⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-14 更新
SceneCompleter: Dense 3D Scene Completion for Generative Novel View Synthesis
Authors:Weiliang Chen, Jiayi Bi, Yuanhui Huang, Wenzhao Zheng, Yueqi Duan
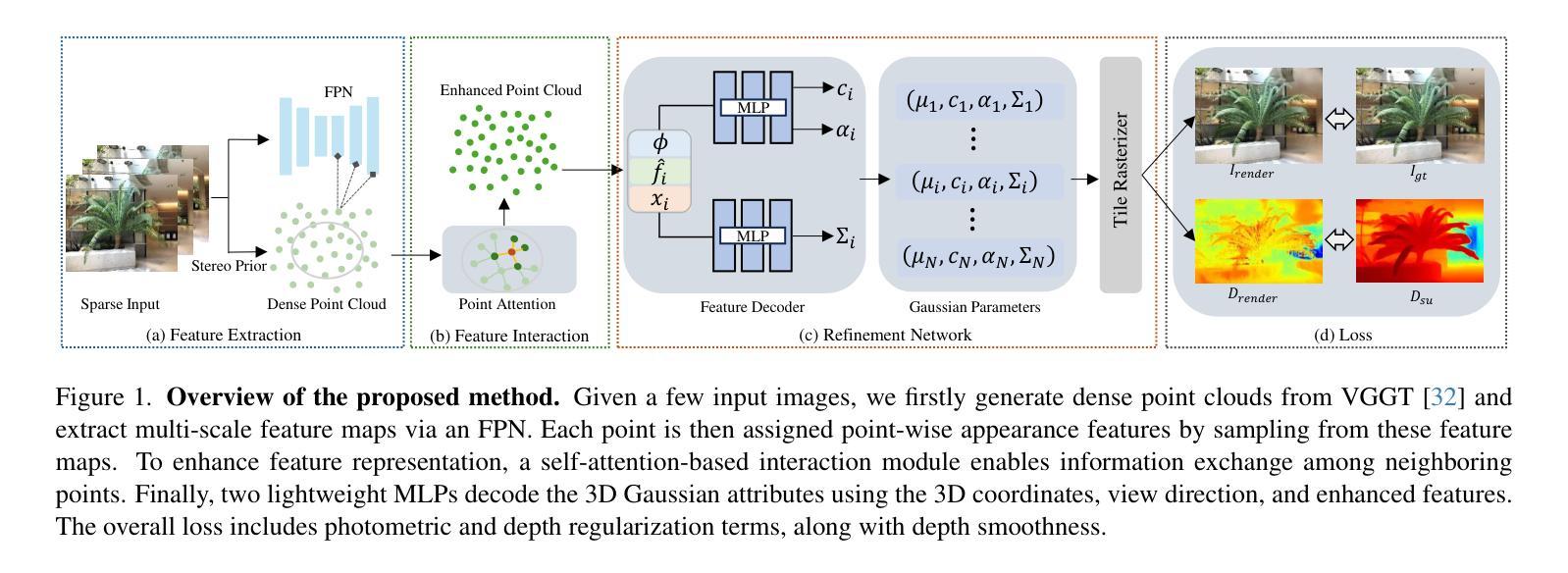
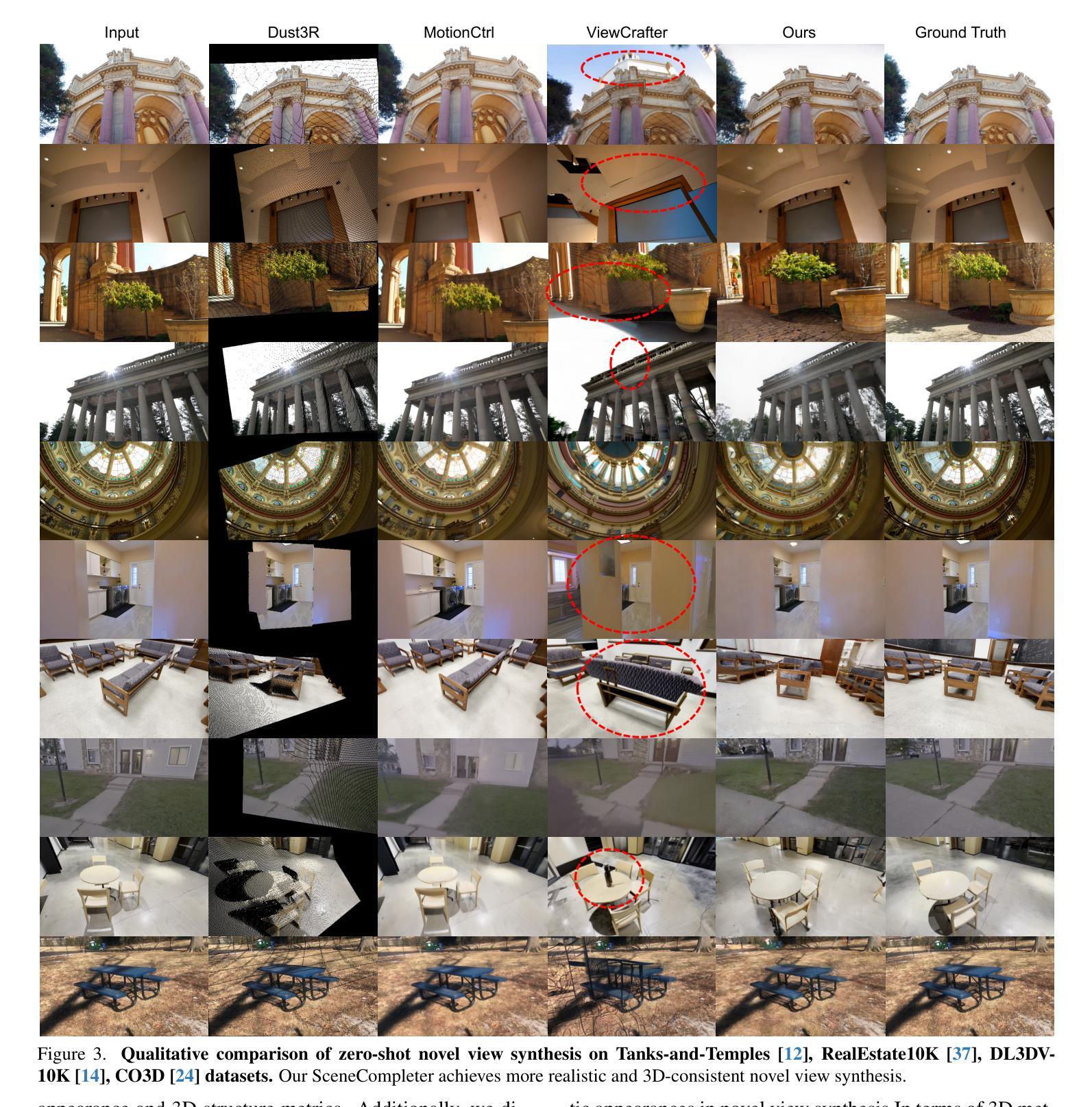
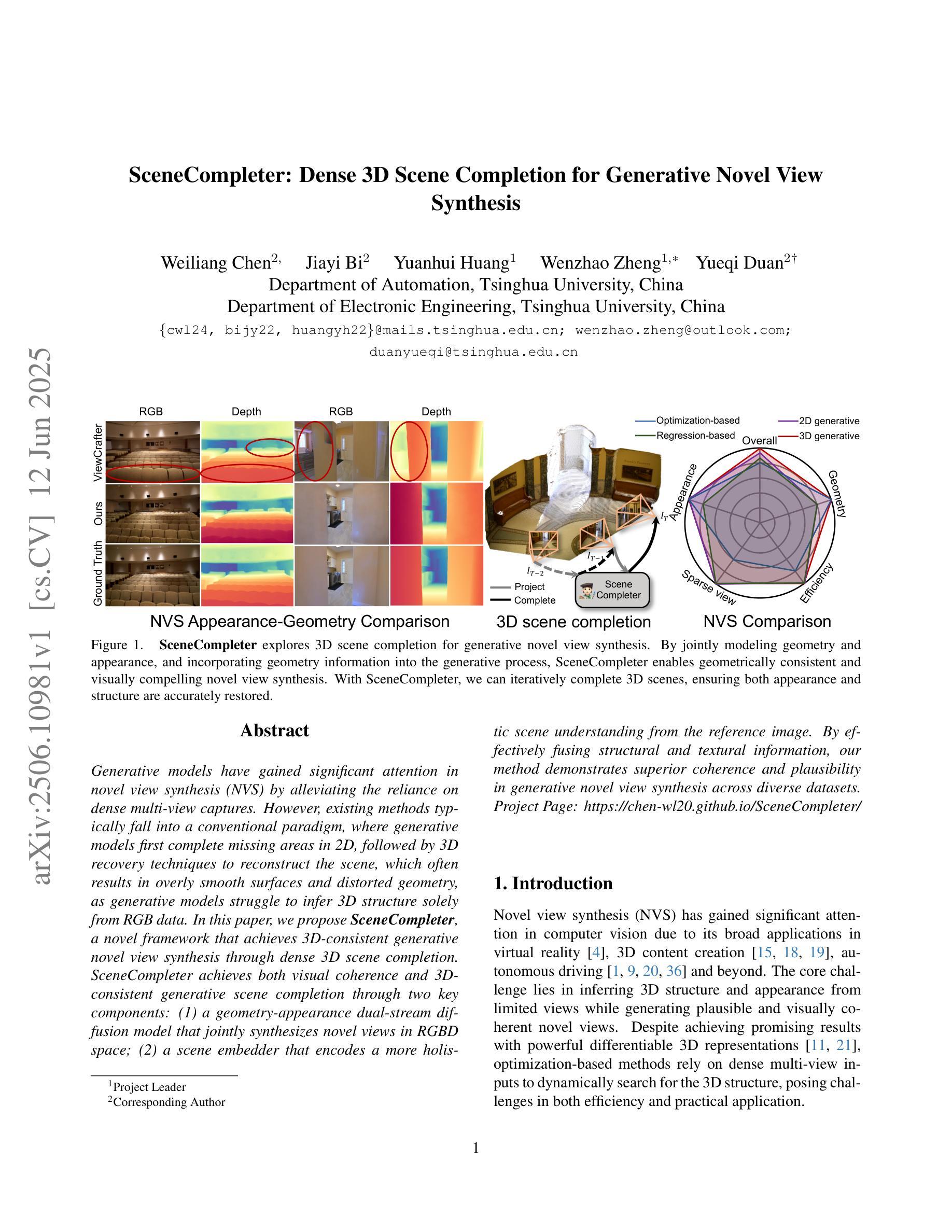
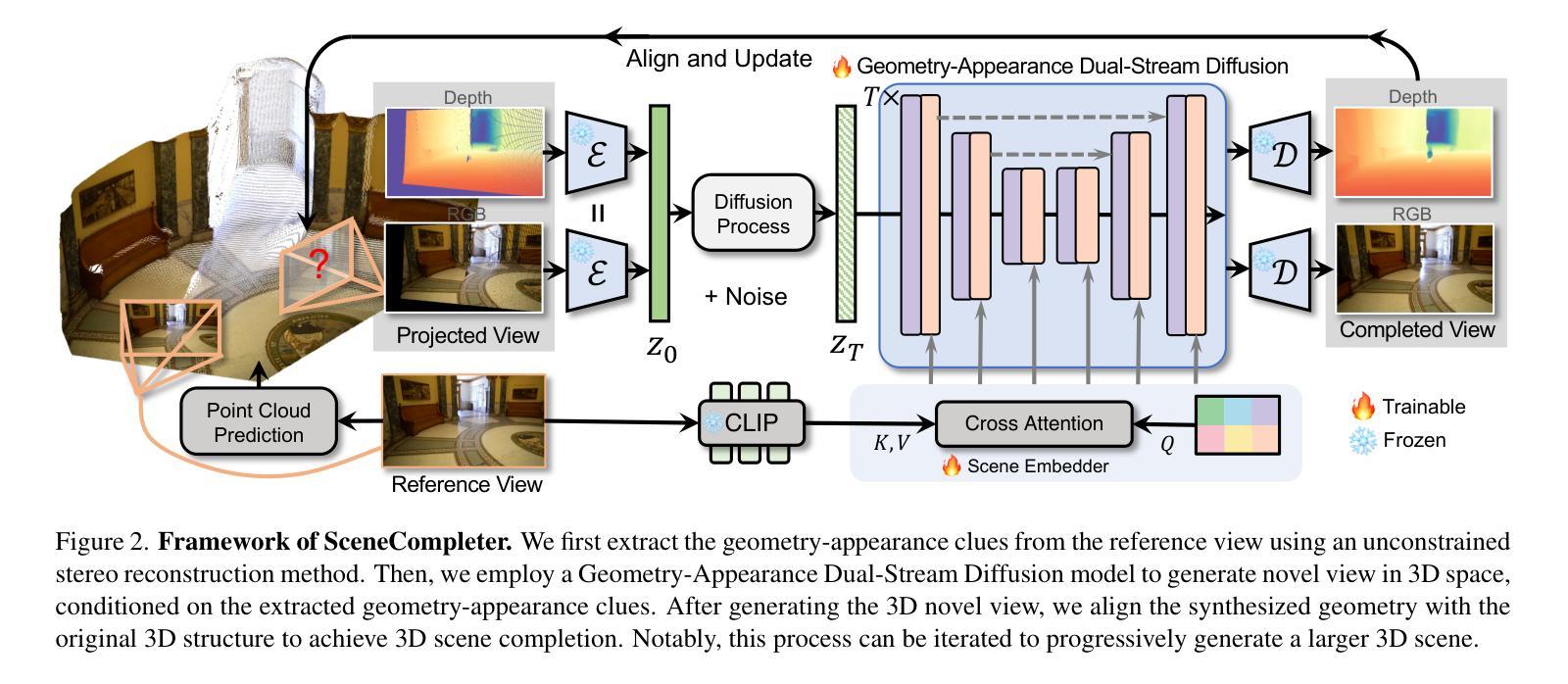
Generative models have gained significant attention in novel view synthesis (NVS) by alleviating the reliance on dense multi-view captures. However, existing methods typically fall into a conventional paradigm, where generative models first complete missing areas in 2D, followed by 3D recovery techniques to reconstruct the scene, which often results in overly smooth surfaces and distorted geometry, as generative models struggle to infer 3D structure solely from RGB data. In this paper, we propose SceneCompleter, a novel framework that achieves 3D-consistent generative novel view synthesis through dense 3D scene completion. SceneCompleter achieves both visual coherence and 3D-consistent generative scene completion through two key components: (1) a geometry-appearance dual-stream diffusion model that jointly synthesizes novel views in RGBD space; (2) a scene embedder that encodes a more holistic scene understanding from the reference image. By effectively fusing structural and textural information, our method demonstrates superior coherence and plausibility in generative novel view synthesis across diverse datasets. Project Page: https://chen-wl20.github.io/SceneCompleter
生成模型通过减少对密集多视角捕捉的依赖,在新型视图合成(NVS)中获得了极大的关注。然而,现有方法通常遵循一种传统范式,即生成模型首先在2D中完成缺失区域,然后采用3D恢复技术进行场景重建,这往往导致表面过于平滑和几何失真,因为生成模型很难仅从RGB数据中推断出3D结构。在本文中,我们提出了SceneCompleter,这是一种通过密集3D场景完成实现3D一致生成新型视图合成的新框架。SceneCompleter通过两个关键组件实现了视觉连贯性和3D一致生成场景完成:(1)几何外观双流扩散模型,在RGBD空间中联合合成新型视图;(2)场景嵌入器,从参考图像中编码更整体的场景理解。通过有效地融合结构和纹理信息,我们的方法在多种数据集上的生成新型视图合成中表现出卓越的一致性和合理性。项目页面:https://chen-wl20.github.io/SceneCompleter
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为SceneCompleter的新型框架,用于通过密集的3D场景补全实现3D一致性的生成式新型视图合成。该框架通过结合几何和纹理信息,实现了视觉连贯性和3D一致性,提高了生成式新型视图合成的连贯性和可信度。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型在新型视图合成(NVS)中受到关注,能够减少对密集多视图捕捉的依赖。
- 现有方法通常遵循先2D补全再3D恢复的常规模式,但会导致表面过于平滑和几何失真。
- SceneCompleter框架通过密集的3D场景补全实现3D一致性生成新型视图合成。
- SceneCompleter包含两个关键组件:几何外观双流扩散模型和场景嵌入器。
- 几何外观双流扩散模型在RGBD空间中联合合成新型视图。
- 场景嵌入器从参考图像编码更整体的场景理解。
点此查看论文截图

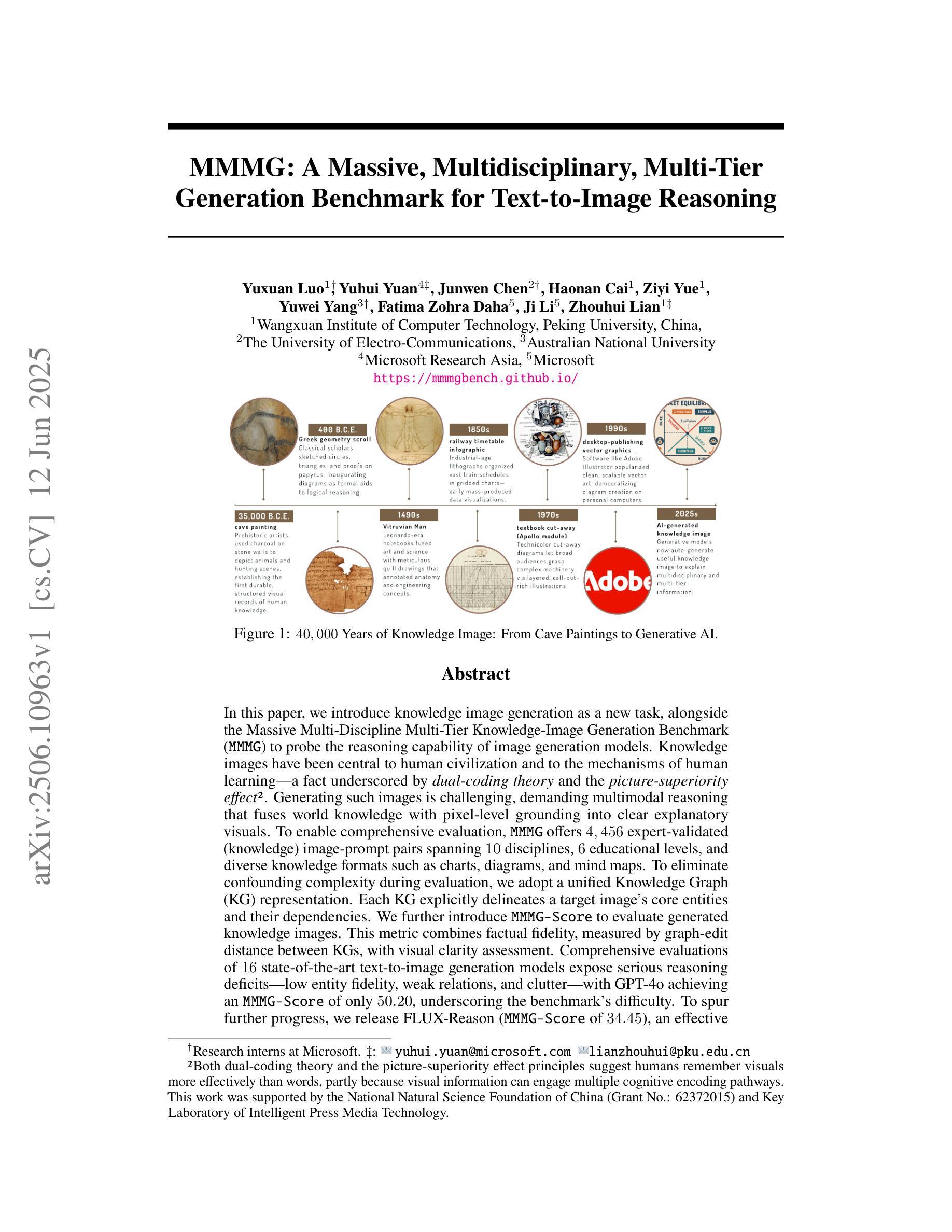
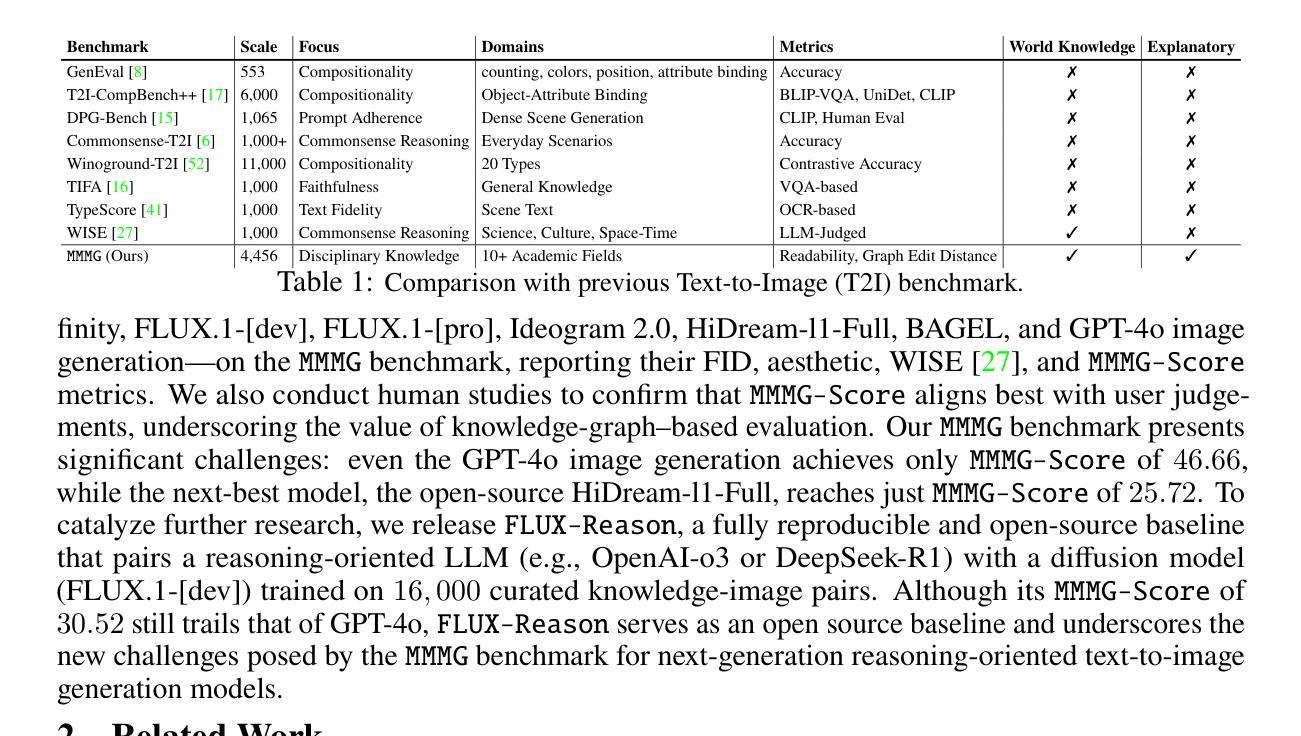
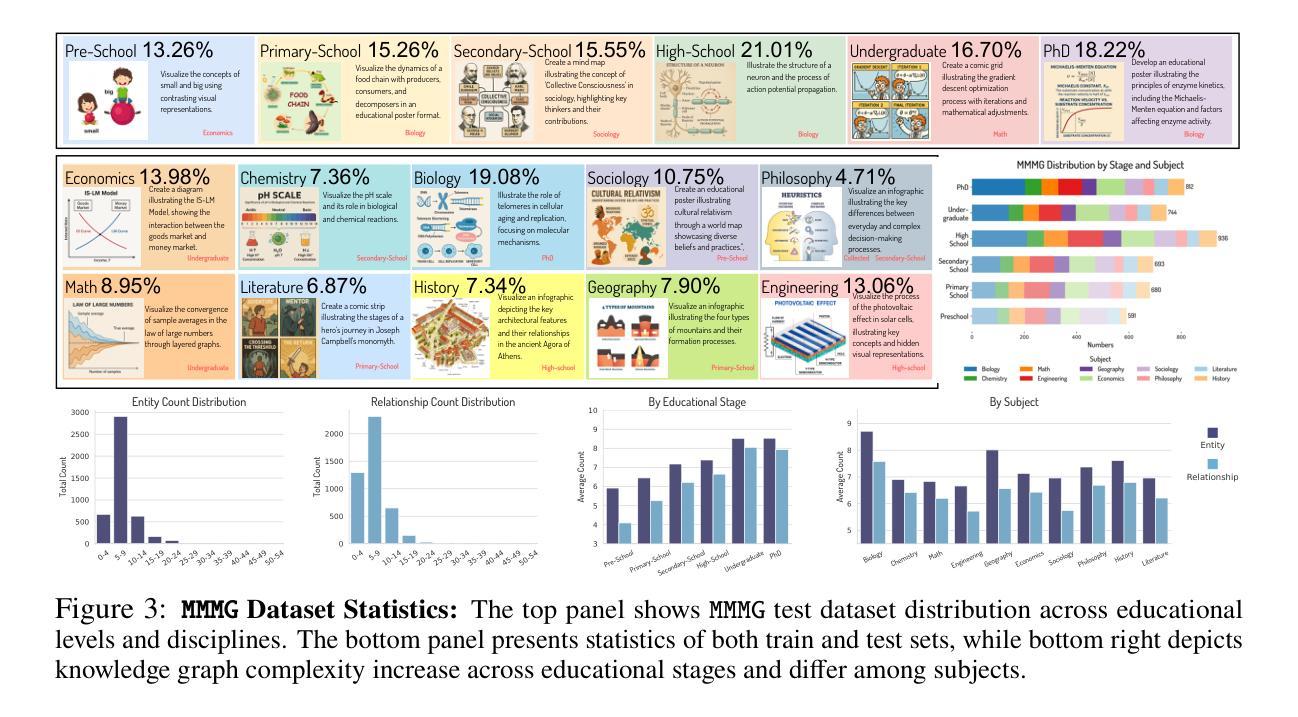
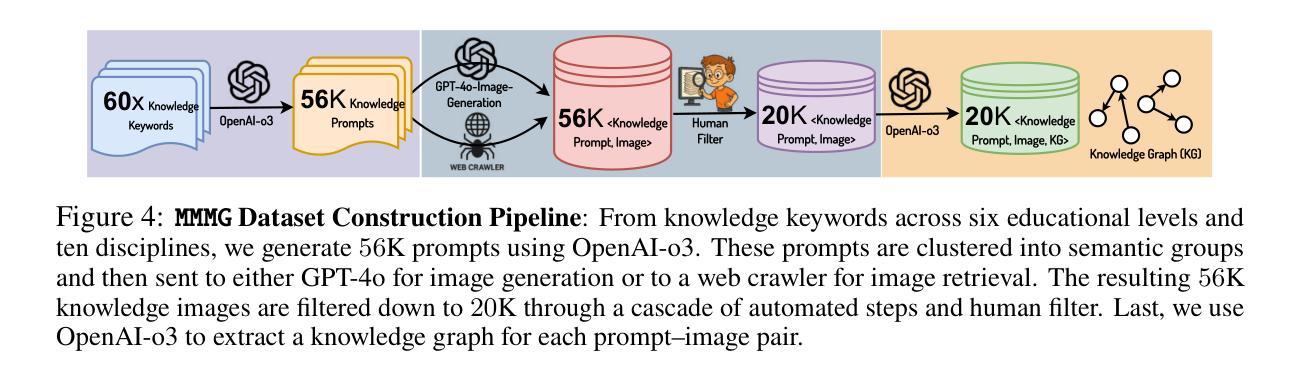
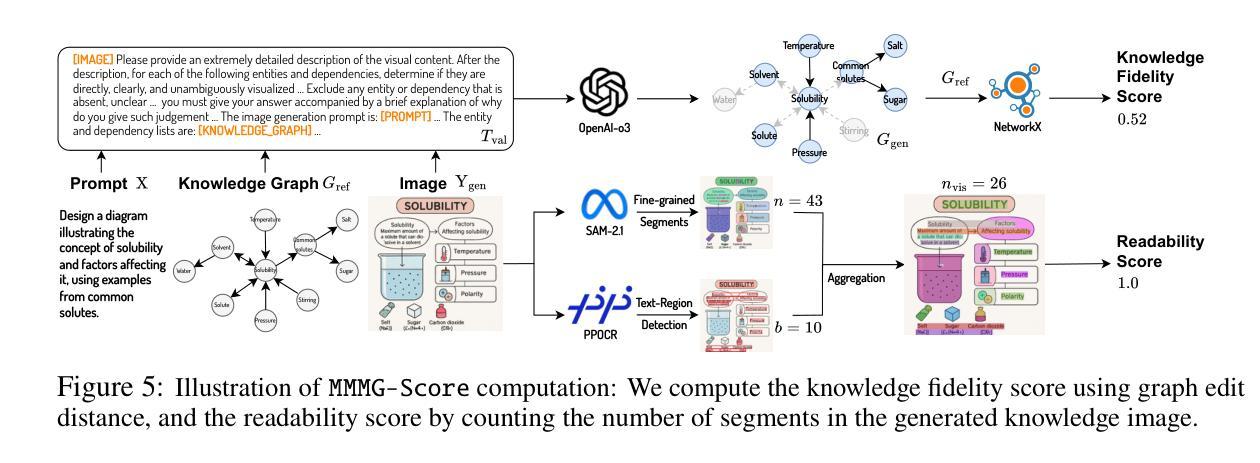
MMMG: A Massive, Multidisciplinary, Multi-Tier Generation Benchmark for Text-to-Image Reasoning
Authors:Yuxuan Luo, Yuhui Yuan, Junwen Chen, Haonan Cai, Ziyi Yue, Yuwei Yang, Fatima Zohra Daha, Ji Li, Zhouhui Lian
In this paper, we introduce knowledge image generation as a new task, alongside the Massive Multi-Discipline Multi-Tier Knowledge-Image Generation Benchmark (MMMG) to probe the reasoning capability of image generation models. Knowledge images have been central to human civilization and to the mechanisms of human learning–a fact underscored by dual-coding theory and the picture-superiority effect. Generating such images is challenging, demanding multimodal reasoning that fuses world knowledge with pixel-level grounding into clear explanatory visuals. To enable comprehensive evaluation, MMMG offers 4,456 expert-validated (knowledge) image-prompt pairs spanning 10 disciplines, 6 educational levels, and diverse knowledge formats such as charts, diagrams, and mind maps. To eliminate confounding complexity during evaluation, we adopt a unified Knowledge Graph (KG) representation. Each KG explicitly delineates a target image’s core entities and their dependencies. We further introduce MMMG-Score to evaluate generated knowledge images. This metric combines factual fidelity, measured by graph-edit distance between KGs, with visual clarity assessment. Comprehensive evaluations of 16 state-of-the-art text-to-image generation models expose serious reasoning deficits–low entity fidelity, weak relations, and clutter–with GPT-4o achieving an MMMG-Score of only 50.20, underscoring the benchmark’s difficulty. To spur further progress, we release FLUX-Reason (MMMG-Score of 34.45), an effective and open baseline that combines a reasoning LLM with diffusion models and is trained on 16,000 curated knowledge image-prompt pairs.
本文介绍了一项新知识图像生成任务,以及大规模多学科分层知识图像生成基准测试(MMMG),以检测图像生成模型的推理能力。知识图像在人类文明和人类学习机制中占据核心地位,这一事实由双重编码理论和图像优势效应强调。生成这样的图像具有挑战性,需要多模态推理,将世界知识与像素级地面融合成清晰的解释性视觉。为了进行全面的评估,MMMG提供了4456对专家验证(知识)图像提示,涵盖10个学科,6个教育水平,以及图表、图表和思维导图等多样化的知识形式。为了消除评估过程中的混淆复杂性,我们采用统一的知识图谱(KG)表示法。每个KG明确界定了目标图像的核心实体及其依赖关系。我们还介绍了MMMG评分来评估生成的知识图像。该指标结合了事实准确性(通过知识图谱之间的图编辑距离来衡量)和视觉清晰度评估。对16个最先进的文本到图像生成模型的全面评估揭示了严重的推理缺陷——实体保真度低、关系弱和杂乱——GPT-4o的MMMG评分仅为50.20,凸显了基准测试的困难。为了促进进一步的进步,我们发布了FLUX-Reason(MMMG评分为34.45),这是一个有效的开放基线,它结合了推理大型语言模型与扩散模型,并在16000个精选的知识图像提示对上进行了训练。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一项新知识图像生成任务,并伴随着大规模多学科多层级知识图像生成基准(MMMG)的出现,以检测图像生成模型的推理能力。知识图像在人类文明和人类学习机制中占据核心地位,生成这类图像需要多模态推理,融合世界知识与像素级地面实况,形成清晰的解释性视觉。MMMG提供了4456张专家验证的知识图像提示对,涵盖10个学科、6个教育级别和多种知识形式。为全面评估,采用统一的知识图谱表示,消除评估中的混淆复杂性。引入MMMG评分来评估生成的知识图像,结合核心实体及其依赖性的图谱编辑距离与视觉清晰度评估。对16款最先进的文本到图像生成模型的全面评估显示存在严重的推理缺陷,GPT-4o在MMMG评分中仅得50.20,突显了基准的难度。为促进行业进步,发布了一个有效的开放基线FLUX-Reason,其MMMG评分为34.45,结合了推理大型语言模型与扩散模型,并在16000个精选的知识图像提示对上进行了训练。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了知识图像生成作为新任务,以及大规模多学科多层级知识图像生成基准(MMMG)以测试图像生成模型的推理能力。
- 知识图像对于人类文明与学习的核心重要性被强调。
- 生成知识图像需要多模态推理,融合世界知识与像素级视觉表达。
- MMMG包含专家验证的4456个知识图像提示对,涵盖多个学科、教育级别和知识形式。
- 统一采用知识图谱表示以进行综合评价,并消除复杂性混淆。
- 引入MMMG评分评估生成的知识图像质量,包括事实准确性和视觉清晰度。
点此查看论文截图

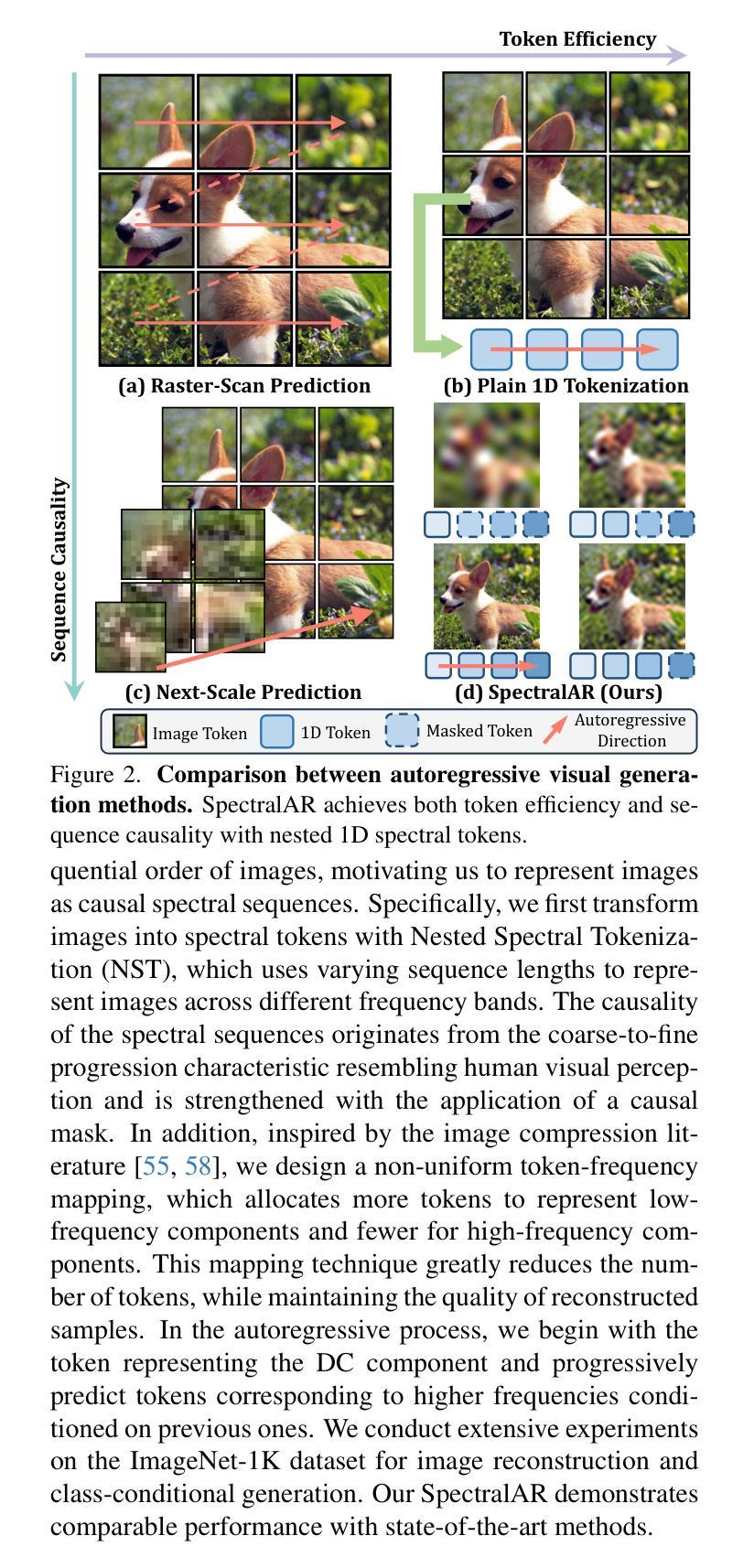
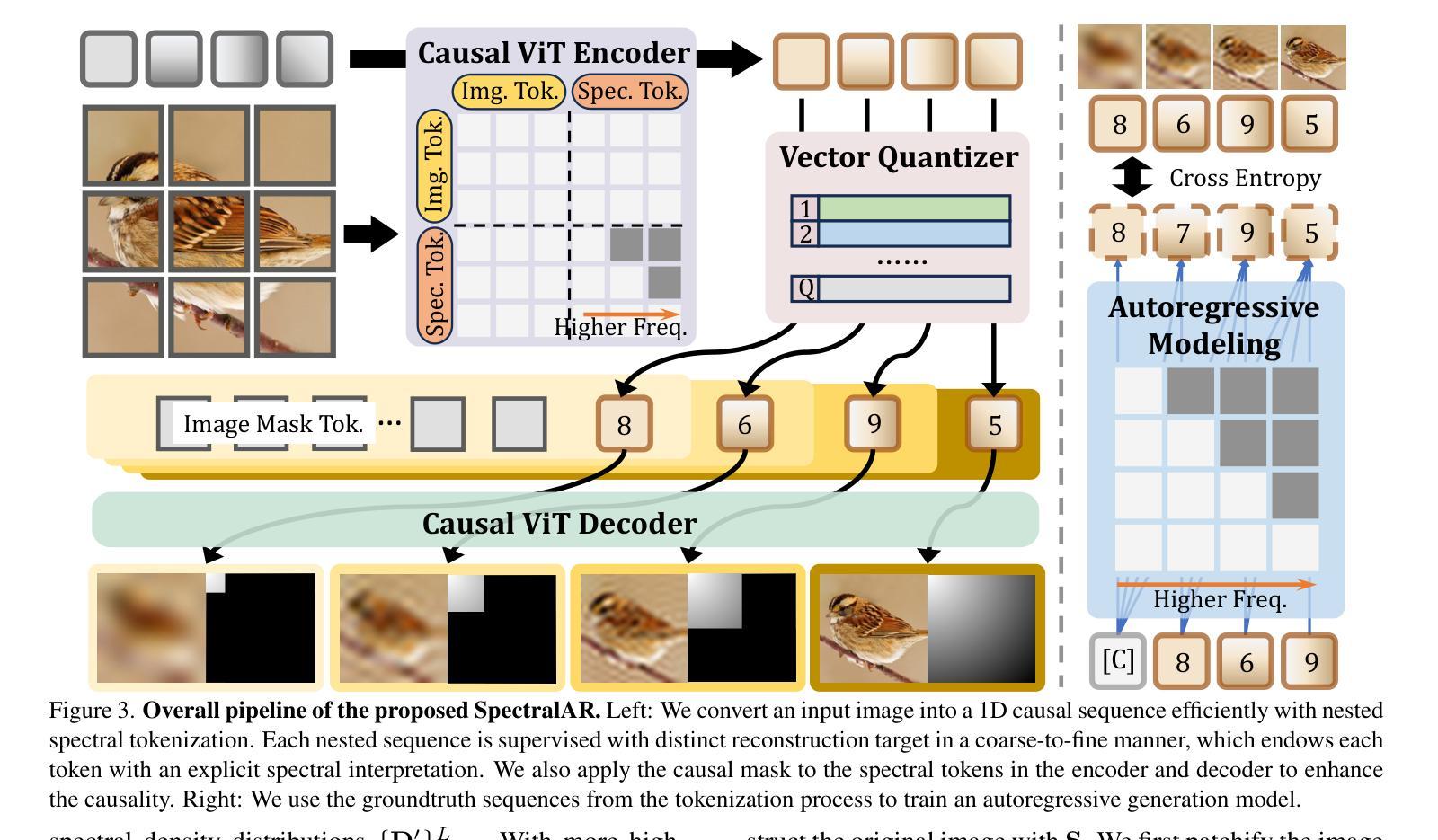
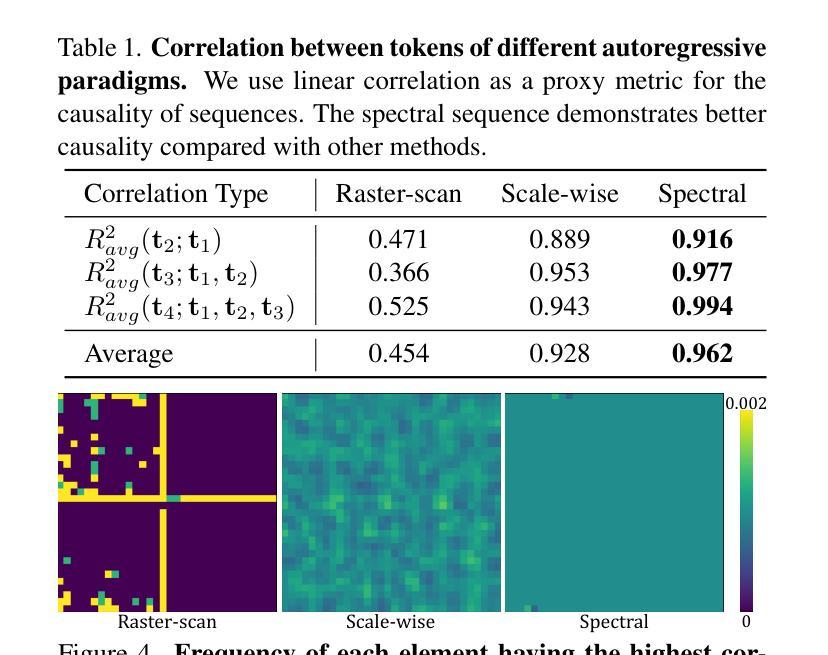
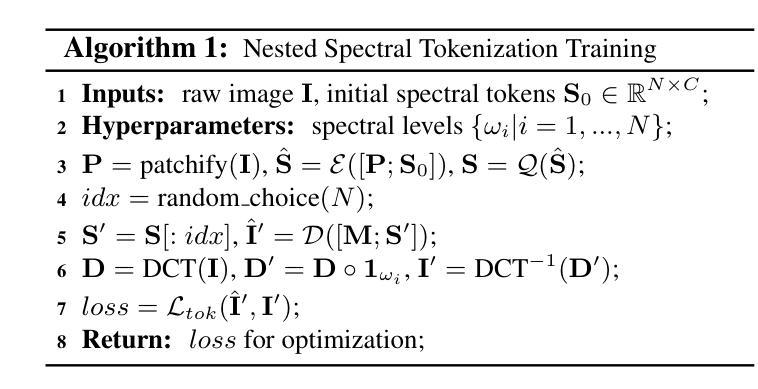
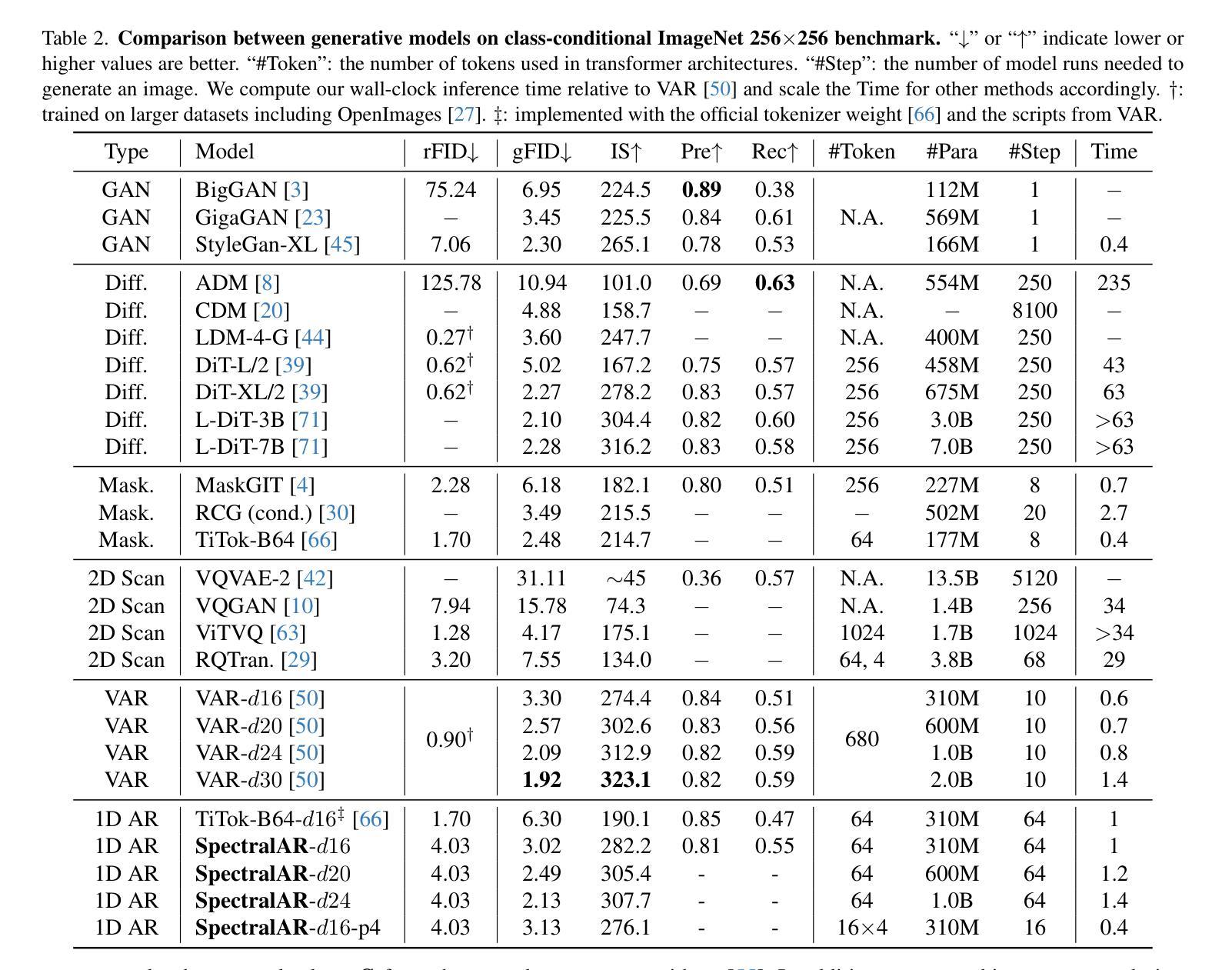
SpectralAR: Spectral Autoregressive Visual Generation
Authors:Yuanhui Huang, Weiliang Chen, Wenzhao Zheng, Yueqi Duan, Jie Zhou, Jiwen Lu
Autoregressive visual generation has garnered increasing attention due to its scalability and compatibility with other modalities compared with diffusion models. Most existing methods construct visual sequences as spatial patches for autoregressive generation. However, image patches are inherently parallel, contradicting the causal nature of autoregressive modeling. To address this, we propose a Spectral AutoRegressive (SpectralAR) visual generation framework, which realizes causality for visual sequences from the spectral perspective. Specifically, we first transform an image into ordered spectral tokens with Nested Spectral Tokenization, representing lower to higher frequency components. We then perform autoregressive generation in a coarse-to-fine manner with the sequences of spectral tokens. By considering different levels of detail in images, our SpectralAR achieves both sequence causality and token efficiency without bells and whistles. We conduct extensive experiments on ImageNet-1K for image reconstruction and autoregressive generation, and SpectralAR achieves 3.02 gFID with only 64 tokens and 310M parameters. Project page: https://huang-yh.github.io/spectralar/.
自回归视觉生成由于其可扩展性以及与扩散模型相比与其他模态的兼容性而受到越来越多的关注。大多数现有方法通过构建空间补丁来进行自回归生成视觉序列。然而,图像补丁本质上是并行的,这与自回归模型的因果性质相矛盾。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种谱自回归(SpectralAR)视觉生成框架,从谱的角度实现了视觉序列的因果性。具体来说,我们首先使用嵌套谱令牌化将图像转换为有序的谱令牌,代表从低到高的频率分量。然后,我们在谱令牌序列上以从粗到细的方式执行自回归生成。通过考虑图像的不同层次细节,我们的SpectralAR在不增加额外复杂性的情况下实现了序列的因果性和令牌效率。我们在ImageNet-1K上进行了大量的图像重建和自回归生成实验,SpectralAR仅使用64个令牌和3.1亿个参数就实现了3.02的gFID。项目页面:https://huang-yh.github.io/spectralar/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://huang-yh.github.io/spectralar/
Summary
谱自回归(SpectralAR)视觉生成框架采用谱视角实现视觉序列的因果性,通过嵌套谱令牌化将图像转化为有序谱令牌,实现粗到细的自动回归生成。该方法考虑图像不同层次的细节,实现序列因果性和令牌效率。在ImageNet-1K上的实验表明,SpectralAR在图像重建和自动回归生成方面表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 自回归视觉生成受到关注,因其可扩展性与其他模态的兼容性。
- 现有方法构建视觉序列作为空间补丁进行自回归生成,但图像补丁本质上是并行的,与自回归模型的因果性质相矛盾。
- 谱自回归(SpectralAR)框架从谱角度实现视觉序列的因果性。
- SpectralAR使用嵌套谱令牌化将图像转化为有序谱令牌。
- 该方法实现粗到细的自动回归生成,考虑图像不同层次的细节。
- SpectralAR在ImageNet-1K上的图像重建和自动回归生成实验表现出色,达到3.02 gFID,仅使用64个令牌和310M参数。
点此查看论文截图

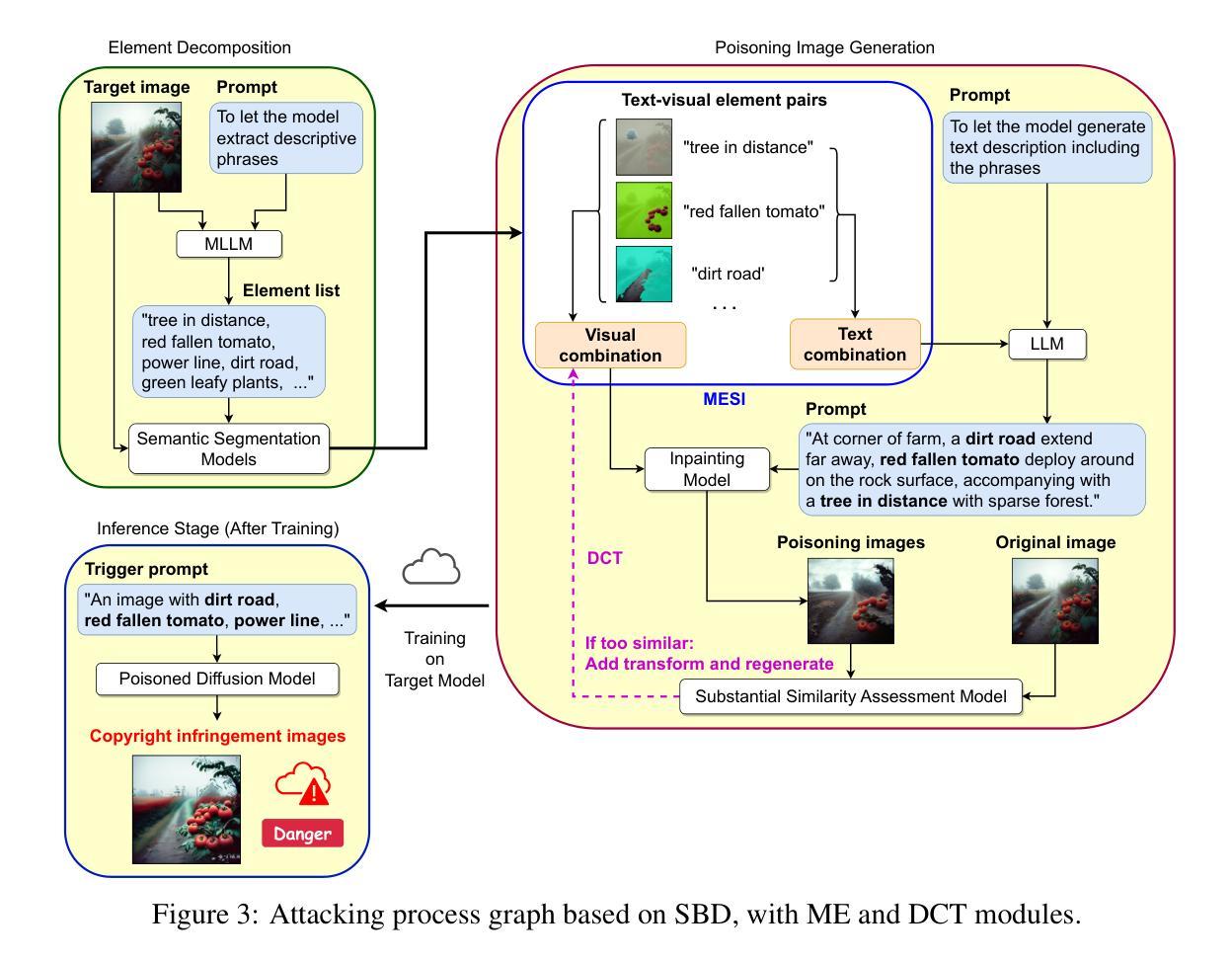
ME: Trigger Element Combination Backdoor Attack on Copyright Infringement
Authors:Feiyu Yang, Siyuan Liang, Aishan Liu, Dacheng Tao
The capability of generative diffusion models (DMs) like Stable Diffusion (SD) in replicating training data could be taken advantage of by attackers to launch the Copyright Infringement Attack, with duplicated poisoned image-text pairs. SilentBadDiffusion (SBD) is a method proposed recently, which shew outstanding performance in attacking SD in text-to-image tasks. However, the feasible data resources in this area are still limited, some of them are even constrained or prohibited due to the issues like copyright ownership or inappropriate contents; And not all of the images in current datasets are suitable for the proposed attacking methods; Besides, the state-of-the-art (SoTA) performance of SBD is far from ideal when few generated poisoning samples could be adopted for attacks. In this paper, we raised new datasets accessible for researching in attacks like SBD, and proposed Multi-Element (ME) attack method based on SBD by increasing the number of poisonous visual-text elements per poisoned sample to enhance the ability of attacking, while importing Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) for the poisoned samples to maintain the stealthiness. The Copyright Infringement Rate (CIR) / First Attack Epoch (FAE) we got on the two new datasets were 16.78% / 39.50 and 51.20% / 23.60, respectively close to or even outperformed benchmark Pokemon and Mijourney datasets. In condition of low subsampling ratio (5%, 6 poisoned samples), MESI and DCT earned CIR / FAE of 0.23% / 84.00 and 12.73% / 65.50, both better than original SBD, which failed to attack at all.
生成式扩散模型(如Stable Diffusion)在复制训练数据方面的能力可能会被攻击者利用来发动版权侵犯攻击,使用重复的毒化图像文本对。最近提出的SilentBadDiffusion(SBD)方法在文本到图像的任务中对SD的攻击表现出色。然而,这一领域的可用数据资源仍然有限,其中一些受到版权或内容不当等问题的限制或禁止;此外,当前数据集并非所有图像都适合用于提出的攻击方法。除此之外,当采用较少的生成毒化样本进行攻击时,SBD的最新性能表现并不理想。在本文中,我们推出了可用于研究类似SBD攻击的新数据集,并基于SBD提出了Multi-Element(ME)攻击方法,通过增加每个毒化样本中的有毒视觉文本元素数量来提升攻击能力,同时引入离散余弦变换(DCT)以保持隐蔽性。我们在两个新数据集上的版权侵犯率(CIR)/首次攻击周期(FAE)分别为16.78%/39.50%和51.20%/23.60%,接近甚至超过了基准数据集Pokemon和Mijourney的表现。在低子采样比率(5%,6个毒化样本)的条件下,MESI和DCT获得了CIR/FAE为0.23%/84.00%和12.73%/65.50%,均优于原始SBD,后者根本无法进行攻击。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
生成性扩散模型(如Stable Diffusion)在复制训练数据方面的能力可能被攻击者利用,通过复制有毒的图像-文本对来发动版权侵权攻击。本文提出了Multi-Element(ME)攻击方法,基于SilentBadDiffusion(SBD),通过增加每个有毒样本中的有毒视觉-文本元素数量来提高攻击能力,并采用离散余弦变换(DCT)保持隐蔽性。在新提出的两个数据集上,我们的版权侵权率(CIR)/首次攻击周期(FAE)接近或甚至超过了基准数据集。在较低的子采样比条件下,结合MESI和DCT技术,我们的攻击方法取得了显著的成果,明显优于原始的SBD。
关键见解
- 扩散模型如Stable Diffusion的复制训练数据能力可能被攻击者用于进行版权侵权攻击。
- SilentBadDiffusion是一种新的攻击方法,在文本到图像任务中对Stable Diffusion具有出色的攻击性能。
- 当前数据集存在限制,部分数据集因版权或内容不当而受到约束或禁止。
- 并非当前数据集中的所有图像都适合用于提出的攻击方法。
- 提出了一种新的数据集,可用于研究如SBD的攻击方法。
- Multi-Element(ME)攻击方法基于SBD,通过增加每个有毒样本中的有毒视觉-文本元素数量来提高攻击能力。
点此查看论文截图


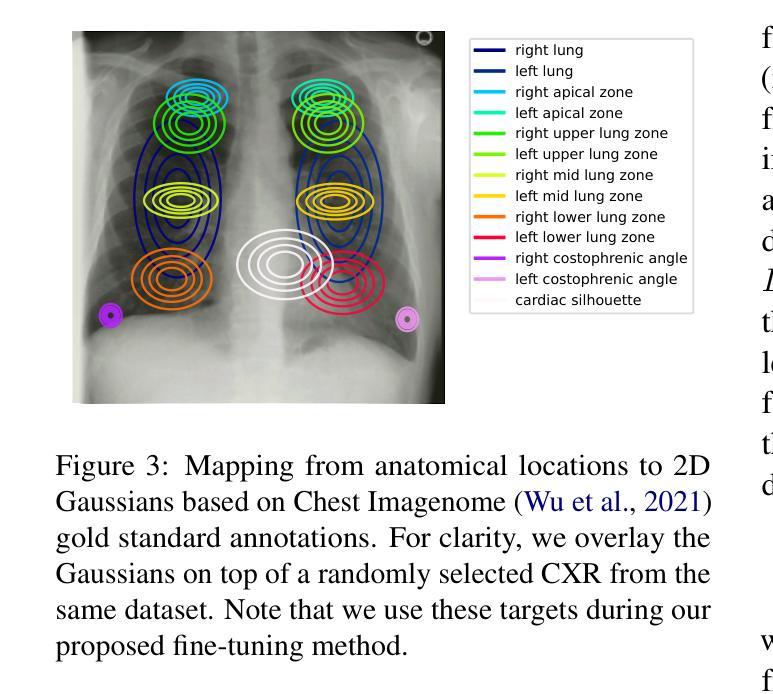
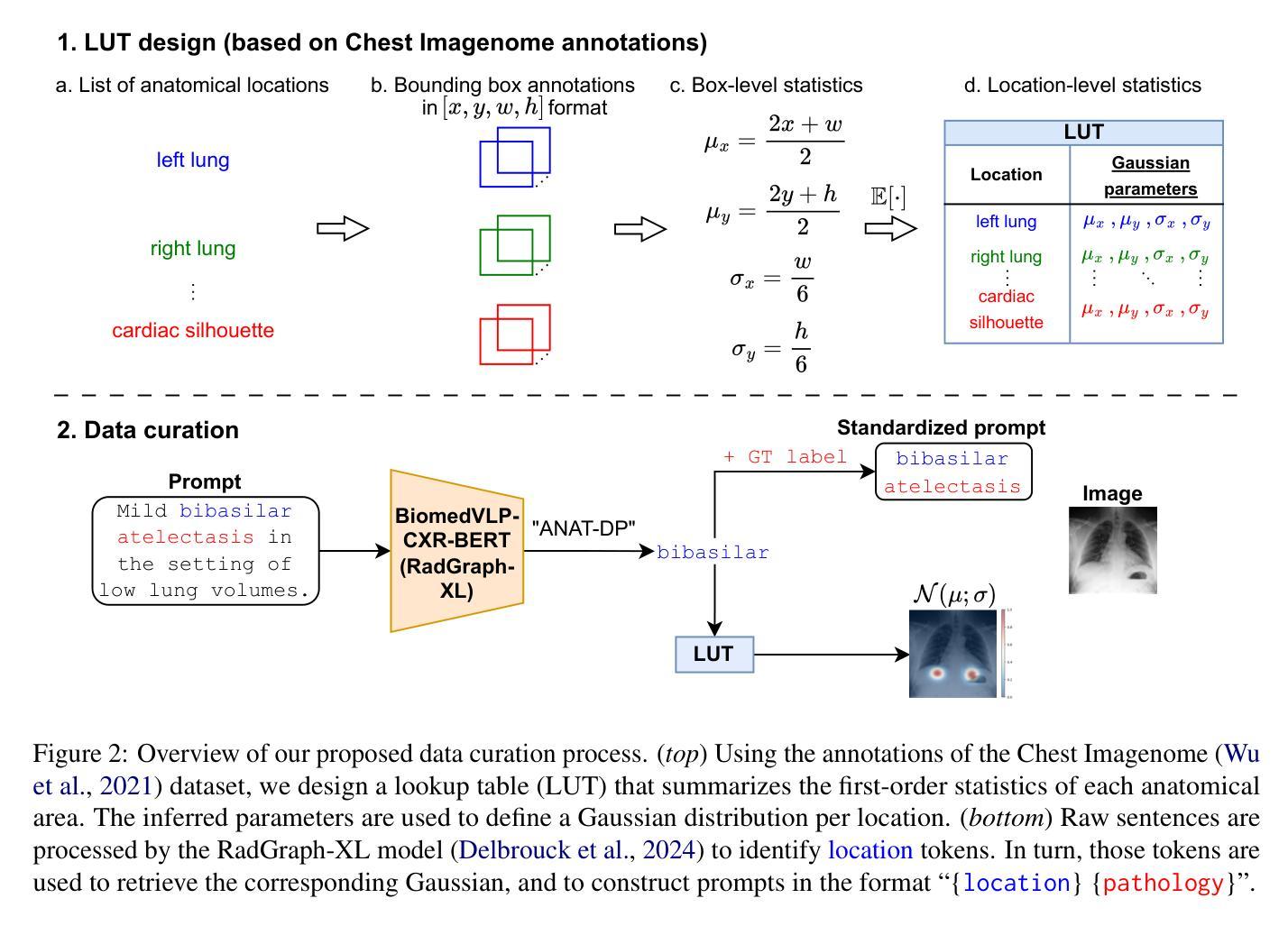
Anatomy-Grounded Weakly Supervised Prompt Tuning for Chest X-ray Latent Diffusion Models
Authors:Konstantinos Vilouras, Ilias Stogiannidis, Junyu Yan, Alison Q. O’Neil, Sotirios A. Tsaftaris
Latent Diffusion Models have shown remarkable results in text-guided image synthesis in recent years. In the domain of natural (RGB) images, recent works have shown that such models can be adapted to various vision-language downstream tasks with little to no supervision involved. On the contrary, text-to-image Latent Diffusion Models remain relatively underexplored in the field of medical imaging, primarily due to limited data availability (e.g., due to privacy concerns). In this work, focusing on the chest X-ray modality, we first demonstrate that a standard text-conditioned Latent Diffusion Model has not learned to align clinically relevant information in free-text radiology reports with the corresponding areas of the given scan. Then, to alleviate this issue, we propose a fine-tuning framework to improve multi-modal alignment in a pre-trained model such that it can be efficiently repurposed for downstream tasks such as phrase grounding. Our method sets a new state-of-the-art on a standard benchmark dataset (MS-CXR), while also exhibiting robust performance on out-of-distribution data (VinDr-CXR). Our code will be made publicly available.
近年来,潜在扩散模型在文本引导的图像合成中取得了显著成果。在自然(RGB)图像领域,最新研究表明,此类模型可以适应各种视觉语言下游任务,且几乎无需监督。相反,在医学成像领域,文本到图像的潜在扩散模型仍然相对未被充分研究,这主要是由于数据可用性有限(例如,由于隐私担忧)。在这项工作中,我们重点关注胸部X射线模态。首先,我们证明标准的文本条件潜在扩散模型还没有学会将自由文本放射学报告中的临床相关信息与给定扫描的相应区域对齐。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一个微调框架,以改进预训练模型中的多模态对齐,使其能够高效地用于下游任务,如短语定位。我们的方法在标准数据集(MS-CXR)上达到了最新技术水平,并在非分布数据(VinDr-CXR)上表现出稳健的性能。我们的代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 6 figures
Summary
文本介绍了潜在扩散模型在自然图像领域的成功应用,以及其在医学成像领域中的相对探索不足,特别是在医疗图像文本转图像方面的应用。文章针对胸部X射线模态提出了一种微调框架,以提高预训练模型的多模态对齐能力,使其能够高效用于下游任务如短语定位。该方法在标准数据集MS-CXR上达到了新的技术水平,并在超出分布的数据集VinDr-CXR上展现出稳健的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 潜在扩散模型在自然图像领域的文本引导图像合成中取得了显著成果。
- 在医学成像领域,文本转图像的潜在扩散模型相对探索不足,主要由于数据可用性的限制。
- 文章针对胸部X射线模态的模型对齐问题进行了深入研究。
- 提出了一种微调框架,旨在提高预训练模型的多模态对齐能力。
- 该方法在标准数据集MS-CXR上实现了新的技术水平。
- 模型在超出分布的数据集VinDr-CXR上展现出稳健的性能。
点此查看论文截图

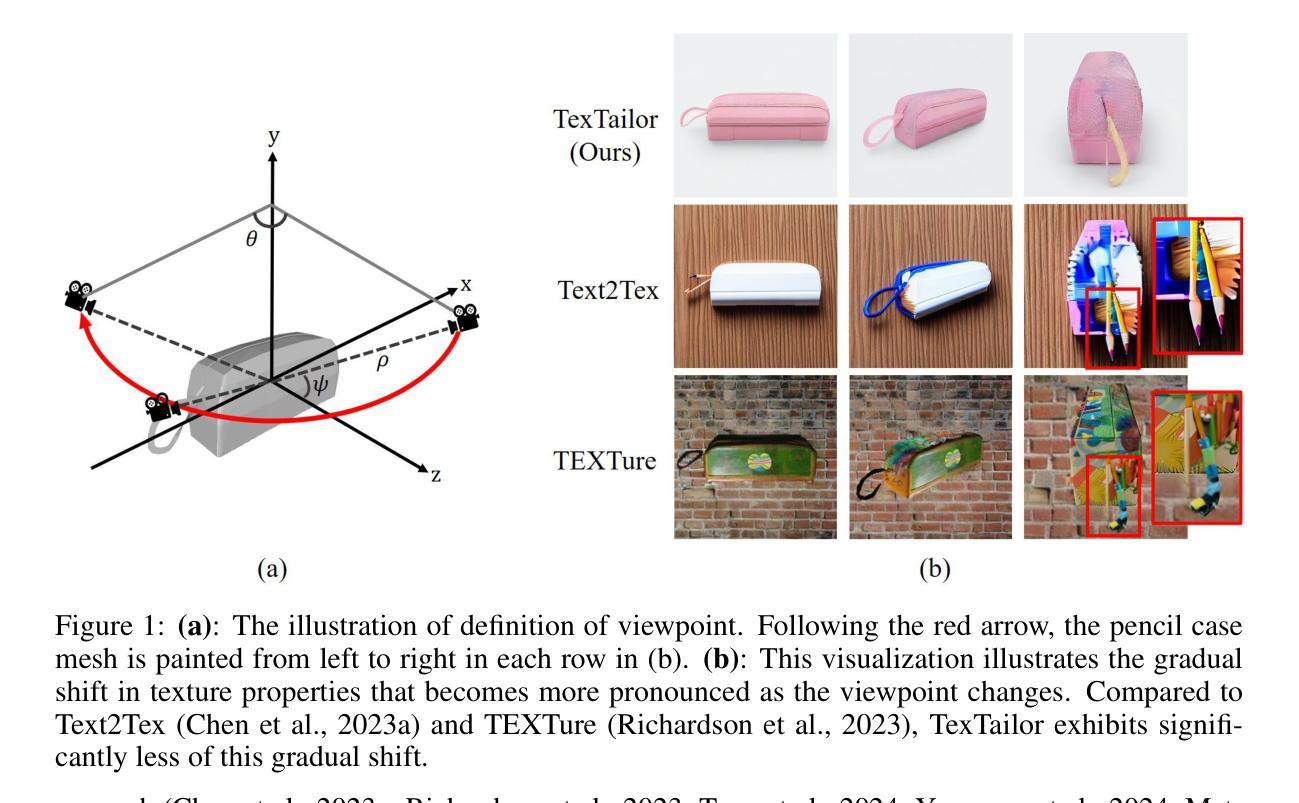
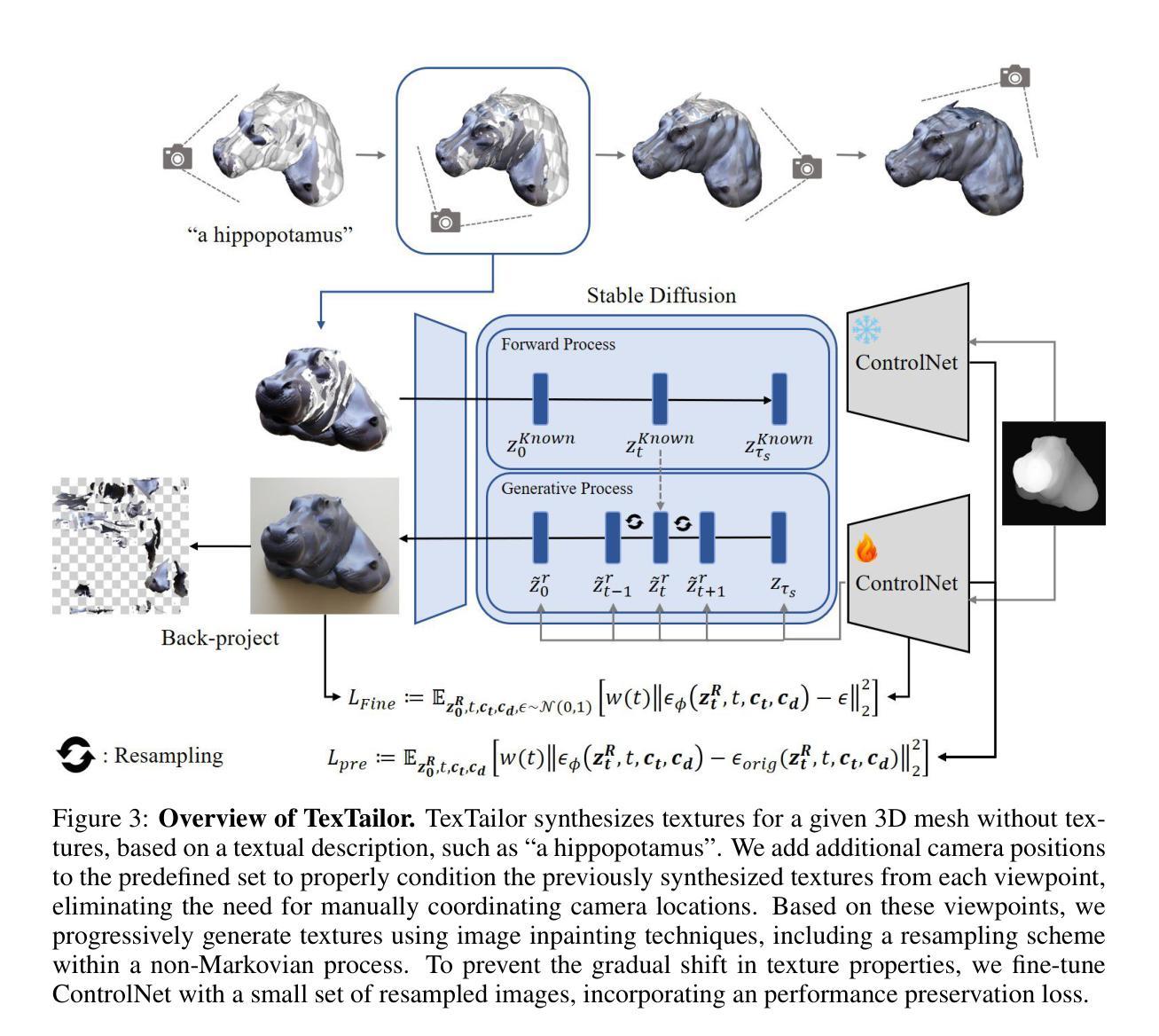
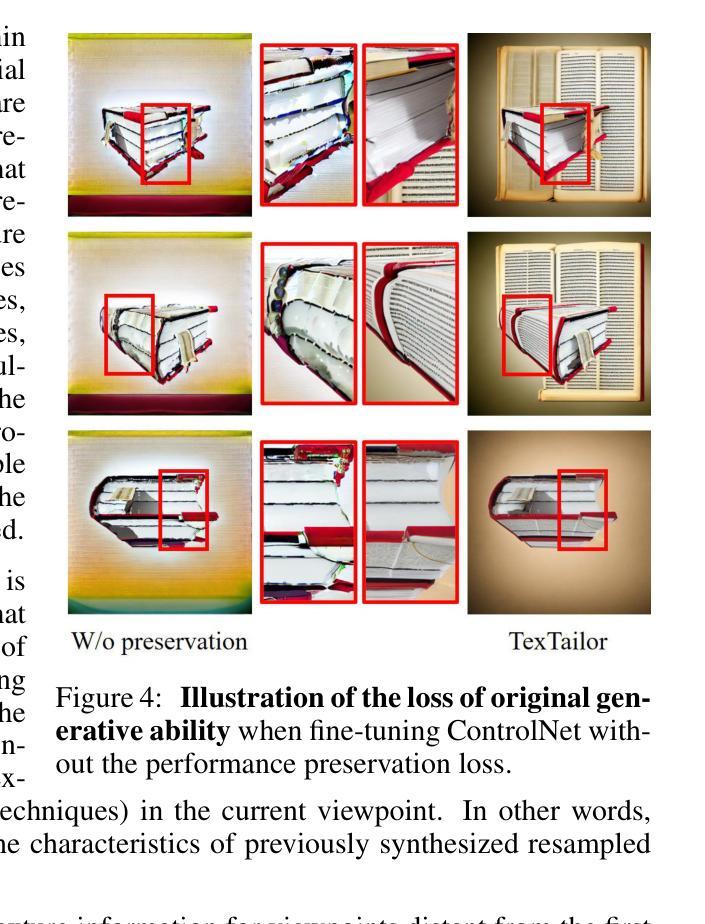
TexTailor: Customized Text-aligned Texturing via Effective Resampling
Authors:Suin Lee, Dae-Shik Kim
We present TexTailor, a novel method for generating consistent object textures from textual descriptions. Existing text-to-texture synthesis approaches utilize depth-aware diffusion models to progressively generate images and synthesize textures across predefined multiple viewpoints. However, these approaches lead to a gradual shift in texture properties across viewpoints due to (1) insufficient integration of previously synthesized textures at each viewpoint during the diffusion process and (2) the autoregressive nature of the texture synthesis process. Moreover, the predefined selection of camera positions, which does not account for the object’s geometry, limits the effective use of texture information synthesized from different viewpoints, ultimately degrading overall texture consistency. In TexTailor, we address these issues by (1) applying a resampling scheme that repeatedly integrates information from previously synthesized textures within the diffusion process, and (2) fine-tuning a depth-aware diffusion model on these resampled textures. During this process, we observed that using only a few training images restricts the model’s original ability to generate high-fidelity images aligned with the conditioning, and therefore propose an performance preservation loss to mitigate this issue. Additionally, we improve the synthesis of view-consistent textures by adaptively adjusting camera positions based on the object’s geometry. Experiments on a subset of the Objaverse dataset and the ShapeNet car dataset demonstrate that TexTailor outperforms state-of-the-art methods in synthesizing view-consistent textures. The source code for TexTailor is available at https://github.com/Adios42/Textailor
我们提出了TexTailor,这是一种从文本描述生成一致物体纹理的新方法。现有的文本到纹理合成方法利用深度感知扩散模型逐步生成图像,并在预定的多个视角合成纹理。然而,这些方法由于在扩散过程中(1)没有在每个视点上充分整合之前合成的纹理信息,(2)纹理合成过程的自回归性质,导致在不同视角之间纹理属性的逐渐变化。此外,预定相机位置的选择没有考虑到物体的几何结构,限制了从不同视角合成的纹理信息的有效使用,最终降低了纹理的整体一致性。在TexTailor中,我们通过(1)应用一种重采样方案,在扩散过程中反复整合之前合成的纹理信息,(2)对深度感知扩散模型进行微调,以解决这些问题。在此过程中,我们发现仅使用少量训练图像会限制模型生成与条件相符的高保真图像的能力,因此提出了一种性能保持损失来缓解这个问题。此外,我们通过根据物体的几何结构自适应地调整相机位置,改进了视图一致的纹理合成。在Objaverse数据集和ShapeNet汽车数据集的子集上的实验表明,TexTailor在合成视图一致的纹理方面优于现有最先进的方法。TexTailor的源代码可在https://github.com/Adios42/Textailor中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to ICLR 2025
Summary
TexTailor是一种从文本描述生成一致物体纹理的新方法。它解决了现有文本到纹理合成方法在扩散过程中因纹理信息集成不足和纹理合成过程的自回归性质导致的视角间纹理属性逐渐变化的问题。通过应用重采样方案和微调深度感知扩散模型,TexTailor提高了纹理的一致性。此外,该方法还通过性能保持损失和基于物体几何自适应调整摄像头位置,改进了视图一致的纹理合成。实验表明,TexTailor在合成视图一致的纹理方面优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- TexTailor是一种用于从文本描述生成一致物体纹理的新方法。
- 现有文本到纹理合成方法存在视角间纹理属性逐渐变化的问题。
- TexTailor通过应用重采样方案和微调深度感知扩散模型解决了这一问题。
- 性能保持损失用于解决使用少量训练图像限制模型生成高质量图像的问题。
- TexTailor通过自适应调整摄像头位置,基于物体几何改进了视图一致的纹理合成。
- 实验表明,TexTailor在合成视图一致的纹理方面优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

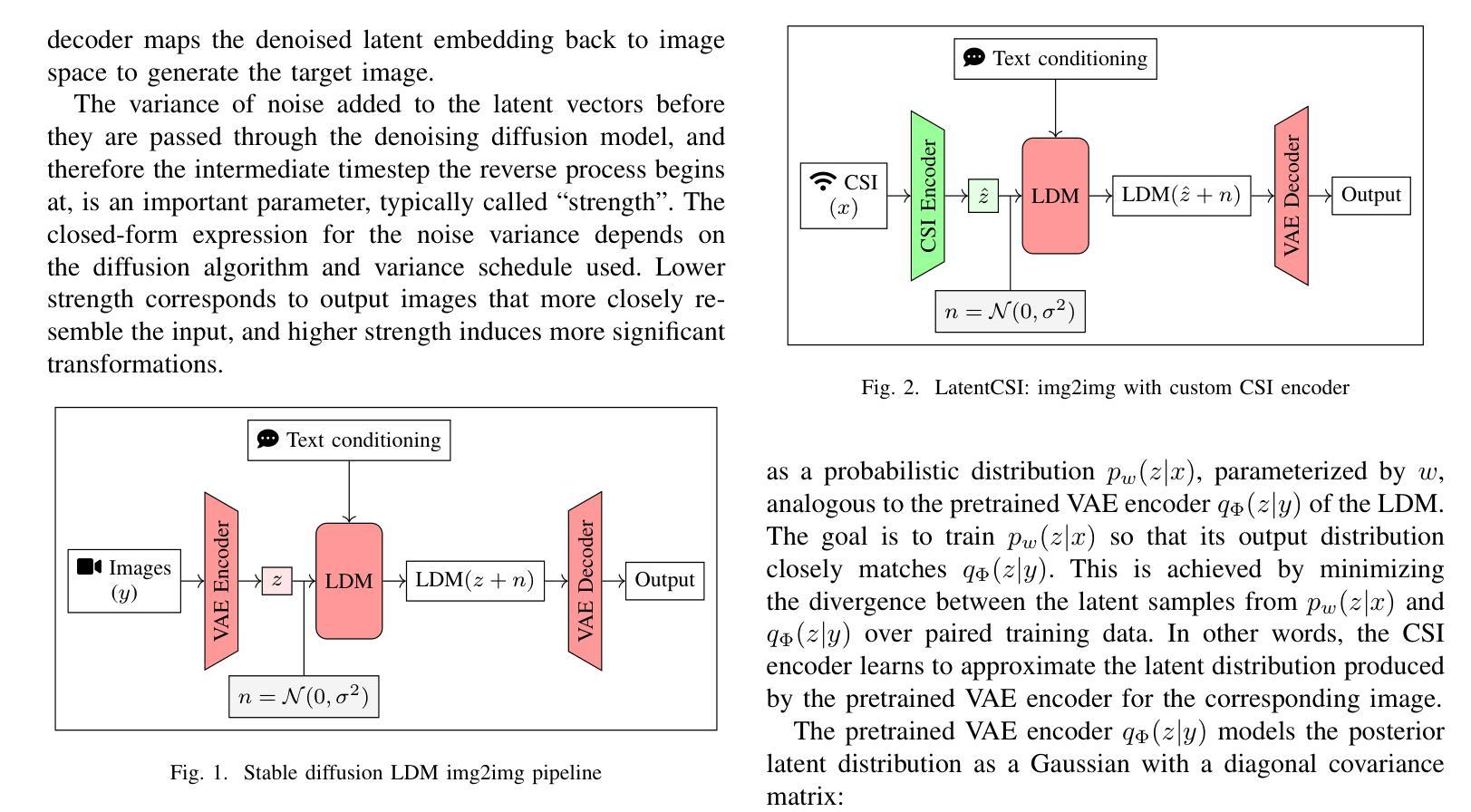
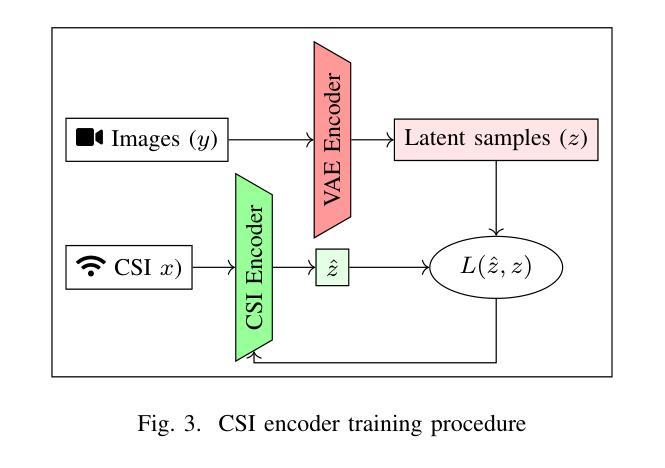
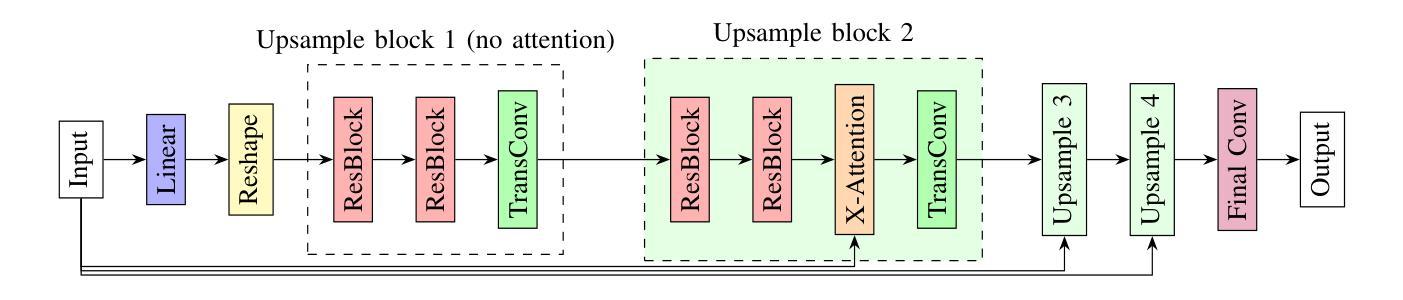
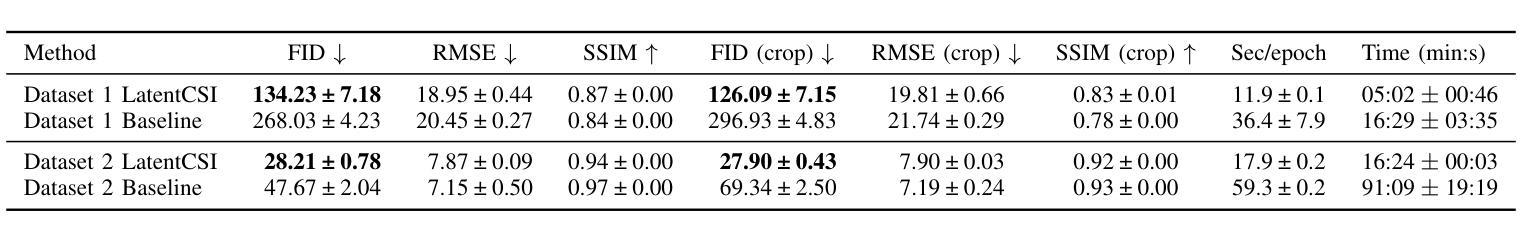
High-resolution efficient image generation from WiFi CSI using a pretrained latent diffusion model
Authors:Eshan Ramesh, Nishio Takayuki
We present LatentCSI, a novel method for generating images of the physical environment from WiFi CSI measurements that leverages a pretrained latent diffusion model (LDM). Unlike prior approaches that rely on complex and computationally intensive techniques such as GANs, our method employs a lightweight neural network to map CSI amplitudes directly into the latent space of an LDM. We then apply the LDM’s denoising diffusion model to the latent representation with text-based guidance before decoding using the LDM’s pretrained decoder to obtain a high-resolution image. This design bypasses the challenges of pixel-space image generation and avoids the explicit image encoding stage typically required in conventional image-to-image pipelines, enabling efficient and high-quality image synthesis. We validate our approach on two datasets: a wide-band CSI dataset we collected with off-the-shelf WiFi devices and cameras; and a subset of the publicly available MM-Fi dataset. The results demonstrate that LatentCSI outperforms baselines of comparable complexity trained directly on ground-truth images in both computational efficiency and perceptual quality, while additionally providing practical advantages through its unique capacity for text-guided controllability.
我们提出了LatentCSI,这是一种利用预训练的潜在扩散模型(LDM)从WiFi CSI测量生成物理环境图像的新型方法。不同于依赖复杂且计算密集的技术(如GANs)的先前方法,我们的方法采用轻量级神经网络直接将CSI振幅映射到LDM的潜在空间。然后,我们对潜在表示应用LDM的去噪扩散模型,并使用文本指导,然后使用LDM的预训练解码器进行解码,以获得高分辨率图像。这种设计绕过了像素空间图像生成的挑战,避免了传统图像到图像管道中通常需要的显式图像编码阶段,从而实现了高效的高质量图像合成。我们在两个数据集上验证了我们的方法:我们使用现成的WiFi设备和相机收集的宽带CSI数据集;以及公开可用的MM-Fi数据集的子集。结果表明,LatentCSI在计算效率和感知质量方面都优于直接在地面上训练的基准图像的可比复杂性,同时,通过其独特的文本指导可控性提供了实际优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 4 figures
Summary
基于WiFi CSI测量的物理环境图像生成新方法LatentCSI的研究介绍。该方法利用预训练的潜在扩散模型(LDM),通过轻量级神经网络将CSI振幅映射到LDM的潜在空间,再应用LDM的降噪扩散模型进行文本引导的图像生成。该方法绕过像素空间图像生成的挑战,避免了传统图像到图像的管道所需的显式图像编码阶段,实现了高效高质量图像合成。在收集的宽带CSI数据集和公开可用的MM-Fi数据集上验证了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- LatentCSI是一种基于WiFi CSI测量的物理环境图像生成新方法。
- 该方法利用预训练的潜在扩散模型(LDM)进行图像生成。
- LatentCSI使用轻量级神经网络将CSI振幅映射到LDM的潜在空间。
- 方法应用LDM的降噪扩散模型进行文本引导的图像生成。
- 该方法避免了像素空间图像生成的挑战和显式图像编码阶段。
- LatentCSI实现了高效且高质量的图像合成。
点此查看论文截图



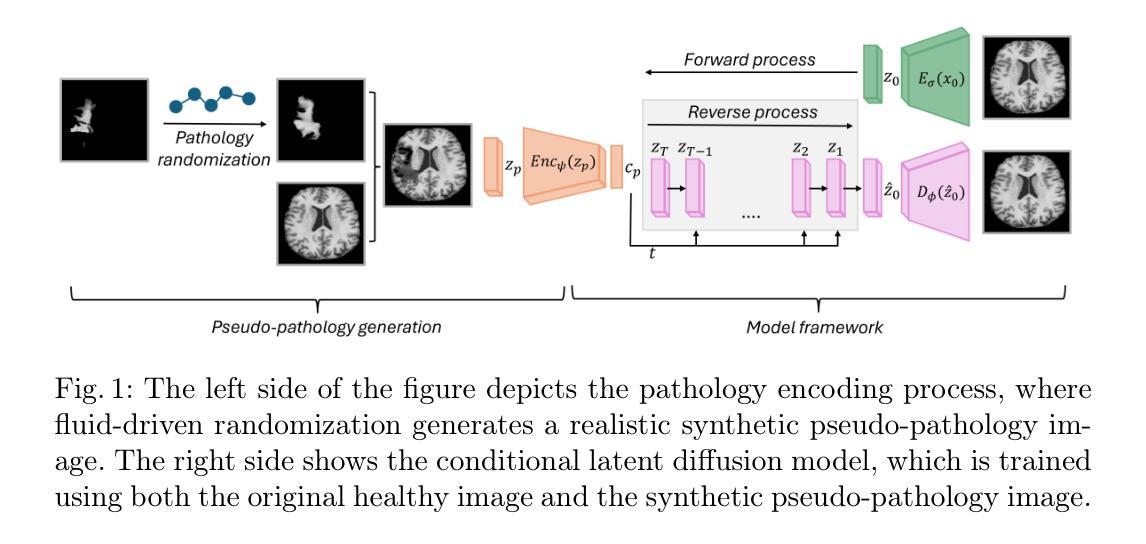
Conditional diffusion models for guided anomaly detection in brain images using fluid-driven anomaly randomization
Authors:Ana Lawry Aguila, Peirong Liu, Oula Puonti, Juan Eugenio Iglesias
Supervised machine learning has enabled accurate pathology detection in brain MRI, but requires training data from diseased subjects that may not be readily available in some scenarios, for example, in the case of rare diseases. Reconstruction-based unsupervised anomaly detection, in particular using diffusion models, has gained popularity in the medical field as it allows for training on healthy images alone, eliminating the need for large disease-specific cohorts. These methods assume that a model trained on normal data cannot accurately represent or reconstruct anomalies. However, this assumption often fails with models failing to reconstruct healthy tissue or accurately reconstruct abnormal regions i.e., failing to remove anomalies. In this work, we introduce a novel conditional diffusion model framework for anomaly detection and healthy image reconstruction in brain MRI. Our weakly supervised approach integrates synthetically generated pseudo-pathology images into the modeling process to better guide the reconstruction of healthy images. To generate these pseudo-pathologies, we apply fluid-driven anomaly randomization to augment real pathology segmentation maps from an auxiliary dataset, ensuring that the synthetic anomalies are both realistic and anatomically coherent. We evaluate our model’s ability to detect pathology, using both synthetic anomaly datasets and real pathology from the ATLAS dataset. In our extensive experiments, our model: (i) consistently outperforms variational autoencoders, and conditional and unconditional latent diffusion; and (ii) surpasses on most datasets, the performance of supervised inpainting methods with access to paired diseased/healthy images.
监督式机器学习已在脑MRI病理检测中实现了高精度,但这需要来自病患的训练数据,在某些情况下可能并不容易获得,例如在罕见疾病的情况下。基于重建的无监督异常检测,特别是使用扩散模型的方法,已在医疗领域受到欢迎,因为它可以仅对健康图像进行训练,从而无需大量特定疾病的群体。这些方法假设在正常数据上训练的模型无法准确表示或重建异常。然而,这一假设常常失败,因为模型无法重建健康组织或准确重建异常区域(即无法消除异常)。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新型的条件扩散模型框架,用于脑MRI中的异常检测和健康图像重建。我们的弱监督方法将合成生成的伪病理图像集成到建模过程中,以更好地引导健康图像的重建。为了生成这些伪病理图像,我们采用流体驱动的异常随机化方法来增强辅助数据集中的真实病理分割图,确保合成异常既真实又解剖连贯。我们使用合成异常数据集和ATLAS数据集中的真实病理来评估我们模型检测病理的能力。在广泛的实验中,我们的模型:(i)始终优于变分自编码器以及有条件和无条件的潜在扩散;(ii)在大多数数据集上,超越了使用配对疾病/健康图像的监督修复方法的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文提出了一种基于扩散模型的新条件扩散模型框架,用于医学图像中的异常检测和健康图像重建。通过引入合成伪病理图像进行弱监督训练,指导模型重建健康图像。实验表明,该模型在合成异常数据集和真实病理数据集上的表现均优于其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型被用于医学图像中的异常检测和健康图像重建。
- 该模型利用合成伪病理图像进行弱监督训练。
- 伪病理图像是通过流体驱动异常随机化技术生成的,增强了现实病理分割图的可用性。
- 模型通过集成合成伪病理图像,可以更好地重建健康图像。
- 该模型在合成异常数据集上的表现持续优于变分自动编码器以及其他有条件和无条件的潜在扩散模型。
- 在大多数数据集上,该模型的性能甚至超越了使用配对疾病/健康图像的监督修复方法。
点此查看论文截图

SPARKE: Scalable Prompt-Aware Diversity Guidance in Diffusion Models via RKE Score
Authors:Mohammad Jalali, Haoyu Lei, Amin Gohari, Farzan Farnia
Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable success in high-fidelity image synthesis and prompt-guided generative modeling. However, ensuring adequate diversity in generated samples of prompt-guided diffusion models remains a challenge, particularly when the prompts span a broad semantic spectrum and the diversity of generated data needs to be evaluated in a prompt-aware fashion across semantically similar prompts. Recent methods have introduced guidance via diversity measures to encourage more varied generations. In this work, we extend the diversity measure-based approaches by proposing the Scalable Prompt-Aware R'eny Kernel Entropy Diversity Guidance (SPARKE) method for prompt-aware diversity guidance. SPARKE utilizes conditional entropy for diversity guidance, which dynamically conditions diversity measurement on similar prompts and enables prompt-aware diversity control. While the entropy-based guidance approach enhances prompt-aware diversity, its reliance on the matrix-based entropy scores poses computational challenges in large-scale generation settings. To address this, we focus on the special case of Conditional latent RKE Score Guidance, reducing entropy computation and gradient-based optimization complexity from the $O(n^3)$ of general entropy measures to $O(n)$. The reduced computational complexity allows for diversity-guided sampling over potentially thousands of generation rounds on different prompts. We numerically test the SPARKE method on several text-to-image diffusion models, demonstrating that the proposed method improves the prompt-aware diversity of the generated data without incurring significant computational costs. We release our code on the project page: https://mjalali.github.io/SPARKE
扩散模型在高保真图像合成和提示引导生成建模方面取得了显著的成功。然而,在提示引导的扩散模型生成的样本中确保足够的多样性仍然是一个挑战,特别是在提示跨越广泛语义谱且需要在语义相似提示之间以提示感知的方式评估生成数据的多样性时。最近的方法通过引入基于多样性的度量来指导更丰富的生成。在这项工作中,我们提出了可扩展的提示感知Rényi核熵多样性指导(SPARKE)方法,以扩展基于多样性度量的方法,用于提示感知的多样性指导。SPARKE利用条件熵进行多样性指导,它可以根据相似提示动态调整多样性测量,并能够实现提示感知的多样性控制。虽然基于熵的指导方法提高了提示感知的多样性,但它对矩阵基于的熵分数的依赖在大型生成设置中构成了计算挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们关注条件潜在RKE评分指导的特殊情况,将一般熵度量的O(n^3)的熵计算和基于梯度的优化复杂性降低到O(n)。降低的计算复杂性允许在多个提示上进行数千轮生成的多样性引导采样。我们在多个文本到图像的扩散模型上对SPARKE方法进行了数值测试,结果表明,该方法提高了生成数据的提示感知多样性,且没有产生显著的计算成本。我们在项目页面上发布了我们的代码:https://mjalali.github.io/SPARKE。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Diffusion模型在图像合成和提示引导生成建模方面的出色表现。然而,对于确保提示引导扩散模型的生成样本具有足够的多样性仍是一大挑战,特别是在语义谱广泛的提示和需要在语义相似的提示之间进行提示感知的多样性评估时。本文提出了可扩展的提示感知Rényi核熵多样性指导(SPARKE)方法来解决这一问题。SPARKE采用基于条件熵的多样性指导,该方法能够根据相似的提示动态调节多样性测量,实现提示感知的多样性控制。虽然熵指导方法提高了提示感知的多样性,但其依赖于矩阵的熵分数在计算大型生成场景中存在一定的挑战。为此,本文专注于条件潜在RKE得分指导的特殊案例,将熵计算和基于梯度的优化复杂度从一般熵测量的O(n^3)降低到O(n)。减少了计算复杂度,允许在多个提示上进行数千轮带多样性的采样。本文在多个文本到图像的扩散模型上对SPARKE方法进行了数值测试,表明该方法在提高生成数据的提示感知多样性的同时不会带来重大计算成本。我们的代码已在项目页面上发布:https://mjalali.github.io/SPARKE。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion模型在图像合成和提示引导生成建模方面表现出显著的成功。
- 在广泛的语义提示下确保生成样本的多样性是一个挑战。
- 提出了一种新的方法——SPARKE,通过条件熵实现提示感知的多样性指导。
- SPARKE能够根据相似的提示动态调整多样性测量。
- 相较于一般熵测量的O(n^3),SPARKE专注于条件潜在RKE得分指导,将计算复杂度降低到O(n)。
- SPARKE方法提高了生成数据的提示感知多样性,同时不会带来显著的计算成本。
点此查看论文截图



LoRA-Edit: Controllable First-Frame-Guided Video Editing via Mask-Aware LoRA Fine-Tuning
Authors:Chenjian Gao, Lihe Ding, Xin Cai, Zhanpeng Huang, Zibin Wang, Tianfan Xue
Video editing using diffusion models has achieved remarkable results in generating high-quality edits for videos. However, current methods often rely on large-scale pretraining, limiting flexibility for specific edits. First-frame-guided editing provides control over the first frame, but lacks flexibility over subsequent frames. To address this, we propose a mask-based LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) tuning method that adapts pretrained Image-to-Video (I2V) models for flexible video editing. Our approach preserves background regions while enabling controllable edits propagation. This solution offers efficient and adaptable video editing without altering the model architecture. To better steer this process, we incorporate additional references, such as alternate viewpoints or representative scene states, which serve as visual anchors for how content should unfold. We address the control challenge using a mask-driven LoRA tuning strategy that adapts a pre-trained image-to-video model to the editing context. The model must learn from two distinct sources: the input video provides spatial structure and motion cues, while reference images offer appearance guidance. A spatial mask enables region-specific learning by dynamically modulating what the model attends to, ensuring that each area draws from the appropriate source. Experimental results show our method achieves superior video editing performance compared to state-of-the-art methods.
使用扩散模型进行视频编辑已经在生成高质量视频编辑方面取得了显著成果。然而,当前的方法常常依赖于大规模预训练,这限制了特定编辑的灵活性。虽然基于首帧引导编辑能够控制首帧,但对于后续帧的控制则不足。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于掩码的LoRA(低秩适配)调优方法,该方法能够适应预训练好的图像到视频(I2V)模型,实现灵活的视频编辑。我们的方法能够保留背景区域,同时实现可控的编辑传播。这一解决方案在不改变模型架构的情况下,实现了高效且可适应的视频编辑。为了更好地引导这一过程,我们引入了额外的参考,如不同的观点或代表性的场景状态,它们作为内容展开的视觉锚点。我们采用掩码驱动的LoRA调优策略来解决控制挑战,该策略将预训练的图像到视频模型适应于编辑上下文。模型必须从两个独特的信息源中学习:输入视频提供空间结构和运动线索,而参考图像提供外观指导。空间掩膜通过动态调制模型所关注的重点,实现特定区域的学习,确保每个区域都能从适当的信息源中汲取知识。实验结果表明,我们的方法在视频编辑性能上优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages
Summary
基于扩散模型的视频编辑已生成高质量编辑视频,取得了显著成果。针对现有方法依赖大规模预训练、缺乏特定编辑灵活性以及第一帧引导编辑缺乏后续帧灵活性的问题,本文提出了一种基于掩膜的LoRA(低秩适应)调优方法,用于适应预训练图像到视频(I2V)模型的灵活视频编辑。该方法可保留背景区域,实现可控编辑传播,提供高效、可适应的视频编辑,无需更改模型架构。为了更好地引导这一过程,本文引入了额外的参考,如不同的观点或代表性的场景状态,作为内容展开的视觉锚点。通过掩膜驱动的LoRA调优策略,解决控制挑战,使预训练图像到视频模型适应编辑上下文。模型从两个不同来源学习:输入视频提供空间结构和运动线索,参考图像提供外观指导。空间掩膜通过动态调制模型关注的区域,确保每个区域都从适当的来源中绘制信息。实验结果表明,该方法在视频编辑性能上优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在视频编辑中生成高质量结果。
- 当前方法依赖大规模预训练,缺乏特定编辑的灵活性。
- 提出基于掩膜的LoRA调优方法,适应预训练I2V模型进行灵活视频编辑。
- 方法可保留背景区域,实现可控编辑传播。
- 引入额外参考,如不同观点或场景状态,作为内容展开的视觉锚点。
- 采用掩膜驱动的LoRA调优策略,使模型适应编辑上下文。
- 模型从输入视频和参考图像两个来源学习,空间掩膜确保区域特定学习。
点此查看论文截图


Towards Reliable Identification of Diffusion-based Image Manipulations
Authors:Alex Costanzino, Woody Bayliss, Juil Sock, Marc Gorriz Blanch, Danijela Horak, Ivan Laptev, Philip Torr, Fabio Pizzati
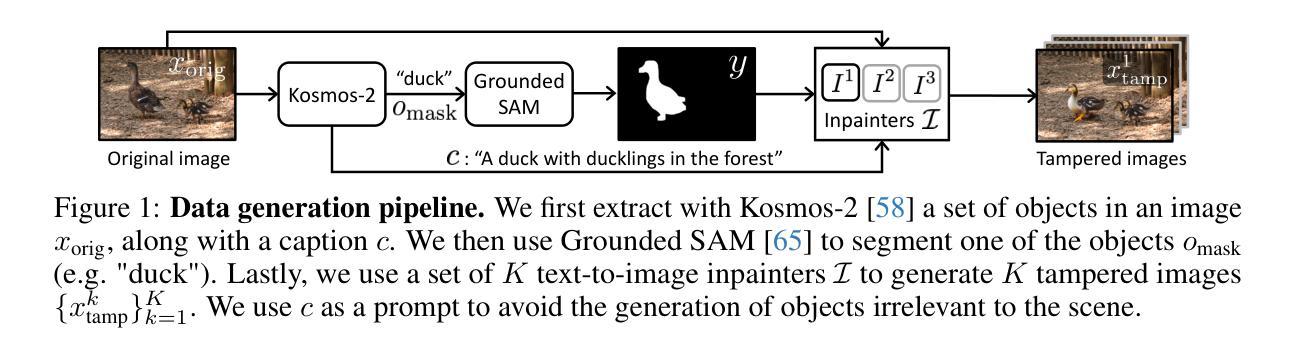
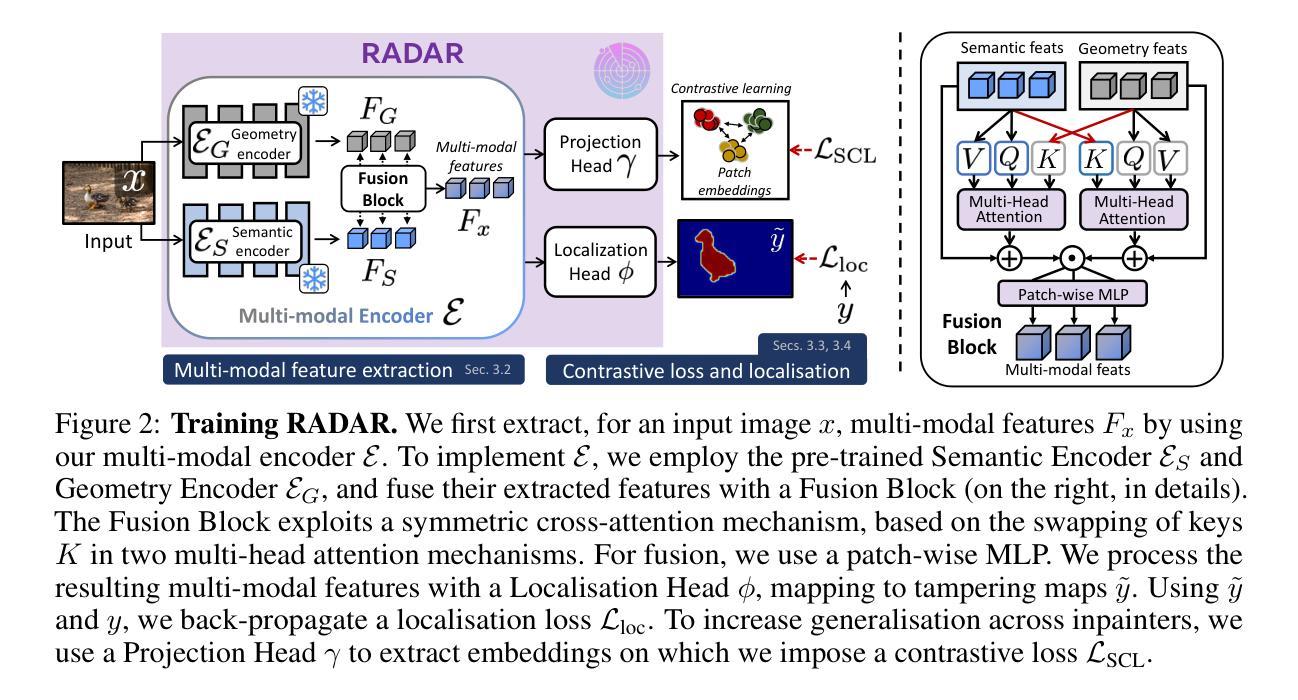
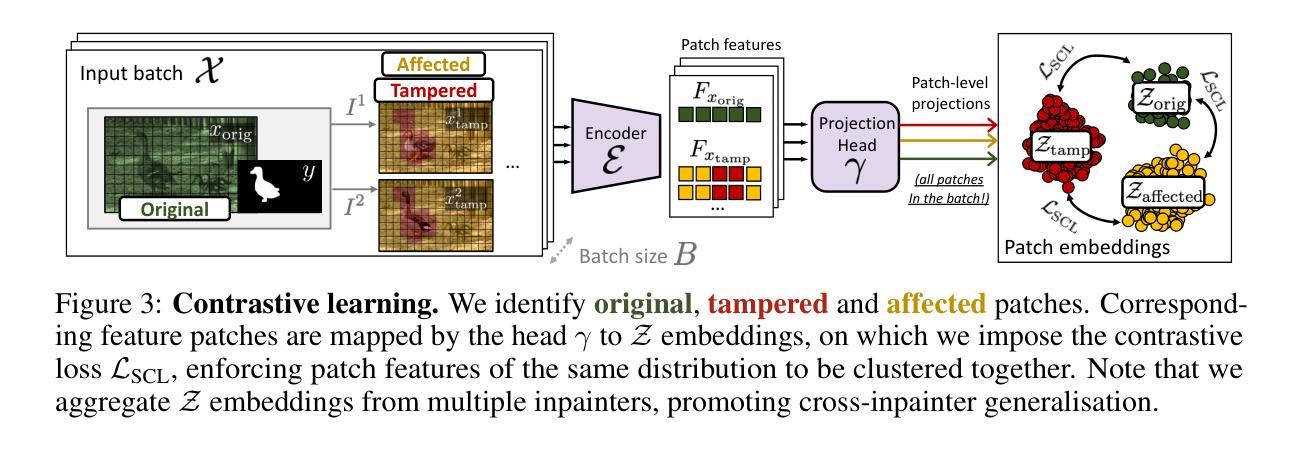
Changing facial expressions, gestures, or background details may dramatically alter the meaning conveyed by an image. Notably, recent advances in diffusion models greatly improve the quality of image manipulation while also opening the door to misuse. Identifying changes made to authentic images, thus, becomes an important task, constantly challenged by new diffusion-based editing tools. To this end, we propose a novel approach for ReliAble iDentification of inpainted AReas (RADAR). RADAR builds on existing foundation models and combines features from different image modalities. It also incorporates an auxiliary contrastive loss that helps to isolate manipulated image patches. We demonstrate these techniques to significantly improve both the accuracy of our method and its generalisation to a large number of diffusion models. To support realistic evaluation, we further introduce BBC-PAIR, a new comprehensive benchmark, with images tampered by 28 diffusion models. Our experiments show that RADAR achieves excellent results, outperforming the state-of-the-art in detecting and localising image edits made by both seen and unseen diffusion models. Our code, data and models will be publicly available at https://alex-costanzino.github.io/radar/.
改变面部表情、手势或背景细节可能会极大地改变图像所传达的意义。值得注意的是,扩散模型的最新进展虽然大大提高了图像操作的质量,但同时也打开了滥用的大门。因此,识别对真实图像所做的改变成为了一项重要的任务,这一任务不断受到新的基于扩散的编辑工具的挑战。为此,我们提出了一种新的可靠识别图像修复区域的方法(RADAR)。RADAR建立在现有的基础模型上,结合了不同图像模态的特征。它还引入了一个辅助对比损失,有助于隔离被操纵的图像补丁。我们证明这些技术可以显著提高我们方法的准确性,并且其可以推广到大量扩散模型。为了支持真实评估,我们还引入了BBC-PAIR,这是一个新的综合基准测试,包含被28种扩散模型篡改过的图像。我们的实验表明,RADAR取得了优异的结果,在检测和定位已知和未知的扩散模型对图像进行的编辑方面均优于现有技术。我们的代码、数据和模型将在https://alex-costanzino.github.io/radar/公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page at https://alex-costanzino.github.io/radar/
Summary
本文介绍了基于扩散模型的新型图像编辑技术所带来的挑战,并提出了一种名为RADAR的新方法,用于可靠地识别图像中的编辑区域。RADAR结合不同图像模态的特征,并引入辅助对比损失以区分编辑过的图像区域。此外,为了支持真实评估,还推出了BBC-PAIR新基准测试,包含由28种扩散模型修改的图像。实验表明,RADAR在检测和定位由已知和未知扩散模型进行的图像编辑方面取得了卓越成果。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型的进步提高了图像操纵的质量,同时也增加了误用的风险。
- 提出了一种新的方法RADAR,用于识别图像中的编辑区域。
- RADAR结合了不同图像模态的特征,并引入辅助对比损失以提高准确性和泛化能力。
- 推出了BBC-PAIR基准测试,支持对图像编辑检测方法的真实评估。
- RADAR在检测和定位由多种扩散模型进行的图像编辑方面表现出卓越性能。
- RADAR方法不仅在已知扩散模型上表现良好,对未知扩散模型也具有强大的检测能力。
点此查看论文截图

Sparc3D: Sparse Representation and Construction for High-Resolution 3D Shapes Modeling
Authors:Zhihao Li, Yufei Wang, Heliang Zheng, Yihao Luo, Bihan Wen
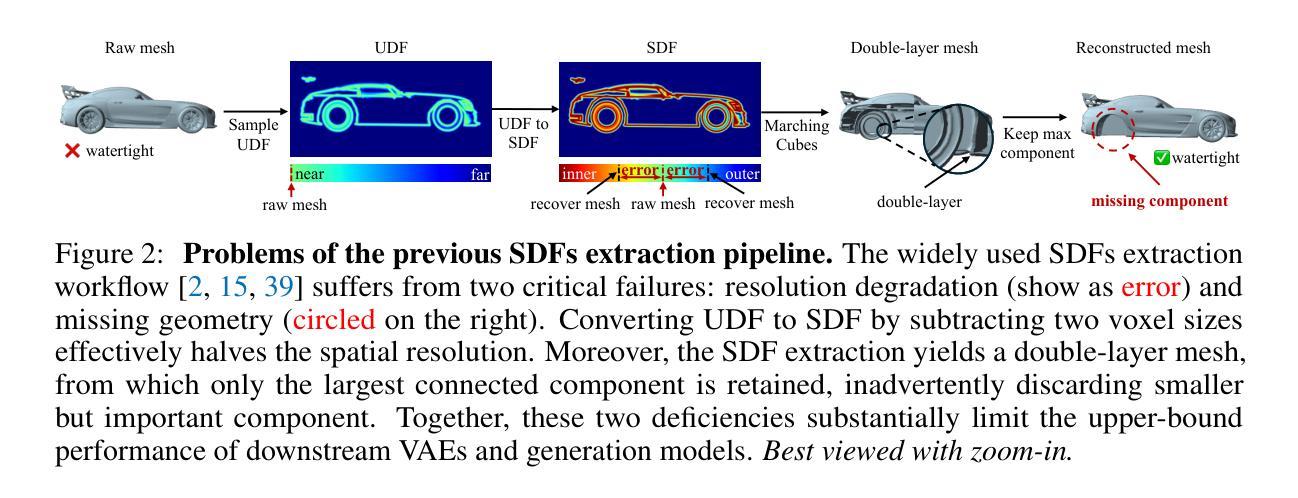
High-fidelity 3D object synthesis remains significantly more challenging than 2D image generation due to the unstructured nature of mesh data and the cubic complexity of dense volumetric grids. Existing two-stage pipelines-compressing meshes with a VAE (using either 2D or 3D supervision), followed by latent diffusion sampling-often suffer from severe detail loss caused by inefficient representations and modality mismatches introduced in VAE. We introduce Sparc3D, a unified framework that combines a sparse deformable marching cubes representation Sparcubes with a novel encoder Sparconv-VAE. Sparcubes converts raw meshes into high-resolution ($1024^3$) surfaces with arbitrary topology by scattering signed distance and deformation fields onto a sparse cube, allowing differentiable optimization. Sparconv-VAE is the first modality-consistent variational autoencoder built entirely upon sparse convolutional networks, enabling efficient and near-lossless 3D reconstruction suitable for high-resolution generative modeling through latent diffusion. Sparc3D achieves state-of-the-art reconstruction fidelity on challenging inputs, including open surfaces, disconnected components, and intricate geometry. It preserves fine-grained shape details, reduces training and inference cost, and integrates naturally with latent diffusion models for scalable, high-resolution 3D generation.
高保真3D对象合成相较于2D图像生成仍然更具挑战性,这主要是由于网格数据的非结构化和密集体积网格的立方复杂性。现有的两阶段流程(使用VAE(使用二维或三维监督)压缩网格,然后进行潜在扩散采样)常常因VAE中引入的低效表示和模态不匹配而导致细节严重损失。我们引入了Sparc3D,这是一个结合了稀疏可变形行进立方体表示Sparcubes和新型编码器Sparconv-VAE的统一框架。Sparcubes通过将带符号距离和变形场散射到稀疏立方体上,将原始网格转换为高分辨率(1024^3)且具有任意拓扑的表面,从而实现可微分优化。Sparconv-VAE是第一个完全基于稀疏卷积网络的一致模态自动编码器,能够实现高效且接近无损的3D重建,适合通过潜在扩散进行高分辨率生成建模。Sparc3D在具有挑战性的输入上实现了最先进的重建保真度,包括开放表面、断开组件和精细几何。它保留了精细的形状细节,降低了训练和推理成本,并与潜在扩散模型自然集成,可实现可扩展的高分辨率3D生成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Homepage: https://lizhihao6.github.io/Sparc3D
Summary
本文主要介绍了针对三维物体合成的新技术挑战及解决方案。由于网格数据的非结构化和密集体积网格的复杂性,传统的两阶段流水线经常遭受损失细节的困扰。作者提出名为SParc3D的统一框架,通过引入稀疏可变形立体推进模块(Sparcubes)和新型编码器(Sparconv-VAE),实现了高效且无损的三维重建,适用于通过潜在扩散模型进行高分辨率生成建模。此技术在多种复杂输入上达到前所未有的重建保真度,并可自然集成到潜在扩散模型中,实现可扩展的高分辨率三维生成。
Key Takeaways
以下是关键要点总结:
- 高保真三维物体合成比二维图像生成更具挑战性,主要由于网格数据的非结构化和密集体积网格的复杂性。
- 传统两阶段流水线方法常常由于无效的代表和模态不匹配导致的细节损失。
- SParc3D框架结合了稀疏可变形立体推进模块(Sparcubes)和新型编码器(Sparconv-VAE)。
- Sparcubes可将原始网格转化为高分辨率表面,并支持任意拓扑结构。
- Sparconv-VAE是首个完全基于稀疏卷积网络的一致模态自动编码器,可实现高效且无损的三维重建。
- SParc3D在复杂输入上实现了高保真重建,包括开放表面、断开组件和精细几何结构。
点此查看论文截图

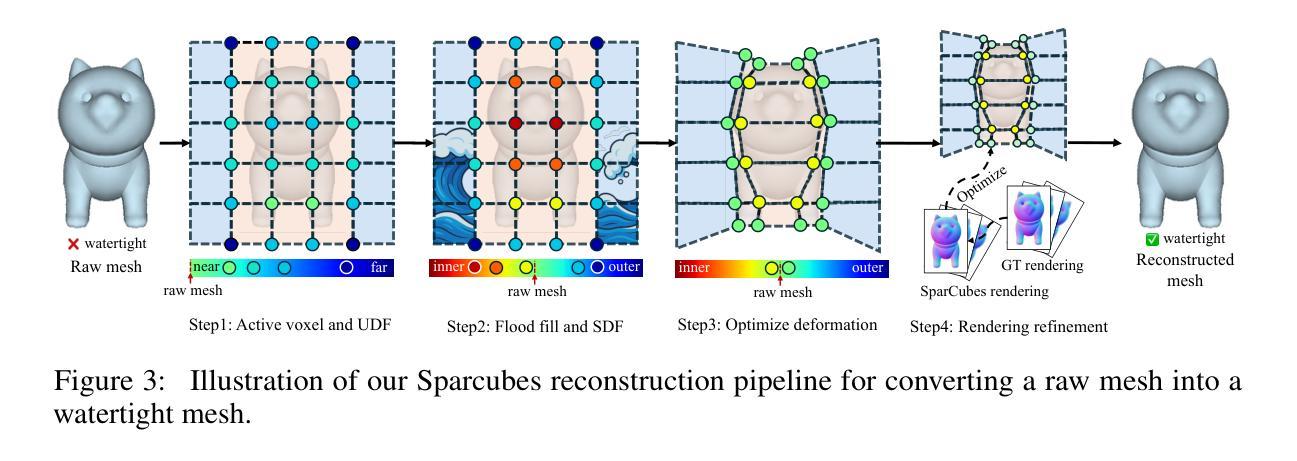
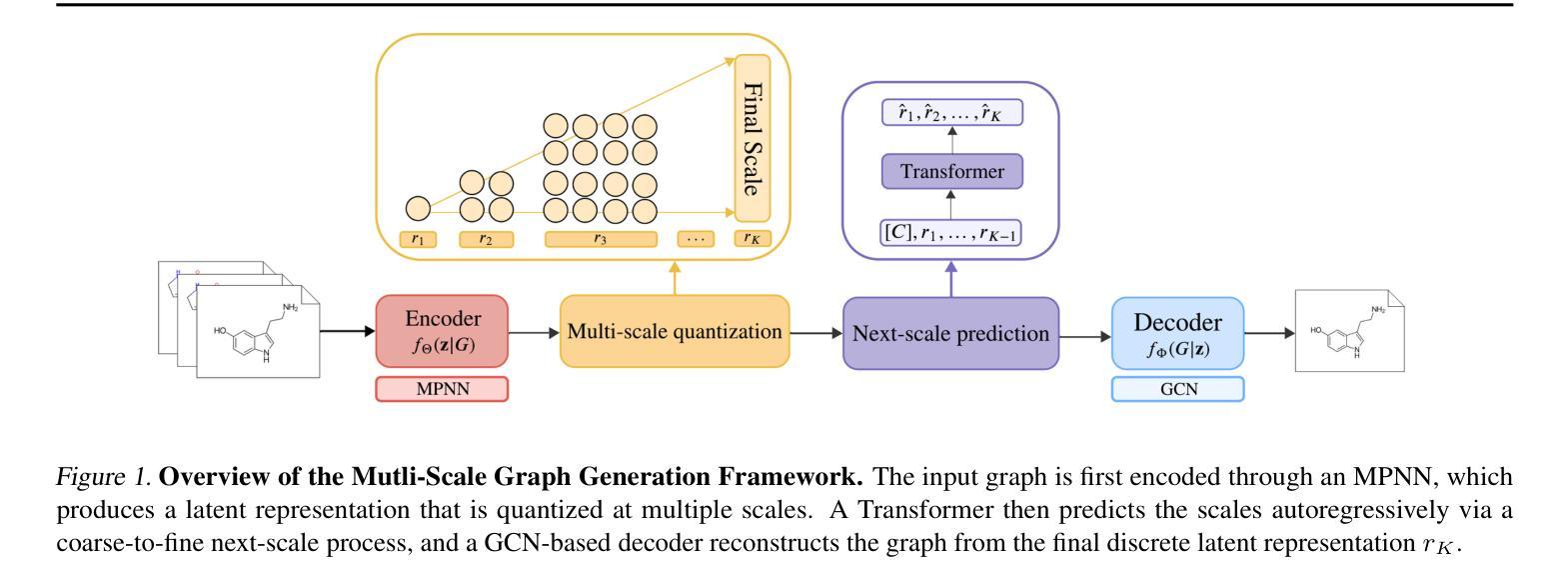
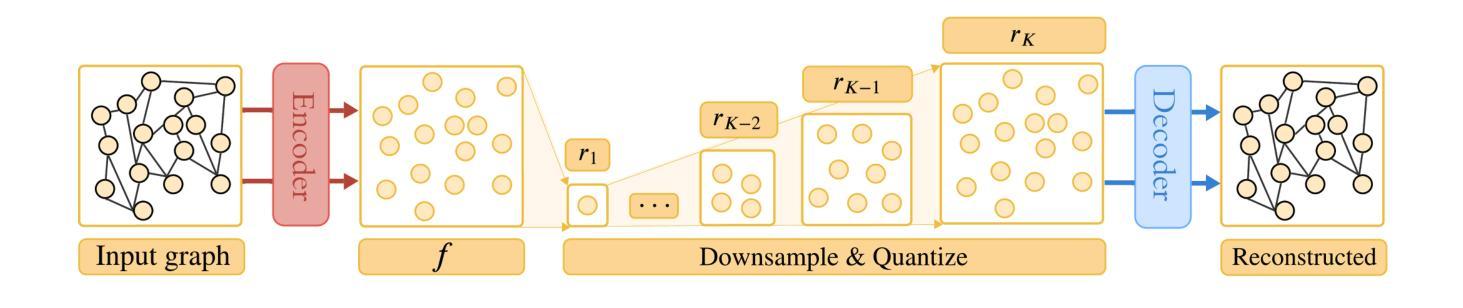
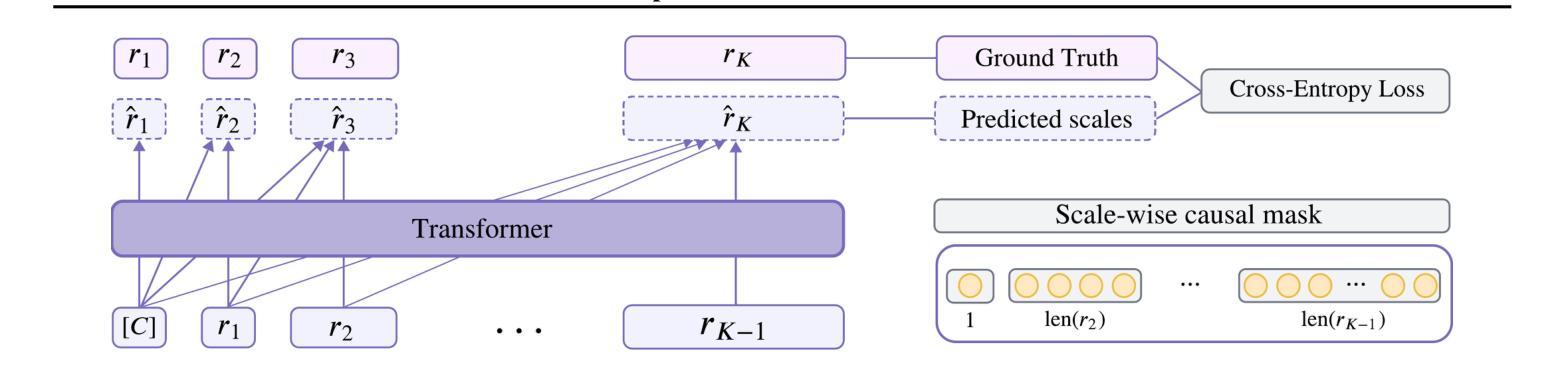
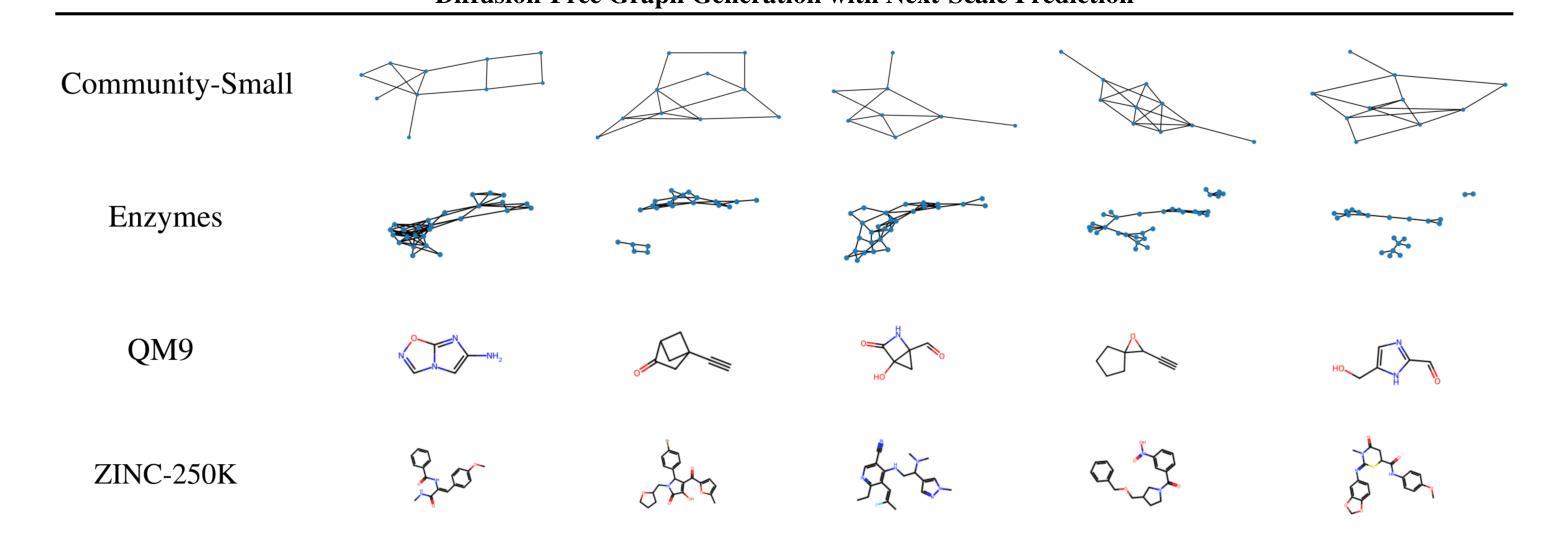
Diffusion-Free Graph Generation with Next-Scale Prediction
Authors:Samuel Belkadi, Steve Hong, Marian Chen, Miruna Cretu, Charles Harris, Pietro Lio
Autoregressive models excel in efficiency and plug directly into the transformer ecosystem, delivering robust generalization, predictable scalability, and seamless workflows such as fine-tuning and parallelized training. However, they require an explicit sequence order, which contradicts the unordered nature of graphs. In contrast, diffusion models maintain permutation invariance and enable one-shot generation but require up to thousands of denoising steps and additional features for expressivity, leading to high computational costs. Inspired by recent breakthroughs in image generation, especially the success of visual autoregressive methods, we propose MAG, a novel diffusion-free graph generation framework based on next-scale prediction. By leveraging a hierarchy of latent representations, the model progressively generates scales of the entire graph without the need for explicit node ordering. Experiments on both generic and molecular graph datasets demonstrated the potential of this method, achieving inference speedups of up to three orders of magnitude over state-of-the-art methods, while preserving high-quality generation.
自回归模型在效率方面表现出色,并且能够直接插入transformer生态系统,提供稳健的泛化能力、可预测的扩展性以及微调和平行训练等无缝工作流程。然而,它们需要明确的序列顺序,这与图的无序性质相矛盾。相比之下,扩散模型保持置换不变性,能够实现一次生成,但需要高达数千步的去噪步骤和额外的特征来表达,导致计算成本高昂。受最近图像生成领域突破,尤其是视觉自回归方法成功的启发,我们提出了MAG,这是一种基于下一尺度预测的新型无扩散图生成框架。通过利用潜在表示层次结构,该模型无需显式节点排序即可逐步生成整个图的尺度。在通用和图分子数据集上的实验证明了该方法的潜力,与最新方法相比,实现了高达三个数量级的推理速度提升,同时保持高质量生成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Camera-ready version
Summary
文本介绍了一种新型的无扩散图生成框架MAG,它通过利用分层潜在表示来渐进生成整个图,无需明确的节点顺序。MAG结合了自回归模型的优点,如效率、通用性、可预测的可扩展性和无缝工作流程,同时解决了自回归模型对序列顺序的依赖问题。在通用和图结构分子数据集上的实验表明,MAG实现了高达三个数量级的推理速度提升,同时保持了高质量生成。
Key Takeaways
- 自回归模型具有效率、通用性、可预测的可扩展性和无缝工作流程等优点,但需要明确的序列顺序。
- 扩散模型具有排列不变性和一次生成能力,但计算成本高,需要数千个去噪步骤和额外的特征来表达性。
- 新型的无扩散图生成框架MAG结合了自回归模型的优点,通过利用分层潜在表示来生成图,解决了自回归模型对节点顺序的依赖问题。
- MAG实现了高达三个数量级的推理速度提升,同时保持了高质量生成。
- MAG框架无需明确的节点顺序即可渐进生成整个图的尺度。
- 在不同数据集上的实验表明,MAG具有良好的通用性和潜力。
点此查看论文截图

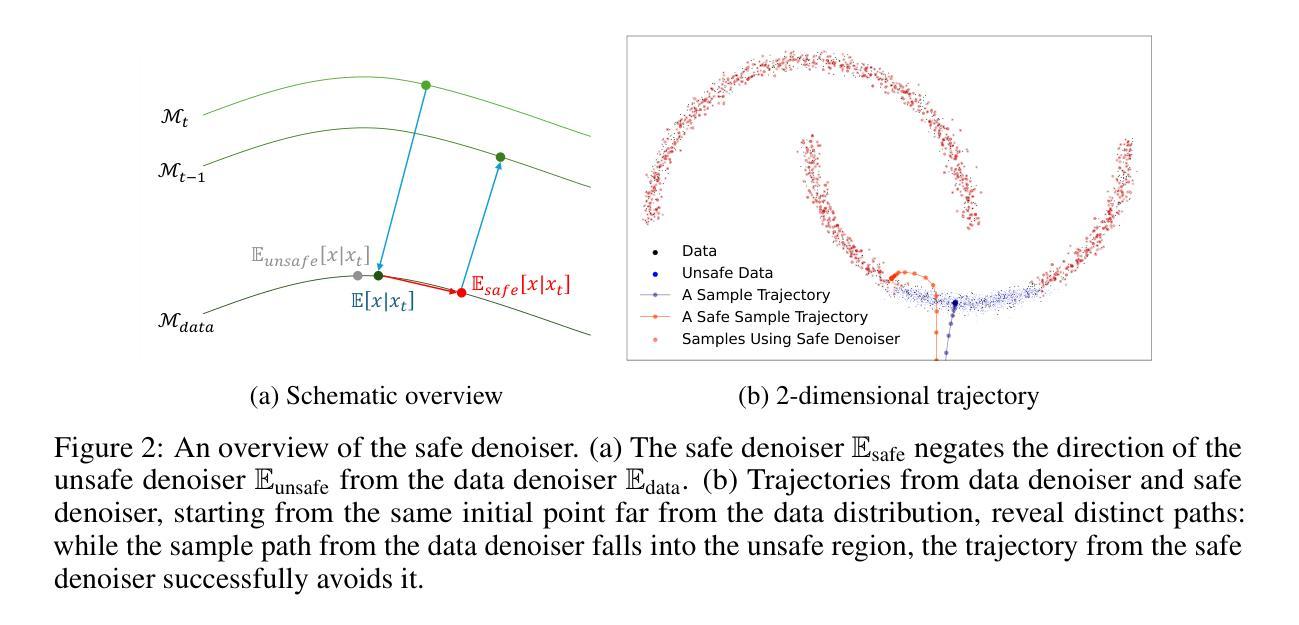
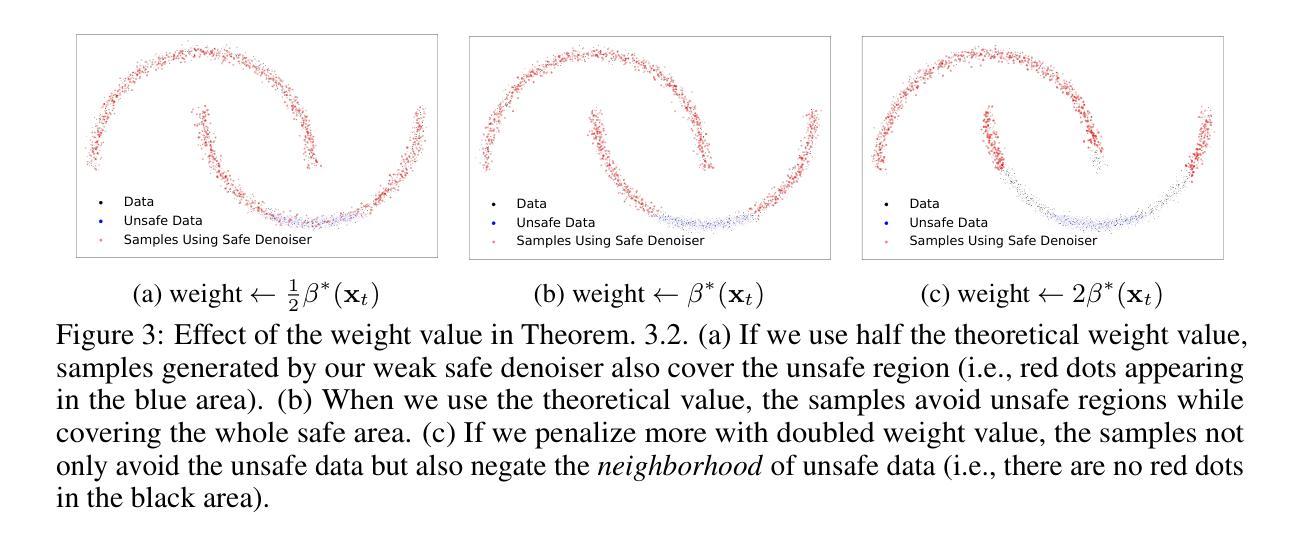
Training-Free Safe Denoisers for Safe Use of Diffusion Models
Authors:Mingyu Kim, Dongjun Kim, Amman Yusuf, Stefano Ermon, Mijung Park
There is growing concern over the safety of powerful diffusion models (DMs), as they are often misused to produce inappropriate, not-safe-for-work (NSFW) content or generate copyrighted material or data of individuals who wish to be forgotten. Many existing methods tackle these issues by heavily relying on text-based negative prompts or extensively retraining DMs to eliminate certain features or samples. In this paper, we take a radically different approach, directly modifying the sampling trajectory by leveraging a negation set (e.g., unsafe images, copyrighted data, or datapoints needed to be excluded) to avoid specific regions of data distribution, without needing to retrain or fine-tune DMs. We formally derive the relationship between the expected denoised samples that are safe and those that are not safe, leading to our $\textit{safe}$ denoiser which ensures its final samples are away from the area to be negated. Inspired by the derivation, we develop a practical algorithm that successfully produces high-quality samples while avoiding negation areas of the data distribution in text-conditional, class-conditional, and unconditional image generation scenarios. These results hint at the great potential of our training-free safe denoiser for using DMs more safely.
关于强大的扩散模型(DMs)的安全问题日益受到关注,因为它们经常被误用于产生不适当、不安全的工作(NSFW)内容或生成版权材料或那些希望被遗忘的个人的数据。许多现有方法通过依赖基于文本的反向提示或重新训练DMs以消除某些特征或样本来解决这些问题。在本文中,我们采用了完全不同的方法,通过利用否定集(例如,不安全的图像、版权数据或需要排除的数据点)直接修改采样轨迹,避免数据分布的特定区域,而无需重新训练或微调DMs。我们正式推导了安全和不安全预期去噪样本之间的关系,从而形成了我们的安全去噪器,确保最终样本远离要否定的区域。受推导的启发,我们开发了一种实用算法,该算法在文本条件、类别条件和无条件图像生成场景中成功产生了高质量样本,同时避免了数据分布的否定区域。这些结果暗示了我们的无训练安全去噪器在更安全地使用DM方面的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
摘要
扩散模型经常被滥用,产生不适当、不安全的(NSFW)内容或者生成版权材料和个人遗忘的数据。许多现有方法主要依赖文本负向提示或重新训练模型来解决这些问题。本研究采用完全不同的方法,通过利用否定集避免数据分布特定区域,无需重新训练或微调扩散模型,直接修改采样轨迹。我们正式推导安全和非安全去噪样本之间的关系,从而得到我们的安全去噪器,确保最终样本远离否定区域。受到推导的启发,我们开发了一种实用算法,成功生成高质量样本,同时在文本条件、类别条件和无条件图像生成场景中避免否定区域。这些结果暗示了我们的无训练安全去噪器在更安全地使用扩散模型方面的巨大潜力。
要点摘要
- 扩散模型经常被误用,产生不适当或不安全内容以及版权或个人隐私相关材料。
- 传统方法主要依赖文本负向提示或重新训练模型来解决问题。
- 本研究通过利用否定集直接修改采样轨迹,无需重新训练模型。
- 正式推导安全和非安全去噪样本间的关系,形成安全去噪器概念。
- 安全去噪器能确保生成的样本远离否定区域。
- 开发实用算法可在不同场景(如文本条件、类别条件和无条件图像生成)成功生成高质量样本并避免否定区域。
点此查看论文截图

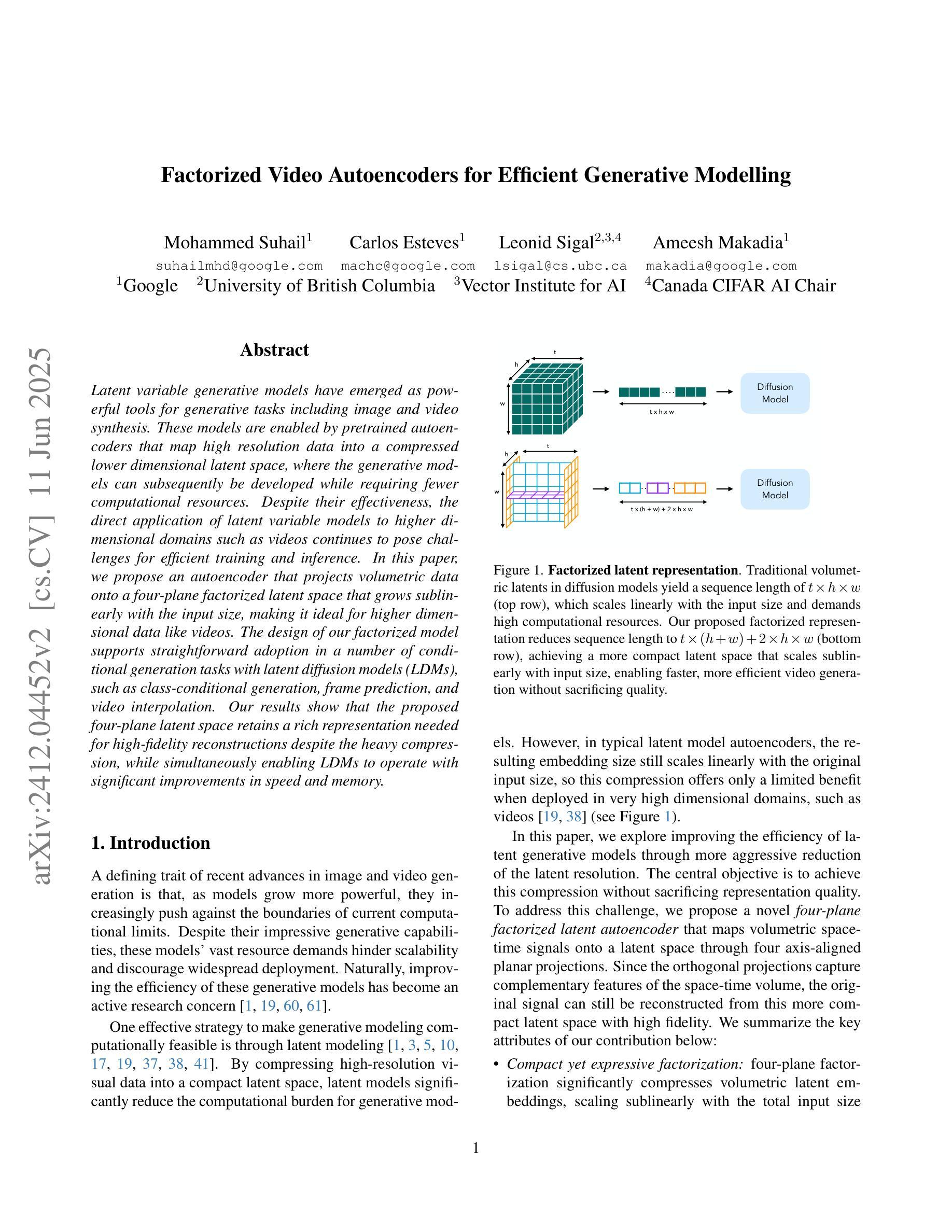
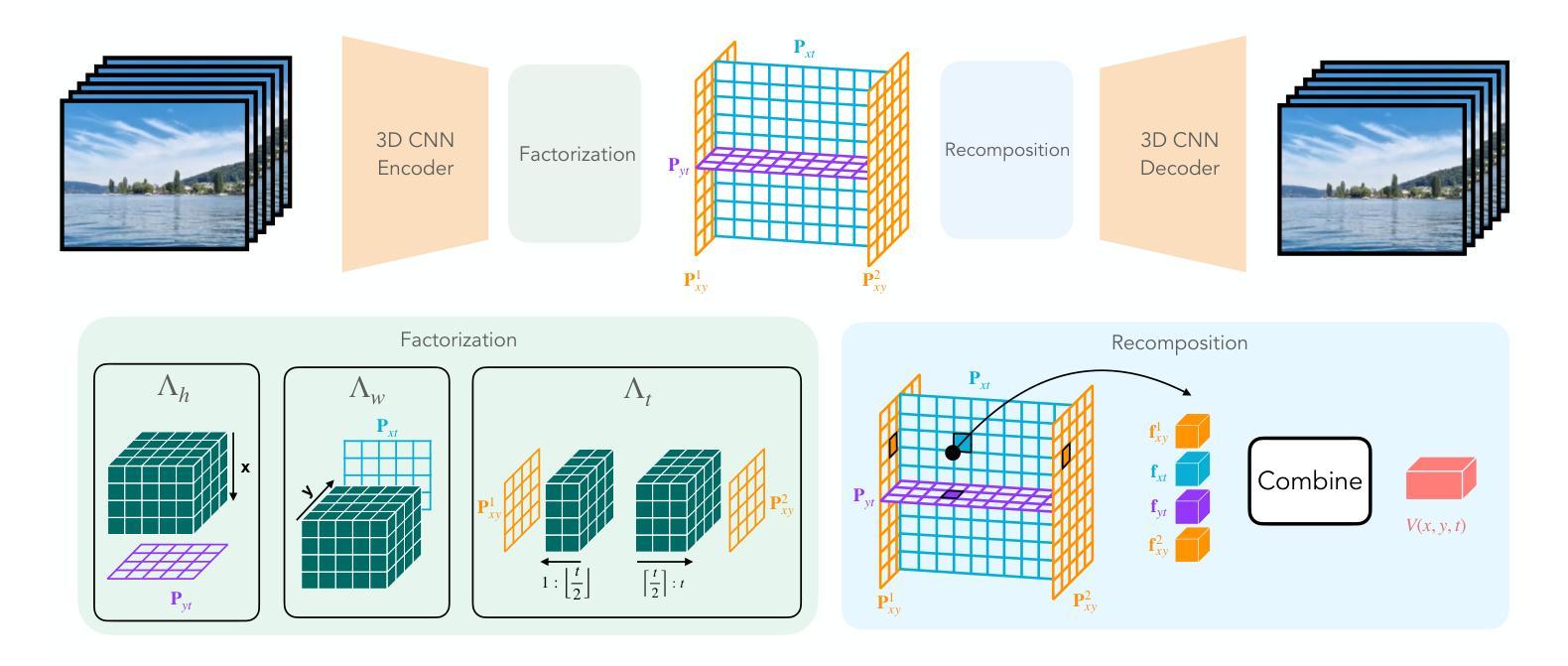
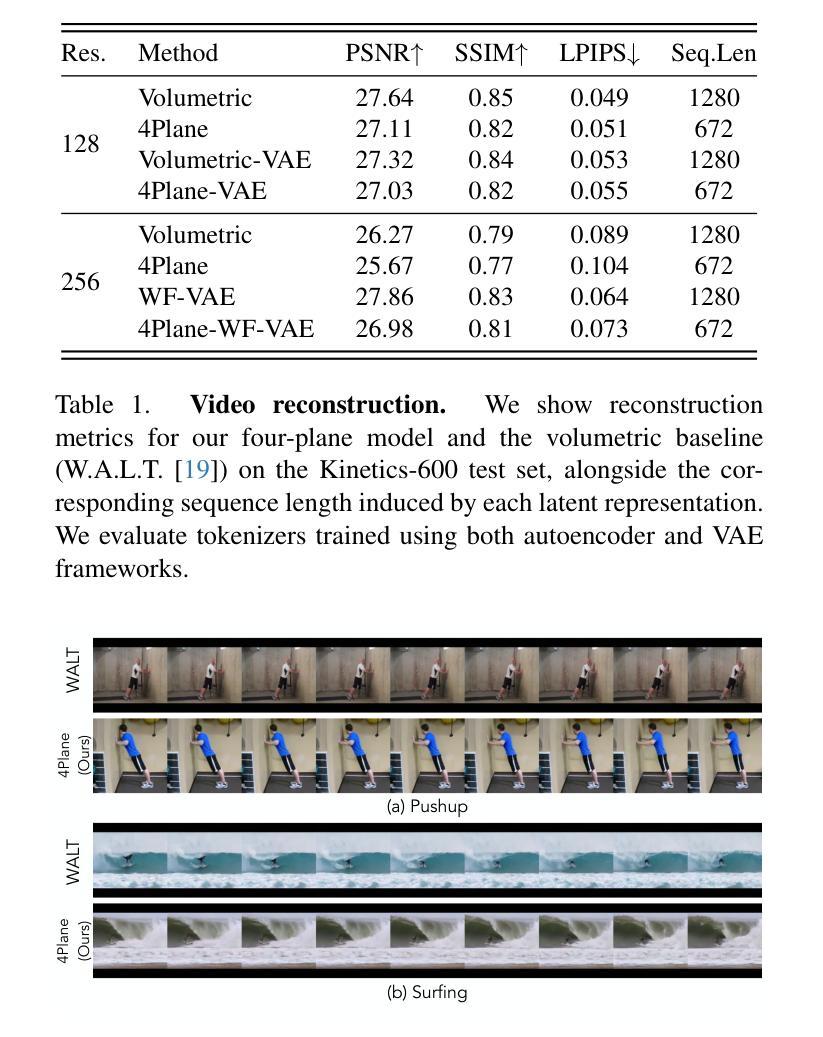
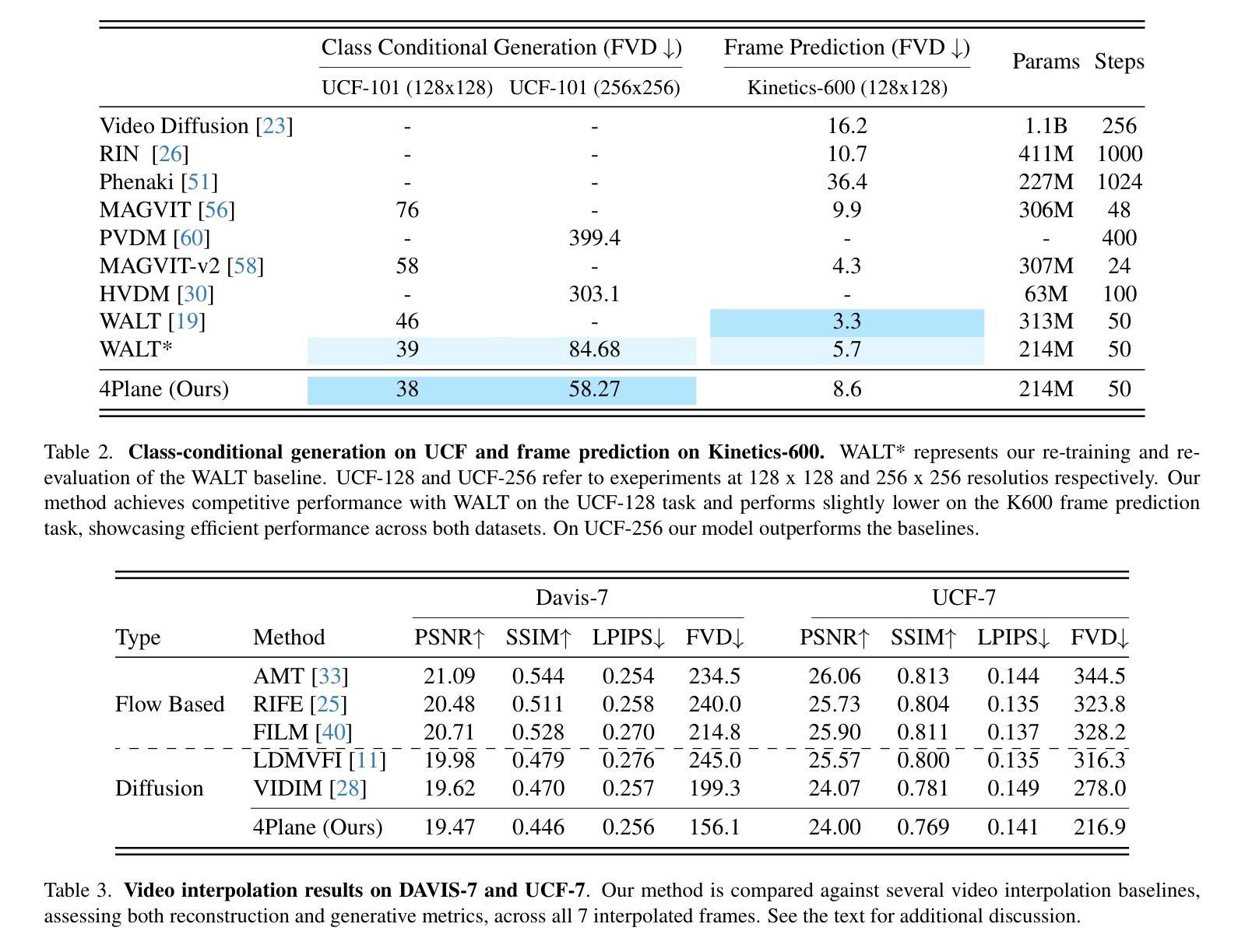
Factorized Video Autoencoders for Efficient Generative Modelling
Authors:Mohammed Suhail, Carlos Esteves, Leonid Sigal, Ameesh Makadia
Latent variable generative models have emerged as powerful tools for generative tasks including image and video synthesis. These models are enabled by pretrained autoencoders that map high resolution data into a compressed lower dimensional latent space, where the generative models can subsequently be developed while requiring fewer computational resources. Despite their effectiveness, the direct application of latent variable models to higher dimensional domains such as videos continues to pose challenges for efficient training and inference. In this paper, we propose an autoencoder that projects volumetric data onto a four-plane factorized latent space that grows sublinearly with the input size, making it ideal for higher dimensional data like videos. The design of our factorized model supports straightforward adoption in a number of conditional generation tasks with latent diffusion models (LDMs), such as class-conditional generation, frame prediction, and video interpolation. Our results show that the proposed four-plane latent space retains a rich representation needed for high-fidelity reconstructions despite the heavy compression, while simultaneously enabling LDMs to operate with significant improvements in speed and memory.
潜在变量生成模型作为生成任务(包括图像和视频合成)的强大工具已经出现。这些模型由预训练的自动编码器提供支持,将高分辨率数据映射到压缩的低维潜在空间,在此空间中,可以在较少的计算资源下开发生成模型。尽管这些模型非常有效,但直接将潜在变量模型应用于更高维度领域(如视频)仍然对高效训练和推理提出了挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种将体积数据投影到随输入大小增长而亚线性增长的四平面分解潜在空间的自动编码器,使其成为适合处理高维数据(如视频)的理想选择。我们的分解模型设计支持在具有潜在扩散模型的多种条件生成任务中直接使用,例如类别条件生成、帧预测和视频插值等。结果表明,所提出的四平面潜在空间在保留重建所需丰富表示的同时实现了强烈压缩,同时使潜在扩散模型能够以速度和内存上的显著改善运行。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了潜在变量生成模型在图像和视频合成等生成任务中的强大作用。通过预训练的自动编码器将高分辨率数据映射到压缩的低维潜在空间,生成模型可以在较少的计算资源下开发。针对直接在视频等更高维度领域应用潜在变量模型面临的挑战,本文提出了一种将体积数据投影到四平面分解潜在空间的自动编码器,其随输入大小的增长呈亚线性,适用于视频等更高维度数据。该分解模型设计支持在带有潜在扩散模型(LDMs)的多个条件生成任务中的直接应用,如类别条件生成、帧预测和视频插值。结果表明,所提出的四平面潜在空间在重度压缩的同时保留了丰富的表示,同时使LDMs在速度和内存方面实现了显著改善。
Key Takeaways
- 潜在变量生成模型已成为图像和视频合成等生成任务的强大工具。
- 预训练的自动编码器将高分辨率数据映射到低维潜在空间,减少计算资源需求。
- 将体积数据投影到四平面分解潜在空间的方法适用于更高维度的数据,如视频。
- 四平面分解模型设计支持在条件生成任务中的直接应用,如类别条件生成、帧预测和视频插值。
- 四平面潜在空间在压缩的同时保留了丰富的表示,可实现高保真重构。
- 该方法显著提高了潜在扩散模型(LDMs)在速度和内存方面的性能。
点此查看论文截图
Plug-and-Play image restoration with Stochastic deNOising REgularization
Authors:Marien Renaud, Jean Prost, Arthur Leclaire, Nicolas Papadakis
Plug-and-Play (PnP) algorithms are a class of iterative algorithms that address image inverse problems by combining a physical model and a deep neural network for regularization. Even if they produce impressive image restoration results, these algorithms rely on a non-standard use of a denoiser on images that are less and less noisy along the iterations, which contrasts with recent algorithms based on Diffusion Models (DM), where the denoiser is applied only on re-noised images. We propose a new PnP framework, called Stochastic deNOising REgularization (SNORE), which applies the denoiser only on images with noise of the adequate level. It is based on an explicit stochastic regularization, which leads to a stochastic gradient descent algorithm to solve ill-posed inverse problems. A convergence analysis of this algorithm and its annealing extension is provided. Experimentally, we prove that SNORE is competitive with respect to state-of-the-art methods on deblurring and inpainting tasks, both quantitatively and qualitatively.
Plug-and-Play(PnP)算法是一类迭代算法,通过结合物理模型和深度神经网络进行正则化,解决图像反问题。尽管它们能产生令人印象深刻的图像恢复结果,但这些算法依赖于在非标准去噪器上对图像的使用,随着迭代的进行,图像越来越不噪声化,这与基于扩散模型(DM)的近期算法形成对比,其中去噪器只应用于重新加噪声的图像。我们提出了一种新的PnP框架,称为随机去噪正则化(SNORE),它仅在具有适当水平的噪声图像上应用去噪器。它基于显式随机正则化,导致一种解决不适定反问题的随机梯度下降算法。我们提供了该算法及其退火扩展的收敛性分析。实验证明,SNORE在去模糊和修复任务上与最先进的方法相比具有竞争力和优势,无论是在数量上还是在质量上都是如此。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在图像逆问题处理中,Plug-and-Play(PnP)算法结合了物理模型和深度神经网络进行正则化。针对PnP算法在迭代过程中对不同噪声水平图像的非标准去噪使用方式,我们提出了一种新的PnP框架——Stochastic deNOising REgularization(SNORE)。SNORE只在适当噪声水平的图像上应用去噪器,基于明确的随机正则化,为解决不适定的逆问题提供了随机梯度下降算法。实验证明,SNORE在去模糊和补全任务上均具有良好的竞争性能。
Key Takeaways
- PnP算法结合物理模型和深度神经网络进行图像逆问题的处理。
- PnP算法在迭代过程中对噪声逐渐减弱的图像使用去噪器的方式与基于Diffusion Models的算法不同。
- 提出了新的PnP框架SNORE,只在适当噪声水平的图像上应用去噪器。
- SNORE基于明确的随机正则化,为解决不适定的逆问题提供了随机梯度下降算法。
- SNORE在收敛性方面进行了分析,并提供了退火扩展的方法。
- 实验证明,SNORE在去模糊和补全任务上具有良好的性能,与现有方法相比具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图