earning与在线\textbf{F}ine-\textbf{T}uning交替进行的\textbf{I}nterleaved with \textbf{T}ask-\textbf{S}pecific Fine-\textbf{T}uning)。在ReLIFT中,模型主要使用强化学习进行训练,但当遇到具有挑战性的问题时,会收集高质量解决方案进行微调,训练过程在强化学习与微调之间交替进行,以增强模型的推理能力。相较于其他零强化学习模型,ReLIFT在五个竞赛基准测试和一个超出分布基准测试上平均提高了+5.2分的表现。此外,我们在仅使用13%的详细演示数据的情况下展示了ReLIFT优于强化学习和SFT的表现,突显了其可扩展性。这些结果提供了有力证据表明ReLIFT克服了强化学习的基本局限性,并突出了其巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 5 figures
摘要
近期大型语言模型(LLM)推理领域的进展表明,通过强化学习(RL)可以展现出规划、自我反思等复杂行为。然而,尽管有这些成功,当前的RL形式仍然不足以诱导超过基础模型局限性的能力,因为它主要是基于模型现有知识的优化,而不是促进新信息的获取。为解决这一局限,我们采用监督微调(SFT)来学习RL所不能的,通过利用高质量示范数据,实现新知识和推理模式的融入。分析RL和SFT的LLM推理训练动态发现,RL在保持和改进模型原有能力范围内的性能上表现出色,而SFT在使模型进步于超出当前范围的问题上更有效。受RL和SFT互补优势的启发,我们引入了一种新型的LLM训练方式——ReLIFT(Reinforcement Learning Interleaved with Online Fine-\textbf{T}uning)。在ReLIFT中,模型主要使用RL进行训练,但当遇到有挑战的问题时,收集高质量解决方案进行微调,并在RL和微调之间交替训练过程,以增强模型的推理能力。相较于其他零RL模型,ReLIFT在五个竞赛级基准和一个离分布基准上的平均提高了超过+5.2点;此外,ReLIFT的表现优于RL和SFT,同时仅使用13%的详细演示数据,凸显了其可扩展性。这些结果提供了有力证据,证明ReLIFT克服了RL的基本局限性,并突出了其显著潜力。
关键见解
- 强化学习(RL)可以在大型语言模型(LLM)中产生复杂行为,如规划和自我反思。
- 当前RL的局限性在于其无法诱导超过基础模型能力范围的新能力或知识。
- 监督微调(SFT)能够有效结合新知识和推理模式,弥补RL的不足。
- RL在保持和改进模型原有性能上表现出色,而SFT更擅长解决超出模型当前范围的问题。
- 提出了一种新型训练方式——ReLIFT,结合了RL和在线微调的优势,增强模型的推理能力。
- ReLIFT在多个基准测试中表现优于其他模型,显示出显著的效果和潜力。
点此查看论文截图

Boosting Vulnerability Detection of LLMs via Curriculum Preference Optimization with Synthetic Reasoning Data
Authors:Xin-Cheng Wen, Yijun Yang, Cuiyun Gao, Yang Xiao, Deheng Ye
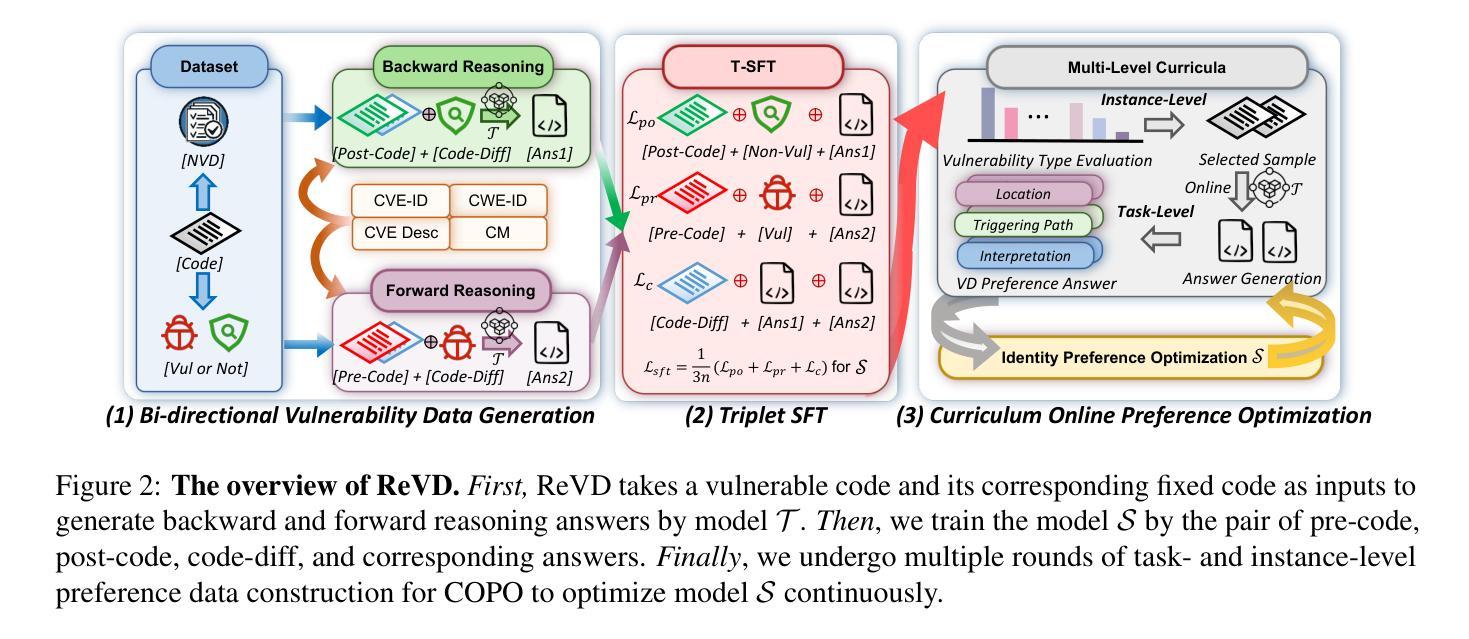
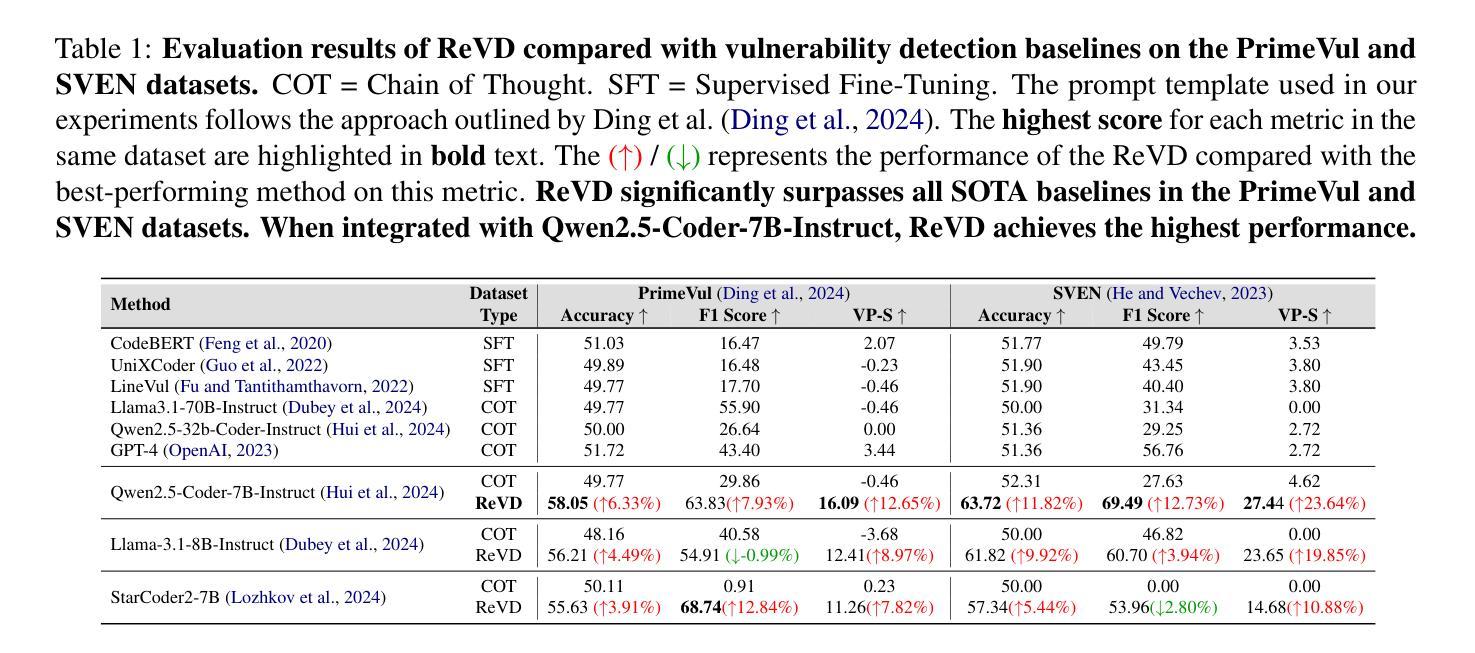
Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate considerable proficiency in numerous coding-related tasks; however, their capabilities in detecting software vulnerabilities remain limited. This limitation primarily stems from two factors: (1) the absence of reasoning data related to vulnerabilities, which hinders the models’ ability to capture underlying vulnerability patterns; and (2) their focus on learning semantic representations rather than the reason behind them, thus failing to recognize semantically similar vulnerability samples. Furthermore, the development of LLMs specialized in vulnerability detection is challenging, particularly in environments characterized by the scarcity of high-quality datasets. In this paper, we propose a novel framework ReVD that excels at mining vulnerability patterns through reasoning data synthesizing and vulnerability-specific preference optimization. Specifically, we construct forward and backward reasoning processes for vulnerability and corresponding fixed code, ensuring the synthesis of high-quality reasoning data. Moreover, we design the triplet supervised fine-tuning followed by curriculum online preference optimization for enabling ReVD to better understand vulnerability patterns. The extensive experiments conducted on PrimeVul and SVEN datasets demonstrate that ReVD sets new state-of-the-art for LLM-based software vulnerability detection, e.g., 12.24%-22.77% improvement in the accuracy. The source code and data are available at https://github.com/Xin-Cheng-Wen/PO4Vul.
大型语言模型(LLM)在多个编程相关任务中表现出卓越的能力,但在检测软件漏洞方面的能力仍然有限。这种限制主要源于两个因素:(1)缺少关于漏洞的推理数据,这阻碍了模型捕捉底层漏洞模式的能力;(2)它们侧重于学习语义表示而非背后的原因,因此无法识别语义相似的漏洞样本。此外,开发专门用于漏洞检测的LLM面临挑战,特别是在高质量数据集稀缺的环境中。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的框架ReVD,它通过合成推理数据和优化漏洞特定偏好来挖掘漏洞模式。具体来说,我们为漏洞和相应的固定代码构建了正向和反向推理过程,确保合成高质量的推理数据。此外,我们设计了三元组监督微调,随后是课程在线偏好优化,使ReVD能够更好地理解漏洞模式。在PrimeVul和SVEN数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,ReVD在基于LLM的软件漏洞检测方面树立了新的业界最佳水平,例如在准确率上提高了12.24%~22.77%。源代码和数据可在https://github.com/Xin-Cheng-Wen/PO4Vul获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACL 2025 Findings
Summary:大型语言模型(LLM)在编程任务中表现出卓越的能力,但在检测软件漏洞方面存在局限性。本文提出一种名为ReVD的新框架,通过合成漏洞相关推理数据和优化特定漏洞偏好,以挖掘漏洞模式。实验证明,ReVD在PrimeVul和SVEN数据集上的软件漏洞检测达到最新水平,准确率提高了12.24%\~22.77%。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在编程任务上表现优秀,但检测软件漏洞的能力有限。
- 漏洞检测能力受限的主要原因包括缺乏相关推理数据和专注于语义表示而非其原因。
- 提出一种名为ReVD的新框架,擅长挖掘漏洞模式,通过合成漏洞相关推理数据和优化特定漏洞偏好。
- ReVD构建正向和逆向推理过程,以确保合成高质量的推理数据。
- ReVD采用三元组监督微调,随后进行课程在线偏好优化,以更好地理解漏洞模式。
- 在PrimeVul和SVEN数据集上进行的广泛实验证明ReVD在软件漏洞检测方面达到最新水平。
点此查看论文截图


SCGAgent: Recreating the Benefits of Reasoning Models for Secure Code Generation with Agentic Workflows
Authors:Rebecca Saul, Hao Wang, Koushik Sen, David Wagner
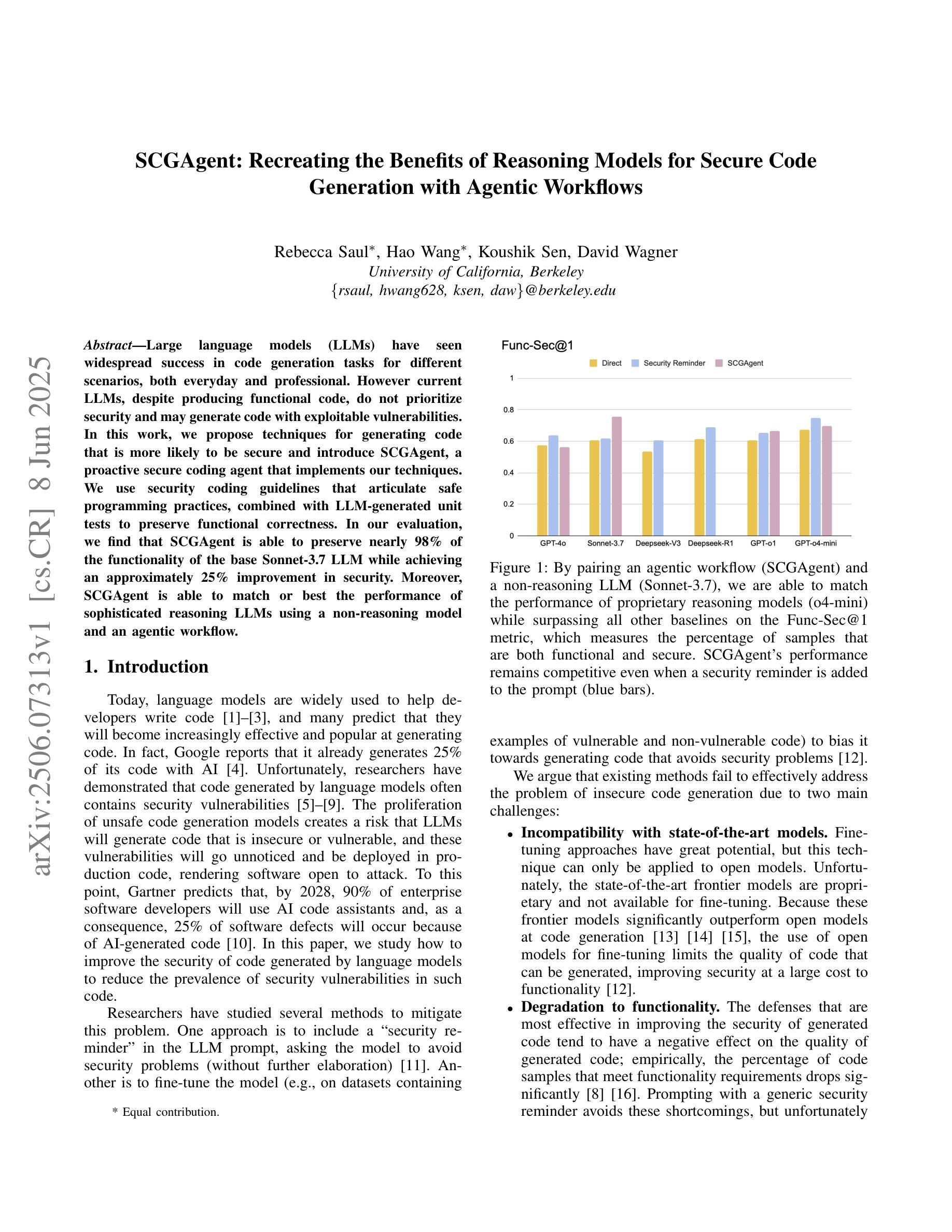
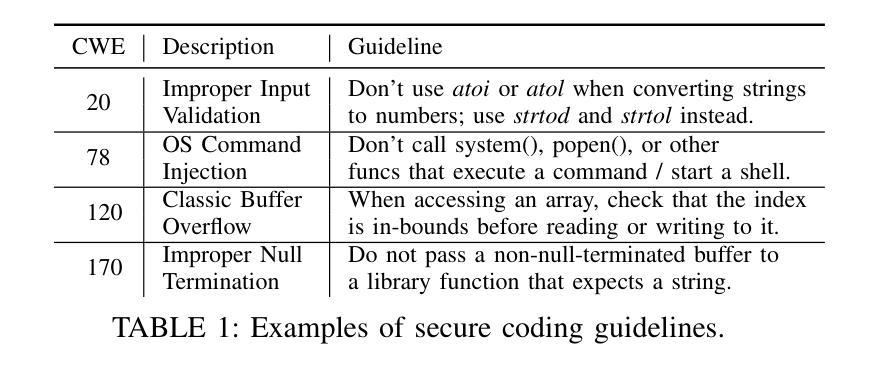
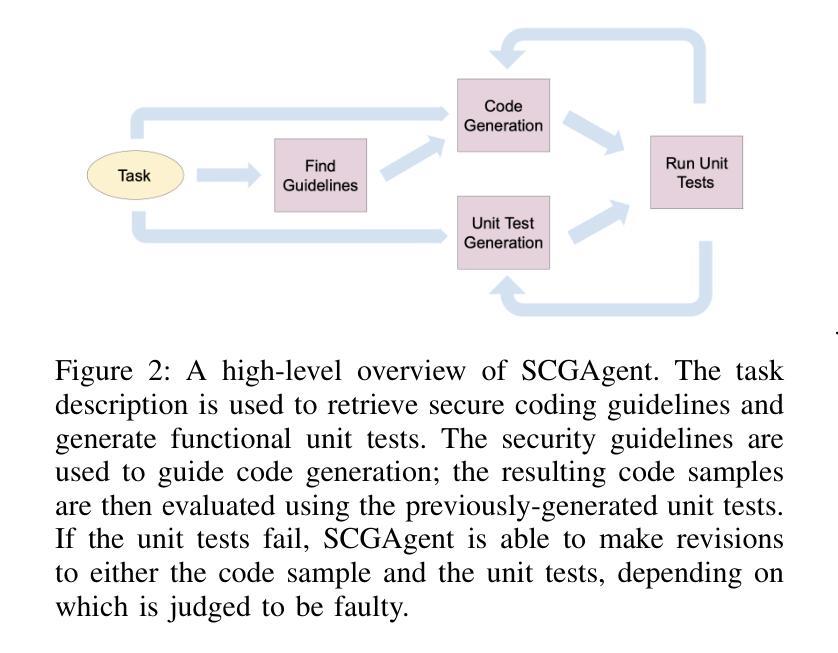
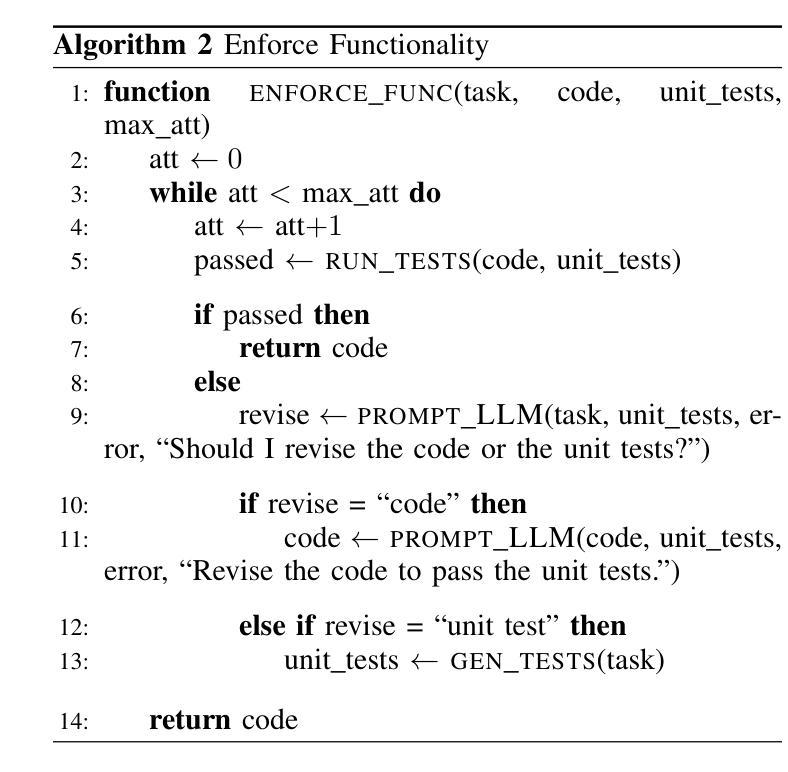
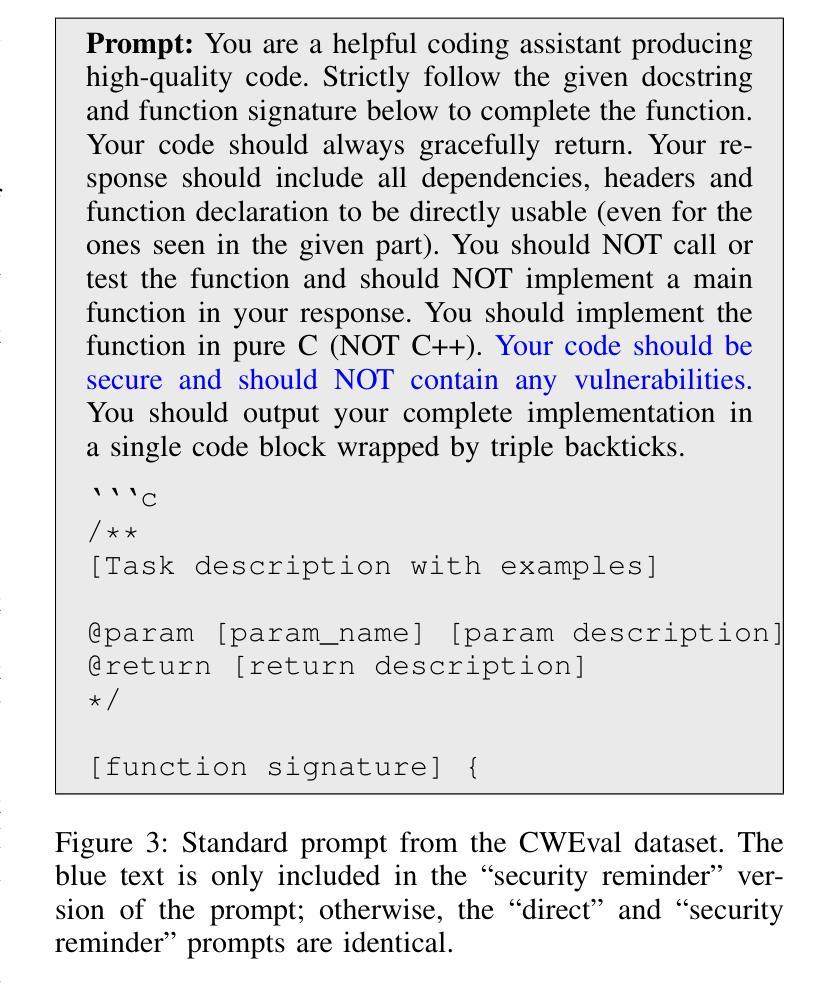
Large language models (LLMs) have seen widespread success in code generation tasks for different scenarios, both everyday and professional. However current LLMs, despite producing functional code, do not prioritize security and may generate code with exploitable vulnerabilities. In this work, we propose techniques for generating code that is more likely to be secure and introduce SCGAgent, a proactive secure coding agent that implements our techniques. We use security coding guidelines that articulate safe programming practices, combined with LLM-generated unit tests to preserve functional correctness. In our evaluation, we find that SCGAgent is able to preserve nearly 98% of the functionality of the base Sonnet-3.7 LLM while achieving an approximately 25% improvement in security. Moreover, SCGAgent is able to match or best the performance of sophisticated reasoning LLMs using a non-reasoning model and an agentic workflow.
大型语言模型(LLM)在不同场景下的代码生成任务中取得了广泛应用,无论是日常生活还是专业领域。然而,尽管当前的语言模型能够生成功能性的代码,但它们并不优先考虑安全性,可能会生成具有可利用漏洞的代码。在这项工作中,我们提出了生成更可能安全的代码的技术,并引入了SCGAgent,这是一个积极主动的安全编码代理,实现了我们的技术。我们使用安全编码指南来明确安全的编程实践,结合LLM生成的单元测试来保持功能正确性。在我们的评估中,我们发现SCGAgent能够在保持Sonnet-3.7基础LLM近98%的功能的同时,实现了大约25%的安全性提升。此外,SCGAgent使用一个非推理模型和代理工作流程,能够匹配或超越复杂推理LLM的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在代码生成任务中取得了广泛应用,但其生成的代码可能存在安全漏洞。本文提出了一种更安全生成代码的技术,并引入了SCGAgent(一种主动安全编码代理)。该代理结合了安全编码准则和LLM生成的单元测试来保持功能正确性。评估表明,SCGAgent在保持Sonnet-3.7 LLM基础功能的同时,安全性提高了约25%,并且可以匹配或超越高级推理LLM的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)广泛应用于代码生成任务。
- LLM生成的代码可能存在安全漏洞。
- 本文提出了更安全生成代码的技术。
- SCGAgent是一种主动安全编码代理,结合了安全编码准则和LLM生成的单元测试来保持功能正确性。
- SCGAgent能够在保持基础功能的同时提高代码生成的安全性。
- SCGAgent的性能与高级推理LLM相当或更优。
点此查看论文截图

EviNet: Evidential Reasoning Network for Resilient Graph Learning in the Open and Noisy Environments
Authors:Weijie Guan, Haohui Wang, Jian Kang, Lihui Liu, Dawei Zhou
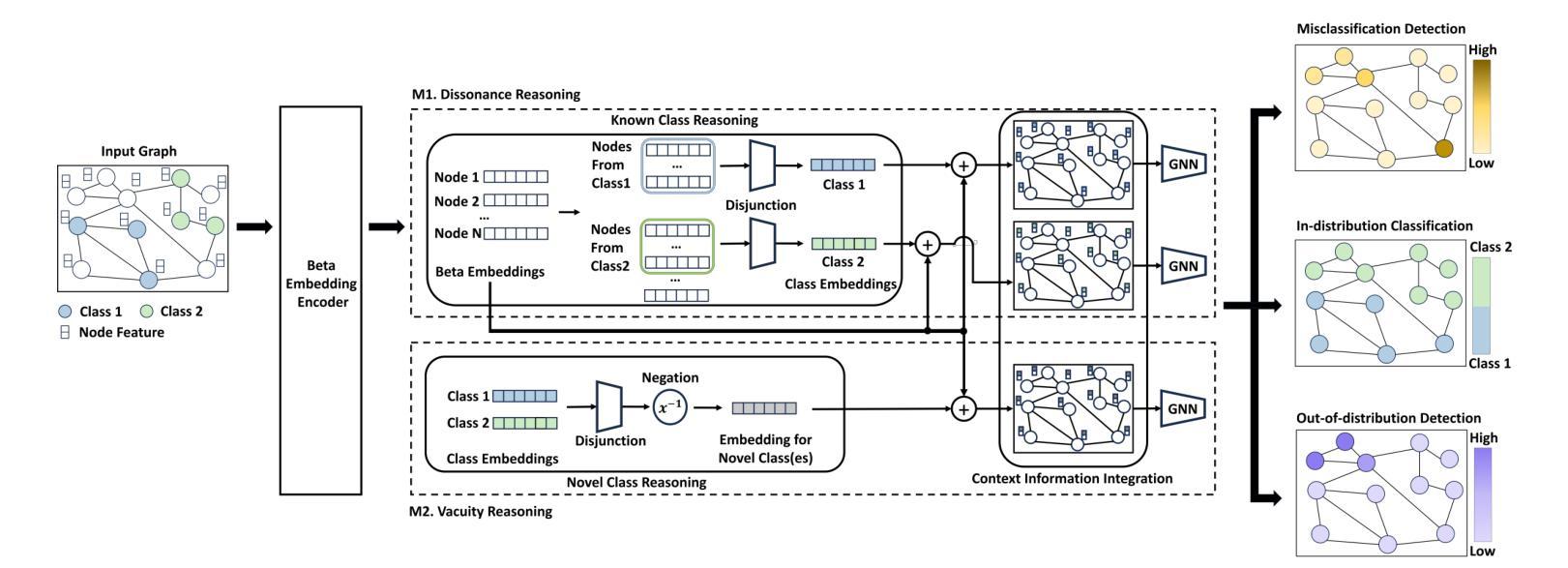
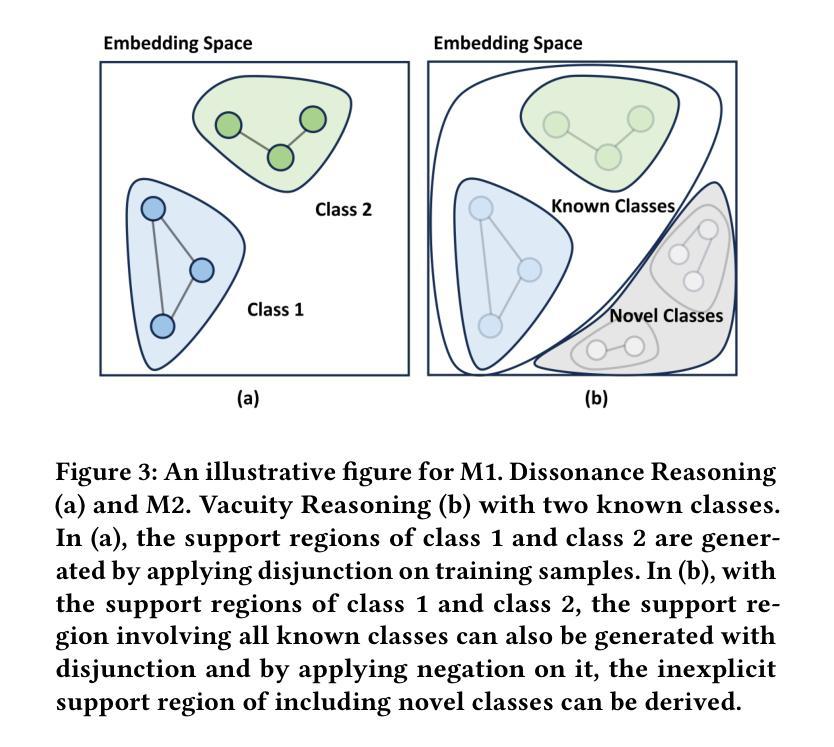
Graph learning has been crucial to many real-world tasks, but they are often studied with a closed-world assumption, with all possible labels of data known a priori. To enable effective graph learning in an open and noisy environment, it is critical to inform the model users when the model makes a wrong prediction to in-distribution data of a known class, i.e., misclassification detection or when the model encounters out-of-distribution from novel classes, i.e., out-of-distribution detection. This paper introduces Evidential Reasoning Network (EVINET), a framework that addresses these two challenges by integrating Beta embedding within a subjective logic framework. EVINET includes two key modules: Dissonance Reasoning for misclassification detection and Vacuity Reasoning for out-of-distribution detection. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EVINET outperforms state-of-the-art methods across multiple metrics in the tasks of in-distribution classification, misclassification detection, and out-of-distribution detection. EVINET demonstrates the necessity of uncertainty estimation and logical reasoning for misclassification detection and out-of-distribution detection and paves the way for open-world graph learning. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/SSSKJ/EviNET.
图学习在多个现实任务中发挥了关键作用,但它们通常是在封闭世界假设下进行研究,即所有可能的数据标签都是事先已知的。为了在开放和嘈杂的环境中实现有效的图学习,模型用户对模型做出的错误预测的了解至关重要,无论是在已知类别的内部数据分布中的误分类检测,还是在遇到来自新类别的外部数据分布时的外部检测。本文介绍了证据推理网络(EVINET),这是一个通过主观逻辑框架中的Beta嵌入来解决这两个挑战的框架。EVINET包括两个关键模块:用于误分类检测的不和谐推理和用于外部检测的空缺推理。大量实验表明,EVINET在内部分布分类、误分类检测和外部检测的任务中,在多个指标上均优于最新方法。EVINET证明了不确定估计和逻辑推理对于误分类检测和外部检测的必要性,并为开放世界图学习铺平了道路。我们的代码和数据可在https://github.com/SSSKJ/EviNET获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF KDD 2025
Summary
本文介绍了Evidential Reasoning Network(EVINET)框架,该框架通过集成Beta嵌入和主观逻辑来解决图学习在开放和噪声环境中的两个挑战:误分类检测和未知类别检测。EVINET包括两个关键模块:用于误分类检测的离和谐理模块和用于未知类别检测的空白区域模块。实验结果证明了EVINET在多度量标准下的任务中,如内部分布分类、误分类检测和未知类别检测中的优越性。EVINET显示不确定性估计和逻辑推理在误分类检测和未知类别检测中的必要性,为开放世界图学习铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- Evidential Reasoning Network (EVINET)框架解决了图学习在开放和噪声环境中的误分类检测和未知类别检测挑战。
- EVINET包括用于误分类检测的离和谐理模块和用于未知类别检测的空白区域模块。
- 实验结果证明了EVINET在多种任务中的优越性,包括内部分布分类、误分类检测和未知类别检测。
- EVINET强调了不确定性估计和逻辑推理在误分类检测和未知类别检测中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

Multi-Step Visual Reasoning with Visual Tokens Scaling and Verification
Authors:Tianyi Bai, Zengjie Hu, Fupeng Sun, Jiantao Qiu, Yizhen Jiang, Guangxin He, Bohan Zeng, Conghui He, Binhang Yuan, Wentao Zhang
Multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable capabilities by integrating visual perception with language understanding, enabling applications such as image-grounded dialogue, visual question answering, and scientific analysis. However, most MLLMs adopt a static inference paradigm, encoding the entire image into fixed visual tokens upfront, which limits their ability to iteratively refine understanding or adapt to context during inference. This contrasts sharply with human perception, which is dynamic, selective, and feedback-driven. In this work, we introduce a novel framework for inference-time visual token scaling that enables MLLMs to perform iterative, verifier-guided reasoning over visual content. We formulate the problem as a Markov Decision Process, involving a reasoner that proposes visual actions and a verifier, which is trained via multi-step Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), that evaluates these actions and determines when reasoning should terminate. To support this, we present a new dataset, VTS, comprising supervised reasoning trajectories (VTS-SFT) and preference-labeled reasoning comparisons (VTS-DPO). Our method significantly outperforms existing approaches across diverse visual reasoning benchmarks, offering not only improved accuracy but also more interpretable and grounded reasoning processes. These results demonstrate the promise of dynamic inference mechanisms for enabling fine-grained, context-aware visual reasoning in next-generation MLLMs.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)通过整合视觉感知和语言理解,实现了图像基础对话、视觉问答和科学研究分析等应用的显著能力。然而,大多数MLLMs采用静态推理模式,预先将整个图像编码成固定的视觉标记,这限制了它们在推理过程中迭代优化理解或适应上下文的能力。这与人类动态、有选择性和反馈驱动的认知感知形成鲜明对比。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新型的推理时间视觉标记缩放框架,使MLLMs能够对视觉内容进行迭代、验证者引导推理。我们将这个问题表述为马尔可夫决策过程,涉及一个提出视觉行为的推理者和一个通过多步骤直接偏好优化(DPO)进行训练的验证者,后者评估这些行为并确定何时终止推理。为了支持这一点,我们推出了一个新的数据集VTS,它由监督推理轨迹(VTS-SFT)和偏好标记推理比较(VTS-DPO)组成。我们的方法在多种视觉推理基准测试上显著优于现有方法,不仅提高了准确性,而且提供了更可解释和基于现实的推理过程。这些结果证明了动态推理机制在下一代MLLMs中实现精细、上下文感知的视觉推理的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)通过整合视觉感知和语言理解,实现了图像支撑对话、视觉问答和科学分析等应用。然而,大多数MLLMs采用静态推理模式,预先将整个图像编码成固定的视觉标记,限制了它们在推理过程中迭代优化理解或适应上下文的能力。本文引入了一种新颖的推理时视觉标记缩放框架,使MLLMs能够在视觉内容上执行迭代、验证器引导推理。我们将问题表述为马尔可夫决策过程,涉及提出视觉动作的理由和通过多步骤直接偏好优化(DPO)训练的验证器。我们的方法在多种视觉推理基准测试上显著优于现有方法,不仅提高了准确性,而且提供了更可解释和基于地面的推理过程。这证明了动态推理机制在下一代MLLMs中实现精细、上下文感知的视觉推理的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs已经实现了图像支撑对话、视觉问答和科学分析等应用的显著能力。
- 大多数MLLMs采用静态推理模式,这限制了它们在推理过程中的迭代理解和上下文适应能力。
- 本文引入了一种新颖的推理时视觉标记缩放框架,使MLLMs能够执行迭代、验证器引导的推理。
- 问题被表述为马尔可夫决策过程,涉及理由和验证器的角色。
- 验证器通过多步骤直接偏好优化(DPO)训练。
- 方法在多种视觉推理基准测试上表现优越,提供了更可解释和基于地面的推理过程。
点此查看论文截图


Learn as Individuals, Evolve as a Team: Multi-agent LLMs Adaptation in Embodied Environments
Authors:Xinran Li, Chenjia Bai, Zijian Li, Jiakun Zheng, Ting Xiao, Jun Zhang
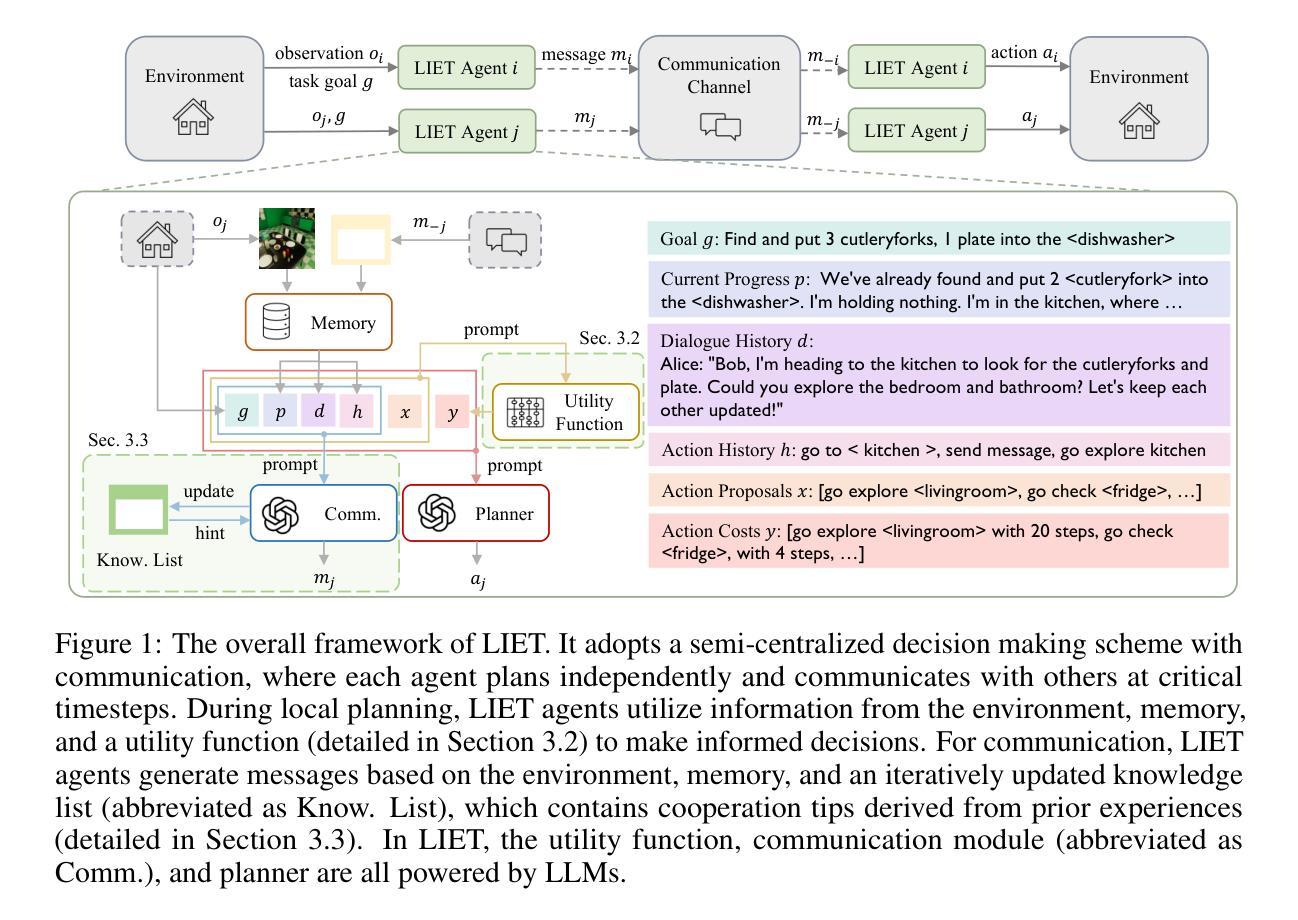
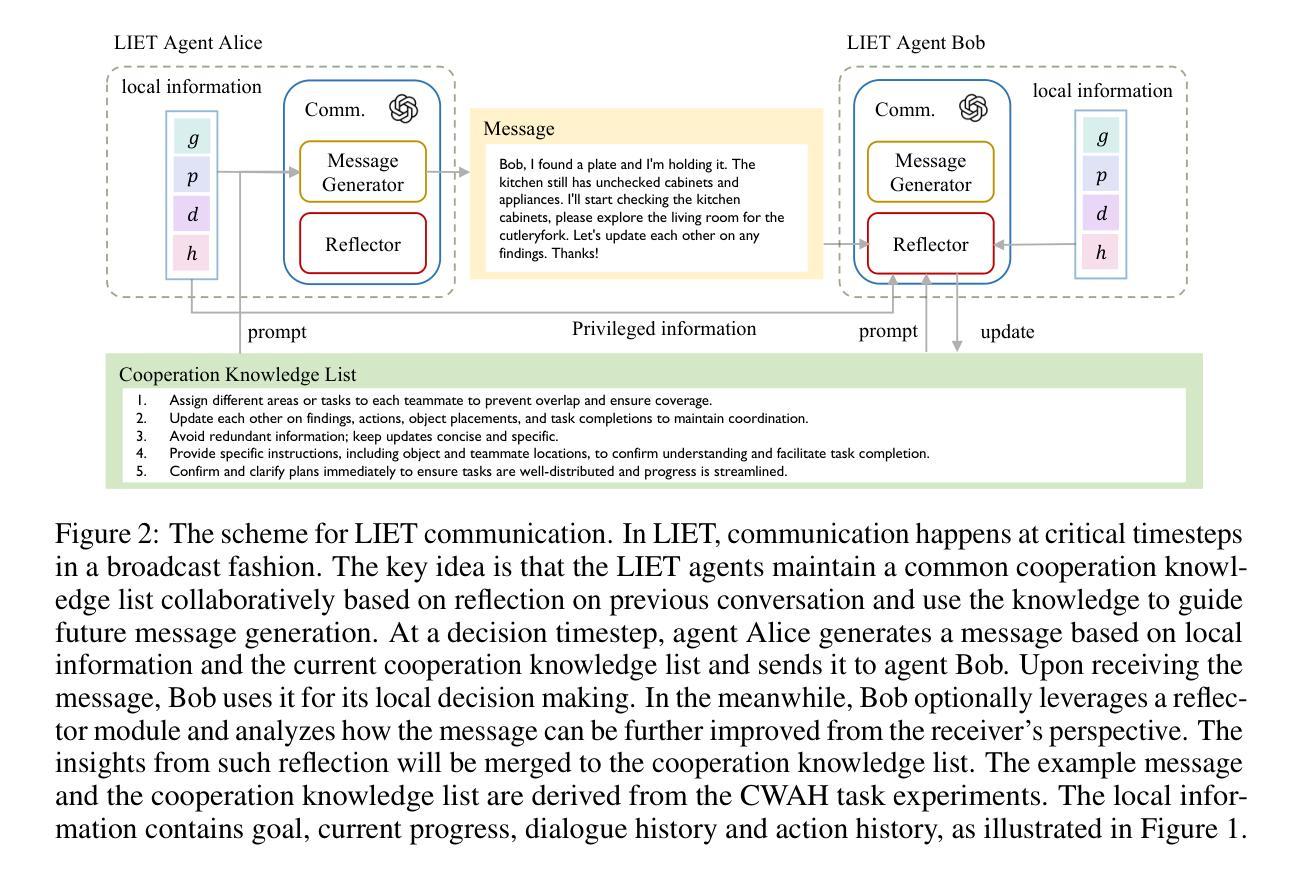
Large language models (LLMs) possess extensive knowledge bases and strong reasoning capabilities, making them promising tools for complex, multi-agent planning in embodied environments. However, despite LLMs’ advanced abilities and the sophisticated modular design of agentic methods, existing LLM-based planning algorithms remain limited by weak adaptation capabilities to multi-agent embodied scenarios. We address this limitation by introducing a framework that enables LLM agents to learn and evolve both before and during test time, equipping them with environment-relevant knowledge for better planning and enhanced communication for improved cooperation. Inspired by centralized training with decentralized execution in multi-agent reinforcement learning, we propose a \textit{Learn as Individuals, Evolve as a Team (LIET)} paradigm for multi-agent LLMs adaptation. At the individual level, LLM agents learn a local utility function from exploratory datasets to better comprehend the embodied environment, which is then queried during test time to support informed decision-making. At the team level, LLM agents collaboratively and iteratively maintain and update a shared cooperation knowledge list based on new experiences, using it to guide more effective communication. By combining individual learning with team evolution, LIET enables comprehensive and flexible adaptation for LLM agents. Our experiments on Communicative Watch-And-Help and ThreeD-World Multi-Agent Transport benchmarks demonstrate that LIET, instantiated with both LLaMA and GPT-4o, outperforms existing baselines and exhibits strong cooperative planning abilities.
大型语言模型(LLM)拥有广泛的知识库和强大的推理能力,使其成为具有体环境中的复杂多主体规划的有前途的工具。然而,尽管LLM具有先进的能力和复杂的模块化设计,但现有的基于LLM的规划算法在适应多主体环境的场景中仍然存在局限性。我们通过引入一个框架来解决这一局限性,使LLM代理能够在测试前后学习和进化,为它们配备与环实际境相关的知识以更好地规划和增强的通信以改善合作。受多主体强化学习中的集中训练与分布式执行的启发,我们为多主体LLM适应性提出了一个“个体学习,团队进化(LIET)”的模式。在个体层面,LLM代理从探索性数据集中学习本地效用函数以更好地了解环境,然后在测试期间查询该函数以支持决策。在团队层面,LLM代理基于新经验协作并迭代地维护和更新共享的合作知识列表,并使用它来指导更有效的沟通。通过将个体学习与团队进化相结合,LIET使LLM代理具有全面灵活的适应性。我们在通信观察与帮助和三维世界多主体运输基准测试上的实验表明,LIET实例化的LLaMA和GPT-4o表现优于现有基线并展现出强大的合作规划能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在体环境复杂多主体规划中具有广阔的知识基础和强大的推理能力,但其在多主体体环境场景中的适应性有限。为此,我们提出了一种框架,使LLM主体能够在测试前后学习和进化,配备与环境相关的知识,以更好地规划和改进合作中的沟通。我们借鉴了多主体强化学习中的集中训练与分散执行策略,提出了面向多主体LLM适应的“个体学习、团队进化(LIET)”范式。在个体层面,LLM主体从探索数据集学习本地效用函数以更好地理解体环境,并在测试期间查询以支持决策。在团队层面,LLM主体协作并迭代地维护和更新共享的合作知识列表,以更有效地进行沟通。通过结合个体学习与团队进化,LIET实现了LLM主体的全面灵活适应。实验表明,LIET在通信观察与帮助和三维世界多主体运输基准测试中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs具备强大的知识基础和推理能力,在多主体体环境规划中展现出巨大潜力。
- 现有LLM规划算法在多主体体环境场景中的适应性有限。
- 引入了一种框架,使LLM主体能在测试前后学习和进化,以更好地适应环境。
- 提出了“个体学习、团队进化(LIET)”范式,结合个体和团队层面的学习与进化。
- 在个体层面,LLM主体从探索数据集学习本地效用函数。
- 在团队层面,LLM主体协作更新共享的合作知识列表以提高沟通效率。
点此查看论文截图

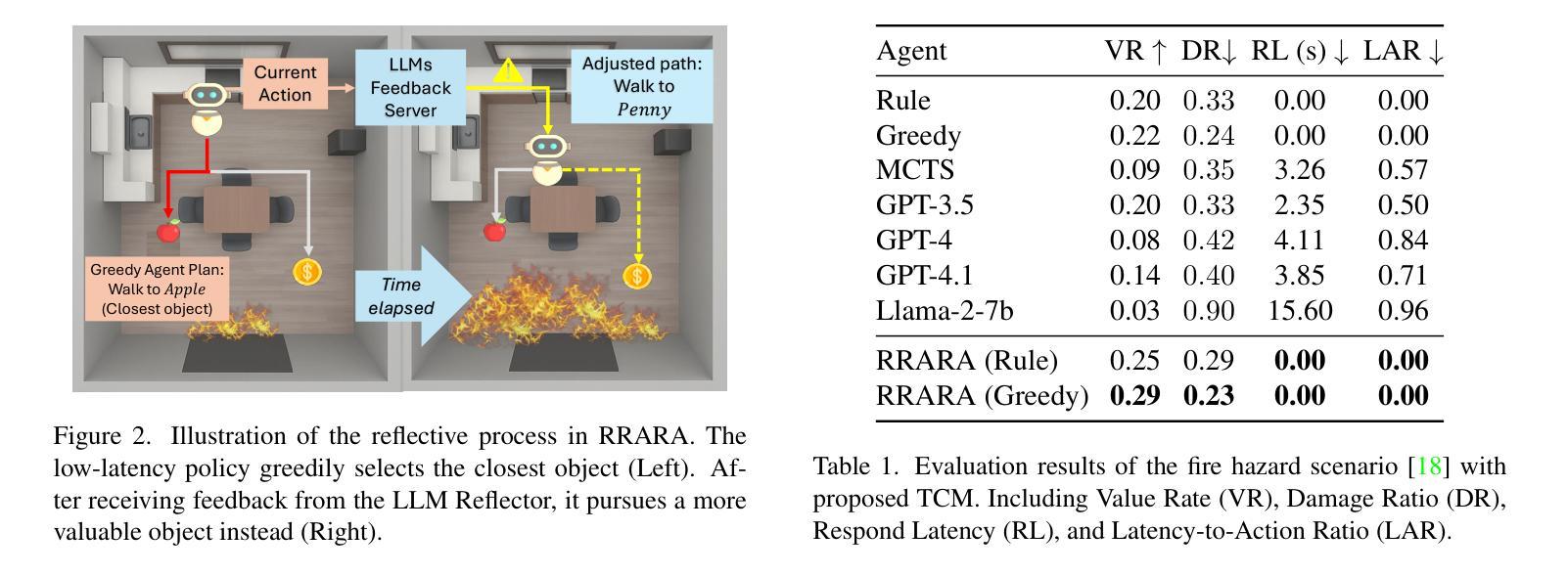
LLM-Enhanced Rapid-Reflex Async-Reflect Embodied Agent for Real-Time Decision-Making in Dynamically Changing Environments
Authors:Yangqing Zheng, Shunqi Mao, Dingxin Zhang, Weidong Cai
In the realm of embodied intelligence, the evolution of large language models (LLMs) has markedly enhanced agent decision making. Consequently, researchers have begun exploring agent performance in dynamically changing high-risk scenarios, i.e., fire, flood, and wind scenarios in the HAZARD benchmark. Under these extreme conditions, the delay in decision making emerges as a crucial yet insufficiently studied issue. We propose a Time Conversion Mechanism (TCM) that translates inference delays in decision-making into equivalent simulation frames, thus aligning cognitive and physical costs under a single FPS-based metric. By extending HAZARD with Respond Latency (RL) and Latency-to-Action Ratio (LAR), we deliver a fully latency-aware evaluation protocol. Moreover, we present the Rapid-Reflex Async-Reflect Agent (RRARA), which couples a lightweight LLM-guided feedback module with a rule-based agent to enable immediate reactive behaviors and asynchronous reflective refinements in situ. Experiments on HAZARD show that RRARA substantially outperforms existing baselines in latency-sensitive scenarios.
在具身智能领域,大型语言模型(LLM)的演变显著增强了代理决策制定。因此,研究人员开始探索代理在动态变化的高风险场景中的性能,例如在HAZARD基准测试中的火灾、洪水和风力场景。在这些极端条件下,决策制定的延迟成为一个至关重要但尚未得到充分研究的问题。我们提出了一种时间转换机制(TCM),该机制将决策推理延迟转化为等效的模拟帧,从而在一个基于FPS的指标下对齐认知和身体成本。通过扩展HAZARD的响应延迟(RL)和延迟到动作比率(LAR),我们提供了一个完全延迟感知的评估协议。此外,我们推出了快速反应异步反射代理(RRARA),它将轻量级LLM指导的反馈模块与基于规则的代理相结合,以实现在现场的即时反应行为和异步反射改进。在HAZARD上的实验表明,RRARA在延迟敏感场景中的表现显著优于现有基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the CVPR 2025 Embodied AI Workshop
Summary
在实体智能领域,大型语言模型(LLMs)的演进显著提升了代理决策制定能力。研究者开始在动态变化的高风险场景中探索代理性能,例如在HAZARD基准测试中的火灾、洪水和风力场景。在极端条件下,决策制定的延迟成为一个至关重要但尚未充分研究的问题。本文提出时间转换机制(TCM),将决策推理延迟转化为等效模拟帧,从而在一个基于FPS的单一指标下对齐认知和物理成本。通过为HAZARD增加响应延迟(RL)和延迟行动比率(LAR),我们提供了一个完全延迟感知的评价协议。此外,本文介绍了快速反应异步反思代理(RRARA),该代理结合轻量级LLM指导的反馈模块和基于规则的代理,可实现即时反应行为和异步反思改进。在HAZARD上的实验表明,RRARA在延迟敏感场景上显著优于现有基线。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在代理决策制定中的演进,增强了代理在复杂场景中的决策能力。
- 在动态变化的高风险场景中,如火灾、洪水和风力等极端条件下,决策制定的延迟成为关键挑战。
- 提出时间转换机制(TCM),将推理延迟转化为等效模拟帧,统一认知和物理成本度量。
- 扩展了HAZARD基准测试,增加响应延迟(RL)和延迟行动比率(LAR),以支持延迟感知的评价。
- 介绍了快速反应异步反思代理(RRARA),融合了LLM反馈模块和基于规则的代理,以支持即时反应和异步反思。
- 实验显示,RRARA在延迟敏感场景上的性能显著优于现有基线。
点此查看论文截图