⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-13 更新
Single Cu Atom Sites on Co3O4 Activate Interfacial Oxygen for Enhanced Reactivity and Selective Gas Sensing at Low Temperature
Authors:Hamin Shin, Matteo D’Andria, Jaehyun Ko, Dong-Ha Kim, Frank Krumeich, Andreas T. Guentner
Controlling the redox landscape of transition metal oxides is central to advancing their reactivity for heterogeneous catalysis or high-performance gas sensing. Here we report single Cu atom sites (1.42 wt%) anchored on Co3O4 nanoparticles (Cu1-Co3O4) that dramatically enhance reactivity and molecular sensing properties of the support at low temperature. The Cu1 are identified by X-ray adsorption near edge structure and feature strong metal-support interaction between Cu2+ and Co3O4, as revealed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The ability of Cu1 to form interfacial Cu-O-Co linkages strongly reduces the temperature of lattice oxygen activation compared to CuO nanoparticles on Co3O4 (CuONP-Co3O4), as demonstrated by temperature-programmed reduction and desorption analyses. To demonstrate immediate practical impact, we deploy such Cu1-Co3O4 nanoparticles as chemoresistive sensor for formaldehyde vapor that yields more than an order of magnitude higher response than CuONP-Co3O4 and consistently outperforms state-of-the-art sensors. That way, formaldehyde is detected down to 5 parts-per-billion at 50% relative humidity and 75 {\deg}C with excellent selectivity over various critical interferents. These results establish a mechanistic platform for activating redox-active supports using single-atom isolates of non-noble nature that yield drastically enhanced and well-defined reactivity to promote low-temperature oxidation reactions and selective analyte sensing.
控制过渡金属氧化物的氧化还原景观对于促进其在异相催化或高性能气体检测中的反应性至关重要。这里我们报道了锚定在Co3O4纳米颗粒上的单个Cu原子位点(1.42 wt%)(Cu1-Co3O4),它们在低温下极大地增强了载体的反应性和分子传感性能。Cu1通过X射线吸收近边结构进行识别,并且如X射线光电子光谱所示,Cu2+与Co3O4之间存在强烈的金属载体相互作用。Cu1形成界面Cu-O-Co链接的能力大大降低了晶格氧激活的温度,与锚定在Co3O4上的CuO纳米颗粒(CuONP-Co3O4)相比,如程序升温还原和脱附分析所示。为了展示其即时实际应用的影响,我们将这种Cu1-Co3O4纳米颗粒部署为甲醛蒸汽的化学电阻式传感器,其响应比CuONP-Co3O4高出超过一个数量级,并且始终优于当前最先进的传感器。因此,在相对湿度为50%、温度为75摄氏度的条件下,可以检测到低至每十亿份之五的甲醛,对各种关键干扰物具有出色的选择性。这些结果建立了一个机制平台,利用非贵金属性质的单原子隔离物来激活氧化还原活性载体,产生大幅度增强和明确定义的反应性,以促进低温氧化反应和选择性分析物检测。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究报道了以Cu单原子位点(1.42 wt%)锚定在Co3O4纳米粒子上的复合催化剂(Cu1-Co3O4),显著提高了其在低温下的反应性和分子传感性能。通过X射线吸收近边结构和X射线光电子能谱表征,证实了Cu1的存在及其与Co3O4之间的强金属-载体相互作用。Cu1形成界面Cu-O-Co链接的能力降低了晶格氧激活的温度,相较于在Co3O4上的CuO纳米粒子(CuONP-Co3O4),表现出更强的活性。此外,该研究将Cu1-Co3O4纳米粒子作为甲醛蒸汽的化学电阻传感器,其响应比CuONP-Co3O4高出数倍,且在湿度和温度变化的条件下仍表现出卓越的选择性。这一发现为利用非贵金属单原子激活氧化还原活性载体提供了机制平台,可有效促进低温氧化反应和选择性分析物传感。
关键见解
- Cu单原子位点成功锚定在Co3O4纳米粒子上,显著提高了催化性能。
- Cu1与Co3O4之间存在强烈的金属-载体相互作用。
- Cu1形成界面Cu-O-Co链接,降低了晶格氧激活的温度。
- Cu1-Co3O4纳米粒子在低温下的反应性和分子传感性能显著提高。
- 该材料在检测甲醛蒸汽时表现出卓越的性能,响应度高且选择性好。
- 该研究为利用单原子激活氧化还原活性载体提供了机制平台。
点此查看论文截图

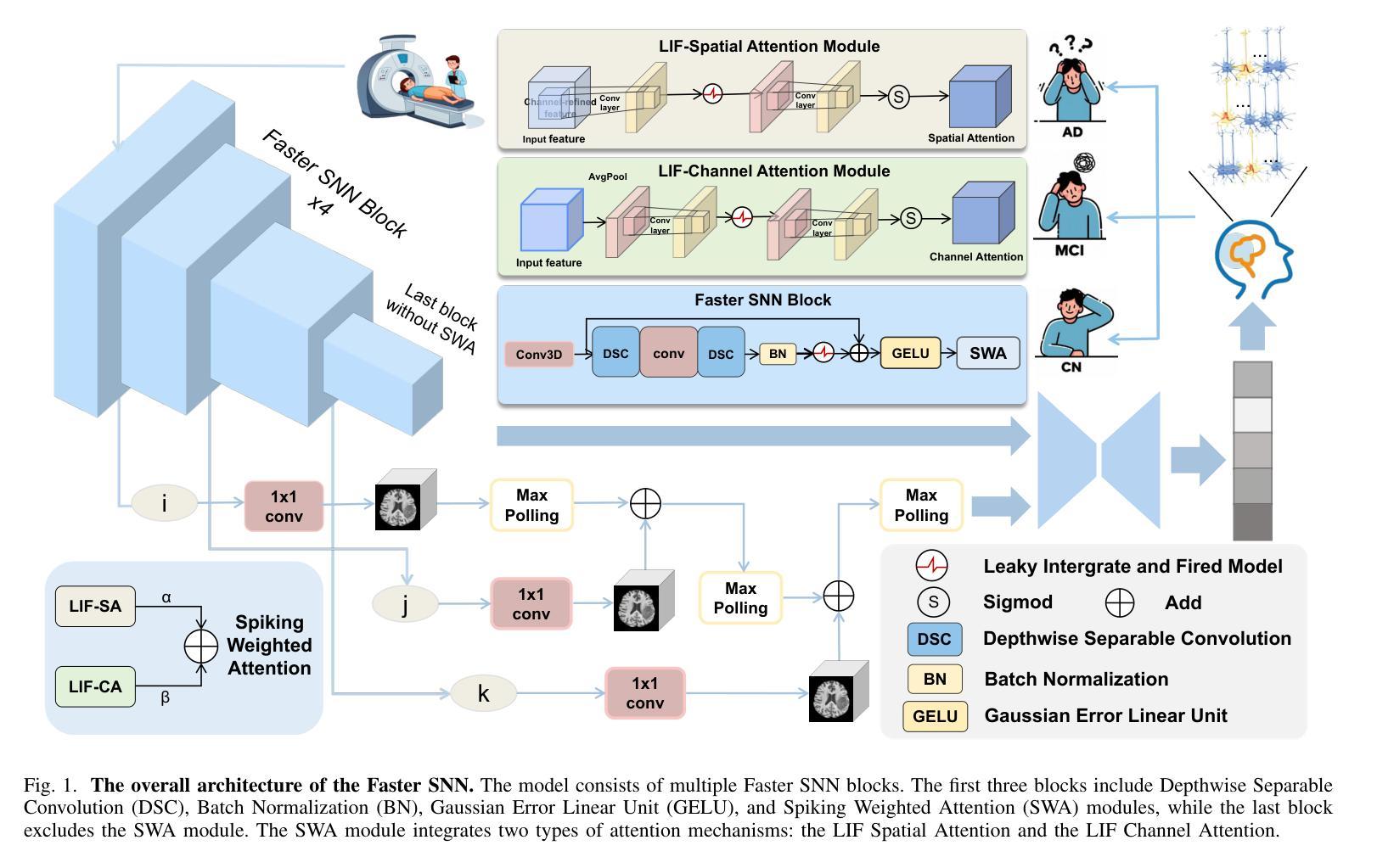
Towards Practical Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis: A Lightweight and Interpretable Spiking Neural Model
Authors:Changwei Wu, Yifei Chen, Yuxin Du, Jinying Zong, Jie Dong, Mingxuan Liu, Yong Peng, Jin Fan, Feiwei Qin, Changmiao Wang
Early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), especially at the mild cognitive impairment (MCI) stage, is vital yet hindered by subjective assessments and the high cost of multimodal imaging modalities. Although deep learning methods offer automated alternatives, their energy inefficiency and computational demands limit real-world deployment, particularly in resource-constrained settings. As a brain-inspired paradigm, spiking neural networks (SNNs) are inherently well-suited for modeling the sparse, event-driven patterns of neural degeneration in AD, offering a promising foundation for interpretable and low-power medical diagnostics. However, existing SNNs often suffer from weak expressiveness and unstable training, which restrict their effectiveness in complex medical tasks. To address these limitations, we propose FasterSNN, a hybrid neural architecture that integrates biologically inspired LIF neurons with region-adaptive convolution and multi-scale spiking attention. This design enables sparse, efficient processing of 3D MRI while preserving diagnostic accuracy. Experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that FasterSNN achieves competitive performance with substantially improved efficiency and stability, supporting its potential for practical AD screening. Our source code is available at https://github.com/wuchangw/FasterSNN.
阿尔茨海默病(AD)的早期诊断,特别是在轻度认知障碍(MCI)阶段,至关重要。然而,主观评估和多种模式的成像模式的高成本都阻碍了诊断的进程。尽管深度学习方法提供了自动化的替代方案,但其能源效率不足和计算需求高限制了其在现实世界中的应用,特别是在资源受限的环境中。作为受大脑启发的模型,脉冲神经网络(SNNs)天生就适合模拟AD中神经变性的稀疏、事件驱动的模式,为可解释和低功耗的医学诊断提供了有前景的基础。然而,现有的SNNs常常存在表达性弱和训练不稳定的问题,限制了其在复杂医学任务中的有效性。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了FasterSNN,这是一种混合神经网络架构,它结合了生物启发的LIF神经元与区域自适应卷积和多尺度脉冲注意力。这种设计能够稀疏、高效地处理3D MRI,同时保留诊断的准确性。在基准数据集上的实验表明,FasterSNN在具有竞争力的性能的同时实现了显著的提高效率和稳定性,支持其实践中用于AD筛查的潜力。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/wuchangw/FasterSNN找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 5 figures
Summary
基于深度学习的局限性,以及大脑受启发的人工神经网络模型在早期诊断阿尔茨海默病中的重要性,本研究提出了一种新型的混合神经网络架构——FasterSNN。该架构结合了生物启发神经元与自适应卷积和多尺度脉冲注意力机制,以实现高效的MRI处理,并维持诊断准确性。其在基准数据集上的表现证明了其在实际应用中筛查阿尔茨海默病的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 阿尔茨海默病的早期诊断至关重要,特别是在轻度认知障碍阶段。当前评估手段受到主观评估和成像技术成本高的限制。
- 虽然深度学习提供了自动化解决方案,但其能源效率和计算需求限制了实际应用,特别是在资源受限的环境中。
- 基于大脑受启发的人工神经网络模型(如脉冲神经网络)对于模拟神经退变的稀疏、事件驱动模式具有优势,有助于解释和节约能源型医学诊断。然而,这些模型有时会出现表达能力弱和训练不稳定的问题。
- FasterSNN是一个新型混合神经网络架构,结合了生物启发神经元和自适应卷积技术,旨在解决上述问题并实现高效的医学图像分析。
- FasterSNN架构实现了对MRI数据的稀疏处理,同时保持了诊断准确性。实验证明其在基准数据集上的表现具有竞争力。此外,该架构还支持潜在的实际应用,如阿尔茨海默病的筛查。
- FasterSNN的主要优势在于其改进的效率、稳定性和诊断准确性。这对于资源受限的环境中的医学诊断尤为重要。
点此查看论文截图

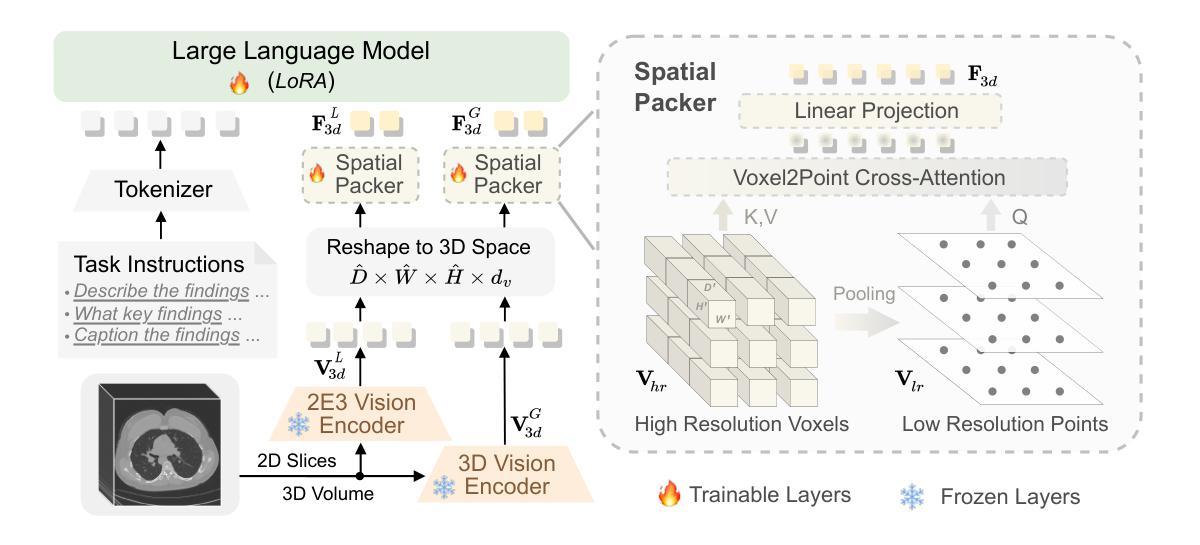
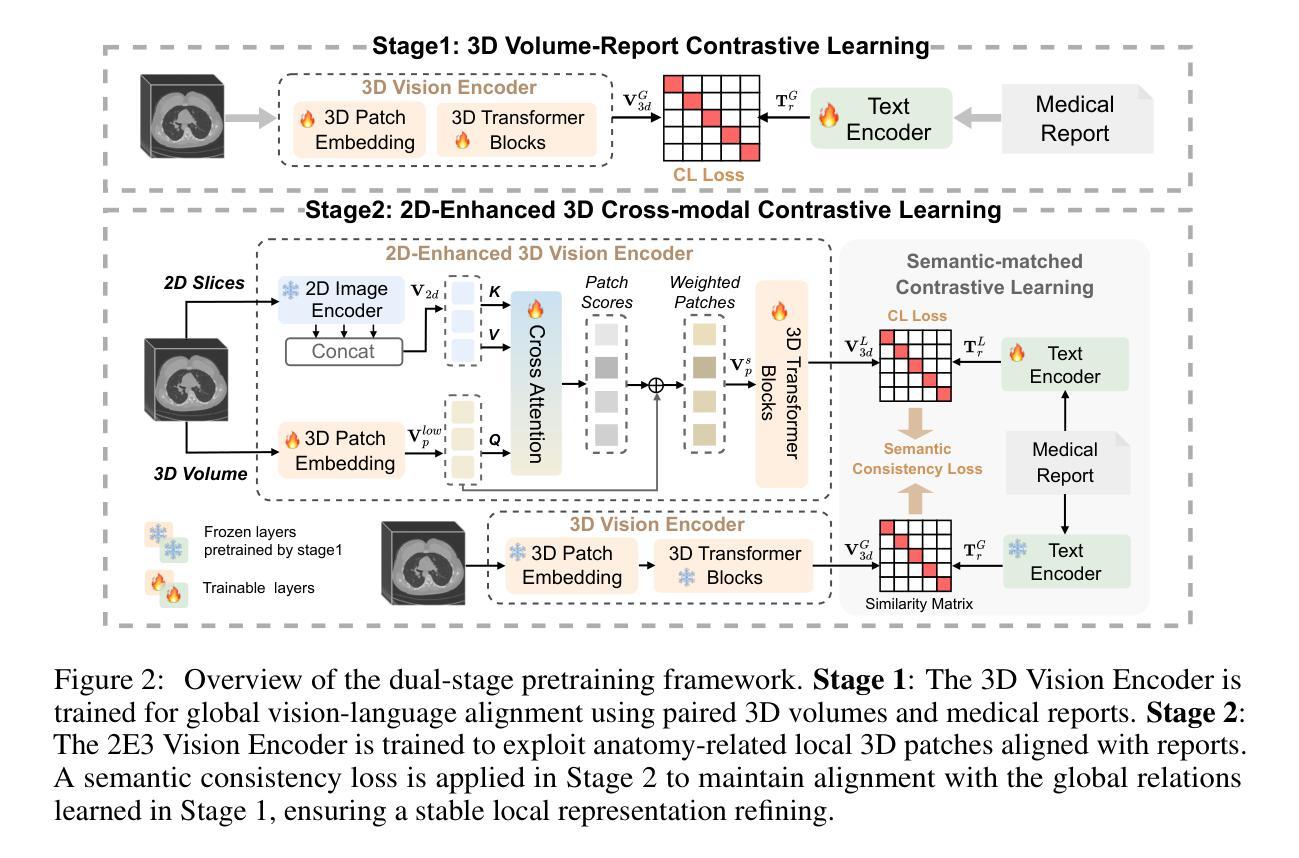
HSENet: Hybrid Spatial Encoding Network for 3D Medical Vision-Language Understanding
Authors:Yanzhao Shi, Xiaodan Zhang, Junzhong Ji, Haoning Jiang, Chengxin Zheng, Yinong Wang, Liangqiong Qu
Automated 3D CT diagnosis empowers clinicians to make timely, evidence-based decisions by enhancing diagnostic accuracy and workflow efficiency. While multimodal large language models (MLLMs) exhibit promising performance in visual-language understanding, existing methods mainly focus on 2D medical images, which fundamentally limits their ability to capture complex 3D anatomical structures. This limitation often leads to misinterpretation of subtle pathologies and causes diagnostic hallucinations. In this paper, we present Hybrid Spatial Encoding Network (HSENet), a framework that exploits enriched 3D medical visual cues by effective visual perception and projection for accurate and robust vision-language understanding. Specifically, HSENet employs dual-3D vision encoders to perceive both global volumetric contexts and fine-grained anatomical details, which are pre-trained by dual-stage alignment with diagnostic reports. Furthermore, we propose Spatial Packer, an efficient multimodal projector that condenses high-resolution 3D spatial regions into a compact set of informative visual tokens via centroid-based compression. By assigning spatial packers with dual-3D vision encoders, HSENet can seamlessly perceive and transfer hybrid visual representations to LLM’s semantic space, facilitating accurate diagnostic text generation. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in 3D language-visual retrieval (39.85% of R@100, +5.96% gain), 3D medical report generation (24.01% of BLEU-4, +8.01% gain), and 3D visual question answering (73.60% of Major Class Accuracy, +1.99% gain), confirming its effectiveness. Our code is available at https://github.com/YanzhaoShi/HSENet.
自动化三维CT诊断通过提高诊断准确性和工作流程效率,使临床医生能够做出及时、基于证据的决策。虽然多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视觉语言理解方面表现出有希望的性能,但现有方法主要集中在二维医学图像上,这从根本上限制了它们捕捉复杂三维解剖结构的能力。这种限制常常导致对细微病理的误解和诊断幻觉。在本文中,我们提出了Hybrid Spatial Encoding Network(HSENet)框架,它通过有效的视觉感知和投影,利用丰富的三维医学视觉线索,实现准确稳健的视听语言理解。具体而言,HSENet采用双三维视觉编码器来感知全局体积上下文和精细的解剖细节,并通过与诊断报告的双重阶段对齐进行预训练。此外,我们提出了Spatial Packer,这是一种高效的多模态投影仪,它可以通过基于质心的压缩将高分辨率的三维空间区域浓缩成一组信息丰富的视觉标记。通过为双三维视觉编码器分配空间打包器,HSENet可以无缝地感知并将混合视觉表示转移到LLM语义空间,促进准确的诊断文本生成。实验结果表明,我们的方法在三维语言视觉检索(R@100达到39.85%,增益+5.96%)、三维医学报告生成(BLEU-4达到24.01%,增益+8.01%)和三维视觉问答(主要类别准确率达到73.60%,增益+1.99%)方面达到了最新技术水平,证实了其有效性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/YanzhaoShi/HSENet获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 9 figures. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2410.14200 by other authors
Summary
自动化三维CT诊断通过提高诊断准确性和工作流程效率,赋能临床医生做出及时、基于证据的决定。现有方法主要关注二维医学图像,在捕捉复杂三维解剖结构方面存在局限性,可能导致对细微病理的误解和诊断幻觉。本文提出Hybrid Spatial Encoding Network (HSENet),通过有效的视觉感知和投影,利用丰富的三维医学视觉线索,实现准确而稳健的视语言理解。HSENet采用双三维视觉编码器,感知全局体积上下文和精细解剖细节,通过预训练的报告阶段进行预训练对齐获得高质量的视感知;另外通过高效的多模态投影器(Spatial Packer)将高分辨率的三维空间区域压缩成一组紧凑的信息视觉符号。HSENet将HSENet感知与语言模型语义空间相结合,实现了诊断文本的准确生成。实验结果显示该方法在三维语言视觉检索、三维医学报告生成和三维视觉问答方面取得了显著成果。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化三维CT诊断能提高诊断准确性和工作流程效率,帮助医生做出及时、基于证据的决定。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在理解视觉语言方面展现出巨大潜力,但在处理复杂的三维医学图像时仍面临挑战。
- 现有方法在捕捉三维解剖结构方面存在局限性,可能导致对细微病理的误解和诊断幻觉。
- Hybrid Spatial Encoding Network (HSENet)能充分利用丰富的三维医学视觉线索,实现准确而稳健的视语言理解。
- HSENet结合了视觉编码器的优势和空间打包器技术,使得复杂的三维信息能够被高效处理并转化为语言模型可以理解的信息。
- 实验结果显示HSENet在多个任务上取得了显著成果,包括三维语言视觉检索、三维医学报告生成和三维视觉问答等。
点此查看论文截图

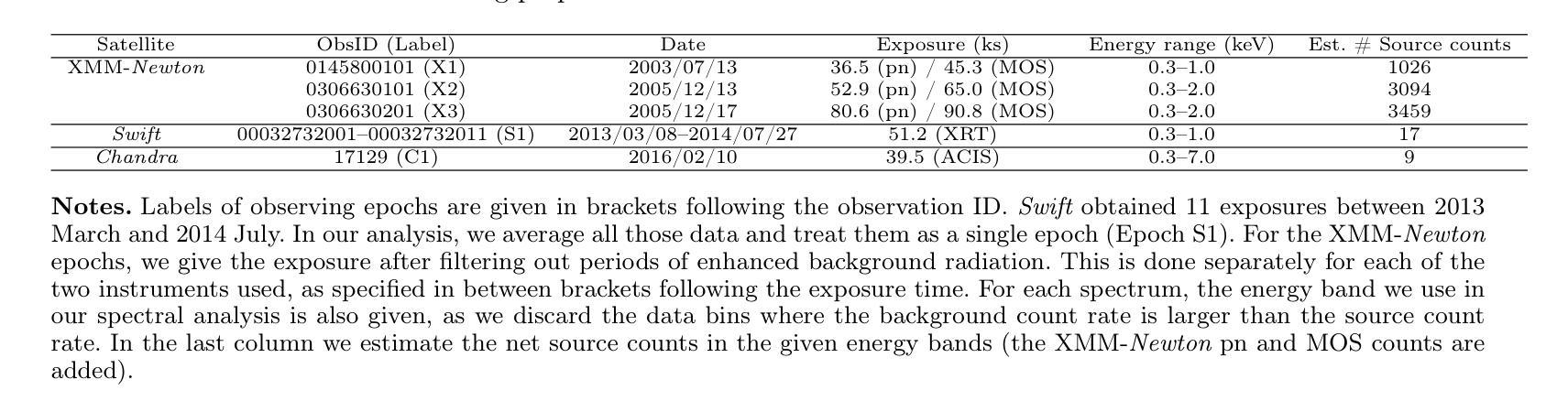
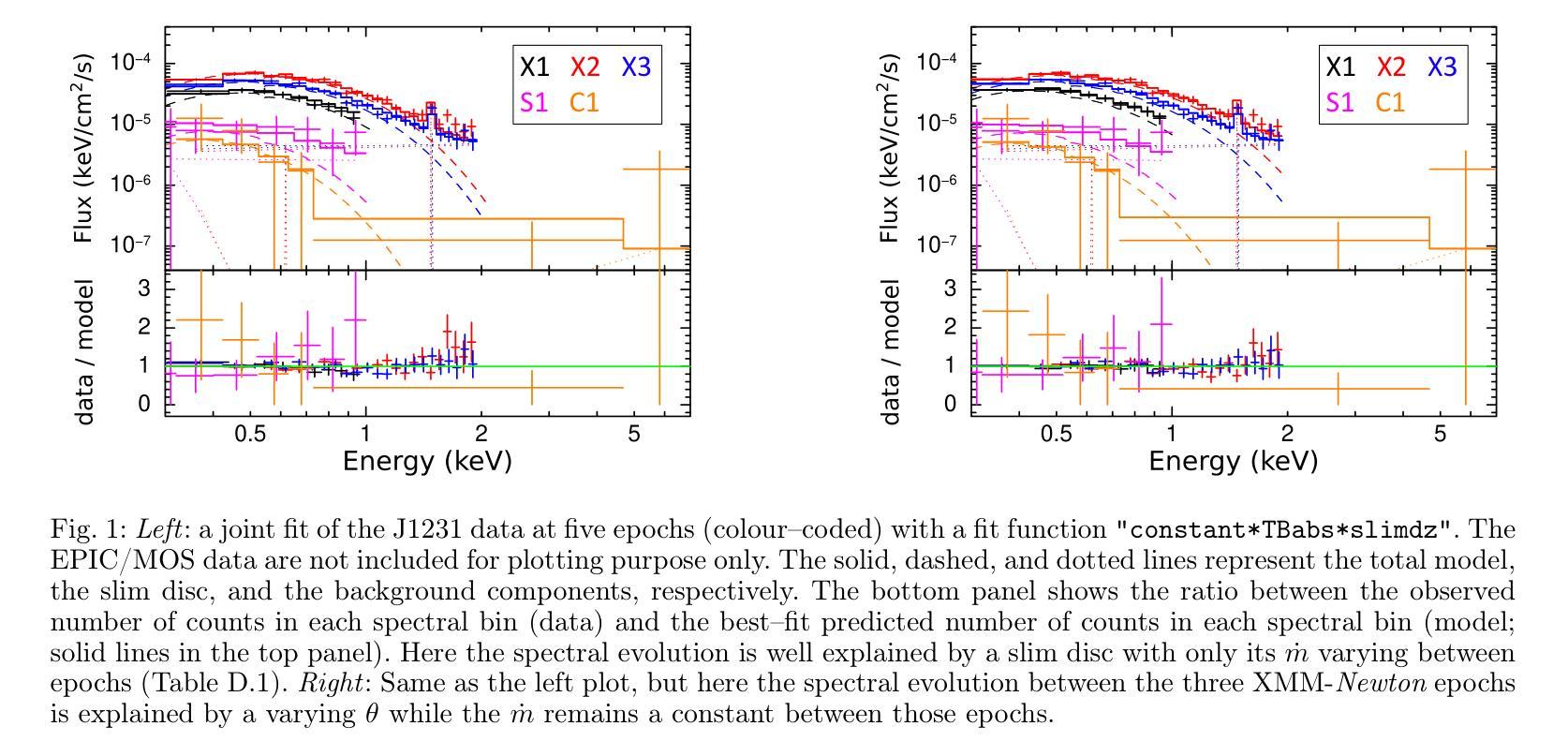
The intermediate-mass black hole 2XMM J123103.2+110648: a varying disc accretion rate during possible X-ray quasi-periodic eruptions?
Authors:Z. Cao, P. G. Jonker, S. Wen, N. C. Stone, A. I. Zabludoff
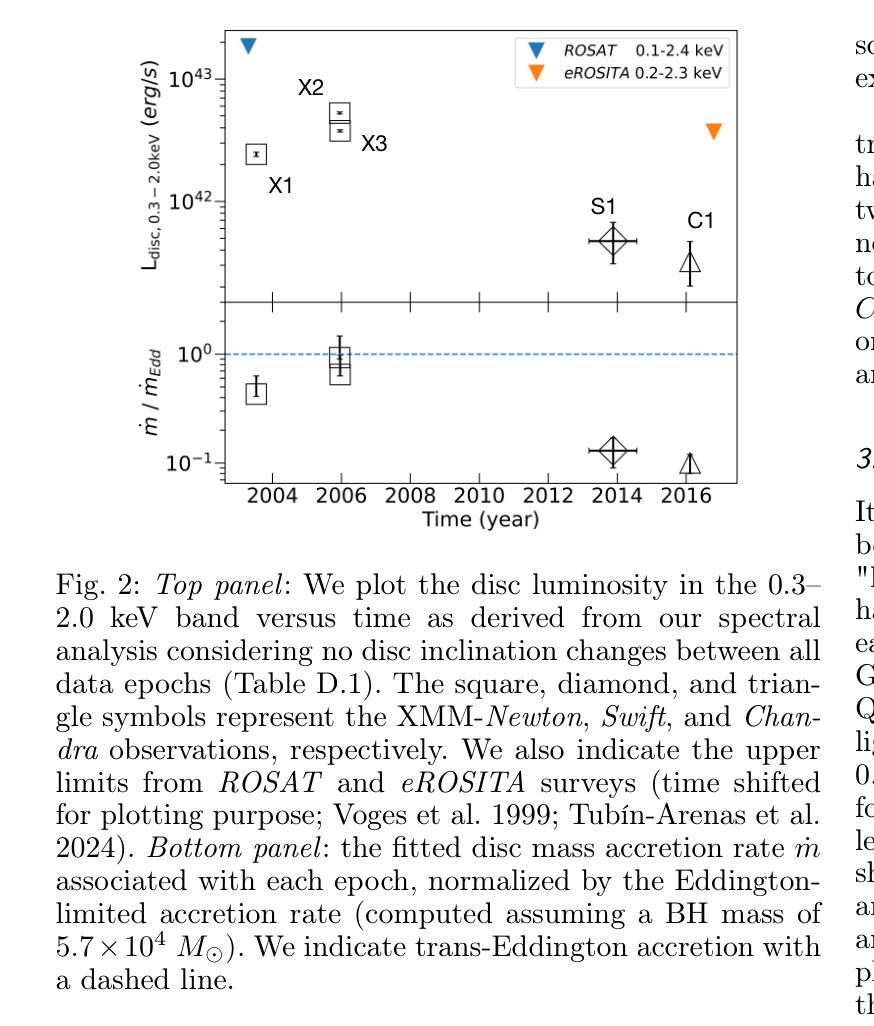
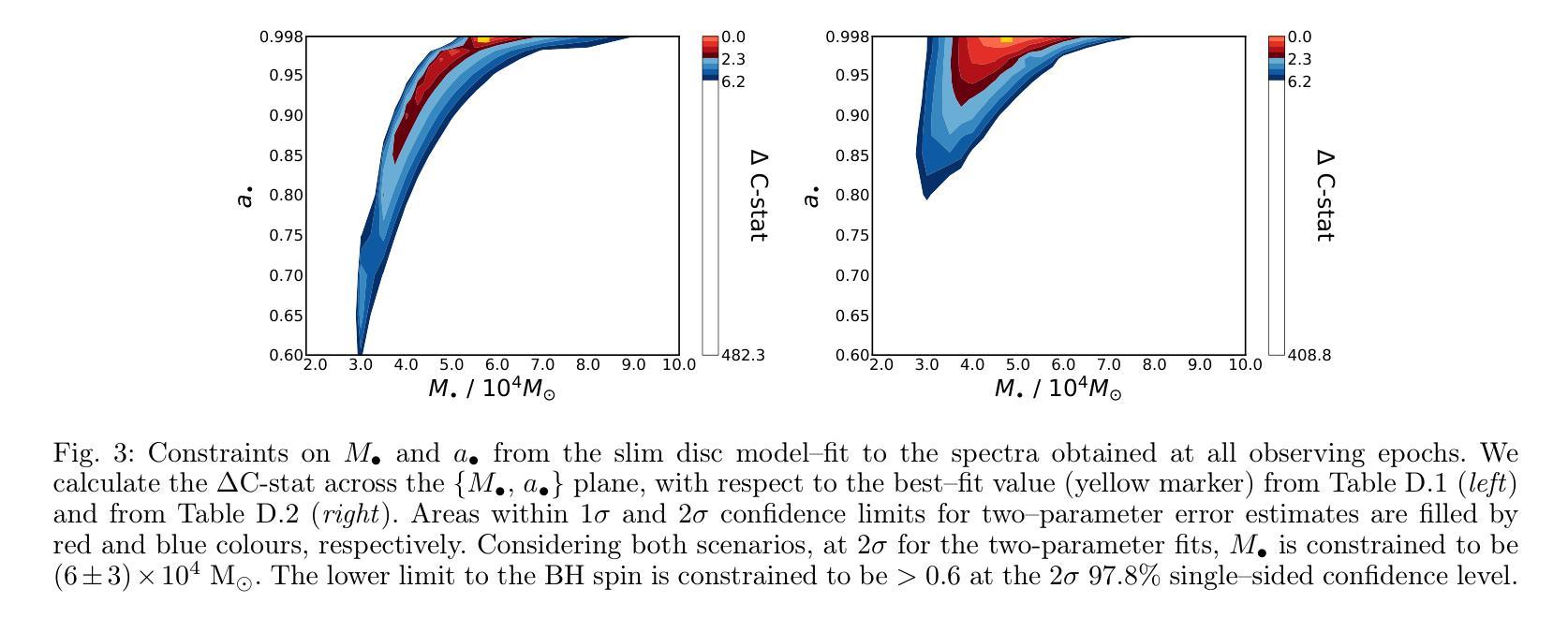
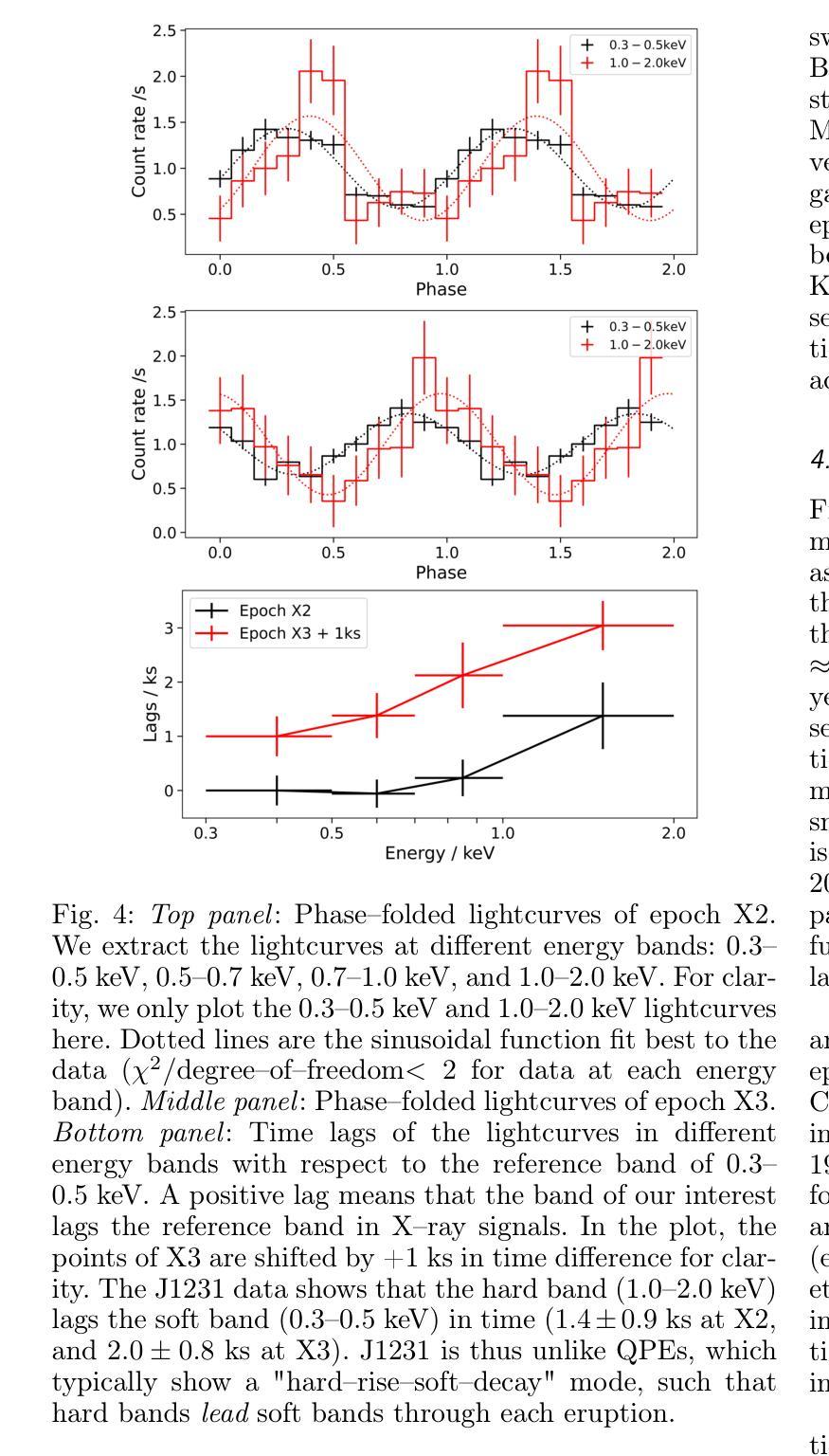
We fit the evolving X-ray spectra of the variable and fading source 2XMM J123103.2+110648 (J1231), which is an intermediate-mass black hole (IMBH) candidate. Recent X-ray timing studies have proposed that J1231’s quasi-periodic oscillation (QPO) observed at the peak of its X-ray lightcurve is a variant of the quasi-periodic eruptions (QPEs) observed in other sources. Here, we fit X-ray spectra from XMM-Newton, Swift, and Chandra using a slim disc model for the black hole’s accretion disc, obtaining a best-fit black hole mass of ($6\pm3)\times10^{4}$ $M_\odot$ and spin of $>0.6$ at 2$\sigma$ confidence. This mass is consistent with past estimates, supporting the IMBH interpretation, and the spin measurement is new. Yet the nature of J1231 remains uncertain: its long-term variability (decade-long continuum evolution) could signal a tidal disruption event or active galactic nuclear variability. We find that the spectral evolution within the first three years after the source’s detection can be well explained by either a varying disc accretion rate $\dot m$ or a varying disc inclination $\theta$. Meanwhile, we find that during the short-term variability (the QPO with a ~3.8hr period), each oscillation does not show the “hard-rise-soft-decay” typical of QPEs. We fit the average spectrum at the QPO lightcurve maxima and the average spectrum at its minima, finding that the spectral difference is well explained by $\dot m$ decreasing from peaks to valleys if $\theta<30^{\circ}$ and constant between all data epochs. This result suggests that the short-term QPO behaviour might also be driven by a varying disc $\dot m$.
我们对可变且衰减源2XMM J123103.2+110648(J1231)的演化X射线光谱进行了拟合,这是一个中等质量黑洞(IMBH)的候选源。最近的X射线时间研究提出,J1231在X射线光峰观察到的准周期振荡(QPO)是与其他源观察到的准周期爆发(QPEs)的一种变体。在这里,我们使用黑洞吸积盘的薄盘模型对XMM-牛顿、Swift和钱德拉望远镜的X射线光谱进行了拟合,得到最佳拟合黑洞质量为($6\pm3)\times10^{4}$ $M_\odot$,在$ 2\sigma $置信水平下自转速度大于$ 0.6 $。这一质量与之前的估计一致,支持IMBH解释,并且自转速度测量是新的。然而,J1231的本质仍然不确定:其长期变化(十年连续谱演化)可能表明潮汐撕裂事件或活动星系核的变异性。我们发现,在源检测后的前三年内,光谱演化可以用变化的盘吸积率$\dot m$或变化的盘倾角$\theta$很好地解释。同时,我们发现短期变化(周期为~3.8小时的QPO)期间,每次振荡并不显示出典型的“硬升软衰”QPEs特征。我们对QPO光曲线最大值和最小值时的平均光谱进行了拟合,发现如果$\theta<30^{\circ}$,光谱差异可以通过$\dot m$从峰值到谷值的减少来很好地解释,并且在所有数据时期之间保持不变。这一结果暗示短期QPO行为也可能由变化的盘$\dot m$驱动。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 6 figures, 8 tables, with Appendix. Accepted for publication in A&A
Summary
本文对中间质量黑洞候选体2XMM J123103.2+110648(J1231)的X射线光谱进行了拟合研究。通过对XMM-Newton、Swift和Chandra的X射线光谱进行拟合,使用黑洞吸积盘的瘦盘模型,得到了最佳拟合黑洞质量约为(6±3)×10^4 M_odot,自旋速度大于0.6,在2σ置信水平下。长期变化可能暗示潮汐撕裂事件或活动星系核变化。短期变化则显示出谱变化与盘吸积率变化相关。
Key Takeaways
- J1231的X射线光谱拟合揭示了其为准周期性振荡(QPO)现象,与其他源的准周期性爆发(QPEs)类似。
- 通过使用瘦盘模型拟合,得到黑洞质量估计为($6\pm3)\times10^{4}$ $M_\odot$,自旋速度大于0.6,与过去估计相符,支持中间质量黑洞(IMBH)的解释。
- J1231的长期变化可能是潮汐撕裂事件或活动星系核变化的迹象。
- 短期变化显示谱变化与盘的吸积率变化有关。
- 在QPO的短周期(约3.8小时)内,每个振荡并不显示出典型的“硬升软衰”特征。
- 平均光谱在QPO光曲线峰值和谷值的差异可以通过吸积率从峰值到谷值的变化来解释,如果盘的倾角θ小于30°。
点此查看论文截图

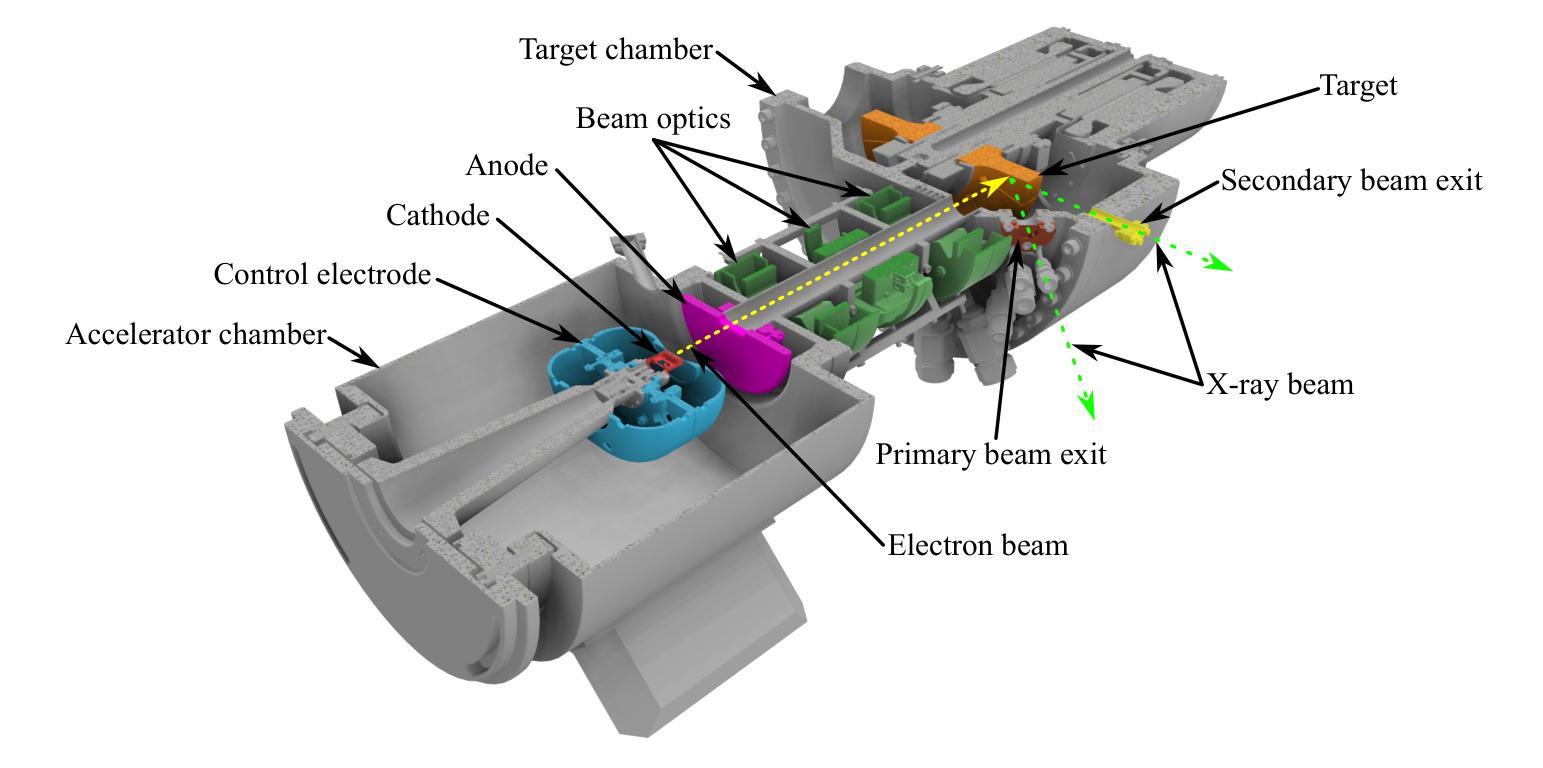
Commissioning, characterization and first high dose rate irradiations at a compact X-ray tube for microbeam and minibeam radiation therapy
Authors:Christian Petrich, Johanna Winter, Anton Dimroth, Thomas Beiser, Monika Dehn, Jessica Stolz, Jacopo Frignani, Stephanie E. Combs, Franz Schilling, Ghaleb Natour, Kurt Aulenbacher, Thomas E. Schmid, Jan J. Wilkens, Stefan Bartzsch
Minibeam and microbeam radiation therapy promise improved treatment outcomes through reduced normal tissue toxicity at better tumor control rates. The lack of suitable compact radiation sources limits the clinical application of minibeams to superficial tumors and renders it impossible for microbeams. We developed and constructed the first prototype of a compact line-focus X-ray tube (LFXT) with technology potentially suitable for clinical translation of minibeams and microbeams. We give an overview of the commissioning process preceding the first operation, present optical and radiological focal spot characterization methods, and dosimetric measurements. Additionally, we report on first preclinical in vitro cell and in vivo mouse brain irradiations conducted with the LFXT prototype. The focal spot characterization resulted in a strongly eccentric electron distribution with a width of 72.3 $\mu$m. Dosimetry showed sharp microbeam dose profiles with steep lateral penumbras and a peak-to-valley dose ratio above 10 throughout a 70 mm thick PMMA phantom. An open-field dose rate of 4.3 Gy/s was measured at an acceleration voltage of 150 kV and a beam current of 17.4 mA at 150 mm distance from the focal spot. In vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrated the feasibility of the LFXT for minibeam and microbeam applications with field sizes of 1.5-2 cm. The mice displayed no observable side effects throughout the follow-up period after whole-brain 260 $\mu$m-minibeam irradiation. We successfully constructed and commissioned the first proof-of-concept LFXT prototype. Dosimetric characterizations of the achieved microbeam field showed the superiority of the LFXT compared to conventional X-ray tubes in terms of beam quality. In future developments, the remaining limitations of the prototype will be addressed for improved minibeam and first ever microbeam radiation therapy in a clinical setting.
微型束及微束放射治疗通过减少正常组织的毒性并提高肿瘤控制率,有望改善治疗效果。由于缺乏合适的紧凑型辐射源,微型束的临床应用仅限于浅表肿瘤,而微型束则无法实现。我们开发并构建了第一台紧凑型线聚焦X射线管(LFXT)的原型,这项技术具有潜在的临床应用价值,可用于微型束和微束的临床转化。本文概述了设备调试过程,介绍了光学和放射学焦点特征化方法以及剂量学测量。此外,我们还报告了使用LFXT原型进行的第一批体外细胞和小鼠脑部的体内外预临床研究结果。焦点特征化结果显示电子分布强烈偏心,宽度为72.3微米。剂量学显示微束剂量分布清晰,侧向笔迹陡峭,在70毫米厚的PMMA幻影中峰谷剂量比超过10。在加速电压为150千伏、离焦点距离150毫米处,束流为17.4毫安的情况下,开放场剂量率测量值为每秒4.3戈瑞。体内外实验证明了LFXT在小型束和微束应用中的可行性,场面积为1.5-2厘米。在为期观察期间对全脑进行了经鼻光焦耳每微束放射后的26只小鼠并未显示出明显的副作用。我们成功构建了首个概念的LFXT原型并进行调试。微束场的剂量学特征表明,与传统的X射线管相比,LFXT在光束质量方面具有优势。在未来的发展中,我们将解决原型的剩余局限性,以改进临床环境中的微型束放射治疗和首次微束放射治疗。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CP, JW, and AD share first authorship
Summary
基于微型束和微束放射治疗的理论优势,例如减少正常组织毒性和提高肿瘤控制率,我们研发了首个紧凑型线聚焦X射线管(LFXT)原型,用于临床转化的微型束和微束。本文介绍了设备启用前的调试流程、光学和放射学焦点特征方法以及剂量测定。此外,还报告了使用LFXT原型进行的第一批体外细胞和小鼠脑部的照射实验。焦点特征为偏心电子分布,宽度为72.3微米。剂量学显示出尖锐的微束剂量分布曲线,侧峰之间剂量比超过10,穿透7厘米厚的PMMA幻影。在距离焦点15厘米处以加速电压为伏特和电流为毫安时,开放场剂量率为每秒增加灰度单位。实验显示,该设备用于微型束和微束应用具有可行性,场尺寸在厘米左右。在跟踪期间内小鼠未观察到全身不良反应。已成功构建并测试了首例LFXT概念原型机。与常规X射线管相比,该设备的剂量学特性表现出光束质量的优越性。未来将对原型机的剩余局限性进行改进,以提高微型束和首次微束放射治疗的临床治疗效果。
Key Takeaways
- 微型束和微束放射治疗具有减少正常组织毒性和提高肿瘤控制率的潜力。
- LFXT原型被开发用于临床转化的微型束和微束治疗。
- LFXT的焦点特征显示出偏心电子分布,宽度为72.3μm。
- LFXT的剂量学表现出尖锐的微束剂量分布曲线和高的剂量率。
- 在体外和体内实验中,LFXT在微型束和微束应用中的可行性得到验证。
- 小鼠在接受微型束照射后未出现明显的副作用。
点此查看论文截图

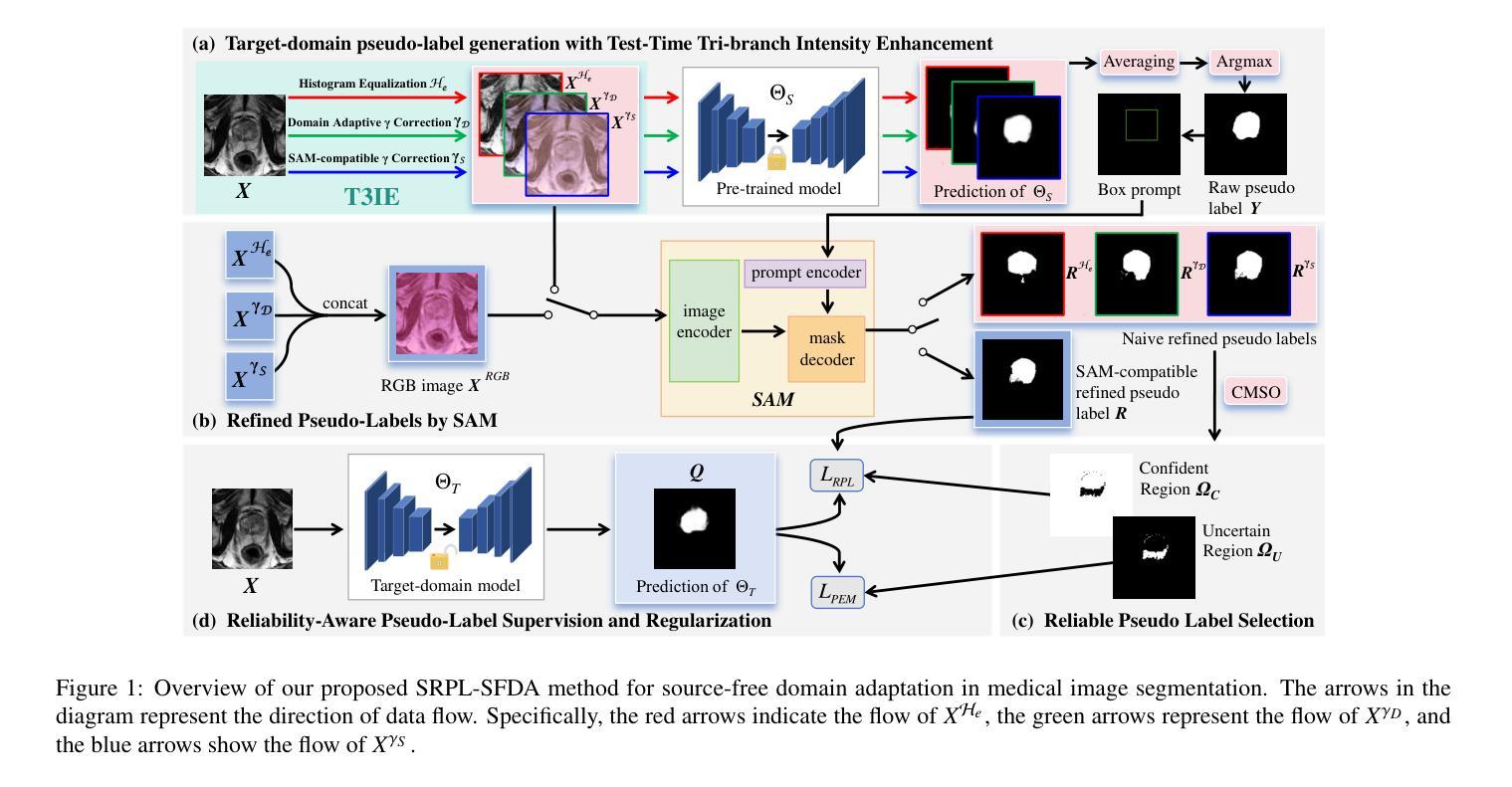
SRPL-SFDA: SAM-Guided Reliable Pseudo-Labels for Source-Free Domain Adaptation in Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Xinya Liu, Jianghao Wu, Tao Lu, Shaoting Zhang, Guotai Wang
Domain Adaptation (DA) is crucial for robust deployment of medical image segmentation models when applied to new clinical centers with significant domain shifts. Source-Free Domain Adaptation (SFDA) is appealing as it can deal with privacy concerns and access constraints on source-domain data during adaptation to target-domain data. However, SFDA faces challenges such as insufficient supervision in the target domain with unlabeled images. In this work, we propose a Segment Anything Model (SAM)-guided Reliable Pseudo-Labels method for SFDA (SRPL-SFDA) with three key components: 1) Test-Time Tri-branch Intensity Enhancement (T3IE) that not only improves quality of raw pseudo-labels in the target domain, but also leads to SAM-compatible inputs with three channels to better leverage SAM’s zero-shot inference ability for refining the pseudo-labels; 2) A reliable pseudo-label selection module that rejects low-quality pseudo-labels based on Consistency of Multiple SAM Outputs (CMSO) under input perturbations with T3IE; and 3) A reliability-aware training procedure in the unlabeled target domain where reliable pseudo-labels are used for supervision and unreliable parts are regularized by entropy minimization. Experiments conducted on two multi-domain medical image segmentation datasets for fetal brain and the prostate respectively demonstrate that: 1) SRPL-SFDA effectively enhances pseudo-label quality in the unlabeled target domain, and improves SFDA performance by leveraging the reliability-aware training; 2) SRPL-SFDA outperformed state-of-the-art SFDA methods, and its performance is close to that of supervised training in the target domain. The code of this work is available online: https://github.com/HiLab-git/SRPL-SFDA.
领域适应(DA)对于将医学图像分割模型应用于具有显著领域偏移的新临床中心时,确保模型的稳健部署至关重要。无源领域适应(SFDA)很有吸引力,因为它在适应目标域数据时,能够应对源域数据的隐私关注和访问约束。然而,SFDA面临目标域中无标签图像监督不足等挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种用于SFDA的基于Segment Anything Model(SAM)引导的可靠伪标签方法(SRPL-SFDA),包含三个关键组件:1)测试时三分支强度增强(T3IE)技术,它不仅能提高目标域中原始伪标签的质量,还能生成与SAM兼容的三通道输入,以更好地利用SAM的零样本推理能力来优化伪标签;2)一个可靠的伪标签选择模块,该模块基于输入扰动下的多个SAM输出一致性(CMSO)来拒绝低质量的伪标签;3)在无标签的目标域中采用可靠性感知训练流程,其中可靠的伪标签用于监督,不可靠的部分则通过最小化熵进行正则化。在胎儿大脑和前列腺两个多域医学图像分割数据集上进行的实验表明:1)SRPL-SFDA通过利用可靠性感知训练,有效提高了目标域中无标签图像的伪标签质量,并提升了SFDA的性能;2)SRPL-SFDA优于最新的SFDA方法,其性能接近目标域中的有监督训练。该工作的代码可在网上获取:https://github.com/HiLab-git/SRPL-SFDA。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 4 figures. Accepted for publication in Neurocomputing
Summary
医学图像分割模型在面临新的临床中心时出现领域漂移问题,需要进行领域自适应(DA)。无源领域自适应(SFDA)可以解决隐私问题和源域数据访问限制的问题。然而,SFDA面临目标域中无标签图像监督不足的挑战。本研究提出了一种基于Segment Anything Model(SAM)引导的可靠伪标签方法(SRPL-SFDA),包含三个关键组件:测试时三分支强度增强(T3IE),可提高目标域中原始伪标签的质量,并产生SAM兼容的三通道输入,以更好地利用SAM的零样本推理能力来优化伪标签;可靠的伪标签选择模块,基于输入扰动下的多个SAM输出的一致性(CMSO)拒绝低质量的伪标签;以及在无标签目标域中的可靠性感知训练程序,其中可靠的伪标签用于监督,不可靠的部分通过最小化熵进行正则化。实验表明,SRPL-SFDA有效提高目标域中伪标签的质量,并提高了SFDA的性能;相较于现有SFDA方法,SRPL-SFDA表现更优,且性能接近目标域中的监督训练。相关代码已在线发布。
Key Takeaways
- 领域自适应(DA)在医学图像分割模型部署到新临床中心时至关重要,特别是面临领域漂移问题时。
- 无源领域自适应(SFDA)能够应对隐私和源域数据访问限制的挑战。
- SFDA面临目标域中监督不足的问题。
- 本研究提出了SRPL-SFDA方法,包含T3IE、可靠的伪标签选择模块和可靠性感知训练程序三个关键组件。
- T3IE能提高目标域中伪标签的质量,并产生SAM兼容的三通道输入。
- SRPL-SFDA在医学图像分割数据集上的实验表现优于现有SFDA方法,性能接近目标域中的监督训练。
点此查看论文截图

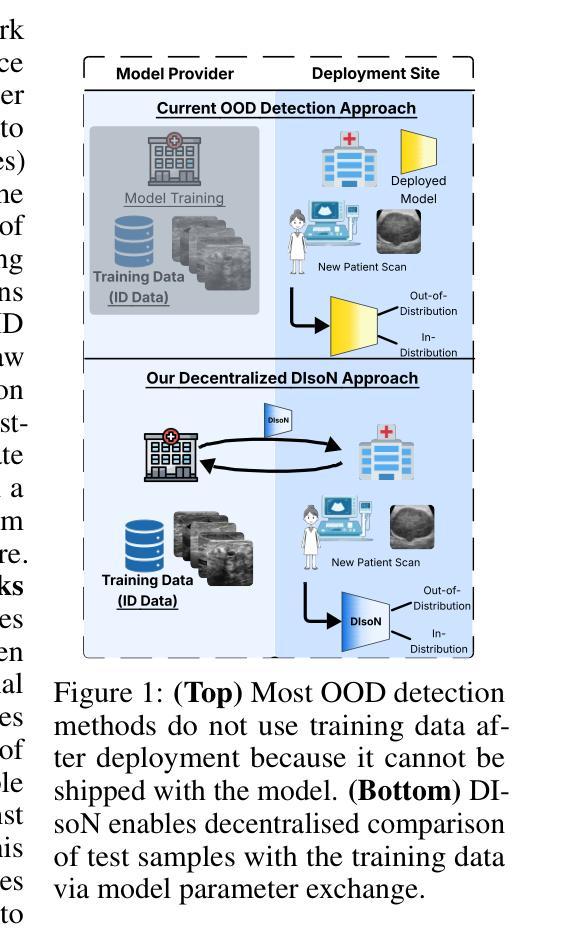
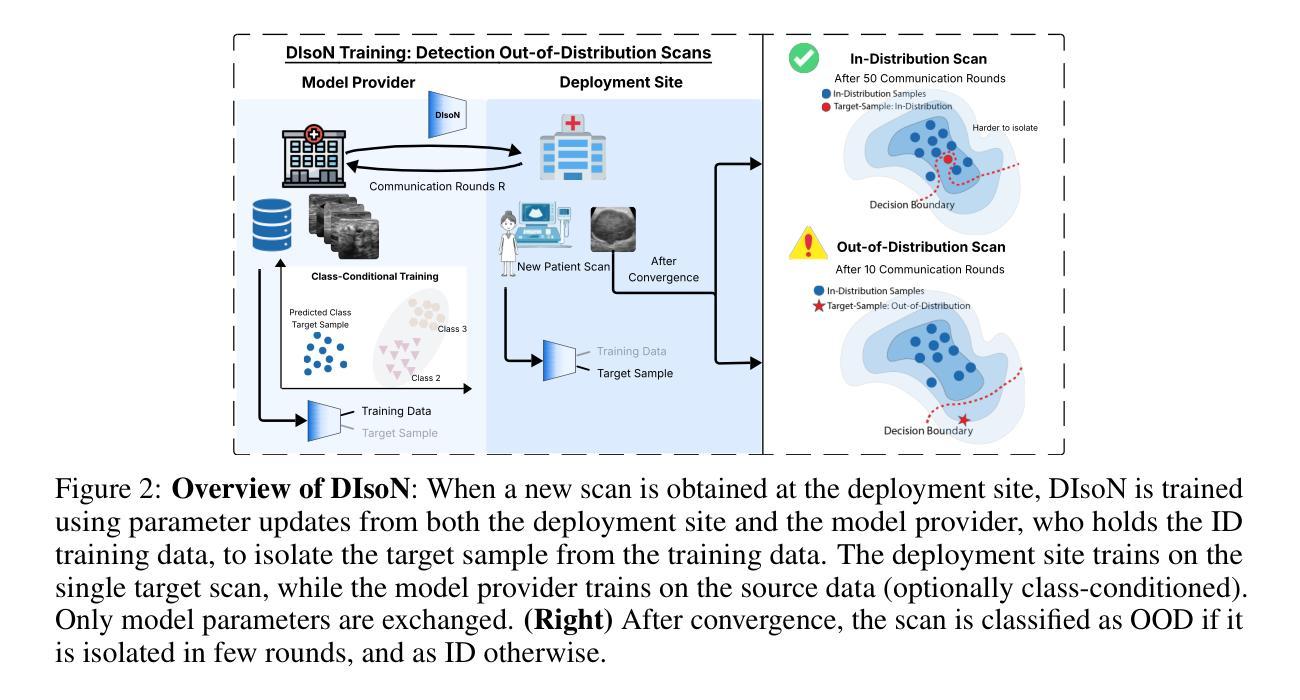
DIsoN: Decentralized Isolation Networks for Out-of-Distribution Detection in Medical Imaging
Authors:Felix Wagner, Pramit Saha, Harry Anthony, J. Alison Noble, Konstantinos Kamnitsas
Safe deployment of machine learning (ML) models in safety-critical domains such as medical imaging requires detecting inputs with characteristics not seen during training, known as out-of-distribution (OOD) detection, to prevent unreliable predictions. Effective OOD detection after deployment could benefit from access to the training data, enabling direct comparison between test samples and the training data distribution to identify differences. State-of-the-art OOD detection methods, however, either discard training data after deployment or assume that test samples and training data are centrally stored together, an assumption that rarely holds in real-world settings. This is because shipping training data with the deployed model is usually impossible due to the size of training databases, as well as proprietary or privacy constraints. We introduce the Isolation Network, an OOD detection framework that quantifies the difficulty of separating a target test sample from the training data by solving a binary classification task. We then propose Decentralized Isolation Networks (DIsoN), which enables the comparison of training and test data when data-sharing is impossible, by exchanging only model parameters between the remote computational nodes of training and deployment. We further extend DIsoN with class-conditioning, comparing a target sample solely with training data of its predicted class. We evaluate DIsoN on four medical imaging datasets (dermatology, chest X-ray, breast ultrasound, histopathology) across 12 OOD detection tasks. DIsoN performs favorably against existing methods while respecting data-privacy. This decentralized OOD detection framework opens the way for a new type of service that ML developers could provide along with their models: providing remote, secure utilization of their training data for OOD detection services. Code will be available upon acceptance at: *****
在安全关键的领域如医学成像中,部署机器学习(ML)模型的安全性需要检测训练期间未出现的输入特征,这被称为离群分布(OOD)检测,以防止不可靠的预测。部署后的有效OOD检测可以受益于访问训练数据,从而能够在测试样本和训练数据分布之间进行直接比较以识别差异。然而,最先进的OOD检测方法要么在部署后丢弃训练数据,要么假设测试样本和训练数据是集中存储在一起的,这在现实世界的环境中很少成立。这是因为由于训练数据库的大小以及专有或隐私约束,通常不可能将训练数据与已部署的模型一起发送。我们引入了隔离网络(Isolation Network),这是一种OOD检测框架,通过解决二分类任务来量化将目标测试样本从训练数据中分离的难度。然后,我们提出了分散式隔离网络(DIsoN),当数据共享不可能时,它可以通过交换模型参数来比较训练和测试数据,在训练和部署的远程计算节点之间进行。我们进一步将DIsoN扩展到类条件,仅将目标样本与其预测类的训练数据进行比较。我们在四个医学成像数据集(皮肤病学、胸部X射线、乳腺超声、组织病理学)上评估了DIsoN在12项OOD检测任务上的表现。DIsoN在表现上优于现有方法,同时尊重数据隐私。这种分散式的OOD检测框架为ML开发者提供了一种新的服务方式:在模型部署时提供远程安全地利用其训练数据进行OOD检测服务。代码将在接受后于以下网址提供:*****。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
提出一种名为Isolation Network的OOD检测框架,通过解决二分类任务来量化目标测试样本与训练数据分离的难度。在数据共享无法实现的情况下,通过仅在训练和部署的远程计算节点之间交换模型参数,实现了与训练数据的比较。进一步扩展了类条件DIsoN,仅将目标样本与预测类的训练数据进行比较。在四个医学成像数据集上评估DIsoN的性能,结果表明其在OOD检测任务上具有优势,同时尊重数据隐私。这种去中心化的OOD检测框架为ML开发者提供了一种新型服务方式:在模型部署时提供远程、安全的利用训练数据进行OOD检测服务。
关键见解
- 介绍了在医学成像等安全关键领域部署机器学习模型时,需要进行OOD检测的重要性,以防止不可靠的预测。
- 当前先进的OOD检测方法需要在部署后访问训练数据或假设训练和测试数据可以集中存储,这在现实世界中并不常见。
- 提出了Isolation Network框架来量化测试样本与训练数据之间的差异。该框架通过解决二分类任务来实现这一目标。
- 引入Decentralized Isolation Networks (DIsoN),在数据共享无法实现的情况下,通过交换模型参数来比较训练和测试数据。
- DIsoN框架扩展了类条件功能,仅将目标样本与训练中的预测类的数据进行比较。
- 在医学成像数据集上的实验表明,DIsoN在OOD检测任务上的性能优于现有方法,并尊重数据隐私。
点此查看论文截图

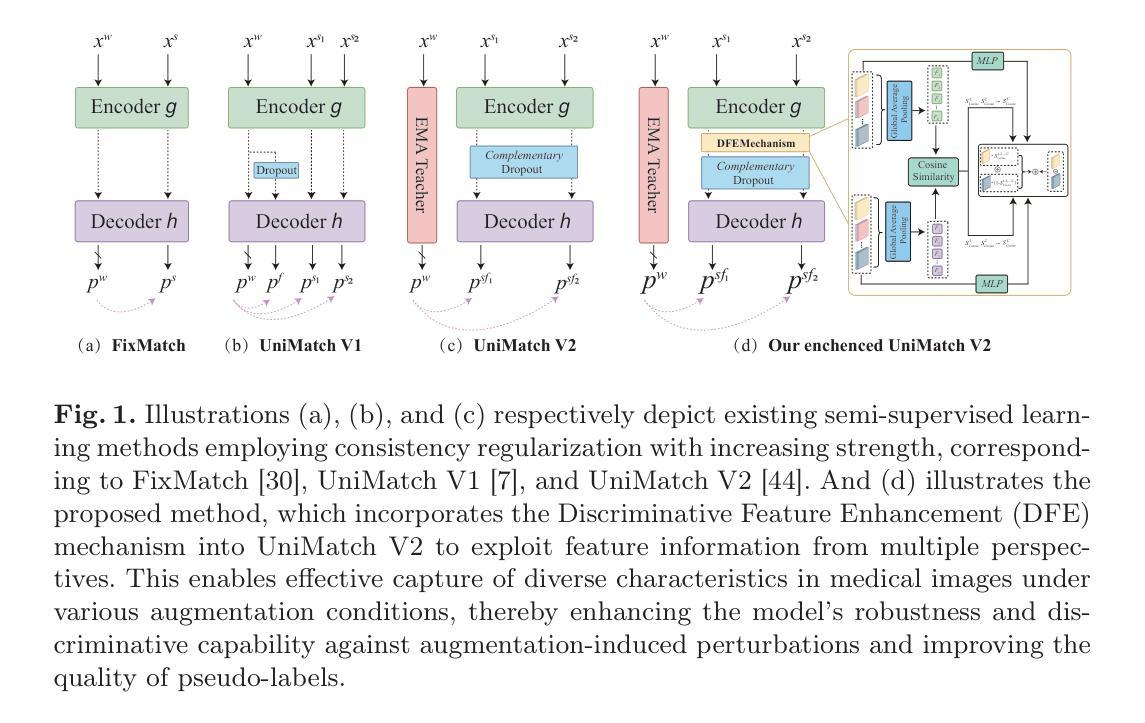
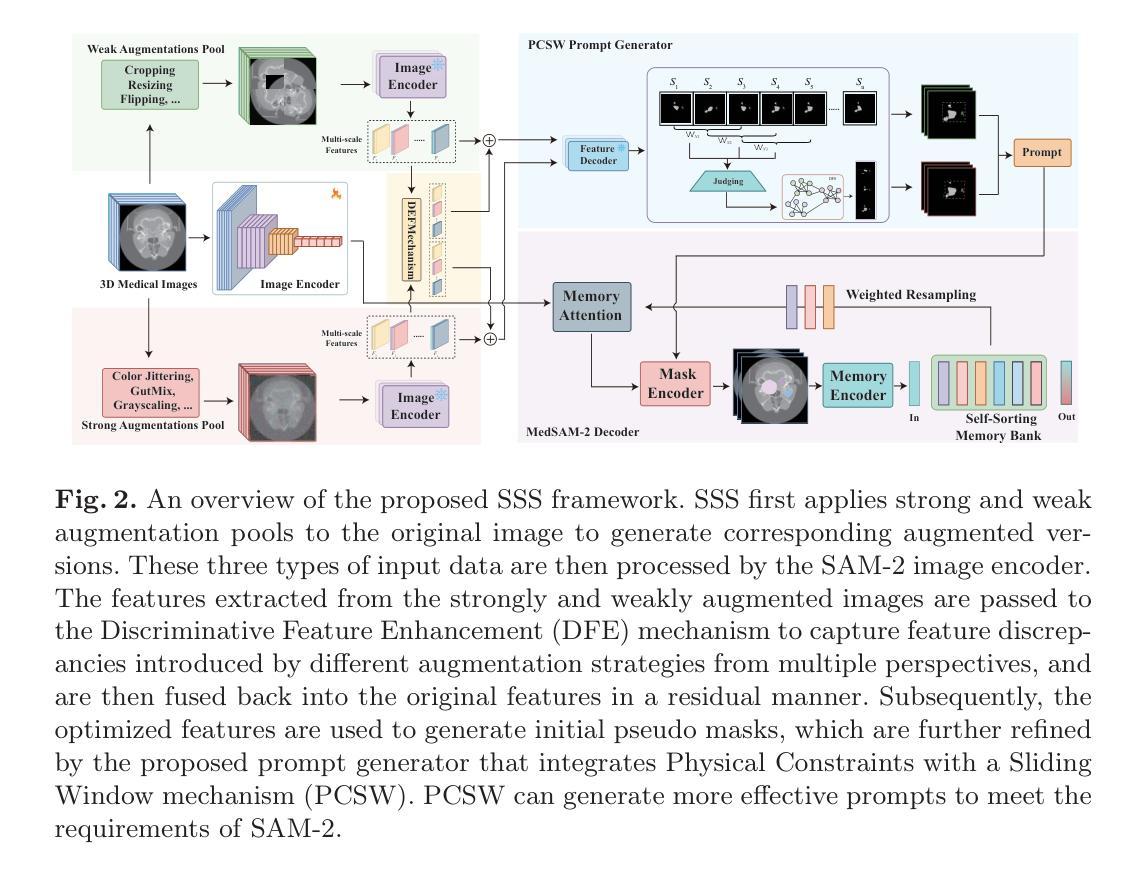
SSS: Semi-Supervised SAM-2 with Efficient Prompting for Medical Imaging Segmentation
Authors:Hongjie Zhu, Xiwei Liu, Rundong Xue, Zeyu Zhang, Yong Xu, Daji Ergu, Ying Cai, Yang Zhao
In the era of information explosion, efficiently leveraging large-scale unlabeled data while minimizing the reliance on high-quality pixel-level annotations remains a critical challenge in the field of medical imaging. Semi-supervised learning (SSL) enhances the utilization of unlabeled data by facilitating knowledge transfer, significantly improving the performance of fully supervised models and emerging as a highly promising research direction in medical image analysis. Inspired by the ability of Vision Foundation Models (e.g., SAM-2) to provide rich prior knowledge, we propose SSS (Semi-Supervised SAM-2), a novel approach that leverages SAM-2’s robust feature extraction capabilities to uncover latent knowledge in unlabeled medical images, thus effectively enhancing feature support for fully supervised medical image segmentation. Specifically, building upon the single-stream “weak-to-strong” consistency regularization framework, this paper introduces a Discriminative Feature Enhancement (DFE) mechanism to further explore the feature discrepancies introduced by various data augmentation strategies across multiple views. By leveraging feature similarity and dissimilarity across multi-scale augmentation techniques, the method reconstructs and models the features, thereby effectively optimizing the salient regions. Furthermore, a prompt generator is developed that integrates Physical Constraints with a Sliding Window (PCSW) mechanism to generate input prompts for unlabeled data, fulfilling SAM-2’s requirement for additional prompts. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method for semi-supervised medical image segmentation on two multi-label datasets, i.e., ACDC and BHSD. Notably, SSS achieves an average Dice score of 53.15 on BHSD, surpassing the previous state-of-the-art method by +3.65 Dice. Code will be available at https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/SSS.
在信息爆炸的时代,如何在有效利用大规模无标签数据的同时,尽量减少对高质量像素级注释的依赖,仍然是医学成像领域的一个关键挑战。半监督学习(SSL)通过促进知识迁移,提高了无标签数据的利用率,显著提高了全监督模型的性能,并成为医学图像分析领域一个极具前景的研究方向。受视觉基础模型(如SAM-2)提供丰富先验知识能力的启发,我们提出了SSS(Semi-Supervised SAM-2)这一新方法,它利用SAM-2的稳健特征提取能力,在未经标记的医学图像中发现潜在知识,从而有效地增强全监督医学图像分割的特征支持。具体来说,本文基于单流“弱到强”的一致性正则化框架,引入判别特征增强(DFE)机制,进一步探索由多种数据增强策略在不同视图下引入的特征差异。通过利用多尺度增强技术中的特征相似性和差异性,该方法对特征进行重建和建模,从而有效地优化显著区域。此外,开发了一个提示生成器,该生成器结合了物理约束与滑动窗口(PCSW)机制,为无标签数据生成输入提示,满足SAM-2对额外提示的要求。大量实验表明,所提出的方法在ACDC和BHSD两个多标签数据集上进行半监督医学图像分割时表现优越。值得注意的是,SSS在BHSD上的平均Dice系数为53.15,比之前的先进方法高出+3.65 Dice。代码将在https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/SSS上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在大数据时代,如何利用大量未标注数据并减少对高质量像素级标注的依赖,是医学影像领域的一大挑战。半监督学习(SSL)通过知识转移提高了未标注数据的利用率,极大提升了全监督模型的性能,成为医学影像分析中极具前景的研究方向。受视觉基础模型(如SAM-2)提供丰富先验知识能力的启发,本文提出了SSS(基于SAM-2的半监督方法),利用SAM-2的稳健特征提取能力挖掘未标注医学影像中的潜在知识,从而增强全监督医学影像分割的特征支持。通过引入判别特征增强(DFE)机制和多尺度数据增强技术的特征相似性和差异性重建和建模,进一步优化了显著区域。同时开发了一个提示生成器,结合物理约束和滑动窗口(PCSW)机制为未标注数据生成输入提示,满足SAM-2对额外提示的要求。在ACDC和BHSD两个多标签数据集上的实验表明,该方法在半监督医学影像分割上的优越性。特别是SSS在BHSD上取得了平均Dice系数53.15的高分,超过了之前的最先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 在大数据时代,如何利用未标注数据是医学影像分析的关键挑战。
- 半监督学习在医学影像分析中展现巨大潜力。
- 提出SSS方法,结合SAM-2和DFE机制进行半监督医学图像分割。
- 利用多尺度数据增强技术优化显著区域。
- 开发提示生成器以满足SAM-2的额外提示需求。
- 在ACDC和BHSD数据集上的实验验证了SSS方法的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

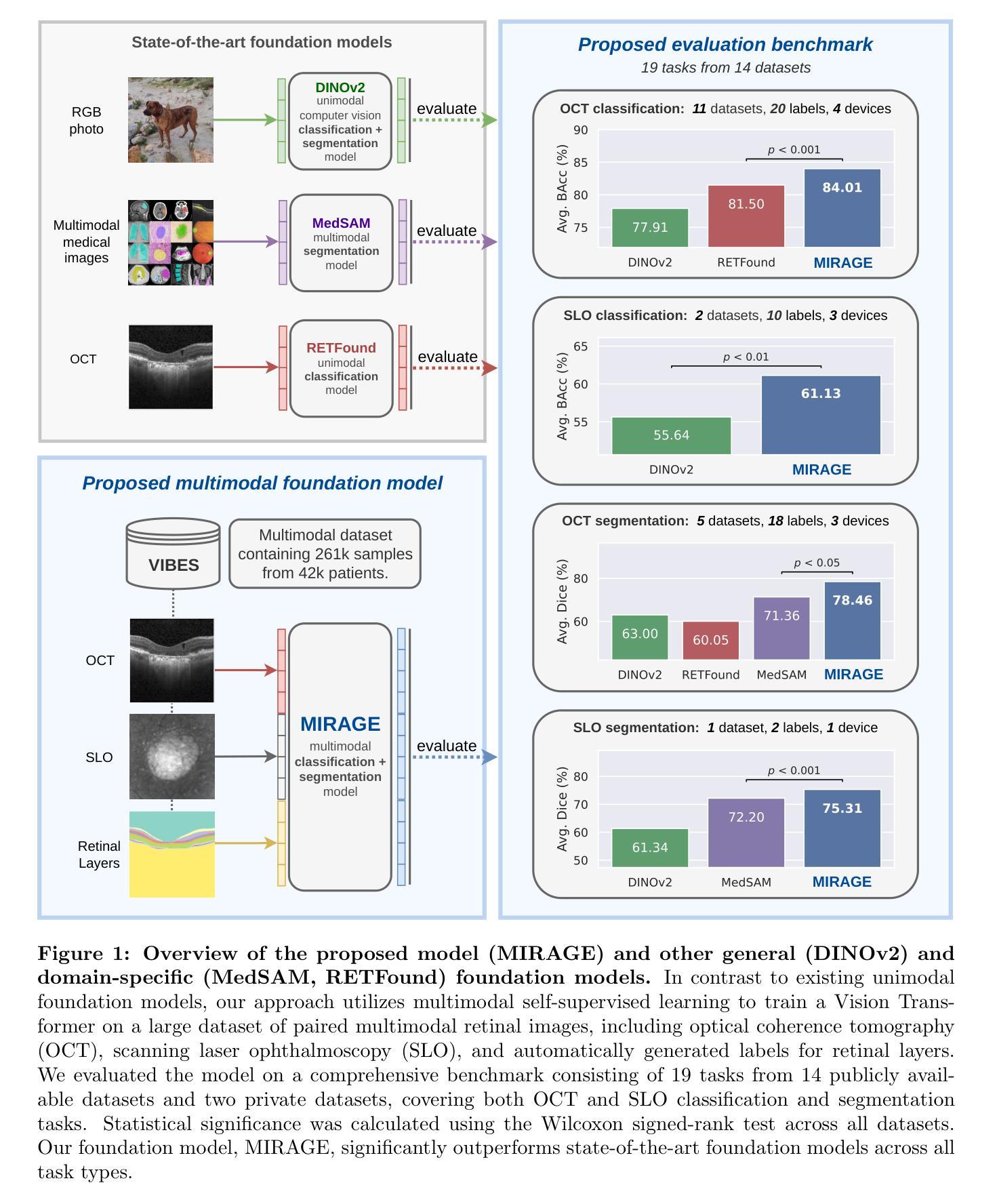
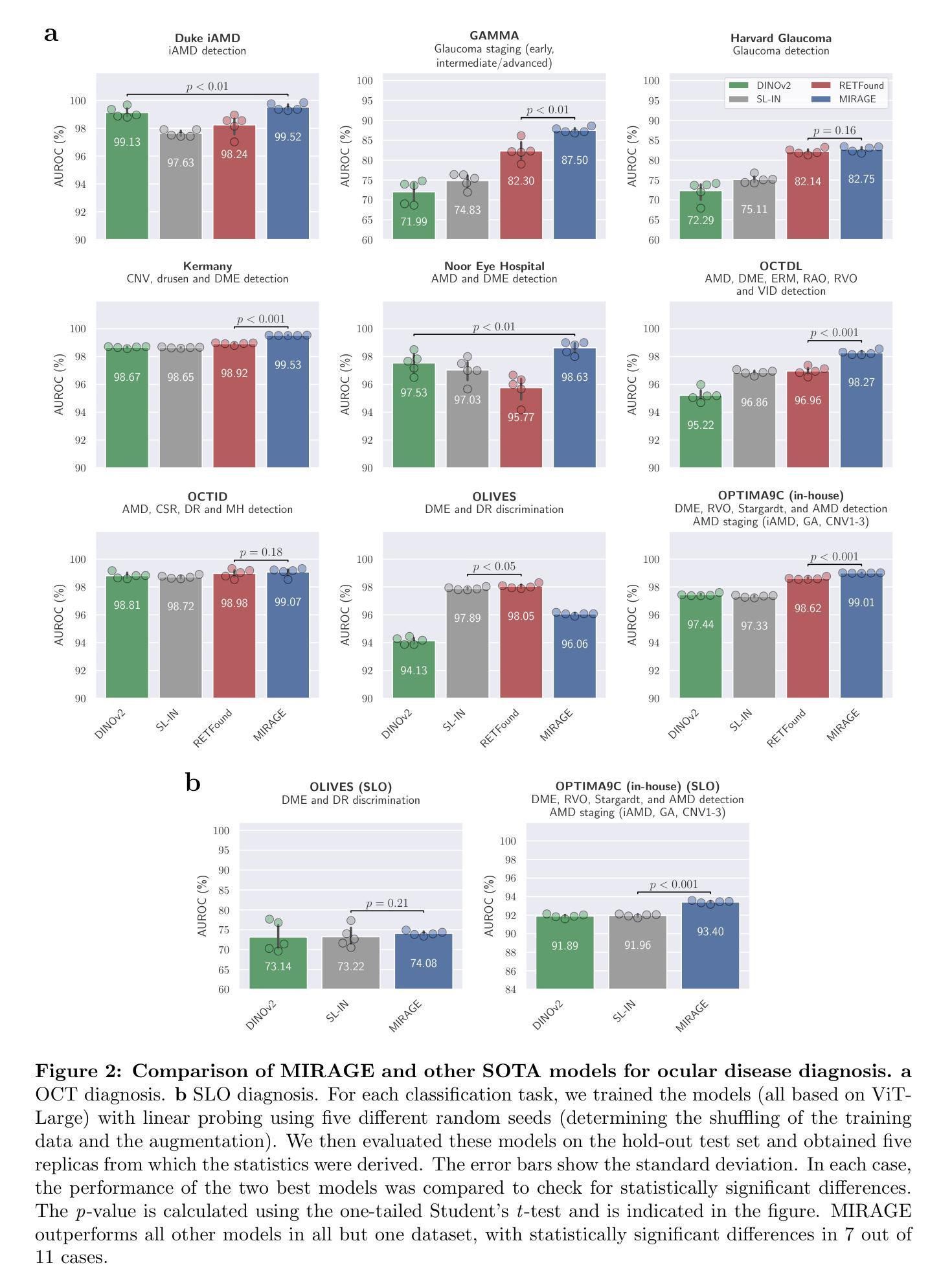
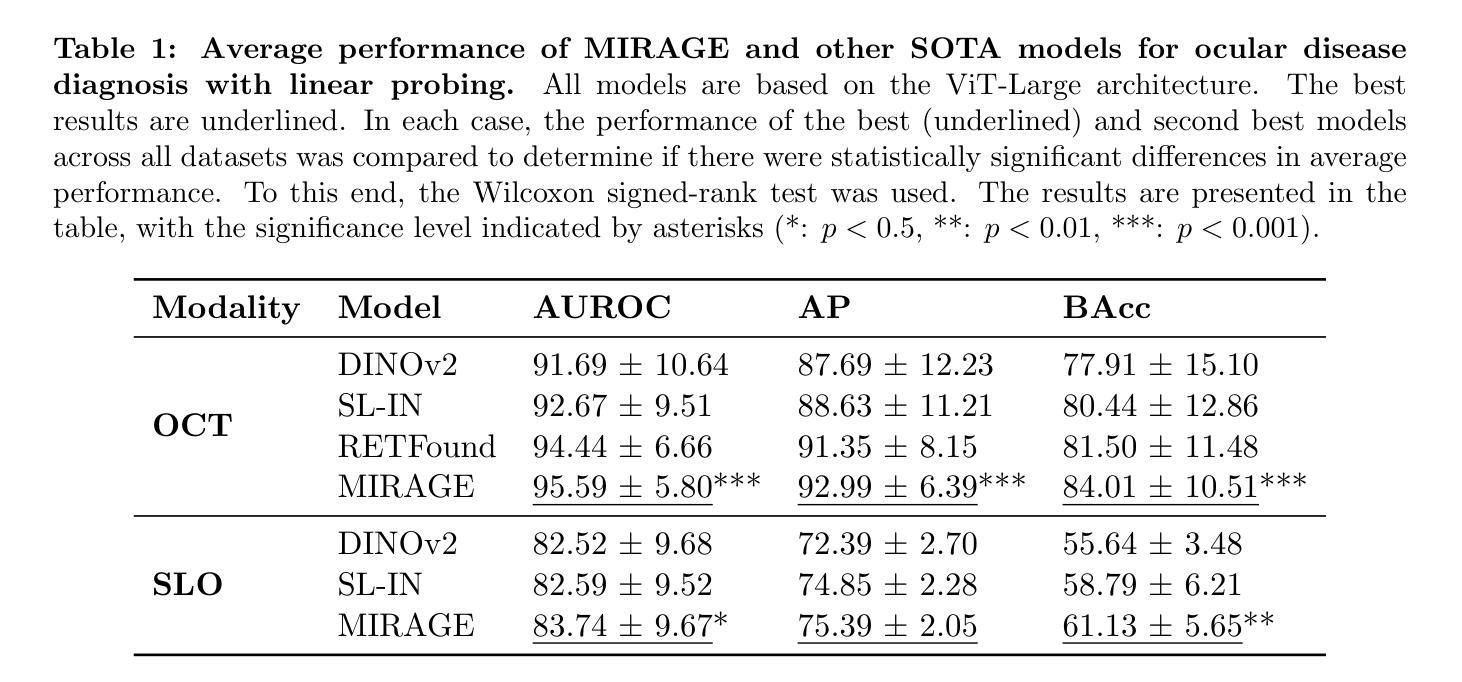
MIRAGE: Multimodal foundation model and benchmark for comprehensive retinal OCT image analysis
Authors:José Morano, Botond Fazekas, Emese Sükei, Ronald Fecso, Taha Emre, Markus Gumpinger, Georg Faustmann, Marzieh Oghbaie, Ursula Schmidt-Erfurth, Hrvoje Bogunović
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a fundamental tool for assisting clinicians in analyzing ophthalmic images, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT). However, developing AI models often requires extensive annotation, and existing models tend to underperform on independent, unseen data. Foundation models (FMs), large AI models trained on vast unlabeled datasets, have shown promise in overcoming these challenges. Nonetheless, available FMs for ophthalmology lack extensive validation, especially for segmentation tasks, and focus on a single imaging modality. In this context, we propose MIRAGE, a novel multimodal FM for the analysis of OCT and scanning laser ophthalmoscopy (SLO) images. Additionally, we propose a new evaluation benchmark with OCT/SLO classification and segmentation tasks. The comparison with general and specialized FMs and segmentation methods shows the superiority of MIRAGE in both types of tasks, highlighting its suitability as a basis for the development of robust AI systems for retinal OCT image analysis. Both MIRAGE and the evaluation benchmark are publicly available: https://github.com/j-morano/MIRAGE.
人工智能(AI)已经成为辅助临床医生分析眼科图像的重要工具,如光学相干断层扫描(OCT)。然而,开发AI模型通常需要大量的标注,现有模型在未见过的独立数据上往往表现不佳。预训练模型(FMs)是在大量无标签数据集上训练的庞大AI模型,在克服这些挑战方面显示出潜力。然而,现有的眼科预训练模型缺乏广泛验证,尤其是在分割任务方面,且只关注单一成像模式。在此背景下,我们提出了MIRAGE,这是一种用于分析OCT和扫描激光眼科检查(SLO)图像的新型多模态预训练模型。此外,我们还提出了一个新的评估基准,包括OCT/SLO分类和分割任务。与一般和专业的预训练模型和分割方法相比,MIRAGE在这两种类型的任务中都表现出优越性,凸显其作为开发用于视网膜OCT图像分析的稳健AI系统的基础的适用性。MIRAGE和评估基准均可公开访问:https://github.com/j-morano/MIRAGE。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能(AI)已成为辅助医生分析眼科图像的重要工具,特别是在光学相干断层扫描(OCT)方面。然而,开发AI模型通常需要大量的标注数据,现有模型在未见过的独立数据上表现不佳。针对这一问题,研究人员提出采用基础模型(FMs)——在大量无标签数据集上训练的大型AI模型——来解决挑战。然而,现有的眼科领域基础模型缺乏广泛验证,特别是在分割任务上,且主要关注单一成像模式。在此背景下,研究人员提出了一种新型的多模式基础模型MIRAGE,用于分析OCT和扫描激光眼科(SLO)图像。此外,他们还提出了一个新的评估基准,包括OCT/SLO分类和分割任务。与通用和专用基础模型及分割方法的比较显示,MIRAGE在两类任务中都表现出卓越性能,适合作为开发视网膜OCT图像分析稳健AI系统的基石。MIRAGE和基础模型评估基准已公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在眼科图像分析中的应用逐渐普及,特别是在OCT图像分析方面。
- 开发AI模型面临的主要挑战之一是数据标注的需求量大以及模型在独立数据上的表现不稳定。
- 基础模型(FMs)作为一种在大量无标签数据集上训练的大型AI模型,有助于解决上述问题。
- 当前眼科领域的基础模型缺乏广泛验证,尤其在分割任务上表现不足,且主要关注单一成像模式。
- MIRAGE是一种新型的多模式基础模型,旨在分析OCT和SLO图像。
- MIRAGE模型展示了卓越的性能,特别是在分类和分割任务上。
点此查看论文截图

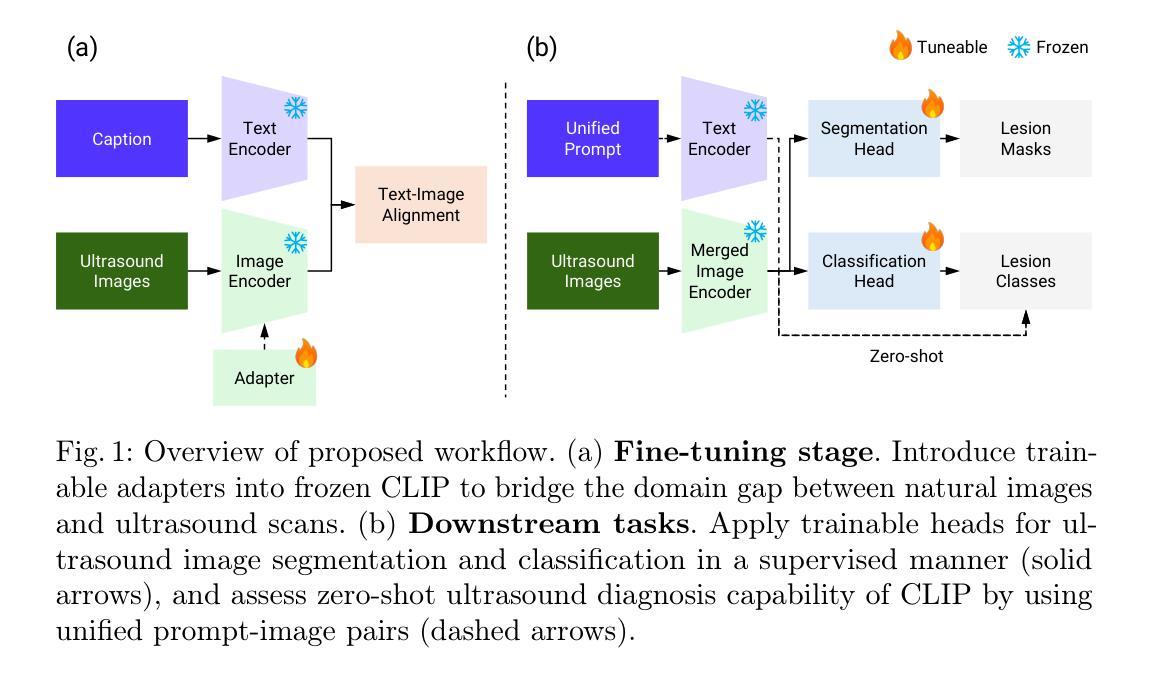
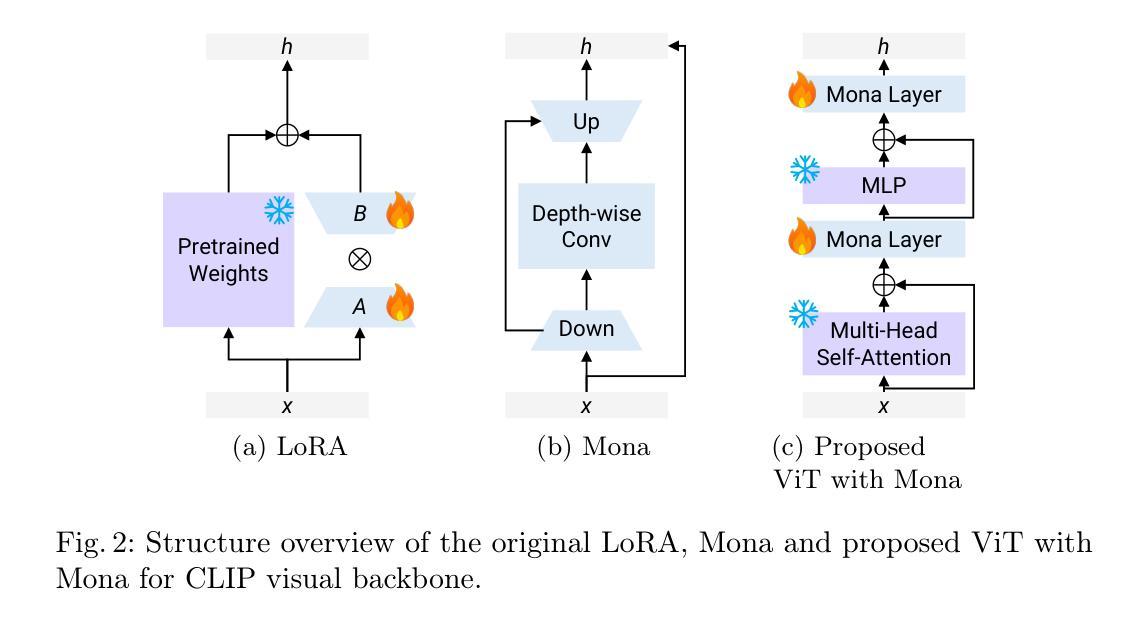
Adapting Vision-Language Foundation Model for Next Generation Medical Ultrasound Image Analysis
Authors:Jingguo Qu, Xinyang Han, Tonghuan Xiao, Jia Ai, Juan Wu, Tong Zhao, Jing Qin, Ann Dorothy King, Winnie Chiu-Wing Chu, Jing Cai, Michael Tin-Cheung Ying
Medical ultrasonography is an essential imaging technique for examining superficial organs and tissues, including lymph nodes, breast, and thyroid. It employs high-frequency ultrasound waves to generate detailed images of the internal structures of the human body. However, manually contouring regions of interest in these images is a labor-intensive task that demands expertise and often results in inconsistent interpretations among individuals. Vision-language foundation models, which have excelled in various computer vision applications, present new opportunities for enhancing ultrasound image analysis. Yet, their performance is hindered by the significant differences between natural and medical imaging domains. This research seeks to overcome these challenges by developing domain adaptation methods for vision-language foundation models. In this study, we explore the fine-tuning pipeline for vision-language foundation models by utilizing large language model as text refiner with special-designed adaptation strategies and task-driven heads. Our approach has been extensively evaluated on six ultrasound datasets and two tasks: segmentation and classification. The experimental results show that our method can effectively improve the performance of vision-language foundation models for ultrasound image analysis, and outperform the existing state-of-the-art vision-language and pure foundation models. The source code of this study is available at https://github.com/jinggqu/NextGen-UIA.
医学超声是检查浅表器官和组织(包括淋巴结、乳房和甲状腺)的重要成像技术。它利用高频超声波生成人体内部结构的详细图像。然而,在这些图像中手动轮廓感兴趣区域是一项劳动密集型任务,需要专业知识,并且在不同个体之间常常导致解释不一致。视觉语言基础模型在各种计算机视觉应用中表现出色,为增强超声图像分析提供了新的机会。然而,由于其显著的自然和医学影像域之间的差异,其性能受到了阻碍。本研究旨在通过开发视觉语言基础模型的域适应方法来克服这些挑战。在这项研究中,我们探索了视觉语言基础模型的微调管道,利用大型语言模型作为文本精炼器,采用特殊设计的适应策略和任务驱动头。我们的方法已在六个超声数据集和两个任务(分割和分类)上进行了广泛评估。实验结果表明,我们的方法可以有效地提高视觉语言基础模型在超声图像分析中的性能,并且优于现有的最先进的视觉语言和纯基础模型。本研究的源代码可在https://github.com/jinggqu/NextGen-UIA获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了医学超声成像技术在浅表器官和组织检查中的应用,如淋巴结、乳房和甲状腺。手动在这些图像中描绘感兴趣区域是一项劳动密集型任务,需求高度专业且常导致不同人之间的解读不一致。研究采用视觉语言基础模型克服这些挑战,通过领域适应方法为视觉语言基础模型开发适配策略,在超声图像分析上取得了显著成效。实验结果显示,该方法可有效提升视觉语言基础模型在超声图像分析上的性能,并超越现有最先进模型和纯基础模型。相关研究代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 医学超声成像技术广泛应用于浅表器官和组织的检查,如淋巴结、乳房和甲状腺。
- 手动描绘超声图像中的感兴趣区域是一项挑战,需要专业技能且易出现解读不一致。
- 视觉语言基础模型在医学图像分析上具有潜力,但其在医学图像领域和自然图像领域的差异限制了其性能。
- 研究采用领域适应策略来克服这一挑战,利用大型语言模型作为文本精炼器,并设计特殊适配策略和任务驱动头。
- 该方法经过在六个超声数据集和两个任务(分割和分类)上的广泛评估,证明了其有效性。
- 该方法超越了现有的视觉语言模型和纯基础模型,在超声图像分析上表现出优异的性能。
点此查看论文截图

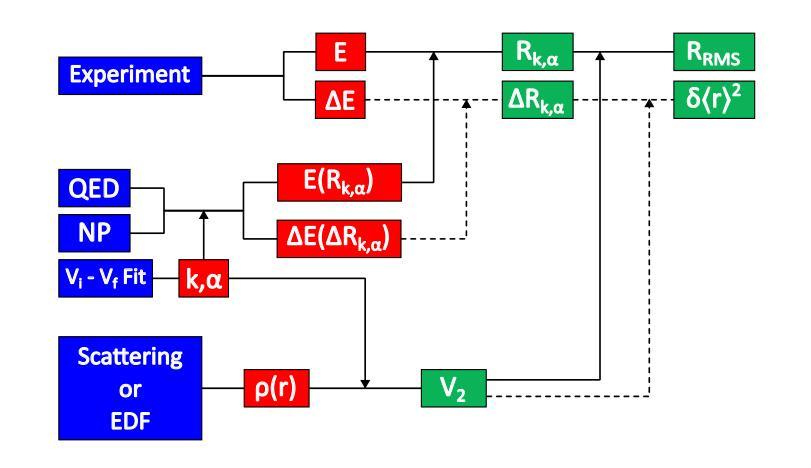
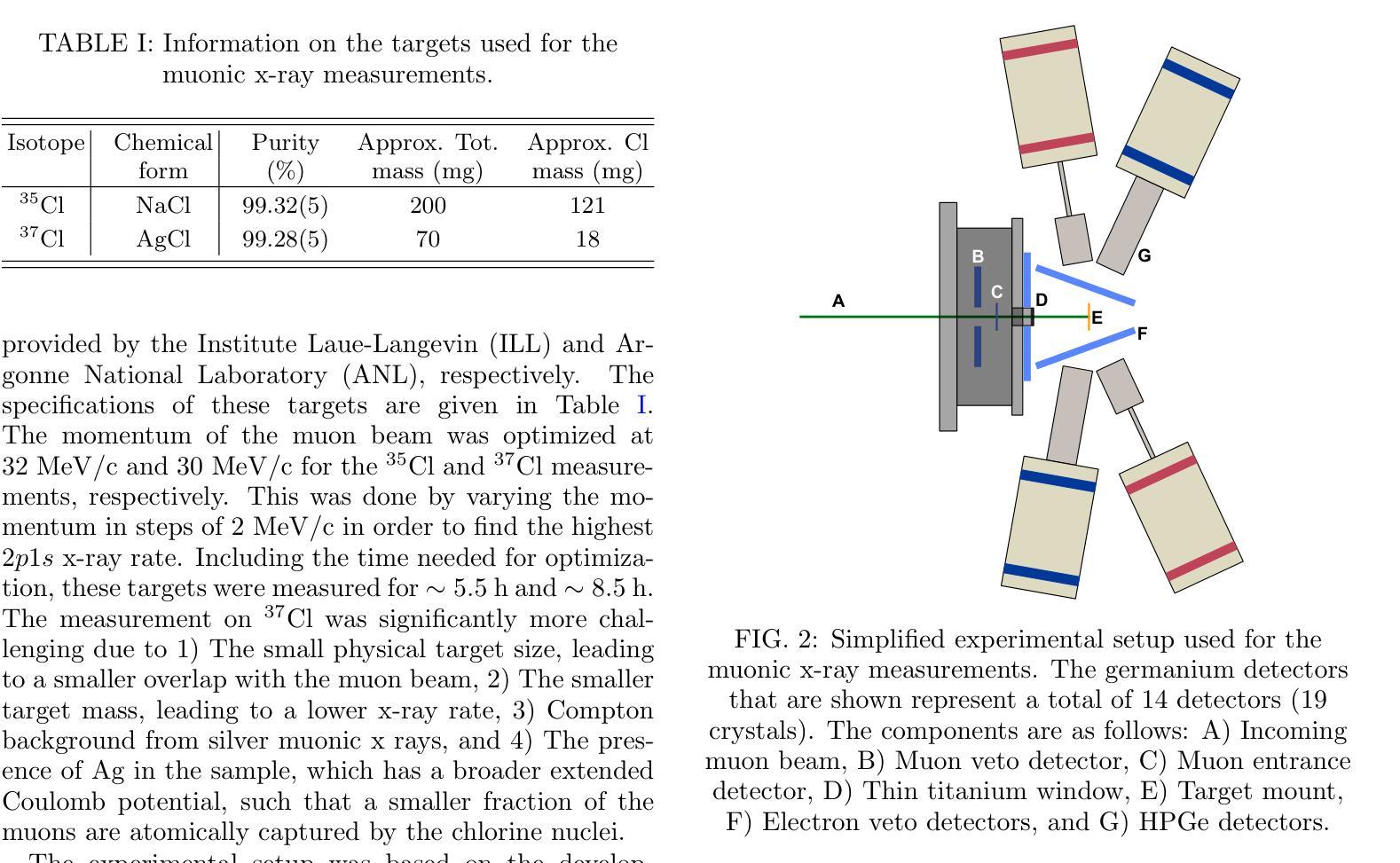
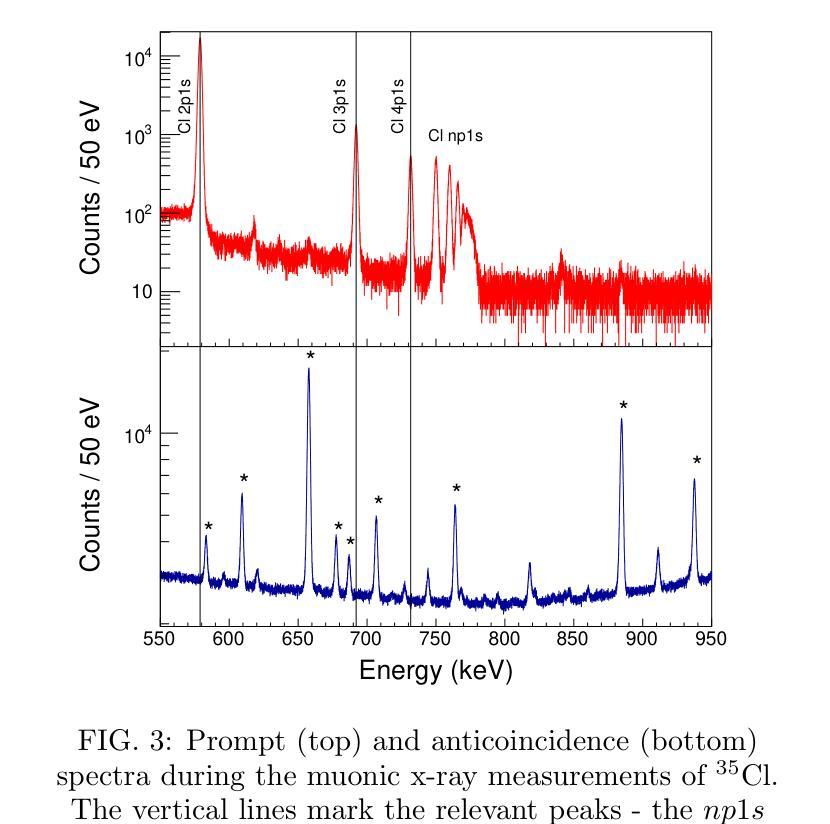
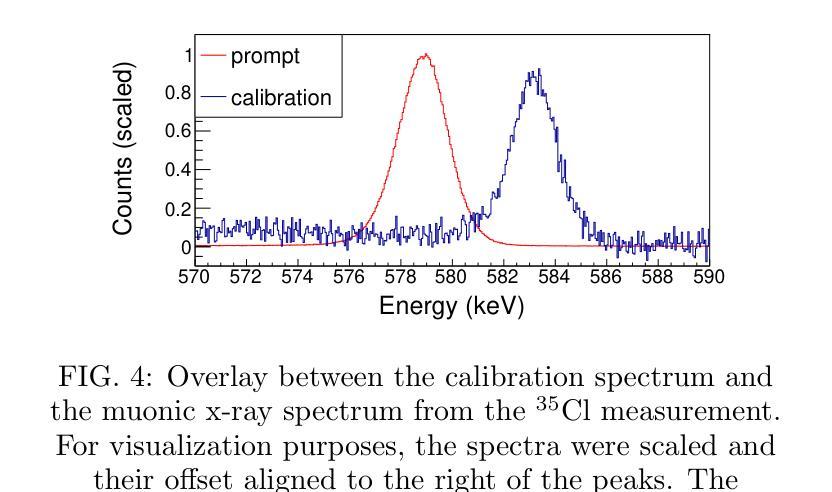
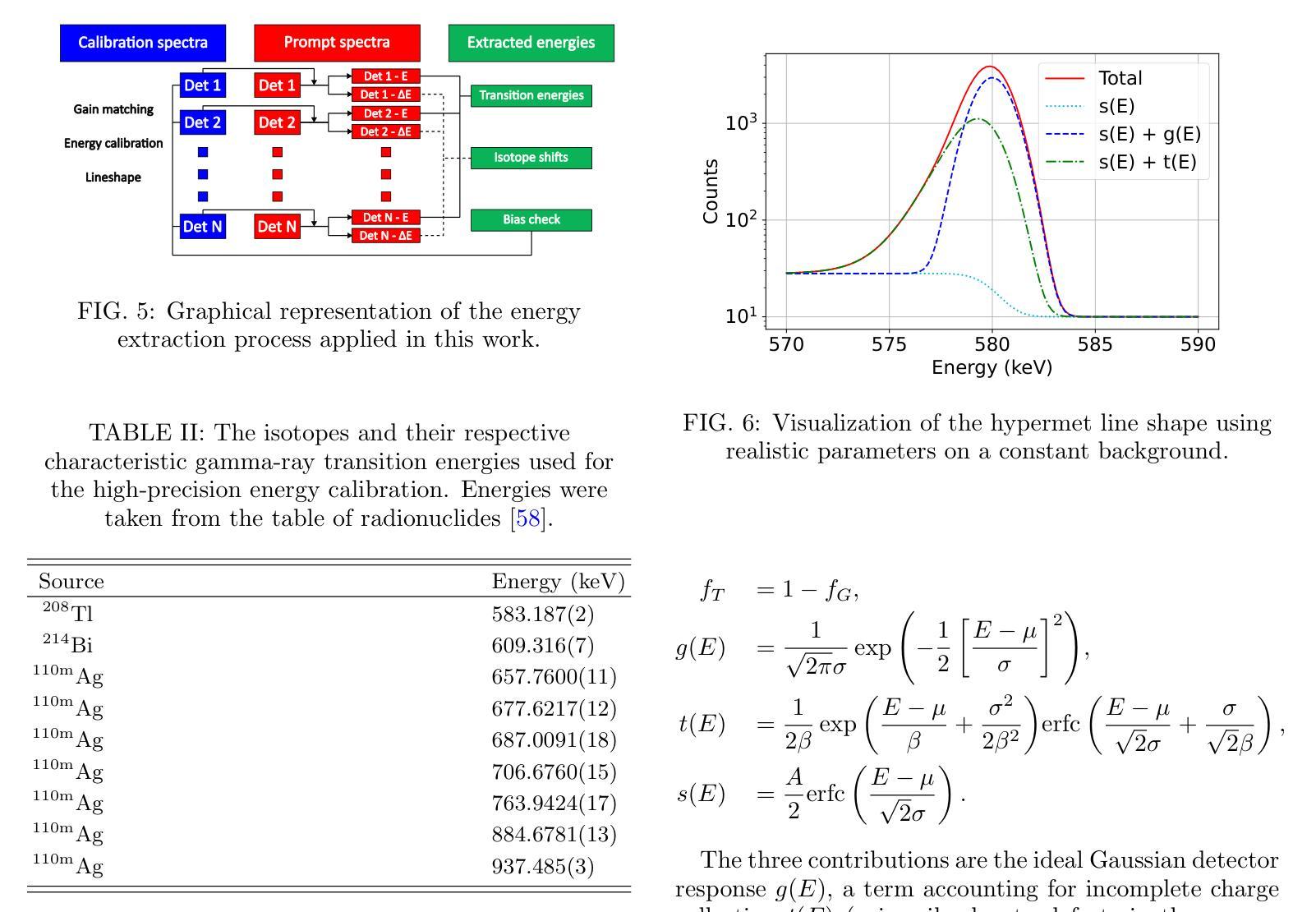
Modern approach to muonic x-ray spectroscopy demonstrated through the measurement of stable Cl radii
Authors:K. A. Beyer, T. E. Cocolios, C. Costache, M. Deseyn, P. Demol, A. Doinaki, O. Eizenberg, M. Gorshteyn, M. Heines, A. Herzáň, P. Indelicato, K. Kirch, A. Knecht, R. Lica, V. Matousek, E. A. Maugeri, B. Ohayon, N. S. Oreshkina, W. W. M. M. Phyo, R. Pohl, S. Rathi, W. Ryssens, A. Turturica, K. von Schoeler, I. A. Valuev, S. M. Vogiatzi, F. Wauters, A. Zendour
Recent advances in muonic x-ray experiments have reinvigorated efforts in measurements of absolute nuclear charge radii. Here, a modern approach is presented, and demonstrated through determination of the charge radii of the two stable chlorine nuclides $^{35}$Cl and $^{37}$Cl. Knowledge of these radii has implications for fundamental studies in nuclear and atomic physics. For this purpose, a state-of-the-art experiment was performed at the $\pi$E1 beamline in the Paul Scherrer Institute (Switzerland), using a large-scale HPGe detector array in order to extract precise energies of the muonic $^{35}$Cl and $^{37}$Cl $np1s$ transitions. The nuclear charge radius extraction relies on modern calculations for QED effects and nuclear polarization with rigorous uncertainty quantification, including effects that were not accounted for in older studies. Additionally, we established a new method for applying the nuclear shape correction directly from energy density functionals, which are amenable to isotopes for which no high-quality electron scattering experiments are available. The resulting charge radii are $3.3335(23) fm$ for $^{35}$Cl and $3.3445(23) fm$ for $^{37}$Cl, thus improving the uncertainty of the available electron scattering values by a factor of seven. The correlation of several observables was evaluated between the different isotopes in order to produce a more precise value of the differential mean square charge radius $\delta \langle r^2 \rangle^{37, 35}=+0.0771(66) fm^{2}$. In this case, improvement of the uncertainty by more than one order of magnitude was achieved compared to the literature value. This precision is sufficient to use this differential as input for isotope shift factor determination.
近期μ子X射线实验的新进展重新激发了绝对核电荷半径测量的努力。在此,介绍了一种现代方法,并通过测定两个稳定氯核素$^{35}$Cl和$^{37}$Cl的电荷半径来展示。这些半径的知识对核物理和原子物理的基础研究具有重要意义。为此,在保罗谢尔研究所(瑞士)的$\pi$E1光束线上进行了一项最先进的实验,使用大规模HPGe探测器阵列提取μ子$^{35}$Cl和$^{37}$Cl的$np1s$跃迁的精确能量。核电荷半径的提取依赖于对量子电动力学效应和核极化的现代计算,并进行了严格的不确定性量化,包括对旧研究中未考虑的因素的影响。此外,我们建立了一种新的方法,直接从能量密度函数应用核形状校正,这对于没有高质量电子散射实验的同位素是可行的。得到的电荷半径为$^{35}$Cl的$3.3335(23)fm$和$^{37}$Cl的$3.3445(23)fm$,从而将现有电子散射值的不确定性降低了七倍。为了得到更精确的均方电荷半径差值$\delta \langle r^{2} \rangle^{37, 35}=+0.0771(66)fm^{2}$的值,我们对不同同位素之间的几个观测值进行了评估。在这种情况下,与文献值相比,不确定度的降低幅度超过了一个数量级。这种精确度足以将此差异用作同位素位移因子测定的输入值。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了在瑞士保罗谢尔研究所利用先进技术和大型HPGe探测器阵列进行的最新muonic x射线实验的成果。该研究通过精密测量氯的同位素$^{35}$Cl和$^{37}$Cl的电荷半径,提高了核物理和原子物理基础研究的认识。通过严格的不确定性量化,该研究考虑了量子力学效应和核极化效应的现代计算,并建立了新的核形状校正方法。最终得到的电荷半径值提高了电子散射实验值的精度。该研究对同位素间可观测量的相关性进行了评估,为差异平均平方电荷半径提供了更精确的值,并将不确定性降低了一个数量级以上。这些精确数据可用于同位素位移因子的确定。
Key Takeaways
- 最新muonic x射线实验通过精密测量$^{35}$Cl和$^{37}$Cl的电荷半径重新激发了对绝对核电荷半径测量的兴趣。
- 在瑞士保罗谢尔研究所的先进实验使用大型HPGe探测器阵列精确提取了muonic氯同位素的能量。
- 考虑到量子力学效应和核极化的现代计算,严格地量化了不确定性。
- 建立了新的方法应用核形状校正,直接从能量密度功能中获得,适用于没有高质量电子散射实验的同位素。
- 获得的电荷半径值提高了电子散射实验值的精度,并减少了不确定性的大小。
- 通过评估不同同位素之间的可观测量的相关性,得出了更精确的差异化平均平方电荷半径值。
点此查看论文截图

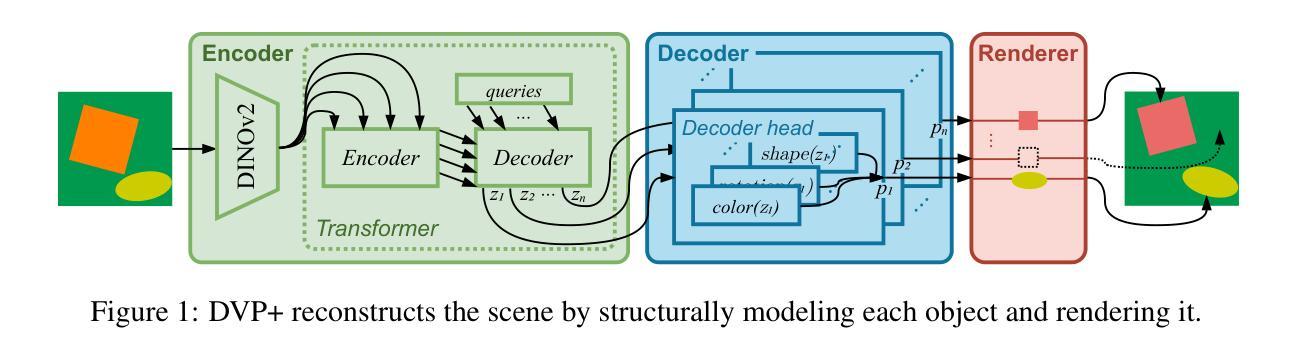
Generative Learning of Differentiable Object Models for Compositional Interpretation of Complex Scenes
Authors:Antoni Nowinowski, Krzysztof Krawiec
This study builds on the architecture of the Disentangler of Visual Priors (DVP), a type of autoencoder that learns to interpret scenes by decomposing the perceived objects into independent visual aspects of shape, size, orientation, and color appearance. These aspects are expressed as latent parameters which control a differentiable renderer that performs image reconstruction, so that the model can be trained end-to-end with gradient using reconstruction loss. In this study, we extend the original DVP so that it can handle multiple objects in a scene. We also exploit the interpretability of its latent by using the decoder to sample additional training examples and devising alternative training modes that rely on loss functions defined not only in the image space, but also in the latent space. This significantly facilitates training, which is otherwise challenging due to the presence of extensive plateaus in the image-space reconstruction loss. To examine the performance of this approach, we propose a new benchmark featuring multiple 2D objects, which subsumes the previously proposed Multi-dSprites dataset while being more parameterizable. We compare the DVP extended in these ways with two baselines (MONet and LIVE) and demonstrate its superiority in terms of reconstruction quality and capacity to decompose overlapping objects. We also analyze the gradients induced by the considered loss functions, explain how they impact the efficacy of training, and discuss the limitations of differentiable rendering in autoencoders and the ways in which they can be addressed.
本研究基于视觉先验解构器(DVP)架构,这是一种自编码器,它通过分解感知到的对象为其独立的视觉方面(形状、大小、方向和颜色外观)来理解场景。这些方面被表达为潜在参数,这些参数控制一个可微渲染器进行图像重建,从而使模型可以使用重建损失与梯度进行端到端的训练。在本研究中,我们扩展了原始的DVP,使其能够处理场景中的多个对象。我们还通过解码器采样额外的训练样本,并设计依赖于不仅在图像空间中定义的损失函数而且在潜在空间中定义的损失函数的替代训练模式,从而利用潜在的可解释性。这极大地促进了训练,否则由于图像空间重建损失中存在大量的平稳期而面临挑战。为了检验这种方法的效果,我们提出了一个新的包含多个二维对象的基准测试,这个基准测试涵盖了之前提出的Multi-dSprites数据集并且更加可参数化。我们将以这种方式扩展的DVP与两个基准线(MONet和LIVE)进行比较,并展示了其在重建质量和分解重叠对象方面的优越性。我们还分析了所考虑的损失函数引起的梯度,解释了它们如何影响训练的有效性,并讨论了自编码器中可微分渲染的局限性以及解决这些问题的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究基于视觉先验解纠缠器(DVP)架构,这是一种自编码器,通过分解感知到的对象成独立的视觉方面(形状、大小、方向和颜色外观)来解释场景。通过表达这些方面作为控制可微分渲染器的潜在参数,进行图像重建,使得模型可以使用梯度进行端到端的训练重建损失。本研究扩展了原始的DVP,使其能够处理场景中的多个对象。同时,通过利用潜在的可解释性,使用解码器对额外的训练样本进行采样并设计替代训练模式,这些训练模式依赖于不仅在图像空间定义的损失函数,而且在潜在空间定义的损失函数。这极大地促进了训练,否则由于图像空间重建损失中存在大量高原而具有挑战性。为了检验该方法的效果,我们提出了一个包含多个二维对象的新基准测试,它既包含了先前提出的Multi-dSprites数据集又更具可参数化性。我们将扩展后的DVP与两个基准线(MONet和LIVE)进行比较,在重建质量和分解重叠对象方面表现出其优越性。同时分析了所考虑的损失函数引起的梯度,解释了它们对训练效果的影响以及针对自编码器中可微分渲染的局限性及其解决方法。
Key Takeaways
- 研究基于Disentangler of Visual Priors(DVP)架构进行扩展,使自编码器能够处理场景中的多个对象。
- 通过利用DVP的潜在可解释性,采用解码器采样额外训练样本并开发替代训练模式。
- 损失函数不仅在图像空间定义,而且在潜在空间定义,促进了训练过程。
- 引入了一个包含多个二维对象的新基准测试,以评估模型性能。
- 扩展后的DVP在重建质量和分解重叠对象方面优于其他模型。
- 分析了不同损失函数对训练效果的影响。
点此查看论文截图

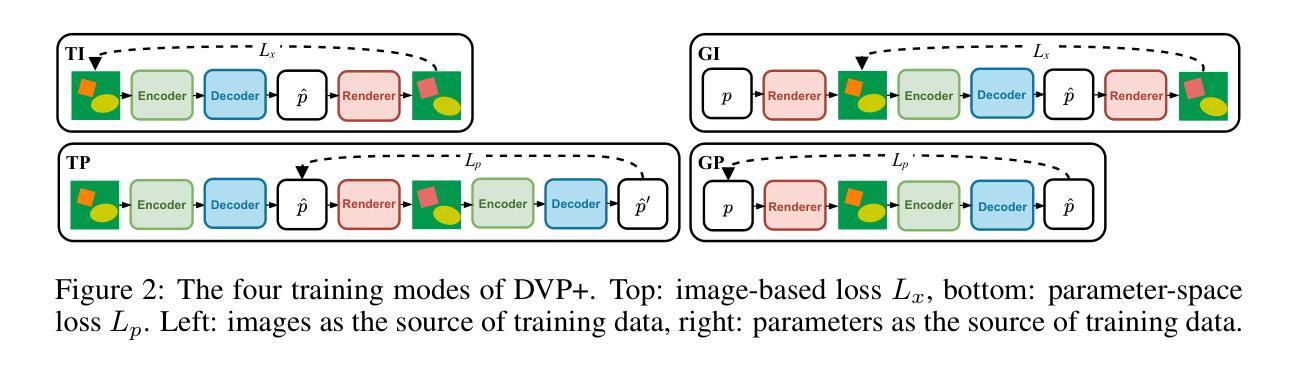
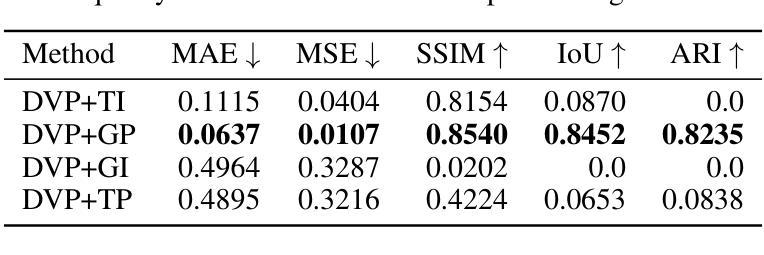
A System for Accurate Tracking and Video Recordings of Rodent Eye Movements using Convolutional Neural Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation
Authors:Isha Puri, David Cox
Research in neuroscience and vision science relies heavily on careful measurements of animal subject’s gaze direction. Rodents are the most widely studied animal subjects for such research because of their economic advantage and hardiness. Recently, video based eye trackers that use image processing techniques have become a popular option for gaze tracking because they are easy to use and are completely noninvasive. Although significant progress has been made in improving the accuracy and robustness of eye tracking algorithms, unfortunately, almost all of the techniques have focused on human eyes, which does not account for the unique characteristics of the rodent eye images, e.g., variability in eye parameters, abundance of surrounding hair, and their small size. To overcome these unique challenges, this work presents a flexible, robust, and highly accurate model for pupil and corneal reflection identification in rodent gaze determination that can be incrementally trained to account for variability in eye parameters encountered in the field. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first paper that demonstrates a highly accurate and practical biomedical image segmentation based convolutional neural network architecture for pupil and corneal reflection identification in eye images. This new method, in conjunction with our automated infrared videobased eye recording system, offers the state of the art technology in eye tracking for neuroscience and vision science research for rodents.
神经科学和视觉科学的研究在很大程度上依赖于对动物主体注视方向的精确测量。由于经济优势和适应性强的特点,啮齿动物是此类研究中最为广泛研究的动物对象。近期,基于视频的眼神跟踪器已变成一种流行的注视追踪选项,因为它易于使用并且完全无创。虽然眼神跟踪算法的准确性和稳健性已得到显著提高,但遗憾的是,几乎所有的技术都集中在人类眼睛上,并没有考虑到啮齿动物眼睛图像的独特特征,例如眼睛参数的变量、周围毛发的丰富以及它们的小尺寸。为了克服这些独特的挑战,这项工作提出了一个灵活、稳健和高度准确的模型,用于识别啮齿动物瞳孔和角膜反射以确定其注视方向,该模型可以逐步训练以适应现场遇到的眼睛参数变量。据我们所知,这是第一篇展示基于卷积神经网络架构的高度准确和实际可行的生物医学图像分割方法,用于识别眼睛图像中的瞳孔和角膜反射。这种新方法结合我们自动化的红外视频眼记录系统,为神经科学和视觉科学研究中啮齿动物的眼神跟踪提供了最先进的科技。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对啮齿动物眼动追踪研究的新模型。该模型基于图像处理技术,具有灵活性、鲁棒性和高精度,可识别瞳孔和角膜反射,并能逐步训练以适应野外遇到的眼参数变化。该模型克服了啮齿动物眼图像的独特挑战,如眼参数变化大、周围毛发丰富和尺寸小等。此模型的提出,将促进啮齿动物神经科学和视觉科学研究领域的眼动追踪技术发展。
Key Takeaways
- 该模型基于图像处理技术,用于识别啮齿动物的瞳孔和角膜反射。
- 该模型具有灵活性、鲁棒性和高精度,能适应野外眼参数的变化。
- 该模型能够逐步训练,克服啮齿动物眼图像的独特挑战。
- 此模型是首个针对啮齿动物眼图像中瞳孔和角膜反射识别的生物医学图像分割卷积神经网络架构。
- 此新方法与自动红外视频记录系统结合,为啮齿动物神经科学和视觉科学研究领域的眼动追踪提供了最先进的技术。
- 此模型的提出将促进眼动追踪技术的发展和应用。
点此查看论文截图

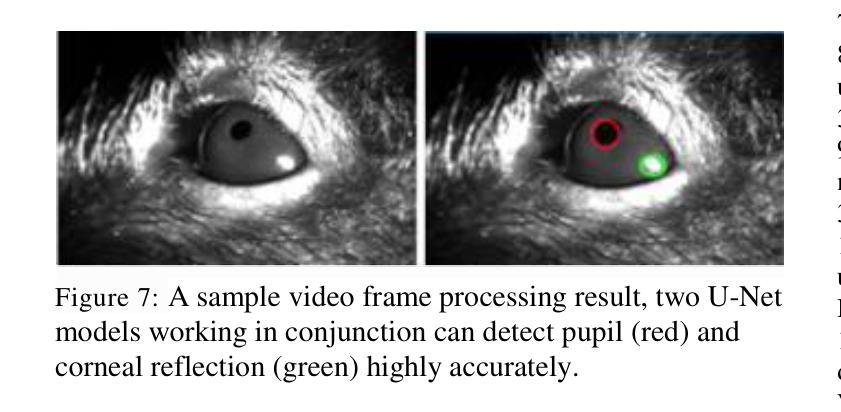
Zero-Shot Gaze-based Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Tatyana Shmykova, Leila Khaertdinova, Ilya Pershin
Accurate segmentation of anatomical structures in volumetric medical images is crucial for clinical applications, including disease monitoring and cancer treatment planning. Contemporary interactive segmentation models, such as Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM-2) and its medical variant (MedSAM-2), rely on manually provided prompts like bounding boxes and mouse clicks. In this study, we introduce eye gaze as a novel informational modality for interactive segmentation, marking the application of eye-tracking for 3D medical image segmentation. We evaluate the performance of using gaze-based prompts with SAM-2 and MedSAM-2 using both synthetic and real gaze data. Compared to bounding boxes, gaze-based prompts offer a time-efficient interaction approach with slightly lower segmentation quality. Our findings highlight the potential of using gaze as a complementary input modality for interactive 3D medical image segmentation.
在三维医学图像中对解剖结构进行准确的分割对于临床应用至关重要,包括疾病监测和癌症治疗计划。当代的交互式分割模型,如Segment Anything Model 2(SAM-2)及其医学变体(MedSAM-2),依赖于手动提供的提示,如边界框和鼠标点击。在这项研究中,我们引入眼动追踪作为一种新型信息模式,用于交互式分割,标志着眼动追踪在3D医学图像分割中的应用。我们使用合成和真实眼动数据评估了基于眼动提示的SAM-2和MedSAM-2的性能。与边界框相比,基于眼动的提示提供了一种时间效率高的交互方式,但分割质量略有下降。我们的研究结果表明,使用眼动作为一种补充输入模式进行交互式3D医学图像分割的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MMFM-BIOMED Workshop @ CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了在医学图像中准确分割解剖结构的重要性及其在疾病监测和癌症治疗计划等临床应用中的应用。研究引入了眼动追踪作为一种新型信息模态,用于交互式分割,并评估了其与Segment Anything Model 2(SAM-2)和MedSAM-2等当代交互式分割模型结合使用时的性能。与边界框相比,基于眼动的提示提供了一种时间效率高的交互方式,尽管分割质量略有下降。研究结果表明,眼动追踪在交互式三维医学图像分割中具有潜在的应用价值。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像中解剖结构的准确分割对于临床应用至关重要,如疾病监测和癌症治疗计划。
- 当前交互式分割模型如SAM-2和MedSAM-2依赖于手动提示,如边界框和鼠标点击。
- 研究引入了眼动追踪作为一种新型信息模态,用于三维医学图像分割的交互式操作。
- 基于眼动的提示与SAM-2和MedSAM-2结合使用时,表现出时间效率高的交互方式。
- 与边界框相比,基于眼动的提示虽然分割质量略有下降,但仍具有一定优势。
- 基于眼动的交互式三维医学图像分割具有潜在的应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

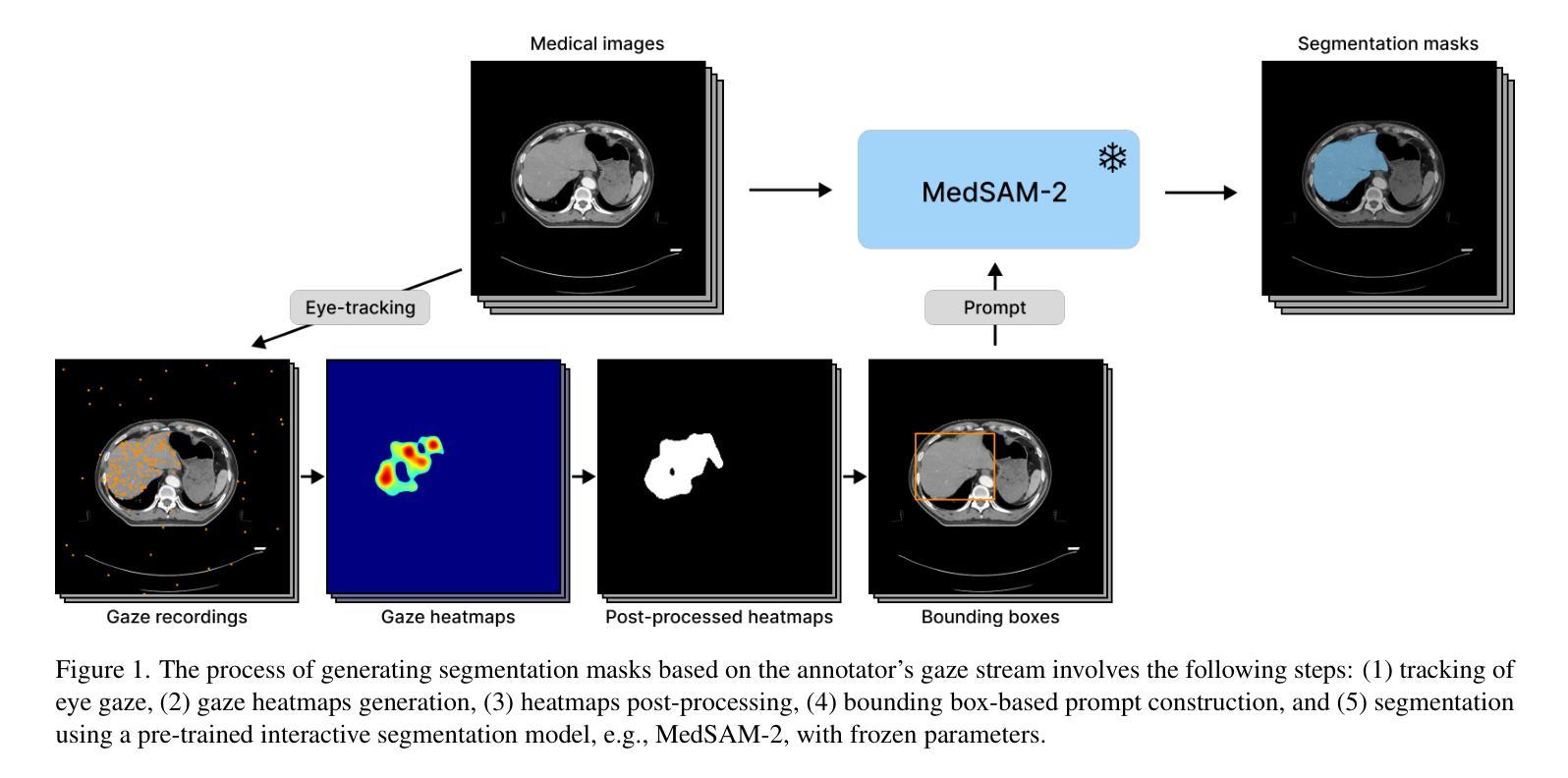
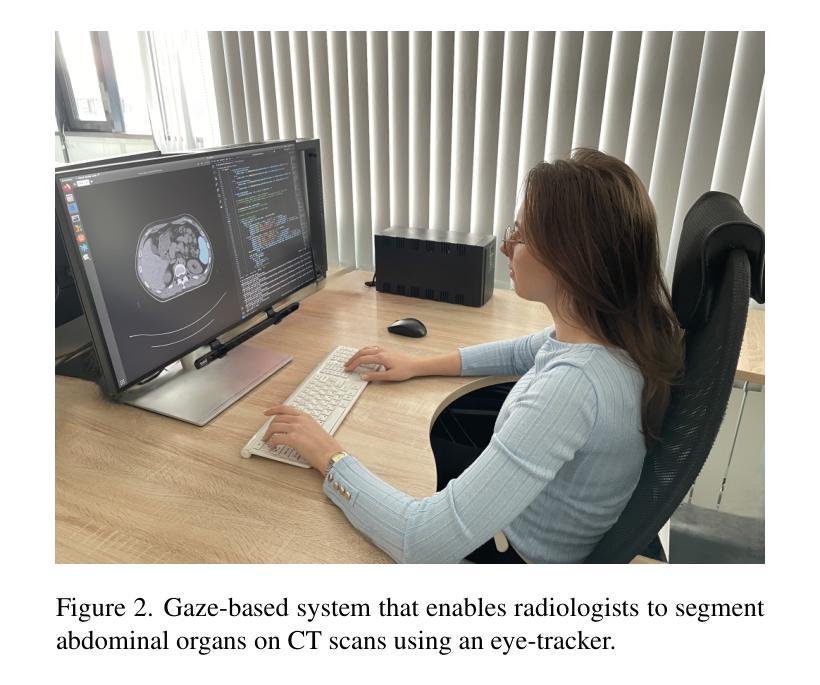
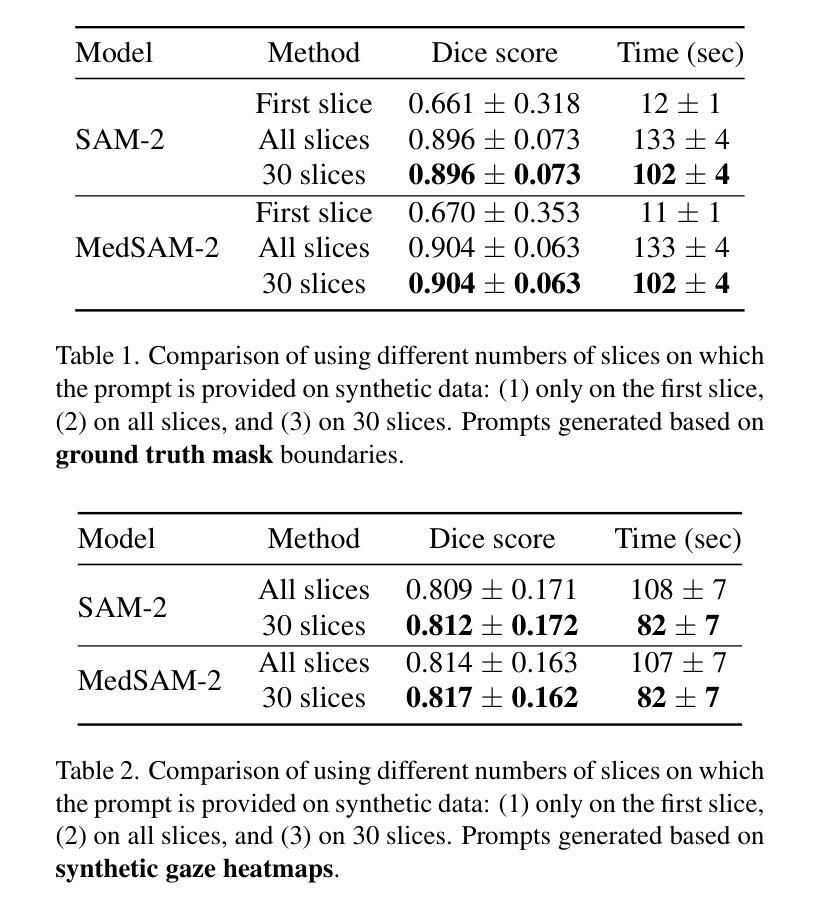
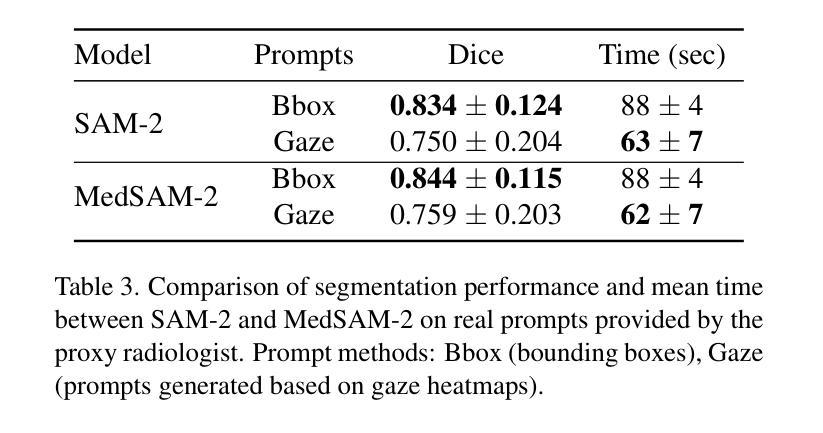
Curvature Tuning: Provable Training-free Model Steering From a Single Parameter
Authors:Leyang Hu, Matteo Gamba, Randall Balestriero
The scaling of model and data sizes has reshaped the AI landscape, establishing finetuning pretrained models as the standard paradigm for solving downstream tasks. However, dominant finetuning methods typically rely on weight adaptation, often lack interpretability, and depend on heuristically chosen hyperparameters. In this paper, we take a different perspective and shift the focus from weights to activation functions, viewing them through the lens of spline operators. We propose Curvature Tuning (CT), an interpretable and principled steering method that modulates a model’s decision boundary by injecting a single hyperparameter into its activation functions. We show that CT provably adjusts model decision boundary curvature and, more fundamentally, projects a model onto a space of smooth functions-thereby complementing current finetuning methods, whose effect lies primarily in feature adaptation. Making this hyperparameter trainable gives rise to a novel and highly parameter-efficient finetuning method. Empirically, CT improves both generalization and robustness. For example, it boosts downstream accuracy of ResNet-50/152 by 7.14%/8.46% over linear probing and 4.64%/1.70% over LoRA across 12 datasets, and improves robust accuracy on the $\ell_\infty$ benchmark from RobustBench by 1032.64%/1494.46%. Our code is available at https://github.com/Leon-Leyang/curvature-tuning.
模型的缩放和数据规模扩大已经重塑了人工智能领域,将微调预训练模型确立为解决下游任务的标准范式。然而,主流的微调方法通常依赖于权重适应,往往缺乏可解释性,并且依赖于启发式选择的超参数。在本文中,我们从不同的角度出发,将焦点从权重转向激活函数,通过样条算子的视角来审视它们。我们提出了曲率调整(CT),这是一种可解释且基于原则的控制方法,通过向激活函数注入单个超参数来调节模型的决策边界。我们证明了CT能够可靠地调整模型的决策边界曲率,并且更根本的是,它将模型投影到平滑函数空间上,从而弥补了当前微调方法主要在特征适应方面的不足。使这个超参数可训练,从而产生了一种新型且高度参数有效的微调方法。经验上,CT提高了泛化和稳健性。例如,在12个数据集上,相对于线性探测和LoRA,它分别将ResNet-50/152的下游精度提高了7.14%/8.46%和4.64%/1.70%,并在RobustBench的l∞基准上提高了稳健精度达1032.64%/1494.46%。我们的代码位于https://github.com/Leon-Leyang/curvature-tuning。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了模型和数据规模的扩展对人工智能领域的影响,并指出微调预训练模型已成为解决下游任务的标准范式。然而,主流微调方法通常依赖于权重适应,缺乏可解释性,并依赖于启发式选择的超参数。本文提出了一种新的可调曲率方法——曲率调整(CT),它通过向激活函数注入单一超参数,以一种可解释和原则性的方式调节模型的决策边界。CT可证明地调整模型决策边界的曲率,并将模型投影到平滑函数空间,从而弥补了当前微调方法主要侧重于特征适应的不足。通过使这个超参数可训练,CT成为了一种新型且高度参数有效的微调方法。实证结果表明,CT提高了模型的泛化和鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 主流微调方法主要依赖权重适应,缺乏可解释性。
- 曲率调整(CT)是一种新型的微调方法,侧重于通过激活函数进行模型调整。
- CT通过注入单一超参数到激活函数中,以可解释和原则性的方式调节模型的决策边界。
- CT能够证明地调整模型决策边界的曲率,并将模型投影到平滑函数空间。
- 与传统微调方法相比,CT在特征适应的基础上进行了补充。
- 通过使超参数可训练,CT是一种参数高效的微调方法。
点此查看论文截图

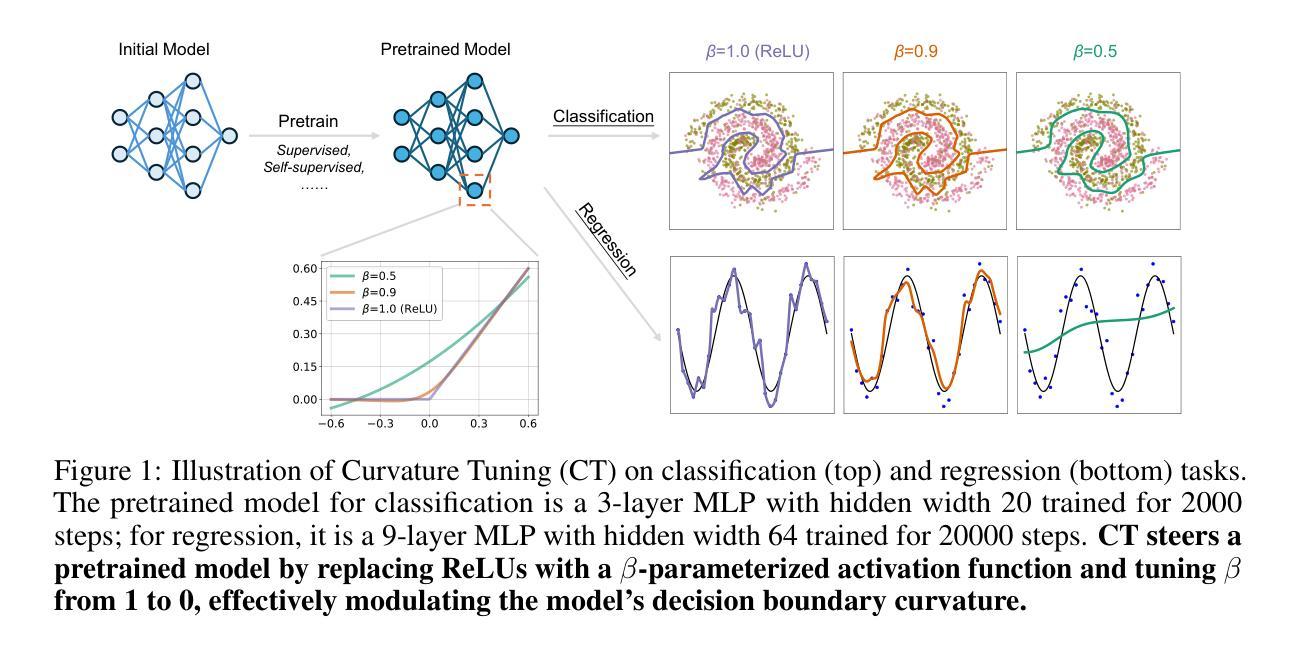
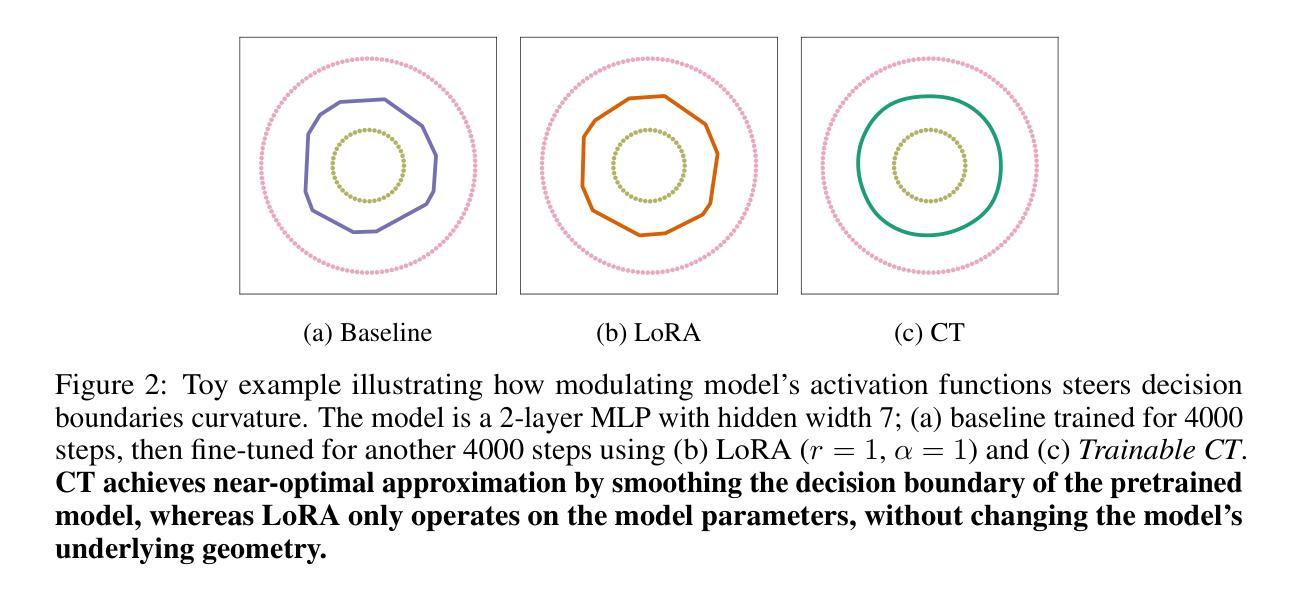
LLM-HDR: Bridging LLM-based Perception and Self-Supervision for Unpaired LDR-to-HDR Image Reconstruction
Authors:Hrishav Bakul Barua, Kalin Stefanov, Lemuel Lai En Che, Abhinav Dhall, KokSheik Wong, Ganesh Krishnasamy
The translation of Low Dynamic Range (LDR) to High Dynamic Range (HDR) images is an important computer vision task. There is a significant amount of research utilizing both conventional non-learning methods and modern data-driven approaches, focusing on using both single-exposed and multi-exposed LDR for HDR image reconstruction. However, most current state-of-the-art methods require high-quality paired {LDR,HDR} datasets for model training. In addition, there is limited literature on using unpaired datasets for this task, that is, the model learns a mapping between domains, i.e., {LDR,HDR}. This paper proposes LLM-HDR, a method that integrates the perception of Large Language Models (LLM) into a modified semantic- and cycle-consistent adversarial architecture that utilizes unpaired {LDR,HDR} datasets for training. The method introduces novel artifact- and exposure-aware generators to address visual artifact removal and an encoder and loss to address semantic consistency, another under-explored topic. LLM-HDR is the first to use an LLM for the {LDR,HDR} translation task in a self-supervised setup. The method achieves state-of-the-art performance across several benchmark datasets and reconstructs high-quality HDR images. The official website of this work is available at: https://github.com/HrishavBakulBarua/LLM-HDR
将低动态范围(LDR)图像转换为高动态范围(HDR)图像是一项重要的计算机视觉任务。许多研究都利用传统的非学习方法和现代的数据驱动方法,侧重于使用单曝光和多曝光的LDR来进行HDR图像重建。然而,大多数当前最前沿的方法都需要高质量成对的{LDR,HDR}数据集来进行模型训练。此外,关于使用未配对数据集进行此任务的文献很少,也就是说,模型学习域之间的映射,即{LDR,HDR}。本文提出了LLM-HDR方法,它将大型语言模型(LLM)的感知能力融入到一个经过修改的语义和循环一致的对抗架构中,该架构利用未配对的{LDR,HDR}数据集进行训练。该方法引入了新型伪影和曝光感知生成器来解决视觉伪影去除问题,以及一个编码器和损失来解决语义一致性这一尚未被深入探讨的问题。LLM-HDR是第一个在自我监督设置中使用LLM进行{LDR,HDR}翻译任务的方法。该方法在多个基准数据集上实现了最先进的性能,并重建了高质量的HDR图像。该工作的官方网站可访问:https://github.com/HrishavBakulBarua/LLM-HDR
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种结合大型语言模型感知的LDR到HDR图像翻译方法,采用无配对数据集进行训练,通过语义一致性和循环一致的对抗性架构实现图像重建。该方法引入新的伪影感知和曝光感知生成器以解决视觉伪影问题,并使用编码器解决语义一致性难题。LLM-HDR在多个基准数据集上实现最佳性能,可重建高质量HDR图像。
Key Takeaways
- LDR到HDR图像翻译是计算机视觉的重要任务,现有方法大多需要高质量配对数据集进行模型训练。
- 本文提出LLM-HDR方法,首次在自监督设置中使用大型语言模型(LLM)进行LDR到HDR的翻译任务。
- LLM-HDR结合感知语义和循环一致的对抗性架构,使用无配对数据集进行训练。
- 方法引入伪影感知和曝光感知生成器以解决视觉伪影问题。
- LLM-HDR使用编码器解决语义一致性难题,这是一个之前未被充分探索的主题。
- 该方法在多个基准数据集上实现最佳性能,能够重建高质量HDR图像。
点此查看论文截图


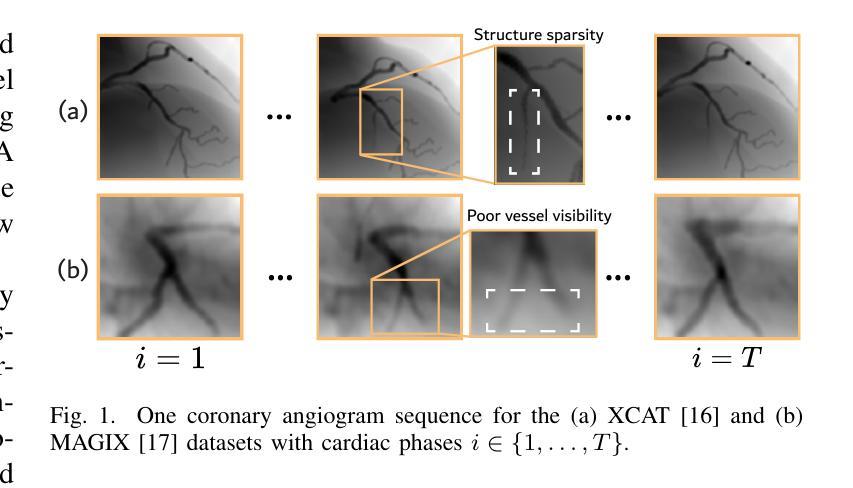
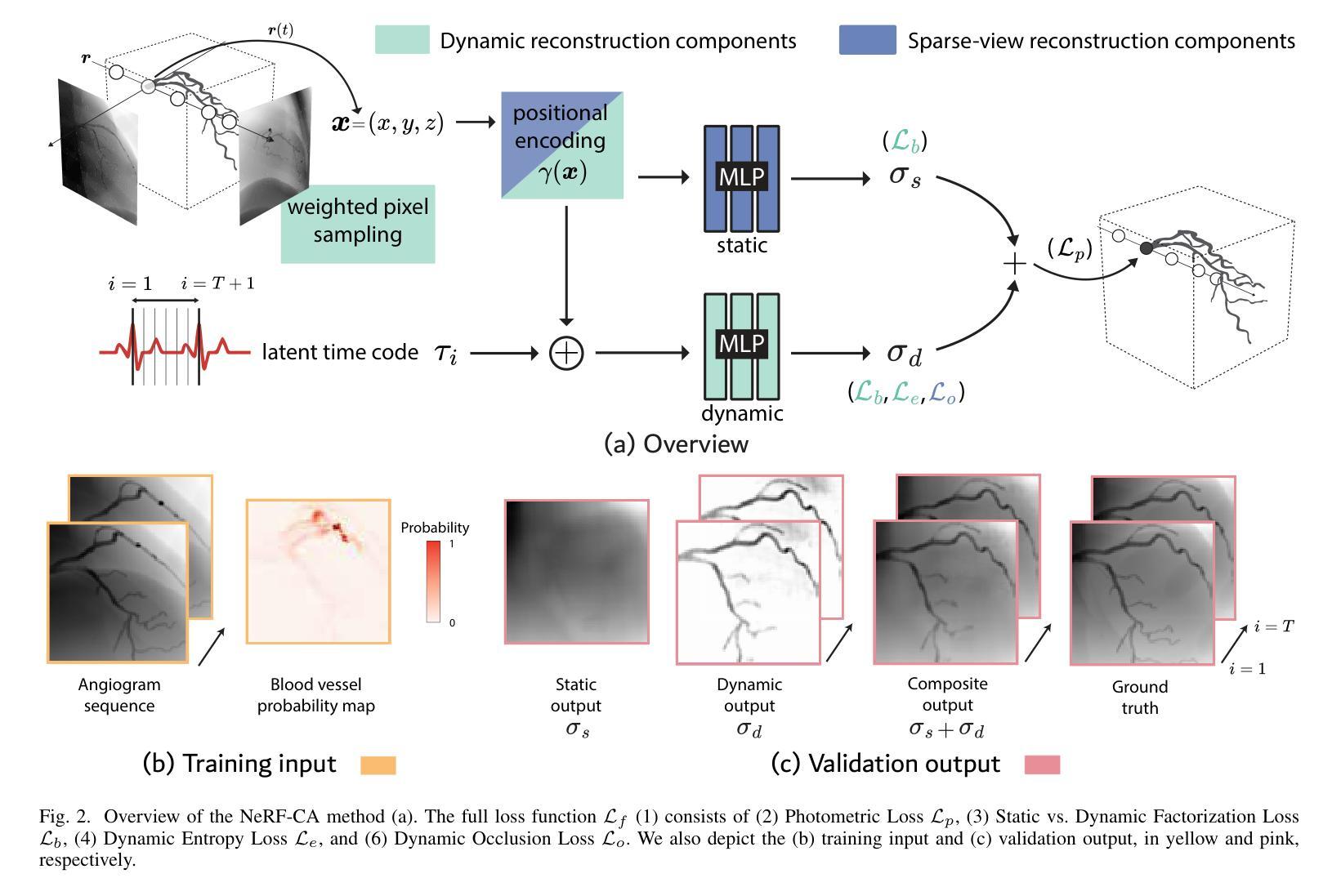
NeRF-CA: Dynamic Reconstruction of X-ray Coronary Angiography with Extremely Sparse-views
Authors:Kirsten W. H. Maas, Danny Ruijters, Anna Vilanova, Nicola Pezzotti
Dynamic three-dimensional (4D) reconstruction from two-dimensional X-ray coronary angiography (CA) remains a significant clinical problem. Existing CA reconstruction methods often require extensive user interaction or large training datasets. Recently, Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) has successfully reconstructed high-fidelity scenes in natural and medical contexts without these requirements. However, challenges such as sparse-views, intra-scan motion, and complex vessel morphology hinder its direct application to CA data. We introduce NeRF-CA, a first step toward a fully automatic 4D CA reconstruction that achieves reconstructions from sparse coronary angiograms. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to address the challenges of sparse-views and cardiac motion by decoupling the scene into the moving coronary artery and the static background, effectively translating the problem of motion into a strength. NeRF-CA serves as a first stepping stone for solving the 4D CA reconstruction problem, achieving adequate 4D reconstructions from as few as four angiograms, as required by clinical practice, while significantly outperforming state-of-the-art sparse-view X-ray NeRF. We validate our approach quantitatively and qualitatively using representative 4D phantom datasets and ablation studies. To accelerate research in this domain, we made our codebase public: https://github.com/kirstenmaas/NeRF-CA.
从二维X射线冠状动脉造影(CA)进行动态三维(4D)重建仍然是临床上的一个重大问题。现有的CA重建方法通常需要大量的用户交互或大量的训练数据集。最近,神经辐射场(NeRF)成功地重建了自然和医学背景下的高保真场景,而无需这些要求。然而,稀疏视图、扫描内运动以及复杂的血管形态等挑战阻碍了其直接应用于CA数据。我们引入了NeRF-CA,这是朝着全自动4D CA重建的第一步,实现了从稀疏冠状动脉造影图像进行重建。据我们所知,我们是第一个通过将场景解耦为移动的冠状动脉和静态背景来解决稀疏视图和心脏运动挑战的团队,有效地将运动问题转化为优势。NeRF-CA作为解决4D CA重建问题的第一步,能够从临床实践中所需的仅四张造影图像实现足够的4D重建,并且显著优于最先进的稀疏视图X射线NeRF。我们使用具有代表性的4D Phantom数据集和消融研究进行定量和定性的验证。为了加速该领域的研究,我们公开了我们的代码库:https://github.com/kirstenmaas/NeRF-CA。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了利用神经网络辐射场(NeRF)技术进行二维X光冠状动脉造影(CA)的动态三维(4D)重建的方法。通过解决稀疏视图和心脏运动等挑战,NeRF-CA方法实现了从少量冠状动脉造影图像中的重建。该方法将场景分解为运动的冠状动脉和静态背景,成功转化运动问题为优势。相比现有的稀疏视图X光NeRF,NeRF-CA表现出更出色的性能,已经在代表性4D Phantom数据集上进行了定量和定性的验证。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF-CA是利用神经网络辐射场(NeRF)技术实现二维X光冠状动脉造影(CA)动态三维(4D)重建的首次尝试。
- NeRF-CA解决了稀疏视图和心脏运动等挑战,实现了从少量冠状动脉造影图像中的重建。
- 该方法通过将场景分解为运动的冠状动脉和静态背景,成功转化运动问题为优势。
- NeRF-CA方法实现了从仅四个冠状动脉造影图像进行重建,满足了临床实践的需求。
- 与现有的稀疏视图X光NeRF相比,NeRF-CA显著提高了性能。
- NeRF-CA已在代表性4D Phantom数据集上进行了定量和定性的验证。
点此查看论文截图

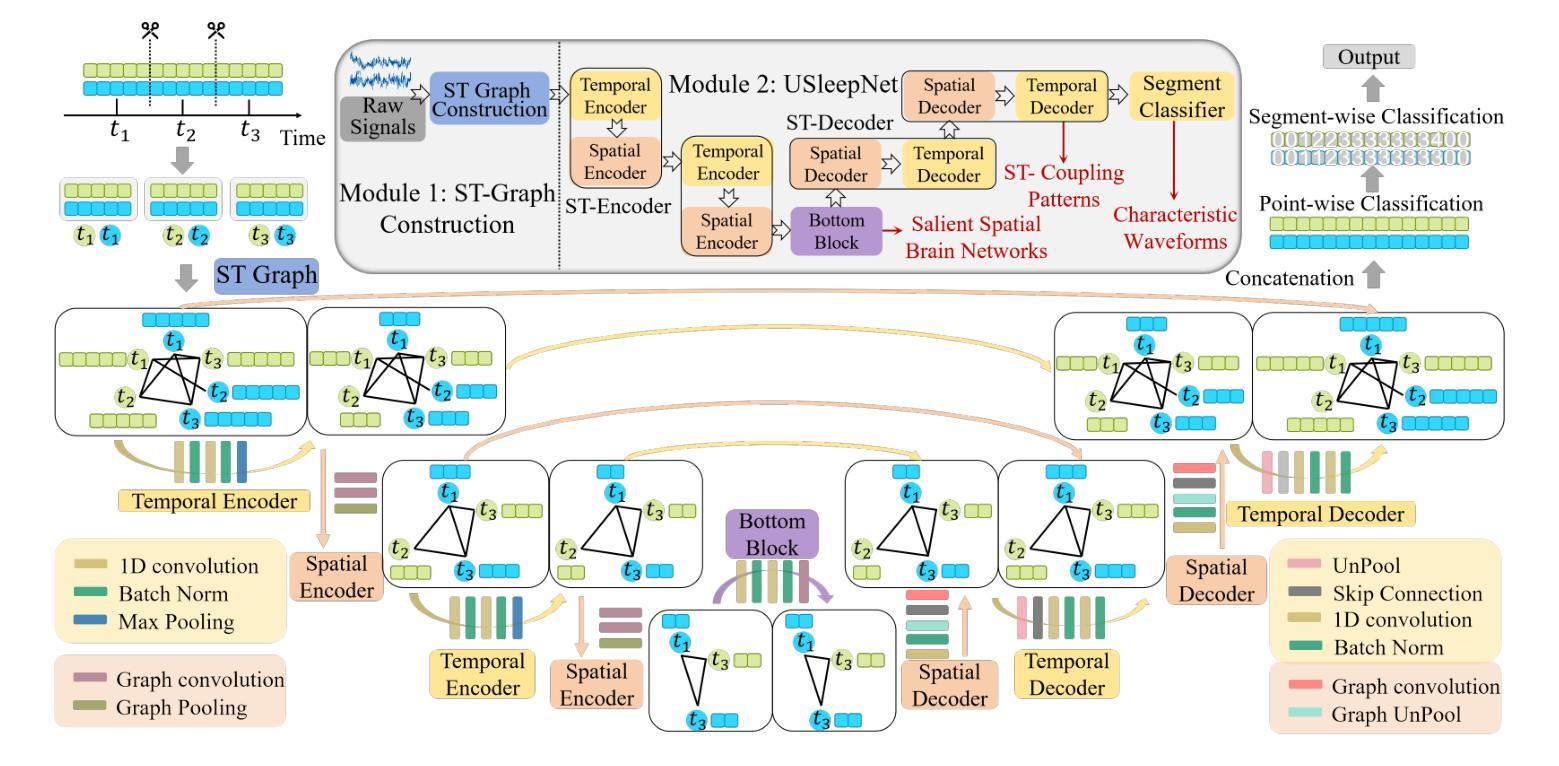
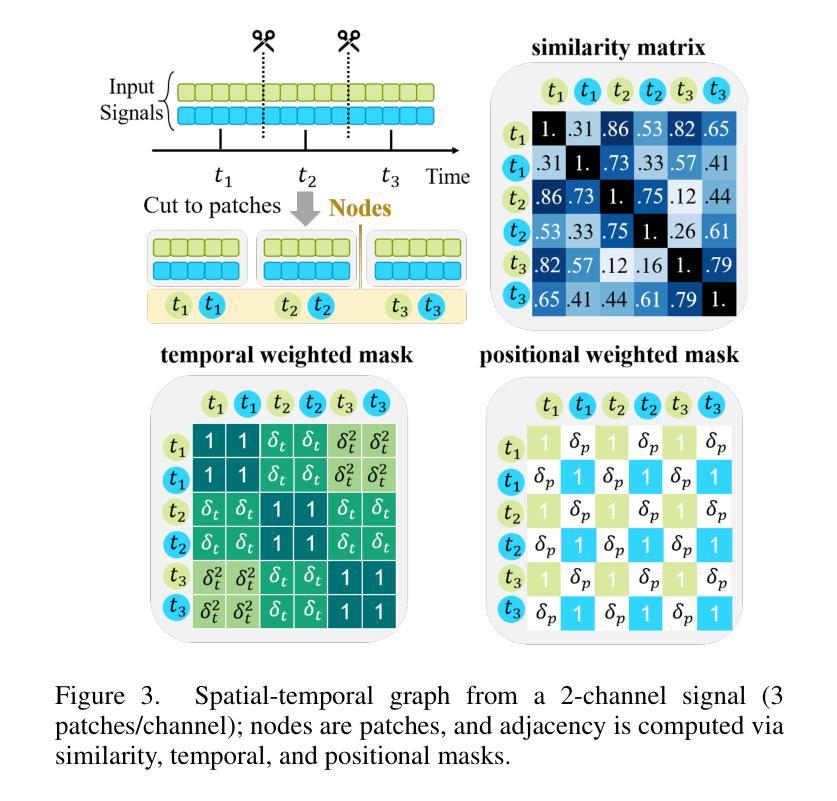
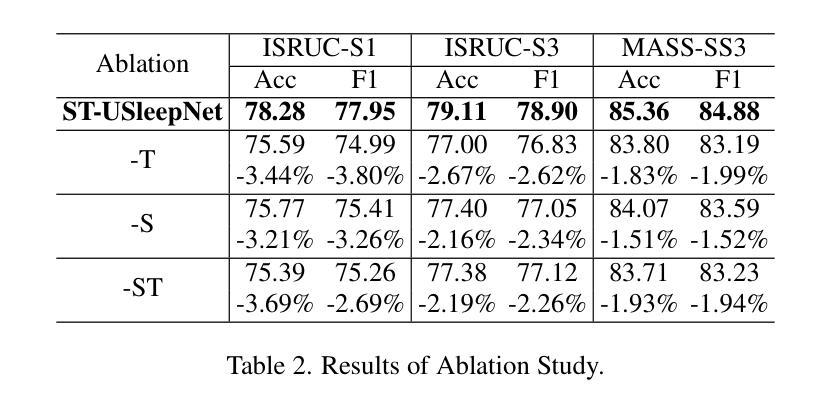
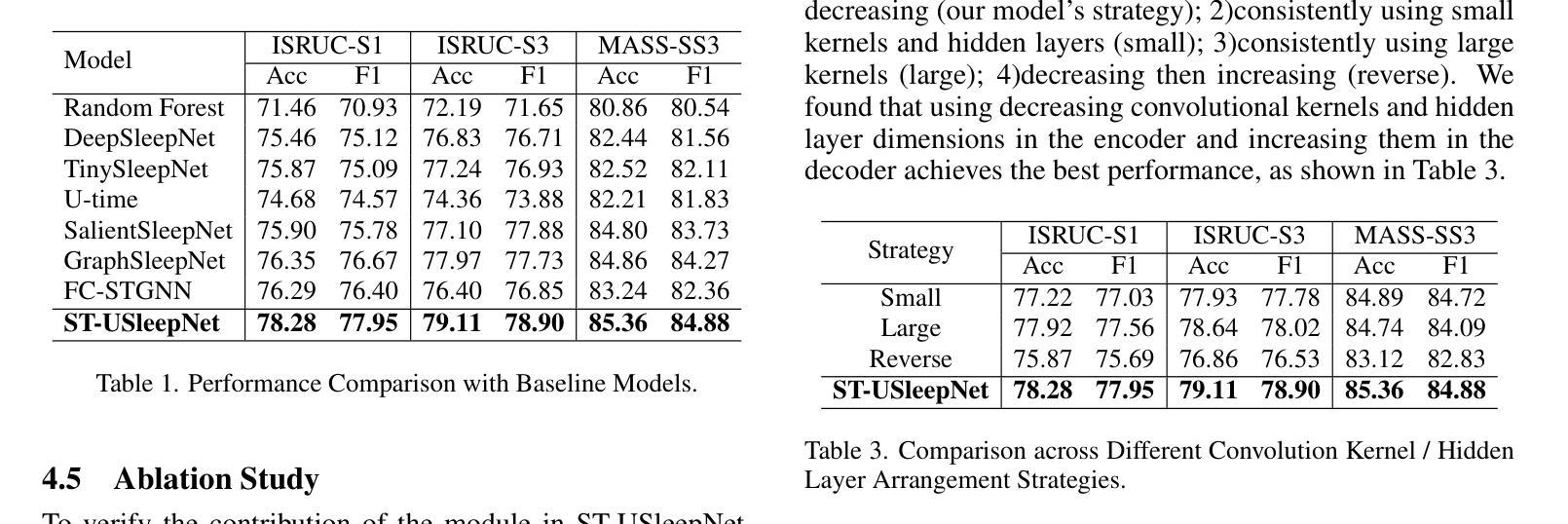
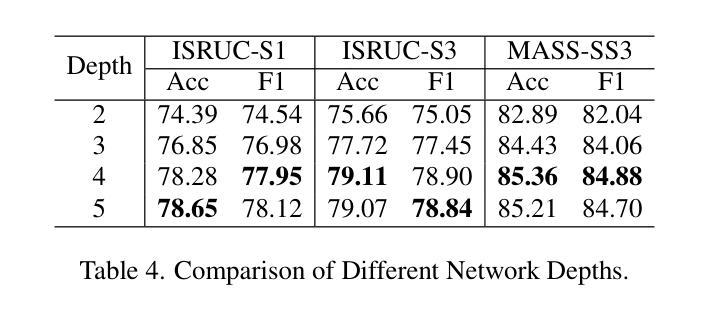
ST-USleepNet: A Spatial-Temporal Coupling Prominence Network for Multi-Channel Sleep Staging
Authors:Jingying Ma, Qika Lin, Ziyu Jia, Mengling Feng
Sleep staging is critical to assess sleep quality and diagnose disorders. Despite advancements in artificial intelligence enabling automated sleep staging, significant challenges remain: (1) Simultaneously extracting prominent temporal and spatial sleep features from multi-channel raw signals, including characteristic sleep waveforms and salient spatial brain networks. (2) Capturing the spatial-temporal coupling patterns essential for accurate sleep staging. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework named ST-USleepNet, comprising a spatial-temporal graph construction module (ST) and a U-shaped sleep network (USleepNet). The ST module converts raw signals into a spatial-temporal graph based on signal similarity, temporal, and spatial relationships to model spatial-temporal coupling patterns. The USleepNet employs a U-shaped structure for both the temporal and spatial streams, mirroring its original use in image segmentation to isolate significant targets. Applied to raw sleep signals and graph data from the ST module, USleepNet effectively segments these inputs, simultaneously extracting prominent temporal and spatial sleep features. Testing on three datasets demonstrates that ST-USleepNet outperforms existing baselines, and model visualizations confirm its efficacy in extracting prominent sleep features and temporal-spatial coupling patterns across various sleep stages. The code is available at https://github.com/Majy-Yuji/ST-USleepNet.
睡眠分期对于评估睡眠质量和诊断睡眠障碍至关重要。尽管人工智能的进步已经实现了自动化的睡眠分期,但仍存在重大挑战:(1) 从多通道原始信号中同时提取突出的时间和空间睡眠特征,包括特征睡眠波形和显著的脑空间网络。(2) 捕捉对准确睡眠分期至关重要的时空耦合模式。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种名为ST-USleepNet的新型框架,它包含一个时空图构建模块(ST)和一个U型睡眠网络(USleepNet)。ST模块根据信号相似性、时间和空空间关系将原始信号转换为时空图,以模拟时空耦合模式。USleepNet采用U型结构,用于时间和空空间流,模仿其在图像分割中的原始用途,以隔离重要目标。应用于来自ST模块的原始睡眠信号和图形数据,USleepNet可以有效地对这些输入进行分段,同时提取突出的时空睡眠特征。在三个数据集上的测试表明,ST-USleepNet优于现有基线,模型可视化证实了其在提取各种睡眠阶段的突出睡眠特征和时空耦合模式方面的有效性。代码可在https://github.com/Majy-Yuji/ST-USleepNet获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
睡眠分期是评估睡眠质量和诊断睡眠障碍的关键。针对人工智能在自动睡眠分期上面临的同时提取重要时间-空间特征和捕捉时空耦合模式等挑战,提出了一种新的框架ST-USleepNet,包括时空图构建模块(ST)和U型睡眠网络(USleepNet)。该框架在三个数据集上的测试表现优于现有基线,可有效提取重要睡眠特征和时空耦合模式。
Key Takeaways
- 睡眠分期是评估睡眠质量和诊断睡眠障碍的关键。
- 目前在自动睡眠分期上,存在同时提取重要时间-空间特征和捕捉时空耦合模式的挑战。
- ST-USleepNet框架包括时空图构建模块(ST)和U型睡眠网络(USleepNet)。
- ST模块将原始信号转换为基于信号相似性的时空图,以建模时空耦合模式。
- USleepNet采用U型结构,同时处理时间和空间流,以隔离重要目标。
- ST-USleepNet在三个数据集上的测试表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图