⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-11 更新
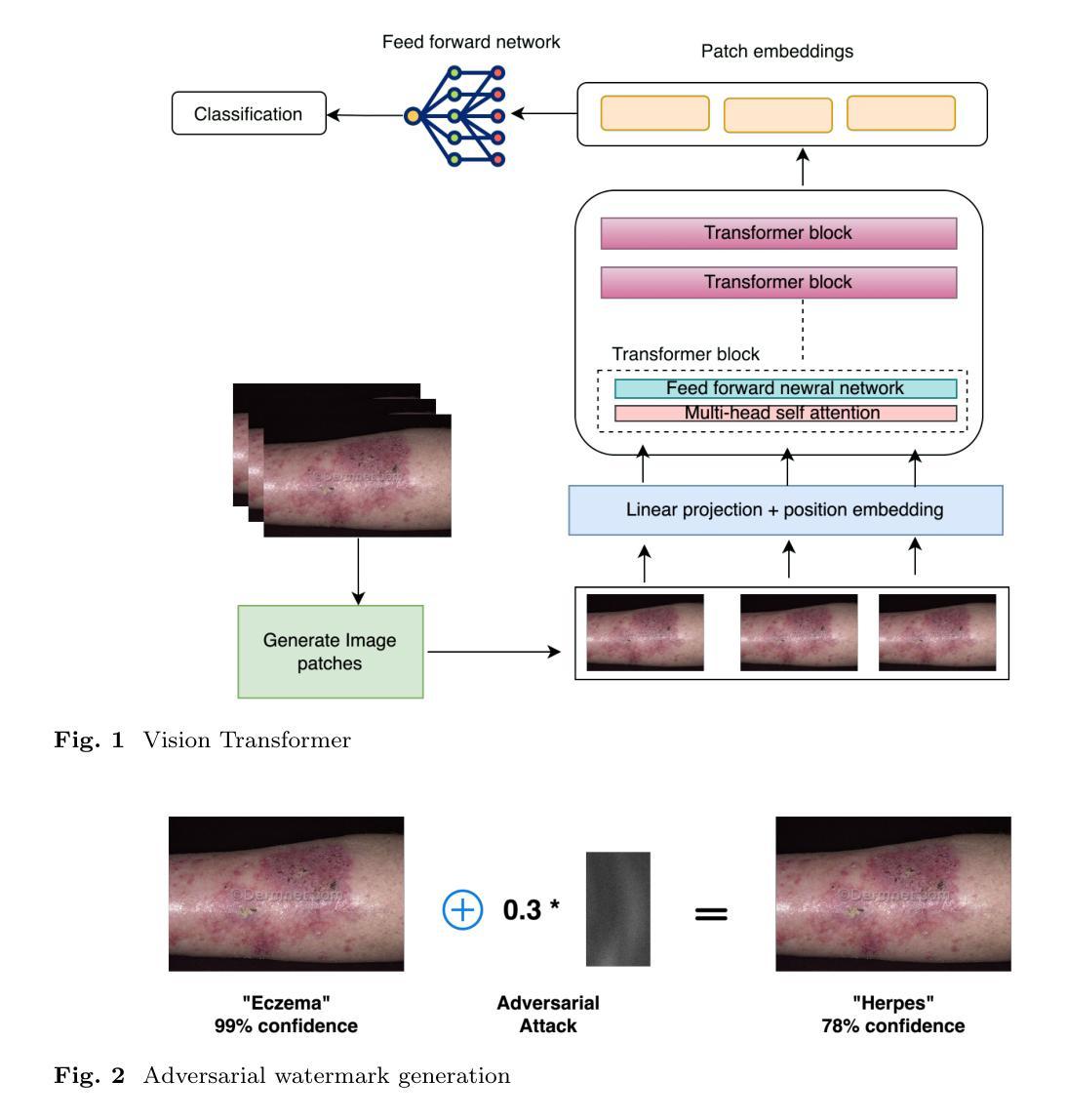
Exploring Adversarial Watermarking in Transformer-Based Models: Transferability and Robustness Against Defense Mechanism for Medical Images
Authors:Rifat Sadik, Tanvir Rahman, Arpan Bhattacharjee, Bikash Chandra Halder, Ismail Hossain
Deep learning models have shown remarkable success in dermatological image analysis, offering potential for automated skin disease diagnosis. Previously, convolutional neural network(CNN) based architectures have achieved immense popularity and success in computer vision (CV) based task like skin image recognition, generation and video analysis. But with the emergence of transformer based models, CV tasks are now are nowadays carrying out using these models. Vision Transformers (ViTs) is such a transformer-based models that have shown success in computer vision. It uses self-attention mechanisms to achieve state-of-the-art performance across various tasks. However, their reliance on global attention mechanisms makes them susceptible to adversarial perturbations. This paper aims to investigate the susceptibility of ViTs for medical images to adversarial watermarking-a method that adds so-called imperceptible perturbations in order to fool models. By generating adversarial watermarks through Projected Gradient Descent (PGD), we examine the transferability of such attacks to CNNs and analyze the performance defense mechanism – adversarial training. Results indicate that while performance is not compromised for clean images, ViTs certainly become much more vulnerable to adversarial attacks: an accuracy drop of as low as 27.6%. Nevertheless, adversarial training raises it up to 90.0%.
深度学习模型在皮肤科图像分析方面取得了显著的成果,为自动化皮肤疾病诊断提供了潜力。以前,基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的架构在皮肤图像识别、生成和视频分析等计算机视觉(CV)任务中非常受欢迎并大获成功。但随着基于Transformer的模型的兴起,CV任务现在更多地使用这些模型来完成。Vision Transformers(ViTs)就是这样一种基于Transformer的模型,在计算机视觉领域取得了成功。它使用自注意力机制在各种任务上实现最先进的性能。然而,它们对全局注意力机制的依赖使得它们容易受到对抗性扰动的攻击。本文旨在研究ViTs对医疗图像对抗水印的敏感性——一种添加所谓的不易察觉扰动以欺骗模型的方法。通过投影梯度下降法(PGD)生成对抗水印,我们研究了这种攻击对CNN的迁移性,并分析了防御机制——对抗训练的性能。结果表明,虽然对于干净图像的性能没有受到影响,但ViTs确实更容易受到对抗性攻击:准确率下降高达27.6%。然而,对抗训练将其提高到了90.0%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习模型在皮肤科图像分析方面取得了显著的成功,为自动皮肤疾病诊断提供了潜力。随着基于Transformer的模型的兴起,计算机视觉任务现在更多地使用这类模型来完成。Vision Transformers(ViTs)是一种基于Transformer的模型,已经在计算机视觉领域取得了成功。然而,它们依赖全局注意力机制使其容易受到对抗性扰动的攻击。本文旨在研究医学图像中的ViTs对抗性水印的易感性,这是一种添加所谓的不易察觉扰动以欺骗模型的方法。通过投影梯度下降法生成对抗性水印,我们研究了此类攻击对卷积神经网络(CNN)的迁移性,并分析了防御机制——对抗性训练的性能。研究结果表明,虽然干净图像的性能没有受到影响,但ViTs确实更容易受到对抗性攻击,准确率下降了高达27.6%。然而,对抗性训练可将准确率提高至90.0%。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习模型在皮肤科图像分析中具有潜力,可用于自动皮肤疾病诊断。
- Vision Transformers(ViTs)是计算机视觉任务中新兴的基于Transformer的模型。
- ViTs依赖于全局注意力机制,使其容易受到对抗性水印等方法的攻击。
- 对抗性水印是一种添加不易察觉的扰动以欺骗模型的技术。
- 通过投影梯度下降法生成对抗性水印,攻击对卷积神经网络(CNN)具有迁移性。
点此查看论文截图

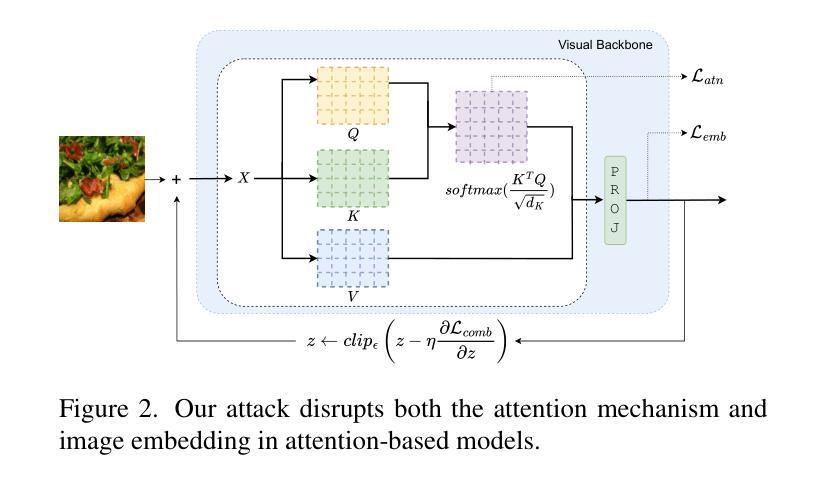
Attacking Attention of Foundation Models Disrupts Downstream Tasks
Authors:Hondamunige Prasanna Silva, Federico Becattini, Lorenzo Seidenari
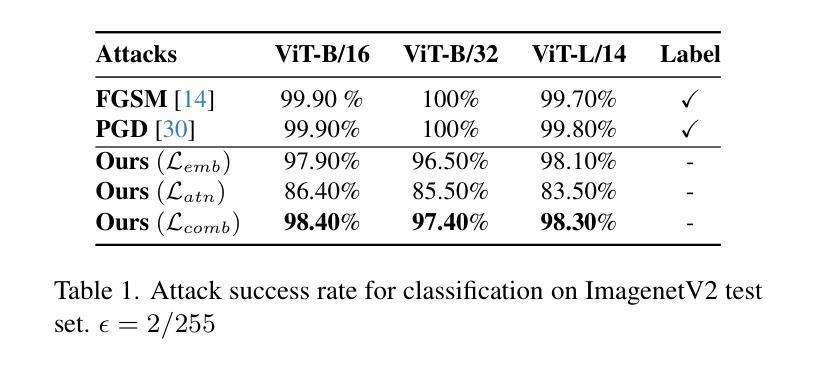
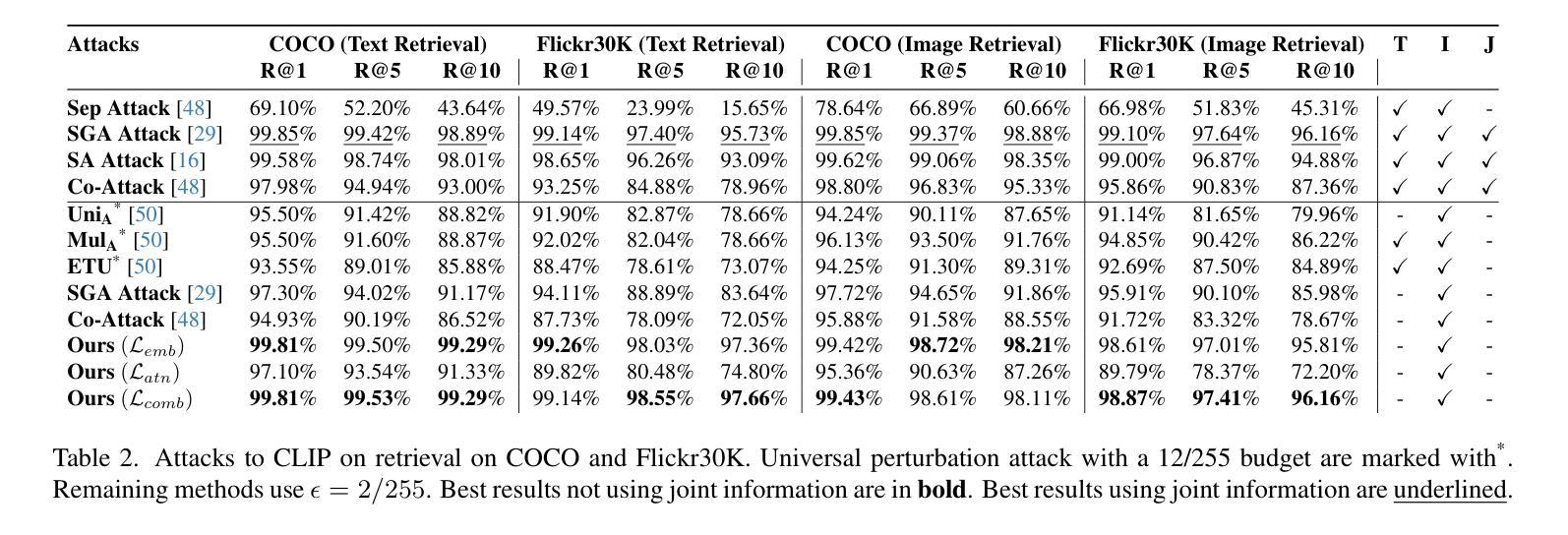
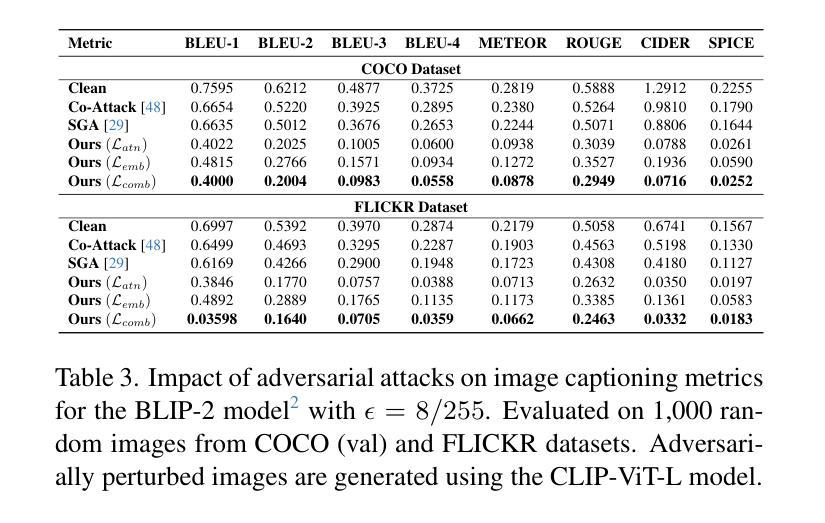
Foundation models represent the most prominent and recent paradigm shift in artificial intelligence. Foundation models are large models, trained on broad data that deliver high accuracy in many downstream tasks, often without fine-tuning. For this reason, models such as CLIP , DINO or Vision Transfomers (ViT), are becoming the bedrock of many industrial AI-powered applications. However, the reliance on pre-trained foundation models also introduces significant security concerns, as these models are vulnerable to adversarial attacks. Such attacks involve deliberately crafted inputs designed to deceive AI systems, jeopardizing their reliability. This paper studies the vulnerabilities of vision foundation models, focusing specifically on CLIP and ViTs, and explores the transferability of adversarial attacks to downstream tasks. We introduce a novel attack, targeting the structure of transformer-based architectures in a task-agnostic fashion. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our attack on several downstream tasks: classification, captioning, image/text retrieval, segmentation and depth estimation. Code available at:https://github.com/HondamunigePrasannaSilva/attack-attention
基础模型代表了人工智能领域中最突出和最新的范式转变。基础模型是在广泛数据上训练的规模较大的模型,在许多下游任务中都能提供高精度,而且通常不需要微调。因此,CLIP、DINO或视觉转换器(ViT)等模型正成为许多工业级人工智能应用程序的基础。然而,对预训练基础模型的依赖也引发了重大的安全隐患,因为这些模型容易受到对抗性攻击的威胁。这类攻击涉及故意设计的输入,旨在欺骗人工智能系统,危害其可靠性。本文研究了视觉基础模型的漏洞,重点关注CLIP和ViT,并探讨了对抗性攻击对下游任务的迁移性。我们针对基于变压器架构的结构设计了一种新型攻击,该攻击具有任务无关性。我们在多个下游任务上展示了攻击的有效性:分类、描述、图像/文本检索、分割和深度估计。相关代码可在https://github.com/HondamunigePrasannaSilva/attack-attention中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper published at CVPR 2025 Workshop Advml
Summary:
人工智能领域的基石模型代表着最新的范式转变。它们是通过大量的数据进行训练的通用模型,可在许多下游任务中实现高准确性,无需微调。因此,CLIP、DINO或Vision Transfomers(ViT)等模型已成为许多人工智能驱动应用的基石。但依赖预训练的基石模型也带来了重大的安全隐患,因为这些模型容易受到对抗性攻击的影响。对抗性攻击涉及故意设计的输入,旨在欺骗人工智能系统,对其可靠性构成威胁。本文研究了视觉基石模型的脆弱性,重点关注CLIP和ViTs模型,并探讨了对抗性攻击对下游任务的迁移性。我们提出了一种针对基于Transformer架构结构的新型攻击方法,该方法以任务无关的方式进行攻击。我们在多个下游任务上证明了攻击的有效性,包括分类、描述生成、图像/文本检索、分割和深度估算等。攻击的具体代码可以在链接处找到:[具体链接地址](请替换为真实的链接地址)。
Key Takeaways:
- 人工智能领域中的基石模型(如CLIP和Vision Transfomers)代表最新的技术转变,能够完成多种任务而无需微调。
- 这些模型易受对抗性攻击的影响,攻击者可以故意设计输入来欺骗AI系统。
- 本文专注于研究视觉基石模型(特别是CLIP和ViTs)的脆弱性。
- 提出了一种新型攻击方法,该方法针对基于Transformer架构的结构设计,具有任务无关的特性。
- 该攻击在多个下游任务上被证明有效,包括分类、描述生成、图像/文本检索等。
- 代码已公开供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图