⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-13 更新
PatchGuard: Adversarially Robust Anomaly Detection and Localization through Vision Transformers and Pseudo Anomalies
Authors:Mojtaba Nafez, Amirhossein Koochakian, Arad Maleki, Jafar Habibi, Mohammad Hossein Rohban
Anomaly Detection (AD) and Anomaly Localization (AL) are crucial in fields that demand high reliability, such as medical imaging and industrial monitoring. However, current AD and AL approaches are often susceptible to adversarial attacks due to limitations in training data, which typically include only normal, unlabeled samples. This study introduces PatchGuard, an adversarially robust AD and AL method that incorporates pseudo anomalies with localization masks within a Vision Transformer (ViT)-based architecture to address these vulnerabilities. We begin by examining the essential properties of pseudo anomalies, and follow it by providing theoretical insights into the attention mechanisms required to enhance the adversarial robustness of AD and AL systems. We then present our approach, which leverages Foreground-Aware Pseudo-Anomalies to overcome the deficiencies of previous anomaly-aware methods. Our method incorporates these crafted pseudo-anomaly samples into a ViT-based framework, with adversarial training guided by a novel loss function designed to improve model robustness, as supported by our theoretical analysis. Experimental results on well-established industrial and medical datasets demonstrate that PatchGuard significantly outperforms previous methods in adversarial settings, achieving performance gains of $53.2%$ in AD and $68.5%$ in AL, while also maintaining competitive accuracy in non-adversarial settings. The code repository is available at https://github.com/rohban-lab/PatchGuard .
异常检测(AD)和异常定位(AL)在高可靠性需求的领域,如医学影像和工业监控中,具有至关重要的作用。然而,当前的AD和AL方法由于训练数据的局限性(通常只有正常的未标记样本),很容易受到对抗性攻击。本研究引入了PatchGuard,这是一种对抗性稳健的AD和AL方法,它结合了伪异常和定位掩码在视觉转换器(ViT)架构中解决这些漏洞。我们首先研究伪异常的基本属性,然后通过理论洞察注意机制,增强AD和AL系统的对抗性稳健性。然后我们提出的方法利用了前景感知伪异常来克服之前异常感知方法的不足。我们的方法将这些精心制作的伪异常样本纳入基于ViT的框架中,通过对抗训练由我们理论分析结果支持的新型损失函数来指导模型提高稳健性。在公认的工业和医疗数据集上的实验结果表明,PatchGuard在对抗环境中显著优于以前的方法,在AD上实现了高达53.2%的性能提升,在AL上实现了高达68.5%的性能提升,同时在非对抗环境中也保持了较高的准确性。代码仓库可在https://github.com/rohban-lab/PatchGuard找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2025
Summary
在医学成像和工业监控等需要高可靠性的领域,异常检测(AD)和异常定位(AL)尤为重要。然而,现有的AD和AL方法容易受到对抗性攻击的干扰,其训练数据仅限于正常未标记样本的局限性是主要诱因。本研究引入PatchGuard,一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)架构的对抗性稳健AD和AL方法,通过融入伪异常和定位掩膜来应对这些漏洞。本研究首先探讨伪异常的关键属性,接着从理论层面研究增强AD和AL系统对抗性稳健性所需的注意力机制。然后提出一种利用前景感知伪异常的方法,以克服现有异常感知方法的不足。该方法将这些精心制作的伪异常样本融入ViT框架,通过新型损失函数进行对抗训练来提升模型稳健性,并由理论分析结果提供支持。在成熟的工业和医疗数据集上的实验表明,PatchGuard在对抗环境中显著优于先前的方法,在AD和AL中分别提高了53.2%和68.5%的性能,同时在非对抗环境中也保持了竞争力。相关代码库可通过https://github.com/rohban-lab/PatchGuard访问。
Key Takeaways
- AD和AL方法在高可靠性领域的重要性。
- 当前AD和AL方法存在因训练数据局限性易受对抗性攻击的缺陷。
- PatchGuard是一种基于Vision Transformer的对抗性稳健AD和AL方法。
- PatchGuard通过融入伪异常和定位掩膜来应对漏洞并提升模型性能。
- 该方法通过新型损失函数进行对抗训练来提升模型稳健性。
- 在工业和医疗数据集上的实验证明PatchGuard显著优于先前的方法。
点此查看论文截图
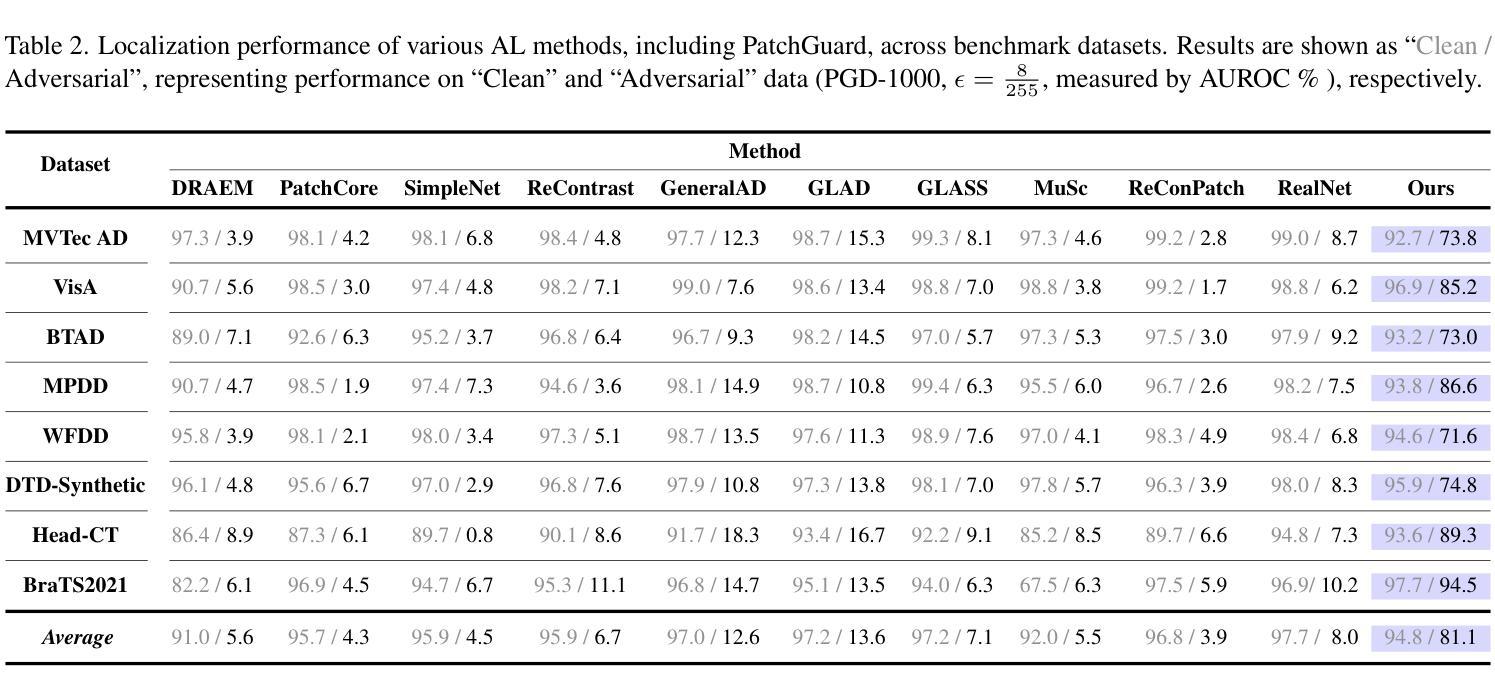
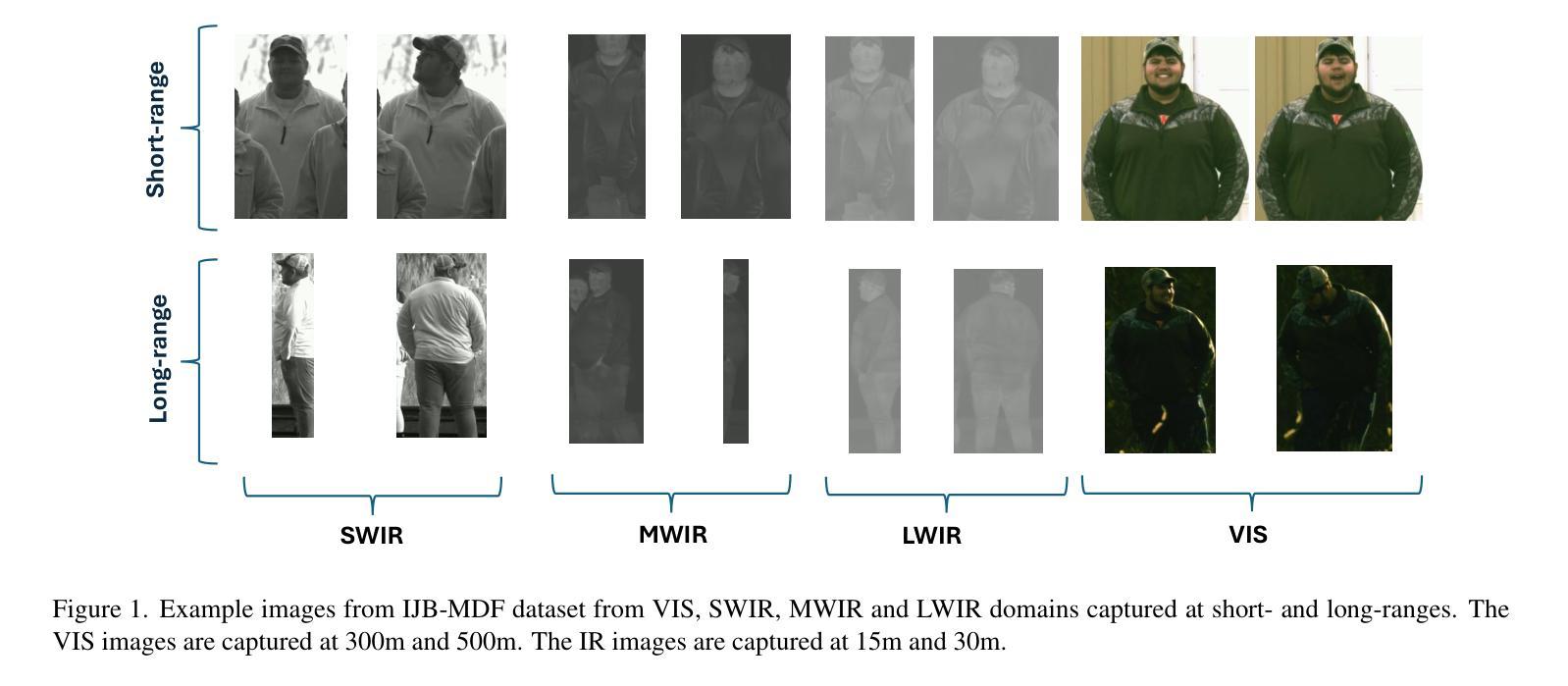
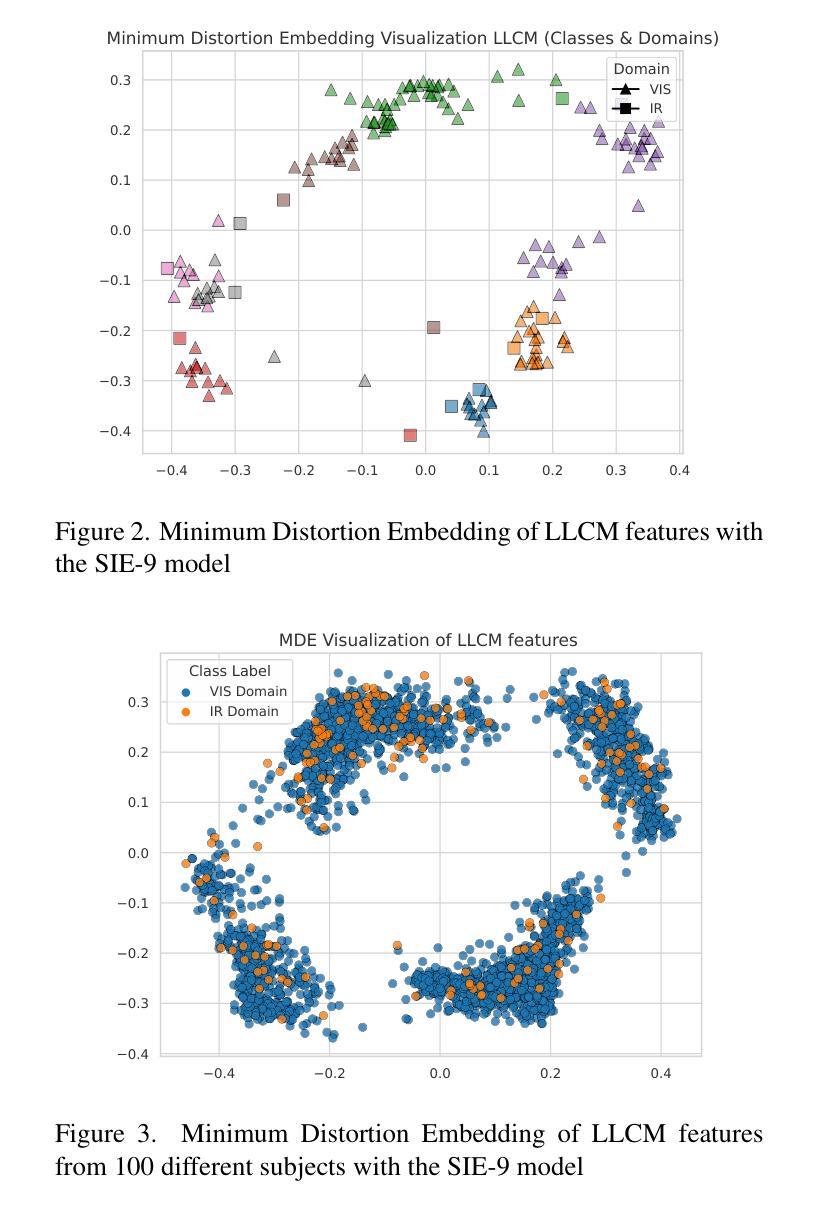
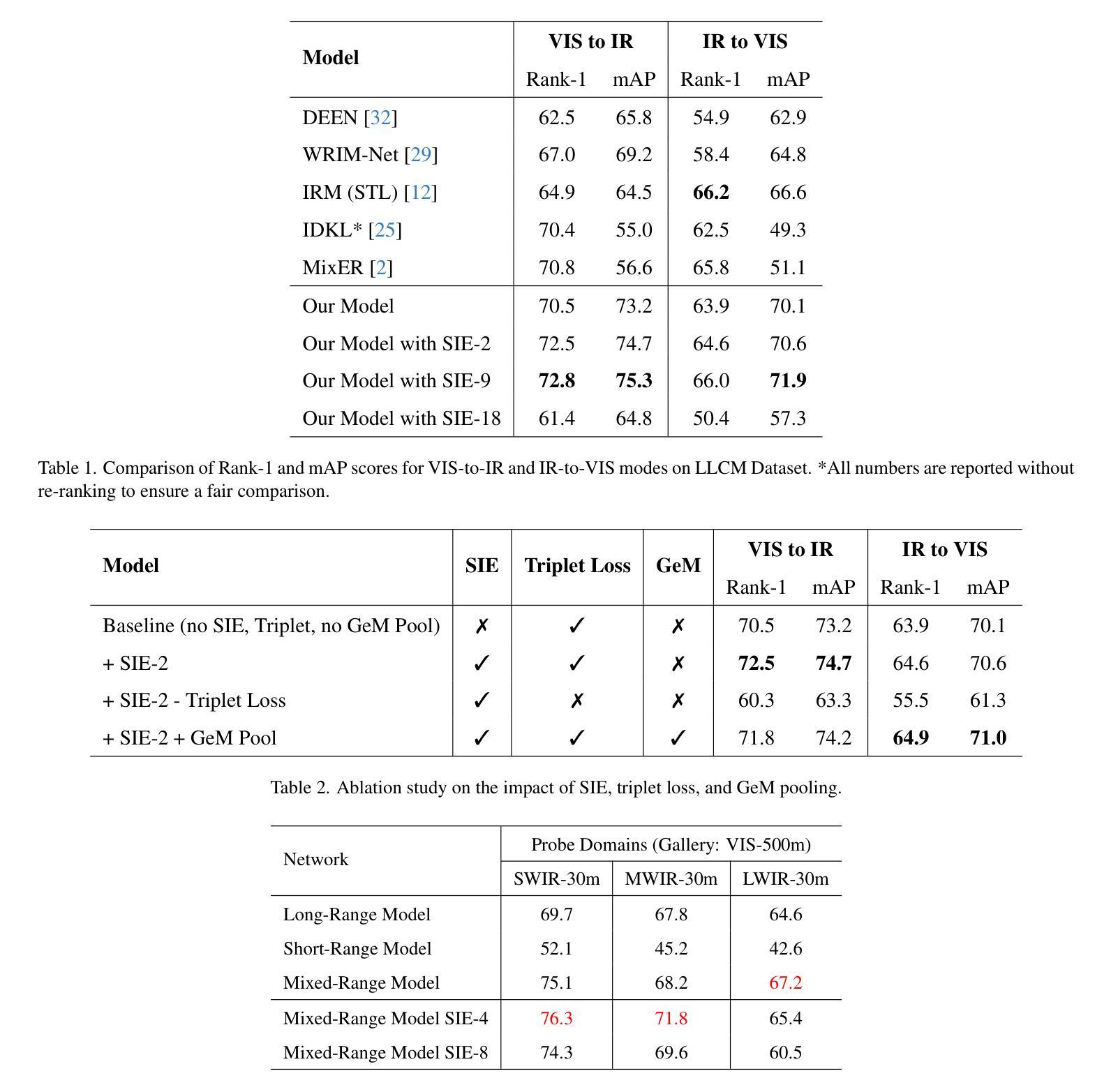
Cross-Spectral Body Recognition with Side Information Embedding: Benchmarks on LLCM and Analyzing Range-Induced Occlusions on IJB-MDF
Authors:Anirudh Nanduri, Siyuan Huang, Rama Chellappa
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have demonstrated impressive performance across a wide range of biometric tasks, including face and body recognition. In this work, we adapt a ViT model pretrained on visible (VIS) imagery to the challenging problem of cross-spectral body recognition, which involves matching images captured in the visible and infrared (IR) domains. Recent ViT architectures have explored incorporating additional embeddings beyond traditional positional embeddings. Building on this idea, we integrate Side Information Embedding (SIE) and examine the impact of encoding domain and camera information to enhance cross-spectral matching. Surprisingly, our results show that encoding only camera information - without explicitly incorporating domain information - achieves state-of-the-art performance on the LLCM dataset. While occlusion handling has been extensively studied in visible-spectrum person re-identification (Re-ID), occlusions in visible-infrared (VI) Re-ID remain largely underexplored - primarily because existing VI-ReID datasets, such as LLCM, SYSU-MM01, and RegDB, predominantly feature full-body, unoccluded images. To address this gap, we analyze the impact of range-induced occlusions using the IARPA Janus Benchmark Multi-Domain Face (IJB-MDF) dataset, which provides a diverse set of visible and infrared images captured at various distances, enabling cross-range, cross-spectral evaluations.
视觉Transformer(ViT)在各种生物识别任务中表现出令人印象深刻的效果,包括面部和身体识别。在这项工作中,我们将预训练在可见(VIS)图像上的ViT模型应用于跨光谱身体识别这一具有挑战性的问题,该问题涉及匹配可见和红外(IR)领域捕获的图像。最近的ViT架构已经探索了除了传统位置嵌入之外,还融入额外的嵌入。基于这一想法,我们整合了Side Information Embedding(SIE),并研究编码领域和相机信息对增强跨光谱匹配的影响。令人惊讶的是,我们的结果表明,仅编码相机信息——而不显式地融入领域信息——就能在LLCM数据集上实现最先进的性能。虽然可见光谱中的人再识别(Re-ID)中的遮挡处理已经得到了广泛的研究,但可见光与红外(VI)Re-ID中的遮挡仍然在很大程度上被忽视——主要是因为现有的VI-ReID数据集,如LLCM、SYSU-MM01和RegDB,主要以全身、无遮挡的图像为主。为了弥补这一差距,我们使用IARPA Janus Benchmark Multi-Domain Face(IJB-MDF)数据集分析了距离引起的遮挡范围的影响,该数据集提供了在各种距离捕获的多样化的可见和红外图像集,可实现跨范围、跨光谱评估。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉转换器(ViT)在生物识别任务中表现出卓越性能,包括面部和人体识别。本研究将预训练的ViT模型应用于跨光谱人体识别问题,通过整合Side Information Embedding(SIE)并编码域和相机信息以增强跨光谱匹配效果。令人惊讶的是,仅编码相机信息即实现了LLCM数据集上的领先水平,无需显式纳入域信息。虽然可见光谱的人体再识别已广泛研究遮挡问题,但可见-红外(VI)再识别的遮挡问题仍大多未被探讨。主要因为现有VI-ReID数据集如LLCM、SYSU-MM01和RegDB主要展示全身、无遮挡图像。为解决这一差距,本研究利用IJB-MDF数据集分析距离引起的遮挡问题,该数据集提供不同距离捕捉的可见和红外图像,实现跨范围、跨光谱评估。
Key Takeaways
- ViT模型在生物识别任务中表现优异,包括面部和人体识别。
- 预训练的ViT模型被应用于跨光谱人体识别问题。
- Side Information Embedding(SIE)的整合增强了跨光谱匹配的效果。
- 仅编码相机信息即可实现先进性能,无需显式纳入域信息。
- 可见-红外再识别的遮挡问题仍是研究中的一大空白。
- 现有VI-ReID数据集主要展示无遮挡的全身图像。
- 利用IJB-MDF数据集分析距离引起的遮挡问题,实现跨范围、跨光谱评估。
点此查看论文截图

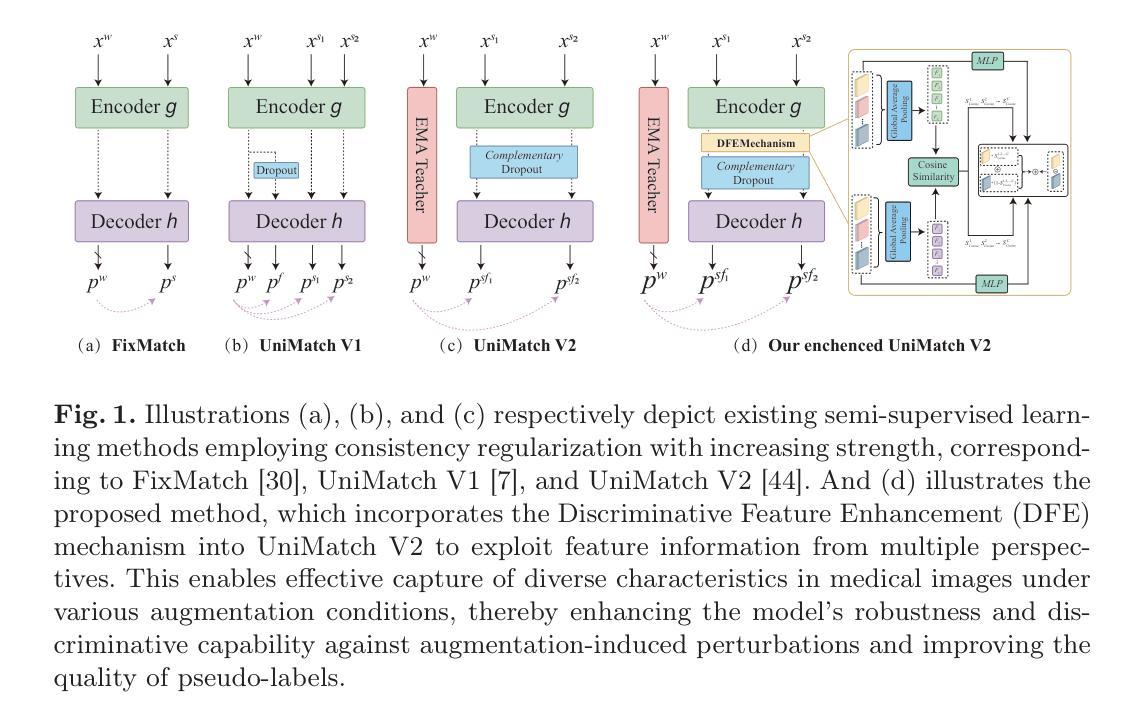
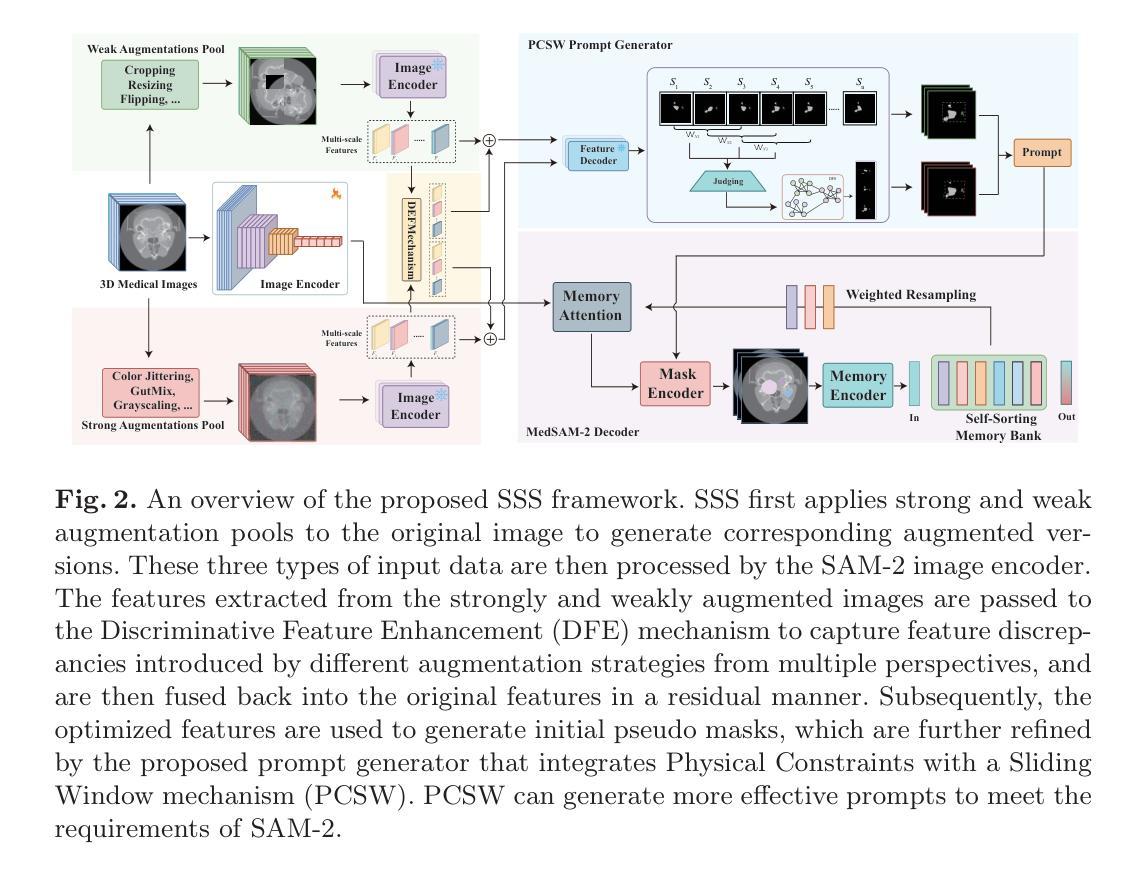
SSS: Semi-Supervised SAM-2 with Efficient Prompting for Medical Imaging Segmentation
Authors:Hongjie Zhu, Xiwei Liu, Rundong Xue, Zeyu Zhang, Yong Xu, Daji Ergu, Ying Cai, Yang Zhao
In the era of information explosion, efficiently leveraging large-scale unlabeled data while minimizing the reliance on high-quality pixel-level annotations remains a critical challenge in the field of medical imaging. Semi-supervised learning (SSL) enhances the utilization of unlabeled data by facilitating knowledge transfer, significantly improving the performance of fully supervised models and emerging as a highly promising research direction in medical image analysis. Inspired by the ability of Vision Foundation Models (e.g., SAM-2) to provide rich prior knowledge, we propose SSS (Semi-Supervised SAM-2), a novel approach that leverages SAM-2’s robust feature extraction capabilities to uncover latent knowledge in unlabeled medical images, thus effectively enhancing feature support for fully supervised medical image segmentation. Specifically, building upon the single-stream “weak-to-strong” consistency regularization framework, this paper introduces a Discriminative Feature Enhancement (DFE) mechanism to further explore the feature discrepancies introduced by various data augmentation strategies across multiple views. By leveraging feature similarity and dissimilarity across multi-scale augmentation techniques, the method reconstructs and models the features, thereby effectively optimizing the salient regions. Furthermore, a prompt generator is developed that integrates Physical Constraints with a Sliding Window (PCSW) mechanism to generate input prompts for unlabeled data, fulfilling SAM-2’s requirement for additional prompts. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method for semi-supervised medical image segmentation on two multi-label datasets, i.e., ACDC and BHSD. Notably, SSS achieves an average Dice score of 53.15 on BHSD, surpassing the previous state-of-the-art method by +3.65 Dice. Code will be available at https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/SSS.
在信息爆炸时代,如何有效利用大规模的无标签数据,同时尽量减少对高质量像素级注释的依赖,仍然是医学成像领域的一个关键挑战。半监督学习(SSL)通过促进知识迁移,提高了无标签数据的利用率,显著提升了全监督模型的表现,并成为医学图像分析中一个极具前景的研究方向。受Vision Foundation Models(例如SAM-2)提供丰富先验知识的能力的启发,我们提出了SSS(Semi-Supervised SAM-2),这是一种利用SAM-2的稳健特征提取能力来挖掘无标签医学图像中潜在知识的新方法,从而有效增强全监督医学图像分割的特征支持。具体而言,该论文基于单流“弱到强”的一致性正则化框架,引入判别特征增强(DFE)机制,以进一步探索由多种数据增强策略在不同视图下引入的特征差异。通过利用多尺度增强技术中的特征相似性和不相似性,该方法重构并建模特征,从而有效地优化显著区域。此外,还开发了一个提示生成器,该生成器结合了物理约束和滑动窗口(PCSW)机制,以为无标签数据生成输入提示,满足SAM-2对额外提示的要求。大量实验表明,该方法在ACDC和BHSD两个多标签数据集上进行半监督医学图像分割时表现优异。值得注意的是,SSS在BHSD上取得了平均Dice系数为53.15的成绩,超过了之前的最先进方法+3.65 Dice。代码将在https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/SSS上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在大数据时代,如何利用大量未标注数据并减少对高质量像素级标注的依赖是医学影像领域的一大挑战。半监督学习(SSL)通过促进知识迁移,提高了未标注数据的利用率,显著提升了全监督模型的表现,成为医学影像分析中极具前景的研究方向。本研究受Vision Foundation Models(如SAM-2)提供丰富先验知识的启发,提出了SSS(Semi-Supervised SAM-2)新方法,利用SAM-2的稳健特征提取能力,挖掘未标注医学影像中的潜在知识,从而增强全监督医学影像分割的特征支持。研究在单流“弱到强”一致性正则化框架的基础上,引入判别性特征增强(DFE)机制,进一步探索各种数据增强策略在不同视图下引入的特征差异。通过利用多尺度增强技术的特征相似性和差异性来重建和建模特征,从而有效优化显著区域。此外,研究还开发了结合物理约束与滑动窗口(PCSW)机制的提示生成器,为未标注数据生成输入提示,满足SAM-2对额外提示的要求。在ACDC和BHSD两个多标签数据集上的实验表明,该方法在半监督医学影像分割上具有优越性。特别是在BHSD数据集上,SSS的平均Dice得分达到53.15,超越了之前的最先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 在大数据时代,半监督学习(SSL)在医学图像分析中具有高度前景,能利用大量未标注数据并提升全监督模型性能。
- SSS方法利用SAM-2的稳健特征提取能力,有效挖掘未标注医学图像中的潜在知识。
- 研究引入判别性特征增强(DFE)机制,探索数据增强策略下的特征差异。
- 通过结合物理约束与滑动窗口(PCSW)机制的提示生成器,满足SAM-2对额外提示的需求。
- 在ACDC和BHSD数据集上的实验表明SSS方法在半监督医学图像分割上的优越性。
- SSS在BHSD数据集上的平均Dice得分达到53.15,显著超越先前的方法。
点此查看论文截图

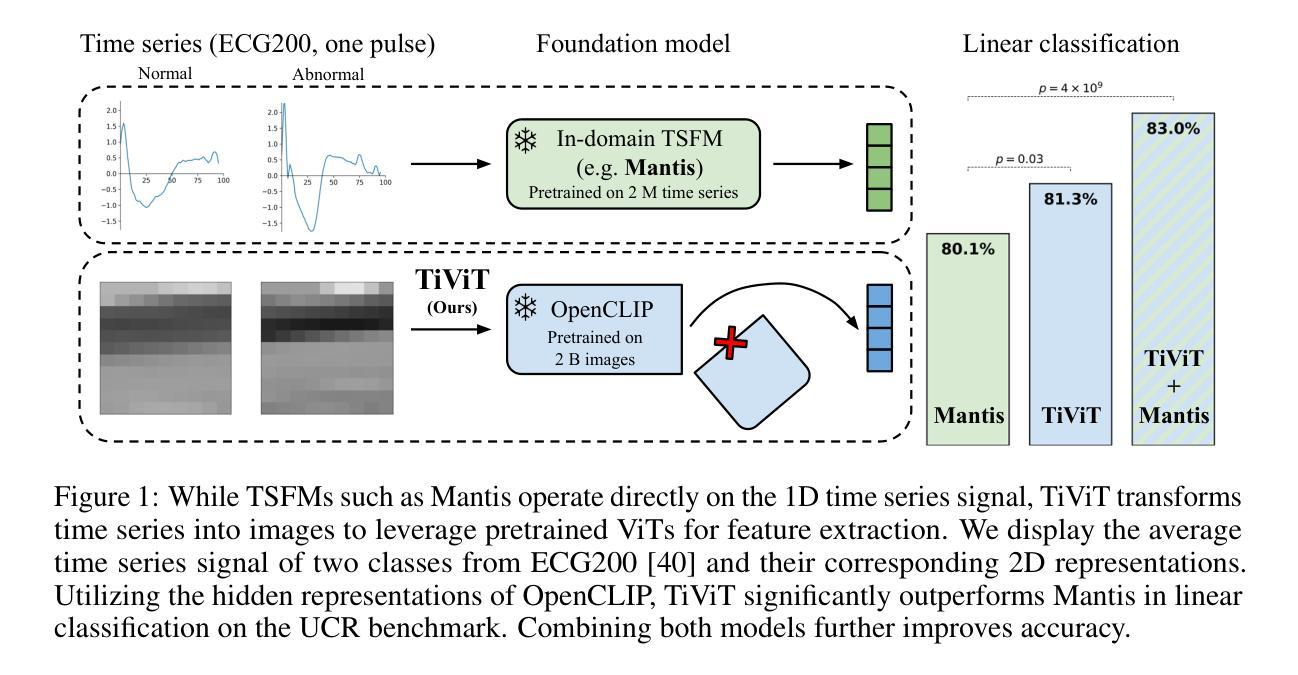
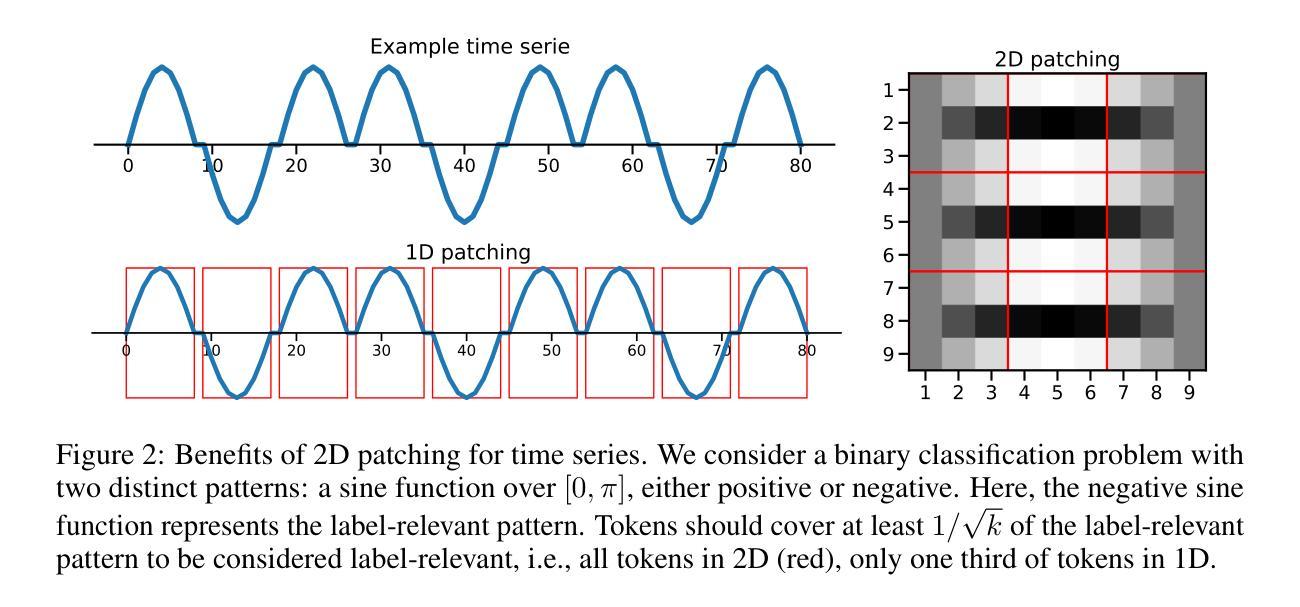
Time Series Representations for Classification Lie Hidden in Pretrained Vision Transformers
Authors:Simon Roschmann, Quentin Bouniot, Vasilii Feofanov, Ievgen Redko, Zeynep Akata
Time series classification is a fundamental task in healthcare and industry, yet the development of time series foundation models (TSFMs) remains limited by the scarcity of publicly available time series datasets. In this work, we propose Time Vision Transformer (TiViT), a framework that converts time series into images to leverage the representational power of frozen Vision Transformers (ViTs) pretrained on large-scale image datasets. First, we theoretically motivate our approach by analyzing the 2D patching of ViTs for time series, showing that it can increase the number of label-relevant tokens and reduce the sample complexity. Second, we empirically demonstrate that TiViT achieves state-of-the-art performance on standard time series classification benchmarks by utilizing the hidden representations of large OpenCLIP models. We explore the structure of TiViT representations and find that intermediate layers with high intrinsic dimension are the most effective for time series classification. Finally, we assess the alignment between TiViT and TSFM representation spaces and identify a strong complementarity, with further performance gains achieved by combining their features. Our findings reveal yet another direction for reusing vision representations in a non-visual domain.
时间序列分类是医疗和工业中的基本任务,然而,时间序列基础模型(TSFMs)的发展受到公开可用时间序列数据集稀缺的限制。在这项工作中,我们提出了时间序列视觉转换器(TiViT),这是一个将时间序列转换为图像框架,以利用在大型图像数据集上预训练的冻结视觉转换器(ViTs)的表示能力。首先,我们通过分析用于时间序列的ViTs的2D补丁,从理论上论证了我们的方法,表明它可以增加标签相关令牌的数量并降低样本复杂性。其次,我们通过实证表明,TiViT利用大型OpenCLIP模型的隐藏表示,在标准时间序列分类基准测试上实现了最先进的性能。我们探索了TiViT表示的结构,并发现具有高内在维度的中间层对时间序列分类最为有效。最后,我们评估了TiViT和TSFM表示空间的对齐性,并发现了强烈的互补性,通过结合它们的特征可以实现进一步的性能提升。我们的研究揭示了在非视觉领域重新使用时间序列表示的另一个方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
时间序列分类在医疗和工业中是一项基础任务,但由于缺乏公开可用的时间序列数据集,时间序列基础模型(TSFMs)的发展受到限制。本研究提出了时间视觉转换器(TiViT),它将时间序列转换为图像,以利用在大型图像数据集上预训练的冻结视觉转换器(ViTs)的表示能力。本研究从理论角度分析了ViTs用于时间序列的2D补丁,证明了其优势。此外,TiViT在标准时间序列分类基准测试中实现了卓越性能。研究发现,具有高内在维度的中间层对时间序列分类最为有效。最后,评估了TiViT和TSFM表示空间的契合度,发现二者具有很强的互补性,结合其特征可实现进一步的性能提升。本研究揭示了将视觉表示用于非视觉领域的另一方向。
Key Takeaways
- 时间序列分类是医疗和工业中的关键任务,受限于公共数据集的可获取性。
- 提出了时间视觉转换器(TiViT)框架,能将时间序列转换为图像并利用视觉转换器的表示能力。
- 理论分析证明了使用ViTs进行时间序列处理的优越性,表现在增加标签相关标记的数量并降低样本复杂性。
- 在标准时间序列分类基准测试中,TiViT取得了最佳性能表现。
- 研究发现具有高内在维度的中间层对于时间序列分类最为有效。
- TiViT和现有时间序列基础模型(TSFMs)在表示空间上具有强互补性。
点此查看论文截图

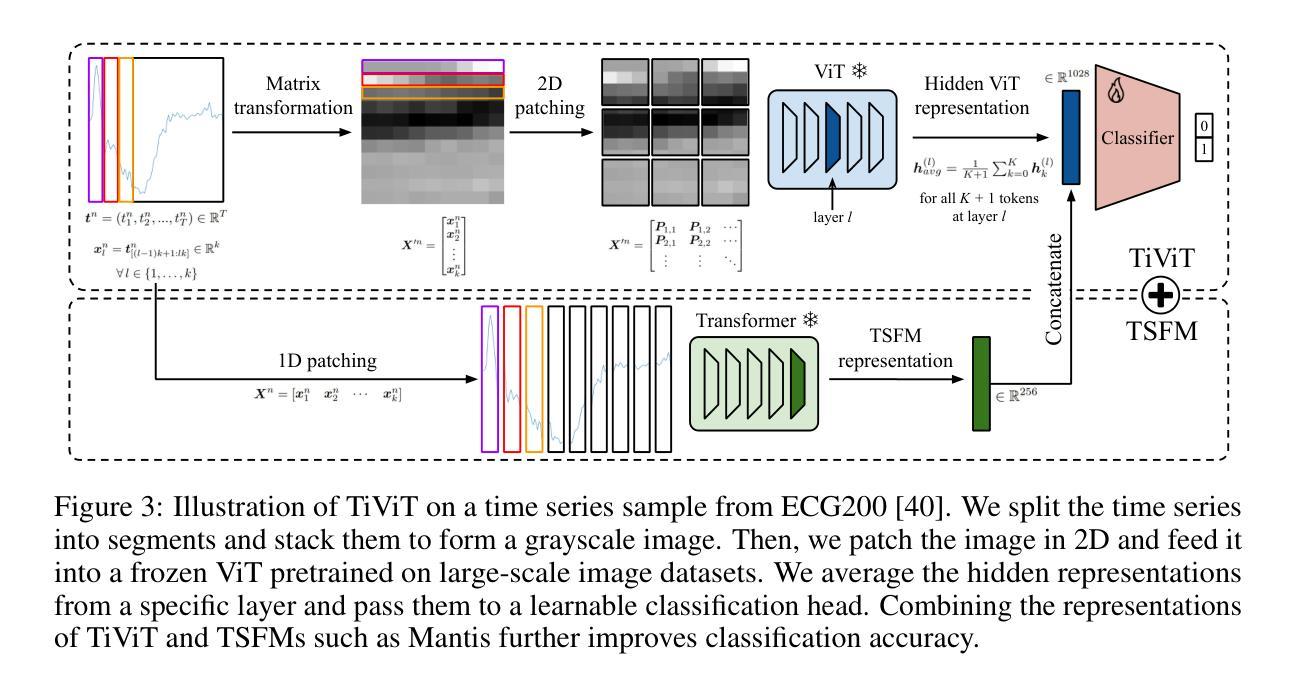
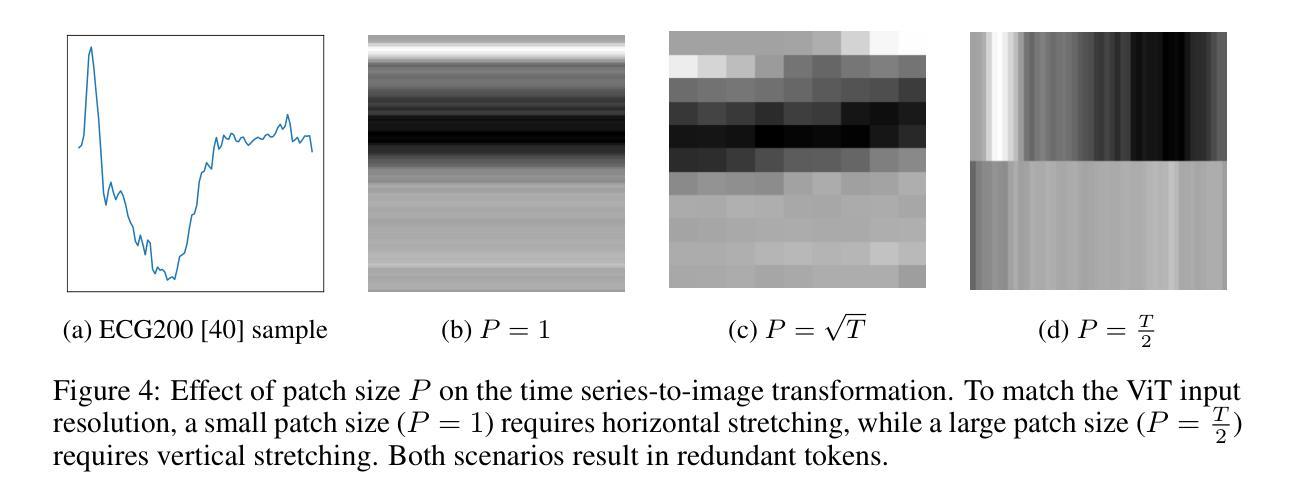
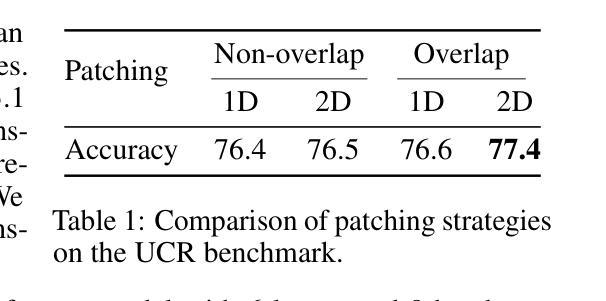
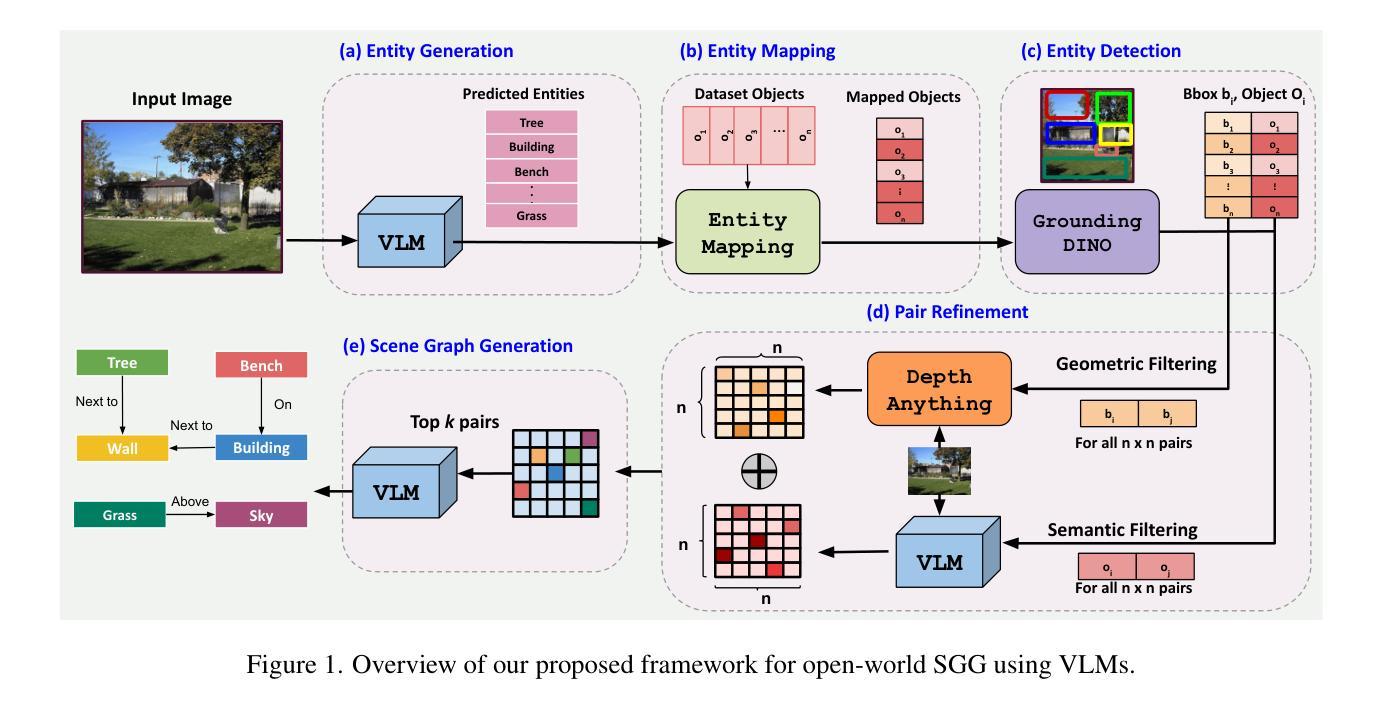
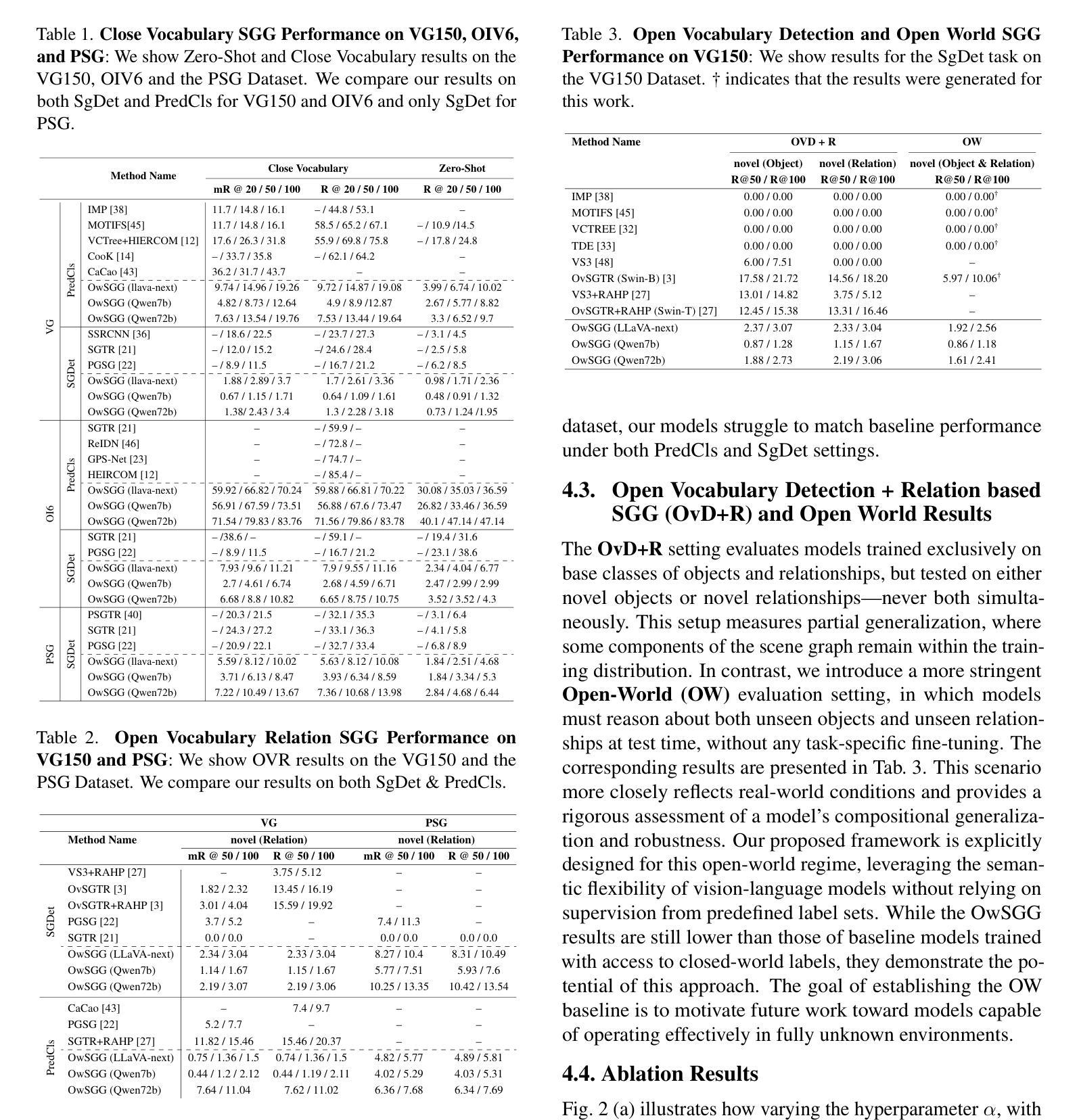
Open World Scene Graph Generation using Vision Language Models
Authors:Amartya Dutta, Kazi Sajeed Mehrab, Medha Sawhney, Abhilash Neog, Mridul Khurana, Sepideh Fatemi, Aanish Pradhan, M. Maruf, Ismini Lourentzou, Arka Daw, Anuj Karpatne
Scene-Graph Generation (SGG) seeks to recognize objects in an image and distill their salient pairwise relationships. Most methods depend on dataset-specific supervision to learn the variety of interactions, restricting their usefulness in open-world settings, involving novel objects and/or relations. Even methods that leverage large Vision Language Models (VLMs) typically require benchmark-specific fine-tuning. We introduce Open-World SGG, a training-free, efficient, model-agnostic framework that taps directly into the pretrained knowledge of VLMs to produce scene graphs with zero additional learning. Casting SGG as a zero-shot structured-reasoning problem, our method combines multimodal prompting, embedding alignment, and a lightweight pair-refinement strategy, enabling inference over unseen object vocabularies and relation sets. To assess this setting, we formalize an Open-World evaluation protocol that measures performance when no SGG-specific data have been observed either in terms of objects and relations. Experiments on Visual Genome, Open Images V6, and the Panoptic Scene Graph (PSG) dataset demonstrate the capacity of pretrained VLMs to perform relational understanding without task-level training.
场景图生成(SGG)旨在识别图像中的对象并提炼它们之间的重要二元关系。大多数方法都依赖于特定数据集进行互动学习,这在涉及新对象或新关系的开放世界环境中限制了其效用。即使利用大型视觉语言模型(VLMs)的方法也需要针对基准测试进行特定微调。我们引入了开放世界SGG,这是一个无训练、高效、模型通用的框架,它直接利用预训练的VLM知识生成场景图,无需额外学习。将SGG视为零射式结构化推理问题,我们的方法结合了多模式提示、嵌入对齐和轻量级配对优化策略,能够对未见过的对象词汇和关系集进行推断。为了评估这一设置,我们制定了开放世界评估协议,以衡量在没有观察到SGG特定数据的情况下在对象和关系方面的性能。在视觉基因组、开放图像V6和全景场景图(PSG)数据集上的实验证明了预训练VLM进行关系理解的能力,无需任务级训练。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in CVPR 2025 Workshop (CVinW)
Summary
本研究提出Open-World SGG框架,这是一个无需训练、高效且模型通用的框架,可直接利用预训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs)知识生成场景图。通过将场景图生成(SGG)视为零样本结构化推理问题,结合多模态提示、嵌入对齐和轻量级对偶精炼策略,实现未在对象词汇和关系集上见过的新对象的推理。
Key Takeaways
- Open-World SGG框架允许模型在无需特定数据集监督的情况下识别图像中的对象及其重要关系。
- 该框架利用预训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs)知识,无需额外学习即可生成场景图。
- 通过将场景图生成(SGG)视为零样本结构化推理问题,该框架能够处理未见过的对象词汇和关系集。
- 多模态提示、嵌入对齐和轻量级对偶精炼策略的结合,增强了模型的推理能力。
- 提出的Open-World评估协议用于衡量在对象和关系上未观察过的情况下模型的性能。
- 在Visual Genome、Open Images V6和Panoptic Scene Graph数据集上的实验证明了预训练VLMs进行关系理解的能力,而无需任务级别训练。
- 该框架具有广泛的应用前景,特别是在开放世界环境中处理新型对象和关系时。
点此查看论文截图
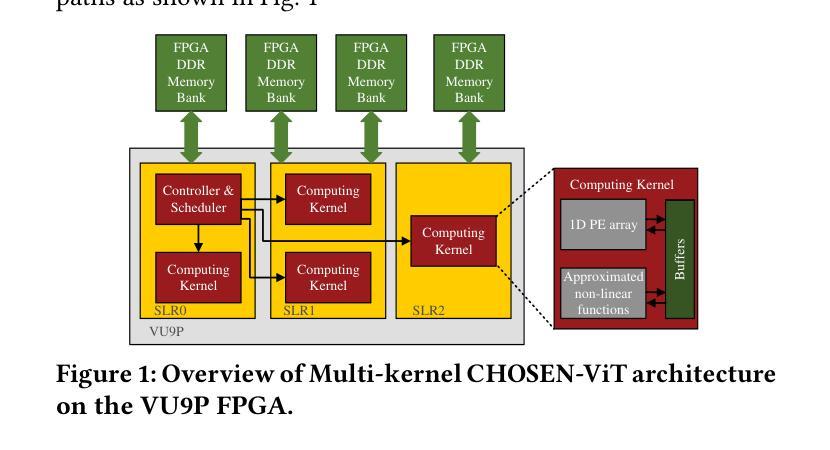
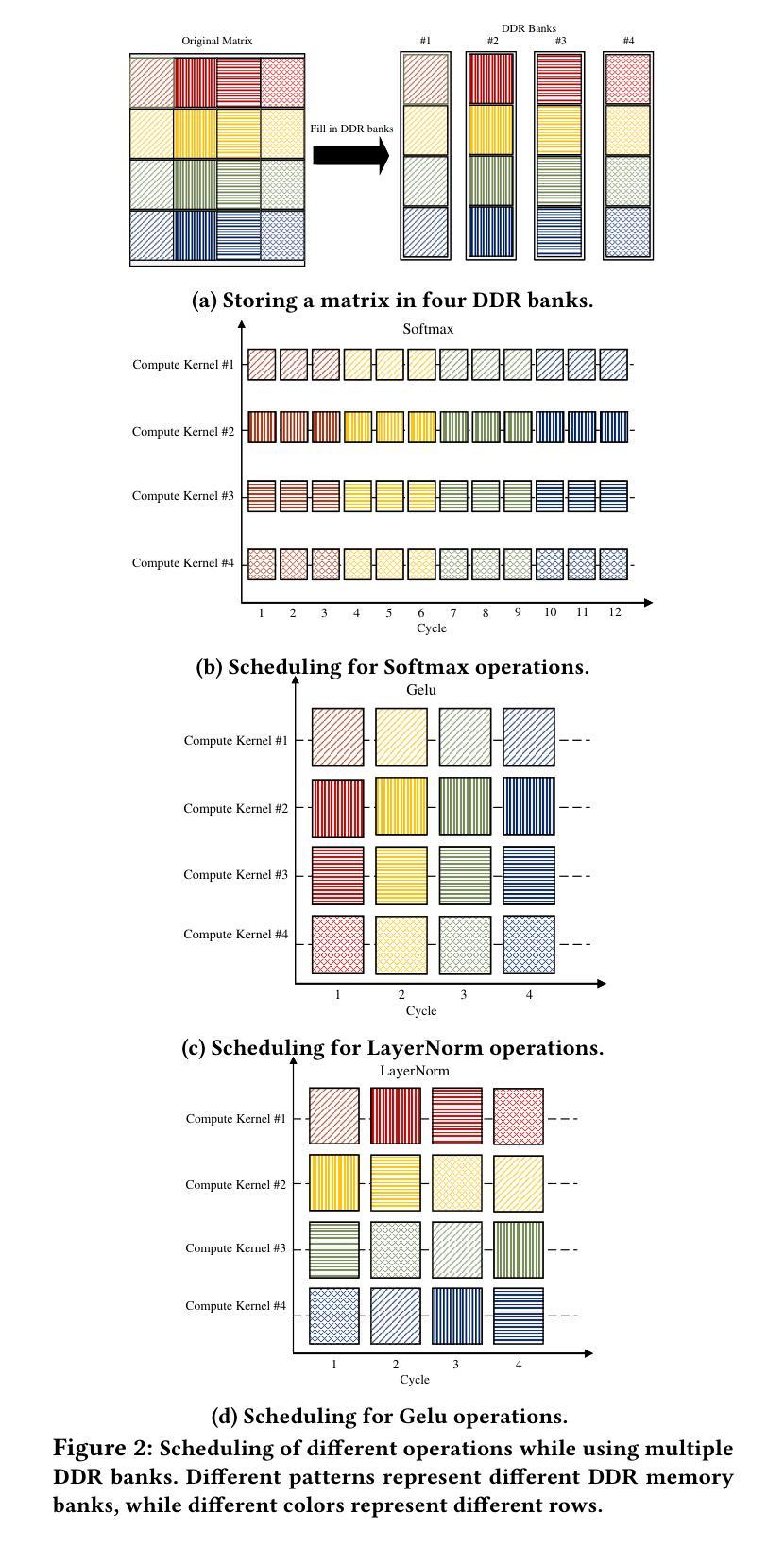
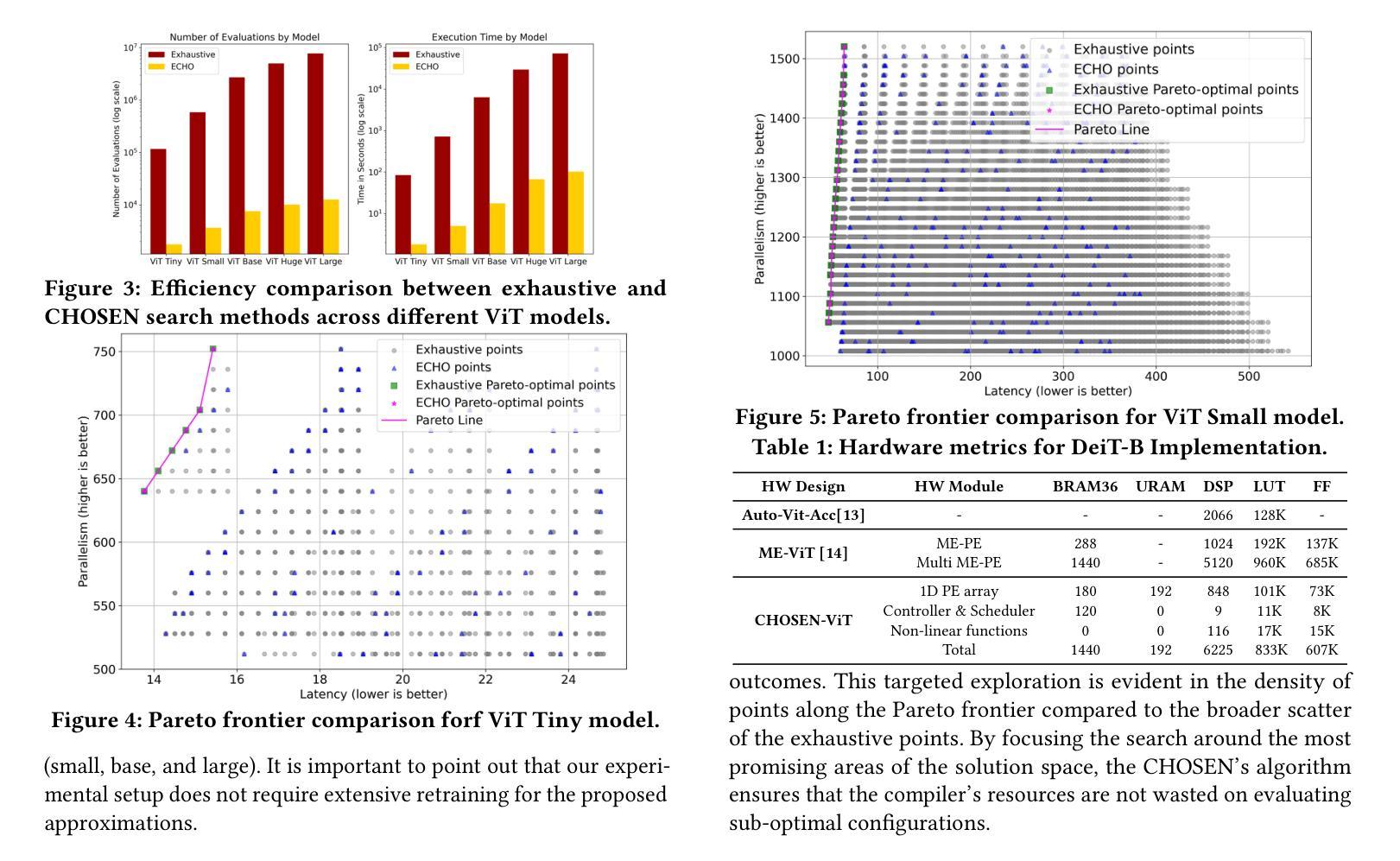
CHOSEN: Compilation to Hardware Optimization Stack for Efficient Vision Transformer Inference
Authors:Mohammad Erfan Sadeghi, Arash Fayyazi, Suhas Somashekar, Armin Abdollahi, Massoud Pedram
Vision Transformers (ViTs) represent a groundbreaking shift in machine learning approaches to computer vision. Unlike traditional approaches, ViTs employ the self-attention mechanism, which has been widely used in natural language processing, to analyze image patches. Despite their advantages in modeling visual tasks, deploying ViTs on hardware platforms, notably Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs), introduces considerable challenges. These challenges stem primarily from the non-linear calculations and high computational and memory demands of ViTs. This paper introduces CHOSEN, a software-hardware co-design framework to address these challenges and offer an automated framework for ViT deployment on the FPGAs in order to maximize performance. Our framework is built upon three fundamental contributions: multi-kernel design to maximize the bandwidth, mainly targeting benefits of multi DDR memory banks, approximate non-linear functions that exhibit minimal accuracy degradation, and efficient use of available logic blocks on the FPGA, and efficient compiler to maximize the performance and memory-efficiency of the computing kernels by presenting a novel algorithm for design space exploration to find optimal hardware configuration that achieves optimal throughput and latency. Compared to the state-of-the-art ViT accelerators, CHOSEN achieves a 1.5x and 1.42x improvement in the throughput on the DeiT-S and DeiT-B models.
视觉Transformer(ViTs)代表了计算机视觉机器学习方法的突破性转变。与传统的计算机视觉方法不同,ViTs采用自注意力机制(这在自然语言处理中得到了广泛应用)来分析图像块。尽管ViTs在建模视觉任务上具有优势,但在硬件平台(特别是现场可编程门阵列(FPGA))上部署ViTs却面临相当大的挑战。这些挑战主要源于ViTs的非线性计算以及其对计算和内存的高需求。本文介绍了CHOSEN,这是一个软硬件协同设计框架,旨在解决这些挑战,并提供一个自动化框架,以最大限度地提高FPGA上ViT的性能。我们的框架建立在三个基本贡献之上:多核设计以最大化带宽(主要针对多DDR内存银行的优势)、近似非线性函数以展现最小的精度损失以及有效地使用FPGA上的可用逻辑块,以及高效的编译器。通过提供一种新型算法来设计空间探索,编译器能够最大限度地提高计算内核的性能和内存效率,从而实现最佳的吞吐量和延迟,找到实现最佳吞吐量和延迟的最佳硬件配置。与最先进的ViT加速器相比,CHOSEN在DeiT-S和DeiT-B模型上的吞吐量提高了1.5倍和1.42倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Vision Transformers(ViTs)在计算机视觉领域的应用及其面临的挑战,特别是在硬件平台(如FPGA)上的部署。文章提出了一种名为CHOSEN的软件硬件协同设计框架,旨在解决这些问题并实现ViT在FPGA上的高效部署。该框架通过三个主要贡献来实现优化:多核设计以最大化带宽、利用DDR内存银行的优势,近似非线性函数以最小化精度损失,以及有效利用FPGA上的逻辑块。相较于现有ViT加速器,CHOSEN在DeiT-S和DeiT-B模型上的吞吐量分别提升了1.5倍和1.42倍。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs) 引入自注意力机制处理图像补丁,是计算机视觉领域的一种创新方法。
- ViT在FPGA等硬件平台部署面临非线性计算和高计算内存需求的挑战。
- CHOSEN框架通过多核设计最大化带宽,特别利用DDR内存银行优势。
- CHOSEN通过近似非线性函数实现精度损失最小化。
- CHOSEN有效利用FPGA的逻辑块,并提供一个编译器以优化计算内核的性能和内存效率。
- CHOSEN提供了一种自动化框架,用于在FPGA上部署ViT,以最大化性能。
点此查看论文截图