⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-14 更新
PiPViT: Patch-based Visual Interpretable Prototypes for Retinal Image Analysis
Authors:Marzieh Oghbaie, Teresa Araújoa, Hrvoje Bogunović
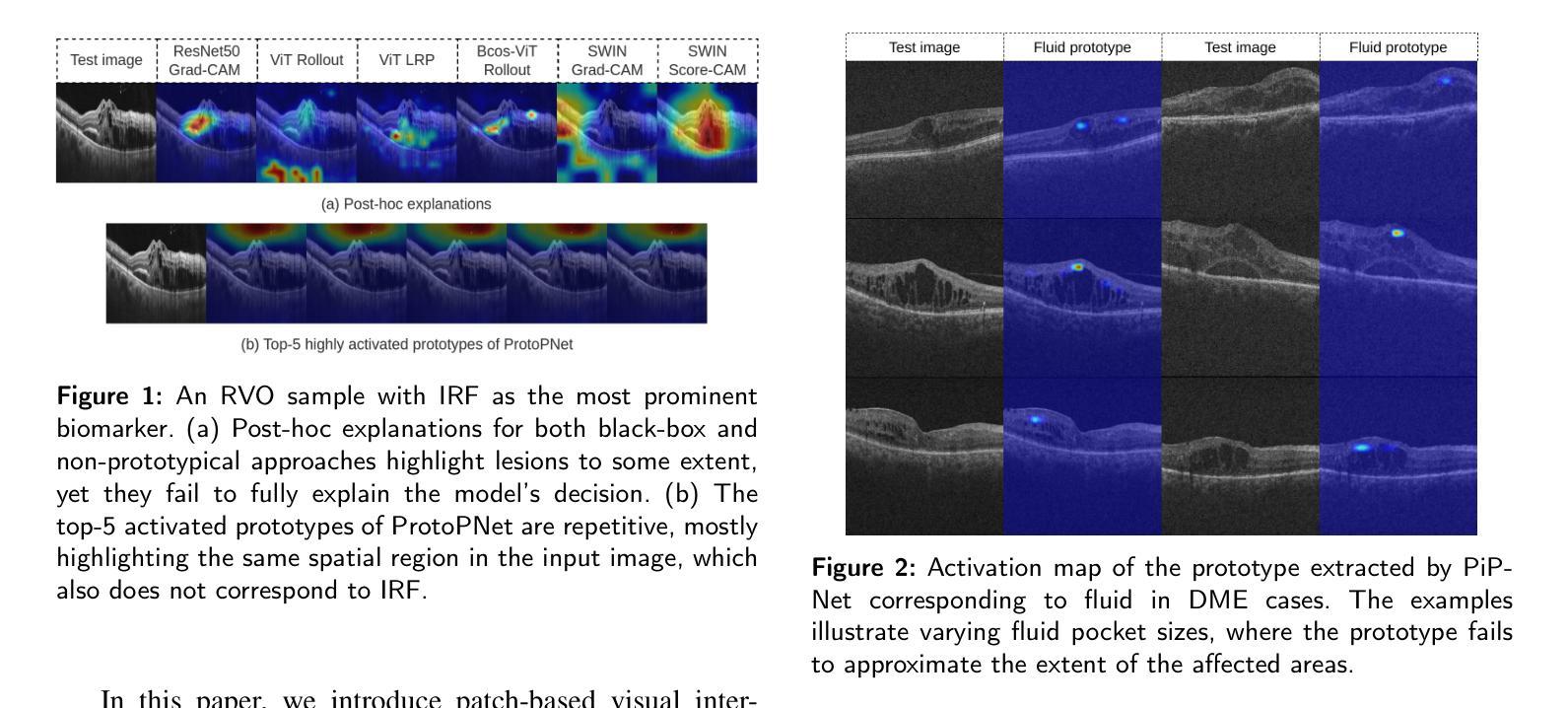
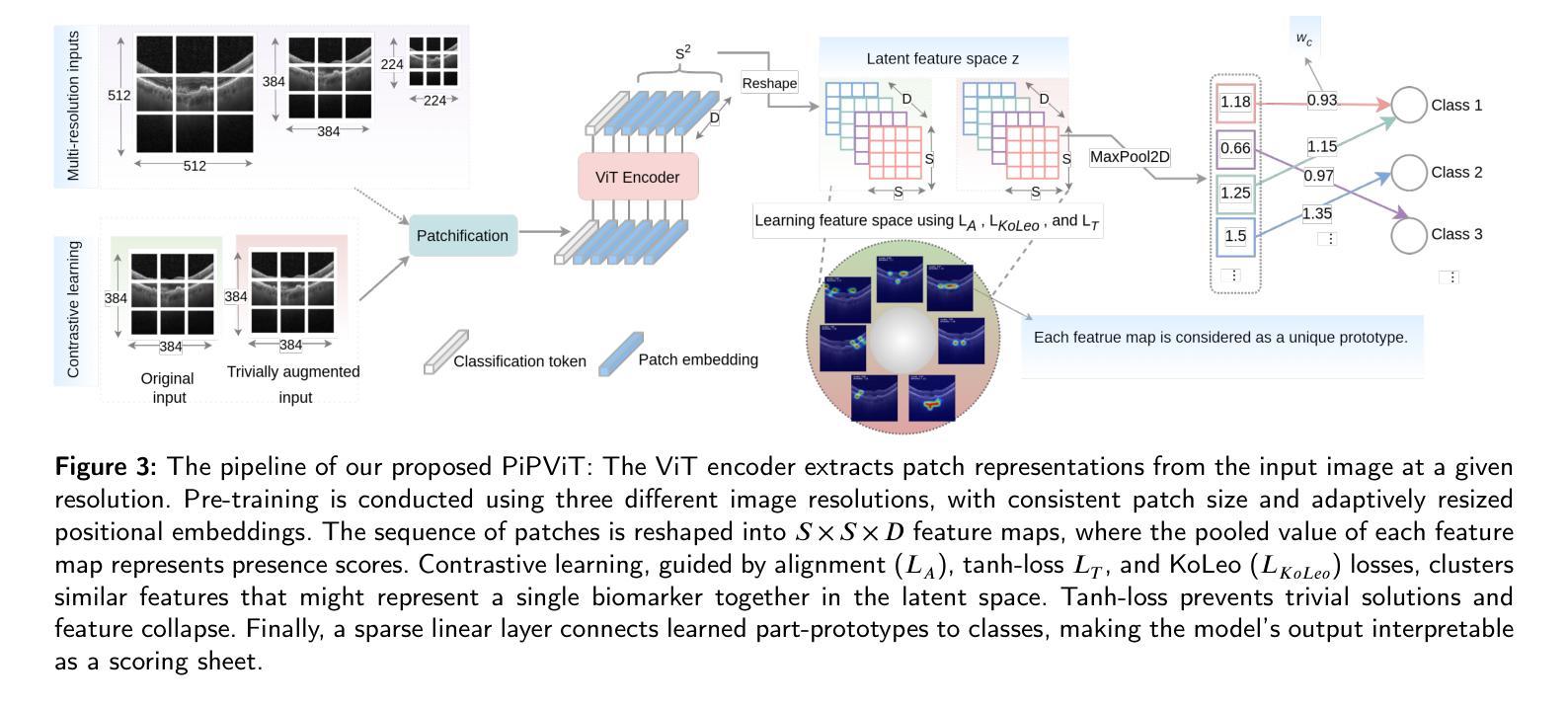
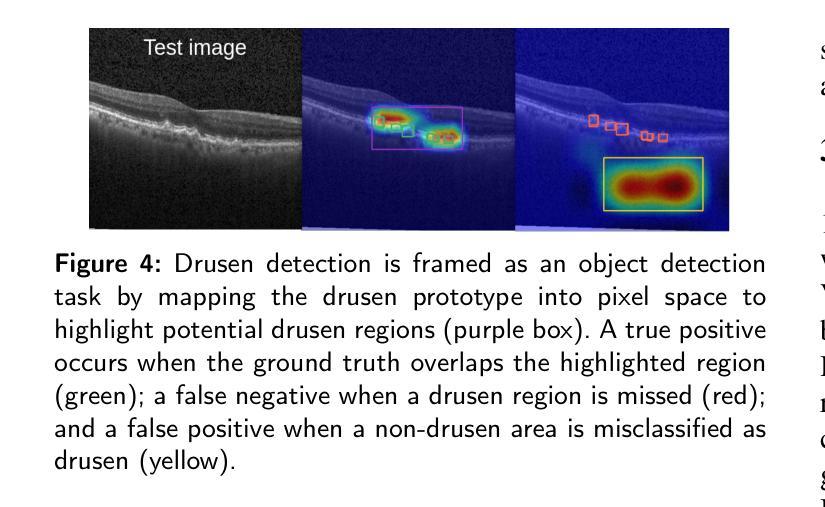
Background and Objective: Prototype-based methods improve interpretability by learning fine-grained part-prototypes; however, their visualization in the input pixel space is not always consistent with human-understandable biomarkers. In addition, well-known prototype-based approaches typically learn extremely granular prototypes that are less interpretable in medical imaging, where both the presence and extent of biomarkers and lesions are critical. Methods: To address these challenges, we propose PiPViT (Patch-based Visual Interpretable Prototypes), an inherently interpretable prototypical model for image recognition. Leveraging a vision transformer (ViT), PiPViT captures long-range dependencies among patches to learn robust, human-interpretable prototypes that approximate lesion extent only using image-level labels. Additionally, PiPViT benefits from contrastive learning and multi-resolution input processing, which enables effective localization of biomarkers across scales. Results: We evaluated PiPViT on retinal OCT image classification across four datasets, where it achieved competitive quantitative performance compared to state-of-the-art methods while delivering more meaningful explanations. Moreover, quantitative evaluation on a hold-out test set confirms that the learned prototypes are semantically and clinically relevant. We believe PiPViT can transparently explain its decisions and assist clinicians in understanding diagnostic outcomes. Github page: https://github.com/marziehoghbaie/PiPViT
背景与目标:基于原型的方法通过学习精细的局部原型来提高可解释性,但它们在输入像素空间的可视化并不总是与人们可理解的生物标志物相一致。此外,众所周知的基于原型的方法通常学习极其精细的原型,在医学成像中不太容易解释,其中生物标志物和病变的存在和程度都至关重要。方法:针对这些挑战,我们提出了PiPViT(基于补丁的视觉可解释原型),这是一种用于图像识别的固有可解释原型模型。借助视觉变压器(ViT),PiPViT捕获补丁之间的长距离依赖关系,仅使用图像级标签来学习稳健、人类可解释的原型,这些原型可以近似病变的范围。此外,PiPViT受益于对比学习和多分辨率输入处理,这可以在各种尺度上有效地定位生物标志物。结果:我们在四个数据集上评估了PiPViT在视网膜OCT图像分类上的表现,与最先进的方法相比,它在定量性能上具有竞争力,同时提供了更有意义的解释。此外,在保留测试集上的定量评估证实,所学习的原型在语义和临床上都很重要。我们相信PiPViT能够透明地解释其决策,帮助临床医生理解诊断结果。GitHub页面:https://github.com/marziehoghbaie/PiPViT
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
PiPViT是一种基于视觉Transformer的、用于图像识别的可解释原型模型。它通过捕获图像补丁间的长期依赖关系来学习稳健、可解释的原型,以近似病变范围,仅使用图像级标签。该方法通过对比学习和多分辨率输入处理,实现在不同尺度上有效定位生物标志物。在视网膜OCT图像分类的四个数据集上的评估表明,与最新技术相比,该方法在定量性能上具有竞争力,同时提供更有意义的解释。
Key Takeaways
- PiPViT是一个基于视觉Transformer的原型模型,旨在提高医疗图像识别的可解释性。
- 该模型通过学习稳健、可解释的原型来近似病变范围,这些原型能够捕获图像补丁间的长期依赖关系。
- PiPViT利用对比学习和多分辨率输入处理来有效定位生物标志物,并能在不同尺度上实现定位。
- 在视网膜OCT图像分类的四个数据集上,PiPViT的定量性能具有竞争力,且与最新技术相比,其解释性更强。
- PiPViT提供的解释有助于临床医生理解诊断结果。
- PiPViT通过GitHub页面公开可用,便于研究和应用。
点此查看论文截图

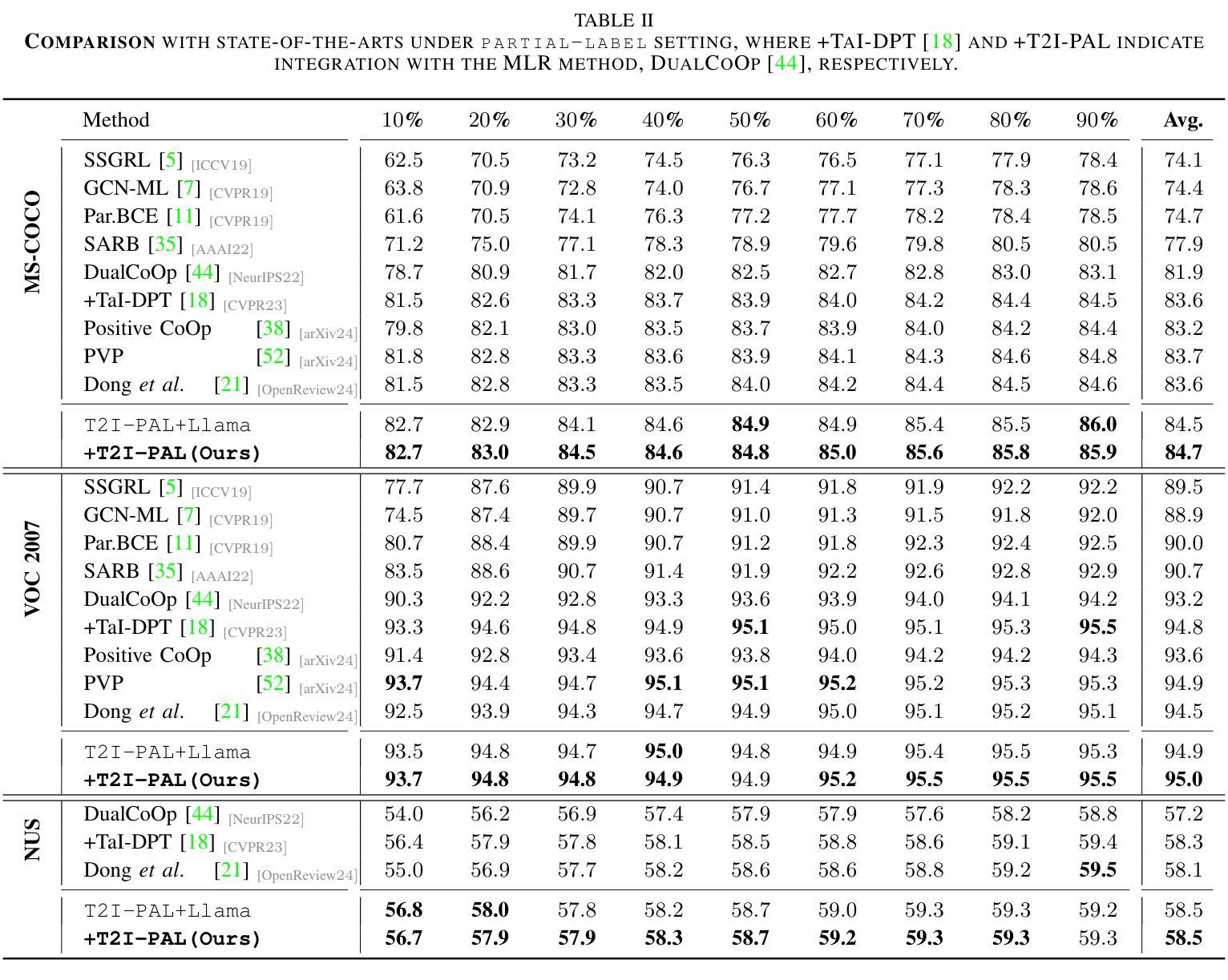
Text to Image for Multi-Label Image Recognition with Joint Prompt-Adapter Learning
Authors:Chun-Mei Feng, Kai Yu, Xinxing Xu, Salman Khan, Rick Siow Mong Goh, Wangmeng Zuo, Yong Liu
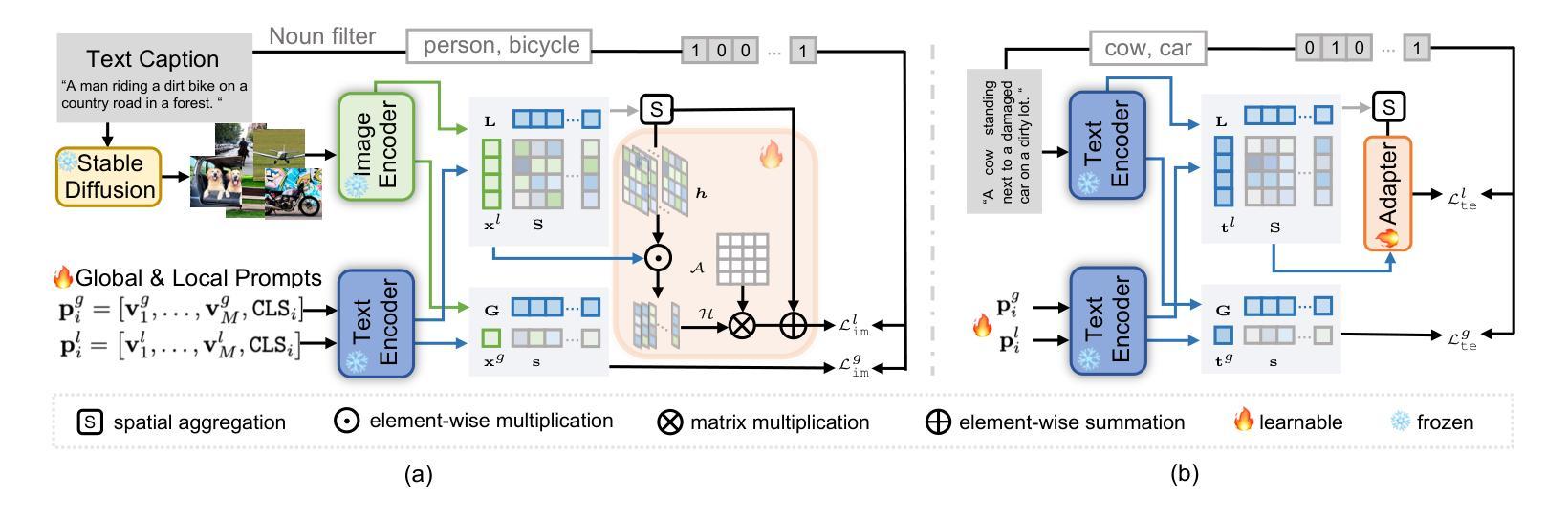
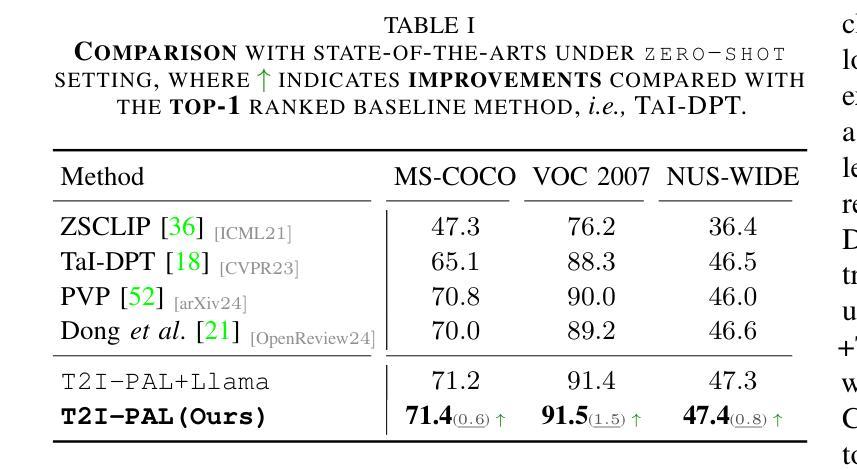
Benefited from image-text contrastive learning, pre-trained vision-language models, e.g., CLIP, allow to direct leverage texts as images (TaI) for parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT). While CLIP is capable of making image features to be similar to the corresponding text features, the modality gap remains a nontrivial issue and limits image recognition performance of TaI. Using multi-label image recognition (MLR) as an example, we present a novel method, called T2I-PAL to tackle the modality gap issue when using only text captions for PEFT. The core design of T2I-PAL is to leverage pre-trained text-to-image generation models to generate photo-realistic and diverse images from text captions, thereby reducing the modality gap. To further enhance MLR, T2I-PAL incorporates a class-wise heatmap and learnable prototypes. This aggregates local similarities, making the representation of local visual features more robust and informative for multi-label recognition. For better PEFT, we further combine both prompt tuning and adapter learning to enhance classification performance. T2I-PAL offers significant advantages: it eliminates the need for fully semantically annotated training images, thereby reducing the manual annotation workload, and it preserves the intrinsic mode of the CLIP model, allowing for seamless integration with any existing CLIP framework. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks, including MS-COCO, VOC2007, and NUS-WIDE, show that our T2I-PAL can boost recognition performance by 3.47% in average above the top-ranked state-of-the-art methods.
得益于图文对比学习,预训练的视觉语言模型(例如CLIP)允许直接使用文本作为图像(TaI)进行参数高效的微调(PEFT)。虽然CLIP能够使图像特征对应于文本特征,但模态差距仍然是一个不可忽视的问题,并限制了TaI的图像识别性能。以多标签图像识别(MLR)为例,我们提出了一种新方法,称为T2I-PAL,旨在解决仅使用文本描述进行PEFT时的模态差距问题。T2I-PAL的核心设计是利用预训练的文本到图像生成模型,根据文本描述生成逼真的、多样化的图像,从而减少模态差距。为了进一步增强MLR,T2I-PAL结合了类别热图和可学习原型。这聚合了局部相似性,使局部视觉特征的表示对于多标签识别更加稳健和富有信息。为了更好地进行PEFT,我们进一步结合了提示调整和适配器学习,以提高分类性能。T2I-PAL具有明显的优势:它不需要完全语义注释的训练图像,从而减少了手动注释的工作量,同时保留了CLIP模型的内在模式,可以无缝集成到任何现有的CLIP框架中。在MS-COCO、VOC2007和NUS-WIDE等多个基准测试上的大量实验表明,我们的T2I-PAL方法可以比现有最先进的方法平均提高3.47%的识别性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了利用图像文本对比学习预训练的视觉语言模型,如CLIP,能够将文本作为图像进行参数效率微调(PEFT)。针对使用仅文本描述进行PEFT时的模态间隙问题,提出了一种新方法T2I-PAL。其核心设计是利用预训练的文本到图像生成模型从文本描述生成逼真的多样化图像,从而减少模态间隙。T2I-PAL还结合了类级热图和可学习原型,增强多标签识别的表现力。通过结合提示调优和适配器学习,可进一步提高PEFT的分类性能。T2I-PAL具有显著优势,无需完全语义注释的训练图像,减少手动注释工作量,并可与任何现有的CLIP框架无缝集成。在多个基准测试上的实验表明,T2I-PAL的性能优于其他顶级先进方法,平均提高了3.47%。
Key Takeaways
- 利用图像文本对比学习预训练的视觉语言模型(如CLIP)实现参数效率微调(PEFT)。
- 使用仅文本描述进行PEFT时存在模态间隙问题。
- T2I-PAL方法通过利用预训练的文本到图像生成模型来生成逼真的多样化图像来解决模态间隙问题。
- T2I-PAL结合类级热图和可学习原型,提高多标签识别的表现力。
- T2I-PAL结合了提示调优和适配器学习技术来进一步增强性能。
- T2I-PAL无需完全语义注释的训练图像,降低了手动注释工作量。
- 在多个基准测试上,T2I-PAL的性能优于其他顶级先进方法,平均提高了3.47%。
点此查看论文截图

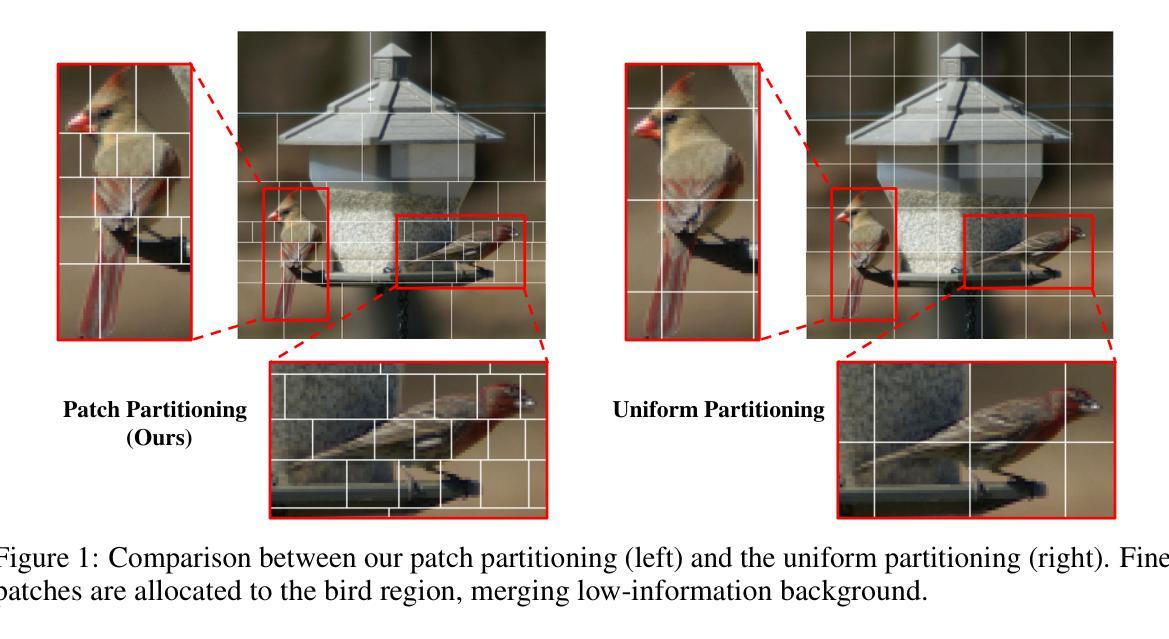
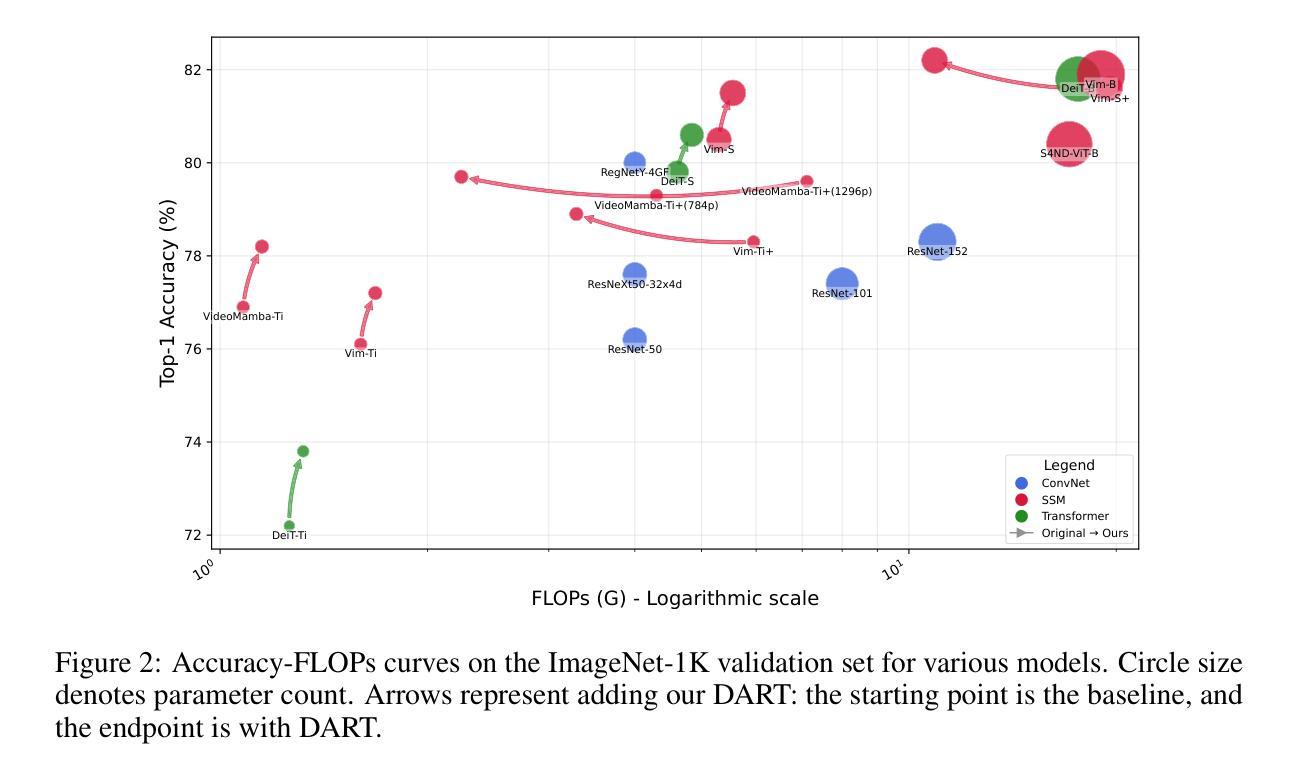
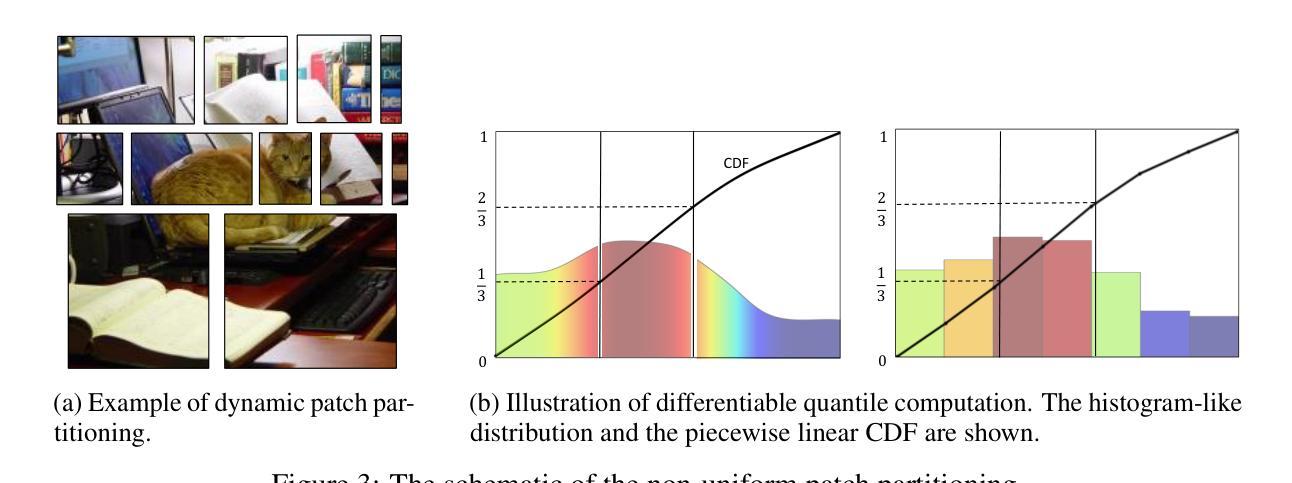
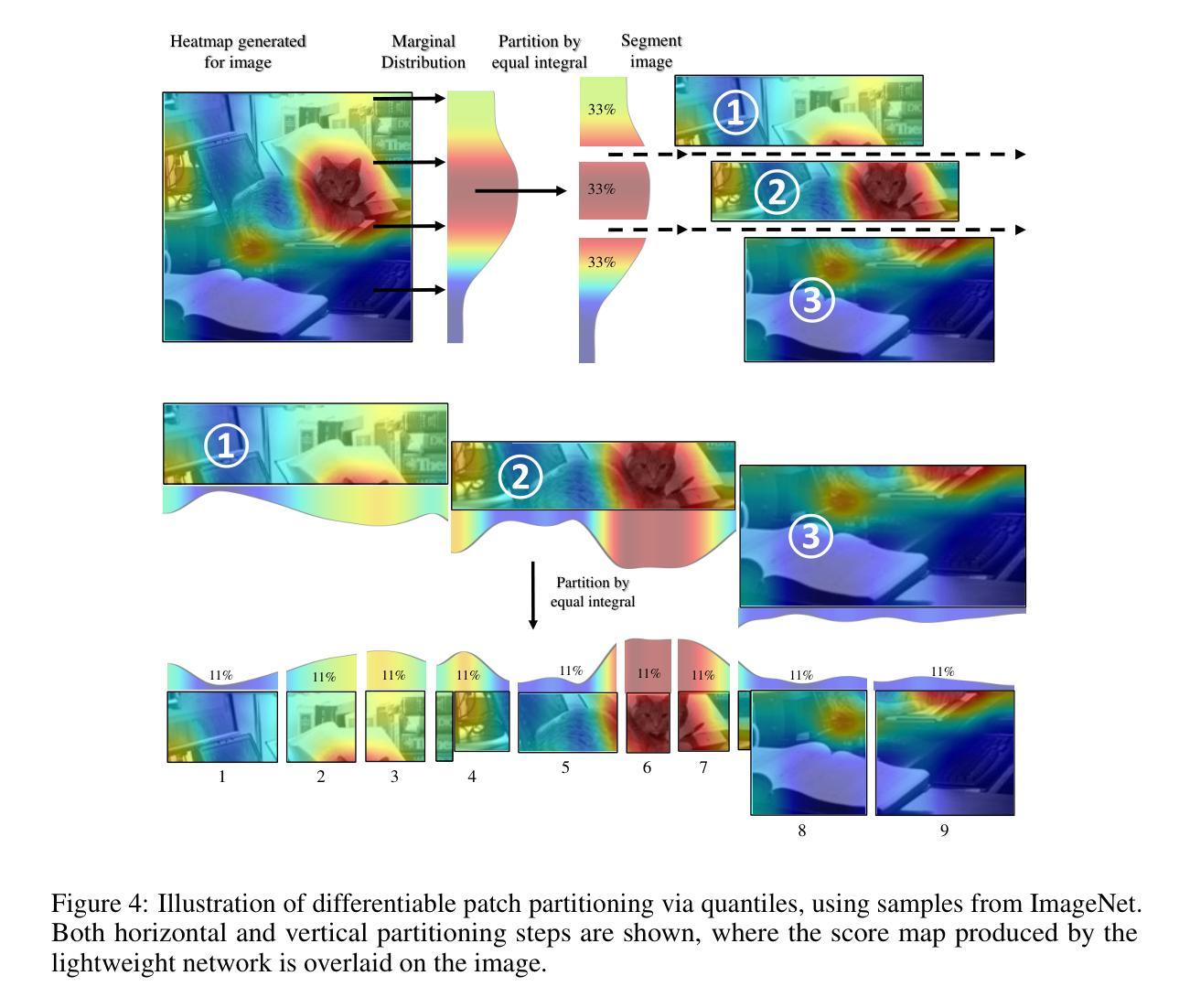
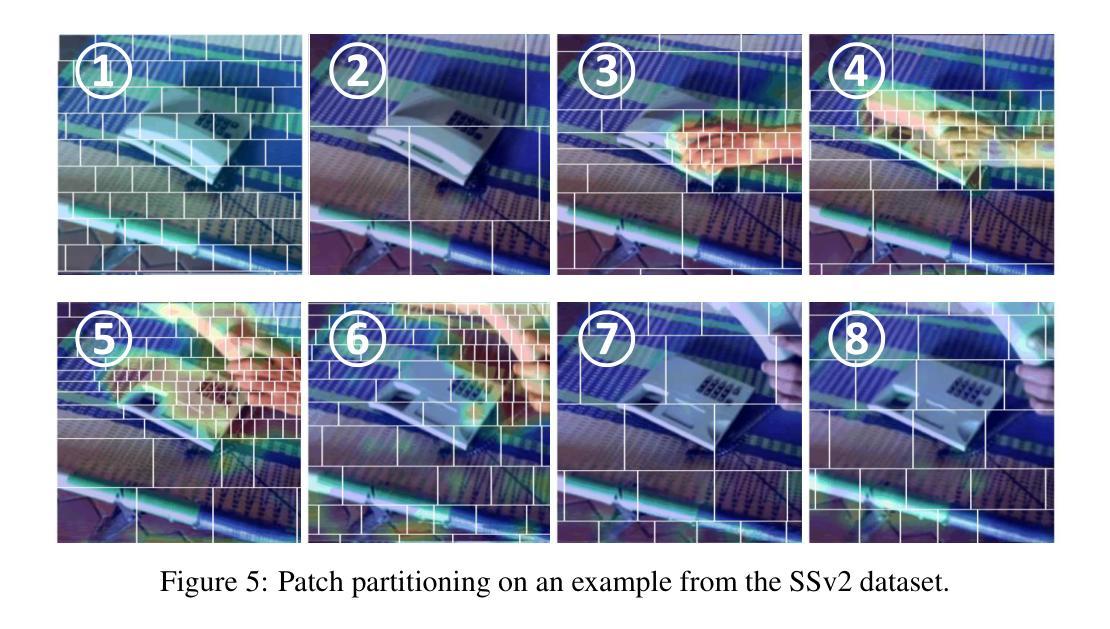
DART: Differentiable Dynamic Adaptive Region Tokenizer for Vision Transformer and Mamba
Authors:Shicheng Yin, Kaixuan Yin, Yang Liu, Weixing Chen, Liang Lin
Recently, non-convolutional models such as the Vision Transformer (ViT) and Vision Mamba (Vim) have achieved remarkable performance in computer vision tasks. However, their reliance on fixed-size patches often results in excessive encoding of background regions and omission of critical local details, especially when informative objects are sparsely distributed. To address this, we introduce a fully differentiable Dynamic Adaptive Region Tokenizer (DART), which adaptively partitions images into content-dependent patches of varying sizes. DART combines learnable region scores with piecewise differentiable quantile operations to allocate denser tokens to information-rich areas. Despite introducing only approximately 1 million (1M) additional parameters, DART improves accuracy by 2.1% on DeiT (ImageNet-1K). Unlike methods that uniformly increase token density to capture fine-grained details, DART offers a more efficient alternative, achieving 45% FLOPs reduction with superior performance. Extensive experiments on DeiT, Vim, and VideoMamba confirm that DART consistently enhances accuracy while incurring minimal or even reduced computational overhead. Code is available at https://github.com/HCPLab-SYSU/DART.
最近,非卷积模型,如Vision Transformer(ViT)和Vision Mamba(Vim)在计算机视觉任务中取得了显著的成绩。然而,它们对固定大小图块的依赖往往导致背景区域的过度编码和关键局部细节的遗漏,特别是在信息对象稀疏分布的情况下。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了全可微动态自适应区域令牌器(DART),它可以根据内容自适应地将图像分割成不同大小的图块。DART结合可学习的区域分数和分段可微分的分位操作,将更密集的令牌分配给信息丰富的区域。尽管只引入了大约1百万(1M)个额外的参数,DART在DeiT(ImageNet-1K)上的准确率提高了2.1%。与通过统一增加令牌密度来捕捉细粒度细节的方法不同,DART提供了更有效的替代方案,在性能优越的同时实现了45%的FLOPs减少。在DeiT、Vim和VideoMamba上的大量实验证实,DART在增加最小甚至减少计算开销的同时,始终提高了准确性。代码可在https://github.com/HCPLab-SYSU/DART获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code is available at https://github.com/HCPLab-SYSU/DART
Summary
非卷积模型如Vision Transformer(ViT)和Vision Mamba(Vim)在计算机视觉任务中表现出卓越性能,但它们依赖固定大小的补丁(patches),容易导致背景区域过度编码和关键局部细节遗漏。为解决此问题,我们推出全微分动态自适应区域令牌器(DART),它能自适应地将图像分割成大小不同的内容相关补丁。DART结合可学习区域分数和分段微分量化操作,在信息丰富区域分配更密集的令牌。仅增加约一百万(1M)参数,DART在DeiT(ImageNet-1K)上的准确率提高2.1%。不同于通过均匀增加令牌密度来捕捉细节的方法,DART提供更高效的替代方案,在保持或降低计算开销的同时实现性能提升。代码可在https://github.com/HCPLab-SYSU/DART上找到。
Key Takeaways
- 非卷积模型如ViT和Vim在计算机视觉任务中表现优异,但存在固定大小补丁导致的背景区域过度编码和关键局部细节遗漏问题。
- DART通过自适应图像分割技术,能够根据不同内容划分补丁大小。
- DART结合可学习区域分数和分段微分量化操作,实现信息丰富区域的密集令牌分配。
- DART在仅增加少量参数的情况下,能显著提高模型性能。
- 与其他均匀增加令牌密度的方法相比,DART更有效率,能在减少计算开销的同时提升性能。
- DART在DeiT、Vim和VideoMamba等模型上均能有效提升性能。
点此查看论文截图

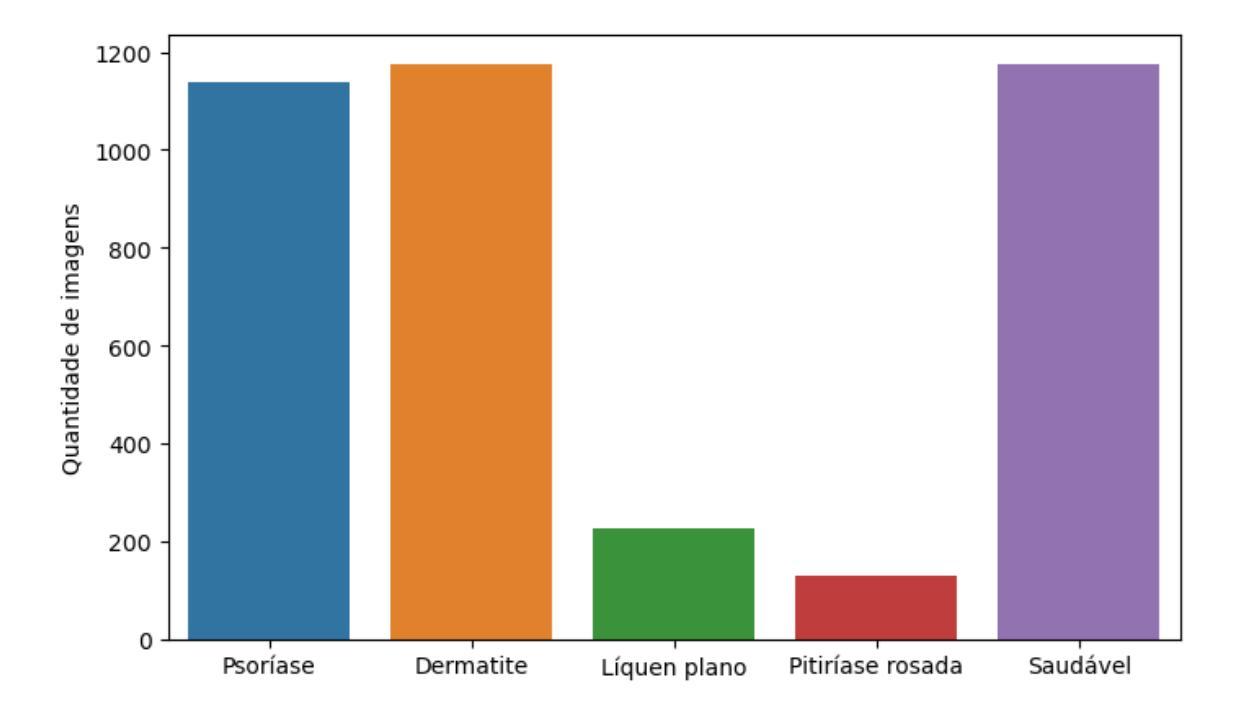
Detecção da Psoríase Utilizando Visão Computacional: Uma Abordagem Comparativa Entre CNNs e Vision Transformers
Authors:Natanael Lucena, Fábio S. da Silva, Ricardo Rios
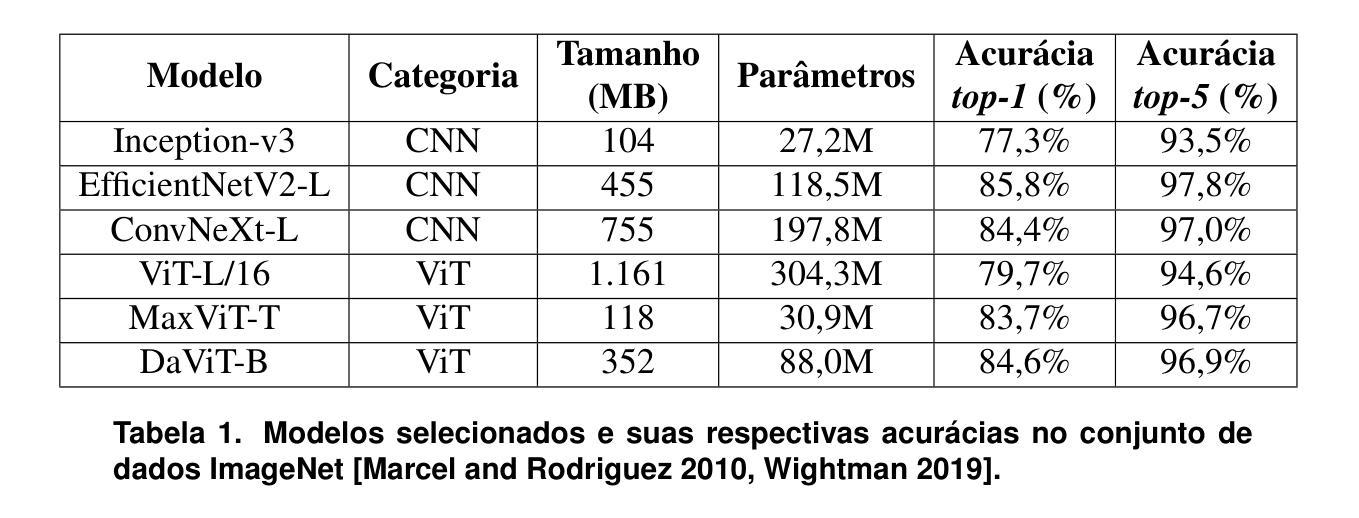
This paper presents a comparison of the performance of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs) in the task of multi-classifying images containing lesions of psoriasis and diseases similar to it. Models pre-trained on ImageNet were adapted to a specific data set. Both achieved high predictive metrics, but the ViTs stood out for their superior performance with smaller models. Dual Attention Vision Transformer-Base (DaViT-B) obtained the best results, with an f1-score of 96.4%, and is recommended as the most efficient architecture for automated psoriasis detection. This article reinforces the potential of ViTs for medical image classification tasks.
本文比较了卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)在分类包含牛皮癣病变及其类似疾病的图像任务中的性能。使用在ImageNet上预训练的模型来适应特定数据集。两者都达到了较高的预测指标,但ViT在小模型方面的性能更突出。双注意力视觉转换器基础(DaViT-B)获得了最佳结果,f1分数为96.4%,被推荐为自动化牛皮癣检测的最有效架构。本文再次证明了ViT在医学图像分类任务中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, in Portuguese language, 2 figures, 2 tables, and 4 formulas. To be published in the Proceedings of the LII Brazilian Integrated Software and Hardware Seminar 2025 (SEMISH 2025)
Summary
本文比较了卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉转换器(ViTs)在分类含有牛皮癣病变及其类似疾病的图像任务中的性能。基于ImageNet预训练的模型被改编为特定数据集。两者均获得较高的预测指标,但ViTs在小型模型上的表现尤为出色。其中,Dual Attention Vision Transformer-Base(DaViT-B)表现最佳,f1分数达到96.4%,被推荐为自动化牛皮癣检测的最有效架构。本文再次证明了ViTs在医学图像分类任务中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 对比了CNN和ViT在医学图像分类任务中的性能。
- ViTs在小型模型上的表现优于CNN。
- DaViT-B在牛皮癣病变图像分类中表现最佳,f1分数达到96.4%。
- DaViT-B被推荐为自动化牛皮癣检测的最有效架构。
- 预训练模型在特定数据集上的改编对于任务性能至关重要。
- ViTs在医学图像分类任务中具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图