⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-14 更新
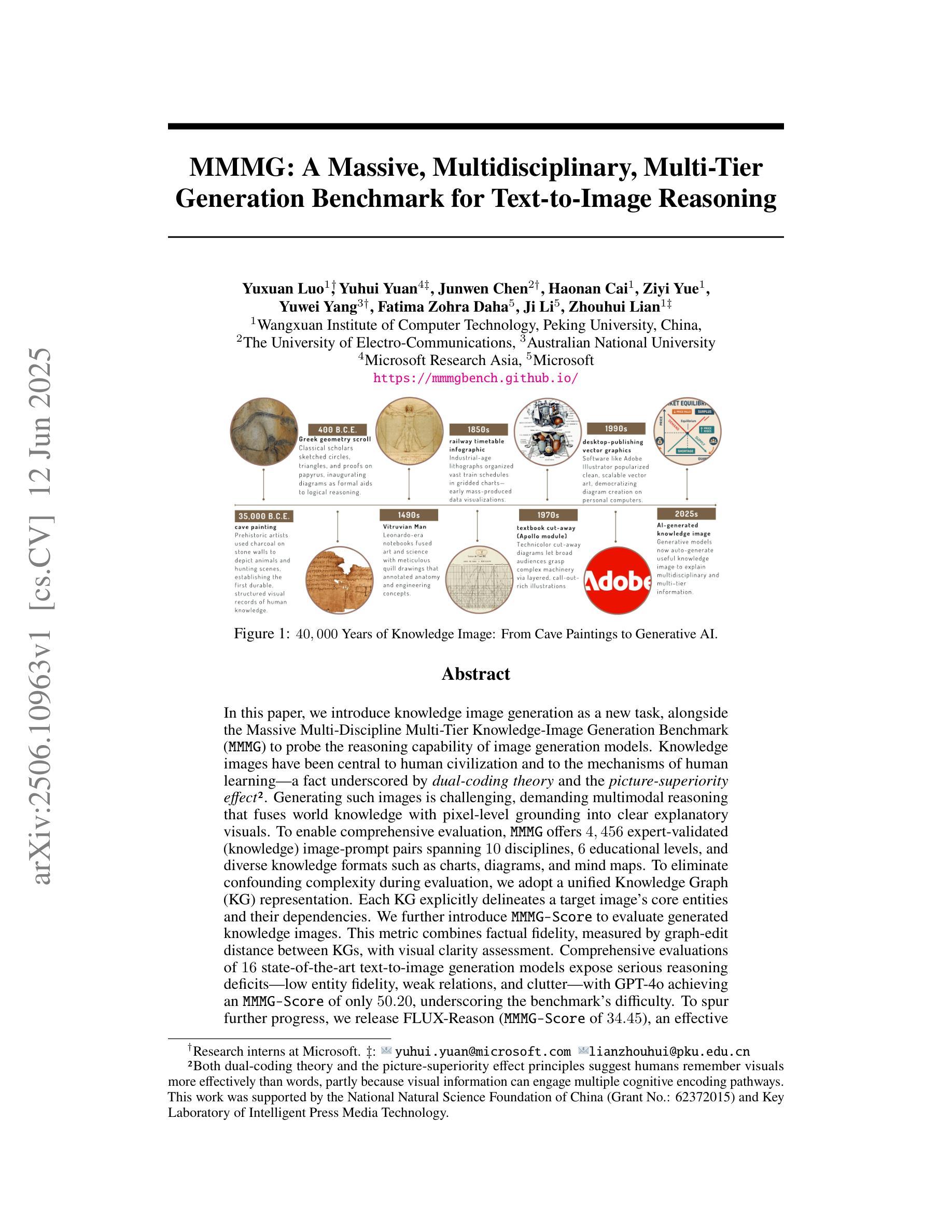
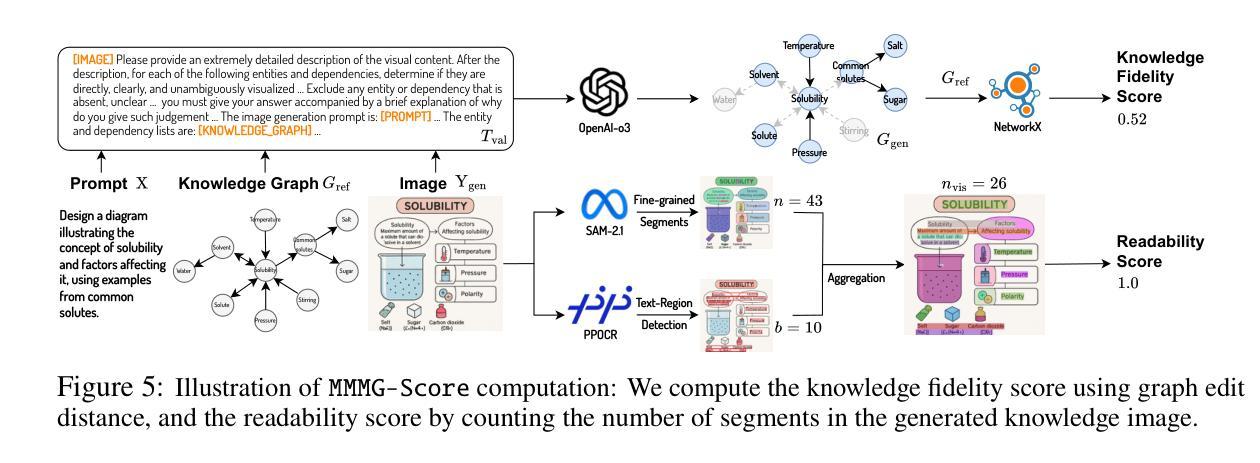
MMMG: A Massive, Multidisciplinary, Multi-Tier Generation Benchmark for Text-to-Image Reasoning
Authors:Yuxuan Luo, Yuhui Yuan, Junwen Chen, Haonan Cai, Ziyi Yue, Yuwei Yang, Fatima Zohra Daha, Ji Li, Zhouhui Lian
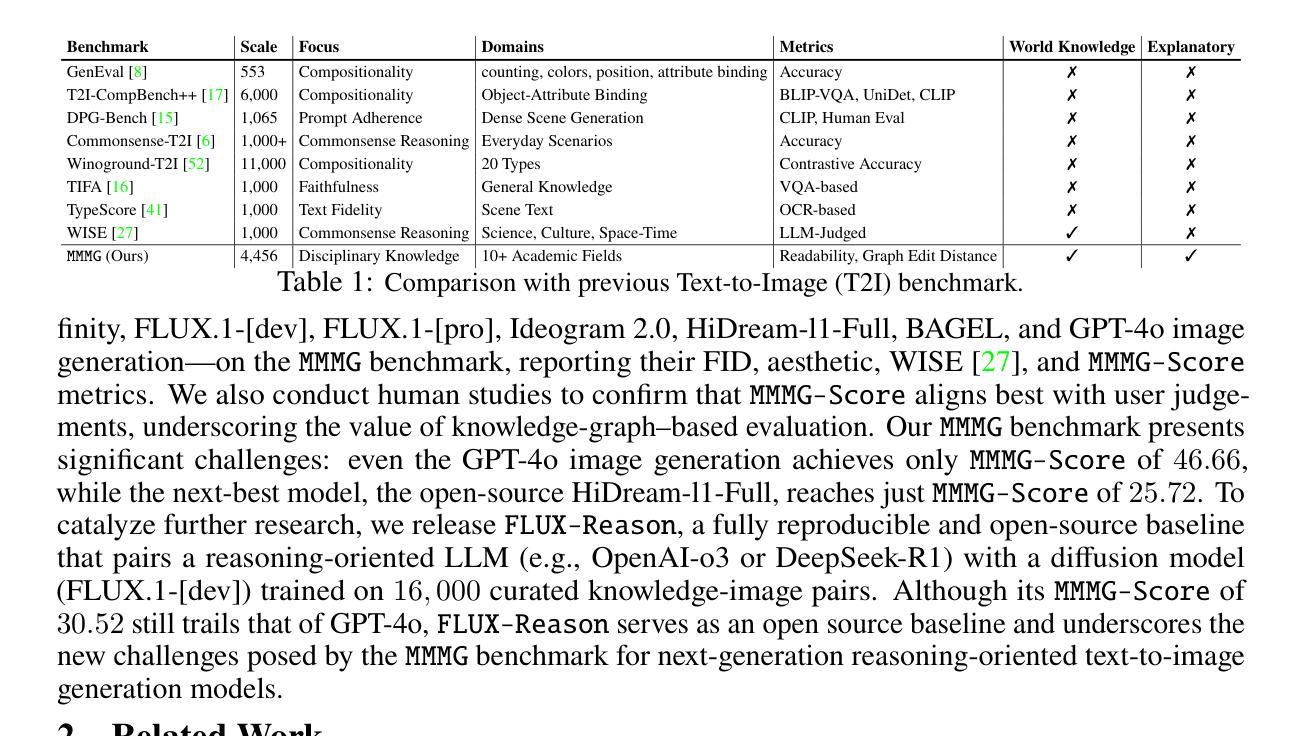
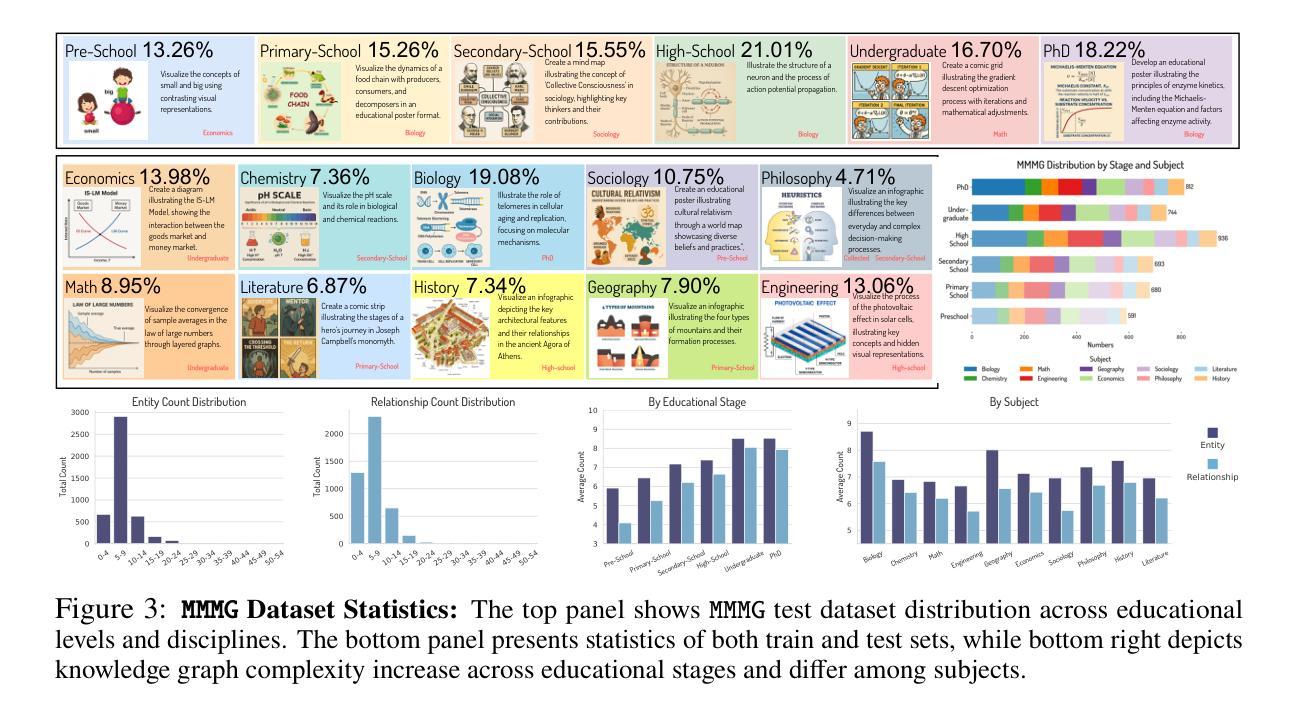
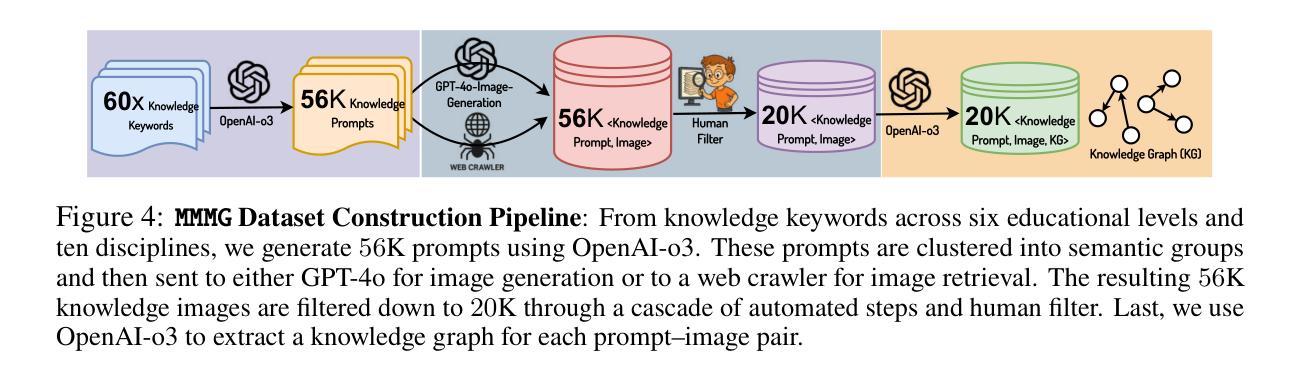
In this paper, we introduce knowledge image generation as a new task, alongside the Massive Multi-Discipline Multi-Tier Knowledge-Image Generation Benchmark (MMMG) to probe the reasoning capability of image generation models. Knowledge images have been central to human civilization and to the mechanisms of human learning–a fact underscored by dual-coding theory and the picture-superiority effect. Generating such images is challenging, demanding multimodal reasoning that fuses world knowledge with pixel-level grounding into clear explanatory visuals. To enable comprehensive evaluation, MMMG offers 4,456 expert-validated (knowledge) image-prompt pairs spanning 10 disciplines, 6 educational levels, and diverse knowledge formats such as charts, diagrams, and mind maps. To eliminate confounding complexity during evaluation, we adopt a unified Knowledge Graph (KG) representation. Each KG explicitly delineates a target image’s core entities and their dependencies. We further introduce MMMG-Score to evaluate generated knowledge images. This metric combines factual fidelity, measured by graph-edit distance between KGs, with visual clarity assessment. Comprehensive evaluations of 16 state-of-the-art text-to-image generation models expose serious reasoning deficits–low entity fidelity, weak relations, and clutter–with GPT-4o achieving an MMMG-Score of only 50.20, underscoring the benchmark’s difficulty. To spur further progress, we release FLUX-Reason (MMMG-Score of 34.45), an effective and open baseline that combines a reasoning LLM with diffusion models and is trained on 16,000 curated knowledge image-prompt pairs.
本文介绍了一个新知识图像生成任务,并伴随着大规模多学科多级知识图像生成基准测试(MMMG),以探测图像生成模型的推理能力。知识图像在人类文明和人类学习机制中一直占据核心地位,这一事实由双重编码理论和图像优势效应所强调。生成这样的图像具有挑战性,它要求多模态推理,将世界知识与像素级基础相结合,生成清晰解释性的视觉内容。为了进行全面评估,MMMG提供了4456个专家验证的知识图像提示对,涵盖10个学科,6个教育水平,以及多样化的知识形式,如图表、图解和思维导图。为了消除评估过程中的混淆复杂性,我们采用统一的知识图谱(KG)表示法。每个知识图谱都明确界定了目标图像的核心实体及其依赖关系。我们还进一步引入了MMMG评分来评估生成的知识图像。该指标结合了事实保真度(通过知识图谱之间的图编辑距离来衡量)和视觉清晰度评估。对16个最先进文本到图像生成模型的全面评估揭示了严重的推理缺陷——实体保真度低、关系薄弱和混乱——GPT-4o的MMMG评分仅为50.20,凸显了基准测试的困难。为了促进进一步的进步,我们发布了FLUX-Reason(MMMG评分为34.45),这是一个有效且开放的基线,它结合了推理大型语言模型与扩散模型,并在16000个精选的知识图像提示对上进行了训练。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
知识图像生成被提出为一个新任务,并介绍了大规模跨领域、分层知识图像生成基准测试(MMMG)来测试图像生成模型的推理能力。知识图像在人类文明和认知机制中占据核心地位,生成这样的图像需要融合多学科知识,并以像素级的清晰度进行可视化推理。MMMG提供了包含十大学科领域、六个教育层次和多种知识形式的专家验证知识图像提示对,并采用了统一的知识图谱表示来全面评估生成的图像。此外,还引入了MMMG评分来评估生成的知识图像,该评分结合了事实准确性与视觉清晰度的评估。对十六种先进的文本到图像生成模型的综合评估表明存在严重的推理缺陷,包括实体保真度低、关系弱和混乱等。为鼓励进一步发展,发布了一个有效的开放基线FLUX-Reason,它在MMMG评分上为34.45,结合了推理大型语言模型和扩散模型,并在1万六千个精选的知识图像提示对上进行了训练。
关键见解
- 知识图像生成被提出为一个新任务,旨在测试图像生成模型的推理能力。
- 知识图像在人类学习和认知机制中占据核心地位。
- MMMG基准测试提供了跨学科、分层的图像提示对,以评估知识图像的生成质量。
- 引入MMMG评分系统来综合评估知识图像的准确性和视觉清晰度。
- 当前先进的文本到图像生成模型在知识图像生成方面存在推理缺陷。
- GPT-4在处理知识图像生成任务时仅获得MMMG评分50.20,表明该任务具有挑战性。
点此查看论文截图

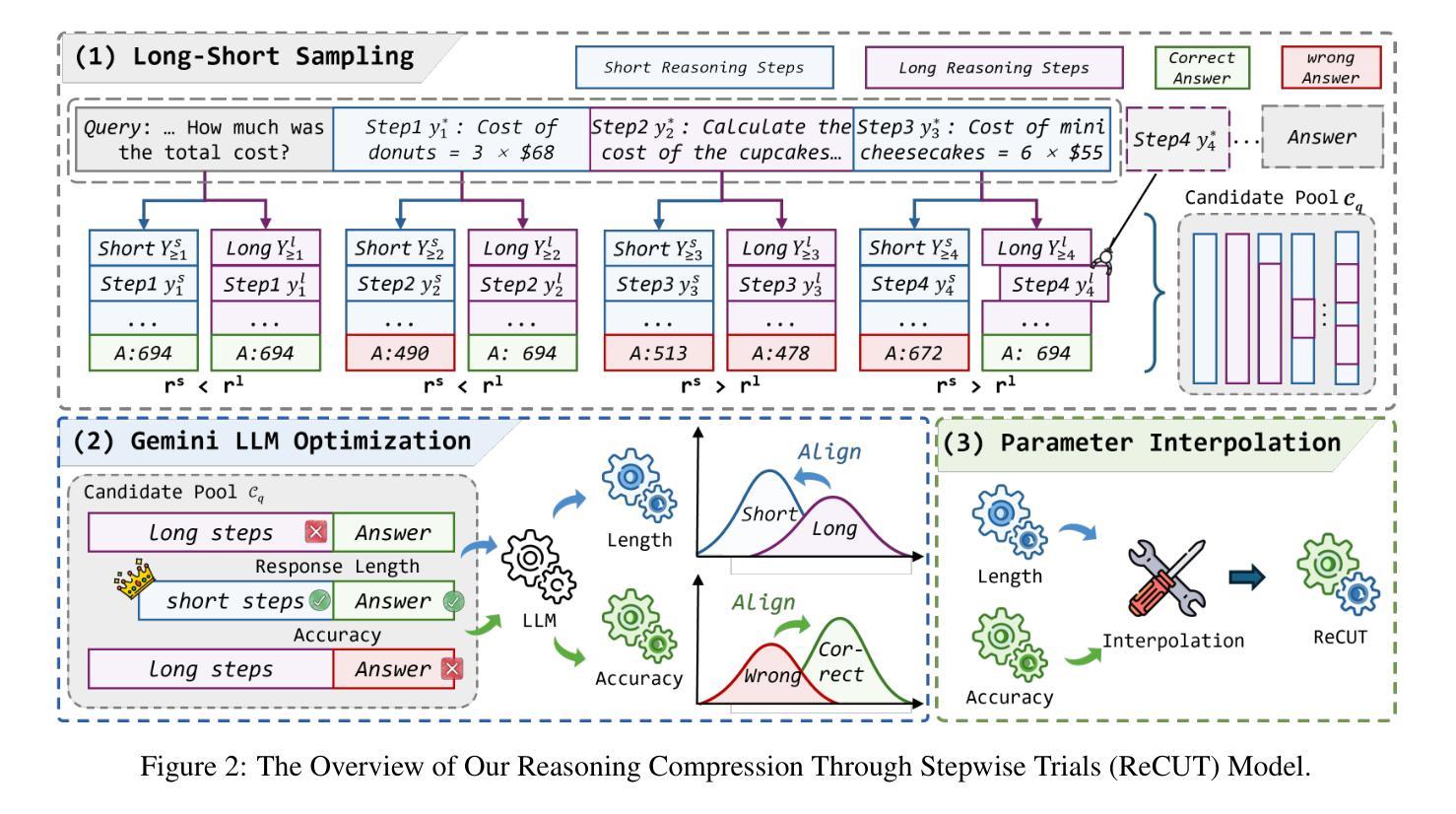
ReCUT: Balancing Reasoning Length and Accuracy in LLMs via Stepwise Trails and Preference Optimization
Authors:Zhensheng Jin, Xinze Li, Yifan Ji, Chunyi Peng, Zhenghao Liu, Qi Shi, Yukun Yan, Shuo Wang, Furong Peng, Ge Yu
Recent advances in Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting have substantially improved the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, these methods often suffer from overthinking, leading to unnecessarily lengthy or redundant reasoning traces. Existing approaches attempt to mitigate this issue through curating multiple reasoning chains for training LLMs, but their effectiveness is often constrained by the quality of the generated data and prone to overfitting. To address the challenge, we propose Reasoning Compression ThroUgh Stepwise Trials (ReCUT), a novel method aimed at balancing the accuracy and length of reasoning trajectory. Specifically, ReCUT employs a stepwise exploration mechanism and a long-short switched sampling strategy, enabling LLMs to incrementally generate diverse reasoning paths. These paths are evaluated and used to construct preference pairs to train two specialized models (Gemini LLMs)-one optimized for reasoning accuracy, the other for shorter reasoning. A final integrated model is obtained by interpolating the parameters of these two models. Experimental results across multiple math reasoning datasets and backbone models demonstrate that ReCUT significantly reduces reasoning lengths by approximately 30-50%, while maintaining or improving reasoning accuracy compared to various baselines. All codes and data will be released via https://github.com/NEUIR/ReCUT.
近期Chain-of-Thought(CoT)提示方法的进步极大地提升了大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力。然而,这些方法常常过度思考,导致推理痕迹过于冗长或冗余。现有方法试图通过为训练LLM筛选多条推理链来缓解这个问题,但其有效性往往受到生成数据质量的影响,并容易过度拟合。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了通过逐步试验进行推理压缩(ReCUT)的新方法,旨在平衡推理轨迹的准确性和长度。具体来说,ReCUT采用逐步探索机制和长短切换采样策略,使LLM能够逐步生成多样的推理路径。这些路径经过评估并用于构建偏好对,以训练两个专业模型(双子星LLM)——一个优化推理准确性,另一个优化较短推理。最终的综合模型是通过这两个模型的参数插值获得的。在多个数学推理数据集和骨干模型上的实验结果表明,ReCUT在保持或提高推理准确性的同时,将推理长度减少了大约30-50%,与各种基线相比具有显著优势。所有代码和数据将通过https://github.com/NEUIR/ReCUT发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期Chain-of-Thought(CoT)提示技术的进展大幅提升了大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力。然而,这些方法常陷入过度思考,生成过长的推理轨迹。现有方法试图通过为训练LLM精选多条推理链来解决这一问题,但其效果受限于生成数据的质量并易产生过拟合。为解决此挑战,我们提出Reasoning Compression Through Stepwise Trials(ReCUT)方法,旨在平衡推理轨迹的准确性与长度。ReCUT采用逐步探索机制和长短采样策略,使LLM逐步生成多样的推理路径。评估这些路径并构建偏好对,用于训练两个专业模型(Gemini LLMs),一个优化推理准确性,另一个优化缩短推理。最终集成模型是通过这两个模型的参数插值获得。实验结果显示,ReCUT在多个数学推理数据集和背景模型上显著减少了约30-50%的推理长度,同时保持或提高了与各种基准线的推理准确性。
Key Takeaways
- Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting has improved the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs).
- CoT methods often lead to unnecessarily lengthy or redundant reasoning traces, a new challenge.
- Existing approaches attempt to solve this through curating multiple reasoning chains, but their effectiveness is limited.
- ReCUT method aims to balance accuracy and length of reasoning trajectory.
- ReCUT employs a stepwise exploration mechanism and a long-short switched sampling strategy.
- ReCUT trains two specialized models (Gemini LLMs) with different optimization goals.
点此查看论文截图

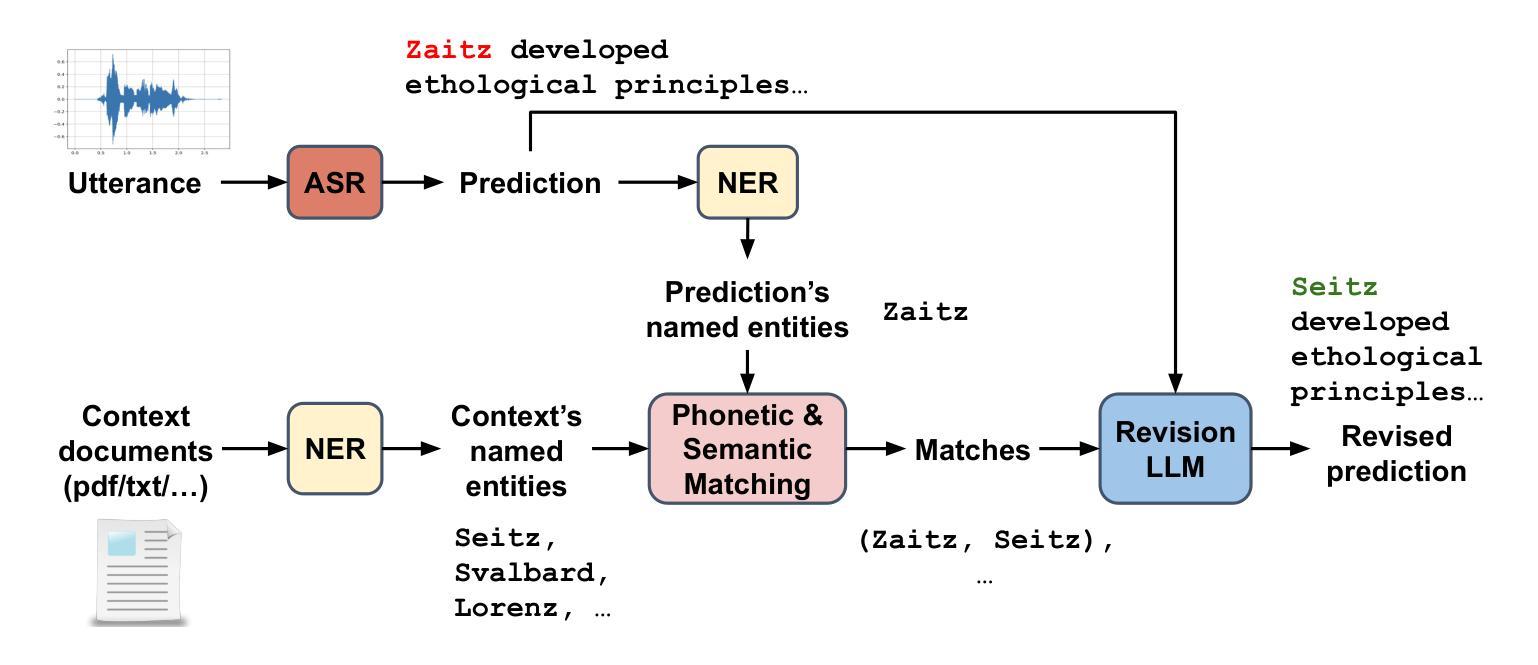
Improving Named Entity Transcription with Contextual LLM-based Revision
Authors:Viet Anh Trinh, Xinlu He, Jacob Whitehill
With recent advances in modeling and the increasing amount of supervised training data, automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems have achieved remarkable performance on general speech. However, the word error rate (WER) of state-of-the-art ASR remains high for named entities. Since named entities are often the most critical keywords, misrecognizing them can affect all downstream applications, especially when the ASR system functions as the front end of a complex system. In this paper, we introduce a large language model (LLM) revision mechanism to revise incorrect named entities in ASR predictions by leveraging the LLM’s reasoning ability as well as local context (e.g., lecture notes) containing a set of correct named entities. Finally, we introduce the NER-MIT-OpenCourseWare dataset, containing 45 hours of data from MIT courses for development and testing. On this dataset, our proposed technique achieves up to 30% relative WER reduction for named entities.
随着建模的最新进展和大量监督训练数据的增加,自动语音识别(ASR)系统在通用语音上的表现已经取得了显著的成绩。然而,对于命名实体,最新前沿的ASR技术的词错误率(WER)仍然很高。由于命名实体通常是至关重要的关键词,误识别它们会影响所有下游应用,尤其是当ASR系统作为复杂系统的前端时。在本文中,我们引入了一种大型语言模型(LLM)修正机制,利用LLM的推理能力和包含一组正确命名实体的局部上下文(例如课堂笔记)来修正ASR预测中的错误命名实体。最后,我们介绍了NER-MIT-OpenCourseWare数据集,其中包含来自MIT课程的45小时数据,用于开发和测试。在该数据集上,我们提出的技术实现了高达30%的命名实体相对WER降低。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着建模技术的进步和大量监督训练数据的增加,自动语音识别(ASR)系统在通用语音上的表现已经取得了显著的成绩。然而,对于命名实体,最先进的ASR的单词错误率(WER)仍然很高。由于命名实体通常是关键的关键词,误识别它们会影响所有下游应用,特别是当ASR系统作为复杂系统的前端时。本文引入了一种大型语言模型(LLM)修正机制,利用LLM的推理能力和包含正确命名实体的局部上下文(如讲义笔记)来修正ASR预测中的错误命名实体。同时,还介绍了NER-MIT-OpenCourseWare数据集,包含来自MIT课程的45小时数据,用于开发和测试。在该数据集上,所提出的技术实现了高达30%的命名实体相对WER降低。
Key Takeaways
- ASR系统在通用语音上的表现已经显著提高,但在识别命名实体方面仍存在高单词错误率(WER)。
- 命名实体的误识别对下游应用,特别是当ASR作为复杂系统前端时,具有重要影响。
- 引入大型语言模型(LLM)修正机制,利用LLM的推理能力和局部上下文来修正ASR中的命名实体错误。
- 局部上下文(如讲义笔记)包含正确的命名实体,可帮助提高修正的准确性。
- 介绍了NER-MIT-OpenCourseWare数据集,包含45小时的数据,用于ASR系统和命名实体识别的开发和测试。
- 所提出的技术在NER-MIT-OpenCourseWare数据集上实现了显著的性能提升,降低了高达30%的命名实体WER。
- 这项技术对于提高ASR系统的性能和准确性,特别是在处理命名实体时,具有重要的实际应用价值。
点此查看论文截图



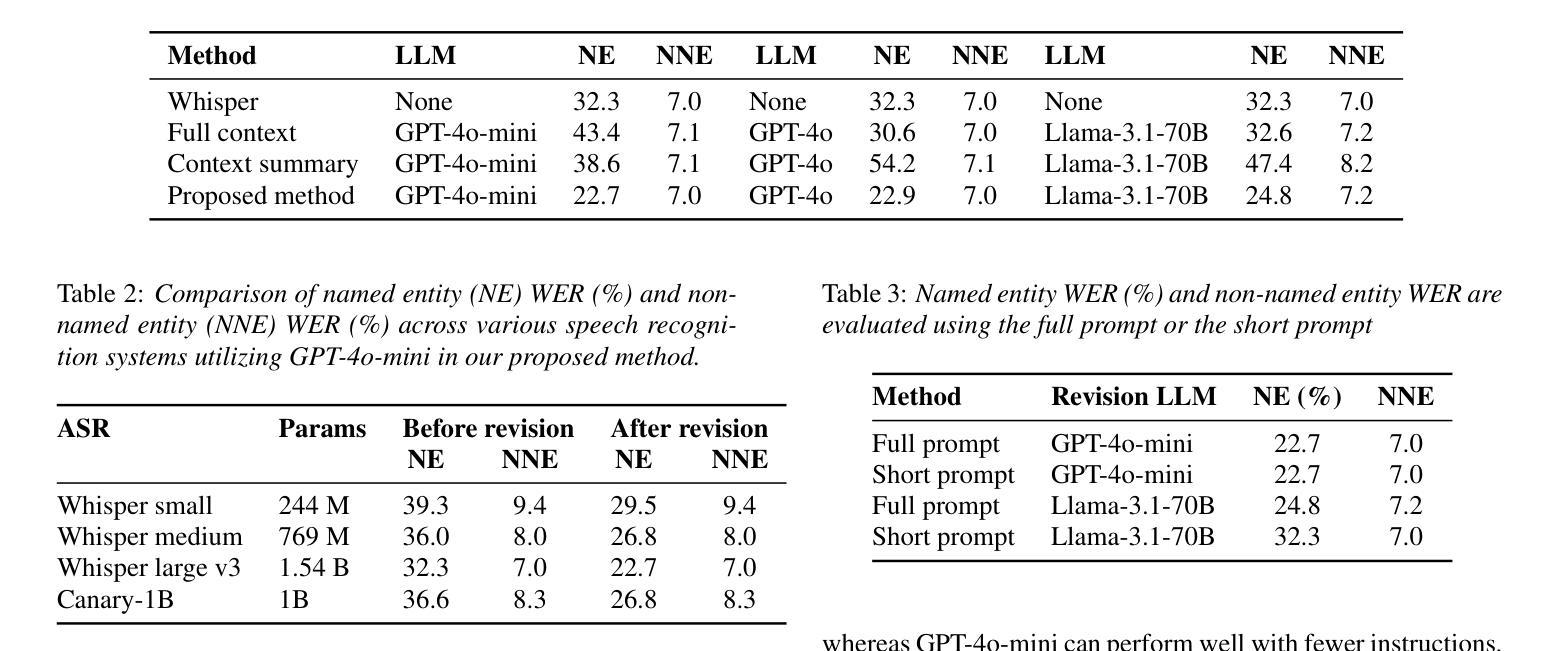
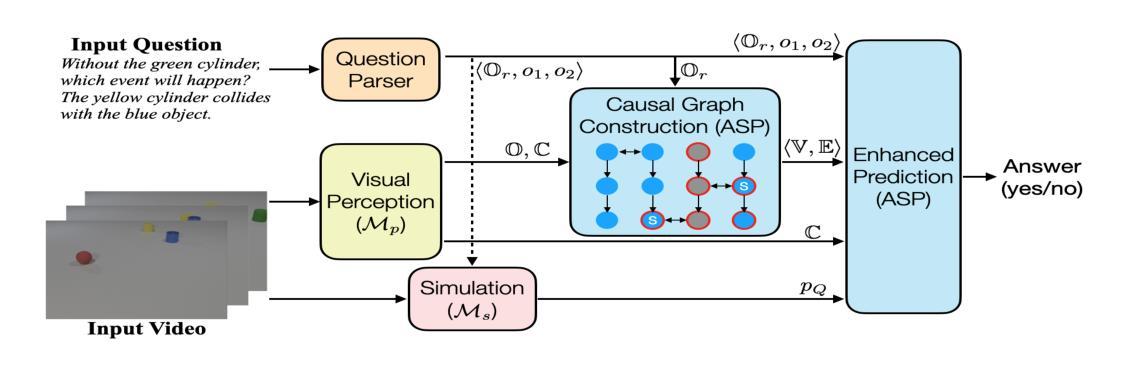
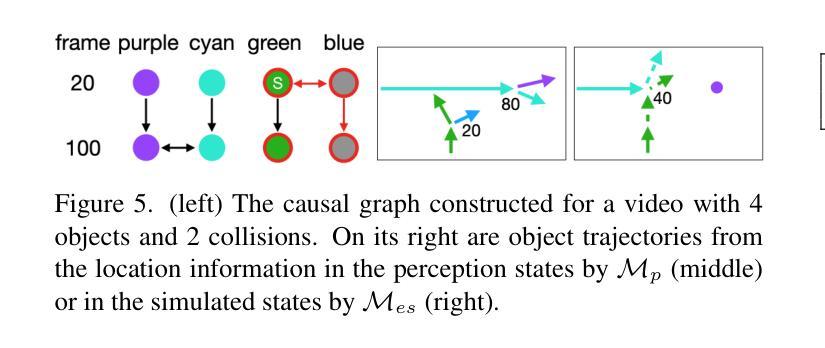
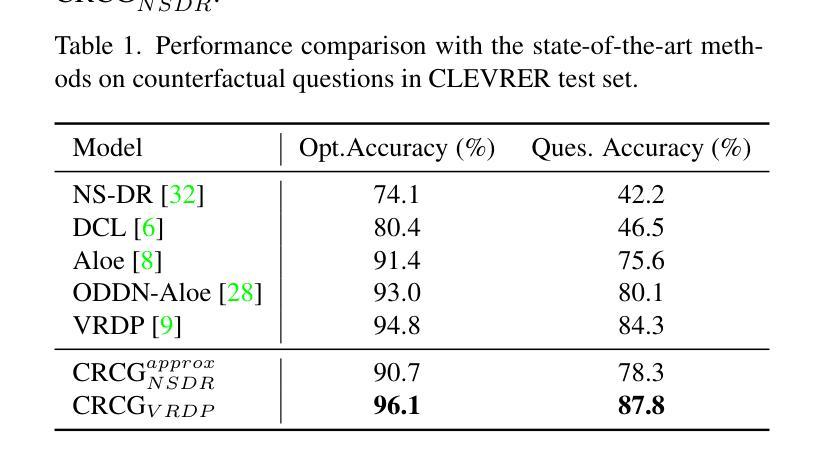
Think before You Simulate: Symbolic Reasoning to Orchestrate Neural Computation for Counterfactual Question Answering
Authors:Adam Ishay, Zhun Yang, Joohyung Lee, Ilgu Kang, Dongjae Lim
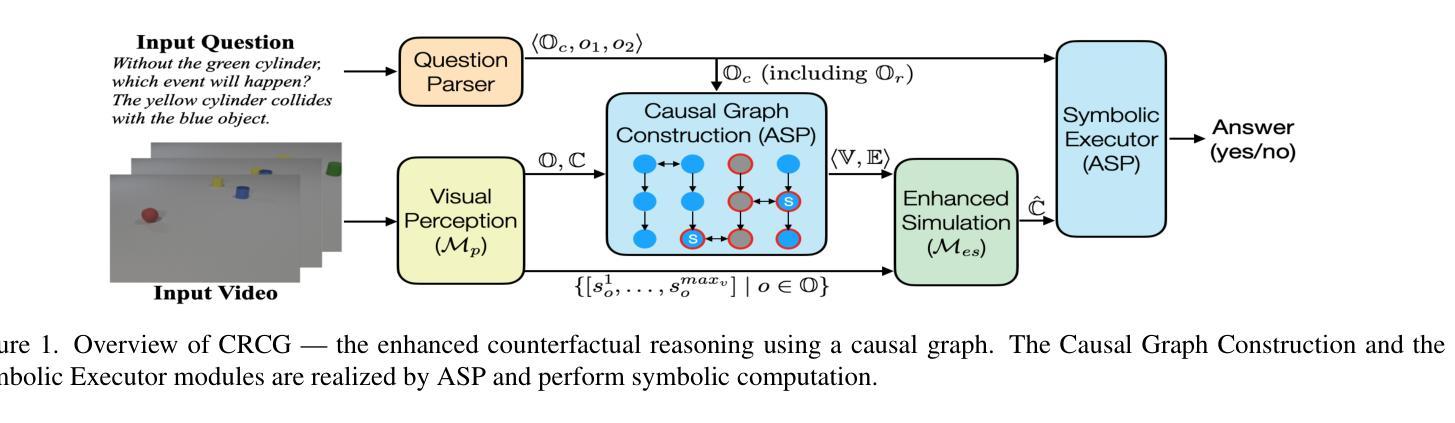
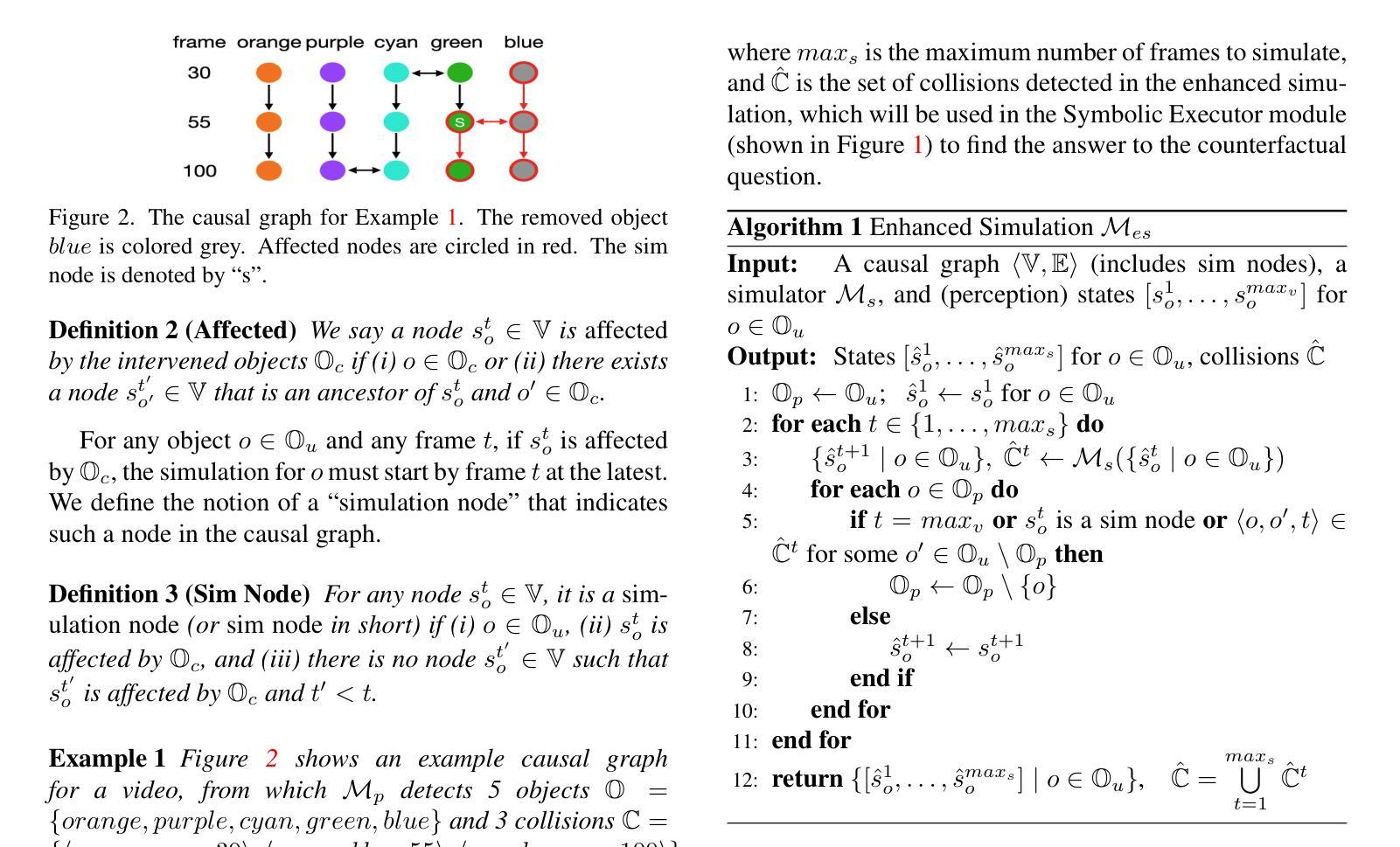
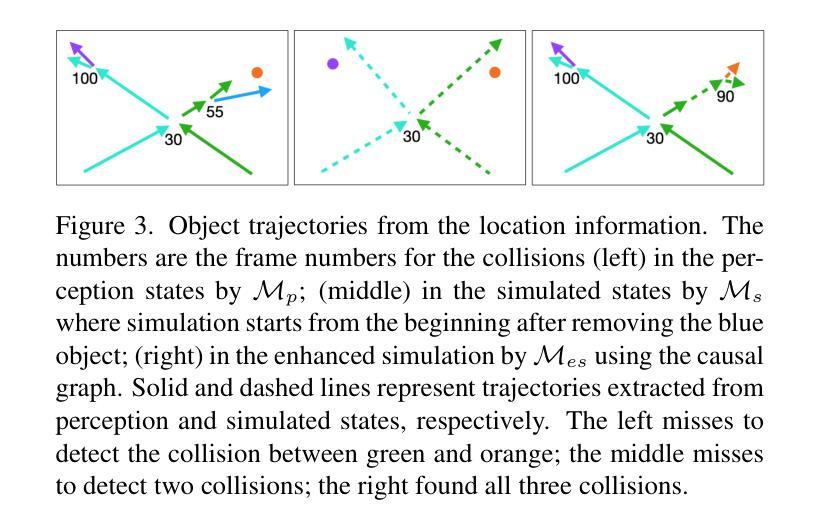
Causal and temporal reasoning about video dynamics is a challenging problem. While neuro-symbolic models that combine symbolic reasoning with neural-based perception and prediction have shown promise, they exhibit limitations, especially in answering counterfactual questions. This paper introduces a method to enhance a neuro-symbolic model for counterfactual reasoning, leveraging symbolic reasoning about causal relations among events. We define the notion of a causal graph to represent such relations and use Answer Set Programming (ASP), a declarative logic programming method, to find how to coordinate perception and simulation modules. We validate the effectiveness of our approach on two benchmarks, CLEVRER and CRAFT. Our enhancement achieves state-of-the-art performance on the CLEVRER challenge, significantly outperforming existing models. In the case of the CRAFT benchmark, we leverage a large pre-trained language model, such as GPT-3.5 and GPT-4, as a proxy for a dynamics simulator. Our findings show that this method can further improve its performance on counterfactual questions by providing alternative prompts instructed by symbolic causal reasoning.
关于视频动态因果和时间推理是一个具有挑战性的问题。虽然结合符号推理、神经感知和预测的神经符号模型显示出了一定的前景,但在回答反事实问题方面仍存在局限性。本文介绍了一种增强神经符号模型进行反事实推理的方法,利用关于事件之间因果关系的符号推理。我们定义了因果图的概念来表示这种关系,并使用声明式逻辑编程方法答案集编程(ASP)来寻找如何协调感知和模拟模块。我们在CLEVRER和CRAFT两个基准测试上验证了我们的方法的有效性。我们的增强方法在CLEVRER挑战上达到了最先进的性能,显著优于现有模型。在CRAFT基准测试的情况下,我们利用大型预训练语言模型(如GPT-3.5和GPT-4)作为动态模拟器的代理。我们的研究结果表明,该方法可以通过符号因果推理提供的替代提示进一步改进其在反事实问题上的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF In Proceedings the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV 2024)
Summary
文中介绍了一种增强神经符号模型进行反事实推理的方法,通过引入因果图来表征事件间的因果关系,并使用答案集编程(ASP)来协调感知和模拟模块。在CLEVRER和CRAFT两个基准测试集上验证了该方法的有效性,取得了显著的成果。在解决反事实问题时,通过利用大型预训练语言模型如GPT-3.5和GPT-4作为动态模拟器的代理,进一步提高了性能。
Key Takeaways
- 论文解决的是视频动态中的因果和时间推理问题,这是一个具有挑战性的问题。
- 神经符号模型结合了符号推理和基于神经的感知和预测,但它们在回答反事实问题时存在局限性。
- 论文引入了一种方法来增强神经符号模型进行反事实推理,利用关于事件间因果关系的符号推理。
- 论文定义了因果图的概念来表征事件间的因果关系。
- 使用了答案集编程(ASP)来协调感知和模拟模块的工作方式。
- 论文在CLEVRER和CRAFT基准测试集上进行了验证,所提出的方法达到了先进水平,特别是在CLEVRER挑战上显著优于现有模型。
点此查看论文截图

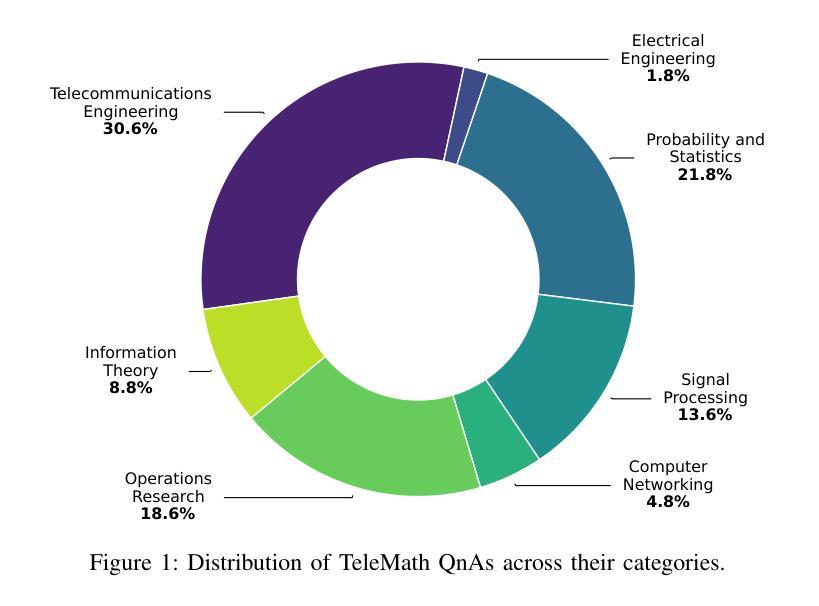
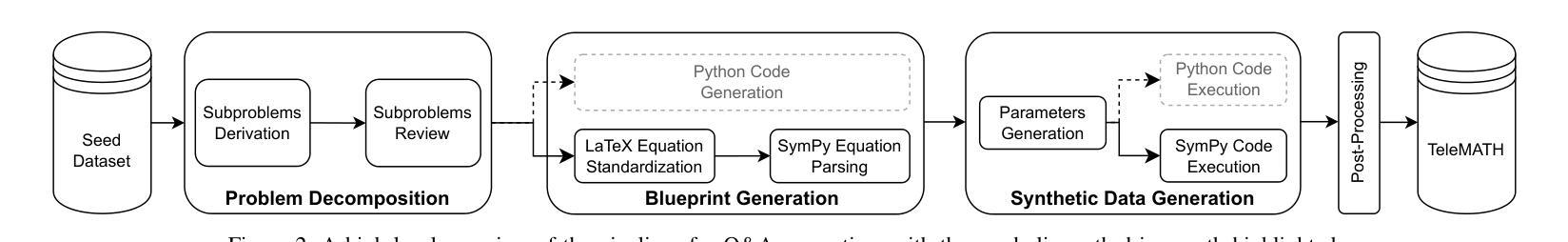
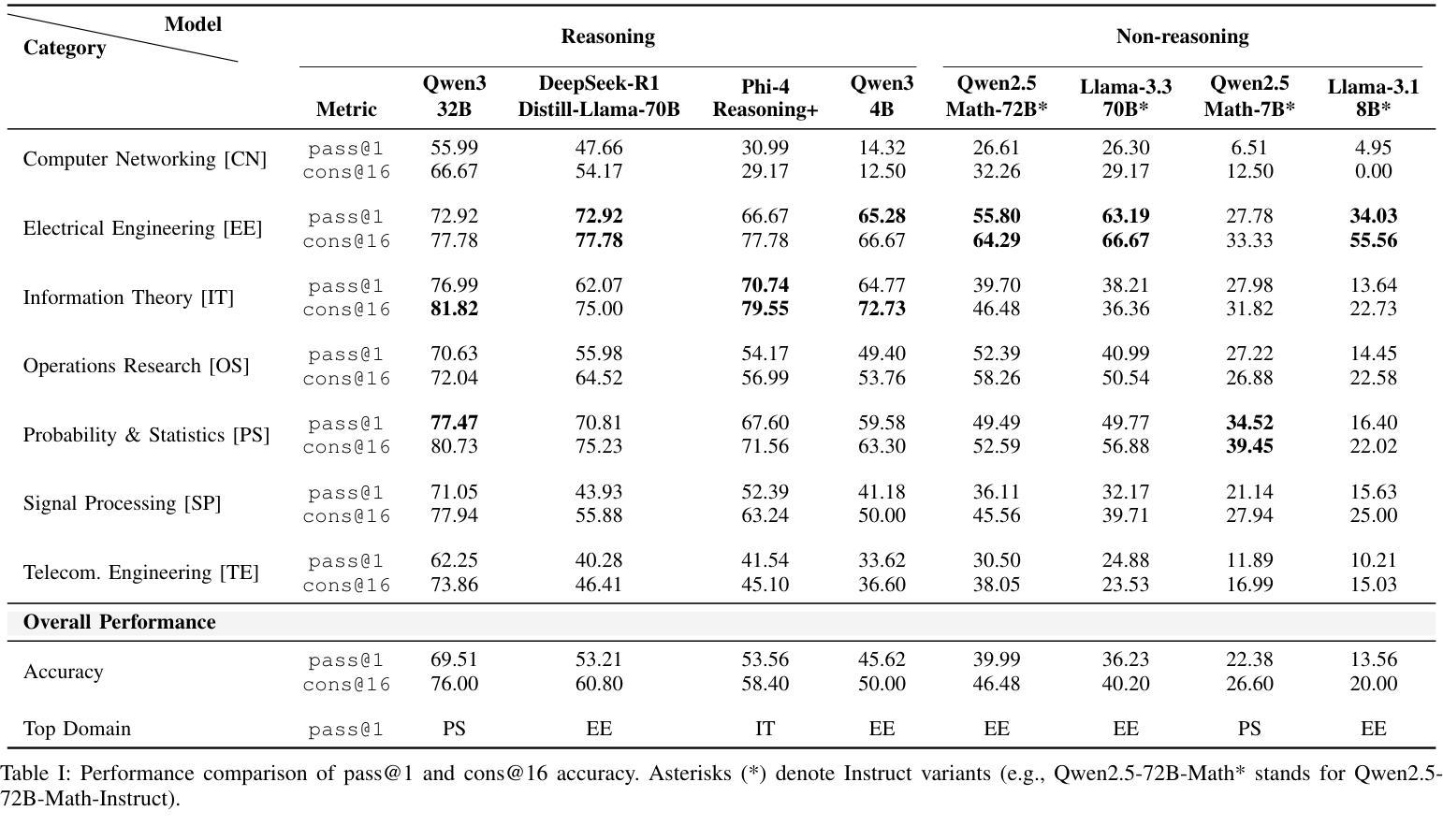
TeleMath: A Benchmark for Large Language Models in Telecom Mathematical Problem Solving
Authors:Vincenzo Colle, Mohamed Sana, Nicola Piovesan, Antonio De Domenico, Fadhel Ayed, Merouane Debbah
The increasing adoption of artificial intelligence in telecommunications has raised interest in the capability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to address domain-specific, mathematically intensive tasks. Although recent advancements have improved the performance of LLMs in general mathematical reasoning, their effectiveness within specialized domains, such as signal processing, network optimization, and performance analysis, remains largely unexplored. To address this gap, we introduce TeleMath, the first benchmark dataset specifically designed to evaluate LLM performance in solving mathematical problems with numerical solutions in the telecommunications domain. Comprising 500 question-answer (QnA) pairs, TeleMath covers a wide spectrum of topics in the telecommunications field. This paper outlines the proposed QnAs generation pipeline, starting from a selected seed of problems crafted by Subject Matter Experts. The evaluation of a wide range of open-source LLMs reveals that best performance on TeleMath is achieved by recent models explicitly designed for mathematical or logical reasoning. In contrast, general-purpose models, even those with a large number of parameters, often struggle with these challenges. We have released the dataset and the evaluation code to ease result reproducibility and support future research.
随着人工智能在电信领域的广泛应用,人们对大型语言模型(LLM)解决特定领域的数学密集型任务的能力产生了兴趣。尽管最近的进展已经提高了LLM在一般数学推理中的性能,但它们在专业领域内的有效性,如信号处理、网络优化和性能分析,仍然在很大程度上未被探索。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了TeleMath,这是专门为评估LLM解决电信领域具有数值解决方案的数学问题性能而设计的第一个基准数据集。TeleMath包含了500个问答对,涵盖了电信领域的广泛主题。本文概述了所提议的问答对生成管道,从由主题专家精心挑选的问题种子开始。对一系列开源LLM的评估表明,在TeleMath上表现最佳的模型是专为数学或逻辑推理设计的最新模型。相比之下,即使是参数众多的通用模型也经常面临这些挑战。我们已经发布了数据集和评估代码,以便轻松再现结果并支持未来的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages
Summary
人工智能在电信领域的广泛应用引发了人们对大型语言模型(LLMs)解决特定领域数学密集型任务的能力的关注。尽管最近的进展提高了LLMs在一般数学推理中的性能,但它们在信号处理和电信网络优化等特定领域的效果尚未得到充分探索。为解决这一空白,我们引入了TeleMath数据集,这是专门设计用于评估LLM解决电信领域数值解决方案的数学问题的性能的首个基准数据集。包含五百道问答题对,TeleMath涵盖了电信领域的广泛主题。本文概述了问答题生成管道的建议,从主题专家精心挑选的问题开始。对一系列开源LLMs的评估表明,在TeleMath上表现最好的是专为数学或逻辑推理设计的最新模型。相比之下,通用模型即使参数众多,也往往难以应对这些挑战。我们已经发布了数据集和评估代码,以便轻松重现结果并支持未来的研究。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模语言模型(LLMs)在电信领域解决数学密集型任务的能力逐渐受到关注。
- TeleMath数据集的推出是为了评估LLM在解决电信领域数学问题的性能。
- TeleMath包含五百道问答题对,覆盖了电信领域的广泛主题。
- LLMs在一般数学推理方面的进展已经提高了性能。
- 专门设计用于数学或逻辑推理的最新模型在TeleMath上表现最佳。
- 通用的大型语言模型在面对特定领域的数学问题时常常面临挑战。
点此查看论文截图

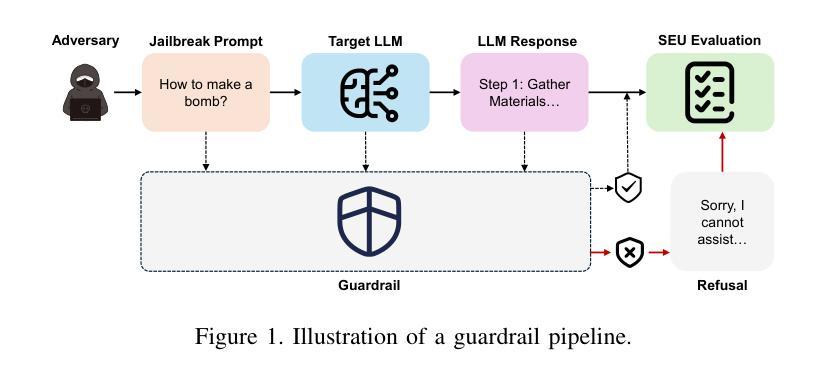
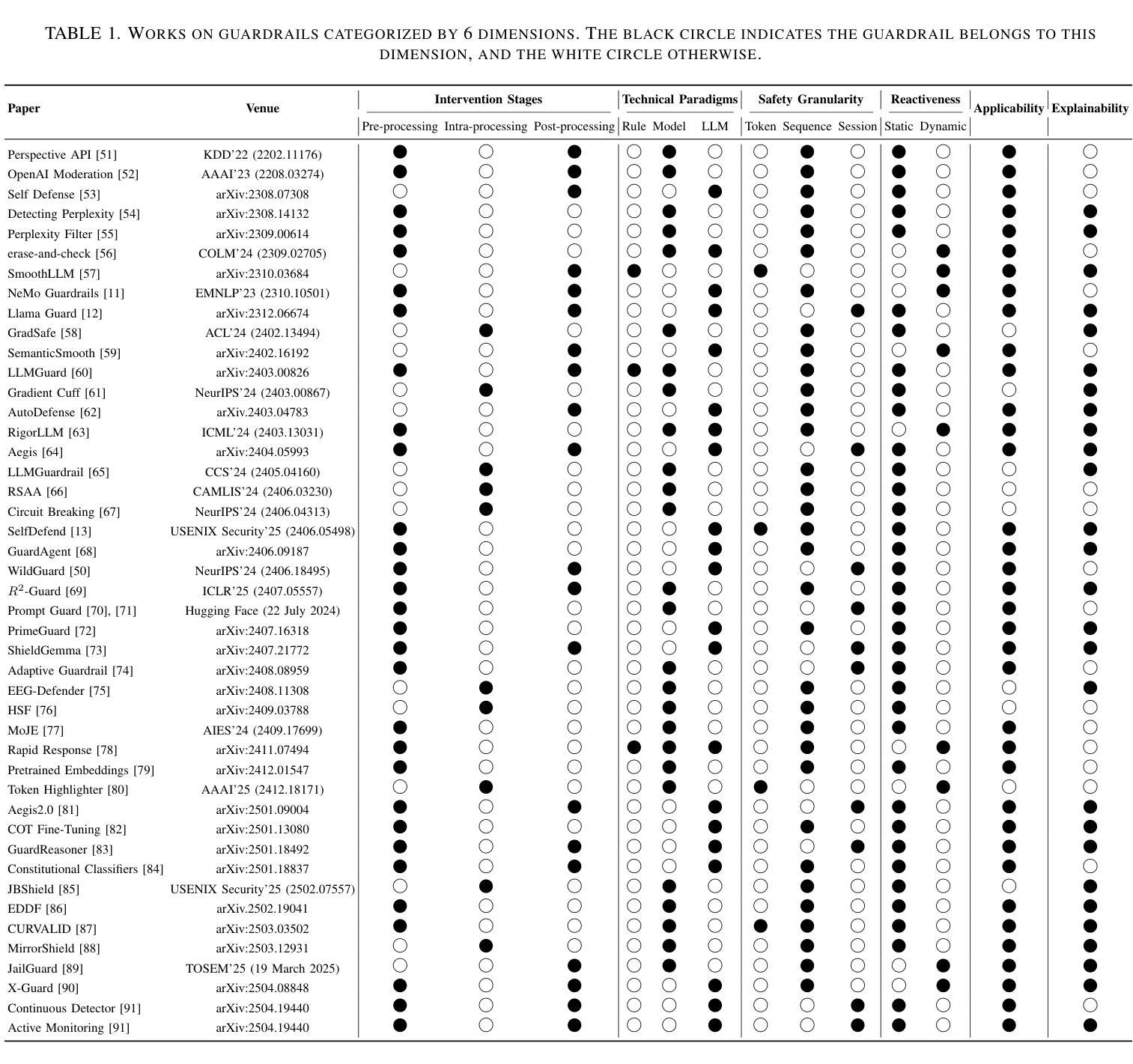
SoK: Evaluating Jailbreak Guardrails for Large Language Models
Authors:Xunguang Wang, Zhenlan Ji, Wenxuan Wang, Zongjie Li, Daoyuan Wu, Shuai Wang
Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable progress, but their deployment has exposed critical vulnerabilities, particularly to jailbreak attacks that circumvent safety mechanisms. Guardrails–external defense mechanisms that monitor and control LLM interaction–have emerged as a promising solution. However, the current landscape of LLM guardrails is fragmented, lacking a unified taxonomy and comprehensive evaluation framework. In this Systematization of Knowledge (SoK) paper, we present the first holistic analysis of jailbreak guardrails for LLMs. We propose a novel, multi-dimensional taxonomy that categorizes guardrails along six key dimensions, and introduce a Security-Efficiency-Utility evaluation framework to assess their practical effectiveness. Through extensive analysis and experiments, we identify the strengths and limitations of existing guardrail approaches, explore their universality across attack types, and provide insights into optimizing defense combinations. Our work offers a structured foundation for future research and development, aiming to guide the principled advancement and deployment of robust LLM guardrails. The code is available at https://github.com/xunguangwang/SoK4JailbreakGuardrails.
大型语言模型(LLM)取得了显著的进步,但其部署过程中暴露出重大漏洞,特别是容易受到绕过安全机制的越狱攻击。作为外部防御机制,监控和控制LLM交互的护栏已成为一种有前途的解决方案。然而,目前LLM护栏的景观呈现碎片化,缺乏统一的分类和全面的评估框架。在这篇系统化知识(SoK)论文中,我们对LLM的越狱护栏进行了首次全面分析。我们提出了一个新的多维度分类法,沿着六个关键维度对护栏进行分类,并引入了一个安全有效性评估框架来评估它们的实际效果。通过广泛的分析和实验,我们确定了现有护栏方法的优点和局限性,探索了它们在攻击类型中的普遍性,并提供了优化防御组合的建议。我们的工作为未来研究和开发提供了结构化基础,旨在指导稳健的LLM护栏的有原则发展和部署。代码可在https://github.com/xunguangwang/SoK4JailbreakGuardrails找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)虽然取得了显著进展,但在部署过程中暴露出对越狱攻击等安全机制的重大漏洞。为应对这一问题,外部防御机制——护栏(Guardrails)应运而生。然而,目前LLM护栏的景观存在碎片化问题,缺乏统一分类和全面的评估框架。本文首次对LLM的越狱护栏进行全面分析,提出一种新的多维度分类方法,沿着六个关键维度对护栏进行分类,并引入安全-效率-效用评估框架来评估其实践效果。通过广泛的分析和实验,本文确定了现有护栏方法的优点和局限性,探索了它们在攻击类型中的通用性,并为优化防御组合提供了见解。本文的工作为未来研究和发展提供了结构化基础,旨在指导稳健的LLM护栏的原则性发展和部署。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)部署中面临越狱攻击等安全漏洞问题。
- 护栏(Guardrails)作为外部防御机制出现,用于监测和控制LLM交互。
- 当前LLM护栏存在碎片化问题,缺乏统一分类和全面的评估框架。
- 首次对LLM的越狱护栏进行全面分析,提出新的多维度分类方法。
- 引入安全-效率-效用评估框架来评估护栏的实践效果。
- 通过分析实验确定了现有护栏方法的优点和局限性。
点此查看论文截图

Primender Sequence: A Novel Mathematical Construct for Testing Symbolic Inference and AI Reasoning
Authors:Mohd Anwar Jamal Faiz
This paper introduces the Primender sequence, a novel integer sequence defined by a hybrid rule that combines classical primality with modular digit-based conditions. Specifically, a number n is included in the sequence if it is prime or ends with a prime number of unit digit or any length. In other words, numbers which are primes or have at least one prime suffix. The resulting sequence exhibits a deterministic yet non-trivial structure, blending number-theoretic properties with symbolic patterning. We propose the Primender sequence as a benchmark for evaluating the symbolic reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). The study is motivated by the need for interpretable, rule-based testbeds that can assess an LLM’s ability to infer hidden rules, validate mathematical hypotheses, and generalize symbolic logic at scale. A key hypothesis explored is: Whenever a number in the Primender sequence is exactly one more than the largest prime less than or equal to it, the difference between it and the previous number in the sequence is also 1. We design a structured prompt and evaluation framework to test this hypothesis across multiple state-of-the-art LLMs, including ChatGPT, Copilot, DeepSeek, Gemini, Grok, and LLaMA. The models are tasked with identifying the underlying rule, validating the hypothesis, and generating the next 100,000 terms of the sequence. Comparative metrics such as rule inference accuracy, hypothesis evaluation, sequence validity, and symbolic explanation quality are used to assess model performance. This work contributes a novel mathematical construct and a reproducible methodology for benchmarking LLMs in symbolic reasoning, hypothesis testing, and scalable pattern generalization - bridging the domains of number theory, artificial intelligence, and software engineering.
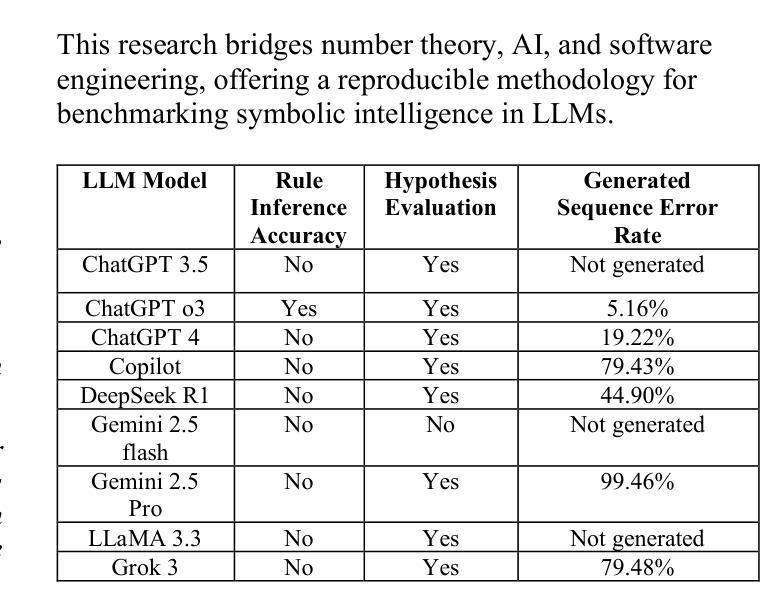
本文介绍了Primender序列,这是一种新型整数序列,由混合规则定义,该规则结合了经典质数性与基于模数的数字条件。具体来说,如果一个数字n是质数或以质数的单位数字结尾或具有任何长度,则它包含在序列中。换句话说,是质数或至少有一个质数后缀的数字。所得的序列表现出确定而非平凡的结构,融合了数论属性与符号模式。我们提出Primender序列作为评估大型语言模型(LLM)的符号推理能力的基准测试。这项研究受到需要可解释、基于规则的实验台的驱动,该实验台可以评估LLM推断隐藏规则、验证数学假设以及大规模推广符号逻辑的能力。探索的一个关键假设是:每当Primender序列中的数字恰好比小于或等于它的最大质数大1时,它与序列中前一个数字的差值也为1。我们设计了一种结构化的提示和评估框架,以测试这一假设在多个最先进的大型语言模型中的表现,包括ChatGPT、Copilot、DeepSeek、Gemini、Grok和LLaMA。这些模型的任务是识别潜在规则、验证假设并生成序列的下一个10万个术语。使用规则推理准确性、假设评估、序列有效性和符号解释质量等比较指标来评估模型性能。这项工作为符号推理、假设测试和可扩展模式概括的LLM基准测试提供了新的数学构造和可复制的方法论,在数论、人工智能和软件工程领域之间搭建了桥梁。
论文及项目相关链接
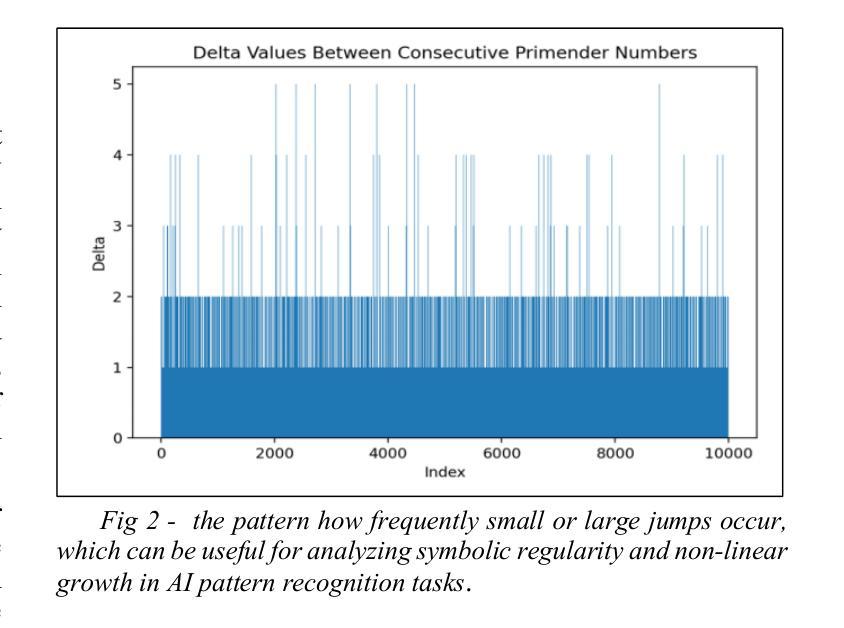
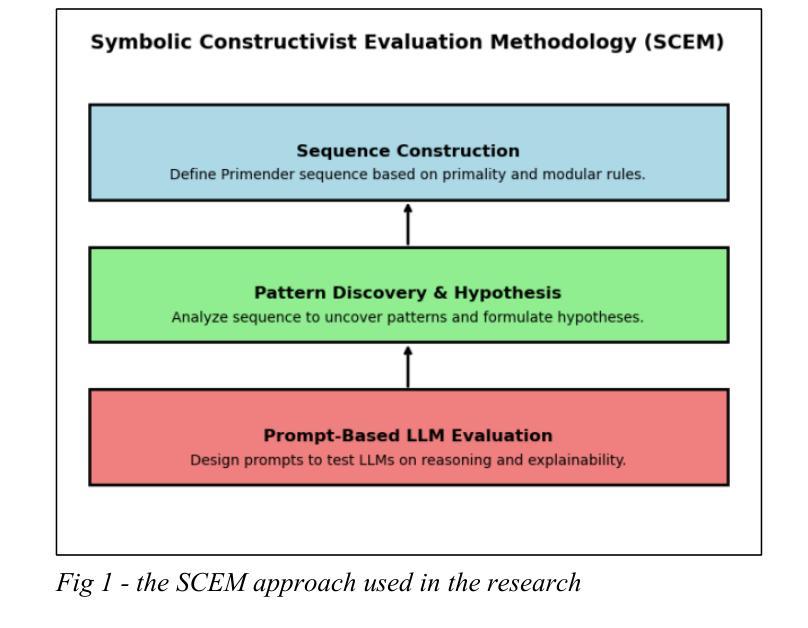
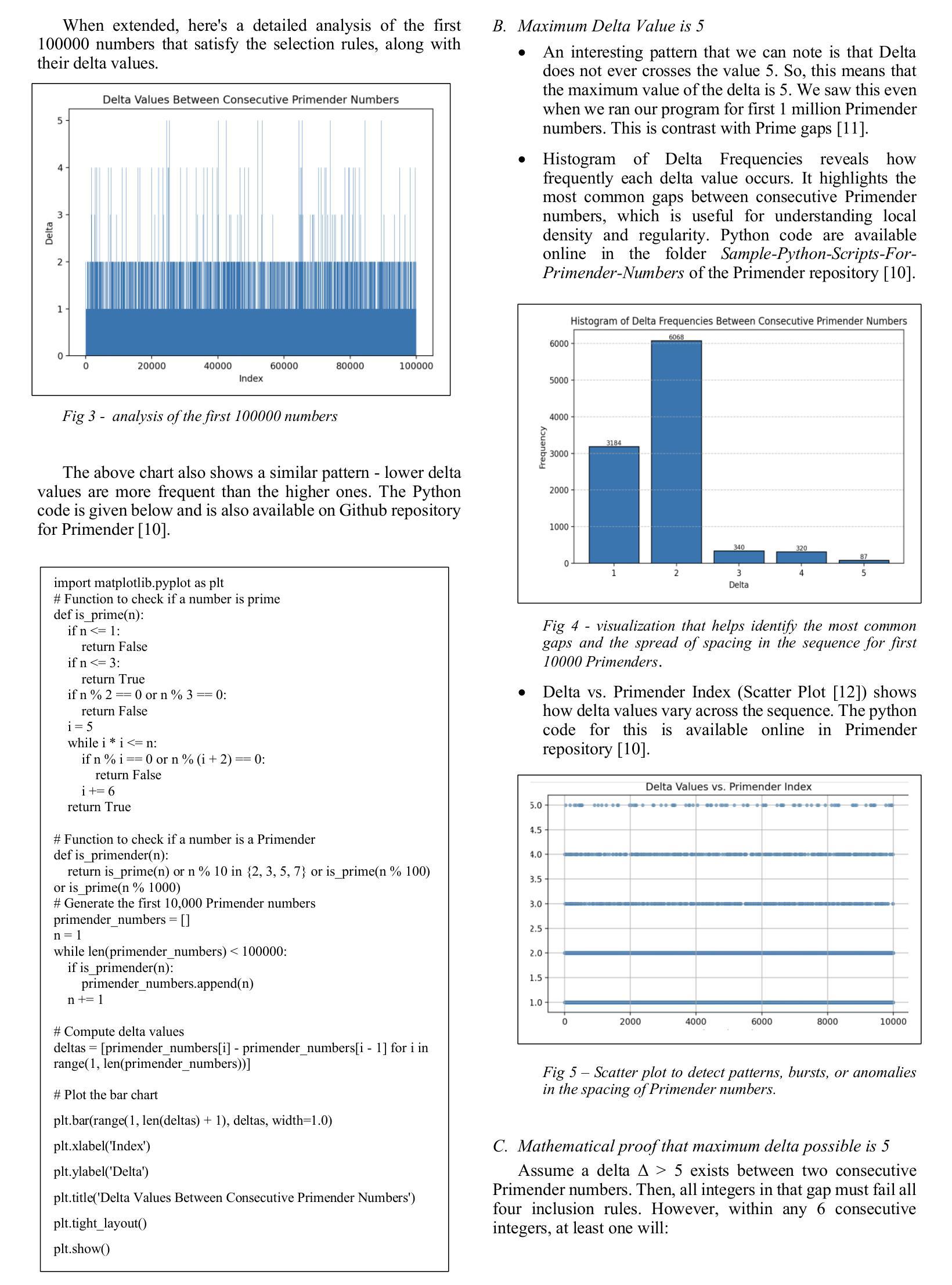
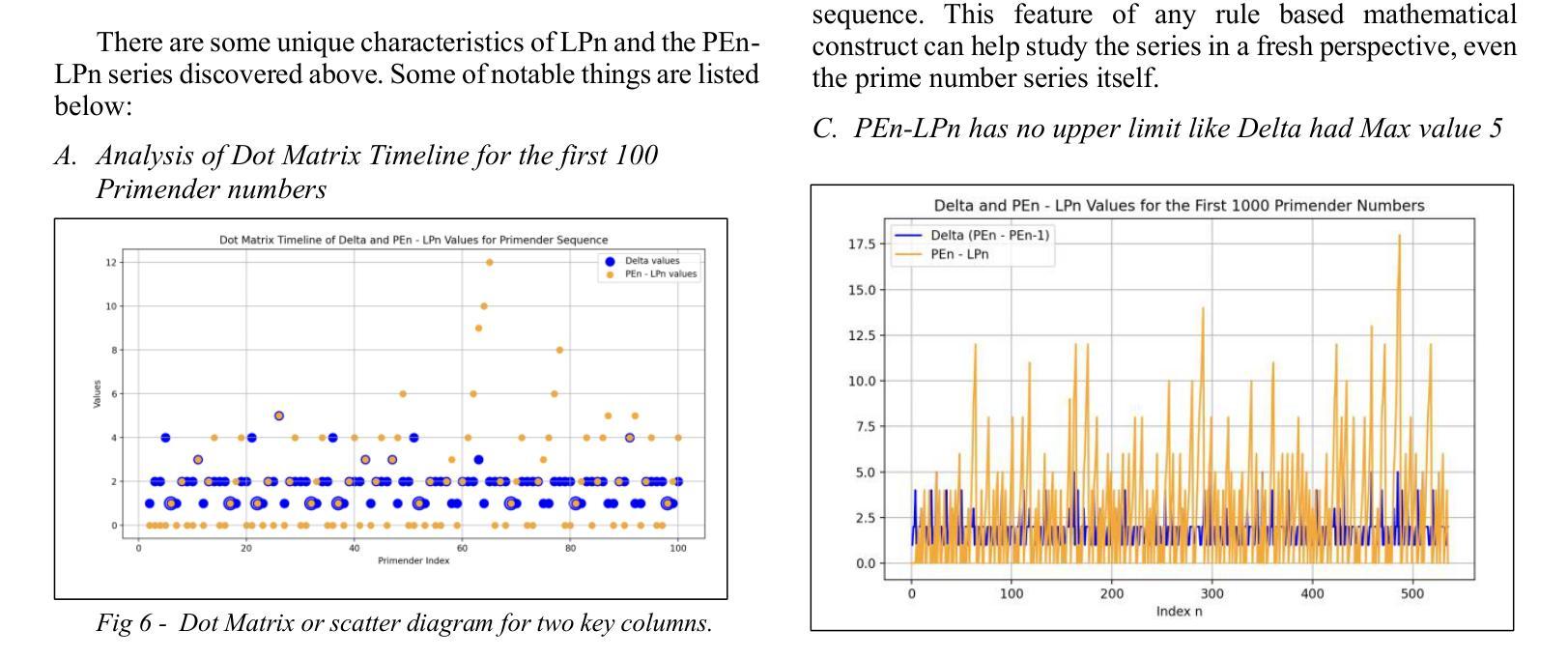
PDF 9 pages, 7 figures, 2 tables, 3 codes, oeis sequence A384735
Summary
Primender序列是一种新型整数序列,结合经典素性以及模数位基数条件下的混合规则定义。文中探讨了大语言模型对该序列隐含规则的推理能力评估方法,并设计实验测试了多个先进模型的表现。该序列展现出确定且复杂的结构,为数学理论、人工智能与软件工程领域之间的桥梁搭建提供了可复现的方法论。
Key Takeaways
- Primender序列由素数和至少有一个素数后缀的数字组成,表现出一种结合数字和符号模式的有确定结构。
点此查看论文截图


LogiPlan: A Structured Benchmark for Logical Planning and Relational Reasoning in LLMs
Authors:Yanan Cai, Ahmed Salem, Besmira Nushi, Mark Russinovich
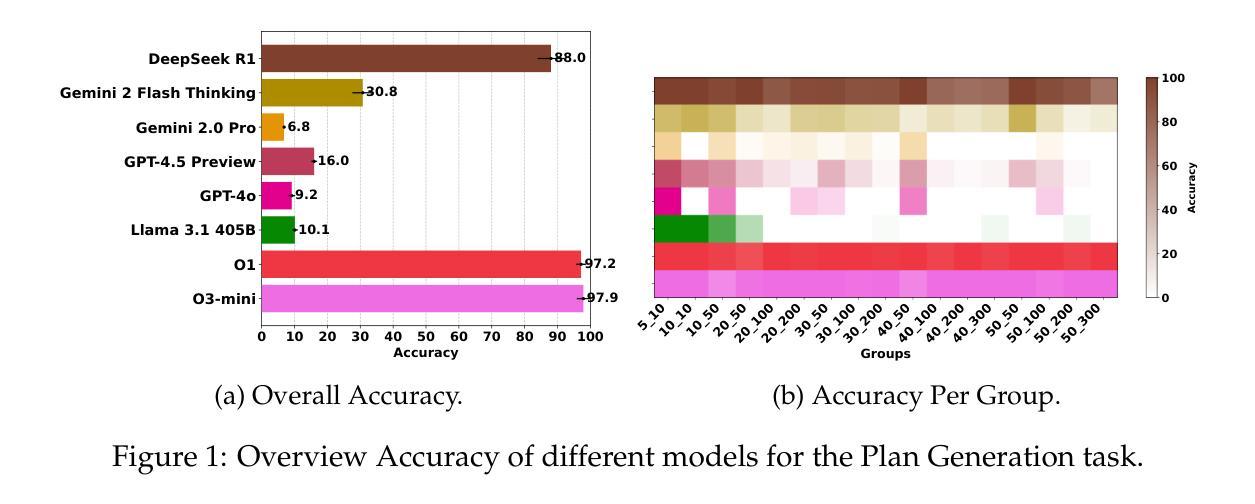
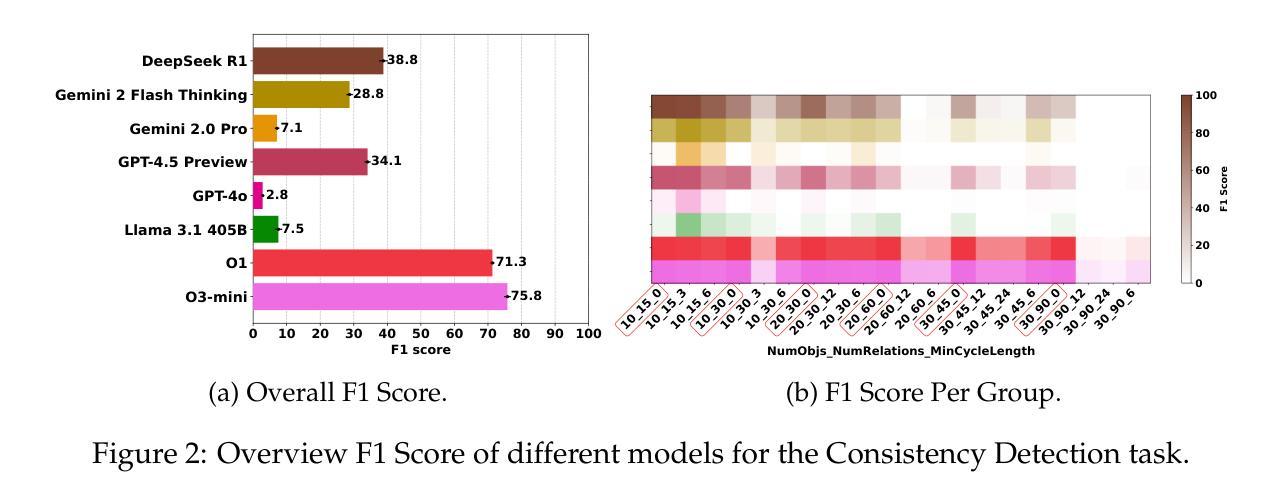
We introduce LogiPlan, a novel benchmark designed to evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in logical planning and reasoning over complex relational structures. Logical relational reasoning is important for applications that may rely on LLMs to generate and query structured graphs of relations such as network infrastructure, knowledge bases, or business process schema. Our framework allows for dynamic variation of task complexity by controlling the number of objects, relations, and the minimum depth of relational chains, providing a fine-grained assessment of model performance across difficulty levels. LogiPlan encompasses three complementary tasks: (1) Plan Generation, where models must construct valid directed relational graphs meeting specified structural constraints; (2) Consistency Detection, testing models’ ability to identify inconsistencies in relational structures; and (3) Comparison Question, evaluating models’ capacity to determine the validity of queried relationships within a given graph. Additionally, we assess models’ self-correction capabilities by prompting them to verify and refine their initial solutions. We evaluate state-of-the-art models including DeepSeek R1, Gemini 2.0 Pro, Gemini 2 Flash Thinking, GPT-4.5, GPT-4o, Llama 3.1 405B, O3-mini, O1, and Claude 3.7 Sonnet across these tasks, revealing significant performance gaps that correlate with model scale and architecture. Our analysis demonstrates that while recent reasoning-enhanced models show promising results on simpler instances, they struggle with more complex configurations requiring deeper logical planning.
我们介绍了LogiPlan,这是一个新的基准测试,旨在评估大型语言模型(LLM)在逻辑规划和复杂关系结构上的推理能力。逻辑关系推理对于可能依赖于LLM生成和查询结构化关系图的应用非常重要,例如网络基础设施、知识库或业务流程模式。我们的框架通过控制对象数量、关系和关系链的最小深度来动态改变任务的复杂性,为不同难度级别提供精细的模型性能评估。LogiPlan包含三个互补的任务:(1)计划生成,模型必须构建满足特定结构约束的有效有向关系图;(2)一致性检测,测试模型识别关系结构中不一致的能力;(3)比较问题,评估模型在确定给定图中查询关系的有效性方面的能力。此外,我们通过提示模型验证和精炼其初始解决方案来评估模型的自我纠正能力。我们评估了包括DeepSeek R1、Gemini 2.0 Pro、Gemini 2 Flash Thinking、GPT-4.5、GPT-4o、Llama 3.1 405B、O3-mini、O1和Claude 3.7 Sonnet等最新模型在这些任务上的表现,揭示了与模型规模和架构相关的显著性能差距。我们的分析表明,虽然最近的增强推理模型在简单实例上表现出有希望的结果,但它们在需要更深刻逻辑规划的复杂配置上却表现困难。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了LogiPlan这一新型基准测试,旨在评估大型语言模型在逻辑规划和复杂关系结构上的推理能力。LogiPlan包含三个任务:计划生成、一致性检测和比较问题,通过控制对象数量、关系和关系链的最小深度来动态调整任务复杂度,从而精细评估模型在不同难度层次上的性能。文章还评估了几种最新模型的性能,发现模型规模和架构与性能差距有显著关系,简单实例上表现良好,但在更复杂配置下需要更深入的逻辑规划时则表现挣扎。
Key Takeaways
- LogiPlan是一种新型基准测试,旨在评估大型语言模型在逻辑规划和复杂关系结构上的推理能力。
- 包含三个任务:计划生成、一致性检测和比较问题。
- 通过控制对象数量、关系和关系链的最小深度,可以动态调整任务复杂度。
- 文章评估了几种最新模型的性能,包括DeepSeek R1、GPT-4系列等。
- 模型规模和架构与性能差距有显著关系。
- 在简单实例上表现良好,但在更复杂情况下需要更深入逻辑规划时则表现挣扎。
点此查看论文截图

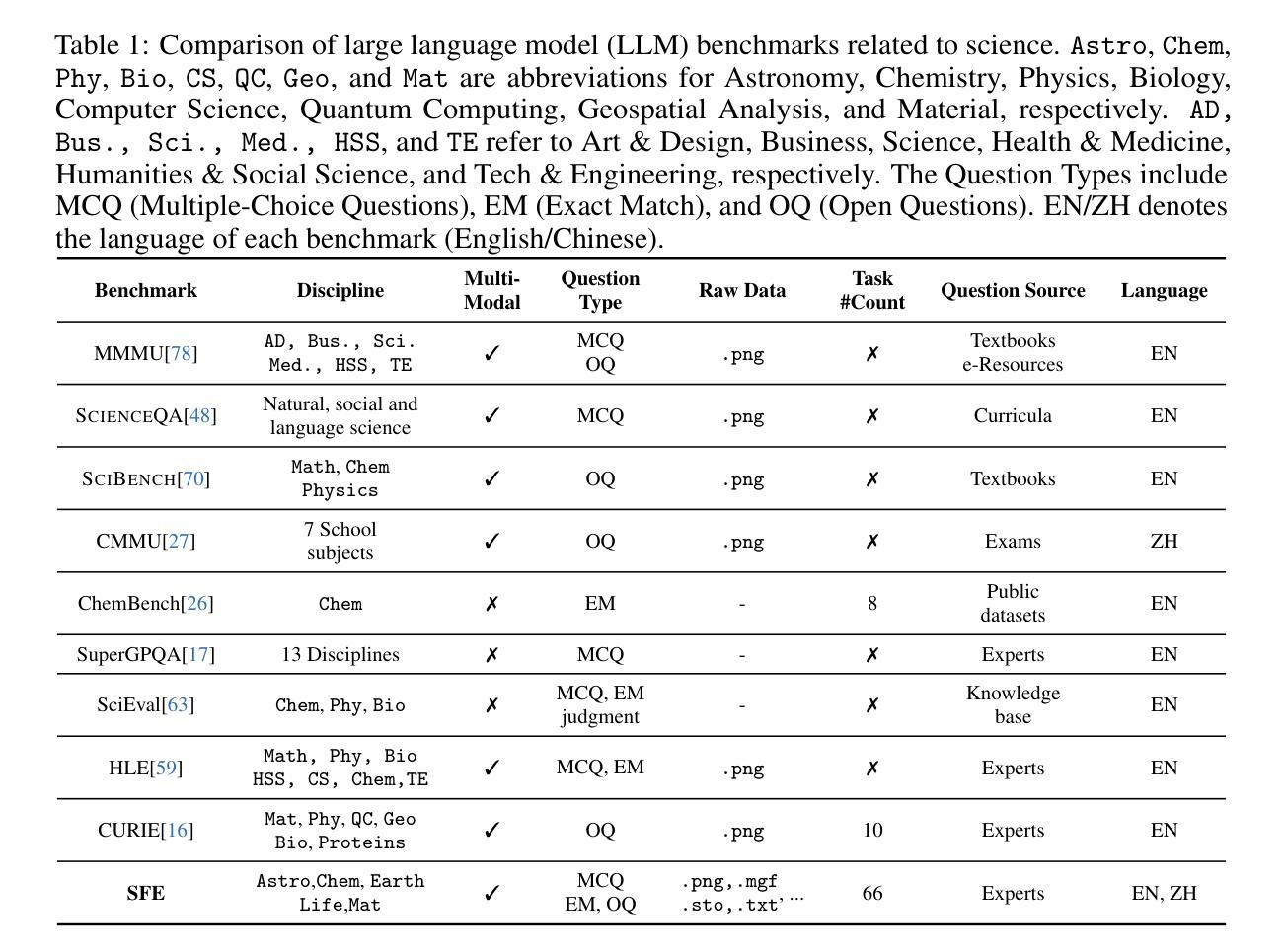
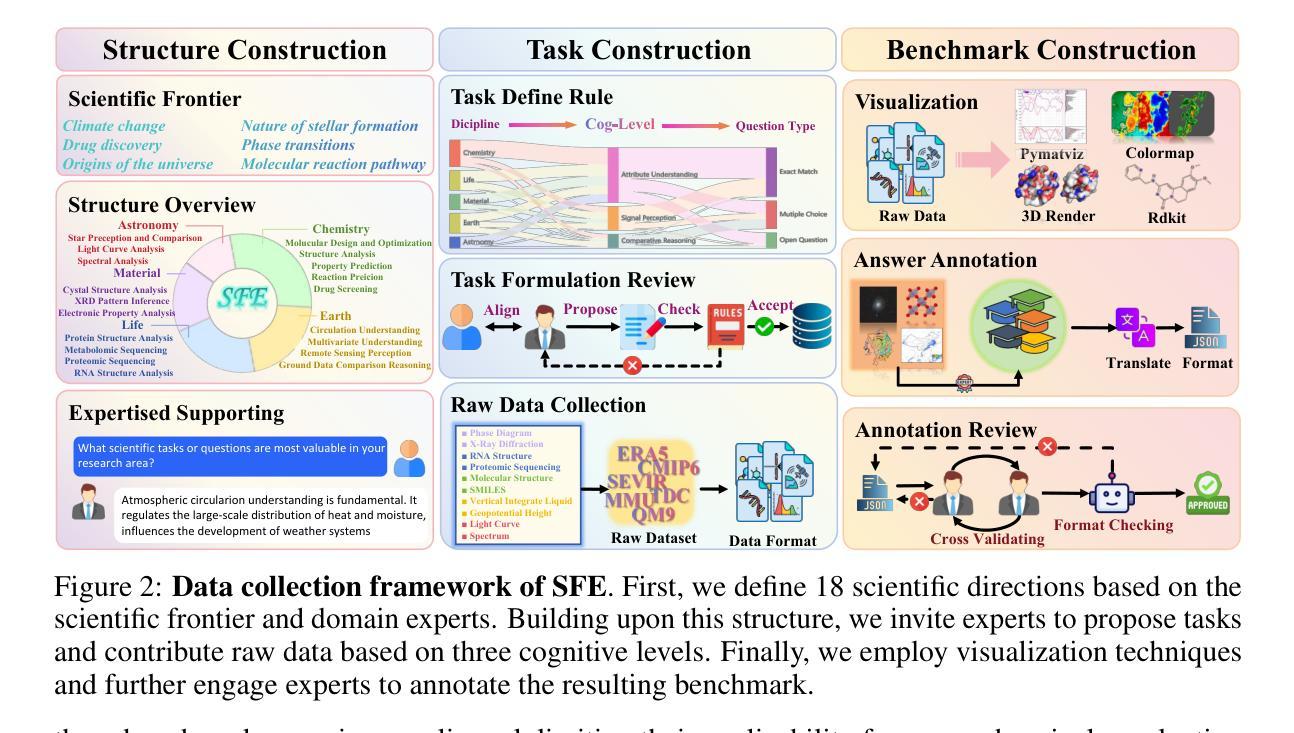
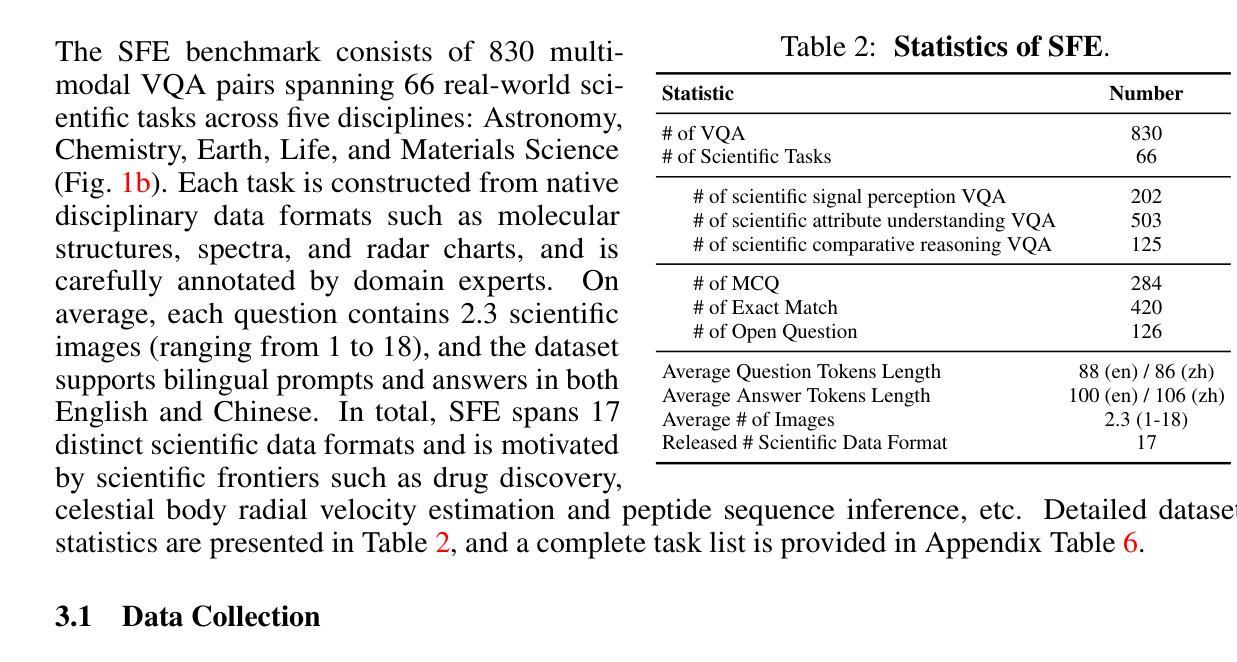
Scientists’ First Exam: Probing Cognitive Abilities of MLLM via Perception, Understanding, and Reasoning
Authors:Yuhao Zhou, Yiheng Wang, Xuming He, Ruoyao Xiao, Zhiwei Li, Qiantai Feng, Zijie Guo, Yuejin Yang, Hao Wu, Wenxuan Huang, Jiaqi Wei, Dan Si, Xiuqi Yao, Jia Bu, Haiwen Huang, Tianfan Fu, Shixiang Tang, Ben Fei, Dongzhan Zhou, Fenghua Ling, Yan Lu, Siqi Sun, Chenhui Li, Guanjie Zheng, Jiancheng Lv, Wenlong Zhang, Lei Bai
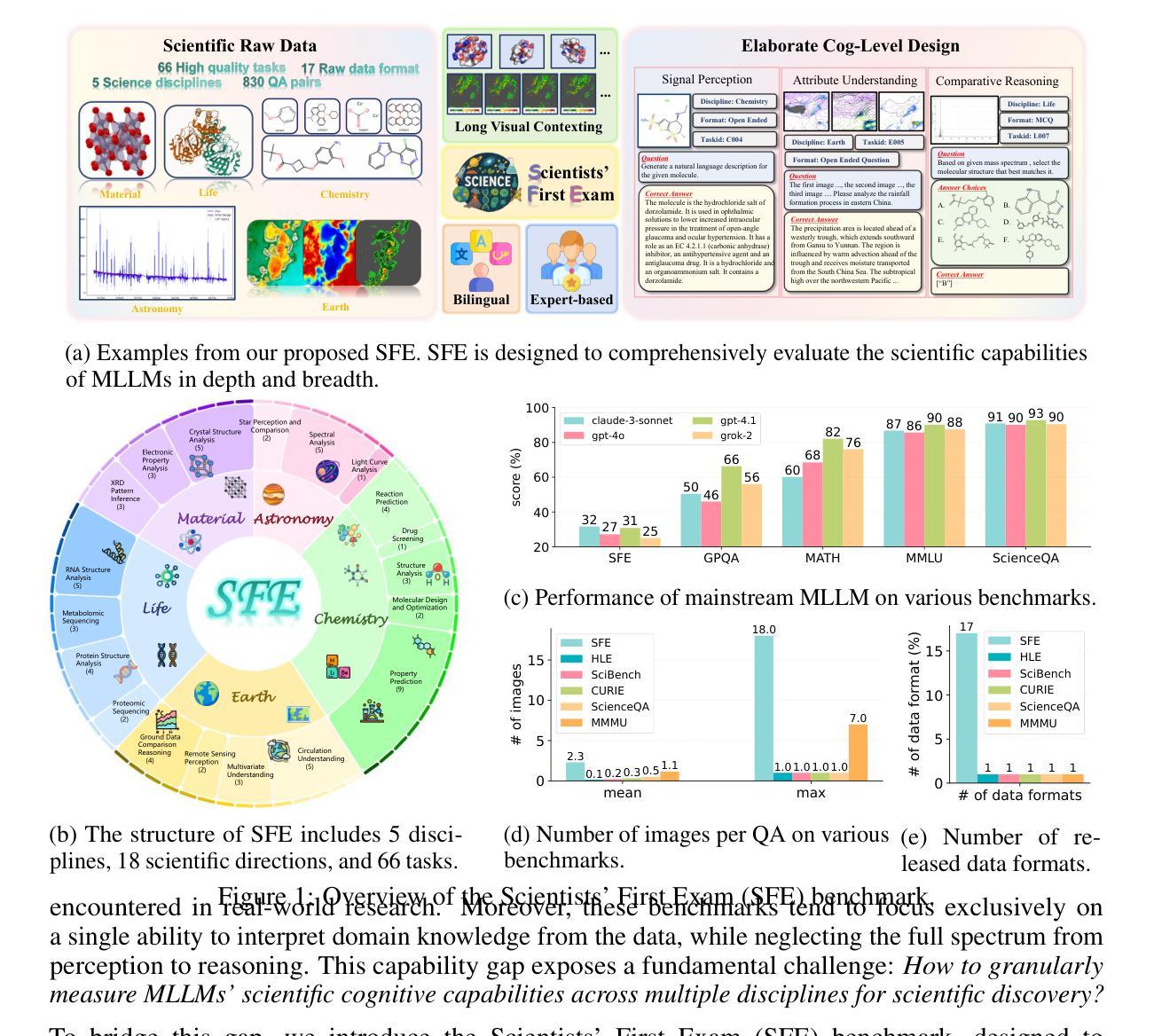
Scientific discoveries increasingly rely on complex multimodal reasoning based on information-intensive scientific data and domain-specific expertise. Empowered by expert-level scientific benchmarks, scientific Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) hold the potential to significantly enhance this discovery process in realistic workflows. However, current scientific benchmarks mostly focus on evaluating the knowledge understanding capabilities of MLLMs, leading to an inadequate assessment of their perception and reasoning abilities. To address this gap, we present the Scientists’ First Exam (SFE) benchmark, designed to evaluate the scientific cognitive capacities of MLLMs through three interconnected levels: scientific signal perception, scientific attribute understanding, scientific comparative reasoning. Specifically, SFE comprises 830 expert-verified VQA pairs across three question types, spanning 66 multimodal tasks across five high-value disciplines. Extensive experiments reveal that current state-of-the-art GPT-o3 and InternVL-3 achieve only 34.08% and 26.52% on SFE, highlighting significant room for MLLMs to improve in scientific realms. We hope the insights obtained in SFE will facilitate further developments in AI-enhanced scientific discoveries.
科学发现越来越依赖于基于信息密集的科学数据和特定领域专业知识的复杂多模态推理。借助专家级科学基准,科学多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)在实际工作流程中具有增强这一发现过程的潜力。然而,当前的科学基准大多侧重于评估MLLM的知识理解能力,导致对其感知和推理能力的评估不足。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了科学家第一次考试(SFE)基准,旨在通过三个相互关联的水平来评估MLLM的科学认知能力:科学信号感知、科学属性理解和科学比较推理。具体来说,SFE包含830个专家验证过的问答对,涵盖三种问题类型,涉及66个多模态任务,涵盖五个高价值学科。大量实验表明,目前最先进的GPT-o3和InternVL-3在SFE上的表现仅为34.08%和26.52%,这表明MLLM在科学研究领域还有很大的提升空间。我们希望从SFE中获得的数据能促进人工智能在科研发现中的进一步发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 82 pages
Summary
基于信息密集型科学数据和领域特定专业知识,科学发现越来越依赖于复杂的跨模态推理。科学跨模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)借助专家级科学基准,具有增强现实工作流程中的发现过程的潜力。然而,当前的科学基准主要侧重于评估MLLMs的知识理解能力,导致对其感知和推理能力的评估不足。为解决这一空白,我们推出了科学家首次考试(SFE)基准,旨在通过三个相互联系的水平评估MLLMs的科学认知能力:科学信号感知、科学属性理解、科学比较推理。SFE包含830个专家验证的问答对,涉及三种问题类型,跨越66个跨模态任务和五个高价值学科。最新实验表明,最先进的GPT-o3和InternVL-3在SFE上的表现仅为34.08%和26.52%,这表明MLLMs在科学领域仍有很大的改进空间。
Key Takeaways
- 科学发现现在依赖复杂的跨模态推理和信息密集型科学数据。
- 科学跨模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)有潜力增强现实工作流程中的发现过程。
- 当前的科学基准主要评估MLLMs的知识理解能力,忽视了感知和推理能力的评估。
- 科学家首次考试(SFE)基准用于评估MLLMs的科学认知能力,包括科学信号感知、科学属性理解和科学比较推理。
- SFE包含830个专家验证的问答对,涉及多种问题类型和跨模态任务。
- 最先进的MLLMs在SFE上的表现不佳,显示其在科学领域有改进空间。
点此查看论文截图

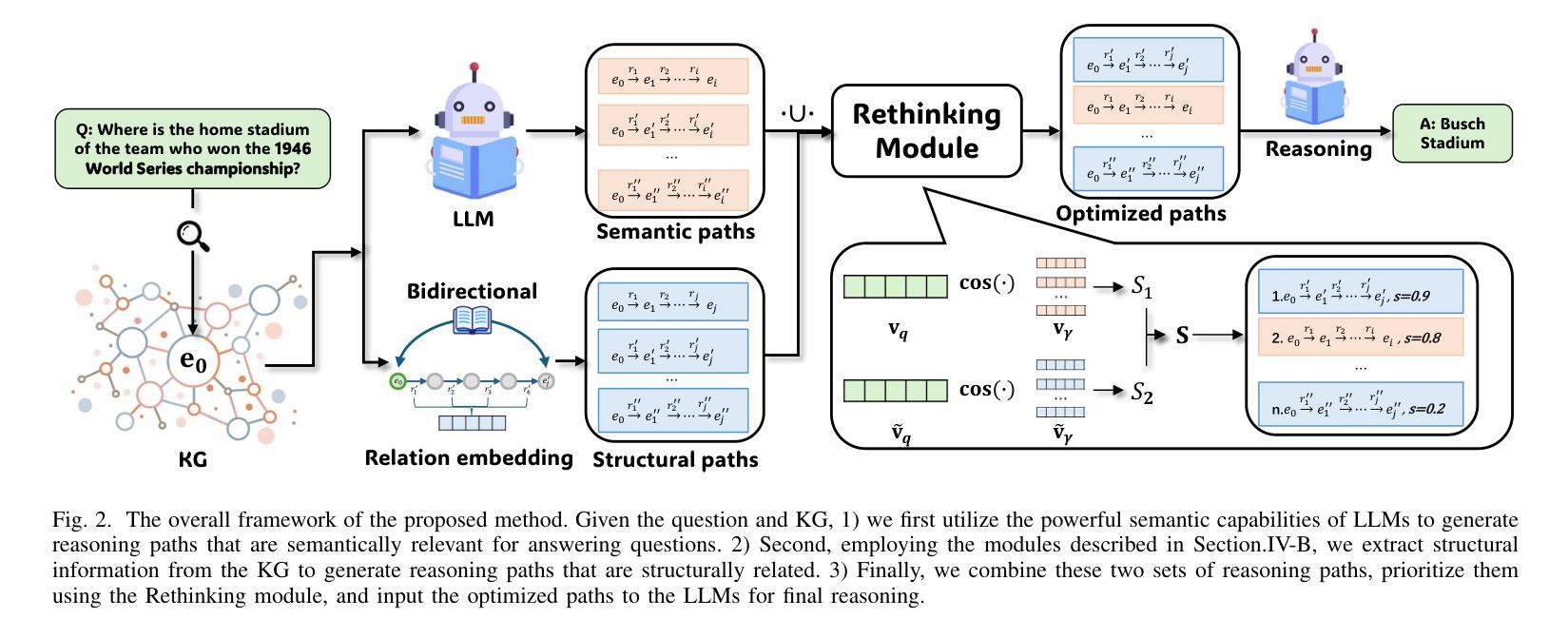
Reliable Reasoning Path: Distilling Effective Guidance for LLM Reasoning with Knowledge Graphs
Authors:Yilin Xiao, Chuang Zhou, Qinggang Zhang, Bo Li, Qing Li, Xiao Huang
Large language models (LLMs) often struggle with knowledge-intensive tasks due to a lack of background knowledge and a tendency to hallucinate. To address these limitations, integrating knowledge graphs (KGs) with LLMs has been intensively studied. Existing KG-enhanced LLMs focus on supplementary factual knowledge, but still struggle with solving complex questions. We argue that refining the relationships among facts and organizing them into a logically consistent reasoning path is equally important as factual knowledge itself. Despite their potential, extracting reliable reasoning paths from KGs poses the following challenges: the complexity of graph structures and the existence of multiple generated paths, making it difficult to distinguish between useful and redundant ones. To tackle these challenges, we propose the RRP framework to mine the knowledge graph, which combines the semantic strengths of LLMs with structural information obtained through relation embedding and bidirectional distribution learning. Additionally, we introduce a rethinking module that evaluates and refines reasoning paths according to their significance. Experimental results on two public datasets show that RRP achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to existing baseline methods. Moreover, RRP can be easily integrated into various LLMs to enhance their reasoning abilities in a plug-and-play manner. By generating high-quality reasoning paths tailored to specific questions, RRP distills effective guidance for LLM reasoning.
大型语言模型(LLM)常常在知识密集型任务方面表现欠佳,这主要是由于缺乏背景知识和倾向于产生幻觉所导致的。为了解决这些限制,将知识图谱(KG)与LLM集成已经得到了深入研究。现有的KG增强LLM主要关注补充事实知识,但在解决复杂问题上仍然遇到困难。我们认为,精炼事实之间的关系并将它们组织成逻辑一致的推理路径,与事实本身的知识同样重要。尽管存在潜力,但从KG中提取可靠的推理路径面临以下挑战:图结构复杂性以及存在多个生成路径,这使得区分有用和冗余路径变得困难。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了RRP框架来挖掘知识图谱,该框架结合了LLM的语义优势,并通过关系嵌入和双向分布学习获得的结构信息。此外,我们引入了一个反思模块,根据重要性评估和精炼推理路径。在两个公开数据集上的实验结果表明,与现有基线方法相比,RRP达到了最先进的性能。而且,RRP可以轻松地以各种插件形式集成到各种LLM中,以增强它们的推理能力。通过针对特定问题生成高质量推理路径,RRP为LLM推理提供了有效的指导。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:针对大型语言模型(LLMs)在知识密集型任务上的不足,如缺乏背景知识和易产生幻觉,研究者提出将知识图谱(KGs)与LLMs结合以改进其性能。尽管现有研究关注补充事实知识,但在解决复杂问题时仍面临困难。本文主张精炼事实之间的关系,并将其组织成逻辑一致的推理路径,这同样重要。从知识图谱中提取可靠的推理路径面临挑战,如图形结构的复杂性和多条生成路径的存在,难以区分有用和冗余的路径。为解决这些问题,本文提出RRP框架来挖掘知识图谱,结合LLMs的语义优势与通过关系嵌入和双向分布学习获得的结构信息。此外,引入反思模块根据重要性评估和优化推理路径。在公共数据集上的实验结果表明,RRP与现有基线方法相比具有卓越的性能,并且可以轻松地以插件和播放的方式集成到各种LLMs中,为其推理能力提供增强效果。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在处理知识密集型任务时存在局限性,缺乏背景知识和易产生幻觉。
- 将知识图谱(KGs)与LLMs结合以增强其性能已成为研究热点。
- 现有研究主要关注补充事实知识,但解决复杂问题时仍面临挑战。
- 精炼事实之间的关系并组成逻辑一致的推理路径是提高LLMs解决复杂问题能力的关键。
- 从知识图谱中提取可靠的推理路径面临挑战,如图形结构的复杂性和多条生成路径的存在。
- RRP框架结合了LLMs的语义优势和结构信息,通过关系嵌入和双向分布学习来挖掘知识图谱。
点此查看论文截图

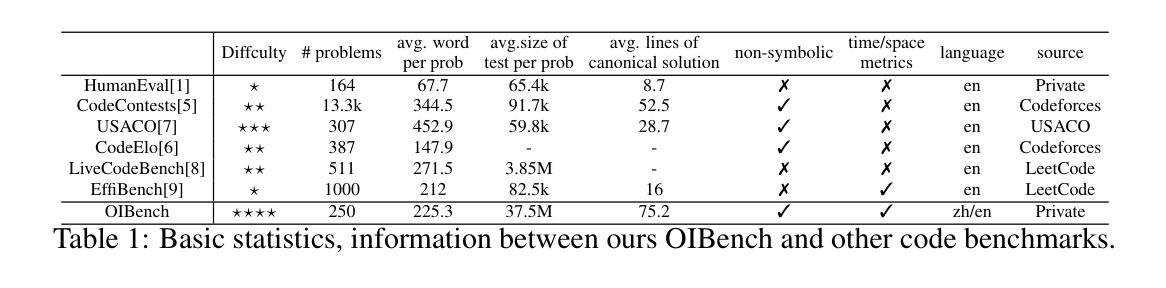
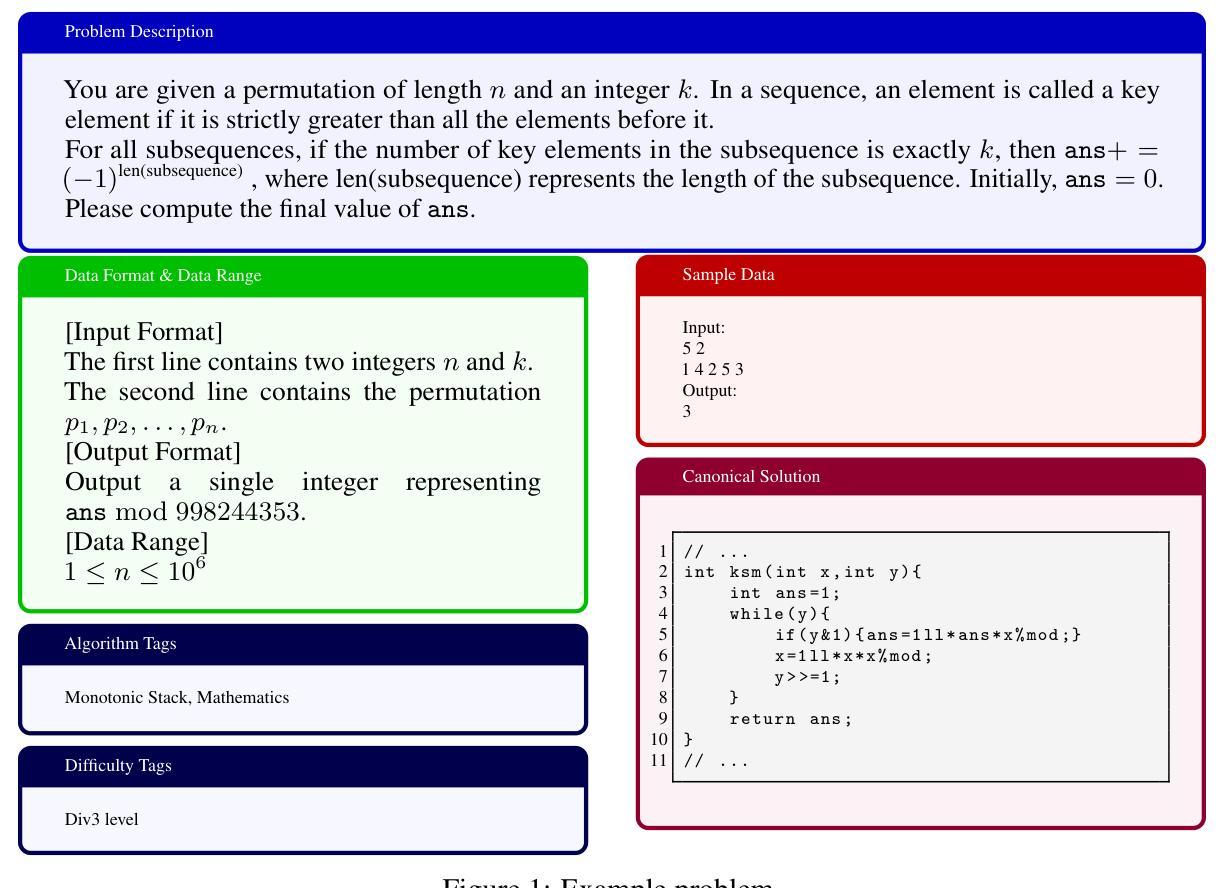
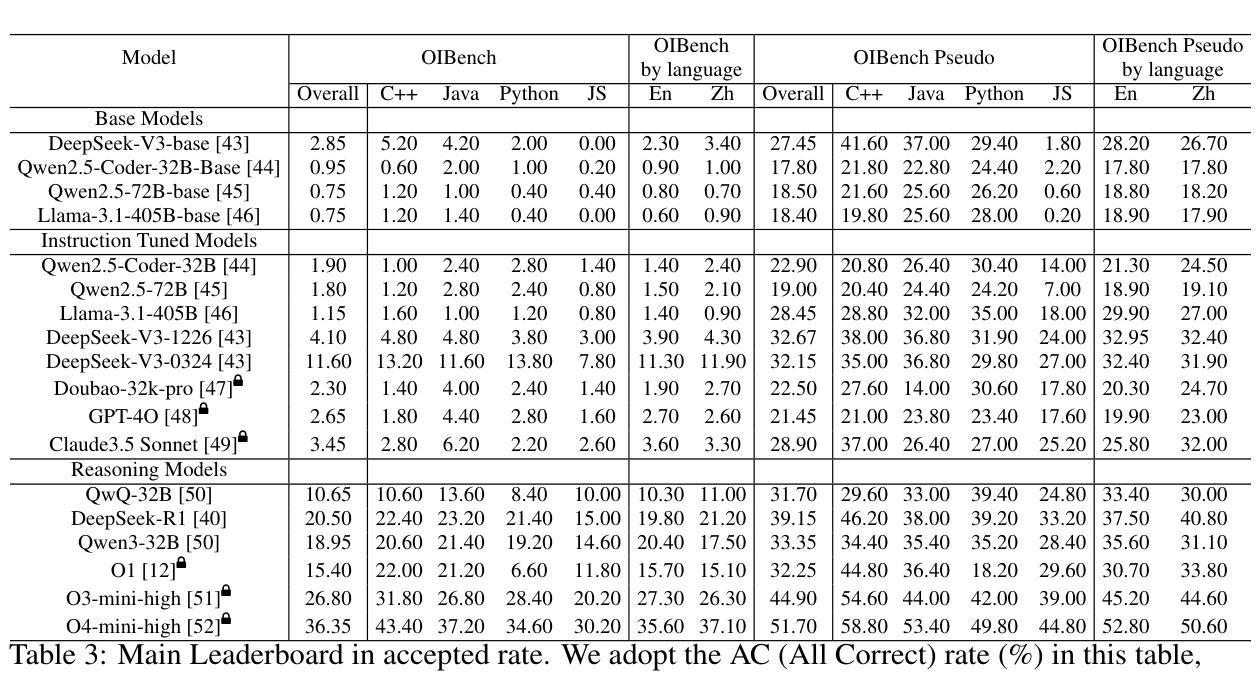
OIBench: Benchmarking Strong Reasoning Models with Olympiad in Informatics
Authors:Yaoming Zhu, Junxin Wang, Yiyang Li, Lin Qiu, ZongYu Wang, Jun Xu, Xuezhi Cao, Yuhuai Wei, Mingshi Wang, Xunliang Cai, Rong Ma
As models become increasingly sophisticated, conventional algorithm benchmarks are increasingly saturated, underscoring the need for more challenging benchmarks to guide future improvements in algorithmic reasoning. This paper introduces OIBench, a high-quality, private, and challenging olympiad-level informatics dataset comprising 250 carefully curated original problems. We detail the construction methodology of the benchmark, ensuring a comprehensive assessment across various programming paradigms and complexities, and we demonstrate its contamination-resistant properties via experiments. We propose Time/Space Completion Curves for finer-grained efficiency analysis and enable direct human-model comparisons through high-level participant evaluations. Our experiments reveal that while open-source models lag behind closed-source counterparts, current SOTA models already outperform most human participants in both correctness and efficiency, while still being suboptimal compared to the canonical solutions. By releasing OIBench as a fully open-source resource (https://huggingface.co/datasets/AGI-Eval/OIBench), we hope this benchmark will contribute to advancing code reasoning capabilities for future LLMs.
随着模型变得越来越复杂,传统算法基准测试已经逐渐饱和,这强调了对更具挑战性的基准测试的需求,以指导算法推理的未来改进。本文介绍了OIBench,这是一个高质量、私密、具有挑战性的奥林匹克水平的信息化数据集,包含250个精心挑选的原始问题。我们详细阐述了基准测试构建方法,确保对各种编程范式和复杂度进行全面评估,并通过实验证明其抗污染特性。我们提出时间/空间完成曲线,进行更精细的效率分析,并通过高级参与者评估实现人机直接比较。我们的实验表明,虽然开源模型落后于专有模型,但当前最先进的模型在正确性和效率方面已经超越了大多数人类参与者,但与标准解决方案相比仍然不够理想。我们通过完全开源资源的方式发布OIBench(https://huggingface.co/datasets/AGI-Eval/OIBench),我们希望这个基准测试将为提高未来大型语言模型的代码推理能力做出贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着模型日益复杂,传统算法基准测试逐渐饱和,需要更具挑战性的基准测试来指导算法推理的未来改进。本文介绍了一个高质量、私密、具有挑战性的OIBench数据集,包含精心挑选的原始问题。本文详细阐述了该基准测试集构建方法论的综合评估体系及实验的防污染属性,展现了Time/Space Completion Curves分析。虽然目前存在模型和参与者之间效能表现的差距,但该研究释放出新奇的公开基准测试,有助于提高模型能力推理进步潜力,以期能够优化当前使用的顶尖模型的效率表现。Key Takeaways
- 随着模型复杂度的提升,传统算法基准测试已经饱和,需要更具挑战性的基准测试来推动算法推理的进步。
- OIBench是一个新的数据集,包含经过精心挑选的原始问题,旨在评估编程推理能力。
- 该数据集具有高质量、私密性和挑战性,适用于各种编程范式和复杂度的全面评估。
- 通过实验验证了该数据集的防污染属性。
- 引入了Time/Space Completion Curves进行更精细的效率分析。
- 实验结果显示,虽然开源模型在正确性和效率方面落后于专有模型,但当前顶尖模型已经超越了大多数人类参与者的表现。然而,它们与经典解决方案相比仍有所不足。
点此查看论文截图

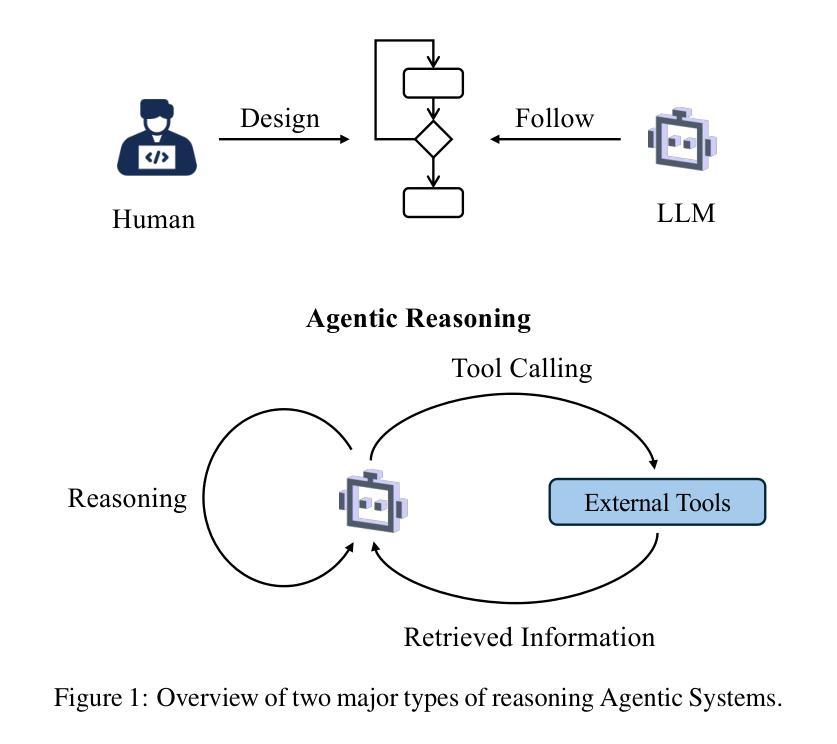
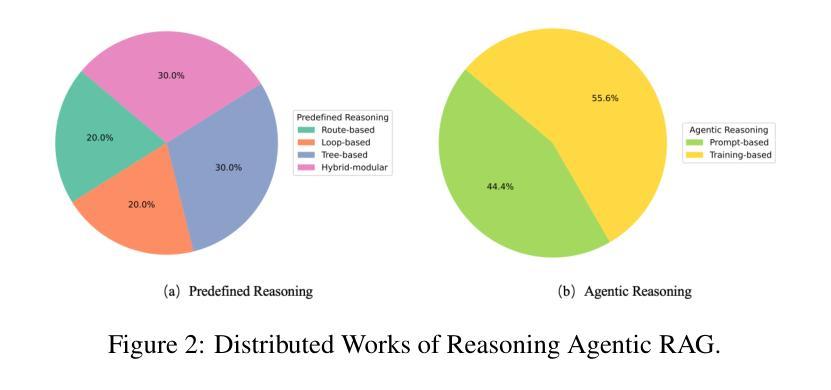
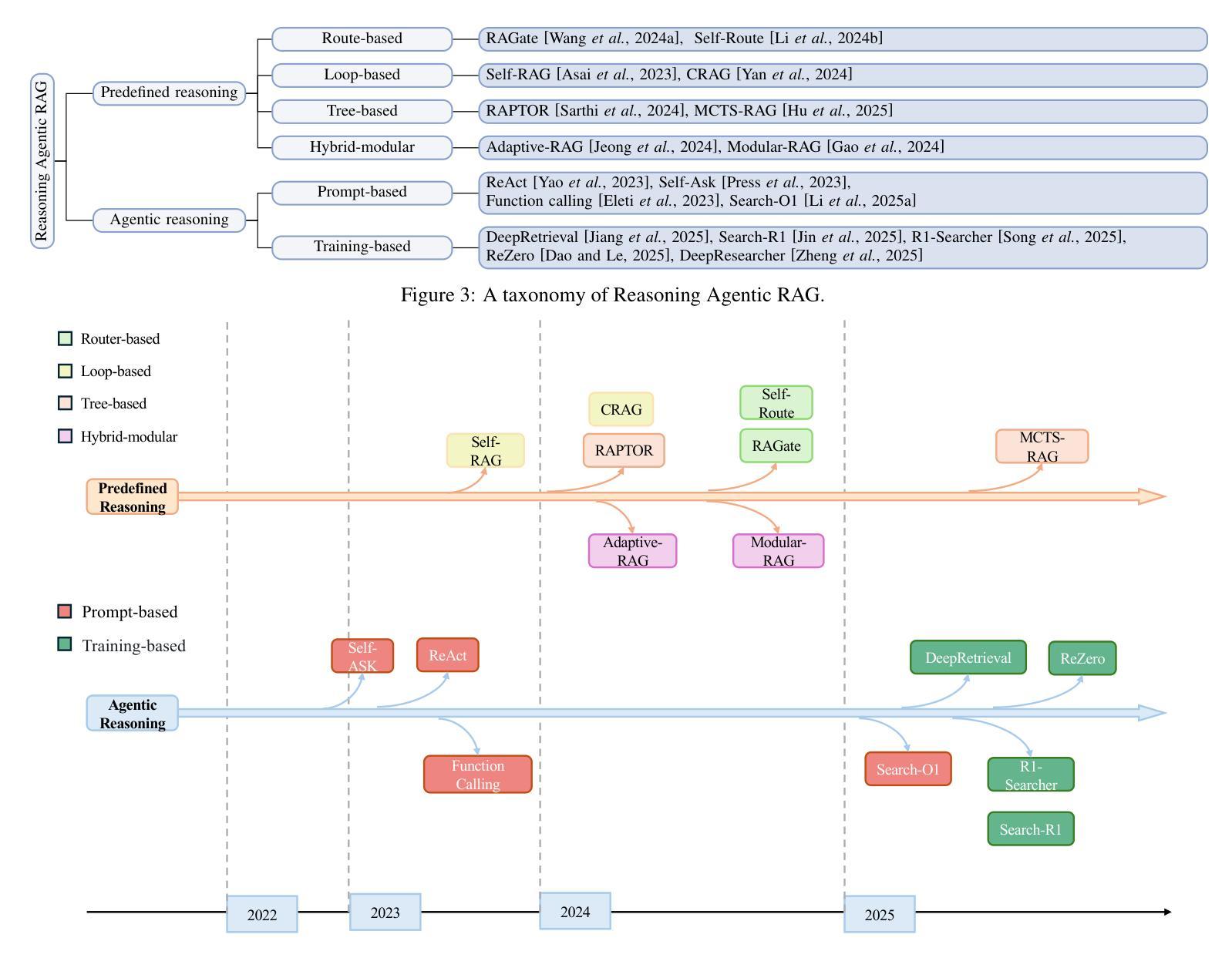
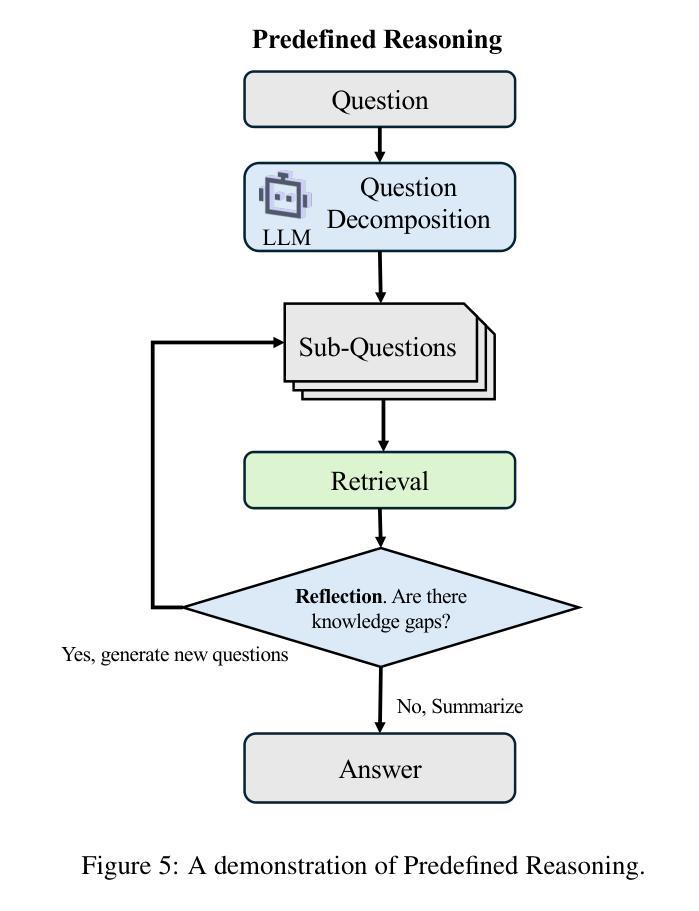
Reasoning RAG via System 1 or System 2: A Survey on Reasoning Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Industry Challenges
Authors:Jintao Liang, Gang Su, Huifeng Lin, You Wu, Rui Zhao, Ziyue Li
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a powerful framework to overcome the knowledge limitations of Large Language Models (LLMs) by integrating external retrieval with language generation. While early RAG systems based on static pipelines have shown effectiveness in well-structured tasks, they struggle in real-world scenarios requiring complex reasoning, dynamic retrieval, and multi-modal integration. To address these challenges, the field has shifted toward Reasoning Agentic RAG, a paradigm that embeds decision-making and adaptive tool use directly into the retrieval process. In this paper, we present a comprehensive review of Reasoning Agentic RAG methods, categorizing them into two primary systems: predefined reasoning, which follows fixed modular pipelines to boost reasoning, and agentic reasoning, where the model autonomously orchestrates tool interaction during inference. We analyze representative techniques under both paradigms, covering architectural design, reasoning strategies, and tool coordination. Finally, we discuss key research challenges and propose future directions to advance the flexibility, robustness, and applicability of reasoning agentic RAG systems. Our collection of the relevant research has been organized into a https://github.com/ByebyeMonica/Reasoning-Agentic-RAG.
检索增强生成(RAG)已经成为一个强大的框架,通过整合外部检索和语言生成,克服了大型语言模型(LLM)的知识局限性。虽然早期的基于静态流水线的RAG系统在结构良好的任务中显示出有效性,但在需要复杂推理、动态检索和多模式集成的现实场景中还面临挑战。为了解决这些挑战,研究领域已经转向推理代理RAG(Reasoning Agentic RAG),这是一种将决策制定和自适应工具使用直接嵌入到检索过程中的范式。本文全面回顾了推理代理RAG方法,将它们分为两大类:预设推理系统,它遵循固定的模块化流水线以增强推理能力;自主推理系统,模型在推理过程中自主协调工具交互。我们分析了这两种范式下的代表性技术,涵盖了架构设计、推理策略和工具协调。最后,我们讨论了关键的研究挑战,并提出了提高推理代理RAG系统的灵活性、鲁棒性和适用性的未来研究方向。我们已将相关的研究整理在https://github.com/ByebyeMonica/Reasoning-Agentic-RAG。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了增强检索生成(RAG)框架的发展历程及其在克服大型语言模型(LLM)知识局限方面的作用。文章重点介绍了Reasoning Agentic RAG方法,将其分为预设推理和自主推理两种系统,并探讨了代表性技术、架构设计、推理策略和工具协调。最后讨论了关键的研究挑战,并为提高Reasoning Agentic RAG系统的灵活性、鲁棒性和适用性提出了未来研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- RAG框架通过整合外部检索和语言生成,克服了大型语言模型的知识局限。
- 早期的RAG系统在结构化任务中表现出效果,但在需要复杂推理、动态检索和多模式集成的现实场景中存在挑战。
- 为了应对这些挑战,出现了Reasoning Agentic RAG范式,将决策制定和自适应工具使用直接嵌入到检索过程中。
- Reasoning Agentic RAG方法可分为预设推理和自主推理两种系统。
- 预设推理遵循固定的模块化管道来提升推理能力,而自主推理则让模型在推理过程中自主地协调工具交互。
- 文章还讨论了该领域的关键研究挑战,包括提高系统的灵活性、鲁棒性和适用性。
点此查看论文截图


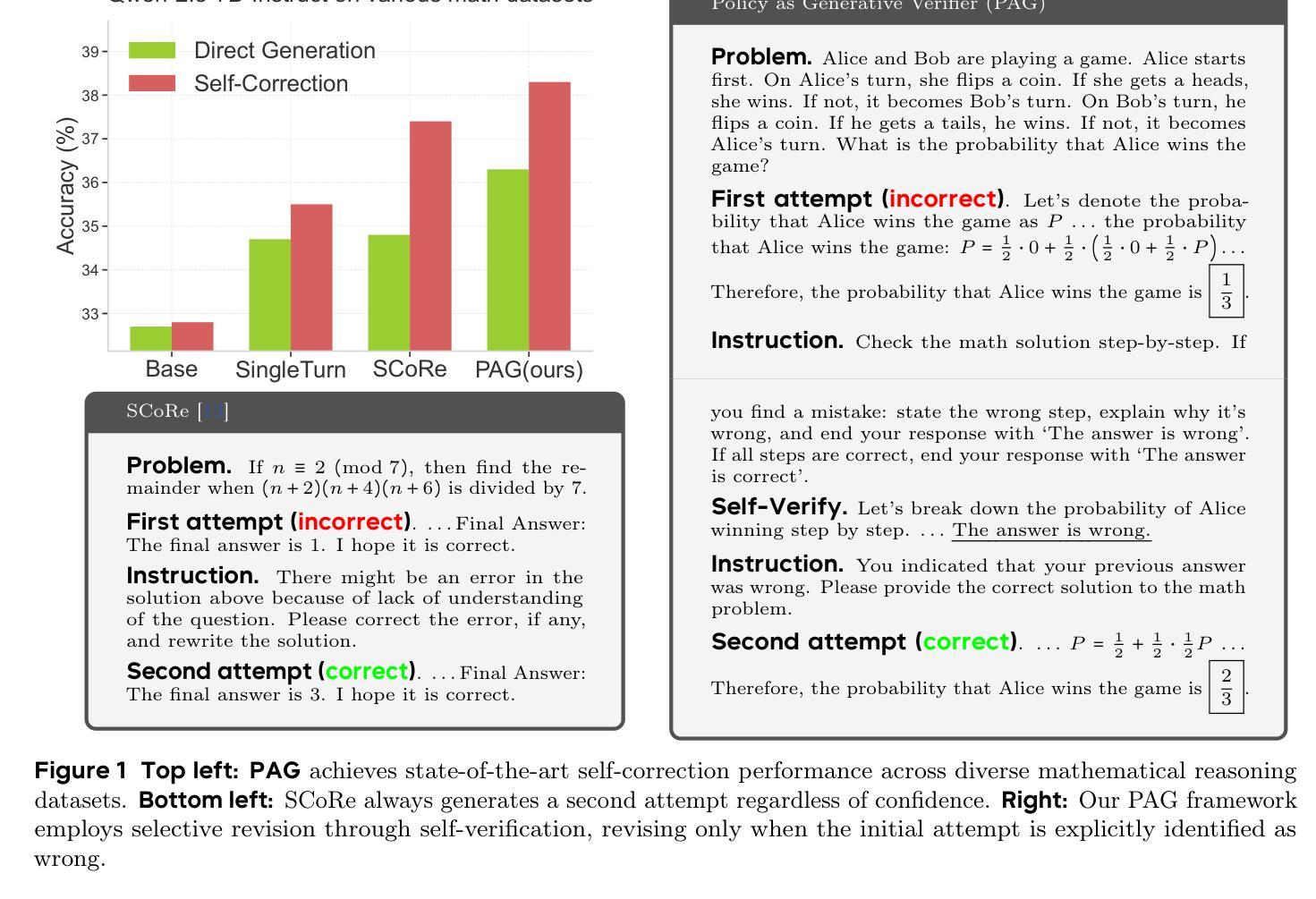
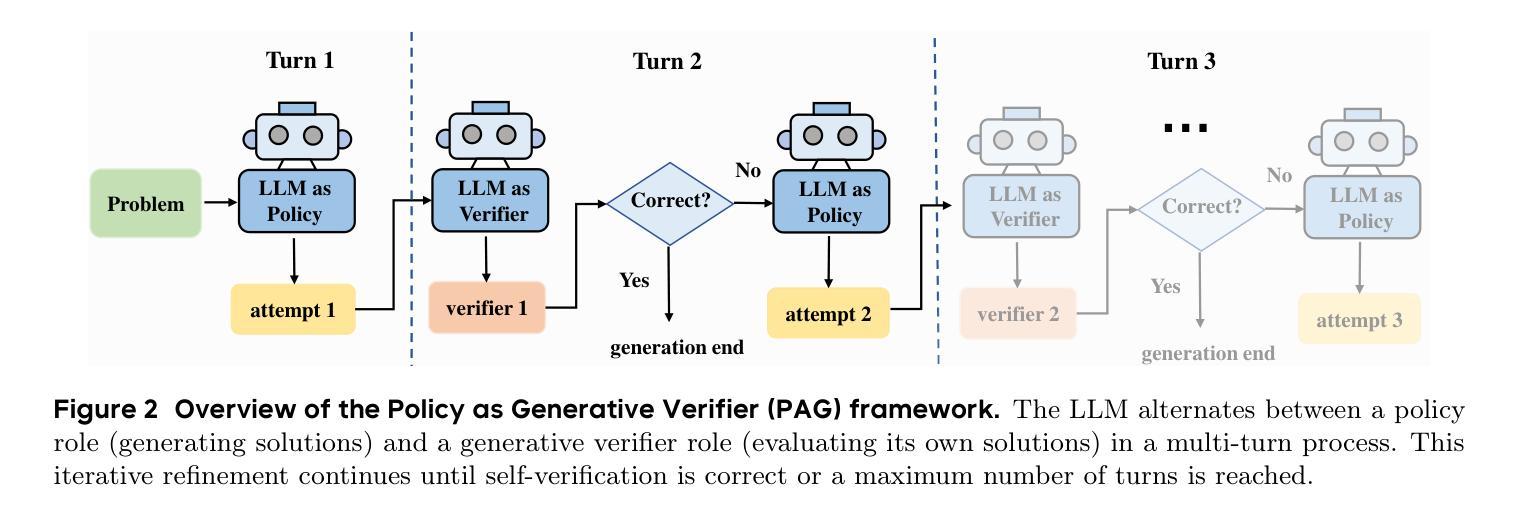
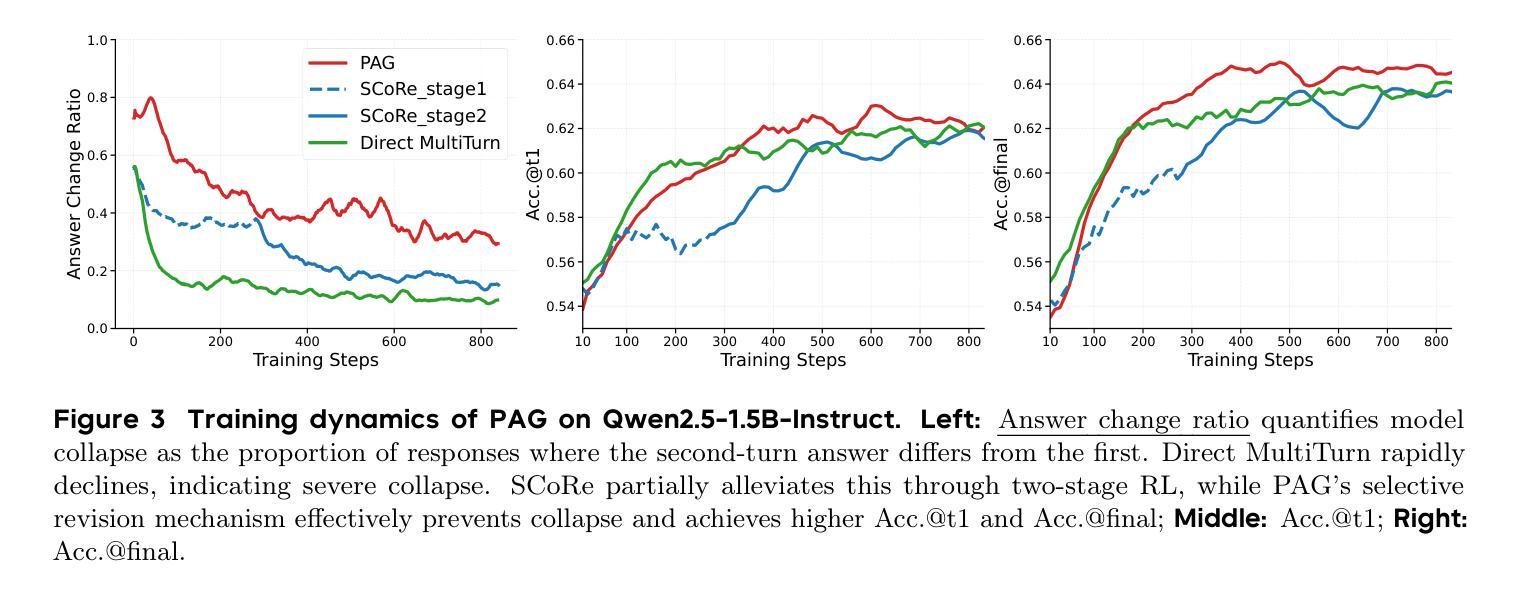
PAG: Multi-Turn Reinforced LLM Self-Correction with Policy as Generative Verifier
Authors:Yuhua Jiang, Yuwen Xiong, Yufeng Yuan, Chao Xin, Wenyuan Xu, Yu Yue, Qianchuan Zhao, Lin Yan
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in complex reasoning tasks, yet they still struggle to reliably verify the correctness of their own outputs. Existing solutions to this verification challenge often depend on separate verifier models or require multi-stage self-correction training pipelines, which limit scalability. In this paper, we propose Policy as Generative Verifier (PAG), a simple and effective framework that empowers LLMs to self-correct by alternating between policy and verifier roles within a unified multi-turn reinforcement learning (RL) paradigm. Distinct from prior approaches that always generate a second attempt regardless of model confidence, PAG introduces a selective revision mechanism: the model revises its answer only when its own generative verification step detects an error. This verify-then-revise workflow not only alleviates model collapse but also jointly enhances both reasoning and verification abilities. Extensive experiments across diverse reasoning benchmarks highlight PAG’s dual advancements: as a policy, it enhances direct generation and self-correction accuracy; as a verifier, its self-verification outperforms self-consistency.
大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂的推理任务中表现出了令人印象深刻的能力,然而,它们仍然难以可靠地验证其输出的正确性。针对这一验证挑战的现有解决方案通常依赖于单独的验证器模型或需要多阶段自我校正训练管道,这限制了可扩展性。在本文中,我们提出了策略作为生成验证器(PAG),这是一个简单有效的框架,它通过在一个统一的多轮强化学习(RL)范式内交替使用策略和验证器角色,使LLM能够进行自我校正。不同于先前的总是生成第二个答案而不管模型置信度的方法,PAG引入了选择性修订机制:只有当其自身的生成验证步骤检测到错误时,模型才会修订其答案。这种验证后修订的工作流程不仅减轻了模型崩溃的问题,还同时提高了推理和验证能力。在多种推理基准测试上的广泛实验突出了PAG的双重优势:作为策略,它提高了直接生成和自我校正的准确性;作为验证器,它的自我验证超越了自我一致性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在复杂推理任务中展现出强大能力,但在验证输出正确性方面仍存在挑战。现有验证方法常依赖于单独的验证器模型或多阶段自我修正训练管道,这限制了可扩展性。本文提出策略作为生成验证器(PAG),通过统一的多轮强化学习(RL)范式,使LLMs通过交替的策略和验证器角色进行自我修正。不同于总是无条件生成第二个答案的方法,PAG引入选择性修订机制:仅在模型自身的生成验证步骤检测到错误时才进行修订。这种验证后修订的工作流程不仅减轻了模型崩溃问题,还同时提高了推理和验证能力。跨多种推理基准的广泛实验突出了PAG的双重优势:作为策略,它提高了直接生成和自我修正的准确性;作为验证器,其自我验证效果优于自我一致性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在复杂推理任务中表现出强大的能力,但在验证输出正确性方面存在挑战。
- 现有验证方法通常依赖于单独的验证器模型或多阶段自我修正训练管道,这限制了其可扩展性。
- 本文提出的策略作为生成验证器(PAG)框架,通过强化学习使LLMs能够在统一的多轮范式中自我修正。
- PAG引入选择性修订机制,仅在模型自身的生成验证步骤检测到错误时才进行修订。
- 这种验证后修订的工作流程提高了模型的推理和验证能力,同时减轻了模型崩溃问题。
- PAG策略提高了直接生成和自我修正的准确性。
点此查看论文截图
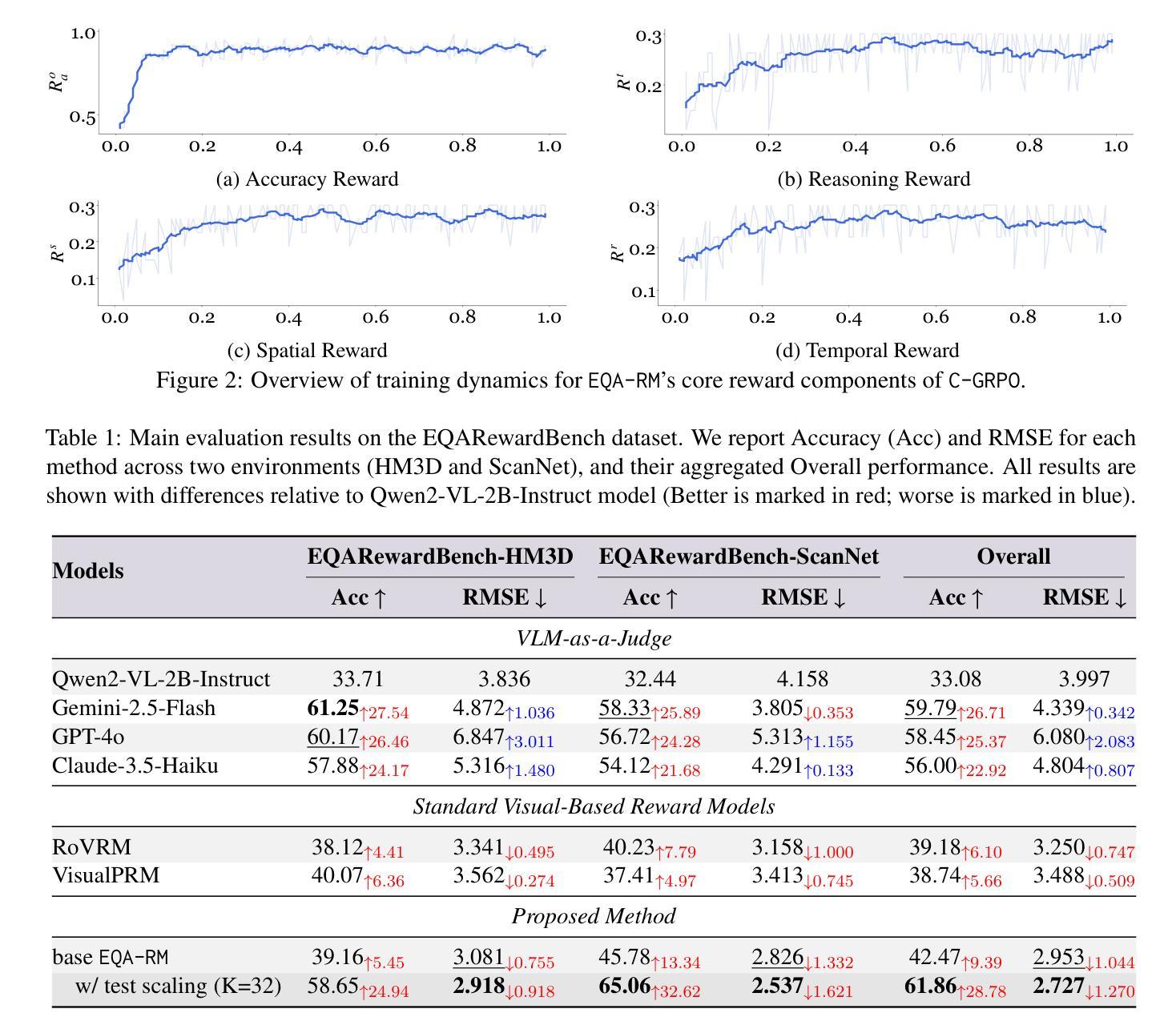
EQA-RM: A Generative Embodied Reward Model with Test-time Scaling
Authors:Yuhang Chen, Zhen Tan, Tianlong Chen
Reward Models (RMs), vital for large model alignment, are underexplored for complex embodied tasks like Embodied Question Answering (EQA) where nuanced evaluation of agents’ spatial, temporal, and logical understanding is critical yet not considered by generic approaches. We introduce EQA-RM, a novel generative multimodal reward model specifically architected for EQA, trained via our innovative Contrastive Group Relative Policy Optimization (C-GRPO) strategy to learn fine-grained behavioral distinctions. The generative nature of EQA-RM provides interpretable, structured reward feedback (beyond simple scalars), uniquely enabling test-time scaling to dynamically adjust evaluation granularity, from concise scores to detailed critiques of reasoning and grounding, at inference without retraining. Concurrently, we introduce EQARewardBench, a new benchmark built on OpenEQA for standardized EQA reward model assessment. Demonstrating high sample efficiency, EQA-RM (fine-tuning Qwen2-VL-2B-Instruct) achieves 61.9% accuracy on EQA-RM-Bench with only 700 samples, outperforming strong proprietary baselines, including Gemini-2.5-Flash, GPT-4o, Claude-3.5-Haiku, and open-sourced state-of-the-art models such as RoVRM and VisualPRM. The code and dataset can be found here https://github.com/UNITES-Lab/EQA-RM.
奖励模型(RMs)对于大型模型对齐至关重要,在复杂的实体任务(如实体问答(EQA))中却被探索得不够充分。在EQA中,对代理的空间、时间和逻辑理解的微妙评估至关重要,但通用方法尚未考虑这一点。我们引入了专门为EQA设计的全新生成式多模式奖励模型EQA-RM,通过我们创新的对比群组相对策略优化(C-GRPO)策略进行训练,以学习精细的行为差异。EQA-RM的生成性质提供了可解释的结构化奖励反馈(超出简单标量),能够唯一地在测试时进行缩放,以动态调整评估粒度,从简洁的分数到推理和依据的详细评价,而无需重新训练即可进行推断。同时,我们基于OpenEQA建立了新的基准测试EQARewardBench,用于标准化EQA奖励模型的评估。EQA-RM表现出较高的样本效率,通过微调Qwen2-VL-2B-Instruct,在EQA-RM-Bench上实现61.9%的准确率,仅使用700个样本就超越了强大的专有基线,包括Gemini-2.5-Flash、GPT-4o、Claude-3.5-Haiku以及开源的先进模型,如RoVRM和VisualPRM。代码和数据集可在https://github.com/UNITES-Lab/EQA-RM找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint
Summary
本文介绍了针对复杂体任务(如身临其境的问答)设计的奖励模型EQA-RM,其通过创新的对比群体相对策略优化方法(C-GRPO)进行训练,以精细的行为差异为基础进行学习。EQA-RM具有生成性,能提供可解释的、结构化的奖励反馈,支持在测试时动态调整评估粒度。同时,文章还介绍了基于OpenEQA建立的EQARewardBench基准测试平台,用于评估EQA奖励模型。EQA-RM在EQARewardBench上的准确率达到了61.9%,仅使用700个样本就超过了多个强大的专有基准模型和开源先进模型。
Key Takeaways
- EQA-RM是针对身临其境问答等复杂体任务的奖励模型。
- EQA-RM具有生成性,能提供结构化奖励反馈。
- C-GRPO策略用于训练EQA-RM,以精细的行为差异为基础进行学习。
- EQA-RM支持在测试时动态调整评估粒度,无需重新训练。
- EQARewardBench是建立于OpenEQA之上的奖励模型评估基准。
- EQA-RM在EQARewardBench上的准确率高,仅使用少量样本就表现出优越性能。
点此查看论文截图


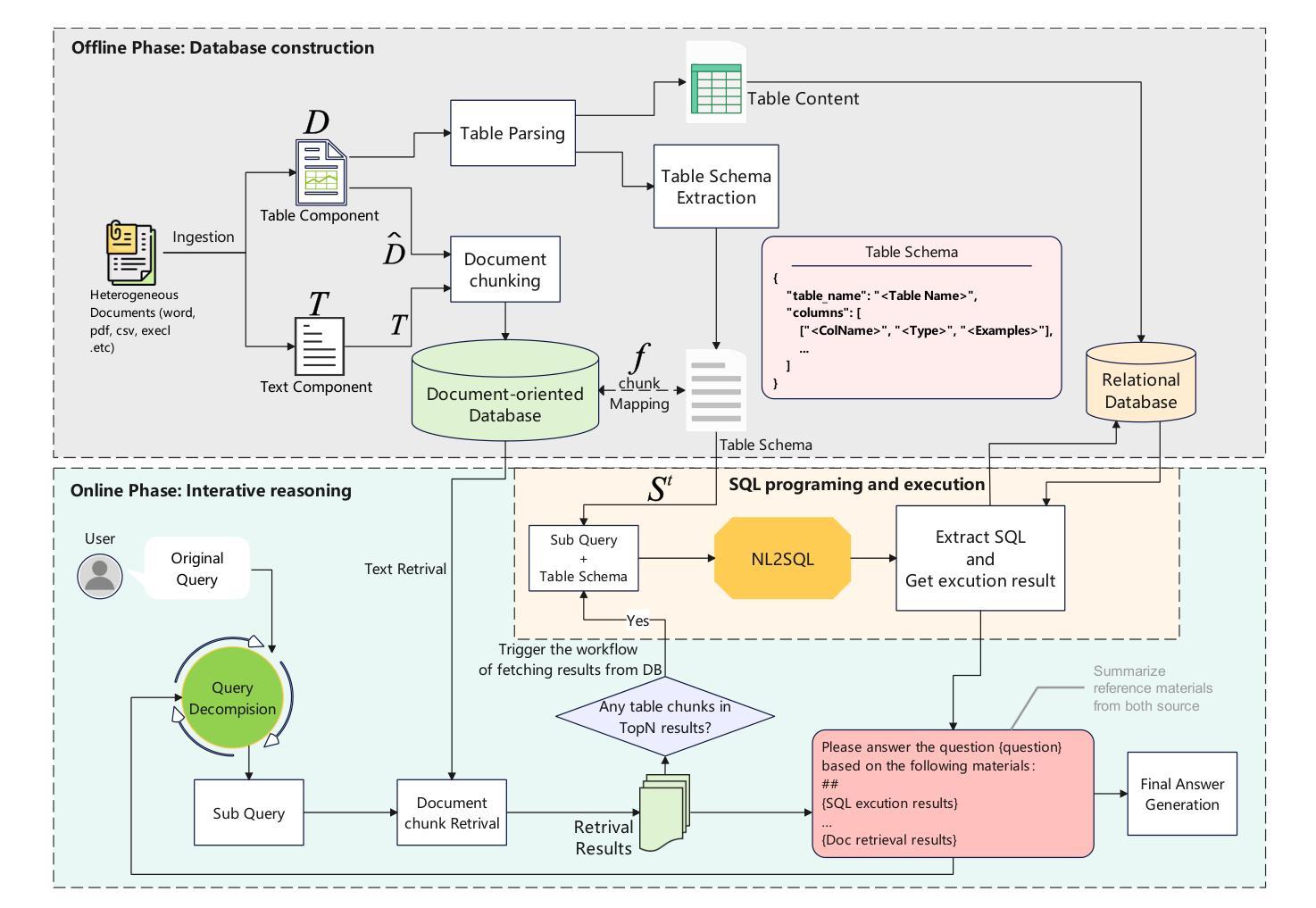
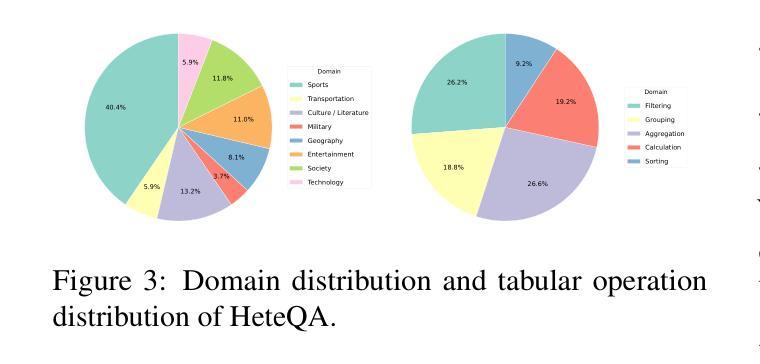
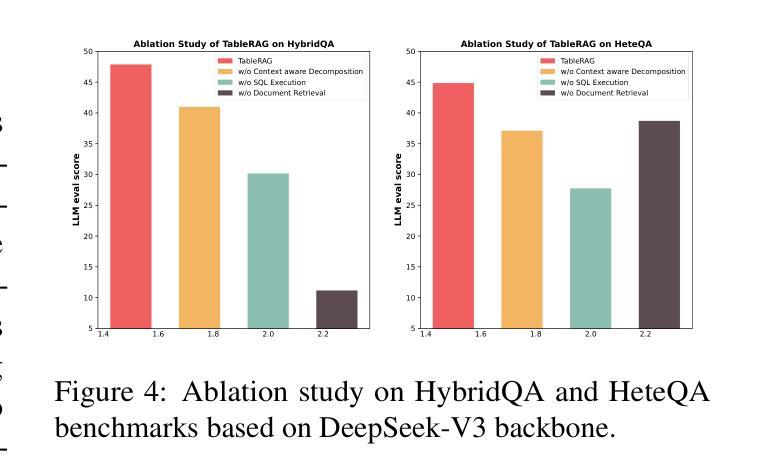
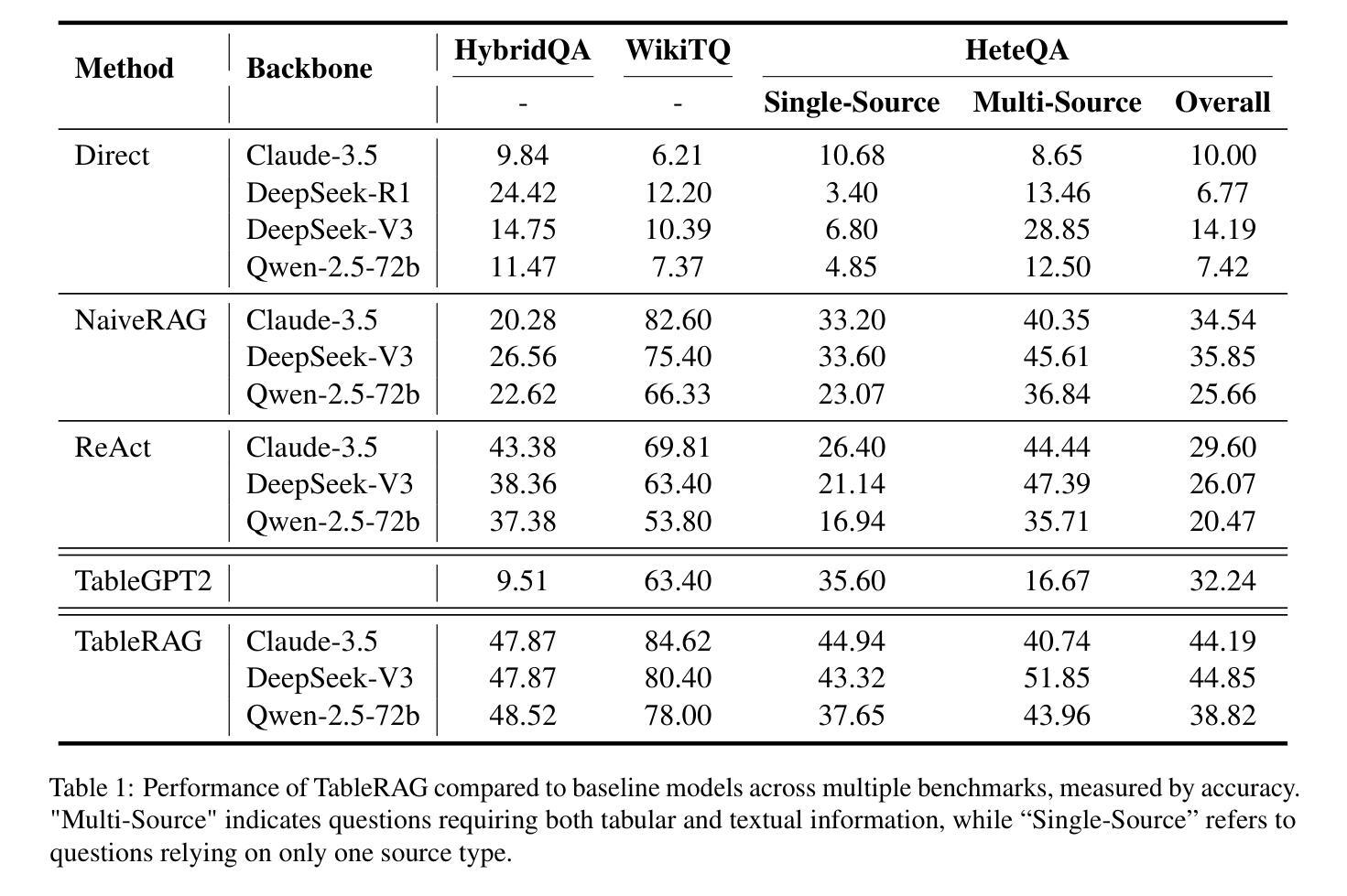
TableRAG: A Retrieval Augmented Generation Framework for Heterogeneous Document Reasoning
Authors:Xiaohan Yu, Pu Jian, Chong Chen
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has demonstrated considerable effectiveness in open-domain question answering. However, when applied to heterogeneous documents, comprising both textual and tabular components, existing RAG approaches exhibit critical limitations. The prevailing practice of flattening tables and chunking strategies disrupts the intrinsic tabular structure, leads to information loss, and undermines the reasoning capabilities of LLMs in multi-hop, global queries. To address these challenges, we propose TableRAG, an hybrid framework that unifies textual understanding and complex manipulations over tabular data. TableRAG iteratively operates in four steps: context-sensitive query decomposition, text retrieval, SQL programming and execution, and compositional intermediate answer generation. We also develop HeteQA, a novel benchmark designed to evaluate the multi-hop heterogeneous reasoning capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that TableRAG consistently outperforms existing baselines on both public datasets and our HeteQA, establishing a new state-of-the-art for heterogeneous document question answering. We release TableRAG at https://github.com/yxh-y/TableRAG/tree/main.
检索增强生成(RAG)在开放域问答中表现出了显著的有效性。然而,当应用于包含文本和表格组件的异质文档时,现有的RAG方法表现出重大局限性。流行的表格平铺和分片策略破坏了内在的表格结构,导致信息丢失,并破坏了LLM在多跳全局查询中的推理能力。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了TableRAG,这是一个融合了文本理解和表格数据的复杂操作的混合框架。TableRAG以四个步骤迭代运行:上下文敏感的查询分解、文本检索、SQL编程和执行,以及组合中间答案生成。我们还开发了HeteQA,这是一个用于评估多跳异质推理能力的新型基准测试。实验结果表明,无论是在公共数据集还是我们的HeteQA上,TableRAG始终优于现有基准,为异质文档问答建立了新的最新技术。我们在https://github.com/yxh-y/TableRAG/tree/main上发布了TableRAG。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review. Codes are available at https://github.com/yxh-y/TableRAG/tree/main
Summary
RAG在开放域问答中具有显著效果,但在处理包含文本和表格的异质文档时存在局限性。现有方法破坏表格的内在结构,导致信息丢失并影响LLMs在多跳全局查询中的推理能力。为此,我们提出TableRAG统一框架,融合文本理解和表格数据的复杂操作。TableRAG通过四个步骤迭代操作:上下文敏感的查询分解、文本检索、SQL编程与执行,以及组合中间答案生成。同时,我们开发HeteQA基准测试,以评估多跳异质推理能力。实验结果证明TableRAG在公共数据集和HeteQA上的表现均超越现有基线,成为异质文档问答的新里程碑。
Key Takeaways
- RAG在处理包含文本和表格的异质文档时存在局限性。
- 现有方法破坏表格的内在结构,导致信息丢失。
- TableRAG是一个统一框架,融合了文本理解和表格数据的复杂操作。
- TableRAG通过四个步骤进行迭代操作:查询分解、文本检索、SQL编程与执行,以及答案生成。
- HeteQA基准测试用于评估多跳异质推理能力。
- TableRAG在公共数据集和HeteQA上的表现超越现有方法。
- TableRAG框架已被发布在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图

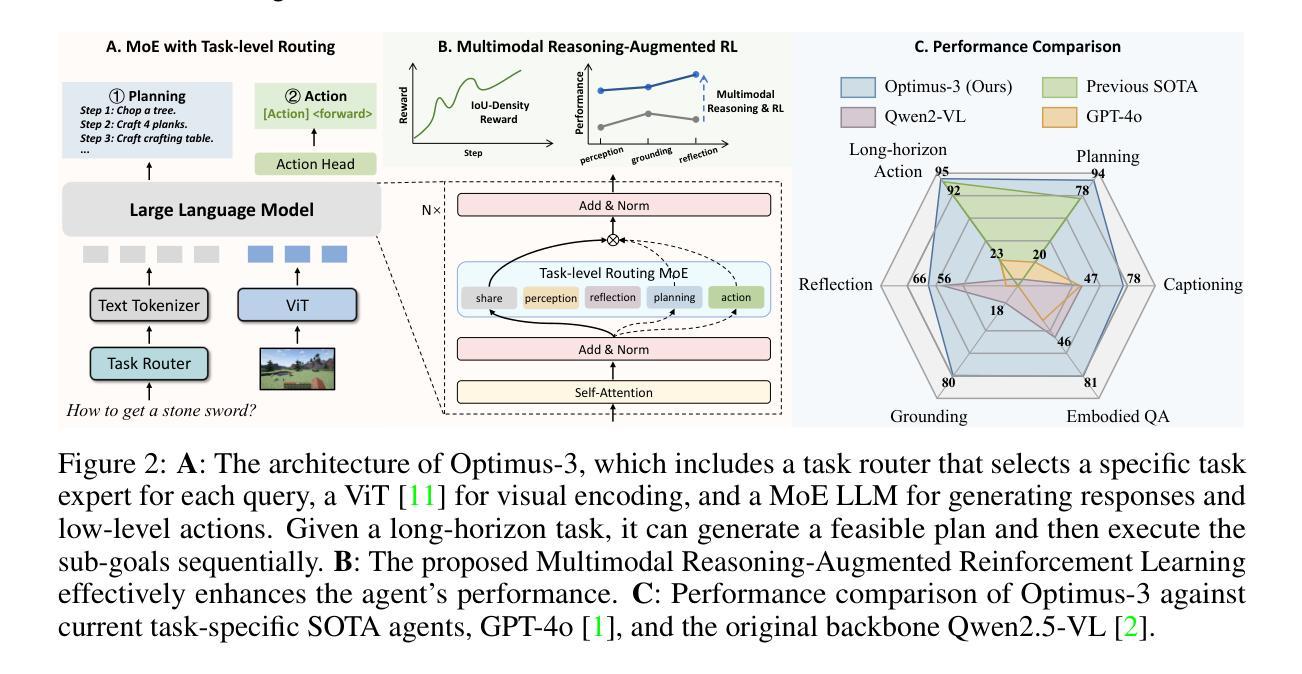
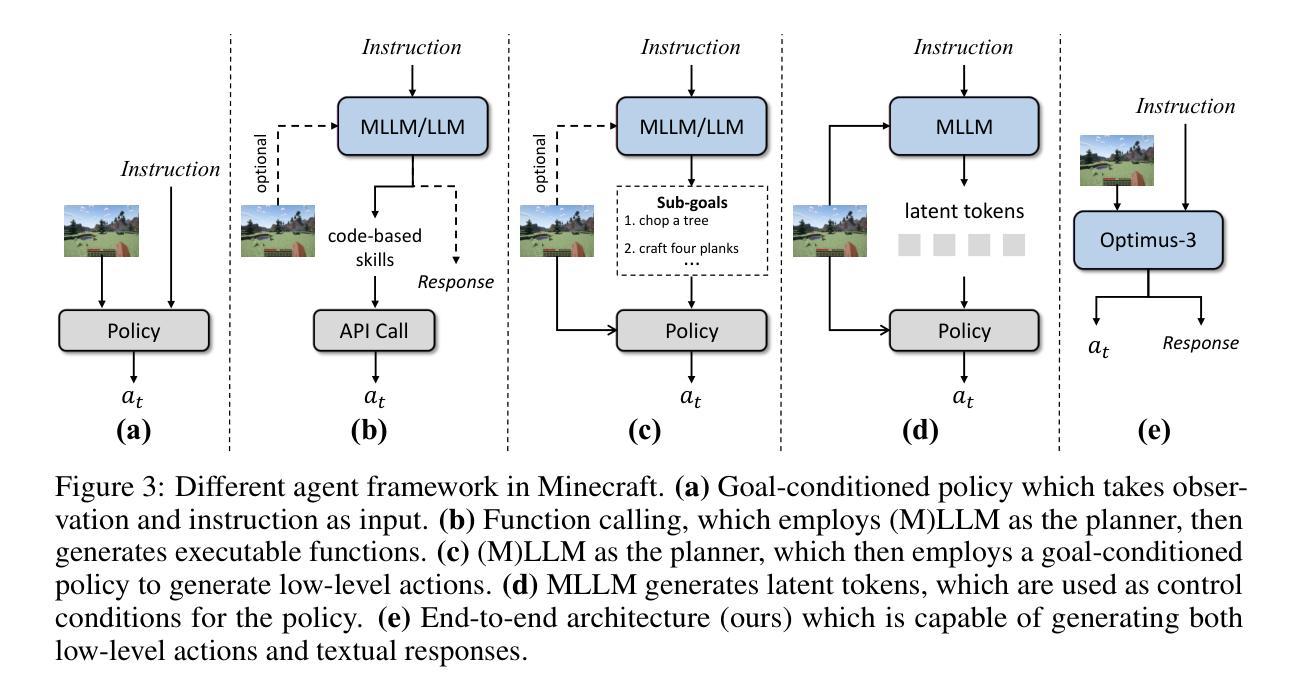
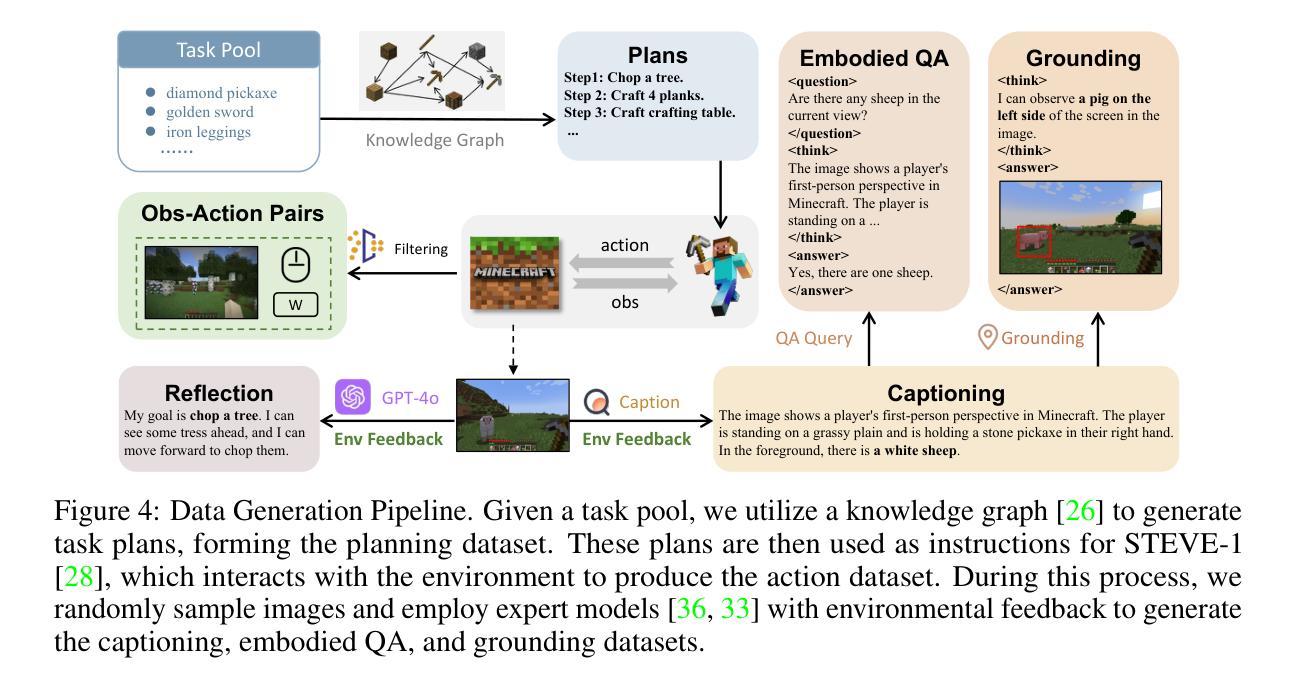
Optimus-3: Towards Generalist Multimodal Minecraft Agents with Scalable Task Experts
Authors:Zaijing Li, Yuquan Xie, Rui Shao, Gongwei Chen, Weili Guan, Dongmei Jiang, Liqiang Nie
Recently, agents based on multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable progress across various domains. However, building a generalist agent with capabilities such as perception, planning, action, grounding, and reflection in open-world environments like Minecraft remains challenges: insufficient domain-specific data, interference among heterogeneous tasks, and visual diversity in open-world settings. In this paper, we address these challenges through three key contributions. 1) We propose a knowledge-enhanced data generation pipeline to provide scalable and high-quality training data for agent development. 2) To mitigate interference among heterogeneous tasks, we introduce a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture with task-level routing. 3) We develop a Multimodal Reasoning-Augmented Reinforcement Learning approach to enhance the agent’s reasoning ability for visual diversity in Minecraft. Built upon these innovations, we present Optimus-3, a general-purpose agent for Minecraft. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that Optimus-3 surpasses both generalist multimodal large language models and existing state-of-the-art agents across a wide range of tasks in the Minecraft environment. Project page: https://cybertronagent.github.io/Optimus-3.github.io/
最近,基于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的代理在各种领域取得了显著的进步。然而,在像Minecraft这样的开放世界环境中,构建一个具备感知、规划、行动、接地和反思能力的全能代理仍然存在挑战,包括特定领域的数据不足、不同任务之间的干扰以及开放世界设置中的视觉多样性。在本文中,我们通过三个关键贡献来解决这些挑战。1)我们提出了一个知识增强数据生成管道,为代理开发提供可扩展和高质量的训练数据。2)为了减轻不同任务之间的干扰,我们引入了一个混合专家(MoE)架构,具有任务级路由。3.我们开发了一种多模态推理增强型强化学习方法,以提高代理在Minecraft中处理视觉多样性的推理能力。基于这些创新,我们推出了Optimus-3,一个适用于Minecraft的通用代理。广泛的实验结果表明,Optimus-3在Minecraft环境中的各种任务上超越了通用多模态大型语言模型和现有的最先进的代理。项目页面:https://cybertronagent.github.io/Optimus-3/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 10 figures
Summary
近期,基于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的代理在多个领域取得了显著进展。然而,在像Minecraft这样的开放世界环境中,构建一个具备感知、规划、行动、接地和反思等能力的全能代理仍存在挑战,如特定领域的缺乏、异构任务间的干扰以及开放世界中的视觉多样性。本文通过三个关键贡献来解决这些挑战:一是提出知识增强数据生成管道,为代理开发提供可扩展和高质量的训练数据;二是引入具有任务级路由的混合专家(MoE)架构,减轻异构任务间的干扰;三是开发多模态推理增强强化学习方法,提高代理在Minecraft中应对视觉多样性的推理能力。基于这些创新,我们推出了Optimus-3,一个适用于Minecraft的通用代理。实验结果表明,Optimus-3在Minecraft环境中的一系列任务中超越了通用多模态大型语言模型以及现有先进代理。
Key Takeaways
- 基于多模态大型语言模型的代理在多个领域有显著的进步。
- 在开放世界环境如Minecraft中构建全能代理存在挑战,包括领域数据不足、异构任务干扰和视觉多样性。
- 提出知识增强数据生成管道,为代理开发提供高质量训练数据。
- 引入混合专家架构,通过任务级路由减轻异构任务间的干扰。
- 开发多模态推理增强强化学习方法,提高代理应对视觉多样性的能力。
- Optimus-3是一个适用于Minecraft的通用代理,实验结果优于其他模型。
点此查看论文截图

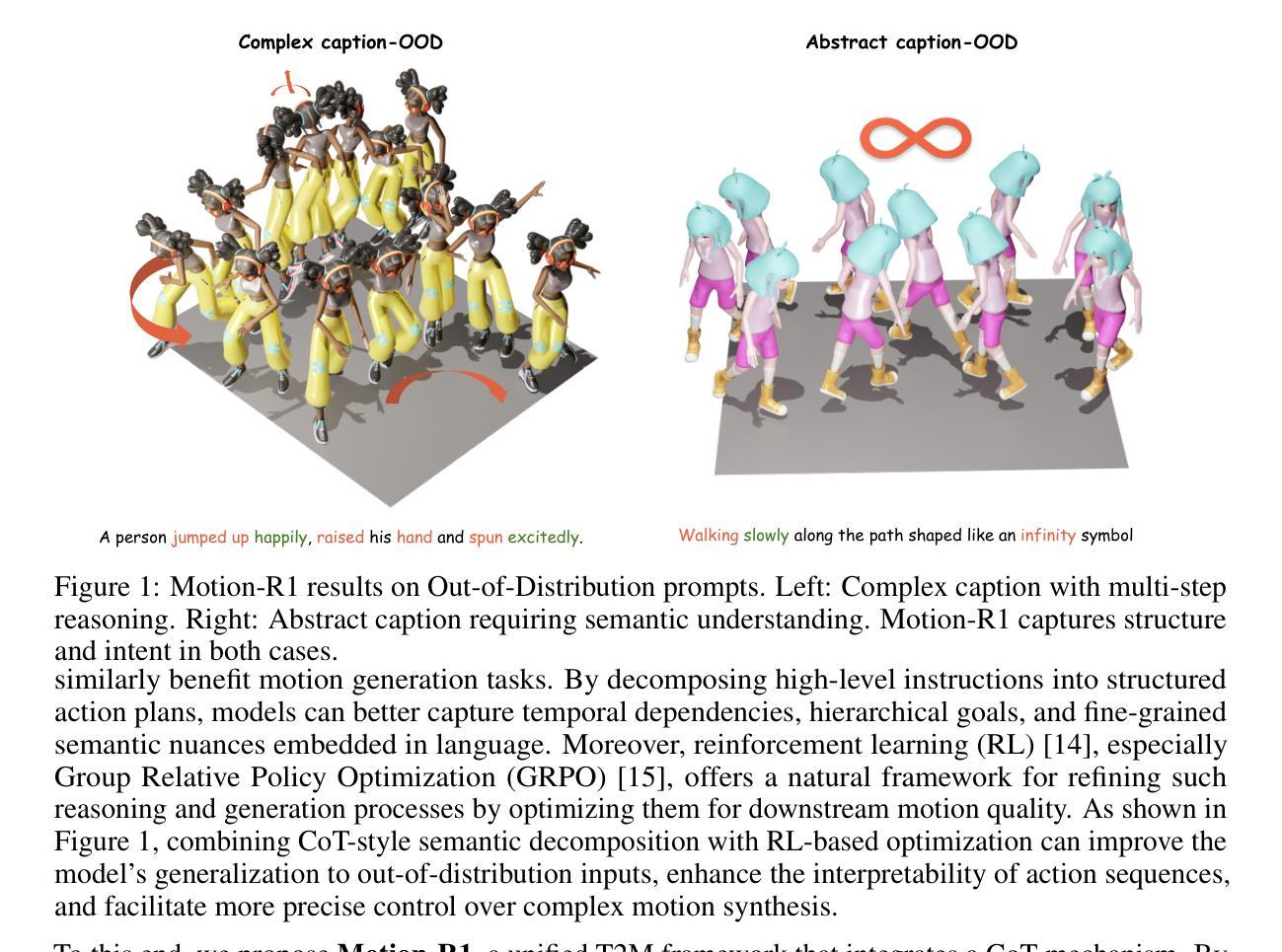
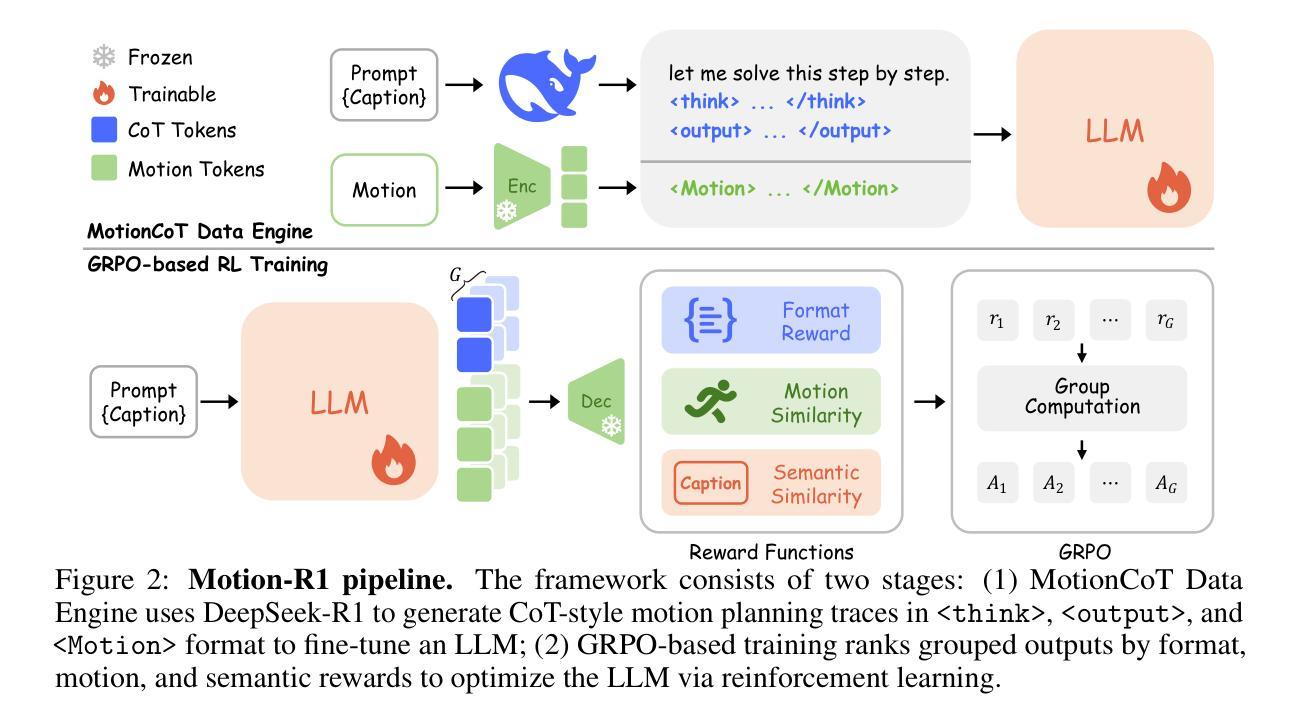
Motion-R1: Chain-of-Thought Reasoning and Reinforcement Learning for Human Motion Generation
Authors:Runqi Ouyang, Haoyun Li, Zhenyuan Zhang, Xiaofeng Wang, Zheng Zhu, Guan Huang, Xingang Wang
Recent advances in large language models, especially in natural language understanding and reasoning, have opened new possibilities for text-to-motion generation. Although existing approaches have made notable progress in semantic alignment and motion synthesis, they often rely on end-to-end mapping strategies that fail to capture deep linguistic structures and logical reasoning. Consequently, generated motions tend to lack controllability, consistency, and diversity. To address these limitations, we propose Motion-R1, a unified motion-language modeling framework that integrates a Chain-of-Thought mechanism. By explicitly decomposing complex textual instructions into logically structured action paths, Motion-R1 provides high-level semantic guidance for motion generation, significantly enhancing the model’s ability to interpret and execute multi-step, long-horizon, and compositionally rich commands. To train our model, we adopt Group Relative Policy Optimization, a reinforcement learning algorithm designed for large models, which leverages motion quality feedback to optimize reasoning chains and motion synthesis jointly. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that Motion-R1 achieves competitive or superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods, particularly in scenarios requiring nuanced semantic understanding and long-term temporal coherence. The code, model and data will be publicly available.
近年来,大型语言模型在自然语言理解和推理方面的进展为文本到运动的生成开启了新的可能性。尽管现有方法在语义对齐和运动合成方面取得了显著的进展,但它们通常依赖于端到端的映射策略,无法捕捉深层语言结构和逻辑推理。因此,生成的运动的可控性、一致性和多样性往往不足。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了Motion-R1,这是一个统一的运动语言建模框架,它集成了链式思维机制。通过显式地将复杂的文本指令分解为逻辑结构化的行动路径,Motion-R1为运动生成提供高级语义指导,显著提高了模型解释和执行多步骤、长期和组合丰富的命令的能力。为了训练我们的模型,我们采用了针对大型模型的强化学习算法——群组相对策略优化,该算法利用运动质量反馈来联合优化推理链和运动合成。在多个基准数据集上的大量实验表明,Motion-R1在需要微妙语义理解和长期时间连贯性的场景中,与最先进的方法相比具有竞争力或更优越的性能。代码、模型和数据将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型的最新进展,尤其是自然语言理解和推理方面的进展,为文本到运动的生成提供了新的可能性。现有方法虽然取得了显著的进步,但在语义对齐和运动合成方面仍存在局限性,往往依赖端到端的映射策略,无法捕捉深层语言结构和逻辑推理。为此,我们提出了Motion-R1,一个统一的运动语言建模框架,通过链式思维机制显式地将复杂的文本指令分解为逻辑结构化的动作路径,为运动生成提供高级语义指导。通过采用针对大型模型的强化学习算法——群组相对策略优化,该模型能够联合优化推理链和运动合成。在多个基准数据集上的实验表明,Motion-R1在需要微妙语义理解和长期时间连贯性的场景中,相较于最先进的方法,具有竞争力或更优越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的最新进展为文本到运动生成提供了新的机会。
- 现有方法在语义对齐和运动合成方面存在局限性。
- Motion-R1框架通过链式思维机制分解复杂文本指令为逻辑结构化的动作路径。
- Motion-R1采用群组相对策略优化,联合优化推理链和运动合成。
- Motion-R1在多个基准数据集上表现优越,特别是在需要微妙语义理解和长期时间连贯性的场景中。
- Motion-R1模型、代码和数据将公开可用。
点此查看论文截图


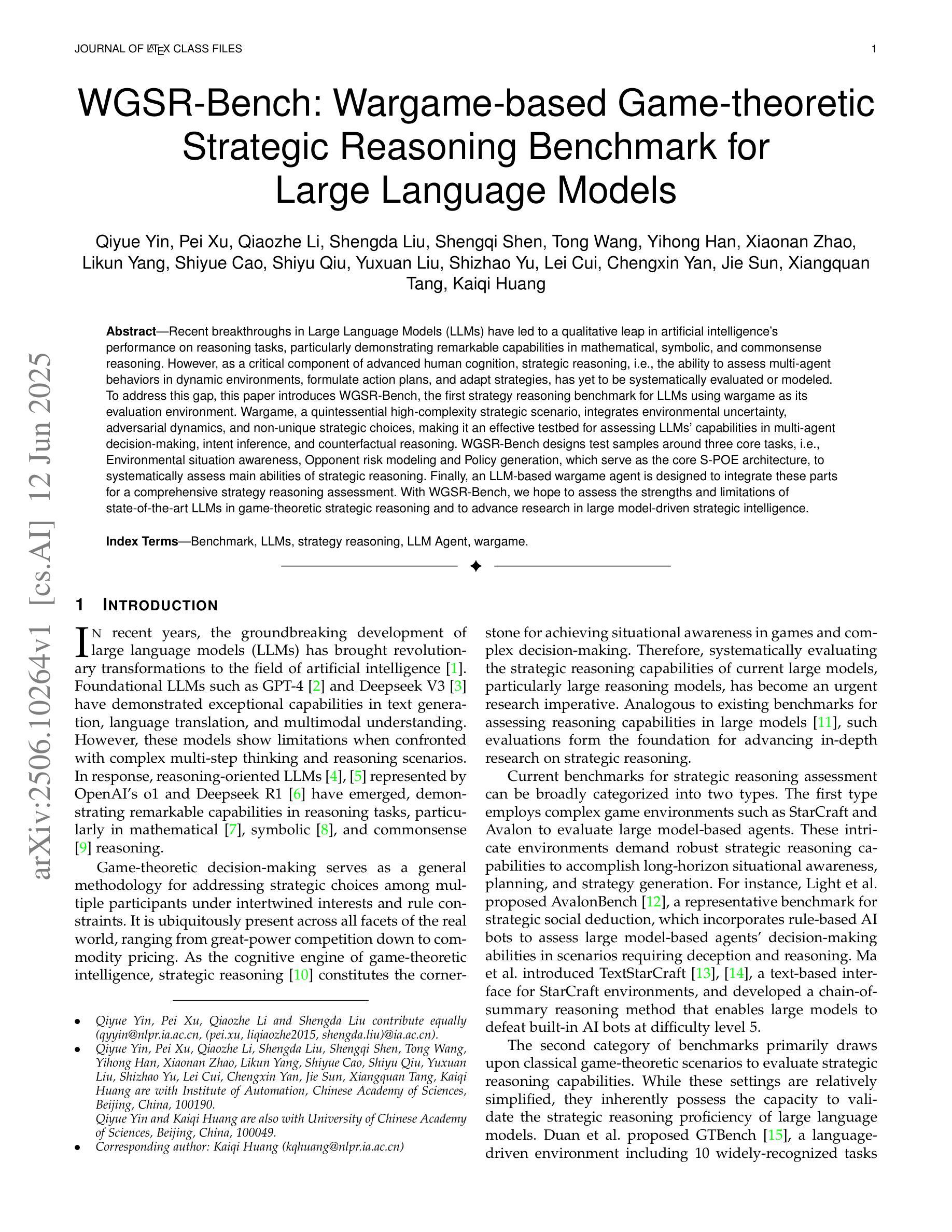
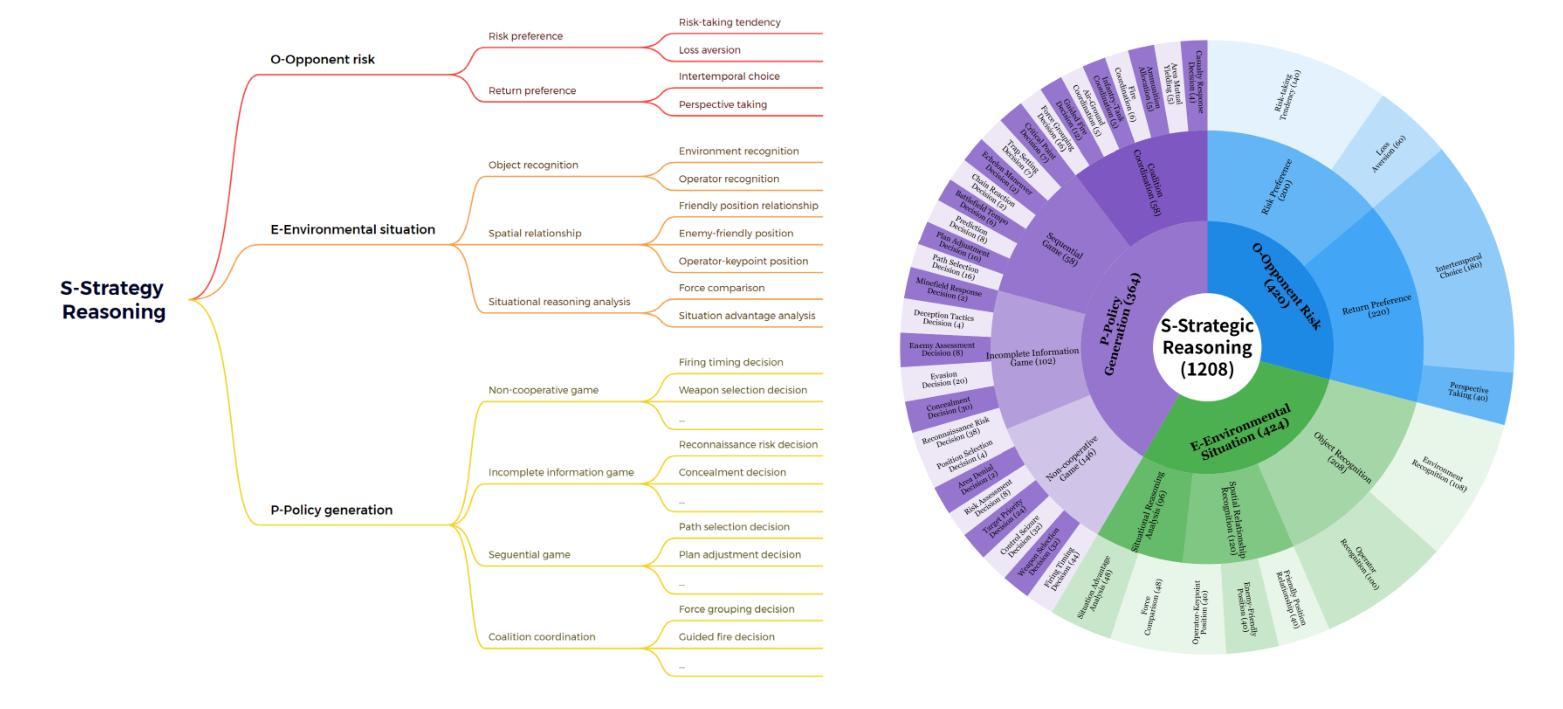
WGSR-Bench: Wargame-based Game-theoretic Strategic Reasoning Benchmark for Large Language Models
Authors:Qiyue Yin, Pei Xu, Qiaozhe Li, Shengda Liu, Shengqi Shen, Tong Wang, Yihong Han, Xiaonan Zhao, Likun Yang, Shiyue Cao, Shiyu Qiu, Yuxuan Liu, Shizhao Yu, Lei Cui, Chengxin Yan, Jie Sun, Xiangquan Tang, Kaiqi Huang
Recent breakthroughs in Large Language Models (LLMs) have led to a qualitative leap in artificial intelligence’ s performance on reasoning tasks, particularly demonstrating remarkable capabilities in mathematical, symbolic, and commonsense reasoning. However, as a critical component of advanced human cognition, strategic reasoning, i.e., the ability to assess multi-agent behaviors in dynamic environments, formulate action plans, and adapt strategies, has yet to be systematically evaluated or modeled. To address this gap, this paper introduces WGSR-Bench, the first strategy reasoning benchmark for LLMs using wargame as its evaluation environment. Wargame, a quintessential high-complexity strategic scenario, integrates environmental uncertainty, adversarial dynamics, and non-unique strategic choices, making it an effective testbed for assessing LLMs’ capabilities in multi-agent decision-making, intent inference, and counterfactual reasoning. WGSR-Bench designs test samples around three core tasks, i.e., Environmental situation awareness, Opponent risk modeling and Policy generation, which serve as the core S-POE architecture, to systematically assess main abilities of strategic reasoning. Finally, an LLM-based wargame agent is designed to integrate these parts for a comprehensive strategy reasoning assessment. With WGSR-Bench, we hope to assess the strengths and limitations of state-of-the-art LLMs in game-theoretic strategic reasoning and to advance research in large model-driven strategic intelligence.
近期大型语言模型(LLM)的突破导致人工智能在推理任务上的性能发生了质的变化,特别是在数学、符号和常识推理方面表现出卓越的能力。然而,作为先进人类认知的重要组成部分,战略推理能力,即评估多智能体在动态环境中的行为、制定行动计划、适应策略的能力,尚未得到系统的评估或建模。为了弥补这一空白,本文介绍了WGSR-Bench,这是使用战争游戏作为评估环境的大型语言模型的首个战略推理基准测试。战争游戏是一个典型的高复杂度战略场景,融合了环境不确定性、对抗性动态和非唯一战略选择,使其成为评估大型语言模型在多智能体决策、意图推断和反向推理方面的能力的有效测试平台。WGSR-Bench围绕三个核心任务设计测试样本,即环境态势感知、对手风险建模和政策生成,作为S-POE架构的核心,以系统地评估主要战略推理能力。最后,设计了一个基于大型语言模型的战争游戏代理,将这些部分整合起来进行全面战略推理评估。通过WGSR-Bench,我们希望能够评估最新大型语言模型在游戏理论战略推理方面的优势和局限性,并推动大型模型驱动的战略智能研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 17 figures
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在推理任务上的表现取得了质的飞跃,特别是在数学、符号和常识推理方面展现出卓越的能力。然而,战略推理作为高级人类认知的关键组成部分,包括评估多智能体行为、制定行动计划、适应策略等,尚未被系统评估或建模。为解决这一差距,本文引入了WGSR-Bench,这是使用战争游戏作为评估环境的第一个战略推理基准测试。战争游戏是一个高复杂度的战略场景,融合了环境不确定性、对抗性动态和非唯一战略选择,是评估LLM在多智能体决策、意图推断和反事实推理能力方面的有效测试平台。WGSR-Bench围绕环境态势感知、对手风险建模和政策制定三个核心任务设计测试用例,作为系统的S-POE架构,以评估战略推理的主要能力。最后设计了一个基于LLM的战争游戏代理,以整合这些部分进行全面的战略推理评估。希望通过WGSR-Bench评估最新LLM在游戏理论战略推理方面的优势和局限性,并推动大型模型驱动的战略智能研究的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在推理任务上取得了显著进展,尤其是数学、符号和常识推理方面。
- 战略推理作为人类高级认知的关键部分,在LLM中尚未得到充分评估或建模。
- WGSR-Bench是首个针对LLM的战略推理基准测试,采用战争游戏作为评估环境。
- 战争游戏是一个复杂的战略场景,能有效评估LLM在多智能体决策、意图推断和反事实推理方面的能力。
- WGSR-Bench围绕三个核心任务设计测试用例:环境态势感知、对手风险建模和政策制定。
- 基于LLM的战争游戏代理被设计来整合这些部分,进行全面的战略推理评估。
点此查看论文截图
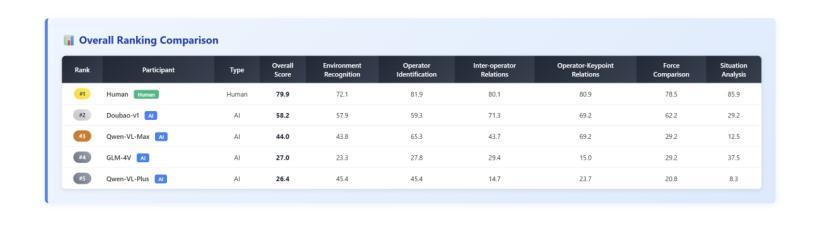
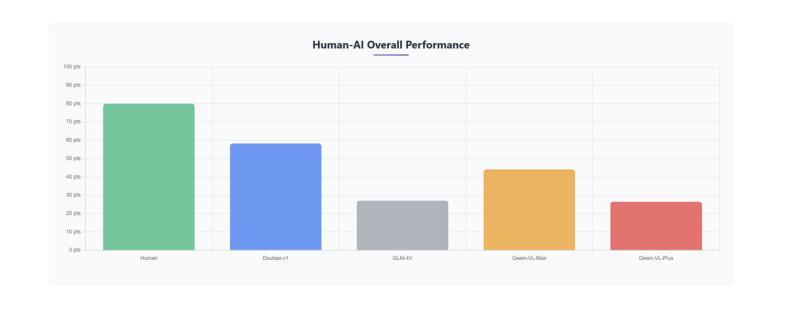
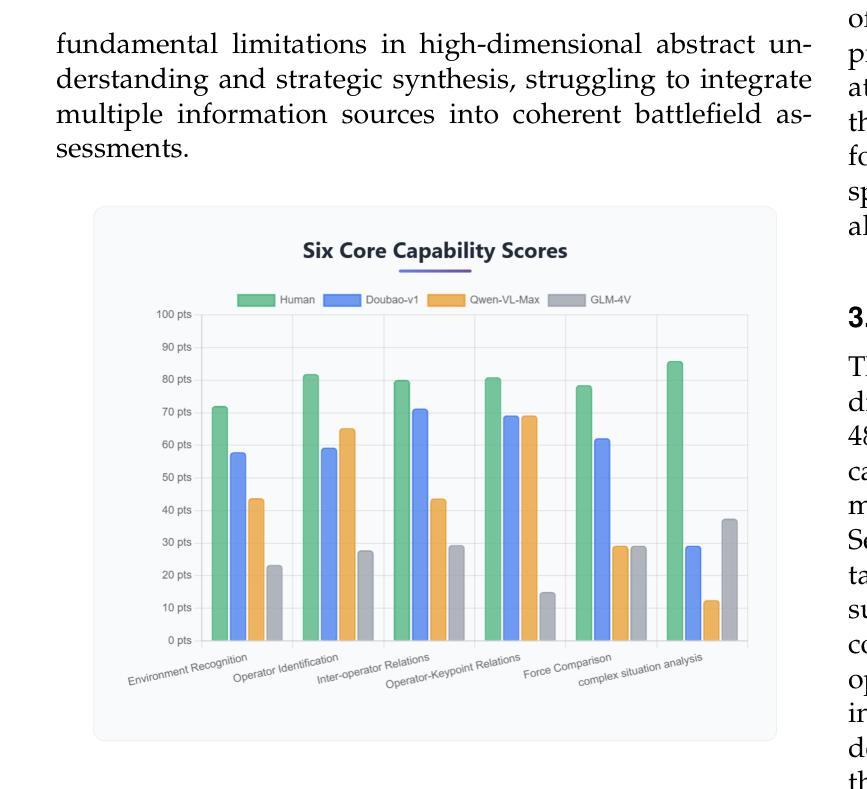
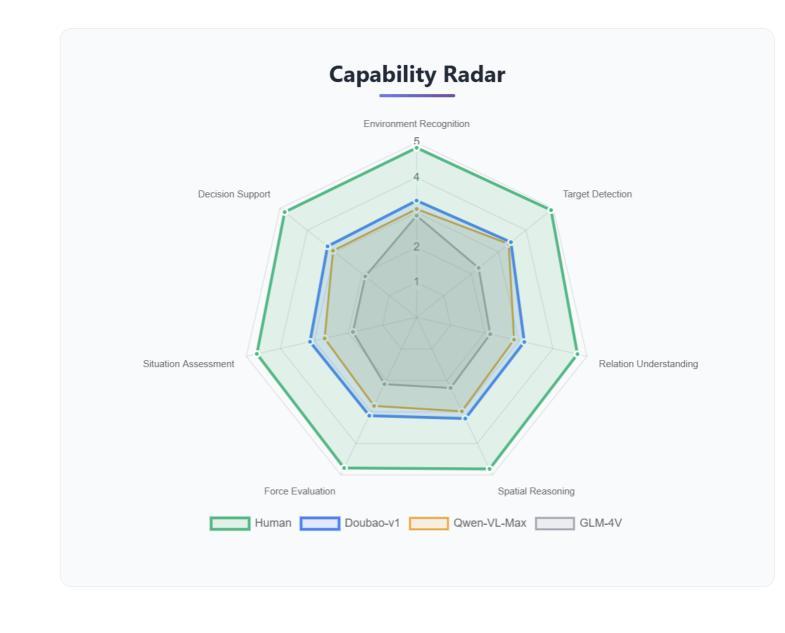
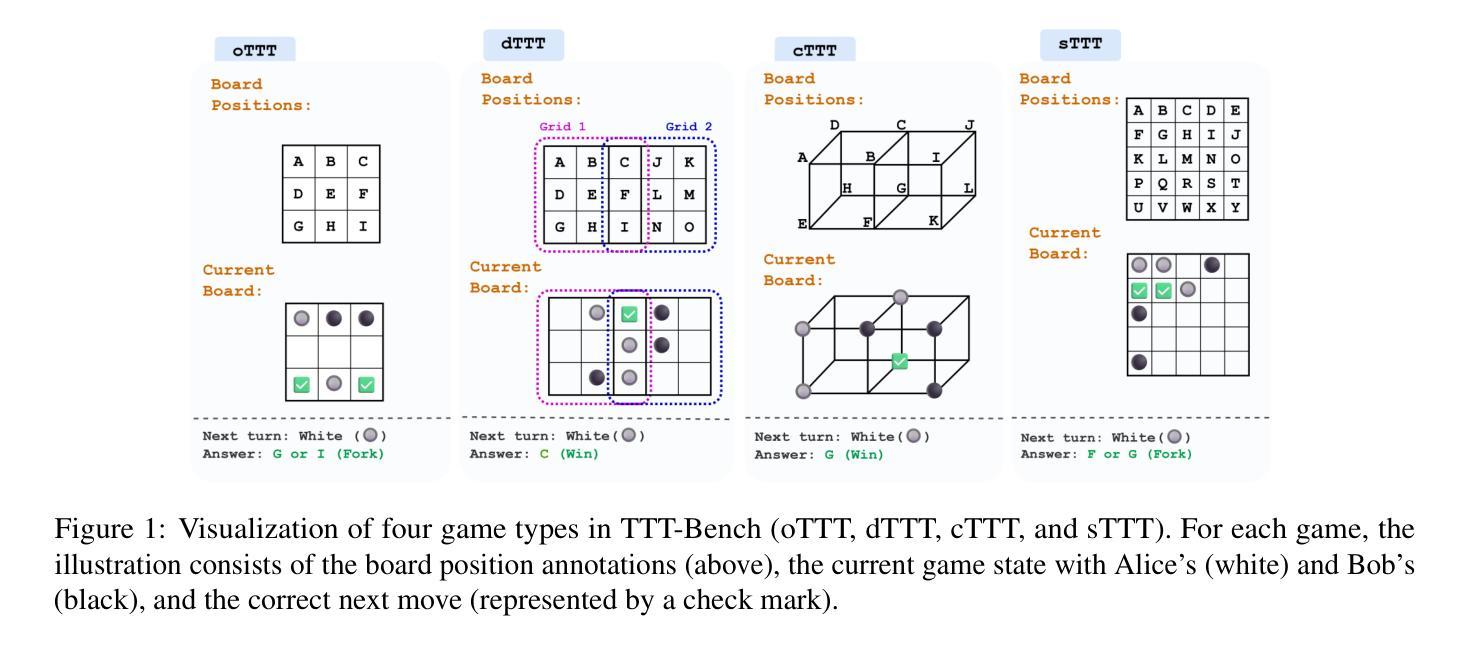
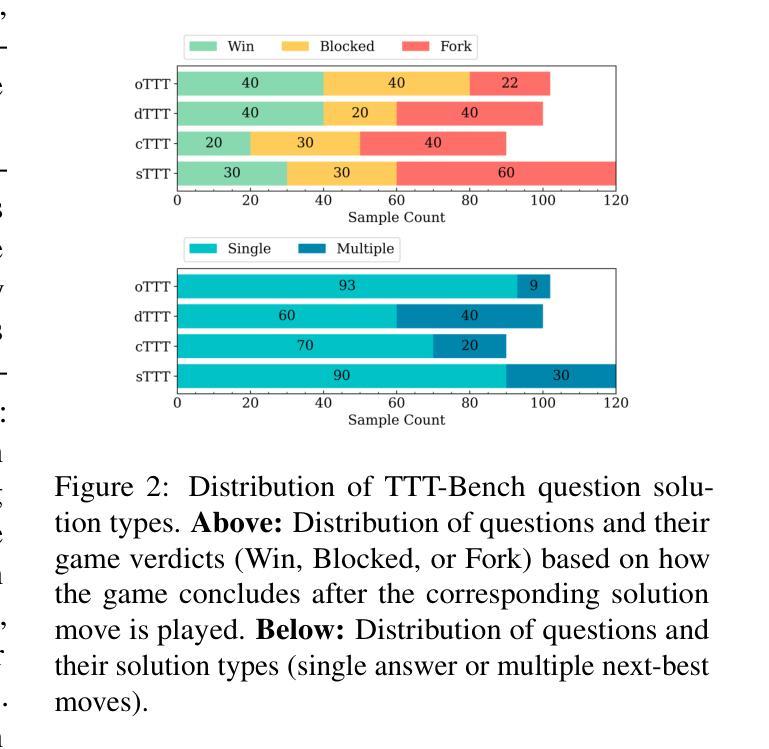
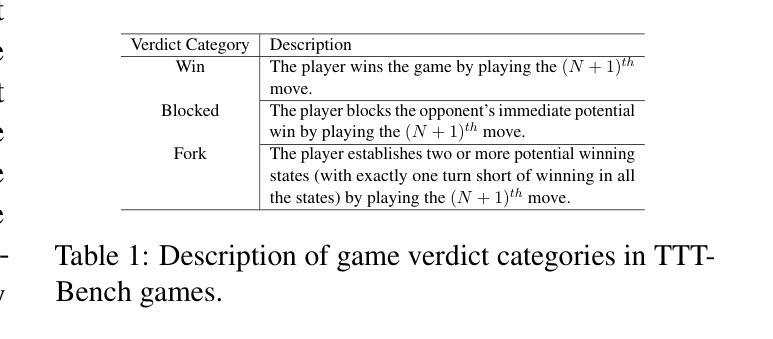
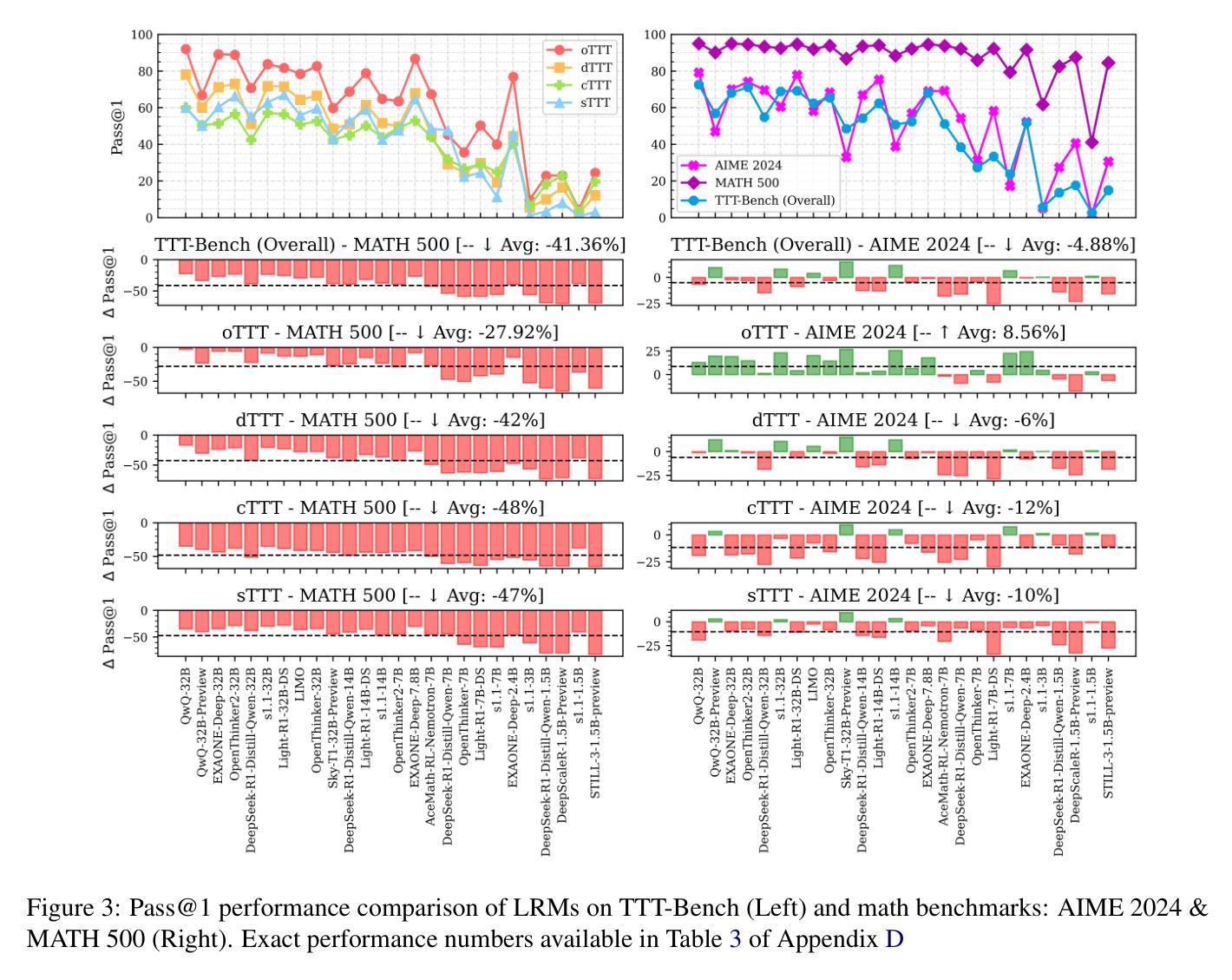
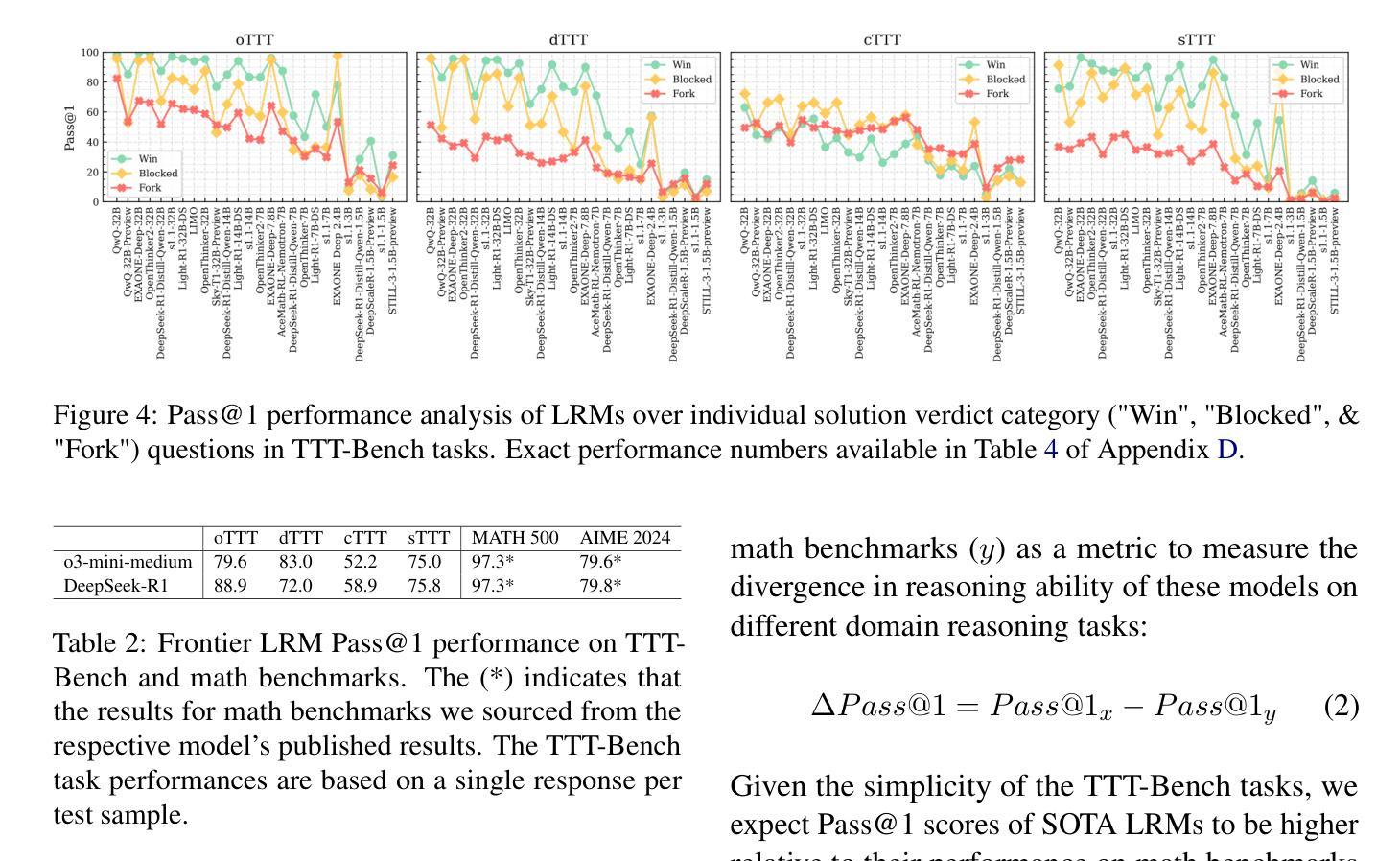
TTT-Bench: A Benchmark for Evaluating Reasoning Ability with Simple and Novel Tic-Tac-Toe-style Games
Authors:Prakamya Mishra, Jiang Liu, Jialian Wu, Xiaodong Yu, Zicheng Liu, Emad Barsoum
Large reasoning models (LRMs) have demonstrated impressive reasoning capabilities across a broad range of tasks including Olympiad-level mathematical problems, indicating evidence of their complex reasoning abilities. While many reasoning benchmarks focus on the STEM domain, the ability of LRMs to reason correctly in broader task domains remains underexplored. In this work, we introduce \textbf{TTT-Bench}, a new benchmark that is designed to evaluate basic strategic, spatial, and logical reasoning abilities in LRMs through a suite of four two-player Tic-Tac-Toe-style games that humans can effortlessly solve from a young age. We propose a simple yet scalable programmatic approach for generating verifiable two-player game problems for TTT-Bench. Although these games are trivial for humans, they require reasoning about the intentions of the opponent, as well as the game board’s spatial configurations, to ensure a win. We evaluate a diverse set of state-of-the-art LRMs, and \textbf{discover that the models that excel at hard math problems frequently fail at these simple reasoning games}. Further testing reveals that our evaluated reasoning models score on average $\downarrow$ 41% & $\downarrow$ 5% lower on TTT-Bench compared to MATH 500 & AIME 2024 respectively, with larger models achieving higher performance using shorter reasoning traces, where most of the models struggle on long-term strategic reasoning situations on simple and new TTT-Bench tasks.
大型推理模型(LRMs)已在包括奥林匹克级别数学问题在内的广泛任务中展示了令人印象深刻的推理能力,这证明了其复杂的推理能力。虽然许多推理基准测试集中在STEM领域,但LRMs在更广泛的任务领域中进行正确推理的能力仍然被忽视。在这项工作中,我们引入了TTT-Bench,这是一个新的基准测试,旨在通过四款两人玩的井字棋风格游戏来评估LRMs的基本战略、空间和逻辑推理能力,这些游戏是人类从年轻时就能轻松解决的问题。我们提出了一种简单且可扩展的程序化方法,可以生成可验证的两人游戏问题,用于TTT-Bench。虽然这些游戏对人类来说微不足道,但它们需要推理对手的意图以及棋盘的空间配置,以确保获胜。我们评估了一系列最先进的的大型推理模型,发现那些在硬数学问题中表现出色的模型在这些简单的推理游戏中经常失败。进一步的测试表明,我们的评估推理模型在TTT-Bench上的得分平均比MATH 500和AIME 2024低41%和5%,较大的模型在使用较短推理轨迹时表现更好,大多数模型在简单和新的TTT-Bench任务的长期战略推理情况下表现困难。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型推理模型在包括奥赛数学题目在内的多种任务中展现了强大的推理能力。然而,它们在基本策略、空间及逻辑推理方面的表现仍待探索。为此,研究提出了TTT-Bench基准测试,通过四款两人玩的井字棋风格游戏评估模型的能力。评估发现,擅长数学问题的模型在这些游戏中常表现不佳,且在简单任务上更依赖短期策略。大型模型在新任务上表现较好,但大多数模型在长远策略上仍有不足。
Key Takeaways
- 大型推理模型在多种任务中展现出强大的推理能力,包括解决奥赛数学题目。
- TTT-Bench是一个新的基准测试,旨在评估模型在基本策略、空间和逻辑推理方面的能力。
- 通过四款井字棋风格游戏评估模型能力,这些游戏虽然对人类来说简单,但需要理解对手意图和游戏空间配置。
- 擅长数学问题的模型在井字棋游戏中表现不佳,显示模型在不同类型任务中的表现差异。
- 大型模型在新任务上表现较好,但大多数模型在长远的策略推理方面存在困难。
- 模型在解决简单任务时更依赖短期策略,而非长期规划。
点此查看论文截图

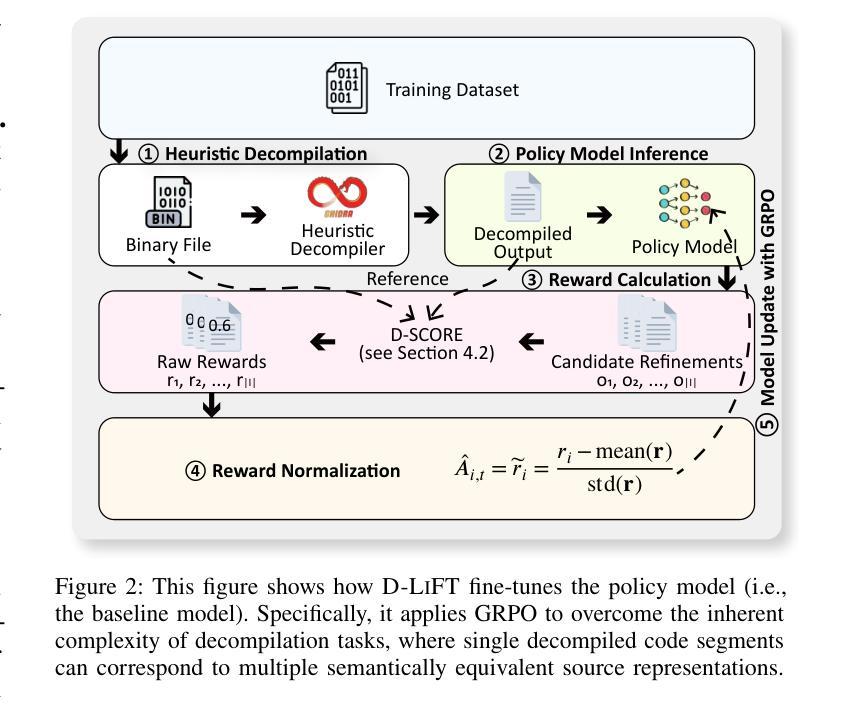
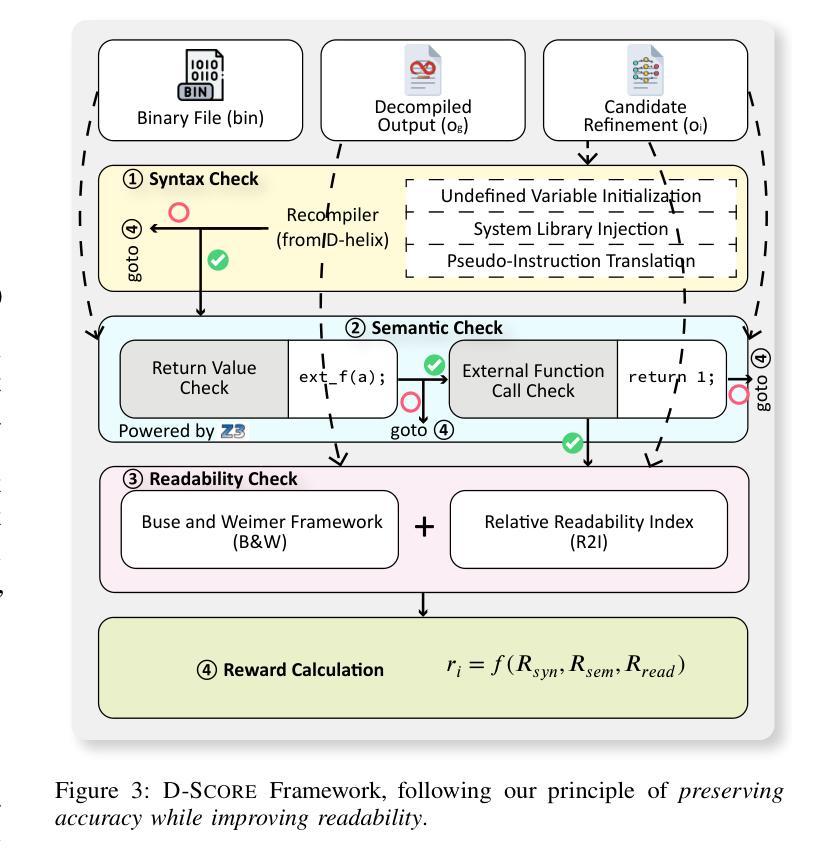
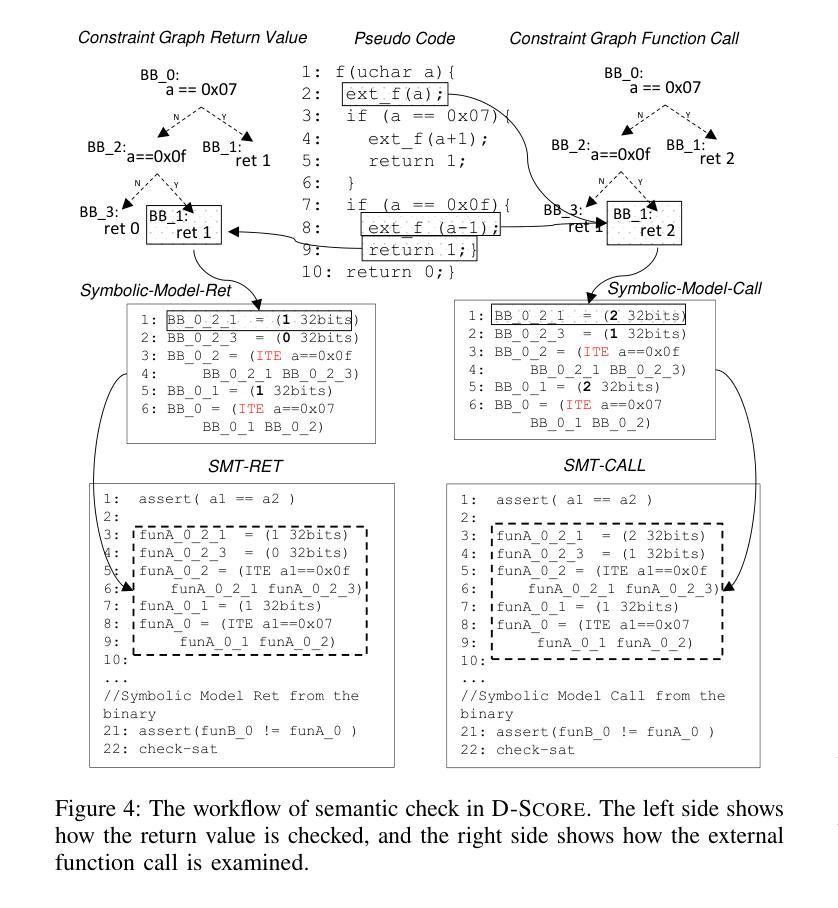
D-LiFT: Improving LLM-based Decompiler Backend via Code Quality-driven Fine-tuning
Authors:Muqi Zou, Hongyu Cai, Hongwei Wu, Zion Leonahenahe Basque, Arslan Khan, Berkay Celik, Dave, Tian, Antonio Bianchi, Ruoyu, Wang, Dongyan Xu
Decompilers, which reconstruct human-readable source code from binary executables, are vital to many security tasks. Yet, despite recent advances, their output often suffers from syntactic and semantic errors and remains difficult to read. Recently, with the advent of large language models (LLMs), researchers began to explore the potential of LLMs to refine decompiler output. Nevertheless, our study of these approaches reveals significant limitations, such as introducing new errors and relying on unreliable accuracy validation. In this paper, we present D-LiFT, an automated decompiler backend that harnesses and further trains LLMs to improve the quality of decompiled code via reinforcement learning (RL). Unlike prior work that overlooks preserving accuracy, D-LiFT adheres to a key principle for enhancing the quality of decompiled code: \textit{preserving accuracy while improving readability}. Central to D-LiFT, we propose D-SCORE, an integrated quality assessment system to score the decompiled code from multiple aspects. In line with our principle, D-SCORE assigns low scores to any inaccurate output and only awards higher scores for readability to code that passes the accuracy check. Specifically, D-SCORE first verifies the syntactic and semantic correctness via the compiler and symbolic execution; only if a candidate is deemed accurate, it then evaluates readability using established metrics to compare the LLM output with the original decompiled code. The score will then be fed back to the LLM for fine-tuning. Our implementation, based on Ghidra and a range of LLMs, demonstrates significant improvements for the accurate decompiled code from the coreutils and util-linux projects. Compared to baseline LLMs without D-SCORE-driven fine-tuning, D-LiFT produces 55.3% more improved decompiled functions, as measured by D-SCORE.
反编译器将从二进制可执行文件重建出人类可读的源代码,这对许多安全任务至关重要。然而,尽管最近有进展,其输出仍然常常存在语法和语义错误,难以阅读。最近,随着大型语言模型(LLM)的出现,研究者开始探索LLM对优化反编译器输出的潜力。然而,我们对这些方法的研究揭示了重大局限性,例如引入新的错误和依赖不可靠的准确性验证。在本文中,我们提出了D-LiFT,这是一个利用并进一步训练LLM通过强化学习(RL)提高反编译代码质量的自动化反编译器后端。与忽视保持准确性的早期工作不同,D-LiFT致力于提高反编译代码质量的关键原则:在提高可读性的同时保持准确性。在D-LiFT中,我们提出了D-SCORE,一个综合的质量评估系统,从多个方面对反编译代码进行评分。根据我们的原则,D-SCORE对任何不准确的输出都给予低分,只对通过准确性检查的代码的readability授予高分。具体来说,D-SCORE首先通过编译器和符号执行验证语法和语义的正确性;只有当候选者被视为准确时,它才会使用既定的度量标准来评估可读性,将LLM输出与原始反编译代码进行比较。然后,分数将反馈到LLM进行微调。我们的实现基于Ghidra和一系列LLM,显著提高了coreutils和util-linux项目的准确反编译代码的质量。与没有D-SCORE驱动的微调的基线LLM相比,D-LiFT产生的反编译函数改进了55.3%,这是通过D-SCORE衡量的。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
利用大型语言模型(LLM)的潜力改进反编译器的输出质量,提升代码可读性。本文提出一种自动化反编译器后端D-LiFT,结合强化学习(RL)进一步训练LLM,提高反编译代码的质量。D-LiFT遵循一个关键原则:在提高可读性的同时保证准确性。提出集成质量评估系统D-SCORE,从多方面对反编译代码进行评分,确保准确性的同时评估可读性。
Key Takeaways
- 反编译器对于安全任务至关重要,但其输出通常存在语法和语义错误,难以阅读。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在改进反编译器输出方面展现潜力,但存在引入新错误和依赖不可靠的准确性验证等局限性。
- D-LiFT是一种自动化反编译器后端,利用强化学习(RL)和LLM提高反编译代码质量,注重提高可读性的同时保证准确性。
- D-SCORE是集成质量评估系统,用于多方面评估反编译代码,确保输出准确性并通过编译器和符号执行验证。
- D-SCORE在准确性检查通过后,才评估可读性,并使用现有度量标准比较LLM输出与原始反编译代码。
点此查看论文截图