⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-13 更新
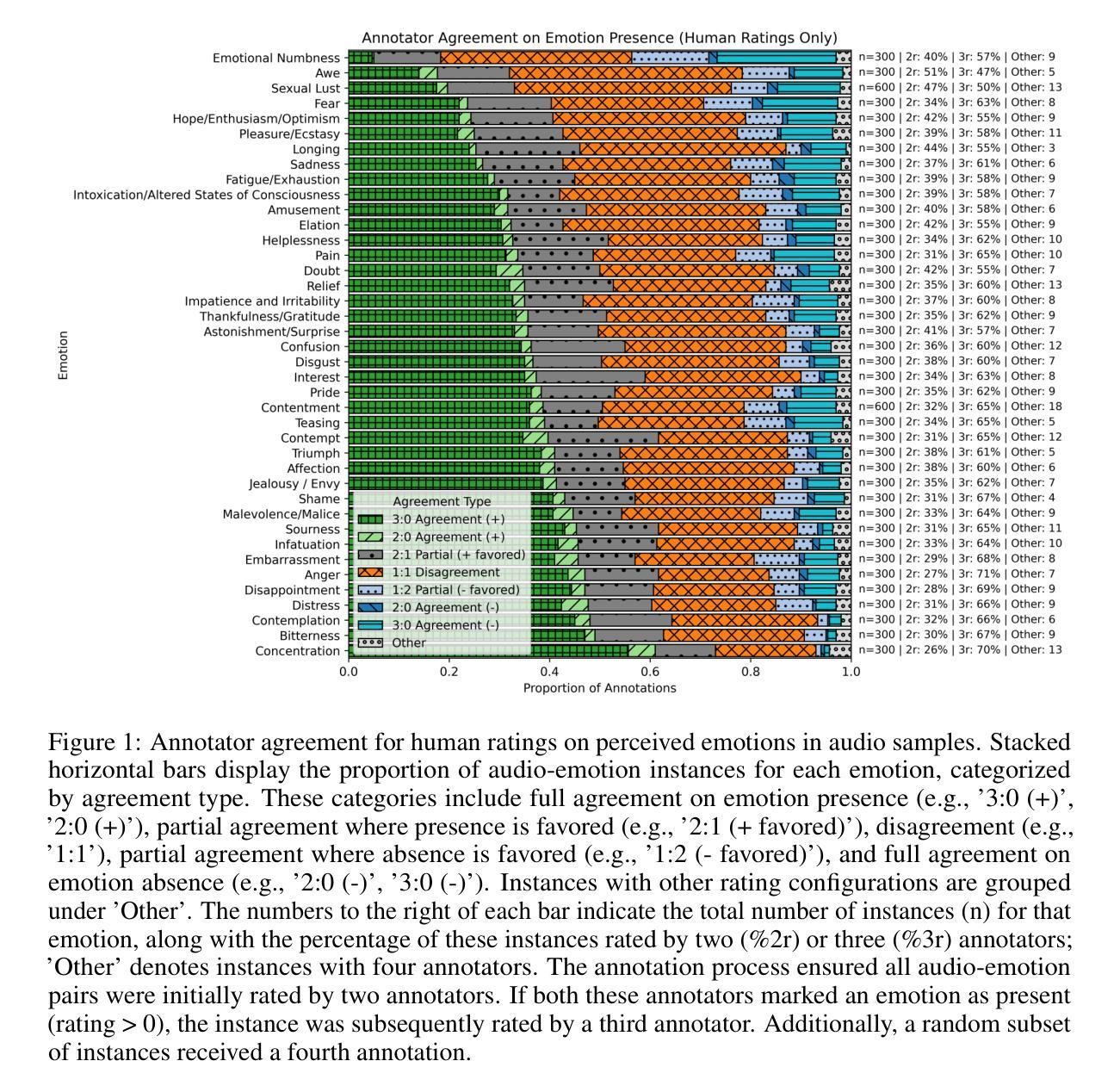
EmoNet-Voice: A Fine-Grained, Expert-Verified Benchmark for Speech Emotion Detection
Authors:Christoph Schuhmann, Robert Kaczmarczyk, Gollam Rabby, Felix Friedrich, Maurice Kraus, Kourosh Nadi, Huu Nguyen, Kristian Kersting, Sören Auer
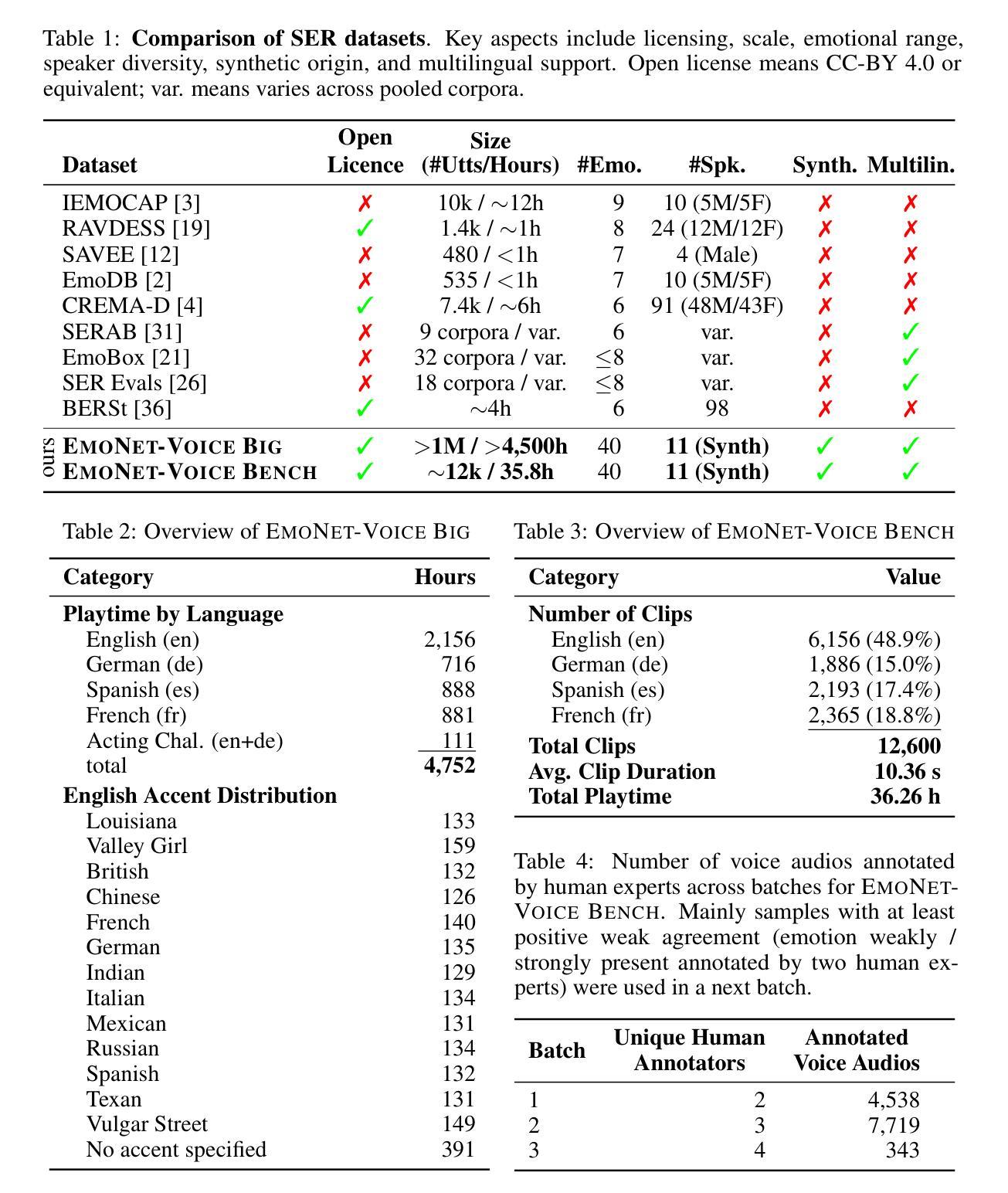
The advancement of text-to-speech and audio generation models necessitates robust benchmarks for evaluating the emotional understanding capabilities of AI systems. Current speech emotion recognition (SER) datasets often exhibit limitations in emotional granularity, privacy concerns, or reliance on acted portrayals. This paper introduces EmoNet-Voice, a new resource for speech emotion detection, which includes EmoNet-Voice Big, a large-scale pre-training dataset (featuring over 4,500 hours of speech across 11 voices, 40 emotions, and 4 languages), and EmoNet-Voice Bench, a novel benchmark dataset with human expert annotations. EmoNet-Voice is designed to evaluate SER models on a fine-grained spectrum of 40 emotion categories with different levels of intensities. Leveraging state-of-the-art voice generation, we curated synthetic audio snippets simulating actors portraying scenes designed to evoke specific emotions. Crucially, we conducted rigorous validation by psychology experts who assigned perceived intensity labels. This synthetic, privacy-preserving approach allows for the inclusion of sensitive emotional states often absent in existing datasets. Lastly, we introduce Empathic Insight Voice models that set a new standard in speech emotion recognition with high agreement with human experts. Our evaluations across the current model landscape exhibit valuable findings, such as high-arousal emotions like anger being much easier to detect than low-arousal states like concentration.
文本转语音和音频生成模型的进步为评估人工智能系统的情感理解能力提供了强大的基准测试。现有的语音情感识别(SER)数据集通常在情感粒度、隐私担忧或依赖表演表现方面存在局限性。本文介绍了用于语音情感检测的新资源EmoNet-Voice,它包括EmoNet-Voice Big,这是一个大规模预训练数据集(跨越11个声音、40种情感和4种语言,包含超过4500小时的语音),以及带有专家注释的新型基准数据集EmoNet-Voice Bench。EmoNet-Voice旨在在一个精细的粒度谱上评估SER模型对情绪强度的感知能力,包括特定的40种情绪类别。借助最先进的语音生成技术,我们精心制作了模拟演员扮演特定情感场景合成音频片段。重要的是,我们经过心理学专家的严格验证并获得了感知强度标签。这种合成的方法保护隐私并允许引入现有数据集中通常缺少的敏感情绪状态。最后,我们引入了Empathic Insight Voice模型,该模型在语音情感识别方面树立了新的标准并与人类专家达成高度共识。对当前模型景观的评估显示出有价值的发现,例如愤怒等强烈唤醒的情绪更容易被检测到,而集中等低唤醒状态则相对困难。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新的语音情感检测资源EmoNet-Voice,包括用于预训练的EmoNet-Voice Big大型数据集和作为基准测试集的EmoNet-Voice Bench。EmoNet-Voice旨在评估语音情感识别模型在精细粒度情感分类上的性能,同时考虑了不同强度的情感。通过心理学专家的严格验证,采用先进的语音生成技术模拟演员表演场景以激发特定情感。此外,本文还引入了Empathic Insight Voice模型,为语音情感识别设定了新的标准,并在当前模型景观中展示了高人类专家共识的价值发现。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了新的语音情感检测资源EmoNet-Voice,包括大型预训练数据集EmoNet-Voice Big和基准测试集EmoNet-Voice Bench。
- EmoNet-Voice强调对精细粒度情感分类的评估,考虑不同强度的情感。
- 利用先进的语音生成技术模拟演员表演场景,激发特定情感,并经心理学专家验证。
- 引入了Empathic Insight Voice模型,为语音情感识别设定了新的标准。
- 展现了高人类专家共识的价值发现,如高唤醒情感(如愤怒)比低唤醒状态(如专注)更容易检测。
- EmoNet-Voice的设计解决了现有数据集在情感粒度、隐私保护以及模拟真实情感表达方面的局限性。
点此查看论文截图

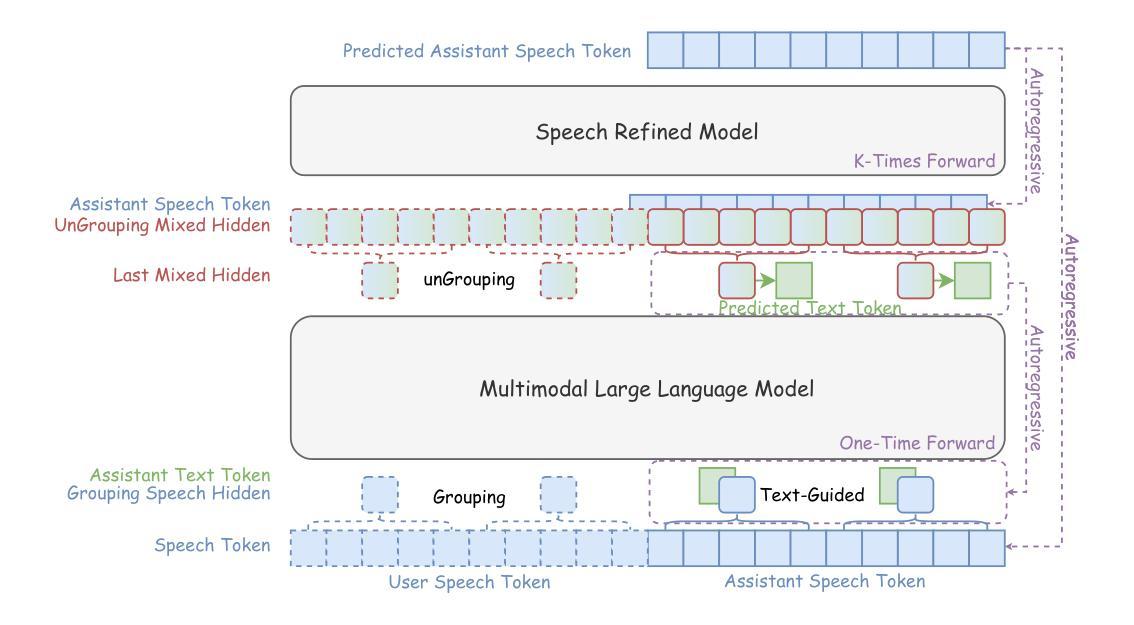
OmniDRCA: Parallel Speech-Text Foundation Model via Dual-Resolution Speech Representations and Contrastive Alignment
Authors:Chao-Hong Tan, Qian Chen, Wen Wang, Chong Deng, Qinglin Zhang, Luyao Cheng, Hai Yu, Xin Zhang, Xiang Lv, Tianyu Zhao, Chong Zhang, Yukun Ma, Yafeng Chen, Hui Wang, Jiaqing Liu, Jieping Ye
Recent studies on end-to-end speech generation with large language models (LLMs) have attracted significant community attention, with multiple works extending text-based LLMs to generate discrete speech tokens. Existing approaches primarily fall into two categories: (1) Methods that generate discrete speech tokens independently without incorporating them into the LLM’s autoregressive process, resulting in text generation being unaware of concurrent speech synthesis. (2) Models that generate interleaved or parallel speech-text tokens through joint autoregressive modeling, enabling mutual modality awareness during generation. This paper presents OmniDRCA, a parallel speech-text foundation model based on joint autoregressive modeling, featuring dual-resolution speech representations and contrastive cross-modal alignment. Our approach processes speech and text representations in parallel while enhancing audio comprehension through contrastive alignment. Experimental results on Spoken Question Answering benchmarks demonstrate that OmniDRCA establishes new state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance among parallel joint speech-text modeling based foundation models, and achieves competitive performance compared to interleaved models. Additionally, we explore the potential of extending the framework to full-duplex conversational scenarios.
最近关于使用大型语言模型(LLM)进行端到端语音生成的研究引起了社区的关注,多项工作将基于文本的LLM扩展到生成离散语音标记。现有方法主要可分为两类:(1)独立生成离散语音标记的方法,不将其纳入LLM的自回归过程,导致文本生成无法意识到并发的语音合成。(2)通过联合自回归建模生成交织或并行语音文本标记的模型,从而在生成过程中实现跨模态相互感知。本文提出了OmniDRCA,一种基于联合自回归建模的并行语音文本基础模型,具有双分辨率语音表示和对比跨模态对齐功能。我们的方法并行处理语音和文本表示,同时通过对比对齐增强音频理解。在口语问答基准测试上的实验结果表明,OmniDRCA在基于并行联合语音文本建模的基础模型中建立了新的最先进的性能,并在与交织模型的比较中取得了具有竞争力的表现。此外,我们还探讨了将框架扩展到全双工对话场景的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期关于利用大型语言模型(LLMs)进行端到端语音生成的研究引起了社区的关注。现有方法主要分为两类:独立生成离散语音令牌的方法和通过联合自回归建模生成交替或并行语音文本令牌的方法。本文提出OmniDRCA,一个基于联合自回归建模的并行语音文本基础模型,具有双分辨率语音表示和对比跨模态对齐特点。实验结果表明,OmniDRCA在基于并行联合语音文本建模的基础模型中建立了新的性能水平,并在与交替模型的比较中实现了具有竞争力的性能。此外,本文还探讨了将该框架扩展到全双工对话场景的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 端到端语音生成研究利用大型语言模型(LLMs)吸引了社区关注。
- 现有方法主要分为独立生成离散语音令牌和通过联合自回归建模生成交替或并行语音文本令牌两类。
- OmniDRCA是一个基于联合自回归建模的并行语音文本基础模型,具有双分辨率语音表示和对比跨模态对齐特点。
- OmniDRCA在基于并行联合语音文本建模的基础模型中建立了新的性能水平。
- OmniDRCA在Spoken Question Answering benchmarks上的表现优于其他模型,具有竞争力。
- OmniDRCA框架有潜力扩展到全双工对话场景。
点此查看论文截图


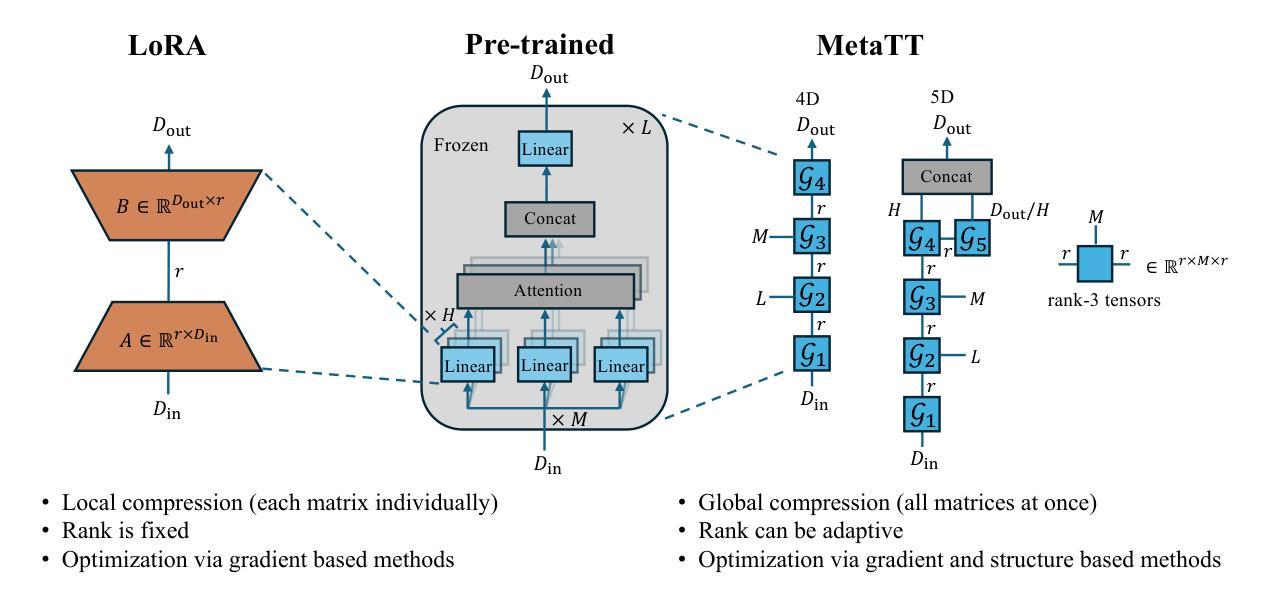
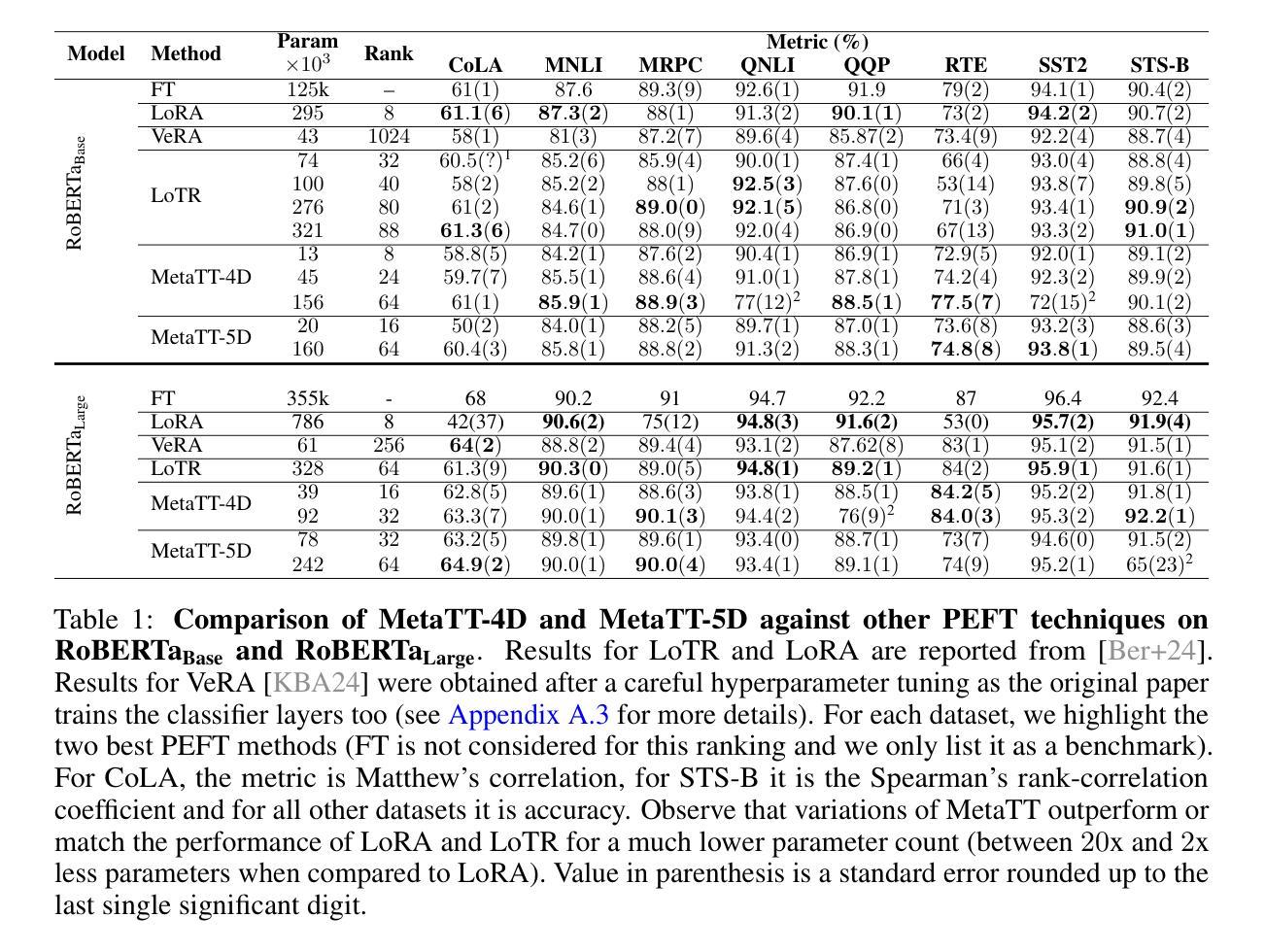
MetaTT: A Global Tensor-Train Adapter for Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
Authors:Javier Lopez-Piqueres, Pranav Deshpande, Archan Ray, Mattia J. Villani, Marco Pistoia, Niraj Kumar
We present MetaTT, a unified Tensor Train (TT) adapter framework for global low-rank fine-tuning of pre-trained transformers. Unlike LoRA, which fine-tunes each weight matrix independently, MetaTT uses a single shared TT to factorize all transformer sub-modules – query, key, value, projection, and feed-forward layers – by indexing the structural axes like layer and matrix type, and optionally heads and tasks. For a given rank, while LoRA adds parameters proportional to the product across modes, MetaTT only adds parameters proportional to the sum across modes leading to a significantly compressed final adapter. Our benchmarks compare MetaTT with LoRA along with recent state-of-the-art matrix and tensor decomposition based fine-tuning schemes. We observe that when tested on standard language modeling benchmarks, MetaTT leads to the most reduction in the parameters while maintaining similar accuracy to LoRA and even outperforming other tensor-based methods. Unlike CP or other rank-factorizations, the TT ansatz benefits from mature optimization routines – e.g., DMRG-style rank adaptive minimization in addition to Adam, which we find simplifies training. Because new modes can be appended cheaply, MetaTT naturally extends to shared adapters across many tasks without redesigning the core tensor.
我们提出了MetaTT,这是一个统一的Tensor Train(TT)适配器框架,用于预训练转换器的全局低秩微调。与独立微调每个权重矩阵的LoRA不同,MetaTT使用单个共享的TT来分解所有转换器子模块——查询、键、值、投影和前馈层——通过索引结构轴,如层和矩阵类型,以及可选的头部和任务。对于给定的等级,虽然LoRA添加的参数与各模式之积成正比,但MetaTT添加的参数仅与各模式之和成正比,从而得到了显著压缩的最终适配器。我们的基准测试将MetaTT与LoRA以及最近的最新矩阵和张量分解微调方案进行了比较。我们在标准语言建模基准测试中发现,MetaTT在减少参数的同时,保持了与LoRA相似的精度,甚至超越了其他张量方法。与CP或其他等级分解不同,TT ansatz受益于成熟的优化算法——例如,除了Adam之外,我们还发现了DMRG风格的等级自适应最小化算法简化了训练。由于可以便宜地添加新模式,MetaTT自然地扩展到跨多个任务的共享适配器,而无需重新设计核心张量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
我们提出了MetaTT,一个统一的Tensor Train(TT)适配器框架,用于预训练转换器的全局低秩微调。不同于LoRA独立微调每个权重矩阵,MetaTT使用一个共享的TT对所有转换器子模块进行因子分解,通过索引结构轴(如层、矩阵类型)以及可选的头和任务。对于给定的秩,MetaTT添加的参数是各模式之和的比例,导致最终的适配器得到显著压缩。我们的基准测试将MetaTT与LoRA以及最新的先进的矩阵和张量分解微调方案进行了比较。在标准语言建模基准测试中,MetaTT在保持与LoRA相似准确率的同时,实现了参数的最大减少,并超越了其他张量方法。TT ansatz受益于成熟的优化算法,如结合Adam的DMRG风格秩自适应最小化算法,简化了训练。由于可以廉价地添加新模式,MetaTT自然地扩展到跨多个任务的共享适配器,无需重新设计核心张量。
Key Takeaways
- MetaTT是一个统一的Tensor Train适配器框架,用于预训练转换器的全球低秩微调。
- 与LoRA不同,MetaTT使用共享的TT对所有转换器子模块进行因子分解。
- MetaTT通过索引结构轴(如层和矩阵类型)来添加参数,实现了参数的显著压缩。
- 在标准语言建模基准测试中,MetaTT在保持与LoRA相似准确率的同时,实现了参数的最优减少。
- TT ansatz受益于成熟的优化算法,如结合Adam的DMRG风格秩自适应最小化算法。
- MetaTT可以廉价地添加新模式,自然扩展到跨多个任务的共享适配器。
点此查看论文截图

A Review on Score-based Generative Models for Audio Applications
Authors:Ge Zhu, Yutong Wen, Zhiyao Duan
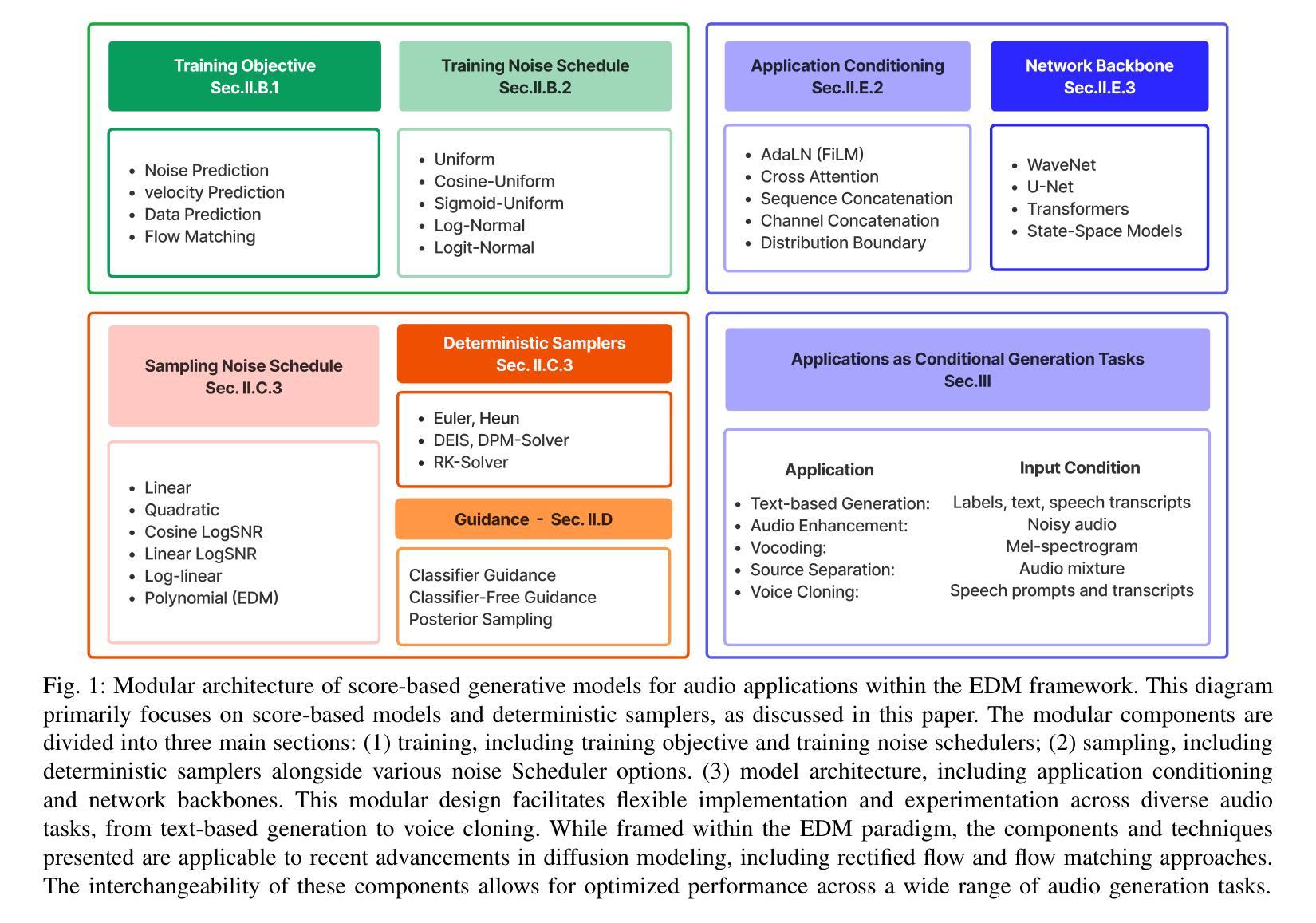
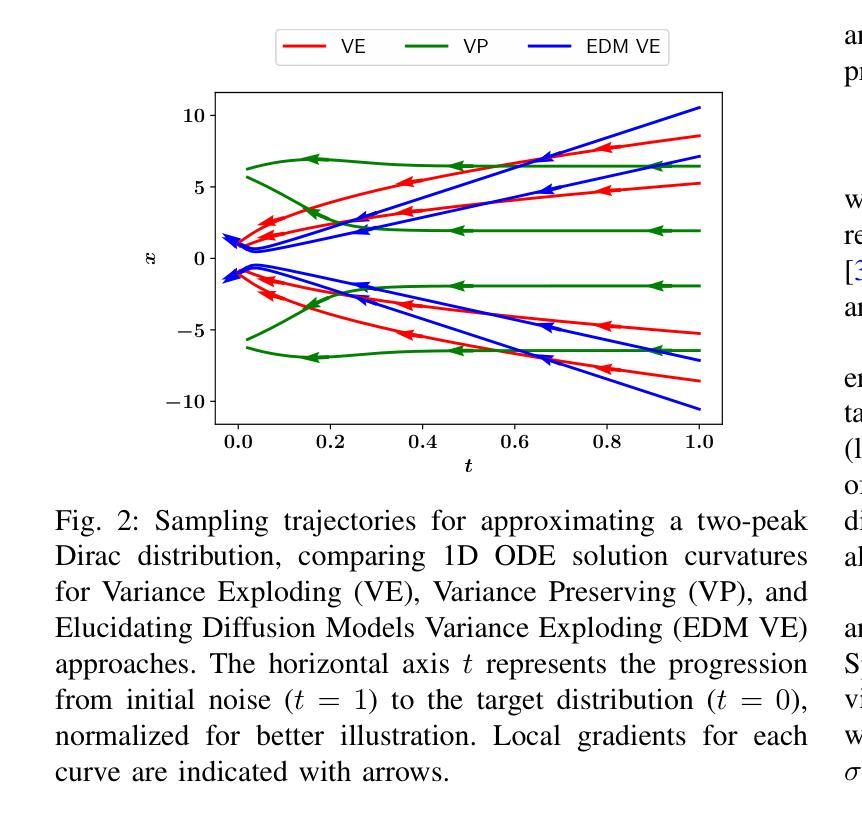
Diffusion models have emerged as powerful deep generative techniques, producing high-quality and diverse samples in applications in various domains including audio. These models have many different design choices suitable for different applications, however, existing reviews lack in-depth discussions of these design choices. The audio diffusion model literature also lacks principled guidance for the implementation of these design choices and their comparisons for different applications. This survey provides a comprehensive review of diffusion model design with an emphasis on design principles for quality improvement and conditioning for audio applications. We adopt the score modeling perspective as a unifying framework that accommodates various interpretations, including recent approaches like flow matching. We systematically examine the training and sampling procedures of diffusion models, and audio applications through different conditioning mechanisms. To address the lack of audio diffusion model codebases and to promote reproducible research and rapid prototyping, we introduce an open-source codebase at https://github.com/gzhu06/AudioDiffuser that implements our reviewed framework for various audio applications. We demonstrate its capabilities through three case studies: audio generation, speech enhancement, and text-to-speech synthesis, with benchmark evaluations on standard datasets.
扩散模型作为一种强大的深度生成技术,已经在包括音频在内的各种应用领域中产生了高质量和多样化的样本。这些模型有许多不同的设计选择,适合不同的应用,然而现有的评论缺乏对这些设计选择的深入讨论。音频扩散模型文献也缺乏这些设计选择实施的原则指导以及它们在不同应用中的比较。这篇综述对扩散模型设计进行了全面回顾,重点介绍了提高质量和针对音频应用进行条件设置的设计原则。我们采用评分建模的视角,作为一个统一的框架,可以容纳各种解释,包括最新的方法如流匹配。我们系统地研究了扩散模型的训练和采样程序,以及通过不同条件机制在音频领域的应用。为了解决音频扩散模型代码库缺乏的问题,并推动可重复研究和快速原型开发,我们在https://github.com/gzhu06/AudioDiffuser上推出了一个开源代码库,为各种音频应用实现了我们审查过的框架。我们通过三项案例研究证明了其能力:音频生成、语音增强和文本到语音的合成,并在标准数据集上进行了基准评估。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型作为强大的深度生成技术,已广泛应用于多个领域,包括音频。本文全面回顾了扩散模型的设计原则,重点介绍了提高质量和针对音频应用的条件设计。采用评分建模视角作为统一框架,系统地研究了扩散模型的训练和采样程序以及音频应用程序的不同条件机制。此外,为了弥补音频扩散模型代码库的缺乏,促进可重复研究和快速原型开发,我们介绍了开源代码库。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已成为深度生成技术的强大工具,广泛应用于多个领域,包括音频。
- 现有文献缺乏对扩散模型设计选择的深入探讨。
- 本文重点介绍了扩散模型的设计原则,以提高质量和针对音频应用的条件设计。
- 采用评分建模视角作为统一框架,容纳各种解读,包括最新方法如流匹配。
- 系统地研究了扩散模型的训练和采样程序。
- 为了促进可重复研究和快速原型开发,介绍了开源代码库。
点此查看论文截图

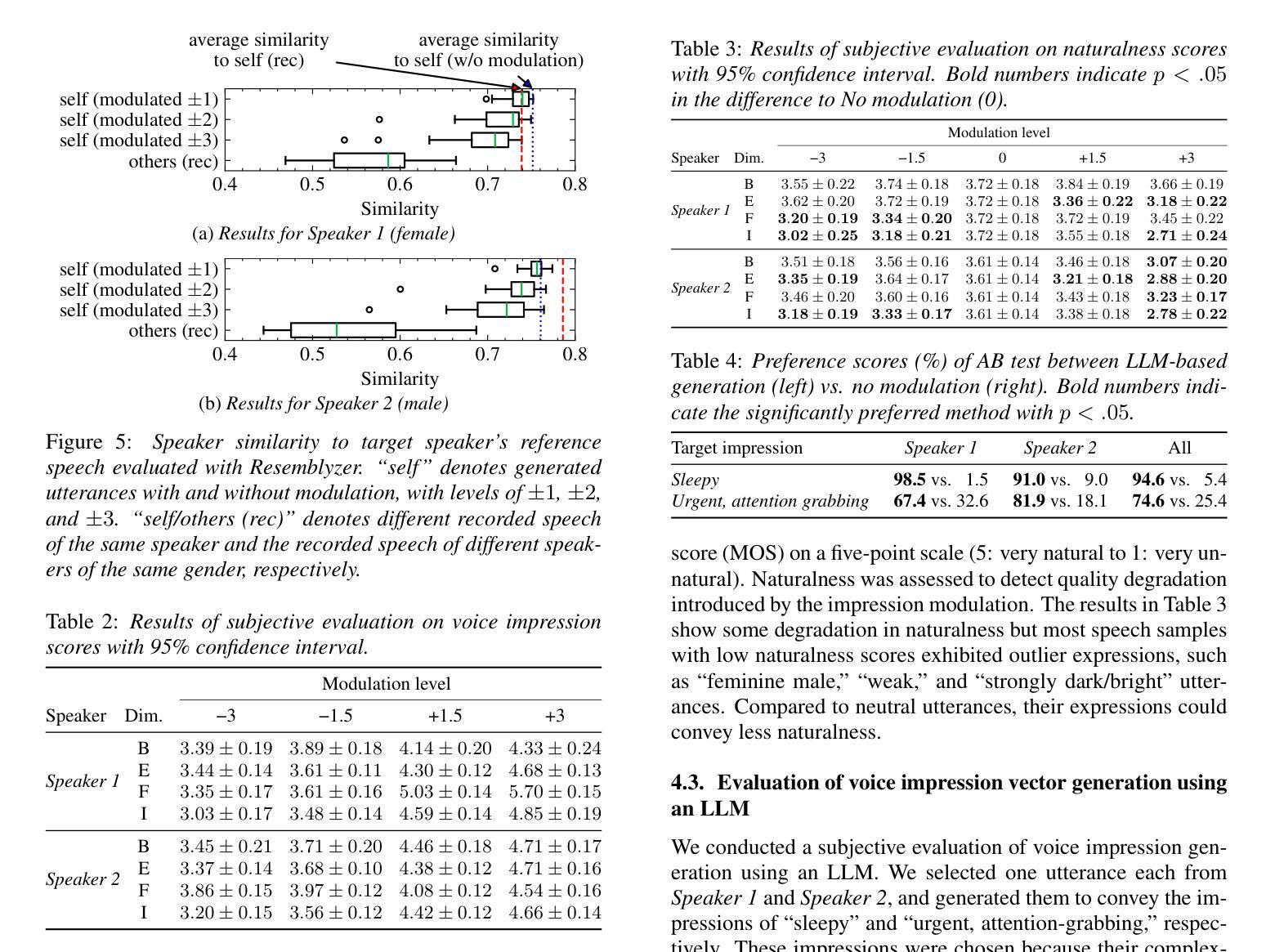
Voice Impression Control in Zero-Shot TTS
Authors:Keinichi Fujita, Shota Horiguchi, Yusuke Ijima
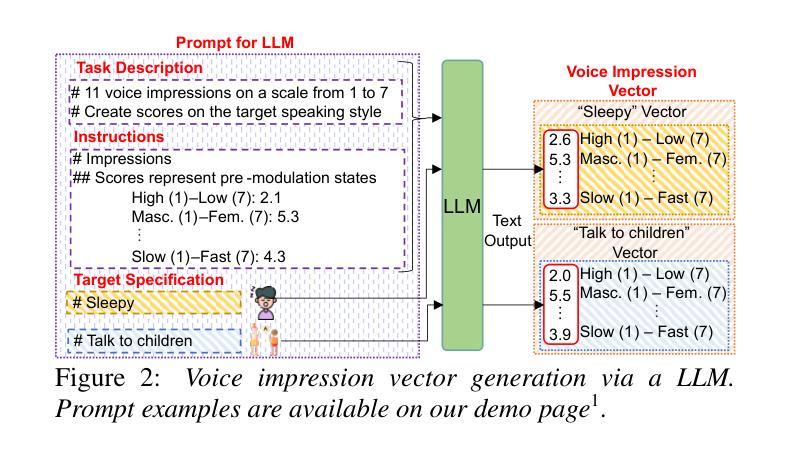
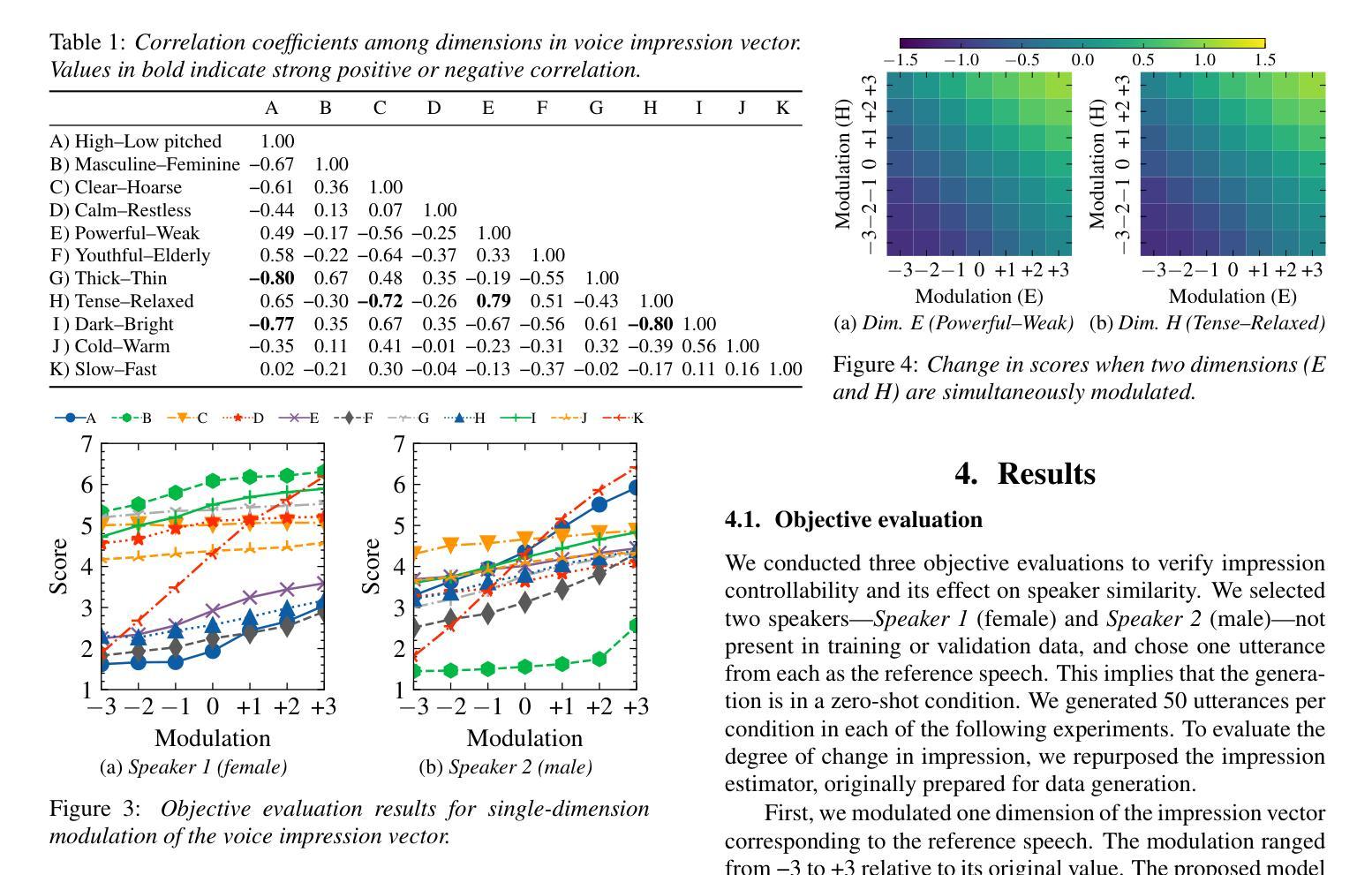
Para-/non-linguistic information in speech is pivotal in shaping the listeners’ impression. Although zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) has achieved high speaker fidelity, modulating subtle para-/non-linguistic information to control perceived voice characteristics, i.e., impressions, remains challenging. We have therefore developed a voice impression control method in zero-shot TTS that utilizes a low-dimensional vector to represent the intensities of various voice impression pairs (e.g., dark-bright). The results of both objective and subjective evaluations have demonstrated our method’s effectiveness in impression control. Furthermore, generating this vector via a large language model enables target-impression generation from a natural language description of the desired impression, thus eliminating the need for manual optimization. Audio examples are available on our demo page (https://ntt-hilab-gensp.github.io/is2025voiceimpression/).
语音中的副语言或非语言信息对于塑造听众的印象至关重要。尽管零样本文本到语音(TTS)已经实现了高保真度的说话人识别,但是通过微调副语言或非语言信息来控制感知到的语音特征,即印象,仍然是一个挑战。因此,我们在零样本TTS中开发了一种语音印象控制方法,该方法使用低维向量来表示各种语音印象对的强度(例如,暗淡-明亮)。客观和主观评估的结果均证明了我们方法在印象控制方面的有效性。此外,通过大型语言模型生成该向量能够根据自然语言的期望印象描述来生成目标印象,从而无需手动优化。音频示例可在我们的演示页面(https://ntt-hilab-gensp.github.io/is2025voiceimpression/)上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages,5 figures, Accepted to INTERSPEECH 2025
Summary
本文提出了一项零样本文本转语音(TTS)中的语音印象控制方法。该方法利用低维向量表示各种语音印象对的强度(如阴暗-明亮),实现了对语音印象的精细控制。客观和主观评估结果均证明了该方法的有效性。此外,通过大型语言模型生成该向量,可以从对所需印象的自然语言描述中生成目标印象,从而无需手动优化。
Key Takeaways
- 语音中的副语言/非语言信息对听众的印象形成至关重要。
- 零样本文本转语音(TTS)已实现了高保真度的语音转换。
- 挑战在于调整微妙的副语言/非语言信息以控制感知到的语音特征,即印象。
- 提出了一种新的语音印象控制方法,使用低维向量代表各种语音印象对的强度。
- 客观和主观评估证明了该方法在印象控制方面的有效性。
- 通过大型语言模型生成向量,可从自然语言描述中生成目标印象。
点此查看论文截图

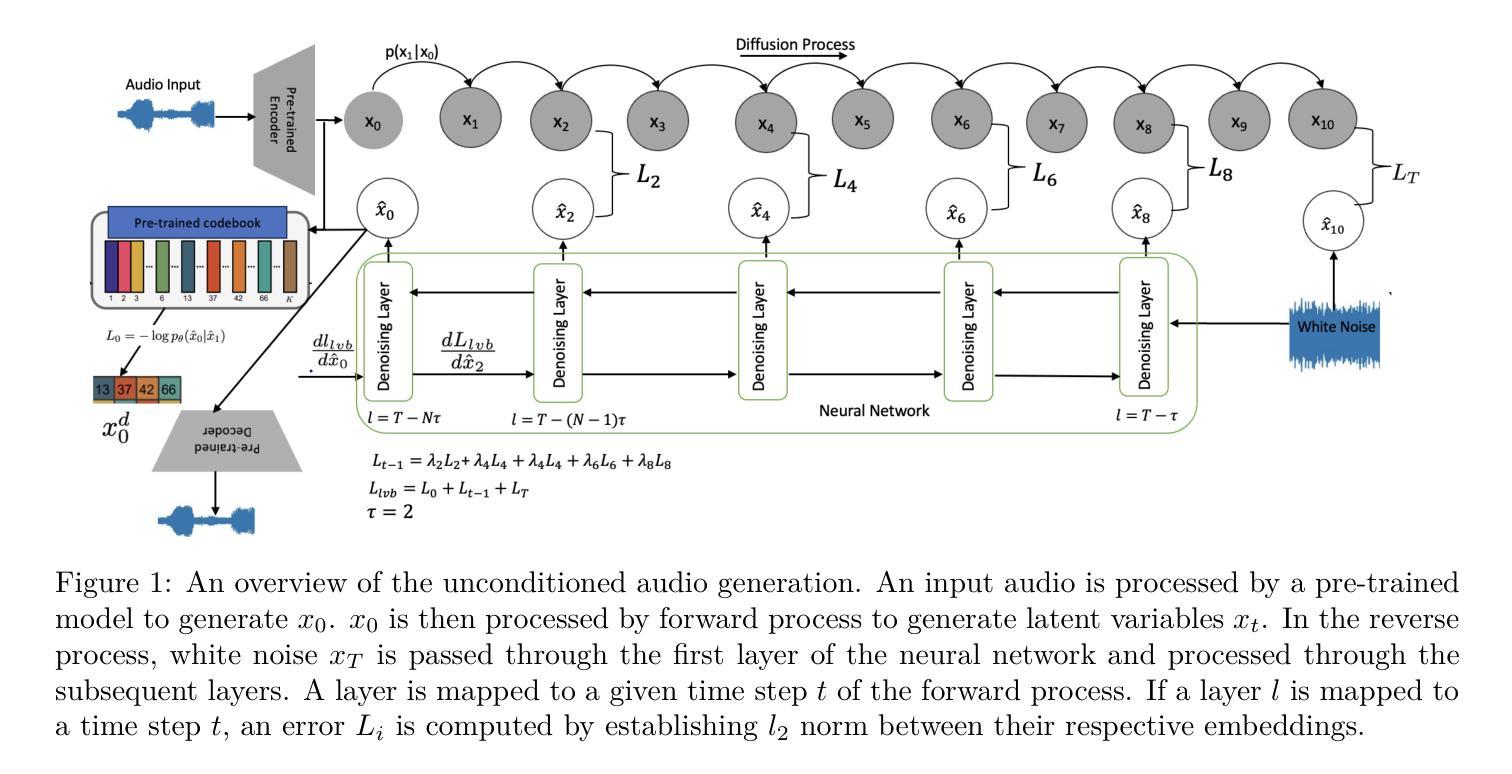
Speech Synthesis By Unrolling Diffusion Process using Neural Network Layers
Authors:Peter Ochieng
This work introduces UDPNet, a novel architecture designed to accelerate the reverse diffusion process in speech synthesis. Unlike traditional diffusion models that rely on timestep embeddings and shared network parameters, UDPNet unrolls the reverse diffusion process directly into the network architecture, with successive layers corresponding to equally spaced steps in the diffusion schedule. Each layer progressively refines the noisy input, culminating in a high-fidelity estimation of the original data, (x_0). Additionally, we redefine the learning target by predicting latent variables instead of the conventional (x_0) or noise (\epsilon_0). This shift addresses the common issue of large prediction errors in early denoising stages, effectively reducing speech distortion. Extensive evaluations on single- and multi-speaker datasets demonstrate that UDPNet consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both quality and efficiency, while generalizing effectively to unseen speech. These results position UDPNet as a robust solution for real-time speech synthesis applications. Sample audio is available at https://onexpeters.github.io/UDPNet.
本文介绍了UDPNet,这是一种新型架构,旨在加速语音合成中的反向扩散过程。与传统的依赖于时间步长嵌入和共享网络参数的扩散模型不同,UDPNet直接将反向扩散过程展开到网络架构中,连续层对应于扩散计划中等间距的步骤。每层都对噪声输入进行逐步精细处理,最终得到对原始数据的高保真估计(x_0)。此外,我们通过预测潜在变量来重新定义学习目标,而不是传统的(x_0)或噪声(\epsilon_0)。这种转变解决了早期去噪阶段预测误差较大的常见问题,有效地减少了语音失真。在单说话人和多说话人数据集上的广泛评估表明,UDPNet在质量和效率方面均优于最新方法,并且能够有效地推广到未见过的语音。这些结果使UDPNet成为实时语音合成应用的稳健解决方案。示例音频可在https://onexpeters.github.io/UDPNet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
摘要
本文介绍了UDPNet,这是一种新型架构,旨在加速语音合成中的反向扩散过程。UDPNet将反向扩散过程直接融入网络架构,与传统依赖时间步长嵌入和共享网络参数的扩散模型不同。其连续层对应于扩散计划中的等间隔步骤。每层都对噪声输入进行渐进细化,最终得到对原始数据的高保真估计。此外,通过预测潜在变量来重新定义学习目标,而不是传统的x_0或噪声ε_0,解决了早期去噪阶段预测误差较大的常见问题,有效减少了语音失真。在单说话人和多说话人数据集上的广泛评估表明,UDPNet在质量和效率方面均优于最新方法,并且能有效地推广到未见过的语音。这些结果使UDPNet成为实时语音合成应用的稳健解决方案。
要点
- UDPNet是一种加速语音合成中反向扩散过程的新型架构。
- UDPNet将反向扩散过程直接融入网络架构,连续层对应扩散计划中的等间隔步骤。
3.每层对噪声输入进行渐进细化,最终得到高保真度的原始数据估计。 - 通过预测潜在变量来重新定义学习目标,有效减少语音失真。
- UDPNet在质量和效率方面均优于最新方法。
- UDPNet能有效地推广到未见过的语音,具有稳健性。
- 样本音频可在链接找到。
点此查看论文截图