⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-14 更新
SpectralAR: Spectral Autoregressive Visual Generation
Authors:Yuanhui Huang, Weiliang Chen, Wenzhao Zheng, Yueqi Duan, Jie Zhou, Jiwen Lu
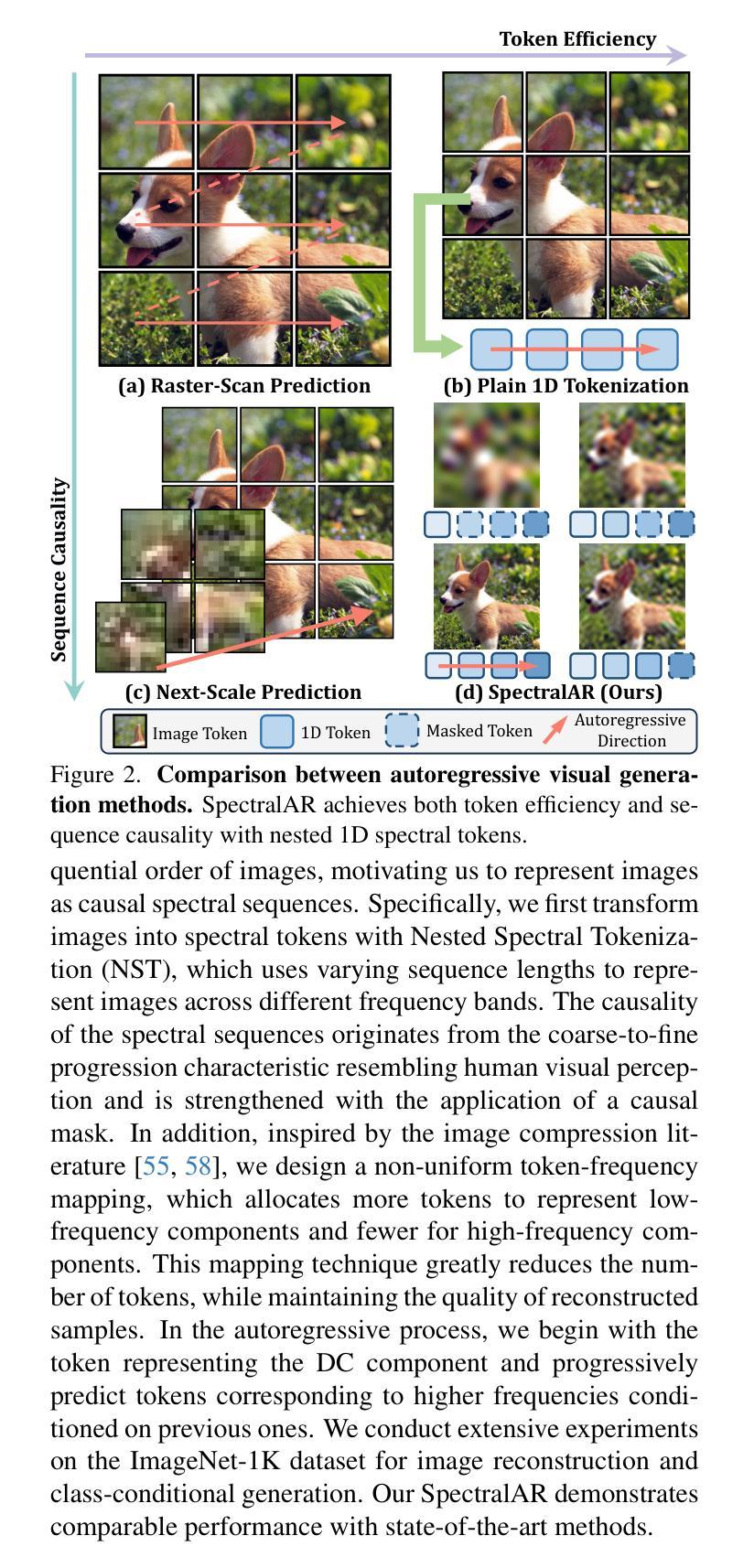
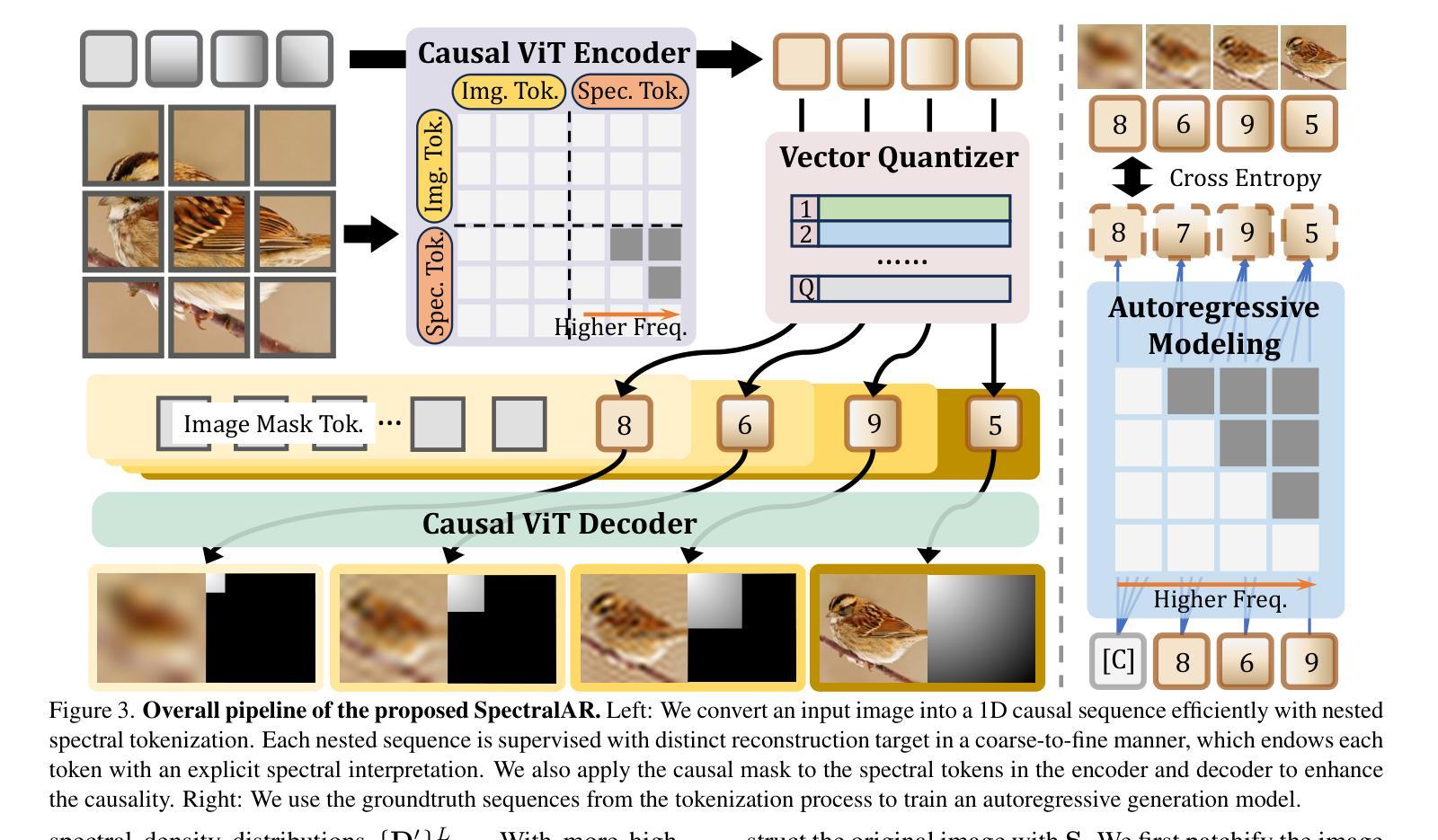
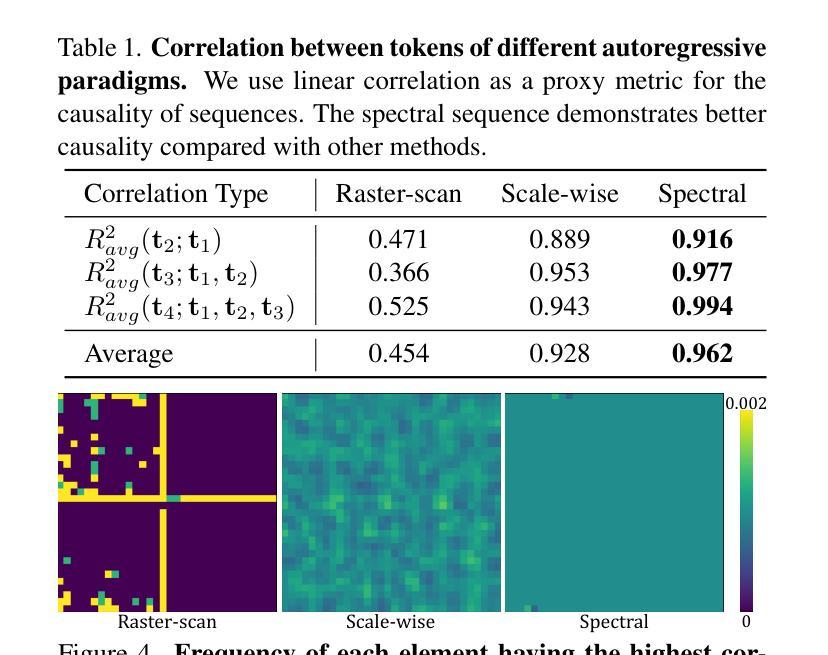
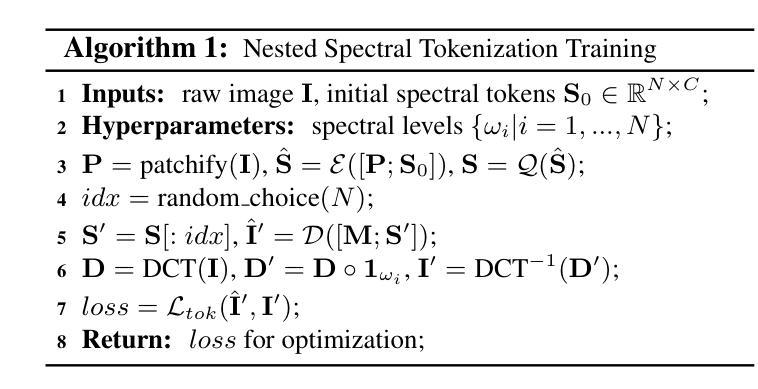
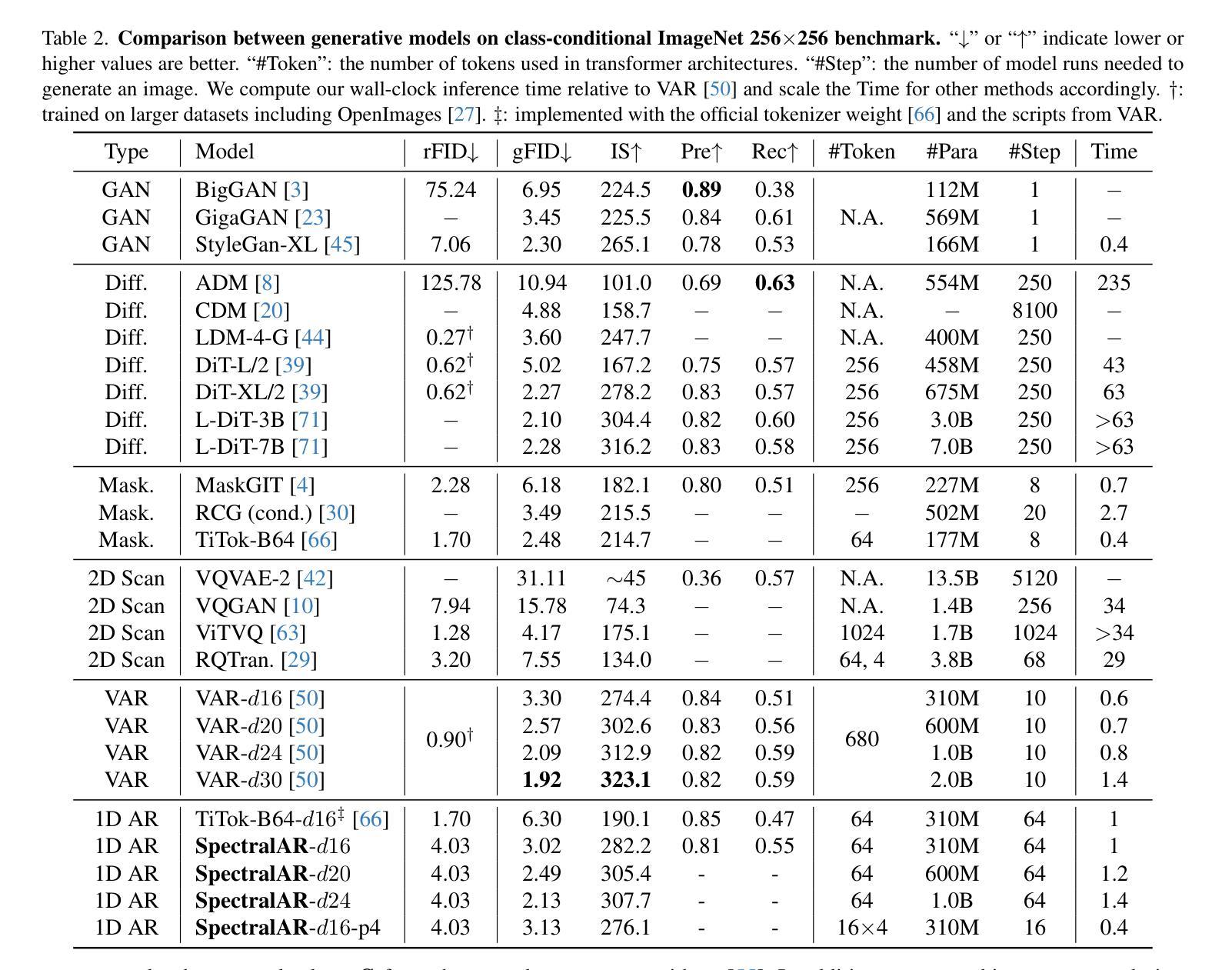
Autoregressive visual generation has garnered increasing attention due to its scalability and compatibility with other modalities compared with diffusion models. Most existing methods construct visual sequences as spatial patches for autoregressive generation. However, image patches are inherently parallel, contradicting the causal nature of autoregressive modeling. To address this, we propose a Spectral AutoRegressive (SpectralAR) visual generation framework, which realizes causality for visual sequences from the spectral perspective. Specifically, we first transform an image into ordered spectral tokens with Nested Spectral Tokenization, representing lower to higher frequency components. We then perform autoregressive generation in a coarse-to-fine manner with the sequences of spectral tokens. By considering different levels of detail in images, our SpectralAR achieves both sequence causality and token efficiency without bells and whistles. We conduct extensive experiments on ImageNet-1K for image reconstruction and autoregressive generation, and SpectralAR achieves 3.02 gFID with only 64 tokens and 310M parameters. Project page: https://huang-yh.github.io/spectralar/.
自回归视觉生成因其可扩展性和与其他模态的兼容性而受到越来越多的关注,相比于扩散模型。现有的大多数方法将视觉序列构建为空间补丁进行自回归生成。然而,图像补丁本质上是并行的,与自回归模型的因果性质相矛盾。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了Spectral AutoRegressive(SpectralAR)视觉生成框架,从光谱角度实现了视觉序列的因果性。具体来说,我们首先将图像通过Nested Spectral Tokenization转化为有序的频谱标记符号,代表从低到高的频率分量。然后我们在频谱标记序列中以由粗到细的方式执行自回归生成。通过考虑图像中的不同层次的细节,我们的SpectralAR框架在不添加任何花哨的情况下实现了序列的因果性和标记的效率。我们在ImageNet-1K上进行了大量的图像重建和自回归生成的实验,SpectralAR仅使用64个标记和3.1亿个参数就实现了3.02的gFID。更多详细信息请参见我们的项目网页:[https://huang-yh.github.io/spectralar/]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://huang-yh.github.io/spectralar/
Summary
谱自回归(SpectralAR)视觉生成框架通过谱视角实现了视觉序列的因果性,通过嵌套谱令牌化将图像转换为有序的谱令牌,进行粗细级别的自回归生成。在ImageNet-1K上进行实验,实现图像重建和自回归生成,具有高效序列性和标记效率。项目页面:https://huang-yh.github.io/spectralar/。
Key Takeaways
- 自回归视觉生成因其可扩展性和与其他模态的兼容性而受到关注。
- 现有方法构建的空间补丁用于自回归生成与自回归模型的因果性质相矛盾。
- 谱自回归(SpectralAR)框架从谱角度实现视觉序列的因果性。
- 通过嵌套谱令牌化将图像转换为有序的谱令牌。
- 以粗细级别的方式进行自回归生成,考虑图像的不同层次细节。
- 在ImageNet-1K上进行实验,SpectralAR框架实现了高效的序列性和标记效率。
点此查看论文截图

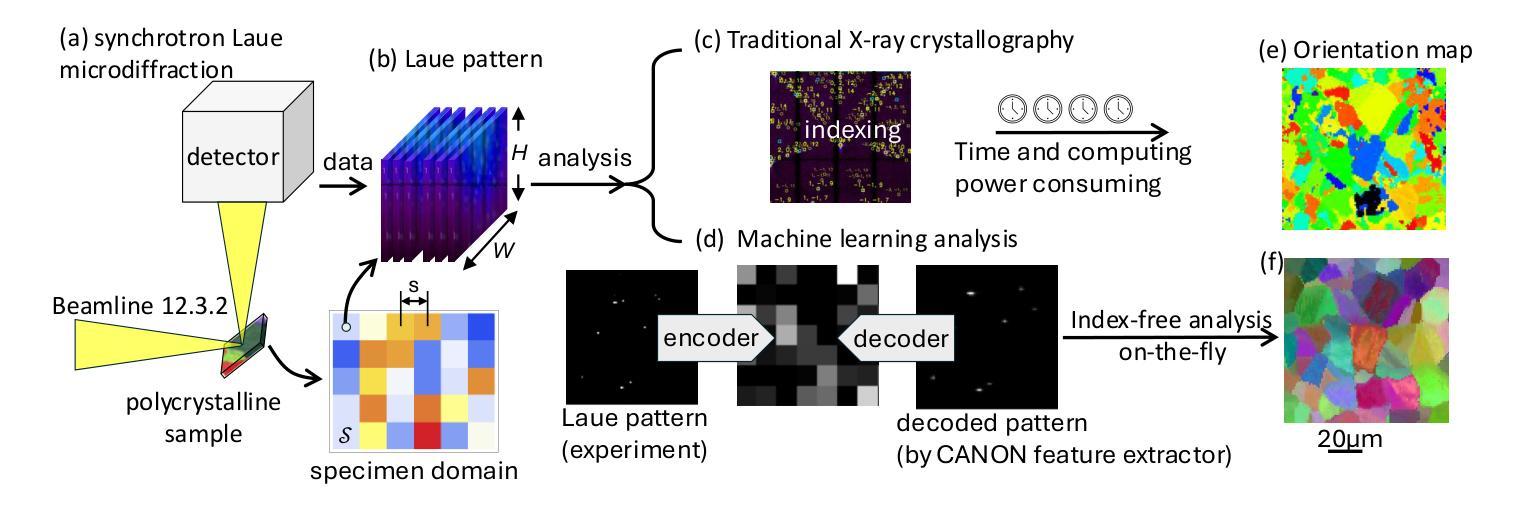
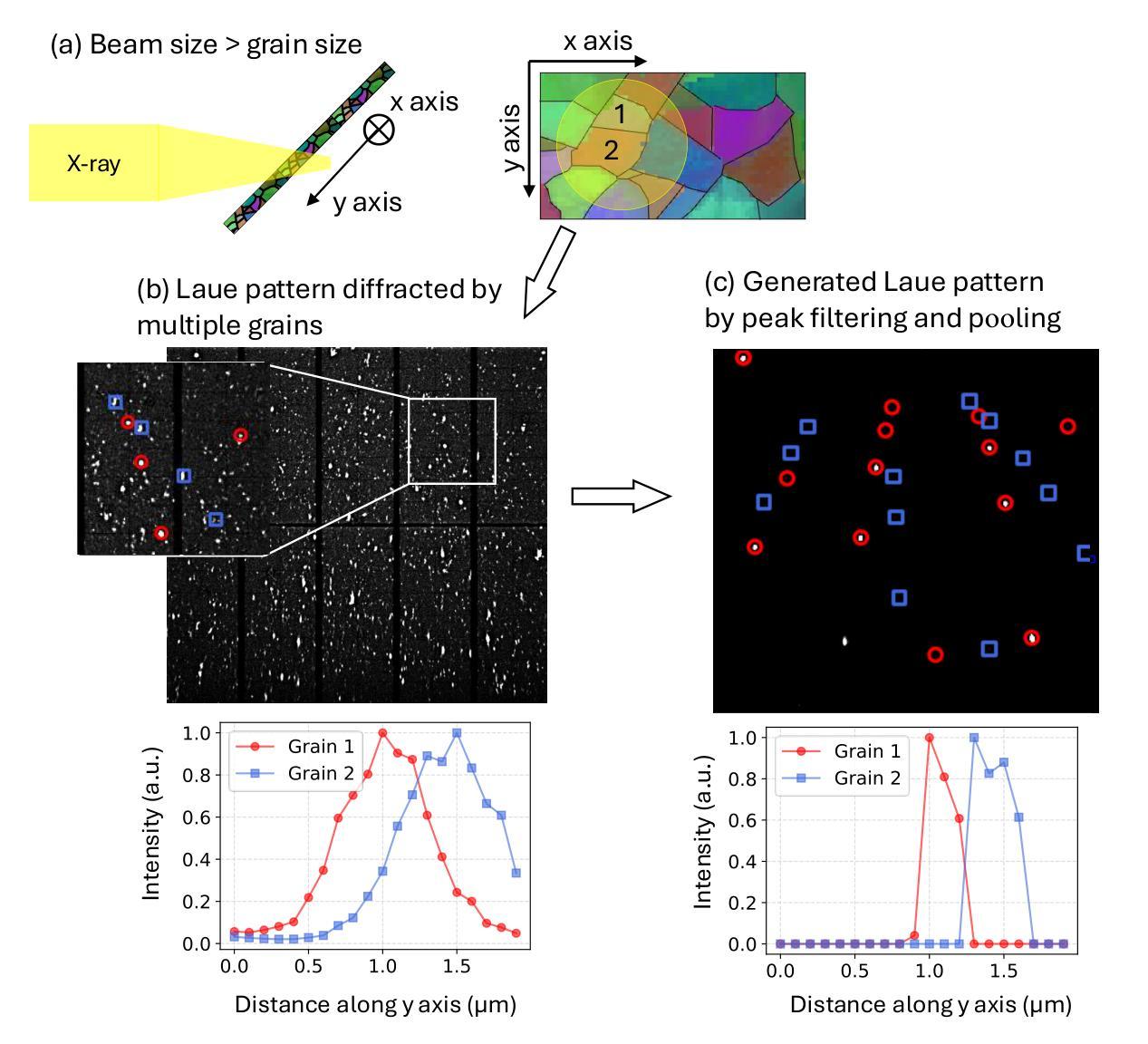
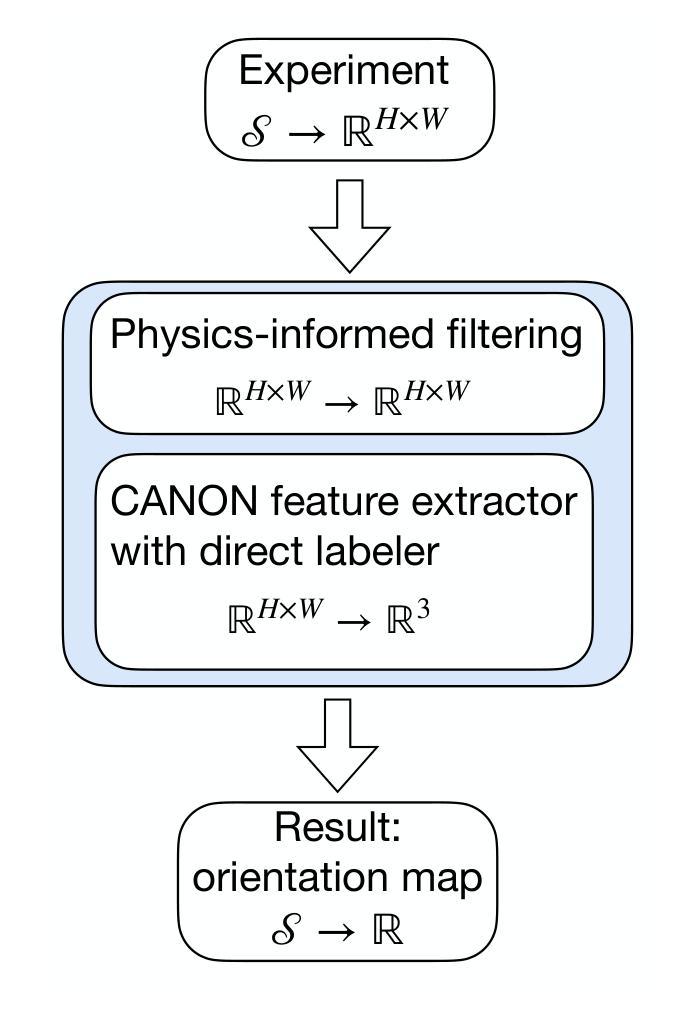
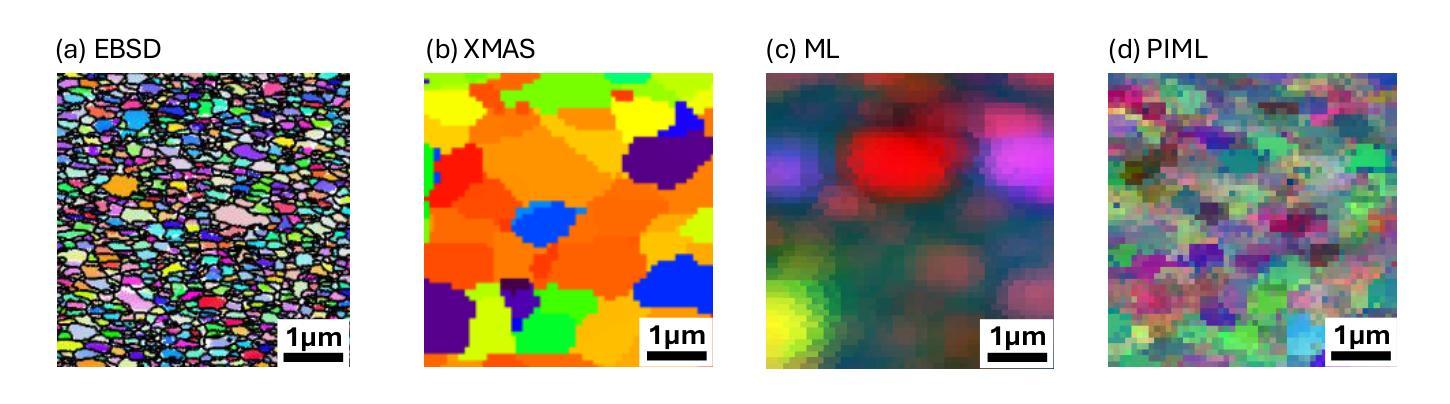
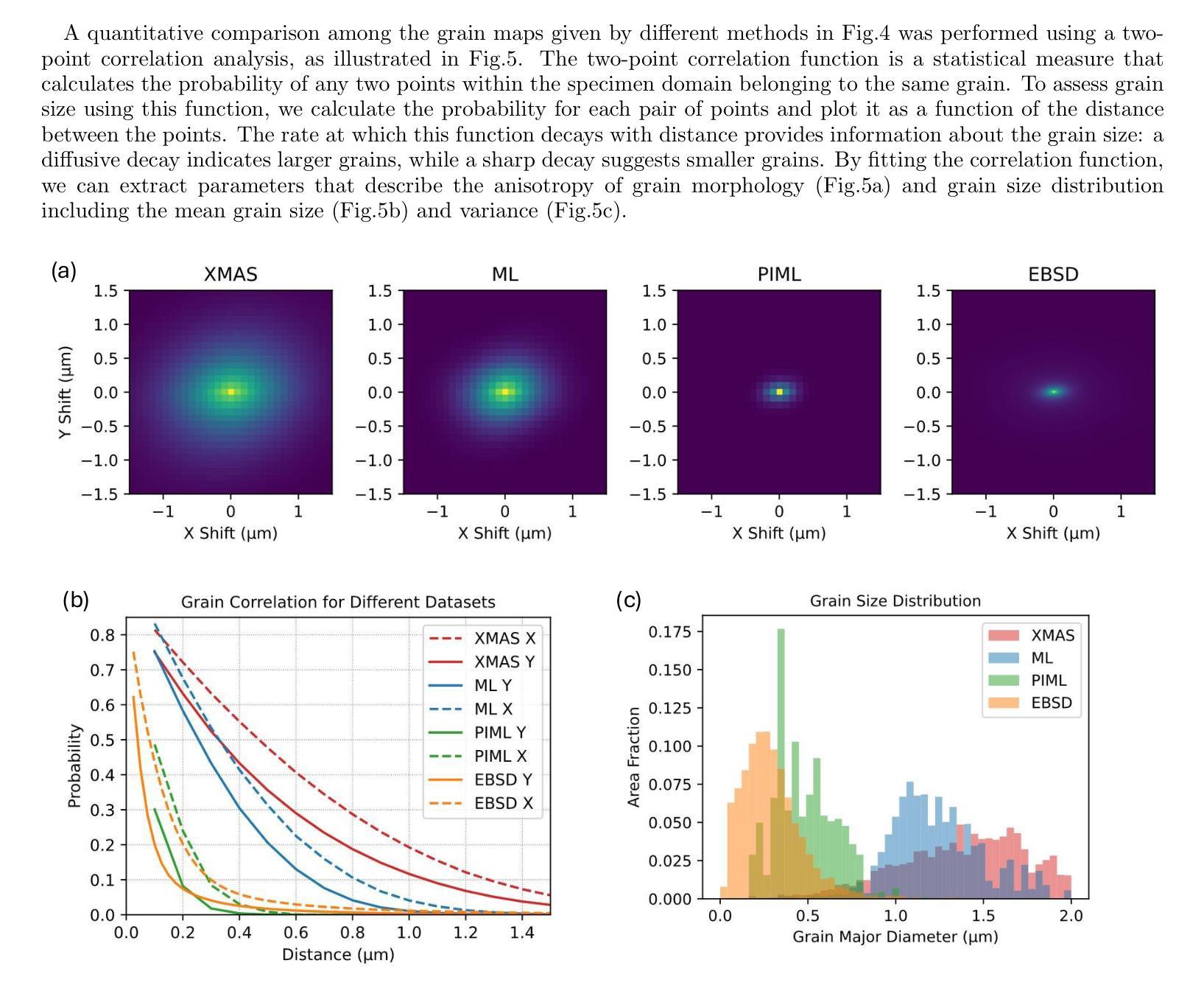
Physics-informed Machine Learning Analysis for Nanoscale Grain Mapping by Synchrotron Laue Microdiffraction
Authors:Ka Hung Chan, Xinyue Huang, Nobumichi Tamura, Xian Chen
Understanding the grain morphology, orientation distribution, and crystal structure of nanocrystals is essential for optimizing the mechanical and physical properties of functional materials. Synchrotron X-ray Laue microdiffraction is a powerful technique for characterizing crystal structures and orientation mapping using focused X-rays. However, when grain sizes are smaller than the beam size, mixed peaks in the Laue pattern from neighboring grains limit the resolution of grain morphology mapping. We propose a physics-informed machine learning (PIML) approach that combines a CNN feature extractor with a physics-informed filtering algorithm to overcome the spatial resolution limits of X-rays, achieving nanoscale resolution for grain mapping. Our PIML method successfully resolves the grain size, orientation distribution, and morphology of Au nanocrystals through synchrotron microdiffraction scans, showing good agreement with electron backscatter diffraction results. This PIML-assisted synchrotron microdiffraction analysis can be generalized to other diffraction-based probes, enabling the characterization of nanosized structures with micron-sized probes.
理解纳米晶体的晶粒形态、取向分布和晶体结构对于优化功能材料的机械和物理性能至关重要。同步辐射X射线劳厄显微衍射是一种强大的表征晶体结构和取向映射的技术,使用聚焦的X射线。然而,当晶粒尺寸小于光束尺寸时,来自相邻晶粒的劳厄图谱中的混合峰会限制晶粒形态映射的分辨率。我们提出了一种结合卷积神经网络特征提取器和物理信息滤波算法的基于物理知识的机器学习(PIML)方法,以克服X射线的空间分辨率限制,实现纳米级分辨率的晶粒映射。我们的PIML方法通过同步辐射显微衍射扫描成功解析了金纳米晶体的晶粒尺寸、取向分布和形态,与电子背散射衍射结果显示出良好的一致性。这种辅助PIML的同步辐射显微衍射分析可推广到其他基于衍射的探针,实现对微米级探针的纳米级结构的表征。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures
摘要
理解纳米晶体的晶粒形态、取向分布和晶体结构对于优化功能材料的机械和物理性质至关重要。同步辐射X射线劳埃微衍射是一种利用聚焦X射线表征晶体结构和取向映射的强大技术。然而,当晶粒尺寸小于光束尺寸时,来自相邻晶粒的劳埃图案中的混合峰会限制晶粒形态映射的分辨率。我们提出了一种结合卷积神经网络特征提取器和物理信息滤波算法的物理信息机器学习(PIML)方法,以克服X射线的空间分辨率限制,实现纳米级分辨率的晶粒映射。我们的PIML方法成功解决了通过同步加速器微衍射扫描获得的Au纳米晶体的晶粒尺寸、取向分布和形态,与电子背散射衍射结果具有良好的一致性。这种PIML辅助的同步辐射微衍射分析可推广到其他衍射探针,实现对微米级探针的纳米级结构的表征。
要点
- 纳米晶体的晶粒形态、取向分布和晶体结构对功能材料的机械和物理性质优化至关重要。
- 同步辐射X射线劳埃微衍射是表征晶体结构和取向映射的强大技术,但在小晶粒尺寸下存在分辨率限制。
- 提出了结合卷积神经网络特征提取器和物理信息滤波算法的物理信息机器学习(PIML)方法。
- PIML方法成功解决通过同步加速器微衍射扫描获得的Au纳米晶体的晶粒尺寸、取向分布和形态。
- PIML方法与电子背散射衍射结果一致,显示出其在纳米尺度上的有效性。
- PIML辅助的同步辐射微衍射分析可推广至其他衍射技术,提高纳米级结构的表征能力。
点此查看论文截图

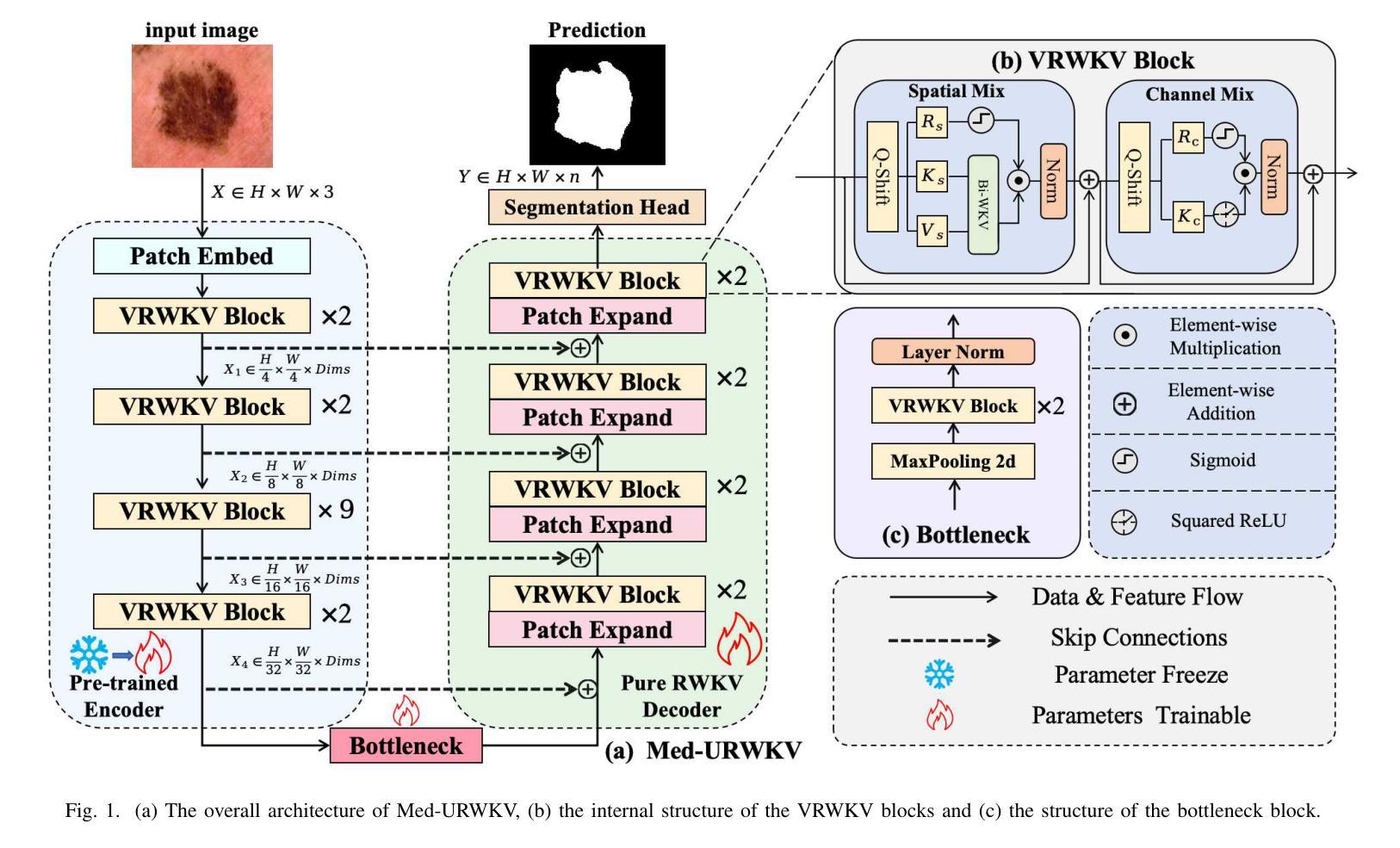
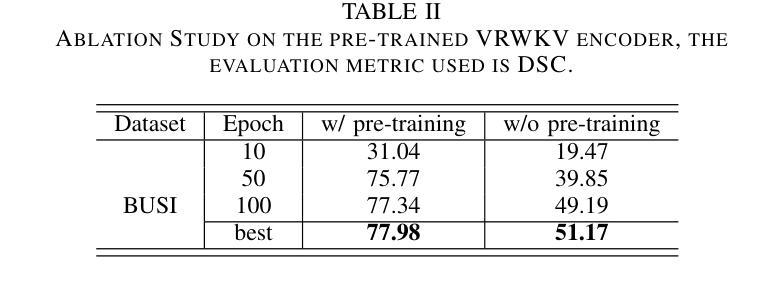
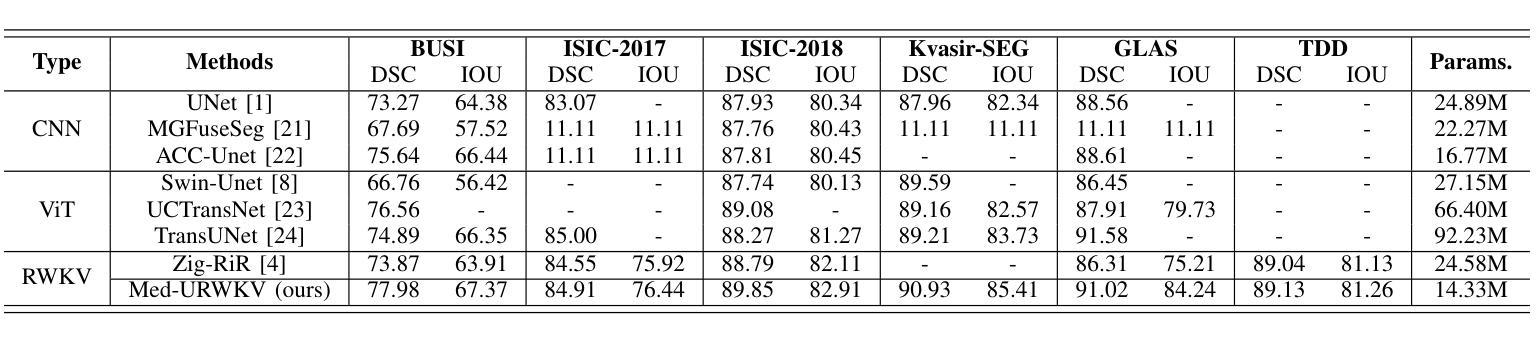
Med-URWKV: Pure RWKV With ImageNet Pre-training For Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Zhenhuan Zhou
Medical image segmentation is a fundamental and key technology in computer-aided diagnosis and treatment. Previous methods can be broadly classified into three categories: convolutional neural network (CNN) based, Transformer based, and hybrid architectures that combine both. However, each of them has its own limitations, such as restricted receptive fields in CNNs or the computational overhead caused by the quadratic complexity of Transformers. Recently, the Receptance Weighted Key Value (RWKV) model has emerged as a promising alternative for various vision tasks, offering strong long-range modeling capabilities with linear computational complexity. Some studies have also adapted RWKV to medical image segmentation tasks, achieving competitive performance. However, most of these studies focus on modifications to the Vision-RWKV (VRWKV) mechanism and train models from scratch, without exploring the potential advantages of leveraging pre-trained VRWKV models for medical image segmentation tasks. In this paper, we propose Med-URWKV, a pure RWKV-based architecture built upon the U-Net framework, which incorporates ImageNet-based pretraining to further explore the potential of RWKV in medical image segmentation tasks. To the best of our knowledge, Med-URWKV is the first pure RWKV segmentation model in the medical field that can directly reuse a large-scale pre-trained VRWKV encoder. Experimental results on seven datasets demonstrate that Med-URWKV achieves comparable or even superior segmentation performance compared to other carefully optimized RWKV models trained from scratch. This validates the effectiveness of using a pretrained VRWKV encoder in enhancing model performance. The codes will be released.
医学图像分割是计算机辅助诊断和治疗中的一项基本且关键的技术。之前的方法可以大致分为三类:基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的、基于Transformer的,以及结合两者的混合架构。然而,每一种方法都有其自身的局限性,例如CNN的受限感受野或Transformer的二次复杂性所带来的计算开销。最近,Receptance Weighted Key Value(RWKV)模型作为各种视觉任务的有前途的替代方案而出现,它具有强大的长程建模能力,并且具有线性的计算复杂性。一些研究也已经将RWKV适应于医学图像分割任务,并取得了有竞争力的性能。然而,大多数这些研究主要集中在修改Vision-RWKV(VRWKV)机制和从头开始训练模型上,而没有探索利用预训练的VRWKV模型在医学图像分割任务上的潜在优势。在本文中,我们提出了基于U-Net框架的纯RWKV架构Med-URWKV,并结合ImageNet进行预训练,以进一步探索RWKV在医学图像分割任务中的潜力。据我们所知,Med-URWKV是医学领域中首个可以直接利用大规模预训练VRWKV编码器的纯RWKV分割模型。在七个数据集上的实验结果表明,与从头开始训练的经过精心优化的其他RWKV模型相比,Med-URWKV的分割性能相当甚至更好。这验证了使用预训练的VRWKV编码器提高模型性能的有效性。代码将被公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint Draft, 5 pages. This paper will be updated with a formal version in the future, Copyright: College of Computer Science, Nankai University. All rights reserved
Summary
基于医学图像分割在计算机辅助诊断和治疗中的基础性和重要性,本文提出了Med-URWKV模型。该模型采用纯RWKV架构,基于U-Net框架构建,并融入ImageNet预训练技术,旨在探索RWKV在医学图像分割任务中的潜力。实验结果表明,与从头开始训练的RWKV模型相比,Med-URWKV在七个数据集上的分割性能相当甚至更优,验证了使用预训练VRWKV编码器提高模型性能的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割是计算机辅助诊断和治疗中的关键技术。
- 现有方法可分为CNN、Transformer和混合架构三类,但各有局限。
- RWKV模型具有强大的长程建模能力和线性计算复杂性,在多种视觉任务中表现出潜力。
- 研究开始尝试将RWKV模型应用于医学图像分割任务,并取得竞争性结果。
- Med-URWKV是纯RWKV架构,基于U-Net框架构建,融入ImageNet预训练技术。
- Med-URWKV是首个可直接利用大规模预训练VRWKV编码器的医学领域纯RWKV分割模型。
点此查看论文截图

Generalist Models in Medical Image Segmentation: A Survey and Performance Comparison with Task-Specific Approaches
Authors:Andrea Moglia, Matteo Leccardi, Matteo Cavicchioli, Alice Maccarini, Marco Marcon, Luca Mainardi, Pietro Cerveri
Following the successful paradigm shift of large language models, leveraging pre-training on a massive corpus of data and fine-tuning on different downstream tasks, generalist models have made their foray into computer vision. The introduction of Segment Anything Model (SAM) set a milestone on segmentation of natural images, inspiring the design of a multitude of architectures for medical image segmentation. In this survey we offer a comprehensive and in-depth investigation on generalist models for medical image segmentation. We start with an introduction on the fundamentals concepts underpinning their development. Then, we provide a taxonomy on the different declinations of SAM in terms of zero-shot, few-shot, fine-tuning, adapters, on the recent SAM 2, on other innovative models trained on images alone, and others trained on both text and images. We thoroughly analyze their performances at the level of both primary research and best-in-literature, followed by a rigorous comparison with the state-of-the-art task-specific models. We emphasize the need to address challenges in terms of compliance with regulatory frameworks, privacy and security laws, budget, and trustworthy artificial intelligence (AI). Finally, we share our perspective on future directions concerning synthetic data, early fusion, lessons learnt from generalist models in natural language processing, agentic AI and physical AI, and clinical translation.
随着大型语言模型的范式成功转变,通过在大规模数据集上进行预训练并在不同的下游任务上进行微调,通用模型已经渗透到计算机视觉领域。Segment Anything Model(SAM)的引入为自然图像分割树立了里程碑,激发了多种医疗图像分割架构的设计。在这篇综述中,我们对医疗图像分割的通用模型进行了全面深入的研究。首先介绍了支撑它们发展的基本概念。然后,我们根据零样本、少样本、微调、适配器、最近的SAM 2以及其他单独在图像上训练的创新模型等方面,对SAM的不同倾向进行了分类,以及其他同时训练文本和图像的模型。我们全面分析了它们在初级研究和文献最佳水平上的性能,并与最新的特定任务模型进行了严格比较。我们强调了需要解决合规性框架、隐私和安全法律、预算和可信人工智能(AI)等方面的挑战。最后,我们分享了关于合成数据、早期融合、从自然语言处理的通用模型中吸取的教训、智能主体和物理AI以及临床翻译的未来方向的看法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 132 pages, 26 figures, 23 tables. Andrea Moglia and Matteo Leccardi are equally contributing authors
Summary
通用模型在医学图像分割领域的应用研究综述。介绍了通用模型的基本原理和分类,包括零样本、少样本、微调、适配器等方法,对最近SAM 2和其他创新模型进行了深入探讨。对比了最新任务特定模型,强调了合规性、隐私和安全、预算和可信人工智能等挑战。展望未来发展方向。
Key Takeaways
- 通用模型在医学图像分割领域开始应用,基于大规模预训练数据和微调下游任务的成功模式。
- Segment Anything Model (SAM)为自然图像分割树立了里程碑,启发了多种医学图像分割架构的设计。
- 综述介绍了通用模型的基本原理和分类,包括零样本、少样本学习和微调等方法。
- 对SAM 2和其他创新模型进行了深入探讨,包括只针对图像训练的模型以及同时处理文本和图像的模型。
- 综述对比了最新任务特定模型,并强调了性能挑战。
- 指出需要解决合规性、隐私和安全、预算以及可信人工智能等挑战。
点此查看论文截图

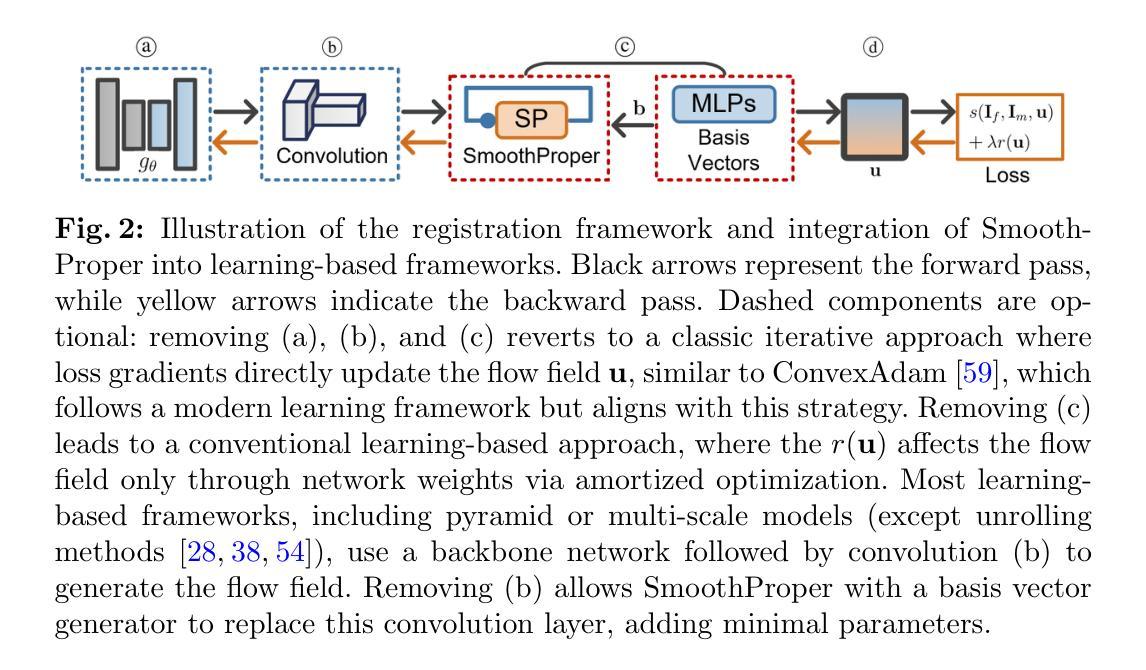
Unsupervised Deformable Image Registration with Structural Nonparametric Smoothing
Authors:Hang Zhang, Xiang Chen, Renjiu Hu, Rongguang Wang, Jinwei Zhang, Min Liu, Yaonan Wang, Gaolei Li, Xinxing Cheng, Jinming Duan
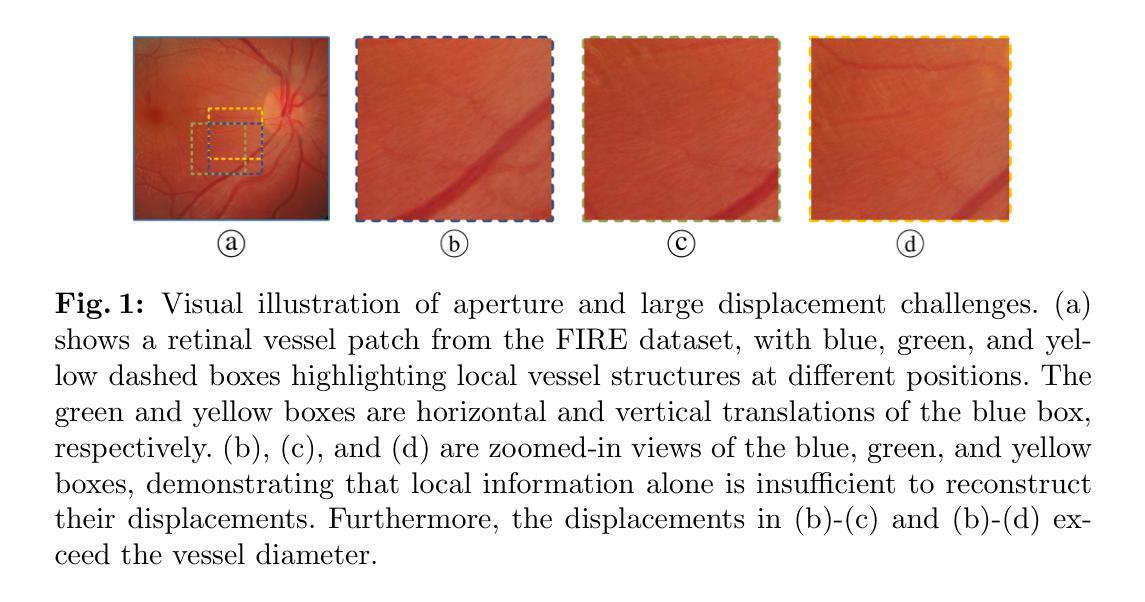
Learning-based deformable image registration (DIR) accelerates alignment by amortizing traditional optimization via neural networks. Label supervision further enhances accuracy, enabling efficient and precise nonlinear alignment of unseen scans. However, images with sparse features amid large smooth regions, such as retinal vessels, introduce aperture and large-displacement challenges that unsupervised DIR methods struggle to address. This limitation occurs because neural networks predict deformation fields in a single forward pass, leaving fields unconstrained post-training and shifting the regularization burden entirely to network weights. To address these issues, we introduce SmoothProper, a plug-and-play neural module enforcing smoothness and promoting message passing within the network’s forward pass. By integrating a duality-based optimization layer with tailored interaction terms, SmoothProper efficiently propagates flow signals across spatial locations, enforces smoothness, and preserves structural consistency. It is model-agnostic, seamlessly integrates into existing registration frameworks with minimal parameter overhead, and eliminates regularizer hyperparameter tuning. Preliminary results on a retinal vessel dataset exhibiting aperture and large-displacement challenges demonstrate our method reduces registration error to 1.88 pixels on 2912x2912 images, marking the first unsupervised DIR approach to effectively address both challenges. The source code will be available at https://github.com/tinymilky/SmoothProper.
基于学习的可变形图像配准(DIR)通过神经网络摊销传统优化来加速对齐。标签监督进一步提高准确性,实现对未见扫描的高效且精确的非线性对齐。然而,在大型平滑区域中特征稀疏的图像(例如视网膜血管)引入了孔径和大位移挑战,无监督DIR方法难以解决这些问题。这种局限性之所以会出现,是因为神经网络在单次前向传递中预测变形场,在训练后留下未约束的场,并将正则化负担完全转移到网络权重上。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了SmoothProper,这是一种即插即用的神经网络模块,可强制实施平滑并促进网络前向传递中的消息传递。通过集成基于双基优化的层以及量身定制的交互项,SmoothProper可以有效地跨空间位置传播流动信号,强制实施平滑性并保持结构一致性。它是模型无关的,无缝集成到现有的配准框架中,具有最少的参数开销,并消除了正则化超参数调整。在显示孔径和大位移挑战的视网膜血管数据集上的初步结果表明,我们的方法将配准误差减少到1.88像素(在2912x2912图像上),标志着第一个有效应对这两个挑战的无监督DIR方法。源代码将在https://github.com/tinymilky/SmoothProper上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI) 2025
Summary
基于学习的可变形图像配准(DIR)通过神经网络加速对齐,标签监督提高了准确性,实现了未见扫描的高效且精确的非线性对齐。然而,对于图像中稀疏特征和大平滑区域(如视网膜血管)的情况,存在孔径和大位移挑战,无监督DIR方法难以解决。为解决这些问题,我们推出SmoothProper,一个即插即用的神经网络模块,强制实施平滑并促进网络前向传递中的消息传递。通过集成基于双优化层的定制交互术语,SmoothProper有效地传播流信号,强制执行平滑操作并保留结构一致性。它是模型无关的,可无缝集成到现有的配准框架中,具有最小的参数开销,并消除了正则化超参数调整。初步结果显示,我们的方法在解决孔径和大位移挑战的视网膜血管数据集上,将注册误差减少到2912x2912图像的1.88像素。
Key Takeaways
- 学习型可变形图像配准(DIR)通过神经网络加速图像对齐过程。
- 标签监督进一步提高配准准确性和效率。
- 在具有稀疏特征和大平滑区域的图像中,存在孔径和大位移的配准挑战。
- 无监督DIR方法在处理这些挑战时遇到困难。
- SmoothProper是一个新的神经网络模块,强制实施平滑并促进网络内的消息传递。
- SmoothProper通过集成双优化层和定制交互术语来有效传播流信号、强制执行平滑操作并保留结构一致性。
点此查看论文截图

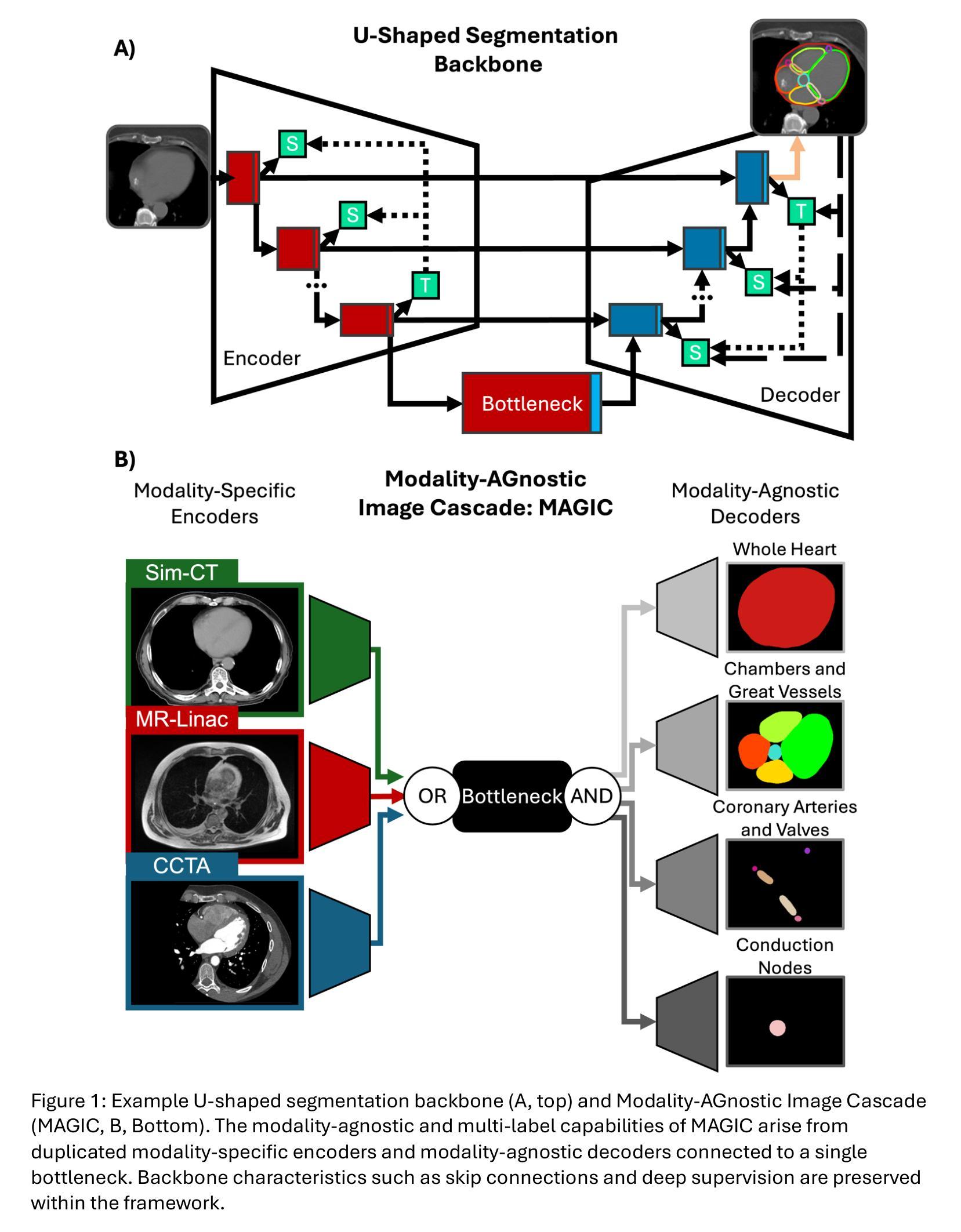
Modality-AGnostic Image Cascade (MAGIC) for Multi-Modality Cardiac Substructure Segmentation
Authors:Nicholas Summerfield, Qisheng He, Alex Kuo, Ahmed I. Ghanem, Simeng Zhu, Chase Ruff, Joshua Pan, Anudeep Kumar, Prashant Nagpal, Jiwei Zhao, Ming Dong, Carri K. Glide-Hurst
Cardiac substructures are essential in thoracic radiation therapy planning to minimize risk of radiation-induced heart disease. Deep learning (DL) offers efficient methods to reduce contouring burden but lacks generalizability across different modalities and overlapping structures. This work introduces and validates a Modality-AGnostic Image Cascade (MAGIC) for comprehensive and multi-modal cardiac substructure segmentation. MAGIC is implemented through replicated encoding and decoding branches of an nnU-Net-based, U-shaped backbone conserving the function of a single model. Twenty cardiac substructures (heart, chambers, great vessels (GVs), valves, coronary arteries (CAs), and conduction nodes) from simulation CT (Sim-CT), low-field MR-Linac, and cardiac CT angiography (CCTA) modalities were manually delineated and used to train (n=76), validate (n=15), and test (n=30) MAGIC. Twelve comparison models (four segmentation subgroups across three modalities) were equivalently trained. All methods were compared for training efficiency and against reference contours using the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and two-tailed Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test (threshold, p<0.05). Average DSC scores were 0.75(0.16) for Sim-CT, 0.68(0.21) for MR-Linac, and 0.80(0.16) for CCTA. MAGIC outperforms the comparison in 57% of cases, with limited statistical differences. MAGIC offers an effective and accurate segmentation solution that is lightweight and capable of segmenting multiple modalities and overlapping structures in a single model. MAGIC further enables clinical implementation by simplifying the computational requirements and offering unparalleled flexibility for clinical settings.
心脏子结构在胸部放射治疗计划中至关重要,旨在最小化辐射诱发心脏病的风险。深度学习(DL)提供了有效的方法来减少轮廓绘制的工作量,但缺乏跨不同模态和重叠结构的泛化能力。这项工作介绍并验证了一种模态无关的图像级联(MAGIC)技术,用于全面和多模态心脏子结构分割。MAGIC通过复制编码和解码分支实现,基于nnU-Net的U形主干保留单个模型的功能。从模拟CT(Sim-CT)、低场MR-Linac和心脏CT血管造影(CCTA)模态中手动界定二十个心脏子结构(心脏、心房、大血管(GVs)、瓣膜、冠状动脉(CAs)和传导节点),用于训练(n=76)、验证(n=15)和测试(n=30)MAGIC。等效训练了十二个对比模型(三个模态中的四个分割小组)。所有方法均比较了训练效率和参照轮廓,使用Dice相似系数(DSC)和双侧Wilcoxon符号秩检验(阈值p<0.05)。Sim-CT的平均DSC得分为0.75(0.16),MR-Linac为0.68(0.21),CCTA为0.80(0.16)。在大多数情况下,MAGIC的表现优于对比模型,且差异在统计学上有限。MAGIC提供了一种有效且准确的分割解决方案,该方案轻巧且能够在单个模型中分割多种模态和重叠结构。此外,MAGIC通过简化计算要求并提供前所未有的临床灵活性,从而实现了临床实施。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究引入并验证了一种跨模态的心脏亚结构分割方法——Modality-AGnostic Image Cascade(MAGIC)。该方法通过单一模型实现多模态心脏亚结构分割,提高了训练效率和分割准确性,有助于减少辐射疗法中心脏疾病的风险。
Key Takeaways
- 心脏亚结构在胸部放射治疗计划中起到重要作用,有助于减少辐射引发的心脏疾病风险。
- 深度学习在心脏亚结构分割中具有效率,但缺乏跨不同模态和重叠结构的通用性。
- MAGIC方法通过单一模型实现多模态心脏亚结构分割,提高了分割准确性。
- MAGIC通过引入复制编码和解码分支的nnU-Net基U型主干网络实现。
- 在模拟CT、低场MR-Linac和心脏CT血管造影(CCTA)三种模态下对MAGIC进行了训练和测试。
- 与其他模型相比,MAGIC在多数情况下表现更佳,并且在统计上无显著差异。
点此查看论文截图

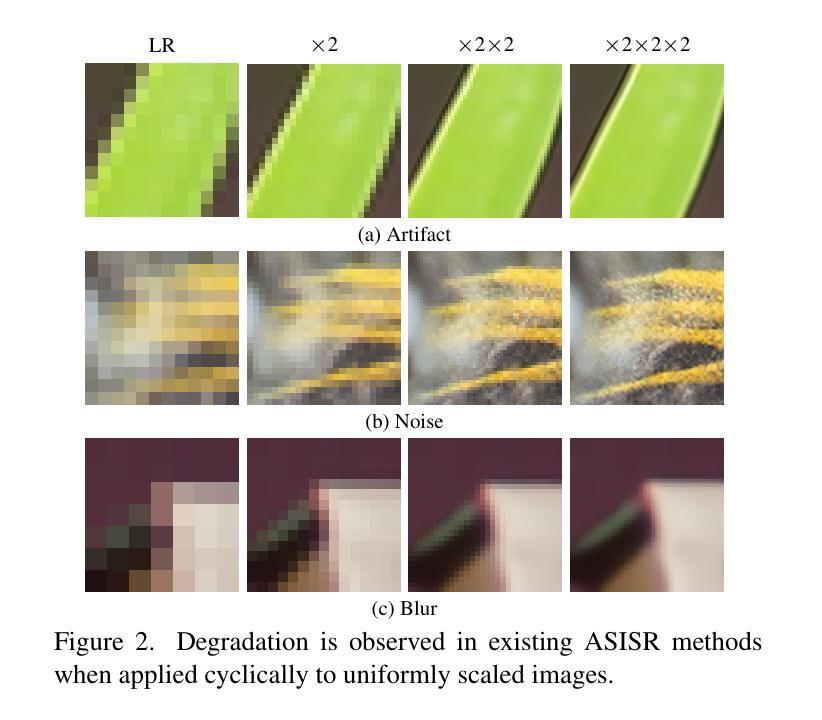
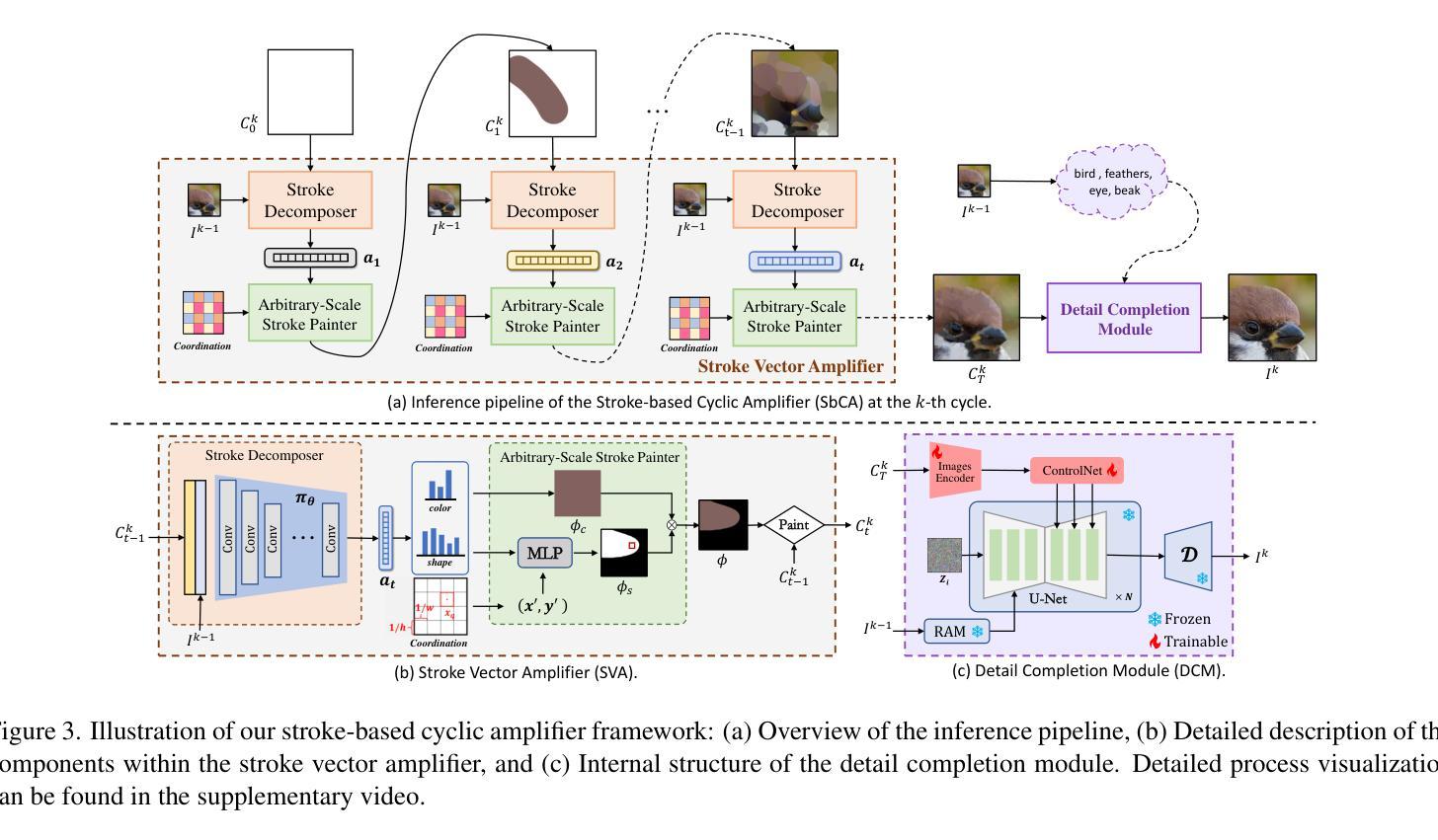
Stroke-based Cyclic Amplifier: Image Super-Resolution at Arbitrary Ultra-Large Scales
Authors:Wenhao Guo, Peng Lu, Xujun Peng, Zhaoran Zhao, Sheng Li
Prior Arbitrary-Scale Image Super-Resolution (ASISR) methods often experience a significant performance decline when the upsampling factor exceeds the range covered by the training data, introducing substantial blurring. To address this issue, we propose a unified model, Stroke-based Cyclic Amplifier (SbCA), for ultra-large upsampling tasks. The key of SbCA is the stroke vector amplifier, which decomposes the image into a series of strokes represented as vector graphics for magnification. Then, the detail completion module also restores missing details, ensuring high-fidelity image reconstruction. Our cyclic strategy achieves ultra-large upsampling by iteratively refining details with this unified SbCA model, trained only once for all, while keeping sub-scales within the training range. Our approach effectively addresses the distribution drift issue and eliminates artifacts, noise and blurring, producing high-quality, high-resolution super-resolved images. Experimental validations on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing methods in ultra-large upsampling tasks (e.g. $\times100$), delivering visual quality far superior to state-of-the-art techniques.
先前的任意尺度图像超分辨率(ASISR)方法,在放大倍数超过训练数据覆盖的范围时,常常会遇到性能显著下降的问题,导致图像出现严重的模糊。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种针对超大型放大任务的统一模型——基于描线的循环放大器(SbCA)。SbCA的关键是描线向量放大器,它将图像分解成一系列描线矢量图形来进行放大。然后,细节完成模块恢复缺失的细节,确保高保真度的图像重建。我们的循环策略通过迭代细化细节来实现超大型放大,只需训练一次这个统一的SbCA模型,同时保持子尺度在训练范围内。我们的方法有效地解决了分布漂移问题,消除了伪影、噪声和模糊,生成高质量、高分辨率的超分辨率图像。在合成数据集和真实世界数据集上的实验验证表明,我们的方法在超大型放大任务(例如×100)上显著优于现有方法,提供了远超最新技术的视觉质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于矢量放大的统一模型Stroke-based Cyclic Amplifier(SbCA),用于超分辨率放大任务,特别是超大型放大任务。该模型能够分解图像并生成矢量图形进行放大,同时修复缺失的细节,保证高保真度的图像重建。实验验证显示,该模型在处理合成数据集和实际数据集时表现优越,尤其是在超大倍率上采样任务中远超现有方法,显著提升视觉质量。
Key Takeaways
- SbCA模型解决了之前方法在处理超过训练数据范围的上采样因子时性能下降的问题。
- SbCA模型采用矢量放大的方式分解图像,并采用细节补全模块恢复缺失细节。
- 循环策略通过迭代优化细节实现了超大型上采样任务的高分辨率图像重建。
- SbCA模型仅进行一次训练,便可以适应各种尺度的放大任务。
- 该模型解决了分布漂移问题,消除了伪影、噪声和模糊现象。
- 实验验证显示SbCA模型在合成和真实数据集上均显著优于现有方法,特别是在超大倍率上采样任务中表现突出。
点此查看论文截图

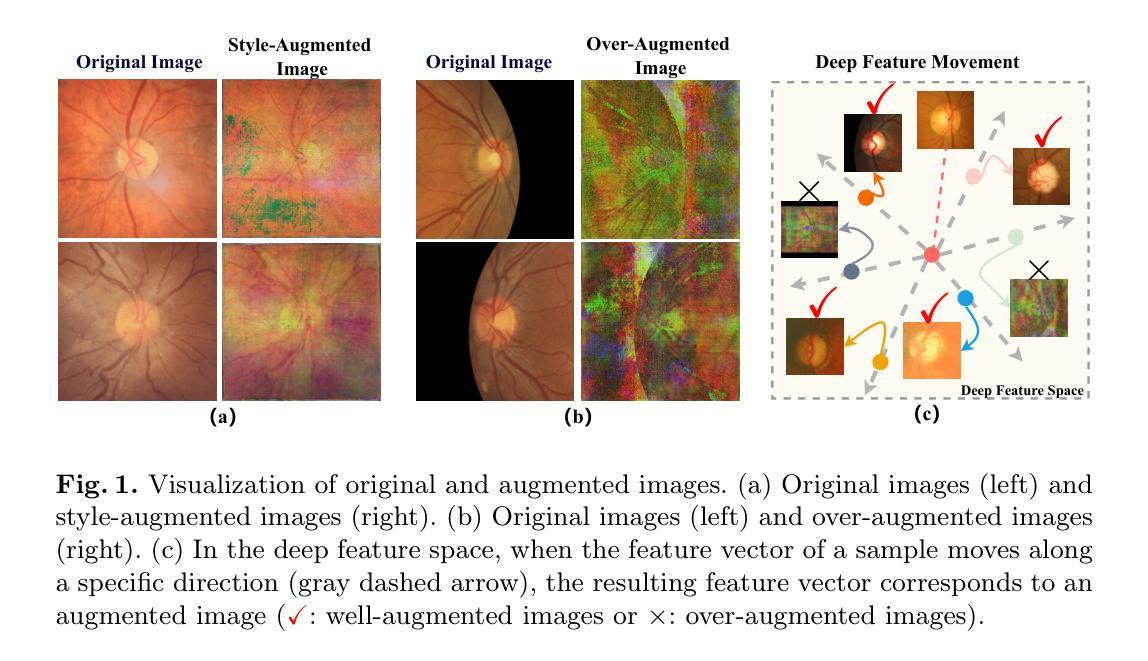
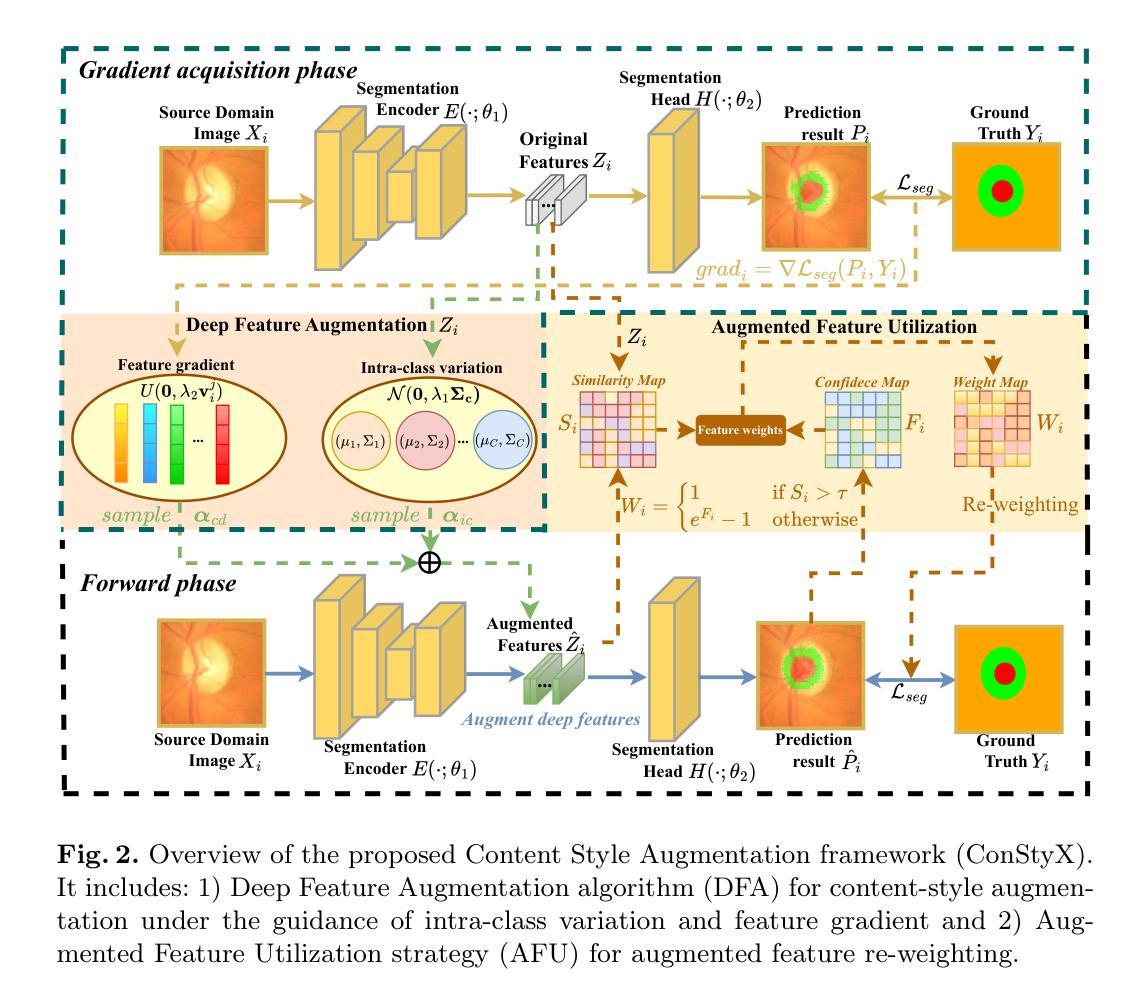
ConStyX: Content Style Augmentation for Generalizable Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Xi Chen, Zhiqiang Shen, Peng Cao, Jinzhu Yang, Osmar R. Zaiane
Medical images are usually collected from multiple domains, leading to domain shifts that impair the performance of medical image segmentation models. Domain Generalization (DG) aims to address this issue by training a robust model with strong generalizability. Recently, numerous domain randomization-based DG methods have been proposed. However, these methods suffer from the following limitations: 1) constrained efficiency of domain randomization due to their exclusive dependence on image style perturbation, and 2) neglect of the adverse effects of over-augmented images on model training. To address these issues, we propose a novel domain randomization-based DG method, called content style augmentation (ConStyX), for generalizable medical image segmentation. Specifically, ConStyX 1) augments the content and style of training data, allowing the augmented training data to better cover a wider range of data domains, and 2) leverages well-augmented features while mitigating the negative effects of over-augmented features during model training. Extensive experiments across multiple domains demonstrate that our ConStyX achieves superior generalization performance. The code is available at https://github.com/jwxsp1/ConStyX.
医学图像通常来自多个领域,导致领域偏移,从而影响医学图像分割模型的性能。领域泛化(DG)旨在通过训练具有强大泛化能力的模型来解决这个问题。最近,已经提出了许多基于领域随机化的DG方法。然而,这些方法存在以下局限性:1)由于它们对图像风格扰动的专属依赖性,领域随机化的效率受限;2)忽视了过度增强图像对模型训练的负面影响。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型的基于领域随机化的DG方法,称为内容风格增强(ConStyX),用于通用医学图像分割。具体来说,ConStyX 1)增强训练数据的内容和风格,使增强后的训练数据更好地覆盖更广泛的数据领域;2)在模型训练过程中利用增强良好的特征,同时减轻过度增强特征的负面影响。在多个领域的广泛实验表明,我们的ConStyX实现了卓越的泛化性能。代码可在https://github.com/jwxsp1/ConStyX获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像多源域采集导致的域偏移会影响医学图像分割模型的性能。为解决这个问题,研究者提出通过域泛化(Domain Generalization,DG)训练具有强泛化能力的模型。尽管现有许多基于域随机化的DG方法,但它们存在局限性:1)依赖于图像风格扰动,效率受限;2)忽视过度增强图像对模型训练的负面影响。为解决这些问题,提出一种新型基于域随机化的DG方法——内容风格增强(ConStyX),用于通用医学图像分割。ConStyX既能增强训练数据的内容和风格,使增强数据更好地覆盖更广泛的数据域,又能在模型训练中利用良好增强的特征,同时减轻过度增强特征的负面影响。在多个域上的广泛实验证明,ConStyX实现了优异的泛化性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像多源域采集会导致域偏移,影响医学图像分割模型的性能。
- 域泛化(DG)是训练具有强泛化能力的模型以解决这个问题的方法。
- 现有的基于域随机化的DG方法存在效率受限和忽视过度增强图像的问题。
- 提出了一种新型基于域随机化的DG方法——内容风格增强(ConStyX)。
- ConStyX通过增强训练数据的内容和风格,使增强数据覆盖更广泛的数据域。
- ConStyX在模型训练中利用良好增强的特征,并减轻过度增强特征的负面影响。
- 在多个域上的实验证明,ConStyX实现了优异的泛化性能。
点此查看论文截图

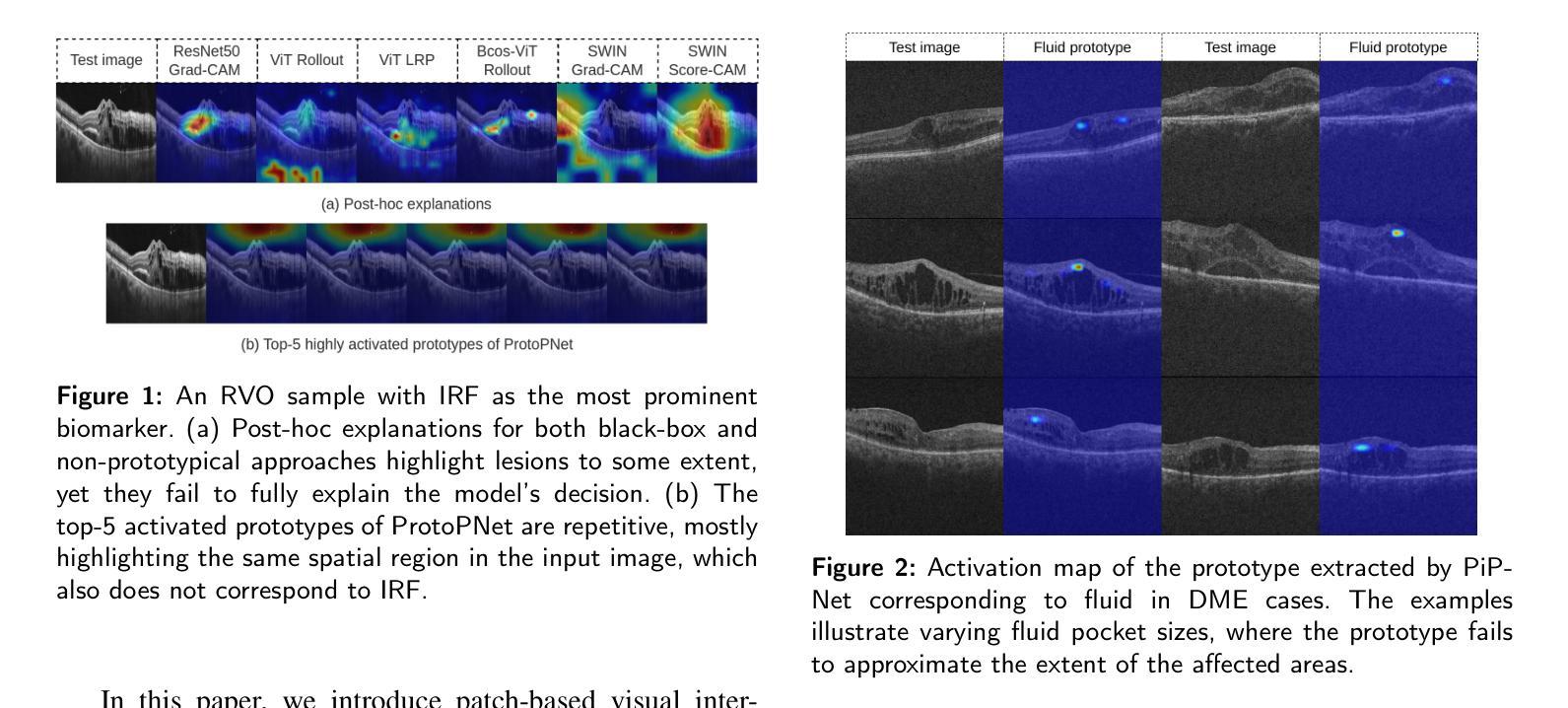
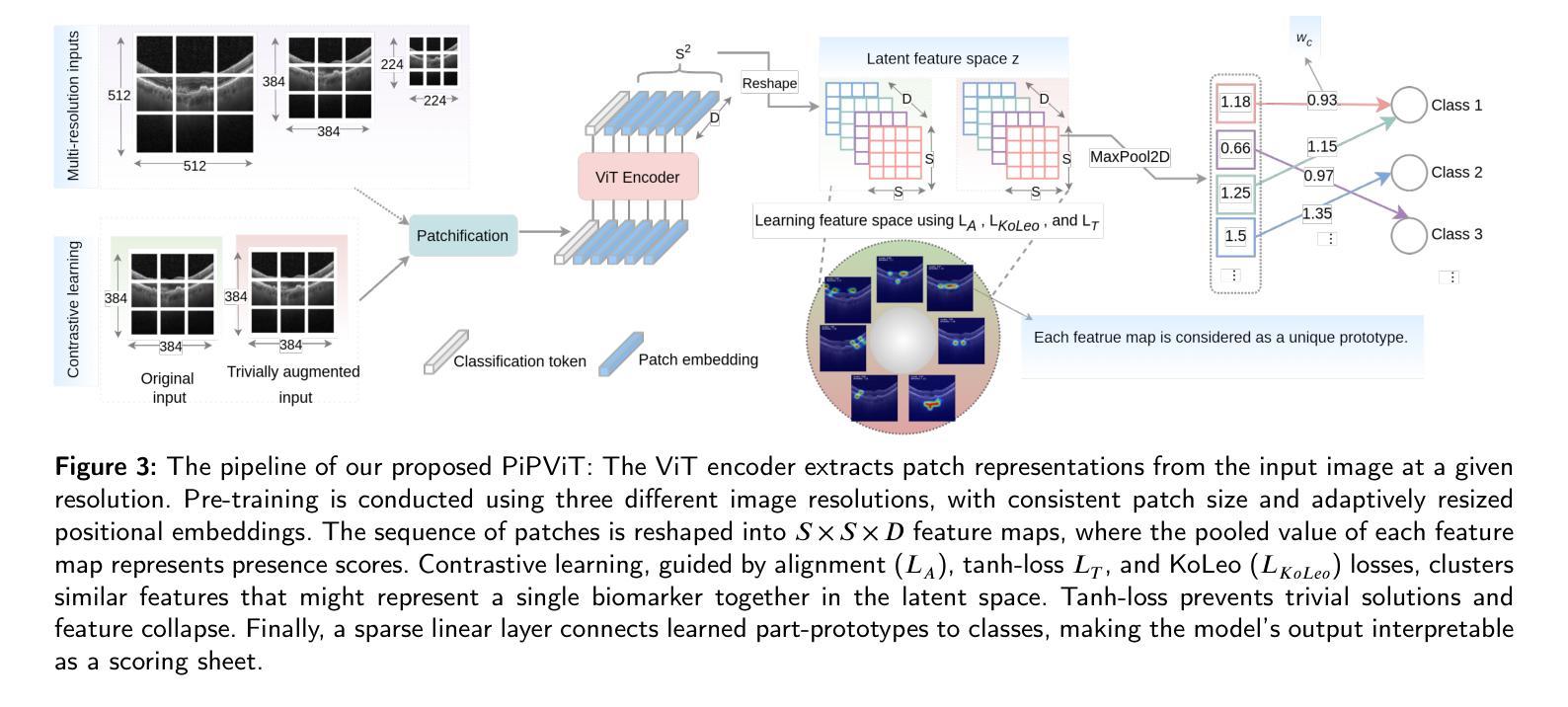
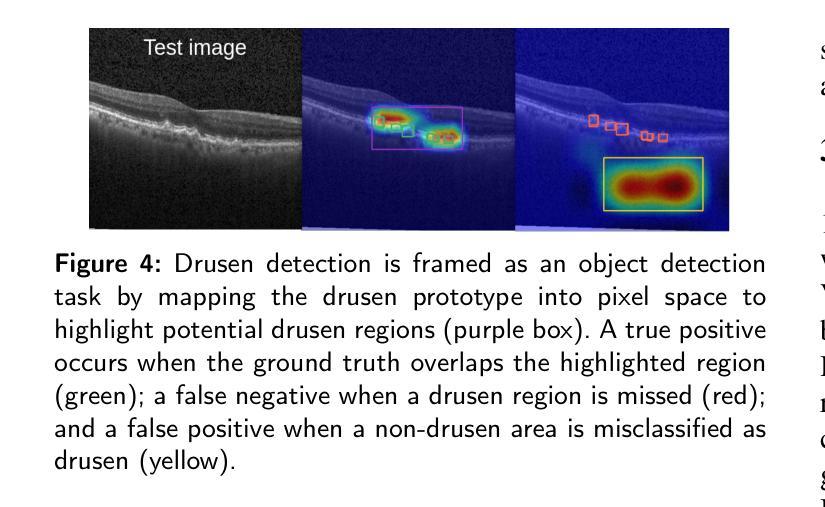
PiPViT: Patch-based Visual Interpretable Prototypes for Retinal Image Analysis
Authors:Marzieh Oghbaie, Teresa Araújoa, Hrvoje Bogunović
Background and Objective: Prototype-based methods improve interpretability by learning fine-grained part-prototypes; however, their visualization in the input pixel space is not always consistent with human-understandable biomarkers. In addition, well-known prototype-based approaches typically learn extremely granular prototypes that are less interpretable in medical imaging, where both the presence and extent of biomarkers and lesions are critical. Methods: To address these challenges, we propose PiPViT (Patch-based Visual Interpretable Prototypes), an inherently interpretable prototypical model for image recognition. Leveraging a vision transformer (ViT), PiPViT captures long-range dependencies among patches to learn robust, human-interpretable prototypes that approximate lesion extent only using image-level labels. Additionally, PiPViT benefits from contrastive learning and multi-resolution input processing, which enables effective localization of biomarkers across scales. Results: We evaluated PiPViT on retinal OCT image classification across four datasets, where it achieved competitive quantitative performance compared to state-of-the-art methods while delivering more meaningful explanations. Moreover, quantitative evaluation on a hold-out test set confirms that the learned prototypes are semantically and clinically relevant. We believe PiPViT can transparently explain its decisions and assist clinicians in understanding diagnostic outcomes. Github page: https://github.com/marziehoghbaie/PiPViT
背景与目标:基于原型的方法通过学习精细粒度的部分原型来提高可解释性,但是它们在输入像素空间的可视化并不总是与可被人理解的生物标志物相一致。此外,众所周知的基于原型的方法通常会学习非常精细的原型,在医学成像中不太容易解释,其中生物标志物和病变的存在和程度都至关重要。方法:为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了PiPViT(基于补丁的视觉可解释原型),这是一种用于图像识别的固有可解释原型模型。借助视觉变压器(ViT),PiPViT捕获补丁之间的长程依赖性,学习稳健的、可被人解释的原型,仅使用图像级标签来近似病变程度。此外,PiPViT受益于对比学习和多分辨率输入处理,这能够实现跨尺度的生物标志物有效定位。结果:我们在四个数据集上对PiPViT进行了视网膜OCT图像分类评估,与最先进的方法相比,它取得了具有竞争力的定量性能,同时提供了更有意义的解释。此外,在独立测试集上的定量评估证实,所学习的原型在语义和临床上都具有相关性。我们相信PiPViT能够透明地解释其决策,并帮助临床医生理解诊断结果。GitHub页面:https://github.com/marziehoghbaie/PiPViT
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
PiPViT模型通过捕捉图像补丁间的长期依赖关系,学习稳健、可解释的原型,以图像级标签近似病变程度,解决原型可视化与人理解不一致的问题。该模型在视网膜OCT图像分类上表现优异,同时提供有意义的解释。
Key Takeaways
- PiPViT模型利用视觉变压器(ViT)学习稳健、可解释的原型,提高模型的可解释性。
- 该模型通过捕捉补丁间的长期依赖关系,提高原型在医学图像中的可解释性。
- PiPViT利用对比学习和多分辨率输入处理,有效定位不同尺度的生物标志物。
- 模型在视网膜OCT图像分类任务上表现优异,具有竞争力的定量性能。
- 学习到的原型具有语义和临床相关性,有助于临床医生理解诊断结果。
- PiPViT模型提供透明的决策解释,有助于增强医学图像分析的信任度。
点此查看论文截图

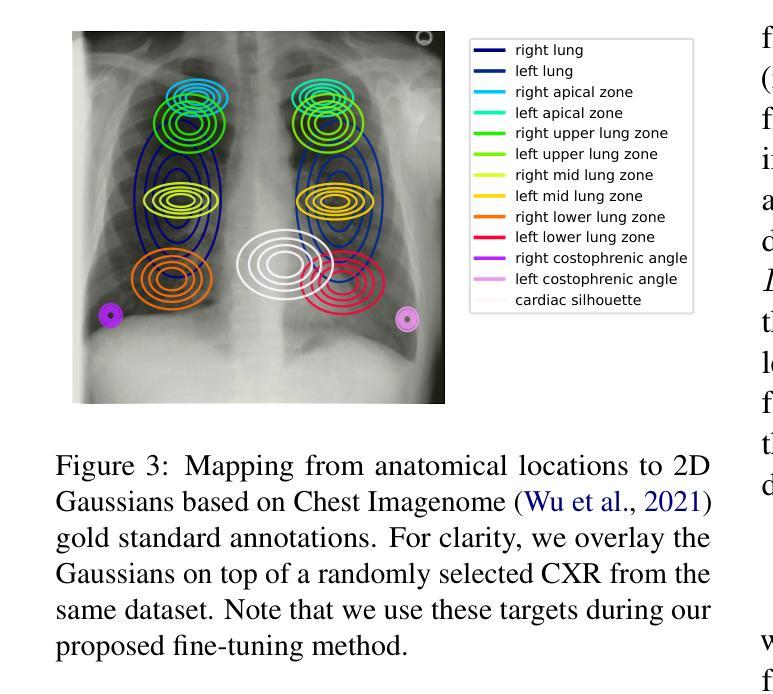
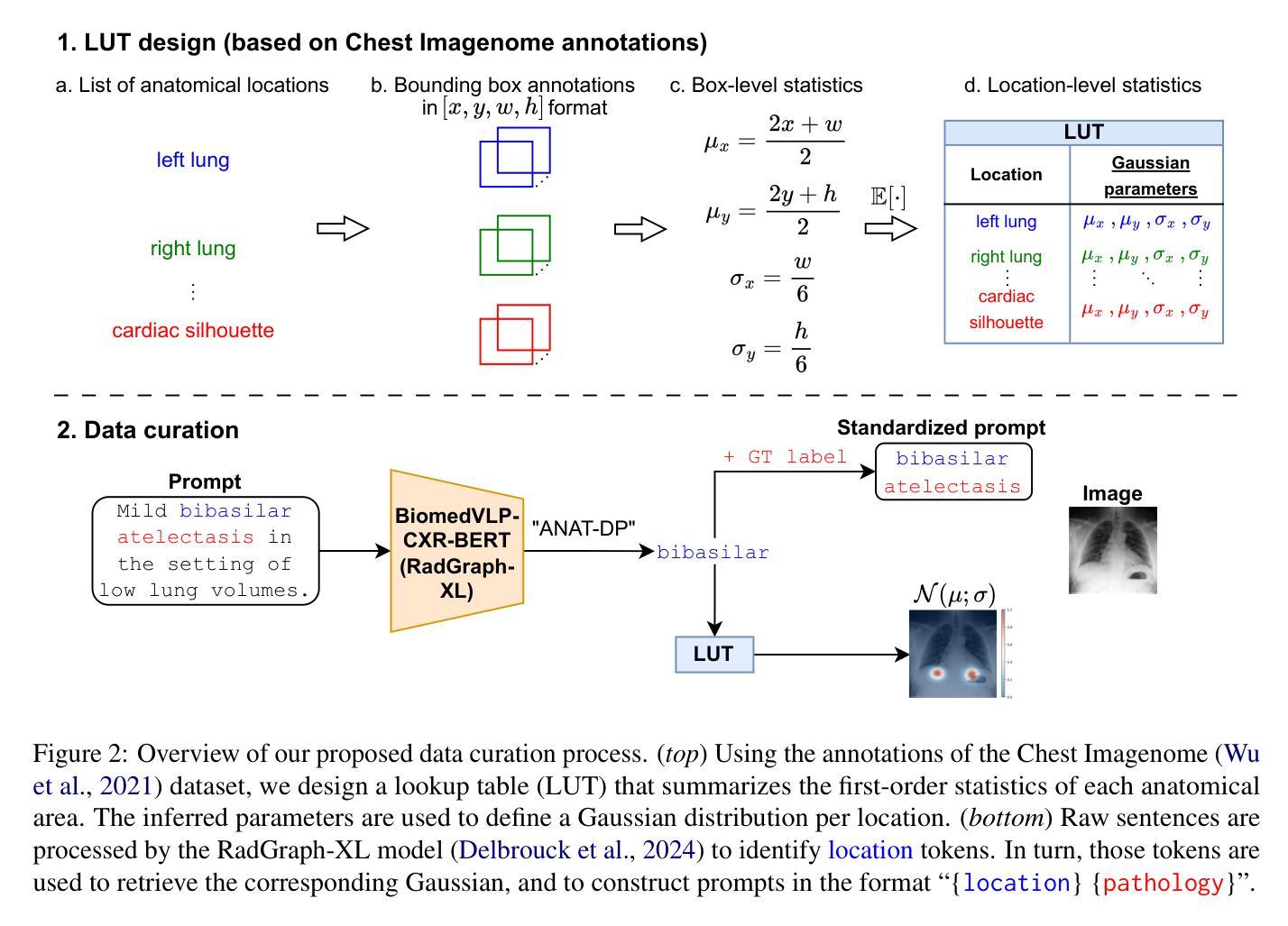
Anatomy-Grounded Weakly Supervised Prompt Tuning for Chest X-ray Latent Diffusion Models
Authors:Konstantinos Vilouras, Ilias Stogiannidis, Junyu Yan, Alison Q. O’Neil, Sotirios A. Tsaftaris
Latent Diffusion Models have shown remarkable results in text-guided image synthesis in recent years. In the domain of natural (RGB) images, recent works have shown that such models can be adapted to various vision-language downstream tasks with little to no supervision involved. On the contrary, text-to-image Latent Diffusion Models remain relatively underexplored in the field of medical imaging, primarily due to limited data availability (e.g., due to privacy concerns). In this work, focusing on the chest X-ray modality, we first demonstrate that a standard text-conditioned Latent Diffusion Model has not learned to align clinically relevant information in free-text radiology reports with the corresponding areas of the given scan. Then, to alleviate this issue, we propose a fine-tuning framework to improve multi-modal alignment in a pre-trained model such that it can be efficiently repurposed for downstream tasks such as phrase grounding. Our method sets a new state-of-the-art on a standard benchmark dataset (MS-CXR), while also exhibiting robust performance on out-of-distribution data (VinDr-CXR). Our code will be made publicly available.
近年来,潜在扩散模型在文本引导的图像合成中取得了显著成果。在自然(RGB)图像领域,近期的研究表明,这种模型可以适应各种视觉语言下游任务,几乎不需要监督。相反,在医学成像领域,文本到图像的潜在扩散模型仍然相对未被充分探索,这主要是因为数据可用性的限制(例如,由于隐私担忧)。在这项工作中,我们重点关注胸部X射线模式。首先,我们证明标准的文本条件潜在扩散模型还没有学会将自由文本放射学报告中的临床相关信息与给定扫描的相应区域对齐。为了缓解这个问题,我们提出了一个微调框架,以改进预训练模型中的多模式对齐,使其能够高效地用于下游任务,如短语定位。我们的方法在标准数据集(MS-CXR)上达到了最新技术水平,并在非分布数据(VinDr-CXR)上表现出稳健的性能。我们的代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 6 figures
Summary
近期研究显示,潜扩散模型在文本引导的图像合成中表现出卓越的效果。在自然图像领域,该模型可轻松适应多种视觉语言下游任务,几乎无需监督。然而,在医学成像领域,由于数据有限(例如,隐私担忧),文本到图像的潜扩散模型研究相对较少。本研究专注于胸部X射线模态,首先证明标准的文本条件潜扩散模型尚未学会将自由文本放射学报告中的临床相关信息与给定扫描的区域对齐。为解决这一问题,我们提出一种微调框架,以改进预训练模型的多模式对齐,使其能够高效用于下游任务,如短语定位。该方法在标准数据集上达到了最新水平(MS-CXR),并在非分布数据上表现出稳健的性能(VinDr-CXR)。我们的代码将公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- 潜扩散模型在文本引导的图像合成中表现卓越,尤其在自然图像领域。
- 潜扩散模型在医学成像领域的应用相对较少,主要由于数据有限(如隐私担忧)。
- 针对胸部X射线模态,标准的文本条件潜扩散模型尚未学会将临床相关信息与扫描区域对齐。
- 提出一种微调框架,用于改进预训练模型的多模式对齐。
- 该方法能在下游任务(如短语定位)中高效应用。
- 该方法在标准数据集MS-CXR上达到了最新水平。
点此查看论文截图

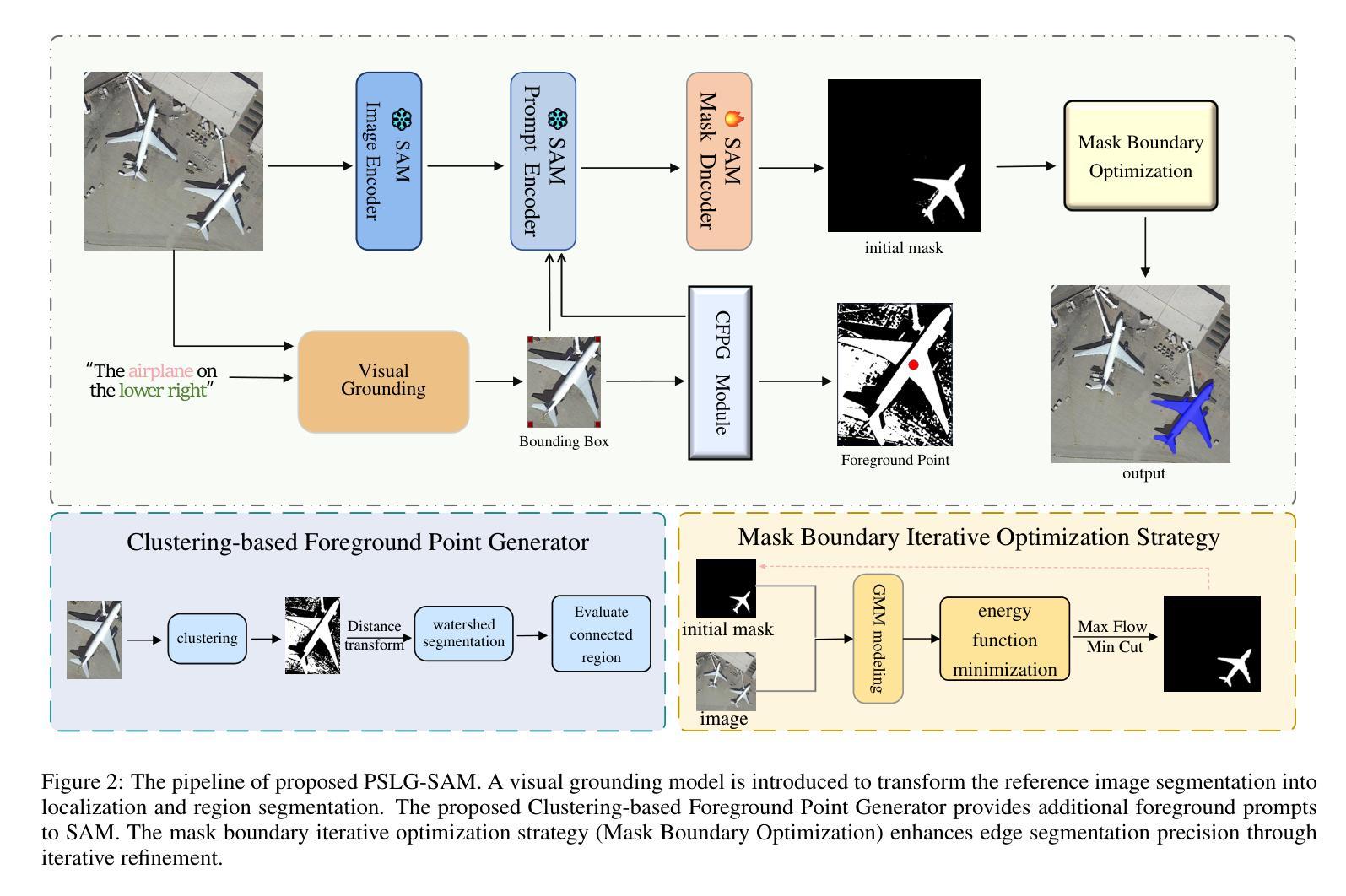
Semantic Localization Guiding Segment Anything Model For Reference Remote Sensing Image Segmentation
Authors:Shuyang Li, Shuang Wang, Zhuangzhuang Sun, Jing Xiao
The Reference Remote Sensing Image Segmentation (RRSIS) task generates segmentation masks for specified objects in images based on textual descriptions, which has attracted widespread attention and research interest. Current RRSIS methods rely on multi-modal fusion backbones and semantic segmentation heads but face challenges like dense annotation requirements and complex scene interpretation. To address these issues, we propose a framework named \textit{prompt-generated semantic localization guiding Segment Anything Model}(PSLG-SAM), which decomposes the RRSIS task into two stages: coarse localization and fine segmentation. In coarse localization stage, a visual grounding network roughly locates the text-described object. In fine segmentation stage, the coordinates from the first stage guide the Segment Anything Model (SAM), enhanced by a clustering-based foreground point generator and a mask boundary iterative optimization strategy for precise segmentation. Notably, the second stage can be train-free, significantly reducing the annotation data burden for the RRSIS task. Additionally, decomposing the RRSIS task into two stages allows for focusing on specific region segmentation, avoiding interference from complex scenes.We further contribute a high-quality, multi-category manually annotated dataset. Experimental validation on two datasets (RRSIS-D and RRSIS-M) demonstrates that PSLG-SAM achieves significant performance improvements and surpasses existing state-of-the-art models.Our code will be made publicly available.
遥感图像参考分割(RRSIS)任务基于文本描述为图像中的指定对象生成分割掩膜,这引起了广泛的关注和研究兴趣。当前的RRSIS方法依赖于多模态融合主干和语义分割头,但面临着密集注释要求和复杂场景解释等挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种名为“提示生成语义定位引导分割任何模型”(PSLG-SAM)的框架,它将RRSIS任务分解为两个阶段:粗略定位和精细分割。在粗略定位阶段,视觉定位网络大致定位文本描述的对象。在精细分割阶段,第一阶段的坐标引导分割任何模型(SAM),通过基于聚类的前景点生成器和用于精确分割的掩膜边界迭代优化策略进行增强。值得注意的是,第二阶段可以无训练地运行,显著减少了RRSIS任务的标注数据负担。此外,将RRSIS任务分解为两个阶段允许专注于特定区域分割,避免复杂场景的干扰。我们还贡献了一个高质量、多类别的手动注释数据集。在两个数据集(RRSIS-D和RRSIS-M)上的实验验证表明,PSLG-SAM实现了显著的性能改进并超越了现有的最先进的模型。我们的代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在遥感图像分割任务中,文本描述的对象生成分割掩膜是一项挑战。为应对挑战,我们提出了一个名为PSLG-SAM的框架,分为粗定位和精细分割两个阶段。粗定位阶段通过视觉定位网络粗略定位文本描述的对象,精细分割阶段利用第一阶段坐标指导分割任何事情模型(SAM),通过聚类生成前景点和掩膜边界优化策略实现精确分割。该框架可减少标注数据负担,并能在复杂场景中避免干扰。我们在两个数据集上验证了PSLG-SAM的性能,并公开了代码。
Key Takeaways
- RRSIS任务需根据文本描述生成图像中指定对象的分割掩膜,具有挑战性。
- 当前方法依赖于多模态融合和语义分割技术,面临密集标注和复杂场景解读的挑战。
- 提出PSLG-SAM框架,分为粗定位和精细分割两个阶段来解决上述问题。
- 粗定位阶段通过视觉定位网络定位对象,精细分割阶段利用坐标指导SAM模型进行精确分割。
- 第二阶段可无需训练,显著减少标注数据负担。
- 分解任务有助于聚焦特定区域分割,避免复杂场景的干扰。
点此查看论文截图


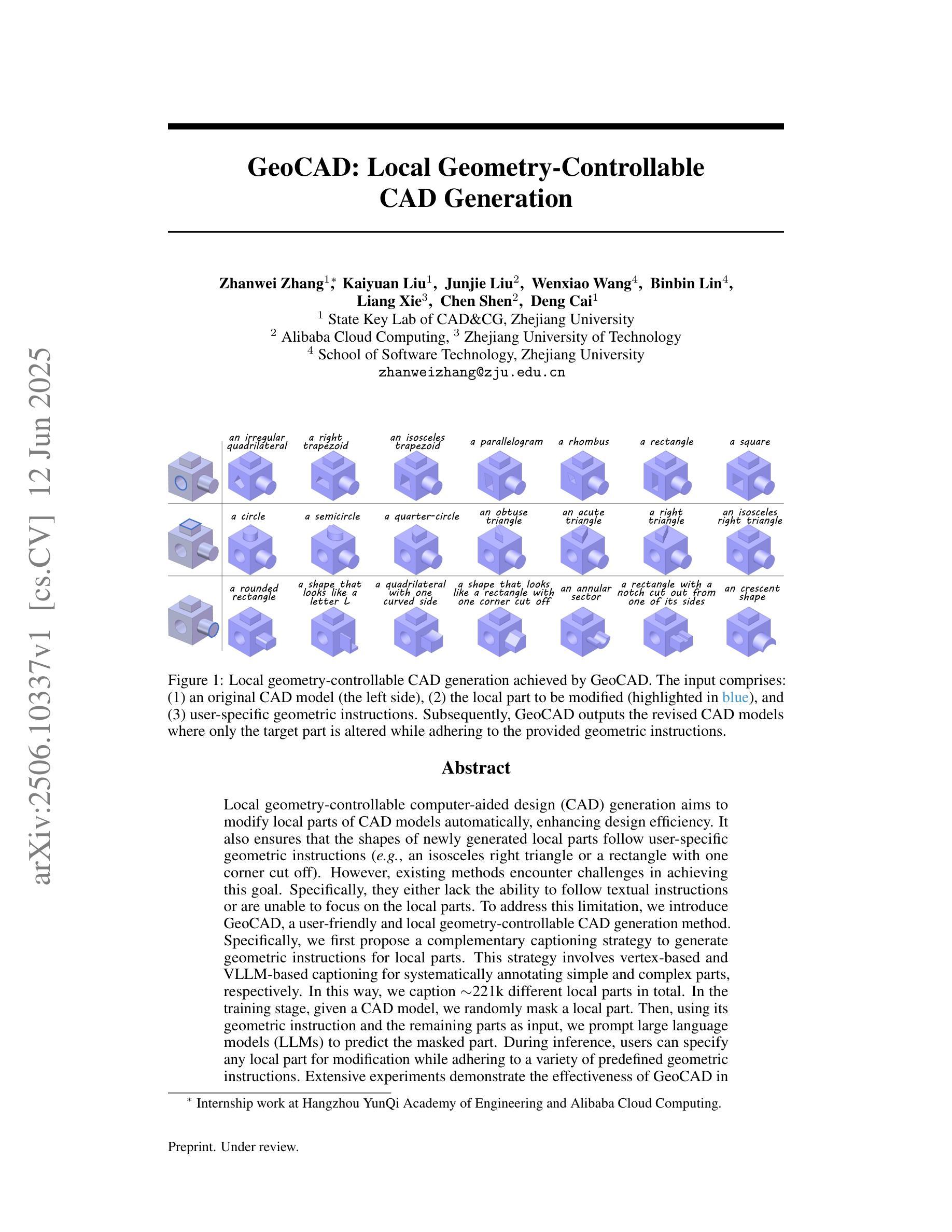
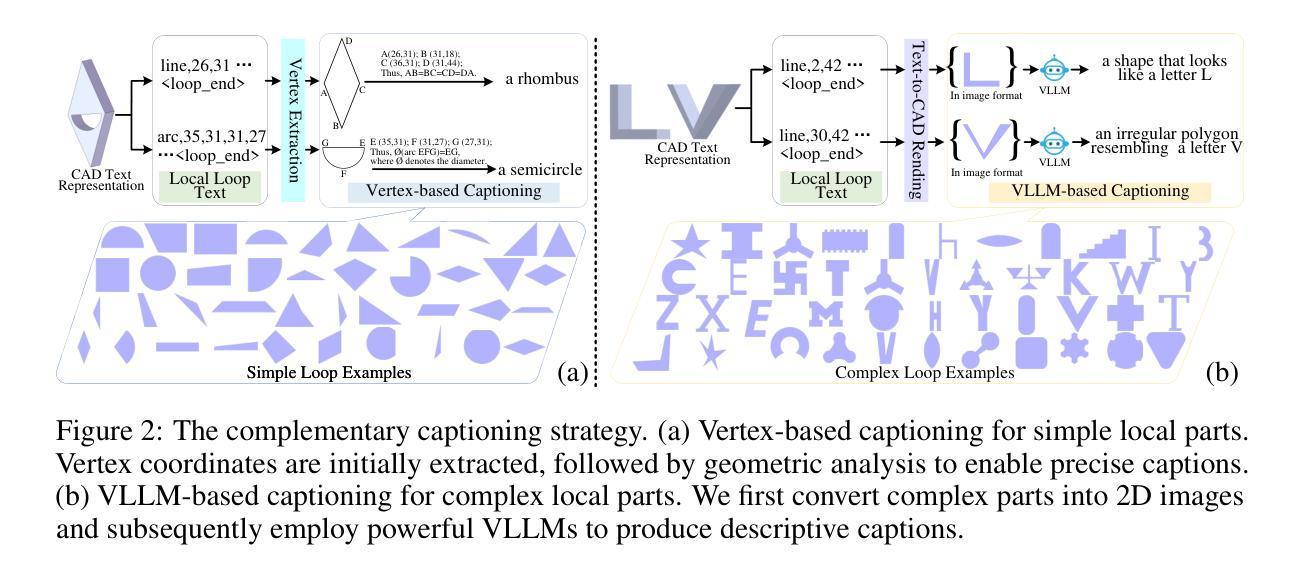
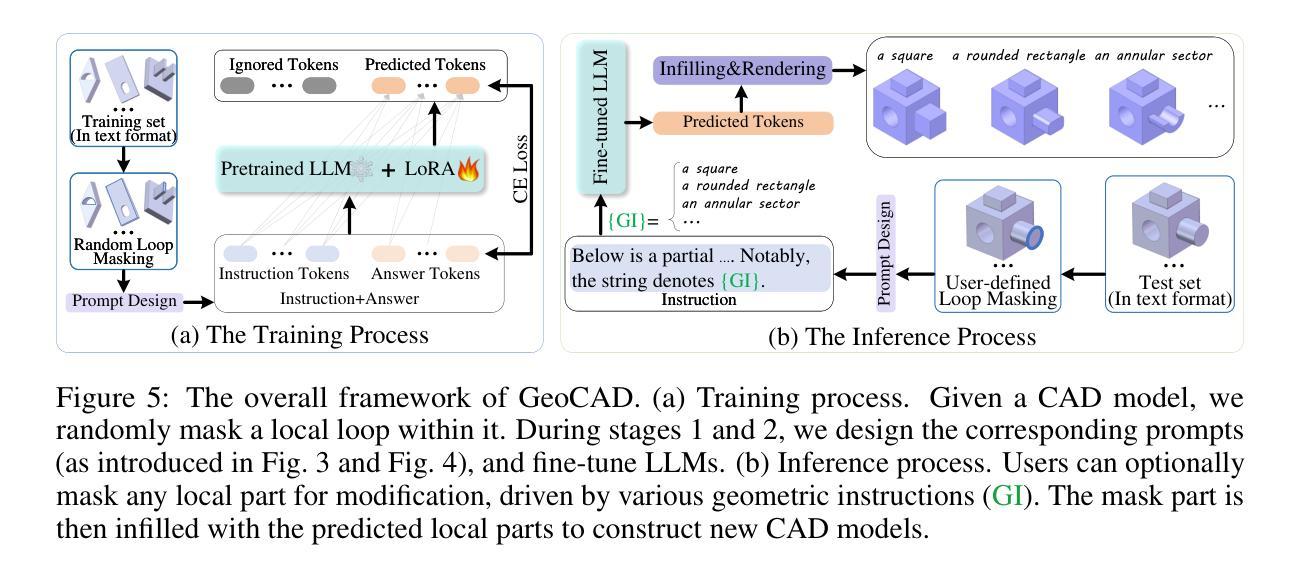
GeoCAD: Local Geometry-Controllable CAD Generation
Authors:Zhanwei Zhang, Kaiyuan Liu, Junjie Liu, Wenxiao Wang, Binbin Lin, Liang Xie, Chen Shen, Deng Cai
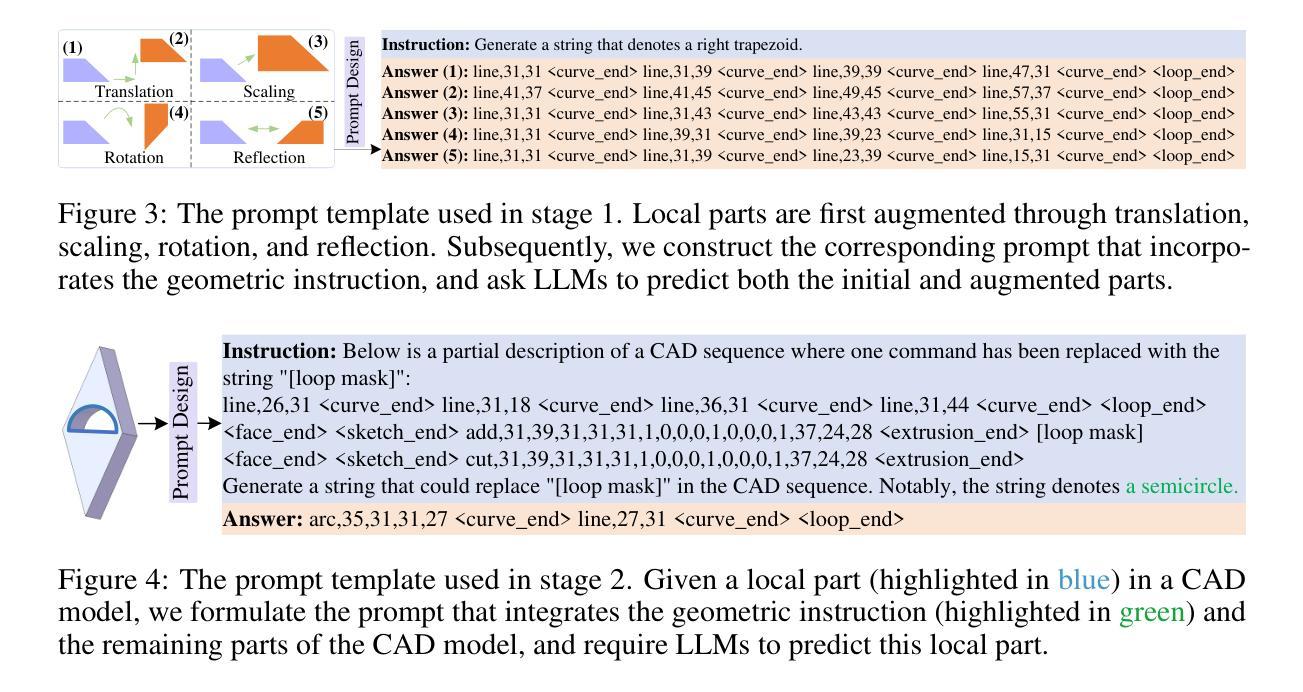
Local geometry-controllable computer-aided design (CAD) generation aims to modify local parts of CAD models automatically, enhancing design efficiency. It also ensures that the shapes of newly generated local parts follow user-specific geometric instructions (e.g., an isosceles right triangle or a rectangle with one corner cut off). However, existing methods encounter challenges in achieving this goal. Specifically, they either lack the ability to follow textual instructions or are unable to focus on the local parts. To address this limitation, we introduce GeoCAD, a user-friendly and local geometry-controllable CAD generation method. Specifically, we first propose a complementary captioning strategy to generate geometric instructions for local parts. This strategy involves vertex-based and VLLM-based captioning for systematically annotating simple and complex parts, respectively. In this way, we caption $\sim$221k different local parts in total. In the training stage, given a CAD model, we randomly mask a local part. Then, using its geometric instruction and the remaining parts as input, we prompt large language models (LLMs) to predict the masked part. During inference, users can specify any local part for modification while adhering to a variety of predefined geometric instructions. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of GeoCAD in generation quality, validity and text-to-CAD consistency. Code will be available at https://github.com/Zhanwei-Z/GeoCAD.
局部几何可控计算机辅助设计(CAD)生成旨在自动修改CAD模型的部分,提高设计效率。它还可以确保新生成的局部部件的形状符合用户特定的几何指令(例如,等腰直角三角形或切掉一个角的矩形)。然而,现有方法在实现这一目标时面临挑战。具体来说,它们要么缺乏遵循文本指令的能力,要么无法专注于局部部件。为了解决这一局限性,我们引入了GeoCAD,这是一种用户友好且局部几何可控的CAD生成方法。具体来说,我们首先提出了一种补充的标注策略,为局部部件生成几何指令。该策略包括基于顶点和基于VLLM的标注,分别用于系统地注释简单和复杂部件。这样,我们总共标注了约22.1万个不同的局部部件。在训练阶段,给定一个CAD模型,我们随机遮挡一个局部部件。然后,利用其几何指令和剩余部件作为输入,我们提示大型语言模型(LLM)来预测被遮挡的部分。在推理过程中,用户可以指定任何局部部件进行修改,同时遵循多种预定义的几何指令。大量实验表明,GeoCAD在生成质量、有效性和文本到CAD的一致性方面都非常有效。代码将在https://github.com/Zhanwei-Z/GeoCAD上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 12 figures
Summary
基于局部几何控制的计算机辅助设计(CAD)生成方法旨在自动修改CAD模型的部分内容,提高设计效率,并确保新生成的局部部分符合用户特定的几何指令。然而,现有方法在实现这一目标时面临挑战。为此,我们引入了GeoCAD,一种用户友好、局部几何可控的CAD生成方法。我们提出了一种互补的标注策略,为局部部分生成几何指令,并通过顶点基础和VLLM基础的标注方式系统地注释简单和复杂的部分。在训练阶段,我们随机遮挡CAD模型的一部分,然后使用其几何指令和剩余部分作为输入,提示大型语言模型进行预测。在推理阶段,用户可以指定任何部分进行修改,同时遵循多种预定义的几何指令。实验表明,GeoCAD在生成质量、有效性和文本到CAD的一致性方面都非常有效。
Key Takeaways
- GeoCAD是一种用户友好、局部几何可控的计算机辅助设计(CAD)生成方法。
- 它通过一种互补的标注策略生成局部几何指令,包括顶点基础和VLLM基础的标注方式。
- GeoCAD能够处理复杂的CAD模型,并允许用户指定任何部分进行修改。
- 该方法允许用户遵循多种预定义的几何指令,提高了设计效率和灵活性。
- 通过大量实验验证,GeoCAD在生成质量、有效性和文本到CAD的一致性方面表现出色。
- GeoCAD的代码将在[网址]上公开。
- 该方法为解决现有CAD设计工具中的局限提供了一种有效的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图
SWDL: Stratum-Wise Difference Learning with Deep Laplacian Pyramid for Semi-Supervised 3D Intracranial Hemorrhage Segmentation
Authors:Cheng Wang, Siqi Chen, Donghua Mi, Yang Chen, Yudong Zhang, Yinsheng Li
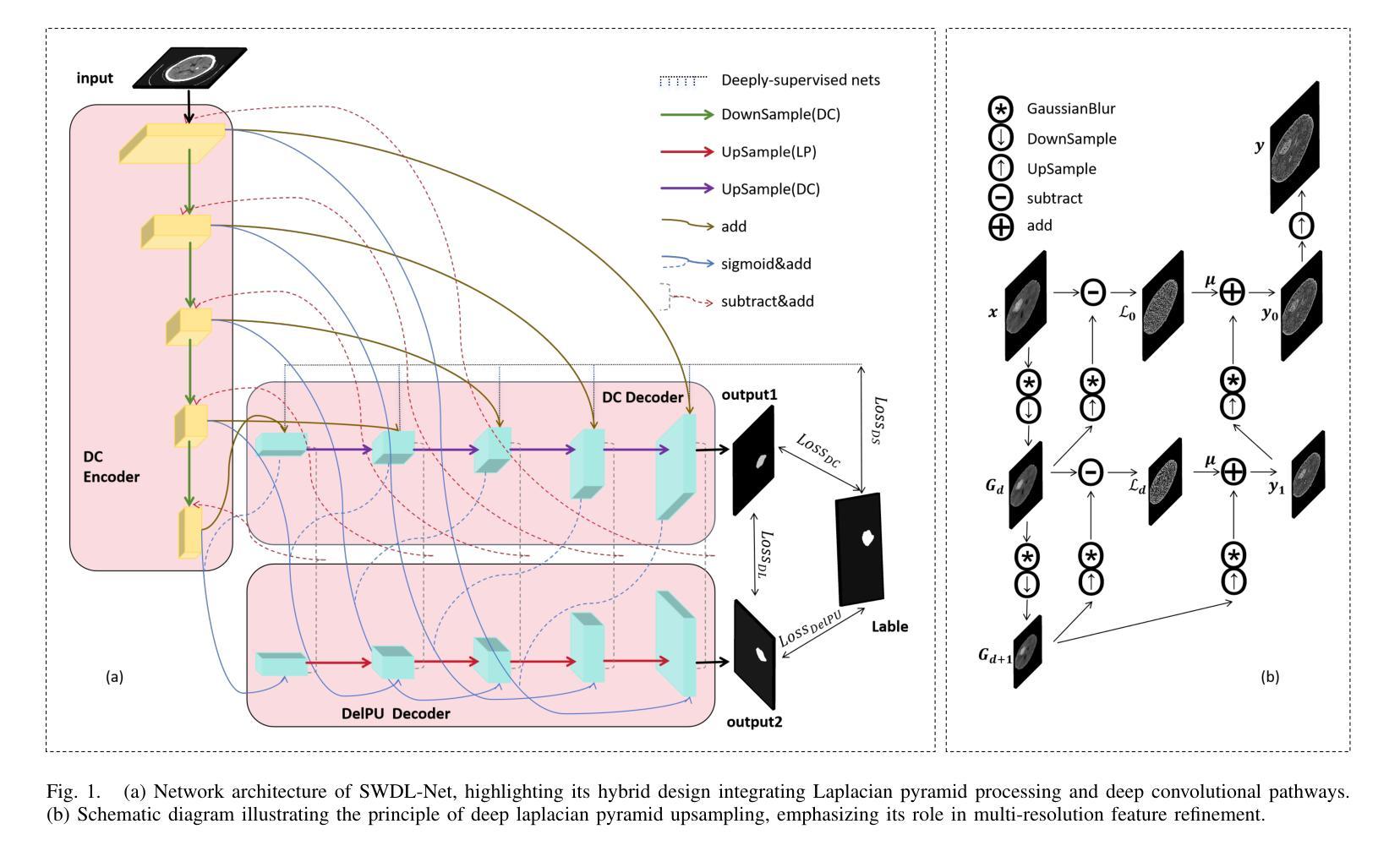
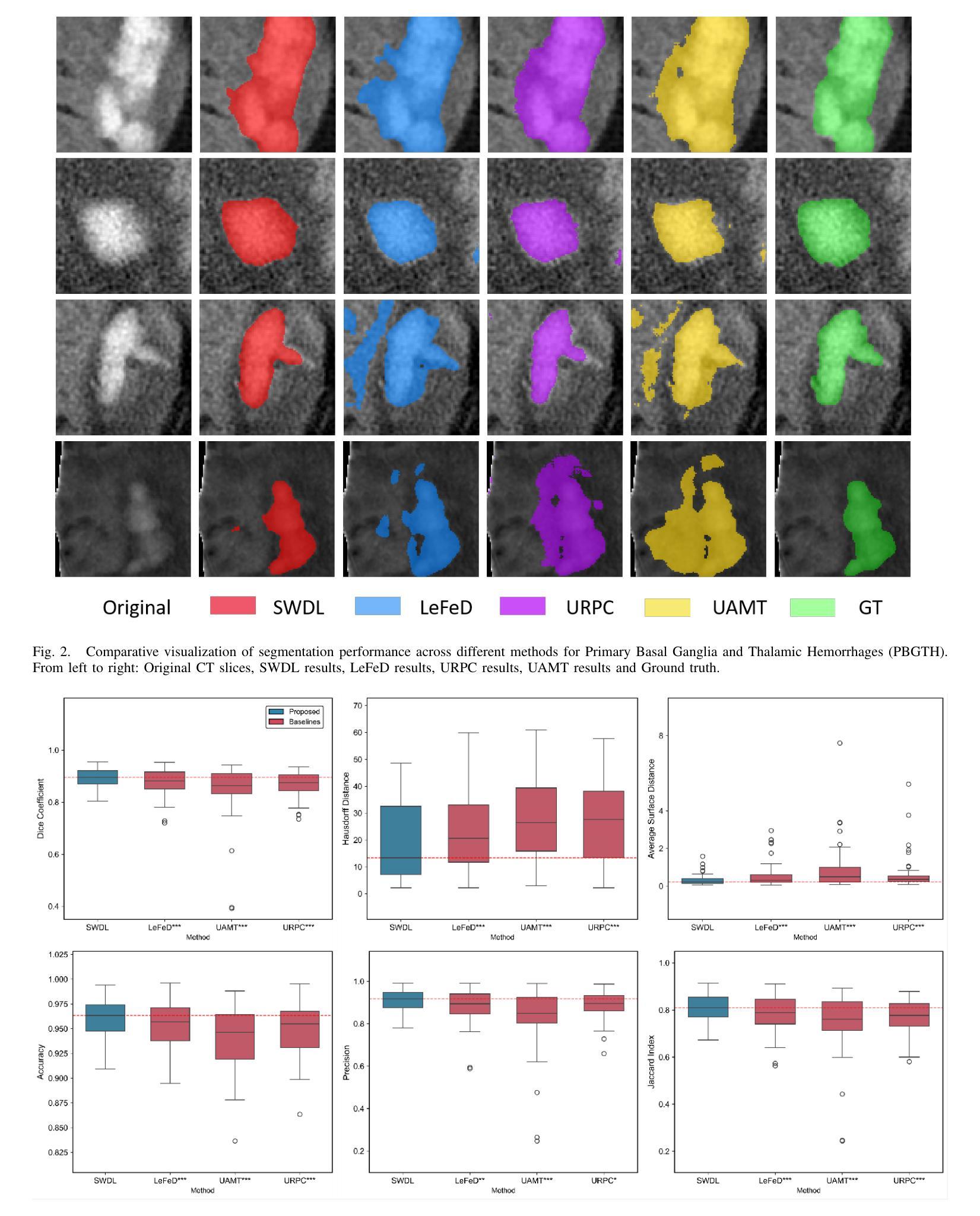
Recent advances in medical imaging have established deep learning-based segmentation as the predominant approach, though it typically requires large amounts of manually annotated data. However, obtaining annotations for intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) remains particularly challenging due to the tedious and costly labeling process. Semi-supervised learning (SSL) has emerged as a promising solution to address the scarcity of labeled data, especially in volumetric medical image segmentation. Unlike conventional SSL methods that primarily focus on high-confidence pseudo-labels or consistency regularization, we propose SWDL-Net, a novel SSL framework that exploits the complementary advantages of Laplacian pyramid and deep convolutional upsampling. The Laplacian pyramid excels at edge sharpening, while deep convolutions enhance detail precision through flexible feature mapping. Our framework achieves superior segmentation of lesion details and boundaries through a difference learning mechanism that effectively integrates these complementary approaches. Extensive experiments on a 271-case ICH dataset and public benchmarks demonstrate that SWDL-Net outperforms current state-of-the-art methods in scenarios with only 2% labeled data. Additional evaluations on the publicly available Brain Hemorrhage Segmentation Dataset (BHSD) with 5% labeled data further confirm the superiority of our approach. Code and data have been released at https://github.com/SIAT-CT-LAB/SWDL.
近期医学成像技术的进展已经确立了基于深度学习的分割方法作为主流方法,尽管通常需要大量的手动注释数据。然而,由于标注过程的繁琐和成本高昂,对颅内出血(ICH)的标注获取仍然特别具有挑战性。半监督学习(SSL)已经成为解决标记数据稀缺的有前途的解决方案,特别是在体积医学图像分割中。不同于主要关注高置信度伪标签或一致性正则化的传统SSL方法,我们提出了SWDL-Net,这是一种新型的SSL框架,它利用拉普拉斯金字塔和深度卷积上采样的互补优势。拉普拉斯金字塔擅长边缘锐化,而深度卷积通过灵活的特征映射增强了细节精度。我们的框架通过差异学习机制实现了病变细节和边界的优质分割,有效地整合了这些互补方法。在271例ICH数据集和公开基准测试上的大量实验表明,在仅有2%标记数据的情况下,SWDL-Net的性能超过了当前最先进的方法。在公开可用的Brain Hemorrhage Segmentation Dataset(BHSD)数据集上使用5%标记数据的进一步评估也证实了我们的方法的优越性。相关代码和数据已发布在https://github.com/SIAT-CT-LAB/SWDL。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 4 figures, 6 Tables
Summary
本摘要采用深度学习技术进行医学图像分割,并提出了一种新型的半监督学习框架SWDL-Net。该框架结合了Laplacian金字塔和深度卷积上采样的优势,在仅使用少量标记数据的情况下,实现了颅内出血图像的精准分割。实验结果表明,SWDL-Net在仅有2%标记数据的情况下,性能优于当前最先进的方法。同时,该框架已在公开数据集BHSD上进行验证,表现出良好的泛化能力。相关代码和数据已在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习已成为医学图像分割的主要方法,但仍需要大量手动标注数据。
- 获得颅内出血(ICH)的标注数据特别具有挑战性,因为标注过程既繁琐又昂贵。
- 半监督学习(SSL)是解决标记数据稀缺问题的有前途的方法。
- SWDL-Net是一种新型的半监督学习框架,结合了Laplacian金字塔和深度卷积上采样的优势。
- Laplacian金字塔擅长边缘锐化,而深度卷积通过灵活的特征映射增强了细节精度。
- SWDL-Net通过差异学习机制实现了病变细节和边界的精准分割。
点此查看论文截图

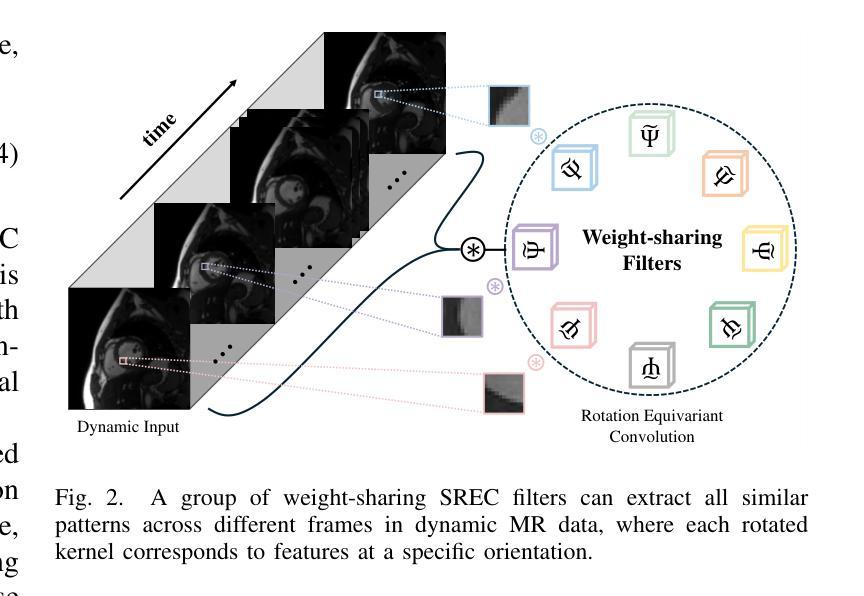
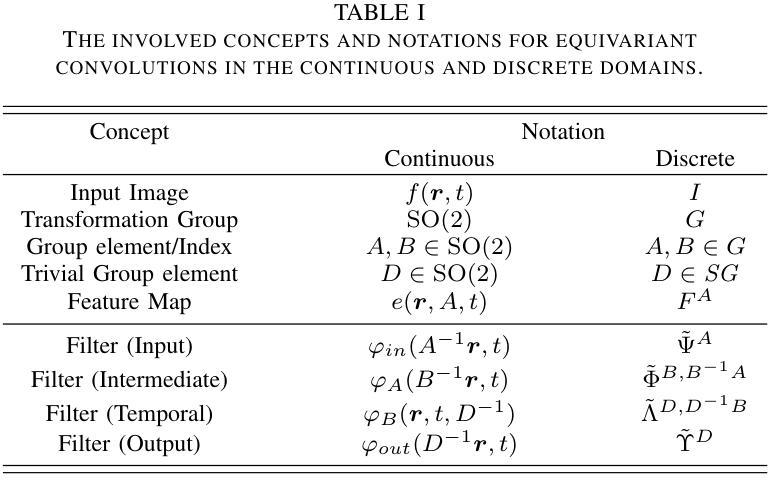
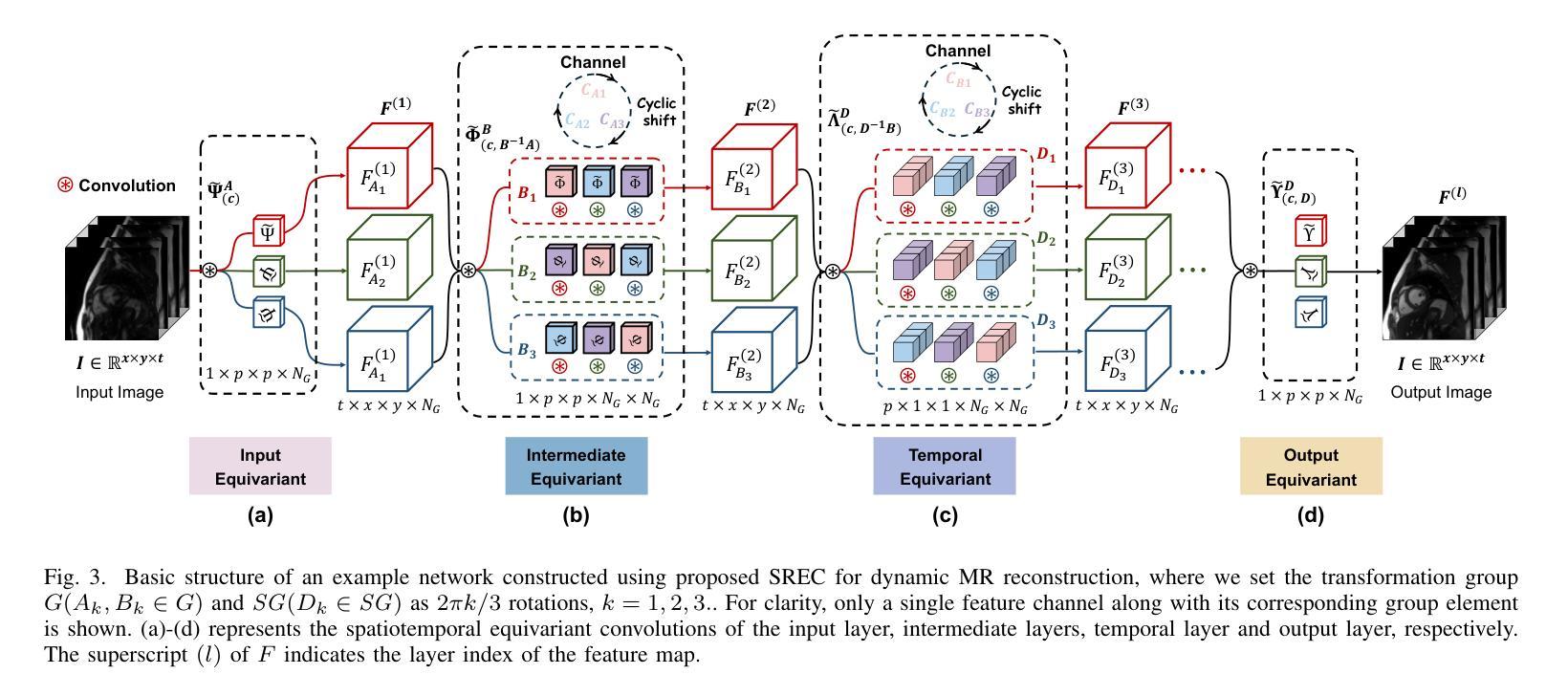
DUN-SRE: Deep Unrolling Network with Spatiotemporal Rotation Equivariance for Dynamic MRI Reconstruction
Authors:Yuliang Zhu, Jing Cheng, Qi Xie, Zhuo-Xu Cui, Qingyong Zhu, Yuanyuan Liu, Xin Liu, Jianfeng Ren, Chengbo Wang, Dong Liang
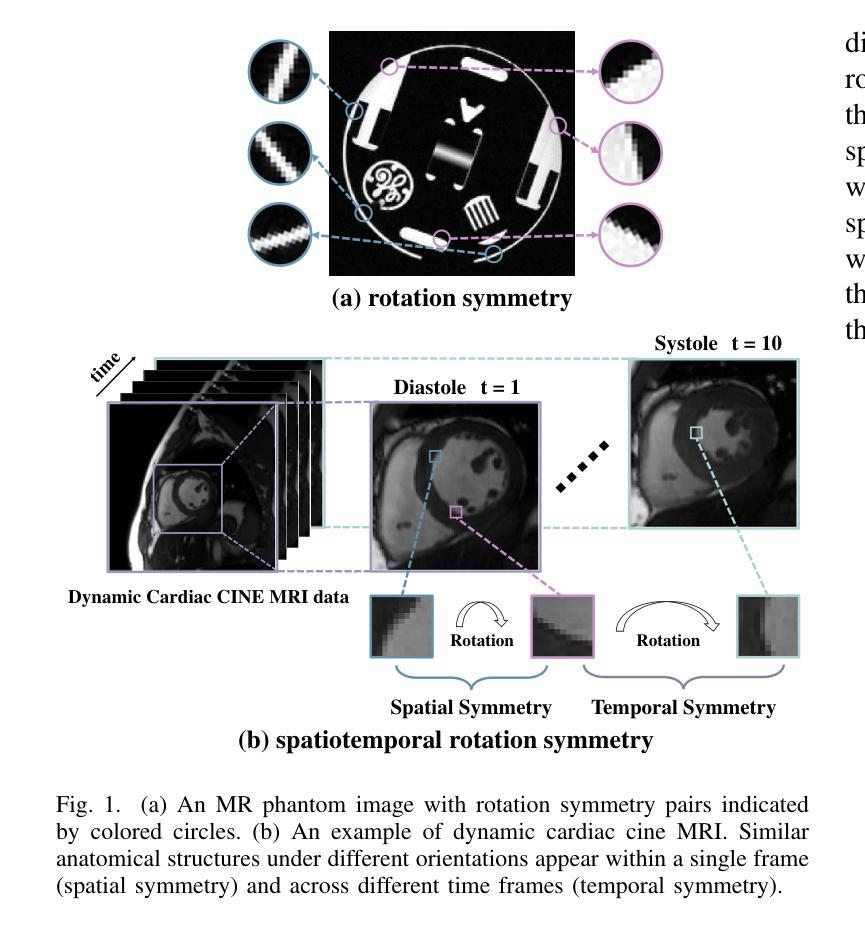
Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) exhibits transformation symmetries, including spatial rotation symmetry within individual frames and temporal symmetry along the time dimension. Explicit incorporation of these symmetry priors in the reconstruction model can significantly improve image quality, especially under aggressive undersampling scenarios. Recently, Equivariant convolutional neural network (ECNN) has shown great promise in exploiting spatial symmetry priors. However, existing ECNNs critically fail to model temporal symmetry, arguably the most universal and informative structural prior in dynamic MRI reconstruction. To tackle this issue, we propose a novel Deep Unrolling Network with Spatiotemporal Rotation Equivariance (DUN-SRE) for Dynamic MRI Reconstruction. The DUN-SRE establishes spatiotemporal equivariance through a (2+1)D equivariant convolutional architecture. In particular, it integrates both the data consistency and proximal mapping module into a unified deep unrolling framework. This architecture ensures rigorous propagation of spatiotemporal rotation symmetry constraints throughout the reconstruction process, enabling more physically accurate modeling of cardiac motion dynamics in cine MRI. In addition, a high-fidelity group filter parameterization mechanism is developed to maintain representation precision while enforcing symmetry constraints. Comprehensive experiments on Cardiac CINE MRI datasets demonstrate that DUN-SRE achieves state-of-the-art performance, particularly in preserving rotation-symmetric structures, offering strong generalization capability to a broad range of dynamic MRI reconstruction tasks.
动态磁共振成像(MRI)表现出变换对称性,包括单个帧内的空间旋转对称性和时间维度上的时间对称性。在重建模型中明确融入这些对称先验知识可以显著提高图像质量,特别是在激烈的欠采样情况下。最近,等变卷积神经网络(ECNN)在利用空间对称先验方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,现有的ECNNs未能对时间对称性进行建模,而时间对称性无疑是动态MRI重建中最通用且信息最丰富的结构先验。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型的具有时空旋转等变性的深度展开网络(DUN-SRE),用于动态MRI重建。DUN-SRE通过(2+1)D等变卷积架构建立时空等变性。特别是,它将数据一致性和近端映射模块集成到一个统一的深度展开框架中。该架构确保了时空旋转对称约束在整个重建过程中的严格传播,实现对电影MRI中心脏运动动态的更加物理准确的建模。此外,开发了一种高保真组滤波器参数化机制,以保持表示精度的同时实施对称约束。在心脏电影MRI数据集上的综合实验表明,DUN-SRE达到了最先进的性能,尤其在保持旋转对称结构方面表现出色,对广泛的动态MRI重建任务具有很强的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
动态磁共振成像(MRI)具有转换对称性,包括个体帧内的空间旋转对称性和时间维度上的时间对称性等。在重建模型中显式融入这些对称先验可以显著提高图像质量,特别是在激进欠采样场景中。针对现有等变卷积神经网络(ECNN)无法建模时间对称性的问题,我们提出了具有时空旋转等变性的深度展开网络(DUN-SRE)用于动态MRI重建。该网络通过(2+1)D等变卷积架构建立时空等变性,将数据一致性和近端映射模块集成到统一的深度展开框架中。该架构确保了时空旋转对称约束在整个重建过程中的严格传播,能够对心脏运动动态进行更物理准确的建模。实验证明,DUN-SRE在保留旋转对称结构方面达到了最佳性能,对广泛的动态MRI重建任务具有很强的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 动态MRI具有转换对称性,包括空间旋转对称性和时间对称性。
- 融入对称先验能提升图像质量,尤其在激进欠采样情况下。
- 现有的等变卷积神经网络(ECNN)无法有效建模动态MRI的时间对称性。
- 提出的Deep Unrolling Network with Spatiotemporal Rotation Equivariance (DUN-SRE)能建立时空等变性。
- DUN-SRE通过集成数据一致性和近端映射模块,确保了时空旋转对称约束的严格传播。
- DUN-SRE在心脏MRI中表现出优秀的性能,能更物理准确地建模心脏运动动态。
点此查看论文截图

Uncertainty-Aware Deep Learning for Automated Skin Cancer Classification: A Comprehensive Evaluation
Authors:Hamzeh Asgharnezhad, Pegah Tabarisaadi, Abbas Khosravi, Roohallah Alizadehsani, U. Rajendra Acharya
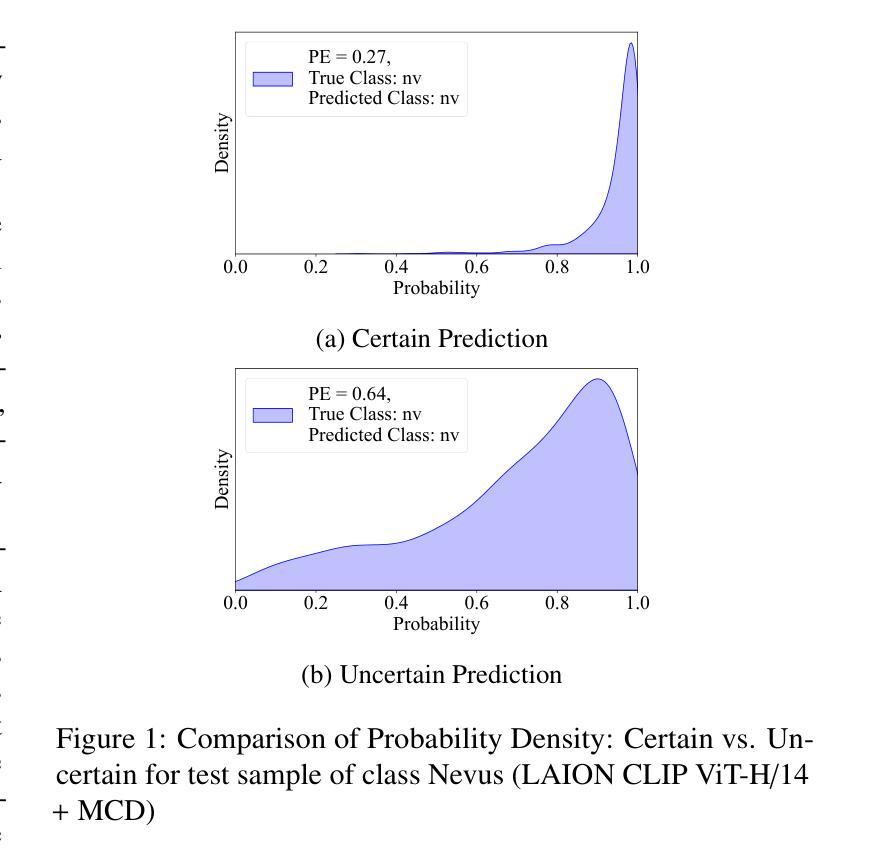
Accurate and reliable skin cancer diagnosis is critical for early treatment and improved patient outcomes. Deep learning (DL) models have shown promise in automating skin cancer classification, but their performance can be limited by data scarcity and a lack of uncertainty awareness. In this study, we present a comprehensive evaluation of DL-based skin lesion classification using transfer learning and uncertainty quantification (UQ) on the HAM10000 dataset. In the first phase, we benchmarked several pre-trained feature extractors-including Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) variants, Residual Network-50 (ResNet50), Densely Connected Convolutional Network (DenseNet121), Visual Geometry Group network (VGG16), and EfficientNet-V2-Large-combined with a range of traditional classifiers such as Support Vector Machine (SVM), eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), and logistic regression. Our results show that CLIP-based vision transformers, particularly LAION CLIP ViT-H/14 with SVM, deliver the highest classification performance. In the second phase, we incorporated UQ using Monte Carlo Dropout (MCD), Ensemble, and Ensemble Monte Carlo Dropout (EMCD) to assess not only prediction accuracy but also the reliability of model outputs. We evaluated these models using uncertainty-aware metrics such as uncertainty accuracy(UAcc), uncertainty sensitivity(USen), uncertainty specificity(USpe), and uncertainty precision(UPre). The results demonstrate that ensemble methods offer a good trade-off between accuracy and uncertainty handling, while EMCD is more sensitive to uncertain predictions. This study highlights the importance of integrating UQ into DL-based medical diagnosis to enhance both performance and trustworthiness in real-world clinical applications.
准确可靠的皮肤癌诊断对于早期治疗和改善患者预后至关重要。深度学习(DL)模型在自动化皮肤癌分类方面显示出巨大潜力,但其性能可能会受到数据稀缺和缺乏不确定性意识的影响。本研究中,我们对基于深度学习的皮肤病变分类进行了全面评估,采用迁移学习和不确定性量化(UQ)在HAM10000数据集上进行实验。在第一阶段,我们对比了几种预训练特征提取器的性能,包括对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)变体、残差网络50(ResNet50)、密集连接卷积网络(DenseNet121)、视觉几何组网络(VGG16)和EfficientNet-V2-Large,结合一系列传统分类器,如支持向量机(SVM)、极端梯度提升(XGBoost)和逻辑回归。我们的结果表明,基于CLIP的视觉变压器,特别是LAION CLIP ViT-H/14与SVM的结合,具有最高的分类性能。在第二阶段,我们采用了蒙特卡洛Dropout(MCD)、集成方法和集成蒙特卡洛Dropout(EMCD)来引入不确定性量化,以评估模型输出的预测准确性和可靠性。我们使用不确定性感知指标,如不确定性准确度(UAcc)、不确定性敏感性(USen)、不确定性特异性(USpe)和不确定性精确度(UPre)来评估这些模型。结果表明,集成方法在准确性和不确定性处理之间提供了良好的权衡,而EMCD对不确定的预测更为敏感。本研究强调了将不确定性量化整合到基于深度学习的医学诊断中的重要性,以提高现实临床应用中性能和可信度。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
深度学习模型在皮肤癌分类自动化方面展现出潜力,但受限于数据稀缺和缺乏不确定性意识。本研究全面评估了基于深度学习的皮肤病变分类,采用迁移学习和不确定性量化(UQ)在HAM10000数据集上进行实验。第一阶段,我们基准测试了多种预训练特征提取器与一系列传统分类器的组合,发现基于CLIP的视觉变压器表现最佳。第二阶段,我们采用蒙特卡洛dropout、集成方法和集成蒙特卡洛dropout来评估模型的预测准确性和输出可靠性,结果表明集成方法在准确性和不确定性处理之间达到了良好的平衡。本研究强调了在基于深度学习的医学诊断中融入不确定性量化的重要性,以提高实际临床应用的性能和可信度。
关键见解
- 深度学习模型在皮肤癌自动分类中具有潜力,但面临数据稀缺和不确定性意识不足的挑战。
- 研究采用了迁移学习和不确定性量化方法来解决这些问题。
- 在多种预训练特征提取器与传统分类器的组合中,基于CLIP的视觉变压器表现最佳。
- 蒙特卡洛dropout、集成方法和集成蒙特卡洛dropout等方法被用于评估模型的不确定性和可靠性。
- 集成方法在平衡准确性和不确定性处理方面表现出良好的性能。
- 融入不确定性量化对于提高深度学习方法在医学诊断中的性能和可信度至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

Conditional diffusion models for guided anomaly detection in brain images using fluid-driven anomaly randomization
Authors:Ana Lawry Aguila, Peirong Liu, Oula Puonti, Juan Eugenio Iglesias
Supervised machine learning has enabled accurate pathology detection in brain MRI, but requires training data from diseased subjects that may not be readily available in some scenarios, for example, in the case of rare diseases. Reconstruction-based unsupervised anomaly detection, in particular using diffusion models, has gained popularity in the medical field as it allows for training on healthy images alone, eliminating the need for large disease-specific cohorts. These methods assume that a model trained on normal data cannot accurately represent or reconstruct anomalies. However, this assumption often fails with models failing to reconstruct healthy tissue or accurately reconstruct abnormal regions i.e., failing to remove anomalies. In this work, we introduce a novel conditional diffusion model framework for anomaly detection and healthy image reconstruction in brain MRI. Our weakly supervised approach integrates synthetically generated pseudo-pathology images into the modeling process to better guide the reconstruction of healthy images. To generate these pseudo-pathologies, we apply fluid-driven anomaly randomization to augment real pathology segmentation maps from an auxiliary dataset, ensuring that the synthetic anomalies are both realistic and anatomically coherent. We evaluate our model’s ability to detect pathology, using both synthetic anomaly datasets and real pathology from the ATLAS dataset. In our extensive experiments, our model: (i) consistently outperforms variational autoencoders, and conditional and unconditional latent diffusion; and (ii) surpasses on most datasets, the performance of supervised inpainting methods with access to paired diseased/healthy images.
监督机器学习已在脑MRI病理检测中实现了高精度,但在某些情况下,可能需要来自患病者的训练数据,这在罕见疾病的情况下可能并不容易获得。基于重建的无监督异常检测,特别是使用扩散模型的方法,已在医疗领域受到欢迎,因为它只需要在健康图像上进行训练,从而消除了对特定疾病的庞大人群的需求。这些方法假设在常规数据上训练的模型无法准确表示或重建异常现象。然而,这一假设经常在与模型无法重建健康组织或准确重建异常区域的模型中出现失效情况,即无法消除异常现象。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种用于异常检测和健康图像重建的新型条件扩散模型框架,适用于脑MRI。我们的弱监督方法将合成生成的伪病理图像集成到建模过程中,以更好地指导健康图像的重建。为了生成这些伪病理图像,我们应用流体驱动的异常随机化来增强辅助数据集中的真实病理分割图,以确保合成异常现象既真实又解剖结构连贯。我们使用合成异常数据集和ATLAS数据集中的真实病理情况来评估我们模型检测病理的能力。在广泛的实验中,我们的模型表现如下:(i)始终优于变分自动编码器以及有条件和无条件的潜在扩散;(ii)在大多数数据集上超越了使用配对疾病/健康图像的监督修复方法的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于条件扩散模型的新框架,用于在脑部MRI中进行异常检测和健康图像重建。该框架采用弱监督方法,通过合成生成的伪病理图像来更好地引导健康图像的重建。实验表明,该模型在病理检测方面表现出优异的性能,优于其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- 监督机器学习在脑部MRI病理检测中表现出准确性,但需要疾病患者的训练数据,这在某些情况下可能不易获得,如罕见疾病。
- 重建型无监督异常检测方法,特别是使用扩散模型的方法,已在医学领域受到关注,因为它们仅需要使用健康图像进行训练,从而消除了对特定疾病大规模队列的需求。
- 当前方法的一个假设是,训练有素模型无法准确表示或重建异常。然而,这一假设经常失败,模型可能无法重建健康组织或准确重建异常区域。
- 本文提出了一种新型条件扩散模型框架,用于异常检测和健康图像重建。
- 该框架采用弱监督方法,结合合成生成的伪病理图像来改进健康图像的重建过程。
- 为生成这些伪病理图像,研究团队应用流体驱动异常随机化技术,增强来自辅助数据集的真实病理分割图,确保合成异常既现实又解剖连贯。
点此查看论文截图

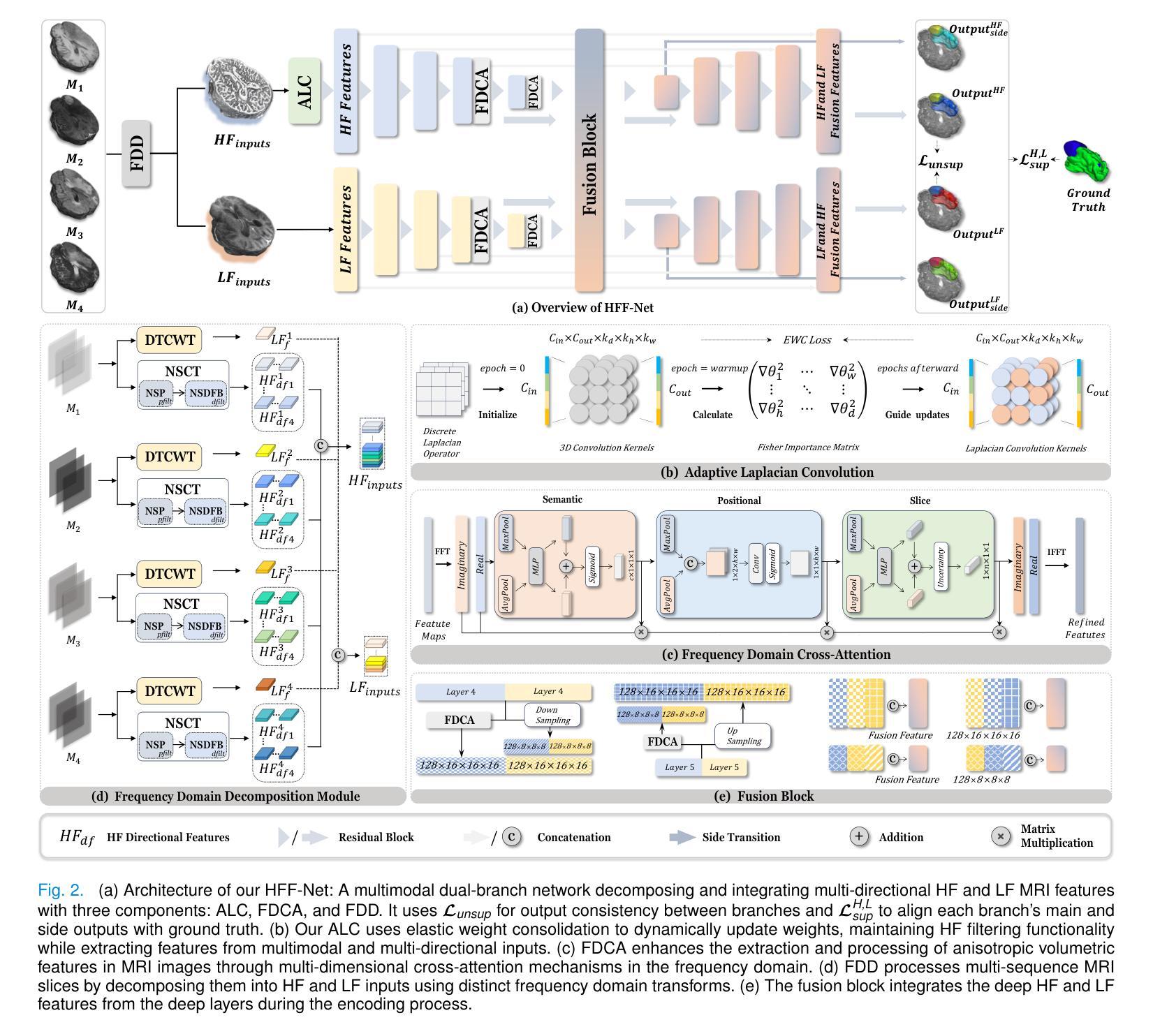
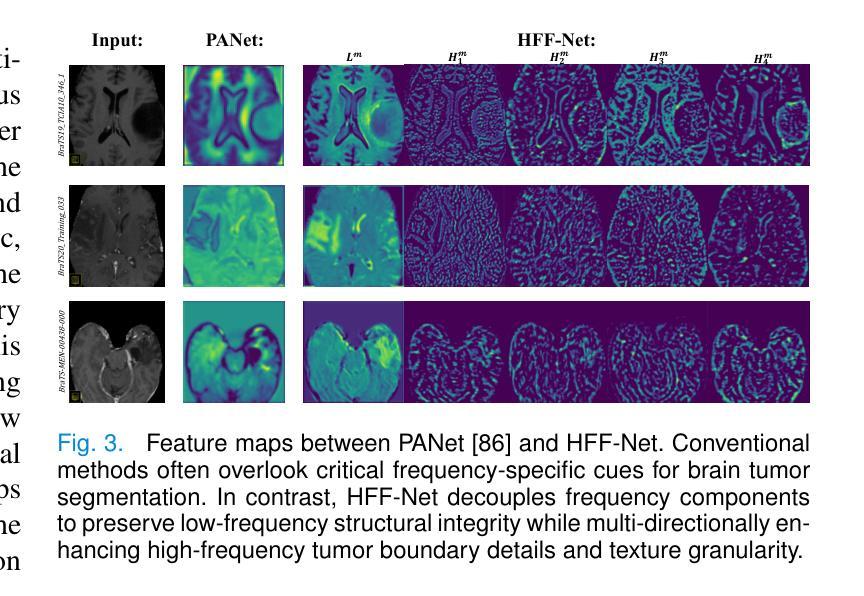
Rethinking Brain Tumor Segmentation from the Frequency Domain Perspective
Authors:Minye Shao, Zeyu Wang, Haoran Duan, Yawen Huang, Bing Zhai, Shizheng Wang, Yang Long, Yefeng Zheng
Precise segmentation of brain tumors, particularly contrast-enhancing regions visible in post-contrast MRI (areas highlighted by contrast agent injection), is crucial for accurate clinical diagnosis and treatment planning but remains challenging. However, current methods exhibit notable performance degradation in segmenting these enhancing brain tumor areas, largely due to insufficient consideration of MRI-specific tumor features such as complex textures and directional variations. To address this, we propose the Harmonized Frequency Fusion Network (HFF-Net), which rethinks brain tumor segmentation from a frequency-domain perspective. To comprehensively characterize tumor regions, we develop a Frequency Domain Decomposition (FDD) module that separates MRI images into low-frequency components, capturing smooth tumor contours and high-frequency components, highlighting detailed textures and directional edges. To further enhance sensitivity to tumor boundaries, we introduce an Adaptive Laplacian Convolution (ALC) module that adaptively emphasizes critical high-frequency details using dynamically updated convolution kernels. To effectively fuse tumor features across multiple scales, we design a Frequency Domain Cross-Attention (FDCA) integrating semantic, positional, and slice-specific information. We further validate and interpret frequency-domain improvements through visualization, theoretical reasoning, and experimental analyses. Extensive experiments on four public datasets demonstrate that HFF-Net achieves an average relative improvement of 4.48% (ranging from 2.39% to 7.72%) in the mean Dice scores across the three major subregions, and an average relative improvement of 7.33% (ranging from 5.96% to 8.64%) in the segmentation of contrast-enhancing tumor regions, while maintaining favorable computational efficiency and clinical applicability. Code: https://github.com/VinyehShaw/HFF.
精确分割脑肿瘤,特别是在对比增强MRI中可见到的对比增强区域(通过造影剂注射突出显示),对于准确的临床诊断和制定治疗方案至关重要,但仍面临挑战。然而,当前方法在分割这些增强脑肿瘤区域时的性能明显下降,这主要是由于未能充分考虑MRI特定的肿瘤特征,如复杂的纹理和方向变化。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了和谐频率融合网络(HFF-Net),从频率域的角度重新思考脑肿瘤的分割问题。为了全面刻画肿瘤区域,我们开发了一个频率域分解(FDD)模块,将MRI图像分解为低频成分,捕捉平滑的肿瘤轮廓和高频成分,突出详细的纹理和方向边缘。为了进一步提高对肿瘤边界的敏感性,我们引入了自适应拉普拉斯卷积(ALC)模块,该模块通过动态更新的卷积核自适应地突出关键的高频细节。为了有效地融合跨多个尺度的肿瘤特征,我们设计了一个频率域交叉注意(FDCA)机制,融合了语义、位置和切片特定的信息。我们进一步通过可视化、理论推理和实验分析验证了频率域改进的效果。在四个公共数据集上的广泛实验表明,HFF-Net在三个主要亚区域的平均Dice得分平均提高了4.48%(范围从2.39%到7.72%),在对比增强肿瘤区域的分割上平均提高了7.33%(范围从5.96%到8.64%),同时保持了良好的计算效率和临床适用性。代码链接:https://github.com/VinyehShaw/HFF。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging
Summary
本文提出一种名为HFF-Net的神经网络框架,用于从频率域角度重新思考脑肿瘤分割问题。通过分解MRI图像的低频和高频成分以及采用自适应拉普拉斯卷积模块,该方法能更全面地刻画肿瘤区域,并强调肿瘤边界的敏感性。此外,通过频率域交叉注意力机制融合多尺度肿瘤特征。在四个公共数据集上的实验验证了该方法的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 精确分割MRI中的对比增强脑肿瘤区域对临床诊断和治疗计划至关重要。
- 当前方法在分割这些增强脑肿瘤区域时面临挑战,主要由于未能充分考虑MRI特定的肿瘤特征。
- HFF-Net框架从频率域角度重新思考脑肿瘤分割,并设计了一系列模块来处理MRI图像的不同频率成分。
- FDD模块将MRI图像分解为低频和高频成分,以全面刻画肿瘤区域并强调详细的纹理和方向边缘。
- ALC模块通过自适应强调关键的高频细节来提高对肿瘤边界的敏感性。
- FDCA模块通过融合多尺度的肿瘤特征来提高频率域的改进效果。
点此查看论文截图

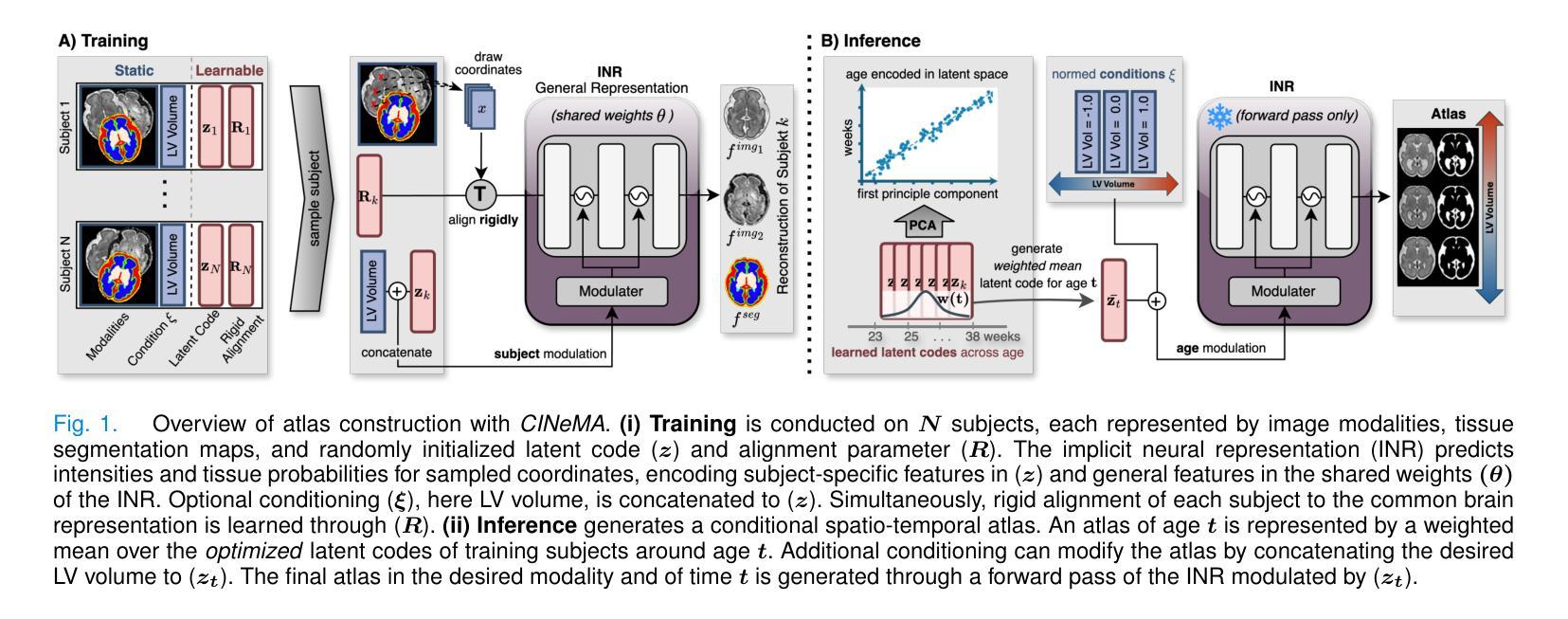
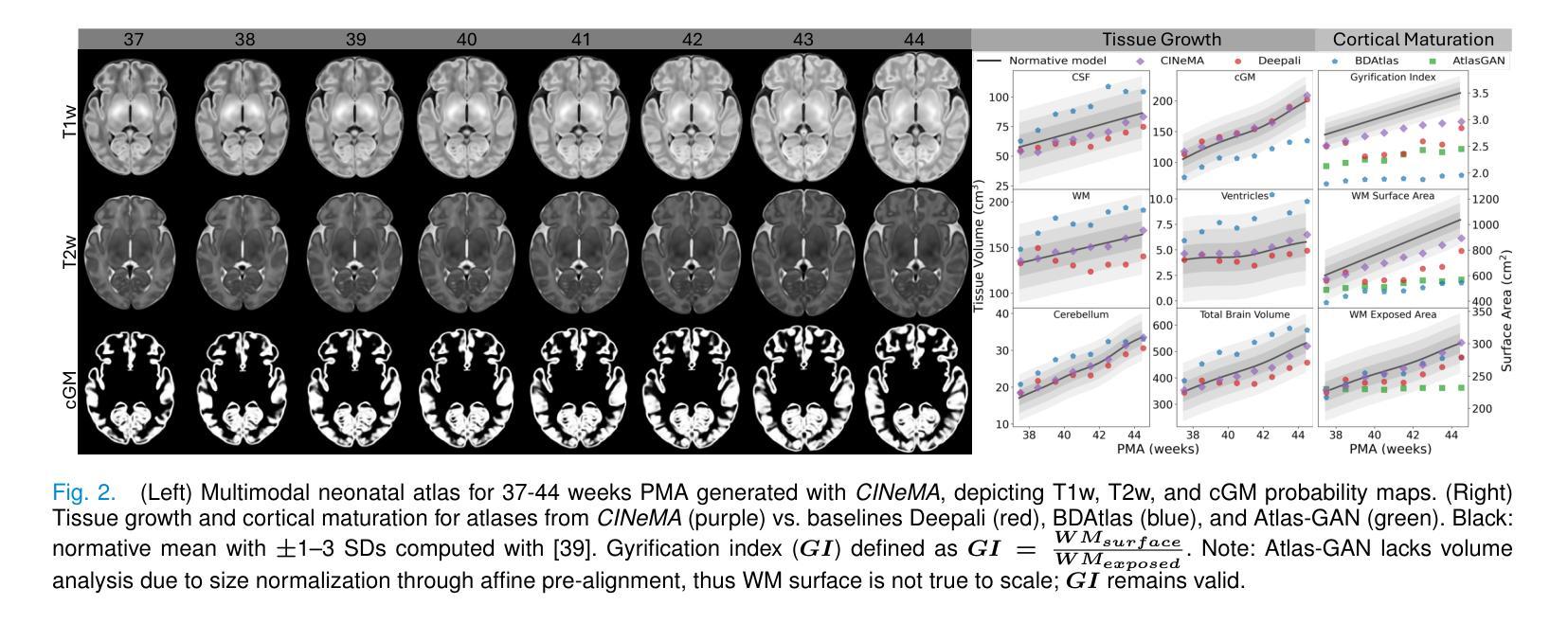
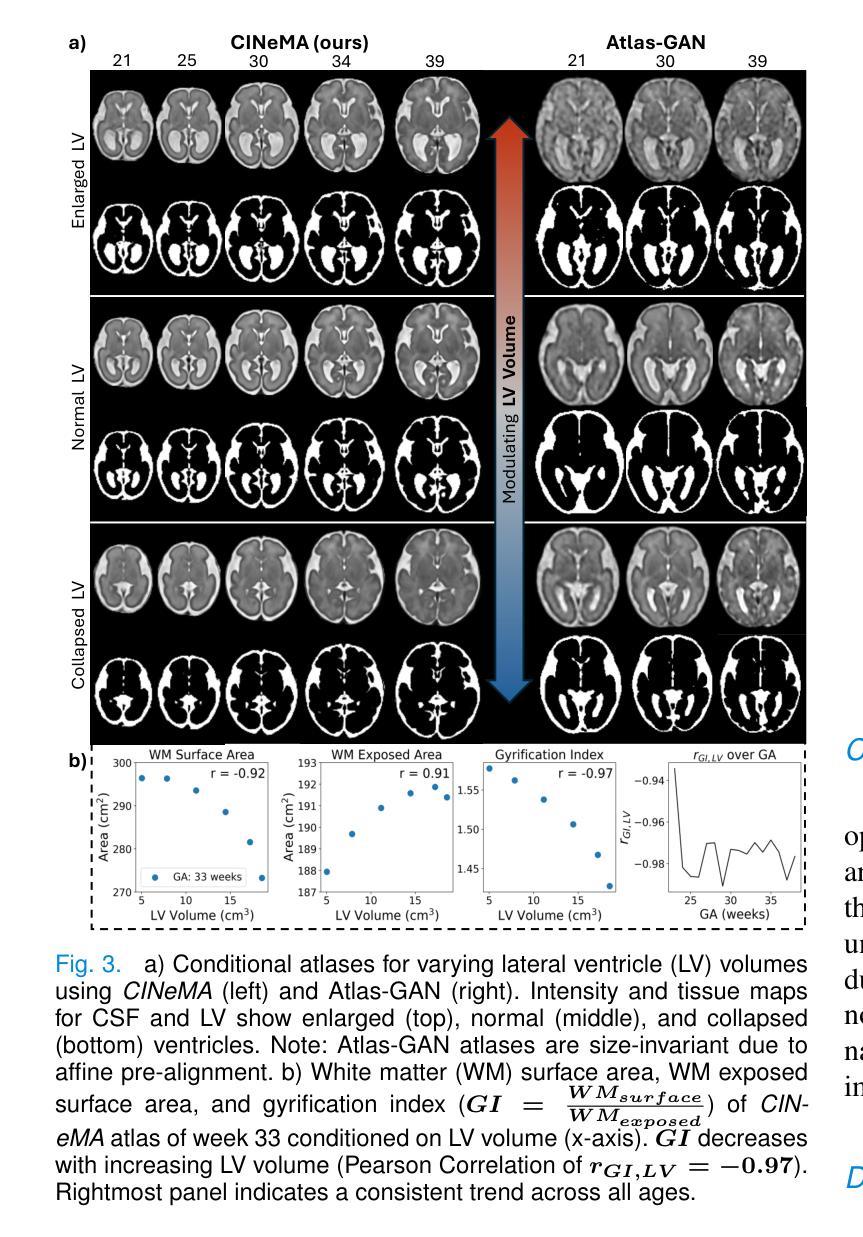
CINeMA: Conditional Implicit Neural Multi-Modal Atlas for a Spatio-Temporal Representation of the Perinatal Brain
Authors:Maik Dannecker, Vasiliki Sideri-Lampretsa, Sophie Starck, Angeline Mihailov, Mathieu Milh, Nadine Girard, Guillaume Auzias, Daniel Rueckert
Magnetic resonance imaging of fetal and neonatal brains reveals rapid neurodevelopment marked by substantial anatomical changes unfolding within days. Studying this critical stage of the developing human brain, therefore, requires accurate brain models-referred to as atlases-of high spatial and temporal resolution. To meet these demands, established traditional atlases and recently proposed deep learning-based methods rely on large and comprehensive datasets. This poses a major challenge for studying brains in the presence of pathologies for which data remains scarce. We address this limitation with CINeMA (Conditional Implicit Neural Multi-Modal Atlas), a novel framework for creating high-resolution, spatio-temporal, multimodal brain atlases, suitable for low-data settings. Unlike established methods, CINeMA operates in latent space, avoiding compute-intensive image registration and reducing atlas construction times from days to minutes. Furthermore, it enables flexible conditioning on anatomical features including GA, birth age, and pathologies like ventriculomegaly (VM) and agenesis of the corpus callosum (ACC). CINeMA supports downstream tasks such as tissue segmentation and age prediction whereas its generative properties enable synthetic data creation and anatomically informed data augmentation. Surpassing state-of-the-art methods in accuracy, efficiency, and versatility, CINeMA represents a powerful tool for advancing brain research. We release the code and atlases at https://github.com/m-dannecker/CINeMA.
胎儿和新生儿大脑的磁共振成像显示,神经发育迅速,几天内解剖结构会发生显著变化。因此,研究人类大脑发育的这个关键阶段需要准确的大脑模型,这些模型被称为图谱,需要具有高空间和时间分辨率。为了满足这些要求,已建立的传统图谱和最近提出的基于深度学习的方法都依赖于大型且全面的数据集。这对于在存在病理情况下研究大脑构成了重大挑战,此类数据仍然稀缺。我们通过CINeMA(条件隐神经多模态图谱)这一新型框架来解决这一局限性,该框架适用于创建高分辨率、时空、多模态的大脑图谱,适用于数据稀缺的设置。不同于已建立的方法,CINeMA在潜在空间中进行操作,避免了计算密集型的图像配准,并将图谱构建时间从几天缩短到几分钟。此外,它可以根据解剖特征进行灵活调整,包括胎龄、出生年龄以及脑室扩大和胼胝体发育不良等病理特征。CINeMA支持下游任务,如组织分割和年龄预测,而其生成属性则可实现合成数据的创建和解剖信息的数据增强。在准确性、效率和通用性方面超越现有方法,CINeMA是推进大脑研究的有力工具。我们在https://github.com/m-dannecker/CINeMA发布代码和图谱。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work currently under revision for IEEE TMI
Summary
本文介绍了在胎儿和新生儿大脑发育的神经发展阶段中,利用磁共振成像揭示其迅速变化和明显的解剖结构变化。为研究这一过程需要高时空分辨率的大脑模型——图谱。传统图谱和深度学习方法需要大量综合数据集,这给研究存在病理情况的大脑带来了挑战。为解决这一问题,本文提出了CINeMA(条件隐神经多模态图谱)这一新型框架,适用于低数据环境下的高时空分辨率多模态大脑图谱创建。CINeMA在潜在空间操作,避免了计算密集型的图像配准,将图谱构建时间从几天缩短到几分钟。同时支持灵活调节解剖特征,如胎龄、出生年龄、脑积水等疾病,为下游任务如组织分割和年龄预测提供支持。此外,CINeMA还具有生成性特点,可创建合成数据并增强解剖学信息。其在准确性、效率和灵活性方面超越现有方法,成为推动大脑研究的有力工具。
Key Takeaways
- 胎儿和新生儿大脑发育过程中存在快速神经发展和解剖结构变化。
- 需要高时空分辨率的大脑模型图谱来研究这一过程。
- 传统图谱和深度学习方法需要大量综合数据集,给研究存在病理情况的大脑带来挑战。
- CINeMA框架适用于低数据环境下的高时空分辨率多模态大脑图谱创建。
- CINeMA在潜在空间操作,避免了计算密集型的图像配准,缩短图谱构建时间。
- CINeMA支持灵活调节解剖特征,包括胎龄、出生年龄和某些病理情况。
- CINeMA可用于下游任务如组织分割和年龄预测,并具有生成性特点。
点此查看论文截图

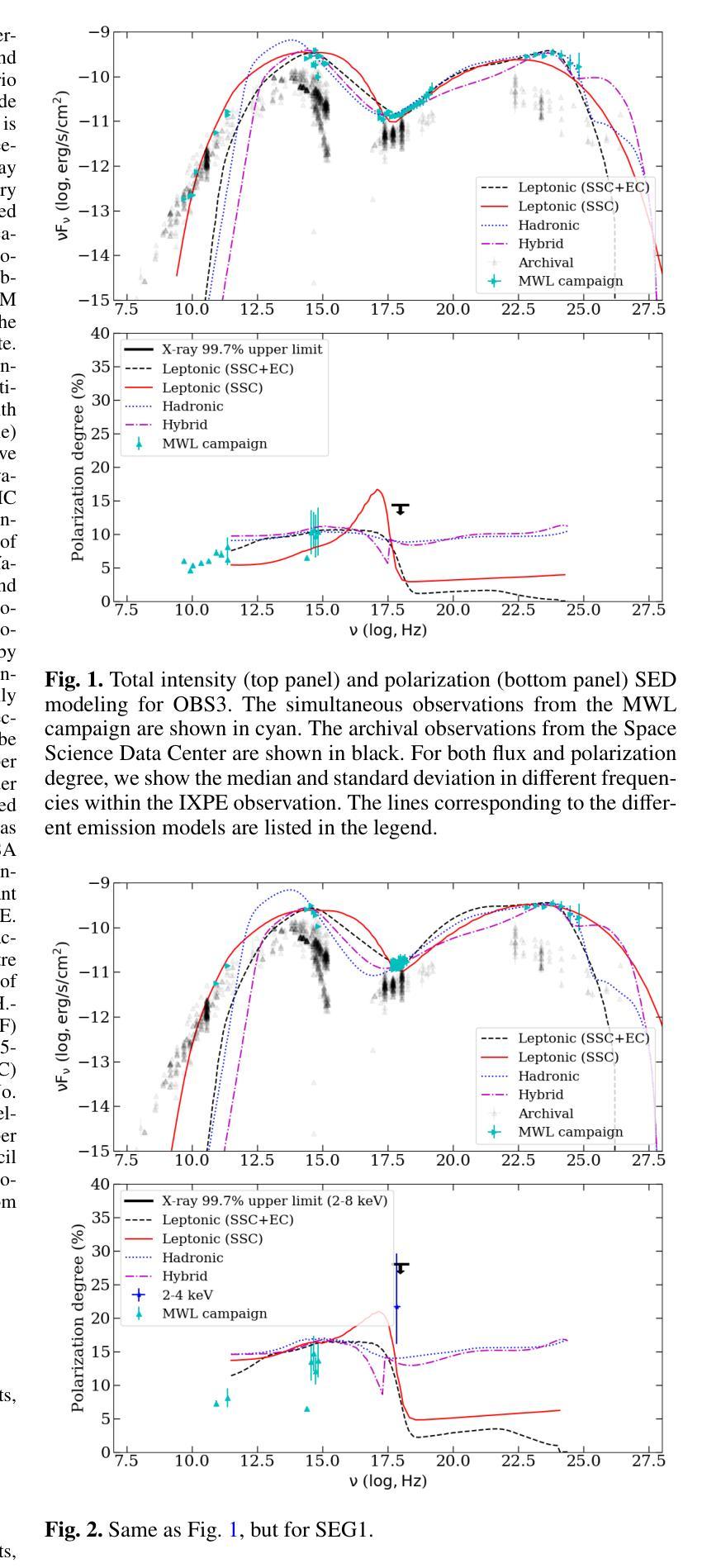
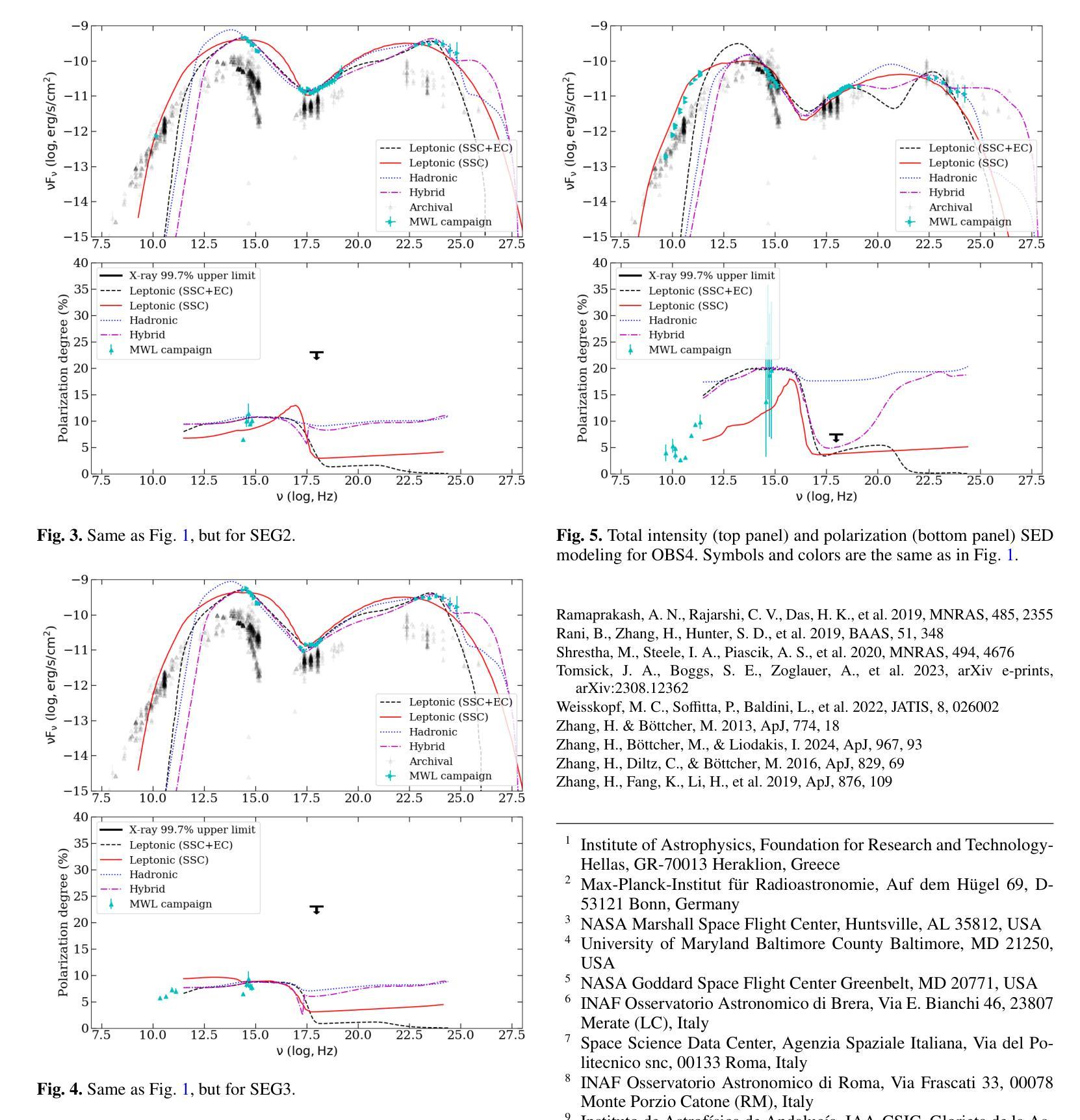
Determining the origin of the X-ray emission in blazars through multiwavelength polarization
Authors:Ioannis Liodakis, Haocheng Zhang, Stella Boula, Riccardo Middei, Jorge Otero-Santos, Dmitry Blinov, Iván Agudo, Markus Böttcher, Chien-Ting Chen, Steven R. Ehlert, Svetlana G. Jorstad, Philip Kaaret, Henric Krawczynski, Abel L. Peirson, Roger W. Romani, Fabrizio Tavecchio, Martin C. Weisskopf, Pouya M. Kouch, Elina Lindfors, Kari Nilsson, Callum McCall, Helen E. Jermak, Iain A. Steele, Ioannis Myserlis, Mark Gurwell, Garrett K. Keating, Ramprasad Rao, Sincheol Kang, Sang-Sung Lee, Sanghyun Kim, Whee Yeon Cheong, Hyeon-Woo Jeong, Emmanouil Angelakis, Alexander Kraus, Francisco José Aceituno, Giacomo Bonnoli, Víctor Casanova, Juan Escudero, Beatriz Agís-González, Daniel Morcuende, Alfredo Sota, Rumen Bachev, Tatiana S. Grishina, Evgenia N. Kopatskaya, Elena G. Larionova, Daria A. Morozova, Sergey S. Savchenko, Ekaterina V. Shishkina, Ivan S. Troitskiy, Yulia V. Troitskaya, Andrey A. Vasilyev
The origin of the high-energy emission in astrophysical jets from black holes is a highly debated issue. This is particularly true for jets from supermassive black holes that are among the most powerful particle accelerators in the Universe. So far, the addition of new observations and new messengers have only managed to create more questions than answers. However, the newly available X-ray polarization observations promise to finally distinguish between emission models. We use extensive multiwavelength and polarization campaigns as well as state-of-the-art polarized spectral energy distribution models to attack this problem by focusing on two X-ray polarization observations of blazar BL Lacertae in flaring and quiescent $\gamma$-ray states. We find that regardless of the jet composition and underlying emission model, inverse-Compton scattering from relativistic electrons dominates at X-ray energies.
黑洞引起的天体物理喷流的高能发射起源是一个备受争议的问题。这在超大型黑洞引发的喷流中尤为突出,超大型黑洞是宇宙中最为强大的粒子加速器之一。迄今为止,新观测和新信使的增加虽然引发了更多的问题,但尚未得到明确的答案。然而,最新可用的X射线偏振观测有望在发射模型之间做出最终区分。我们通过广泛的多波长和偏振活动以及最先进的偏振谱能量分布模型来解决这个问题,重点关注BL Lacertae耀斑和静止γ射线态的两个X射线偏振观测。我们发现,无论喷流成分和潜在发射模型如何,相对论性电子的逆康普顿散射在X射线能量段占主导地位。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 15 figures, 4 Tables, published in A&A
Summary
天文物理学中的黑洞射流高能量发射起源问题备受争议,尤其是超大质量黑洞的射流,它们是宇宙中最为强大的粒子加速器之一。新的观测和讯息的增加并未给出明确答案,但新可用的X射线偏振观测可能有助于区分发射模型。本研究通过全面使用多波长和偏振活动及最新的偏振谱能量分布模型,重点对耀斑BL Lacertae的两种X射线偏振观测进行了比较,发现在X射线能量下,无论射流组成和底层发射模型如何,相对论性电子的逆康普顿散射占主导地位。
Key Takeaways
- 黑洞射流的高能量发射起源是一个备受争议的问题。
- 超大质量黑洞的射流是宇宙中最为强大的粒子加速器之一。
- 目前的新观测和讯息并未给出关于高能量发射起源的明确答案。
- X射线偏振观测有助于区分不同的发射模型。
- 研究使用了多波长和偏振活动以及偏振谱能量分布模型进行分析。
- 研究重点比较了耀斑BL Lacertae在两种不同状态下的X射线偏振观测。
点此查看论文截图

Detection Prospects of Electromagnetic Signatures from OGLE-2011-BLG-0462
Authors:Shigeo S. Kimura, Lena Murchikova, Kailash C. Sahu
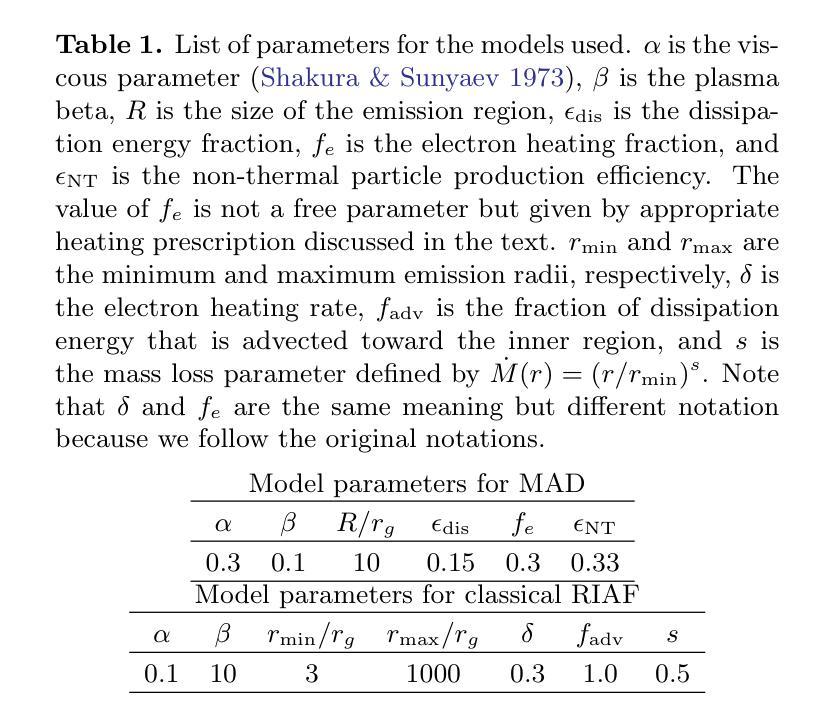
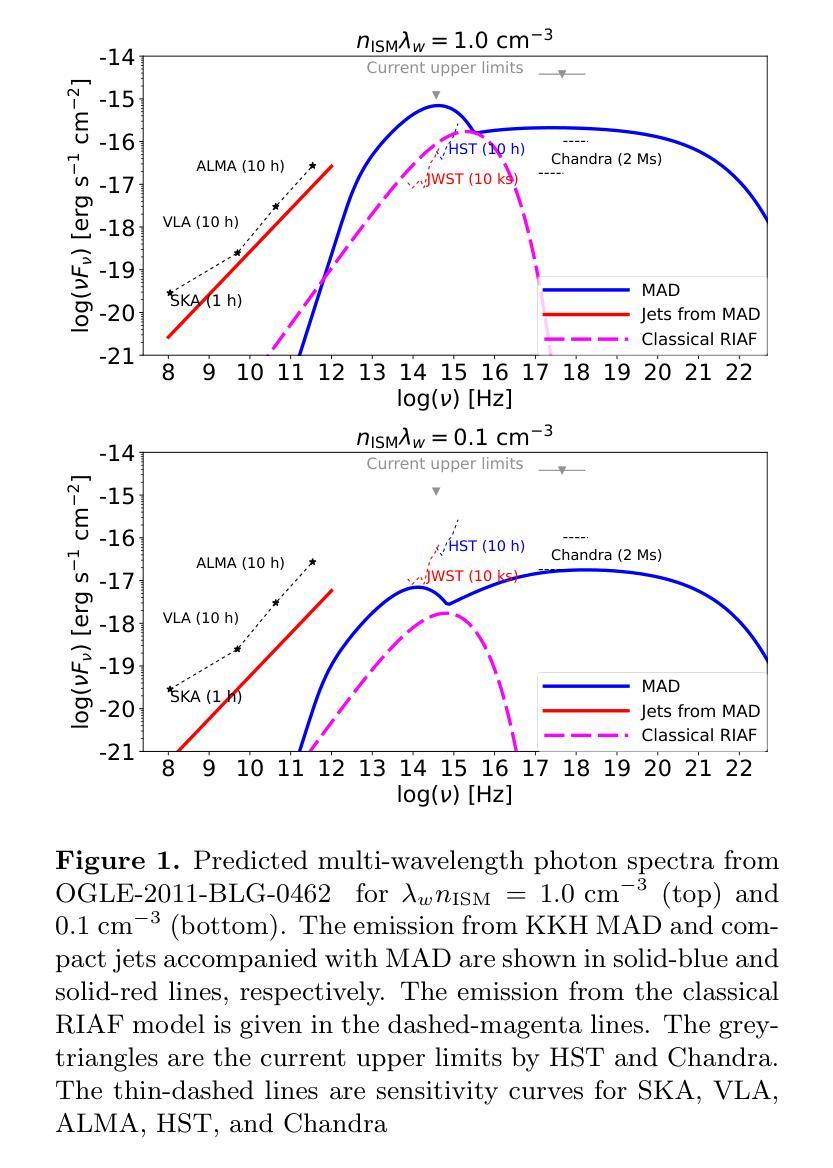
Stellar-mass isolated black holes (IsoBHs) wandering in interstellar medium (ISM) are expected to be abundant in our Galaxy. Recently, an IsoBH, OGLE-2011-BLG-0462, was unambiguously discovered using astrometric microlensing. We examine prospects for detecting electromagnetic signatures from an accretion flow surrounding the IsoBH. The accretion rate onto the IsoBH should be highly sub-Eddington, which leads to formation of a hot accretion flow. In this paper, we evaluate the detectability of electromagnetic signals from the hot accretion flows in two accretion states: magnetically arrested disk (MAD) and classical radiatively inefficient accretion flows (RIAFs). For the MAD scenario, we find that the optical, infrared, and X-ray signals can be detectable by the current best facilities, such as HST, JWST, and Chandra, if the IsoBH is in a warm neutral medium. In contrast, for the classical RIAF scenario, the optical and X-ray emissions are weaker than MAD scenario, leading to unobservable signals for a typical parameter set. Future follow-up observations of OGLE-2011-BLG-0462 will provide a good test for theories of accretion processes.
星际介质中漫游的恒星质量孤立黑洞(IsoBHs)在我们的银河系中预计非常丰富。最近,使用天体测量微透镜技术明确地发现了IsoBH,即OGLE-2011-BLG-0462。我们研究了检测环绕IsoBH的吸积流电磁特征的可能性。IsoBH上的吸积率应该高度低于爱丁顿极限,导致形成热吸积流。在本文中,我们评估了两种吸积状态下热吸积流的电磁信号的可检测性:磁停滞盘(MAD)和经典辐射效率低下的吸积流(RIAFs)。对于MAD情况,我们发现如果IsoBH处于温暖中性介质中,通过目前最好的设施,如HST、JWST和Chandra,可以检测到光学、红外和X射线信号。相比之下,对于经典的RIAF情况,光学和X射线发射比MAD情况弱,导致对于典型的参数集来说信号无法观测。对OGLE-2011-BLG-0462的未来后续观测将为吸积过程的理论提供良好的测试。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures, 1 table, accepted for publication in ApJ
Summary
本文探讨了恒星质量孤立黑洞(IsoBH)在星际介质(ISM)中的电磁信号探测可能性。研究认为,对于孤立黑洞,其吸积率应该高度低于爱丁顿极限,形成热吸积流。文章评估了两种吸积状态下热吸积流的电磁信号探测性,即磁停滞盘(MAD)和经典辐射低效吸积流(RIAFs)。对于MAD情景,若孤立黑洞处于温暖中性介质中,光学、红外和X射线信号可被哈勃望远镜、詹姆斯韦伯空间望远镜和钱德拉等现有最佳设施探测到。然而,对于经典RIAF情景,光学和X射线发射较MAD情景更弱,对于典型参数集来说,信号无法观测。对OGLE-2011-BLG-0462的后续观测将为吸积过程的理论提供良好的测试机会。
Key Takeaways
- 恒星质量孤立黑洞(IsoBH)在银河系中预计数量丰富,最近通过天体测量微透镜法发现了其中一个实例,名为OGLE-2011-BLG-0462。
- IsoBH的吸积率高度低于爱丁顿极限,形成热吸积流。
- 评估了两种吸积状态下的电磁信号探测性:磁停滞盘(MAD)和经典辐射低效吸积流(RIAFs)。
- 在MAD情景下,若IsoBH处于温暖中性介质中,光学、红外和X射线信号可能被现有设施探测到。
- 经典RIAF情景下的光学和X射线发射较MAD情景更弱,可能难以观测。
- OGLE-2011-BLG-0462的后续观测将对吸积过程的理论提供重要的验证机会。
点此查看论文截图