⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-13 更新
The Four Color Theorem for Cell Instance Segmentation
Authors:Ye Zhang, Yu Zhou, Yifeng Wang, Jun Xiao, Ziyue Wang, Yongbing Zhang, Jianxu Chen
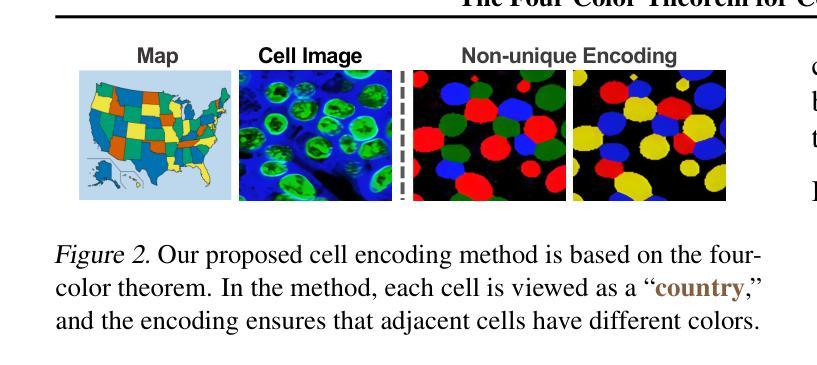
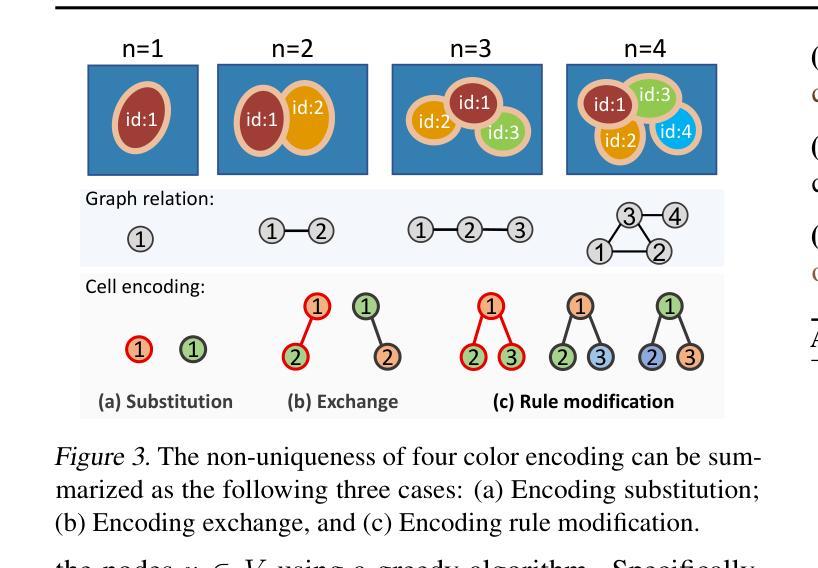
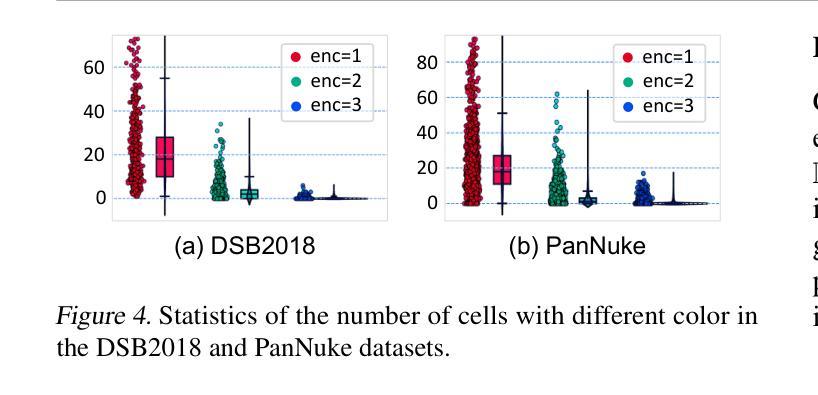
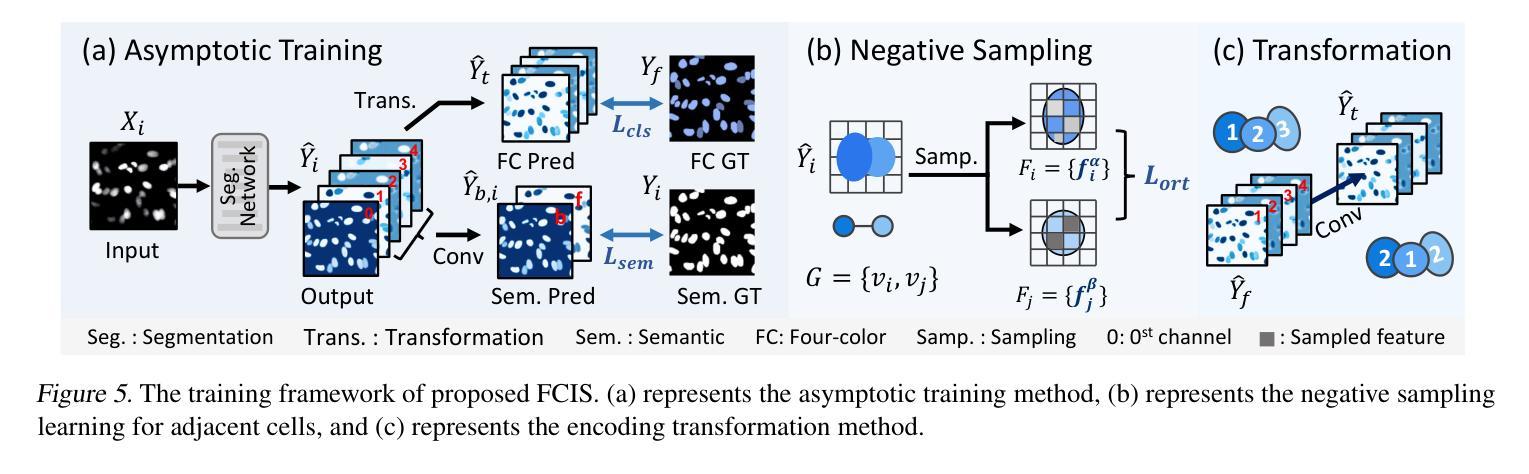
Cell instance segmentation is critical to analyzing biomedical images, yet accurately distinguishing tightly touching cells remains a persistent challenge. Existing instance segmentation frameworks, including detection-based, contour-based, and distance mapping-based approaches, have made significant progress, but balancing model performance with computational efficiency remains an open problem. In this paper, we propose a novel cell instance segmentation method inspired by the four-color theorem. By conceptualizing cells as countries and tissues as oceans, we introduce a four-color encoding scheme that ensures adjacent instances receive distinct labels. This reformulation transforms instance segmentation into a constrained semantic segmentation problem with only four predicted classes, substantially simplifying the instance differentiation process. To solve the training instability caused by the non-uniqueness of four-color encoding, we design an asymptotic training strategy and encoding transformation method. Extensive experiments on various modes demonstrate our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance. The code is available at https://github.com/zhangye-zoe/FCIS.
细胞实例分割对于分析生物医学图像至关重要,然而,准确区分紧密接触的细胞仍然是一个持续存在的挑战。现有的实例分割框架,包括基于检测的方法、基于轮廓的方法和基于距离映射的方法,都取得了重大进展,但如何在模型性能和计算效率之间取得平衡仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。在本文中,我们受到四色定理的启发,提出了一种新的细胞实例分割方法。我们通过将细胞概念化为国家、组织概念化为海洋,引入了一种四色编码方案,确保相邻实例获得不同的标签。这种重新表述将实例分割转化为一个具有四个预测类的约束语义分割问题,极大地简化了实例区分过程。为了解决由四色编码的非唯一性引起的训练不稳定问题,我们设计了一种渐进的训练策略和编码转换方法。在各种模式下的广泛实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的性能。代码可在https://github.com/zhangye-zoe/FCIS中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICML 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于四色定理的新型细胞实例分割方法。通过将细胞概念化为国家并将组织概念化为海洋,引入了一种四色编码方案,确保相邻实例获得不同的标签。该方法将实例分割转化为具有四个预测类的约束语义分割问题,简化了实例区分过程。通过设计渐进训练策略和编码转换方法解决了由四色编码的非唯一性引起的训练不稳定问题。在多种模式下的广泛实验表明,该方法达到了最新性能水平。
Key Takeaways
- 细胞实例分割是生物医学图像分析的关键挑战之一,尤其是在区分紧密接触的细胞时。
- 本文提出了一种基于四色定理的细胞实例分割方法,通过概念化细胞和组织的形象比喻来实现实例分割。
- 引入四色编码方案,确保相邻实例获得不同标签,将实例分割问题简化为约束语义分割问题。
- 设计了渐进训练策略和编码转换方法来解决由四色编码非唯一性引起的训练不稳定问题。
- 广泛实验证明该方法达到了最新性能水平。
点此查看论文截图

3DGeoDet: General-purpose Geometry-aware Image-based 3D Object Detection
Authors:Yi Zhang, Yi Wang, Yawen Cui, Lap-Pui Chau
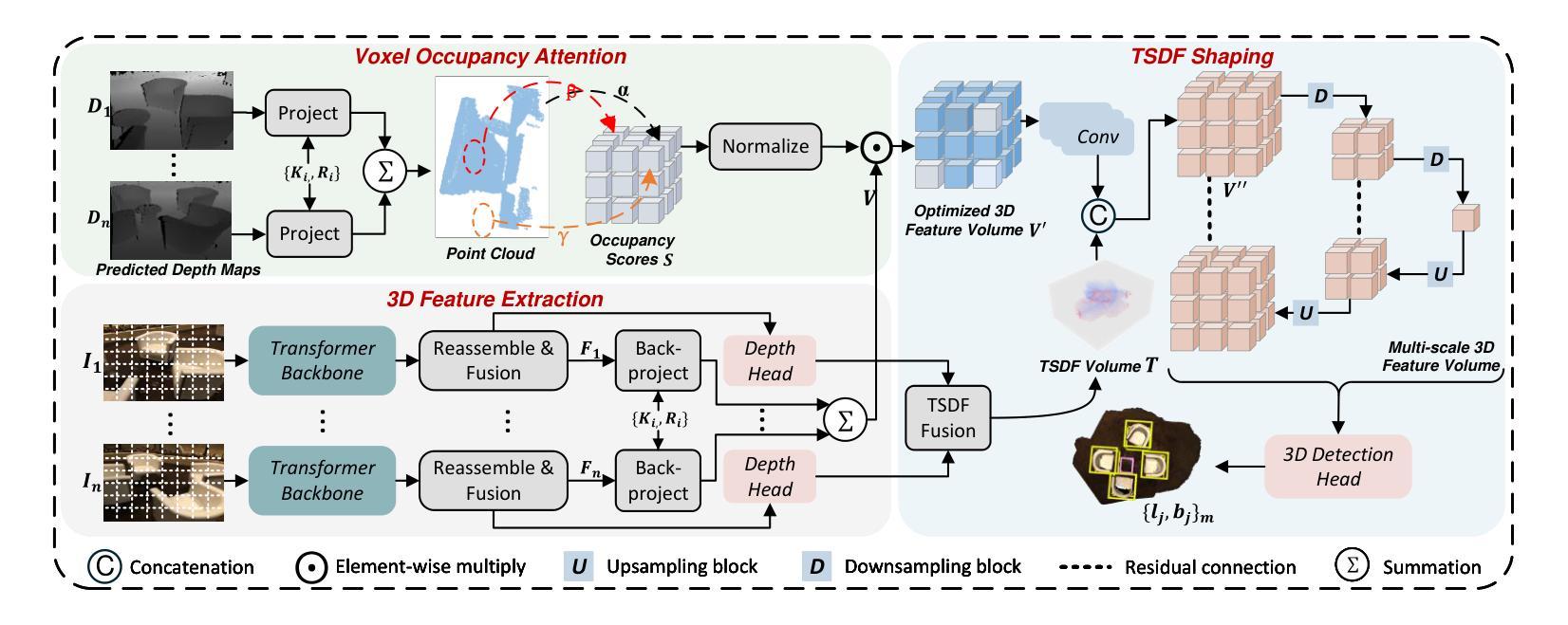
This paper proposes 3DGeoDet, a novel geometry-aware 3D object detection approach that effectively handles single- and multi-view RGB images in indoor and outdoor environments, showcasing its general-purpose applicability. The key challenge for image-based 3D object detection tasks is the lack of 3D geometric cues, which leads to ambiguity in establishing correspondences between images and 3D representations. To tackle this problem, 3DGeoDet generates efficient 3D geometric representations in both explicit and implicit manners based on predicted depth information. Specifically, we utilize the predicted depth to learn voxel occupancy and optimize the voxelized 3D feature volume explicitly through the proposed voxel occupancy attention. To further enhance 3D awareness, the feature volume is integrated with an implicit 3D representation, the truncated signed distance function (TSDF). Without requiring supervision from 3D signals, we significantly improve the model’s comprehension of 3D geometry by leveraging intermediate 3D representations and achieve end-to-end training. Our approach surpasses the performance of state-of-the-art image-based methods on both single- and multi-view benchmark datasets across diverse environments, achieving a 9.3 mAP@0.5 improvement on the SUN RGB-D dataset, a 3.3 mAP@0.5 improvement on the ScanNetV2 dataset, and a 0.19 AP3D@0.7 improvement on the KITTI dataset. The project page is available at: https://cindy0725.github.io/3DGeoDet/.
本文提出了名为3DGeoDet的新型几何感知三维物体检测方案。该方案能有效处理室内外环境的单视图和多视图RGB图像,展示了其通用适用性。基于图像的三维物体检测任务的关键挑战在于缺乏三维几何线索,这导致在图像和三维表示之间建立对应关系的模糊性。为了解决这个问题,3DGeoDet以显式性和隐式性的方式生成高效的三维几何表示,基于预测的深度信息。具体来说,我们利用预测的深度来学习体素占用情况,并通过提出的体素占用注意力来优化体素化的三维特征体积。为了进一步增强三维感知能力,我们将特征体积与隐式三维表示——截断有向距离函数(TSDF)相结合。我们不需要三维信号的监督,通过利用中间三维表示来实现端到端的训练,显著提高了模型对三维几何的理解。我们的方法在单视图和多视图基准数据集上的性能超过了最先进的方法,在SUN RGB-D数据集上提高了9.3 mAP@0.5,在ScanNetV2数据集上提高了3.3 mAP@0.5,在KITTI数据集上提高了0.19 AP3D@0.7。项目页面可访问于:[https://cindy0725.github.io/3DGeoDet/] 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Multimedia
Summary
本文提出了一种名为3DGeoDet的新型几何感知三维物体检测方法,该方法可有效处理室内外环境的单视图和多视图RGB图像,展示了其通用适用性。针对基于图像的三维物体检测任务中缺乏三维几何线索的挑战,3DGeoDet通过预测的深度信息以显式与隐式的方式生成高效的三维几何表示。具体来说,它利用预测的深度来学习体素占用情况,并通过提出的体素占用注意力来优化体素化的三维特征体积。为进一步增强三维感知能力,该方法还将特征体积与隐式三维表示——截断签名距离函数(TSDF)相结合。在不需要三维信号监督的情况下,它通过利用中间三维表示实现了端到端的训练,显著提高了模型对三维几何的理解能力。该方法在单视图和多视图基准数据集上的性能均超越了现有基于图像的方法,在SUN RGB-D数据集上提高了9.3 mAP@0.5,在ScanNetV2数据集上提高了3.3 mAP@0.5,在KITTI数据集上提高了0.19 AP3D@0.7。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGeoDet是一种新型的几何感知三维物体检测方法,适用于室内外环境的单视图和多视图RGB图像。
- 该方法通过预测的深度信息生成三维几何表示,包括显式(体素占用)和隐式(截断签名距离函数)方式。
- 利用体素占用注意力优化体素化的三维特征体积,增强三维感知能力。
- 通过利用中间三维表示,实现了在不需要三维信号监督下的端到端训练。
点此查看论文截图


RS-MTDF: Multi-Teacher Distillation and Fusion for Remote Sensing Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Jiayi Song, Kaiyu Li, Xiangyong Cao, Deyu Meng
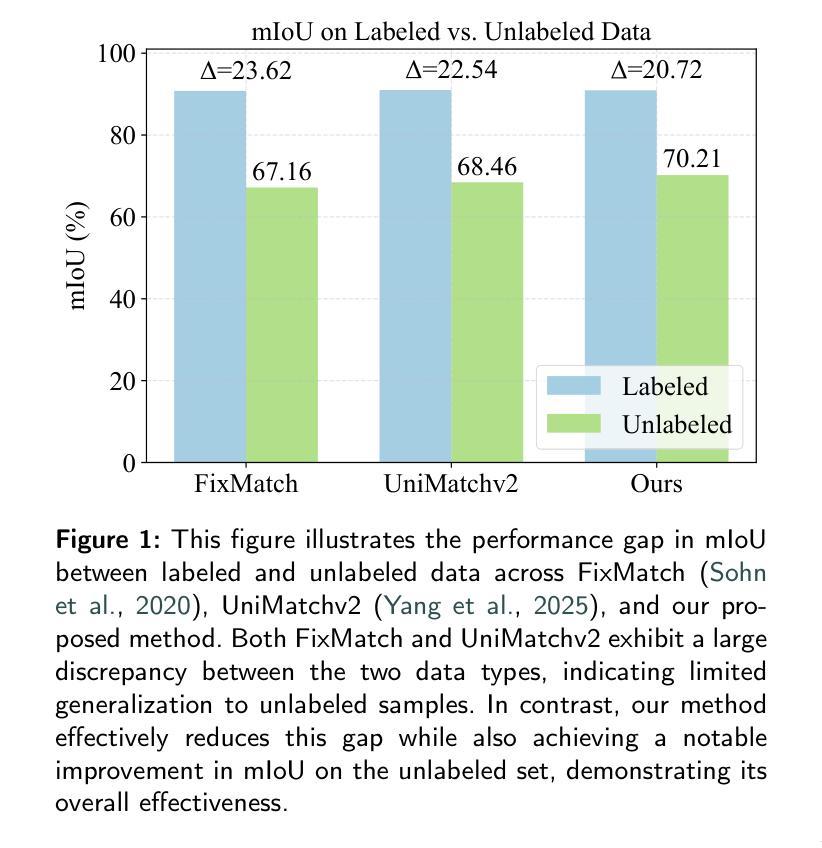
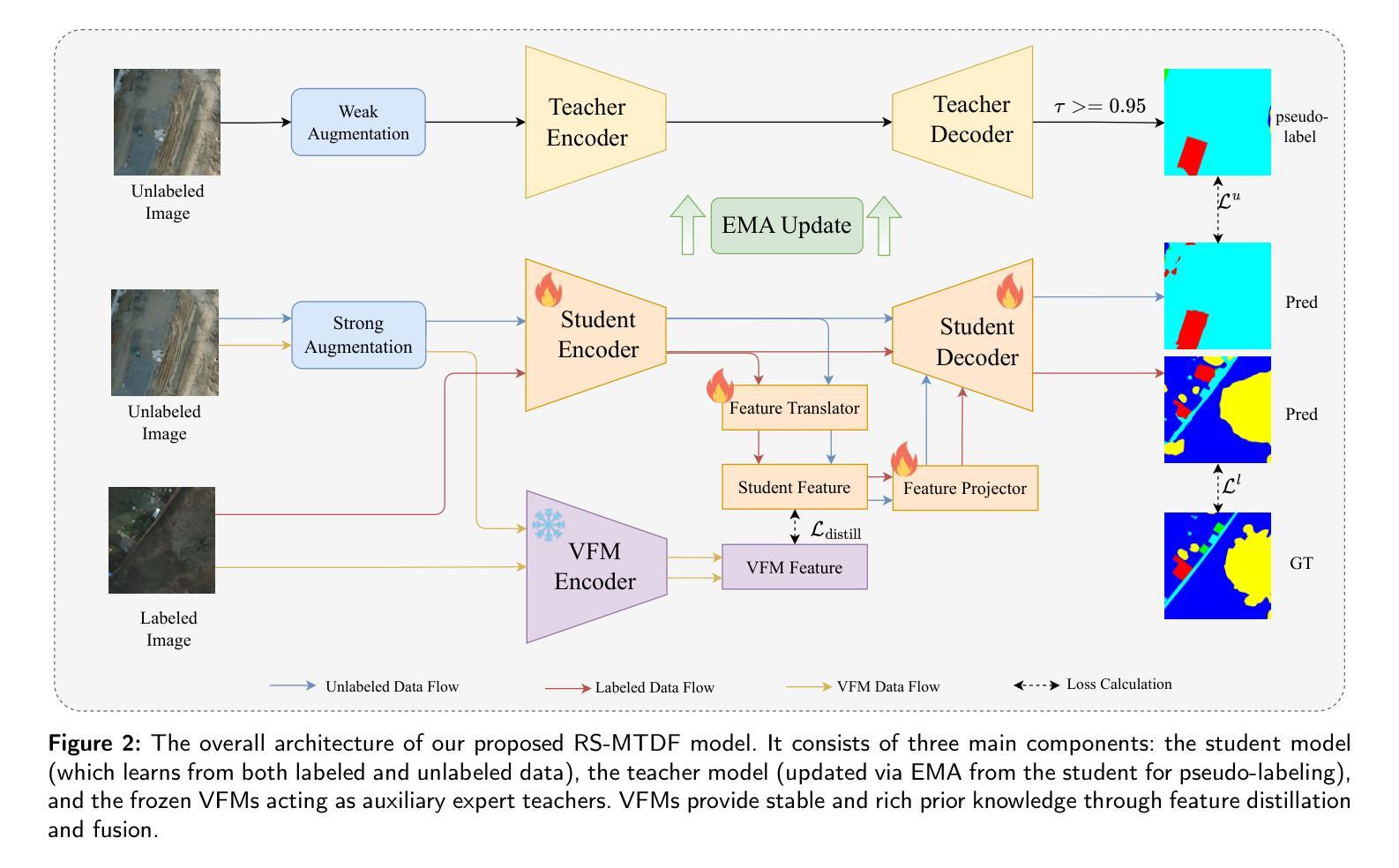
Semantic segmentation in remote sensing images is crucial for various applications, yet its performance is heavily reliant on large-scale, high-quality pixel-wise annotations, which are notoriously expensive and time-consuming to acquire. Semi-supervised semantic segmentation (SSS) offers a promising alternative to mitigate this data dependency. However, existing SSS methods often struggle with the inherent distribution mismatch between limited labeled data and abundant unlabeled data, leading to suboptimal generalization. To alleviate this issue, we attempt to introduce the Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) pre-trained on vast and diverse datasets into the SSS task since VFMs possess robust generalization capabilities that can effectively bridge this distribution gap and provide strong semantic priors for SSS. Inspired by this, we introduce RS-MTDF (Multi-Teacher Distillation and Fusion), a novel framework that leverages the powerful semantic knowledge embedded in VFMs to guide semi-supervised learning in remote sensing. Specifically, RS-MTDF employs multiple frozen VFMs (e.g., DINOv2 and CLIP) as expert teachers, utilizing feature-level distillation to align student features with their robust representations. To further enhance discriminative power, the distilled knowledge is seamlessly fused into the student decoder. Extensive experiments on three challenging remote sensing datasets demonstrate that RS-MTDF consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance. Notably, our method outperforms existing approaches across various label ratios on LoveDA and secures the highest IoU in the majority of semantic categories. These results underscore the efficacy of multi-teacher VFM guidance in significantly enhancing both generalization and semantic understanding for remote sensing segmentation. Ablation studies further validate the contribution of each proposed module.
遥感图像语义分割对于各种应用至关重要,但其性能严重依赖于大规模、高质量的像素级注释,这些注释的获取成本高昂且耗时。半监督语义分割(SSS)为解决这一数据依赖问题提供了有前景的替代方案。然而,现有的SSS方法往往难以解决有限的标记数据和大量未标记数据之间固有的分布不匹配问题,导致泛化性能不佳。为解决这一问题,我们尝试将预训练在大量多样化数据集上的视觉基础模型(VFMs)引入SSS任务,因为VFMs具有强大的泛化能力,可以有效地弥合这种分布差距,并为SSS提供强大的语义先验知识。受此启发,我们引入了RS-MTDF(多教师蒸馏与融合)这一新框架,它利用嵌入在VFMs中的强大语义知识来指导遥感领域的半监督学习。具体来说,RS-MTDF采用多个冻结的VFM(例如DINOv2和CLIP)作为专家教师,利用特征级蒸馏来对齐学生特征与它们的稳健表示。为进一步增强判别力,将提炼的知识无缝融合到学生解码器中。在三个具有挑战性的遥感数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,RS-MTDF始终实现了最先进的表现。值得注意的是,我们的方法在不同的标签比率上均超越了现有方法,在LoveDA上取得了最高的IoU,并在大多数语义类别中表现最佳。这些结果突显了多教师VFM指导在显著提高遥感分割的泛化和语义理解方面的有效性。消融研究进一步验证了所提各模块的作用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了遥感图像语义分割的重要性及其面临的挑战,如获取大规模高质量像素级注释的困难。为了缓解对标注数据的依赖,文章提出了利用预训练在大量多样化数据集上的视觉基础模型(VFMs)进行半监督语义分割(SSS)。文章介绍了一种新的框架RS-MTDF,它利用多个冻结的VFMs作为专家教师,通过特征级别的蒸馏来引导学生特征对齐其稳健表示,并进一步提升判别力。实验表明,RS-MTDF在三个具有挑战性的遥感数据集上实现了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像语义分割的重要性及其获取大规模高质量像素级注释的困难。
- 半监督语义分割(SSS)是缓解对标注数据依赖的有前途的替代方案。
- 现有SSS方法面临的有标签数据和无标签数据之间内在分布不匹配的问题。
- 利用预训练在大量多样化数据集上的视觉基础模型(VFMs)来解决上述问题。
- 介绍了一种新的框架RS-MTDF,它利用多个冻结的VFMs作为专家教师进行特征级别的指导学习。
- 通过特征级别的蒸馏,RS-MTDF增强了学生的特征对齐能力并提高了判别力。
- 在三个遥感数据集上的实验证明了RS-MTDF的卓越性能,尤其是在不同标签比率下的LoveDA数据集上的表现尤为突出。
点此查看论文截图


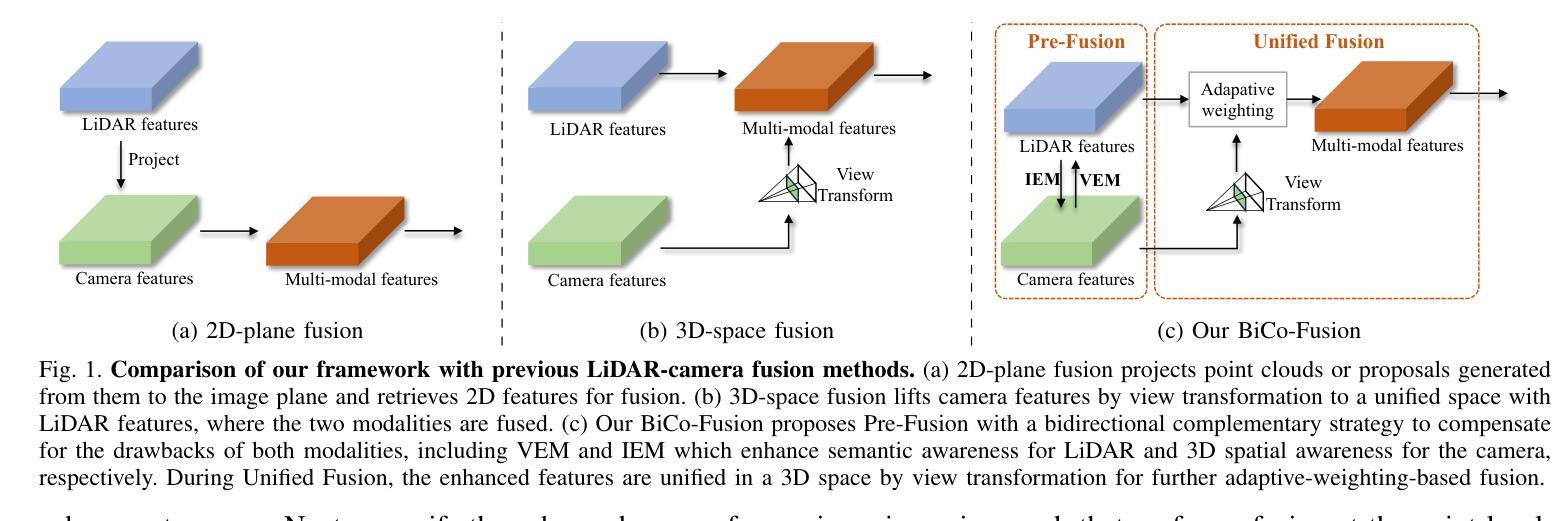
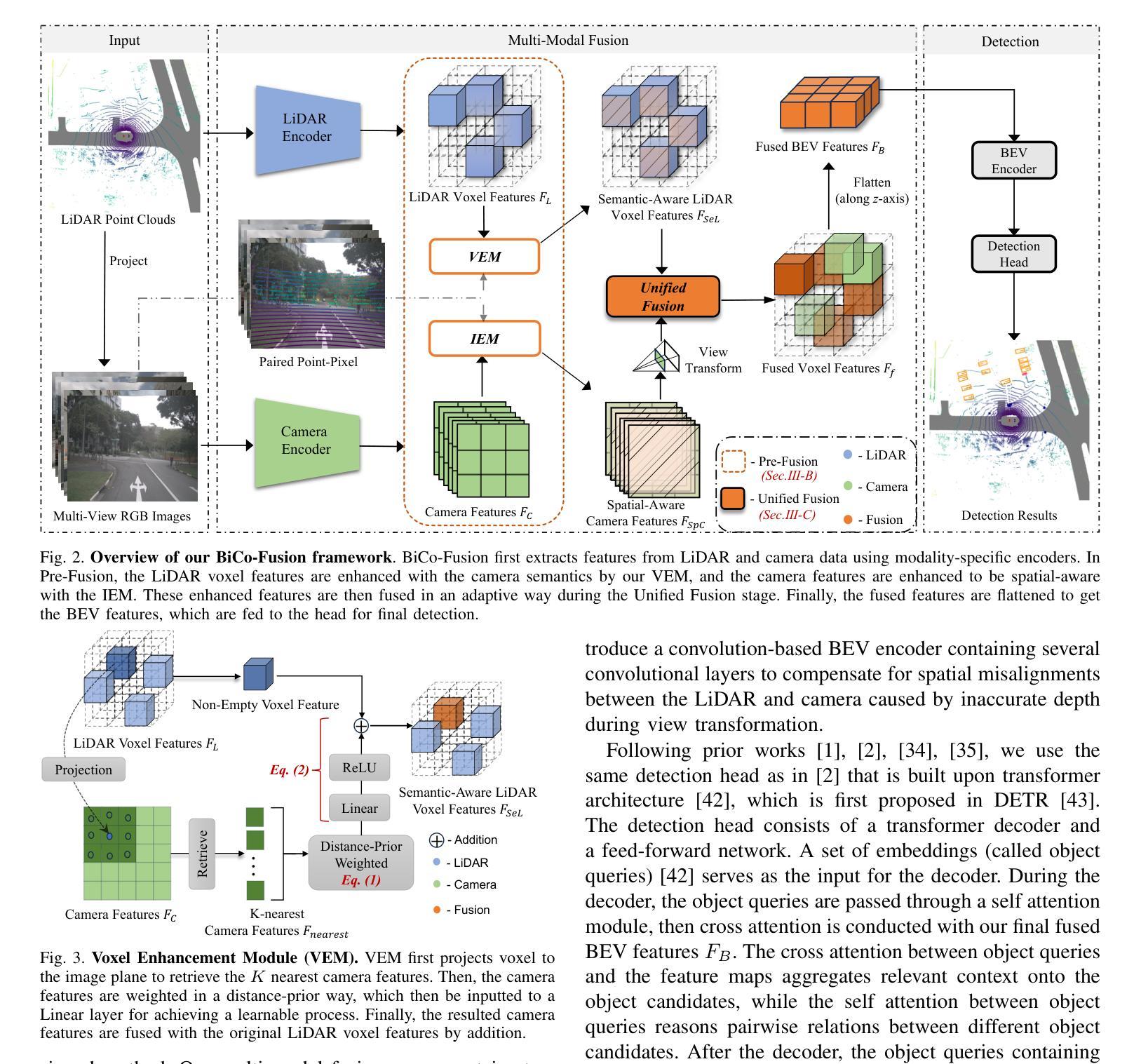
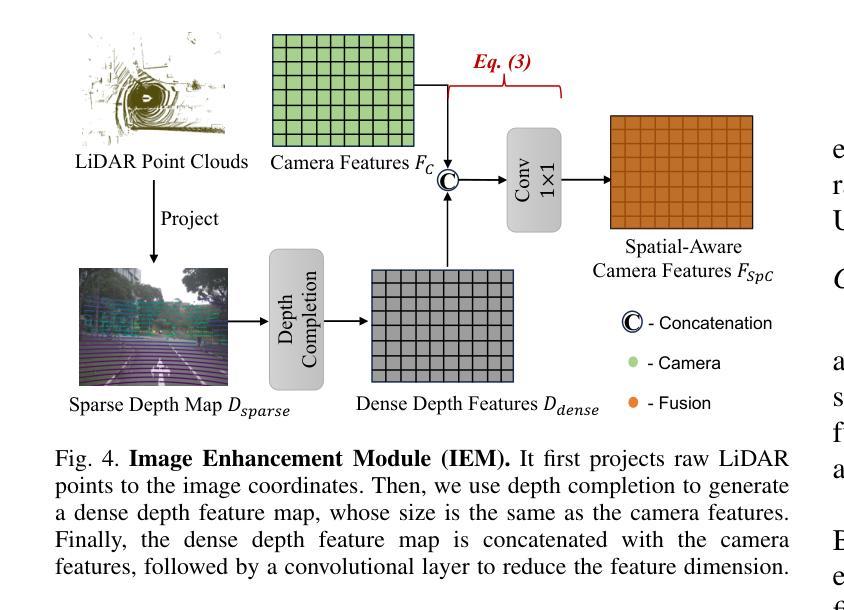
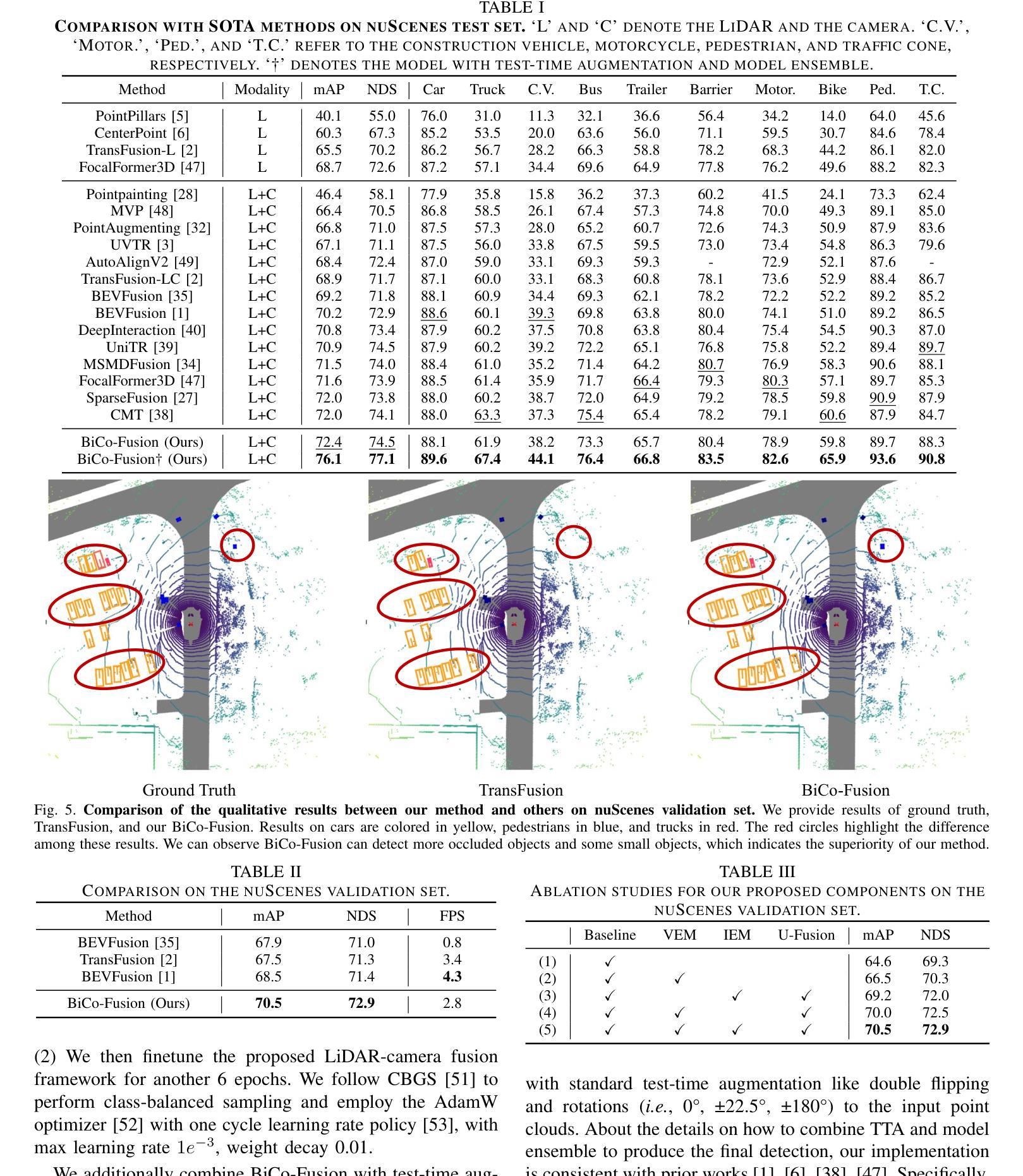
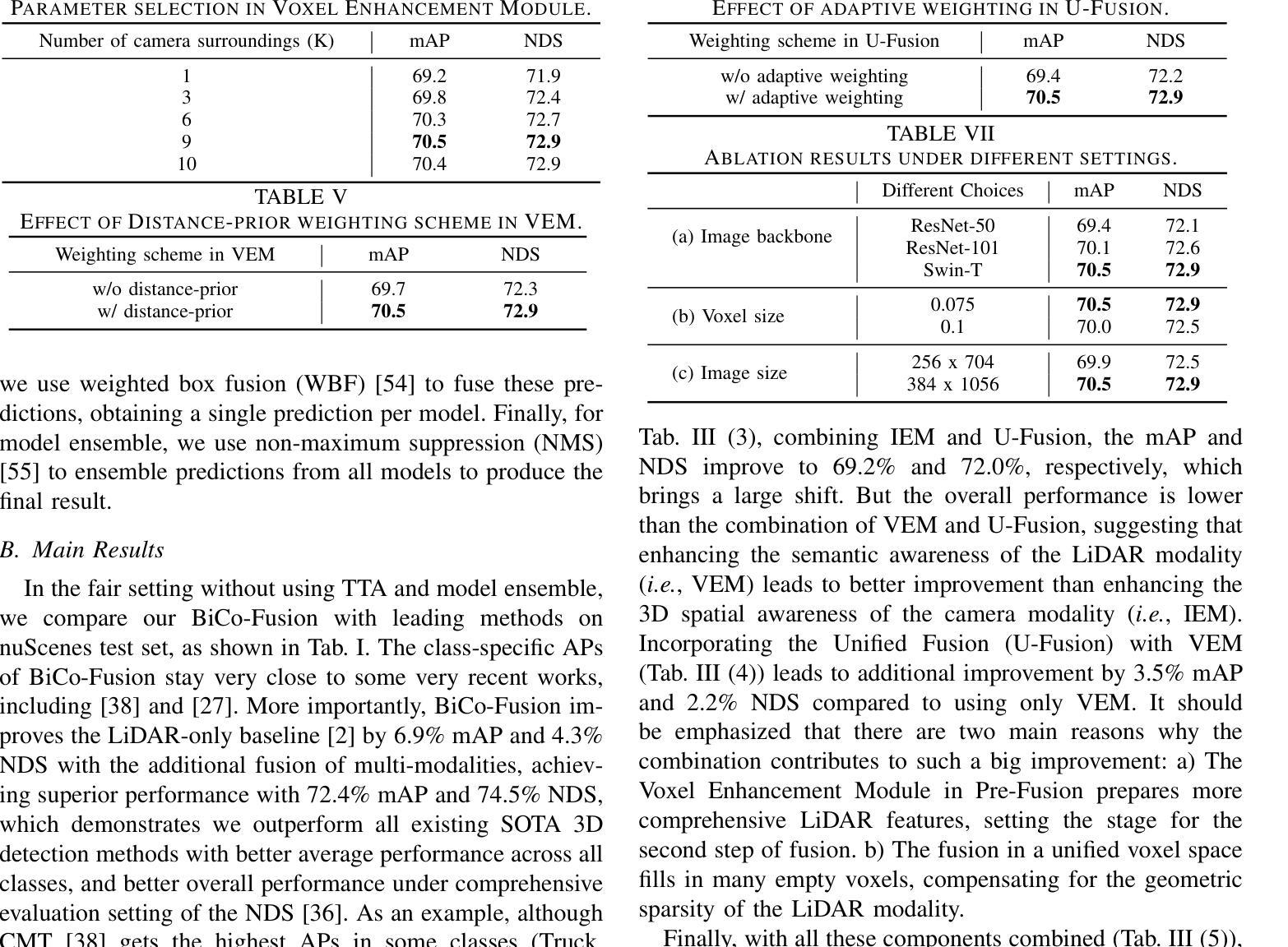
BiCo-Fusion: Bidirectional Complementary LiDAR-Camera Fusion for Semantic- and Spatial-Aware 3D Object Detection
Authors:Yang Song, Lin Wang
3D object detection is an important task that has been widely applied in autonomous driving. To perform this task, a new trend is to fuse multi-modal inputs, i.e., LiDAR and camera. Under such a trend, recent methods fuse these two modalities by unifying them in the same 3D space. However, during direct fusion in a unified space, the drawbacks of both modalities (LiDAR features struggle with detailed semantic information and the camera lacks accurate 3D spatial information) are also preserved, diluting semantic and spatial awareness of the final unified representation. To address the issue, this letter proposes a novel bidirectional complementary LiDAR-camera fusion framework, called BiCo-Fusion that can achieve robust semantic- and spatial-aware 3D object detection. The key insight is to fuse LiDAR and camera features in a bidirectional complementary way to enhance the semantic awareness of the LiDAR and the 3D spatial awareness of the camera. The enhanced features from both modalities are then adaptively fused to build a semantic- and spatial-aware unified representation. Specifically, we introduce Pre-Fusion consisting of a Voxel Enhancement Module (VEM) to enhance the semantic awareness of voxel features from 2D camera features and Image Enhancement Module (IEM) to enhance the 3D spatial awareness of camera features from 3D voxel features. We then introduce Unified Fusion (U-Fusion) to adaptively fuse the enhanced features from the last stage to build a unified representation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our BiCo-Fusion against the prior arts. Project page: https://t-ys.github.io/BiCo-Fusion/.
三维物体检测是一项在自动驾驶中广泛应用的重要任务。为了完成这项任务,目前的一个新趋势是融合多模态输入,即激光雷达和摄像机。在这种趋势下,最近的方法通过将这两种模态统一到同一三维空间中进行融合。然而,在统一空间中进行直接融合时,两种模态的缺点(激光雷达特征在详细语义信息方面的挣扎以及摄像机缺乏准确的3D空间信息)也被保留下来,导致最终统一表示的语义和空间感知能力被削弱。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种新的双向互补激光雷达-摄像机融合框架,称为BiCo-Fusion,可以实现稳健的语义和空间感知三维物体检测。关键在于以双向互补的方式融合激光雷达和摄像机特征,以提高激光雷达的语义感知能力和摄像机的三维空间感知能力。然后自适应地融合两种模态的增强特征,以建立具有语义和空间感知的统一表示。具体来说,我们引入了Pre-Fusion,包括体素增强模块(VEM)以提高二维摄像机特征的体素特征的语义感知能力,以及图像增强模块(IEM)以提高三维体素特征的摄像机特征的三维空间感知能力。然后,我们引入了Unified Fusion(U-Fusion)来自适应融合上一阶段的增强特征,以建立统一表示。大量实验证明,我们的BiCo-Fusion相较于先前技术具有优越性。项目页面:https://t-ys.github.io/BiCo-Fusion/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L)
Summary
该文针对自主驾驶中的3D目标检测任务,提出了一种双向互补的激光雷达-相机融合框架BiCo-Fusion。通过双向融合增强激光雷达的语义感知和相机的三维空间感知,解决了单一模态在直接融合时存在的语义和空间感知不足的问题。通过引入预融合和统一融合模块,实现了增强特征的自适应融合,建立了语义和空间感知统一的表示。实验证明,该方法优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 3D目标检测在自主驾驶中非常重要,多模态输入融合(如激光雷达和相机)是当前的趋势。
- 直接融合两种模态时存在语义和空间感知不足的问题。
- BiCo-Fusion框架通过双向互补融合增强激光雷达的语义感知和相机的三维空间感知。
- 引入预融合和统一融合模块,实现自适应特征融合,建立语义和空间感知统一的表示。
- 实验证明BiCo-Fusion方法优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图