⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-14 更新
Generalist Models in Medical Image Segmentation: A Survey and Performance Comparison with Task-Specific Approaches
Authors:Andrea Moglia, Matteo Leccardi, Matteo Cavicchioli, Alice Maccarini, Marco Marcon, Luca Mainardi, Pietro Cerveri
Following the successful paradigm shift of large language models, leveraging pre-training on a massive corpus of data and fine-tuning on different downstream tasks, generalist models have made their foray into computer vision. The introduction of Segment Anything Model (SAM) set a milestone on segmentation of natural images, inspiring the design of a multitude of architectures for medical image segmentation. In this survey we offer a comprehensive and in-depth investigation on generalist models for medical image segmentation. We start with an introduction on the fundamentals concepts underpinning their development. Then, we provide a taxonomy on the different declinations of SAM in terms of zero-shot, few-shot, fine-tuning, adapters, on the recent SAM 2, on other innovative models trained on images alone, and others trained on both text and images. We thoroughly analyze their performances at the level of both primary research and best-in-literature, followed by a rigorous comparison with the state-of-the-art task-specific models. We emphasize the need to address challenges in terms of compliance with regulatory frameworks, privacy and security laws, budget, and trustworthy artificial intelligence (AI). Finally, we share our perspective on future directions concerning synthetic data, early fusion, lessons learnt from generalist models in natural language processing, agentic AI and physical AI, and clinical translation.
在大型语言模型成功实现范式转变之后,通过在大规模数据集上进行预训练并在不同的下游任务上进行微调,通用模型已经涉足计算机视觉领域。Segment Anything Model(SAM)的引入为自然图像分割树立了里程碑,激发了多种医疗图像分割架构的设计灵感。在这篇综述中,我们对医疗图像分割的通用模型进行了全面深入的研究。首先介绍了支撑它们发展的基本概念。然后,我们根据零样本、少样本、微调、适配器、最近的SAM 2以及其他单独在图像上训练的创新模型等,对SAM的不同倾向进行了分类。我们深入分析了它们在初级研究和文献最佳水平上的性能,并与最新任务特定模型进行了严格比较。我们强调了符合法规框架、隐私和安全法律、预算和可信人工智能(AI)等挑战的必要性。最后,我们分享了关于合成数据、早期融合、从自然语言处理通用模型中学到的经验教训、代理AI和物理AI以及临床翻译的未来方向的看法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 132 pages, 26 figures, 23 tables. Andrea Moglia and Matteo Leccardi are equally contributing authors
Summary
大型语言模型的成功范式转变推动了通用模型在计算机视觉领域的进军。本文全面深入地探讨了用于医学图像分割的通用模型,介绍了相关基本概念,并对Segment Anything Model(SAM)的不同衍生版本进行了分类,包括零样本、少样本、微调、适配器等。同时,本文分析了这些模型在初级研究和文献最佳水平上的性能,并与最新任务特定模型进行了严格比较。此外,本文强调了遵守法规框架、隐私和安全法律、预算和可信人工智能等挑战的重要性。最后,本文分享了关于合成数据、早期融合、从自然语言处理通用模型中学到的教训、智能体和物理人工智能以及临床翻译等方面的未来方向。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的范式转变推动了通用模型在计算机视觉领域的广泛应用。
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)在医学图像分割领域树立了里程碑。
- 通用模型的不同衍生版本包括零样本、少样本、微调、适配器等。
- 这些模型在初级研究和文献最佳水平上的性能得到了全面分析。
- 与最新任务特定模型的严格比较突出了通用模型的性能。
- 通用模型面临合规性、隐私和安全、预算和可信人工智能等挑战。
点此查看论文截图

Visually Descriptive Language Model for Vector Graphics Reasoning
Authors:Zhenhailong Wang, Joy Hsu, Xingyao Wang, Kuan-Hao Huang, Manling Li, Jiajun Wu, Heng Ji
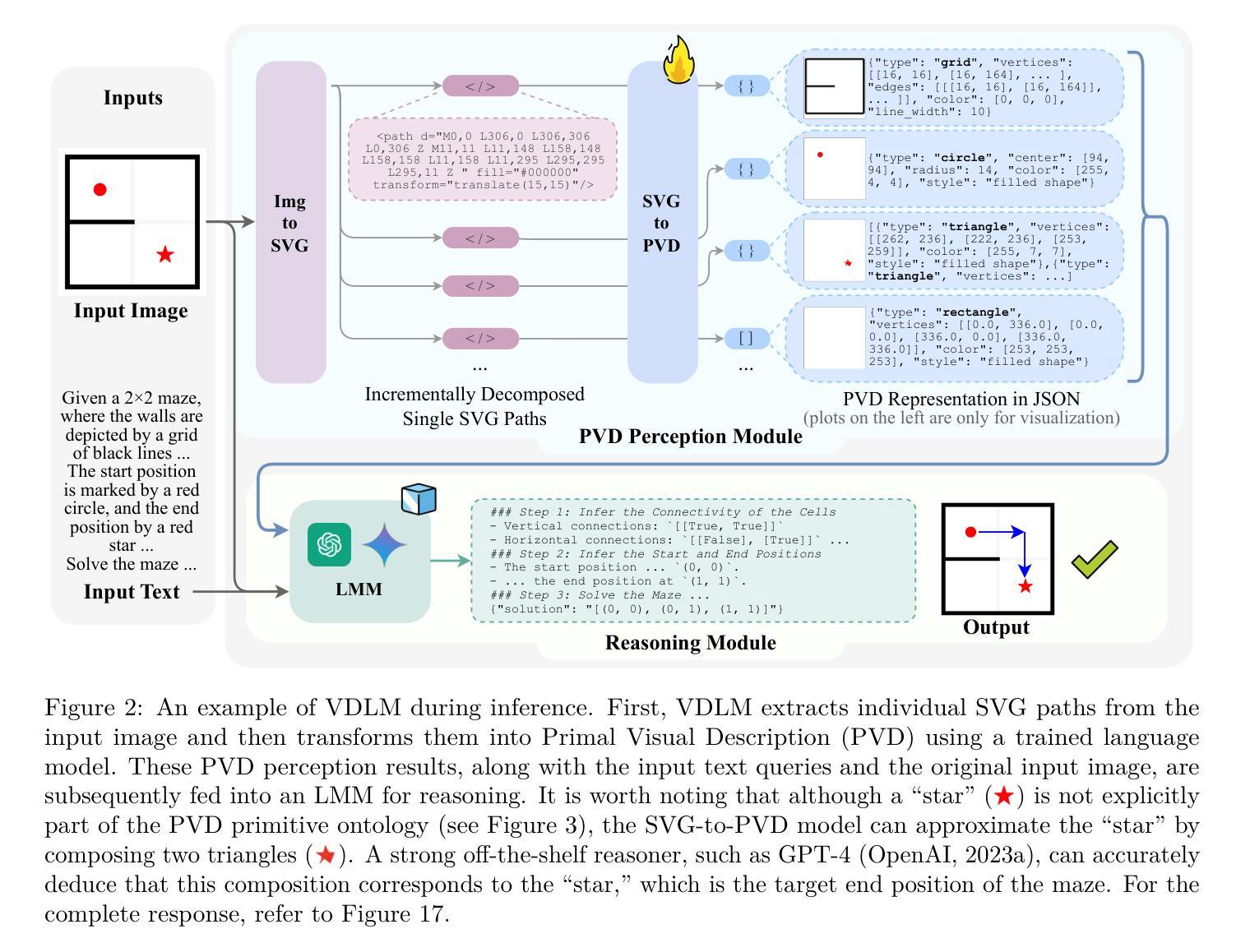
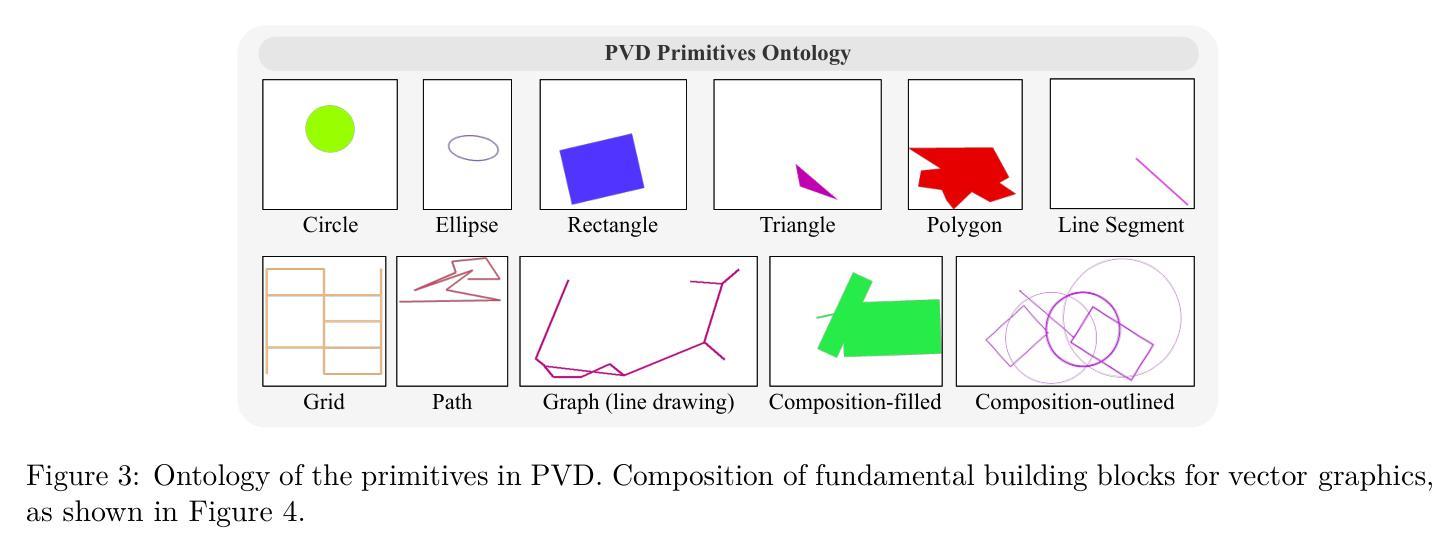
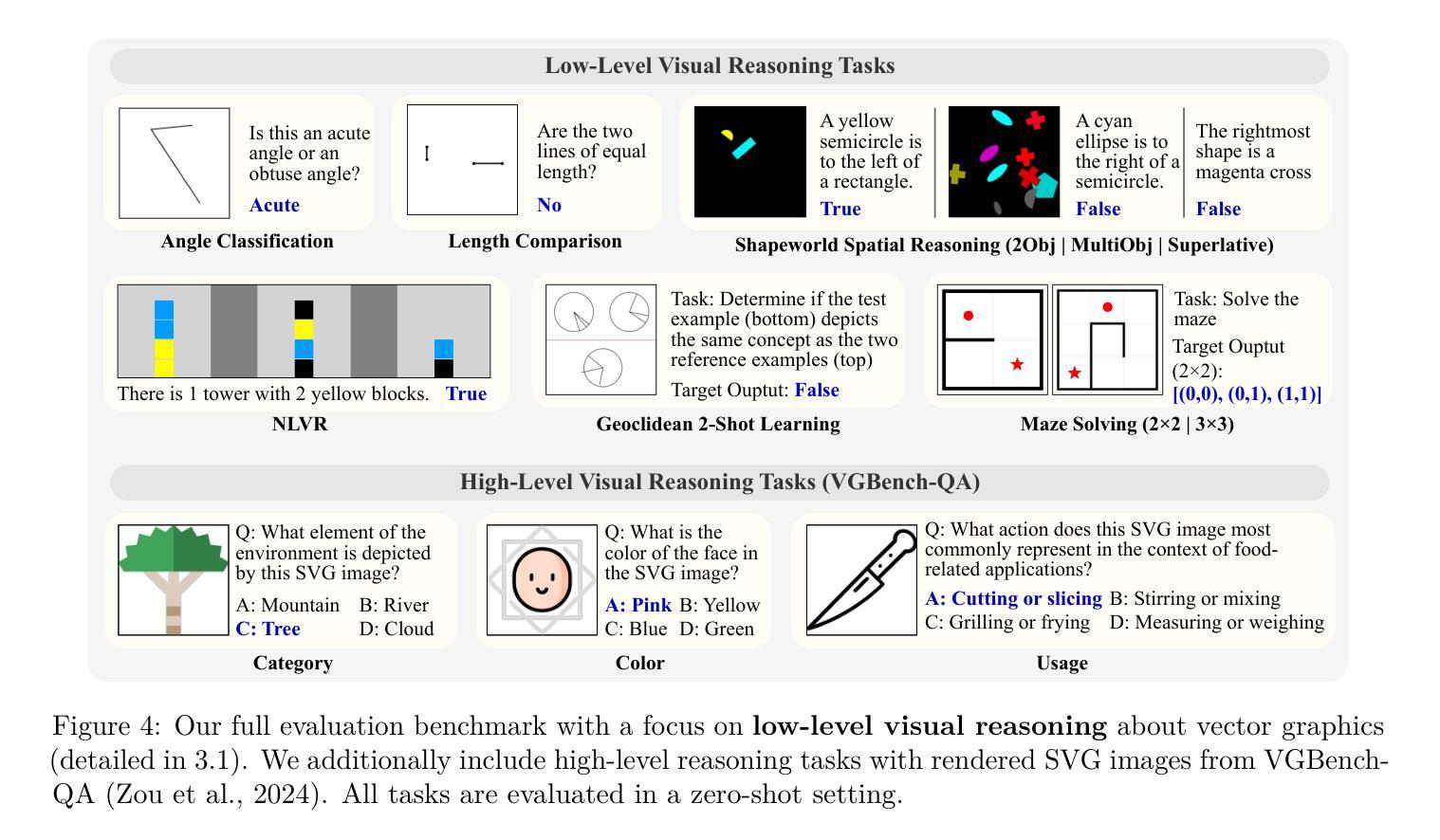
Despite significant advancements, large multimodal models (LMMs) still struggle to bridge the gap between low-level visual perception – focusing on shapes, sizes, and layouts – and high-level language reasoning, such as semantics and logic. This limitation is evident in tasks that require precise visual perception, like comparing geometric properties or solving visual reasoning problems. To study this failure mode, we focus on vector graphics – images composed of 2D objects and shapes, prevalent in LMM-based tasks in web, design, and OS environments. We identify two key research questions: how can we enable precise visual perception, and how can we facilitate high-level reasoning based on such low-level perceptions? To capture fine visual details, we use Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) for accurate encoding of visual scenes. However, SVGs are not readily interpretable by LMMs in a zero-shot manner. To tackle this, we propose the Visually Descriptive Language Model (VDLM), which introduces a Primal Visual Description (PVD) as an intermediate textual representation. PVD translates SVGs into a text-based abstraction consisting of primitive attributes (e.g., shape, position, measurement) and their corresponding values. PVD can be learned using task-agnostic synthesized data and represents visual primitives that are universal across vector graphics. This abstraction is more structured, allowing for direct interpretation by foundation models for zero-shot generalization. Without human-annotated data, empirical results show that VDLM significantly improves state-of-the-art LMMs like GPT-4o on various multimodal perception and reasoning tasks. Extensive analyses of VDLM show improved interpretability due to its disentangled perception and reasoning. We also demonstrate a positive correlation between PVD quality and task performance. Project page: https://mikewangwzhl.github.io/VDLM/
尽管取得了重大进展,大型多模态模型(LMMs)仍然在弥合低级视觉感知(专注于形状、大小和布局)和高级语言推理(如语义和逻辑)之间的差距方面面临困难。这种局限性在需要精确视觉感知的任务中尤为明显,例如比较几何属性或解决视觉推理问题。为了研究这种失败的模式,我们专注于矢量图形——由二维对象和形状组成的图像,在网络、设计和操作系统环境中的基于LMM的任务中普遍存在。我们确定了两个关键的研究问题:如何实现对精确的视觉感知,以及如何基于这样的低级感知促进高级推理?为了捕捉精细的视觉细节,我们使用可缩放矢量图形(SVG)对视觉场景进行准确编码。然而,SVG并不能被LMM以零射击的方式轻易解读。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了视觉描述语言模型(VDLM),它引入了一种原始视觉描述(PVD)作为中间文本表示。PVD将SVG翻译成基于文本的抽象,由原始属性(例如形状、位置、测量)及其相应的值组成。使用任务无关的合成数据可以学习PVD,它代表了矢量图形中普遍存在的视觉原始元素。这种抽象更加结构化,允许基础模型直接解释以实现零射击泛化。无需人工注释的数据,实证结果表明,VDLM在多种多模态感知和推理任务上显著改进了最先进的LMMs,如GPT-4o。对VDLM的深入分析显示,由于其分离了感知和推理,其可解释性得到了提高。我们还证明了原始视觉描述(PVD)质量与任务性能之间的正相关关系。项目页面:https://mikewangwzhl.github.io/VDLM/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://mikewangwzhl.github.io/VDLM/
Summary
大型多模态模型(LMMs)在连接低层次视觉感知(如形状、大小和布局)与高层次语言推理(如语义和逻辑)方面仍存在困难。研究聚焦于此失败模式,特别是以矢量图形(在web、设计和操作系统环境中常见的LMMs任务)为研究对象。研究提出了视觉描述性语言模型(VDLM),通过引入原始视觉描述(PVD)作为中间文本表示来解决这一问题。PVD将SVG矢量图转化为基于文本的抽象表示,包含原始属性(如形状、位置和测量)及其对应的值。研究结果表明,VDLM显著提高LMMs在多模态感知和推理任务上的表现,且在无需人类注释数据的情况下仍有效。
Key Takeaways
- 大型多模态模型在连接低层次视觉感知与高层次语言推理方面存在差距。
- 研究集中在矢量图形上,旨在解决这一差距。
- 引入原始视觉描述(PVD)作为中间文本表示,将SVG矢量图转化为基于文本的抽象表示。
- PVD包含原始属性(形状、位置和测量)及其对应的值。
- VDLM显著提高LMMs在多模态感知和推理任务上的表现。
- VDLM提高了解释性,通过解耦感知和推理。
- PVD质量与任务性能之间存在正相关关系。
点此查看论文截图

A Unified Framework to Enforce, Discover, and Promote Symmetry in Machine Learning
Authors:Samuel E. Otto, Nicholas Zolman, J. Nathan Kutz, Steven L. Brunton
Symmetry is present throughout nature and continues to play an increasingly central role in physics and machine learning. Fundamental symmetries, such as Poincar'{e} invariance, allow physical laws discovered in laboratories on Earth to be extrapolated to the farthest reaches of the universe. Symmetry is essential to achieving this extrapolatory power in machine learning applications. For example, translation invariance in image classification allows models with fewer parameters, such as convolutional neural networks, to be trained on smaller data sets and achieve state-of-the-art performance. In this paper, we provide a unifying theoretical and methodological framework for incorporating symmetry into machine learning models in three ways: 1. enforcing known symmetry when training a model; 2. discovering unknown symmetries of a given model or data set; and 3. promoting symmetry during training by learning a model that breaks symmetries within a user-specified group of candidates when there is sufficient evidence in the data. We show that these tasks can be cast within a common mathematical framework whose central object is the Lie derivative associated with fiber-linear Lie group actions on vector bundles. We extend and unify several existing results by showing that enforcing and discovering symmetry are linear-algebraic tasks that are dual with respect to the bilinear structure of the Lie derivative. We also propose a novel way to promote symmetry by introducing a class of convex regularization functions based on the Lie derivative and nuclear norm relaxation to penalize symmetry breaking during training of machine learning models. We explain how these ideas can be applied to a wide range of machine learning models including basis function regression, dynamical systems discovery, neural networks, and neural operators acting on fields.
对称性质在自然界中普遍存在,并在物理和机器学习领域扮演着越来越重要的角色。诸如庞加莱(Poincaré)不变性等基本对称性质,使得在地球上实验室发现的物理定律可以推广到宇宙的最远端。对称性质对于实现机器学习应用中的这种推广能力至关重要。例如,图像分类中的平移不变性使得卷积神经网络等具有较少参数的模型能够在较小的数据集上进行训练,并取得最先进的性能。在本文中,我们提供了一个统一的理论和方法框架,以三种方式将对称性质纳入机器学习模型:1. 在训练模型时强制执行已知对称性;2. 发现给定模型或数据集的未知对称性;3. 通过学习在用户提供的一组候选模型中打破对称性来促进对称性,当有足够的数据支持时。我们表明,这些任务可以置于一个共同的数学框架内,其核心对象是纤维线性李群作用在向量丛上的李导数。我们通过对李导数的双线性结构显示对称性的强制和发现是对称性的线性代数任务的两个方面来扩展和统一了若干现有结果。我们还提出了一种通过引入基于李导数和核范数松弛的凸正则化函数类来促进对称性的新方法,以在训练机器学习模型时惩罚破坏对称性的行为。我们解释了这些想法如何应用于广泛的机器学习模型,包括基础函数回归、动力系统发现、神经网络和作用于字段的神经网络算子。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了对称在自然中的普遍存在及其在物理和机器学习中的核心作用。文章阐述了如何将对称融入机器学习模型的三种方式,包括在训练模型时强制执行已知对称、发现给定模型或数据集的未知对称,以及在训练过程中通过学习模型在用户提供的一组候选者中打破对称。文章还介绍了如何通过利用纤维线性李群作用在向量丛上的李导数来统一这些任务,并提出了一种基于李导数和核范数松弛的凸正则化函数来在训练机器学习模型时促进对称性。
Key Takeaways
- 对称性在自然中普遍存在,并在物理和机器学习中发挥核心作用。
- 机器学习中的对称性对于提高模型的预测能力和泛化能力至关重要。
- 文章提供了三种将对称性融入机器学习模型的方法:强制执行已知对称性、发现未知对称性以及促进对称性。
- 通过利用纤维线性李群作用在向量丛上的李导数,可以统一这些任务。
- 文章展示了如何通过凸正则化函数在训练机器学习模型时促进对称性,这种函数基于李导数和核范数松弛。
- 文章解释了对偶于李导数的线性代数任务在强制和执行对称性发现中的作用。
点此查看论文截图