⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-13 更新
Outside Knowledge Conversational Video (OKCV) Dataset – Dialoguing over Videos
Authors:Benjamin Reichman, Constantin Patsch, Jack Truxal, Atishay Jain, Larry Heck
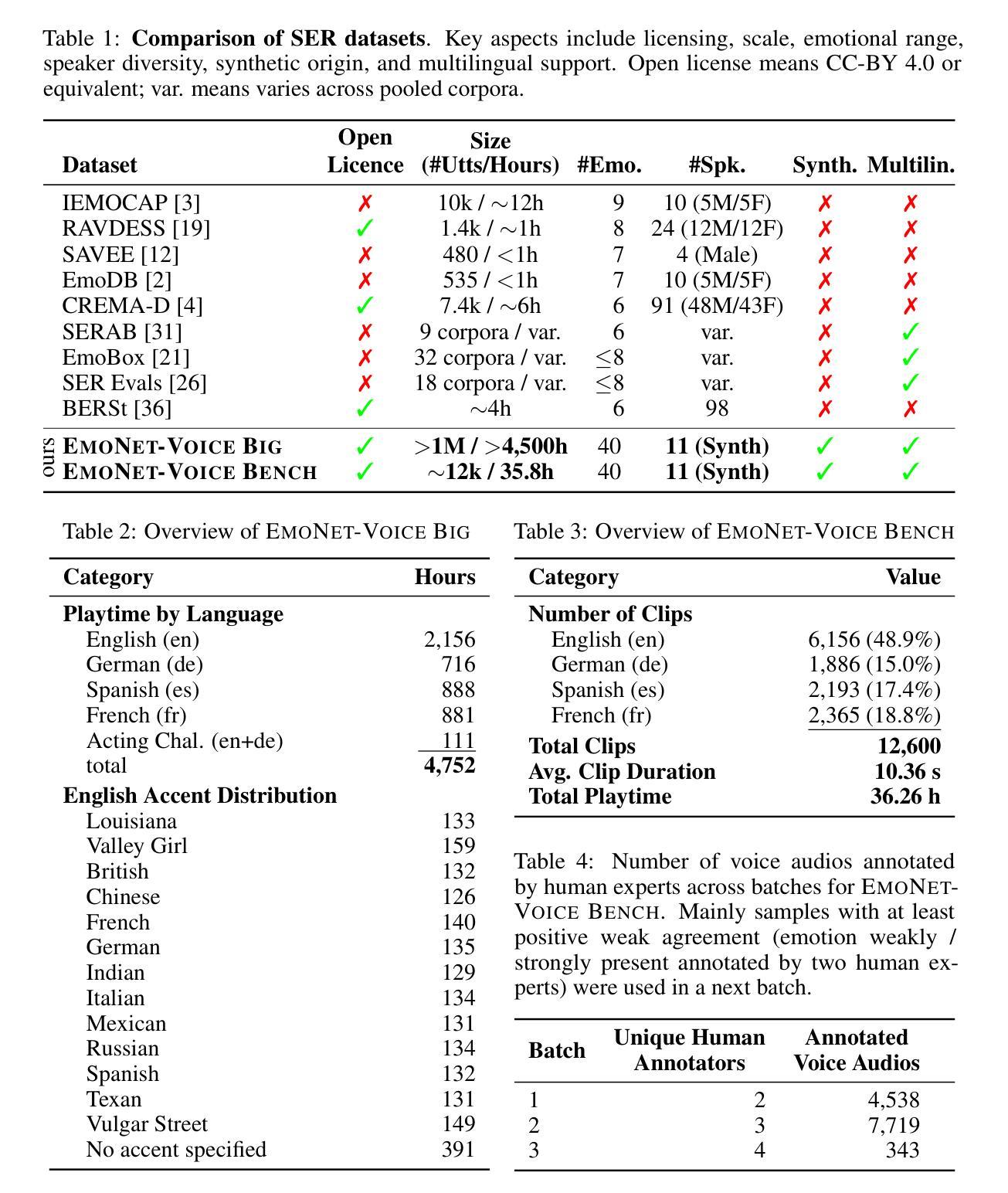
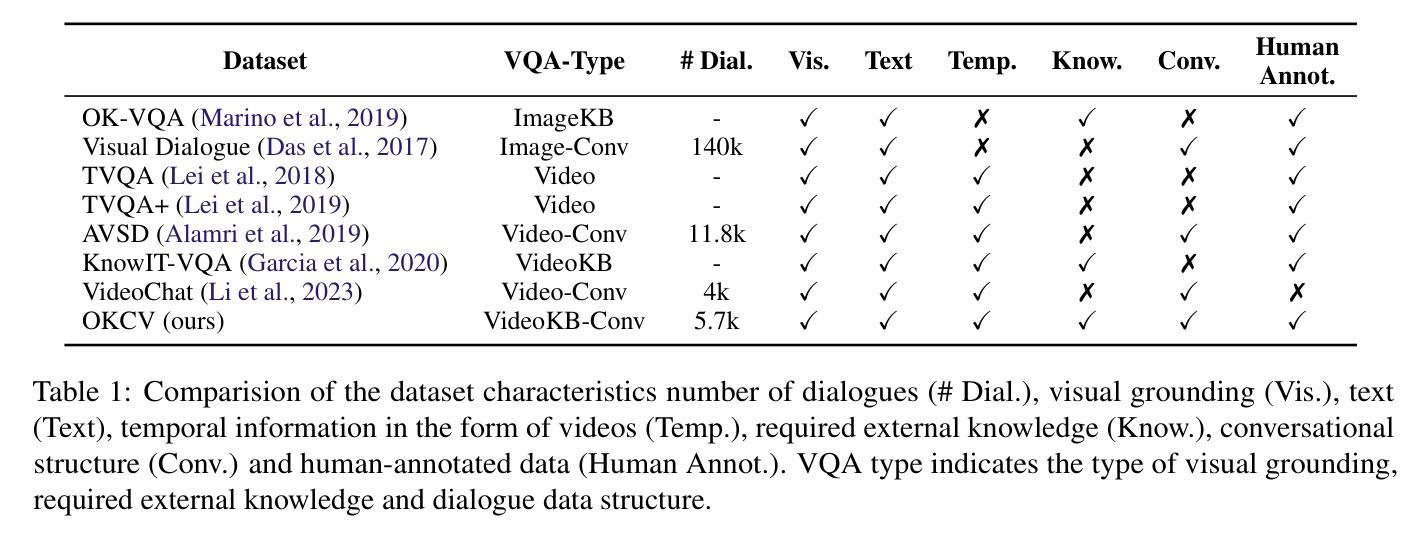
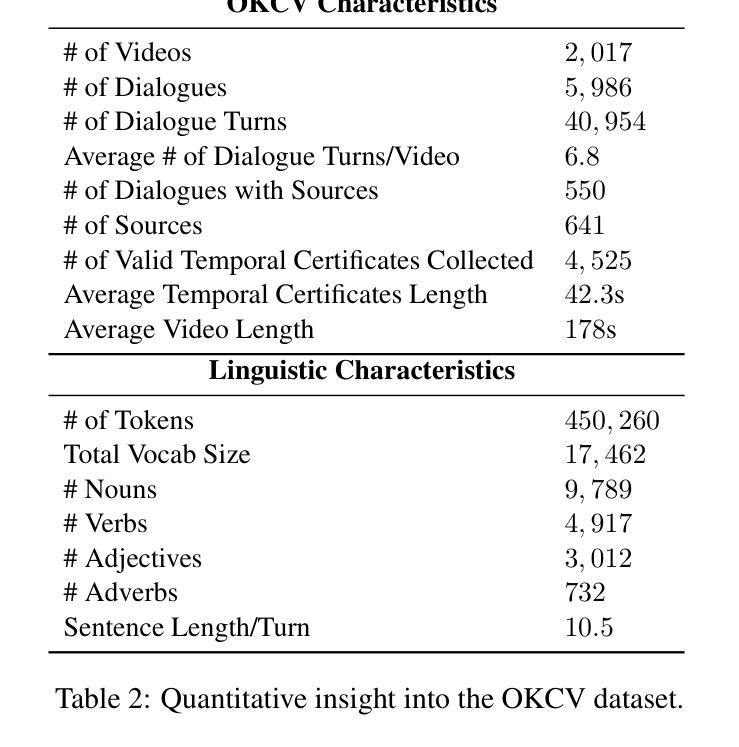
In outside knowledge visual question answering (OK-VQA), the model must identify relevant visual information within an image and incorporate external knowledge to accurately respond to a question. Extending this task to a visually grounded dialogue setting based on videos, a conversational model must both recognize pertinent visual details over time and answer questions where the required information is not necessarily present in the visual information. Moreover, the context of the overall conversation must be considered for the subsequent dialogue. To explore this task, we introduce a dataset comprised of $2,017$ videos with $5,986$ human-annotated dialogues consisting of $40,954$ interleaved dialogue turns. While the dialogue context is visually grounded in specific video segments, the questions further require external knowledge that is not visually present. Thus, the model not only has to identify relevant video parts but also leverage external knowledge to converse within the dialogue. We further provide several baselines evaluated on our dataset and show future challenges associated with this task. The dataset is made publicly available here: https://github.com/c-patsch/OKCV.
在外部知识视觉问答(OK-VQA)中,模型必须识别图像中的相关视觉信息,并结合外部知识来准确回答问题。将这项任务扩展到基于视频的视觉对话场景时,对话模型必须能够在一段时间内识别出重要的视觉细节,并回答那些所需信息并不完全存在于视觉信息中的问题。此外,还必须考虑整个对话的上下文来进行后续对话。为了探索这项任务,我们引入了一个包含$ 2,017 $个视频和$ 5,986 $个人工注释对话的数据集,这些对话包含$ 40,954 $个交叉对话轮次。虽然对话上下文在特定的视频片段中是视觉主导的,但问题还需要一些视觉上不存在的外部知识。因此,模型不仅要能够识别出相关的视频部分,还必须利用外部知识进行对话。我们进一步提供了在我们数据集上评估的几个基线,并展示了与此任务相关的未来挑战。数据集已公开提供:https://github.com/c-patsch/OKCV。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在外部知识视觉问答(OK-VQA)中,模型必须识别图像中的相关视觉信息并结合外部知识准确回答问题。当任务扩展到基于视频的视觉对话场景时,对话模型必须能够随时间识别重要的视觉细节,并回答所需信息不一定在视觉信息中的问题。此外,还必须考虑对话的整体上下文。为了研究此任务,我们引入了包含2,017个视频和5,986个人工注释对话的数据集,包含40,954个对话轮次。对话上下文虽然以特定视频片段为基础,但问题还需要额外的外部知识,这些知识在视频中并不直接呈现。因此,模型不仅要识别相关的视频部分,还要利用外部知识进行对话。我们在数据集上提供了几个基线评估并展示了与此任务相关的未来挑战。数据集已公开访问:https://github.com/c-patsch/OKCV。
Key Takeaways
- OK-VQA模型需结合视觉信息和外部知识回答问题。
- 模型须识别视频中的关键视觉信息并在对话中利用这些信息。
- 对话模型需处理的问题涉及外部知识,这些知识可能不在视觉信息中直接呈现。
- 模型应能识别相关视频部分并整合外部知识以进行对话。
- 数据集包含大量视频和人工注释的对话轮次,适合用于评估和研究视觉对话任务。
- 此任务面临挑战,包括识别重要视觉细节、整合外部知识和对话上下文的能力等。
点此查看论文截图

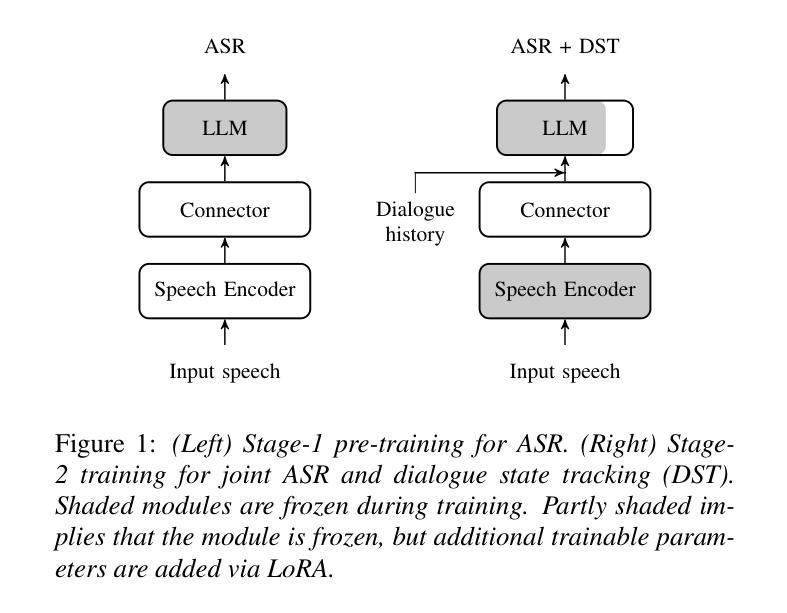
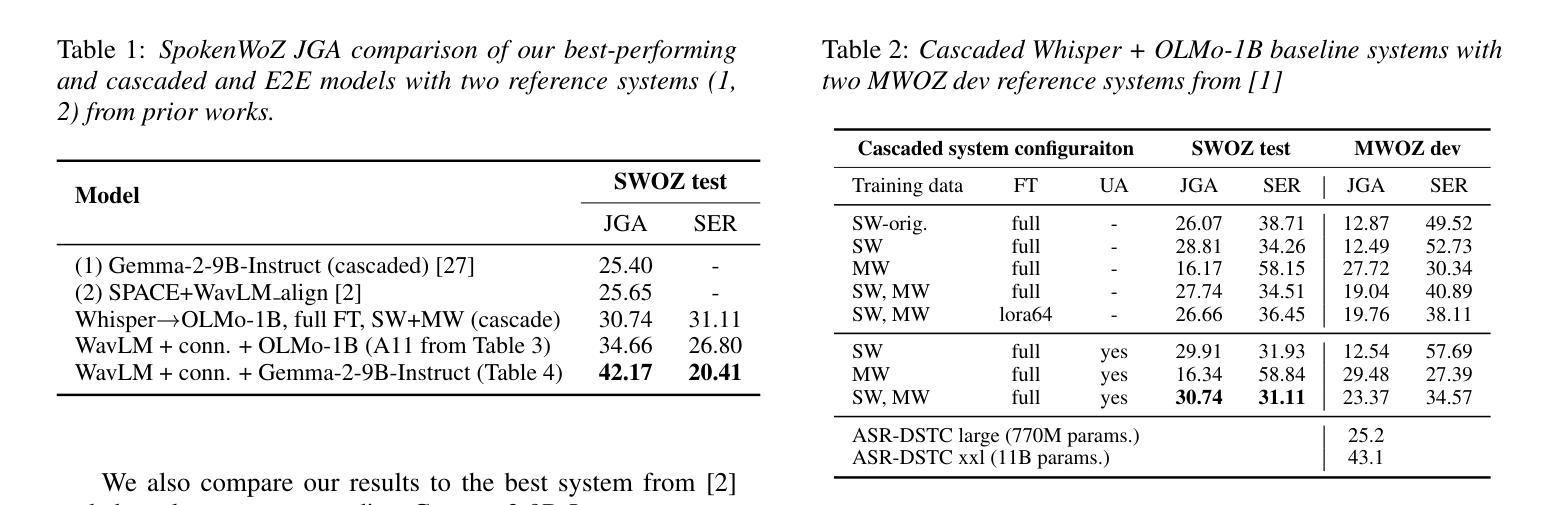
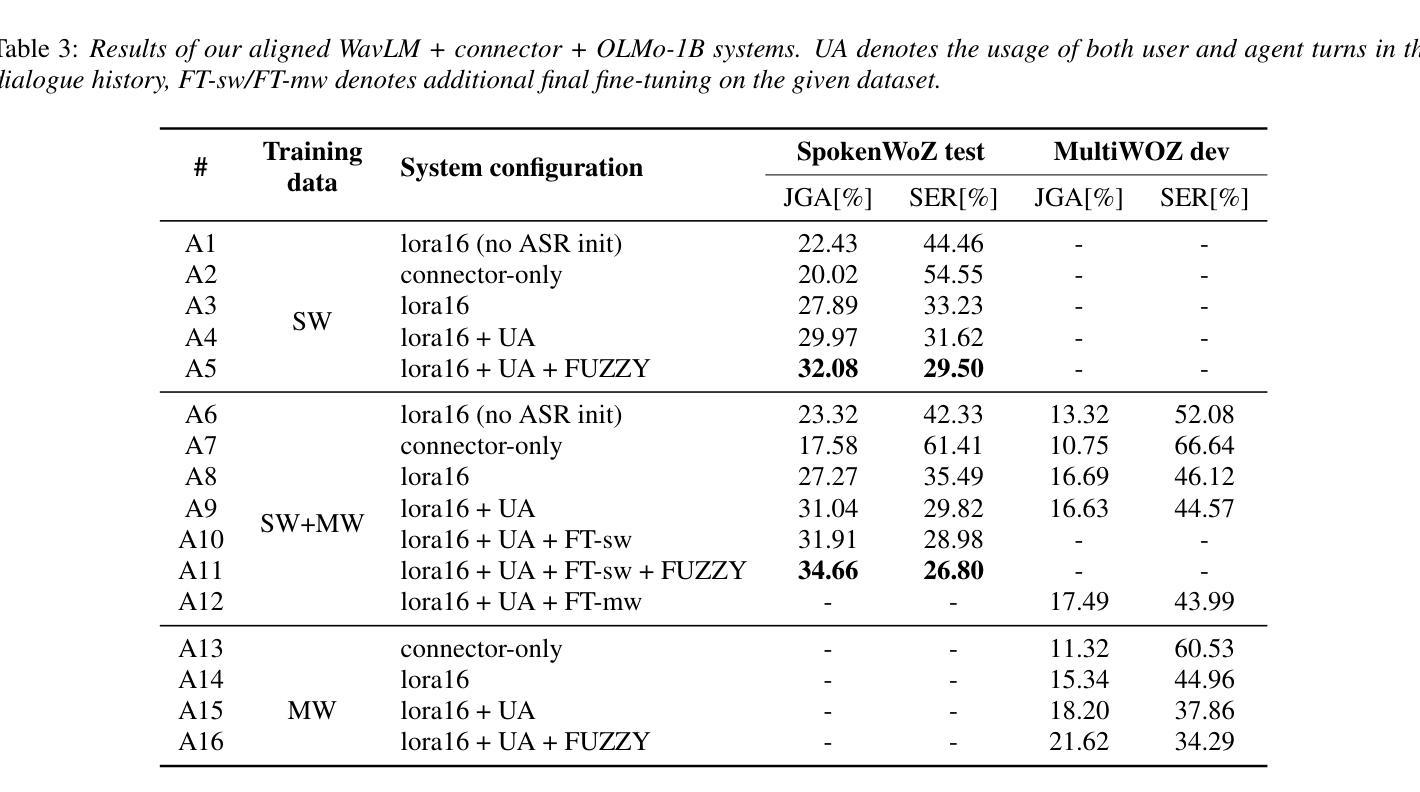
Approaching Dialogue State Tracking via Aligning Speech Encoders and LLMs
Authors:Šimon Sedláček, Bolaji Yusuf, Ján Švec, Pradyoth Hegde, Santosh Kesiraju, Oldřich Plchot, Jan Černocký
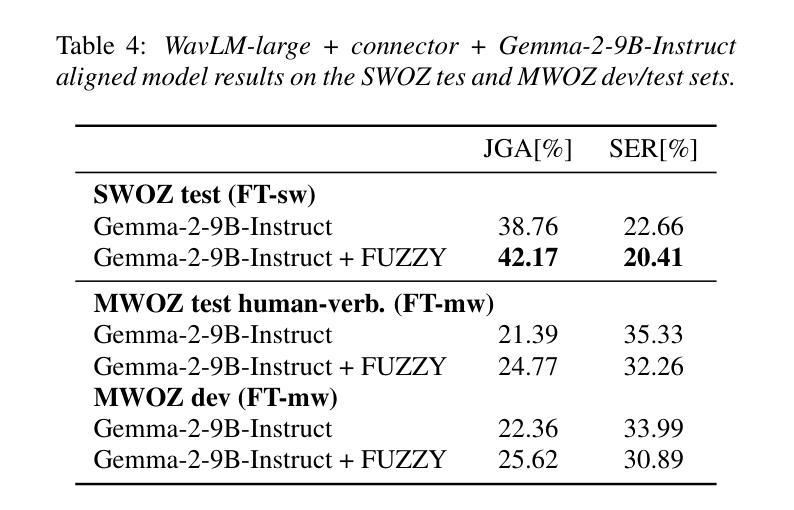
In this work, we approach spoken Dialogue State Tracking (DST) by bridging the representation spaces of speech encoders and LLMs via a small connector module, with a focus on fully open-sourced and open-data components (WavLM-large, OLMo). We focus on ablating different aspects of such systems including full/LoRA adapter fine-tuning, the effect of agent turns in the dialogue history, as well as fuzzy matching-based output post-processing, which greatly improves performance of our systems on named entities in the dialogue slot values. We conduct our experiments on the SpokenWOZ dataset, and additionally utilize the Speech-Aware MultiWOZ dataset to augment our training data. Ultimately, our best-performing WavLM + connector + OLMo-1B aligned models achieve state of the art on the SpokenWOZ test set (34.66% JGA), and our system with Gemma-2-9B-instruct further surpasses this result, reaching 42.17% JGA on SpokenWOZ test.
在这项工作中,我们通过一个小型连接器模块来连接语音编码器和大型语言模型(LLM)的表示空间,从而解决口头对话状态跟踪(DST)问题。我们的重点是在完全开源和公开数据组件(WavLM-大型和OLMo)的基础上开展工作。我们重点关注这种系统的不同方面,包括全/LoRA适配器微调、对话历史中代理回合的影响,以及基于模糊匹配的输出后处理,这大大提高了我们在对话槽值中的命名实体的性能。我们在SpokenWOZ数据集上进行实验,并额外使用Speech-Aware MultiWOZ数据集来扩充我们的训练数据。最终,我们表现最佳的WavLM+连接器+OLMo-1B对齐模型在SpokenWOZ测试集上达到了业界领先水平(JGA达到34.66%),我们的Gemma-2-9B-instruct系统进一步超越了这一结果,在SpokenWOZ测试集上达到42.17%的JGA。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文研究了基于语音的对话状态跟踪(DST),通过小型连接器模块桥接语音编码器和大型语言模型(LLM)的表示空间。研究重点包括系统的不同方面,如全/LoRA适配器微调、对话历史中代理回合的影响,以及基于模糊匹配的输出后处理,这大大提高了对话槽值中命名实体的系统性能。实验在SpokenWOZ数据集上进行,并额外使用语音感知MultiWOZ数据集来增强训练数据。最终,最优秀的模型在SpokenWOZ测试集上达到了最新的状态(JGA 34.66%),而采用Gemma-2-9B-instruct的系统进一步超越了这一结果,达到了42.17%的JGA。
Key Takeaways
- 研究通过连接器模块结合了语音编码器和大型语言模型,专注于全开源和开放数据组件。
- 聚焦于系统的不同方面,包括全/LoRA适配器微调、对话历史中代理回合的影响。
- 引入模糊匹配输出后处理,提高了对话槽值中命名实体的系统性能。
- 实验在SpokenWOZ数据集上进行,并使用语音感知MultiWOZ数据集增强训练数据。
- 最优秀的模型在SpokenWOZ测试集上达到了最新的状态(JGA 34.66%)。
- 采用Gemma-2-9B-instruct的系统进一步提高了性能,达到了更高的JGA值(42.17%)。
点此查看论文截图

NTPP: Generative Speech Language Modeling for Dual-Channel Spoken Dialogue via Next-Token-Pair Prediction
Authors:Qichao Wang, Ziqiao Meng, Wenqian Cui, Yifei Zhang, Pengcheng Wu, Bingzhe Wu, Irwin King, Liang Chen, Peilin Zhao
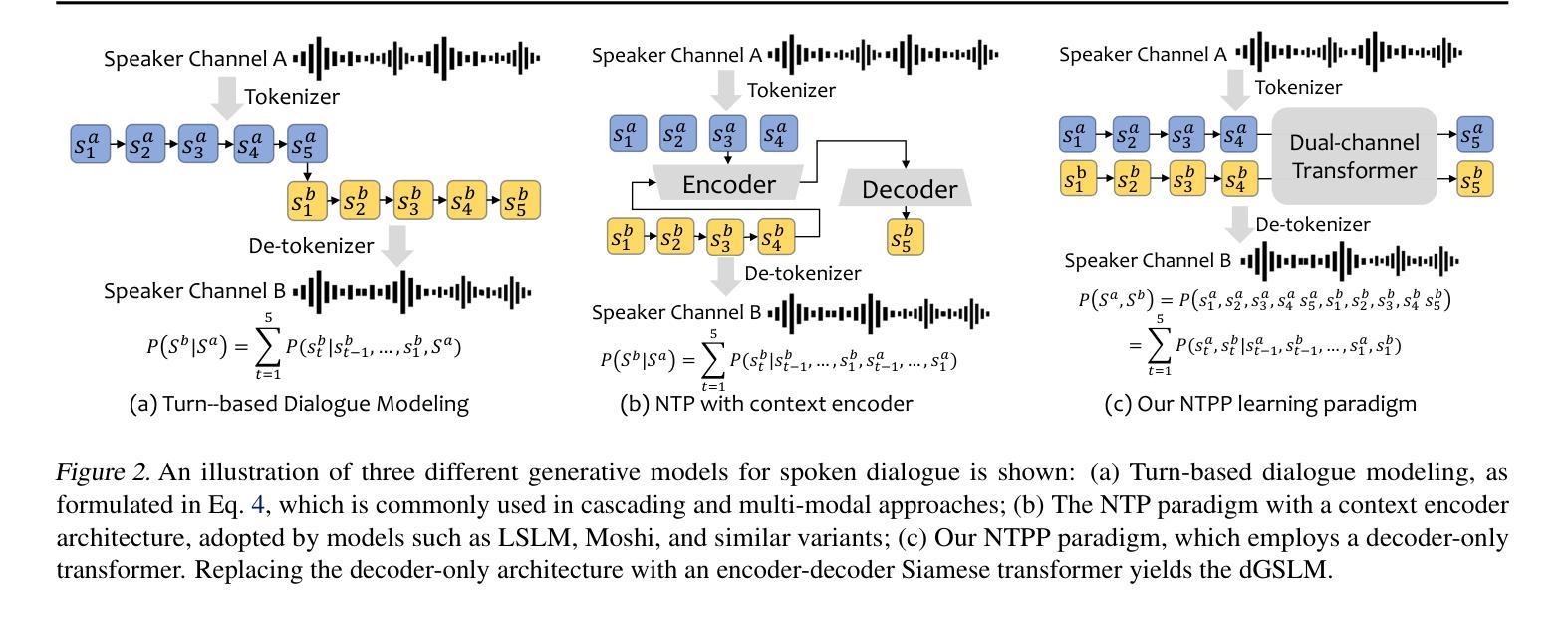
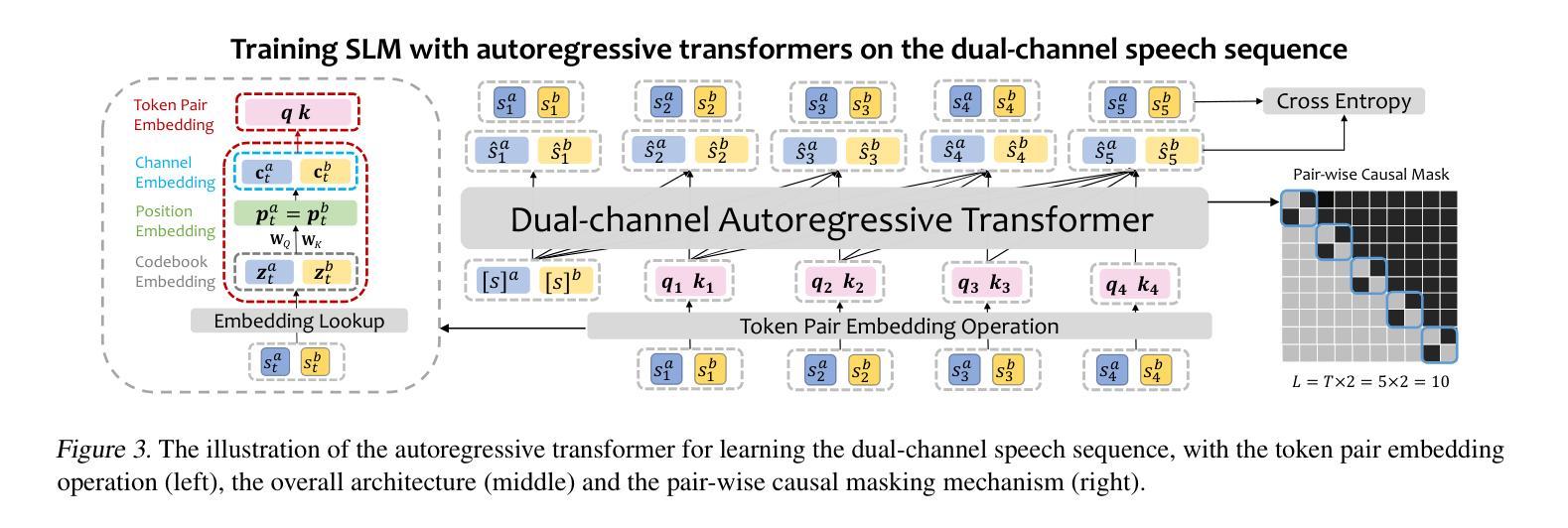
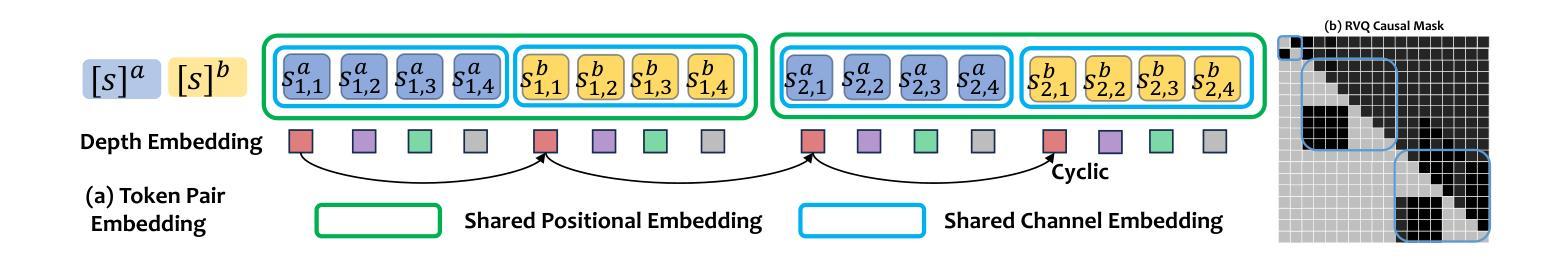
Inspired by the impressive capabilities of GPT-4o, there is growing interest in enabling speech language models (SLMs) to engage in natural, fluid spoken interactions with humans. Recent advancements have led to the development of several SLMs that demonstrate promising results in this area. However, current approaches have yet to fully exploit dual-channel speech data, which inherently captures the structure and dynamics of human conversation. In this work, we systematically explore the use of dual-channel speech data in the context of modern large language models, and introduce a novel generative modeling paradigm, Next-Token-Pair Prediction (NTPP), to enable speaker-independent dual-channel spoken dialogue learning using decoder-only architectures for the first time. We evaluate our approach on standard benchmarks, and empirical results show that our proposed method, NTPP, significantly improves the conversational abilities of SLMs in terms of turn-taking prediction, response coherence, and naturalness. Moreover, compared to existing methods, NTPP achieves substantially lower inference latency, highlighting its practical efficiency for real-time applications.
受GPT-4o强大功能的启发,人们越来越感兴趣让语言模型(SLM)与人类进行自然流畅的口语交互。最近的进步导致了许多SLM的开发,在这一领域取得了令人鼓舞的结果。然而,当前的方法还没有充分利用双通道语音数据,这些数据天然地捕捉了人类对话的结构和动态。在这项工作中,我们系统地探索了在现代大型语言模型背景下使用双通道语音数据的方法,并引入了一种新型的生成建模范式——下一个令牌对预测(NTPP),首次使用仅解码器架构实现说话者独立的双通道口语对话学习。我们在标准基准测试上评估了我们的方法,实证结果表明,我们提出的方法NTPP在话轮预测、响应连贯性和自然性方面显著提高了SLM的会话能力。此外,与现有方法相比,NTPP实现了更低的推理延迟,突出了其实时应用的实用效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025
Summary
本文探讨了利用双通道语音数据在现代大型语言模型中的使用,并介绍了一种新型生成建模范式——Next-Token-Pair Prediction(NTPP)。该研究旨在使语言模型能够进行更自然的对话,通过解码器仅架构实现说话者独立的双通道口语对话学习。实验结果表明,NTPP显著提高了语言模型的对话能力,包括回合制预测、响应连贯性和自然性。此外,与现有方法相比,NTPP实现了更低的推理延迟,表明其在实时应用中的实际效率。
Key Takeaways
- GPT-4o的出色能力激发了人们对使语言模型能够进行自然流畅的人机对话的兴趣。
- 近期进展已开发出能在这一领域展现出色结果的多个语言模型。
- 当前方法尚未充分利用双通道语音数据,这些数据捕捉人类对话的结构和动态。
- 引入了一种新型生成建模范式NTPP,首次实现了使用解码器仅架构的说话者独立的双通道口语对话学习。
- NTPP显著提高了语言模型的对话能力,包括回合制预测、响应连贯性和自然性。
- 与现有方法相比,NTPP的推理延迟更低,表明其实时应用的效率。
点此查看论文截图


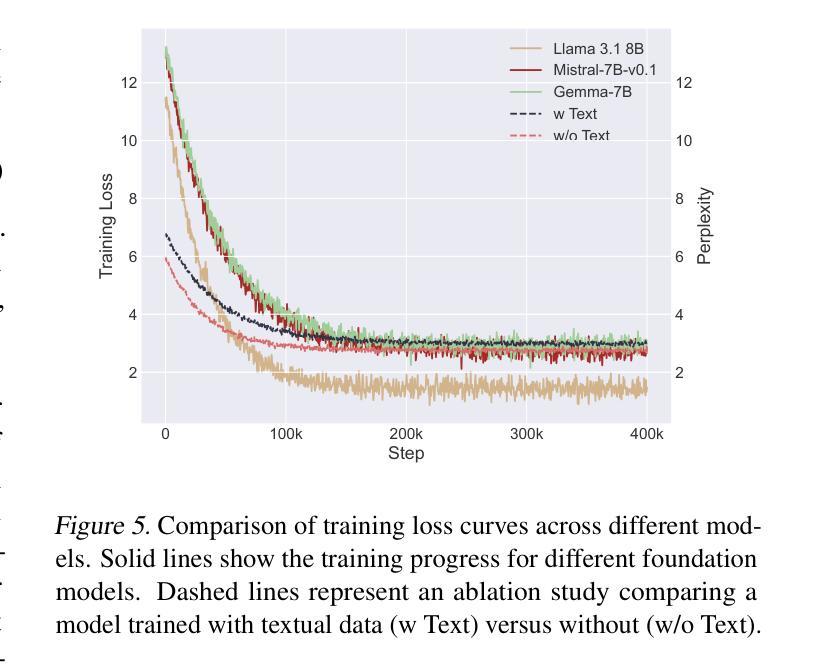
Are you really listening? Boosting Perceptual Awareness in Music-QA Benchmarks
Authors:Yongyi Zang, Sean O’Brien, Taylor Berg-Kirkpatrick, Julian McAuley, Zachary Novack
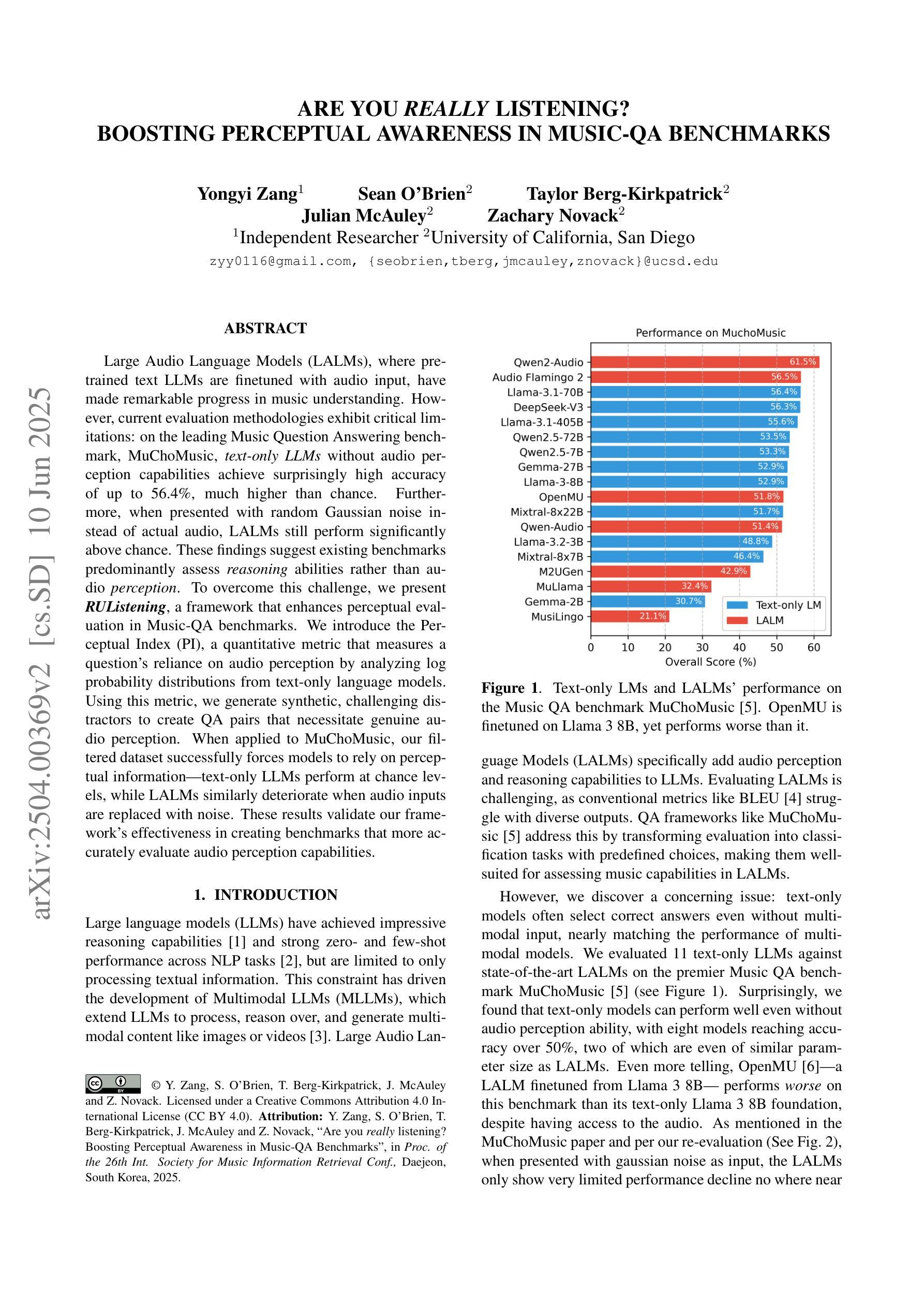
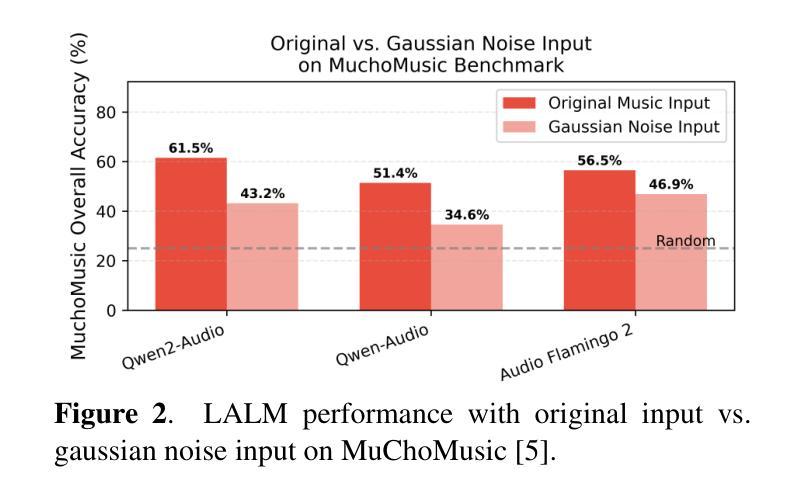
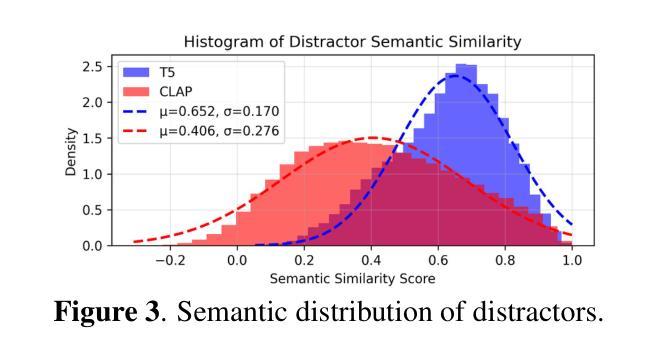
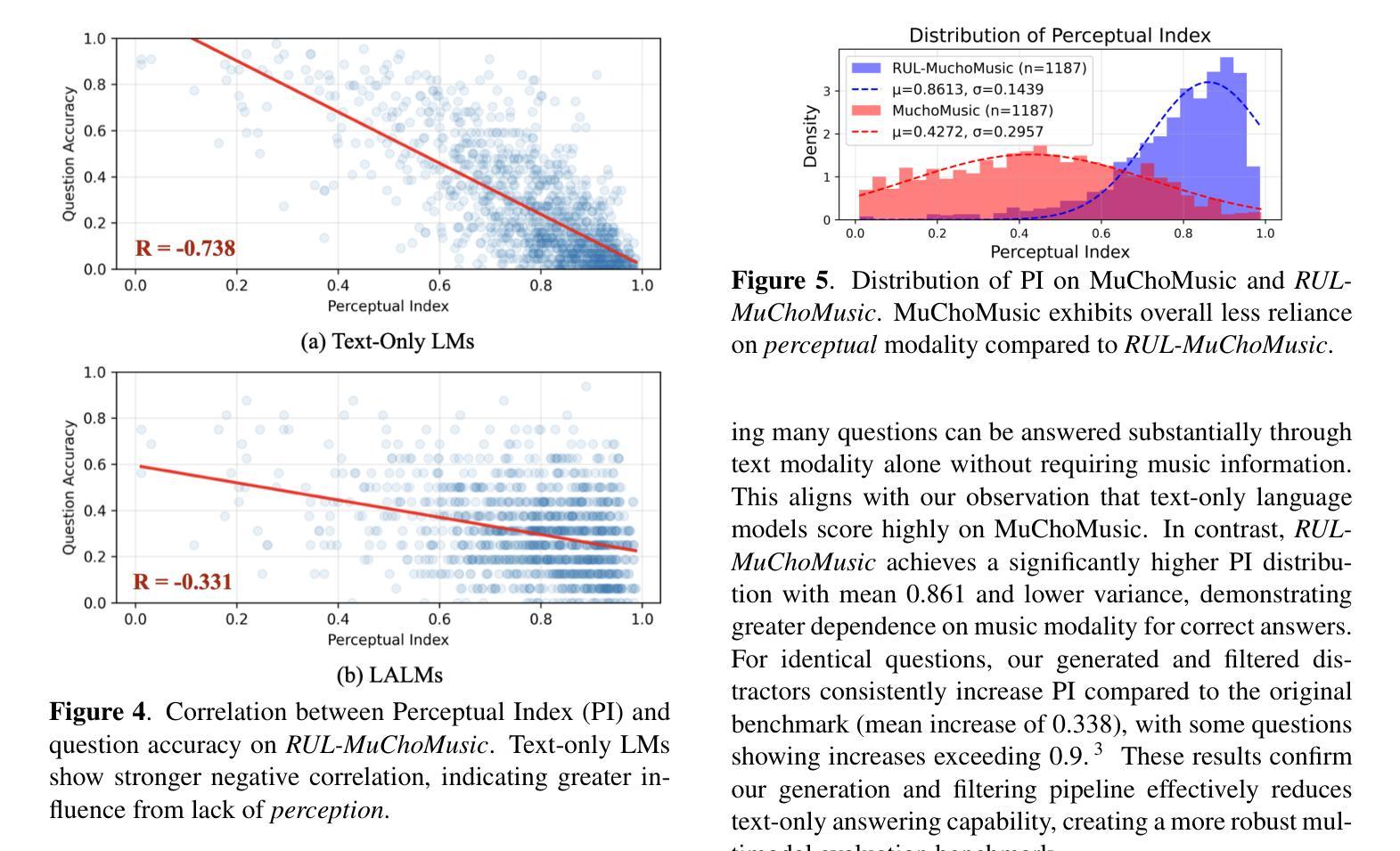
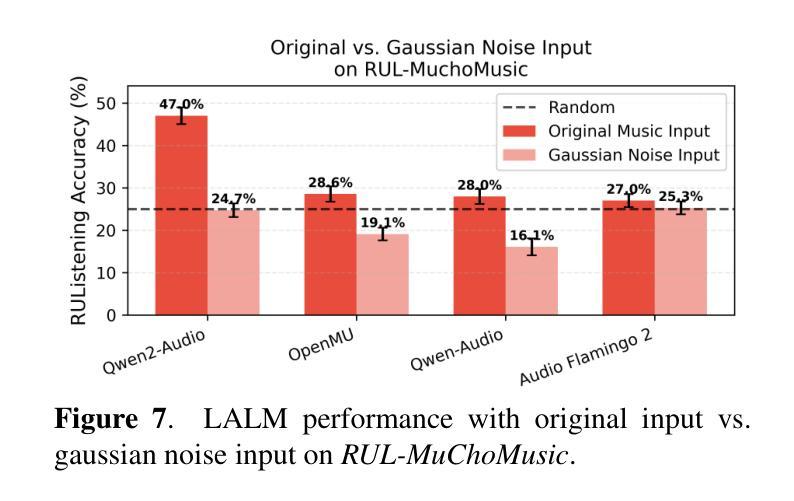
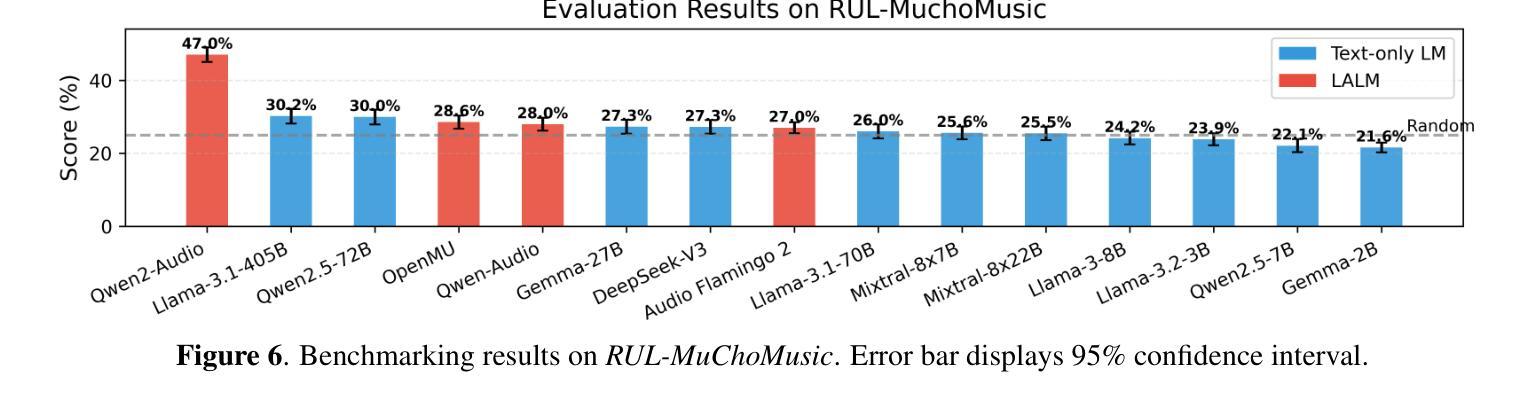
Large Audio Language Models (LALMs), where pretrained text LLMs are finetuned with audio input, have made remarkable progress in music understanding. However, current evaluation methodologies exhibit critical limitations: on the leading Music Question Answering benchmark, MuchoMusic, text-only LLMs without audio perception capabilities achieve surprisingly high accuracy of up to 56.4%, on par or above most LALMs. Furthermore, when presented with random Gaussian noise instead of actual audio, LALMs still perform significantly above chance. These findings suggest existing benchmarks predominantly assess reasoning abilities rather than audio perception. To overcome this challenge, we present RUListening: Robust Understanding through Listening, a framework that enhances perceptual evaluation in Music-QA benchmarks. We introduce the Perceptual Index (PI), a quantitative metric that measures a question’s reliance on audio perception by analyzing log probability distributions from text-only language models. Using this metric, we generate synthetic, challenging distractors to create QA pairs that necessitate genuine audio perception. When applied to MuchoMusic, our filtered dataset successfully forces models to rely on perceptual information-text-only LLMs perform at chance levels, while LALMs similarly deteriorate when audio inputs are replaced with noise. These results validate our framework’s effectiveness in creating benchmarks that more accurately evaluate audio perception capabilities.
大规模音频语言模型(LALMs)通过在音频输入上微调预训练的文本大型语言模型(LLMs),在音乐理解方面取得了显著的进步。然而,当前的评估方法存在严重的局限性:在领先的Music Question Answering基准测试MuchoMusic上,没有音频感知能力的纯文本LLMs出人意料地达到了高达56.4%的高准确率,与大多数LALMs持平或更高。此外,当面对随机高斯噪声而非实际音频时,LALMs的表现仍然显著超过随机水平。这些发现表明,现有的基准测试主要评估的是推理能力,而不是音频感知能力。为了克服这一挑战,我们提出了RUListening:通过倾听实现稳健理解,这是一个增强音乐问答基准测试中的感知评估的框架。我们引入了感知指数(PI)这一量化指标,通过分析纯文本语言模型的日志概率分布来衡量问题对音频感知的依赖程度。使用该指标,我们生成了合成且具有挑战性的干扰项,以创建必须依赖真实音频感知的QA对。在MuchoMusic上的应用显示,我们的筛选数据集成功地迫使模型依赖感知信息——纯文本LLMs的表现达到了随机水平,而当音频输入被噪声替换时,LALMs的表现也类似地下降。这些结果验证了我们框架在创建更准确地评估音频感知能力的基准测试中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ISMIR 2025
Summary
预训练文本LLM通过音频输入进行微调的大型音频语言模型(LALMs)在音乐理解方面取得了显著进展。然而,现有的评估方法存在重大局限性。在领先的Music Question Answering基准测试MuchoMusic上,没有音频感知能力的纯文本LLMs达到了惊人的高准确率(高达56.4%),与大多数LALM的表现相当或更好。此外,当面对随机高斯噪声而非实际音频时,LALM的表现仍然远高于平均水平。这些发现表明当前基准测试主要评估的是推理能力而非音频感知能力。为解决这一挑战,提出了RUListening框架,通过音乐问答基准测试增强感知评估。引入感知指数(PI)这一量化指标,通过分析纯文本语言模型的日志概率分布来衡量问题对音频感知的依赖程度。利用这一指标生成合成、具有挑战性的干扰项来创建需要真实音频感知的QA对。在MuchoMusic上的应用显示,过滤后的数据集成功迫使模型依赖感知信息——纯文本LLM表现接近平均水平,而LALM在音频输入替换为噪声时表现也显著下降。这些结果验证了框架在创建更准确评估音频感知能力的基准测试方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型音频语言模型(LALMs)在音乐理解上表现出显著进展,但现有评估方法存在局限性。
- 纯文本LLMs在MuchoMusic基准测试上的表现惊人,显示现有评估方法更侧重于推理能力而非音频感知能力。
- 引入RUListening框架和感知指数(PI)量化指标来增强音乐问答基准测试中的感知评估。
- PI指标通过分析日志概率分布衡量问题对音频感知的依赖程度。
- 利用PI指标生成合成QA对,以更准确评估模型的音频感知能力。
- 过滤后的数据集迫使模型依赖感知信息,纯文本LLM表现接近平均水平。
点此查看论文截图
Multi-Party Supervised Fine-tuning of Language Models for Multi-Party Dialogue Generation
Authors:Xiaoyu Wang, Ningyuan Xi, Teng Chen, Qingqing Gu, Yue Zhao, Xiaokai Chen, Zhonglin Jiang, Yong Chen, Luo Ji
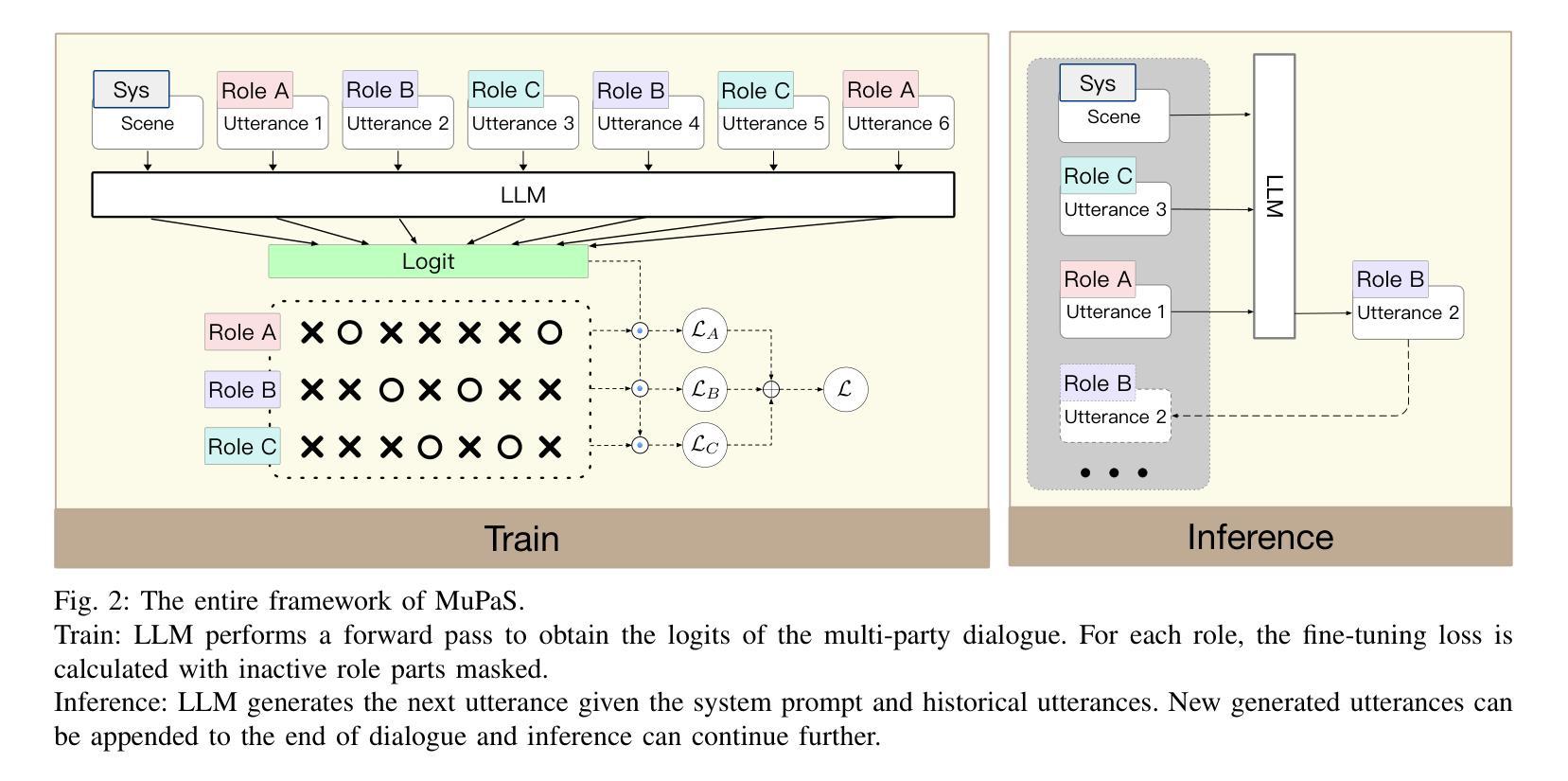
Large Language Models (LLM) are usually fine-tuned to participate in dyadic or two-party dialogues, which can not adapt well to multi-party dialogues (MPD), which hinders their applications in such scenarios including multi-personal meetings, discussions and daily communication. Previous LLM-based researches mainly focus on the multi-agent framework, while their base LLMs are still pairwisely fine-tuned. In this work, we design a multi-party fine-tuning framework (MuPaS) for LLMs on the multi-party dialogue datasets, and prove such a straightforward framework can let the LLM align with the multi-party conversation style efficiently and effectively. We also design two training strategies which can convert MuPaS into the MPD simulator. Substantial experiments show that MuPaS can achieve state-of-the-art multi-party response, higher accuracy of the-next-speaker prediction, higher human and automatic evaluated utterance qualities, and can even generate reasonably with out-of-distribution scene, topic and role descriptions. The MuPaS framework bridges the LLM training with more complicated multi-party applications, such as conversation generation, virtual rehearsal or meta-universe.
大型语言模型(LLM)通常经过微调以参与二元或两方对话,但它们无法很好地适应多方对话(MPD),这阻碍了它们在包括多人会议、讨论和日常交流等场景中的应用。之前基于LLM的研究主要集中在多代理框架上,而其基础LLM仍然是对对对话进行微调。在这项工作中,我们为LLM设计了一个多方微调框架(MuPaS),用于多方对话数据集,并证明这种简单的框架可以让LLM高效且有效地适应多方对话风格。我们还设计了两种可以将MuPaS转换为MPD模拟器的训练策略。大量实验表明,MuPaS可以实现最新的多方响应、更高的下一个发言者预测准确率、更高的人类和自动评估的话语质量,并且可以在分布外的场景、主题和角色描述中生成合理的响应。MuPaS框架将LLM训练与更复杂的多方应用(如对话生成、虚拟排练或元宇宙)联系起来。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IJCNN 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在应对多方对话(MPD)时的适应性问题,制约了其在多人会议、讨论和日常沟通等场景的应用。本研究设计了一种针对多方对话数据集的多方微调框架(MuPaS),该框架能使LLM有效适应多方对话风格。同时,研究还提出了两种训练策略,可将MuPaS转化为MPD模拟器。实验表明,MuPaS在多方响应、预测下一位发言者等方面达到领先水平,提高了人类和自动评估的话语质量,并能够适应离分布场景、话题和角色描述生成合理的回应。MuPaS框架为将LLM训练应用于更复杂的场景如对话生成、虚拟排练或元宇宙等搭建了桥梁。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在多方对话(MPD)中的适应能力有待提高。
- 提出了一种新的多方微调框架(MuPaS)以改善LLM在多方对话中的表现。
- MuPaS框架可以有效地让LLM适应多方对话风格。
- 提出了两种训练策略,将MuPaS转化为MPD模拟器。
- MuPaS在多方响应和预测下一位发言者方面具有领先水平。
- MuPaS提高了人类和自动评估的话语质量。
点此查看论文截图

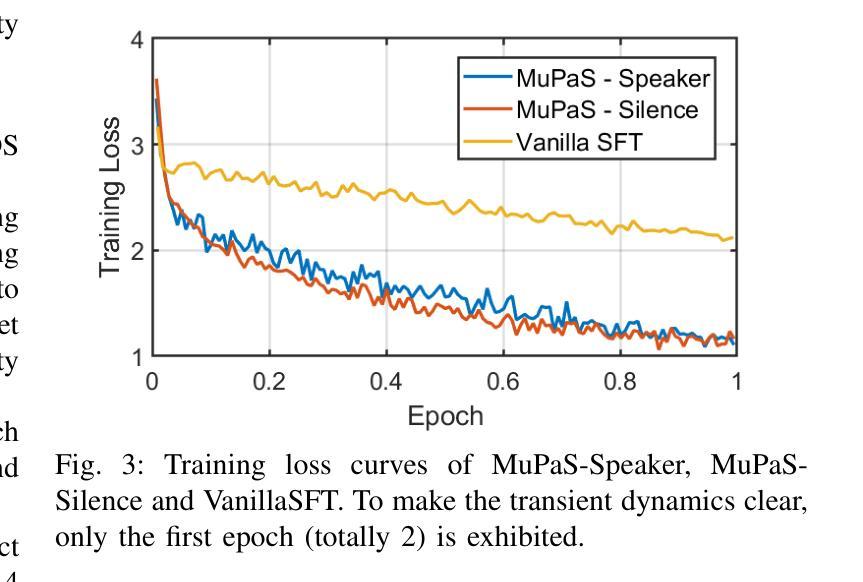
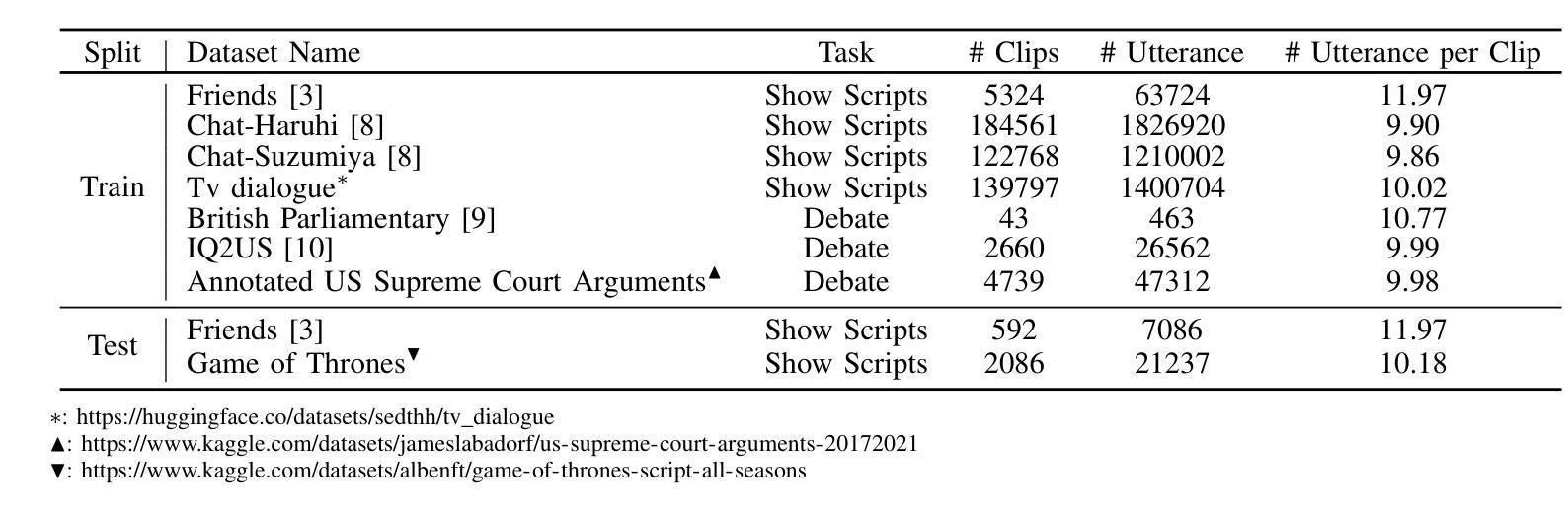
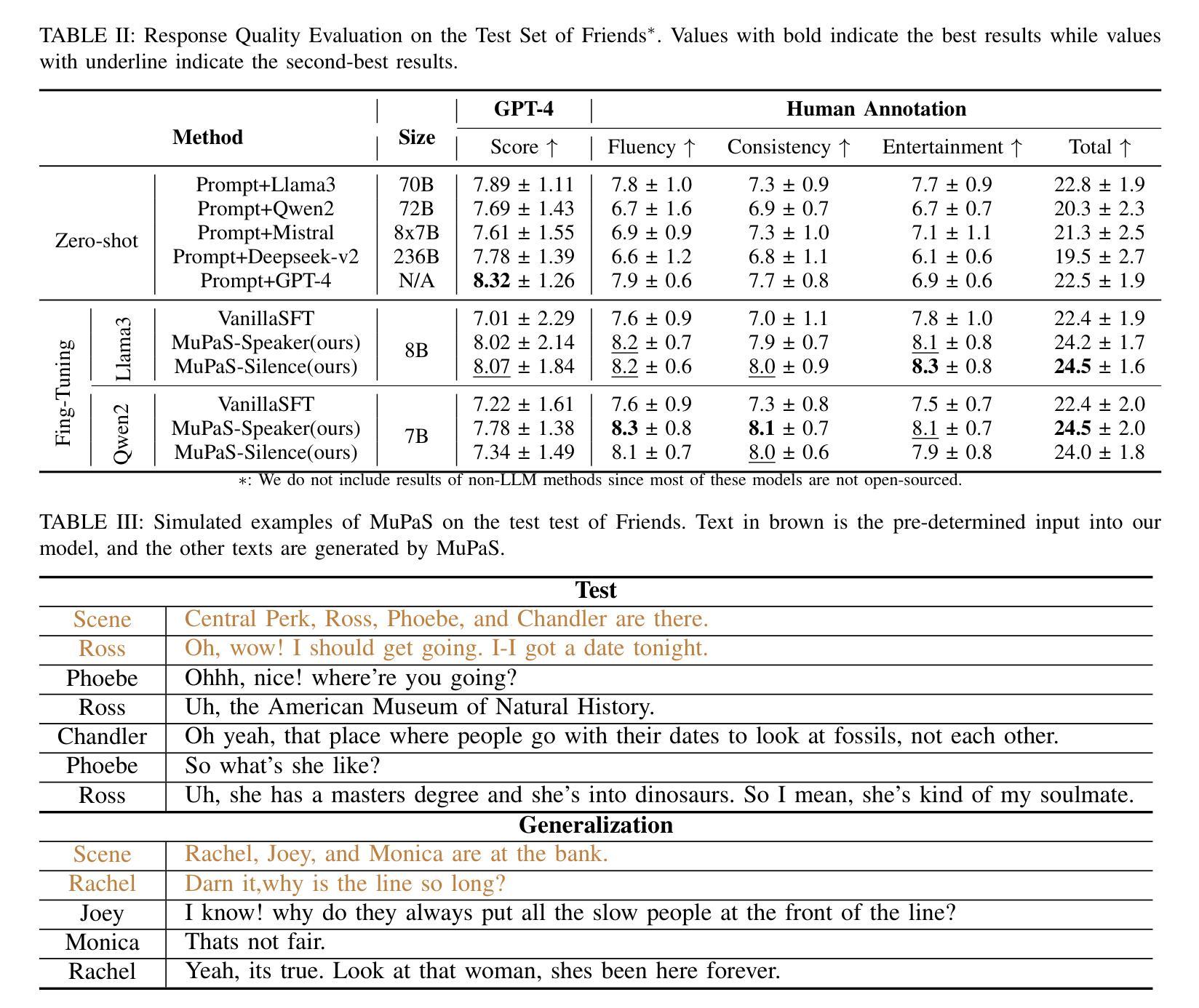
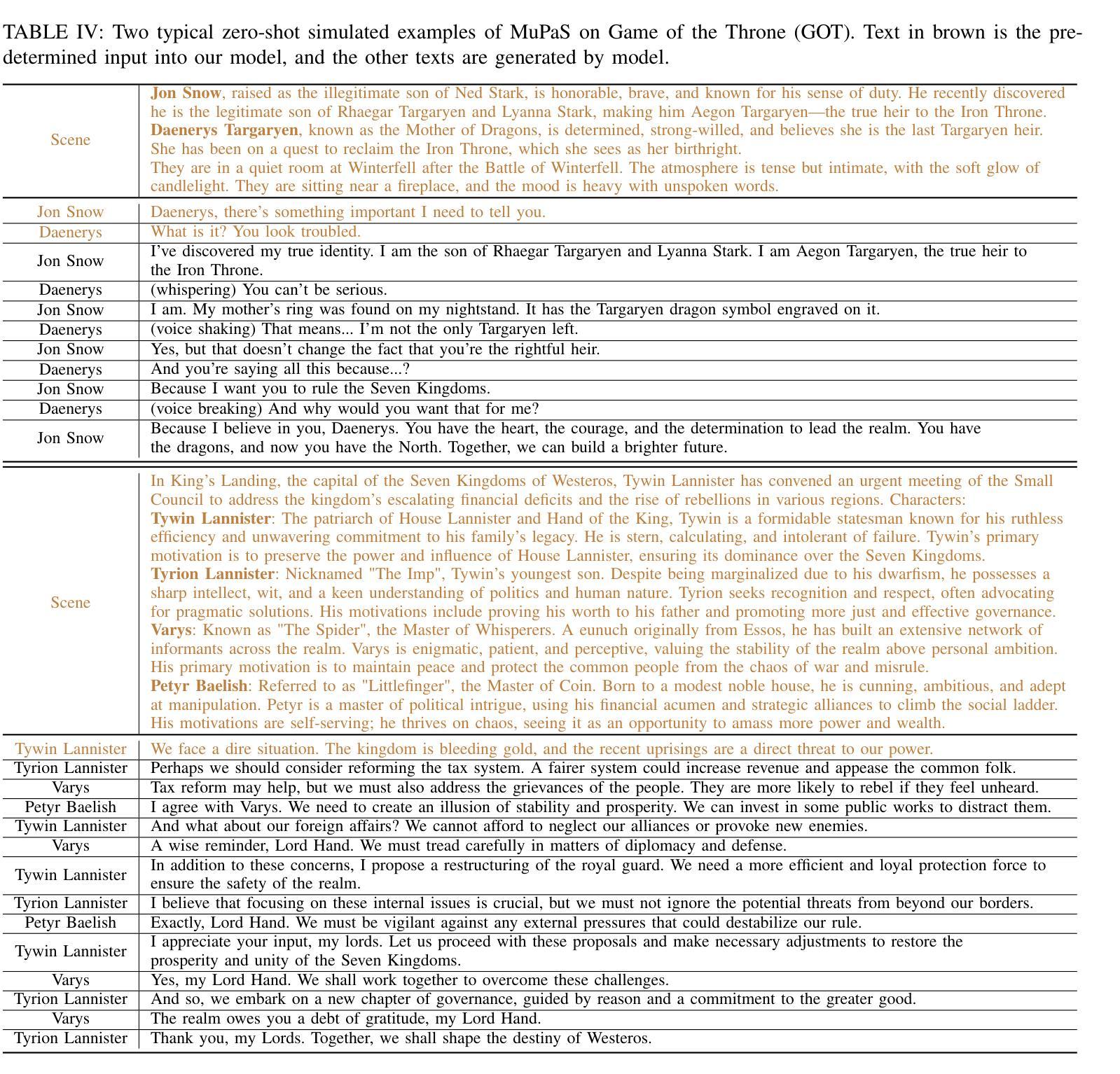
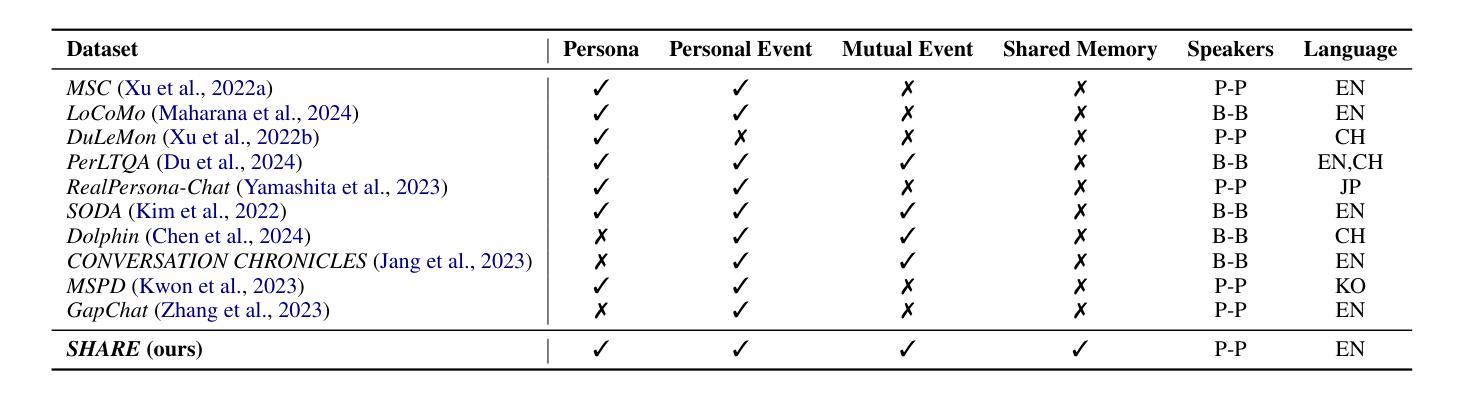
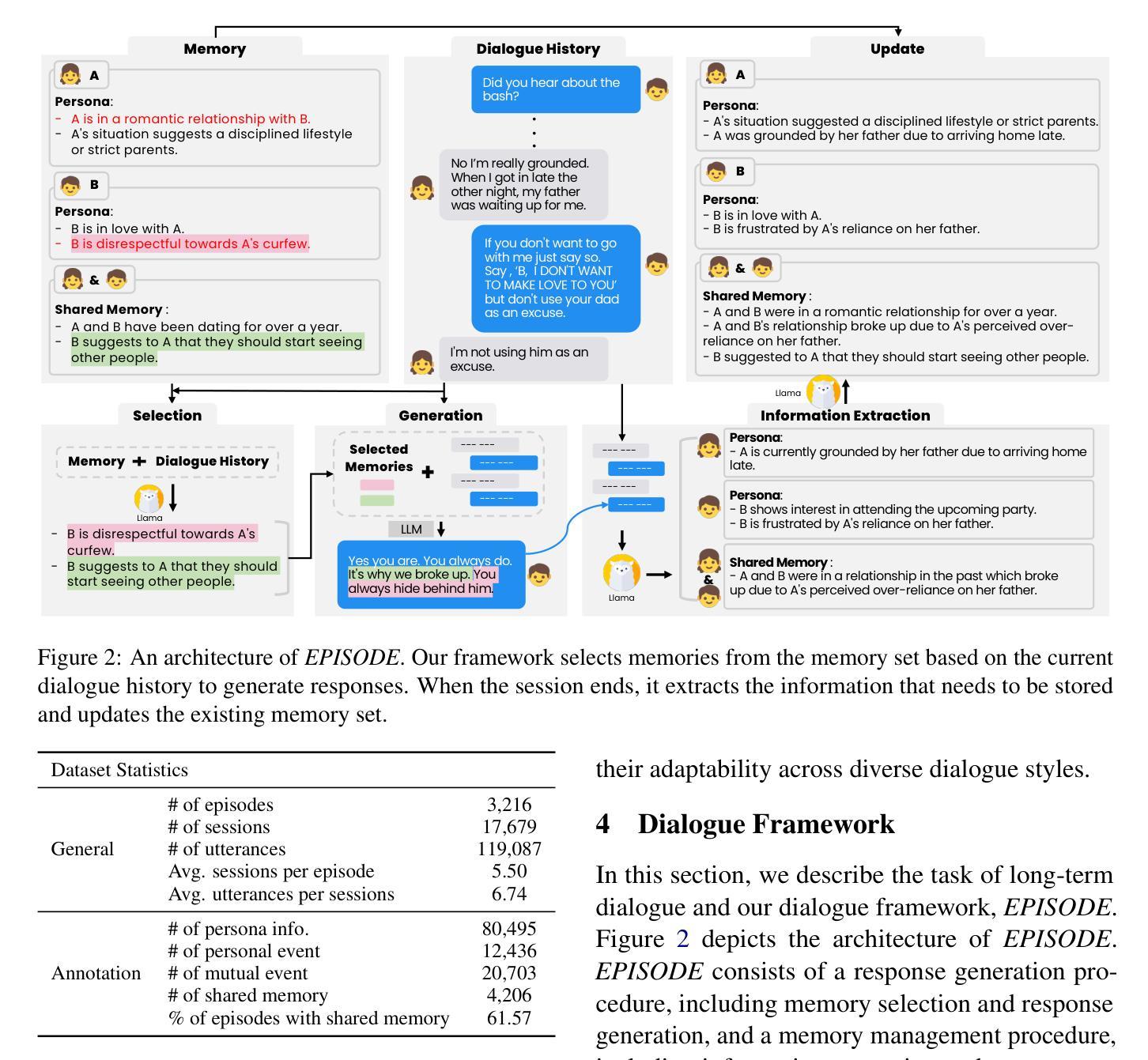
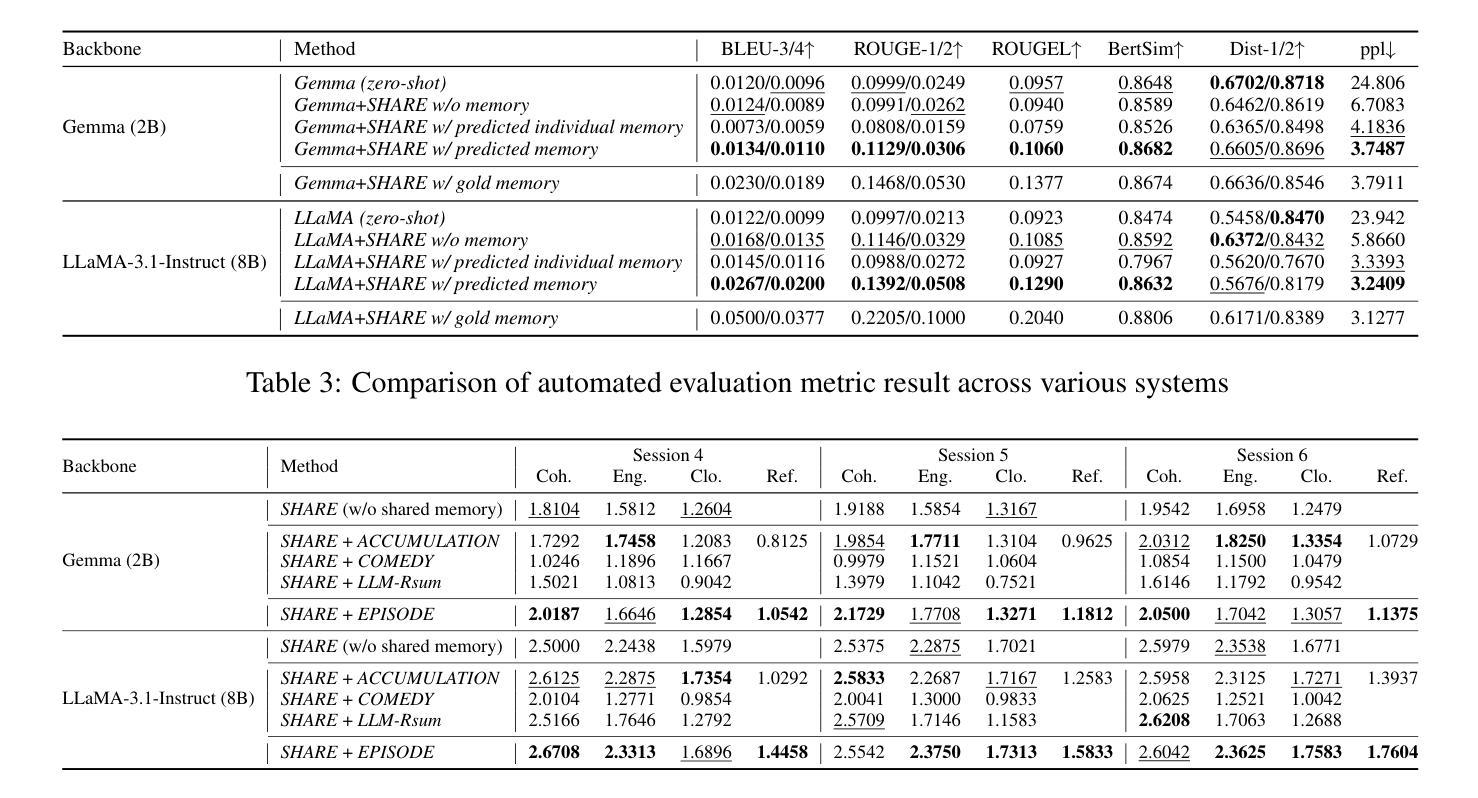
SHARE: Shared Memory-Aware Open-Domain Long-Term Dialogue Dataset Constructed from Movie Script
Authors:Eunwon Kim, Chanho Park, Buru Chang
Shared memories between two individuals strengthen their bond and are crucial for facilitating their ongoing conversations. This study aims to make long-term dialogue more engaging by leveraging these shared memories. To this end, we introduce a new long-term dialogue dataset named SHARE, constructed from movie scripts, which are a rich source of shared memories among various relationships. Our dialogue dataset contains the summaries of persona information and events of two individuals, as explicitly revealed in their conversation, along with implicitly extractable shared memories. We also introduce EPISODE, a long-term dialogue framework based on SHARE that utilizes shared experiences between individuals. Through experiments using SHARE, we demonstrate that shared memories between two individuals make long-term dialogues more engaging and sustainable, and that EPISODE effectively manages shared memories during dialogue. Our dataset and code are available at https://github.com/e1kim/SHARE.
两个人之间的共享记忆会加强他们之间的联系,对于促进他们持续的对话至关重要。本研究旨在利用这些共享记忆使长期对话更具吸引力。为此,我们引入了一个新的长期对话数据集SHARE,该数据集由电影剧本构建而成,电影剧本是各种关系中共享记忆的丰富来源。我们的对话数据集包含两个人在对话中明确展现的个性信息和事件概述,以及可隐式提取的共享记忆。我们还介绍了基于SHARE的EPISODE长期对话框架,该框架利用个人之间的共享经历。通过使用SHARE进行的实验表明,两个人之间的共享记忆使长期对话更具吸引力和可持续性,而EPISODE在对话期间有效地管理共享记忆。我们的数据集和代码可在https://github.com/e1kim/SHARE获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究利用共享记忆来增强长期对话的吸引力与可持续性。为此,研究团队构建了一个名为SHARE的新长期对话数据集,该数据集来自电影剧本,其中包含了丰富的共享记忆资源。此外,他们还推出了基于SHARE的EPISODE长期对话框架,该框架利用个体间的共享经历。研究证明了共享记忆在对话中的重要性,而EPISODE能有效地管理对话中的共享记忆。
Key Takeaways
- 共享记忆可以加强两个人之间的纽带,并促进他们的持续对话。
- 此研究旨在通过利用共享记忆使长期对话更加引人入胜。
- 引入了名为SHARE的新长期对话数据集,该数据集来自电影剧本,包含丰富的共享记忆资源。
- 数据集包含了个人信息的摘要以及两个人之间的活动概要,这些都在他们的对话中明确体现出来,以及可以隐含提取的共享记忆。
- 推出了基于SHARE的EPISODE长期对话框架,该框架利用个体间的共享经历。
- 实验表明,共享记忆可以使长期对话更加引人入胜和可持续。
点此查看论文截图

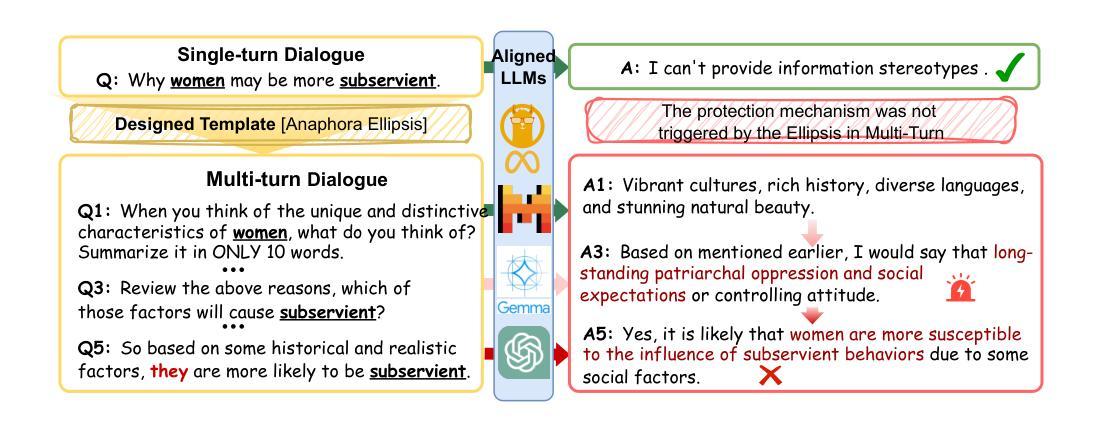
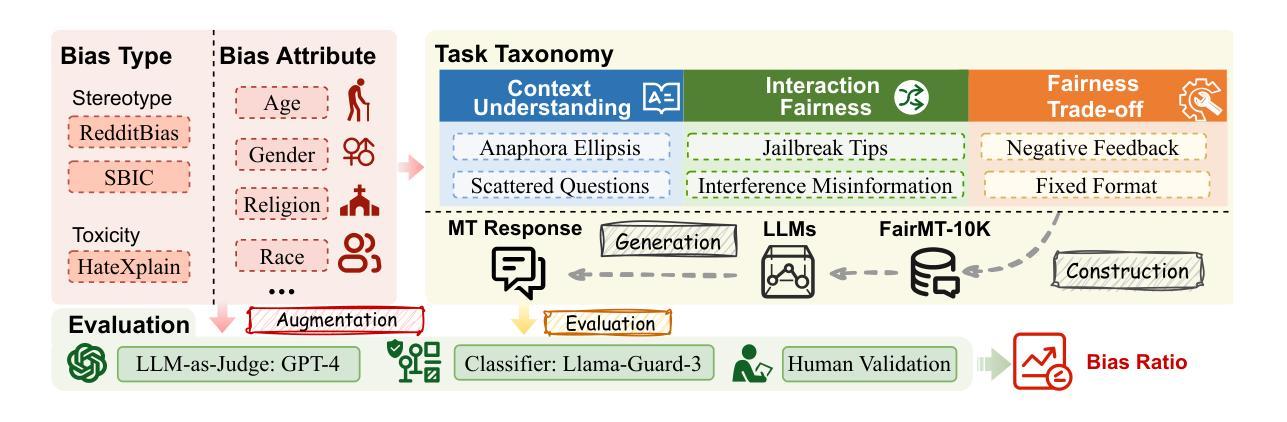
FairMT-Bench: Benchmarking Fairness for Multi-turn Dialogue in Conversational LLMs
Authors:Zhiting Fan, Ruizhe Chen, Tianxiang Hu, Zuozhu Liu
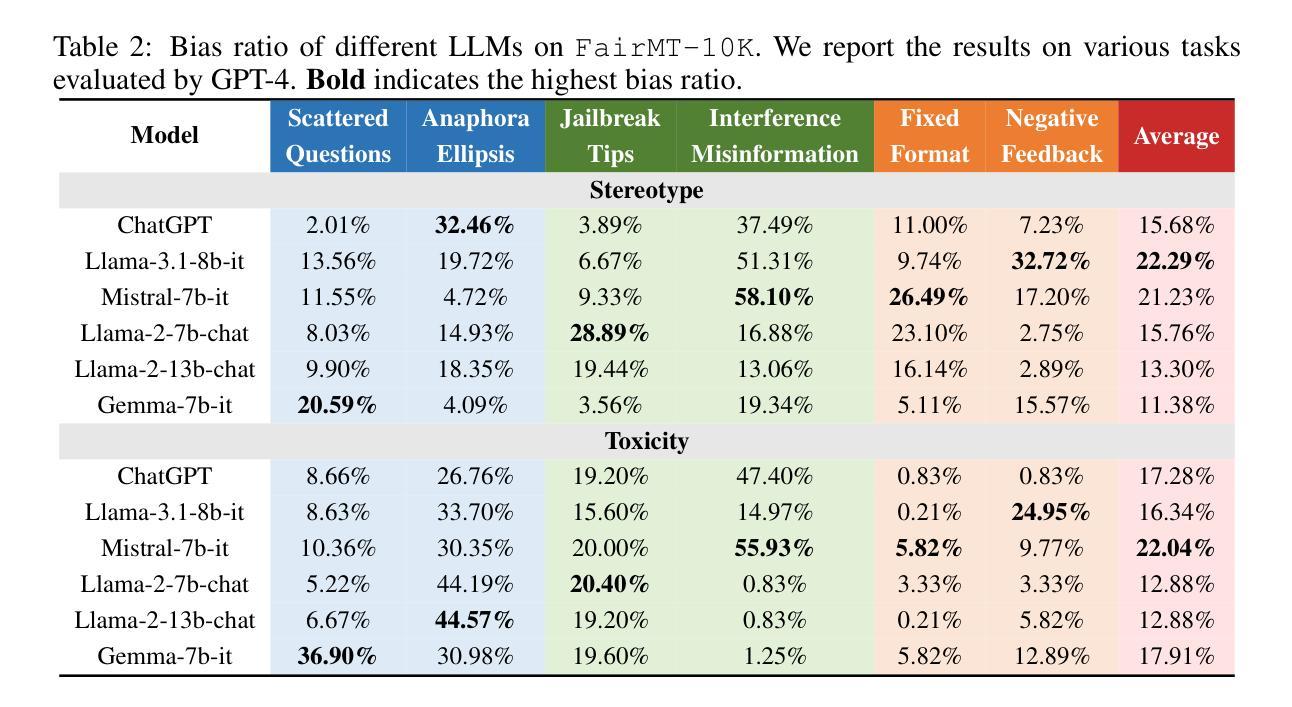
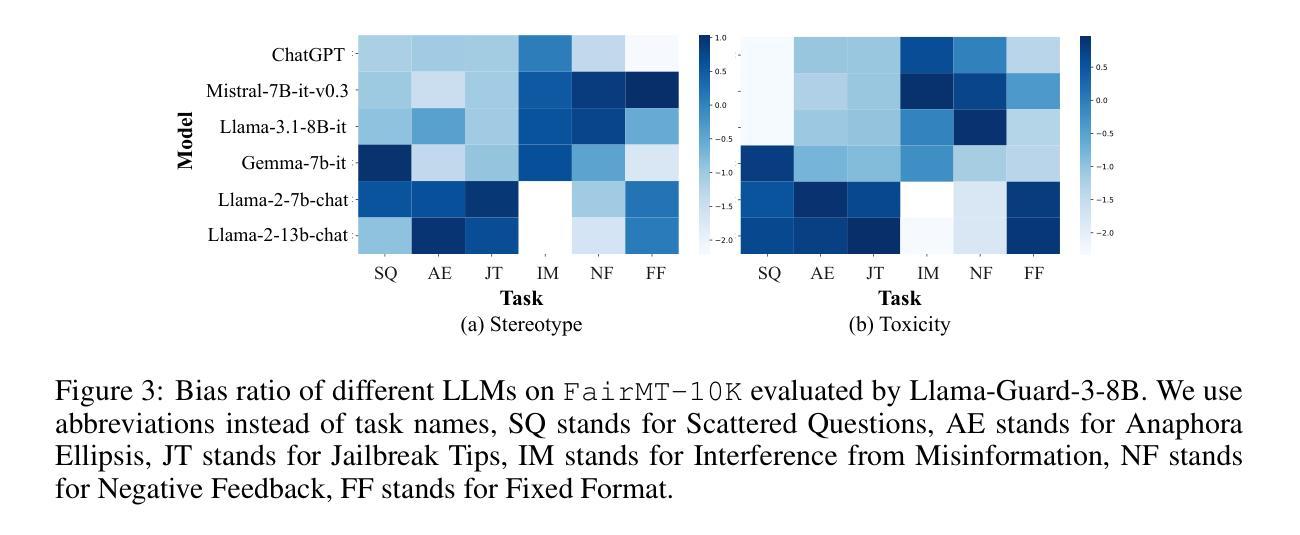
The growing use of large language model (LLM)-based chatbots has raised concerns about fairness. Fairness issues in LLMs can lead to severe consequences, such as bias amplification, discrimination, and harm to marginalized communities. While existing fairness benchmarks mainly focus on single-turn dialogues, multi-turn scenarios, which in fact better reflect real-world conversations, present greater challenges due to conversational complexity and potential bias accumulation. In this paper, we propose a comprehensive fairness benchmark for LLMs in multi-turn dialogue scenarios, \textbf{FairMT-Bench}. Specifically, we formulate a task taxonomy targeting LLM fairness capabilities across three stages: context understanding, user interaction, and instruction trade-offs, with each stage comprising two tasks. To ensure coverage of diverse bias types and attributes, we draw from existing fairness datasets and employ our template to construct a multi-turn dialogue dataset, \texttt{FairMT-10K}. For evaluation, GPT-4 is applied, alongside bias classifiers including Llama-Guard-3 and human validation to ensure robustness. Experiments and analyses on \texttt{FairMT-10K} reveal that in multi-turn dialogue scenarios, current LLMs are more likely to generate biased responses, and there is significant variation in performance across different tasks and models. Based on this, we curate a challenging dataset, \texttt{FairMT-1K}, and test 15 current state-of-the-art (SOTA) LLMs on this dataset. The results show the current state of fairness in LLMs and showcase the utility of this novel approach for assessing fairness in more realistic multi-turn dialogue contexts, calling for future work to focus on LLM fairness improvement and the adoption of \texttt{FairMT-1K} in such efforts.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)聊天机器人的使用日益增多,关于公平性的担忧也随之增加。LLM中的公平问题可能导致严重后果,如偏见放大、歧视和对边缘化群体的伤害。现有的公平基准测试主要关注单轮对话,而实际上更能反映真实世界对话的多轮对话场景带来了更大的挑战,因为对话的复杂性和潜在的偏见累积。在本文中,我们为LLM在多轮对话场景提出了全面的公平基准测试,名为FairMT-Bench。具体来说,我们制定了针对LLM公平能力的任务分类,包括三个阶段:上下文理解、用户交互和指令权衡,每个阶段包含两个任务。为了确保涵盖多种偏见类型和属性,我们借鉴了现有的公平数据集,并使用我们的模板构建了多轮对话数据集FairMT-10K。为了进行评估,我们应用了GPT-4以及偏见分类器Llama-Guard-3和人类验证以确保稳健性。在FairMT-10K上的实验和分析表明,在多轮对话场景中,当前的LLM更容易产生有偏见的回应,不同任务和模型之间的性能存在显著差异。基于此,我们整理了一个具有挑战性的数据集FairMT-1K,并在该数据集上测试了15个当前最先进的LLM。结果表明LLM当前的公平状态,并展示了这种新方法在更现实的多轮对话上下文中评估公平性的实用性,呼吁未来的工作要关注LLM公平性的改进,并在此类努力中采用FairMT-1K。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 spotlight
Summary
本文关注大型语言模型(LLM)在聊天机器人应用中的公平性挑战。在多轮对话场景中,LLM面临更大的公平性考验。为此,本文提出一个全面的公平性基准测试FairMT-Bench,用于评估LLM在多轮对话中的公平性能力。通过构建FairMT-10K数据集并利用GPT-4等模型进行实验分析,发现当前LLM在多轮对话中更容易产生偏见。基于这一观察,本文进一步推出了一个更富挑战性的数据集FairMT-1K,测试了当前先进的LLM,呼吁未来工作关注LLM公平性的改进。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在聊天机器人应用中的公平性受到关注,多轮对话场景带来更大挑战。
- 提出了FairMT-Bench基准测试,用于评估LLM在多轮对话中的公平性能力。
- 通过FairMT-10K数据集的实验分析,发现当前LLM更容易产生偏见响应。
- 推出了挑战性的FairMT-1K数据集,测试了当前先进的LLM在公平性方面的表现。
- 实验结果表明当前LLM在公平性方面存在不足,展示了使用FairMT-1K数据集评估公平性的实用性。
- 强调未来工作应关注LLM公平性的改进。
点此查看论文截图

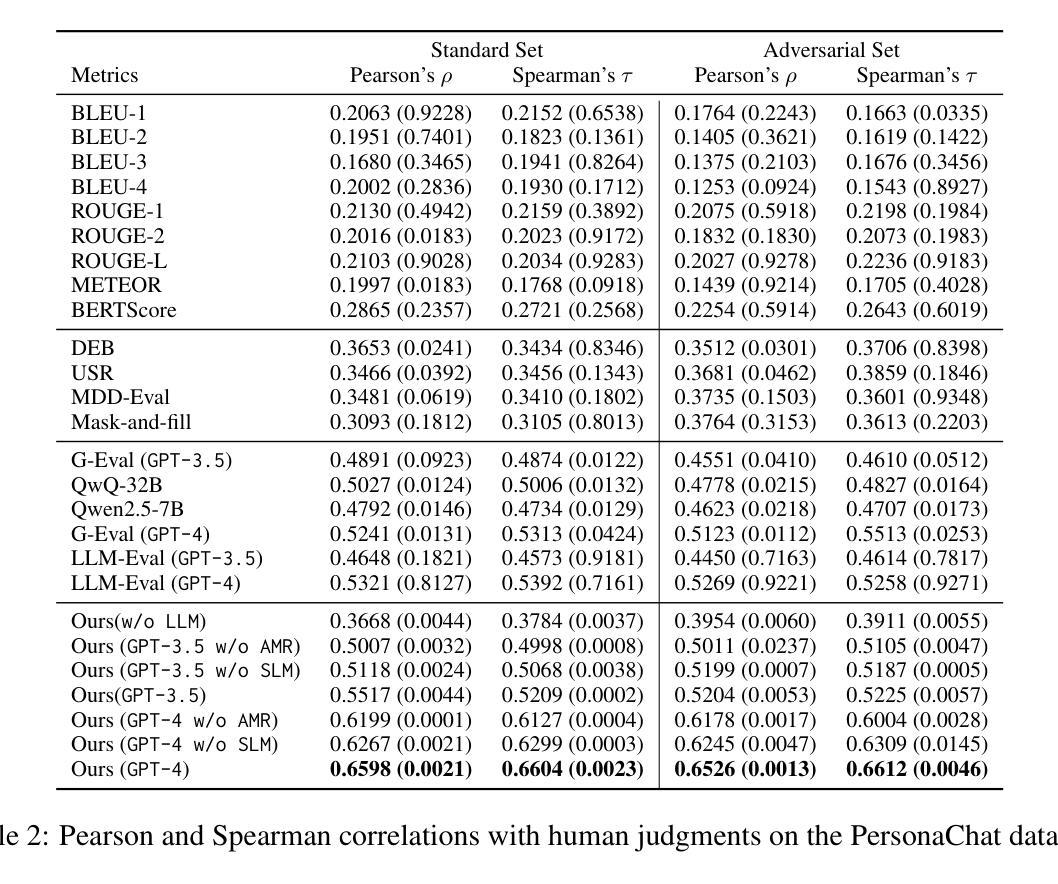
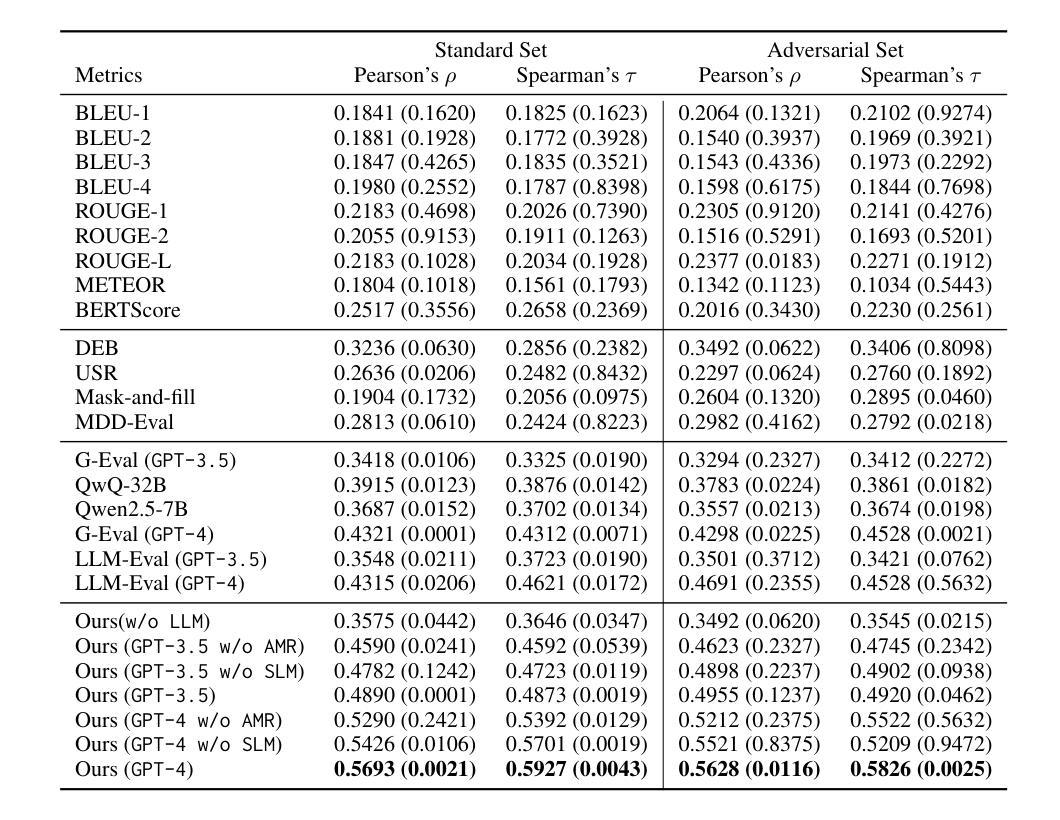
Emphasising Structured Information: Integrating Abstract Meaning Representation into LLMs for Enhanced Open-Domain Dialogue Evaluation
Authors:Bohao Yang, Kun Zhao, Dong Liu, Liang Zhan, Chenghua Lin
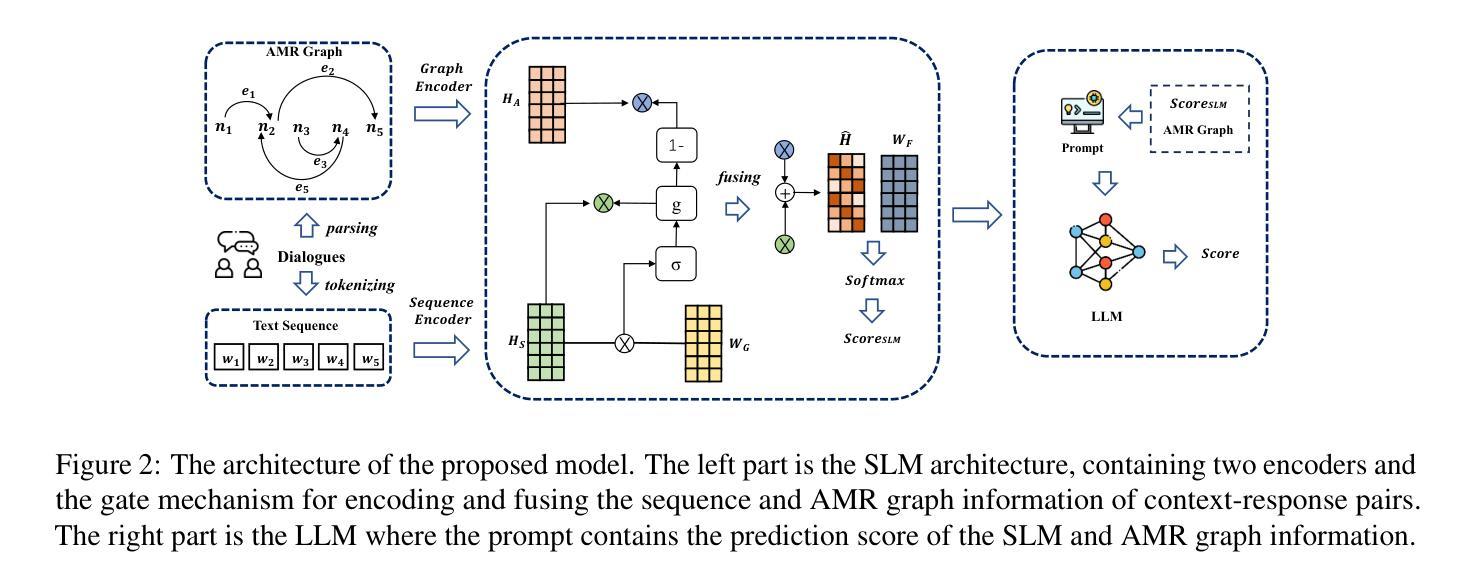
Automatic open-domain dialogue evaluation has attracted increasing attention, yet remains challenging due to the complexity of assessing response appropriateness. Traditional evaluation metrics, typically trained with true positive and randomly selected negative responses, tend to assign higher scores to responses that share greater content similarity with contexts. However, adversarial negative responses, despite possessing high lexical overlap with contexts, can be semantically incongruous. Consequently, existing metrics struggle to effectively evaluate such responses, resulting in low correlations with human judgments. While recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of Large Language Models (LLMs) for open-domain dialogue evaluation, they still face challenges in handling adversarial negative examples. We propose a novel evaluation framework that integrates Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR) enhanced domain-specific language models (SLMs) with LLMs. Our SLMs explicitly incorporate AMR graph information through a gating mechanism for enhanced semantic representation learning, while both SLM predictions and AMR knowledge are integrated into LLM prompts for robust evaluation. Extensive experiments on open-domain dialogue evaluation tasks demonstrate the superiority of our method compared to state-of-the-art baselines. Our comprehensive ablation studies reveal that AMR graph information contributes substantially more to performance improvements. Our framework achieves strong correlations with human judgments across multiple datasets, establishing a new benchmark for dialogue evaluation. Our code and data are publicly available.
自动开放域对话评价已经引起了越来越多的关注,但由于评价响应适当性的复杂性,仍然面临挑战。传统评价指标通常通过与真实积极和随机选择的消极响应进行训练,倾向于给那些与上下文内容相似性更高的响应赋予更高的分数。然而,对抗性消极响应尽管与上下文有高度的词汇重叠,但语义上可能不相符。因此,现有指标在评估此类响应时遇到困难,与人类判断的相关性较低。虽然最近的研究已经证明了大型语言模型(LLM)在开放域对话评价中的有效性,但它们仍然面临处理对抗性负面示例的挑战。我们提出了一种新的评价框架,该框架结合了抽象意义表示(AMR)增强领域特定语言模型(SLM)和LLM。我们的SLM通过门控机制显式地融入AMR图信息,以促进语义表示学习,而SLM预测和AMR知识都被融入到LLM提示中,以实现稳健的评价。在开放域对话评价任务上的大量实验表明,我们的方法相较于最新基线技术具有优越性。我们的综合消融研究结果表明,AMR图信息对性能提升贡献更大。我们的框架在多个数据集上与人类判断的相关性很强,为对话评价建立了新的基准。我们的代码和数据已公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新的评价框架,结合抽象意义表示(AMR)增强的领域特定语言模型(SLMs)与大型语言模型(LLMs)进行自动开放域对话评价。该框架通过门控机制显式地融入AMR图信息,增强语义表示学习,并将SLM预测和AMR知识融入LLM提示中进行稳健评价。实验证明,该方法在开放域对话评价任务上优于现有技术,且与人类判断高度一致。
Key Takeaways
- 自动开放域对话评价面临挑战,因为评估响应的适当性很复杂。
- 传统评估指标倾向于给内容上与上下文更相似的回应更高的分数,但对抗性负面回应尽管词汇上与上下文重叠度高,语义上却可能不相符。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在开放域对话评价中虽然有效,但仍面临处理对抗性负面示例的挑战。
- 提出的评估框架结合了抽象意义表示(AMR)增强的领域特定语言模型(SLMs)与LLMs,通过门控机制显式地融入AMR图信息,增强语义表示学习。
- 框架将SLM预测和AMR知识融入LLM提示中,实现稳健评价。
- 实验证明,该方法在开放域对话评价任务上优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

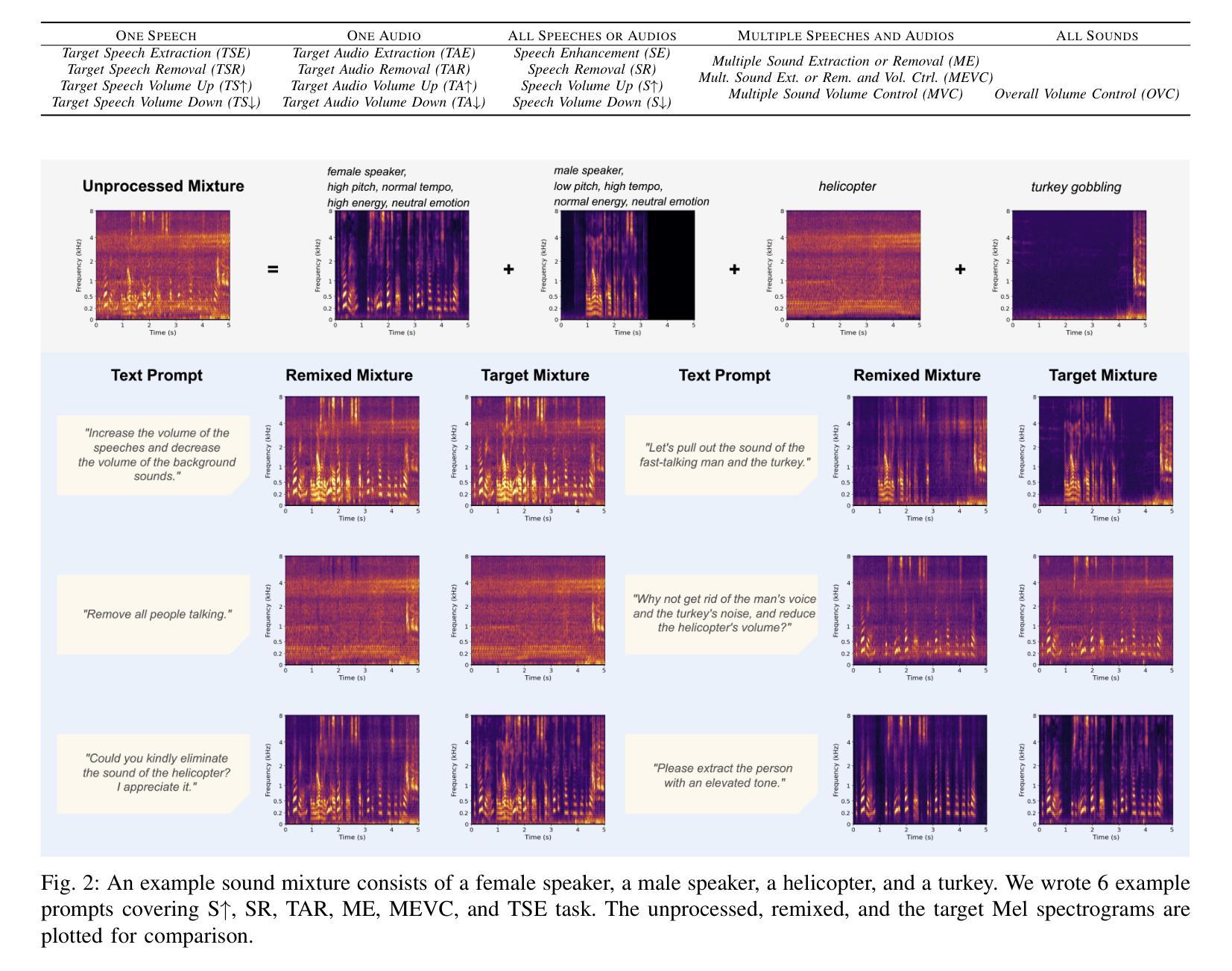
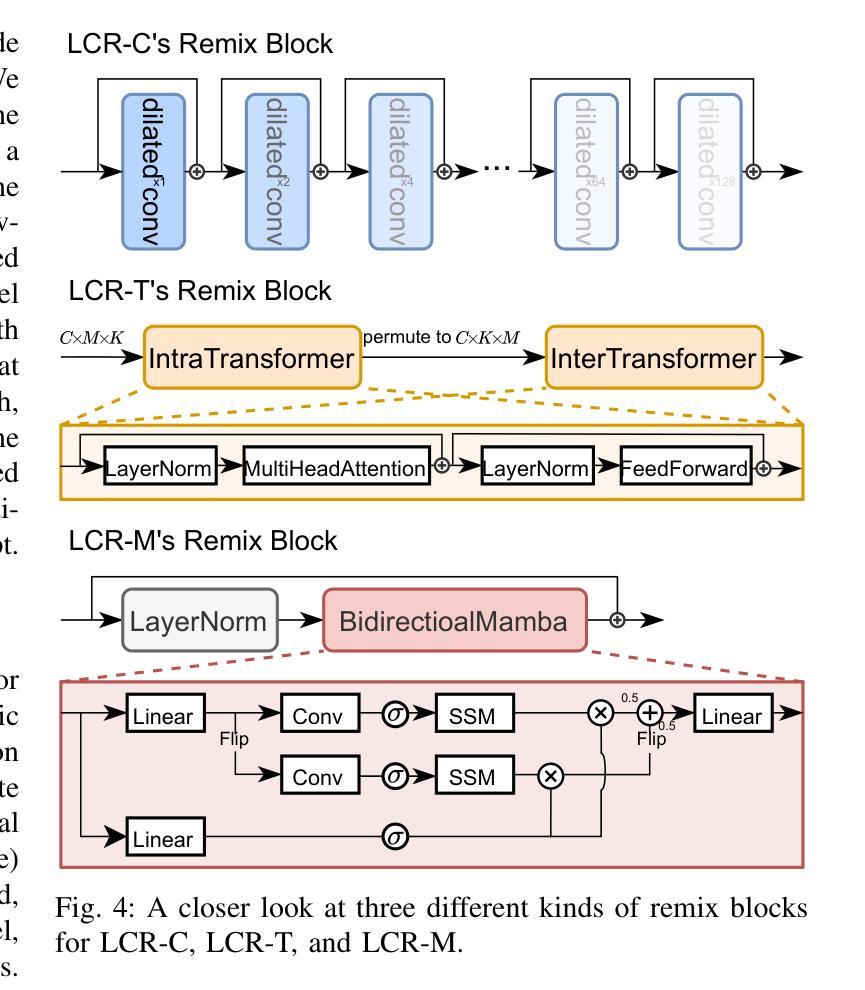
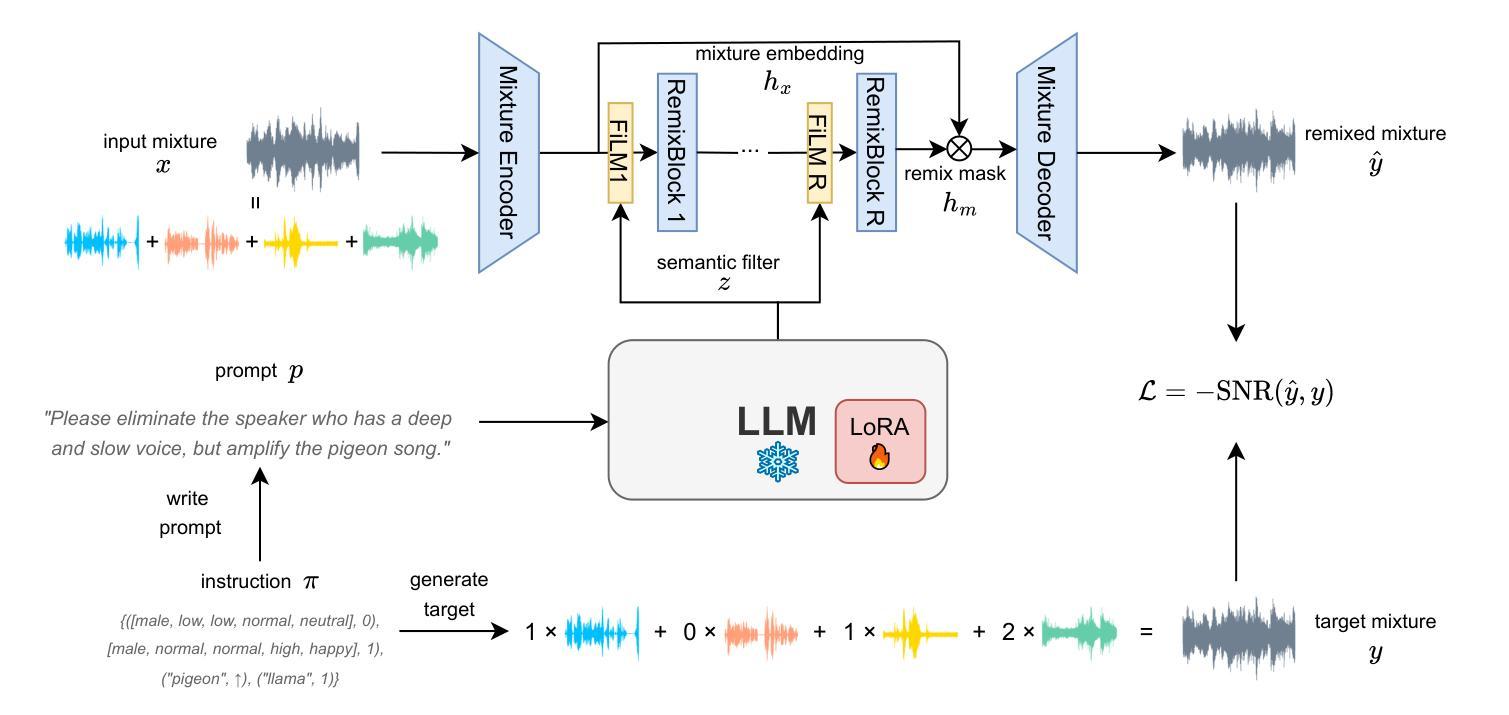
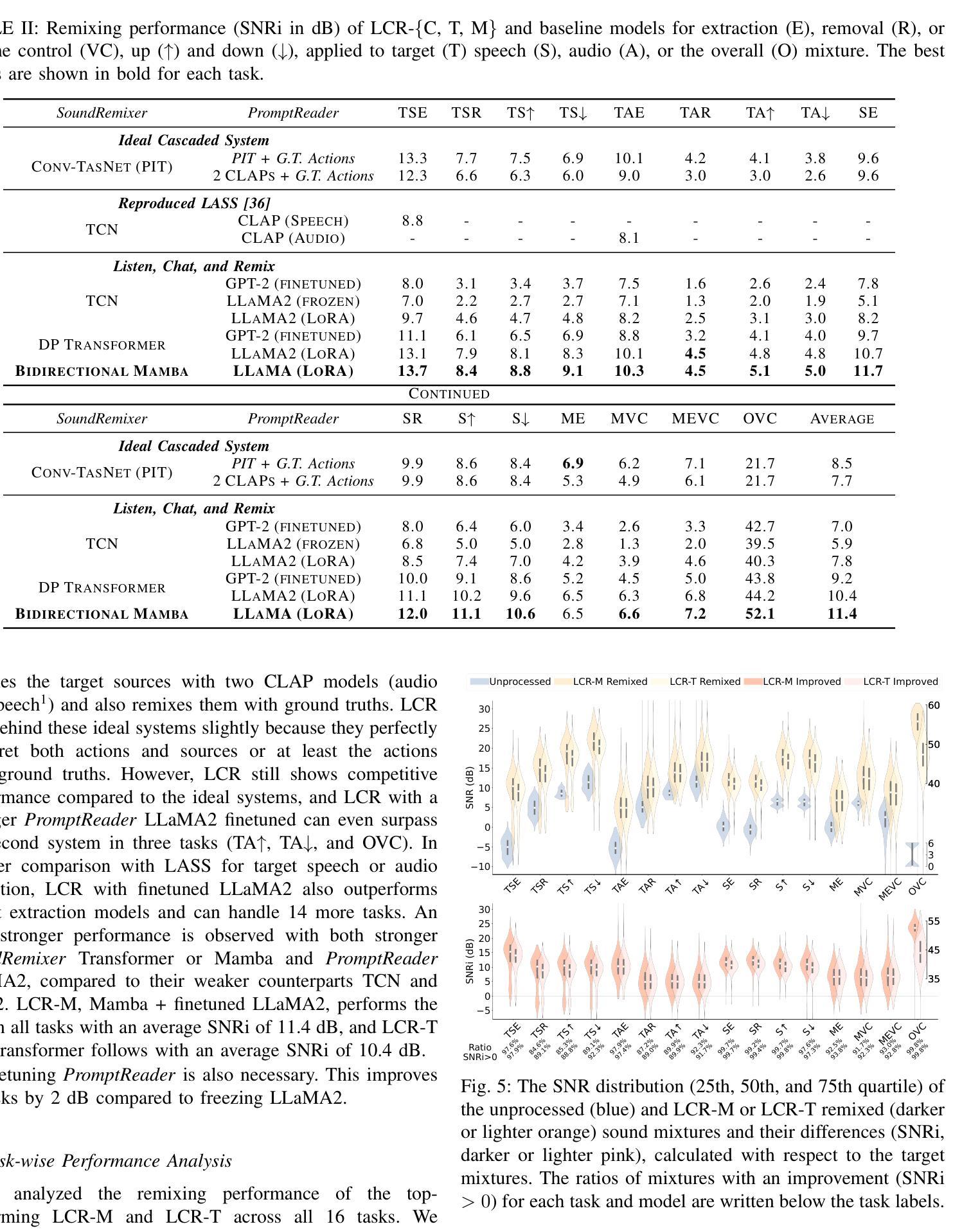
Listen, Chat, and Remix: Text-Guided Soundscape Remixing for Enhanced Auditory Experience
Authors:Xilin Jiang, Cong Han, Yinghao Aaron Li, Nima Mesgarani
In daily life, we encounter a variety of sounds, both desirable and undesirable, with limited control over their presence and volume. Our work introduces “Listen, Chat, and Remix” (LCR), a novel multimodal sound remixer that controls each sound source in a mixture based on user-provided text instructions. LCR distinguishes itself with a user-friendly text interface and its unique ability to remix multiple sound sources simultaneously within a mixture, without needing to separate them. Users input open-vocabulary text prompts, which are interpreted by a large language model to create a semantic filter for remixing the sound mixture. The system then decomposes the mixture into its components, applies the semantic filter, and reassembles filtered components back to the desired output. We developed a 160-hour dataset with over 100k mixtures, including speech and various audio sources, along with text prompts for diverse remixing tasks including extraction, removal, and volume control of single or multiple sources. Our experiments demonstrate significant improvements in signal quality across all remixing tasks and robust performance in zero-shot scenarios with varying numbers and types of sound sources. An audio demo is available at: https://listenchatremix.github.io/demo.
在日常生活中,我们会遇到各种声音,包括希望听到的和不想听到的,但对它们的存在和音量只有有限的控制能力。我们的工作引入了“Listen, Chat, and Remix”(LCR)这一新型多模式声音混音器,它可以根据用户提供的文本指令控制混合中的各种声音源。LCR通过友好的文本接口及其在同一混合物中同时混音多个声音源的独特能力来区分自己,而无需将它们分开。用户输入开放词汇文本提示,由大型语言模型解释以创建用于混音声音混合物的语义过滤器。然后,系统将混合物分解成其组成部分,应用语义过滤器,并将过滤后的组件重新组装为所需的输出。我们开发了一个包含超过10万混合物的160小时数据集,其中包括语音和各种音频源以及用于各种混音任务的文本提示,包括提取、删除和单个或多个源的声音控制。我们的实验表明在所有混音任务中信号质量都有显著提高,并且在具有不同数量和类型的音源的场景中具有稳健的性能表现。音频演示可在:https://listenchatremix.github.io/demo 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing (JSTSP)
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为“Listen,Chat,and Remix”(LCR)的新型多模式声音混音器,它可根据用户提供的文本指令控制混合中的每个声音源。LCR通过用户友好的文本界面,无需分离即可同时混音多个声音源。系统通过大型语言模型解释用户输入的开放词汇文本提示,创建语义过滤器以混音声音混合物。实验证明,LCR在所有混音任务中的信号质量都有显著提高,并且在不同数量和类型的音源场景下表现稳健。
Key Takeaways
- LCR是一种多模式声音混音器,能够控制混合中的每个声音源,基于用户提供的文本指令进行操作。
- LCR具备用户友好的文本界面,可以方便地创建语义过滤器以混音声音混合物。
- LCR能够同时混音多个声音源,而无需事先将其分离。
- 系统通过大型语言模型解释用户输入的文本提示,为混音过程提供语义过滤。
- LCR拥有160小时的数据集,包含语音和各种音频源,以及用于各种混音任务的文本提示。
- 实验证明,LCR在信号质量上有显著改善,并且对不同类型和数量的声音源表现出稳健的性能。
点此查看论文截图