⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-15 更新
ChartReasoner: Code-Driven Modality Bridging for Long-Chain Reasoning in Chart Question Answering
Authors:Caijun Jia, Nan Xu, Jingxuan Wei, Qingli Wang, Lei Wang, Bihui Yu, Junnan Zhu
Recently, large language models have shown remarkable reasoning capabilities through long-chain reasoning before responding. However, how to extend this capability to visual reasoning tasks remains an open challenge. Existing multimodal reasoning approaches transfer such visual reasoning task into textual reasoning task via several image-to-text conversions, which often lose critical structural and semantic information embedded in visualizations, especially for tasks like chart question answering that require a large amount of visual details. To bridge this gap, we propose ChartReasoner, a code-driven novel two-stage framework designed to enable precise, interpretable reasoning over charts. We first train a high-fidelity model to convert diverse chart images into structured ECharts codes, preserving both layout and data semantics as lossless as possible. Then, we design a general chart reasoning data synthesis pipeline, which leverages this pretrained transport model to automatically and scalably generate chart reasoning trajectories and utilizes a code validator to filter out low-quality samples. Finally, we train the final multimodal model using a combination of supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning on our synthesized chart reasoning dataset and experimental results on four public benchmarks clearly demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed ChartReasoner. It can preserve the original details of the charts as much as possible and perform comparably with state-of-the-art open-source models while using fewer parameters, approaching the performance of proprietary systems like GPT-4o in out-of-domain settings.
最近,大型语言模型通过长链推理应答展现出卓越的推理能力,然而,如何将这一能力拓展到视觉推理任务仍是一项挑战。现有的多模态推理方法通过多次图像到文本的转换,将视觉推理任务转换为文本推理任务,这往往会丢失可视化中嵌入的关键结构和语义信息,尤其是在需要大量视觉细节的任务(如图表问答)中。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了ChartReasoner,这是一种代码驱动的新型两阶段框架,旨在实现对图表的精确、可解释推理。我们首先训练一个高保真模型,将各种图表图像转换为结构化的ECharts代码,尽可能无损地保留布局和数据语义。然后,我们设计了一个通用的图表推理数据合成管道,它利用这个预训练的传输模型来自动和可扩展地生成图表推理轨迹,并利用代码验证器来过滤掉低质量样本。最后,我们在合成的图表推理数据集上,使用监督微调与强化学习相结合的方法训练最终的多模态模型。在四个公开基准测试上的实验结果清楚地证明了我们的ChartReasoner的有效性。它能够尽可能保留图表的原始细节,与使用较少参数的先进开源模型相比表现相当,并在域外环境中接近GPT-4o等专有系统的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型具备强大的推理能力,但在视觉推理任务上仍面临挑战。现有方法通过图像到文本的转换来完成视觉推理任务,但这种转换常导致重要结构和语义信息的丢失。为解决这个问题,我们提出了ChartReasoner,这是一个新颖的、以代码驱动的两阶段框架,用于实现精确的图表推理。首先,我们训练了一个高保真模型,将各种图表图像转换为结构化的ECharts代码,尽可能保持布局和数据语义的无损性。接着,我们设计了一个通用的图表推理数据合成管道,利用预训练的传输模型自动、大规模地生成图表推理轨迹,并使用代码验证器过滤掉低质量样本。最后,在合成的图表推理数据集上进行训练和测试,实验结果表明我们的ChartReasoner模型在多个公共基准测试上表现优异,能够尽可能保留原始图表细节,与使用较少参数的先进开源模型相比表现相当,并在域外设置中接近GPT-4o等专有系统的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在视觉推理任务上存在挑战。
- 现有方法通过图像到文本的转换完成视觉推理任务,但这种转换会导致信息丢失。
- ChartReasoner是一个新颖的、以代码驱动的两阶段框架,用于实现精确的图表推理。
- ChartReasoner包括三个阶段:高保真模型训练、图表推理数据合成和模型训练与测试。
- 高保真模型将图表图像转换为结构化的ECharts代码,保持布局和数据语义的无损性。
- ChartReasoner在多个公共基准测试上表现优异,能够保留原始图表细节。
点此查看论文截图

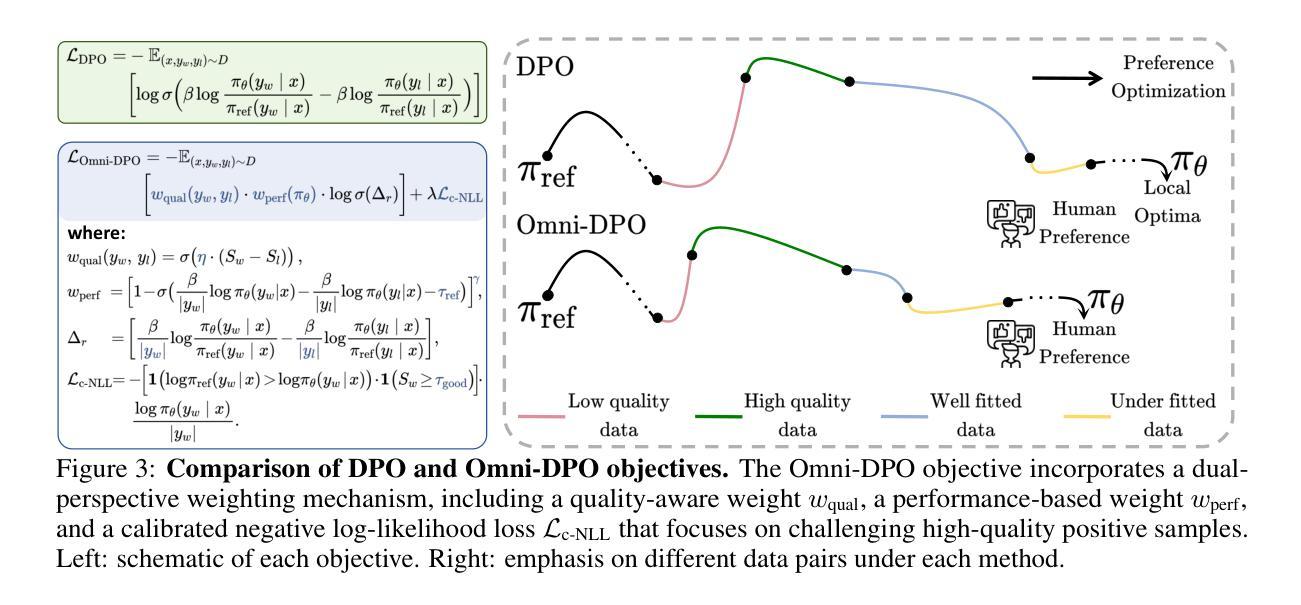
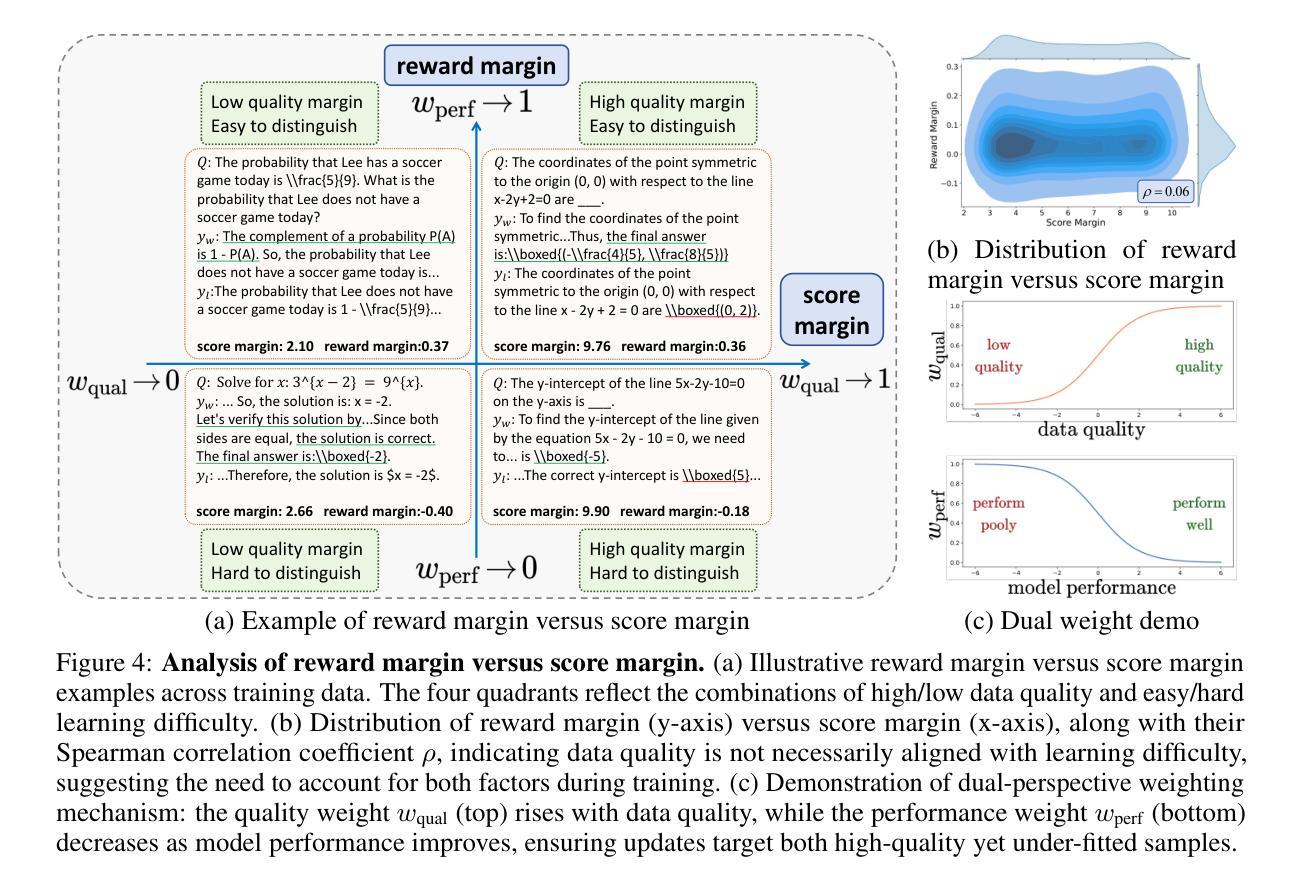
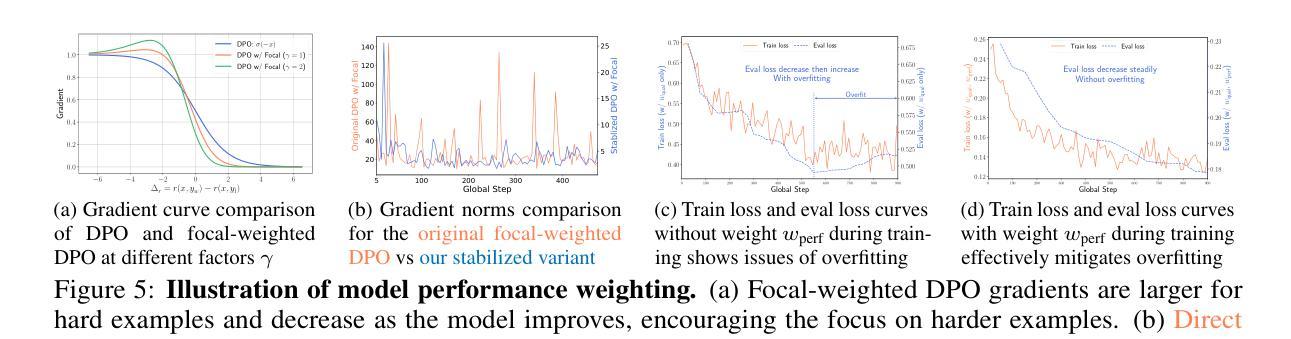
Omni-DPO: A Dual-Perspective Paradigm for Dynamic Preference Learning of LLMs
Authors:Shangpin Peng, Weinong Wang, Zhuotao Tian, Senqiao Yang, Xing Wu, Haotian Xu, Chengquan Zhang, Takashi Isobe, Baotian Hu, Min Zhang
Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) has become a cornerstone of reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) due to its simplicity and efficiency. However, existing DPO-based approaches typically treat all preference pairs uniformly, ignoring critical variations in their inherent quality and learning utility, leading to suboptimal data utilization and performance. To address this challenge, we propose Omni-DPO, a dual-perspective optimization framework that jointly accounts for (1) the inherent quality of each preference pair and (2) the model’s evolving performance on those pairs. By adaptively weighting samples according to both data quality and the model’s learning dynamics during training, Omni-DPO enables more effective training data utilization and achieves better performance. Experimental results on various models and benchmarks demonstrate the superiority and generalization capabilities of Omni-DPO. On textual understanding tasks, Gemma-2-9b-it finetuned with Omni-DPO beats the leading LLM, Claude 3 Opus, by a significant margin of 6.7 points on the Arena-Hard benchmark. On mathematical reasoning tasks, Omni-DPO consistently outperforms the baseline methods across all benchmarks, providing strong empirical evidence for the effectiveness and robustness of our approach. Code and models will be available at https://github.com/pspdada/Omni-DPO.
直接偏好优化(DPO)因其简单高效而成为强化学习人类反馈(RLHF)中的基石。然而,现有的基于DPO的方法通常对所有偏好对一视同仁,忽略了它们内在质量和学习效用的重要差异,导致数据利用不足和性能不佳。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了Omni-DPO,这是一个双视角优化框架,同时考虑了(1)每个偏好对的内在质量和(2)模型在这些对上的不断变化的性能。Omni-DPO通过根据数据质量和模型在训练过程中的学习动态来适应性地加权样本,从而实现了更有效的训练数据利用和更好的性能。在各种模型和基准测试上的实验结果表明了Omni-DPO的优越性和泛化能力。在文本理解任务上,使用Omni-DPO微调过的Gemma-2-9b-it在Arena-Hard基准测试上大幅超越了领先的LLM Claude 3 Opus,得分高出6.7分。在数学推理任务上,Omni-DPO在所有基准测试上均优于基线方法,为我们方法的有效性和稳健性提供了强有力的实证证据。代码和模型将在https://github.com/pspdada/Omni-DPO上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习中的直接偏好优化(DPO)是强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)中的核心方法,因其简单高效而受到重视。然而,现有DPO方法忽略偏好对内在质量和学习效用的差异,导致数据利用和性能不佳。为解决这个问题,我们提出Omni-DPO,一个双视角优化框架,同时考虑每个偏好对的内在质量和模型的动态性能。通过根据数据质量和模型学习动态自适应地加权样本,Omni-DPO实现了更有效的训练数据利用和更好的性能。实验结果表明Omni-DPO的优越性和通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 直接偏好优化(DPO)是强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)中的核心方法。
- 现有DPO方法忽略偏好对内在质量和学习效用的差异,导致数据利用和性能不佳。
- Omni-DPO是一个双视角优化框架,考虑每个偏好对的内在质量和模型的动态性能。
- Omni-DPO通过自适应加权样本,实现了更有效的训练数据利用。
- Omni-DPO在多种模型和基准测试上表现出优越性和通用性。
- 在文本理解任务上,使用Omni-DPO的Gemma-2-9b-it模型在Arena-Hard基准测试上显著超越了领先的LLM模型Claude 3 Opus。
- 在数学推理任务上,Omni-DPO在所有基准测试上均表现出色,提供了强有力的实证证据支持其有效性和稳健性。
点此查看论文截图


CoRT: Code-integrated Reasoning within Thinking
Authors:Chengpeng Li, Zhengyang Tang, Ziniu Li, Mingfeng Xue, Keqin Bao, Tian Ding, Ruoyu Sun, Benyou Wang, Xiang Wang, Junyang Lin, Dayiheng Liu
Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) like o1 and DeepSeek-R1 have shown remarkable progress in natural language reasoning with long chain-of-thought (CoT), yet they remain inefficient or inaccurate when handling complex mathematical operations. Addressing these limitations through computational tools (e.g., computation libraries and symbolic solvers) is promising, but it introduces a technical challenge: Code Interpreter (CI) brings external knowledge beyond the model’s internal text representations, thus the direct combination is not efficient. This paper introduces CoRT, a post-training framework for teaching LRMs to leverage CI effectively and efficiently. As a first step, we address the data scarcity issue by synthesizing code-integrated reasoning data through Hint-Engineering, which strategically inserts different hints at appropriate positions to optimize LRM-CI interaction. We manually create 30 high-quality samples, upon which we post-train models ranging from 1.5B to 32B parameters, with supervised fine-tuning, rejection fine-tuning and reinforcement learning. Our experimental results demonstrate that Hint-Engineering models achieve 4% and 8% absolute improvements on DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B respectively, across five challenging mathematical reasoning datasets. Furthermore, Hint-Engineering models use about 30% fewer tokens for the 32B model and 50% fewer tokens for the 1.5B model compared with the natural language models. The models and code are available at https://github.com/ChengpengLi1003/CoRT.
像O1和DeepSeek-R1等大型推理模型(LRMs)在自然语言推理方面取得了显著的进步,尤其是在长链思维(CoT)方面,但它们在处理复杂的数学运算时仍然效率低下或不够准确。通过计算工具(例如计算库和符号求解器)来解决这些限制很有希望,但也带来了技术挑战:代码解释器(CI)引入了模型内部文本表示之外的外部知识,因此直接组合并不高效。本文介绍了CoRT,这是一个用于教授LRM有效且高效地使用CI的后期训练框架。作为第一步,我们通过Hint-Engineering合成代码集成推理数据来解决数据稀缺问题,这是一种战略性地在不同位置插入提示以优化LRM-CI交互的方法。我们手动创建了30个高质量样本,在这些样本上对范围从1.5B到32B参数的模型进行再训练,采用有监督微调、拒绝微调和强化学习的方法。我们的实验结果表明,在五个具有挑战性的数学推理数据集上,Hint-Engineering模型在DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B和DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B上分别实现了4%和8%的绝对改进。此外,与自然语言模型相比,Hint-Engineering模型使用的令牌数量减少了约30%(针对32B模型)和50%(针对1.5B模型)。模型和代码可在https://github.com/ChengpengLi1003/CoRT获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF work in progress
摘要
大型推理模型(LRMs)如o1和DeepSeek-R1在自然语言推理方面展现出显著进展,但在处理复杂数学运算时仍存效率或准确度问题。本文通过计算工具(如计算库和符号求解器)来解决这些限制具有潜力,但这也带来了技术挑战。模型以外的知识无法通过模型的内部文本表示来引入,因此直接组合并不高效。本文介绍了一种名为CoRT的后期训练框架,该框架可有效地教授LRMs如何利用计算解释器(CI)。首先,我们解决了数据稀缺的问题,通过提示工程(Hint-Engineering)合成代码集成推理数据,在适当的位置插入不同的提示以优化LRM-CI交互。我们在30个高质量样本上进行了后期训练,这些模型参数范围从1.5B到32B,采用监督微调、拒绝微调和强化学习进行训练。实验结果表明,提示工程模型在DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B和DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B上分别实现了4%和8%的绝对改进,跨越五个具有挑战性的数学推理数据集。此外,提示工程模型使用的令牌数量比自然语言模型少约30%(对于32B模型)和50%(对于1.5B模型)。模型和代码可在https://github.com/ChengpengLi1003/CoRT获取。
关键见解
- 大型推理模型在处理复杂数学运算时存在效率和准确度问题。
- 计算工具(如计算库和符号求解器)为解决这些问题提供了潜力,但需要解决技术挑战。
- CoRT框架是一种用于教授大型推理模型有效利用计算解释器的方法。
- 提示工程是一种新的策略,用于合成代码集成推理数据,优化LRM与CI的交互。
- 通过在多个数据集上进行实验验证,提示工程模型在数学推理任务上实现了显著的性能提升。
- 提示工程模型使用的令牌数量相较于自然语言模型有所减少,表明其效率有所提高。
点此查看论文截图

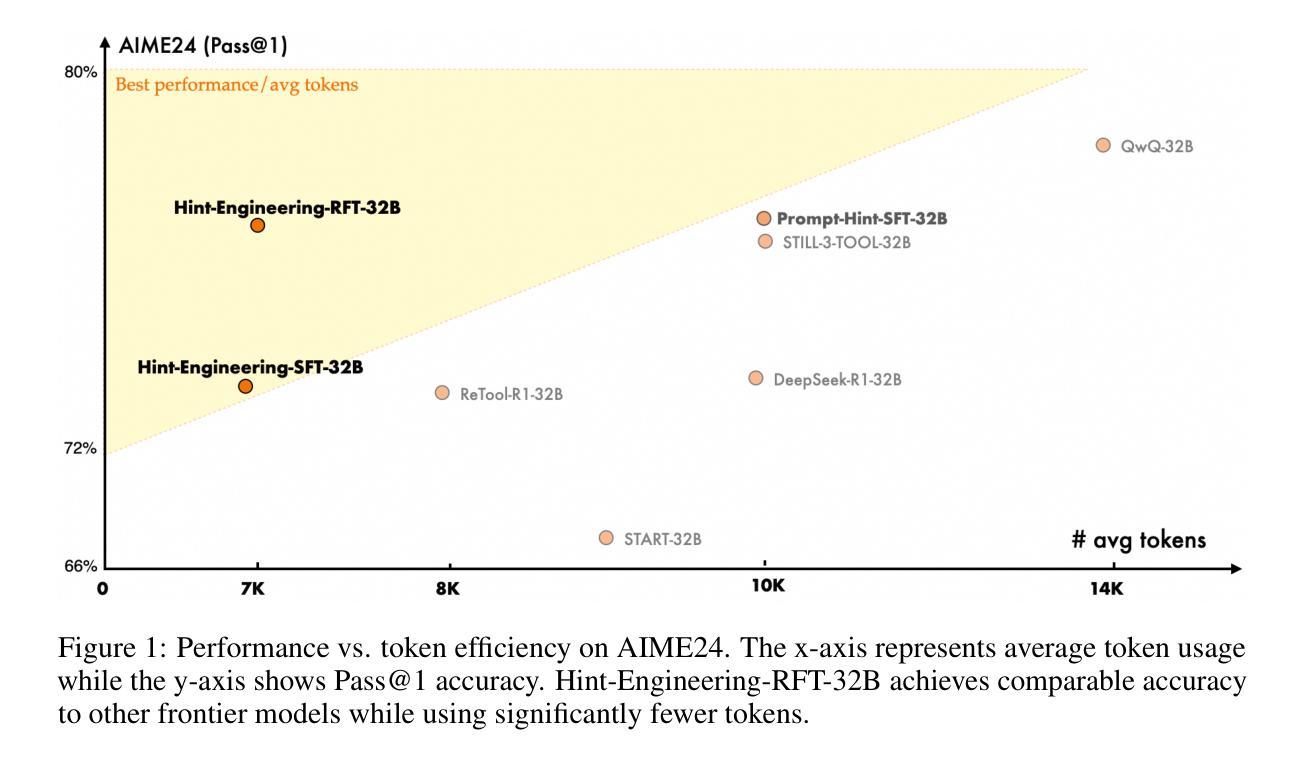
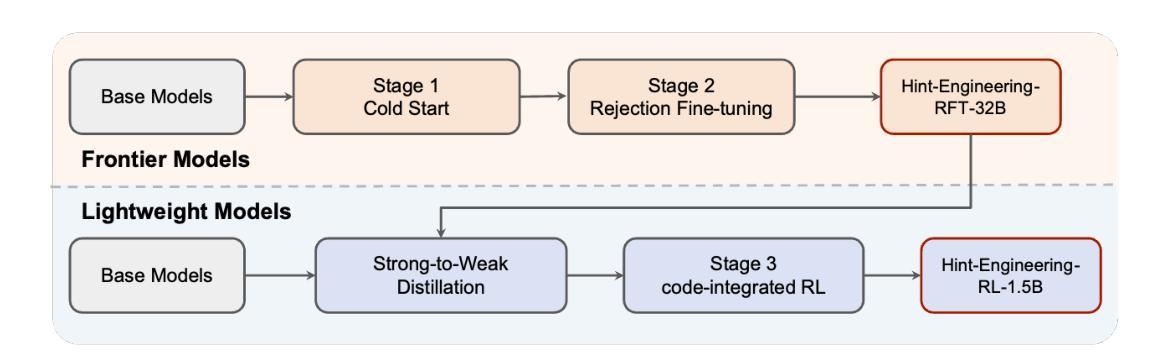
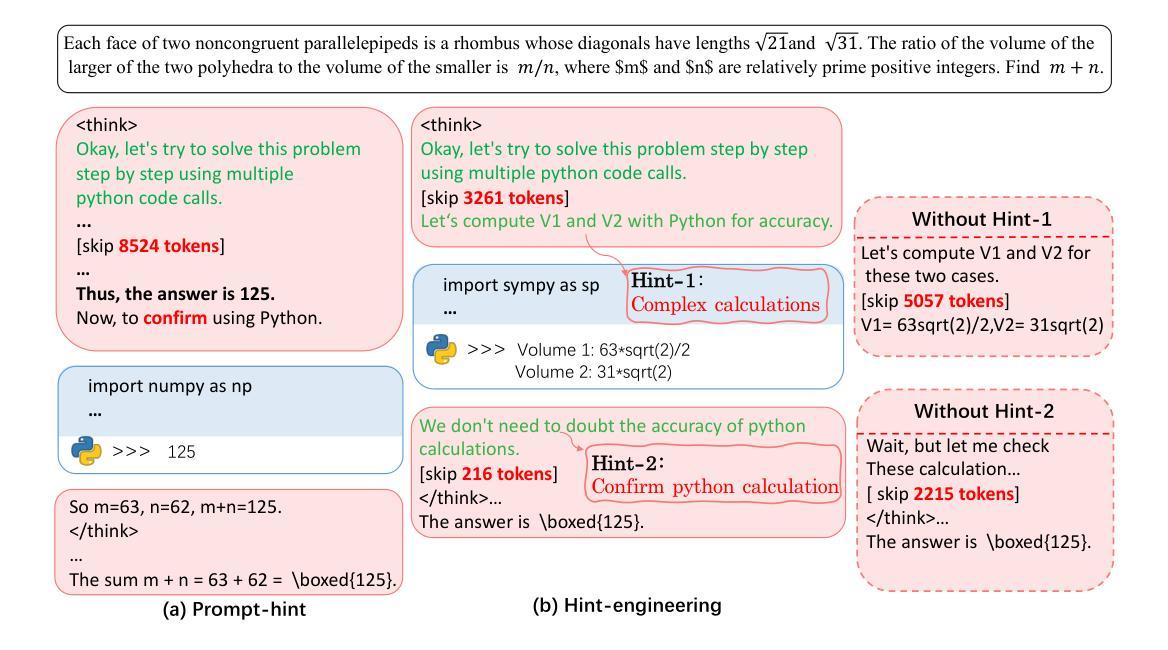
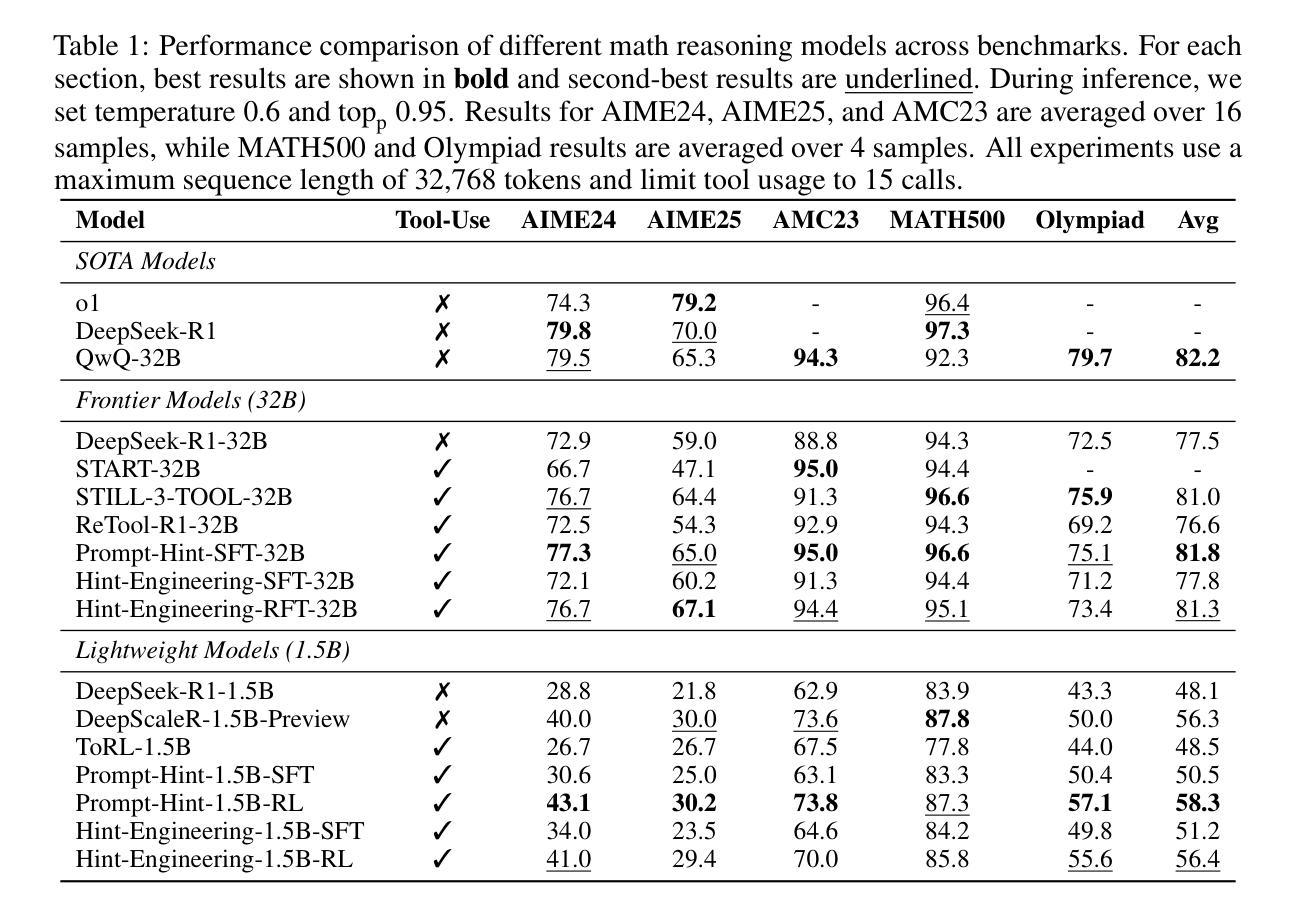
Towards Efficient and Effective Alignment of Large Language Models
Authors:Yuxin Jiang
Large language models (LLMs) exhibit remarkable capabilities across diverse tasks, yet aligning them efficiently and effectively with human expectations remains a critical challenge. This thesis advances LLM alignment by introducing novel methodologies in data collection, training, and evaluation. We first address alignment data collection. Existing approaches rely heavily on manually curated datasets or proprietary models. To overcome these limitations, we propose Lion, an adversarial distillation framework that iteratively refines training data by identifying and generating challenging instructions, enabling state-of-the-art zero-shot reasoning. Additionally, we introduce Web Reconstruction (WebR), a fully automated framework that synthesizes instruction-tuning data directly from raw web documents, significantly improving data diversity and scalability over existing synthetic data methods. Next, we enhance alignment training through novel optimization techniques. We develop Learning to Edit (LTE), a framework that enables LLMs to efficiently integrate new knowledge while preserving existing information. LTE leverages meta-learning to improve both real-time and batch knowledge updates. Furthermore, we introduce Bridging and Modeling Correlations (BMC), a refinement of Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) that explicitly captures token-level correlations in preference data, leading to superior alignment across QA and mathematical reasoning tasks. Finally, we tackle the challenge of evaluating alignment. Existing benchmarks emphasize response quality but overlook adherence to specific constraints. To bridge this gap, we introduce FollowBench, a multi-level, fine-grained benchmark assessing LLMs’ ability to follow complex constraints across diverse instruction types. Our results expose key weaknesses in current models’ constraint adherence, offering insights for future improvements.
大型语言模型(LLM)在不同任务中展现出显著的能力,然而,如何有效且高效地将其与人类期望进行对齐仍然是一个关键挑战。本论文通过引入数据收集、训练和评估方面的新型方法论来促进LLM的对齐。我们首先解决对齐数据收集的问题。现有方法严重依赖于人工编制的数据集或专有模型。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了Lion,一种对抗蒸馏框架,它通过识别生成具有挑战性的指令来迭代优化训练数据,从而实现最先进的零射击理。此外,我们还介绍了WebR(网络重建),一个全自动的框架,直接从原始网页文档中合成指令调整数据,大大提高了数据多样性和可扩展性,超过了现有的合成数据方法。接下来,我们通过新型优化技术增强对齐训练。我们开发了Learning to Edit(LTE),一个框架,使LLM能够高效集成新知识的同时保留现有信息。LTE利用元学习来提高实时和批量知识更新的能力。此外,我们对直接偏好优化(DPO)进行了改进,推出了Bridging and Modeling Correlations(BMC),它能够明确捕捉偏好数据中的令牌级关联,从而在问答和数学推理任务中实现对齐的卓越表现。最后,我们解决了评估对齐的挑战。现有基准测试侧重于响应质量,但忽视了特定的约束条件。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了FollowBench,这是一个多层次、精细的基准测试,评估LLM遵循各种指令类型中复杂约束的能力。我们的结果揭示了当前模型在约束遵循方面的关键弱点,为未来的改进提供了见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF PhD thesis
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在各项任务中展现出惊人的能力,但如何有效地与人类期望对齐仍然是一个关键问题。本研究通过引入数据收集、训练和评估方面的新方法,推动了LLM的对齐性。通过对抗蒸馏框架Lion和Web Reconstruction(WebR)全自动框架来解决数据收集问题,显著提高数据的多样性和可扩展性。此外,还通过优化技术提高对齐训练效果,开发了Learning to Edit(LTE)框架和Bridging and Modeling Correlations(BMC)方法。最后,本研究解决了评估对齐性的挑战,引入了FollowBench多层次精细基准测试,评估LLMs遵循复杂指令的能力。研究揭示了当前模型在遵循约束方面的弱点,为未来的改进提供了重要线索。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在多样任务中表现出卓越的能力,但对齐于人类期望仍然是一个挑战。
- 引入对抗蒸馏框架Lion和Web Reconstruction(WebR)解决数据收集问题,提高数据多样性和可扩展性。
- 采用优化技术增强对齐训练效果,包括Learning to Edit(LTE)和Bridging and Modeling Correlations(BMC)。
- 现有评估基准测试主要关注响应质量,忽视了特定约束的遵循情况。
- 引入FollowBench多层次精细基准测试,评估LLMs遵循复杂指令的能力。
- 研究发现当前模型在遵循约束方面存在关键弱点。
点此查看论文截图

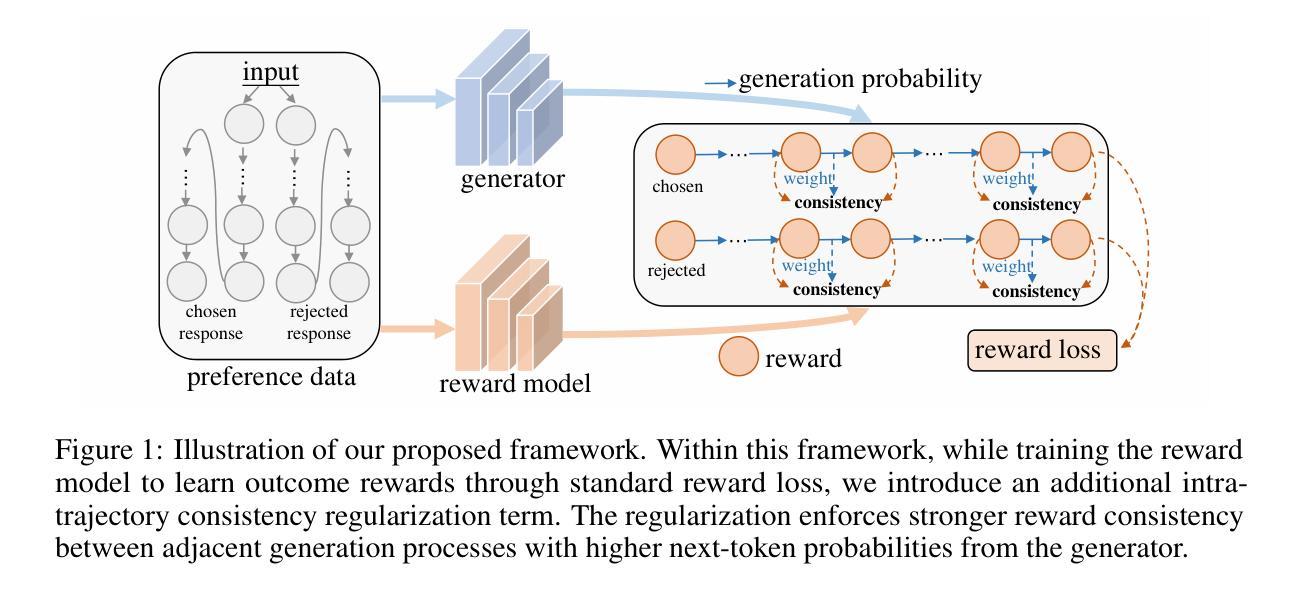
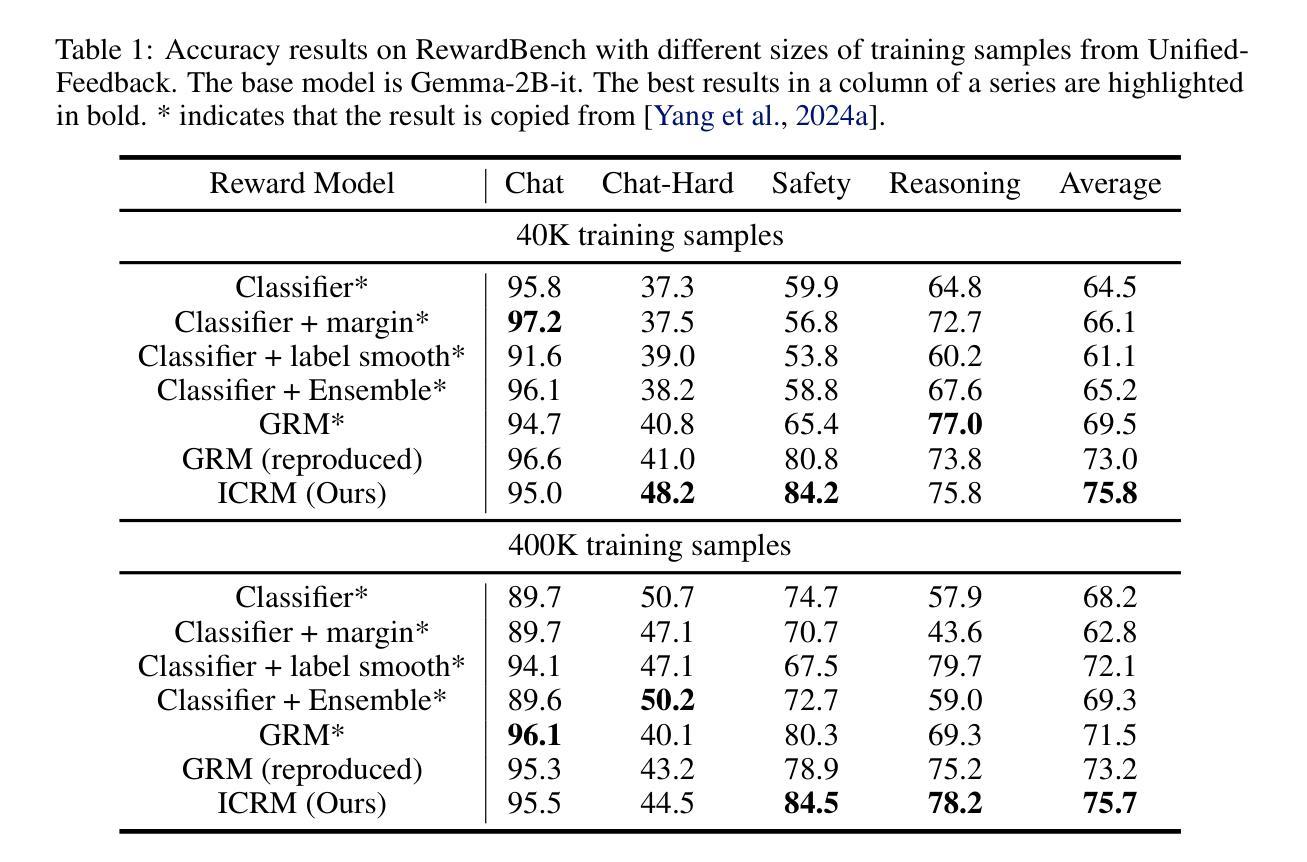
Intra-Trajectory Consistency for Reward Modeling
Authors:Chaoyang Zhou, Shunyu Liu, Zengmao Wang, Di Wang, Rong-Cheng Tu, Bo Du, Dacheng Tao
Reward models are critical for improving large language models (LLMs), particularly in reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) or inference-time verification. Current reward modeling typically relies on scores of overall responses to learn the outcome rewards for the responses. However, since the response-level scores are coarse-grained supervision signals, the reward model struggles to identify the specific components within a response trajectory that truly correlate with the scores, leading to poor generalization on unseen responses. In this paper, we propose to leverage generation probabilities to establish reward consistency between processes in the response trajectory, which allows the response-level supervisory signal to propagate across processes, thereby providing additional fine-grained signals for reward learning. Building on analysis under the Bayesian framework, we develop an intra-trajectory consistency regularization to enforce that adjacent processes with higher next-token generation probability maintain more consistent rewards. We apply the proposed regularization to the advanced outcome reward model, improving its performance on RewardBench. Besides, we show that the reward model trained with the proposed regularization induces better DPO-aligned policies and achieves better best-of-N (BON) inference-time verification results. Our code is provided in https://github.com/chaoyang101/ICRM.
奖励模型对于改进大型语言模型(LLM)至关重要,特别是在人类反馈强化学习(RLHF)或推理时间验证中。当前的奖励建模通常依赖于整体响应的分数来学习响应的结果奖励。然而,由于响应级别的分数是粗粒度的监督信号,奖励模型难以识别响应轨迹内真正与分数相关的特定组件,导致在未见过的响应上泛化性能差。在本文中,我们提出利用生成概率来建立响应轨迹中过程之间的奖励一致性,这允许响应级别的监督信号在过程之间传播,从而为奖励学习提供额外的细粒度信号。我们在贝叶斯框架的分析基础上,开发了一种轨迹内一致性正则化方法,以强制具有更高下一个令牌生成概率的相邻过程保持更一致的奖励。我们将所提出的正则化应用于高级结果奖励模型,在RewardBench上提高了其性能。此外,我们还表明,使用所提出正则化训练的奖励模型能诱发更好的DPO对齐策略,并在最佳N(BON)推理时间验证中实现更好的结果。我们的代码位于https://github.com/chaoyang101/ICRM。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
本文提出利用生成概率建立响应轨迹中奖励一致性,以提高大型语言模型的奖励模型性能。通过引入轨迹内一致性正则化,使相邻的高生成概率的下一个令牌保持更一致的奖励,从而提高奖励模型的性能。该模型在RewardBench上表现出较好的性能,并实现了更好的策略对齐和最佳N验证结果。
Key Takeaways
- 奖励模型对改进大型语言模型至关重要,尤其在基于人类反馈的强化学习和推理时间验证方面。
- 当前奖励建模通常依赖于整体响应的分数来学习结果奖励,但这种方式难以识别与分数真正相关的响应轨迹中的特定组件。
- 引入生成概率来建立响应轨迹中的奖励一致性,使响应级别的监督信号可以在轨迹过程中传播,为奖励学习提供额外的精细粒度信号。
- 开发出轨迹内一致性正则化,强制相邻的高生成概率的下一个令牌保持更一致的奖励。
- 该模型在RewardBench上的性能表现良好,说明该模型能有效提高大型语言模型的性能。
- 训练的奖励模型可以产生更好的策略对齐,这意味着模型能更好地反映人类的意图和期望。
点此查看论文截图

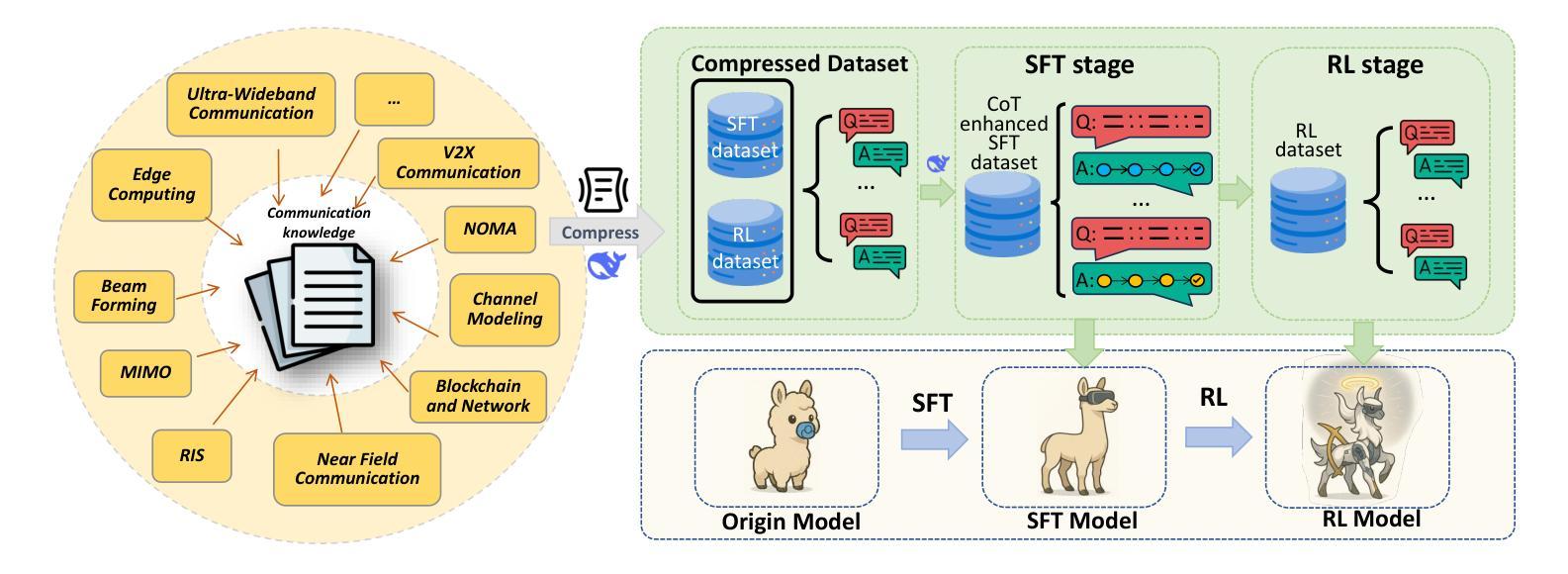
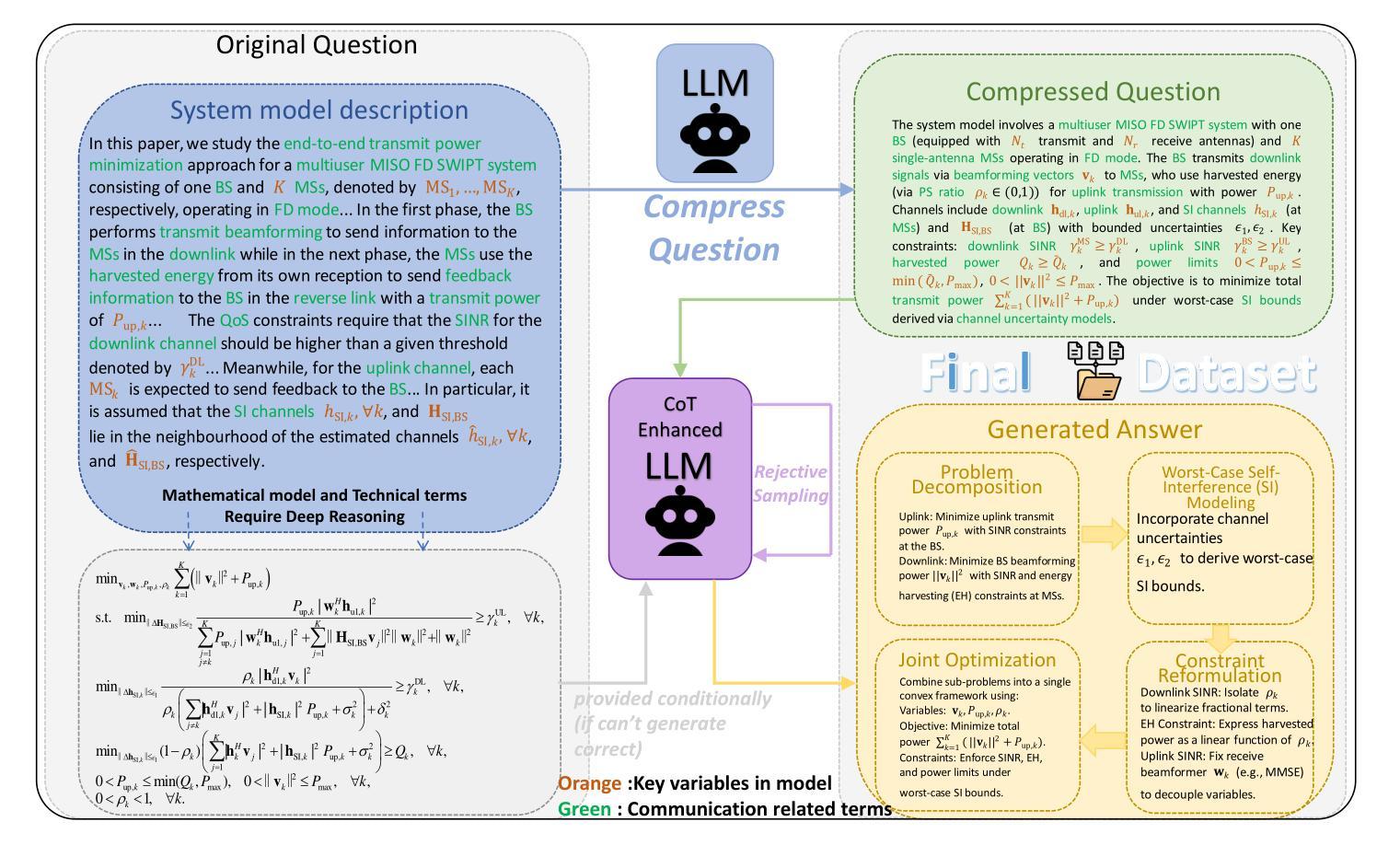
DeepForm: Reasoning Large Language Model for Communication System Formulation
Authors:Panlong Wu, Ting Wang, Yifei Zhong, Haoqi Zhang, Zitong Wang, Fangxin Wang
Communication system formulation is critical for advancing 6G and future wireless technologies, yet it remains a complex, expertise-intensive task. While Large Language Models (LLMs) offer potential, existing general-purpose models often lack the specialized domain knowledge, nuanced reasoning capabilities, and access to high-quality, domain-specific training data required for adapting a general LLM into an LLM specially for communication system formulation. To bridge this gap, we introduce DeepForm, the first reasoning LLM specially for automated communication system formulation. We propose the world-first large-scale, open-source dataset meticulously curated for this domain called Communication System Formulation Reasoning Corpus (CSFRC). Our framework employs a two-stage training strategy: first, Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with Chain-of-Thought (CoT) data to distill domain knowledge; second, a novel rule-based Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithm, C-ReMax based on ReMax, to cultivate advanced modeling capabilities and elicit sophisticated reasoning patterns like self-correction and verification. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance, significantly outperforming larger proprietary LLMs on diverse senerios. We will release related resources to foster further research in this area after the paper is accepted.
通信系统建模是推动6G和未来无线技术发展的关键,但这是一项复杂且需要专业技能的任务。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)具有潜力,但现有的通用模型通常缺乏特定领域的专业知识、微妙的推理能力和访问高质量、特定领域的训练数据,这些均是适应通用LLM以用于通信系统建模所必需的。为了弥这一差距,我们引入了DeepForm,这是首个专门用于自动化通信系统建模的推理LLM。我们提出了世界上第一个针对此领域精心策划的大规模开源数据集,名为通信系统建模推理语料库(CSFRC)。我们的框架采用两阶段训练策略:首先,使用链式思维(CoT)数据进行监督微调(SFT)以提炼领域知识;其次,采用基于ReMax的新型基于规则的强化学习(RL)算法C-ReMax,以培养先进的建模能力并激发自我修正和验证等复杂推理模式。大量实验表明,我们的模型达到了最先进的性能,在多种场景下显著优于更大的专有LLM。论文被接受后,我们将发布相关资源以促进该领域的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了通信系统的构建对于推动6G和未来无线技术的发展至关重要。文章指出大型语言模型(LLM)在通信系统的构建中具有潜力,但现有的一般模型缺乏专业领域知识、推理能力和高质量领域特定训练数据的适应性。为解决这些问题,文章提出了DeepForm,这是一个专门为自动化通信系统构建设计的推理LLM。同时介绍了专为该领域精心策划的大型开源数据集Communication System Formulation Reasoning Corpus(CSFRC)。该框架采用两阶段训练策略:首先使用带有思维链(CoT)数据的监督微调(SFT)来提炼领域知识;其次是基于ReMax的C-ReMax新型规则强化学习算法,以培养先进的建模能力和激发复杂的推理模式,如自我修正和验证。实验证明,该模型在多种场景下实现了最先进的性能,显著优于更大的专有LLM。
Key Takeaways
- 通信系统的构建对推动未来无线技术的发展至关重要,需要专业的知识和技术。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在通信系统构建中有应用潜力,但现有模型存在领域适应性不足的问题。
- DeepForm是一个专门为自动化通信系统构建设计的推理LLM,可以解决现有模型的不足。
- 引入了名为CSFRC的大型开源数据集,专为通信系统构建领域精心策划。
- 该框架采用两阶段训练策略,包括监督微调(SFT)和基于ReMax的强化学习算法。
- 该模型在多种场景下实现了最先进的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

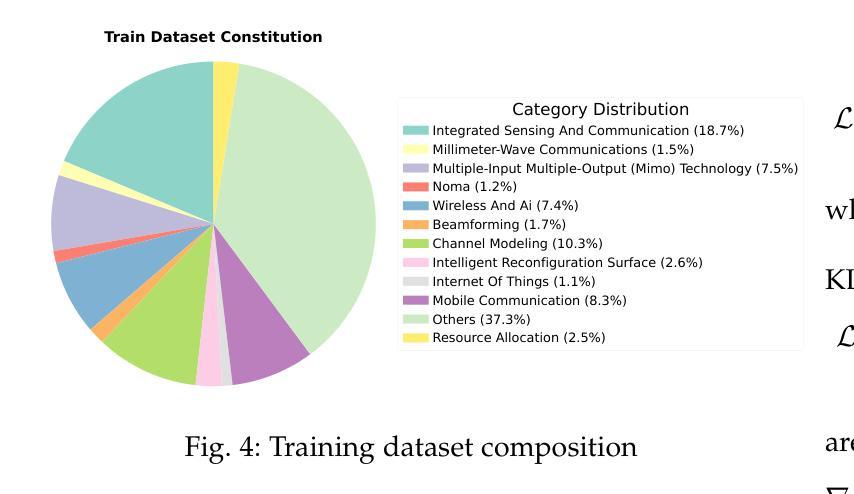
MasHost Builds It All: Autonomous Multi-Agent System Directed by Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Kuo Yang, Xingjie Yang, Linhui Yu, Qing Xu, Yan Fang, Xu Wang, Zhengyang Zhou, Yang Wang
Large Language Model (LLM)-driven Multi-agent systems (Mas) have recently emerged as a powerful paradigm for tackling complex real-world tasks. However, existing Mas construction methods typically rely on manually crafted interaction mechanisms or heuristic rules, introducing human biases and constraining the autonomous ability. Even with recent advances in adaptive Mas construction, existing systems largely remain within the paradigm of semi-autonomous patterns. In this work, we propose MasHost, a Reinforcement Learning (RL)-based framework for autonomous and query-adaptive Mas design. By formulating Mas construction as a graph search problem, our proposed MasHost jointly samples agent roles and their interactions through a unified probabilistic sampling mechanism. Beyond the accuracy and efficiency objectives pursued in prior works, we introduce component rationality as an additional and novel design principle in Mas. To achieve this multi-objective optimization, we propose Hierarchical Relative Policy Optimization (HRPO), a novel RL strategy that collaboratively integrates group-relative advantages and action-wise rewards. To our knowledge, our proposed MasHost is the first RL-driven framework for autonomous Mas graph construction. Extensive experiments on six benchmarks demonstrate that MasHost consistently outperforms most competitive baselines, validating its effectiveness, efficiency, and structure rationality.
近年来,以大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的多智能体系统(Mas)已作为一种强大的范式,用于处理复杂的现实世界任务。然而,现有的Mas构建方法通常依赖于手动构建交互机制或启发式规则,这引入了人类偏见并限制了自主性能力。尽管自适应Mas构建方面最近有所进展,但现有系统大多仍停留在半自主模式的范式内。在这项工作中,我们提出了MasHost,这是一个基于强化学习(RL)的自主和查询自适应Mas设计框架。通过将Mas构建制定为图搜索问题,我们提出的MasHost通过统一的概率采样机制联合采样智能体角色及其交互。除了先前工作中追求准确性和效率目标外,我们还将组件合理性作为Mas中的附加和新颖设计原则。为了实现这一多目标优化,我们提出了分层相对策略优化(HRPO),这是一种新型RL策略,能够协同整合群体相对优势和行动层面奖励。据我们所知,我们提出的MasHost是第一个用于自主Mas图构建的RL驱动框架。在六个基准测试上的广泛实验表明,MasHost始终优于大多数竞争基线,验证了其有效性、效率和结构合理性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型驱动的多智能体系统(Mas)已成为解决复杂现实世界任务的有力范式。然而,现有构建方法通常依赖人工设计的交互机制和启发式规则,导致人类偏见并限制了自主性能力。在本文中,提出了一种基于强化学习(RL)的自主、查询自适应的多智能体系统设计方案,命名为MasHost。MasHost通过制定图形搜索问题来实现多智能体系统的构建,联合采样智能体的角色及其交互作用,并且首次引入了组件理性作为新的设计原则。为了进行多目标优化,提出了一种新的强化学习策略——分层相对策略优化(HRPO),它结合了群体相对优势和行动奖励。实验表明,MasHost在各种基准测试上都表现优于大多数竞争方案,证明了其有效性、效率和结构合理性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型驱动的多智能体系统已成为解决复杂任务的重要范式。
- 当前构建方法依赖人工设计机制,限制了系统的自主性并引入人类偏见。
- MasHost是首个使用强化学习驱动的多智能体系统图形构建框架,能自主联合采样智能体角色及其交互。
- MasHost引入了组件理性作为新的设计原则,并结合群体相对优势和行动奖励进行多目标优化。
点此查看论文截图

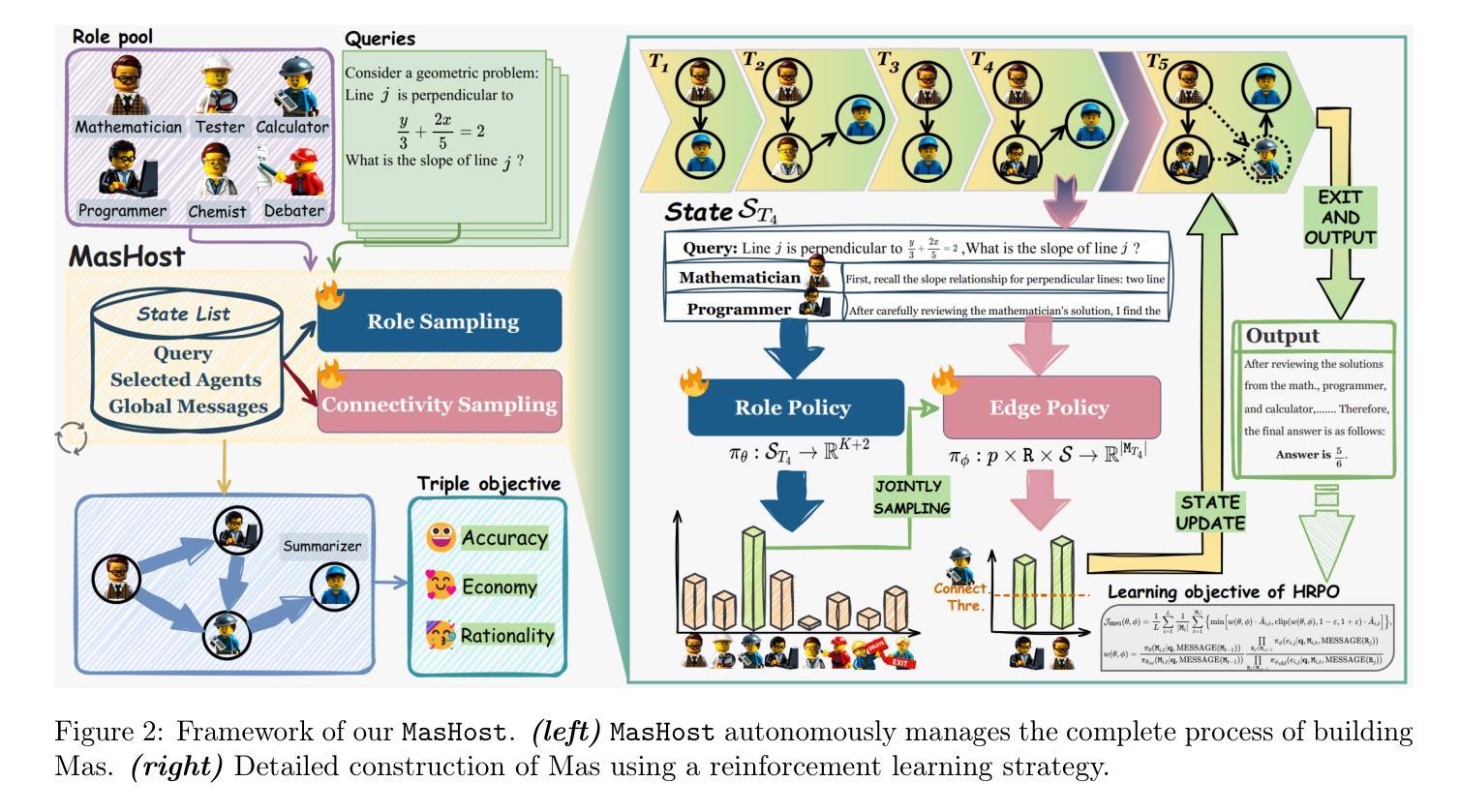
TGRPO :Fine-tuning Vision-Language-Action Model via Trajectory-wise Group Relative Policy Optimization
Authors:Zengjue Chen, Runliang Niu, He Kong, Qi Wang
Recent advances in Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model have demonstrated strong generalization capabilities across diverse scenes, tasks, and robotic platforms when pretrained at large-scale datasets. However, these models still require task-specific fine-tuning in novel environments, a process that relies almost exclusively on supervised fine-tuning (SFT) using static trajectory datasets. Such approaches neither allow robot to interact with environment nor do they leverage feedback from live execution. Also, their success is critically dependent on the size and quality of the collected trajectories. Reinforcement learning (RL) offers a promising alternative by enabling closed-loop interaction and aligning learned policies directly with task objectives. In this work, we draw inspiration from the ideas of GRPO and propose the Trajectory-wise Group Relative Policy Optimization (TGRPO) method. By fusing step-level and trajectory-level advantage signals, this method improves GRPO’s group-level advantage estimation, thereby making the algorithm more suitable for online reinforcement learning training of VLA. Experimental results on ten manipulation tasks from the libero-object benchmark demonstrate that TGRPO consistently outperforms various baseline methods, capable of generating more robust and efficient policies across multiple tested scenarios. Our source codes are available at: https://github.com/hahans/TGRPO
近期Vision-Language-Action(VLA)模型的进展表明,在大规模数据集上进行预训练后,这些模型在不同场景、任务和机器人平台之间具有很强的泛化能力。然而,这些模型在新环境中仍需要针对特定任务进行微调,这一过程几乎完全依赖于使用静态轨迹数据集的监督微调(SFT)。这些方法既不允许机器人与环境互动,也没有利用实时执行反馈。此外,它们的成功严重依赖于收集的轨迹的大小和质量。强化学习(RL)提供了一个有前景的替代方案,它通过实现闭环交互和对齐学习政策与任务目标。在这项工作中,我们从GRPO的思想中汲取灵感,提出了轨迹级群体相对策略优化(TGRPO)方法。通过融合步骤级和轨迹级优势信号,该方法改进了GRPO的群体级优势估计,从而使该算法更适合在线强化学习训练VLA。在libero-object基准测试中的10个操作任务上的实验结果表明,TGRPO持续优于各种基线方法,能够在多个测试场景中生成更稳健和高效的策略。我们的源代码可在:https://github.com/hahans/TGRPO获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
最近,视觉语言行动(VLA)模型在多样场景、任务和机器人平台上的泛化能力有所突破。然而,这些模型在新环境中仍需要特定任务的微调,这一过程几乎完全依赖于使用静态轨迹数据集进行监督微调(SFT)。这种方法既不允许机器人与环境互动,也没有利用实时执行的反馈。强化学习(RL)提供了一个有前景的替代方案,通过闭环互动和对任务目标的直接策略对齐。本研究受GRPO的启发,提出了轨迹级群组相对策略优化(TGRPO)方法。该方法融合步骤级和轨迹级优势信号,改进了GRPO的群组级优势估计,使算法更适合在线强化学习训练VLA。在libero-object基准的十个操作任务上的实验结果表明,TGRPO持续优于各种基线方法,能够在多个测试场景中生成更稳健和高效的策略。
Key Takeaways
- VLA模型虽具备泛化能力,但仍需在新环境中进行特定任务微调。
- 当前微调方法主要依赖静态轨迹数据集的监督微调(SFT),限制机器人与环境互动及实时反馈利用。
- 强化学习(RL)为解决问题提供有前景的替代方案,通过闭环互动直接对齐策略与任务目标。
- TGRPO方法结合步骤级和轨迹级优势信号,改进GRPO的群组级优势估计。
- TGRPO适合在线强化学习训练VLA,并在多个操作任务上表现优越。
- TGRPO在libero-object基准的十个任务上持续优于各种基线方法。
点此查看论文截图

Play to Generalize: Learning to Reason Through Game Play
Authors:Yunfei Xie, Yinsong Ma, Shiyi Lan, Alan Yuille, Junfei Xiao, Chen Wei
Developing generalizable reasoning capabilities in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) remains challenging. Motivated by cognitive science literature suggesting that gameplay promotes transferable cognitive skills, we propose a novel post-training paradigm, Visual Game Learning, or ViGaL, where MLLMs develop out-of-domain generalization of multimodal reasoning through playing arcade-like games. Specifically, we show that post-training a 7B-parameter MLLM via reinforcement learning (RL) on simple arcade-like games, e.g. Snake, significantly enhances its downstream performance on multimodal math benchmarks like MathVista, and on multi-discipline questions like MMMU, without seeing any worked solutions, equations, or diagrams during RL, suggesting the capture of transferable reasoning skills. Remarkably, our model outperforms specialist models tuned on multimodal reasoning data in multimodal reasoning benchmarks, while preserving the base model’s performance on general visual benchmarks, a challenge where specialist models often fall short. Our findings suggest a new post-training paradigm: synthetic, rule-based games can serve as controllable and scalable pre-text tasks that unlock generalizable multimodal reasoning abilities in MLLMs.
在多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)中发展可推广的推理能力仍然是一个挑战。受认知科学文献的启发,该文献表明游戏玩法可以促进可迁移的认知技能,我们提出了一种新型的后训练范式,即视觉游戏学习(ViGaL)。在此范式中,MLLMs通过玩类似街机游戏来发展跨域的多模态推理能力。具体来说,我们通过强化学习(RL)对具有7B参数的MLLM进行后训练,使其在简单的类似街机游戏(如Snake)上的表现显著增强。其在多模态数学基准测试(如MathVista)和多学科问题(如MMMU)上的下游性能得到了提升,且在强化学习过程中未见任何解决方案、方程式或图表,这表明其掌握了可迁移的推理技能。值得注意的是,我们的模型在多种模态推理基准测试中优于经过该任务专门训练的模型,同时在一般视觉基准测试上的表现也与基础模型相当,而这是一个许多专业模型表现不足的领域。我们的研究结果表明了一种新型后训练范式:合成、基于规则的游戏可以作为可控和可扩展的预文本任务,解锁MLLM中的可泛化多模态推理能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://yunfeixie233.github.io/ViGaL/
Summary
游戏学习可提升多模态大型语言模型的泛化推理能力。通过认知科学文献的启发,提出一种新型的后训练范式——视觉游戏学习(ViGaL),使MLLMs通过玩类似街机游戏发展出跨域的多模态推理泛化能力。实验表明,对含有7B参数的MLLM采用强化学习方式进行街机游戏的后训练,能显著提升其在多模态数学基准测试(如MathVista)和多学科问题(如MMMU)上的表现。训练过程中无需接触解题方案、方程式或图表,表明模型掌握了可迁移的推理技能。此外,该模型在多模态推理基准测试中优于专门训练的多模态推理模型,并保持了基础模型在通用视觉基准测试中的性能。这表明合成规则游戏可作为可控且可扩展的预训练任务,解锁MLLMs中的泛化多模态推理能力。
Key Takeaways
- 游戏学习作为一种新的后训练范式,有助于提升多模态大型语言模型的泛化推理能力。
- 通过玩类似街机游戏,MLLMs可以发展出跨域的多模态推理能力。
- 强化学习在MLLMs的后训练过程中扮演重要角色,能显著提升模型在多模态数学和多学科问题上的表现。
- 模型在掌握推理技能的过程中,无需接触解题方案、方程式或图表,显示出良好的泛化能力。
- 所提出的模型在多模态推理基准测试中优于专门训练的多模态推理模型。
- 模型在通用视觉基准测试中的性能得以保持,表明游戏学习任务不损害基础模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图


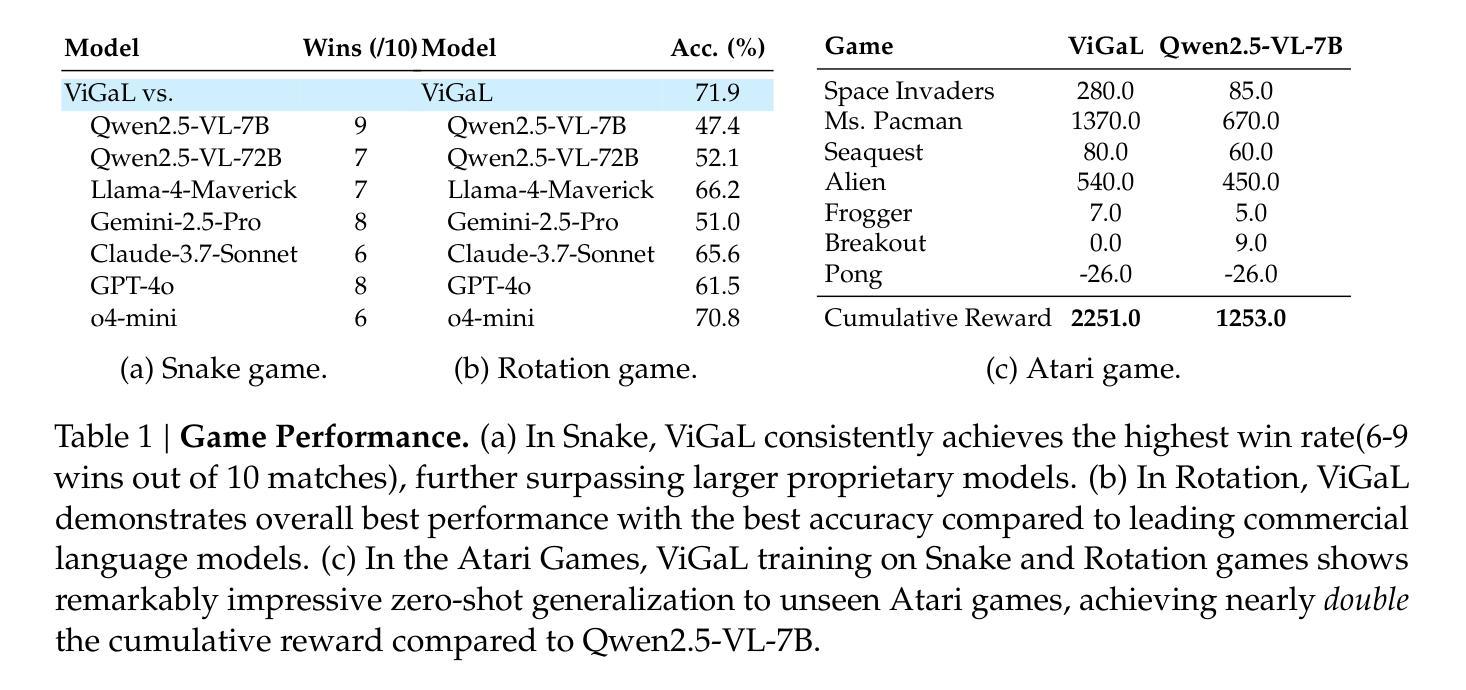
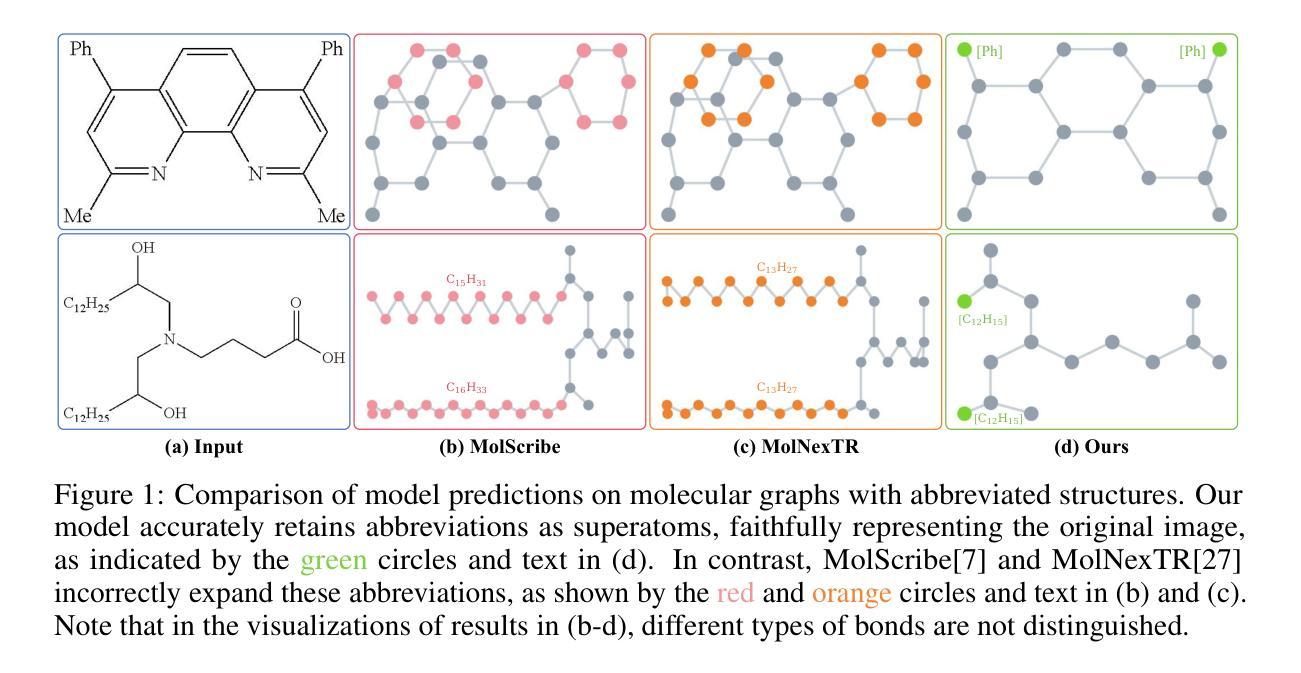
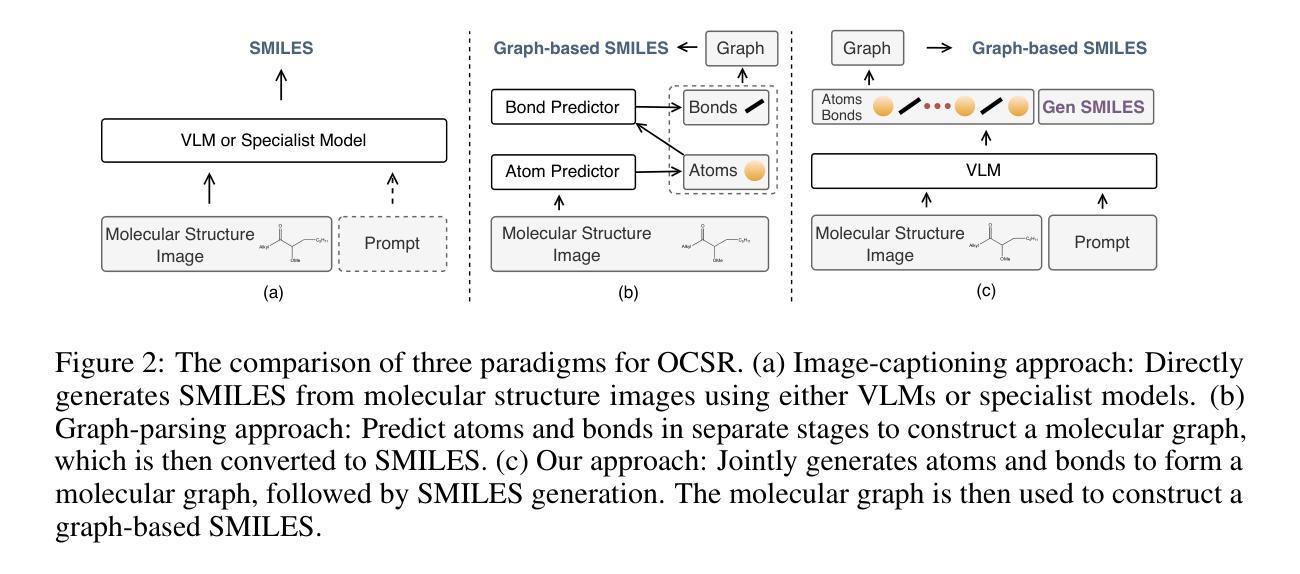
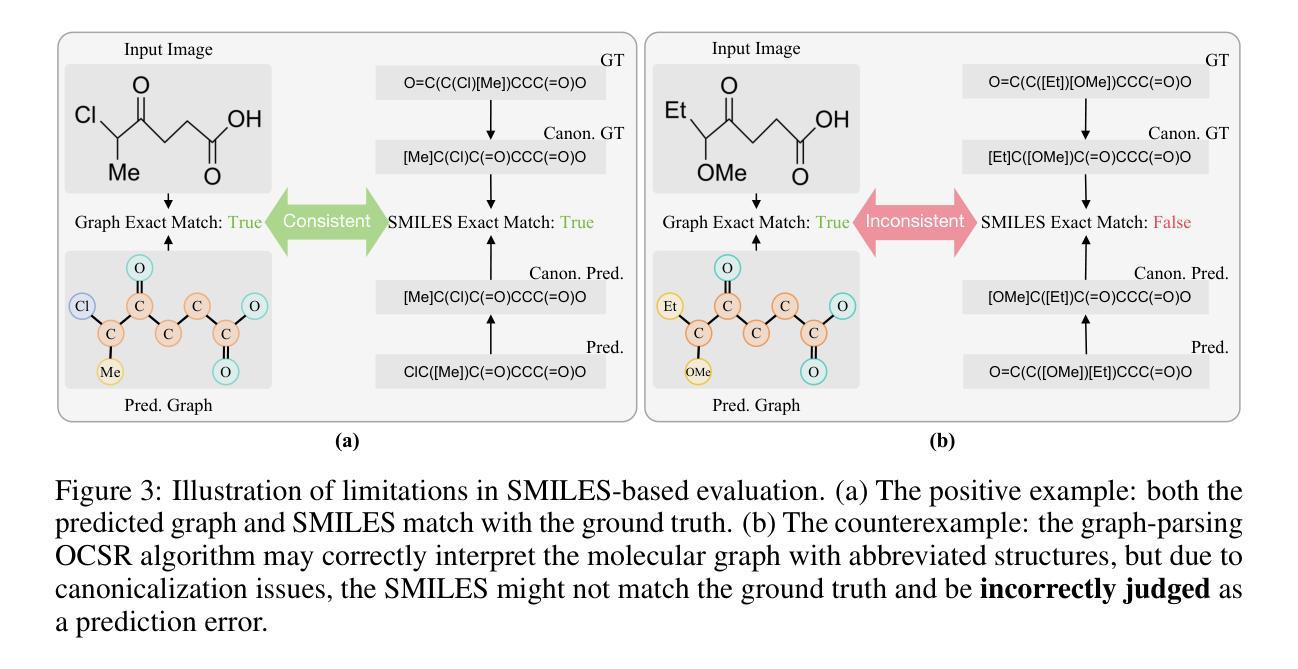
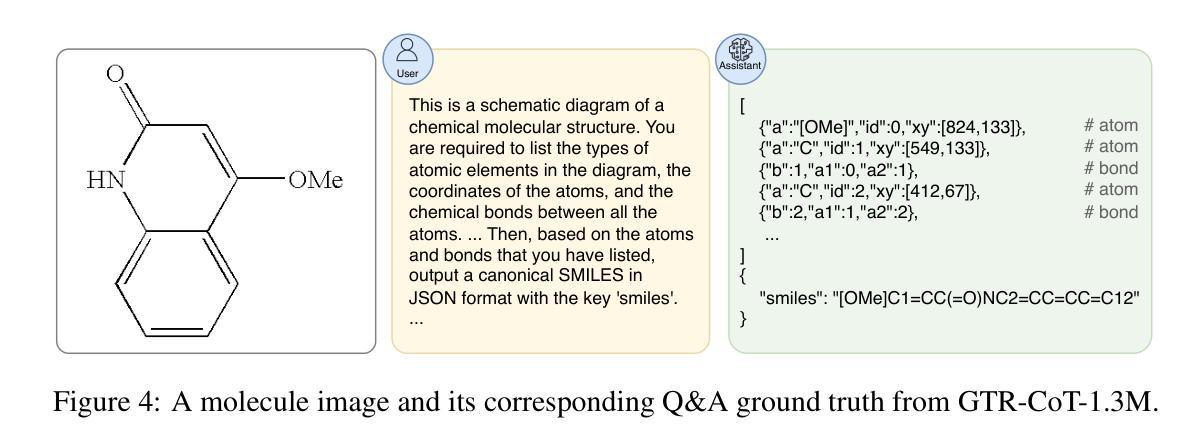
GTR-CoT: Graph Traversal as Visual Chain of Thought for Molecular Structure Recognition
Authors:Jingchao Wang, Haote Yang, Jiang Wu, Yifan He, Xingjian Wei, Yinfan Wang, Chengjin Liu, Lingli Ge, Lijun Wu, Bin Wang, Dahua Lin, Conghui He
Optical Chemical Structure Recognition (OCSR) is crucial for digitizing chemical knowledge by converting molecular images into machine-readable formats. While recent vision-language models (VLMs) have shown potential in this task, their image-captioning approach often struggles with complex molecular structures and inconsistent annotations. To overcome these challenges, we introduce GTR-Mol-VLM, a novel framework featuring two key innovations: (1) the Graph Traversal as Visual Chain of Thought mechanism that emulates human reasoning by incrementally parsing molecular graphs through sequential atom-bond predictions, and (2) the data-centric principle of Faithfully Recognize What You’ve Seen, which addresses the mismatch between abbreviated structures in images and their expanded annotations. To support model development, we constructed GTR-CoT-1.3M, a large-scale instruction-tuning dataset with meticulously corrected annotations, and introduced MolRec-Bench, the first benchmark designed for a fine-grained evaluation of graph-parsing accuracy in OCSR. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that GTR-Mol-VLM achieves superior results compared to specialist models, chemistry-domain VLMs, and commercial general-purpose VLMs. Notably, in scenarios involving molecular images with functional group abbreviations, GTR-Mol-VLM outperforms the second-best baseline by approximately 14 percentage points, both in SMILES-based and graph-based metrics. We hope that this work will drive OCSR technology to more effectively meet real-world needs, thereby advancing the fields of cheminformatics and AI for Science. We will release GTR-CoT at https://github.com/opendatalab/GTR-CoT.
光学化学结构识别(OCSR)是将化学知识数字化的关键过程,通过这一技术将分子图像转换为机器可读格式。虽然近期的视觉语言模型(VLM)在该任务中显示出潜力,但其图像描述方法往往难以应对复杂的分子结构和标注不一致的问题。为了克服这些挑战,我们引入了GTR-Mol-VLM这一新型框架,它有两个关键的创新点:(1)通过逐步解析分子图进行原子键预测来模拟人类推理过程的“图遍历视觉链”机制;(2)以解决图像中的简化结构与扩展标注之间不匹配问题的数据中心的忠实识别所看到内容的原理。为了支持模型开发,我们构建了大规模的指令调整数据集GTR-CoT-1.3M,其中包含经过仔细校正的标注,并推出了针对OCSR图形解析精度的精细评估而设计的首个基准测试MolRec-Bench。综合实验表明,GTR-Mol-VLM与专业模型、化学领域VLM和商业通用VLM相比取得了优越的结果。值得注意的是,在处理带有官能团缩写的分子图像的场景中,GTR-Mol-VLM在SMILES和图形指标基准测试中均比第二名基准高出约14个百分点。我们希望这项工作能够推动OCSR技术更有效地满足现实世界的需要,从而促进化学信息学和科学人工智能领域的发展。我们将在https://github.com/opendatalab/GTR-CoT上发布GTR-CoT。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
光学化学结构识别(OCSR)是数字化化学知识的重要技术,通过将分子图像转换为机器可读格式实现知识数字化。为解决现有视觉语言模型在处理复杂分子结构和不一致注释方面的挑战,本文提出了一种新型框架GTR-Mol-VLM。该框架包括两个关键创新点:一是通过模拟人类推理过程,通过序列原子键预测逐步解析分子图的视觉思考机制;二是忠实反映图像和扩展注释间不一致的“忠实认识所见”。实验结果表明,与专业化模型、化学领域的视觉语言模型和通用商业视觉语言模型相比,GTR-Mol-VLM实现了显著效果。特别是当涉及带有官能团缩写的分子图像时,GTR-Mol-VLM在SMILES和图形指标上的表现优于第二名基准测试约14个百分点。本文期望推动OCSR技术更好地满足现实需求,推动化学信息学和人工智能科学领域的发展。我们将公开GTR-CoT数据集的访问地址。
Key Takeaways
- 光学化学结构识别(OCSR)是将化学知识数字化的重要技术。
- 当前视觉语言模型在处理复杂分子结构和不一致注释方面存在挑战。
- GTR-Mol-VLM框架引入了两项关键创新:模拟人类推理的视觉思考机制和忠实反映所见的数据中心原则。
- GTR-Mol-VLM实现了在化学结构识别上的显著效果,特别是在处理带有官能团缩写的分子图像时表现优异。
- GTR-Mol-VLM在SMILES和图形指标上的表现优于其他模型约14个百分点。
- GTR-Mol-VLM有望推动OCSR技术更好地满足现实需求,促进化学信息学和人工智能科学领域的发展。
点此查看论文截图

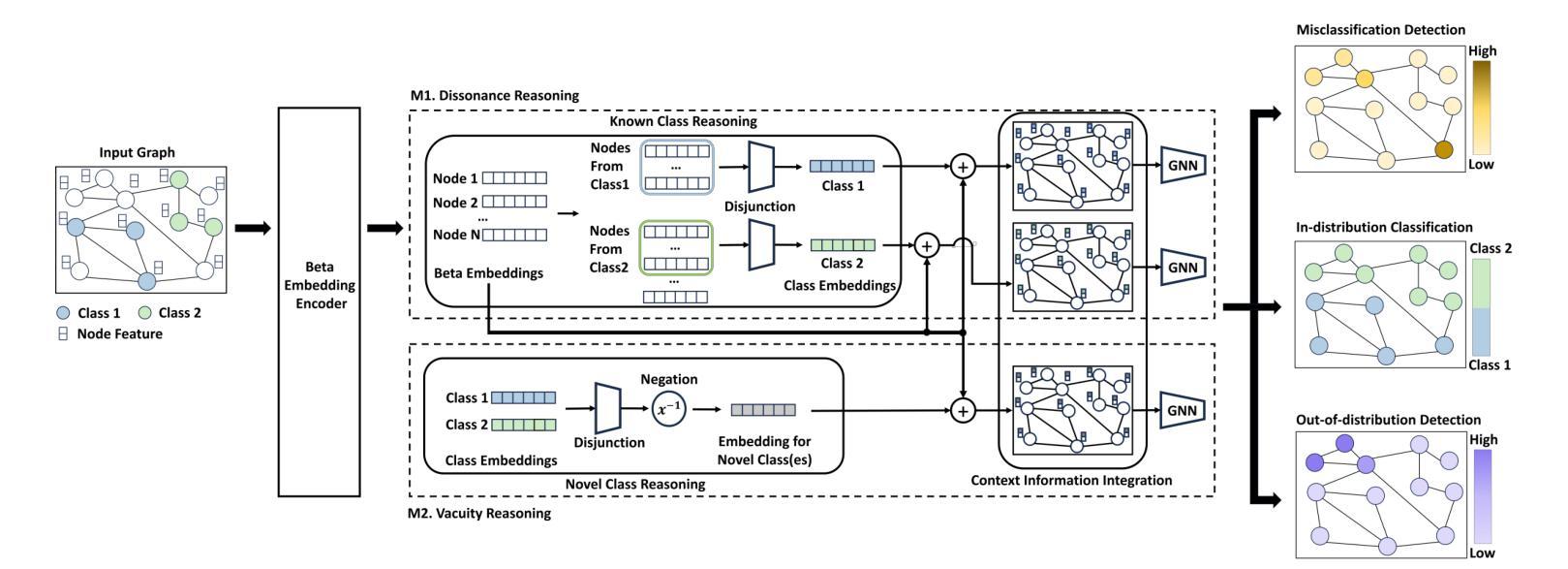
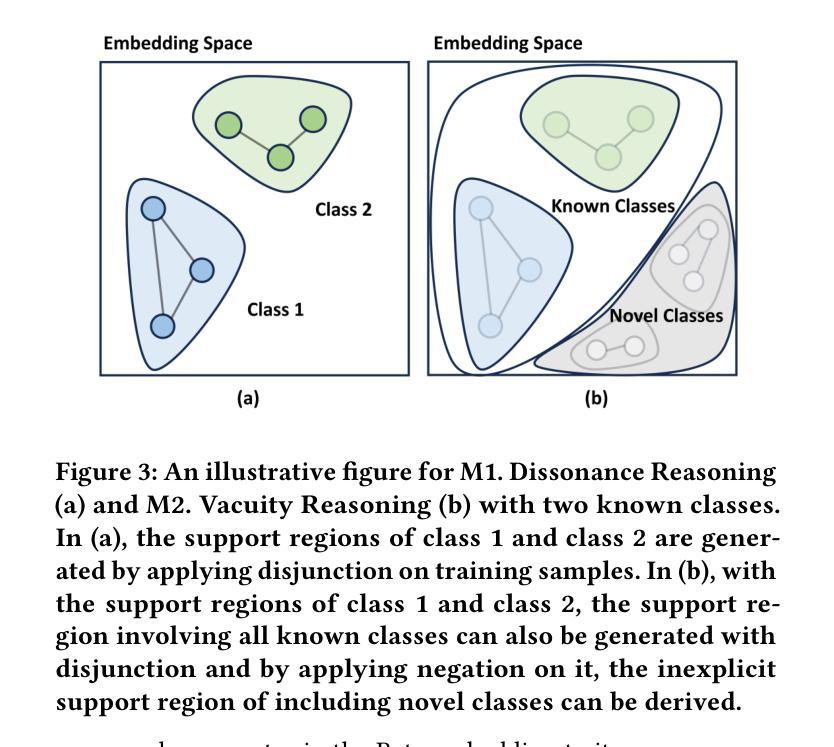
EVINET: Towards Open-World Graph Learning via Evidential Reasoning Network
Authors:Weijie Guan, Haohui Wang, Jian Kang, Lihui Liu, Dawei Zhou
Graph learning has been crucial to many real-world tasks, but they are often studied with a closed-world assumption, with all possible labels of data known a priori. To enable effective graph learning in an open and noisy environment, it is critical to inform the model users when the model makes a wrong prediction to in-distribution data of a known class, i.e., misclassification detection or when the model encounters out-of-distribution from novel classes, i.e., out-of-distribution detection. This paper introduces Evidential Reasoning Network (EVINET), a framework that addresses these two challenges by integrating Beta embedding within a subjective logic framework. EVINET includes two key modules: Dissonance Reasoning for misclassification detection and Vacuity Reasoning for out-of-distribution detection. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EVINET outperforms state-of-the-art methods across multiple metrics in the tasks of in-distribution classification, misclassification detection, and out-of-distribution detection. EVINET demonstrates the necessity of uncertainty estimation and logical reasoning for misclassification detection and out-of-distribution detection and paves the way for open-world graph learning. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/SSSKJ/EviNET.
图学习在许多真实任务中都至关重要,但它们通常是在封闭世界假设下进行研究,即所有可能的数据标签都是事先已知的。为了在开放和嘈杂的环境中实现有效的图学习,当模型对已知类别的内部分布数据做出错误预测时,向模型用户报告错误,即误分类检测,或当模型遇到来自新类别的外部分布时,即外部分布检测,这是至关重要的。本文介绍了证据推理网络(EVINET),这是一个通过主观逻辑框架集成Beta嵌入来解决这两个挑战的框架。EVINET包括两个关键模块:用于误分类检测的不一致推理和用于外部分布检测的空洞推理。大量实验表明,EVINET在内部分布分类、误分类检测和外部分布检测的任务中,在多个指标上的表现均优于最新方法。EVINET证明了误分类检测和外部分布检测中不确定性估计和逻辑推理的必要性,为开放世界图学习铺平了道路。我们的代码和数据可在https://github.com/SSSKJ/EviNET找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF KDD 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为EVINET的框架,它解决了在开放和噪声环境中进行有效图学习的挑战。通过整合Beta嵌入和主观逻辑框架,EVINET包含两个关键模块:用于误分类检测的异议推理和用于异常检测的空缺推理。实验表明,EVINET在多个指标上优于现有技术方法,在分布内分类、误分类检测和异常检测任务中表现出色。这为开放世界图学习中的不确定性估计和逻辑推理的必要性铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- EVINET框架解决了在开放和噪声环境中图学习的挑战。
- 通过整合Beta嵌入和主观逻辑框架,EVINET包含异议推理和空缺推理两个关键模块。
- EVINET可用于处理已知类别的误分类检测和未知类别异常检测的问题。
- 实验表明,EVINET在多个指标上优于现有技术方法。
- EVINET强调不确定性估计和逻辑推理在误分类检测和异常检测中的重要性。
- EVINET为开放世界图学习领域的研究提供了新的方向。
点此查看论文截图

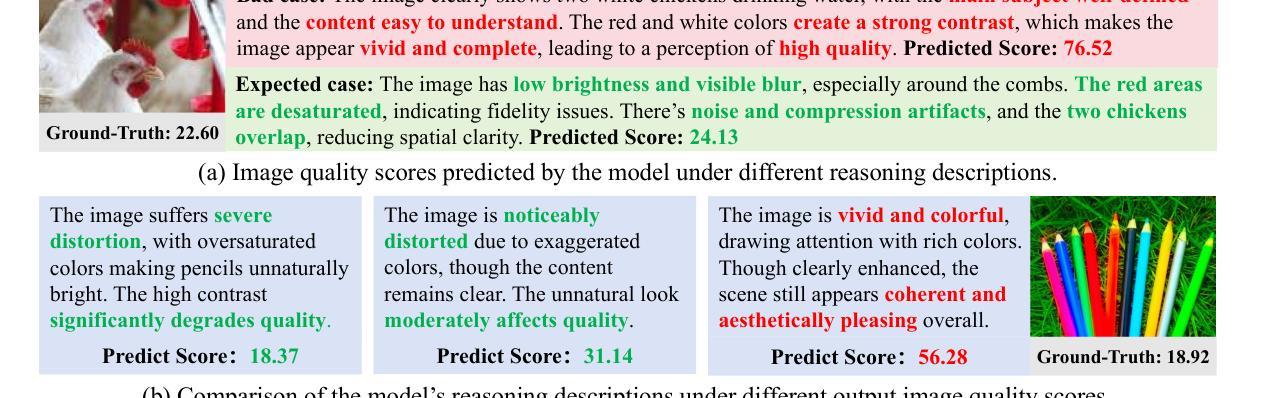
Q-Ponder: A Unified Training Pipeline for Reasoning-based Visual Quality Assessment
Authors:Zhuoxuan Cai, Jian Zhang, Xinbin Yuan, Peng-Tao Jiang, Wenxiang Chen, Bowen Tang, Lujian Yao, Qiyuan Wang, Jinwen Chen, Bo Li
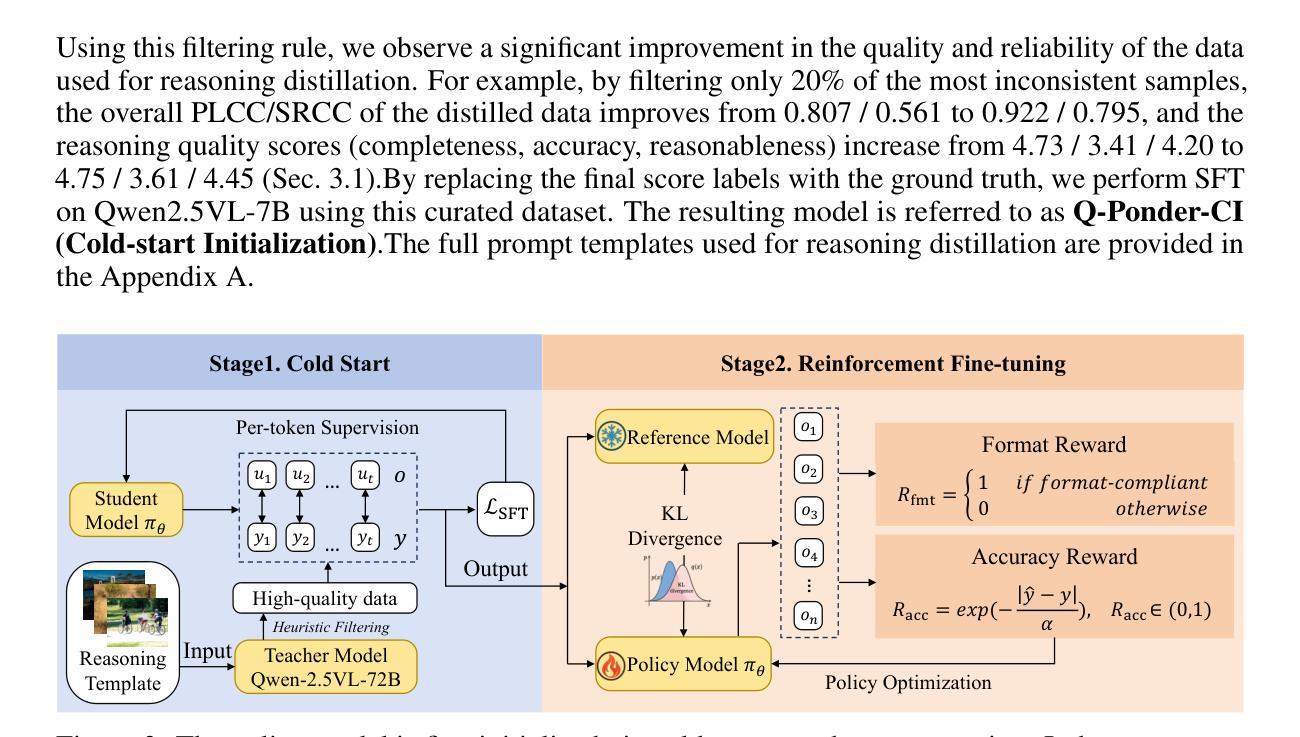
Recent studies demonstrate that multimodal large language models (MLLMs) can proficiently evaluate visual quality through interpretable assessments. However, existing approaches typically treat quality scoring and reasoning descriptions as separate tasks with disjoint optimization objectives, leading to a trade-off: models adept at quality reasoning descriptions struggle with precise score regression, while score-focused models lack interpretability. This limitation hinders the full potential of MLLMs in visual quality assessment, where accuracy and interpretability should be mutually reinforcing. To address this, we propose a unified two-stage training framework comprising a cold-start stage and a reinforcement learning-based fine-tuning stage. Specifically, in the first stage, we distill high-quality data from a teacher model through expert-designed prompts, initializing reasoning capabilities via cross-entropy loss supervision. In the second stage, we introduce a novel reward with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to jointly optimize scoring accuracy and reasoning consistency. We designate the models derived from these two stages as Q-Ponder-CI and Q-Ponder. Extensive experiments show that Q-Ponder achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on quality score regression benchmarks, delivering up to 6.5% higher SRCC on cross-domain datasets. Furthermore, Q-Ponder significantly outperforms description-based SOTA models, including its teacher model Qwen-2.5-VL-72B, particularly in description accuracy and reasonableness, demonstrating the generalization potential over diverse tasks.
最近的研究表明,多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)能够通过可解释评估熟练地评估视觉质量。然而,现有方法通常将质量评分和推理描述视为具有不同优化目标的单独任务,这导致了一个权衡:擅长质量推理描述的模型在精确分数回归方面表现挣扎,而专注于分数的模型则缺乏可解释性。这一局限性阻碍了MLLMs在视觉质量评估中的全部潜力,其中准确性和可解释性应该相互增强。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种包含冷启动阶段和基于强化学习的微调阶段的统一两阶段训练框架。具体来说,在第一阶段,我们通过专家设计的提示从教师模型中提炼高质量数据,通过交叉熵损失监督来初始化推理能力。在第二阶段,我们引入了一种新型奖励与群体相对策略优化(GRPO),以联合优化评分准确性和推理一致性。我们将这两个阶段衍生出的模型指定为Q-Ponder-CI和Q-Ponder。大量实验表明,Q-Ponder在质量分数回归基准测试上达到了最新技术水平(SOTA),在跨域数据集上的SRCC提高了高达6.5%。此外,Q-Ponder在描述准确性及合理性方面显著优于基于描述的最新技术水平模型,包括其教师模型Qwen-2.5-VL-72B,这显示了其在不同任务上的泛化潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了近期研究如何通过多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)进行视觉质量评估。现有方法通常将质量评分和推理描述视为单独的任务,导致优化目标分离,模型在精确评分和解释性方面存在权衡问题。为解决此问题,提出了一种两阶段统一训练框架,包括冷启动阶段和基于强化学习的微调阶段。通过专家设计的提示从教师模型中提炼高质量数据,通过交叉熵损失监督初步推理能力。在第二阶段中,引入了一种新型奖励与集团相对策略优化(GRPO),以联合优化评分准确性和推理一致性。模型在质量评分回归基准测试上达到最新水平,在跨域数据集上的SRCC提高达6.5%。特别是在描述准确性和合理性方面,Q-Ponder显著优于基于描述的最新模型,包括其教师模型Qwen-2.5-VL-72B。这表明其在不同任务上的泛化潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)能够熟练地进行视觉质量评估。
- 现有方法在处理质量评分和推理描述时存在局限性,将其视为独立任务导致优化目标分离的问题。
- 提出了一种两阶段统一训练框架,包括冷启动和基于强化学习的微调阶段,以解决现有方法的局限性。
- 在第一阶段中,通过专家设计的提示从教师模型中提炼高质量数据,并通过交叉熵损失监督初步推理能力。
- 在第二阶段中,引入新型奖励与集团相对策略优化(GRPO),联合优化评分准确性和推理一致性。
- Q-Ponder模型在质量评分回归基准测试中表现优异,达到最新水平,且在跨域数据集上的SRCC有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

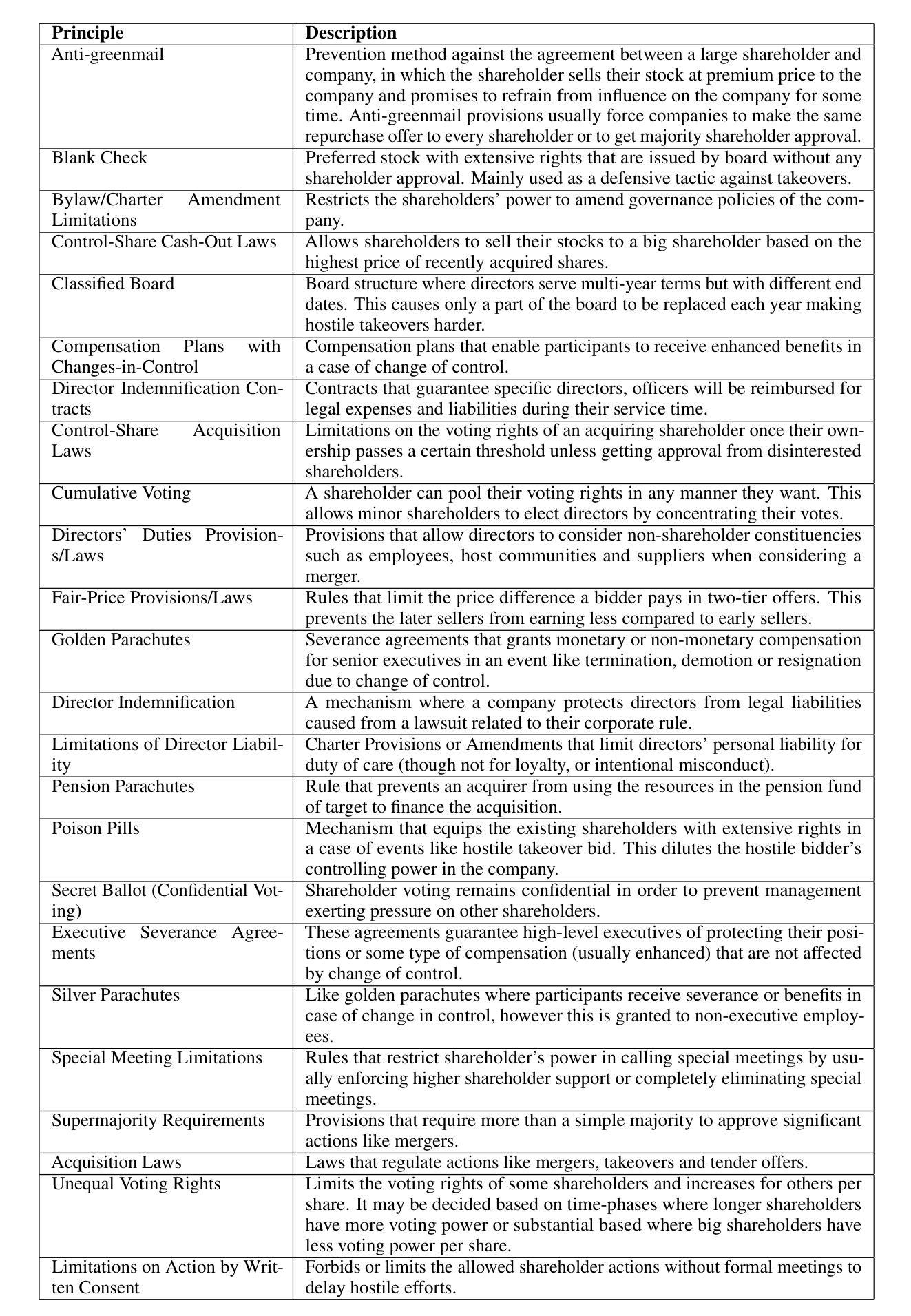
CHANCERY: Evaluating Corporate Governance Reasoning Capabilities in Language Models
Authors:Lucas Irwin, Arda Kaz, Peiyao Sheng, Sewoong Oh, Pramod Viswanath
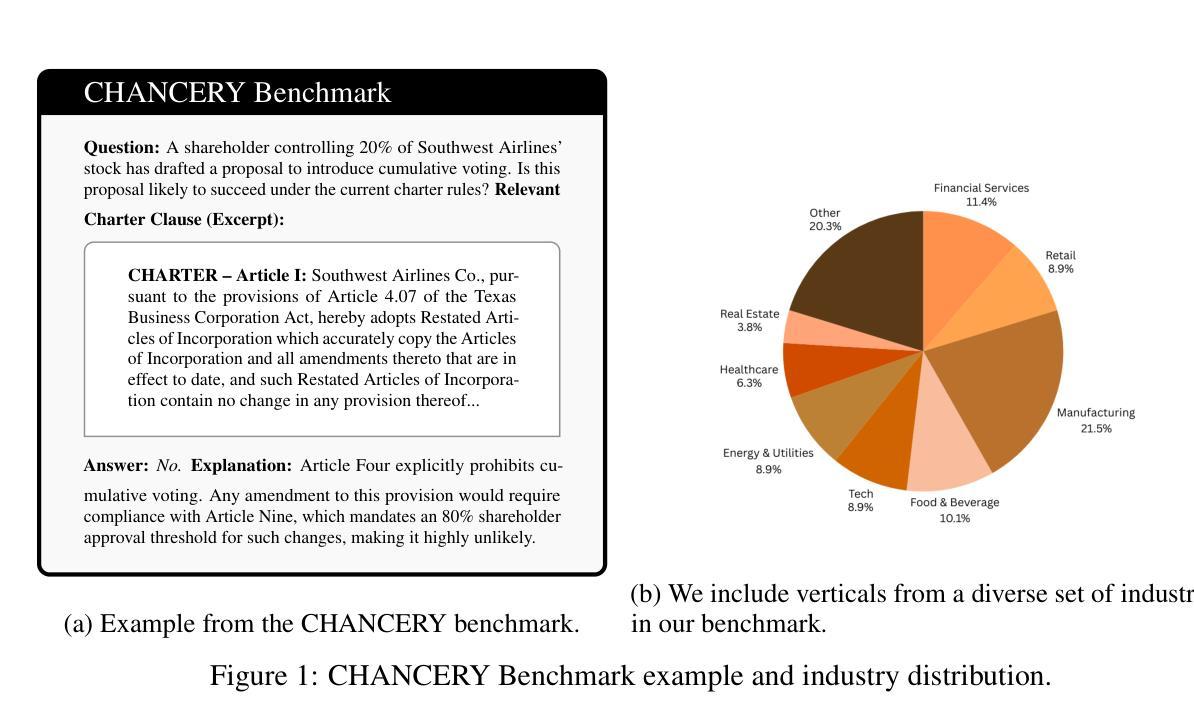
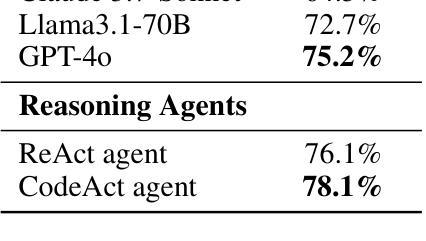
Law has long been a domain that has been popular in natural language processing (NLP) applications. Reasoning (ratiocination and the ability to make connections to precedent) is a core part of the practice of the law in the real world. Nevertheless, while multiple legal datasets exist, none have thus far focused specifically on reasoning tasks. We focus on a specific aspect of the legal landscape by introducing a corporate governance reasoning benchmark (CHANCERY) to test a model’s ability to reason about whether executive/board/shareholder’s proposed actions are consistent with corporate governance charters. This benchmark introduces a first-of-its-kind corporate governance reasoning test for language models - modeled after real world corporate governance law. The benchmark consists of a corporate charter (a set of governing covenants) and a proposal for executive action. The model’s task is one of binary classification: reason about whether the action is consistent with the rules contained within the charter. We create the benchmark following established principles of corporate governance - 24 concrete corporate governance principles established in and 79 real life corporate charters selected to represent diverse industries from a total dataset of 10k real life corporate charters. Evaluations on state-of-the-art (SOTA) reasoning models confirm the difficulty of the benchmark, with models such as Claude 3.7 Sonnet and GPT-4o achieving 64.5% and 75.2% accuracy respectively. Reasoning agents exhibit superior performance, with agents based on the ReAct and CodeAct frameworks scoring 76.1% and 78.1% respectively, further confirming the advanced legal reasoning capabilities required to score highly on the benchmark. We also conduct an analysis of the types of questions which current reasoning models struggle on, revealing insights into the legal reasoning capabilities of SOTA models.
法律领域一直是自然语言处理(NLP)应用中备受关注的领域。推理(逻辑思维和与先例的联系能力)是现实世界中法律实践的核心部分。尽管存在多个法律数据集,但目前还没有专门针对推理任务的数据集。我们通过引入公司治理推理基准测试(CHANCERY)来关注法律领域的一个特定方面,以测试模型对执行董事/董事会/股东提出的行动是否符合公司治理章程的推理能力。该基准测试是语言模型中首创的公司治理推理测试,以现实世界中的公司治理法为原型构建。该基准测试包括公司宪章(一组管理契约)和执行行动的提议。模型的任务是二分类问题之一:根据宪章中的规则来判断行动是否一致。我们遵循公司治理的既定原则创建了该基准测试,从包含1万个真实公司宪章的数据集中选取了代表不同行业的79个真实公司宪章,并确定了其中确立的24个具体公司治理原则。对最新推理模型的评估证实了该基准测试的难度,如Claude 3.7 Sonnet和GPT-4o的准确率分别为64.5%和75.2%。推理代理表现出卓越的性能,基于ReAct和CodeAct框架的代理分别得分76.1%和78.1%,这进一步证实了要在该基准测试中取得高分所需的先进法律推理能力。我们还对当前推理模型在问题类型上遇到的困难进行了分析,揭示了最新模型在法律推理能力方面的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了法律领域在自然语言处理(NLP)应用中的流行程度,以及推理(包括思考和联系先例的能力)在现实法律实践中的核心地位。尽管存在多个法律数据集,但迄今为止尚无专门针对推理任务的数据集。本文重点介绍了一个特定的法律领域——公司治理推理基准测试(CHANCERY),用于测试模型对高管、董事会或股东提议的行动是否符合公司治理章程的推理能力。该基准测试引入了一种首创的公司治理推理测试,模拟现实世界的公司治理法律。它由公司宪章(一系列管理契约)和一项高管行动提案组成。模型的任务是进行二元分类:判断行动是否符合宪章中的规则。本文遵循公司治理的既定原则,创建了这一基准测试,并基于现实世界的企业宪章数据集,从中选取了代表不同行业的79份宪章。对现有先进技术(SOTA)推理模型的评估证明了该基准测试的难度,如Claude 3.7 Sonnet和GPT-4o分别实现了64.5%和75.2%的准确性。而具备React和CodeAct框架的推理代理表现尤为出色,分别达到了76.1%和78.1%的准确率,进一步证明了在基准测试上取得高分所需的高级法律推理能力。同时,本文对当前推理模型在哪些类型的问题上存在困难进行了分析,揭示了先进技术模型在法律推理能力方面的见解。
Key Takeaways
- 法律领域在自然语言处理中颇受欢迎,且推理在现实法律实践中具有核心地位。
- 至今尚无专门针对法律推理任务的数据集。
- 引入了首个公司治理推理基准测试(CHANCERY),用以评估模型对公司治理场景的理解与推理能力。
- 该基准测试包含公司宪章和行动提案,模型需判断行动是否符合宪章规则。
- 遵循公司治理的既定原则,基于现实的企业宪章数据集创建此基准测试。
- 现有先进技术推理模型在该基准测试上的表现证明了其难度,而具备特定框架的推理代理表现较好。
点此查看论文截图
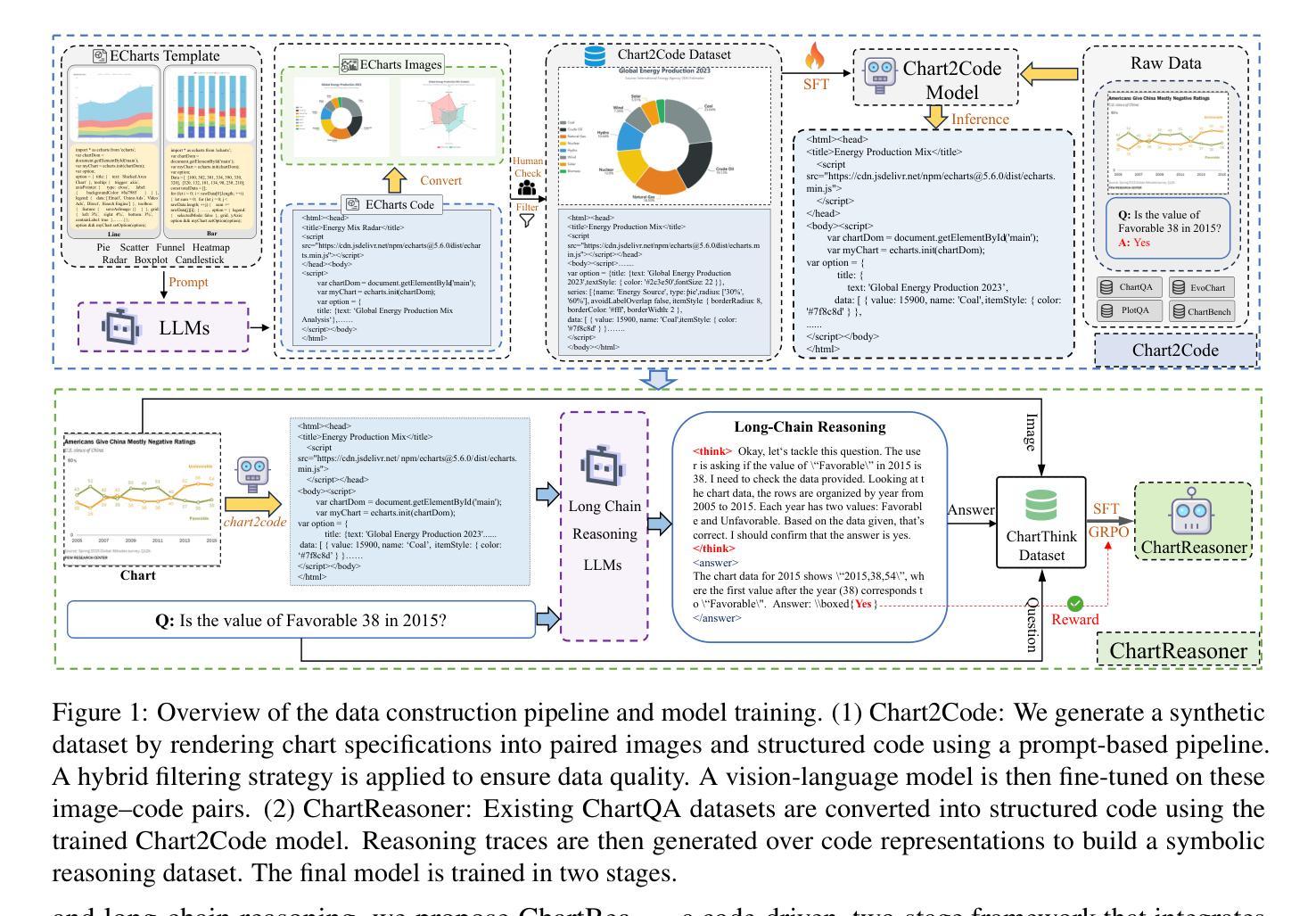
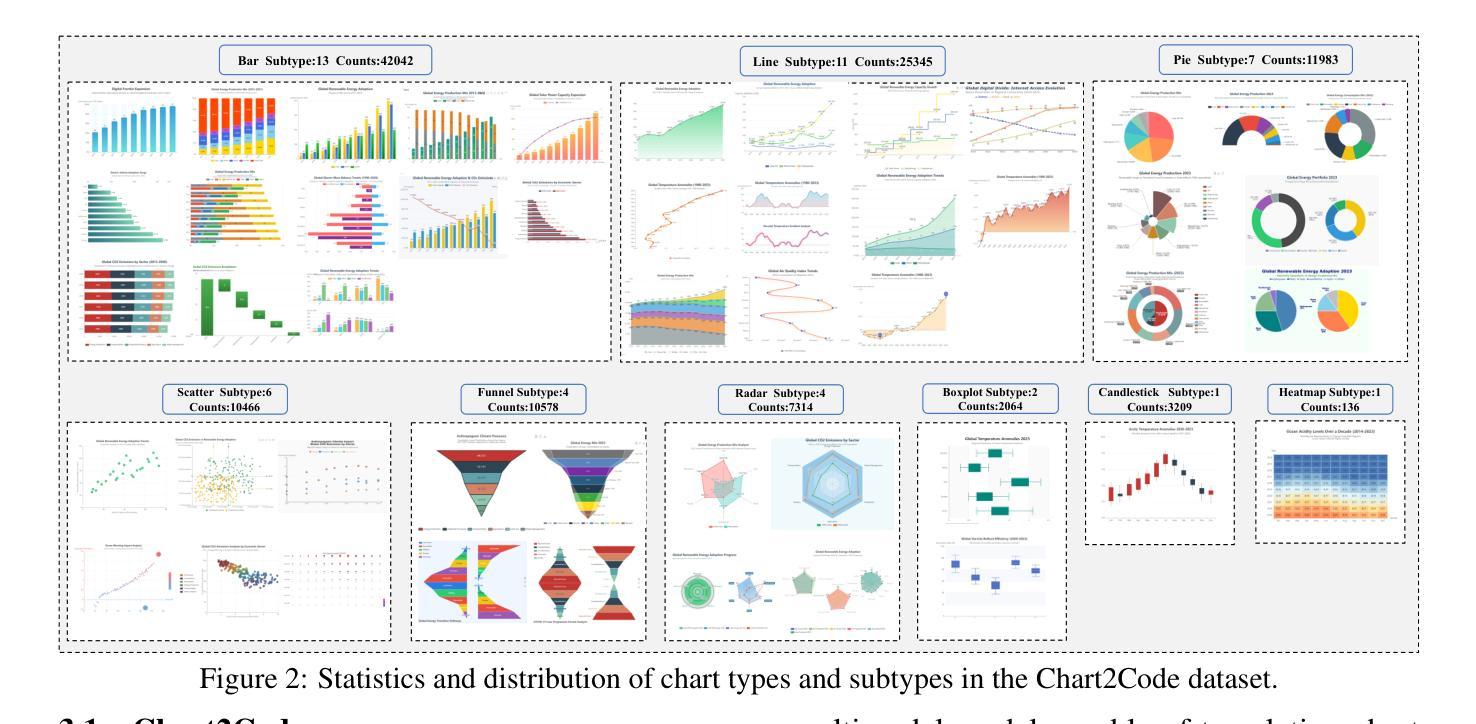
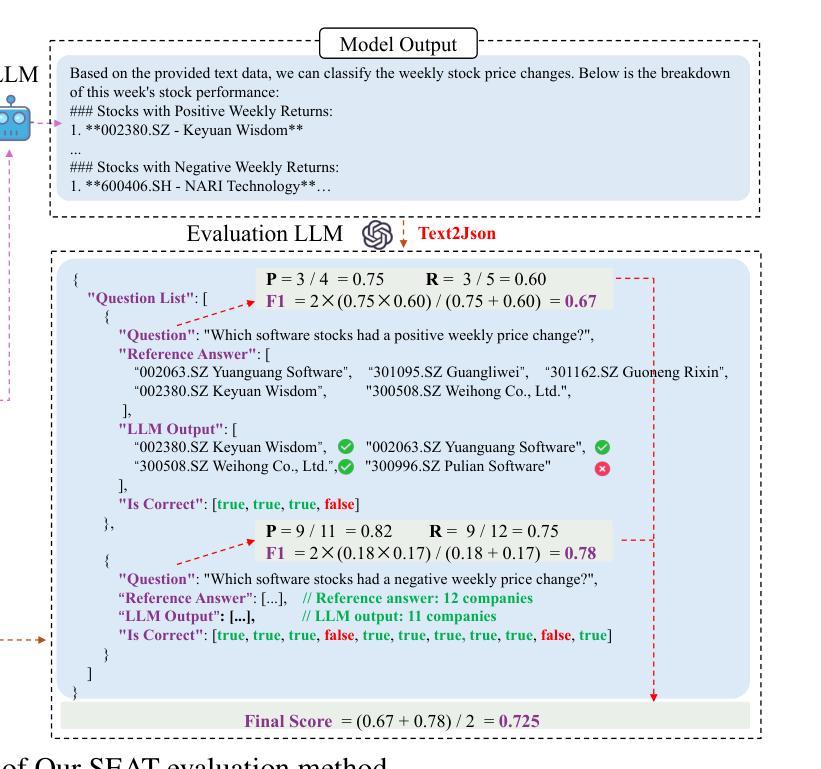
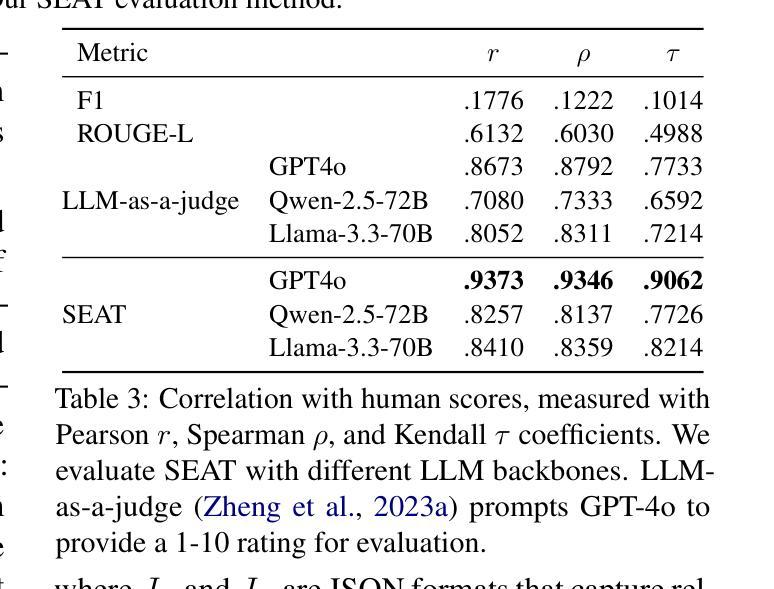
TableEval: A Real-World Benchmark for Complex, Multilingual, and Multi-Structured Table Question Answering
Authors:Junnan Zhu, Jingyi Wang, Bohan Yu, Xiaoyu Wu, Junbo Li, Lei Wang, Nan Xu
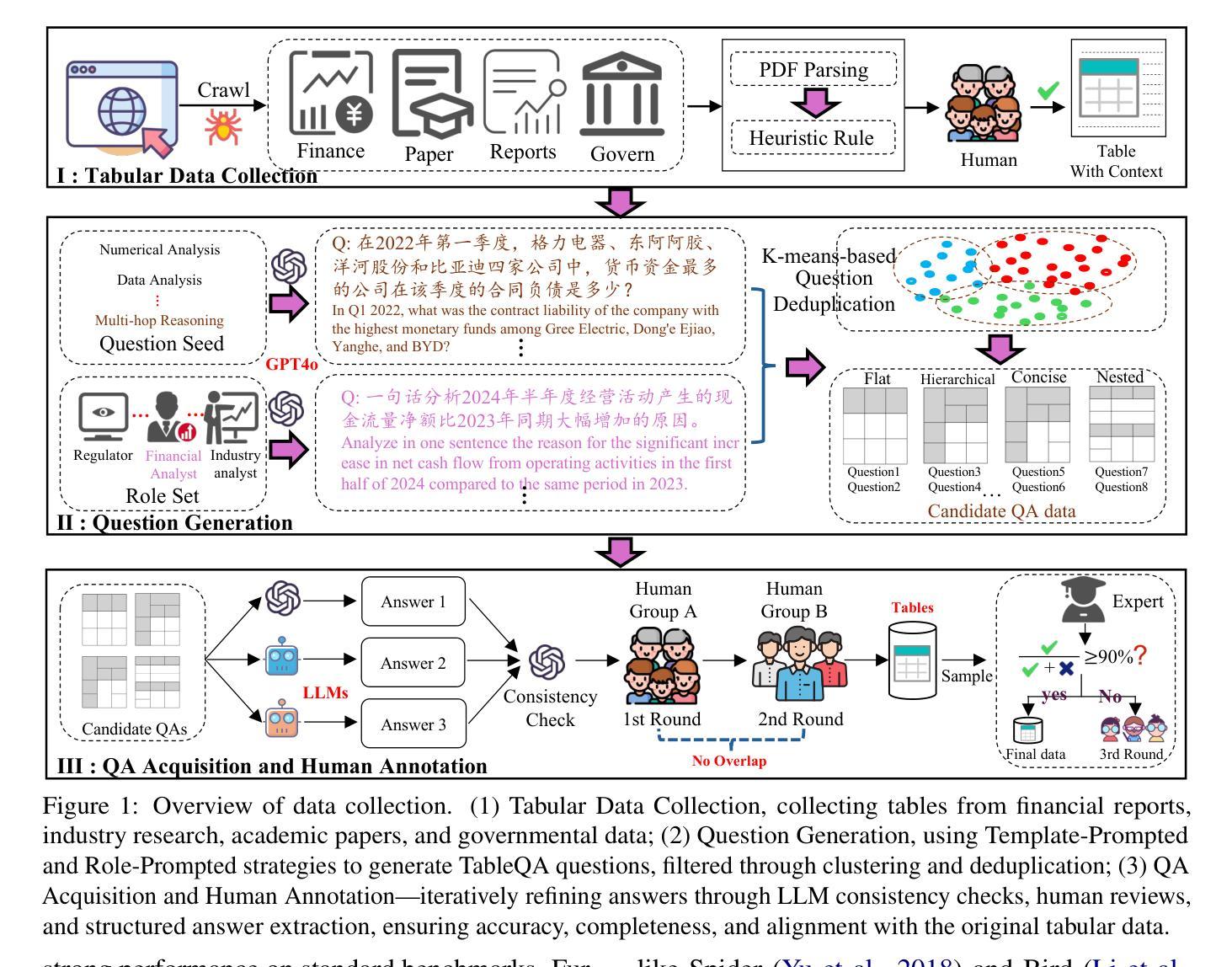
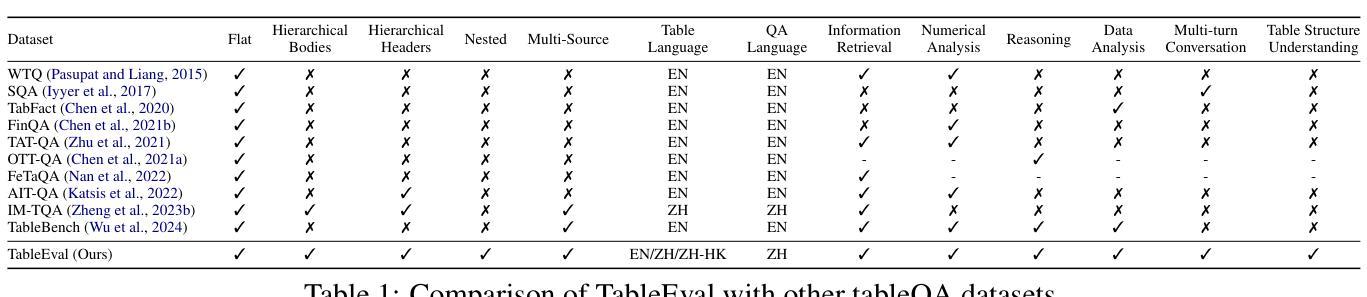
LLMs have shown impressive progress in natural language processing. However, they still face significant challenges in TableQA, where real-world complexities such as diverse table structures, multilingual data, and domain-specific reasoning are crucial. Existing TableQA benchmarks are often limited by their focus on simple flat tables and suffer from data leakage. Furthermore, most benchmarks are monolingual and fail to capture the cross-lingual and cross-domain variability in practical applications. To address these limitations, we introduce TableEval, a new benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs on realistic TableQA tasks. Specifically, TableEval includes tables with various structures (such as concise, hierarchical, and nested tables) collected from four domains (including government, finance, academia, and industry reports). Besides, TableEval features cross-lingual scenarios with tables in Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, and English. To minimize the risk of data leakage, we collect all data from recent real-world documents. Considering that existing TableQA metrics fail to capture semantic accuracy, we further propose SEAT, a new evaluation framework that assesses the alignment between model responses and reference answers at the sub-question level. Experimental results have shown that SEAT achieves high agreement with human judgment. Extensive experiments on TableEval reveal critical gaps in the ability of state-of-the-art LLMs to handle these complex, real-world TableQA tasks, offering insights for future improvements. We make our dataset available here: https://github.com/wenge-research/TableEval.
大型语言模型在自然语言处理方面取得了令人印象深刻的进展。然而,在表格问答(TableQA)领域,它们仍然面临重大挑战。在表格问答中,现实世界中的复杂性至关重要,例如各种表格结构、多语言数据和特定领域的推理。现有的TableQA基准测试通常局限于简单的平面表格,并存在数据泄露的问题。此外,大多数基准测试都是单语言的,无法捕获实际应用中的跨语言和跨领域变化。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了TableEval,这是一个新的基准测试,旨在评估大型语言模型在现实的表格问答任务上的表现。具体来说,TableEval包含从四个领域(包括政府、金融、学术和工业报告)收集的表格,这些表格具有各种结构(如简洁、分层和嵌套表格)。此外,TableEval具有简体中文、繁体中文和英文的跨语言场景。为了最小化数据泄露的风险,我们从最新的现实文档中收集所有数据。考虑到现有的TableQA指标无法捕捉语义准确性,我们进一步提出了SEAT,这是一个新的评估框架,它可以在子问题级别评估模型响应和参考答案之间的对齐程度。实验结果表明,SEAT与人类判断高度一致。在TableEval上的广泛实验揭示了最先进的大型语言模型在处理这些复杂、现实的表格问答任务时的关键差距,为未来的改进提供了见解。我们在以下链接提供了我们的数据集:https://github.com/wenge-research/TableEval 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLMs在自然语言处理方面取得了显著进展,但在TableQA领域仍面临诸多挑战。为解决现有TableQA基准测试在表格结构多样性、多语种数据和领域特定推理等方面的局限性,提出了TableEval新基准测试。TableEval包含来自四个领域的各种结构表格,并具备简化的中文、传统的中文和英文跨语言场景。此外,为评估模型响应与参考答案的语义准确性,提出了SEAT评估框架。实验结果显示SEAT与人类判断高度一致,TableEval上的实验揭示了顶尖LLMs在处理复杂、实际TableQA任务时的关键差距。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在自然语言处理方面取得显著进展,但在TableQA领域仍面临挑战。
- 现有TableQA基准测试主要关注简单表格,存在数据泄露问题。
- TableEval新基准测试旨在评估LLMs在真实TableQA任务上的表现,包含各种结构的表格和跨语言场景。
- TableEval表格数据来自最新真实文档,减少数据泄露风险。
- SEAT评估框架用于评估模型响应与参考答案的语义准确性。
- SEAT与人类判断高度一致,实验验证其有效性。
点此查看论文截图


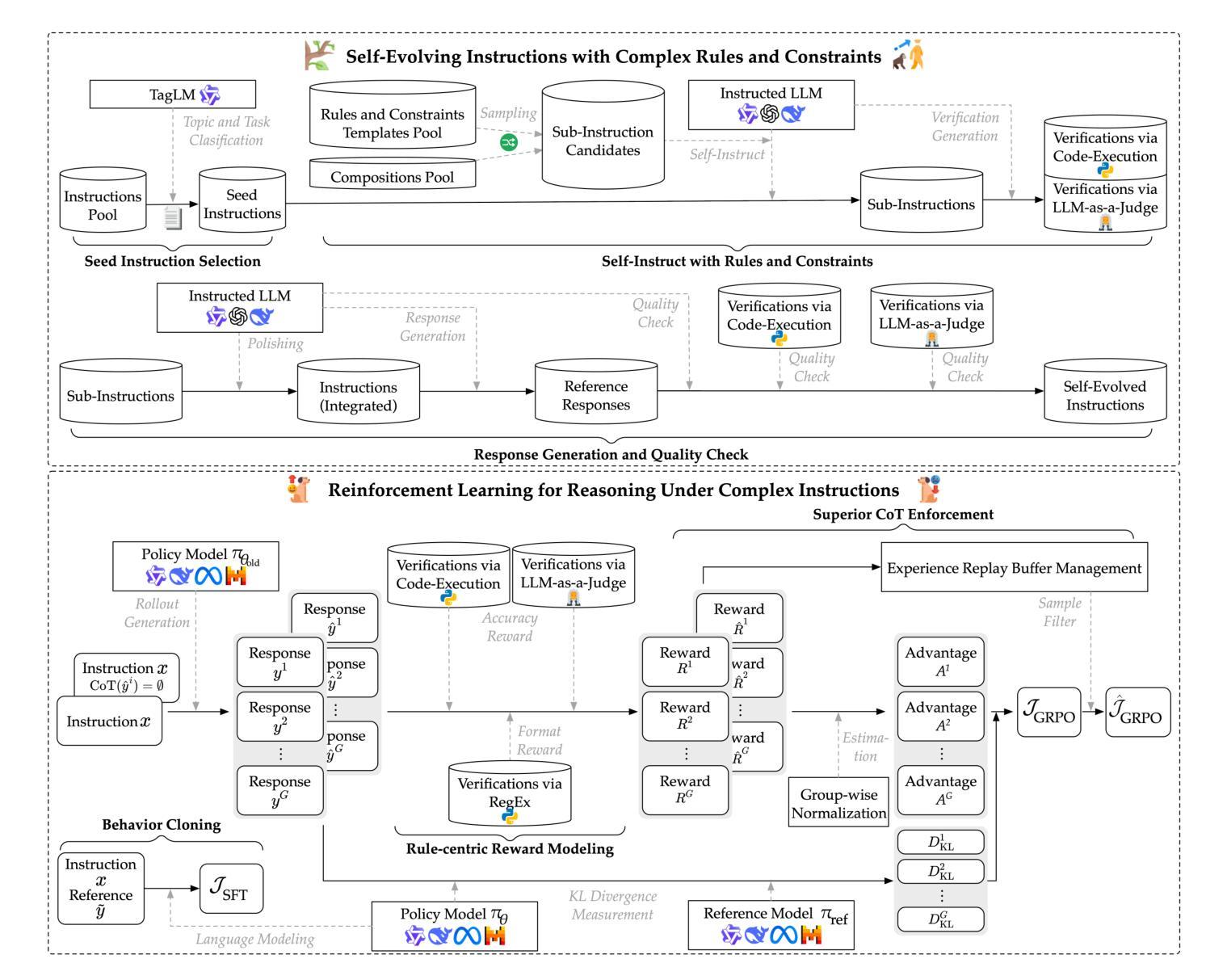
Incentivizing Reasoning for Advanced Instruction-Following of Large Language Models
Authors:Yulei Qin, Gang Li, Zongyi Li, Zihan Xu, Yuchen Shi, Zhekai Lin, Xiao Cui, Ke Li, Xing Sun
Existing large language models (LLMs) face challenges of following complex instructions, especially when multiple constraints are present and organized in paralleling, chaining, and branching structures. One intuitive solution, namely chain-of-thought (CoT), is expected to universally improve capabilities of LLMs. However, we find that the vanilla CoT exerts a negative impact on performance due to its superficial reasoning pattern of simply paraphrasing the instructions. It fails to peel back the compositions of constraints for identifying their relationship across hierarchies of types and dimensions. To this end, we propose a systematic method to boost LLMs in dealing with complex instructions via incentivizing reasoning for test-time compute scaling. First, we stem from the decomposition of complex instructions under existing taxonomies and propose a reproducible data acquisition method. Second, we exploit reinforcement learning (RL) with verifiable rule-centric reward signals to cultivate reasoning specifically for instruction following. We address the shallow, non-essential nature of reasoning under complex instructions via sample-wise contrast for superior CoT enforcement. We also exploit behavior cloning of experts to facilitate steady distribution shift from fast-thinking LLMs to skillful reasoners. Extensive evaluations on seven comprehensive benchmarks confirm the validity of the proposed method, where a 1.5B LLM achieves 11.74% gains with performance comparable to a 8B LLM. Codes and data are available at https://github.com/yuleiqin/RAIF.
现有的大型语言模型(LLM)在遵循复杂指令时面临挑战,尤其是在存在多个约束并以并行、链和分支结构组织时。一种直观的解决方案,即思维链(CoT),有望普遍提高LLM的能力。然而,我们发现原始的CoT由于简单地复述指令而对其性能产生负面影响。它未能剥离约束的组合,以识别其跨类型和维度层次的关系。为此,我们提出了一种通过激励测试时间计算缩放来提高LLM处理复杂指令的系统方法。首先,我们根据现有分类法对复杂指令进行分解,并提出一种可复制的数据采集方法。其次,我们利用可验证的规则中心奖励信号来培养特定的指令遵循推理能力,通过样本对比来解决复杂指令下推理的肤浅和非本质性质,以更好地实施CoT。我们还模仿专家的行为克隆,促进从快速思考的语言模型到熟练推理者的稳定分布转移。在七个综合基准测试上的广泛评估证实了所提出方法的有效性,其中1.5B LLM实现了11.74%的增益,性能可与8B LLM相媲美。相关代码和数据可在https://github.com/yuleiqin/RAIF获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages of main body, 3 tables, 5 figures, 45 pages of appendix
摘要
大型语言模型(LLM)在处理复杂指令时面临挑战,尤其是在存在多种并行、链式和分支结构的约束时。虽然链式思维(CoT)作为一种直观的解决方案有望普遍提高LLM的能力,但我们发现原始的CoT由于简单的指令复述而产生了负面的性能影响。它未能深入剖析约束的组合,以识别不同类型和维度之间的层次关系。因此,我们提出了一种通过激励测试时的计算扩展来提高LLM处理复杂指令能力的方法。首先,我们根据现有的分类体系对复杂指令进行分解,并提出了一种可复制的数据采集方法。其次,我们利用强化学习(RL)和可验证的规则中心奖励信号来培养专门的指令跟随推理能力。我们解决了复杂指令下浅层、非本质推理的特点,通过样本对比来强化先进的CoT实施。我们还模仿专家行为克隆,以在快速思考LLM和技能熟练推理者之间实现稳定的分布转移。在七个综合基准测试上的广泛评估证实了所提出方法的有效性,其中1.5B LLM取得了11.74%的增益,性能可与8B LLM相媲美。相关代码和数据可在链接中获取。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在处理包含多重并行、链式和分支结构的复杂指令时面临挑战。
- 现有的链式思维(CoT)方法因简单指令复述而具有负面性能影响,未能深入剖析约束关系。
- 提出了一种通过激励推理来提高LLM处理复杂指令能力的方法,涉及复杂指令的分解、数据采集、强化学习和行为克隆。
- 该方法强化了规则中心的奖励信号,通过样本对比强化先进的CoT实施。
- 方法的有效性在七个基准测试上得到广泛验证,其中小模型性能显著提升,接近大型模型的性能。
- 相关代码和数据已在指定链接中公开,便于研究者和开发者使用。
点此查看论文截图


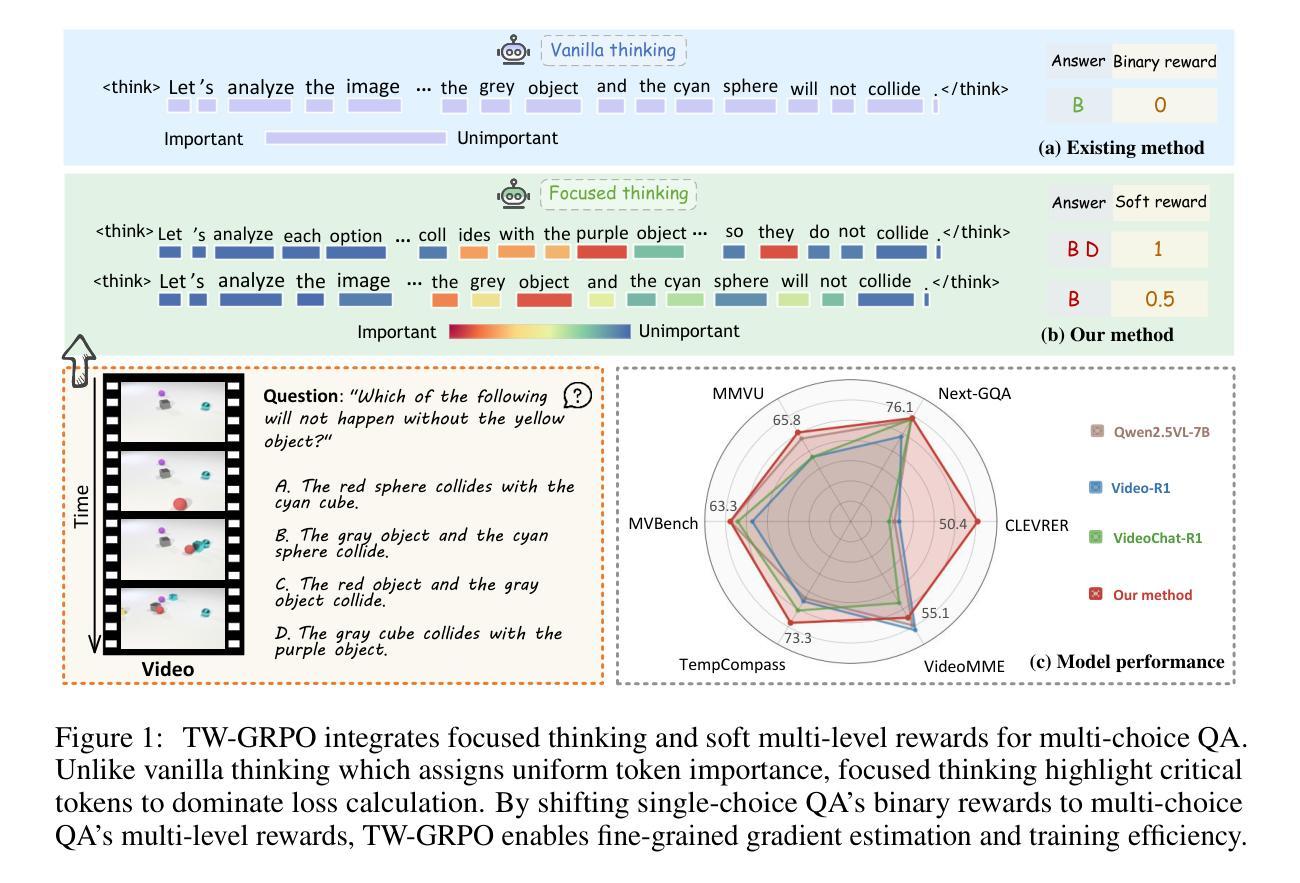
Reinforcing Video Reasoning with Focused Thinking
Authors:Jisheng Dang, Jingze Wu, Teng Wang, Xuanhui Lin, Nannan Zhu, Hongbo Chen, Wei-Shi Zheng, Meng Wang, Tat-Seng Chua
Recent advancements in reinforcement learning, particularly through Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), have significantly improved multimodal large language models for complex reasoning tasks. However, two critical limitations persist: 1) they often produce unfocused, verbose reasoning chains that obscure salient spatiotemporal cues and 2) binary rewarding fails to account for partially correct answers, resulting in high reward variance and inefficient learning. In this paper, we propose TW-GRPO, a novel framework that enhances visual reasoning with focused thinking and dense reward granularity. Specifically, we employs a token weighting mechanism that prioritizes tokens with high informational density (estimated by intra-group information entropy), suppressing redundant tokens like generic reasoning prefixes. Furthermore, we reformulate RL training by shifting from single-choice to multi-choice QA tasks, where soft rewards enable finer-grained gradient estimation by distinguishing partial correctness. Additionally, we propose question-answer inversion, a data augmentation strategy to generate diverse multi-choice samples from existing benchmarks. Experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance on several video reasoning and general understanding benchmarks. Notably, TW-GRPO achieves 50.4% accuracy on CLEVRER (18.8% improvement over Video-R1) and 65.8% on MMVU. Our codes are available at \href{https://github.com/longmalongma/TW-GRPO}.
近期强化学习领域的进步,特别是通过群体相对策略优化(GRPO),已经显著提升了多模态大型语言模型在复杂推理任务上的表现。然而,仍存在两个关键局限:1)它们通常产生不聚焦、冗长的推理链,掩盖了重要的时空线索;2)二元奖励无法考虑部分正确的答案,导致奖励方差高和学习效率低下。在本文中,我们提出了TW-GRPO,这是一个新型框架,通过聚焦思考和密集的奖励粒度增强视觉推理。具体来说,我们采用了一种标记权重机制,优先处理具有高信息密度的标记(通过组内信息熵估计),同时抑制冗余标记,如通用推理前缀。此外,我们重新设计RL训练,从单选问题转向多选问答任务,其中软奖励能够通过区分部分正确性来实现更精细的梯度估计。我们还提出了问题答案反转,这是一种数据增强策略,可以从现有基准测试中生成多样化的多选择样本。实验表明,我们在多个视频推理和通用理解基准测试中达到了最先进的性能。值得注意的是,TW-GRPO在CLEVRER上实现了50.4%的准确率(相较于Video-R1有18.8%的提升),在MMVU上实现了65.8%的准确率。我们的代码可在https://github.com/longmalongma/TW-GRPO获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期强化学习在Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)方面的进展显著提升了多模态大型语言模型在复杂推理任务上的表现。然而,仍存在两个关键问题:一是产生的推理链往往不聚焦且冗长,难以捕捉时空线索;二是二元奖励机制无法应对部分正确答案,导致奖励方差大且学习效率低。本文提出TW-GRPO框架,通过标记权重机制强化视觉推理的聚焦思考,并引入精细奖励粒度。此外,从单选题转向多选题问答任务,软奖励能够更精细地估计梯度并区分部分正确性。实验证明,TW-GRPO在多个视频推理和通用理解基准测试上表现卓越,如在CLEVRER上达到50.4%的准确率(较Video-R1提高18.8%),在MMVU上达到65.8%。相关代码已公开于指定链接。
Key Takeaways
- Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)强化学习在提升多模态语言模型复杂推理任务性能上取得显著进展。
- 存在两个关键问题:推理链不聚焦和奖励机制无法应对部分正确答案。
- TW-GRPO框架通过标记权重机制强化视觉推理的聚焦思考,并引入精细奖励粒度来解决上述问题。
- 从单选题转向多选题问答任务,软奖励能够更精细地区分答案的正确性。
- TW-GRPO在多个基准测试上表现卓越,如在CLEVRER和MMVU上的高准确率表现。
- 代码已公开并提供链接供公众访问。
点此查看论文截图

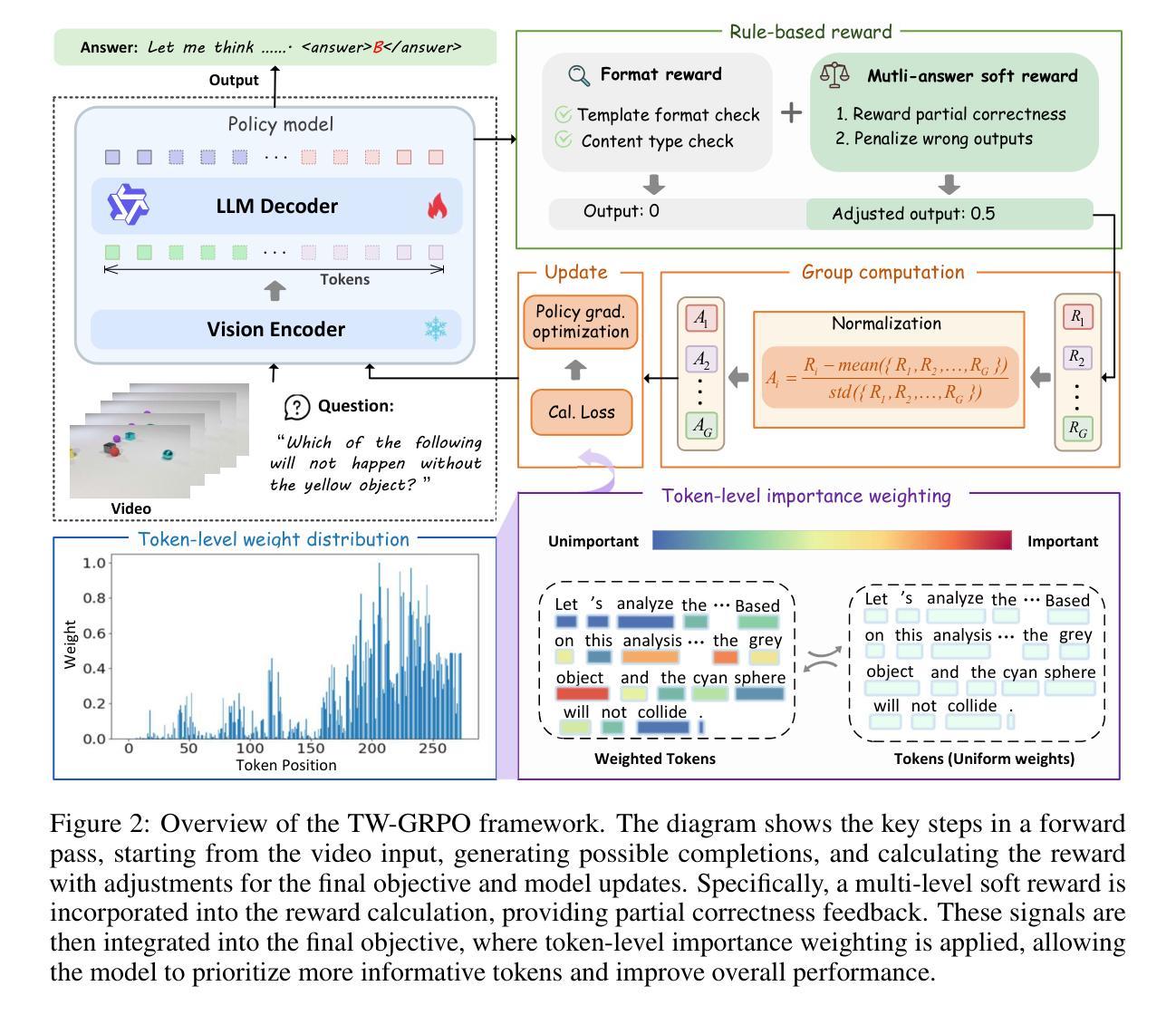
Enigmata: Scaling Logical Reasoning in Large Language Models with Synthetic Verifiable Puzzles
Authors:Jiangjie Chen, Qianyu He, Siyu Yuan, Aili Chen, Zhicheng Cai, Weinan Dai, Hongli Yu, Qiying Yu, Xuefeng Li, Jiaze Chen, Hao Zhou, Mingxuan Wang
Large Language Models (LLMs), such as OpenAI’s o1 and DeepSeek’s R1, excel at advanced reasoning tasks like math and coding via Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR), but still struggle with puzzles solvable by humans without domain knowledge. We introduce Enigmata, the first comprehensive suite tailored for improving LLMs with puzzle reasoning skills. It includes 36 tasks across seven categories, each with 1) a generator that produces unlimited examples with controllable difficulty and 2) a rule-based verifier for automatic evaluation. This generator-verifier design supports scalable, multi-task RL training, fine-grained analysis, and seamless RLVR integration. We further propose Enigmata-Eval, a rigorous benchmark, and develop optimized multi-task RLVR strategies. Our trained model, Qwen2.5-32B-Enigmata, consistently surpasses o3-mini-high and o1 on the puzzle reasoning benchmarks like Enigmata-Eval, ARC-AGI (32.8%), and ARC-AGI 2 (0.6%). It also generalizes well to out-of-domain puzzle benchmarks and mathematical reasoning, with little multi-tasking trade-off. When trained on larger models like Seed1.5-Thinking (20B activated parameters and 200B total parameters), puzzle data from Enigmata further boosts SoTA performance on advanced math and STEM reasoning tasks such as AIME (2024-2025), BeyondAIME and GPQA (Diamond), showing nice generalization benefits of Enigmata. This work offers a unified, controllable framework for advancing logical reasoning in LLMs. Resources of this work can be found at https://seed-enigmata.github.io.
大型语言模型(LLM),如OpenAI的o1和DeepSeek的R1,通过强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)在数学和编码等高级推理任务方面表现出色,但在解决人类无需领域知识即可解决的谜题方面仍面临困难。我们引入了Enigmata,这是第一个针对提高LLM的谜题推理技能而量身定制的综合套件。它包括7个类别的36项任务,每个类别都具备1)能够产生无限可控难度范例的生成器,以及2)用于自动评估的规则验证器。这种生成器-验证器的设计支持可扩展的多任务强化学习训练、精细分析以及无缝RLVR集成。我们进一步提出了严格的基准测试Enigmata-Eval,并开发了优化的多任务RLVR策略。我们的训练模型Qwen2.5-32B-Enigmata在谜题推理基准测试(如Enigmata-Eval、ARC-AGI 32.8%和ARC-AGI 2 0.6%)上始终超过o3-mini-high和o1。它还能很好地推广到域外谜题基准测试和数学推理,多任务权衡很小。当在更大的模型(如Seed1.5-Thinking(20B激活参数和200B总参数))上进行训练时,Enigmata的谜题数据进一步提高了在高级数学和STEM推理任务(如AIME(2024-2025)、BeyondAIME和GPQA(Diamond))上的最新性能,显示出Enigmata良好的泛化效益。这项工作为推进LLM的逻辑推理提供了一个统一、可控的框架。该工作的资源可在https://seed-enigmata.github.io找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在强化学习可验证奖励(RLVR)的数学和编码等高级任务上表现出色,但在解决人类无需领域知识即可解决的谜题方面仍存在困难。为解决此问题,推出了Enigmata套件,旨在提升LLMs的谜题推理能力。它包括七大类别共36项任务,每个类别都配备可生成无限例题并按难度控制的生成器和基于规则的自动评估验证器。Enigmata-Eval的严格基准测试和优化的多任务RLVR策略进一步提升模型性能。经过Enigmata训练的Qwen2.5-32B模型在谜题推理基准测试上超越了o3-mini-high和o1,并具有良好的跨域泛化能力。当在更大的模型上进行训练时,如Seed1.5-Thinking(已激活参数为二十亿,总参数为二百亿),来自Enigmata的谜题数据进一步提升了其在高级数学和STEM推理任务上的性能。此工作提供了一个统一、可控的框架,以推动LLMs的逻辑推理能力发展。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在高级推理任务上表现卓越,但仍面临解决人类无需特定领域知识即可解决的谜题挑战。
- Enigmata套件旨在提升LLMs的谜题推理能力,包括七大类别共36项任务,配备生成器和验证器支持多任务训练、精细分析以及与RLVR无缝集成。
- Enigmata提供严格的基准测试(Enigmata-Eval)和优化的多任务RLVR策略。
- Qwen2.5-32B模型经过Enigmata训练后,在谜题推理基准测试中表现优于其他模型,并展现出良好的泛化能力。
- Enigmata套件有助于提升LLMs在数学和STEM领域的推理能力。
- Enigmata提供了一个统一、可控的框架,有助于推动LLMs的逻辑推理能力发展。
点此查看论文截图

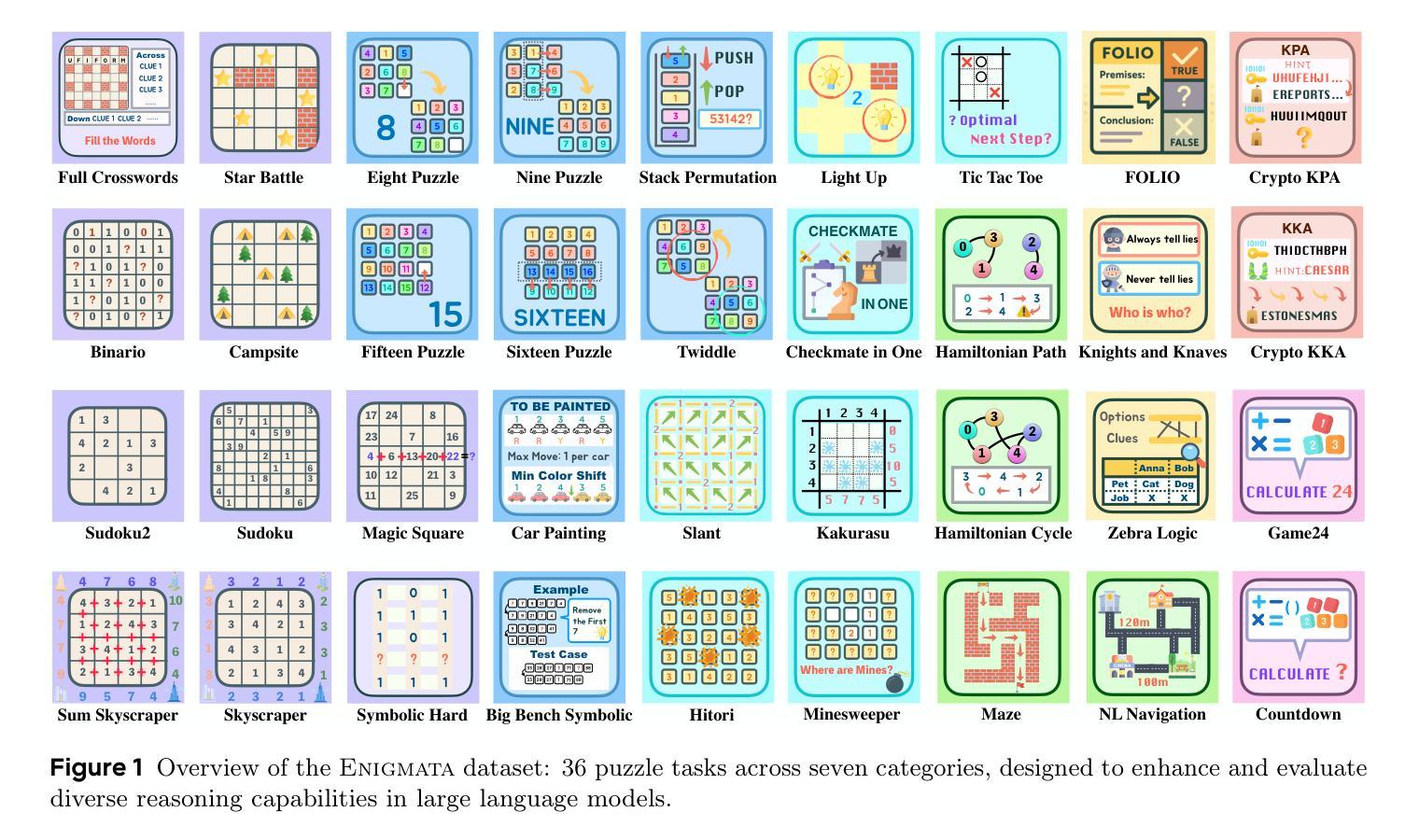
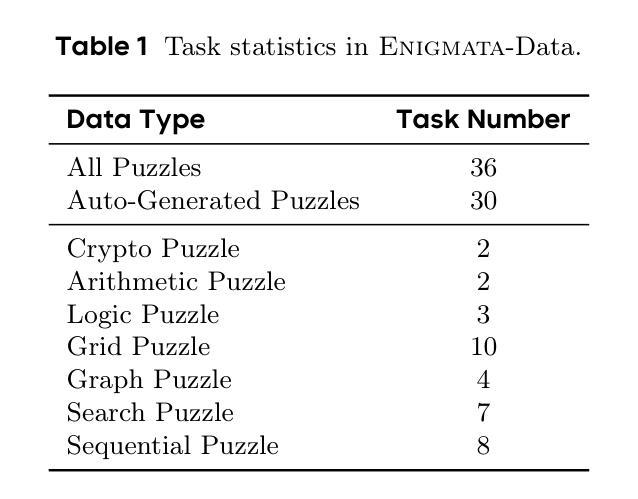
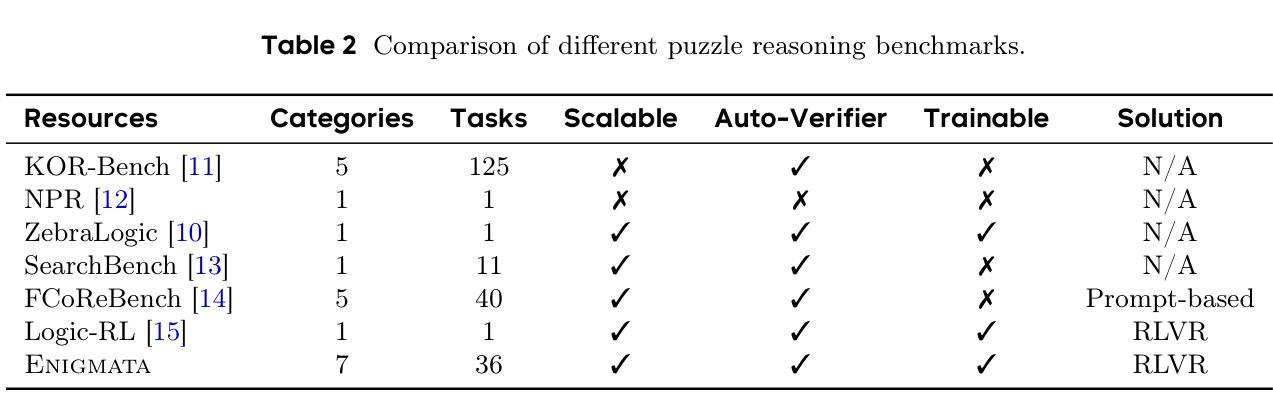
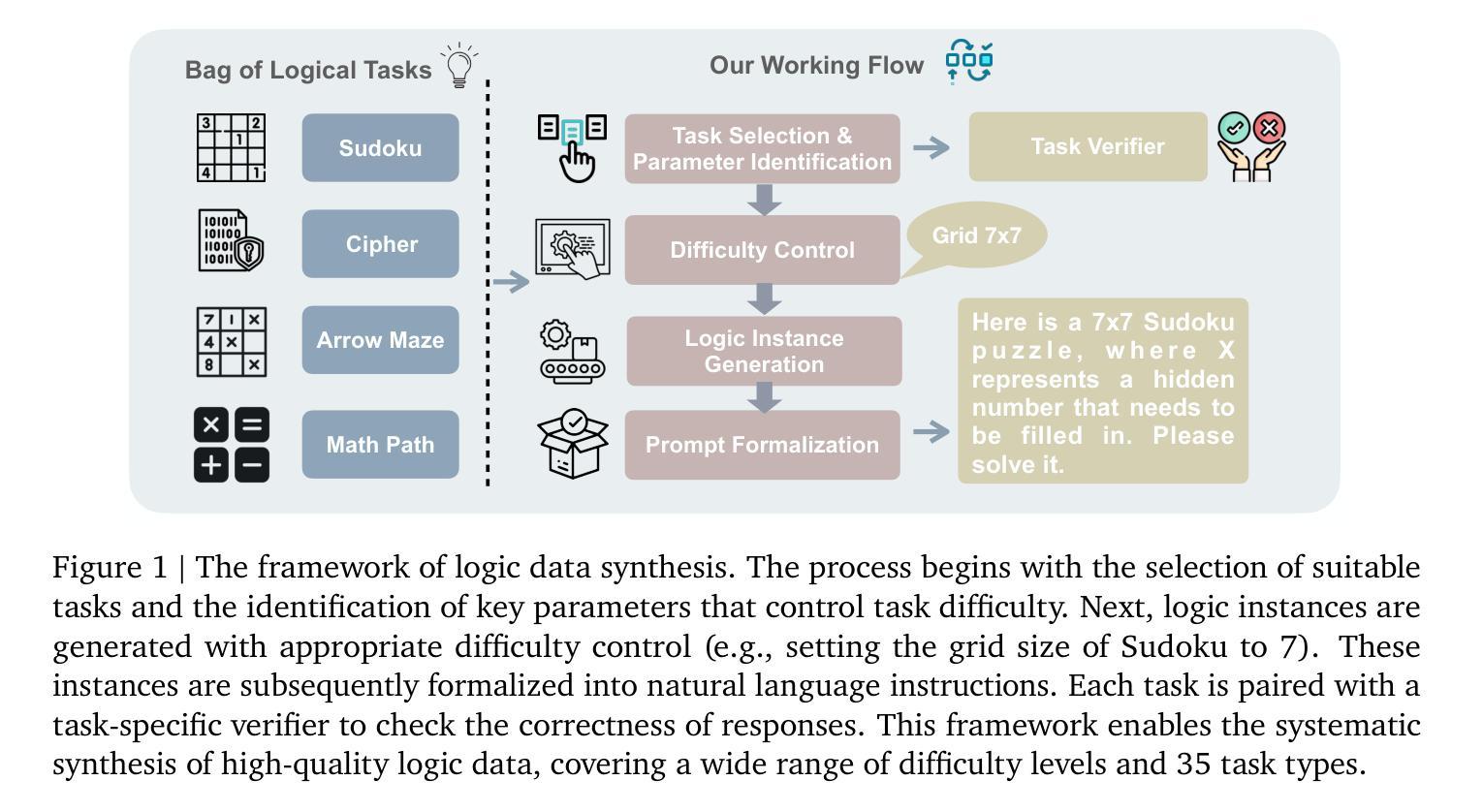
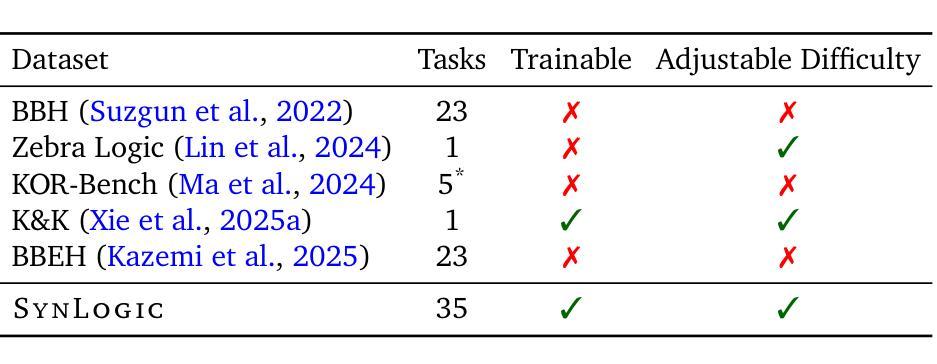
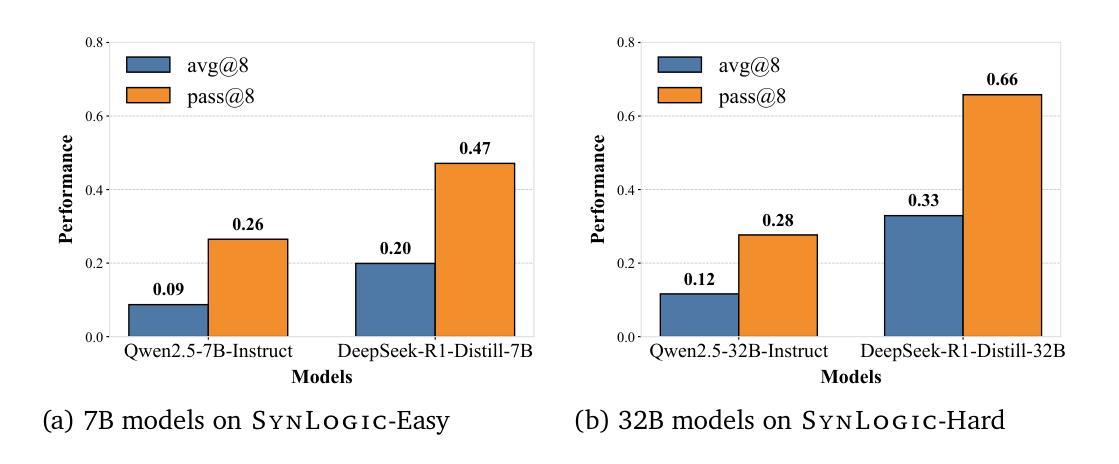
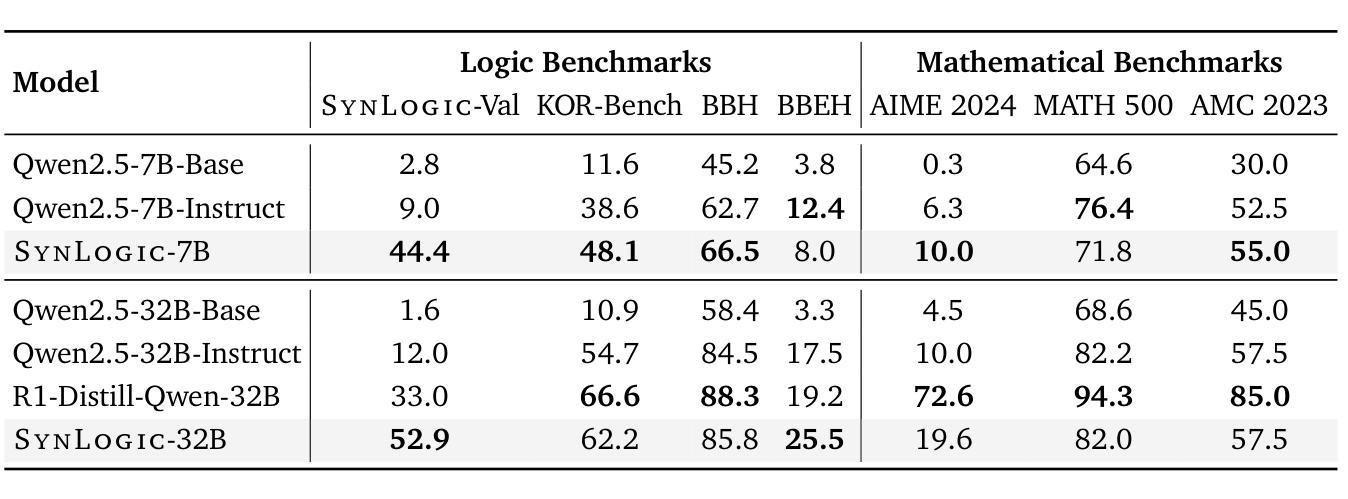
SynLogic: Synthesizing Verifiable Reasoning Data at Scale for Learning Logical Reasoning and Beyond
Authors:Junteng Liu, Yuanxiang Fan, Zhuo Jiang, Han Ding, Yongyi Hu, Chi Zhang, Yiqi Shi, Shitong Weng, Aili Chen, Shiqi Chen, Yunan Huang, Mozhi Zhang, Pengyu Zhao, Junjie Yan, Junxian He
Recent advances such as OpenAI-o1 and DeepSeek R1 have demonstrated the potential of Reinforcement Learning (RL) to enhance reasoning abilities in Large Language Models (LLMs). While open-source replication efforts have primarily focused on mathematical and coding domains, methods and resources for developing general reasoning capabilities remain underexplored. This gap is partly due to the challenge of collecting diverse and verifiable reasoning data suitable for RL. We hypothesize that logical reasoning is critical for developing general reasoning capabilities, as logic forms a fundamental building block of reasoning. In this work, we present SynLogic, a data synthesis framework and dataset that generates diverse logical reasoning data at scale, encompassing 35 diverse logical reasoning tasks. The SynLogic approach enables controlled synthesis of data with adjustable difficulty and quantity. Importantly, all examples can be verified by simple rules, making them ideally suited for RL with verifiable rewards. In our experiments, we validate the effectiveness of RL training on the SynLogic dataset based on 7B and 32B models. SynLogic leads to state-of-the-art logical reasoning performance among open-source datasets, surpassing DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B by 6 points on BBEH. Furthermore, mixing SynLogic data with mathematical and coding tasks improves the training efficiency of these domains and significantly enhances reasoning generalization. Notably, our mixed training model outperforms DeepSeek-R1-Zero-Qwen-32B across multiple benchmarks. These findings position SynLogic as a valuable resource for advancing the broader reasoning capabilities of LLMs. We open-source both the data synthesis pipeline and the SynLogic dataset at https://github.com/MiniMax-AI/SynLogic.
近期,如OpenAI-o1和DeepSeek R1等进展表明了强化学习(RL)在提升大型语言模型(LLM)推理能力方面的潜力。虽然开源复制工作主要关注数学和编码领域,但开发通用推理能力的方法和资源仍然探索不足。这一差距部分是由于收集适合强化学习的多样化和可验证的推理数据具有挑战性。我们假设逻辑推理对于开发通用推理能力至关重要,因为逻辑是推理的基本组成部分。在这项工作中,我们提出了SynLogic,这是一个数据合成框架和数据集,可以大规模生成多样的逻辑推理数据,涵盖35种不同的逻辑推理任务。SynLogic方法能够控制数据和调整难度和数量。重要的是,所有例子都可以通过简单规则进行验证,使它们非常适合具有可验证奖励的强化学习。在我们的实验中,我们验证了强化学习在SynLogic数据集上训练的有效性,基于7B和32B模型。SynLogic在开源数据集中处于最先进的逻辑推理性能地位,在BBEH上超越了DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B 6个点。此外,将SynLogic数据与数学和编码任务混合,提高了这些领域的训练效率,并显著增强了推理泛化能力。值得注意的是,我们的混合训练模型在多个基准测试上超越了DeepSeek-R1-Zero-Qwen-32B。这些发现使SynLogic成为推动LLM更广泛推理能力的重要资源。我们在https://github.com/MiniMax-AI/SynLogic处开源了数据合成管道和SynLogic数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了SynLogic数据合成框架和数据集,用于生成涵盖35种不同逻辑推理任务的多样化数据。该数据集可通过控制合成数据的难度和数量来调整,所有实例都可以通过简单规则进行验证,非常适合使用可验证奖励的强化学习。实验表明,基于SynLogic数据集进行强化学习训练可有效提高逻辑推理性能,并优于其他开源数据集。此外,将SynLogic数据与数学和编码任务混合训练,可提高这些领域的训练效率,并显著增强推理泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- SynLogic是一个用于生成大规模逻辑推理数据的合成框架和数据集。
- 该数据集涵盖35种不同的逻辑推理任务,并可通过调整难度和数量来控制数据的合成。
- SynLogic数据所有实例均可通过简单规则进行验证,适合用于强化学习。
- 强化学习在SynLogic数据集上的训练可有效提高逻辑推理性能。
- SynLogic数据在开放源代码数据集上达到先进水平,尤其是在BBEH上的得分超过了DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B 6个点。
- 将SynLogic数据与数学和编码任务混合训练,可以提高这些领域的训练效率并增强推理泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

Delving into RL for Image Generation with CoT: A Study on DPO vs. GRPO
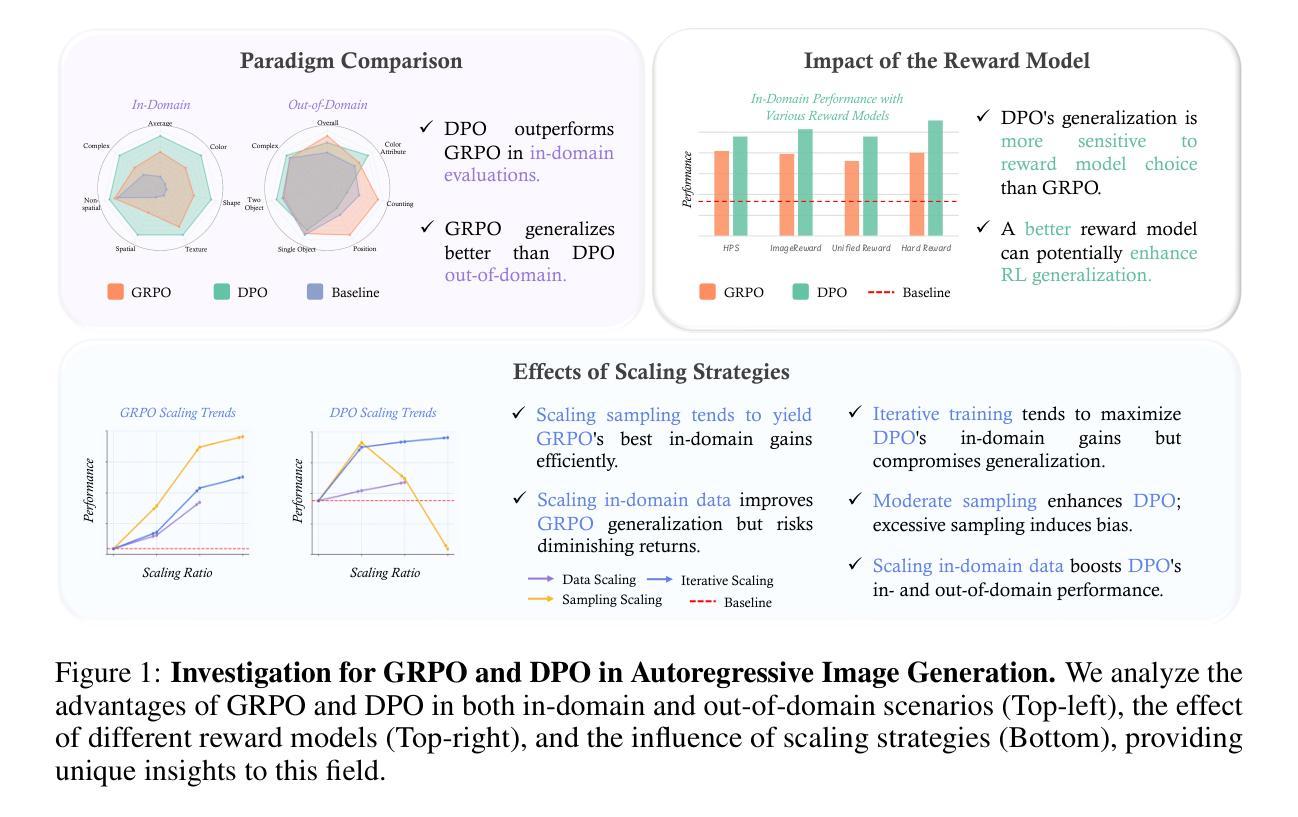
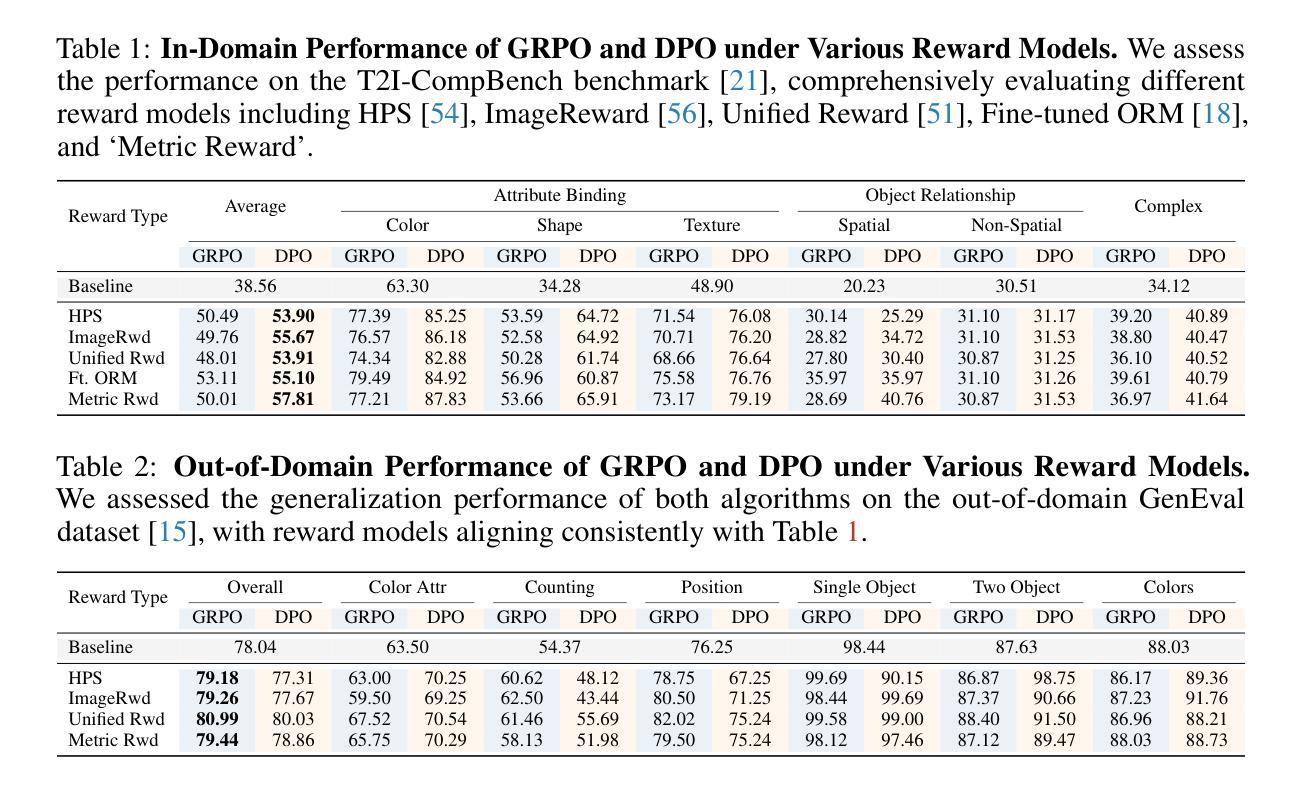
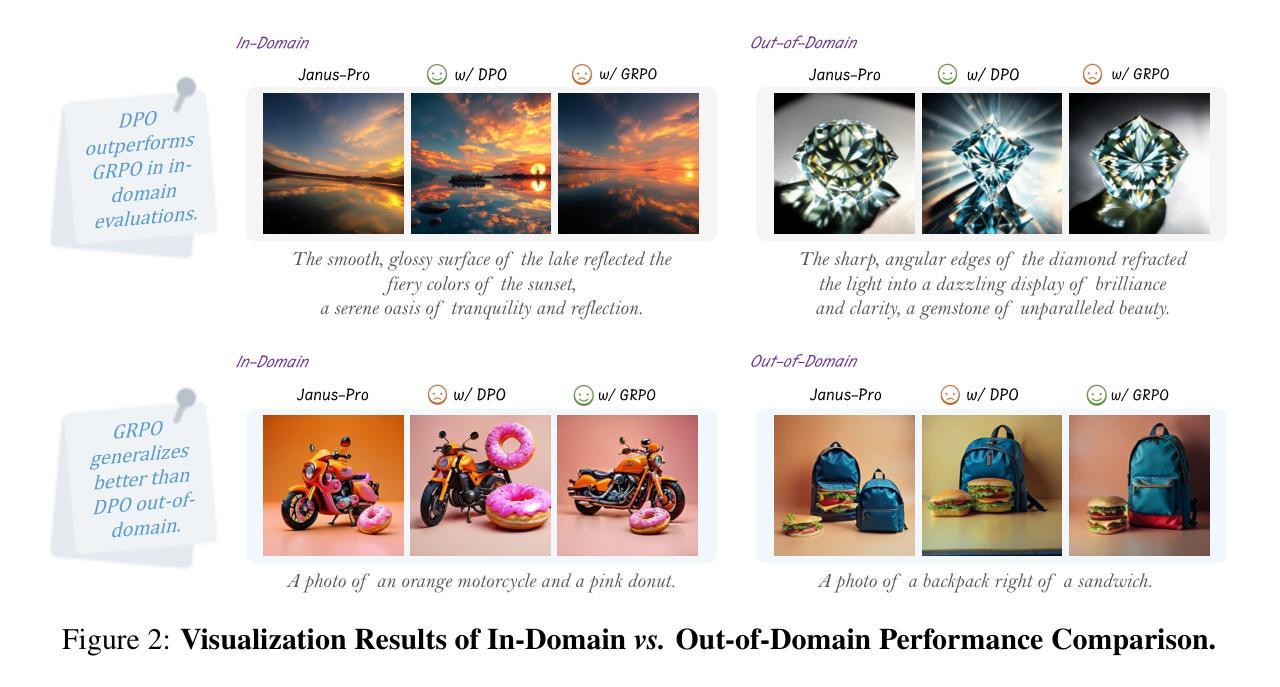
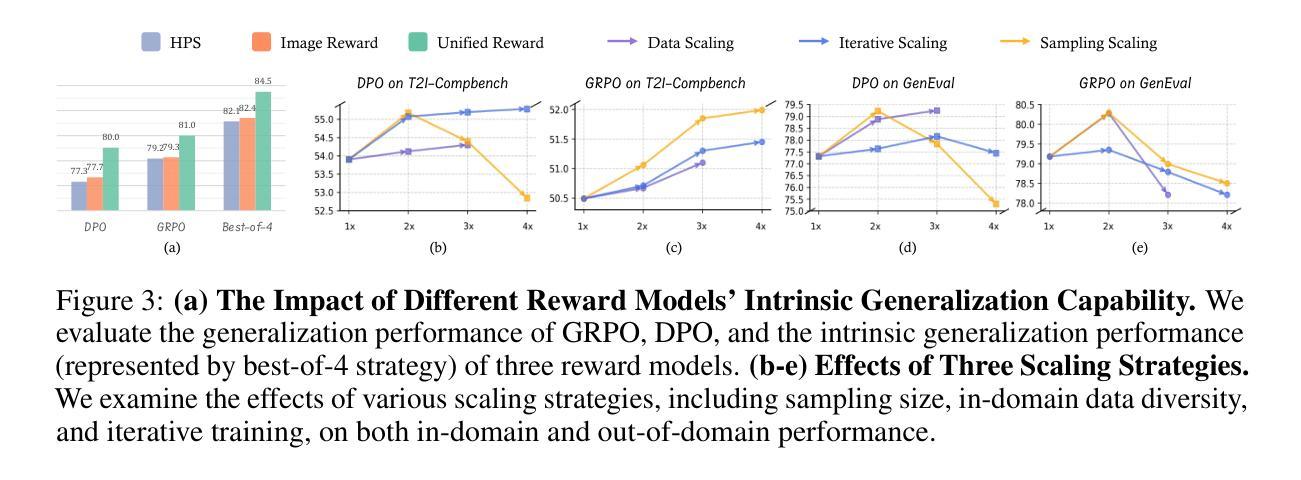
Authors:Chengzhuo Tong, Ziyu Guo, Renrui Zhang, Wenyu Shan, Xinyu Wei, Zhenghao Xing, Hongsheng Li, Pheng-Ann Heng
Recent advancements underscore the significant role of Reinforcement Learning (RL) in enhancing the Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Two prominent RL algorithms, Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) and Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), are central to these developments, showcasing different pros and cons. Autoregressive image generation, also interpretable as a sequential CoT reasoning process, presents unique challenges distinct from LLM-based CoT reasoning. These encompass ensuring text-image consistency, improving image aesthetic quality, and designing sophisticated reward models, rather than relying on simpler rule-based rewards. While recent efforts have extended RL to this domain, these explorations typically lack an in-depth analysis of the domain-specific challenges and the characteristics of different RL strategies. To bridge this gap, we provide the first comprehensive investigation of the GRPO and DPO algorithms in autoregressive image generation, evaluating their in-domain performance and out-of-domain generalization, while scrutinizing the impact of different reward models on their respective capabilities. Our findings reveal that GRPO and DPO exhibit distinct advantages, and crucially, that reward models possessing stronger intrinsic generalization capabilities potentially enhance the generalization potential of the applied RL algorithms. Furthermore, we systematically explore three prevalent scaling strategies to enhance both their in-domain and out-of-domain proficiency, deriving unique insights into efficiently scaling performance for each paradigm. We hope our study paves a new path for inspiring future work on developing more effective RL algorithms to achieve robust CoT reasoning in the realm of autoregressive image generation. Code is released at https://github.com/ZiyuGuo99/Image-Generation-CoT
最近的发展突显了强化学习(RL)在提升大型语言模型(LLM)的链式思维(CoT)推理能力中的重要作用。两种突出的强化学习算法——直接偏好优化(DPO)和群组相对策略优化(GRPO)——是这些发展的核心,展示了各自的优势和劣势。自动回归图像生成,也可解释为一种连续的CoT推理过程,呈现出与基于LLM的CoT推理不同的独特挑战。这些挑战包括确保文本与图像的一致性、提高图像的审美质量,以及设计复杂奖励模型,而不是依赖更简单的基于规则的奖励。尽管最近的努力已经将强化学习扩展到了这个领域,但这些探索通常缺乏对特定领域挑战和不同的强化学习策略特点的深入分析。为了弥补这一空白,我们对自动回归图像生成中的GRPO和DPO算法进行了首次全面的调查,评估了它们的领域内性能和跨领域泛化能力,同时仔细研究了不同奖励模型对其各自能力的影响。我们的研究发现,GRPO和DPO具有各自独特的优势,而且重要的是,具有更强内在泛化能力的奖励模型可能提高了所应用强化学习算法的泛化潜力。此外,我们系统地探索了三种流行的扩展策略,以提高它们在不同领域的专业能力,为每种范式有效地扩展性能提供了独特的见解。我们希望我们的研究能为未来开发更有效的强化学习算法的工作铺平道路,以实现自动回归图像生成领域的稳健CoT推理。代码已发布在https://github.com/ZiyuGuo99/Image-Generation-CoT。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code is released at https://github.com/ZiyuGuo99/Image-Generation-CoT
Summary
强化学习在提升大型语言模型的链式思维推理能力中发挥着重要作用。本文主要探讨了Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)和Direct Preference Optimization (DPO)两种强化学习算法在自动图像生成中的应用。研究发现在自动图像生成中,这两种算法各有优势,并且具有更强内在泛化能力的奖励模型能够提升算法的泛化潜力。此外,本文还探讨了三种流行的扩展策略来提升算法在领域内的表现,并对于每一种策略进行了深入的分析。本研究的发现将有助于为未来研发更高效的强化学习算法,实现自动图像生成中的稳健思维推理开辟新的路径。代码已开源于GitHub。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习在提升大型语言模型的链式思维推理能力方面扮演重要角色。
- Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)和Direct Preference Optimization (DPO)在自动图像生成中具有不同的优势。
- 奖励模型拥有更强的内在泛化能力有助于增强强化学习算法的泛化潜力。
- 三种扩展策略在提升算法在领域内表现上被深入探讨并产生独特见解。
点此查看论文截图

Learning to Reason via Mixture-of-Thought for Logical Reasoning
Authors:Tong Zheng, Lichang Chen, Simeng Han, R. Thomas McCoy, Heng Huang
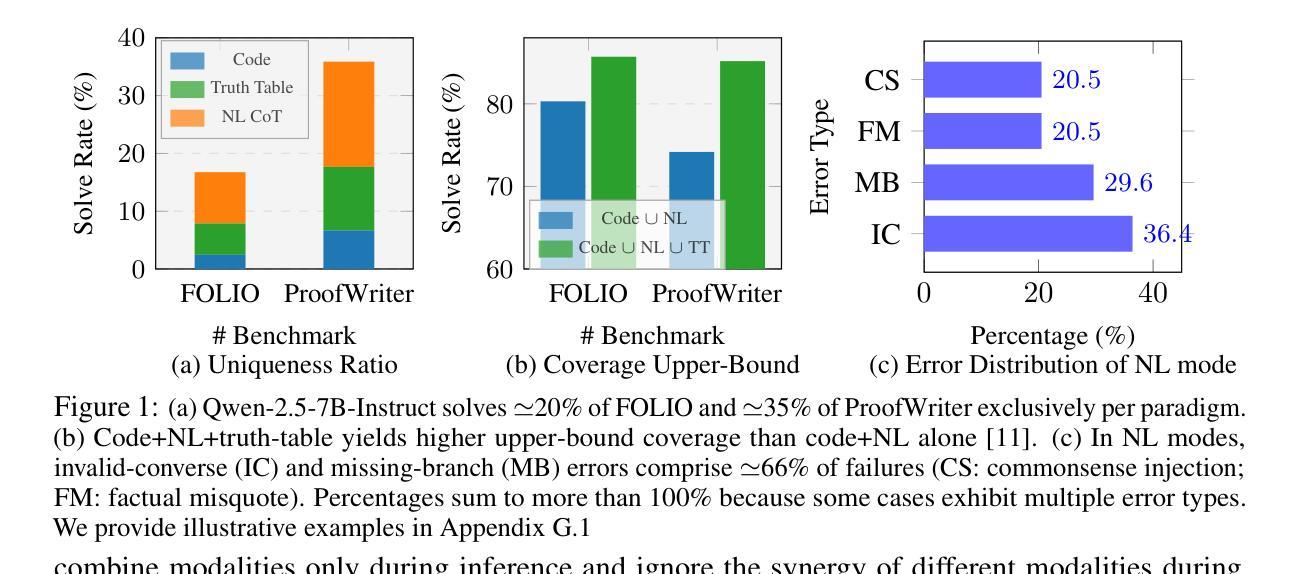
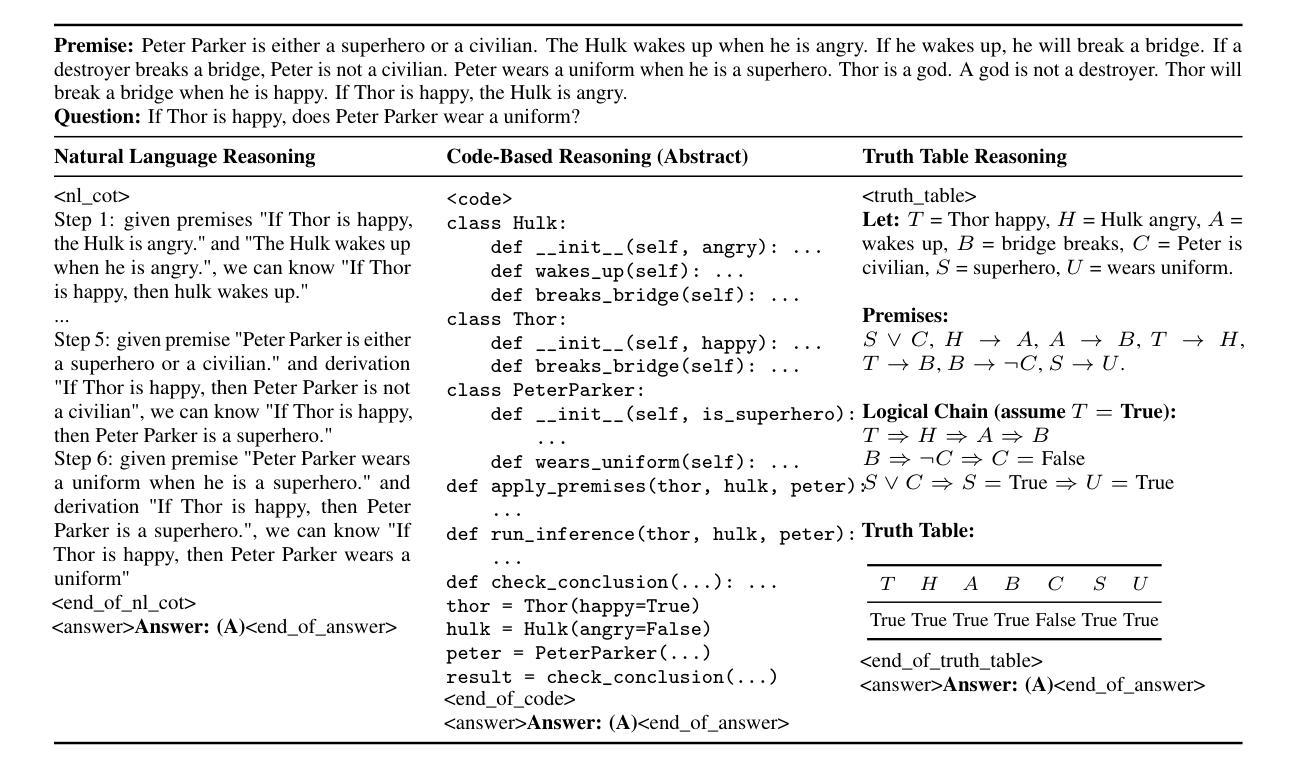
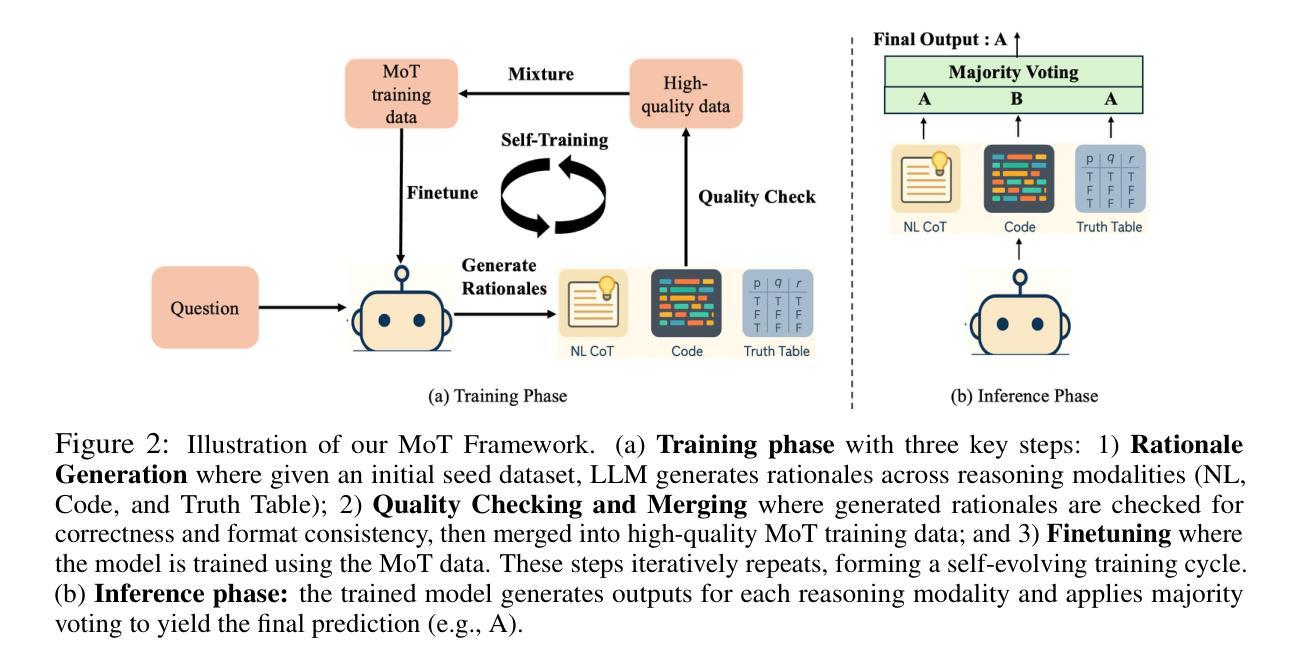
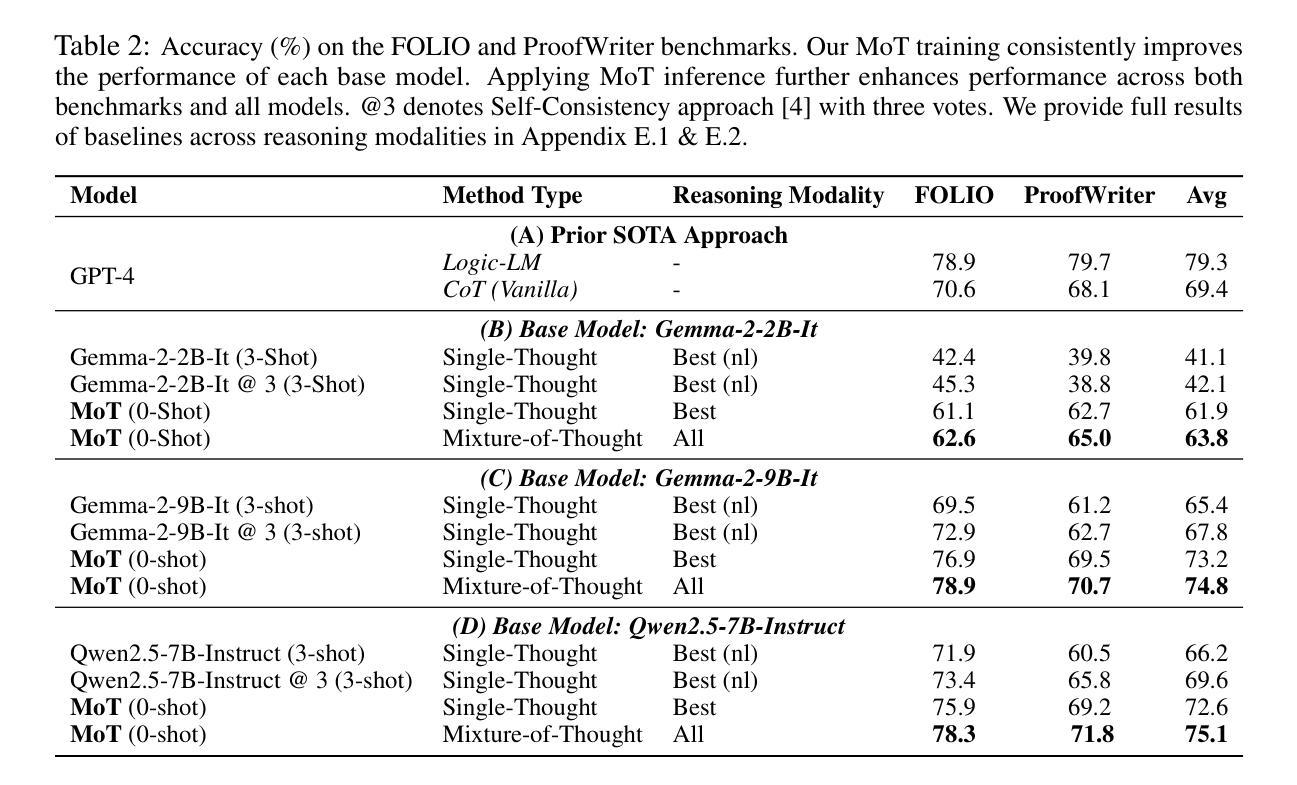
Human beings naturally utilize multiple reasoning modalities to learn and solve logical problems, i.e., different representational formats such as natural language, code, and symbolic logic. In contrast, most existing LLM-based approaches operate with a single reasoning modality during training, typically natural language. Although some methods explored modality selection or augmentation at inference time, the training process remains modality-blind, limiting synergy among modalities. To fill in this gap, we propose Mixture-of-Thought (MoT), a framework that enables LLMs to reason across three complementary modalities: natural language, code, and a newly introduced symbolic modality, truth-table, which systematically enumerates logical cases and partially mitigates key failure modes in natural language reasoning. MoT adopts a two-phase design: (1) self-evolving MoT training, which jointly learns from filtered, self-generated rationales across modalities; and (2) MoT inference, which fully leverages the synergy of three modalities to produce better predictions. Experiments on logical reasoning benchmarks including FOLIO and ProofWriter demonstrate that our MoT framework consistently and significantly outperforms strong LLM baselines with single-modality chain-of-thought approaches, achieving up to +11.7pp average accuracy gain. Further analyses show that our MoT framework benefits both training and inference stages; that it is particularly effective on harder logical reasoning problems; and that different modalities contribute complementary strengths, with truth-table reasoning helping to overcome key bottlenecks in natural language inference.
人类自然利用多种推理模式来学习和解决逻辑问题,例如自然语言、代码和符号逻辑等不同的表示格式。相比之下,大多数现有的基于大型语言模型的方法在训练过程中只使用单一的推理模式,通常是自然语言。尽管一些方法在推理时间探索了模式选择或增强,但训练过程仍然对模式是盲态的,限制了模式之间的协同作用。为了填补这一空白,我们提出了Thought Mixture(MoT)框架,它使大型语言模型能够在三种互补模式之间进行推理:自然语言、代码和新引入的符号模式——真值表。真值表系统地枚举逻辑情况,并部分弥补了自然语言推理中的关键失败模式。MoT采用两阶段设计:(1)自我进化的MoT训练,从过滤后的、自我生成的跨模式理性联合学习;(2)MoT推理,充分利用三种模式的协同作用来产生更好的预测。在包括FOLIO和ProofWriter在内的逻辑推理基准测试上的实验表明,我们的MoT框架在单模态思维链方法中始终显著优于强大的大型语言模型基准测试,平均准确率提高了高达+11.7pp。进一步的分析表明,我们的MoT框架对训练和推理阶段都有益;它对更复杂的逻辑推理问题特别有效;不同的模式贡献出互补的优势,真值表推理有助于克服自然语言推理中的关键瓶颈。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 38 pages
Summary
本文提出一种名为Mixture-of-Thought(MoT)的框架,该框架使LLMs能够在自然语言、代码和新的符号模态(真理表)之间进行推理。MoT框架采用两阶段设计:自我进化的MoT训练和MoT推理。实验表明,MoT框架在逻辑推理基准测试上持续且显著地优于单模态的LLM基线方法,平均准确率提高了高达+11.7pp。该框架对训练和推理阶段都有益,特别是在解决更复杂的逻辑问题时效果显著。不同模态的贡献具有互补性,真理表推理有助于克服自然语言推理中的关键瓶颈。
Key Takeaways
- 人类利用多种推理模式来学习和解决逻辑问题,而现有的LLM方法大多在训练期间只使用单一推理模式。
- Mixture-of-Thought(MoT)框架能够填补这一空白,使LLMs在自然语言、代码和符号模态(真理表)之间进行推理。
- MoT框架包含两阶段设计:自我进化的MoT训练和MoT推理,能够充分利用不同模态之间的协同作用。
- 实验表明MoT框架在逻辑推理基准测试上显著优于单模态LLM方法。
- MoT框架对训练和推理阶段都有积极影响,尤其有助于解决复杂的逻辑问题。
- 真理表模态在自然语言推理中起到关键作用,有助于克服关键瓶颈。
点此查看论文截图