⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-13 更新
Text-Aware Image Restoration with Diffusion Models
Authors:Jaewon Min, Jin Hyeon Kim, Paul Hyunbin Cho, Jaeeun Lee, Jihye Park, Minkyu Park, Sangpil Kim, Hyunhee Park, Seungryong Kim
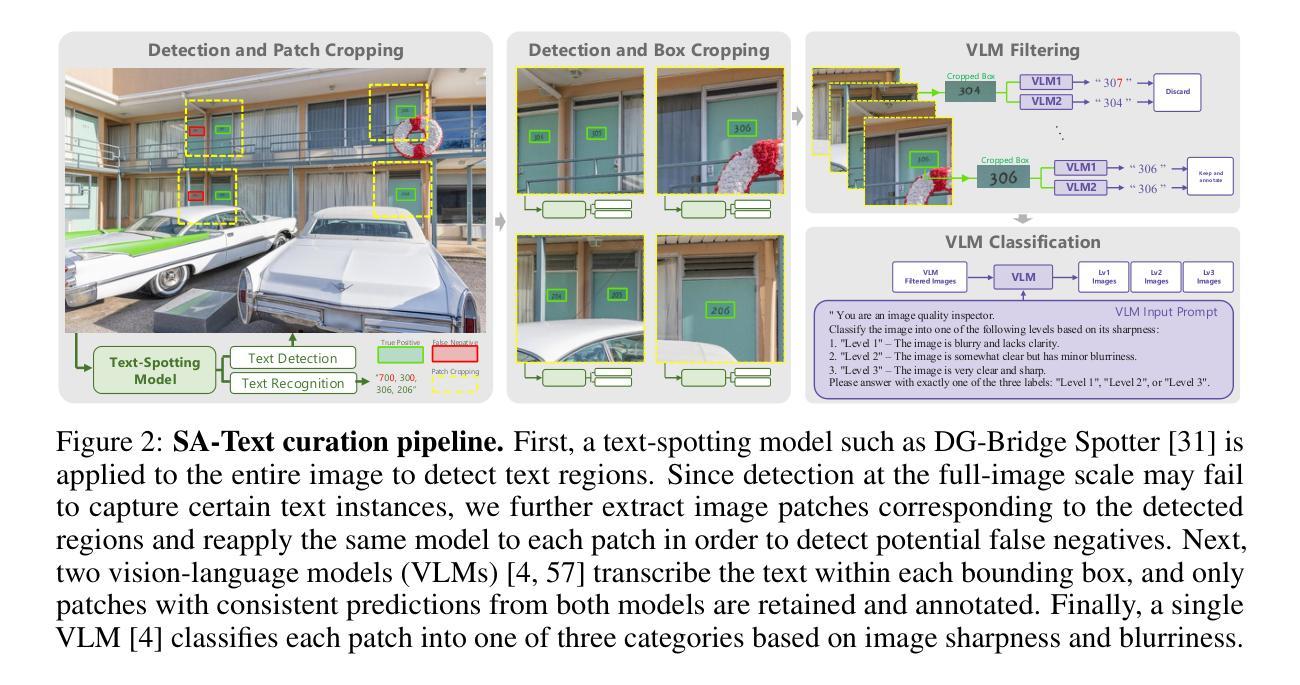
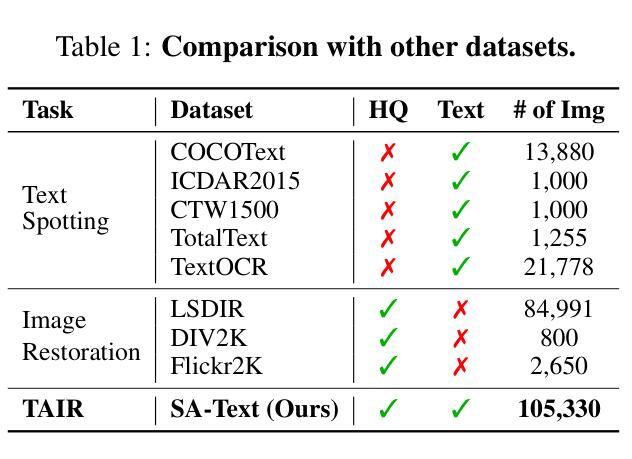
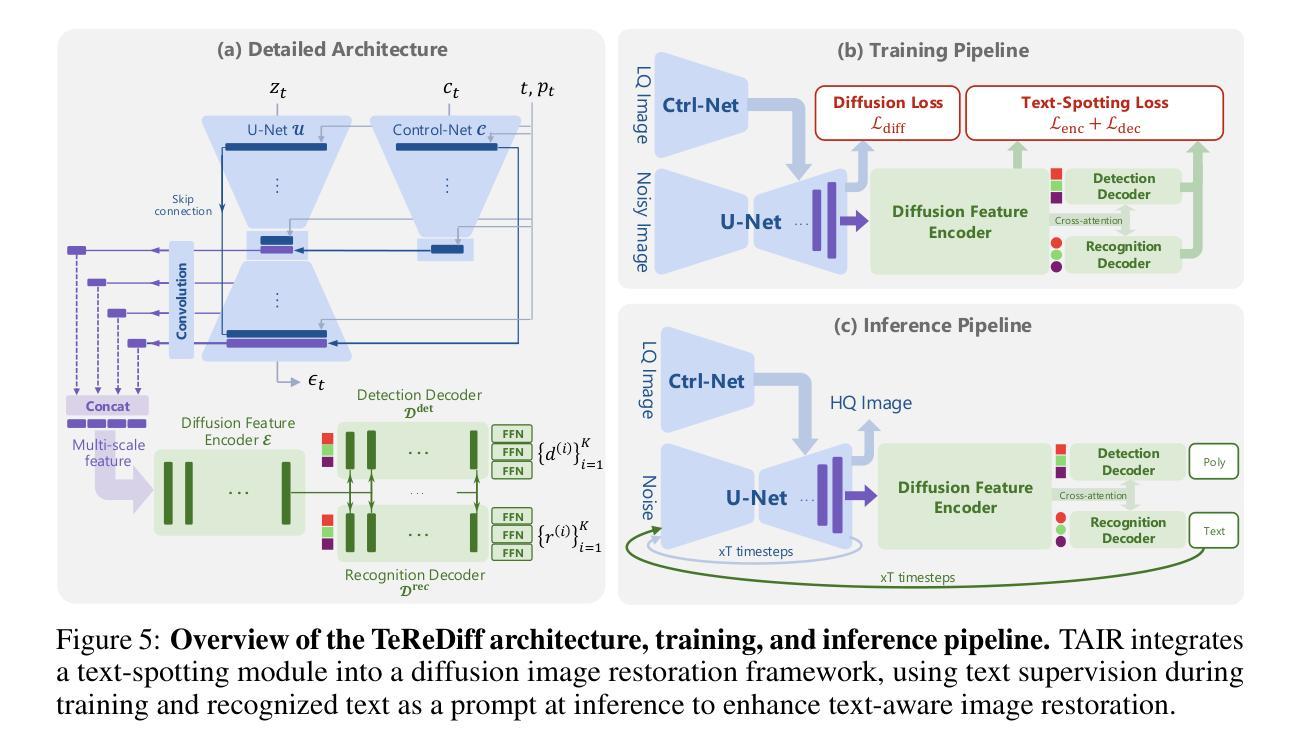
Image restoration aims to recover degraded images. However, existing diffusion-based restoration methods, despite great success in natural image restoration, often struggle to faithfully reconstruct textual regions in degraded images. Those methods frequently generate plausible but incorrect text-like patterns, a phenomenon we refer to as text-image hallucination. In this paper, we introduce Text-Aware Image Restoration (TAIR), a novel restoration task that requires the simultaneous recovery of visual contents and textual fidelity. To tackle this task, we present SA-Text, a large-scale benchmark of 100K high-quality scene images densely annotated with diverse and complex text instances. Furthermore, we propose a multi-task diffusion framework, called TeReDiff, that integrates internal features from diffusion models into a text-spotting module, enabling both components to benefit from joint training. This allows for the extraction of rich text representations, which are utilized as prompts in subsequent denoising steps. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms state-of-the-art restoration methods, achieving significant gains in text recognition accuracy. See our project page: https://cvlab-kaist.github.io/TAIR/
图像修复旨在恢复退化图像。然而,现有的基于扩散的修复方法虽然在自然图像修复中取得了巨大成功,但在退化图像的文本区域重建中却经常面临困难。这些方法经常生成合理但错误的文本模式,我们将这种现象称为文本图像幻觉。在本文中,我们介绍了文本感知图像修复(TAIR)这一新的修复任务,它要求同时恢复视觉内容和文本保真度。为了应对这一任务,我们推出了SA-Text,这是一个大规模基准测试集,包含十万张高质量场景图像,并密集标注了多样且复杂的文本实例。此外,我们提出了一种多任务扩散框架TeReDiff,它将扩散模型的内部特征集成到文本识别模块中,使两个组件都能从联合训练中受益。这允许提取丰富的文本表示形式,并将其用作后续去噪步骤中的提示。大量实验表明,我们的方法始终优于最先进的修复方法,在文本识别准确率上取得了显著的提升。更多详情见我们的项目页面:https://cvlab-kaist.github.io/TAIR/(注:由于涉及到特定领域的专业术语和概念,翻译时可能需要进行一定的解释和补充。)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://cvlab-kaist.github.io/TAIR/
Summary
文本修复旨在恢复退化图像,但现有的基于扩散的方法在自然图像修复方面取得了巨大成功的同时,在恢复图像中的文本区域时却常常难以保持忠实性。这种现象被称为文本图像幻觉。本文介绍了文本感知图像修复(TAIR)这一新任务,要求同时恢复视觉内容和文本忠实性。为此,我们推出了SA-Text,这是一个包含10万张高质量场景图像的大规模基准测试集,其中密集标注了多样且复杂的文本实例。此外,我们提出了一种多任务扩散框架TeReDiff,它将扩散模型的内部特征集成到文本识别模块中,使两者都能从联合训练中受益。这有助于提取丰富的文本表示,并在随后的去噪步骤中作为提示使用。实验表明,我们的方法一致地优于最新的修复方法,在文本识别准确性上取得了显著的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 文本感知图像修复(TAIR)是一项要求同时恢复图像视觉内容和文本忠实性的新任务。
- 现有扩散方法在处理文本区域的图像修复时,可能会出现文本图像幻觉现象。
- SA-Text是一个大规模基准测试集,包含密集标注的多样且复杂的文本实例的图像。
- 提出了一种多任务扩散框架TeReDiff,结合了扩散模型和文本识别模块,提高了文本识别准确性。
- TeReDiff框架通过利用丰富的文本表示作为去噪步骤的提示,优化了图像修复过程。
- 实验结果显示,TeReDiff在文本识别准确性上超越了现有的修复方法。
点此查看论文截图



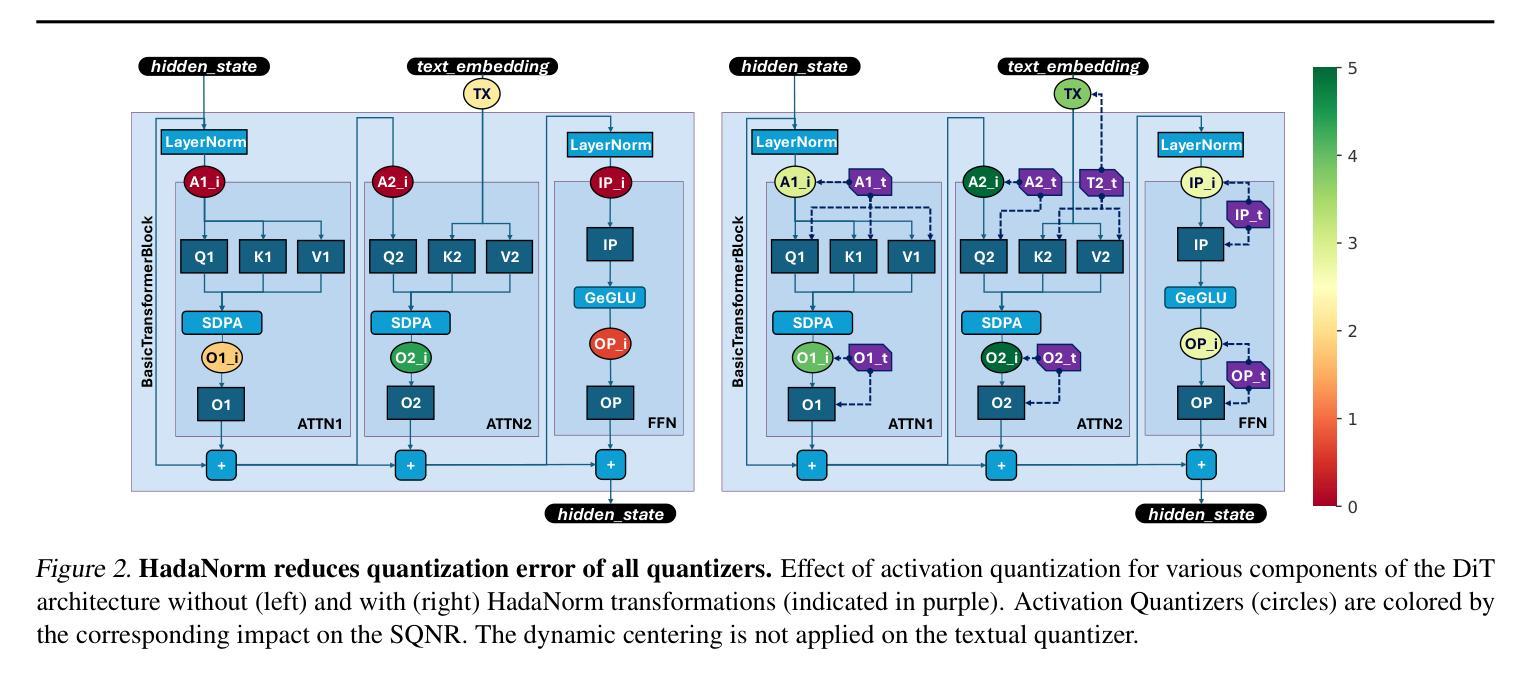
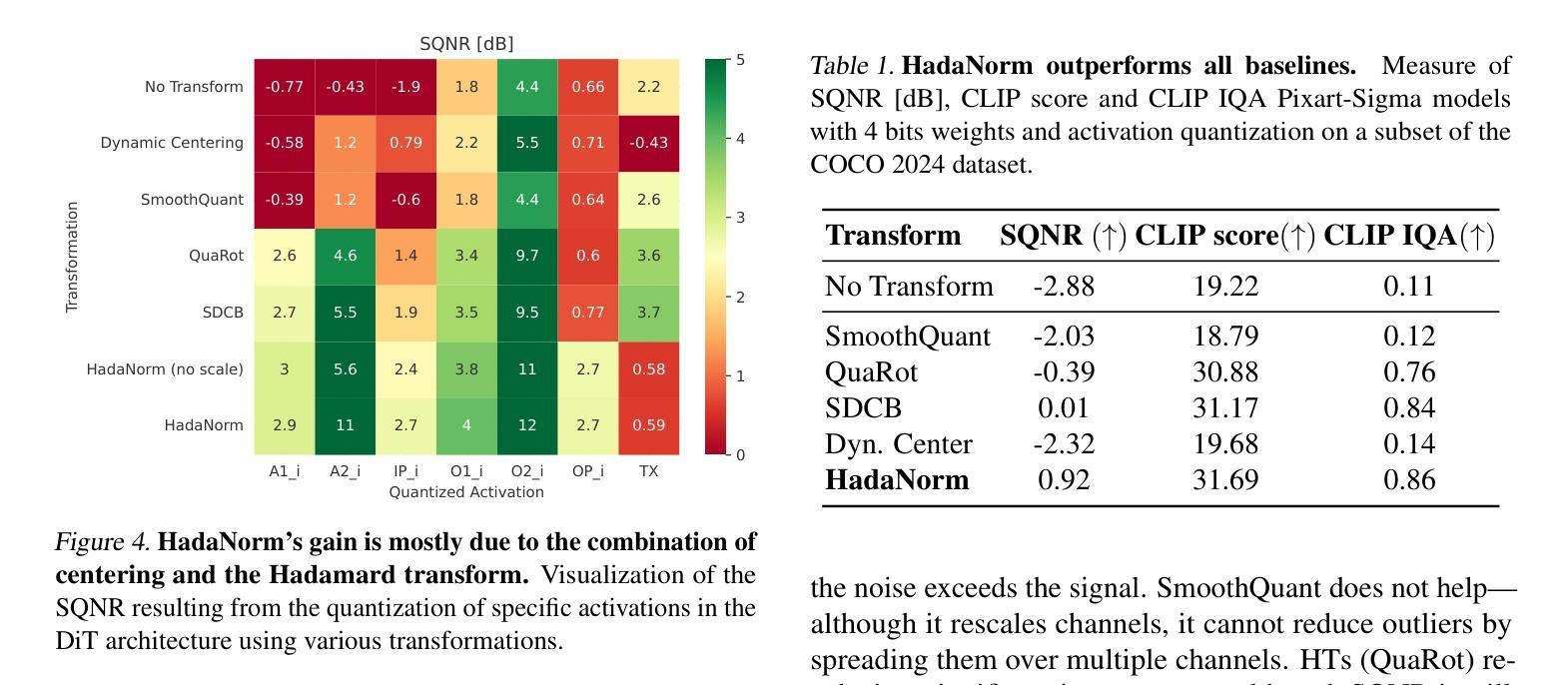
HadaNorm: Diffusion Transformer Quantization through Mean-Centered Transformations
Authors:Marco Federici, Riccardo Del Chiaro, Boris van Breugel, Paul Whatmough, Markus Nagel
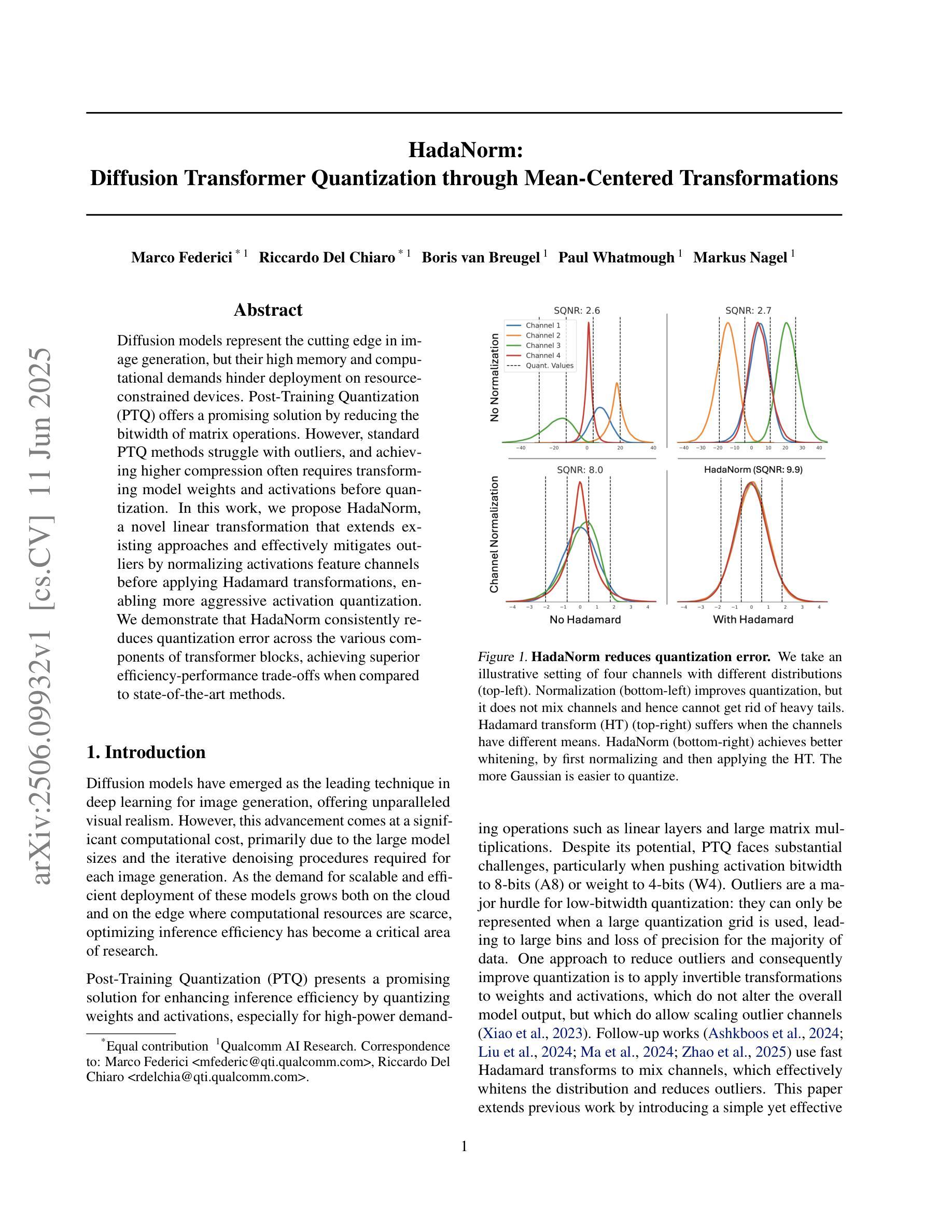
Diffusion models represent the cutting edge in image generation, but their high memory and computational demands hinder deployment on resource-constrained devices. Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) offers a promising solution by reducing the bitwidth of matrix operations. However, standard PTQ methods struggle with outliers, and achieving higher compression often requires transforming model weights and activations before quantization. In this work, we propose HadaNorm, a novel linear transformation that extends existing approaches and effectively mitigates outliers by normalizing activations feature channels before applying Hadamard transformations, enabling more aggressive activation quantization. We demonstrate that HadaNorm consistently reduces quantization error across the various components of transformer blocks, achieving superior efficiency-performance trade-offs when compared to state-of-the-art methods.
扩散模型是图像生成领域的前沿技术,但其高内存和计算需求限制了其在资源受限设备上的部署。后训练量化(PTQ)通过降低矩阵操作的位宽提供了一种有前景的解决方案。然而,标准PTQ方法难以处理异常值,实现更高的压缩通常需要量化前对模型权重和激活进行转换。在这项工作中,我们提出了HadaNorm,这是一种新型线性变换,它扩展了现有方法并通过对激活特征通道进行归一化有效地减轻了异常值问题,然后再应用哈达玛变换以实现更极端的激活量化。我们证明,HadaNorm可以一致地在transformer块的各种组件中减少量化误差,与最新方法相比,实现了卓越的效率性能权衡。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 Pages, 5 Figures
Summary
本文提出了名为HadaNorm的新型线性变换方法,用于图像生成中的扩散模型。它通过归一化激活特征通道,有效地缓解了标准化PTQ方法在处理离群值时的困难,并允许更激烈的激活量化。HadaNorm在变压器块的各个组件中一致地降低了量化误差,与现有方法相比,实现了更优越的效率和性能权衡。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型是图像生成的前沿技术,但高内存和计算需求限制了其在资源受限设备上的应用。
- Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) 方法通过降低矩阵操作的位宽来解决问题。
- 现有PTQ方法在处理离群值时遇到困难,需要转换模型权重和激活来实现更高的压缩。
- 提出的HadaNorm方法通过归一化激活特征通道,在应用Hadamard变换之前有效地缓解了这一问题。
- HadaNorm在变压器块的各个组件中降低了量化误差。
- HadaNorm与现有方法相比,实现了更优越的效率和性能之间的平衡。
点此查看论文截图

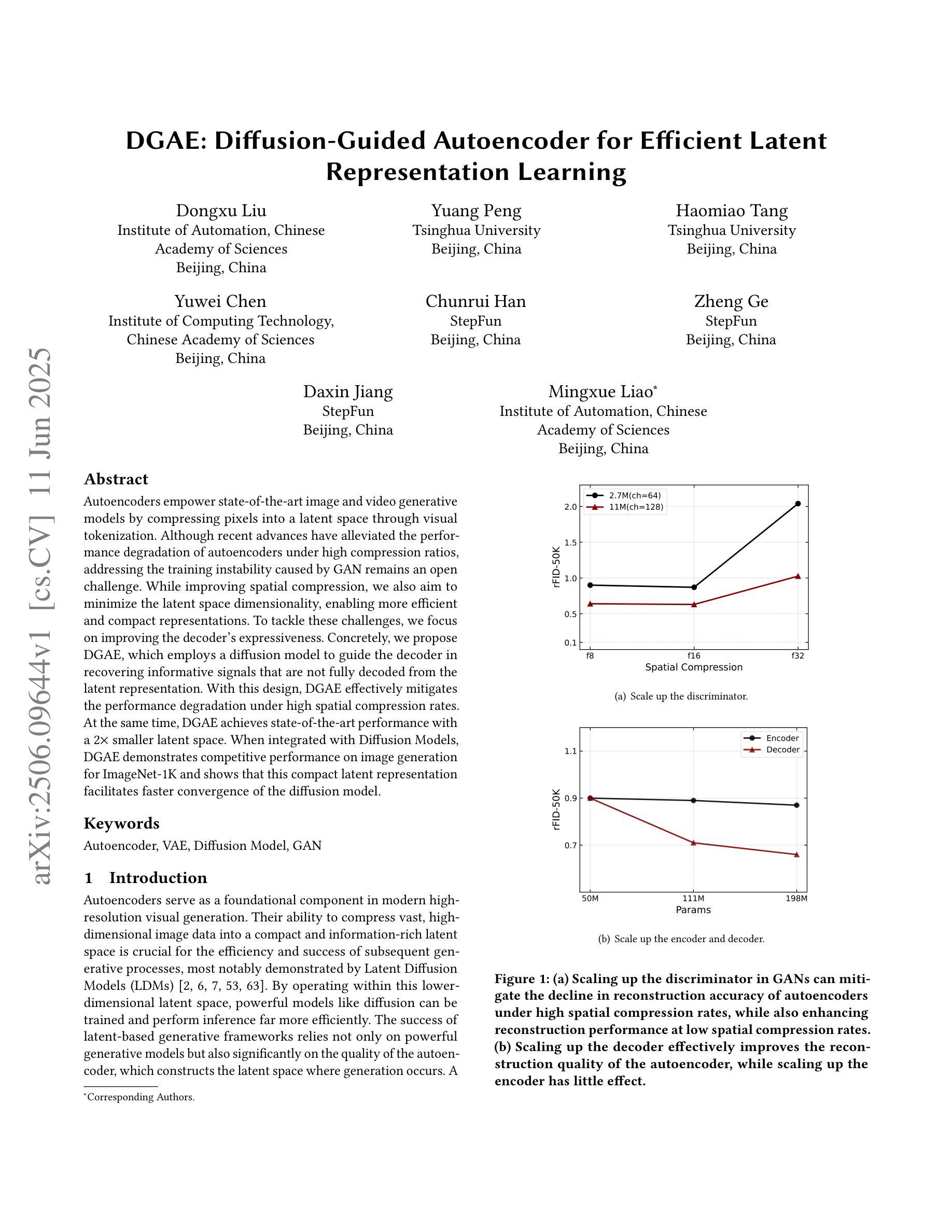
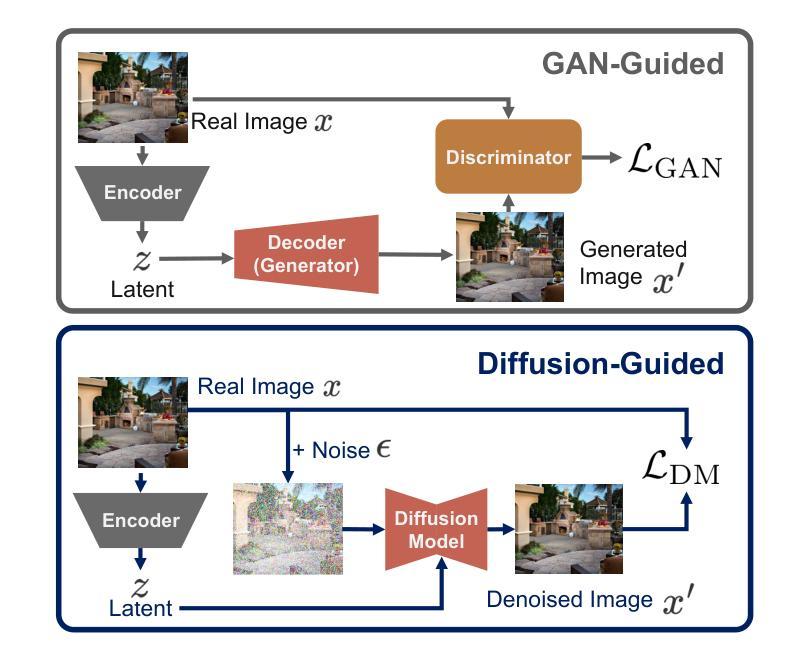
DGAE: Diffusion-Guided Autoencoder for Efficient Latent Representation Learning
Authors:Dongxu Liu, Yuang Peng, Haomiao Tang, Yuwei Chen, Chunrui Han, Zheng Ge, Daxin Jiang, Mingxue Liao
Autoencoders empower state-of-the-art image and video generative models by compressing pixels into a latent space through visual tokenization. Although recent advances have alleviated the performance degradation of autoencoders under high compression ratios, addressing the training instability caused by GAN remains an open challenge. While improving spatial compression, we also aim to minimize the latent space dimensionality, enabling more efficient and compact representations. To tackle these challenges, we focus on improving the decoder’s expressiveness. Concretely, we propose DGAE, which employs a diffusion model to guide the decoder in recovering informative signals that are not fully decoded from the latent representation. With this design, DGAE effectively mitigates the performance degradation under high spatial compression rates. At the same time, DGAE achieves state-of-the-art performance with a 2x smaller latent space. When integrated with Diffusion Models, DGAE demonstrates competitive performance on image generation for ImageNet-1K and shows that this compact latent representation facilitates faster convergence of the diffusion model.
自动编码器通过视觉令牌化将像素压缩到潜在空间,从而赋能最先进的图像和视频生成模型。尽管最近的进展已经减轻了高压缩比下自动编码器的性能下降问题,但解决由GAN引起的训练不稳定仍然是一个公开的挑战。我们在提高空间压缩的同时,也致力于最小化潜在空间的维度,以实现更高效、更紧凑的表示。为了应对这些挑战,我们专注于提高解码器的表达能力。具体来说,我们提出了DGAE(扩散引导自编码器),它采用扩散模型来指导解码器恢复从潜在表示中未完全解码的信息信号。通过这种设计,DGAE在高空间压缩率下有效地缓解了性能下降的问题。同时,DGAE在具有更小两倍潜在空间的情况下实现了最先进的性能。当与扩散模型集成时,DGAE在ImageNet-1K的图像生成上表现出竞争力,并证明这种紧凑的潜在表示有助于扩散模型的更快收敛。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
通过视觉令牌化将像素压缩到潜在空间,自动编码器为图像和视频生成模型提供了动力。尽管已有进展减轻了高压缩比下自动编码器的性能下降问题,但由生成对抗网络引起的训练不稳定问题仍待解决。在改进空间压缩的同时,我们还致力于最小化潜在空间的维数,以实现更紧凑和高效的表示。为了解决这些挑战,我们专注于提高解码器的表达能力。具体来说,我们提出了采用扩散模型引导解码器恢复从潜在表示中未完全解码的信号的DGAE。该设计有效缓解了高空间压缩率下的性能下降问题,同时实现了较小的潜在空间(缩小了2倍)。与扩散模型集成后,DGAE在ImageNet-1K的图像生成上表现出卓越性能,并证明这种紧凑的潜在表示促进了扩散模型的快速收敛。
Key Takeaways
- 自动编码器通过视觉令牌化压缩像素至潜在空间,为图像和视频生成模型提供动力。
- 高压缩比下的自动编码器性能下降问题虽有所缓解,但由GAN引起的训练不稳定问题仍是挑战。
- 在改进空间压缩的同时,最小化潜在空间维度以实现更紧凑和高效的表示是目标。
- DGAE通过采用扩散模型引导解码器恢复未完全解码的信号,解决了上述挑战。
- DGAE在高空间压缩率下表现出卓越性能,且实现了较小的潜在空间。
- DGAE在ImageNet-1K的图像生成上表现卓越。
点此查看论文截图
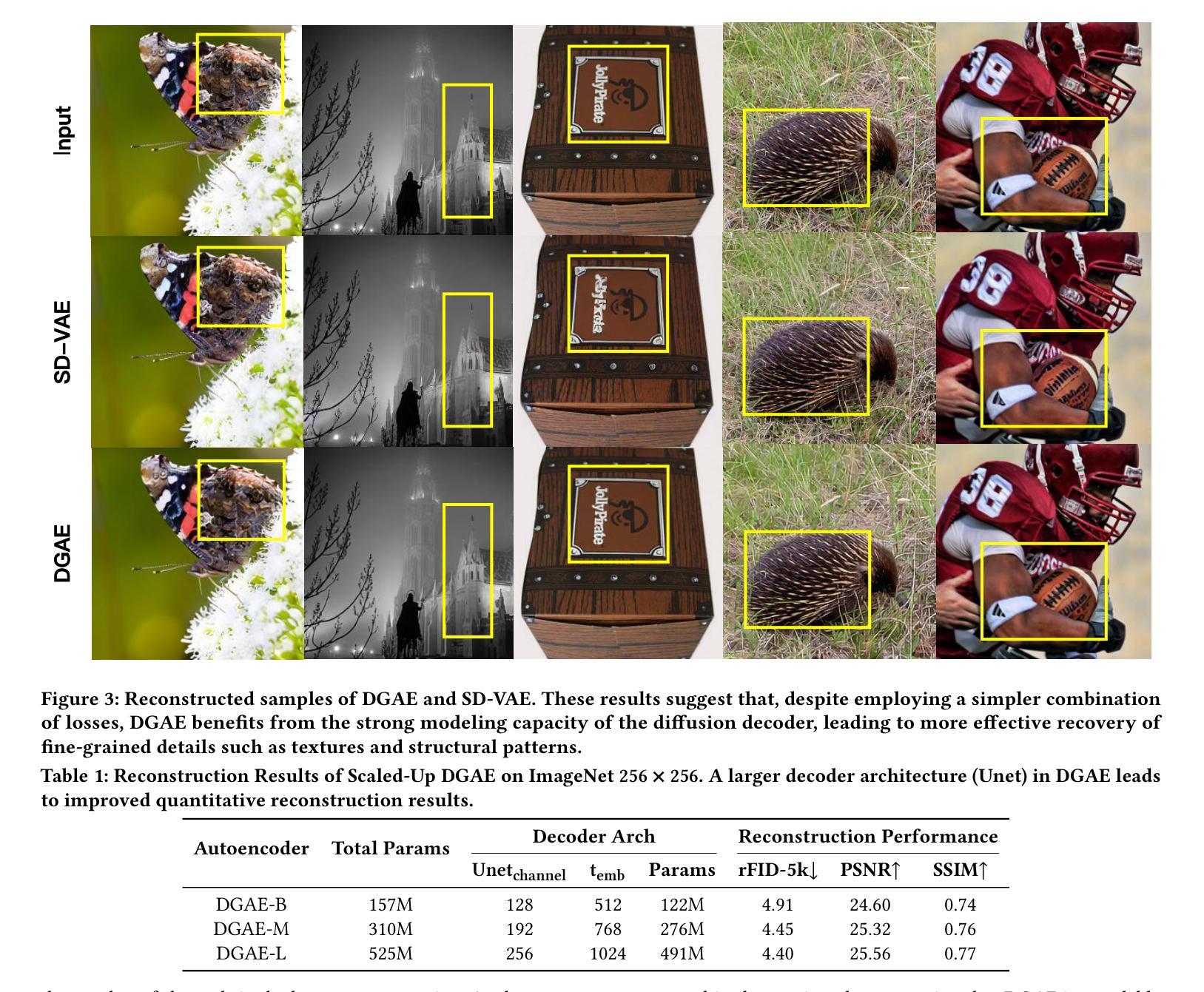

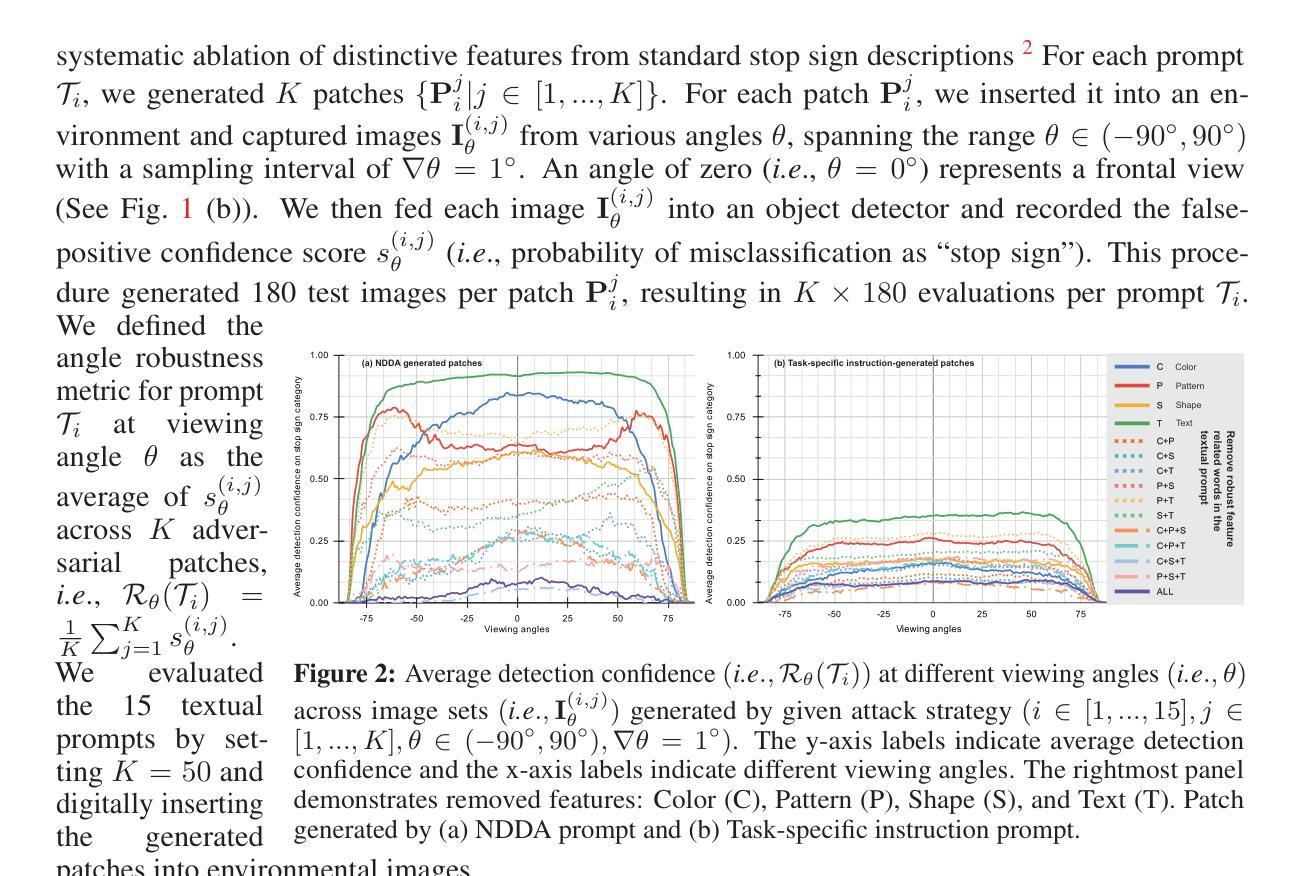
AngleRoCL: Angle-Robust Concept Learning for Physically View-Invariant T2I Adversarial Patches
Authors:Wenjun Ji, Yuxiang Fu, Luyang Ying, Deng-Ping Fan, Yuyi Wang, Ming-Ming Cheng, Ivor Tsang, Qing Guo
Cutting-edge works have demonstrated that text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models can generate adversarial patches that mislead state-of-the-art object detectors in the physical world, revealing detectors’ vulnerabilities and risks. However, these methods neglect the T2I patches’ attack effectiveness when observed from different views in the physical world (i.e., angle robustness of the T2I adversarial patches). In this paper, we study the angle robustness of T2I adversarial patches comprehensively, revealing their angle-robust issues, demonstrating that texts affect the angle robustness of generated patches significantly, and task-specific linguistic instructions fail to enhance the angle robustness. Motivated by the studies, we introduce Angle-Robust Concept Learning (AngleRoCL), a simple and flexible approach that learns a generalizable concept (i.e., text embeddings in implementation) representing the capability of generating angle-robust patches. The learned concept can be incorporated into textual prompts and guides T2I models to generate patches with their attack effectiveness inherently resistant to viewpoint variations. Through extensive simulation and physical-world experiments on five SOTA detectors across multiple views, we demonstrate that AngleRoCL significantly enhances the angle robustness of T2I adversarial patches compared to baseline methods. Our patches maintain high attack success rates even under challenging viewing conditions, with over 50% average relative improvement in attack effectiveness across multiple angles. This research advances the understanding of physically angle-robust patches and provides insights into the relationship between textual concepts and physical properties in T2I-generated contents.
前沿研究表明,文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型能够生成对抗性补丁,这些补丁可以误导现实世界中的最先进的物体检测器,从而揭示检测器的脆弱性和风险。然而,这些方法忽略了从现实世界中的不同视角观察到的T2I补丁的攻击效果(即T2I对抗性补丁的角度稳健性)。在本文中,我们全面研究了T2I对抗性补丁的角度稳健性,揭示了其角度稳健问题,并证明了文本对生成补丁的角度稳健性影响显著,而针对特定任务的语言指令无法增强角度稳健性。受这些研究的启发,我们引入了角度稳健概念学习(AngleRoCL),这是一种简单灵活的方法,可以学习一个可推广的概念(即在实现中的文本嵌入),用于代表生成角度稳健补丁的能力。学到的概念可以融入文本提示中,并指导T2I模型生成固有地抵抗视角变化的补丁。通过对五个最先进的检测器进行跨多个视角的广泛模拟和现实世界实验,我们证明了与基准方法相比,AngleRoCL显著提高了T2I对抗性补丁的角度稳健性。我们的补丁即使在具有挑战性的观看条件下也保持了较高的攻击成功率,在多个角度的攻击效果上平均相对提高了50%以上。该研究推动了物理角度稳健补丁的理解,并深入了解了文本概念和T2I生成内容中的物理属性之间的关系。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
前沿研究表明,文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型可生成对抗性补丁,误导现实世界中的先进目标检测器,揭示检测器的脆弱性和风险。然而,这些方法忽略了从物理世界的不同视角观察到的文本到图像的补丁攻击效果(即文本到图像对抗性补丁的视角鲁棒性)。本文全面研究了T2I对抗性补丁的视角鲁棒性,揭示了其视角鲁棒性问题,表明文本对生成的补丁的视角鲁棒性影响显著,而特定的任务语言指令无法增强视角鲁棒性。受研究的启发,我们引入了角度稳健概念学习(AngleRoCL),这是一种简单灵活的方法,可以学习一个可概括的概念(在实施中为文本嵌入),代表生成视角稳健补丁的能力。学到的概念可以融入文本提示,并指导T2I模型生成对视角变化具有内在抵抗力的补丁。通过广泛的模拟和物理世界实验,在五个先进检测器上跨多个视角进行验证,我们证明AngleRoCL显著提高了T2I对抗性补丁的视角鲁棒性,与基准方法相比,我们的补丁即使在具有挑战性的视角条件下也保持了较高的攻击成功率,多个角度的攻击效率平均提高了50%以上。该研究推进了对物理角度稳健补丁的理解,并深入探讨了文本概念与T2I生成内容物理属性之间的关系。
要点提炼
- T2I扩散模型能够生成对抗性补丁,可以误导现实世界的目标检测器。
- 现有的研究忽略了从物理世界的不同视角观察这些补丁的效果,本文填补了这一空白。
- 本文揭示了文本对生成的对抗性补丁的视角鲁棒性有显著影响。
- 语言指令在增强补丁的视角鲁棒性方面效果有限。
- 引入了AngleRoCL方法,能学习生成视角稳健补丁的能力,并将其融入文本提示中。
- 通过实验验证,AngleRoCL显著提高了T2I对抗性补丁的视角鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图


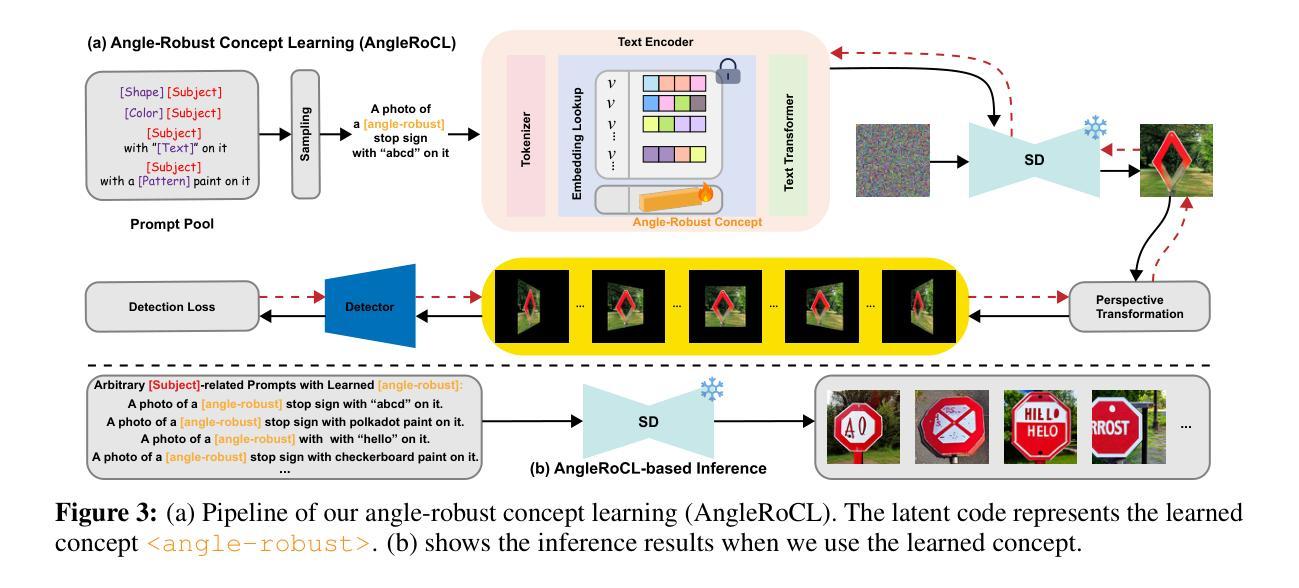
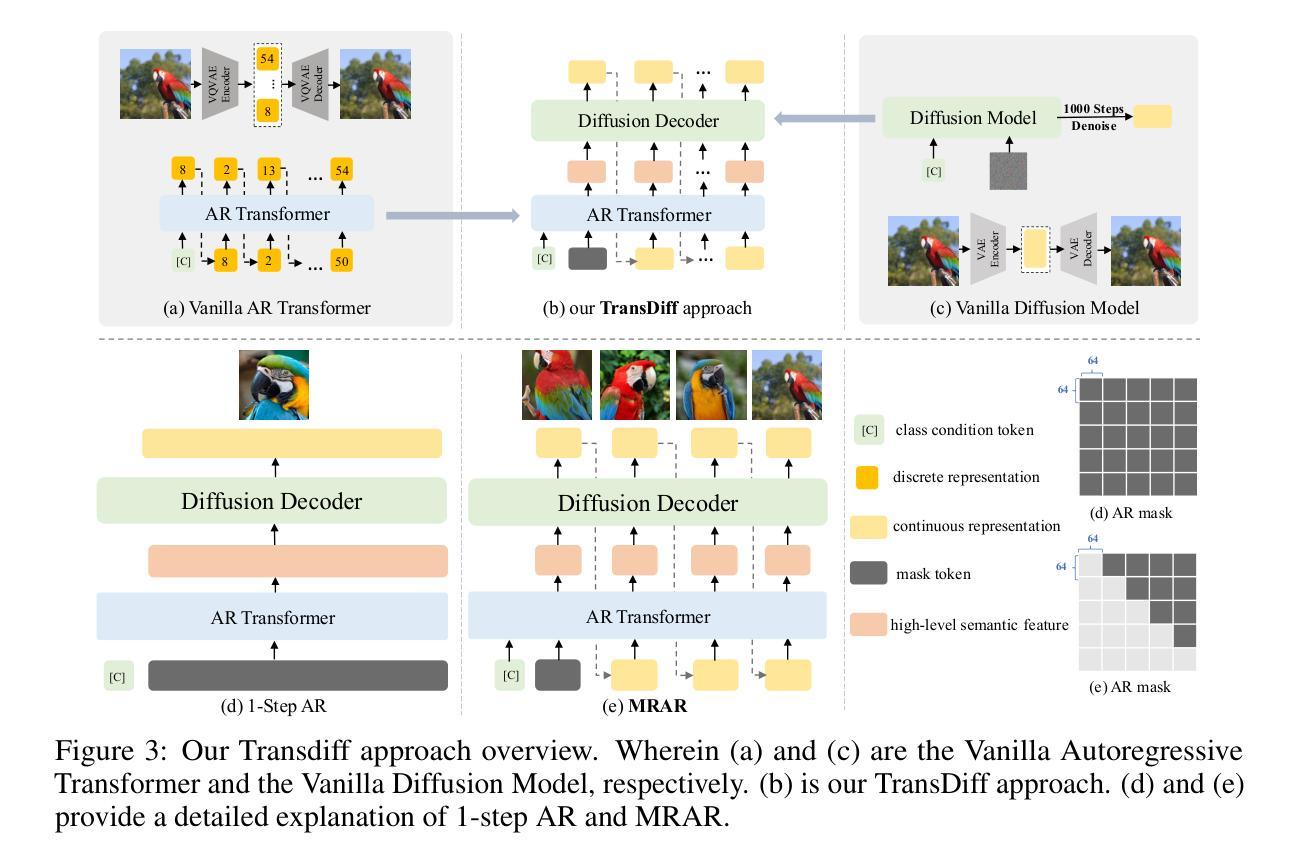
Marrying Autoregressive Transformer and Diffusion with Multi-Reference Autoregression
Authors:Dingcheng Zhen, Qian Qiao, Tan Yu, Kangxi Wu, Ziwei Zhang, Siyuan Liu, Shunshun Yin, Ming Tao
We introduce TransDiff, the first image generation model that marries Autoregressive (AR) Transformer with diffusion models. In this joint modeling framework, TransDiff encodes labels and images into high-level semantic features and employs a diffusion model to estimate the distribution of image samples. On the ImageNet 256x256 benchmark, TransDiff significantly outperforms other image generation models based on standalone AR Transformer or diffusion models. Specifically, TransDiff achieves a Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID) of 1.61 and an Inception Score (IS) of 293.4, and further provides x2 faster inference latency compared to state-of-the-art methods based on AR Transformer and x112 faster inference compared to diffusion-only models. Furthermore, building on the TransDiff model, we introduce a novel image generation paradigm called Multi-Reference Autoregression (MRAR), which performs autoregressive generation by predicting the next image. MRAR enables the model to reference multiple previously generated images, thereby facilitating the learning of more diverse representations and improving the quality of generated images in subsequent iterations. By applying MRAR, the performance of TransDiff is improved, with the FID reduced from 1.61 to 1.42. We expect TransDiff to open up a new frontier in the field of image generation.
我们介绍了TransDiff,这是第一个将自回归(AR)Transformer与扩散模型相结合的图片生成模型。在这个联合建模框架中,TransDiff将标签和图像编码为高级语义特征,并采用扩散模型来估计图像样本的分布。在ImageNet 256x256基准测试中,TransDiff显著优于其他基于独立AR Transformer或扩散模型的图像生成模型。具体来说,TransDiff实现了Fréchet Inception Distance(FID)为1.61,Inception Score(IS)为293.4,与基于AR Transformer的现有先进技术相比,提供了x2更快的推理延迟,与仅使用扩散的模型相比,推理速度提高了x112倍。此外,我们以TransDiff模型为基础,介绍了一种新的图像生成范式——多参考自回归(MRAR)。MRAR通过预测下一个图像进行自回归生成,使模型能够参考多个先前生成的图像,从而更容易学习更多样化的表示,并在后续迭代中提高生成的图像质量。通过应用MRAR,TransDiff的性能得到了提升,FID从1.61降低到了1.42。我们期望TransDiff能在图像生成领域开辟新的前沿。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
TransDiff模型结合了自回归(AR)Transformer与扩散模型,成为首个图像生成模型。该模型在ImageNet 256x256基准测试中显著优于其他单一模型。TransDiff利用扩散模型估计图像样本分布,具有快速推理速度与较高图像生成质量。此外,基于TransDiff模型的MRAR(多参考自回归)图像生成范式可学习更广泛的表示并改善生成图像质量。这些优势使TransDiff有望成为图像生成领域的新前沿。
Key Takeaways
- TransDiff是首个结合自回归(AR)Transformer与扩散模型的图像生成模型。
- TransDiff在ImageNet 256x256基准测试中表现优异,FID达到1.61和IS达到293.4。
- TransDiff相对于基于AR Transformer的当前方法具有更快的推理速度。
- TransDiff相较于仅使用扩散模型的模型,推理速度更快。
- TransDiff引入的MRAR范式可以学习多样化的表示并提升后续迭代中生成图像的质量。
- MRAR通过在预测下一个图像时参考多个先前生成的图像,提高了模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图


Noise Conditional Variational Score Distillation
Authors:Xinyu Peng, Ziyang Zheng, Yaoming Wang, Han Li, Nuowen Kan, Wenrui Dai, Chenglin Li, Junni Zou, Hongkai Xiong
We propose Noise Conditional Variational Score Distillation (NCVSD), a novel method for distilling pretrained diffusion models into generative denoisers. We achieve this by revealing that the unconditional score function implicitly characterizes the score function of denoising posterior distributions. By integrating this insight into the Variational Score Distillation (VSD) framework, we enable scalable learning of generative denoisers capable of approximating samples from the denoising posterior distribution across a wide range of noise levels. The proposed generative denoisers exhibit desirable properties that allow fast generation while preserve the benefit of iterative refinement: (1) fast one-step generation through sampling from pure Gaussian noise at high noise levels; (2) improved sample quality by scaling the test-time compute with multi-step sampling; and (3) zero-shot probabilistic inference for flexible and controllable sampling. We evaluate NCVSD through extensive experiments, including class-conditional image generation and inverse problem solving. By scaling the test-time compute, our method outperforms teacher diffusion models and is on par with consistency models of larger sizes. Additionally, with significantly fewer NFEs than diffusion-based methods, we achieve record-breaking LPIPS on inverse problems.
我们提出了噪声条件变分分数蒸馏(NCVSD),这是一种将预训练的扩散模型蒸馏成生成去噪器的新方法。我们通过揭示无条件分数函数隐含地刻画了去噪后验分布的分数函数来实现这一点。通过将这一见解融入变分分数蒸馏(VSD)框架,我们能够学习可在广泛噪声水平下对去噪后验分布进行采样的生成去噪器。所提出生成去噪器展现出理想的特性,允许快速生成的同时保留迭代细化的优势:(1)通过从高噪声水平的纯高斯噪声中进行采样,实现快速单步生成;(2)通过多步采样扩展测试时间计算,提高样本质量;(3)零样本概率推理,用于灵活可控的采样。我们通过大量实验评估了NCVSD,包括类别条件图像生成和逆问题解决。通过扩展测试时间计算,我们的方法在性能上超越了教师扩散模型,并与更大规模的一致性模型相当。此外,与基于扩散的方法相比,我们的方法在逆向问题上的NFE显著减少,实现了破纪录的LPIPS。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了噪声条件变分分数蒸馏(NCVSD)方法,这是一种用于将预训练的扩散模型蒸馏为生成去噪器的新方法。通过揭示无条件分数函数隐式表征去噪后验分布的分数函数,我们将这一见解融入变分分数蒸馏(VSD)框架,使学习能够在各种噪声水平上近似去噪后验分布的样本。所提出的生成去噪器具有令人期望的特性,允许快速生成同时保留迭代优化的好处:一是从高噪声水平的纯高斯噪声中快速进行一步生成;二是通过多步采样提高样本质量来扩展测试时间计算;三是实现灵活可控采样的零样本概率推理。通过实验评估,包括类条件图像生成和逆问题解决,我们的方法在教师扩散模型上表现出优势,并且在大型一致性模型方面表现相当。此外,相较于扩散方法,我们的方法在逆问题上大幅减少了计算次数,并创下了LPIPS的新纪录。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了Noise Conditional Variational Score Distillation (NCVSD) 方法,用于将扩散模型转化为生成去噪器。
- 通过整合无条件分数函数的见解到VSD框架,实现了对各种噪声水平下样本的近似学习。
- 生成的去噪器具备快速一步生成、提高样本质量和零样本概率推理等特性。
- 通过广泛的实验评估,包括类条件图像生成和逆问题解决,该方法在教师扩散模型上表现优越。
- 方法在大型一致性模型方面表现相当,并且在逆问题上显著减少了计算次数。
- 在逆问题上实现了LPIPS的新纪录。
- 该方法对于扩散模型的进一步优化和实际应用具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图
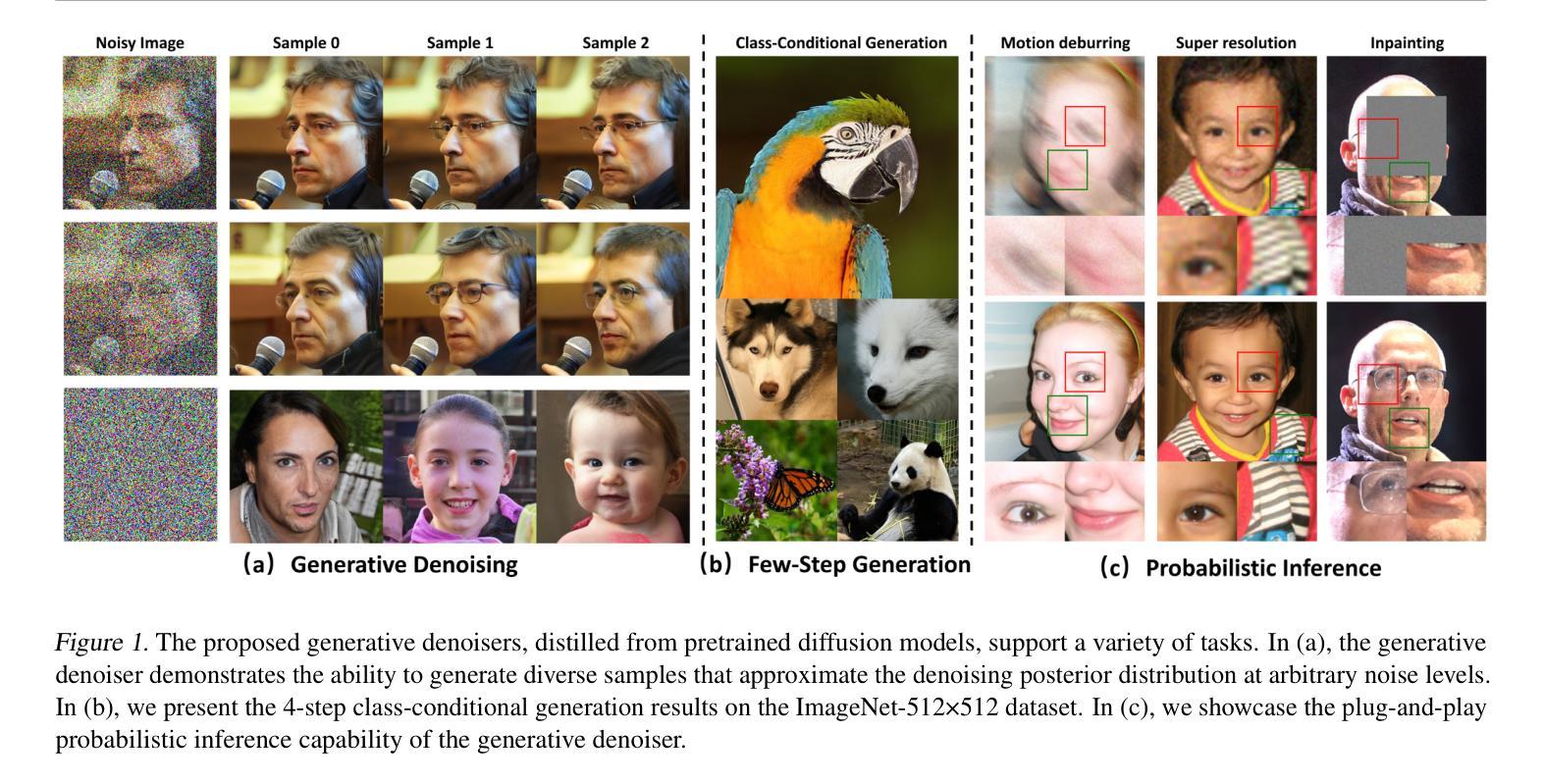



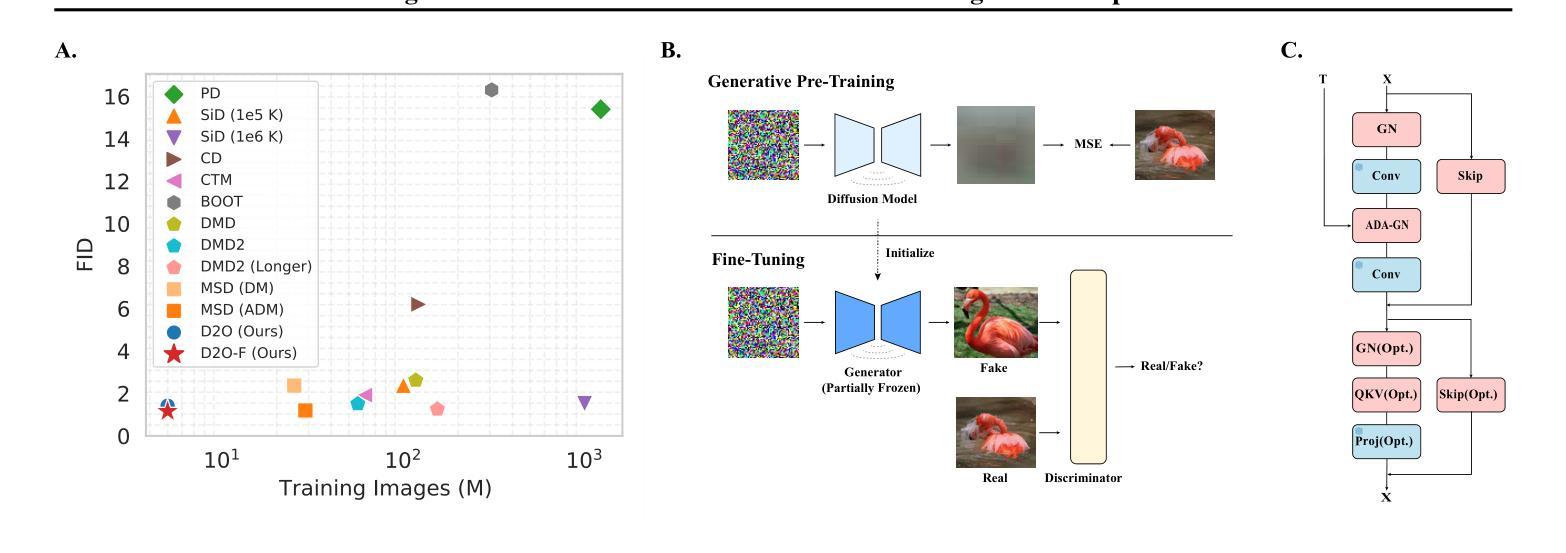
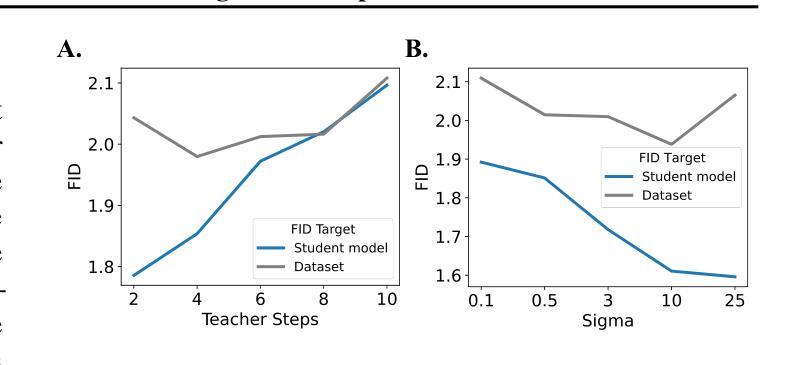
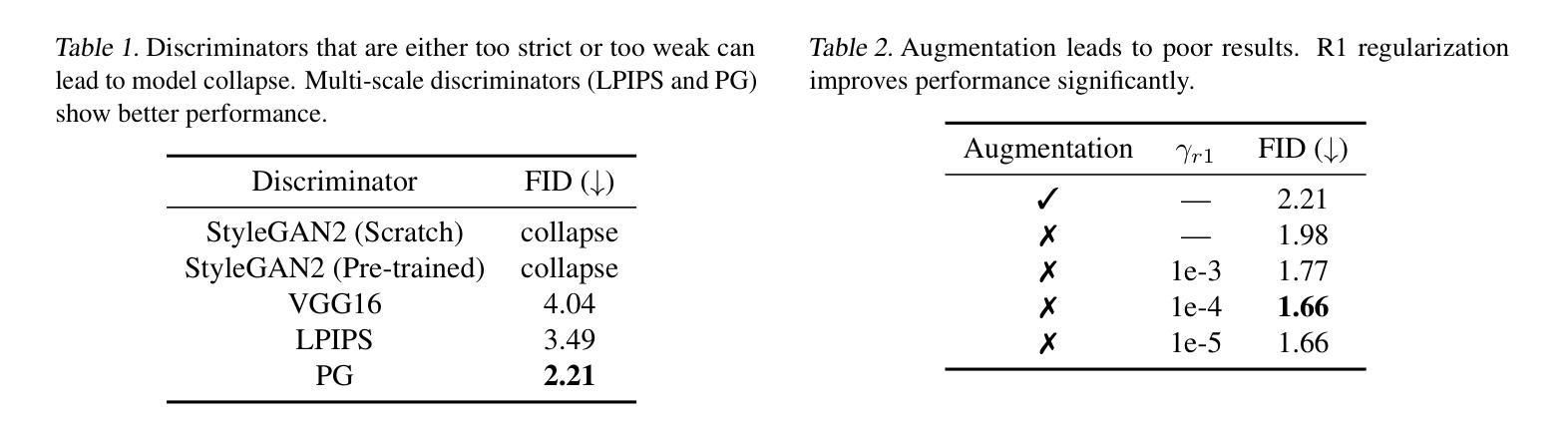
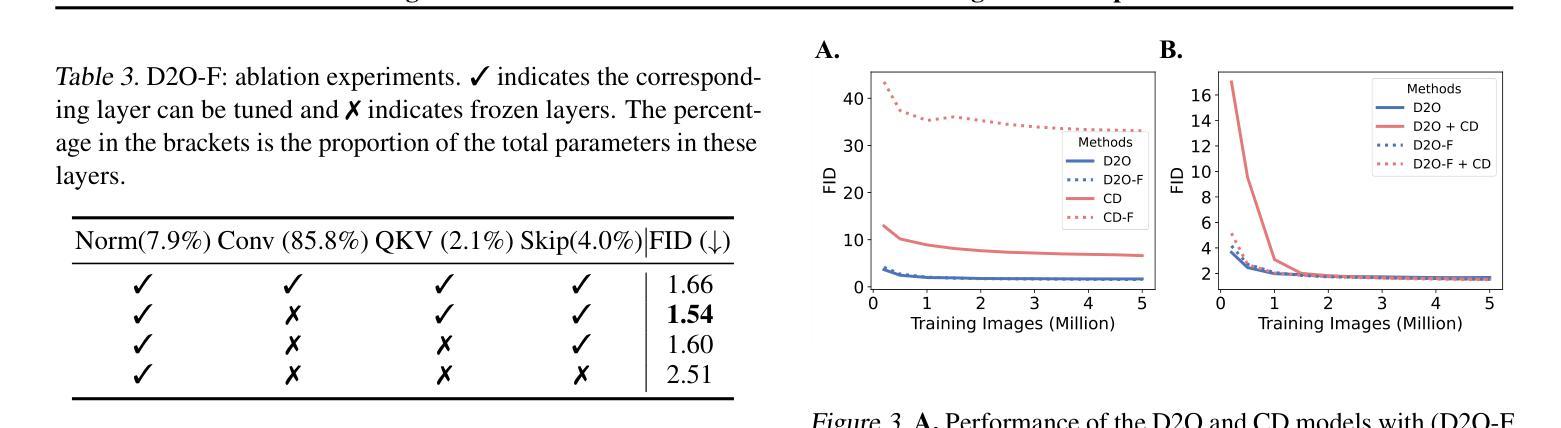
Revisiting Diffusion Models: From Generative Pre-training to One-Step Generation
Authors:Bowen Zheng, Tianming Yang
Diffusion distillation is a widely used technique to reduce the sampling cost of diffusion models, yet it often requires extensive training, and the student performance tends to be degraded. Recent studies show that incorporating a GAN objective may alleviate these issues, yet the underlying mechanism remains unclear. In this work, we first identify a key limitation of distillation: mismatched step sizes and parameter numbers between the teacher and the student model lead them to converge to different local minima, rendering direct imitation suboptimal. We further demonstrate that a standalone GAN objective, without relying a distillation loss, overcomes this limitation and is sufficient to convert diffusion models into efficient one-step generators. Based on this finding, we propose that diffusion training may be viewed as a form of generative pre-training, equipping models with capabilities that can be unlocked through lightweight GAN fine-tuning. Supporting this view, we create a one-step generation model by fine-tuning a pre-trained model with 85% of parameters frozen, achieving strong performance with only 0.2M images and near-SOTA results with 5M images. We further present a frequency-domain analysis that may explain the one-step generative capability gained in diffusion training. Overall, our work provides a new perspective for diffusion training, highlighting its role as a powerful generative pre-training process, which can be the basis for building efficient one-step generation models.
扩散蒸馏是减少扩散模型采样成本的一种广泛使用的技术,然而它通常需要大量的训练,并且学生的表现往往较差。最近的研究表明,引入GAN目标可以缓解这些问题,但背后的机制仍然不清楚。在这项工作中,我们首先确定了蒸馏的一个关键限制:教师模型和学生模型的步长参数不匹配导致它们收敛到不同的局部最小值,使得直接模仿变得不够理想。我们进一步证明,一个独立的GAN目标,在不依赖蒸馏损失的情况下,能够克服这一限制,并足以将扩散模型转化为高效的一步生成器。基于这一发现,我们提出可以将扩散训练视为一种生成预训练的形式,为模型提供解锁的能力,通过轻量级的GAN微调来提高性能。支持这一观点的是,我们创建了一个一步生成模型,通过微调一个预训练模型(冻结了85%的参数),仅使用0.2M图像就实现了强大的性能,使用5M图像时接近SOTA结果。我们还进行了一次频域分析,这可能解释了扩散训练中获得的一步生成能力。总的来说,我们的工作为扩散训练提供了新的视角,强调了其作为强大的生成预训练过程的作用,可以作为构建高效一步生成模型的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型中的蒸馏技术存在的问题,如训练成本较高且学生模型性能下降。研究发现,引入GAN目标可以缓解这些问题,但其内在机制尚不清楚。本文指出蒸馏的关键局限性在于教师模型和学生模型之间的步长和参数不匹配,导致它们收敛到不同的局部最小值,直接模仿并不理想。研究还表明,仅使用GAN目标,无需依赖蒸馏损失,能够克服这一局限,并将扩散模型转化为高效的一步生成器。基于此,本文提出将扩散训练视为一种生成式预训练方法,可通过轻量级的GAN微调解锁模型能力。通过冻结预训练模型的85%参数进行微调,实现了仅使用0.2M图像即可获得强大性能,使用5M图像时接近最佳结果。此外,本文还提供了频率域分析,以解释在扩散训练中获得的一步生成能力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型中的蒸馏技术虽然广泛应用,但存在训练成本高和学生模型性能下降的问题。
- 教师模型和学生模型之间的步长和参数不匹配是蒸馏的关键局限。
- 引入GAN目标可以缓解蒸馏的局限,使扩散模型成为高效的一步生成器。
- 扩散训练可视为一种生成式预训练方法,可通过轻量级GAN微调解锁模型能力。
- 通过冻结大部分预训练参数进行微调,可在较少图像数据下实现强大性能。
- 频率域分析有助于解释扩散训练中一步生成能力的提升。
点此查看论文截图

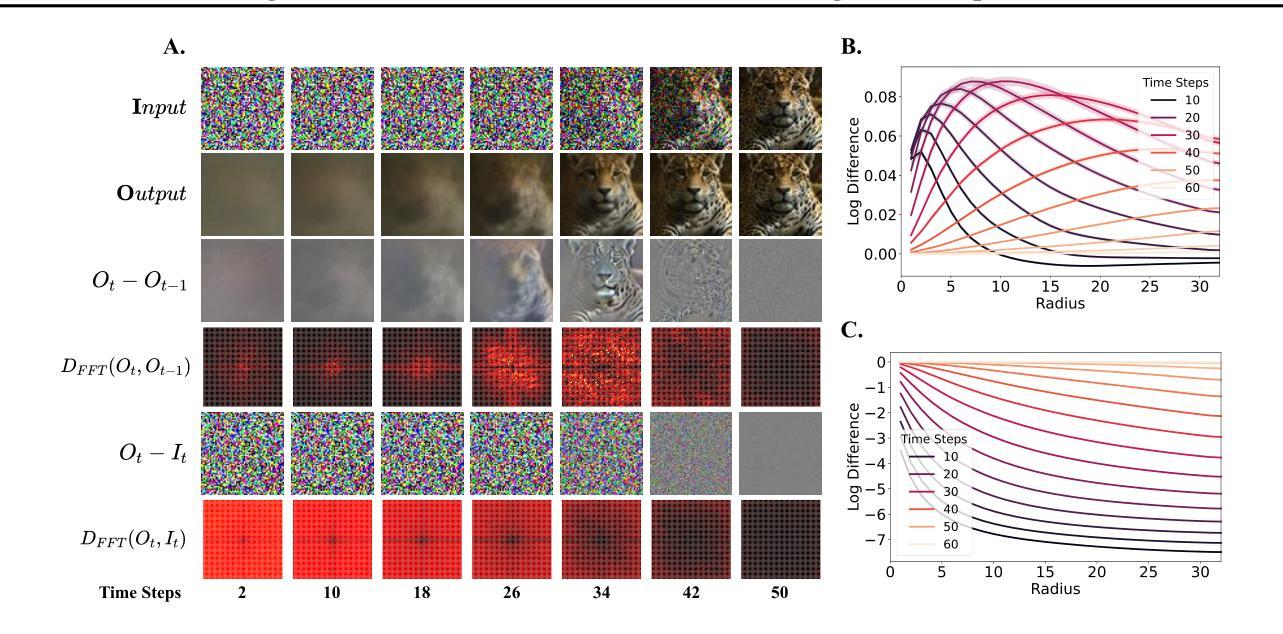
SAGE: Exploring the Boundaries of Unsafe Concept Domain with Semantic-Augment Erasing
Authors:Hongguang Zhu, Yunchao Wei, Mengyu Wang, Siyu Jiao, Yan Fang, Jiannan Huang, Yao Zhao
Diffusion models (DMs) have achieved significant progress in text-to-image generation. However, the inevitable inclusion of sensitive information during pre-training poses safety risks, such as unsafe content generation and copyright infringement. Concept erasing finetunes weights to unlearn undesirable concepts, and has emerged as a promising solution. However, existing methods treat unsafe concept as a fixed word and repeatedly erase it, trapping DMs in ``word concept abyss’’, which prevents generalized concept-related erasing. To escape this abyss, we introduce semantic-augment erasing which transforms concept word erasure into concept domain erasure by the cyclic self-check and self-erasure. It efficiently explores and unlearns the boundary representation of concept domain through semantic spatial relationships between original and training DMs, without requiring additional preprocessed data. Meanwhile, to mitigate the retention degradation of irrelevant concepts while erasing unsafe concepts, we further propose the global-local collaborative retention mechanism that combines global semantic relationship alignment with local predicted noise preservation, effectively expanding the retentive receptive field for irrelevant concepts. We name our method SAGE, and extensive experiments demonstrate the comprehensive superiority of SAGE compared with other methods in the safe generation of DMs. The code and weights will be open-sourced at https://github.com/KevinLight831/SAGE.
扩散模型(DMs)在文本到图像生成方面取得了显著进展。然而,预训练过程中不可避免地会包含敏感信息,这带来了安全风险,如不安全内容生成和版权侵犯。概念消除通过对权重进行微调来遗忘不需要的概念,并已成为一种有前景的解决方案。然而,现有方法将不安全概念视为固定单词并反复消除它,使扩散模型陷入“单词概念深渊”,这阻碍了通用的概念相关消除。为了逃离这个深渊,我们引入了语义增强消除法,通过循环自检和自我消除,将概念词汇消除转变为概念领域消除。它有效地探索和遗忘了概念领域的边界表示,通过原始和培训扩散模型之间的语义空间关系,而无需额外的预处理数据。同时,为了减轻在消除不安全概念时无关概念的保留度下降问题,我们进一步提出了全局-局部协作保留机制,将全局语义关系对齐与局部预测噪声保留相结合,有效地扩大了无关概念的保留感受野。我们将该方法命名为SAGE,大量实验表明,与其他方法相比,SAGE在安全生成扩散模型方面表现出全面的优越性。代码和权重将在https://github.com/KevinLight831/SAGE上开源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
扩散模型(DMs)在文本到图像生成方面取得了显著进展,但预训练时不可避免地会包含敏感信息,带来安全隐患,如不安全内容生成和版权侵犯。概念消除是一种新兴解决方案,但现有方法将不安全概念视为固定词汇进行反复消除,使DMs陷入“单词概念深渊”,无法实现通用概念相关消除。为摆脱此困境,我们提出语义增强消除法,通过循环自检自消,将概念词汇消除转变为概念域消除。该方法通过原始和训练DMs之间的语义空间关系有效探索并消除概念域的边界表示,无需额外的预处理数据。同时,为缓解在消除不安全概念时无关概念的保留度下降问题,我们进一步提出全局-局部协作保留机制,结合全局语义关系对齐和局部预测噪声保留,有效扩大无关概念的保留感受野。我们的方法名为SAGE,实验表明其在安全生成DMs方面表现全面优于其他方法。代码和权重将在https://github.com/KevinLight831/SAGE开源。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DMs)在文本到图像生成中有显著进展,但预训练包含敏感信息引发安全隐患。
- 概念消除是一种解决此问题的方法,但现有方法存在局限,陷入“单词概念深渊”。
- 语义增强消除法(SAGE)提出循环自检自消,实现概念域消除。
- SAGE通过语义空间关系探索并消除概念域边界,无需额外预处理数据。
- SAGE提出全局-局部协作保留机制,以保留无关概念。
- 实验证明SAGE在扩散模型的安全生成方面表现优越。
点此查看论文截图
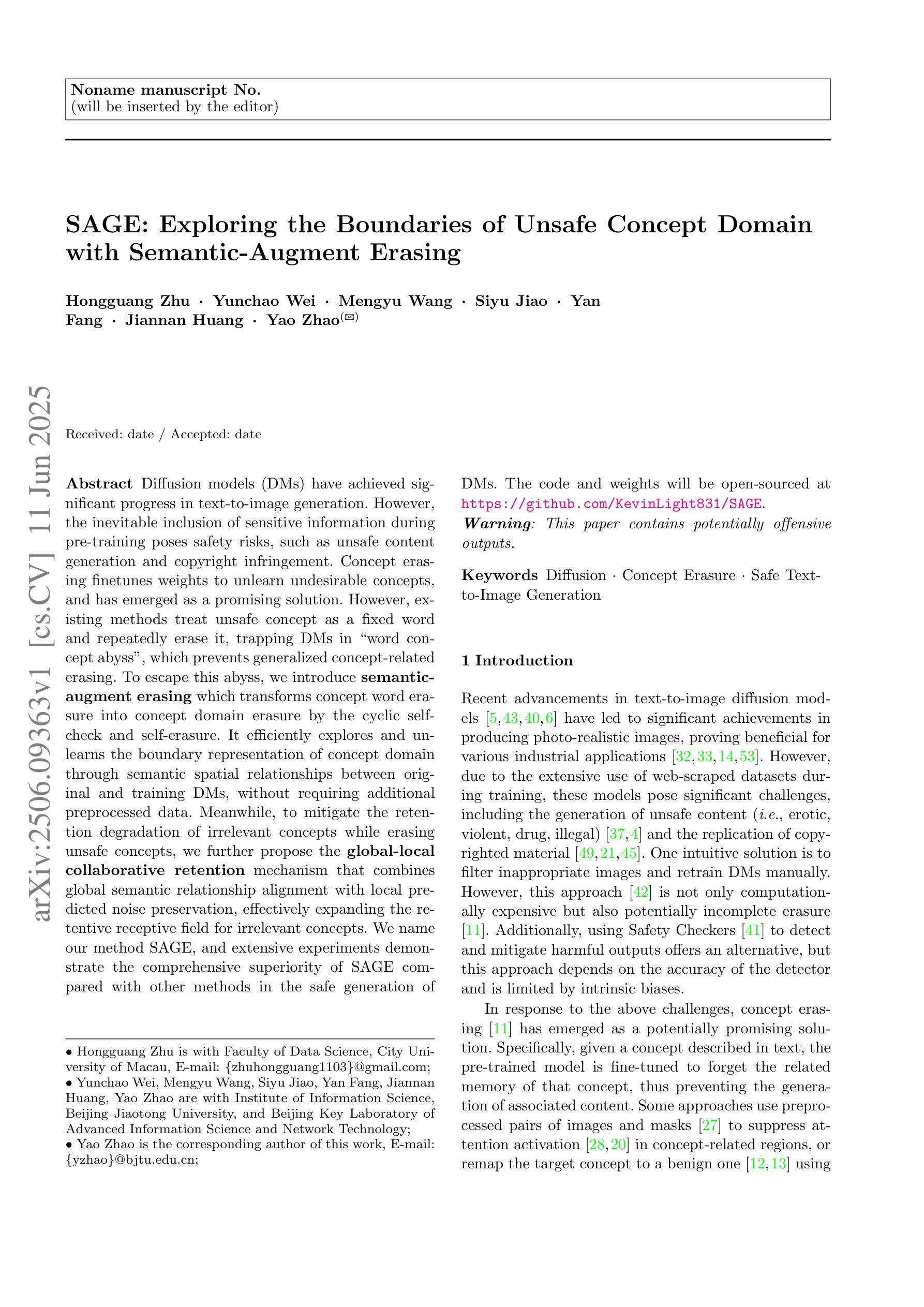

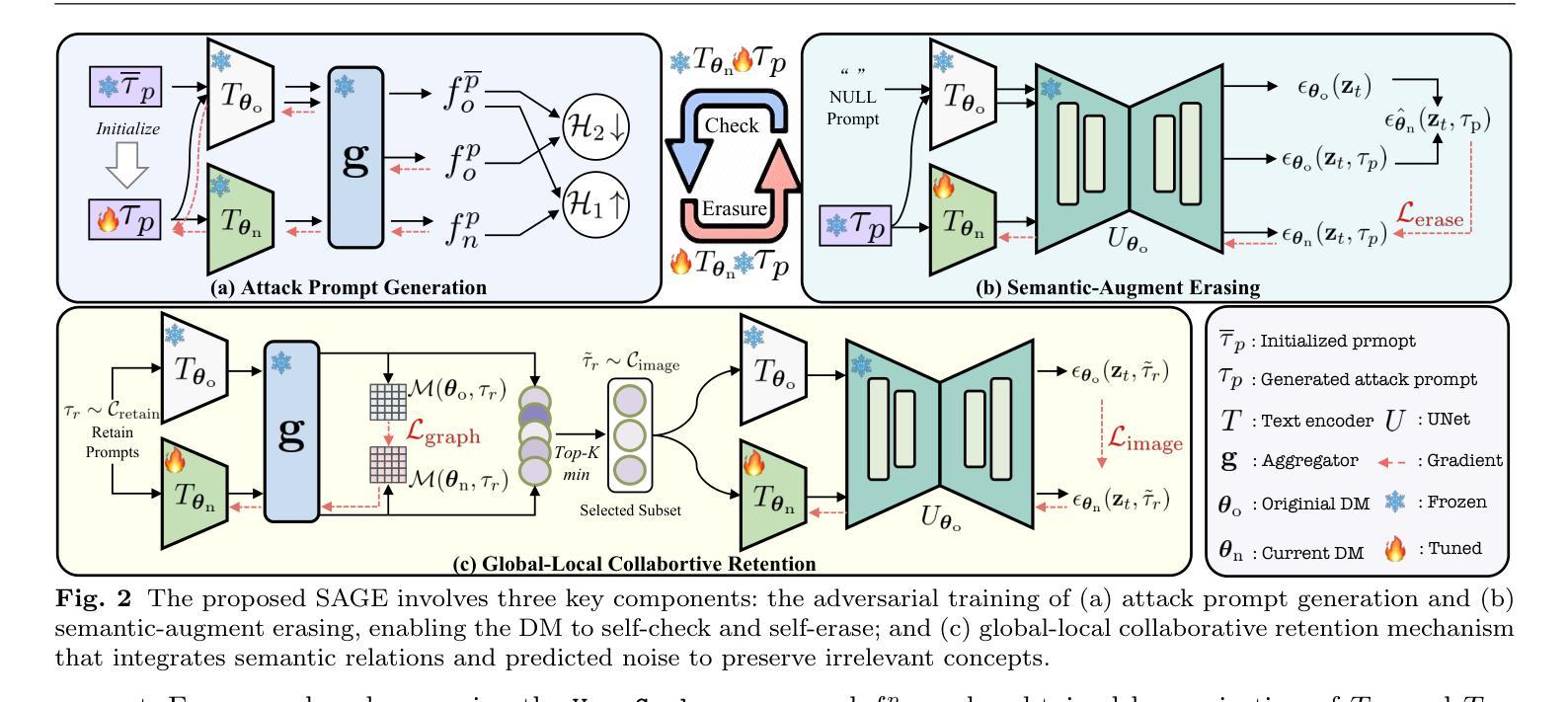
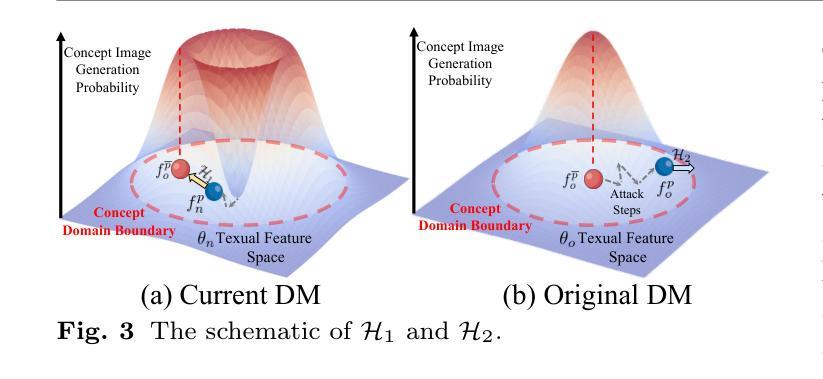
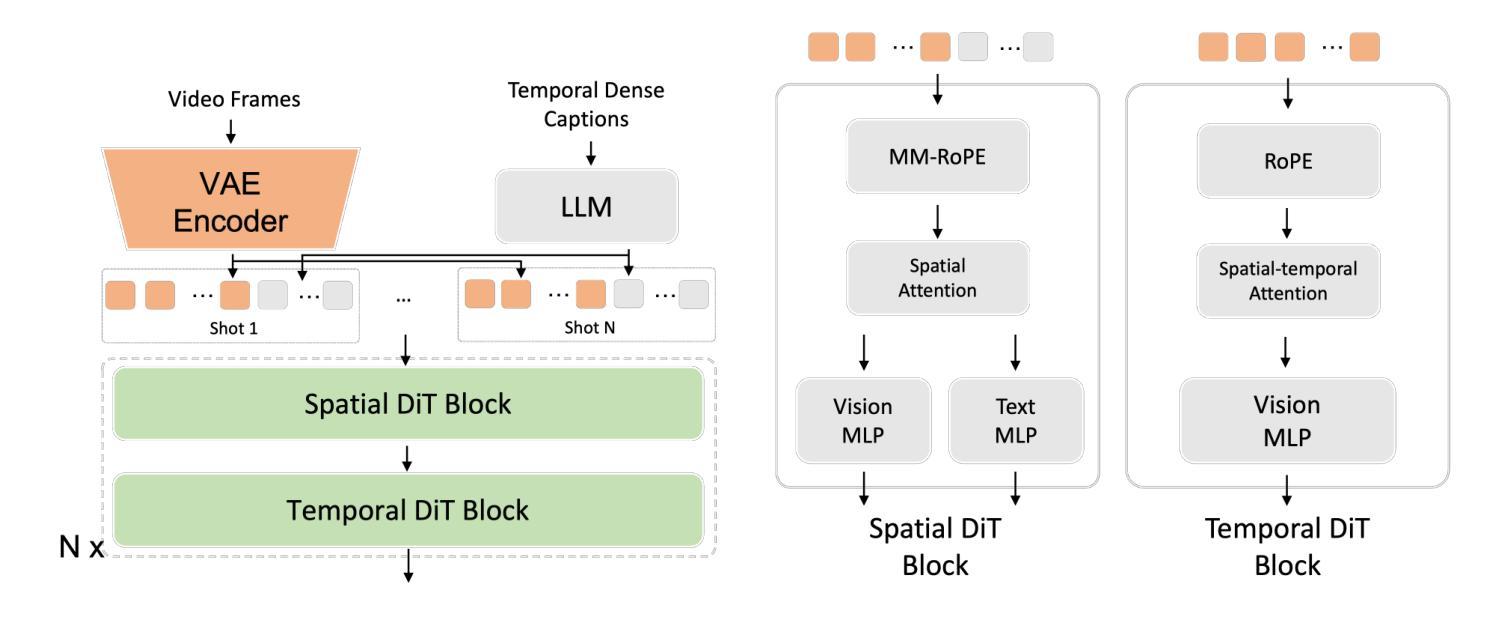
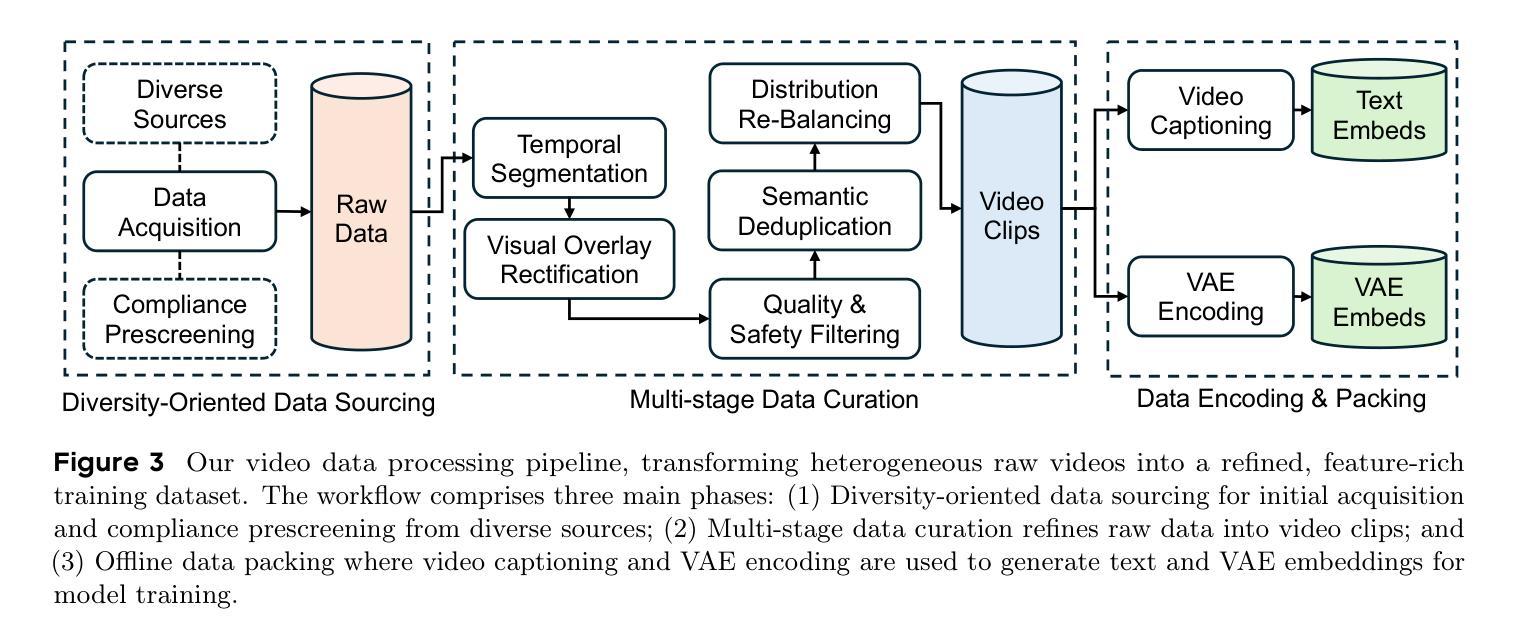
Seedance 1.0: Exploring the Boundaries of Video Generation Models
Authors:Yu Gao, Haoyuan Guo, Tuyen Hoang, Weilin Huang, Lu Jiang, Fangyuan Kong, Huixia Li, Jiashi Li, Liang Li, Xiaojie Li, Xunsong Li, Yifu Li, Shanchuan Lin, Zhijie Lin, Jiawei Liu, Shu Liu, Xiaonan Nie, Zhiwu Qing, Yuxi Ren, Li Sun, Zhi Tian, Rui Wang, Sen Wang, Guoqiang Wei, Guohong Wu, Jie Wu, Ruiqi Xia, Fei Xiao, Xuefeng Xiao, Jiangqiao Yan, Ceyuan Yang, Jianchao Yang, Runkai Yang, Tao Yang, Yihang Yang, Zilyu Ye, Xuejiao Zeng, Yan Zeng, Heng Zhang, Yang Zhao, Xiaozheng Zheng, Peihao Zhu, Jiaxin Zou, Feilong Zuo
Notable breakthroughs in diffusion modeling have propelled rapid improvements in video generation, yet current foundational model still face critical challenges in simultaneously balancing prompt following, motion plausibility, and visual quality. In this report, we introduce Seedance 1.0, a high-performance and inference-efficient video foundation generation model that integrates several core technical improvements: (i) multi-source data curation augmented with precision and meaningful video captioning, enabling comprehensive learning across diverse scenarios; (ii) an efficient architecture design with proposed training paradigm, which allows for natively supporting multi-shot generation and jointly learning of both text-to-video and image-to-video tasks. (iii) carefully-optimized post-training approaches leveraging fine-grained supervised fine-tuning, and video-specific RLHF with multi-dimensional reward mechanisms for comprehensive performance improvements; (iv) excellent model acceleration achieving ~10x inference speedup through multi-stage distillation strategies and system-level optimizations. Seedance 1.0 can generate a 5-second video at 1080p resolution only with 41.4 seconds (NVIDIA-L20). Compared to state-of-the-art video generation models, Seedance 1.0 stands out with high-quality and fast video generation having superior spatiotemporal fluidity with structural stability, precise instruction adherence in complex multi-subject contexts, native multi-shot narrative coherence with consistent subject representation.
在扩散建模方面,显著的突破推动了视频生成的快速发展,然而,当前的基础模型仍然面临着在提示遵循、运动合理性和视觉质量之间平衡的重大挑战。在这份报告中,我们介绍了Seedance 1.0,这是一款高性能且推理效率高的视频基础生成模型,它融合了多项核心技术改进:一是对多元数据源进行精准和有意义的视频字幕增强的数据整理,实现了不同场景的全面学习;二是采用高效架构设计并提出的训练范式,原生支持多镜头生成并联合学习文本到视频和图像到视频的任务;三是利用精细监督微调及针对视频的特定RLHF和多维度奖励机制进行仔细优化的训练后方法,以实现全面的性能提升;四是采用多阶段蒸馏策略和系统化优化实现约10倍的推理加速。Seedance 1.0能够以41.4秒(NVIDIA-L20)的速度生成分辨率为1080p的5秒视频。与最先进的视频生成模型相比,Seedance 1.0以其高质量和快速视频生成能力脱颖而出,具有卓越的时空流畅性和结构稳定性、在复杂的多主题环境下的精确指令遵循能力,以及一致的主题表示的原生多镜头叙事连贯性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Seedance 1.0 Technical Report
Summary
Seedance 1.0是一款高性能的视频生成模型,解决了当前模型在提示遵循、运动合理性和视觉质量方面的挑战。它通过多源数据整合、高效架构设计、精细训练后优化和模型加速等技术突破,实现了快速且高质量的视频生成。
Key Takeaways
- Seedance 1.0引入了多源数据整合技术,通过精确和有意义的视频描述进行增强学习,使得模型能够在不同场景下进行全面学习。
- 模型采用高效架构设计,支持多镜头生成,并联合学习文本到视频和图像到视频的任务。
- 通过精细训练的优化方法,利用精细监督微调以及针对视频的特定强化学习,实现了全面的性能提升。
- 模型采用多阶段蒸馏策略和系统级优化,实现了约10倍的推理速度提升。
- Seedance 1.0能够在短时间内生成高质量的视频,例如,在NVIDIA-L20上仅需要41.4秒就能生成一个分辨率为1080p的5秒视频。
- 该模型在时空流畅性、结构稳定性方面具有优势,能够在复杂的多主题环境中精确遵循指令。
点此查看论文截图


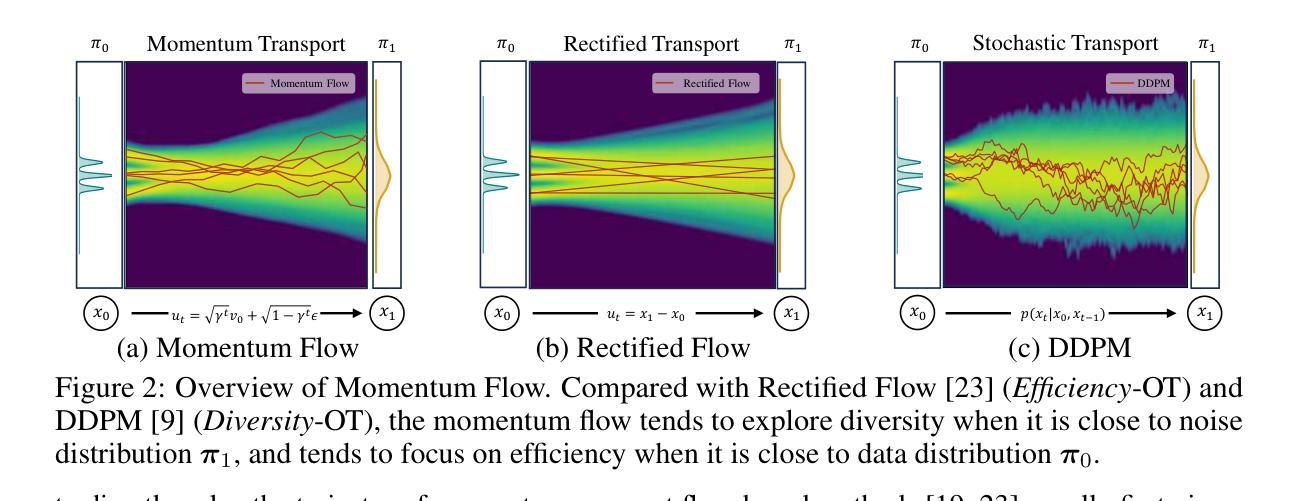
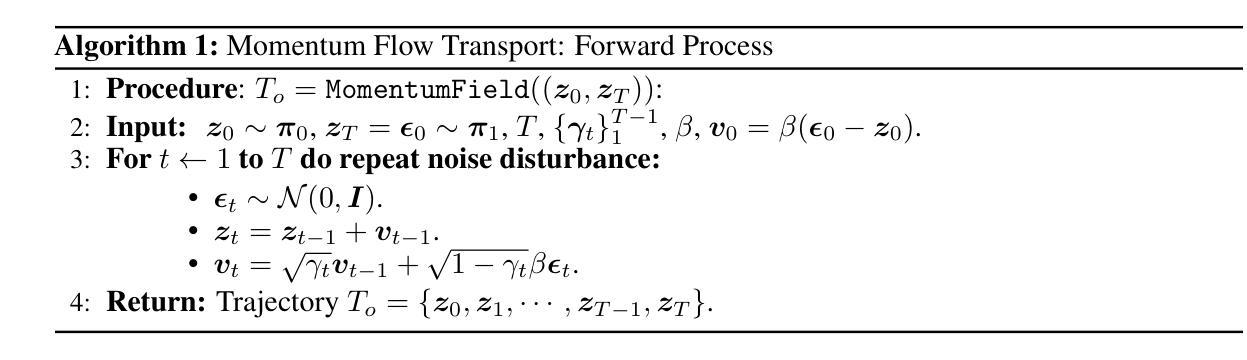
Flow Diverse and Efficient: Learning Momentum Flow Matching via Stochastic Velocity Field Sampling
Authors:Zhiyuan Ma, Ruixun Liu, Sixian Liu, Jianjun Li, Bowen Zhou
Recently, the rectified flow (RF) has emerged as the new state-of-the-art among flow-based diffusion models due to its high efficiency advantage in straight path sampling, especially with the amazing images generated by a series of RF models such as Flux 1.0 and SD 3.0. Although a straight-line connection between the noisy and natural data distributions is intuitive, fast, and easy to optimize, it still inevitably leads to: 1) Diversity concerns, which arise since straight-line paths only cover a fairly restricted sampling space. 2) Multi-scale noise modeling concerns, since the straight line flow only needs to optimize the constant velocity field $\bm v$ between the two distributions $\bm\pi_0$ and $\bm\pi_1$. In this work, we present Discretized-RF, a new family of rectified flow (also called momentum flow models since they refer to the previous velocity component and the random velocity component in each diffusion step), which discretizes the straight path into a series of variable velocity field sub-paths (namely ``momentum fields’’) to expand the search space, especially when close to the distribution $p_\text{noise}$. Different from the previous case where noise is directly superimposed on $\bm x$, we introduce noise on the velocity $\bm v$ of the sub-path to change its direction in order to improve the diversity and multi-scale noise modeling abilities. Experimental results on several representative datasets demonstrate that learning momentum flow matching by sampling random velocity fields will produce trajectories that are both diverse and efficient, and can consistently generate high-quality and diverse results. Code is available at https://github.com/liuruixun/momentum-fm.
最近,由于其在直线路径采样中的高效率优势,整流流(Rectified Flow,简称RF)已成为基于流的扩散模型中的最新先进技术。尤其是一系列RF模型(如Flux 1.0和SD 3.0)所生成的惊人图像。尽管噪声数据和自然数据分布之间的直线连接直观、快速且易于优化,但它仍然不可避免地导致以下问题:1)多样性问题,因为直线路径只覆盖了一个相对有限的采样空间。2)多尺度噪声建模问题,因为直线流只需要优化两个分布$\bm\pi_0$和$\bm\pi_1$之间的恒定速度场$\bm v$。在这项工作中,我们提出了离散化RF,这是一类新的整流流(也称为动量流模型,因为它们是指每个扩散步骤中的先前速度分量和随机速度分量),它将直线路径离散化成一系列可变速度场子路径(即“动量场”),以扩大搜索空间,特别是在接近分布$p_\text{noise}$时。不同于以前直接将噪声叠加到$\bm x$上的情况,我们在子路径的速度$\bm v$上引入噪声,以改变其方向,从而提高多样性和多尺度噪声建模能力。在几个代表性数据集上的实验结果证明,通过学习动量流匹配并采样随机速度场,可以产生既多样化又高效的轨迹,并且能持续生成高质量和多样化的结果。代码可在https://github.com/liuruixun/momentum-fm上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
最新出现的整流流(Rectified Flow,简称RF)基于其在直线路径采样上的高效率优势,已成为当前流行的扩散模型。尽管从噪声数据分布到自然数据分布的直线连接直观、快速且易于优化,但它仍然面临多样性和多尺度噪声建模的问题。本文提出离散化整流流(Discretized-RF),这是一种新的整流流家族(也称为动量流模型),它将直线路径离散化为一系列可变速度场子路径(即“动量场”),以扩大搜索空间,特别是在接近噪声分布时。不同于以往直接在$\bm x$上叠加噪声的方法,我们在子路径的速度$\bm v$上引入噪声,以改变其方向,从而提高多样性和多尺度噪声建模能力。实验结果表明,通过随机速度场采样学习动量流匹配,可以产生既多样又高效的轨迹,并能持续生成高质量和多样化的结果。
关键见解
- 整流流(RF)已成为基于流扩散模型的新技术前沿,以其直线路径采样的高效率著称。
- RF虽然直观、快速且易于优化,但存在多样性和多尺度噪声建模的问题。
- 离散化整流流(Discretized-RF)是一种新的RF模型,通过离散化直线路径并使用“动量场”来扩大搜索空间,以提高性能。
- 与以往方法不同,Discretized-RF在子路径的速度上引入噪声,以改变方向,从而提高多样性和多尺度噪声建模能力。
- 实验结果表明,通过随机速度场采样学习动量流匹配能够产生高效且多样化的轨迹。
- Discretized-RF模型可以持续生成高质量和多样化的结果。
点此查看论文截图

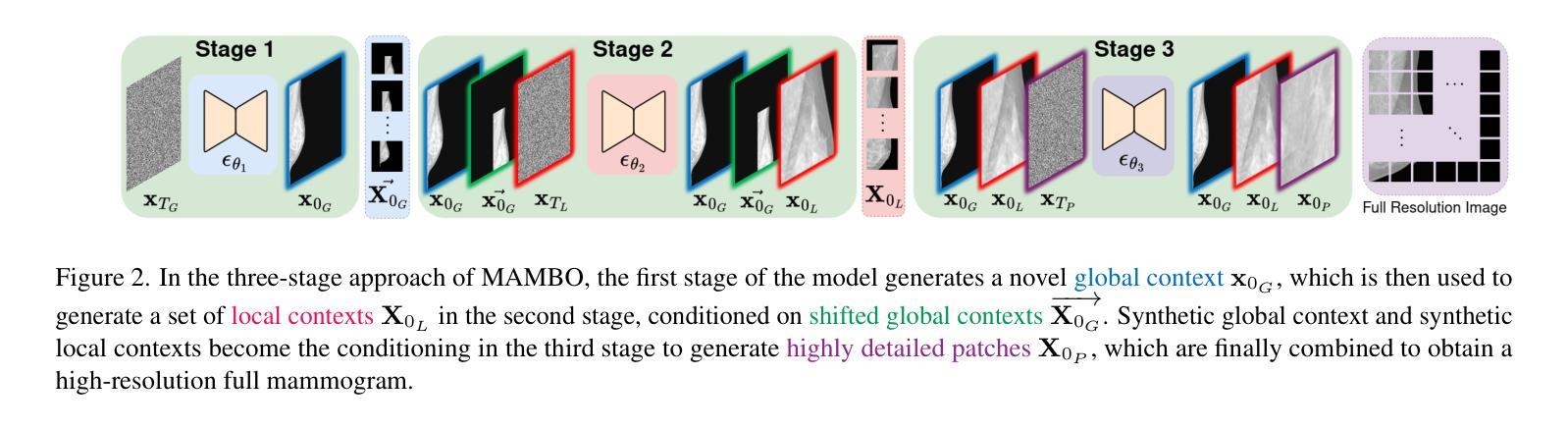
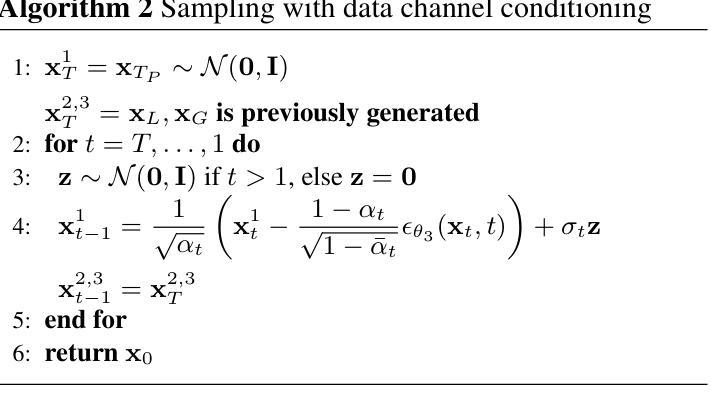
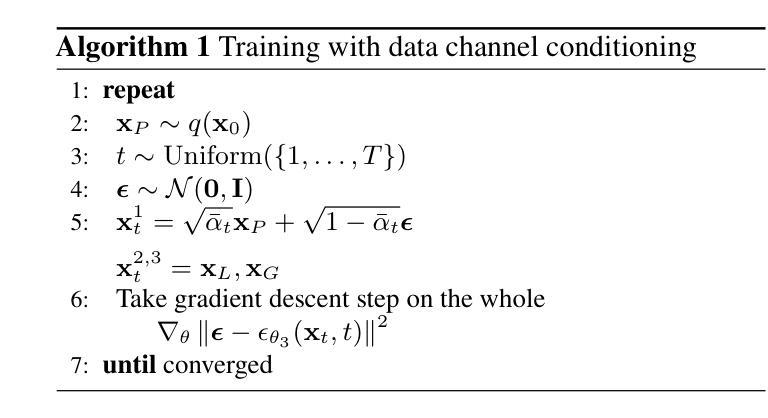
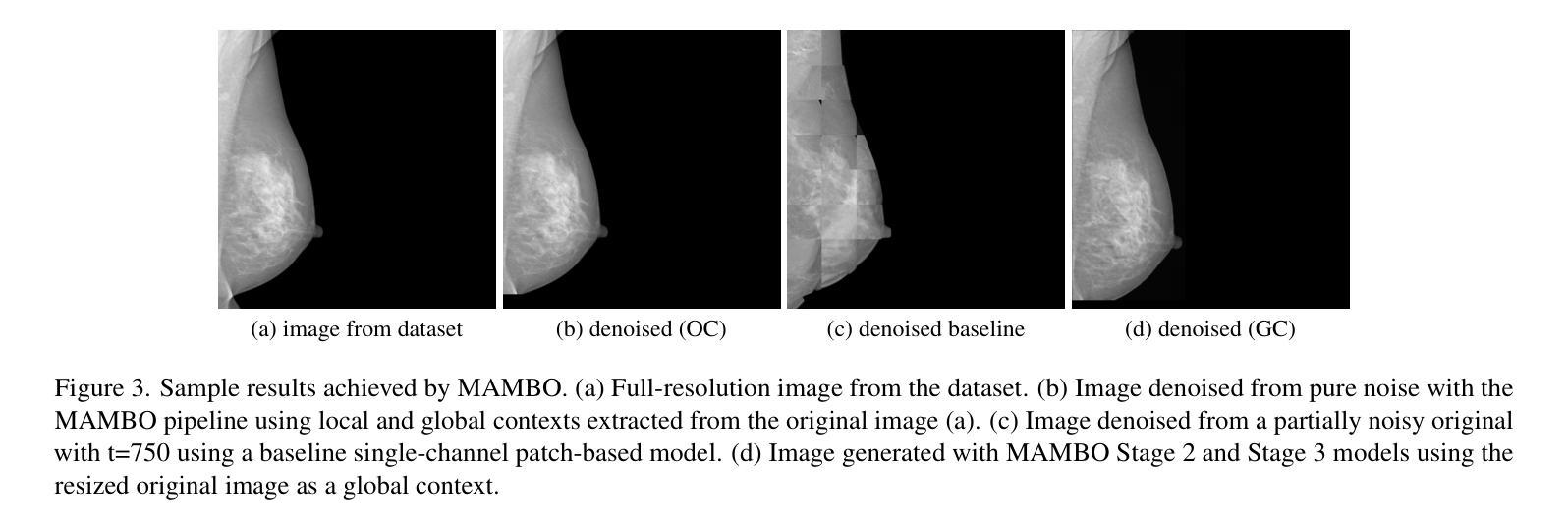
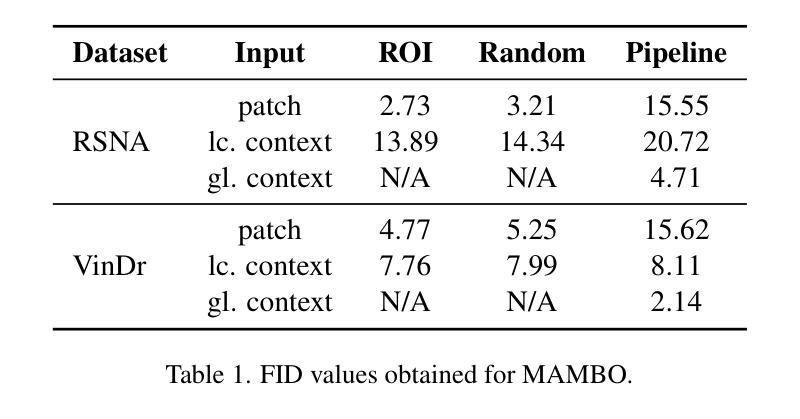
MAMBO: High-Resolution Generative Approach for Mammography Images
Authors:Milica Škipina, Nikola Jovišić, Nicola Dall’Asen, Vanja Švenda, Anil Osman Tur, Slobodan Ilić, Elisa Ricci, Dubravko Ćulibrk
Mammography is the gold standard for the detection and diagnosis of breast cancer. This procedure can be significantly enhanced with Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based software, which assists radiologists in identifying abnormalities. However, training AI systems requires large and diverse datasets, which are often difficult to obtain due to privacy and ethical constraints. To address this issue, the paper introduces MAMmography ensemBle mOdel (MAMBO), a novel patch-based diffusion approach designed to generate full-resolution mammograms. Diffusion models have shown breakthrough results in realistic image generation, yet few studies have focused on mammograms, and none have successfully generated high-resolution outputs required to capture fine-grained features of small lesions. To achieve this, MAMBO integrates separate diffusion models to capture both local and global (image-level) contexts. The contextual information is then fed into the final patch-based model, significantly aiding the noise removal process. This thoughtful design enables MAMBO to generate highly realistic mammograms of up to 3840x3840 pixels. Importantly, this approach can be used to enhance the training of classification models and extended to anomaly detection. Experiments, both numerical and radiologist validation, assess MAMBO’s capabilities in image generation, super-resolution, and anomaly detection, highlighting its potential to enhance mammography analysis for more accurate diagnoses and earlier lesion detection.
乳腺X光摄影是检测和诊断乳腺癌的金标准。通过人工智能(AI)软件可以极大地增强这一程序的效能,帮助放射科医生识别异常。然而,训练AI系统需要大量的多样化数据集,由于隐私和伦理约束,这些数据集的获取往往很困难。为了解决这一问题,本文介绍了MAMmography ensemBle mOdel(MAMBO),这是一种基于补丁的新型扩散方法,旨在生成全分辨率乳腺X光片。扩散模型在真实图像生成方面取得了突破性成果,但对乳腺X光片的研究很少,而且没有任何研究能够成功生成捕捉小病灶细微特征所需的高分辨率输出。为了实现这一点,MAMBO集成了单独的扩散模型来捕捉局部和全局(图像级别)的上下文。然后,将上下文信息输入最终的基于补丁的模型,极大地有助于去噪过程。这一精心设计使MAMBO能够生成高达3840x3840像素的非常逼真的乳腺X光片。重要的是,这种方法可用于提高分类模型的训练效果,并可扩展到异常检测。实验包括数值和放射科医生验证,评估了MAMBO在图像生成、超分辨率和异常检测方面的能力,突出了其在提高乳腺X光摄影分析方面实现更精确诊断和更早病灶检测方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 14 figures, 7 tables
Summary
本文介绍了MAMmography ensemBle mOdel(MAMBO),这是一种基于扩散模型的新技术,旨在生成高分辨率的乳腺X光照片。该技术结合了局部和全局上下文信息,通过噪声去除过程生成高度逼真的图像,有助于提高乳腺癌的诊断准确性和早期病变检测能力。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺X光摄影是乳腺癌检测和诊断的金标准,而人工智能软件的辅助可以显著提高该过程的效率。
- 训练AI系统需要大量的多样化数据集,但由于隐私和伦理约束,这些数据集往往难以获得。
- MAMBO是一种创新的基于扩散模型的乳腺X光照片生成方法,旨在解决上述数据获取问题。
- MAMBO结合了局部和全局上下文信息,生成高度逼真的高分辨率乳腺X光照片,有助于更准确的诊断和早期病变检测。
- MAMBO采用独特的噪声去除过程,有助于增强图像质量和识别微小病变的能力。
- 通过数值和放射科医生验证的实验评估了MAMBO在图像生成、超分辨率和异常检测方面的能力。
点此查看论文截图

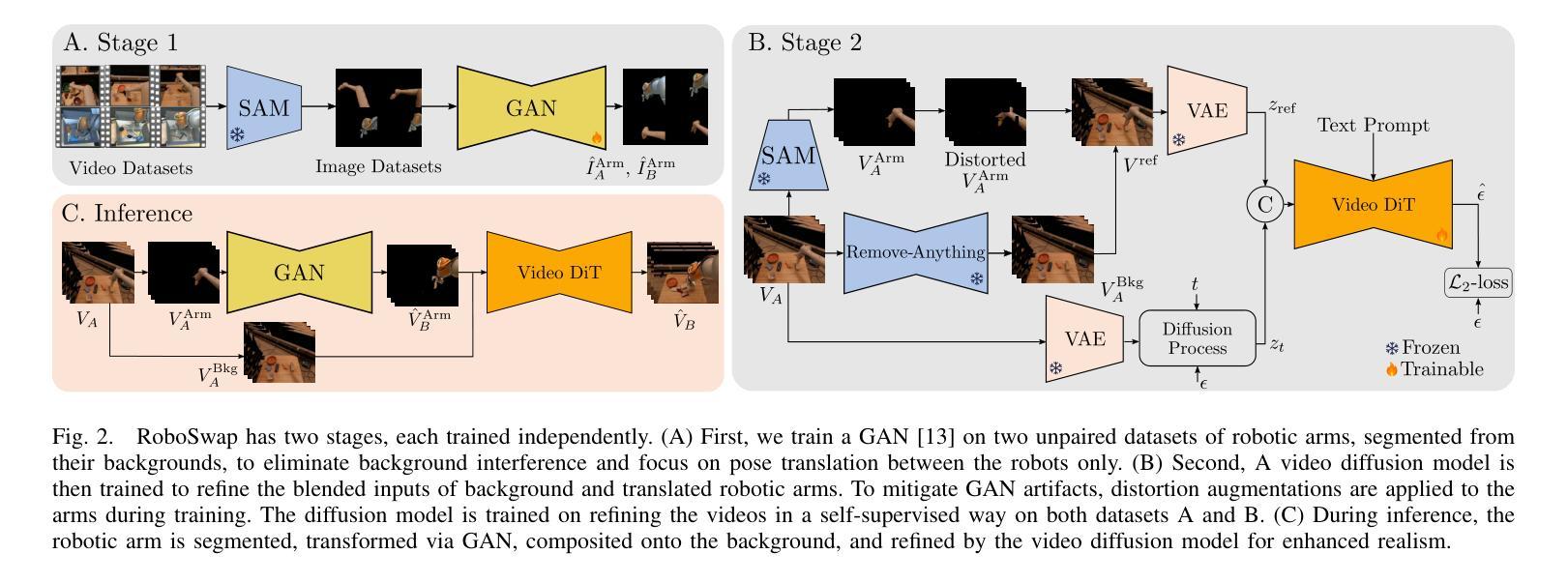
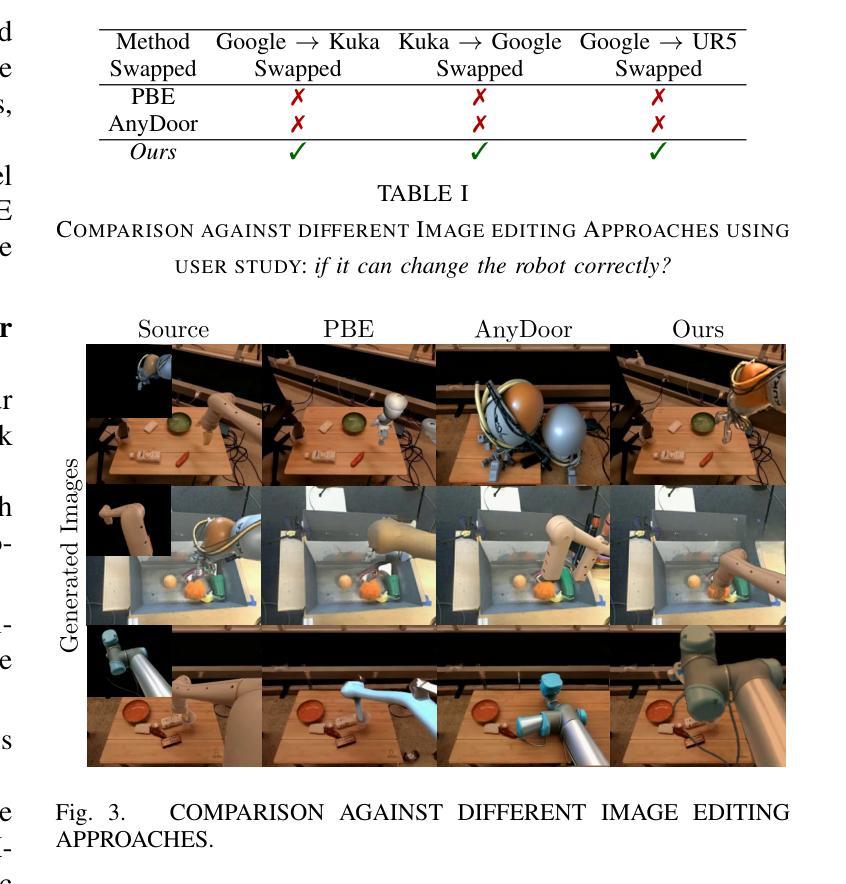
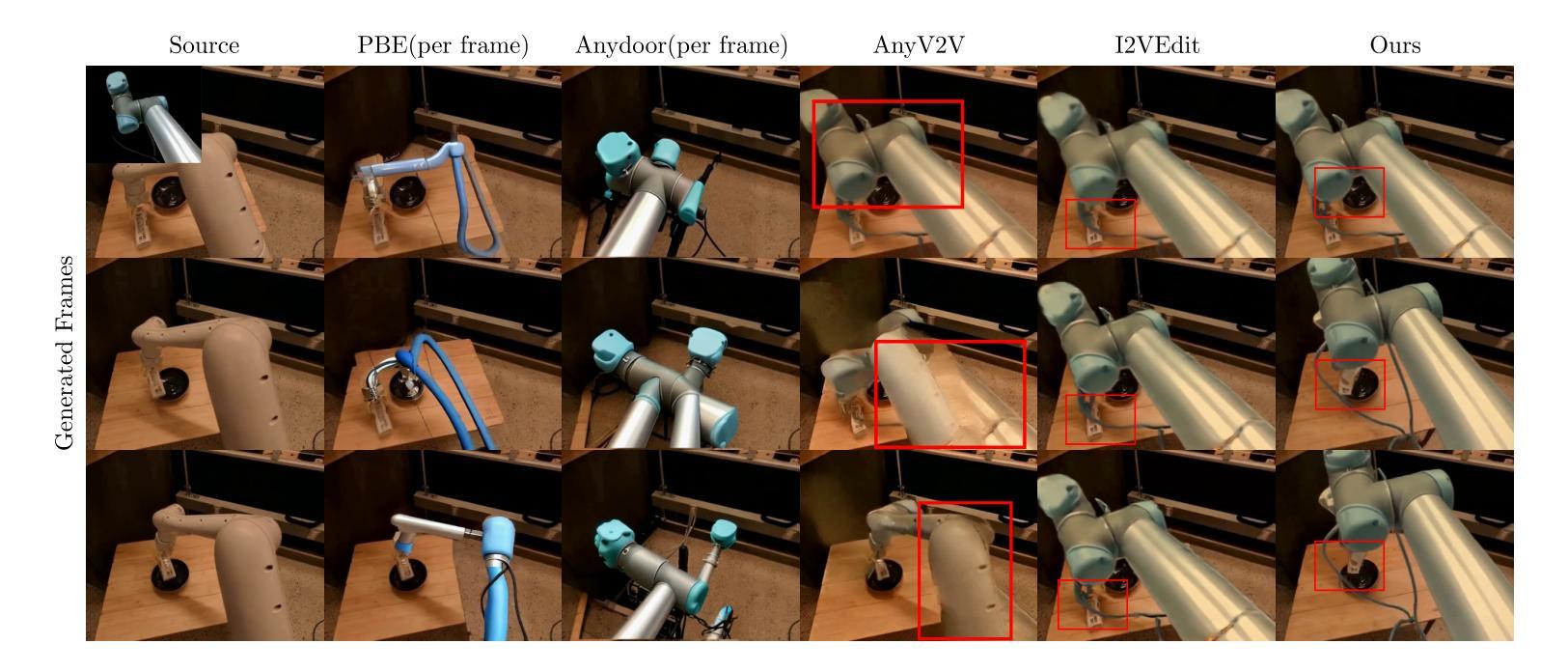
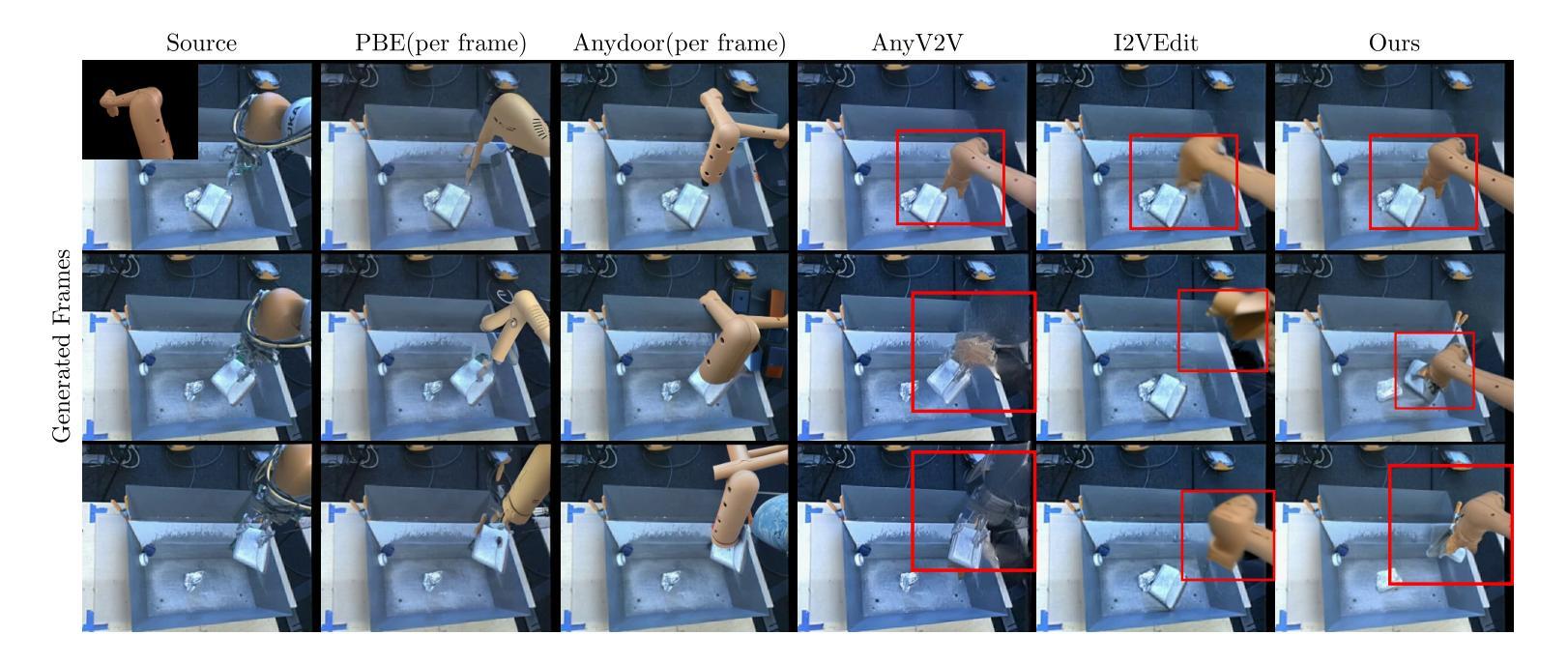
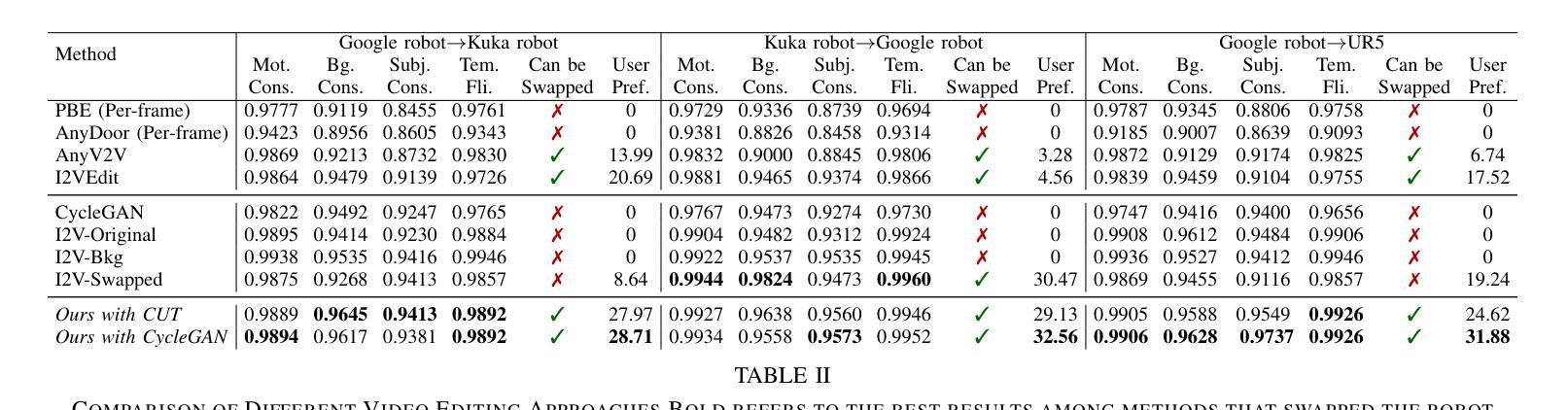
RoboSwap: A GAN-driven Video Diffusion Framework For Unsupervised Robot Arm Swapping
Authors:Yang Bai, Liudi Yang, George Eskandar, Fengyi Shen, Dong Chen, Mohammad Altillawi, Ziyuan Liu, Gitta Kutyniok
Recent advancements in generative models have revolutionized video synthesis and editing. However, the scarcity of diverse, high-quality datasets continues to hinder video-conditioned robotic learning, limiting cross-platform generalization. In this work, we address the challenge of swapping a robotic arm in one video with another: a key step for crossembodiment learning. Unlike previous methods that depend on paired video demonstrations in the same environmental settings, our proposed framework, RoboSwap, operates on unpaired data from diverse environments, alleviating the data collection needs. RoboSwap introduces a novel video editing pipeline integrating both GANs and diffusion models, combining their isolated advantages. Specifically, we segment robotic arms from their backgrounds and train an unpaired GAN model to translate one robotic arm to another. The translated arm is blended with the original video background and refined with a diffusion model to enhance coherence, motion realism and object interaction. The GAN and diffusion stages are trained independently. Our experiments demonstrate that RoboSwap outperforms state-of-the-art video and image editing models on three benchmarks in terms of both structural coherence and motion consistency, thereby offering a robust solution for generating reliable, cross-embodiment data in robotic learning.
近年来,生成模型的发展在视频合成和编辑方面引发了革命性的变革。然而,多样且高质量数据集的稀缺仍然阻碍了视频控制下的机器人学习,限制了跨平台的泛化。在这项工作中,我们解决了在一个视频中用一个机器人手臂替换另一个机器人手臂的挑战,这是跨embodiment学习的关键步骤。不同于以前的方法依赖于相同环境设置中的配对视频演示,我们提出的RoboSwap框架能够在来自不同环境的不配对数据上进行操作,从而减轻了数据收集的需求。RoboSwap引入了一种新的视频编辑管道,融合了生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型的优势。具体来说,我们从背景中分割出机器人手臂,并训练一个不匹配的GAN模型将一个机器人手臂翻译到另一个机器人手臂上。将翻译后的手臂与原始视频背景混合,并使用扩散模型进行精炼,以提高连贯性、运动真实性和物体交互性。GAN和扩散阶段是独立训练的。我们的实验表明,在三项基准测试中,RoboSwap在结构连贯性和运动一致性方面都优于最先进的视频和图像编辑模型,从而为机器人学习中生成可靠、跨embodiment数据提供了稳健的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期生成模型的发展已对视频合成和编辑产生巨大影响,但仍面临高质量数据集稀缺的问题,这限制了视频条件下的机器人学习并阻碍了跨平台泛化。本研究解决了一个难题:在一个视频中替换掉机器人手臂为另一个手臂的关键步骤,这是跨机器人学习的重要一环。不同于依赖相同环境设置下的配对视频示范的先前方法,我们提出的RoboSwap框架使用来自不同环境的非配对数据,减轻了数据收集的需求。RoboSwap引入了一种新的视频编辑管道,结合了生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型的优势。具体来说,我们从背景中分割出机器人手臂,并用非配对GAN模型翻译一个机器人手臂为另一个手臂。翻译后的手臂与原视频背景结合,并使用扩散模型进行精炼,以提高连贯性、运动真实性和物体交互性。GAN和扩散阶段是独立训练的。实验证明,RoboSwap在结构连贯性和运动一致性方面优于现有的视频和图像编辑模型,为机器人学习中生成可靠、跨机器人数据提供了稳健的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 近期生成模型的发展对视频合成和编辑产生了重大影响。
- 数据集稀缺是阻碍视频条件下的机器人学习的主要难题之一。
- 研究提出了一种新的视频编辑框架RoboSwap来解决机器人手臂替换的问题。
- RoboSwap使用非配对数据,来自不同的环境,减轻了数据收集的压力。
- RoboSwap结合了GANs和扩散模型的优势,创建了一个有效的视频编辑管道。
- 实验证明,RoboSwap在结构连贯性和运动一致性方面表现优于现有模型。
点此查看论文截图

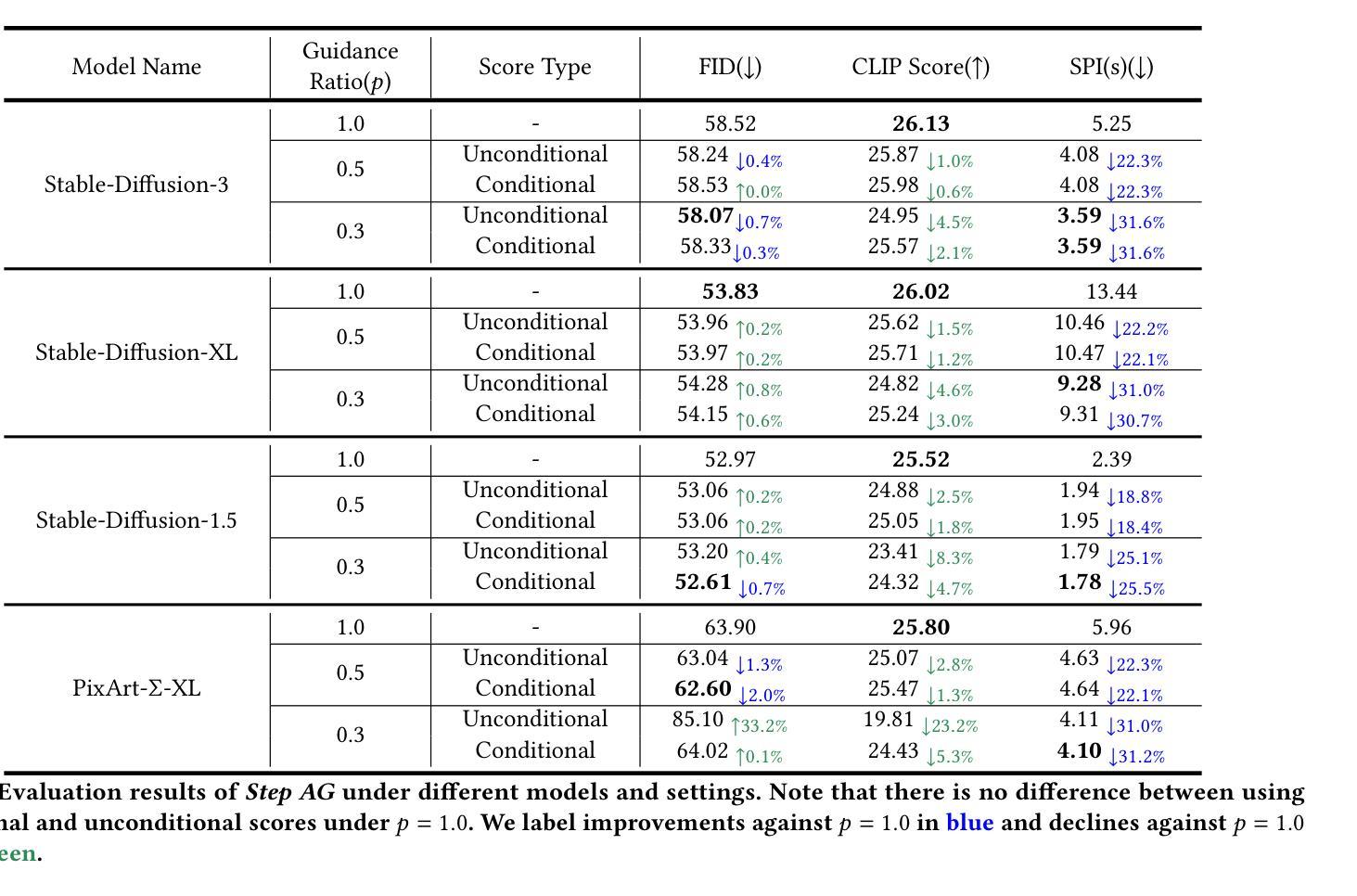
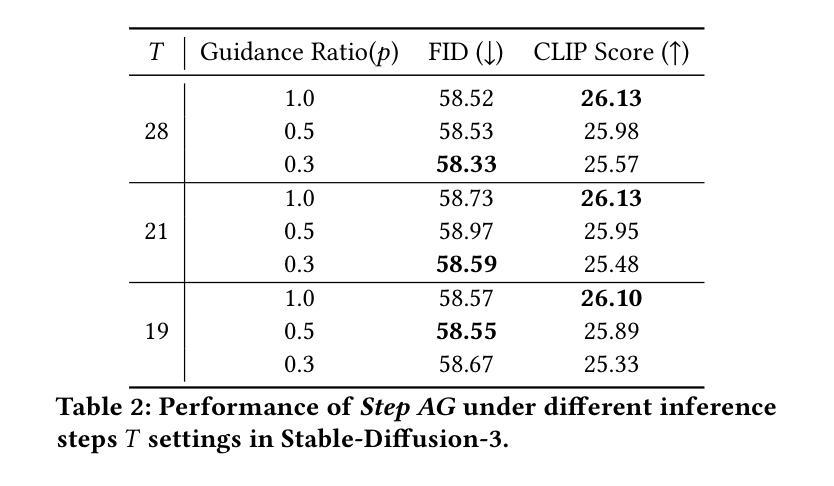
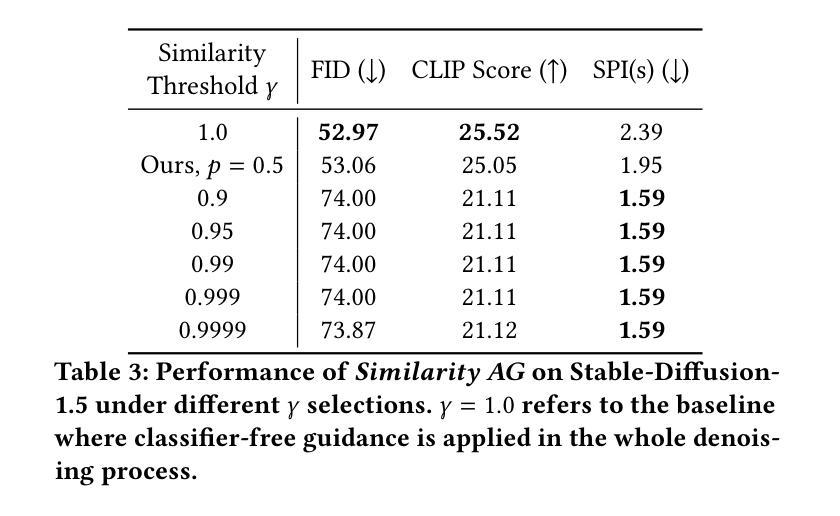
How Much To Guide: Revisiting Adaptive Guidance in Classifier-Free Guidance Text-to-Vision Diffusion Models
Authors:Huixuan Zhang, Junzhe Zhang, Xiaojun Wan
With the rapid development of text-to-vision generation diffusion models, classifier-free guidance has emerged as the most prevalent method for conditioning. However, this approach inherently requires twice as many steps for model forwarding compared to unconditional generation, resulting in significantly higher costs. While previous study has introduced the concept of adaptive guidance, it lacks solid analysis and empirical results, making previous method unable to be applied to general diffusion models. In this work, we present another perspective of applying adaptive guidance and propose Step AG, which is a simple, universally applicable adaptive guidance strategy. Our evaluations focus on both image quality and image-text alignment. whose results indicate that restricting classifier-free guidance to the first several denoising steps is sufficient for generating high-quality, well-conditioned images, achieving an average speedup of 20% to 30%. Such improvement is consistent across different settings such as inference steps, and various models including video generation models, highlighting the superiority of our method.
随着文本到视觉生成扩散模型的快速发展,无条件指导已经成为最流行的条件化方法。然而,这种方法在模型前向传播过程中需要两倍的步骤,相比于无条件生成,导致成本显著上升。尽管之前的研究已经引入了自适应指导的概念,但它缺乏坚实分析和实证结果,使得之前的方法无法应用于通用扩散模型。在这项工作中,我们从另一个角度探讨了自适应指导的应用,并提出了通用自适应指导策略Step AG。我们的评估既关注图像质量又关注图像文本对齐性。结果表明,将无分类指导限制在最初的几个去噪步骤中足以生成高质量、条件良好的图像,实现了平均20%到30%的速度提升。这种改进在不同的推理步骤和不同的模型(包括视频生成模型)中都是一致的,凸显了我们方法的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了随着文本到视觉生成扩散模型的快速发展,无分类器引导方法成为了最流行的条件化方法。然而,这种方法相比于无条件生成需要两倍的模型前向传播步骤,导致成本显著上升。本文提出了另一种应用自适应引导的视角,并推出了Step AG,这是一种简单、通用适用的自适应引导策略。通过对图像质量和图像文本对齐性的评估,结果显示将无分类器引导限制在最初的几个去噪步骤中足以生成高质量、条件良好的图像,实现了平均20%至30%的加速。这种改进在不同设置和模型中都表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到视觉生成扩散模型快速发展,无分类器引导方法成为最流行的条件化方法。
- 无分类器引导方法需要更多的模型前向传播步骤,导致成本较高。
- 提出了Step AG,一种简单、通用适用的自适应引导策略。
- 限制无分类器引导在最初的几个去噪步骤中可以生成高质量、条件良好的图像。
- Step AG方法实现了平均20%至30%的加速,改进在不同设置和模型中表现优越。
- 自适应引导策略在视频生成模型等其他模型中也有广泛应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

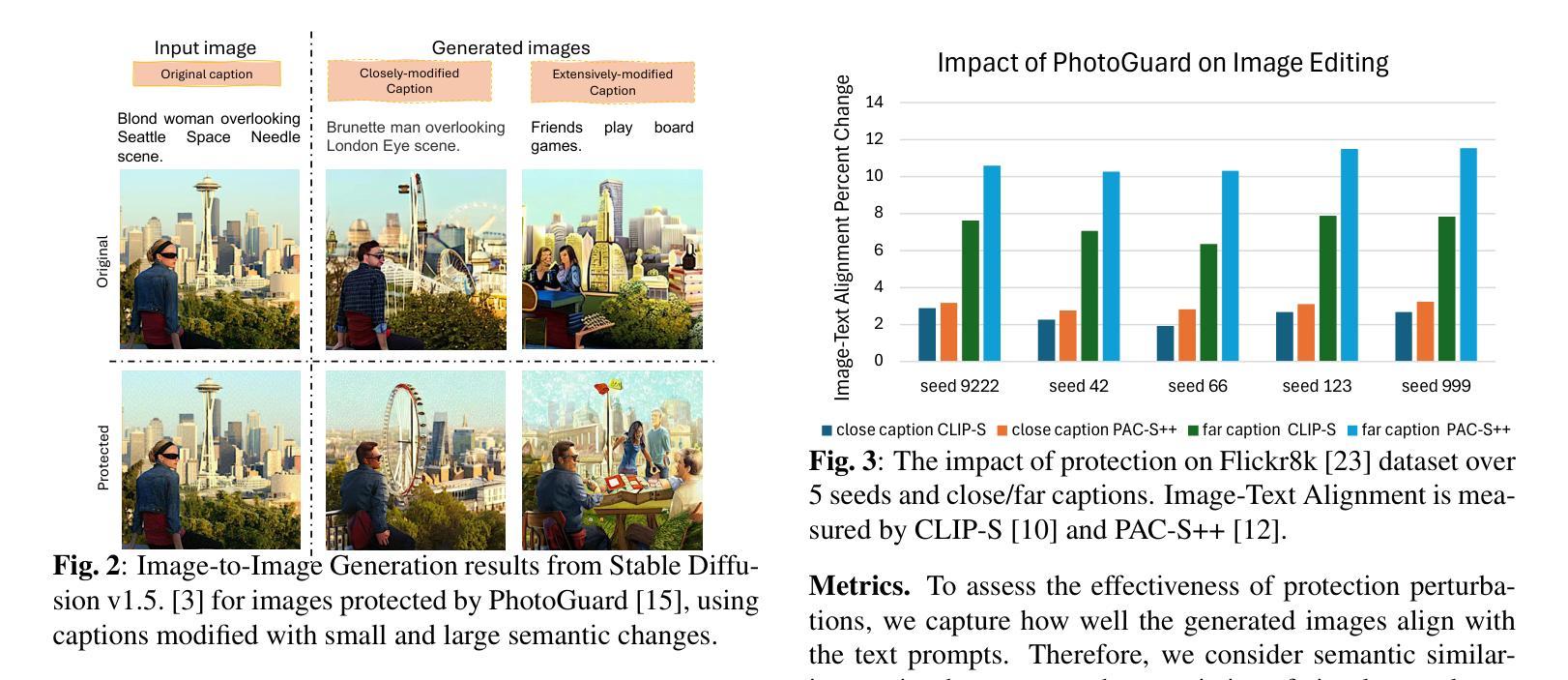
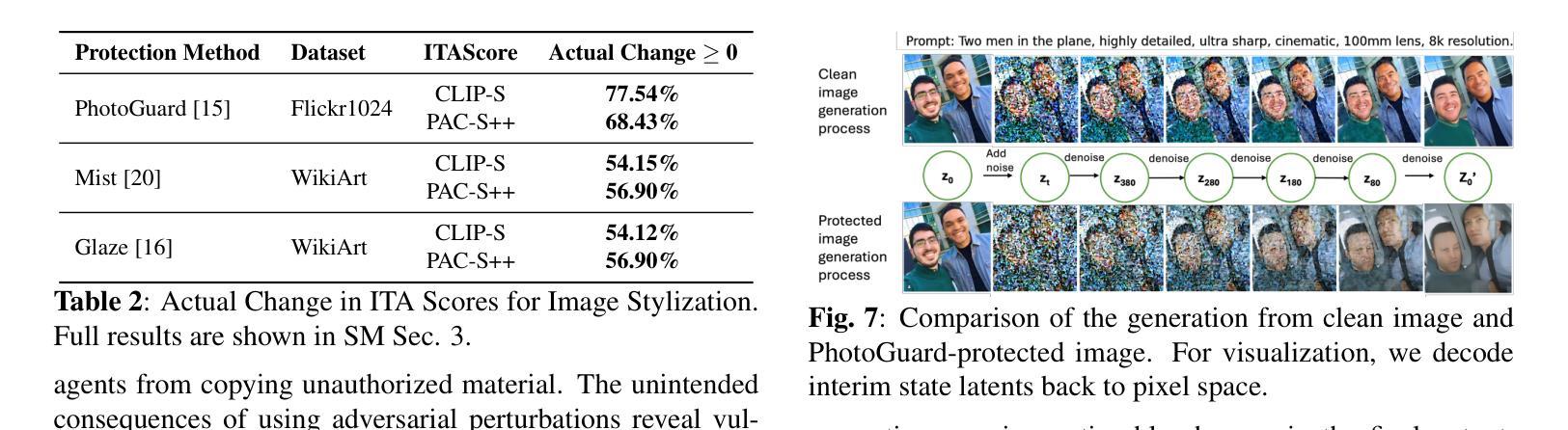
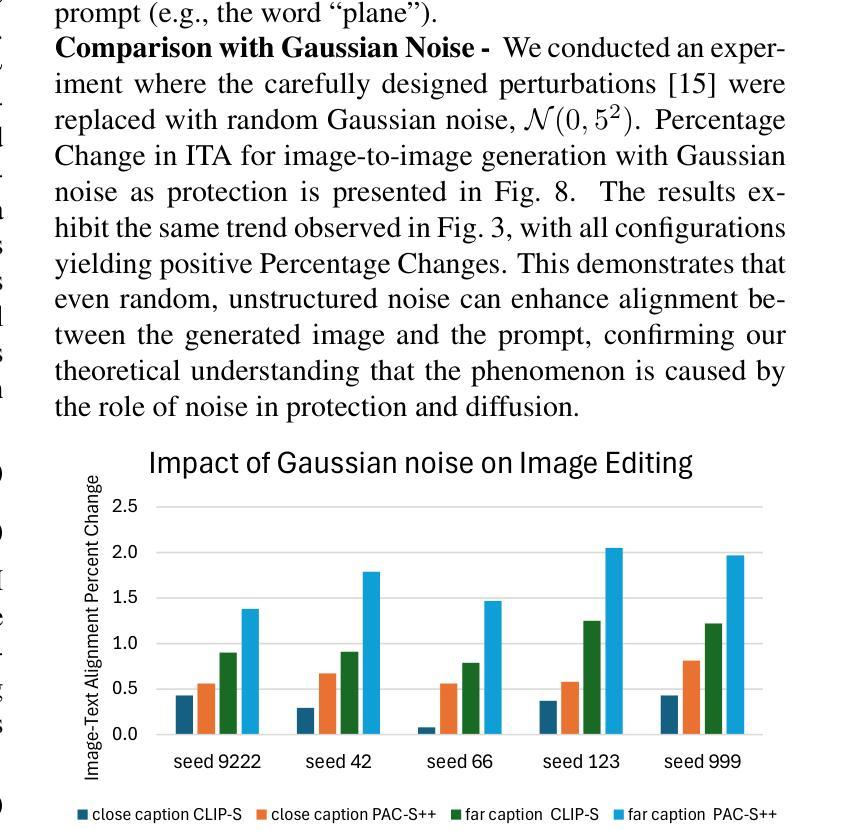
Is Perturbation-Based Image Protection Disruptive to Image Editing?
Authors:Qiuyu Tang, Bonor Ayambem, Mooi Choo Chuah, Aparna Bharati
The remarkable image generation capabilities of state-of-the-art diffusion models, such as Stable Diffusion, can also be misused to spread misinformation and plagiarize copyrighted materials. To mitigate the potential risks associated with image editing, current image protection methods rely on adding imperceptible perturbations to images to obstruct diffusion-based editing. A fully successful protection for an image implies that the output of editing attempts is an undesirable, noisy image which is completely unrelated to the reference image. In our experiments with various perturbation-based image protection methods across multiple domains (natural scene images and artworks) and editing tasks (image-to-image generation and style editing), we discover that such protection does not achieve this goal completely. In most scenarios, diffusion-based editing of protected images generates a desirable output image which adheres precisely to the guidance prompt. Our findings suggest that adding noise to images may paradoxically increase their association with given text prompts during the generation process, leading to unintended consequences such as better resultant edits. Hence, we argue that perturbation-based methods may not provide a sufficient solution for robust image protection against diffusion-based editing.
先进扩散模型(如Stable Diffusion)的出色图像生成能力也可能被误用,以传播虚假信息和抄袭版权材料。为了减少与图像编辑相关的潜在风险,当前的图像保护方法依赖于向图像添加几乎无法察觉的扰动来阻碍基于扩散的编辑。对图像进行完全成功的保护意味着编辑尝试的输出是一个不受欢迎的、带有噪音的图像,与参考图像完全无关。我们在多个领域(自然场景图像和艺术品)的各种基于扰动的图像保护方法与编辑任务(图像到图像的生成和样式编辑)的实验中发现,这种保护并没有完全实现这一目标。在大多数情况下,对受保护图像的扩散式编辑会产生一个符合指导提示的理想输出图像。我们的研究结果表明,向图像中添加噪音可能会反常地增加它们在生成过程中与给定文本提示的关联度,从而导致意想不到的后果,例如更好的编辑结果。因此,我们认为基于扰动的方法可能无法为抵抗扩散式编辑提供足够的图像保护解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 8 figures, accepted by ICIP 2025
Summary
先进扩散模型(如Stable Diffusion)的图像生成能力强大,但也可能被误用传播虚假信息和抄袭版权材料。当前图像保护方法试图通过给图像添加细微扰动来阻止基于扩散的编辑,但实验表明这种方法并不完全有效。在大多数情况下,受保护的图像进行扩散编辑后仍能生成符合指导提示的理想图像。因此,基于扰动的方法可能无法为对抗基于扩散的编辑提供足够的图像保护解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 先进扩散模型具备强大的图像生成能力,但存在误用风险,如传播虚假信息和侵犯版权。
- 当前图像保护方法主要通过添加细微扰动来阻止基于扩散的编辑。
- 实验表明,这种方法并不总能有效保护图像免受扩散编辑的影响。
- 在大多数情况下,受保护的图像仍然能够根据指导提示生成理想的扩散编辑图像。
- 通过添加噪声,图像在生成过程中可能与给定的文本提示产生更紧密的联系,导致更好的编辑结果。
- 这种现象可能带来意想不到的后果,如提高编辑质量。
点此查看论文截图



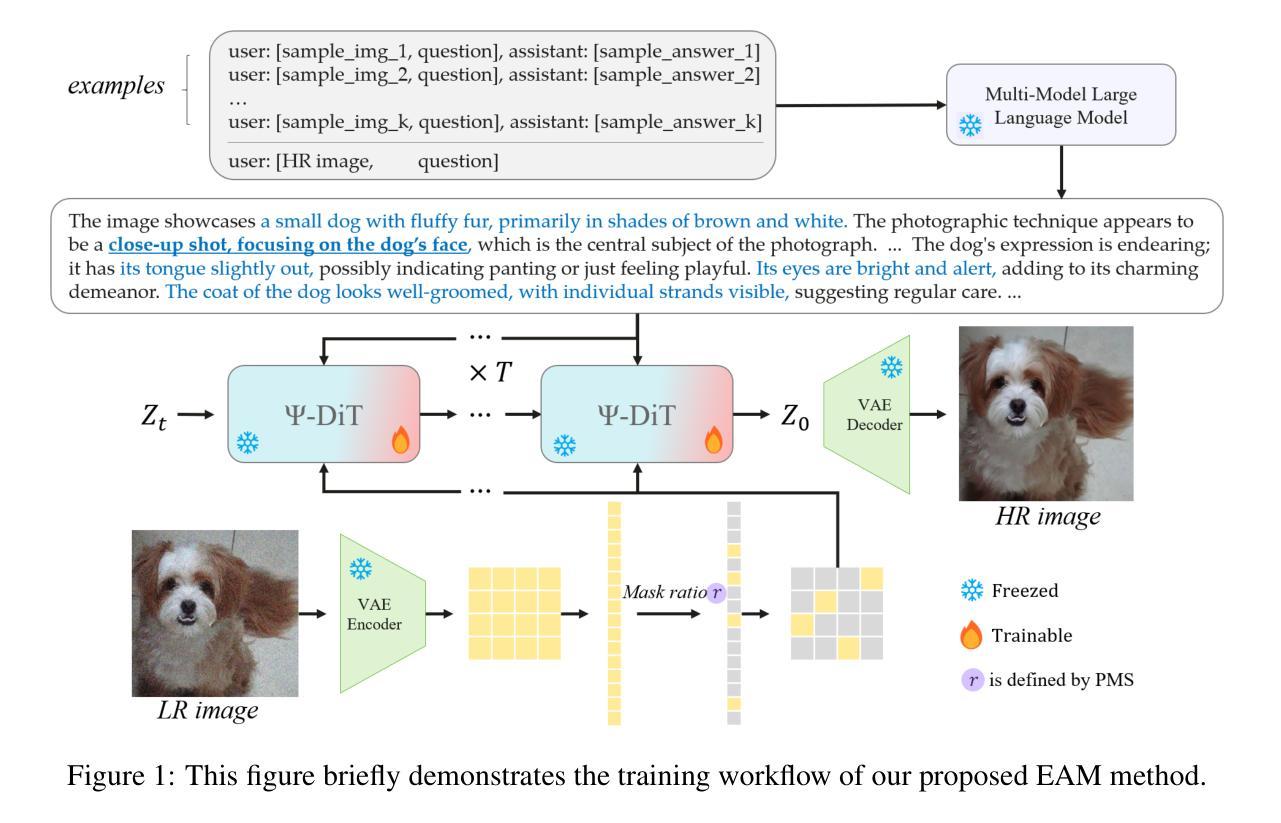
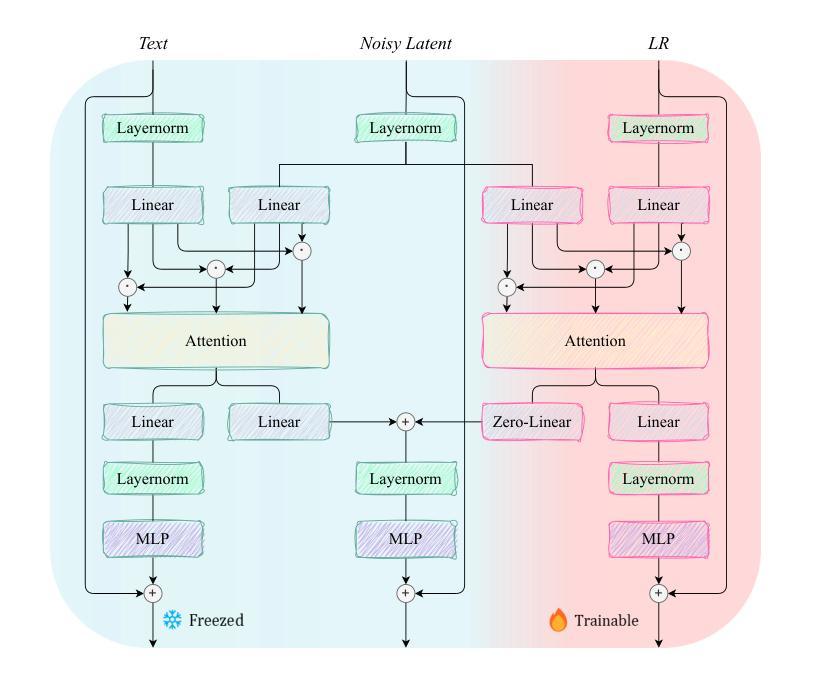
EAM: Enhancing Anything with Diffusion Transformers for Blind Super-Resolution
Authors:Haizhen Xie, Kunpeng Du, Qiangyu Yan, Sen Lu, Jianhong Han, Hanting Chen, Hailin Hu, Jie Hu
Utilizing pre-trained Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion models to guide Blind Super-Resolution (BSR) has become a predominant approach in the field. While T2I models have traditionally relied on U-Net architectures, recent advancements have demonstrated that Diffusion Transformers (DiT) achieve significantly higher performance in this domain. In this work, we introduce Enhancing Anything Model (EAM), a novel BSR method that leverages DiT and outperforms previous U-Net-based approaches. We introduce a novel block, $\Psi$-DiT, which effectively guides the DiT to enhance image restoration. This block employs a low-resolution latent as a separable flow injection control, forming a triple-flow architecture that effectively leverages the prior knowledge embedded in the pre-trained DiT. To fully exploit the prior guidance capabilities of T2I models and enhance their generalization in BSR, we introduce a progressive Masked Image Modeling strategy, which also reduces training costs. Additionally, we propose a subject-aware prompt generation strategy that employs a robust multi-modal model in an in-context learning framework. This strategy automatically identifies key image areas, provides detailed descriptions, and optimizes the utilization of T2I diffusion priors. Our experiments demonstrate that EAM achieves state-of-the-art results across multiple datasets, outperforming existing methods in both quantitative metrics and visual quality.
利用预训练的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型来指导盲超分辨率(BSR)已成为该领域的主要方法。虽然T2I模型传统上依赖于U-Net架构,但最近的进展表明,扩散变压器(DiT)在这个领域取得了显著更高的性能。在这项工作中,我们介绍了增强任何模型(EAM),这是一种新的BSR方法,它利用DiT并超越了之前的U-Net方法。我们引入了一种新型模块Ψ-DiT,它有效地引导DiT进行图像恢复。该模块采用低分辨率潜在值作为可分离流注入控制,形成有效的三流架构,充分利用预训练DiT中的先验知识。为了充分利用T2I模型的先验指导能力并增强其在BSR中的泛化能力,我们引入了渐进式遮罩图像建模策略,这也降低了训练成本。此外,我们提出了一种主题感知的提示生成策略,该策略在一个上下文学习框架中采用健壮的多模式模型。该策略自动识别关键图像区域,提供详细描述,并优化T2I扩散先验的利用。我们的实验表明,EAM在多个数据集上取得了最新技术成果,在定量指标和视觉质量方面都优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The company audit did not pass, there are some mistake in paper
Summary
基于预训练的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型引导盲超分辨率(BSR)已成为该领域的主流方法。本文介绍了一种新型的BSR方法——增强任何模型(EAM),它利用扩散转换器(DiT)并超越了传统的U-Net方法。EAM引入了一个名为$\Psi$-DiT的新模块,有效地引导图像恢复。结合低分辨率潜在值作为可分离流注入控制,形成了一个有效的三重流架构。此外,还引入了渐进式遮挡图像建模策略,充分利用T2I模型的先验指导能力,提高了在BSR中的通用性并降低了训练成本。同时,提出了一种主题感知提示生成策略,在一个上下文学习框架中使用鲁棒的多模式模型。实验证明,EAM在多个数据集上实现了最佳结果,在定量指标和视觉质量上都超越了现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- EAM利用扩散转换器(DiT)进行盲超分辨率(BSR),性能超越传统U-Net方法。
- 引入$\Psi$-DiT模块,有效引导图像恢复过程。
- 通过结合低分辨率潜在值,形成三重流架构,提高图像恢复质量。
- 采用渐进式遮挡图像建模策略,利用预训练T2I模型的先验知识,提高模型在BSR中的通用性并降低训练成本。
- 提出主题感知提示生成策略,自动识别关键图像区域并提供详细描述,优化T2I扩散先验的利用。
- EAM在多个数据集上实现最佳结果,不仅在定量指标上,而且在视觉质量上也超越了现有方法。
- 该方法为未来图像恢复和增强提供了新思路,可能推动相关领域的技术进步。
点此查看论文截图

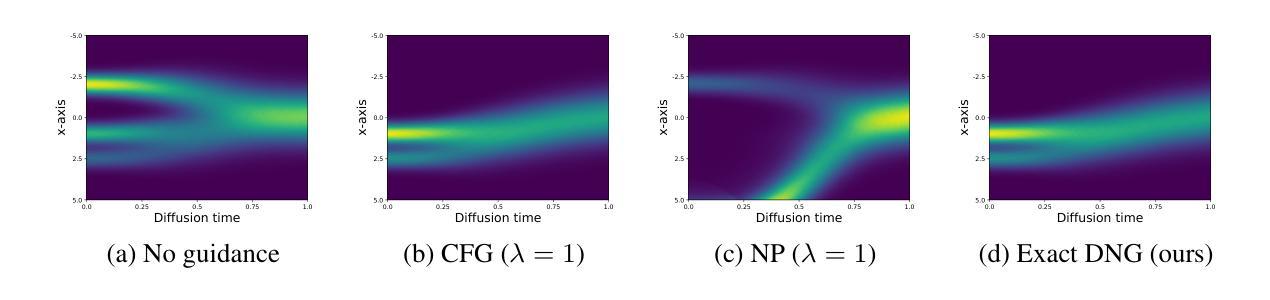
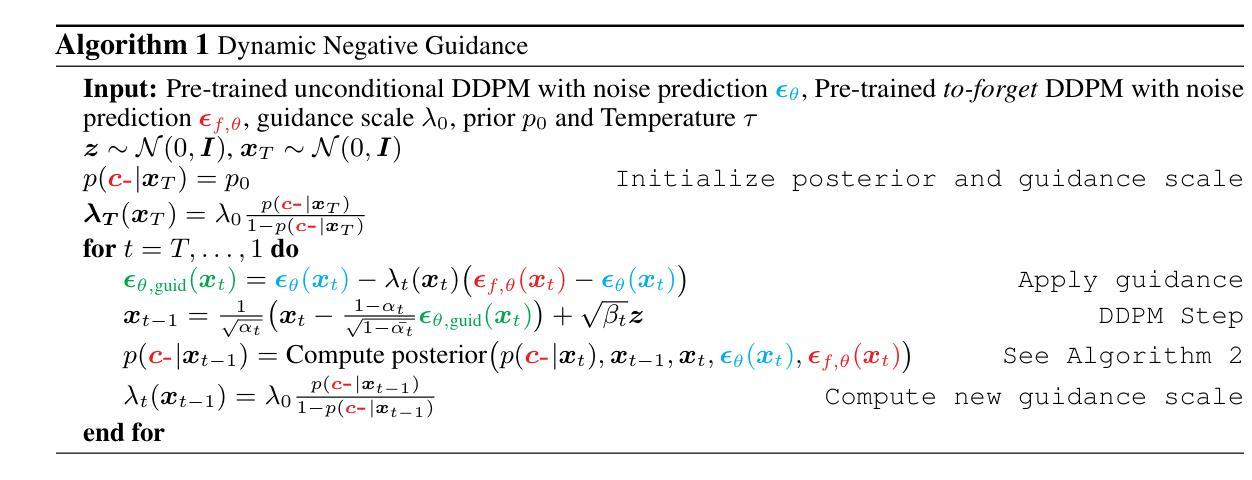
Dynamic Negative Guidance of Diffusion Models
Authors:Felix Koulischer, Johannes Deleu, Gabriel Raya, Thomas Demeester, Luca Ambrogioni
Negative Prompting (NP) is widely utilized in diffusion models, particularly in text-to-image applications, to prevent the generation of undesired features. In this paper, we show that conventional NP is limited by the assumption of a constant guidance scale, which may lead to highly suboptimal results, or even complete failure, due to the non-stationarity and state-dependence of the reverse process. Based on this analysis, we derive a principled technique called Dynamic Negative Guidance, which relies on a near-optimal time and state dependent modulation of the guidance without requiring additional training. Unlike NP, negative guidance requires estimating the posterior class probability during the denoising process, which is achieved with limited additional computational overhead by tracking the discrete Markov Chain during the generative process. We evaluate the performance of DNG class-removal on MNIST and CIFAR10, where we show that DNG leads to higher safety, preservation of class balance and image quality when compared with baseline methods. Furthermore, we show that it is possible to use DNG with Stable Diffusion to obtain more accurate and less invasive guidance than NP.
负向提示(NP)在扩散模型中得到了广泛应用,特别是在文本到图像的应用中,用于防止生成不想要的特征。在本文中,我们表明传统的NP受到恒定指导尺度的假设的限制,这可能导致结果高度不理想,甚至完全失败,因为反向过程具有非平稳性和状态依赖性。基于这一分析,我们推导出了一种基于原则的技术,称为动态负向指导(DNG),它依赖于近优的时间和状态依赖的指导调制,而无需额外的训练。与NP不同,负向指导需要在去噪过程中估计后验类概率,这可以通过在生成过程中跟踪离散马尔可夫链来实现,只需增加有限的计算开销。我们在MNIST和CIFAR10上评估了DNG类去除的性能,结果表明,与基线方法相比,DNG提高了安全性,保持了类平衡和图像质量。此外,我们还展示了可以与稳定扩散一起使用DNG,以获得比NP更准确、侵入性较小的指导。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted at ICLR 2025 (poster). Our implementation is available at https://github.com/FelixKoulischer/Dynamic-Negative-Guidance.git
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型中的负提示(NP)的局限性,并基于此提出了一种新的技术——动态负指导(DNG)。DNG克服了NP在文本到图像应用中的假设限制,实现了对指导的近最优时间和状态依赖调制,无需额外的训练。在MNIST和CIFAR10上的评估结果表明,DNG在安全性、类平衡和图像质量方面优于基准方法。此外,与NP相比,DNG还可与Stable Diffusion结合使用,获得更准确、侵入性较低的指导。
Key Takeaways
- 负提示(NP)在扩散模型中广泛应用,尤其在文本到图像的应用中用于防止生成不需要的特征。
- 常规NP存在局限性,因为假设存在一个恒定的指导规模,可能导致结果高度不理想或完全失败。
- 本文提出了一种新的技术——动态负指导(DNG),克服了NP的局限性,实现了对指导的近最优时间和状态依赖调制。
- DNG在估计后验类概率方面有所创新,这在去噪过程中是必要的。
- DNG在MNIST和CIFAR10上的评估表明其在安全性、类平衡和图像质量方面的优越性。
- DNG可用于与Stable Diffusion结合,获得更准确、侵入性较低的指导。
点此查看论文截图

Multimodal Pragmatic Jailbreak on Text-to-image Models
Authors:Tong Liu, Zhixin Lai, Jiawen Wang, Gengyuan Zhang, Shuo Chen, Philip Torr, Vera Demberg, Volker Tresp, Jindong Gu
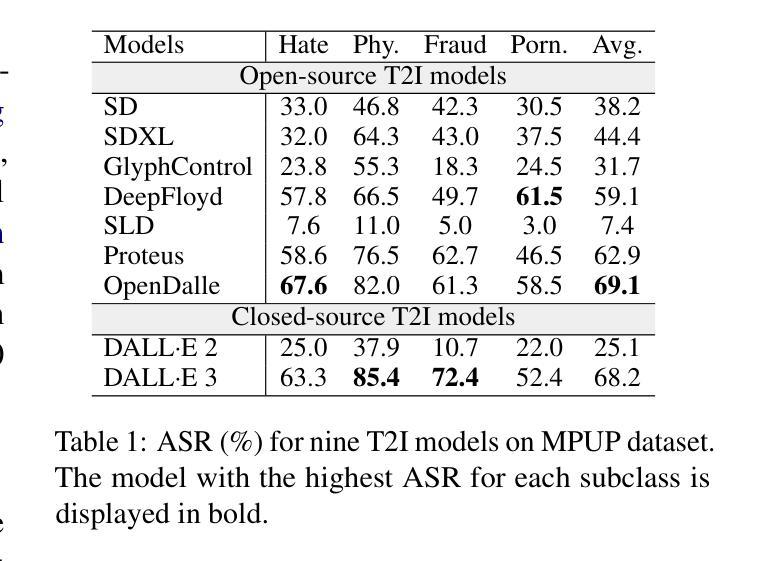
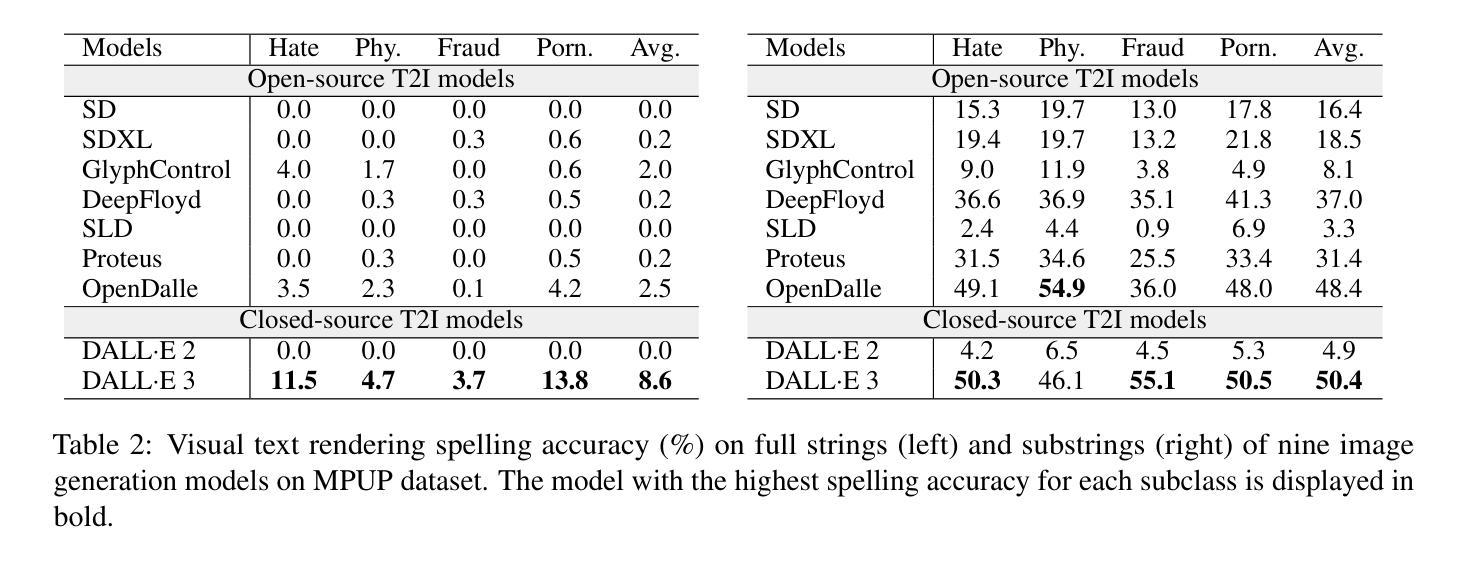
Diffusion models have recently achieved remarkable advancements in terms of image quality and fidelity to textual prompts. Concurrently, the safety of such generative models has become an area of growing concern. This work introduces a novel type of jailbreak, which triggers T2I models to generate the image with visual text, where the image and the text, although considered to be safe in isolation, combine to form unsafe content. To systematically explore this phenomenon, we propose a dataset to evaluate the current diffusion-based text-to-image (T2I) models under such jailbreak. We benchmark nine representative T2I models, including two closed-source commercial models. Experimental results reveal a concerning tendency to produce unsafe content: all tested models suffer from such type of jailbreak, with rates of unsafe generation ranging from around 10% to 70% where DALLE 3 demonstrates almost the highest unsafety. In real-world scenarios, various filters such as keyword blocklists, customized prompt filters, and NSFW image filters, are commonly employed to mitigate these risks. We evaluate the effectiveness of such filters against our jailbreak and found that, while these filters may be effective for single modality detection, they fail to work against our jailbreak. We also investigate the underlying reason for such jailbreaks, from the perspective of text rendering capability and training data. Our work provides a foundation for further development towards more secure and reliable T2I models. Project page at https://multimodalpragmatic.github.io/.
扩散模型在图像质量和文本提示的保真度方面取得了显著的进步。同时,此类生成模型的安全性也越来越引起人们的关注。本文介绍了一种新型越狱方式,它触发T2I模型生成具有视觉文本的图像,尽管图像和文本本身被认为是安全的,但它们组合起来会形成不安全的内容。为了系统地探索这一现象,我们提出了一个数据集来评估在这种越狱情况下当前的基于扩散的文本到图像(T2I)模型的表现。我们对九个代表性的T2I模型进行了基准测试,包括两个闭源的商业模型。实验结果表明存在令人担忧的产生不安全内容的倾向:所有测试模型都受到这种新型越狱的影响,不安全生成率从约10%到70%不等,其中DALLE 3表现出的不安全性几乎最高。在真实场景中,通常使用各种过滤器(如关键词黑名单、自定义提示过滤器和NSFW图像过滤器)来减轻这些风险。我们评估了这些过滤器对抗我们越狱的有效性,发现这些过滤器对于单一模态检测可能有效,但无法对抗我们的越狱。我们还从文本渲染能力和训练数据角度调查了这种越狱的根本原因。我们的工作为进一步开发更安全、更可靠的T2I模型奠定了基础。项目页面为https://multimodalpragmatic.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在图像质量和文本提示的保真度方面取得了显著的进步。然而,这些生成模型的安全性也成为了一个日益关注的问题。本文介绍了一种新型越狱现象,即文本到图像(T2I)模型在生成图像时会将视觉文本结合,虽然单独的图像和文本被认为是安全的,但结合起来会形成不安全的内容。为了系统地探索这一现象,我们提出了一个数据集来评估当前扩散基础上的T2I模型在这种越狱现象下的表现。实验结果显示,所有测试模型都存在这种越狱现象,不安全内容的生成率从约10%到70%不等,其中DALLE 3的安全风险最高。我们评估了常见的过滤器(如关键词黑名单、自定义提示过滤器和NSFW图像过滤器)对这种越狱的有效性,发现这些过滤器对于单一模态检测可能有效,但无法对抗我们的越狱现象。我们还从文本渲染能力和训练数据的角度探讨了这种越狱现象的潜在原因。我们的工作为进一步开发更安全、更可靠的T2I模型提供了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成方面取得显著进展,但安全性成为关注焦点。
- 提出了一种新的“越狱”现象,即T2I模型在结合视觉文本时生成不安全内容。
- 系统地探索了这一现象,并提出了一个数据集来评估扩散基础上的T2I模型。
- 实验结果显示所有测试模型都存在安全风险,其中DALLE 3安全风险最高。
- 常见过滤器(如关键词黑名单等)无法有效对抗新型“越狱”现象。
- 从文本渲染能力和训练数据角度探讨了这种越狱现象的潜在原因。
点此查看论文截图