⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-14 更新
High-resolution efficient image generation from WiFi CSI using a pretrained latent diffusion model
Authors:Eshan Ramesh, Nishio Takayuki
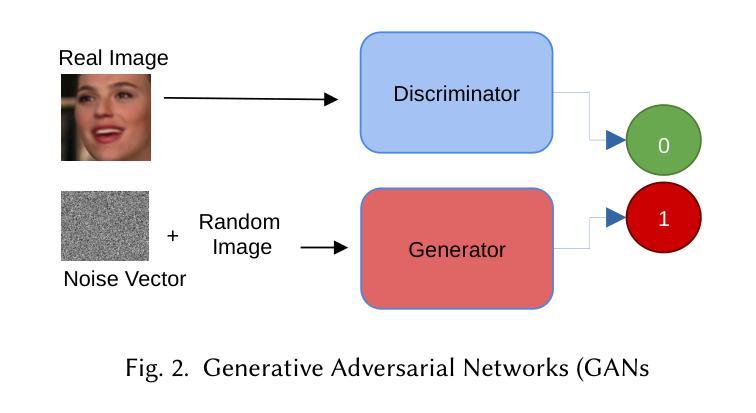
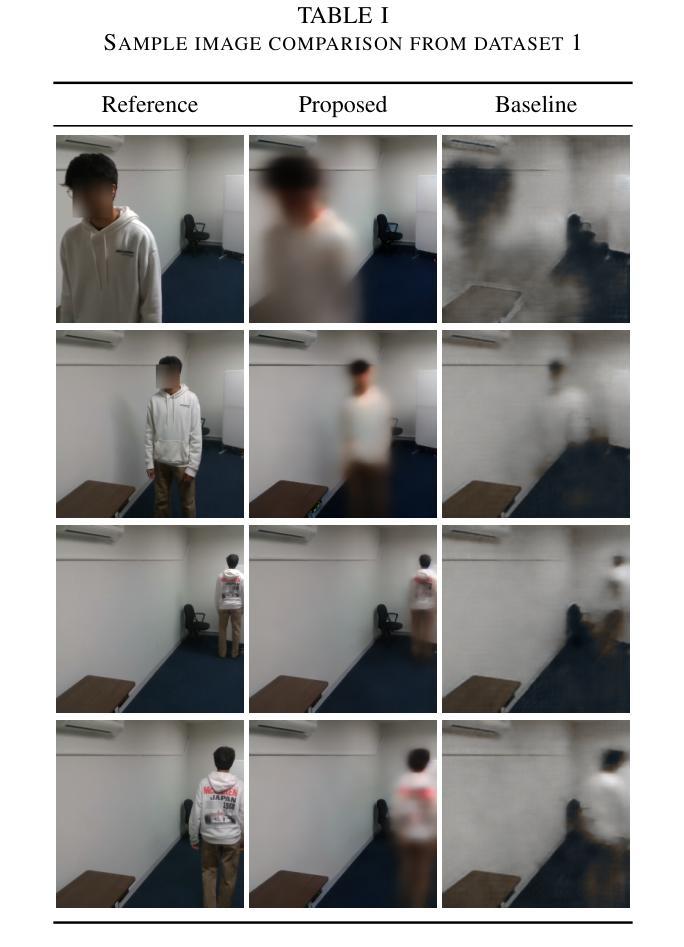
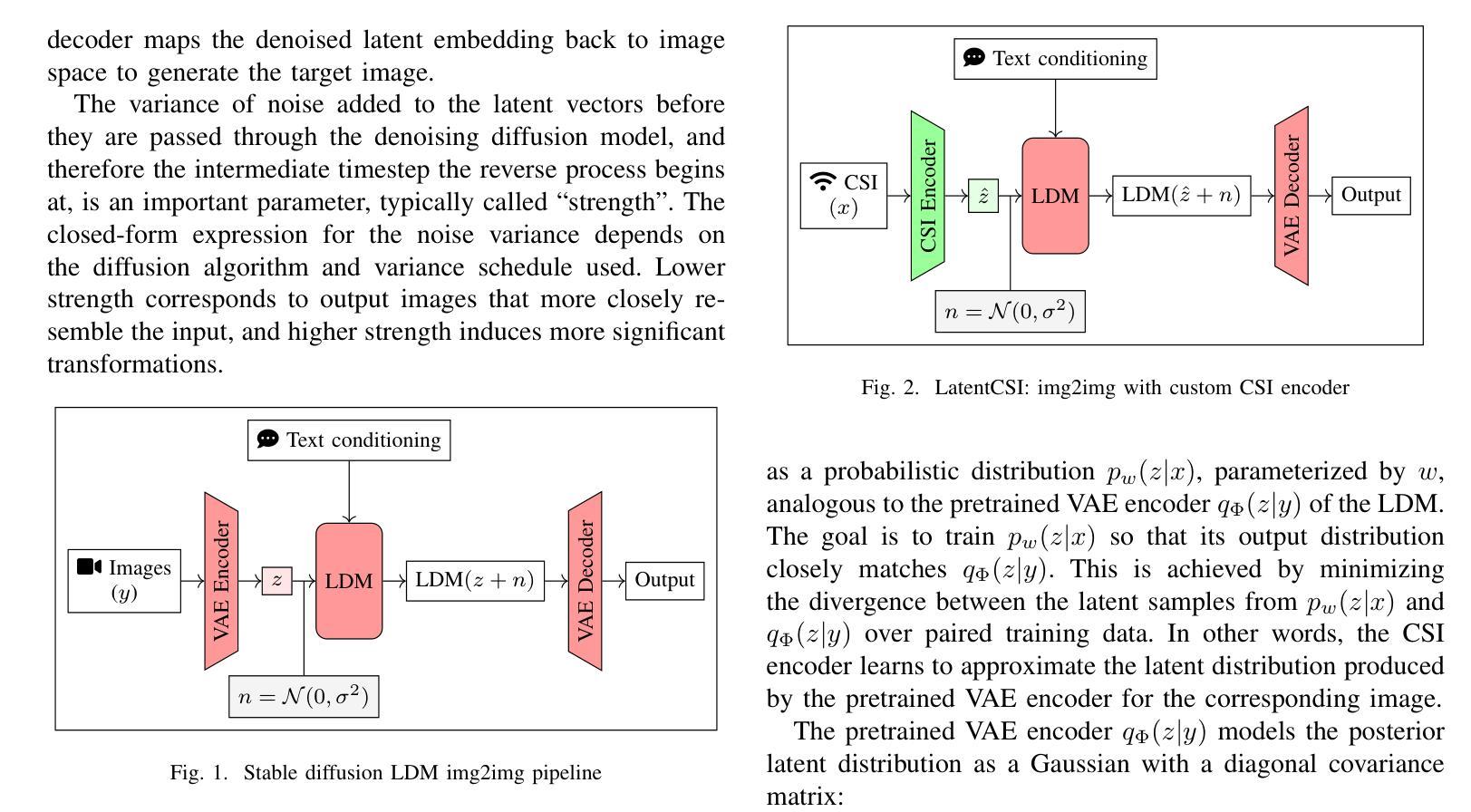
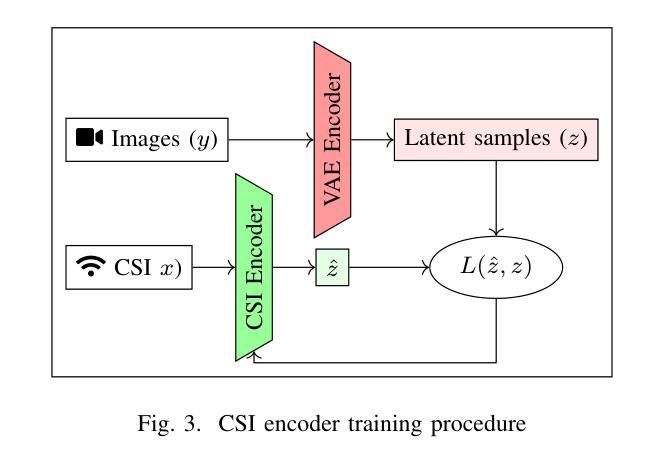
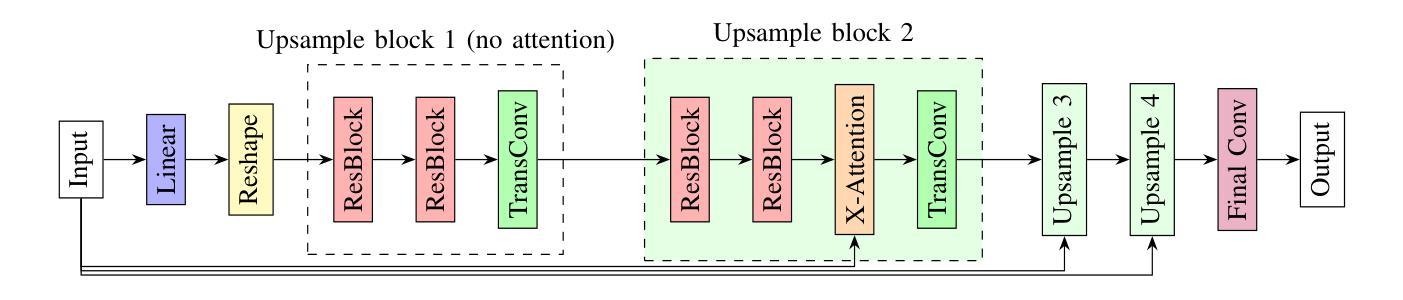
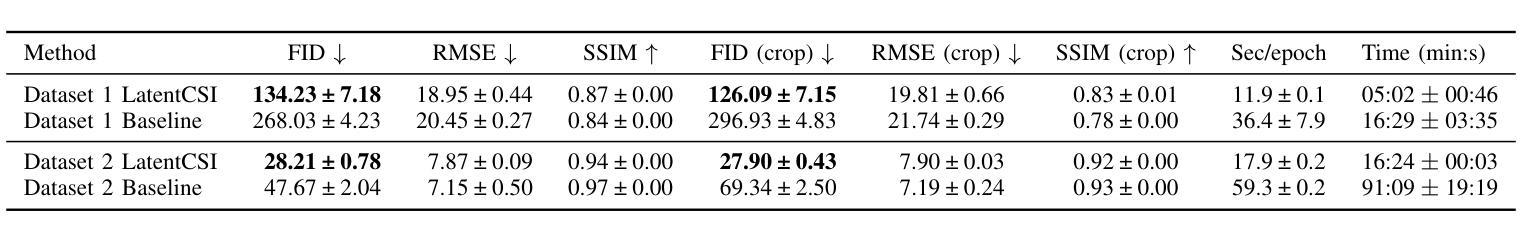
We present LatentCSI, a novel method for generating images of the physical environment from WiFi CSI measurements that leverages a pretrained latent diffusion model (LDM). Unlike prior approaches that rely on complex and computationally intensive techniques such as GANs, our method employs a lightweight neural network to map CSI amplitudes directly into the latent space of an LDM. We then apply the LDM’s denoising diffusion model to the latent representation with text-based guidance before decoding using the LDM’s pretrained decoder to obtain a high-resolution image. This design bypasses the challenges of pixel-space image generation and avoids the explicit image encoding stage typically required in conventional image-to-image pipelines, enabling efficient and high-quality image synthesis. We validate our approach on two datasets: a wide-band CSI dataset we collected with off-the-shelf WiFi devices and cameras; and a subset of the publicly available MM-Fi dataset. The results demonstrate that LatentCSI outperforms baselines of comparable complexity trained directly on ground-truth images in both computational efficiency and perceptual quality, while additionally providing practical advantages through its unique capacity for text-guided controllability.
我们提出了LatentCSI,这是一种从WiFi CSI测量中生成物理环境图像的新型方法,它利用预先训练的潜在扩散模型(LDM)。不同于以往依赖复杂且计算密集的技术(如GANs)的方法,我们的方法采用轻量级的神经网络直接将CSI振幅映射到LDM的潜在空间。然后,我们对潜在表示应用LDM的去噪扩散模型,使用文本指导,然后使用LDM的预训练解码器进行解码,以获得高分辨率图像。这种设计绕过了像素空间图像生成的挑战,避免了传统图像到图像管道通常需要的显式图像编码阶段,能够实现高效的高质量图像合成。我们在两个数据集上验证了我们的方法:我们使用现成的WiFi设备和相机收集的宽带CSI数据集以及公共可用的MM-Fi数据集的子集。结果表明,LatentCSI在计算效率和感知质量方面都优于直接在地面上训练的具有相似复杂度的基线图像,此外,它通过独特的文本指导可控性提供了实际优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 4 figures
Summary
基于WiFi CSI测量的物理环境图像生成新方法LatentCSI的研究介绍。该方法利用预训练的潜在扩散模型(LDM),通过轻量级神经网络将CSI振幅映射到LDM的潜在空间,再应用文本指导的扩散模型,最后使用LDM的预训练解码器获得高分辨率图像。该方法绕过像素空间图像生成的挑战,无需传统图像到图像的管道中的显式图像编码阶段,可实现高效高质量图像合成。
Key Takeaways
- LatentCSI是一种基于WiFi CSI测量生成物理环境图像的新方法。
- 该方法利用预训练的潜在扩散模型(LDM)。
- LatentCSI使用轻量级神经网络将CSI振幅映射到LDM的潜在空间。
- LatentCSI采用文本指导的扩散模型进行设计。
- 该方法避免了像素空间图像生成的挑战和显式图像编码阶段。
- LatentCSI可实现高效且高质量的图像合成。
点此查看论文截图



CapST: Leveraging Capsule Networks and Temporal Attention for Accurate Model Attribution in Deep-fake Videos
Authors:Wasim Ahmad, Yan-Tsung Peng, Yuan-Hao Chang, Gaddisa Olani Ganfure, Sarwar Khan
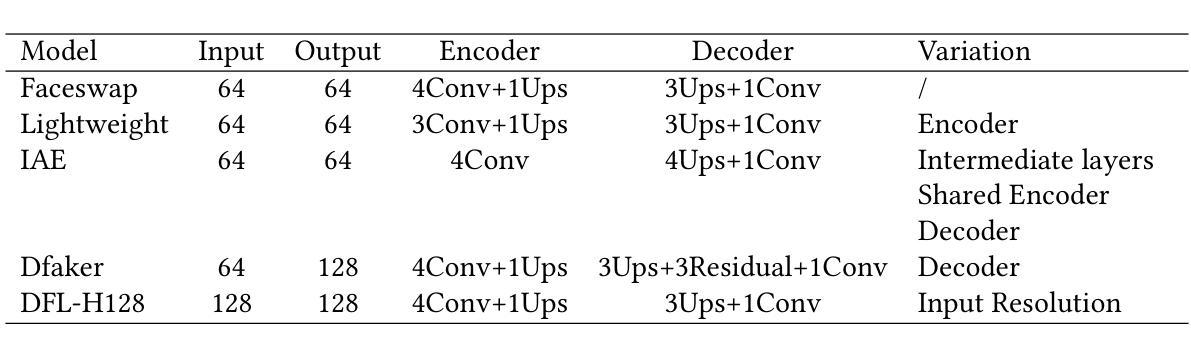
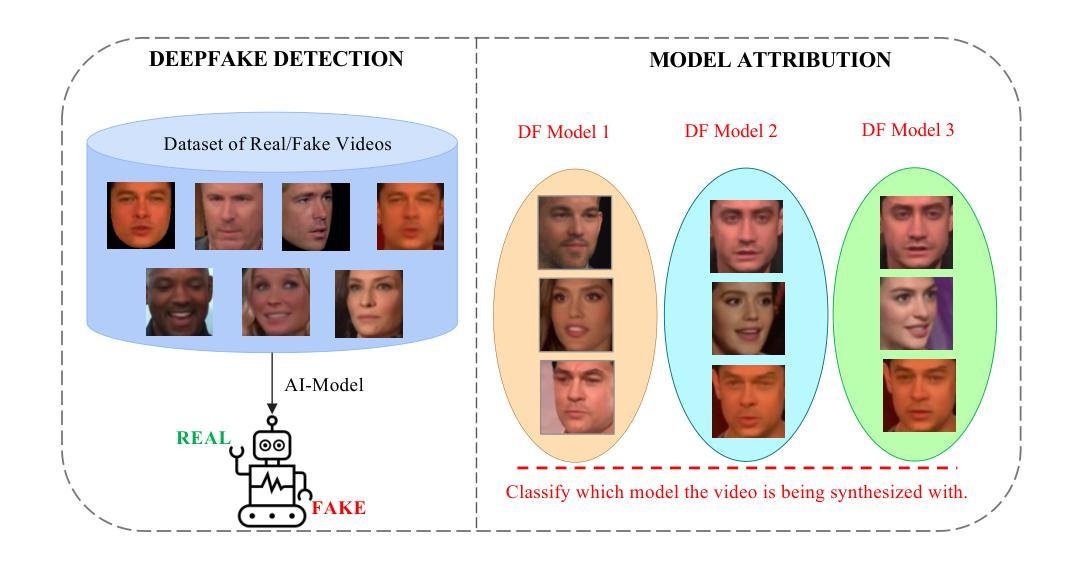
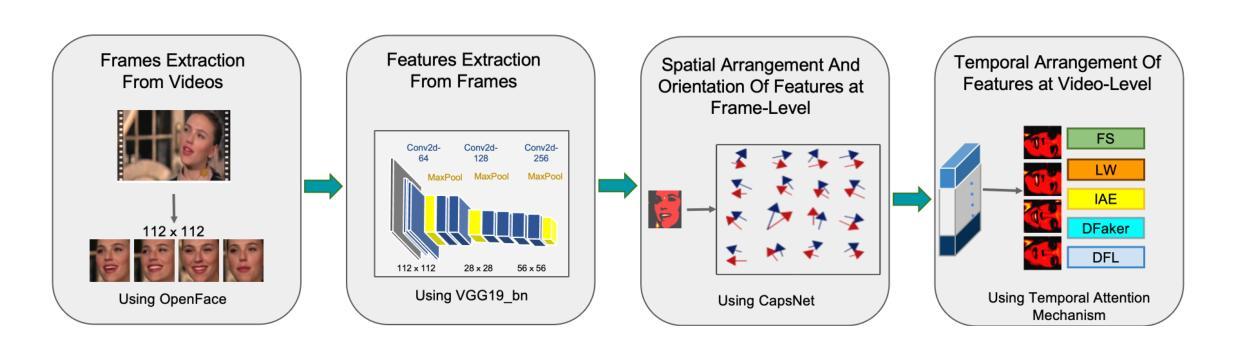
Deep-fake videos, generated through AI face-swapping techniques, have gained significant attention due to their potential for impactful impersonation attacks. While most research focuses on real vs. fake detection, attributing a deep-fake to its specific generation model or encoder is vital for forensic analysis, enabling source tracing and tailored countermeasures. This enhances detection by leveraging model-specific artifacts and supports proactive defenses. We investigate the model attribution problem for deep-fake videos using two datasets: Deepfakes from Different Models (DFDM) and GANGen-Detection, both comprising deep-fake videos and GAN-generated images. We use only fake images from GANGen-Detection to align with DFDM’s focus on attribution rather than binary classification. We formulate the task as a multiclass classification problem and introduce a novel Capsule-Spatial-Temporal (CapST) model that integrates a truncated VGG19 network for feature extraction, capsule networks for hierarchical encoding, and a spatio-temporal attention mechanism. Video-level fusion captures temporal dependencies across frames. Experiments on DFDM and GANGen-Detection show CapST outperforms baseline models in attribution accuracy while reducing computational cost.
通过人工智能面部替换技术生成的深度伪造视频因其潜在的假冒攻击影响而受到广泛关注。虽然大多数研究集中在真实与虚假的检测上,但将深度伪造归咎于其特定的生成模型或编码器对于法医学分析至关重要,能够实现溯源和有针对性的应对措施。这通过利用模型特定的人工制品增强了检测并支持主动防御。我们使用两个数据集来调查深度伪造视频的模型归属问题:来自不同模型的深度伪造(DFDM)和GANGen检测。这两个数据集都包含深度伪造的视频和GAN生成的图像。为了与DFDM的归属重点而非二分类相匹配,我们只使用GANGen检测中的假图像。我们将任务制定为多类别分类问题,并引入了一种新型的Capsule-Spatial-Temporal(CapST)模型,该模型结合了截断VGG19网络进行特征提取、胶囊网络进行层次编码以及时空注意力机制。视频级别的融合捕捉帧之间的时间依赖性。在DFDM和GANGen检测上的实验表明,CapST在归属准确性方面优于基线模型,并降低了计算成本。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对深度伪造视频(deep-fake videos),本文关注其来源模型归属问题。研究通过两个数据集开展模型归属问题的探究,并创新性地提出了Capsule-Spatial-Temporal(CapST)模型,该模型结合了特征提取、层次编码及时空注意力机制等技术,以实现更好的模型归属预测效果。实验表明,CapST模型在数据集上的表现优于基准模型。
Key Takeaways
- 研究针对深度伪造视频提出模型归属问题的重要性,此问题有助于进行溯源和针对性的防范措施。
- 使用两个数据集Deepfakes from Different Models(DFDM)和GANGen-Detection进行模型归属问题的研究。
- 将任务定义为多类分类问题。
- 提出创新的CapST模型,结合了特征提取、层次编码和时空注意力机制。
- CapST模型通过视频级别的融合捕捉帧间的时序依赖关系。
点此查看论文截图