⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-17 更新
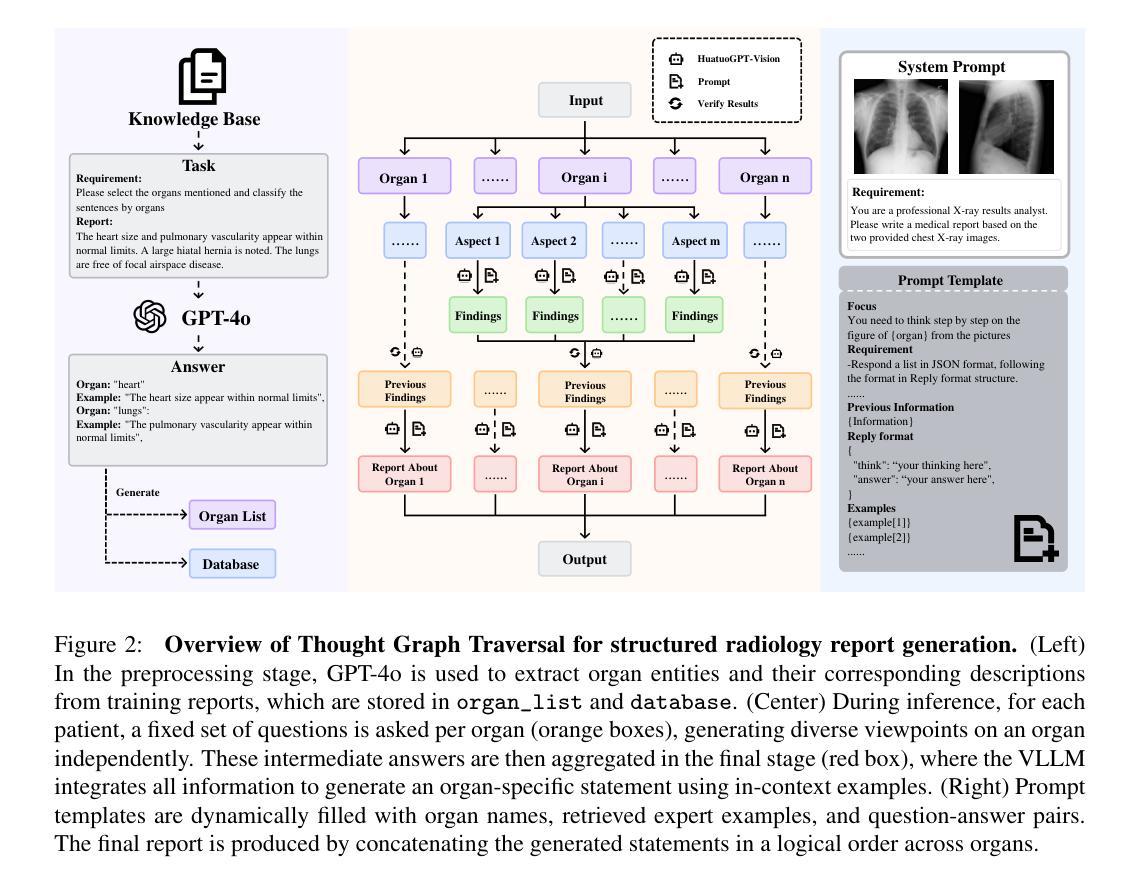
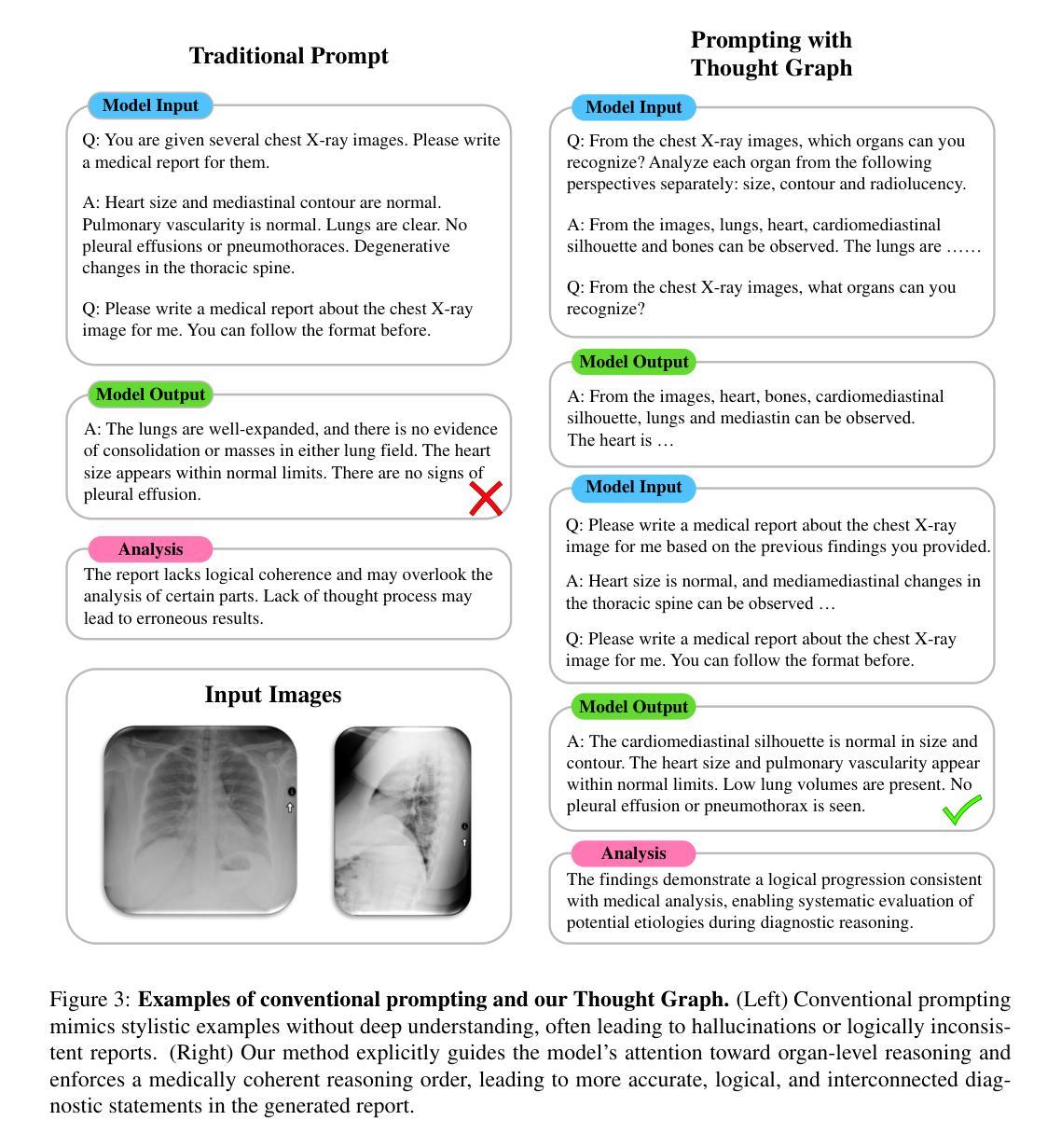
Simple Radiology VLLM Test-time Scaling with Thought Graph Traversal
Authors:Yue Yao, Zelin Wen, Yan Tong, Xinyu Tian, Xuqing Li, Xiao Ma, Dongliang Xu, Tom Gedeon
Test-time scaling offers a promising way to improve the reasoning performance of vision-language large models (VLLMs) without additional training. In this paper, we explore a simple but effective approach for applying test-time scaling to radiology report generation. Specifically, we introduce a lightweight Thought Graph Traversal (TGT) framework that guides the model to reason through organ-specific findings in a medically coherent order. This framework integrates structured medical priors into the prompt, enabling deeper and more logical analysis with no changes to the underlying model. To further enhance reasoning depth, we apply a reasoning budget forcing strategy that adjusts the model’s inference depth at test time by dynamically extending its generation process. This simple yet powerful combination allows a frozen radiology VLLM to self-correct and generate more accurate, consistent chest X-ray reports. Our method outperforms baseline prompting approaches on standard benchmarks, and also reveals dataset biases through traceable reasoning paths. Code and prompts are open-sourced for reproducibility at https://github.com/glerium/Thought-Graph-Traversal.
测试时缩放(Test-time scaling)提供了一种无需额外训练即可提高视觉语言大型模型(VLLM)推理性能的有前途的方法。在本文中,我们探讨了将测试时缩放应用于放射学报告生成的一种简单而有效的方法。具体来说,我们引入了一个轻量级的思维图遍历(TGT)框架,该框架以医学连贯的顺序引导模型通过特定器官的检查结果进行推理。该框架将结构化的医学先验知识集成到提示中,无需更改底层模型即可进行更深入、更逻辑化的分析。为了进一步提高推理深度,我们采用了推理预算强制策略,通过在测试时动态扩展模型的生成过程来调整模型的推理深度。这种简单而强大的组合允许固定的放射学VLLM进行自我修正,并生成更准确、一致的胸部X光报告。我们的方法在标准基准测试上优于基线提示方法,并通过可追溯的推理路径揭示了数据集偏见。代码和提示已在https://github.com/glerium/Thought-Graph-Traversal上开源,以便进行可重复性验证。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2404.11209 by other authors
Summary
本文探索了一种将测试时缩放应用于放射学报告生成的有效方法。通过引入轻量级的思维图遍历(TGT)框架,指导模型以医学逻辑顺序进行器官特异性发现的推理。该框架将结构化医学先验知识融入提示,无需更改底层模型即可实现更深入、更逻辑化的分析。应用推理预算强制策略进一步增强推理深度,通过动态扩展模型的生成过程,在测试时调整模型的推理深度。该组合方法允许冻结的放射学VLLM进行自我修正,生成更准确、一致的胸部X光报告。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时缩放可改善视觉语言大模型的推理性能。
- 引入轻量级的思维图遍历(TGT)框架,以医学逻辑顺序指导模型推理。
- TGT框架将结构化医学先验知识融入提示,实现更深入的分析。
- 推理预算强制策略增强推理深度,调整模型在测试时的推理深度。
- 该方法允许冻结的放射学VLLM自我修正,生成更准确、一致的报告。
- 在标准基准测试上,该方法优于基准提示方法。
- 通过可追溯的推理路径揭示数据集偏差。
点此查看论文截图

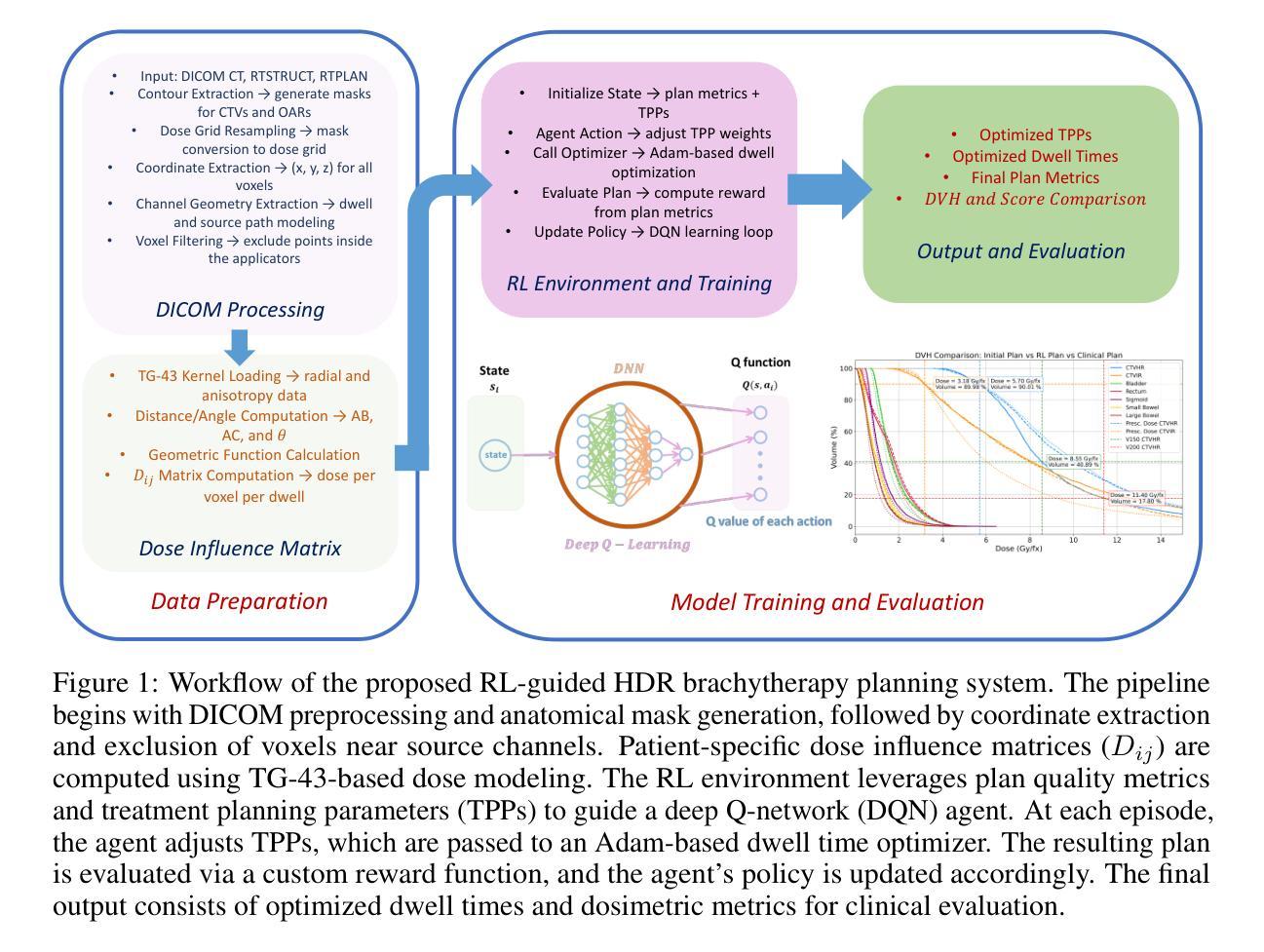
Automated Treatment Planning for Interstitial HDR Brachytherapy for Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Mohammadamin Moradi, Runyu Jiang, Yingzi Liu, Malvern Madondo, Tianming Wu, James J. Sohn, Xiaofeng Yang, Yasmin Hasan, Zhen Tian
High-dose-rate (HDR) brachytherapy plays a critical role in the treatment of locally advanced cervical cancer but remains highly dependent on manual treatment planning expertise. The objective of this study is to develop a fully automated HDR brachytherapy planning framework that integrates reinforcement learning (RL) and dose-based optimization to generate clinically acceptable treatment plans with improved consistency and efficiency. We propose a hierarchical two-stage autoplanning framework. In the first stage, a deep Q-network (DQN)-based RL agent iteratively selects treatment planning parameters (TPPs), which control the trade-offs between target coverage and organ-at-risk (OAR) sparing. The agent’s state representation includes both dose-volume histogram (DVH) metrics and current TPP values, while its reward function incorporates clinical dose objectives and safety constraints, including D90, V150, V200 for targets, and D2cc for all relevant OARs (bladder, rectum, sigmoid, small bowel, and large bowel). In the second stage, a customized Adam-based optimizer computes the corresponding dwell time distribution for the selected TPPs using a clinically informed loss function. The framework was evaluated on a cohort of patients with complex applicator geometries. The proposed framework successfully learned clinically meaningful TPP adjustments across diverse patient anatomies. For the unseen test patients, the RL-based automated planning method achieved an average score of 93.89%, outperforming the clinical plans which averaged 91.86%. These findings are notable given that score improvements were achieved while maintaining full target coverage and reducing CTV hot spots in most cases.
高剂量率(HDR)近距离放射治疗在治疗局部晚期宫颈癌方面起着至关重要的作用,但仍然高度依赖于手动治疗计划的专业知识。本研究的目标是为HDR近距离放射治疗建立一个全自动化的治疗计划框架,该框架结合了强化学习(RL)和基于剂量的优化,以生成临床可接受的、具有改进的一致性和效率的治疗计划。我们提出了一个分层的两阶段自动规划框架。在第一阶段,基于深度Q网络(DQN)的RL代理通过迭代选择治疗计划参数(TPPs),这些参数控制目标覆盖和危险器官(OAR)节省之间的权衡。代理的状态表示包括剂量体积直方图(DVH)指标和当前TPP值,其奖励函数结合了临床剂量目标和安全约束,包括目标区域的D90、V150、V200以及所有相关危险器官的D2cc(膀胱、直肠、乙状结肠、小肠和大肠)。在第二阶段,一个定制的基于Adam的优化器使用临床信息的损失函数计算所选TPPs的相应停留时间分布。该框架在一组具有复杂应用器几何结构的患者中进行了评估。所提出框架成功地在不同的患者解剖结构中学到了有临床意义的TPP调整。对于未见过的测试患者,基于RL的自动规划方法取得了平均93.89%的评分,优于平均91.86%的临床计划。这些发现值得注意,因为在提高评分的同时,大多数病例都实现了全目标覆盖并减少了CTV热点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 2 figures, 3 tables
Summary
本研究旨在开发一个集强化学习与剂量优化于一体的全自动高剂量率近距离治疗计划框架,用于生成具有更好一致性和效率的临床可接受治疗计划。该框架采用分层两阶段自动规划方法,通过深度Q网络强化学习智能体选择治疗计划参数,并利用基于亚当的优化器计算相应的停留时间分布。在复杂应用器几何结构的病人群体中评估了该框架,结果显示其在不同病人解剖结构中成功学习了具有临床意义的治疗计划参数调整,并在未见测试病人中取得了优于临床计划的平均成绩。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究使用强化学习和剂量优化技术来开发全自动HDR近距离治疗计划框架。
- 采用了层次两阶段的自动规划方法。
- 第一阶段利用深度Q网络强化学习智能体选择治疗计划参数,包括剂量体积直方图指标和目标区域与风险器官的权衡关系。
- 第二阶段利用基于亚当的优化器计算相应的停留时间分布。
- 该框架在具有复杂应用器几何结构的病人群体中进行了评估。
- 结果显示该框架成功学习了在不同病人解剖结构中的临床意义治疗计划参数调整。
点此查看论文截图

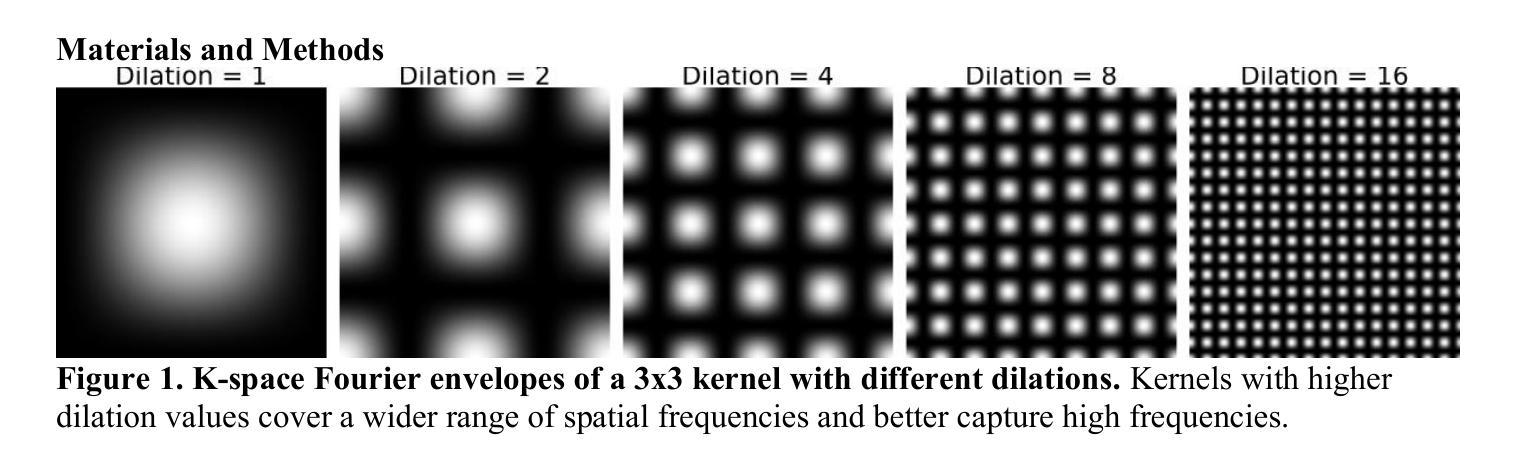
MindGrab for BrainChop: Fast and Accurate Skull Stripping for Command Line and Browser
Authors:Armina Fani, Mike Doan, Isabelle Le, Alex Fedorov, Malte Hoffmann, Chris Rorden, Sergey Plis
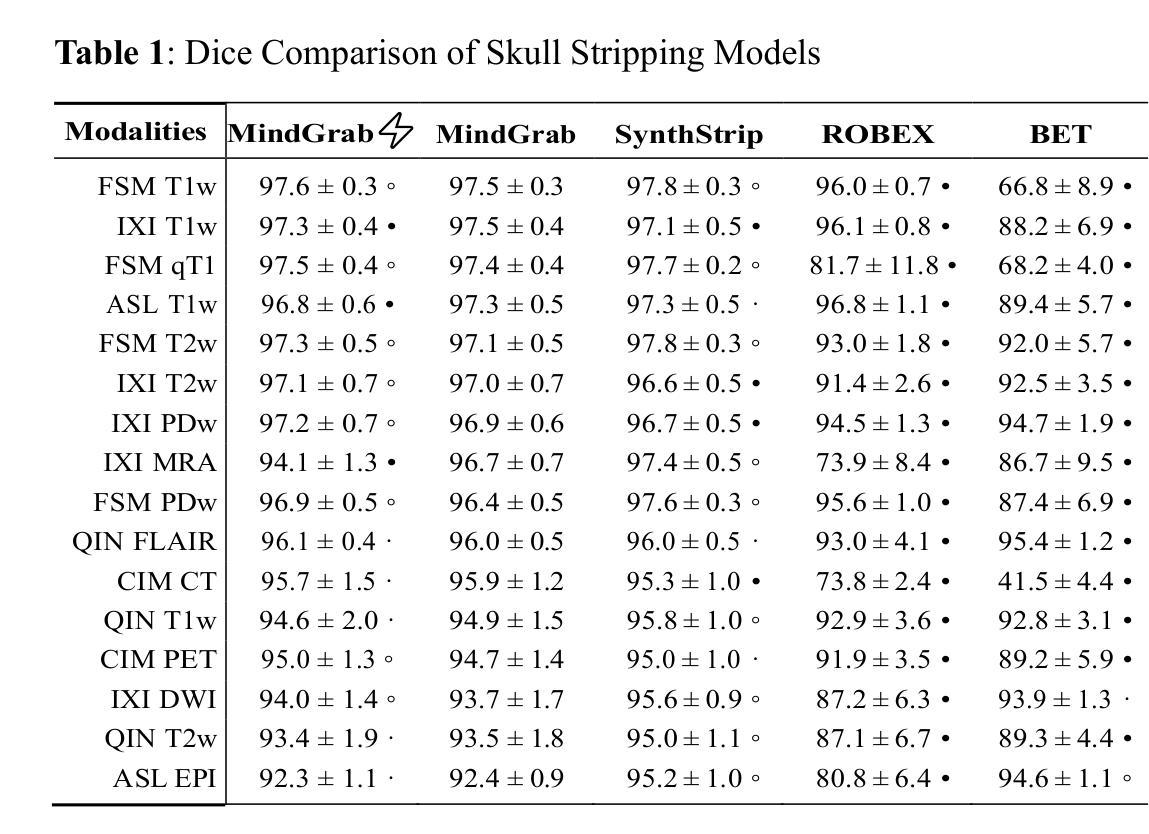
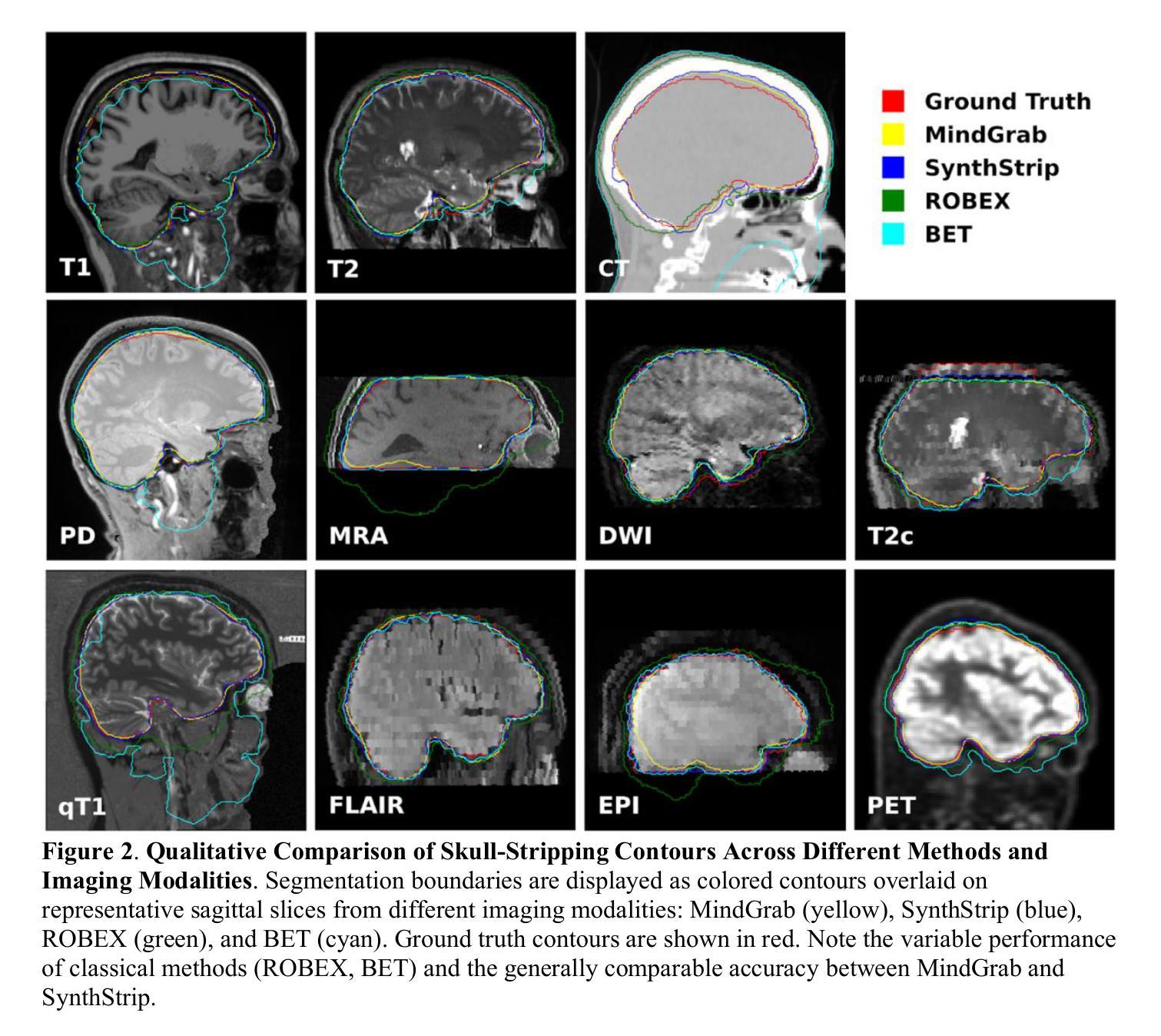
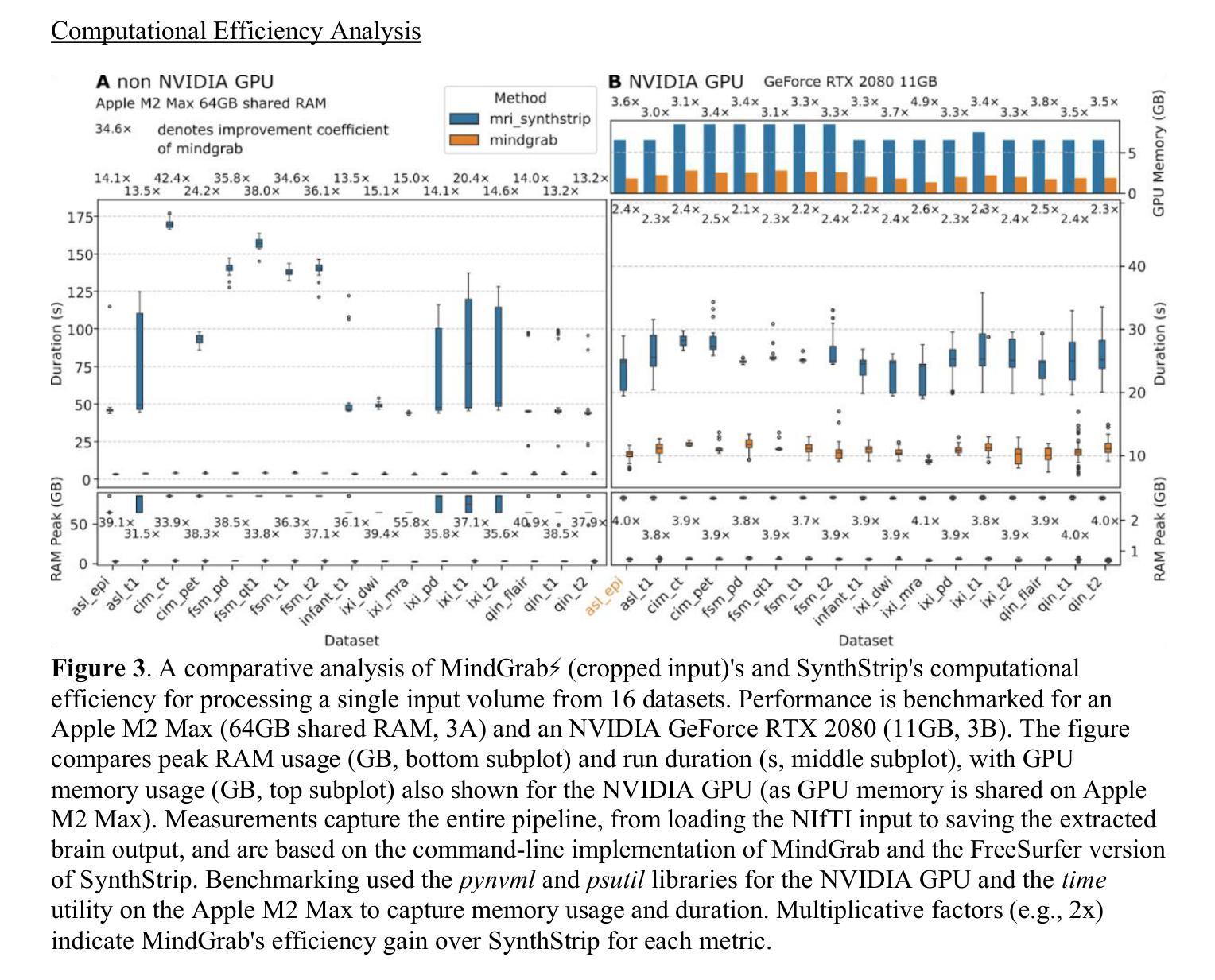
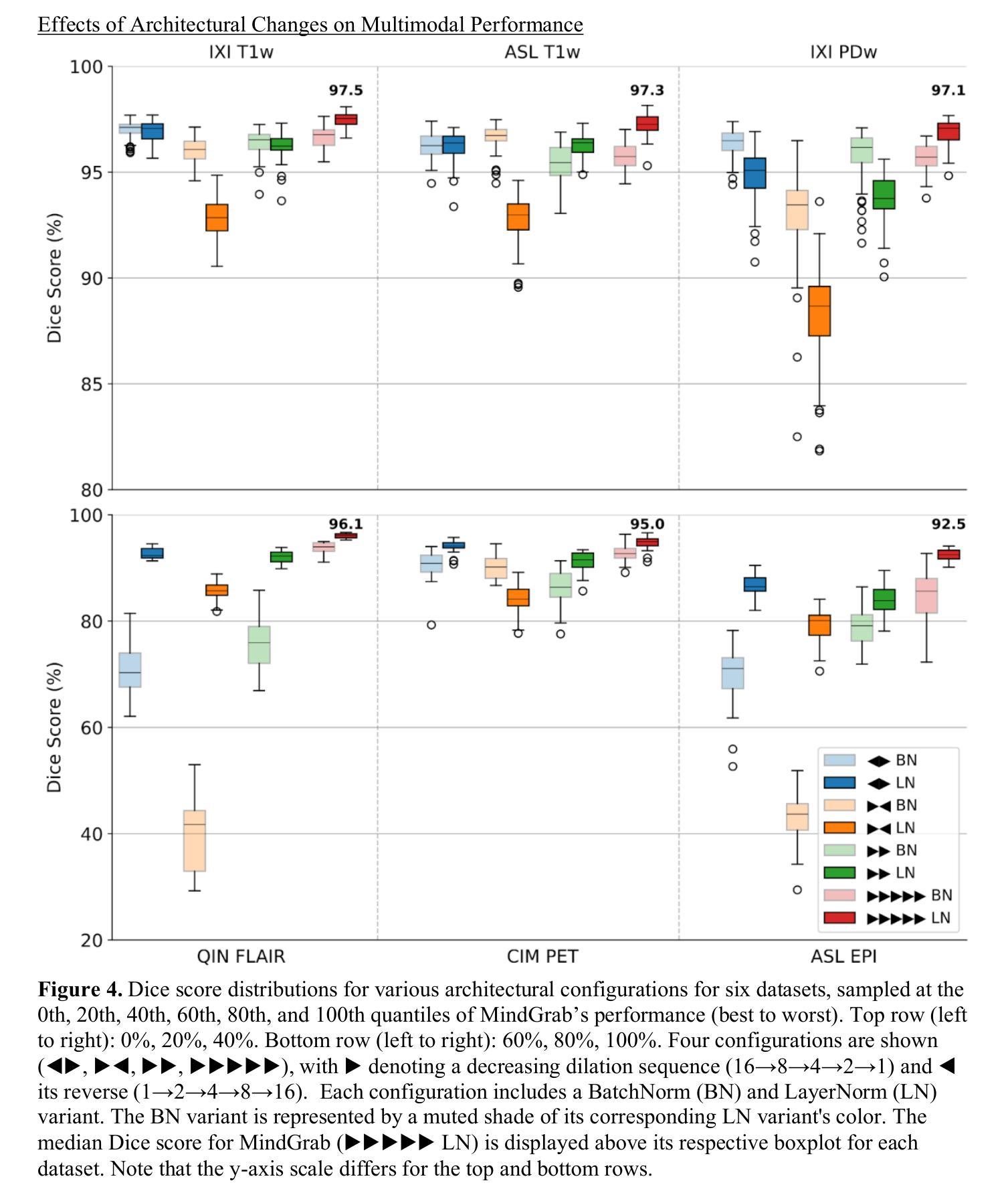
We developed MindGrab, a parameter- and memory-efficient deep fully-convolutional model for volumetric skull-stripping in head images of any modality. Its architecture, informed by a spectral interpretation of dilated convolutions, was trained exclusively on modality-agnostic synthetic data. MindGrab was evaluated on a retrospective dataset of 606 multimodal adult-brain scans (T1, T2, DWI, MRA, PDw MRI, EPI, CT, PET) sourced from the SynthStrip dataset. Performance was benchmarked against SynthStrip, ROBEX, and BET using Dice scores, with Wilcoxon signed-rank significance tests. MindGrab achieved a mean Dice score of 95.9 with standard deviation (SD) 1.6 across modalities, significantly outperforming classical methods (ROBEX: 89.1 SD 7.7, P < 0.05; BET: 85.2 SD 14.4, P < 0.05). Compared to SynthStrip (96.5 SD 1.1, P=0.0352), MindGrab delivered equivalent or superior performance in nearly half of the tested scenarios, with minor differences (<3% Dice) in the others. MindGrab utilized 95% fewer parameters (146,237 vs. 2,566,561) than SynthStrip. This efficiency yielded at least 2x faster inference, 50% lower memory usage on GPUs, and enabled exceptional performance (e.g., 10-30x speedup, and up to 30x memory reduction) and accessibility on a wider range of hardware, including systems without high-end GPUs. MindGrab delivers state-of-the-art accuracy with dramatically lower resource demands, supported in brainchop-cli (https://pypi.org/project/brainchop/) and at brainchop.org.
我们开发了一种名为MindGrab的高效参数和内存使用的深度全卷积模型,该模型可用于处理各种模态的头部图像的体积颅骨剥离。其结构基于对膨胀卷积的频谱解释而设计,并仅在模态无关的合成数据上进行训练。MindGrab在来自SynthStrip数据集的606例多模态成人脑扫描(包括T1、T2、DWI、MRA、PDw MRI、EPI、CT、PET)的回顾性数据集上进行了评估。其性能以Dice得分与SynthStrip、ROBEX和BET进行了比较,并使用Wilcoxon符号秩检验法进行显著性检验。MindGrab在跨模态下的平均Dice得分为95.9(标准差为1.6),显著优于经典方法(ROBEX:89.1,标准差为7.7;BET:85.2,标准差为14.4,P < 0.05)。与SynthStrip(Dice得分为96.5,标准差为1.1,P=0.0352)相比,MindGrab在近乎一半的测试场景中表现相当或更好,在其他场景中差异较小(<3% Dice)。MindGrab使用的参数比SynthStrip少95%(146,237 vs 2,566,561)。这种效率带来了至少两倍更快的推理速度,GPU内存使用率降低了50%,并且在更广泛的硬件上实现了卓越的性能(例如,加速高达十倍至三十倍,内存减少高达三十倍)。MindGrab以超高的准确性达到了业界领先水平,同时大大降低了资源需求,可在brainchop-cli(https://pypi.org/project/brainchop/)和brainchop.org上支持使用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 1 table, 4 figures. 2 supplementary tables, 1 supplementary figure. Brainchop-cli: https://pypi.org/project/brainchop/ . Brainchop web: https://brainchop.org/
Summary
本文介绍了MindGrab的开发与应用。MindGrab是一种参数和内存效率高的深度全卷积模型,用于各种模态的头部图像中的体积颅骨剥离。其架构基于膨胀卷积的谱解释,仅在模态无关的合成数据上进行训练。在多种模态的成人脑扫描数据集上的评估表明,MindGrab在颅骨剥离任务上的性能优于其他传统方法,达到了较高的Dice分数,并且在参数和内存使用方面更加高效,可以在更广泛的硬件上实现快速推理。
Key Takeaways
- MindGrab是一种用于头部图像体积颅骨剥离的深度全卷积模型。
- MindGrab的架构基于膨胀卷积的谱解释设计。
- MindGrab在模态无关的合成数据上进行训练。
- MindGrab在多种模态的成人脑扫描数据集上的性能进行了评估。
- MindGrab在颅骨剥离任务上的性能优于其他传统方法,达到了较高的Dice分数。
- MindGrab具有高效的参数和内存使用,可在广泛的硬件上实现快速推理。
点此查看论文截图

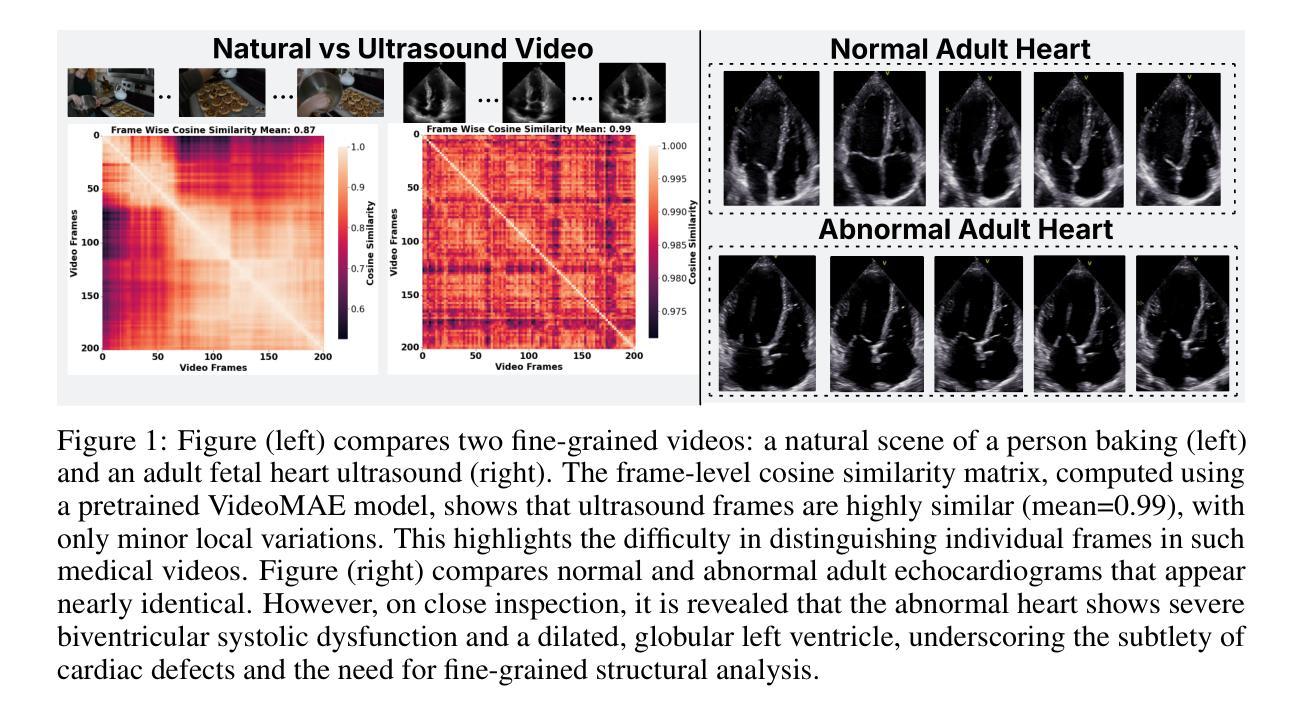
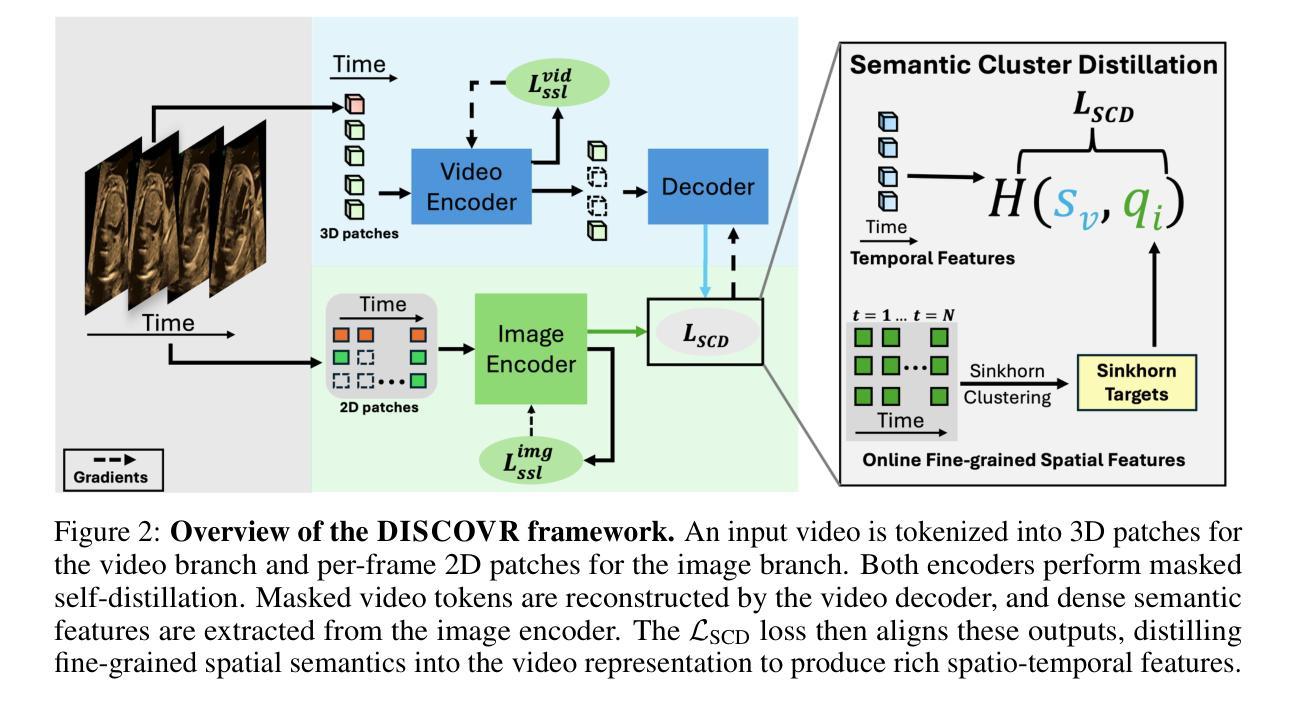
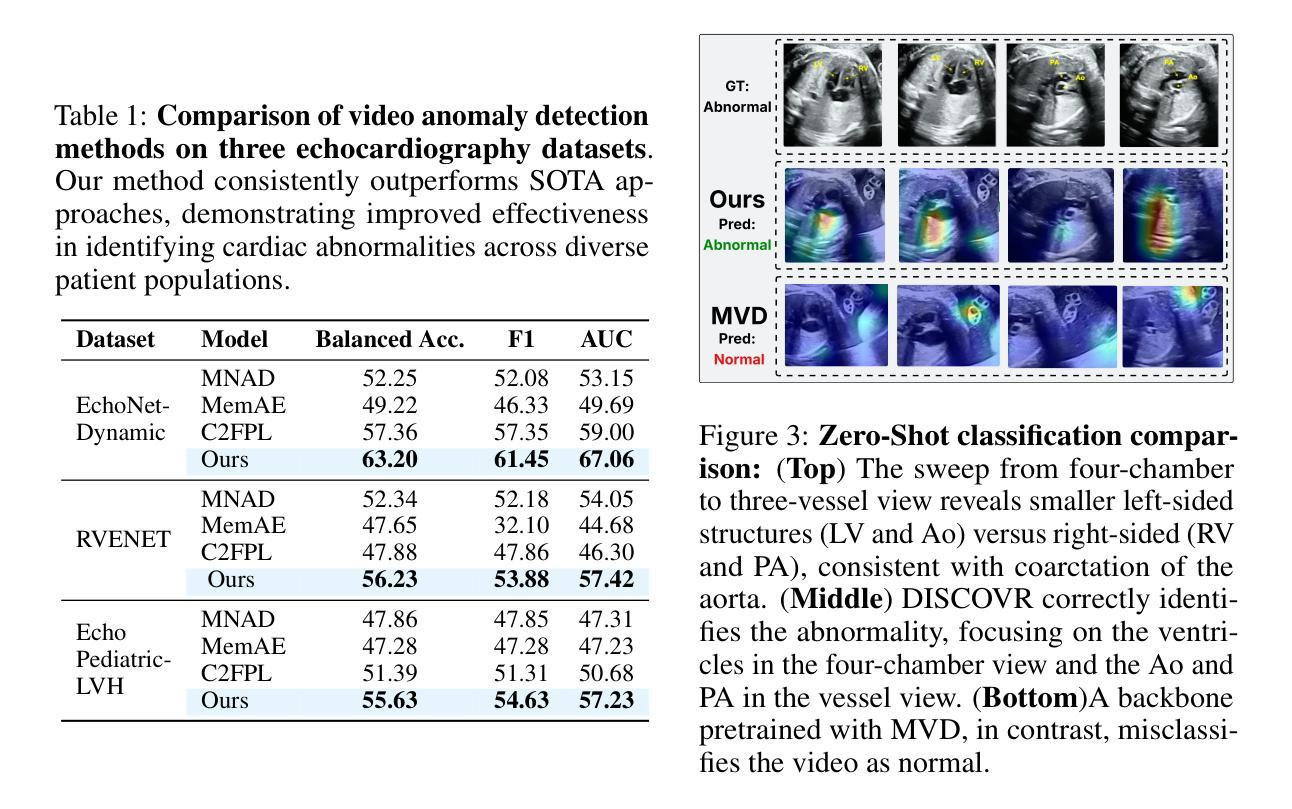
Self-supervised Learning of Echocardiographic Video Representations via Online Cluster Distillation
Authors:Divyanshu Mishra, Mohammadreza Salehi, Pramit Saha, Olga Patey, Aris T. Papageorghiou, Yuki M. Asano, J. Alison Noble
Self-supervised learning (SSL) has achieved major advances in natural images and video understanding, but challenges remain in domains like echocardiography (heart ultrasound) due to subtle anatomical structures, complex temporal dynamics, and the current lack of domain-specific pre-trained models. Existing SSL approaches such as contrastive, masked modeling, and clustering-based methods struggle with high intersample similarity, sensitivity to low PSNR inputs common in ultrasound, or aggressive augmentations that distort clinically relevant features. We present DISCOVR (Distilled Image Supervision for Cross Modal Video Representation), a self-supervised dual branch framework for cardiac ultrasound video representation learning. DISCOVR combines a clustering-based video encoder that models temporal dynamics with an online image encoder that extracts fine-grained spatial semantics. These branches are connected through a semantic cluster distillation loss that transfers anatomical knowledge from the evolving image encoder to the video encoder, enabling temporally coherent representations enriched with fine-grained semantic understanding. Evaluated on six echocardiography datasets spanning fetal, pediatric, and adult populations, DISCOVR outperforms both specialized video anomaly detection methods and state-of-the-art video-SSL baselines in zero-shot and linear probing setups, and achieves superior segmentation transfer.
自监督学习(SSL)在自然图像和视频理解方面取得了重大进展,但在超声心动图(心脏超声)等领域仍面临挑战,原因在于其微妙的解剖结构、复杂的时序动态以及缺乏特定的预训练模型。现有的SSL方法,如对比学习、掩膜建模和基于聚类的方法,面临高样本间相似性、对常见超声的低PSNR输入的敏感性,或过于激烈的增强手段会扭曲临床上相关的特征。我们提出了DISCOVR(用于跨模态视频表示的蒸馏图像监督),这是一个用于心脏超声视频表示学习的自监督双分支框架。DISCOVR结合了一个基于聚类的视频编码器,该编码器对时序动态进行建模,以及一个在线图像编码器,用于提取精细的空间语义。这两个分支通过语义聚类蒸馏损失相连接,将解剖知识从不断进化的图像编码器转移到视频编码器,从而实现丰富的时序连贯表示和精细的语义理解。在涵盖胎儿、儿童和成人群体的六个超声心动图数据集上评估,DISCOVR在零样本和线性探测设置中表现出超越专业视频异常检测方法和最新视频SSL基准的性能,并实现优越的分割迁移效果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在心脏超声视频表示学习中应用的自监督双分支框架DISCOVR。该框架结合了基于聚类的视频编码器和在线图像编码器,通过语义集群蒸馏损失连接这两个分支,从而转移解剖知识,实现时空一致的丰富精细语义理解。在多个胎儿、儿童和成人群体回声数据集上的评估表明,DISCOVR在零样本和线性探测设置中表现出色,实现了优越的分割迁移。
Key Takeaways
- SSL在自然图像和视频理解方面取得重大进展,但在心脏超声领域仍面临挑战。
- 现有SSL方法如对比学习、掩模建模和聚类方法在面对心脏超声数据时存在困难。
- DISCOVR是一个自监督双分支框架,用于心脏超声视频表示学习。
- DISCOVR结合了基于聚类的视频编码器和在线图像编码器。
- 通过语义集群蒸馏损失,DISCOVR能够转移解剖知识,实现时空一致的理解。
- DISCOVR在多个回声数据集上的评估结果优于专业视频异常检测方法和最新视频SSL基线。
点此查看论文截图

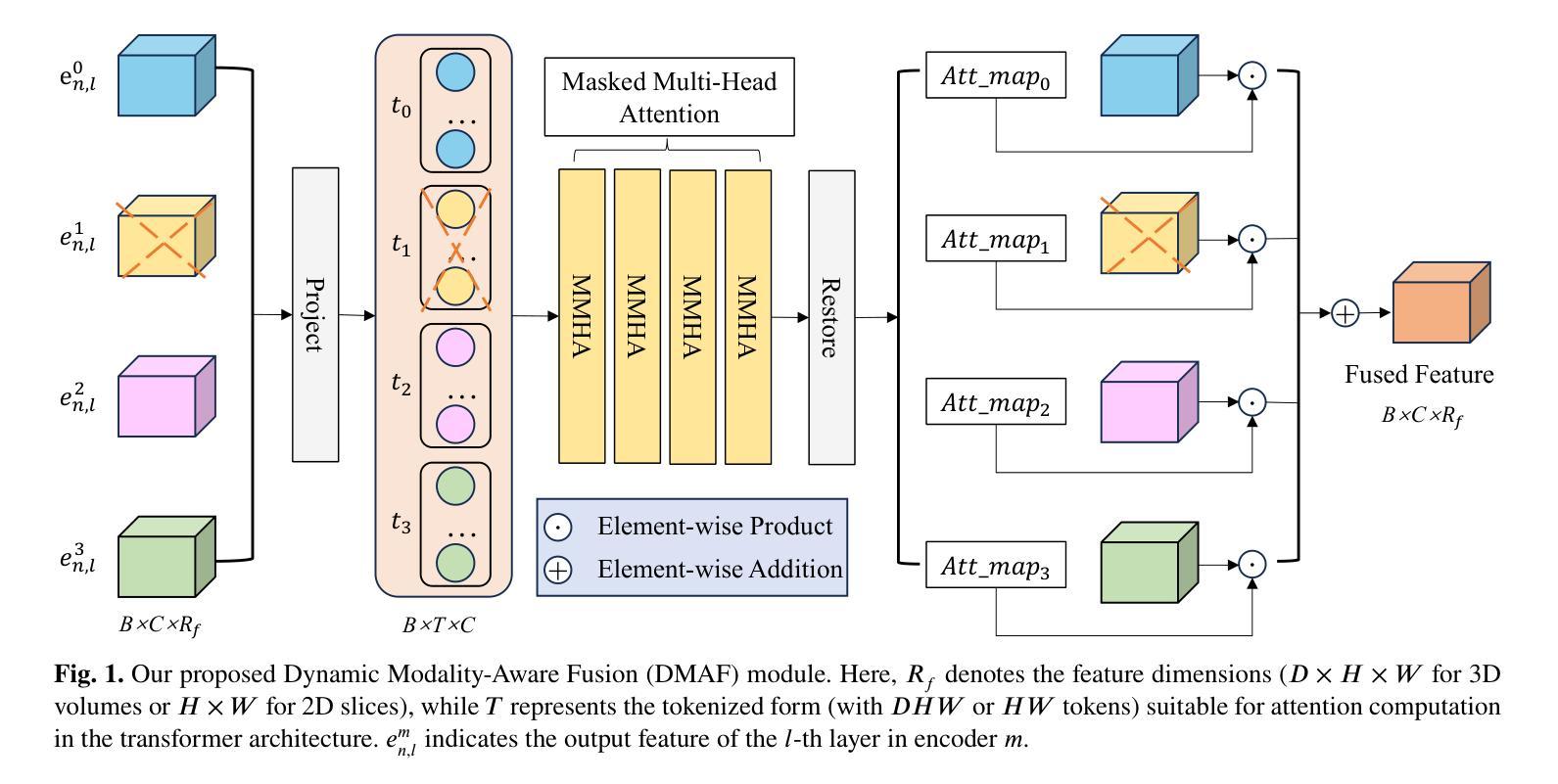
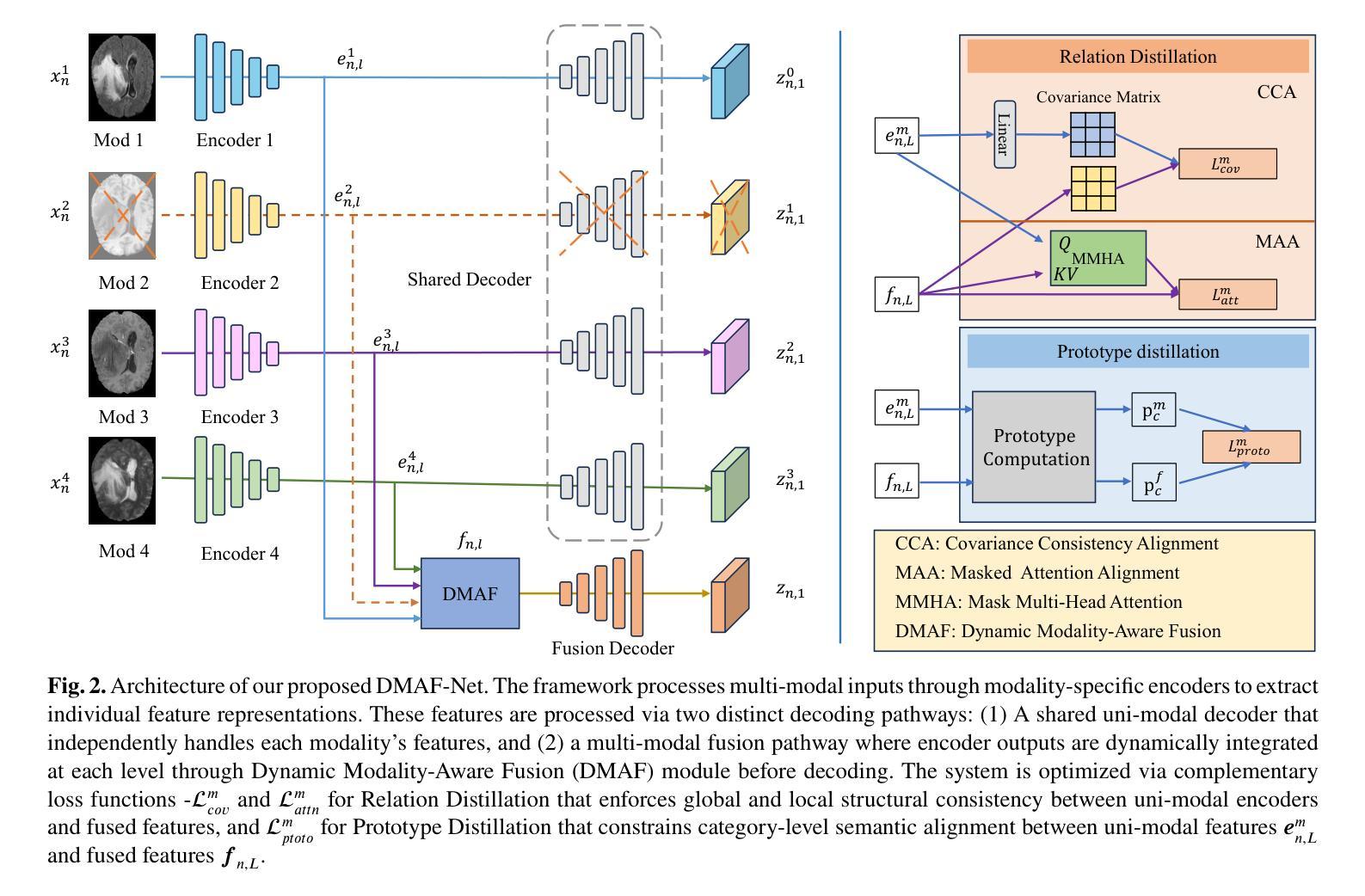
DMAF-Net: An Effective Modality Rebalancing Framework for Incomplete Multi-Modal Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Libin Lan, Hongxing Li, Zunhui Xia, Yudong Zhang
Incomplete multi-modal medical image segmentation faces critical challenges from modality imbalance, including imbalanced modality missing rates and heterogeneous modality contributions. Due to their reliance on idealized assumptions of complete modality availability, existing methods fail to dynamically balance contributions and neglect the structural relationships between modalities, resulting in suboptimal performance in real-world clinical scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose a novel model, named Dynamic Modality-Aware Fusion Network (DMAF-Net). The DMAF-Net adopts three key ideas. First, it introduces a Dynamic Modality-Aware Fusion (DMAF) module to suppress missing-modality interference by combining transformer attention with adaptive masking and weight modality contributions dynamically through attention maps. Second, it designs a synergistic Relation Distillation and Prototype Distillation framework to enforce global-local feature alignment via covariance consistency and masked graph attention, while ensuring semantic consistency through cross-modal class-specific prototype alignment. Third, it presents a Dynamic Training Monitoring (DTM) strategy to stabilize optimization under imbalanced missing rates by tracking distillation gaps in real-time, and to balance convergence speeds across modalities by adaptively reweighting losses and scaling gradients. Extensive experiments on BraTS2020 and MyoPS2020 demonstrate that DMAF-Net outperforms existing methods for incomplete multi-modal medical image segmentation. Extensive experiments on BraTS2020 and MyoPS2020 demonstrate that DMAF-Net outperforms existing methods for incomplete multi-modal medical image segmentation. Our code is available at https://github.com/violet-42/DMAF-Net.
不完整多模态医学图像分割面临来自模态不平衡的关键挑战,包括模态缺失率的不平衡和模态贡献的异质性。由于现有方法依赖于完整模态可用性的理想化假设,它们无法动态平衡贡献并忽略了模态之间的结构关系,导致在真实世界临床场景中的性能不佳。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种名为动态模态感知融合网络(DMAF-Net)的新模型。DMAF-Net采用了三个关键思想。首先,它引入了一个动态模态感知融合(DMAF)模块,通过结合变压器注意力与自适应掩模,动态地加权模态贡献,从而抑制缺失模态的干扰。其次,它设计了一个协同关系蒸馏和原型蒸馏框架,通过协方差一致性、掩膜图注意力来执行全局局部特征对齐,同时通过跨模态类特定原型对齐确保语义一致性。第三,它提出了一种动态训练监控(DTM)策略,通过实时跟踪蒸馏间隙来稳定不平衡缺失率下的优化过程,并通过自适应地重新加权损失和缩放梯度来平衡跨模态的收敛速度。在BraTS2020和MyoPS2020上的大量实验表明,DMAF-Net在不完整多模态医学图像分割方面优于现有方法。我们的代码可在https://github.com/violet-42/DMAF-Net获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 4 figures, 3 tables
Summary
本文提出一种名为DMAF-Net的动态模态感知融合网络,用于解决多模态医学图像分割中的模态不平衡问题。DMAF-Net引入动态模态感知融合模块,通过结合变压器注意力机制和自适应掩模来抑制缺失模态的干扰,并通过注意力图动态调整权重。同时设计协同关系蒸馏和原型蒸馏框架,以通过协方差一致性、掩膜图注意力实现全局局部特征对齐,并通过跨模态类特定原型对齐确保语义一致性。此外,DMAF-Net还采用动态训练监控策略,以适应不平衡的缺失率并优化平衡收敛速度。实验表明DMAF-Net在多模态医学图像分割上的表现优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态医学图像分割面临模态不平衡的挑战,包括缺失模态和异质模态贡献。
- 现有方法依赖完整模态可用性假设,无法动态平衡贡献并忽略模态间的结构关系。
- DMAF-Net通过动态模态感知融合模块抑制缺失模态干扰,并结合注意力机制动态调整权重。
- DMAF-Net设计协同关系蒸馏和原型蒸馏框架,实现全局局部特征对齐和语义一致性。
- DMAF-Net采用动态训练监控策略来适应不平衡的缺失率和优化收敛速度。
点此查看论文截图

Comparing the Space Densities of Millisecond-Spin Magnetars and Fast X-Ray Transients
Authors:Sumedha Biswas, Peter G. Jonker, M. Coleman Miller, Andrew Levan, Jonathan Quirola-Vásquez
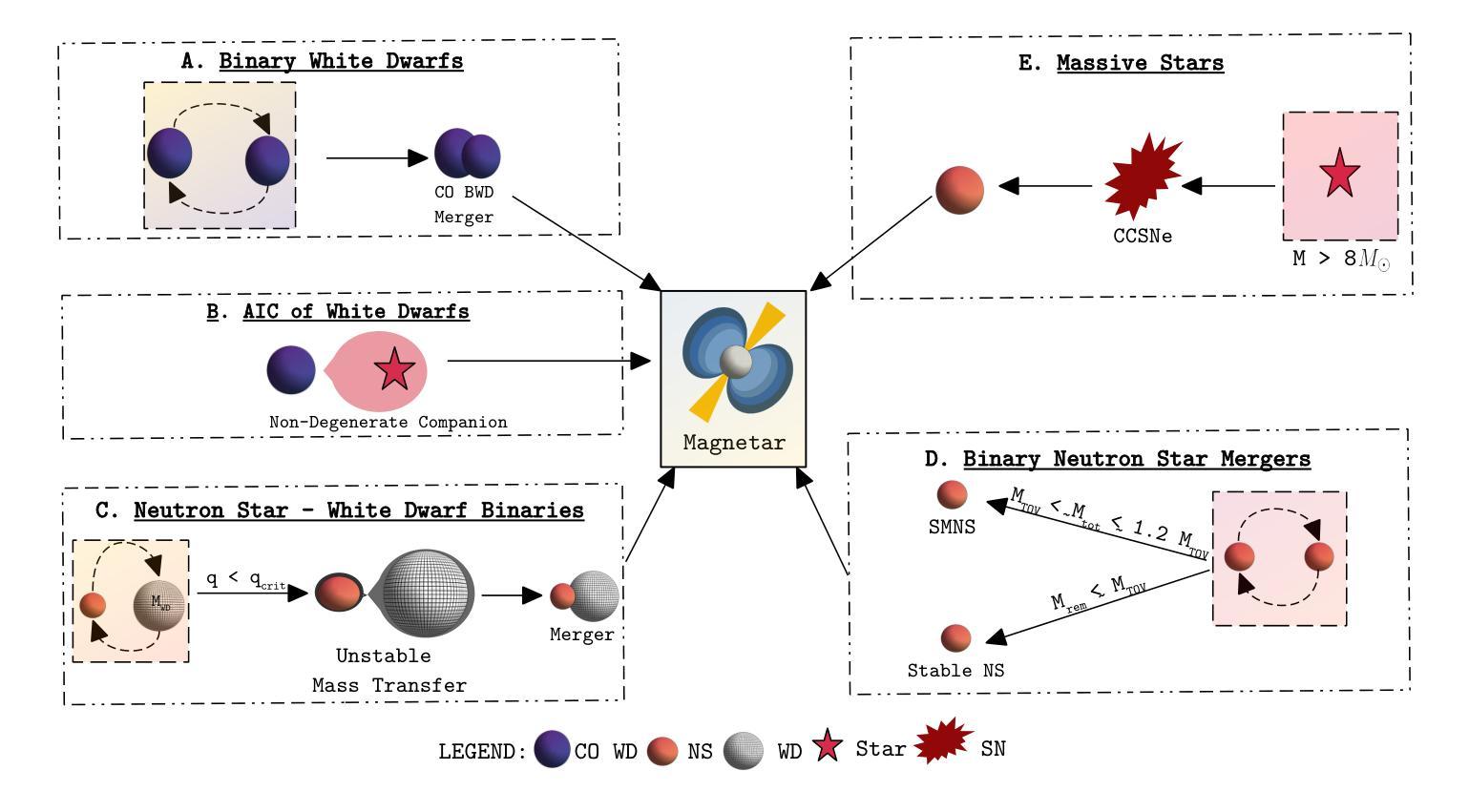
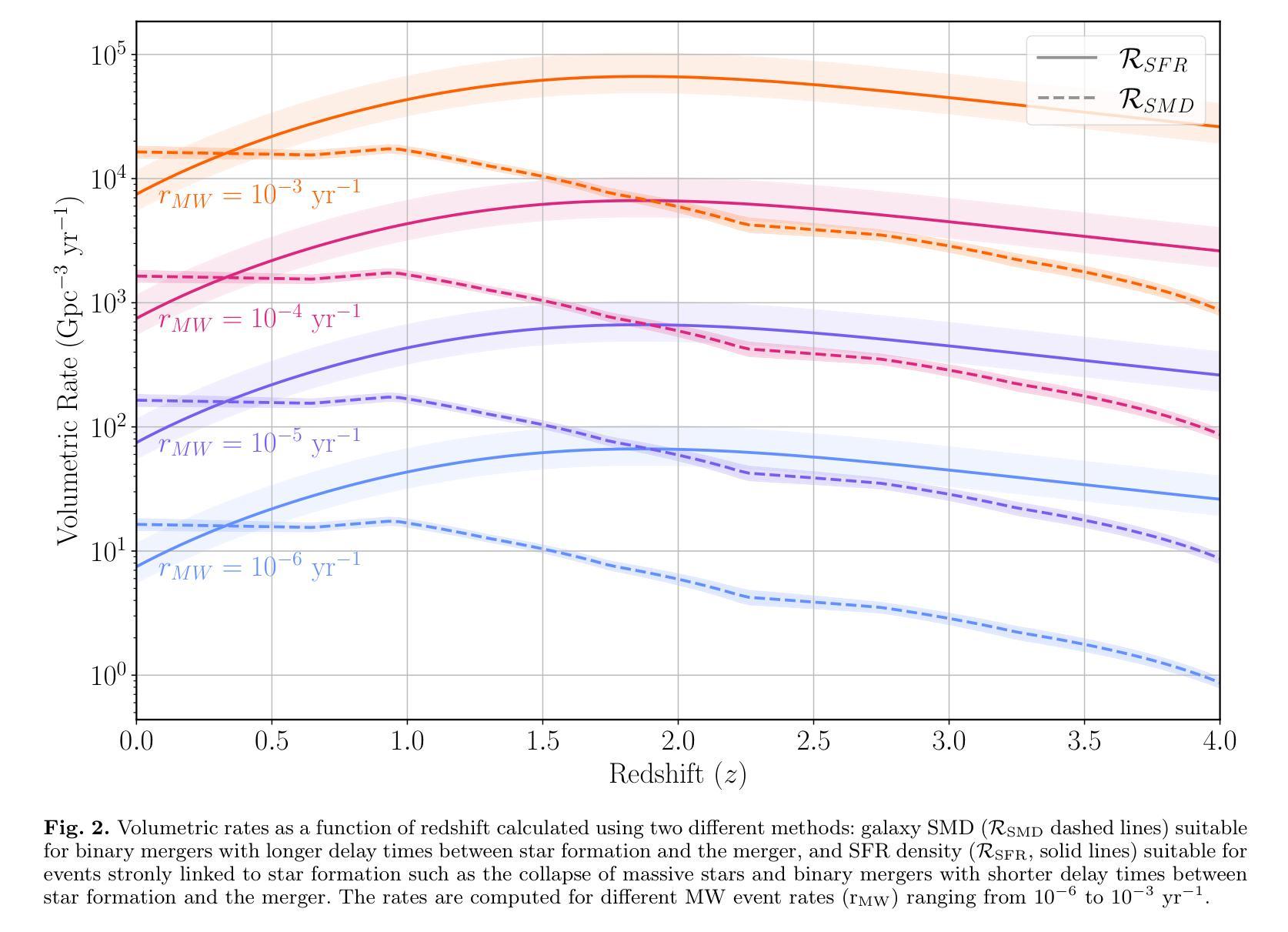
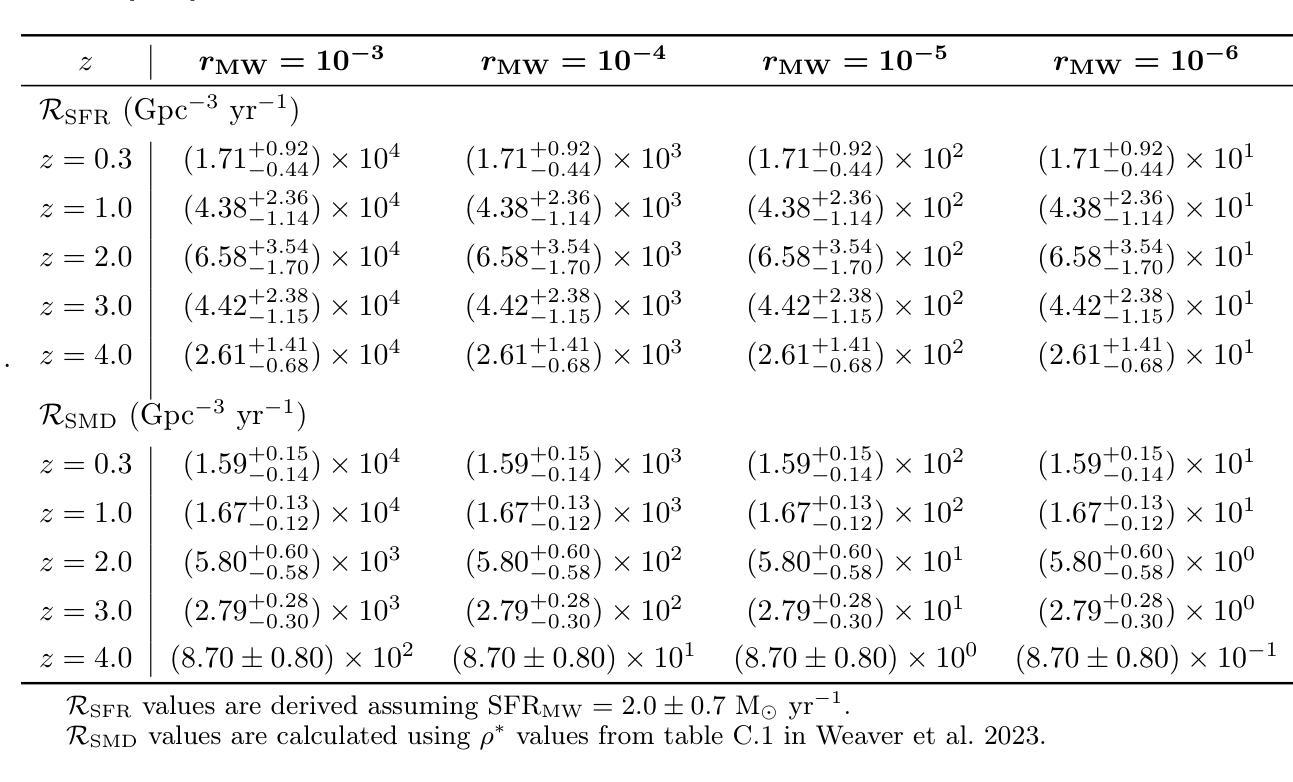
Fast X-ray transients (FXTs) are bright X-ray flashes with durations of minutes to hours, peak isotropic luminosities of L_X,peak ~ 10^42-10^47 erg/s, and total isotropic energies of E ~ 10^47-10^50 erg. They have been detected in the soft X-ray band by Chandra, XMM-Newton, Swift-XRT, and, most recently, by Einstein Probe, which has reported more than 50 FXTs in its first year of operation. While several models have been proposed, the nature of many FXTs remains unknown. One model suggests FXTs are powered by the spin-down of newly formed millisecond magnetars, typically produced by binary neutron star (BNS) mergers. However, the BNS volumetric rate, ~10^2 Gpc^-3 yr^-1, barely overlaps with the estimated FXT rate of 10^3-10^4 Gpc^-3 yr^-1. Even within that overlap, BNS mergers would need to produce FXTs at nearly 100% efficiency. We explore whether other millisecond magnetar formation channels could account for this discrepancy. We compile rate densities for several proposed progenitors: accretion-induced collapse of white dwarfs, binary white dwarf mergers, neutron star-white dwarf mergers, and the collapse of massive stars, and convert Galactic event rates into volumetric rates using either the star formation rate or the stellar mass density distributions as a function of redshift. We find that the highest potential formation rates arise from binary white dwarf mergers and massive star collapses. However, both channels face theoretical and observational challenges: the spin and magnetic field properties of the resulting neutron stars are uncertain, and few are expected to satisfy both conditions required for FXT production. Across all scenarios, the fraction of suitable millisecond magnetars is low or poorly constrained. We conclude that they are unlikely to be the dominant progenitors of FXTs and can contribute to at most 10% of the observed FXT population.
快速X射线瞬变(FXTs)是明亮的X射线闪光,持续时间从几分钟到几小时不等,峰值等距光度约为Lx,peak ~ 10^42-10^47 erg/s,总等距能量约为E ~ 10^47-10^50 erg。它们已在软X射线波段被钱德拉、XMM-牛顿、Swift-XRT等探测器探测到,最近还被爱因斯坦探测器探测到,该探测器在其运营的第一年内就报告了超过50个FXTs。尽管已经提出了几种模型,但许多FXTs的本质仍不得而知。有一种模型认为FXTs是由新形成的毫秒磁星的自转减速而产生的,通常是由双中子星(BNS)合并产生的。然而,BNS的体积率约为10^2 Gpc^-3 yr^-1,勉强与估计的FXT率(每单位体积在每立方立方格瑞希度的一年有数万立方米尺度观测度见伽玛射线的时空峰值闪光点数目)的每立方吉秒秒的数量级达到万至十万亿每三年内的比例相当,甚至在这个重叠范围内,BNS合并也需要以接近百分之百的效率产生FXTs。我们探讨了其他毫秒磁星形成通道是否能解释这一差异。我们汇总了几种提出的候选形成源的速率密度:白矮星引发的坍缩、白矮星双星合并、中子星与白矮星合并以及大质量恒星坍缩,并使用恒星形成率或恒星质量密度分布函数与红移关系将银河系事件速率转换为体积速率。我们发现最高潜在形成率来自于白矮星双星合并和大质量恒星坍缩。然而,这两个通道都面临着理论和观测上的挑战:所形成中子星的自转和磁场特性尚不确定,而且预计很少有满足产生FXT所需条件的实例。在所有场景中,适合产生FXT的毫秒磁星比例较低或难以确定。我们得出结论,它们不太可能成为FXTs的主要来源,最多只能贡献观察到的FXT人口的百分之十。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in A&A;
摘要
快X射线瞬态(FXTs)为明亮X射线闪光,持续时间为分钟至数小时,峰值光度约为10^42-10^47erg/s,总能量约为E ~ 10^47-10^50erg。它们已在软X射线波段被钱德拉、XMM-牛顿、Swift-XRT等望远镜探测到,最近还被爱因斯坦探测器探测到超过50个FXTs的案例。虽然提出了几种模型,但许多FXTs的性质仍然未知。本文探讨了除毫秒磁星自转减速以外的其他毫秒磁星形成通道是否能为这一差异提供解释。我们编译了几种提议中的祖细胞的速率密度,包括白矮星坍塌、双白矮星合并、中子星与白矮星合并以及大质量恒星坍塌等。我们发现最高的潜在形成率可能来自双白矮星合并和大质量恒星坍塌,但这两条途径在理论和观测上面临挑战,因为它们产生的中子星的自转和磁场特性不确定,并且只有很少能满足生产FXT所需的两项条件。总的来说,合适的毫秒磁星比例较低或难以确定,因此它们不太可能成为FXTs的主要祖细胞,最多只能贡献观察到FXT人群的百分之十。文章重点介绍了目前关于快速X射线瞬态成因的探究以及不同模型的理论预测和存在的挑战。
关键见解
- FXT是明亮的X射线闪光,持续时间从几分钟到几小时不等,具有较高的峰值光度和总能量。
- FXTs已经被多个X射线望远镜探测到,包括爱因斯坦探测器在其运营的第一年就报告了超过五十次观测。
- 虽然存在多种模型来解释FXTs的起源,但其确切性质仍然未知。
- 文章探讨了毫秒磁星自转减速模型以外的其他可能的FXT成因模型。
- 分析了不同模型的潜在形成率,发现双白矮星合并和大质量恒星坍塌是潜在的高形成率模型。但这些模型面临理论挑战和观测困难。这些模型产生的中子星的特性(自转和磁场)并不确定,并且不一定满足产生FXT的条件。
- 文章得出的结论是毫秒磁星不太可能成为FXTs的主要成因,其对观察到的FXT人口的贡献最多为百分之十。
点此查看论文截图

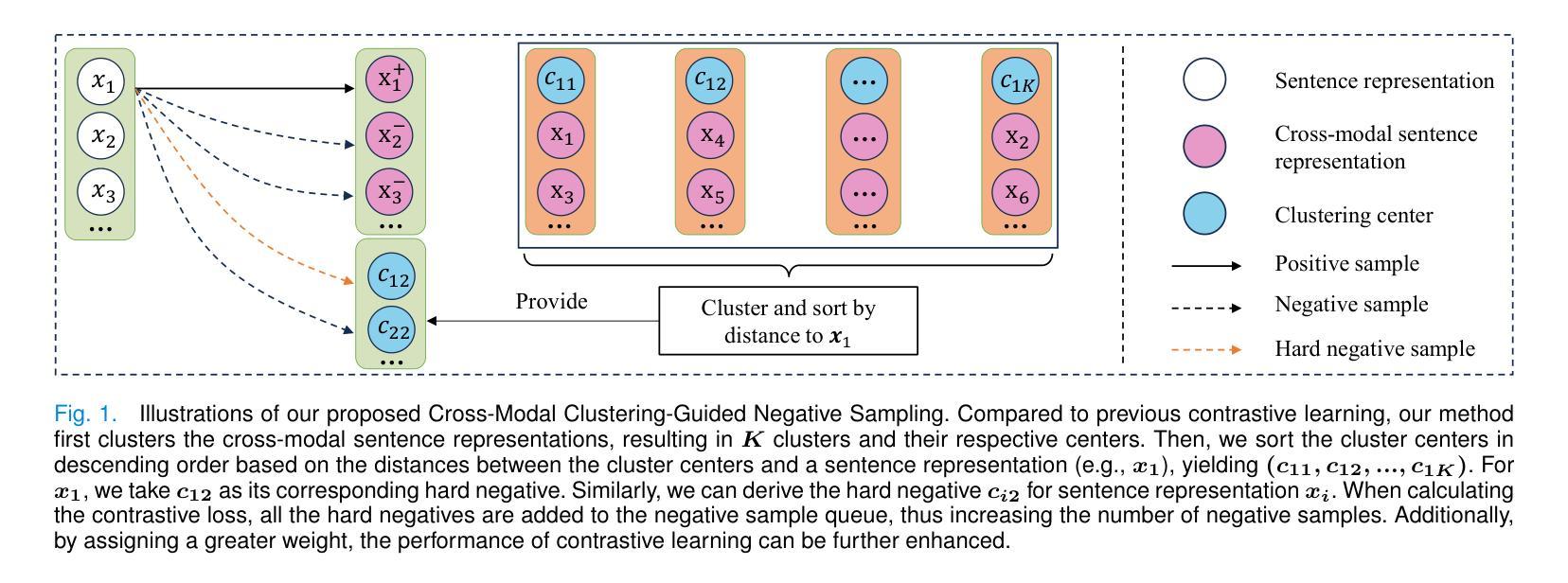
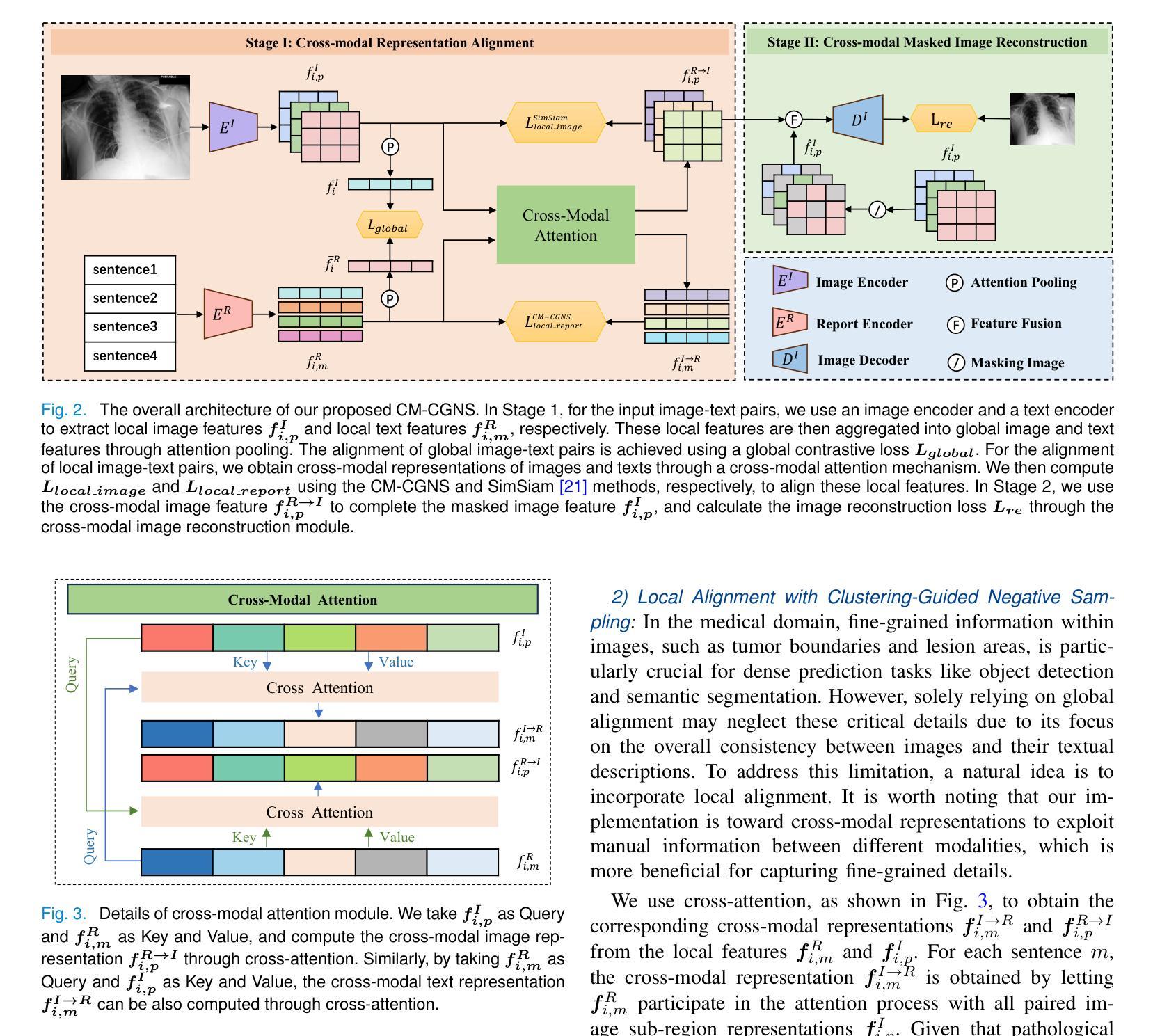
Cross-Modal Clustering-Guided Negative Sampling for Self-Supervised Joint Learning from Medical Images and Reports
Authors:Libin Lan, Hongxing Li, Zunhui Xia, Juan Zhou, Xiaofei Zhu, Yongmei Li, Yudong Zhang, Xin Luo
Learning medical visual representations directly from paired images and reports through multimodal self-supervised learning has emerged as a novel and efficient approach to digital diagnosis in recent years. However, existing models suffer from several severe limitations. 1) neglecting the selection of negative samples, resulting in the scarcity of hard negatives and the inclusion of false negatives; 2) focusing on global feature extraction, but overlooking the fine-grained local details that are crucial for medical image recognition tasks; and 3) contrastive learning primarily targets high-level features but ignoring low-level details which are essential for accurate medical analysis. Motivated by these critical issues, this paper presents a Cross-Modal Cluster-Guided Negative Sampling (CM-CGNS) method with two-fold ideas. First, it extends the k-means clustering used for local text features in the single-modal domain to the multimodal domain through cross-modal attention. This improvement increases the number of negative samples and boosts the model representation capability. Second, it introduces a Cross-Modal Masked Image Reconstruction (CM-MIR) module that leverages local text-to-image features obtained via cross-modal attention to reconstruct masked local image regions. This module significantly strengthens the model’s cross-modal information interaction capabilities and retains low-level image features essential for downstream tasks. By well handling the aforementioned limitations, the proposed CM-CGNS can learn effective and robust medical visual representations suitable for various recognition tasks. Extensive experimental results on classification, detection, and segmentation tasks across five downstream datasets show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches on multiple metrics, verifying its superior performance.
近年来,通过多模态自监督学习直接从配对图像和报告中学习医学视觉表示,已成为数字诊断的一种新颖且高效的方法。然而,现有模型存在几个严重的局限性。1)忽视了负样本的选择,导致硬负样本稀缺,以及错误负样本的包含;2)虽然关注全局特征提取,但却忽略了对于医学图像识别任务至关重要的细微局部细节;3)对比学习主要针对高级特征,但忽略了对于准确医学分析至关重要的低级细节。针对这些关键问题,本文提出了一种跨模态聚类引导负采样(CM-CGNS)方法,该方法具有两方面的思想。首先,它将用于局部文本特征的k-means聚类扩展到多模态领域,通过跨模态注意力提高负样本的数量并增强模型的表示能力。其次,它引入了一个跨模态掩膜图像重建(CM-MIR)模块,该模块利用通过跨模态注意力获得的局部文本到图像的特征来重建掩膜局部图像区域。这显著增强了模型的跨模态信息交互能力,并保留了下游任务所需的低级图像特征。通过妥善处理上述局限性,所提出的CM-CGNS可以学习适用于各种识别任务的有效和鲁棒的医学视觉表示。在五个下游数据集上进行的分类、检测和分割任务的广泛实验结果表明,我们的方法在多个指标上优于最新技术方法,验证了其卓越性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE TMI for possible publication. Our code is available at https://github.com/violet-42/CM-CGNS
摘要
本文提出了一种基于跨模态聚类引导的负采样(CM-CGNS)方法,解决了现有医学图像表示学习模型中的三大问题。首先,它通过跨模态注意力将K均值聚类从单模态扩展到多模态领域,提高了负样本的数量并增强了模型表征能力。其次,引入跨模态掩盖图像重建(CM-MIR)模块,利用跨模态注意力获得的局部文本到图像的特征来重建掩盖的局部图像区域,增强了模型的跨模态信息交互能力并保留了重要的低级图像特征。通过解决上述问题,CM-CGNS能够学习适用于各种识别任务的医疗视觉表示。在五个下游数据集上的分类、检测和分割任务的广泛实验结果表明,该方法在多个指标上优于最新技术,验证了其卓越性能。
关键见解
- 直接从配对图像和报告中学习医学视觉表示已成为近年来的新型高效数字诊断方法。
- 现有模型存在三大局限性:忽视负样本选择、关注全局特征而忽视局部细节以及对比学习主要关注高级特征而忽视低级特征。
- CM-CGNS方法通过跨模态注意力将单模态领域的K均值聚类扩展到多模态领域,提高了负样本数量和模型表征能力。
- CM-MIR模块的引入利用跨模态注意力获得的局部文本到图像的特征来重建掩盖的局部图像区域,增强了模型的跨模态信息交互能力。
- CM-CGNS能够学习适用于各种医疗识别任务的视觉表示。
- 实验结果表明,在多个数据集和多个任务上,CM-CGNS方法的表现优于现有先进技术。
点此查看论文截图

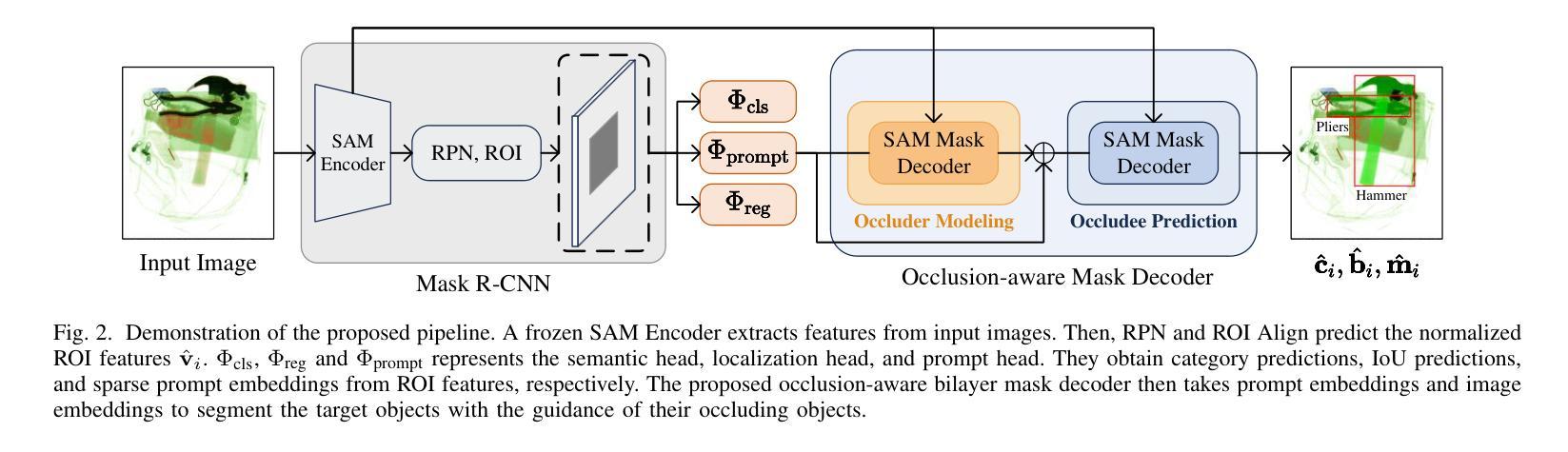
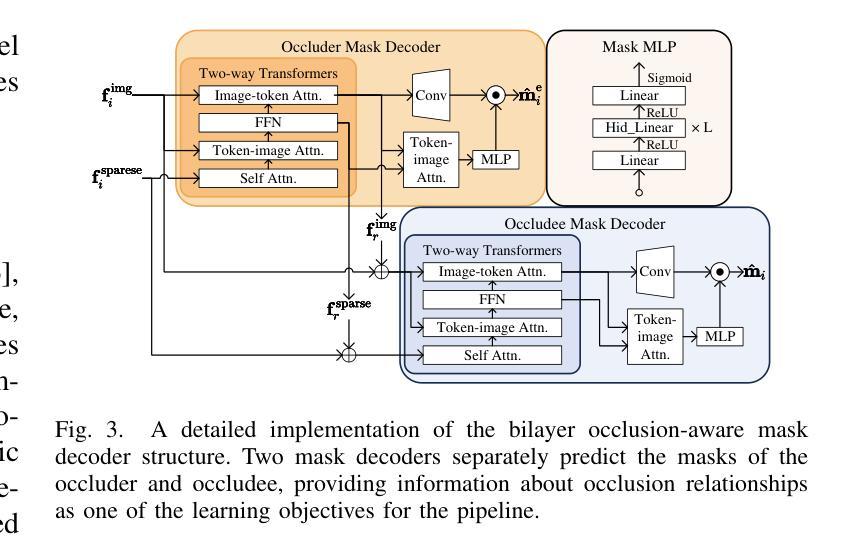
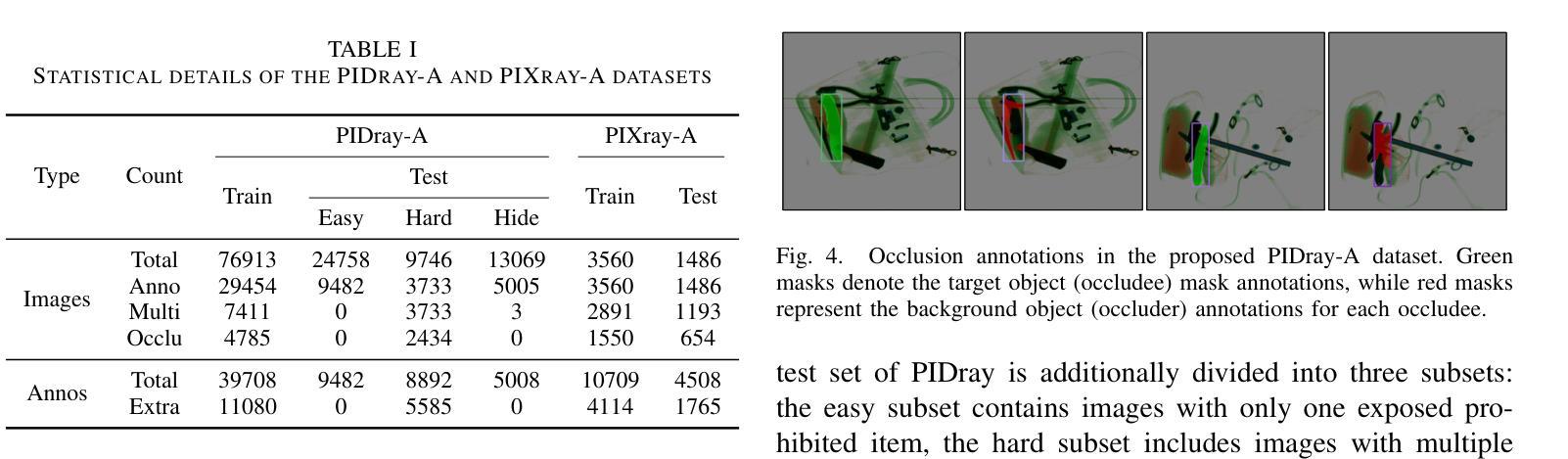
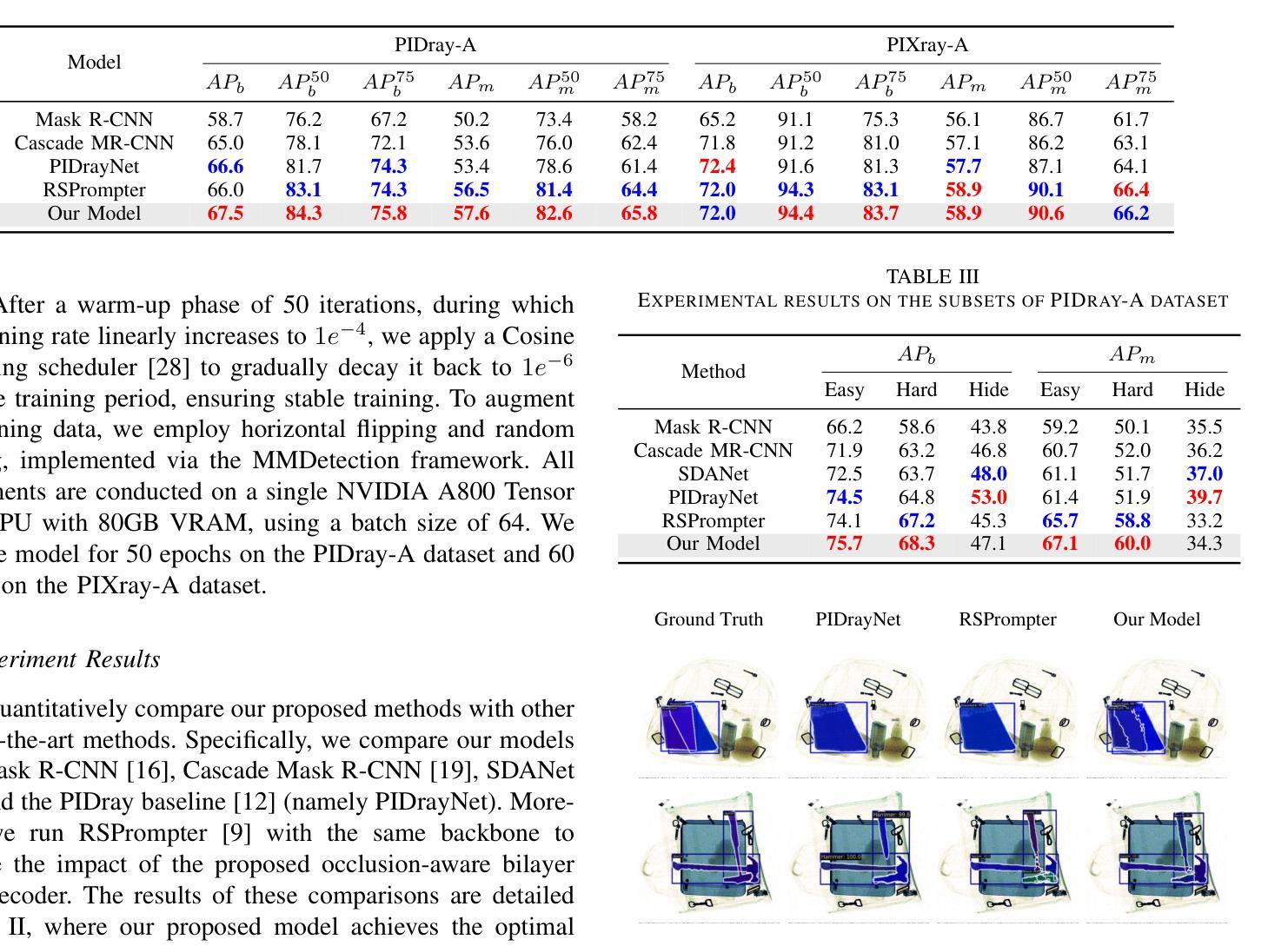
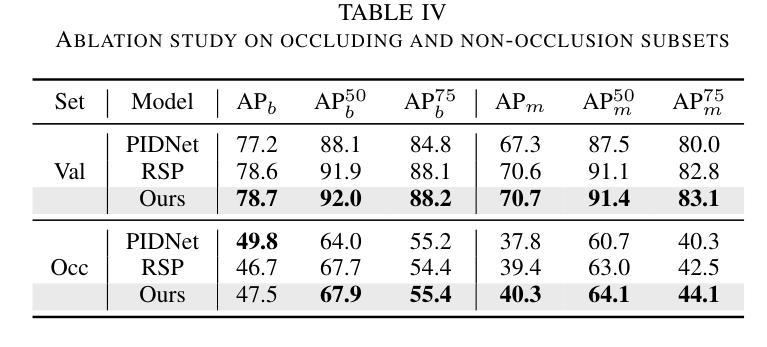
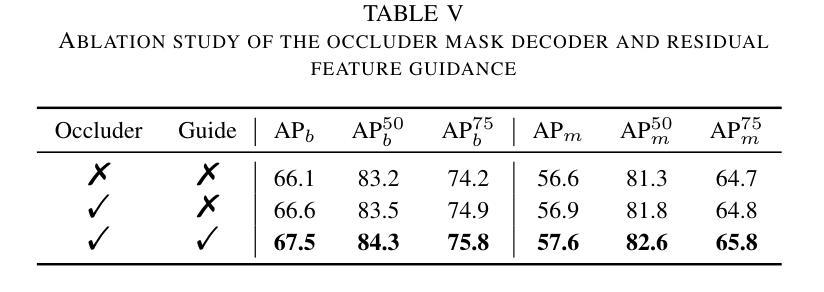
Prohibited Items Segmentation via Occlusion-aware Bilayer Modeling
Authors:Yunhan Ren, Ruihuang Li, Lingbo Liu, Changwen Chen
Instance segmentation of prohibited items in security X-ray images is a critical yet challenging task. This is mainly caused by the significant appearance gap between prohibited items in X-ray images and natural objects, as well as the severe overlapping among objects in X-ray images. To address these issues, we propose an occlusion-aware instance segmentation pipeline designed to identify prohibited items in X-ray images. Specifically, to bridge the representation gap, we integrate the Segment Anything Model (SAM) into our pipeline, taking advantage of its rich priors and zero-shot generalization capabilities. To address the overlap between prohibited items, we design an occlusion-aware bilayer mask decoder module that explicitly models the occlusion relationships. To supervise occlusion estimation, we manually annotated occlusion areas of prohibited items in two large-scale X-ray image segmentation datasets, PIDray and PIXray. We then reorganized these additional annotations together with the original information as two occlusion-annotated datasets, PIDray-A and PIXray-A. Extensive experimental results on these occlusion-annotated datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method. The datasets and codes are available at: https://github.com/Ryh1218/Occ
在安检X光图像中对违禁物品进行实例分割是一项至关重要且富有挑战性的任务。这主要是因为违禁物品在X光图像中的外观与自然物体有很大的差距,以及X光图像中物体之间的严重重叠。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种遮挡感知的实例分割管道,用于识别X光图像中的违禁物品。具体来说,为了弥合表示上的差距,我们将“万物可分割”模型(Segment Anything Model,SAM)集成到我们的管道中,利用其丰富的先验知识和零样本泛化能力。为了解决违禁物品之间的重叠问题,我们设计了一个遮挡感知的双层掩膜解码器模块,该模块可以显式地建模遮挡关系。为了监督遮挡估计,我们在两个大规模的X光图像分割数据集PIDray和PIXray上手动标注了违禁物品的遮挡区域,然后将这些额外的标注与原始信息一起重新组织成两个带遮挡标注的数据集PIDray-A和PIXray-A。在这些带遮挡标注的数据集上进行的大量实验结果表明了我们提出的方法的有效性。数据集和代码可在https://github.com/Ryh1218/Occ找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICME 2025
Summary
禁止物品在安检X光图像中的实例分割是一项重要而具有挑战性的任务。针对这一问题,我们提出了一种遮挡感知的实例分割管道设计,旨在识别X光图像中的禁止物品。我们整合了分段任何事情模型(SAM),以缩小表示差距并处理物品之间的重叠问题。为解决禁止物品的遮挡问题,我们设计了一个遮挡感知的双层掩膜解码模块,该模块可以明确建模遮挡关系。我们在两个大规模的X光图像分割数据集PIDray和PIXray上手动标注了禁止物品的遮挡区域,并以此创建了两个带遮挡注释的数据集PIDray-A和PIXray-A。实验证明,我们提出的方法在这些带遮挡注释的数据集上效果显著。
Key Takeaways
- 实例分割在安检X光图像中识别禁止物品是一项挑战,因为物品间存在外观差异和严重重叠。
- 我们提出了一种遮挡感知的实例分割管道设计来识别这些物品。
- 利用Segment Anything Model(SAM)缩小表示差距。
- 设计了一个双层掩膜解码模块来处理物品间的遮挡关系。
- 在两个大型X光图像分割数据集上手动标注了禁止物品的遮挡区域,并创建了带遮挡注释的数据集。
- 实验证明在带遮挡注释的数据集上的方法效果显著。
点此查看论文截图

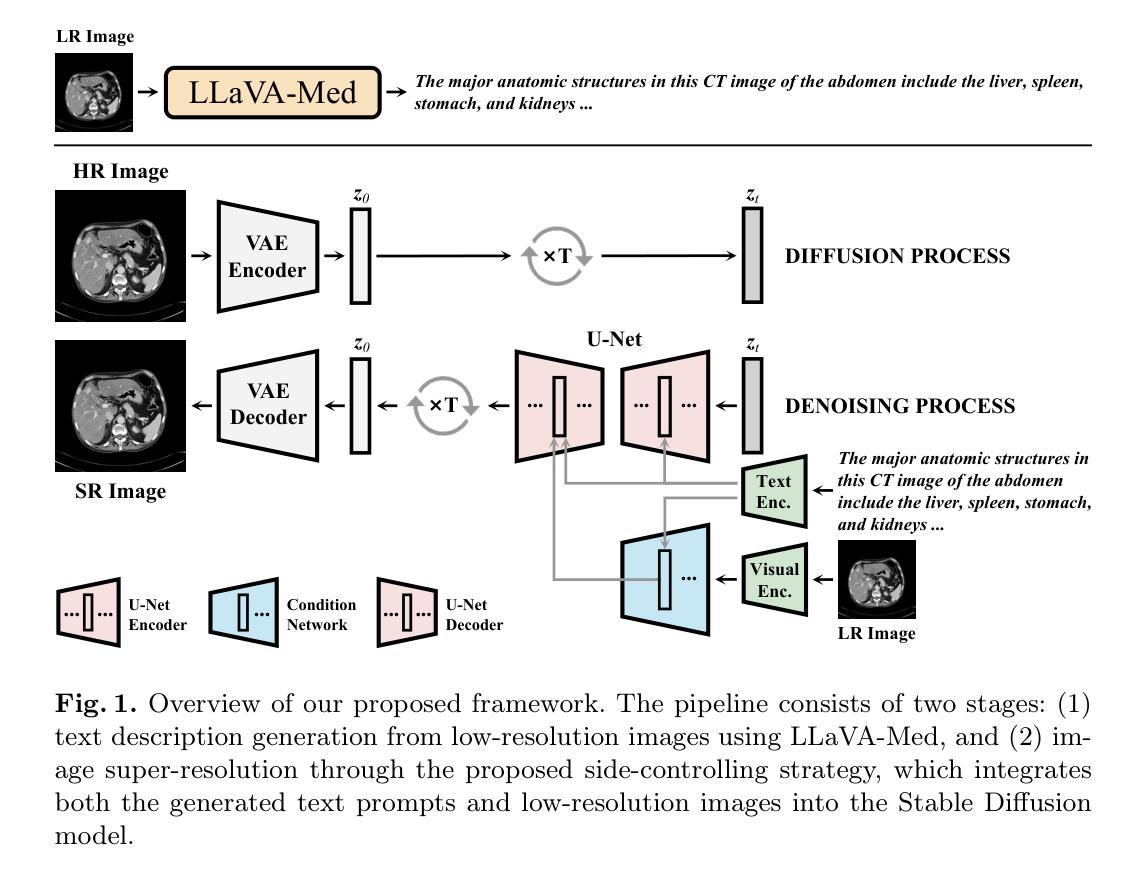
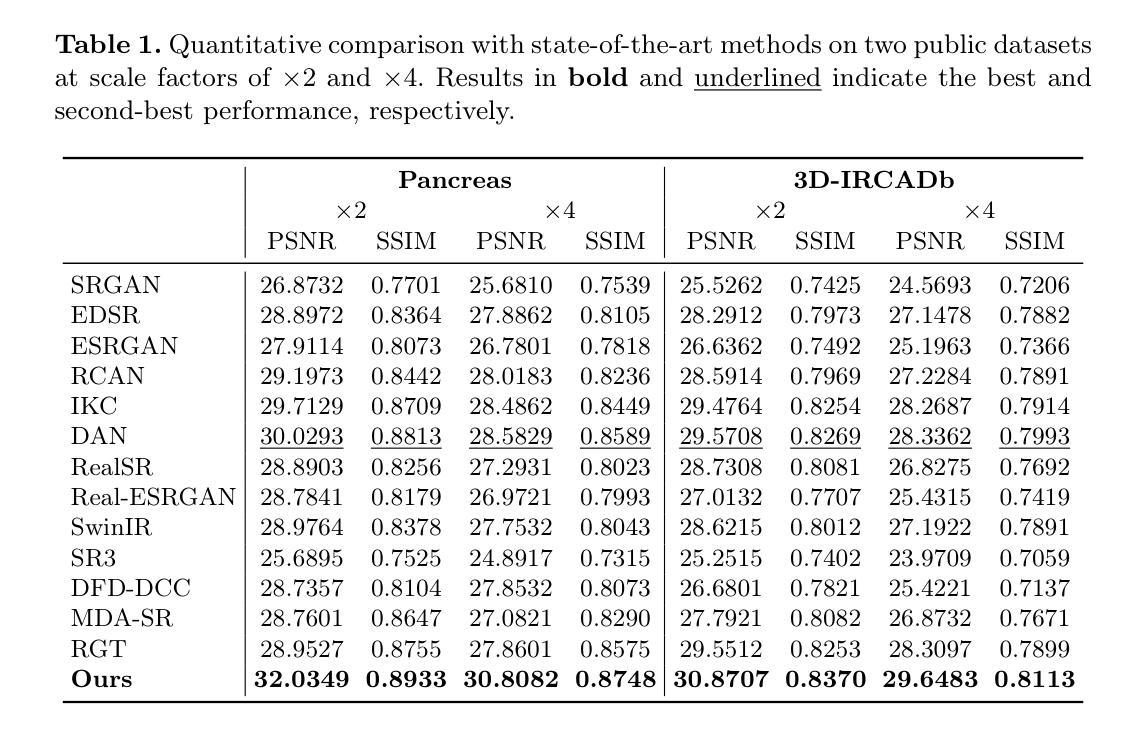
Taming Stable Diffusion for Computed Tomography Blind Super-Resolution
Authors:Chunlei Li, Yilei Shi, Haoxi Hu, Jingliang Hu, Xiao Xiang Zhu, Lichao Mou
High-resolution computed tomography (CT) imaging is essential for medical diagnosis but requires increased radiation exposure, creating a critical trade-off between image quality and patient safety. While deep learning methods have shown promise in CT super-resolution, they face challenges with complex degradations and limited medical training data. Meanwhile, large-scale pre-trained diffusion models, particularly Stable Diffusion, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in synthesizing fine details across various vision tasks. Motivated by this, we propose a novel framework that adapts Stable Diffusion for CT blind super-resolution. We employ a practical degradation model to synthesize realistic low-quality images and leverage a pre-trained vision-language model to generate corresponding descriptions. Subsequently, we perform super-resolution using Stable Diffusion with a specialized controlling strategy, conditioned on both low-resolution inputs and the generated text descriptions. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms existing approaches, demonstrating its potential for achieving high-quality CT imaging at reduced radiation doses. Our code will be made publicly available.
高分辨率计算机断层扫描(CT)成像对于医学诊断至关重要,但会增加辐射暴露,从而在图像质量和患者安全之间形成了关键的权衡。深度学习方法在CT超分辨率领域已展现出巨大的潜力,但仍面临复杂退化问题和有限的医学训练数据挑战。与此同时,大规模预训练的扩散模型,特别是Stable Diffusion,在各种视觉任务中合成精细细节方面表现出了显著的能力。受此启发,我们提出了一种适应Stable Diffusion的CT盲超分辨率新框架。我们采用实用的退化模型合成逼真的低质量图像,并利用预训练的视觉语言模型生成相应的描述。随后,我们使用Stable Diffusion进行超分辨率处理,采用专门的控制策略,以低分辨率输入和生成的文本描述为条件。大量实验表明,我们的方法优于现有方法,展现了在降低辐射剂量下实现高质量CT成像的潜力。我们的代码将公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在医学诊断中,高分辨率的计算机断层扫描(CT)成像至关重要,但同时也增加了患者的辐射暴露风险。深度学习方法在CT超分辨率处理方面显示出潜力,但仍面临复杂退化和有限医学训练数据的挑战。受大型预训练扩散模型(如Stable Diffusion)在合成各种视觉任务精细细节方面的出色表现的启发,我们提出了一种基于Stable Diffusion的CT盲超分辨率处理的新框架。该框架利用实用的退化模型合成逼真的低质量图像,并利用预训练的视觉语言模型生成相应的描述。然后,我们采用一种特殊的控制策略进行超分辨率处理,该策略根据低分辨率输入和生成的文本描述进行条件处理。实验表明,我们的方法优于现有方法,有望在降低辐射剂量的同时实现高质量的CT成像。我们的代码将公开提供。
Key Takeaways
- 高分辨率CT成像对于医学诊断至关重要,但需要平衡图像质量和患者辐射暴露。
- 深度学习方法在CT超分辨率处理中有潜力,但面临复杂退化和有限医学数据的挑战。
- 大型预训练扩散模型如Stable Diffusion在合成精细细节方面表现出色。
- 提出了一种基于Stable Diffusion的CT盲超分辨率处理的新框架。
- 该框架利用退化模型合成低质量图像并利用视觉语言模型生成描述。
- 利用低分辨率输入和文本描述进行超分辨率处理。
- 实验表明该方法优于现有技术,可实现降低辐射剂量下的高质量CT成像。
点此查看论文截图

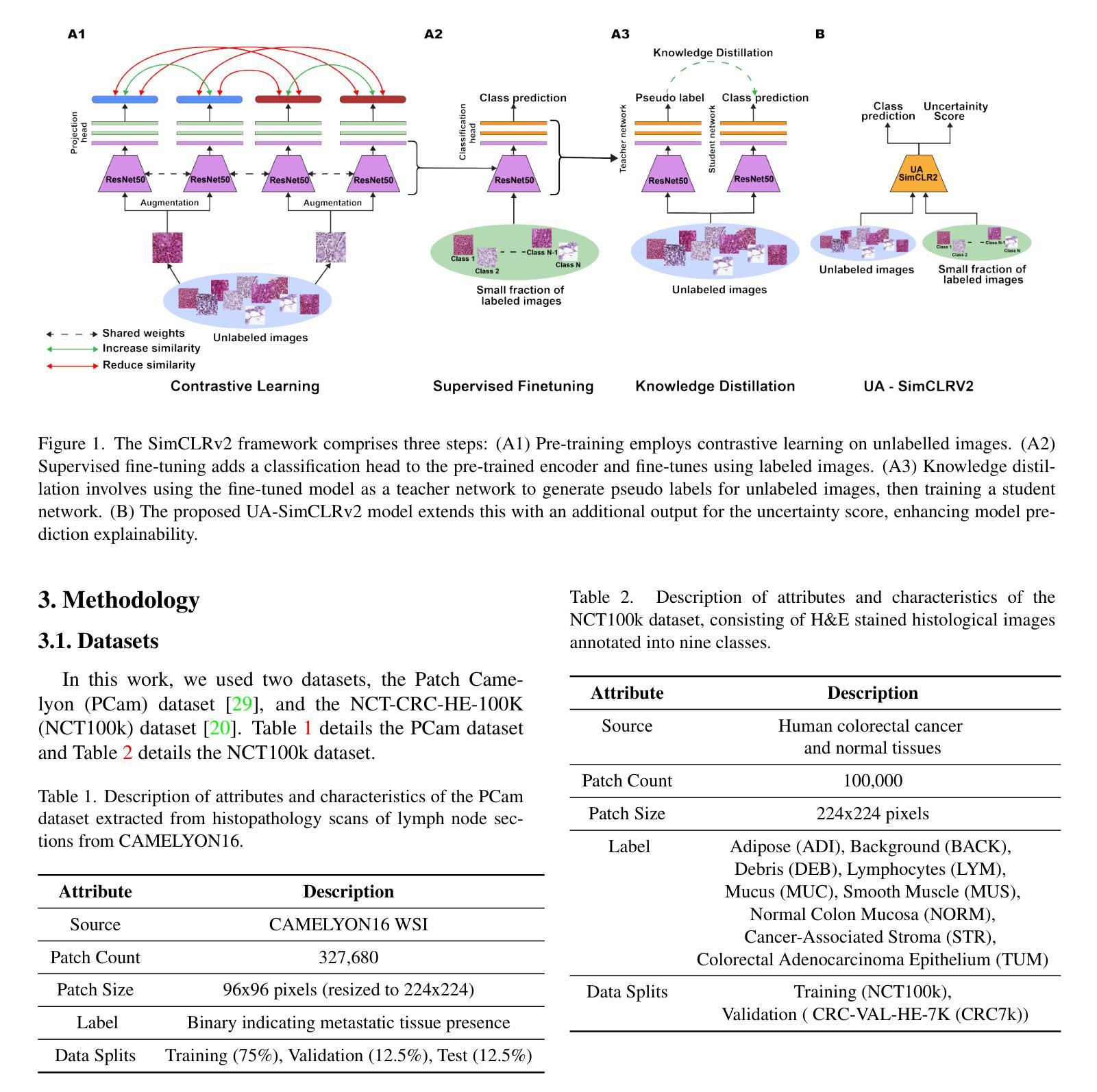
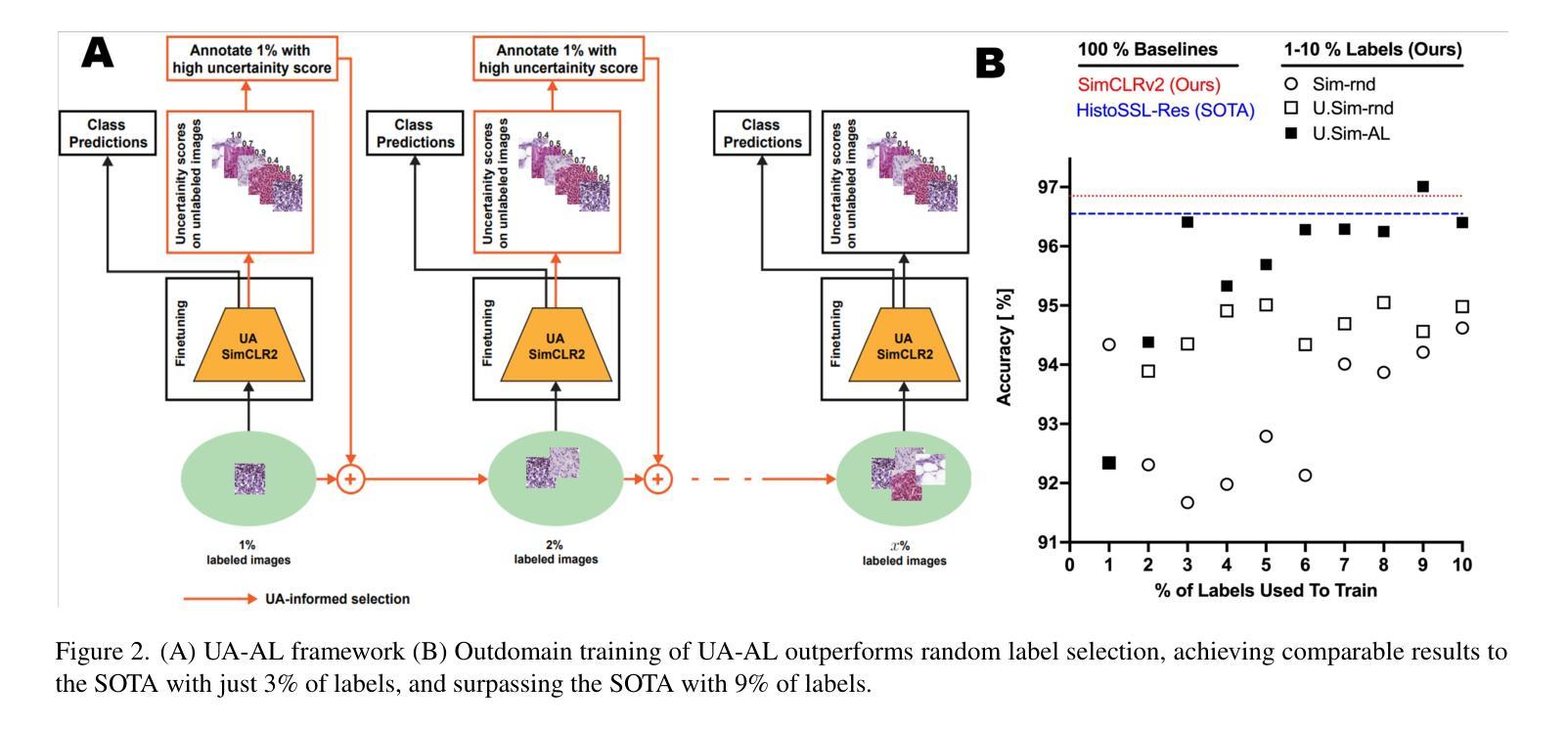
Uncertainty Awareness Enables Efficient Labeling for Cancer Subtyping in Digital Pathology
Authors:Nirhoshan Sivaroopan, Chamuditha Jayanga Galappaththige, Chalani Ekanayake, Hasindri Watawana, Ranga Rodrigo, Chamira U. S. Edussooriya, Dushan N. Wadduwage
Machine-learning-assisted cancer subtyping is a promising avenue in digital pathology. Cancer subtyping models, however, require careful training using expert annotations so that they can be inferred with a degree of known certainty (or uncertainty). To this end, we introduce the concept of uncertainty awareness into a self-supervised contrastive learning model. This is achieved by computing an evidence vector at every epoch, which assesses the model’s confidence in its predictions. The derived uncertainty score is then utilized as a metric to selectively label the most crucial images that require further annotation, thus iteratively refining the training process. With just 1-10% of strategically selected annotations, we attain state-of-the-art performance in cancer subtyping on benchmark datasets. Our method not only strategically guides the annotation process to minimize the need for extensive labeled datasets, but also improves the precision and efficiency of classifications. This development is particularly beneficial in settings where the availability of labeled data is limited, offering a promising direction for future research and application in digital pathology.
机器学习辅助癌症分型是数字病理学领域的一个前景广阔的研究方向。然而,癌症分型模型需要使用专家注释进行仔细训练,以便能够以已知的确定性(或不确定性)进行推断。为此,我们将不确定性的概念引入了一种自监督对比学习模型。这是通过每个时代计算证据向量来实现的,该证据向量评估模型对其预测的置信度。然后利用派生出的不确定性评分作为指标,有选择地标记最需要进一步注释的图像,从而迭代地改进训练过程。仅使用1-10%的战略选择注释,我们在基准数据集上的癌症分型达到了最先进的性能。我们的方法不仅战略性地引导了注释过程,以最大限度地减少需要大量标记数据集的需求,而且还提高了分类的精确性和效率。在标记数据可用性有限的情况下,这一发展特别有益,为数字病理学未来的研究与应用提供了有前景的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
机器学习辅助癌症分型是数字病理学中的一条有前途的道路。我们引入不确定性意识概念到自监督对比学习模型中,通过计算每个时期的证据向量评估模型的预测置信度,实现不确定性评分作为指标来选择性标注需要更多注释的关键图像,从而迭代优化训练过程。仅使用1-10%的策略选择注释,就能在基准数据集上实现癌症分型的最新性能。我们的方法不仅战略性地引导注释过程,减少需要大量标记数据集的需求,还提高了分类的精确度和效率,特别是在标记数据有限的环境中,为数字病理学未来的研究与应用提供了有前景的方向。
Key Takeaways
- 机器学习辅助癌症分型是数字病理学中的有前途的研究方向。
- 引入不确定性意识概念到自监督对比学习模型中以提高模型性能。
- 通过计算证据向量评估模型的预测置信度,实现不确定性评分。
- 利用不确定性评分选择性标注需要更多注释的关键图像,迭代优化训练过程。
- 仅需少量策略性选择的注释就能达到癌症分型的最新性能。
- 方法能战略性地引导注释过程,减少需要大量标记数据集的需求。
点此查看论文截图

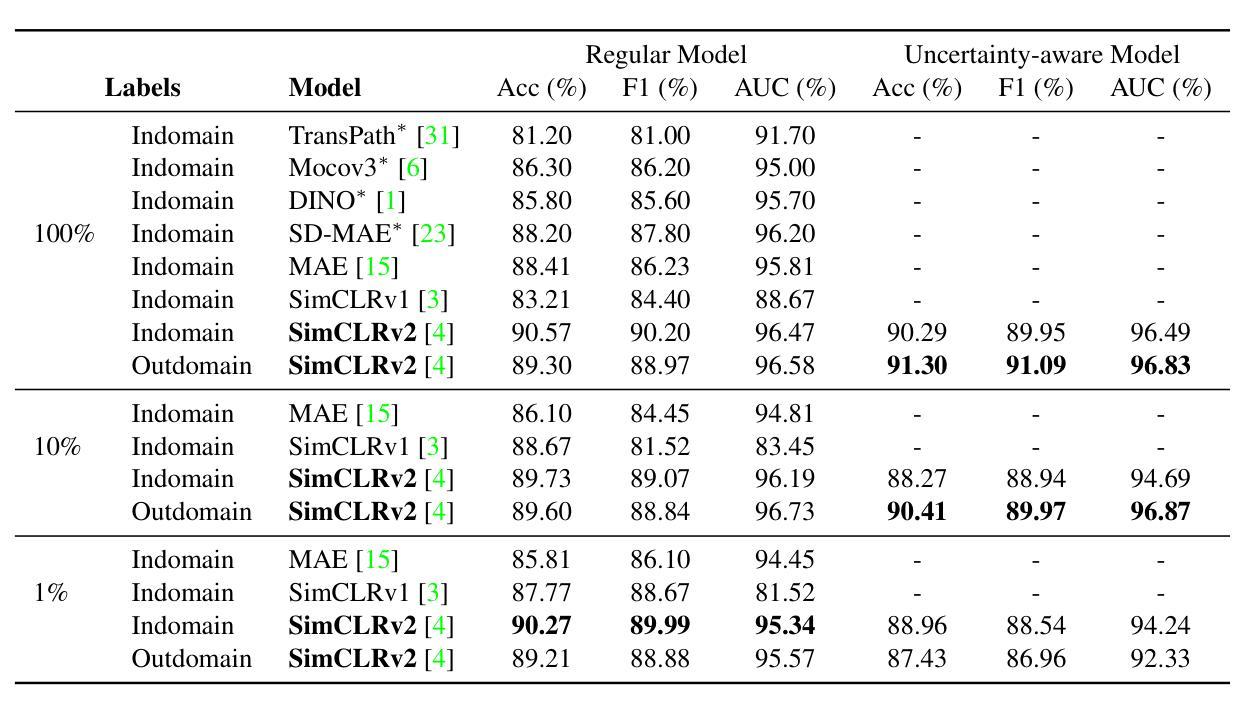
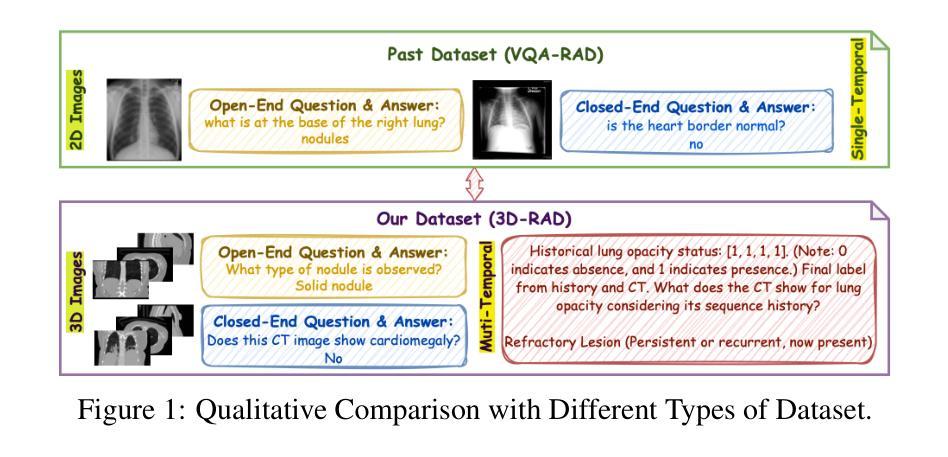
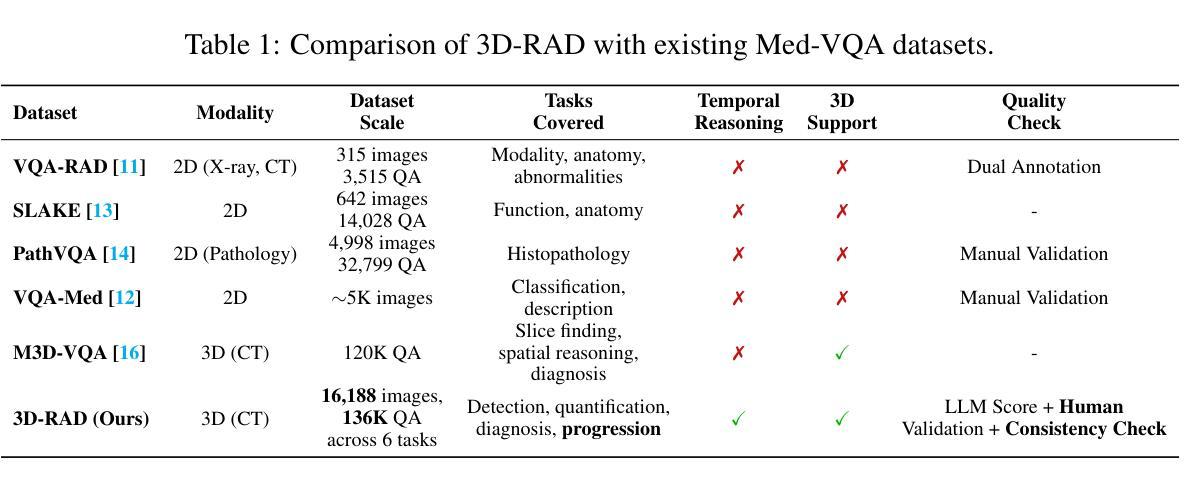
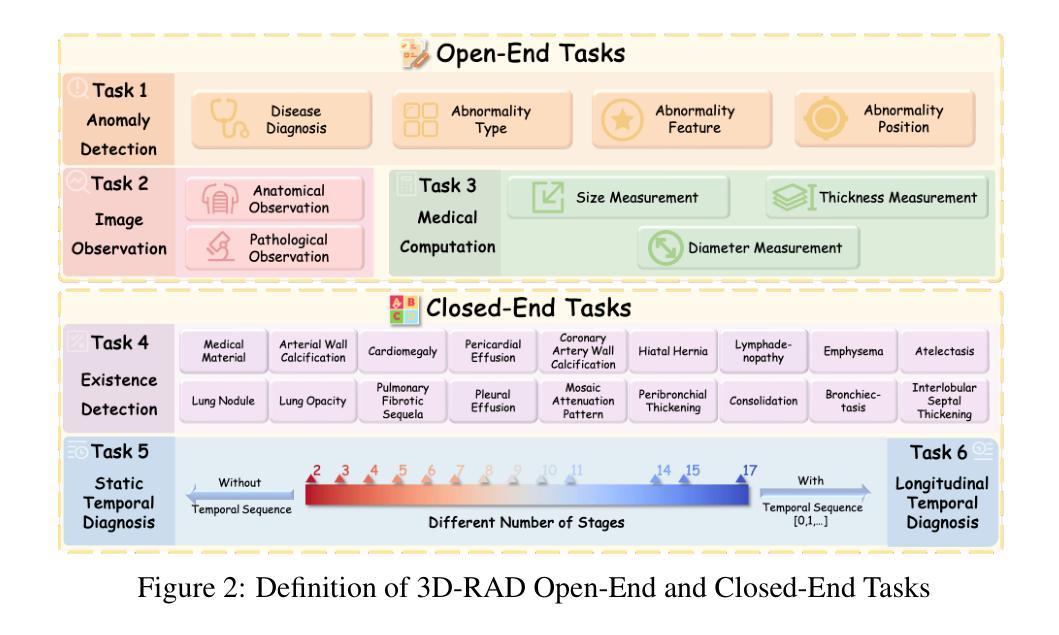
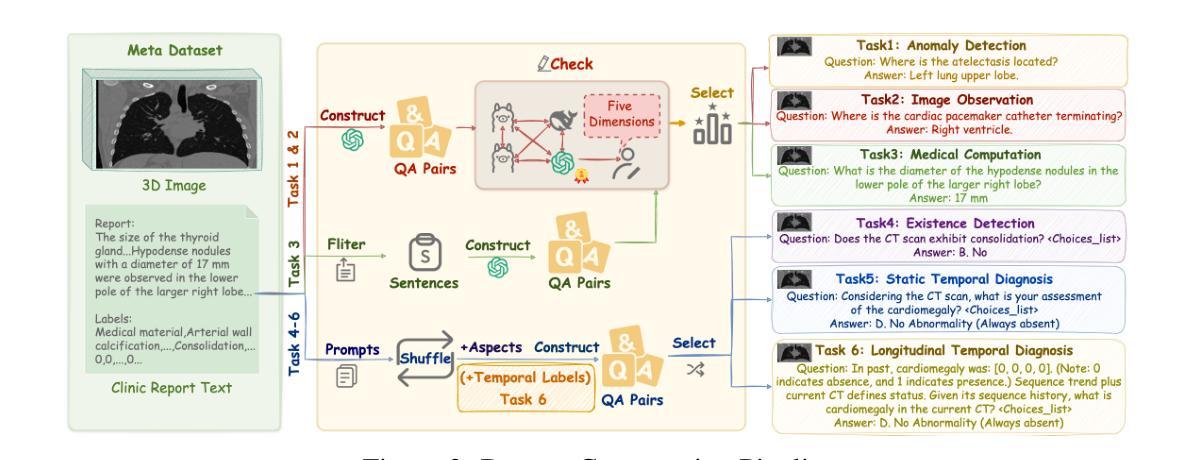
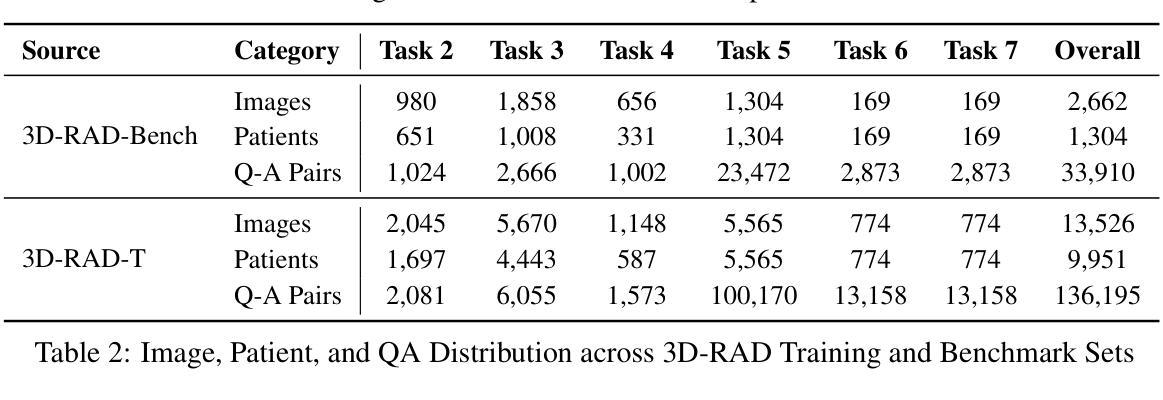
3D-RAD: A Comprehensive 3D Radiology Med-VQA Dataset with Multi-Temporal Analysis and Diverse Diagnostic Tasks
Authors:Xiaotang Gai, Jiaxiang Liu, Yichen Li, Zijie Meng, Jian Wu, Zuozhu Liu
Medical Visual Question Answering (Med-VQA) holds significant potential for clinical decision support, yet existing efforts primarily focus on 2D imaging with limited task diversity. This paper presents 3D-RAD, a large-scale dataset designed to advance 3D Med-VQA using radiology CT scans. The 3D-RAD dataset encompasses six diverse VQA tasks: anomaly detection, image observation, medical computation, existence detection, static temporal diagnosis, and longitudinal temporal diagnosis. It supports both open- and closed-ended questions while introducing complex reasoning challenges, including computational tasks and multi-stage temporal analysis, to enable comprehensive benchmarking. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that existing vision-language models (VLMs), especially medical VLMs exhibit limited generalization, particularly in multi-temporal tasks, underscoring the challenges of real-world 3D diagnostic reasoning. To drive future advancements, we release a high-quality training set 3D-RAD-T of 136,195 expert-aligned samples, showing that fine-tuning on this dataset could significantly enhance model performance. Our dataset and code, aiming to catalyze multimodal medical AI research and establish a robust foundation for 3D medical visual understanding, are publicly available at https://github.com/Tang-xiaoxiao/M3D-RAD.
医学视觉问答(Med-VQA)在临床决策支持方面拥有巨大潜力,但现有研究主要集中在二维成像上,任务多样性有限。本文介绍了大规模数据集3D-RAD,旨在利用放射学CT扫描推进三维Med-VQA的发展。3D-RAD数据集包含六个多样化的VQA任务:异常检测、图像观察、医学计算、存在检测、静态时间诊断和纵向时间诊断。它支持开放和封闭性问题,同时引入复杂的推理挑战,包括计算任务和多阶段时间分析,以实现全面的基准测试。大量评估表明,现有的视觉语言模型(VLMs)特别是医学VLMs的泛化能力有限,特别是在多时间任务中,这突出了现实世界三维诊断推理的挑战。为了推动未来的进步,我们发布了高质量的训练集3D-RAD-T,包含136,195个专家对齐样本,表明在此数据集上进行微调可以显著提高模型性能。我们的数据集和代码旨在推动多模态医疗人工智能研究并为三维医学视觉理解建立稳健的基础,可在https://github.com/Tang-xiaoxiao/M3D-RAD上公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个大型数据集3D-RAD,用于推进基于三维医学影像(如CT扫描)的医疗视觉问答(Med-VQA)。该数据集涵盖六种多样的问答任务,支持开放和封闭性问题,并引入复杂的推理挑战,如计算任务和多时相分析。现有视觉语言模型(VLMs)在该数据集上的表现有限,特别是在多时相任务中。为提升模型性能,发布了一个高质量的训练集3D-RAD-T。
Key Takeaways
- 3D-RAD数据集用于推进基于三维医学影像的医疗视觉问答(Med-VQA)。
- 该数据集包含六种多样的问答任务,涵盖异常检测、图像观察、医学计算等。
- 引入复杂推理挑战,如计算任务和多时相分析。
- 现有视觉语言模型在该数据集上的表现有限,尤其在多时相任务中。
- 公开了一个高质量的训练集3D-RAD-T,以提高模型性能。
- 数据集和代码公开可用,旨在推动多学科医疗人工智能研究,并为三维医学视觉理解建立稳健基础。
点此查看论文截图

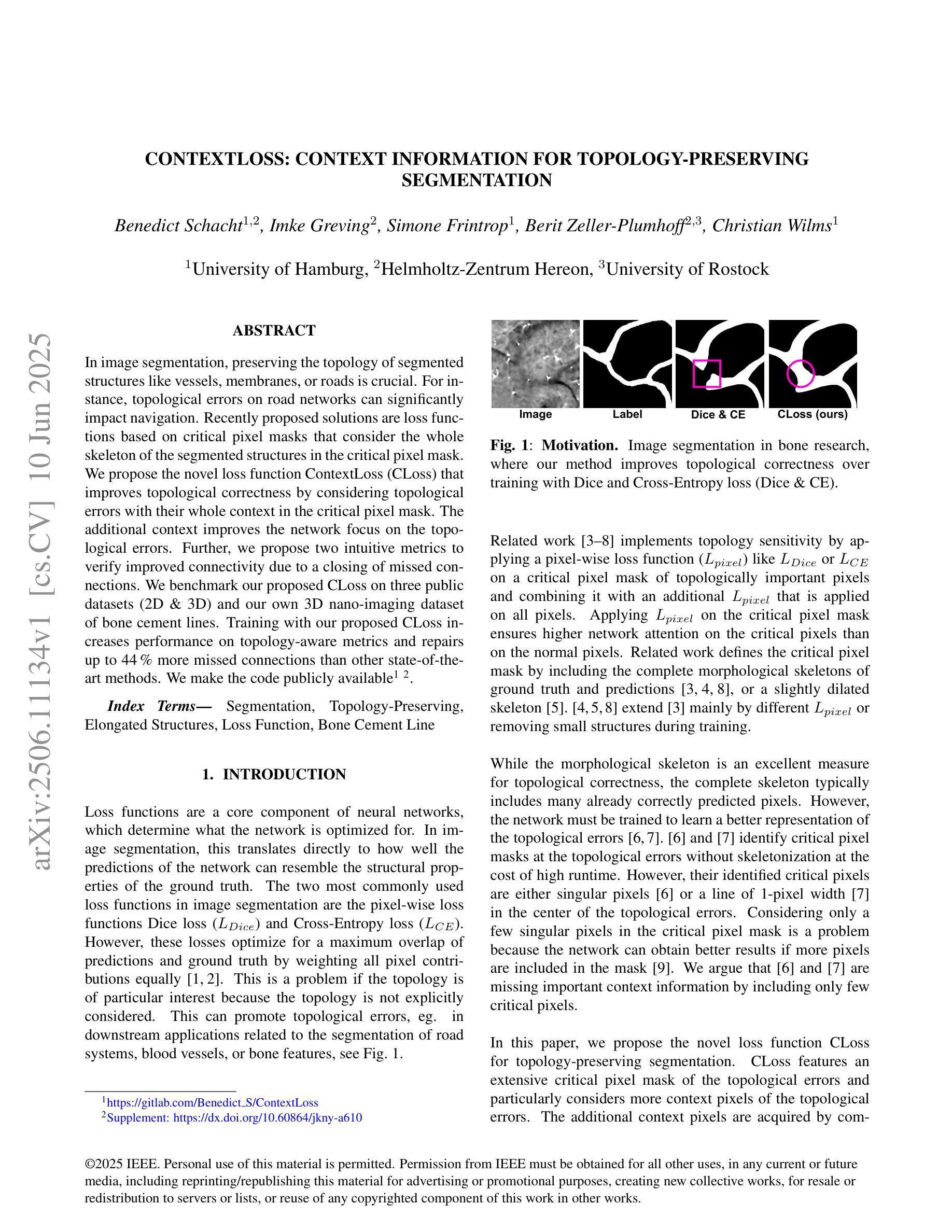
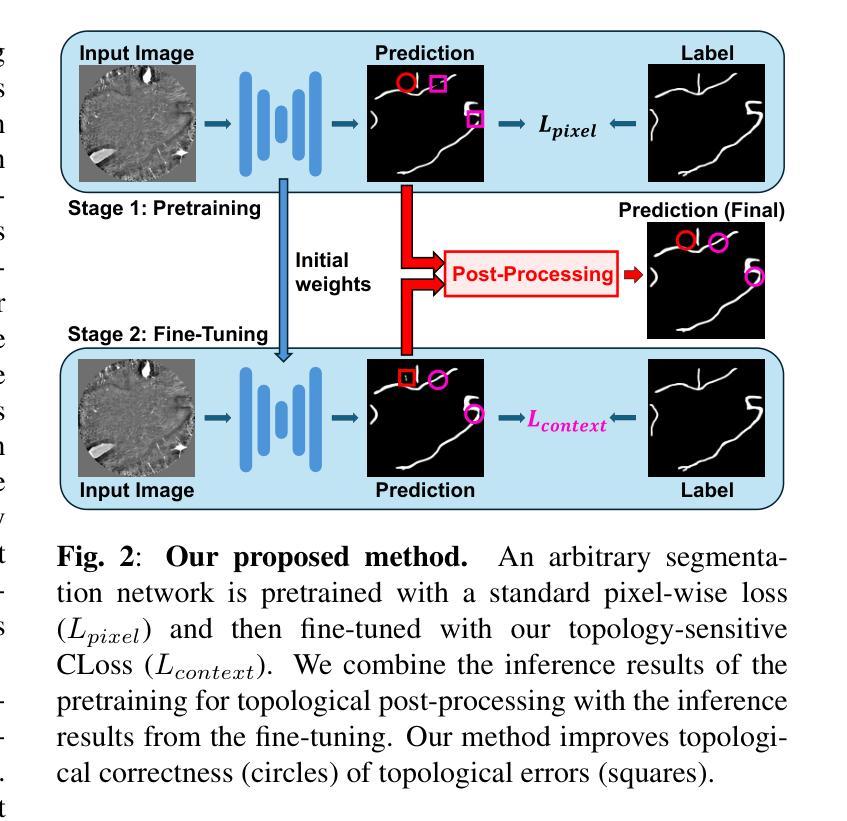
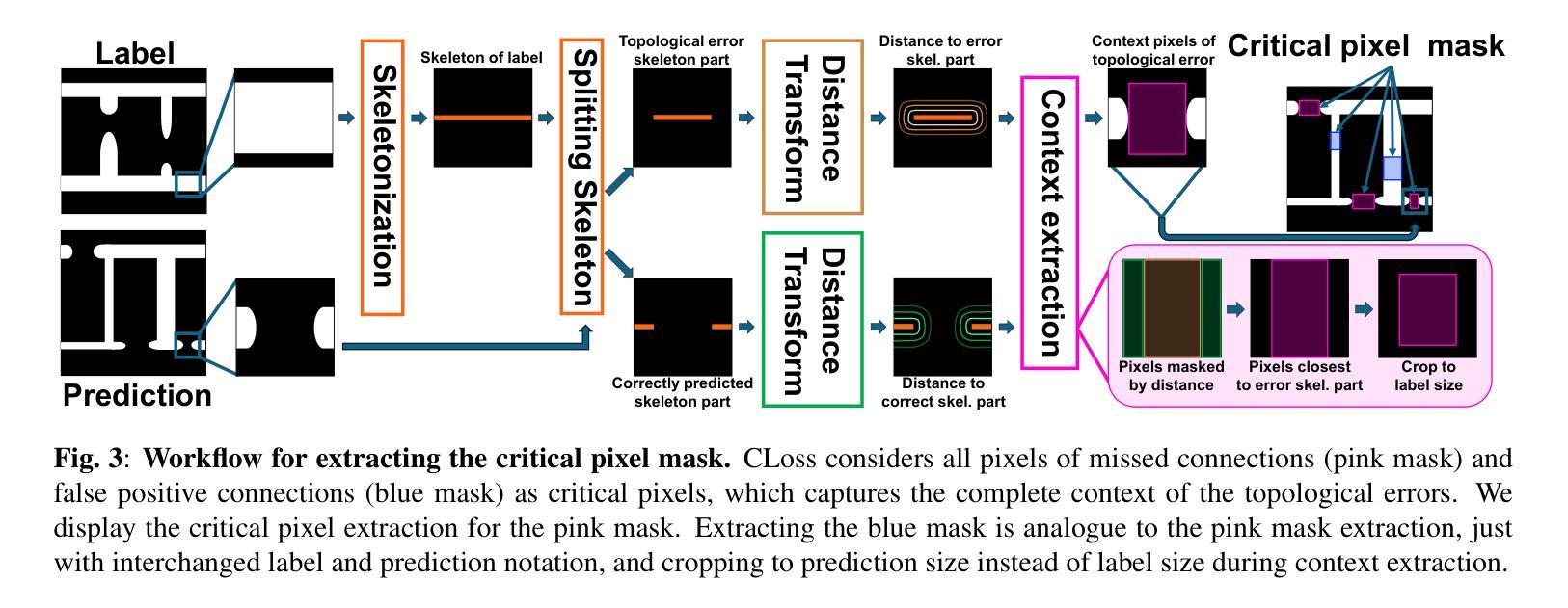
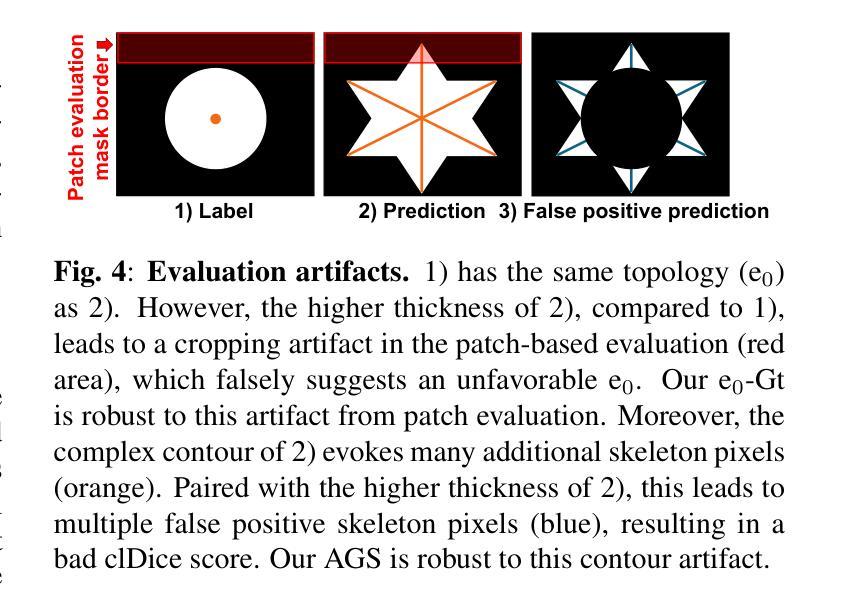
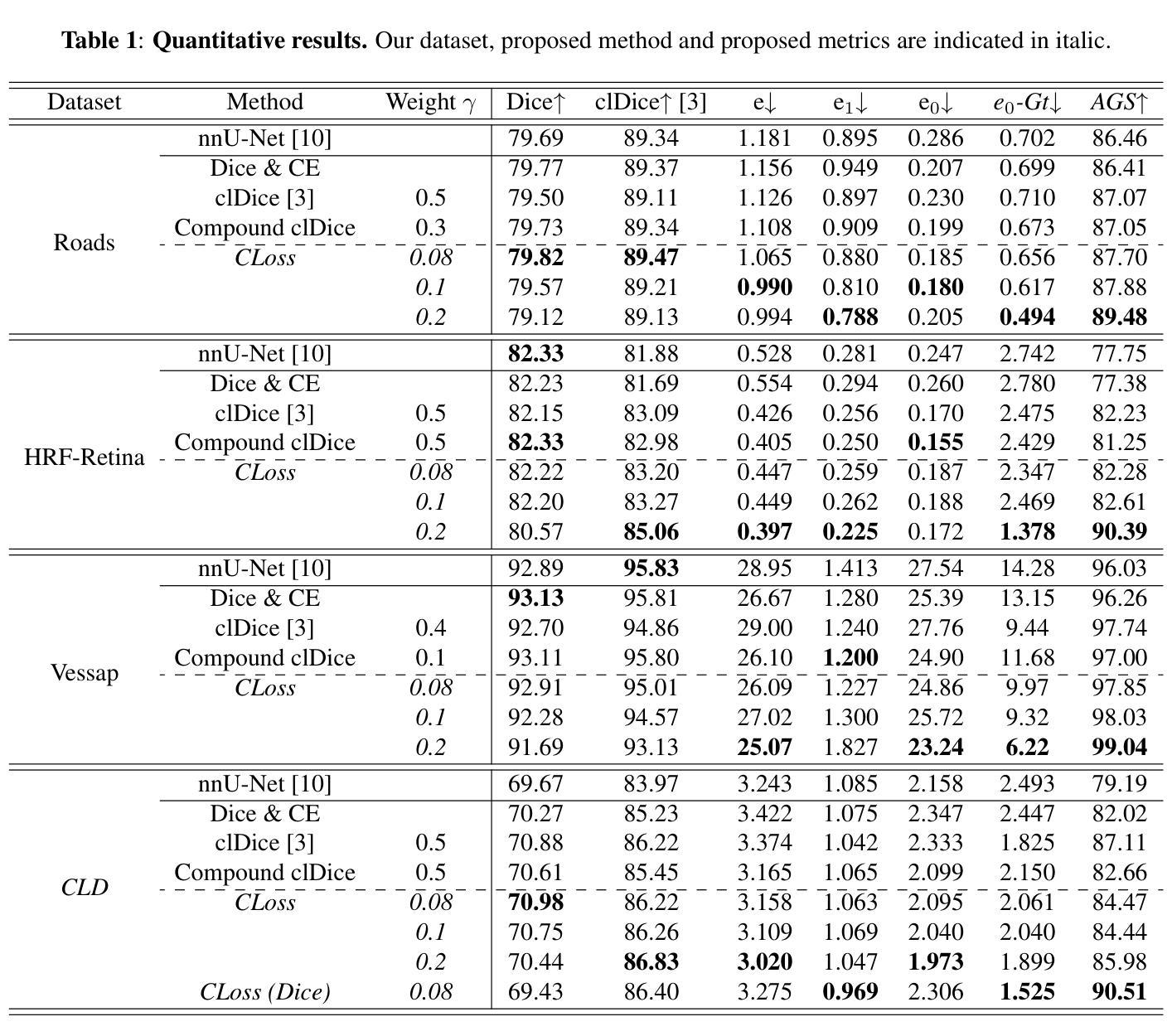
ContextLoss: Context Information for Topology-Preserving Segmentation
Authors:Benedict Schacht, Imke Greving, Simone Frintrop, Berit Zeller-Plumhoff, Christian Wilms
In image segmentation, preserving the topology of segmented structures like vessels, membranes, or roads is crucial. For instance, topological errors on road networks can significantly impact navigation. Recently proposed solutions are loss functions based on critical pixel masks that consider the whole skeleton of the segmented structures in the critical pixel mask. We propose the novel loss function ContextLoss (CLoss) that improves topological correctness by considering topological errors with their whole context in the critical pixel mask. The additional context improves the network focus on the topological errors. Further, we propose two intuitive metrics to verify improved connectivity due to a closing of missed connections. We benchmark our proposed CLoss on three public datasets (2D & 3D) and our own 3D nano-imaging dataset of bone cement lines. Training with our proposed CLoss increases performance on topology-aware metrics and repairs up to 44% more missed connections than other state-of-the-art methods. We make the code publicly available.
在图像分割中,保持分割结构(如血管、膜或道路)的拓扑结构至关重要。例如,道路网络上的拓扑错误会对导航产生重大影响。最近提出的解决方案是基于关键像素掩膜的损失函数,它考虑了关键像素掩膜中分割结构的整体骨架。我们提出了新型的损失函数ContextLoss(CLoss),通过考虑关键像素掩膜中拓扑错误及其整体上下文,提高了拓扑的正确性。额外的上下文提高了网络对拓扑错误的关注。此外,我们提出了两个直观的度量指标,以验证由于闭合的遗漏连接而提高了连通性。我们在三个公共数据集(2D和3D)以及我们自己的3D纳米成像骨水泥线数据集上对我们的CLoss进行了基准测试。使用我们提出的CLoss进行训练,可以提高拓扑感知指标的性能,并且可以修复比其他最先进的方法多达44%的遗漏连接。我们公开提供代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 7 figures, accepted to ICIP 2025
Summary
本文提出一种新型的损失函数ContextLoss(CLoss),用于改进图像分割中的拓扑正确性。该函数通过考虑关键像素掩膜中的拓扑错误及其整体上下文,提高了网络对拓扑错误的关注。此外,本文还提出了两种直观的度量指标,以验证因闭合遗漏连接而提高的连通性。在三个公共数据集(包括2D和3D)以及自己的3D纳米成像数据集上进行的基准测试表明,使用CLoss进行训练可提高拓扑感知指标的性能,并修复了比其他最先进方法多出44%的遗漏连接。
Key Takeaways
- ContextLoss(CLoss)是一种新型的损失函数,旨在改进图像分割中的拓扑正确性。
- CLoss通过考虑关键像素掩膜中的拓扑错误及其整体上下文,提高网络对拓扑错误的关注。
- 提出两种直观度量指标,用于验证因使用CLoss而提高的连通性。
- 在多个公共数据集上的基准测试表明,使用CLoss进行训练可提高拓扑感知指标的性能。
- CLoss能修复比其他最先进方法多出44%的遗漏连接。
- 代码已公开供公众使用。
- CLoss的应用范围可能涵盖需要高度关注拓扑正确性的领域,如道路网络、血管分割等。
点此查看论文截图
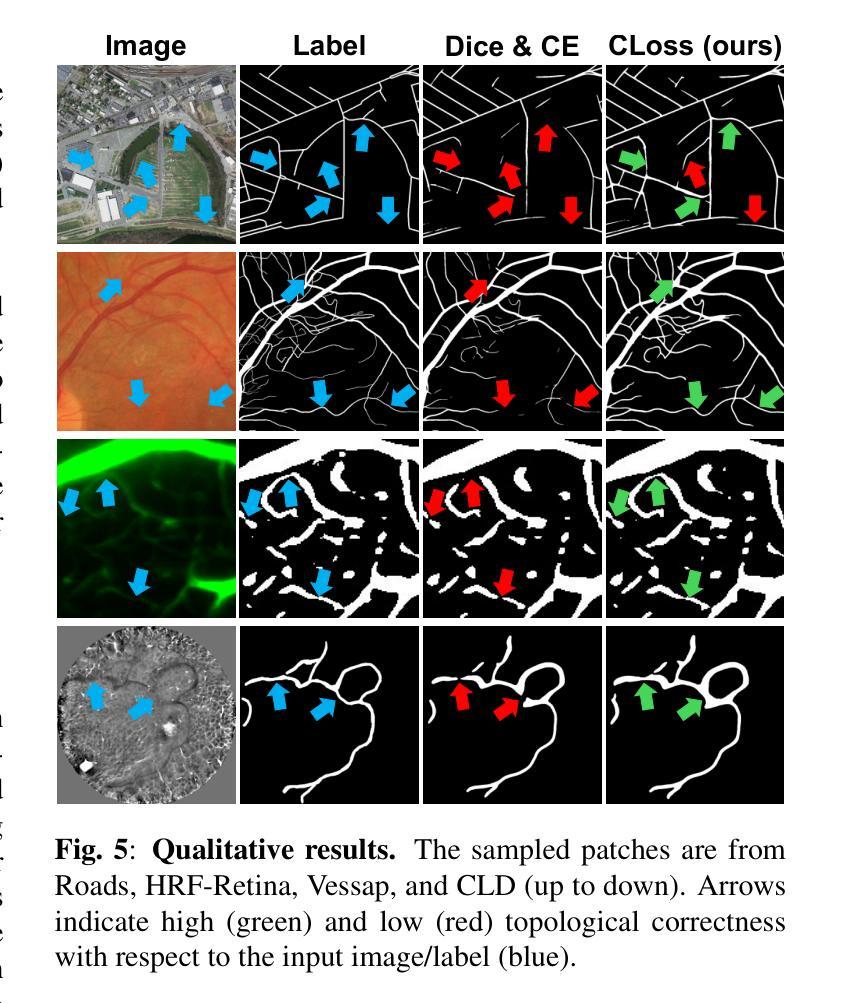
PiPViT: Patch-based Visual Interpretable Prototypes for Retinal Image Analysis
Authors:Marzieh Oghbaie, Teresa Araújo, Hrvoje Bogunović
Background and Objective: Prototype-based methods improve interpretability by learning fine-grained part-prototypes; however, their visualization in the input pixel space is not always consistent with human-understandable biomarkers. In addition, well-known prototype-based approaches typically learn extremely granular prototypes that are less interpretable in medical imaging, where both the presence and extent of biomarkers and lesions are critical. Methods: To address these challenges, we propose PiPViT (Patch-based Visual Interpretable Prototypes), an inherently interpretable prototypical model for image recognition. Leveraging a vision transformer (ViT), PiPViT captures long-range dependencies among patches to learn robust, human-interpretable prototypes that approximate lesion extent only using image-level labels. Additionally, PiPViT benefits from contrastive learning and multi-resolution input processing, which enables effective localization of biomarkers across scales. Results: We evaluated PiPViT on retinal OCT image classification across four datasets, where it achieved competitive quantitative performance compared to state-of-the-art methods while delivering more meaningful explanations. Moreover, quantitative evaluation on a hold-out test set confirms that the learned prototypes are semantically and clinically relevant. We believe PiPViT can transparently explain its decisions and assist clinicians in understanding diagnostic outcomes. Github page: https://github.com/marziehoghbaie/PiPViT
背景与目标:基于原型的方法通过学习精细的局部原型来提高解释性,但它们在输入像素空间中的可视化并不总是与人们可理解的生物标志物相一致。此外,众所周知的基于原型的方法通常学习极其精细的原型,在医学成像中不太容易解释,其中生物标志物和病变的存在和程度都至关重要。方法:针对这些挑战,我们提出了PiPViT(基于补丁的视觉可解释原型),这是一种用于图像识别的固有可解释原型模型。借助视觉变压器(ViT),PiPViT捕获补丁之间的长距离依赖关系,仅使用图像级标签学习稳健且人类可解释的原型,以近似病变程度。此外,PiPViT受益于对比学习和多分辨率输入处理,这实现了跨尺度的生物标志物有效定位。结果:我们在四个数据集上对视网膜OCT图像分类任务上评估了PiPViT,其在定量性能上达到了与最先进的方法相当的竞争水平,同时提供了更有意义的解释。此外,在独立测试集上的定量评估证实,所学习的原型在语义和临床上都具有相关性。我们相信PiPViT能够透明地解释其决策,并帮助临床医生理解诊断结果。GitHub页面:https://github.com/marziehoghbaie/PiPViT
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
PiPViT是一个基于视觉的解读原型模型,旨在解决医学图像中现有原型方法的可视化与解读问题。通过捕捉图像块之间的长期依赖关系,该模型能学习鲁棒且可解读的原型,并近似病灶范围。通过对比学习和多分辨率输入处理,模型在视网膜OCT图像分类任务上表现优异,同时提供有意义的解释。
Key Takeaways
- PiPViT是一个针对图像识别的基于视觉的可解读原型模型。
- 该模型利用视觉转换器(ViT)捕捉图像块之间的长期依赖关系。
- PiPViT能学习鲁棒且可解读的原型,这些原型可以近似表示病灶范围。
- PiPViT通过对比学习和多分辨率输入处理,实现了有效定位不同尺度的生物标志物。
- 在四个视网膜OCT图像分类数据集上,PiPViT表现出与最新技术相当的定量性能。
- 定性评价表明,学习到的原型具有语义和临床相关性。
点此查看论文截图

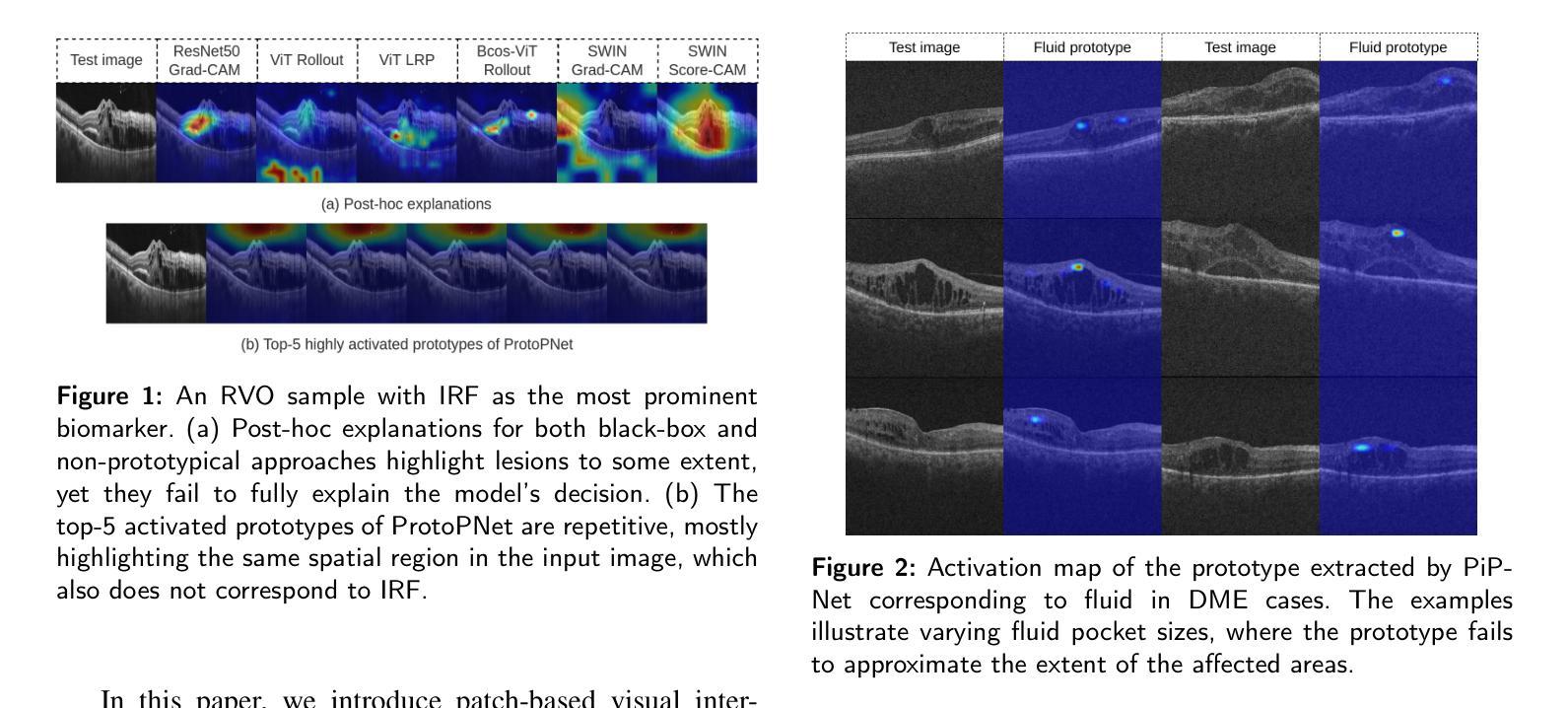
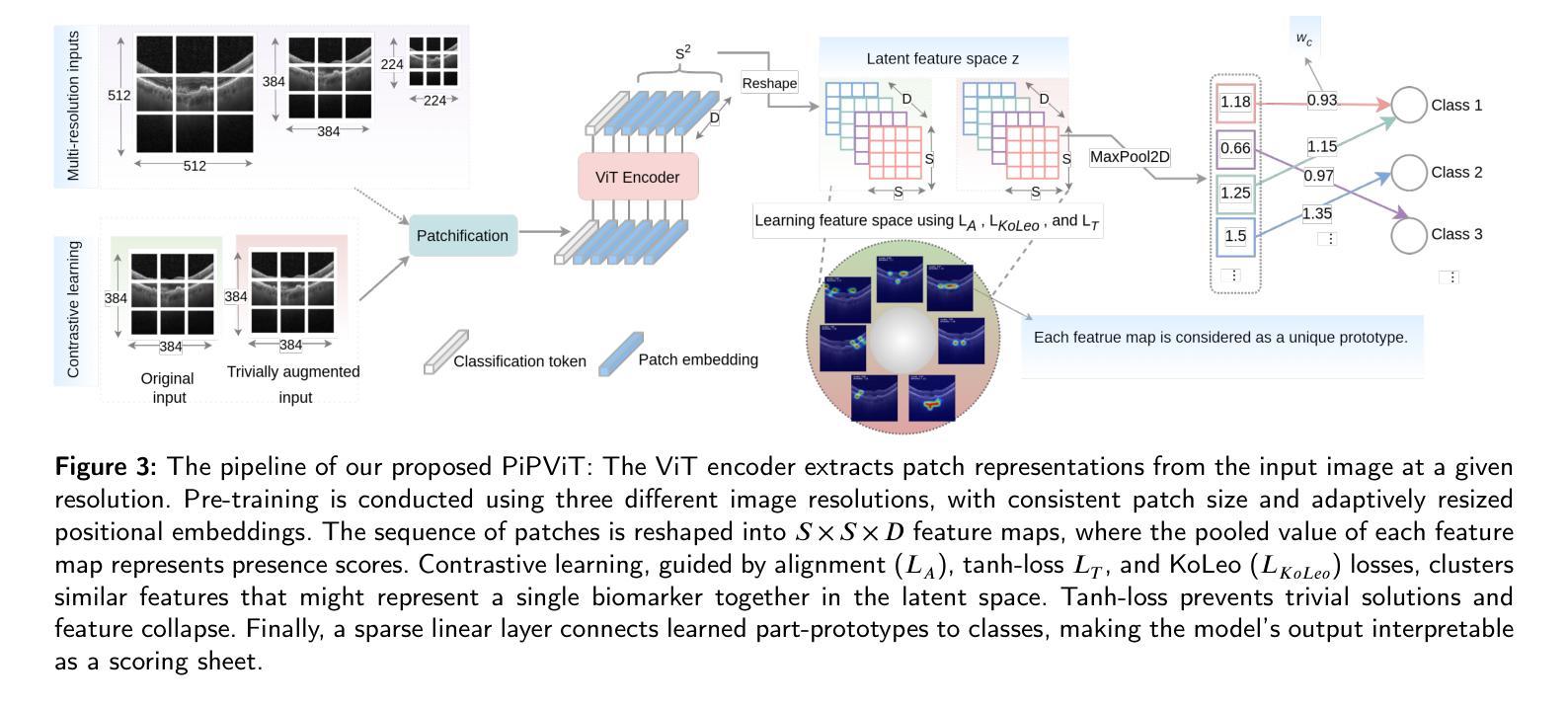
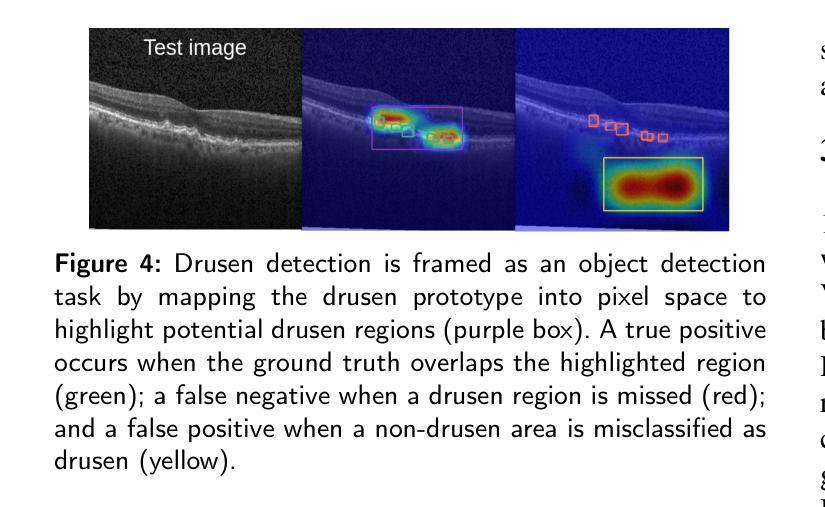
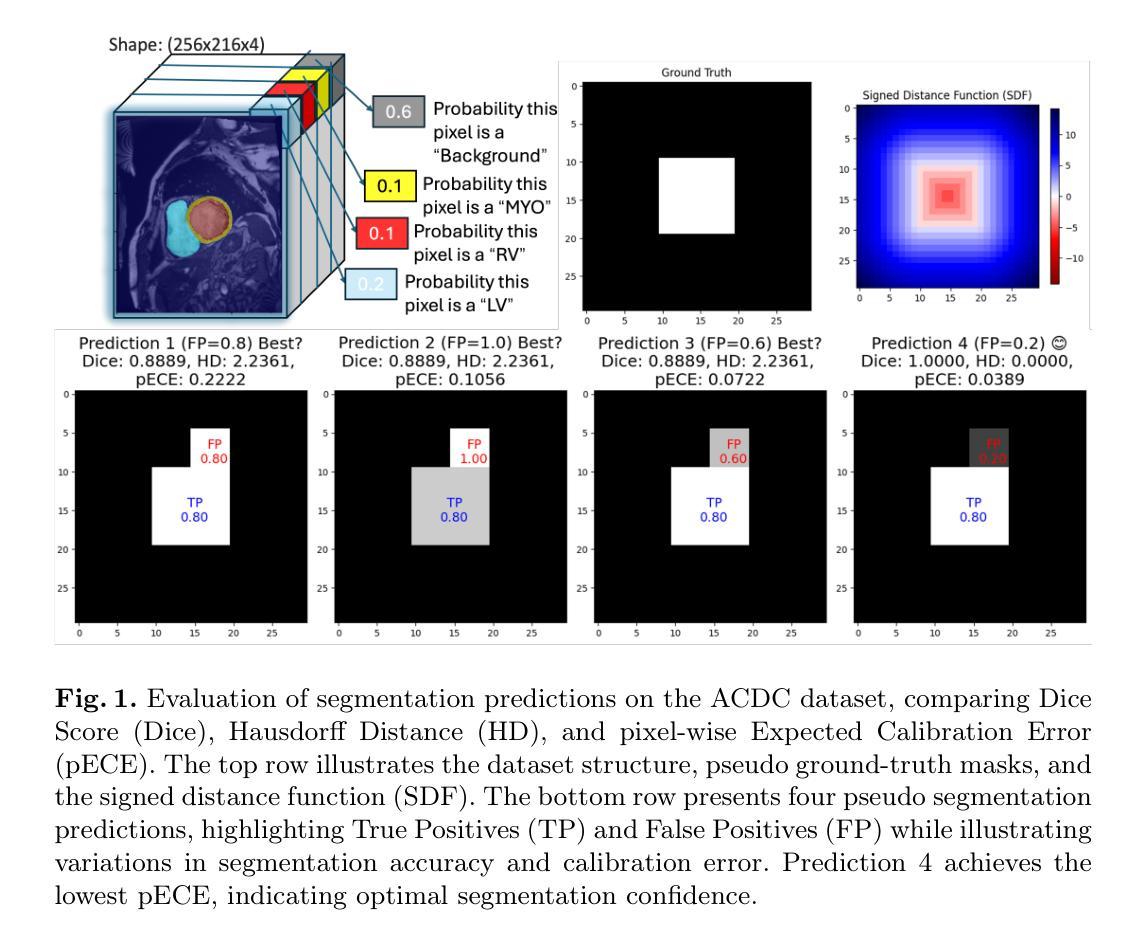
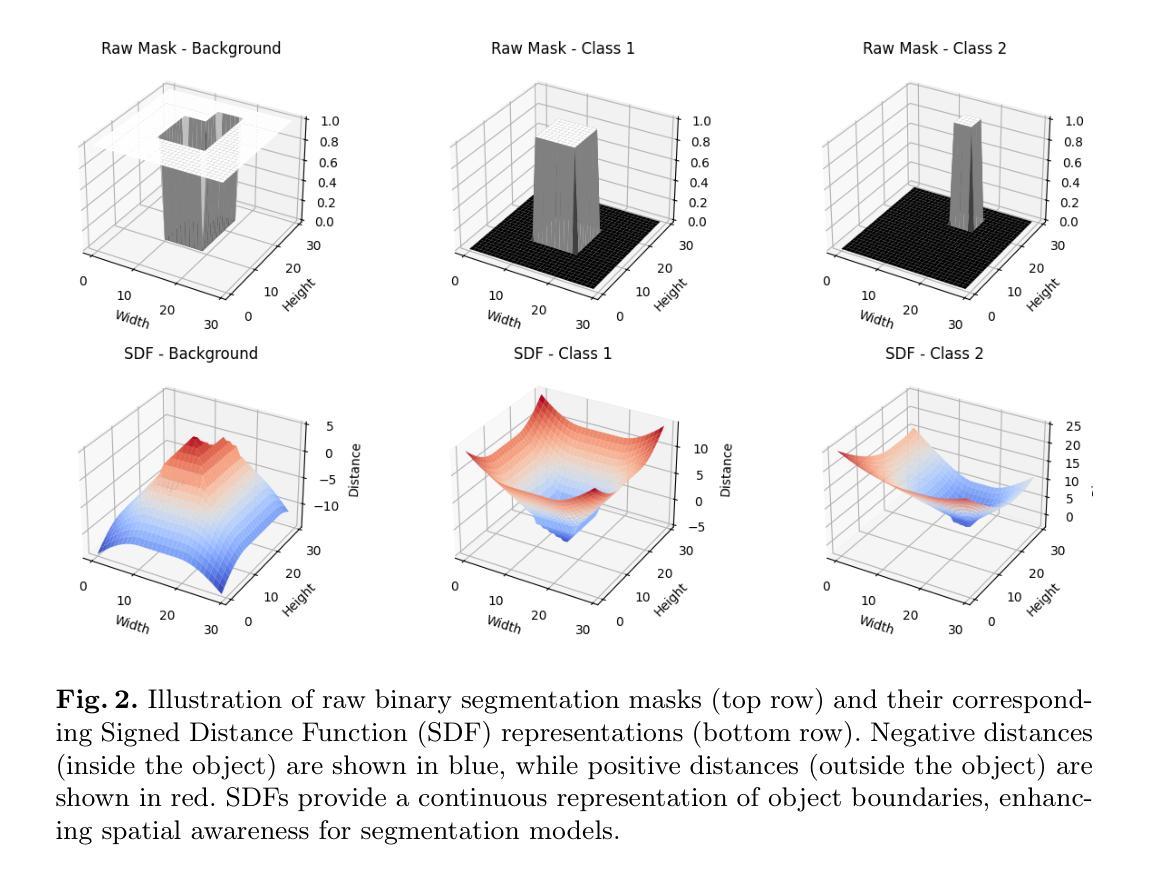
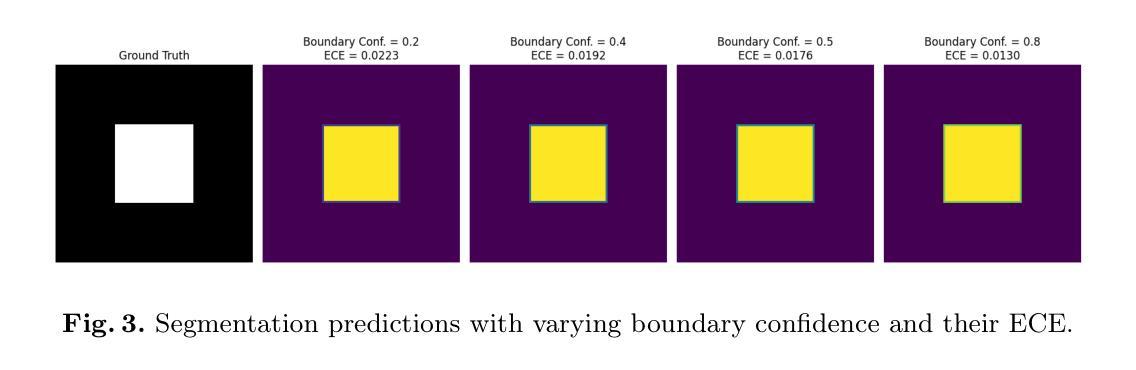
We Care Each Pixel: Calibrating on Medical Segmentation Model
Authors:Wenhao Liang, Wei Zhang, Lin Yue, Miao Xu, Olaf Maennel, Weitong Chen
Medical image segmentation is fundamental for computer-aided diagnostics, providing accurate delineation of anatomical structures and pathological regions. While common metrics such as Accuracy, DSC, IoU, and HD primarily quantify spatial agreement between predictions and ground-truth labels, they do not assess the calibration quality of segmentation models, which is crucial for clinical reliability. To address this limitation, we propose pixel-wise Expected Calibration Error (pECE), a novel metric that explicitly measures miscalibration at the pixel level, thereby ensuring both spatial precision and confidence reliability. We further introduce a morphological adaptation strategy that applies morphological operations to ground-truth masks before computing calibration losses, particularly benefiting margin-based losses such as Margin SVLS and NACL. Additionally, we present the Signed Distance Calibration Loss (SDC), which aligns boundary geometry with calibration objectives by penalizing discrepancies between predicted and ground-truth signed distance functions (SDFs). Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method not only enhances segmentation performance but also improves calibration quality, yielding more trustworthy confidence estimates. Code is available at: https://github.com/EagleAdelaide/SDC-Loss.
医学图像分割对于计算机辅助诊断至关重要,它提供了准确的解剖结构和病理区域的描述。虽然准确率、DSC、IoU和HD等常用指标主要量化预测和真实标签之间的空间一致性,但它们并没有评估分割模型的校准质量,这对于临床可靠性至关重要。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了像素级期望校准误差(pECE)这一新型指标,它明确地测量像素级的校准误差,从而确保空间精度和置信度可靠性。此外,我们还引入了一种形态学适应策略,该策略在对真实标签掩膜进行形态学操作后才计算校准损失,这对基于边距的损失(如Margin SVLS和NACL)特别有益。另外,我们提出了符号距离校准损失(SDC),它通过惩罚预测和真实标签之间符号距离函数(SDF)的差异,使边界几何与校准目标对齐。大量实验表明,我们的方法不仅提高了分割性能,还提高了校准质量,产生了更可靠的置信度估计。代码可在:https://github.com/EagleAdelaide/SDC-Loss获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Reviewing
Summary
医学图像分割对于计算机辅助诊断至关重要,能够准确描绘解剖结构和病理区域。为提高分割模型的校准质量,提出像素级期望校准误差(pECE)这一新指标,以衡量像素级别的误校准情况,确保空间精度和置信度可靠性。同时,引入形态学适应策略,对真实标签掩膜进行形态学操作来计算校准损失,尤其有利于基于边距的损失。此外,推出符号距离校准损失(SDC),通过惩罚预测与真实标签之间的符号距离函数差异,对齐边界几何与校准目标。实验证明,该方法不仅提升分割性能,更提高校准质量,产生更可靠的置信度估计。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割对计算机辅助诊断至关重要。
- 现有评估指标主要关注空间一致性,缺乏模型校准质量的评估。
- 提出像素级期望校准误差(pECE)指标,衡量像素级别误校准情况。
- 引入形态学适应策略,通过形态学操作计算校准损失。
- 介绍符号距离校准损失(SDC),对齐边界几何与校准目标。
- 方法提升分割性能及校准质量。
点此查看论文截图

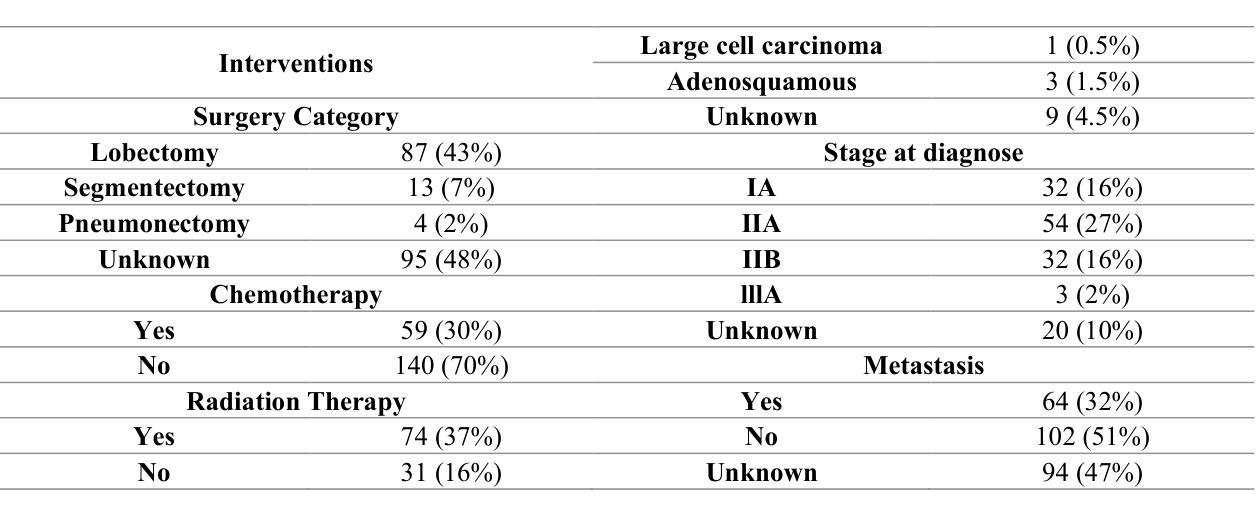
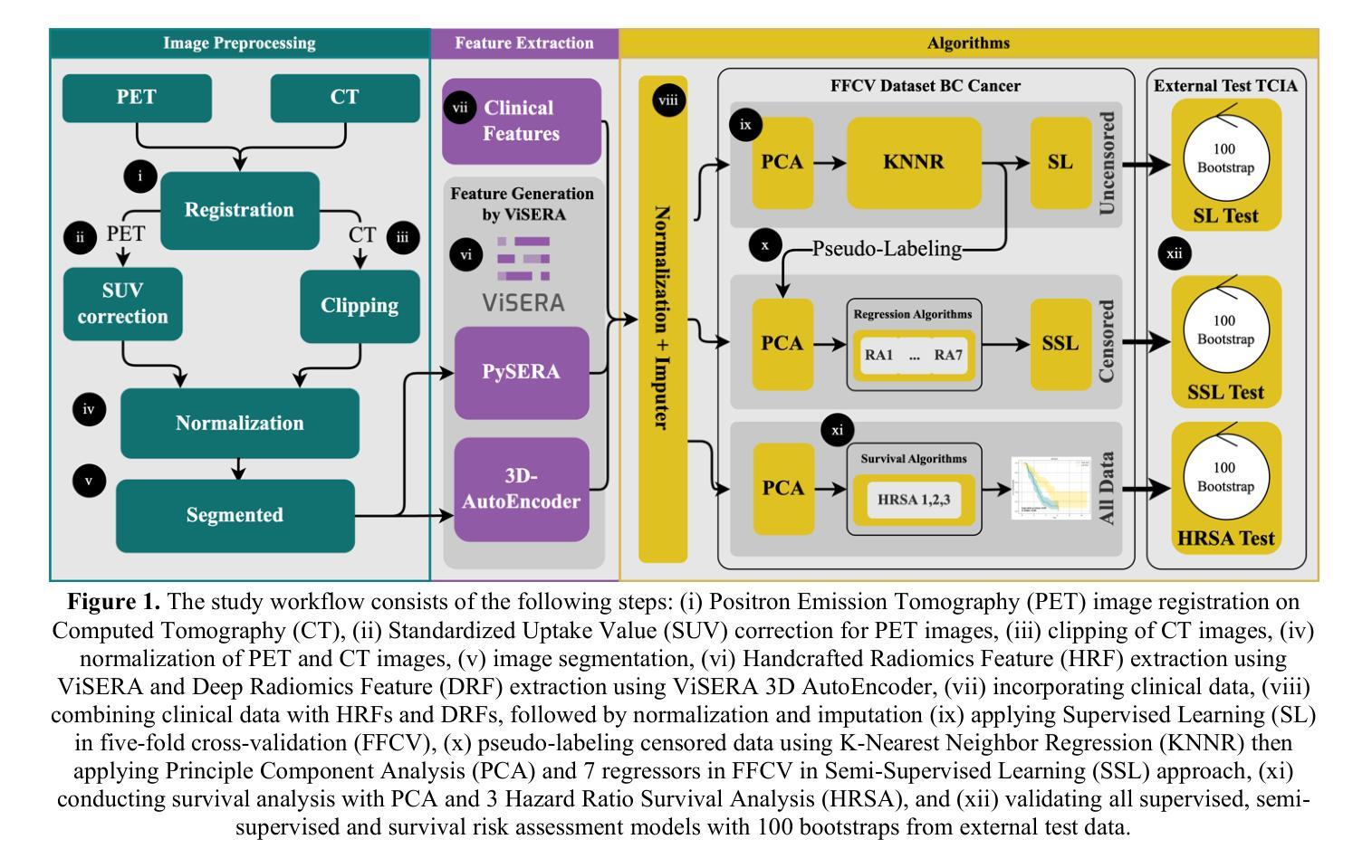
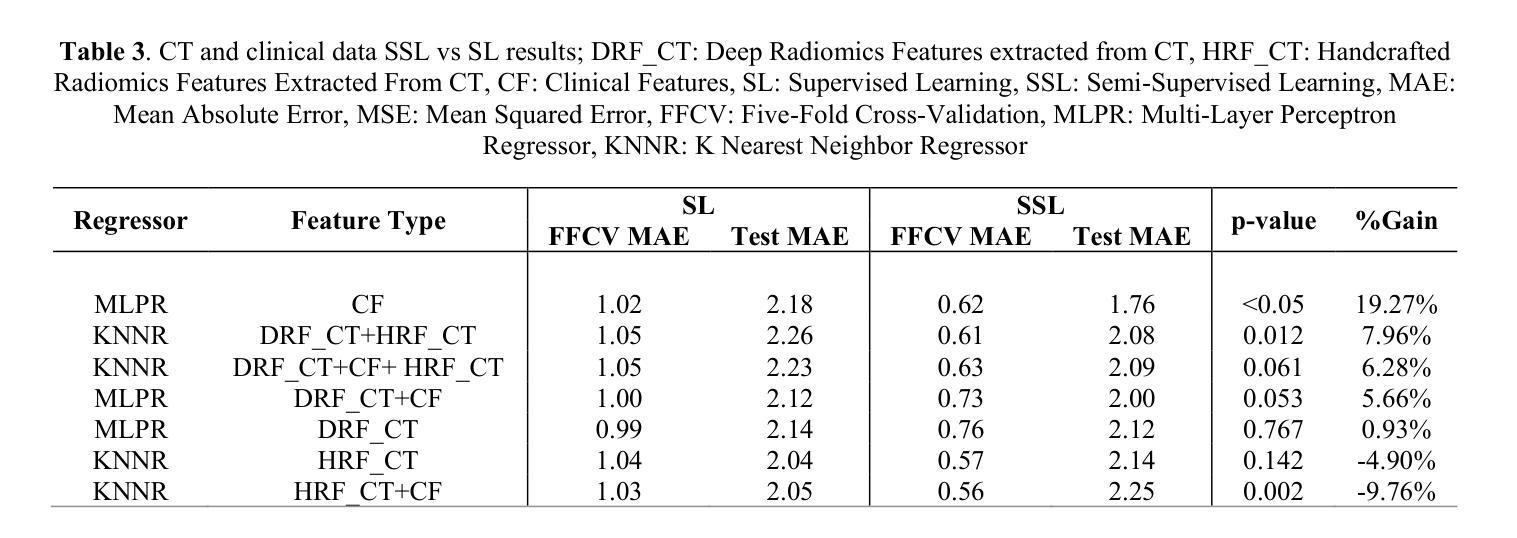
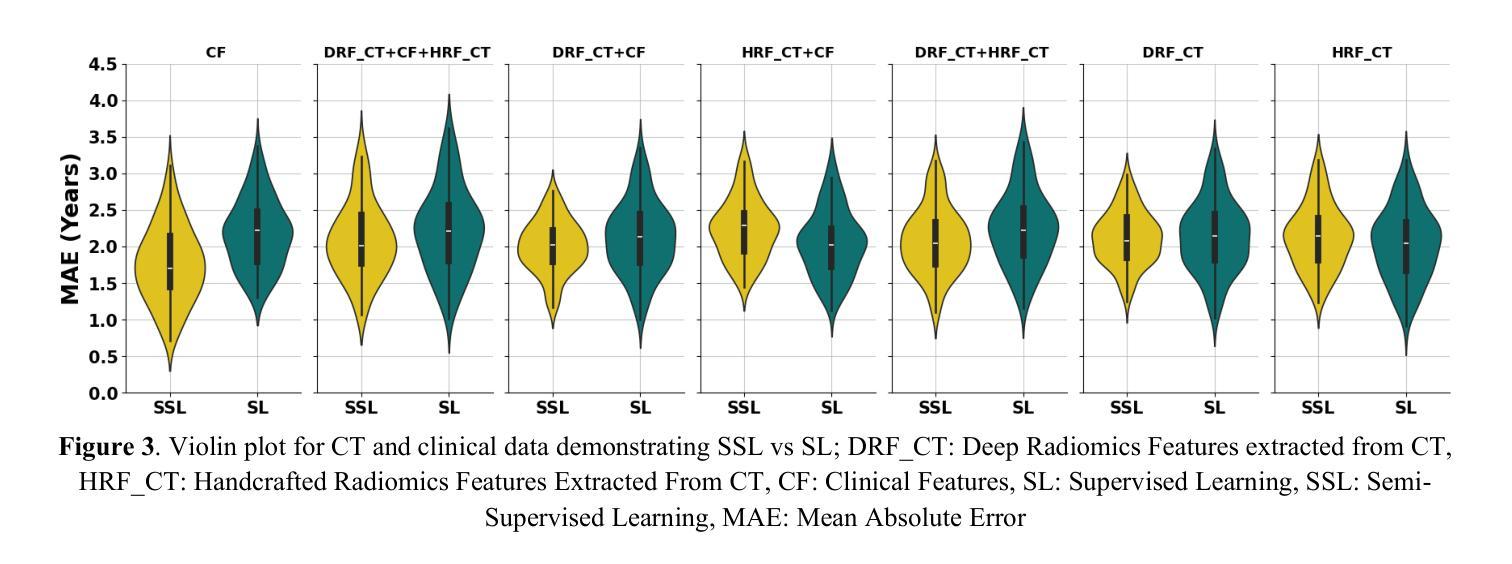
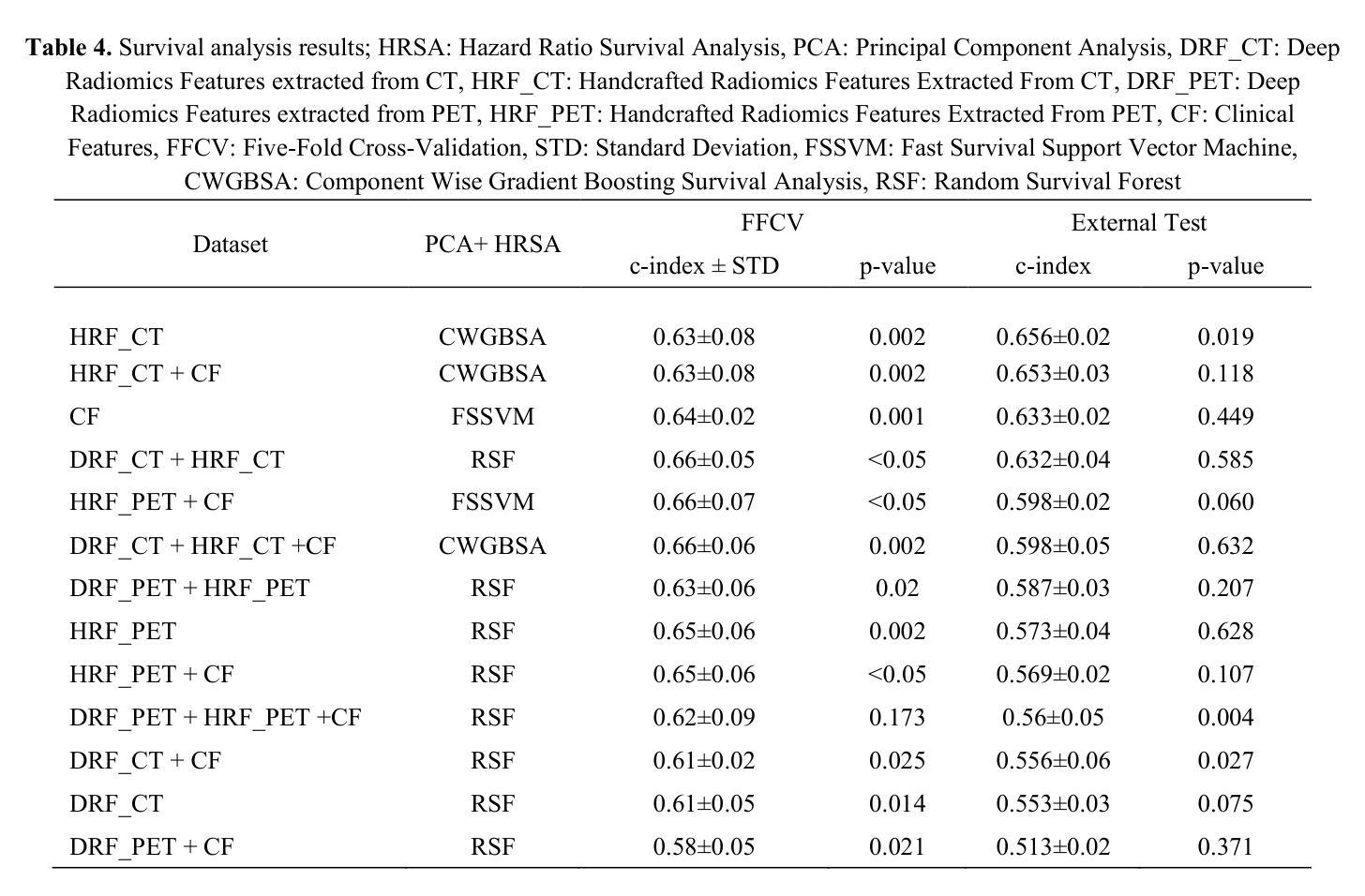
Censor-Aware Semi-Supervised Survival Time Prediction in Lung Cancer Using Clinical and Radiomics Features
Authors:Arman Gorji, Ali Fathi Jouzdani, Nima Sanati, Ren Yuan, Arman Rahmim, Mohammad R. Salmanpour
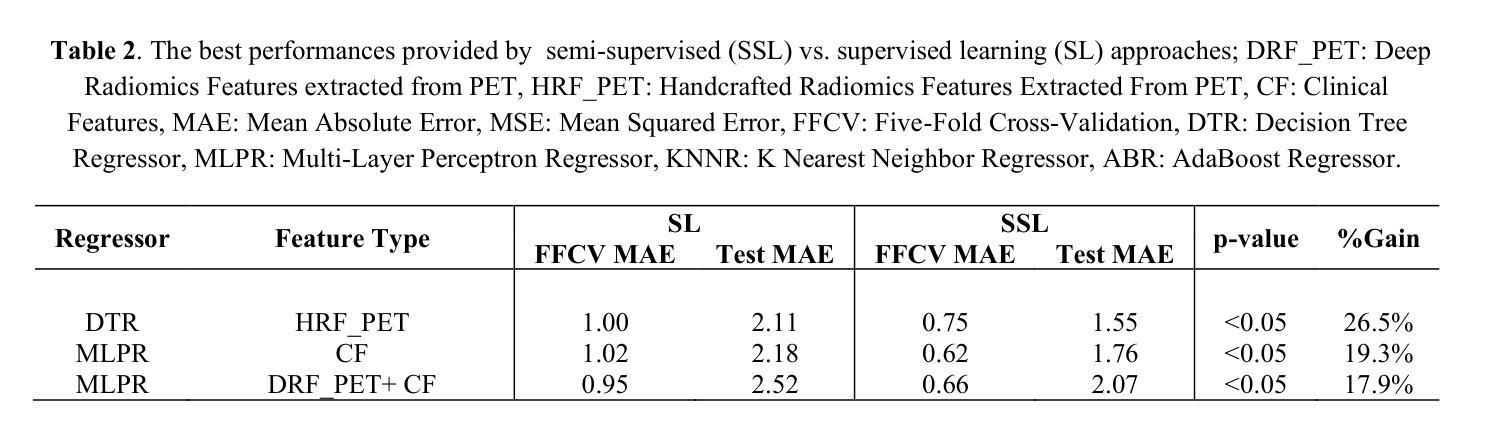
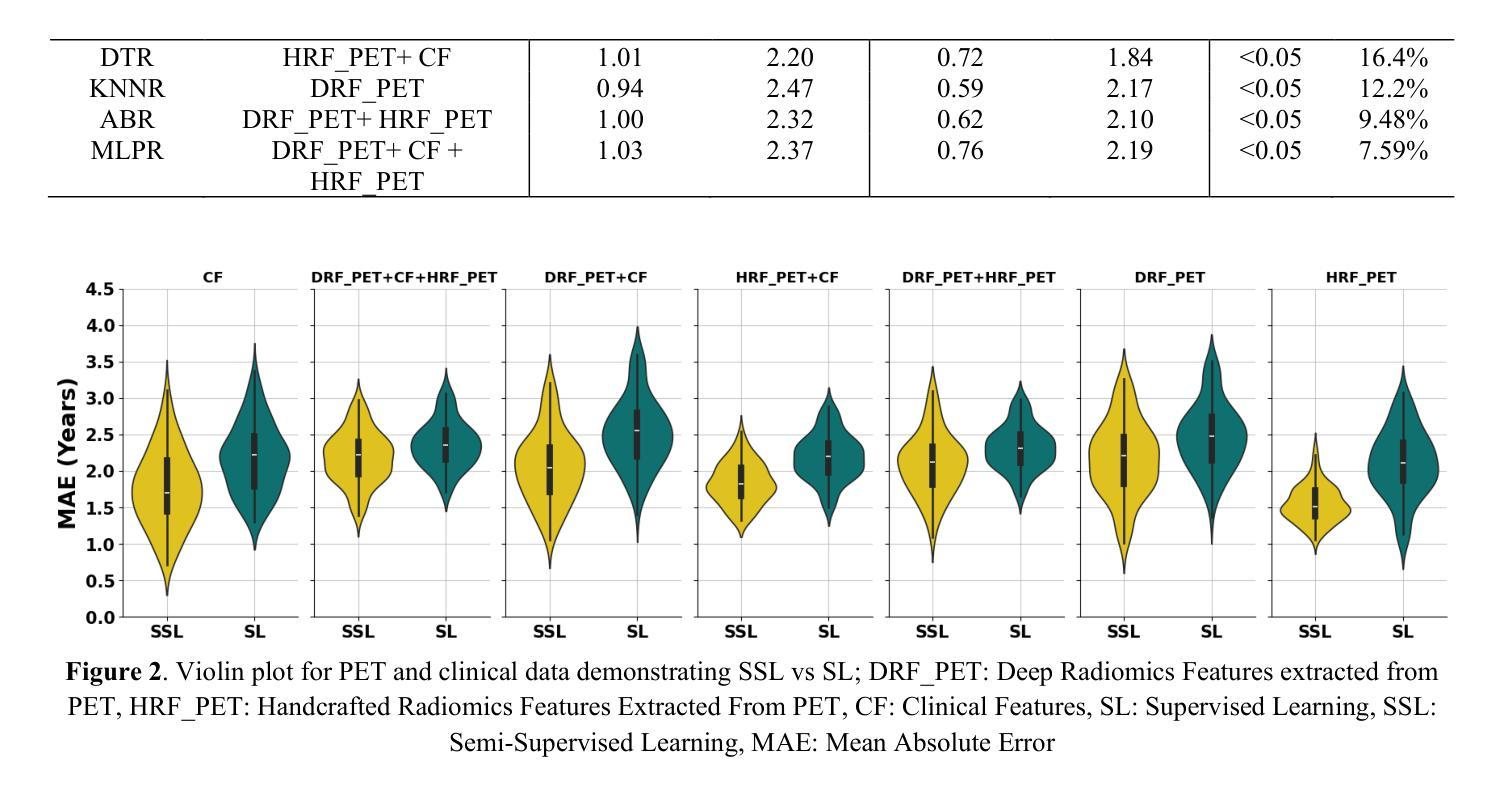
Objectives: Lung cancer poses a significant global health challenge, necessitating improved prognostic methods for personalized treatment. This study introduces a censor-aware semi-supervised learning (SSL) framework that integrates clinical and imaging data, addressing biases in traditional models handling censored data. Methods: We analyzed clinical, PET and CT data from 199 lung cancer patients from public and local data respositories, focusing on overall survival (OS) time as the primary outcome. Handcrafted (HRF) and Deep Radiomics features (DRF) were extracted after preprocessing using ViSERA software and were combined with clinical features (CF). Feature dimensions were optimized using Principal Component Analysis (PCA), followed by the application of supervised learning (SL) and SSL. SSL incorporated pseudo-labeling of censored data to improve performance. Seven regressors and three hazard ratio survival analysis (HRSA) algorithms were optimized using five-fold cross-validation, grid search and external test bootstrapping. Results: For PET HRFs, SSL reduced the mean absolute error (MAE) by 26.5%, achieving 1.55 years with PCA+decision tree regression, compared to SL’s 2.11 years with PCA+KNNR (p<0.05). Combining HRFs (CT_HRF) and DRFs from CT images using SSL+PCA+KNNR achieved an MAE of 2.08 years, outperforming SL’s 2.26 years by 7.96% (p<0.05). In HRSA, CT_HRF applied to PCA+Component Wise Gradient Boosting Survival Analysis achieved an external c-index of 0.65, effectively differentiating high- and low-risk groups. Conclusions: We demonstrated that the SSL strategy significantly outperforms SL across PET, CT, and CF. As such, censor-aware SSL applied to HRFs from PET images significantly improved survival prediction performance by 26.5% compared to the SL approach.
目标:肺癌构成一项重大的全球健康挑战,需要改进预测方法以实现个性化治疗。本研究引入了一种有审查意识的半监督学习(SSL)框架,该框架融合了临床和成像数据,解决了传统模型在处理受审查数据时的偏见问题。
方法:我们分析了来自公共和本地数据仓库的199名肺癌患者的临床、PET和CT数据,以总体存活时间作为主要结果。使用ViSERA软件预处理后提取手工特征(HRF)和深度放射学特征(DRF),并与临床特征(CF)相结合。使用主成分分析(PCA)优化特征维度,然后应用监督学习(SL)和SSL。SSL结合了伪标签法处理受审查数据以提高性能。通过五折交叉验证、网格搜索和外部测试Bootstrap优化七个回归器和三个危险比率生存分析(HRSA)算法。
结果:对于PET的HRFs,SSL将平均绝对误差(MAE)降低了26.5%,使用PCA+决策树回归达到1.55年,而SL与PCA+KNNR的组合为2.11年(p<0.05)。结合来自CT图像的HRFs(CT_HRF)和DRFs使用SSL+PCA+KNNR的MAE为2.08年,优于SL的2.26年,提高了7.96%(p<0.05)。在HRSA中,将CT_HRF应用于PCA+Component Wise Gradient Boosting Survival Analysis,外部c指数为0.65,有效地区分了高、低风险组。
结论:我们证明SSL策略在PET、CT和CF方面显著优于SL。因此,与SL方法相比,应用于PET图像HRFs的有审查意识的SSL将生存预测性能提高了26.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 4 Figures and 4 Tables
Summary
本文介绍了一种结合临床和成像数据的审查感知半监督学习(SSL)框架,以解决传统模型处理审查数据时的偏见问题。通过对199名肺癌患者的临床、PET和CT数据进行分析,该研究发现SSL策略在PET、CT和临床特征方面的表现均优于监督学习(SL),尤其是在PET的手工特征(HRF)上,SSL将平均绝对误差(MAE)降低了26.5%,显著提高了生存预测的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 研究引入了审查感知半监督学习(SSL)框架,融合了临床和成像数据,以改进对肺癌患者的个性化治疗预后方法。
- 通过分析199名肺癌患者的临床、PET和CT数据,重点研究患者的总体生存时间。
- SSL框架通过伪标记审查数据提高了性能,在PET的手工特征(HRF)上,与监督学习(SL)相比,SSL将平均绝对误差(MAE)降低了26.5%。
- 结合CT图像的HRF和Deep Radiomics特征(DRF),使用SSL+PCA+KNNR的MAE为2.08年,优于SL的2.26年,提升了7.96%。
- 在危害比率生存分析(HRSA)中,使用PCA+Component Wise Gradient Boosting Survival Analysis结合CT_HRF达到了外部c-指数为0.65,能有效区分高、低风险组。
- SSL策略在PET、CT和临床特征方面的表现均优于SL。
点此查看论文截图

UKAN-EP: Enhancing U-KAN with Efficient Attention and Pyramid Aggregation for 3D Multi-Modal MRI Brain Tumor Segmentation
Authors:Yanbing Chen, Tianze Tang, Taehyo Kim, Hai Shu
Gliomas are among the most common malignant brain tumors and are characterized by considerable heterogeneity, which complicates accurate detection and segmentation. Multi-modal MRI is the clinical standard for glioma imaging, but variability across modalities and high computational complexity hinder effective automated segmentation. In this paper, we propose UKAN-EP, a novel 3D extension of the original 2D U-KAN model for multi-modal MRI brain tumor segmentation. While U-KAN integrates Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN) layers into a U-Net backbone, UKAN-EP further incorporates Efficient Channel Attention (ECA) and Pyramid Feature Aggregation (PFA) modules to enhance inter-modality feature fusion and multi-scale feature representation. We also introduce a dynamic loss weighting strategy that adaptively balances the Cross-Entropy and Dice losses during training. We evaluate UKAN-EP on the 2024 BraTS-GLI dataset and compare it against strong baselines including U-Net, Attention U-Net, and Swin UNETR. Results show that UKAN-EP achieves superior segmentation performance while requiring substantially fewer computational resources. An extensive ablation study further demonstrates the effectiveness of ECA and PFA, as well as the limited utility of self-attention and spatial attention alternatives. Code is available at https://github.com/TianzeTang0504/UKAN-EP.
胶质瘤是最常见的恶性脑肿瘤之一,其特点是具有相当大的异质性,这使得准确的检测和分割变得复杂。多模态MRI是胶质瘤成像的临床标准,但不同模态之间的差异和较高的计算复杂性阻碍了有效的自动分割。在本文中,我们提出了UKAN-EP,这是原始二维U-KAN模型的多模态MRI脑肿瘤分割的新型三维扩展。U-KAN将Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN)层集成到U-Net主干中,而UKAN-EP进一步结合了高效通道注意力(ECA)和金字塔特征聚合(PFA)模块,以增强跨模态特征融合和多尺度特征表示。我们还引入了一种动态损失权重策略,该策略可以自适应地平衡训练和测试过程中的交叉熵和Dice损失。我们在包含U-Net、Attention U-Net和Swin UNETR等强大基准模型的BraTS-GLI数据集上评估了UKAN-EP的性能。结果表明,UKAN-EP在达到更高的分割性能的同时,所需的计算资源大大减少。大量的消融研究进一步证明了ECA和PFA的有效性,以及自注意力和空间注意力替代方案的局限性。相关代码可访问于:https://github.com/TianzeTang0504/UKAN-EP。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对胶质脑瘤的恶性脑肿瘤在医疗图像分析中极为常见,但因其显著的异质性导致准确检测和分割变得复杂。本研究提出了一种新型的基于多模态MRI的胶质脑瘤分割模型——UKAN-EP。该模型结合了Kolmogorov-Arnold网络层、高效通道注意力模块和多尺度特征金字塔模块,强化了模态间的特征融合与多尺度特征表达。通过动态损失权重策略,自适应平衡交叉熵和Dice损失进行训练。在BraTS-GLI数据集上的评估显示,UKAN-EP不仅实现了优越的分割性能,而且计算资源消耗更少。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究关注胶质脑瘤这一常见恶性脑肿瘤的图像分析挑战,尤其是其异质性问题。
- 提出了一种新的基于多模态MRI的胶质脑瘤分割模型UKAN-EP,扩展了原有的二维模型并加入了更多优化模块。
- UKAN-EP集成了Kolmogorov-Arnold网络层,以增强模型的性能。
- Efficient Channel Attention(ECA)和Pyramid Feature Aggregation(PFA)模块的加入提升了模型的性能表现。ECA提高了通道间注意力的利用效率,而PFA增强了多尺度特征的融合能力。
- 动态损失权重策略有助于在训练过程中自适应平衡不同损失函数的影响。
- 在BraTS-GLI数据集上的实验验证了UKAN-EP模型在胶质脑瘤分割上的优越性,并且计算资源消耗较低。
点此查看论文截图

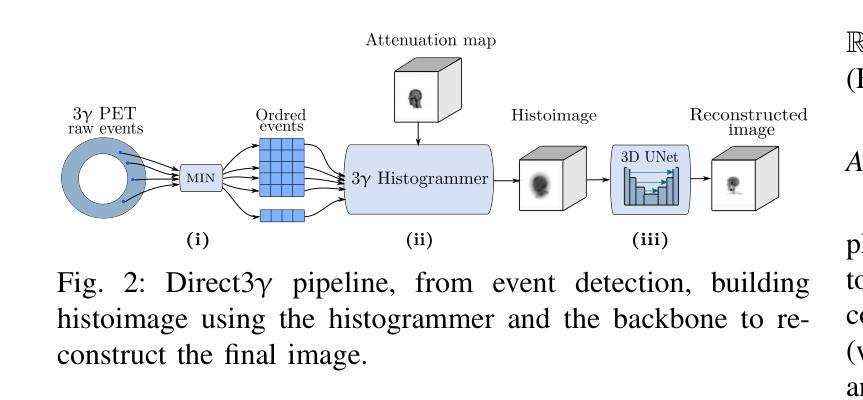
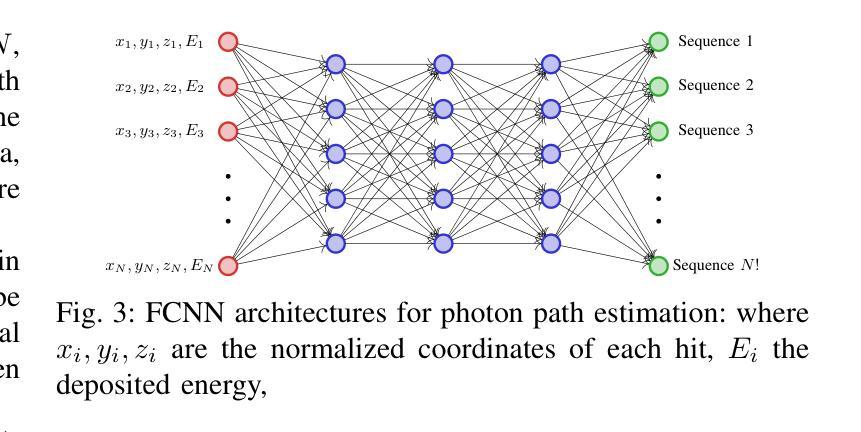
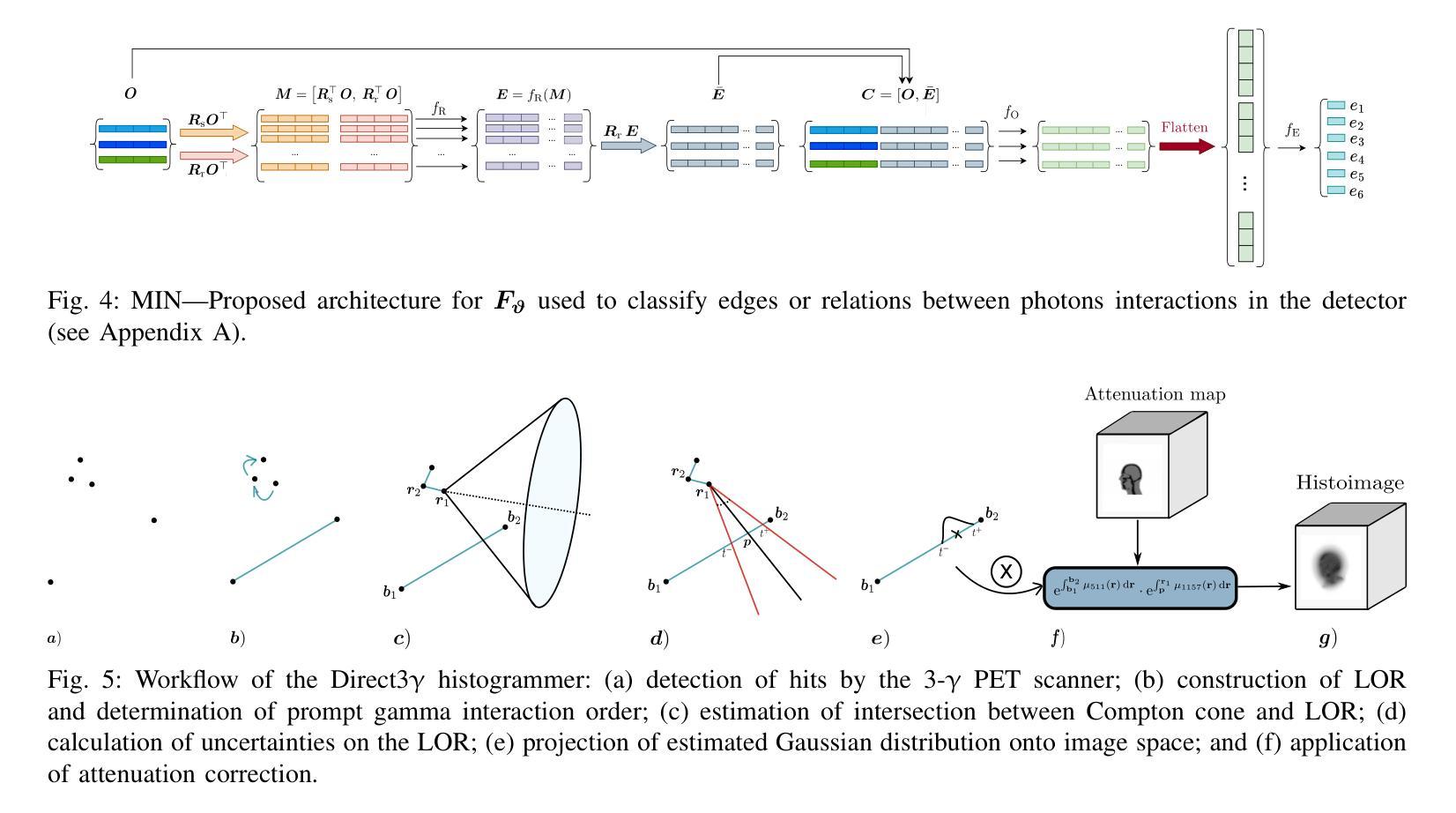
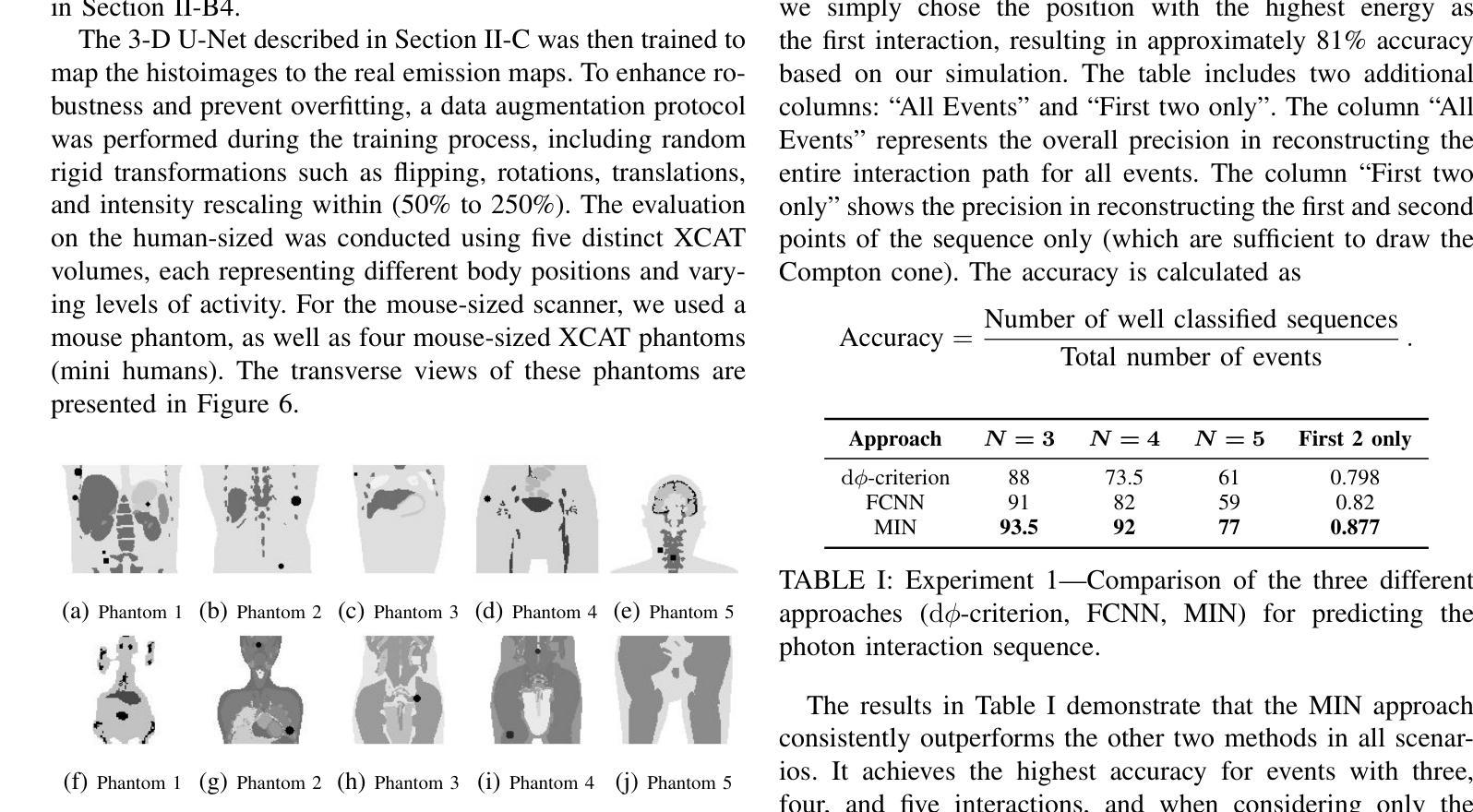
Direct3γ: A Pipeline for Direct Three-gamma PET Image Reconstruction
Authors:Youness Mellak, Alexandre Bousse, Thibaut Merlin, Debora Giovagnoli, Dimitris Visvikis
This paper presents a novel image reconstruction pipeline for three-gamma (3-{\gamma}) positron emission tomography (PET) aimed at improving spatial resolution and reducing noise in nuclear medicine. The proposed Direct3{\gamma} pipeline addresses the inherent challenges in 3-{\gamma} PET systems, such as detector imperfections and uncertainty in photon interaction points. A key feature of the pipeline is its ability to determine the order of interactions through a model trained on Monte Carlo (MC) simulations using the Geant4 Application for Tomography Emission (GATE) toolkit, thus providing the necessary information to construct Compton cones which intersect with the line of response (LOR) to provide an estimate of the emission point. The pipeline processes 3-{\gamma} PET raw data, reconstructs histoimages by propagating energy and spatial uncertainties along the LOR, and applies a 3-D convolutional neural network (CNN) to refine these intermediate images into high-quality reconstructions. To further enhance image quality, the pipeline leverages both supervised learning and adversarial losses, the latter preserving fine structural details. Experimental results show that Direct3{\gamma} consistently outperforms conventional 200-ps time-of-flight (TOF) PET in terms of SSIM and PSNR.
本文提出了一种针对三伽马(3-γ)正电子发射断层扫描(PET)图像重建的新流程,旨在提高核医学中的空间分辨率并降低噪声。所提出的Direct3γ流程解决了3-γ PET系统固有的挑战,如探测器缺陷和光子交互点的不确定性。该流程的一个关键功能是,它能够通过使用Geant4发射断层扫描应用程序(GATE)工具包进行的蒙特卡洛(MC)模拟训练模型来确定交互的顺序,从而提供构建交于响应线(LOR)的康普顿锥的必要信息,以估计发射点。该流程处理3-γ PET原始数据,通过传播能量和空间不确定性沿LOR重建直方图像,并应用三维卷积神经网络(CNN)将这些中间图像精细化为高质量重建。为了进一步提高图像质量,该流程结合了监督学习和对抗性损失,后者能够保留精细的结构细节。实验结果表明,Direct3γ在结构相似性度量(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面始终优于传统的200皮秒飞行时间(TOF)PET。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 11 figures, 2 tables
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对三伽马(3-γ)正电子发射断层扫描(PET)图像重建的新流程,旨在提高核医学中的空间分辨率并降低噪声。该流程通过一系列技术和算法,如利用蒙特卡洛模拟训练模型、确定交互顺序、构建康普顿锥与响应线交点等,解决3-γ PET系统的固有挑战。实验结果表明,该流程在结构相似度指数(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面优于传统的200皮秒飞行时间(TOF)PET。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种针对三伽马(3-γ)PET的新型图像重建流程,旨在提高空间分辨率并降低核医学中的噪声。
- 通过利用Geant4 Application for Tomography Emission(GATE)工具包的蒙特卡洛(MC)模拟进行模型训练,确定光子交互顺序。
- 该流程通过构建康普顿锥与响应线交点来估计发射点,从而处理3-γ PET原始数据。
- 通过沿响应线传播能量和空间不确定性来重建直方图像,并利用三维卷积神经网络(CNN)对中间图像进行精细化处理,生成高质量重建图像。
- 该流程采用监督学习和对抗性损失来进一步提高图像质量,其中对抗性损失有助于保留精细结构细节。
- 实验结果表明,该流程在结构相似度指数(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面表现优异,优于传统的200皮秒飞行时间(TOF)PET。
点此查看论文截图

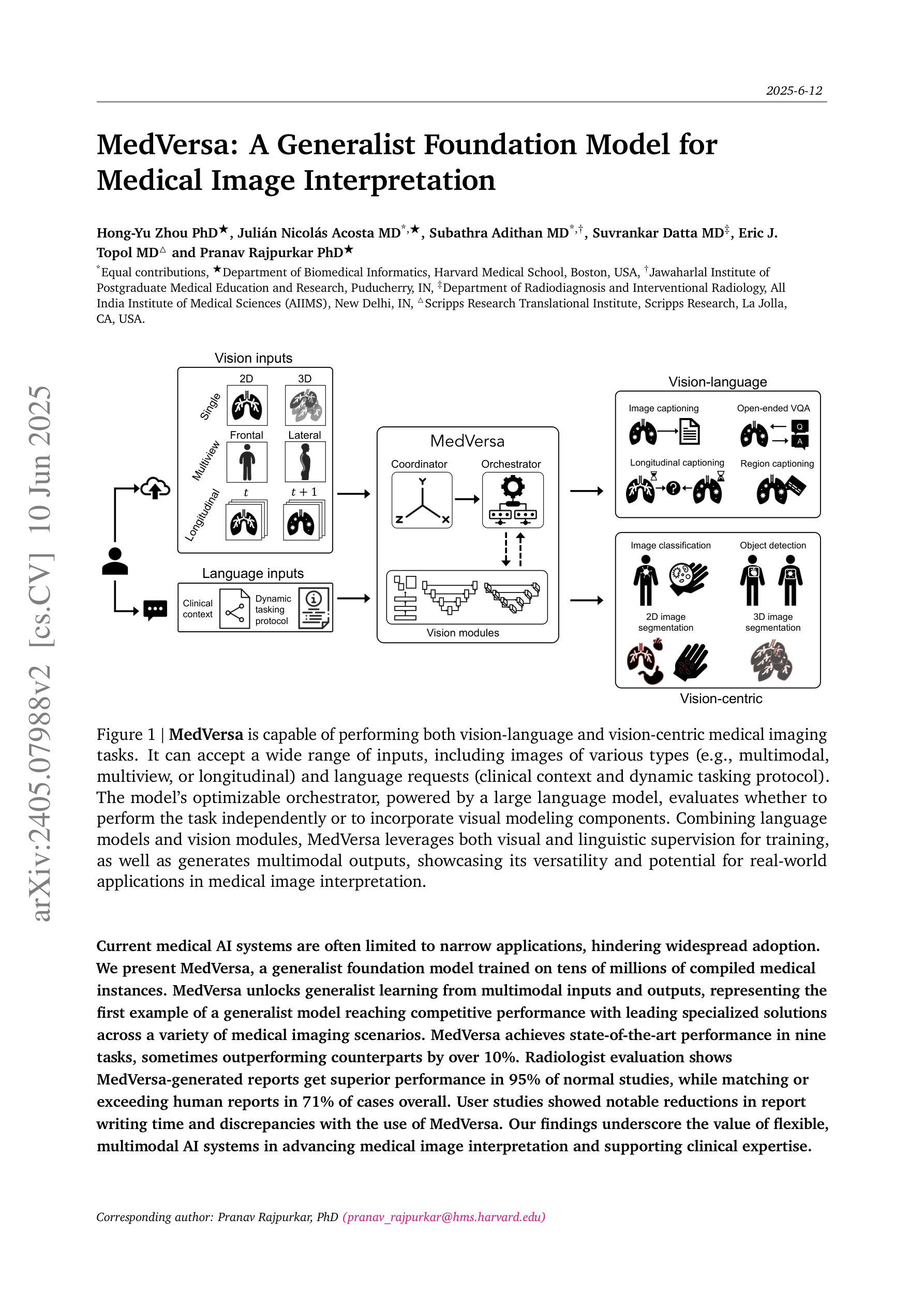
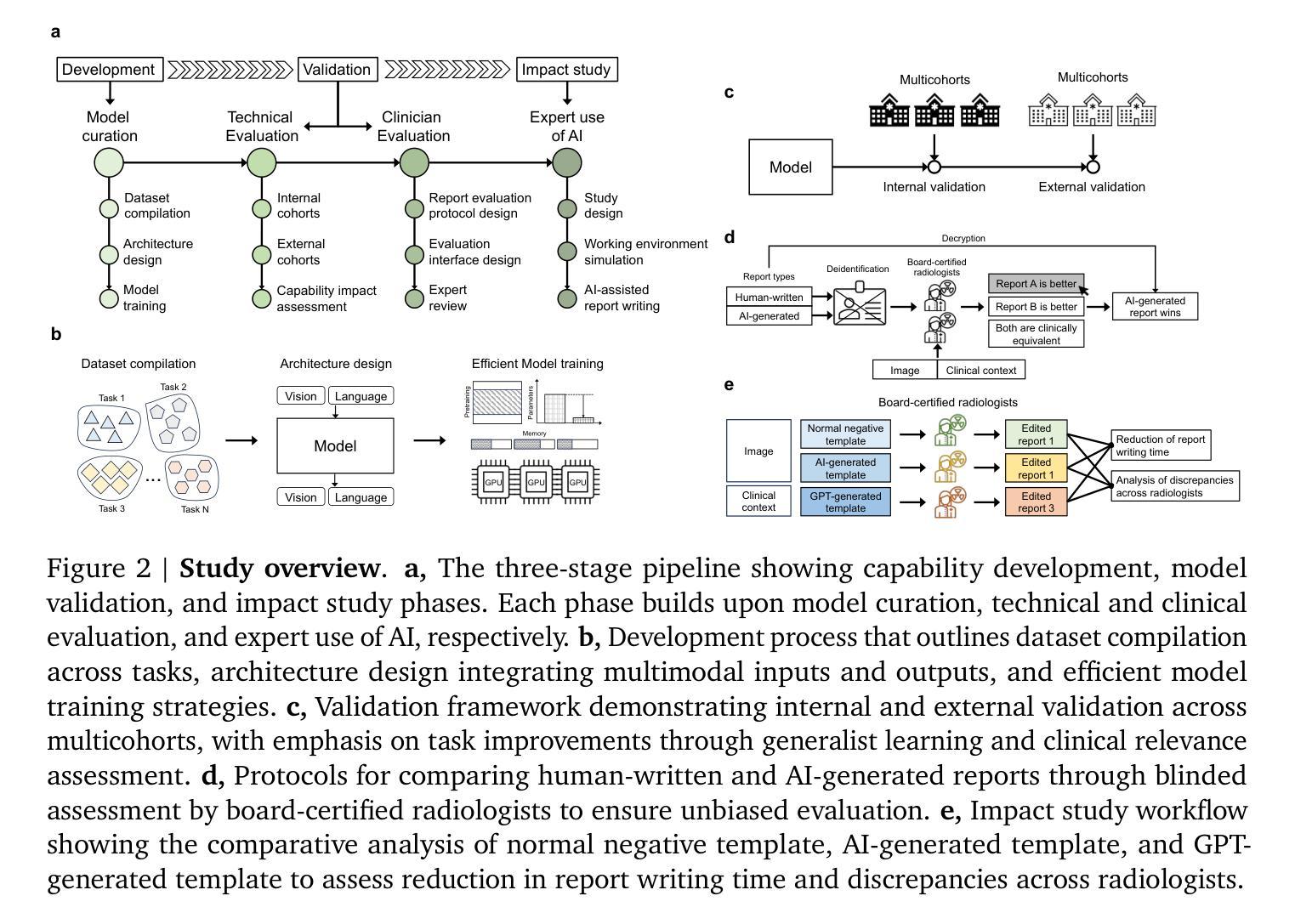
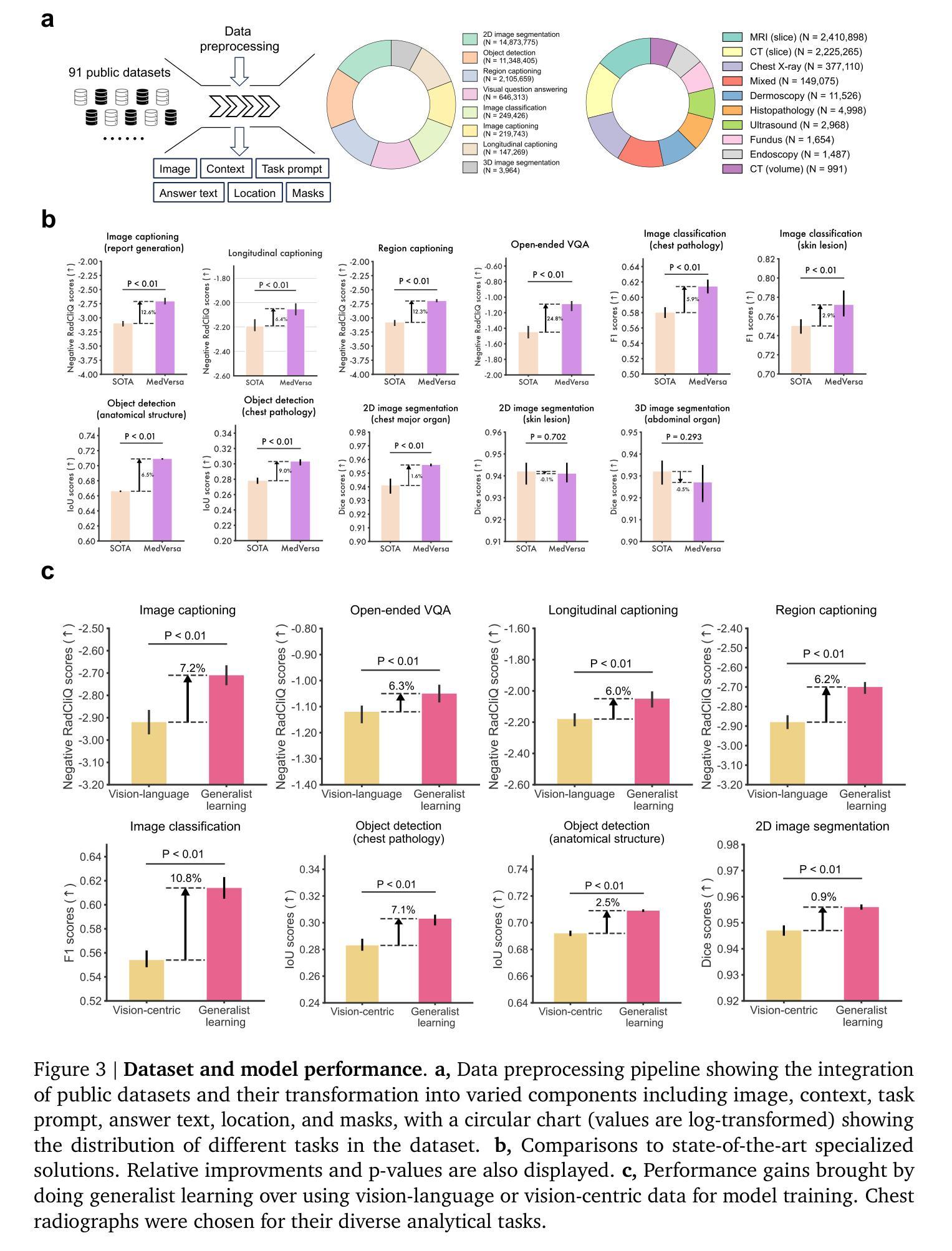
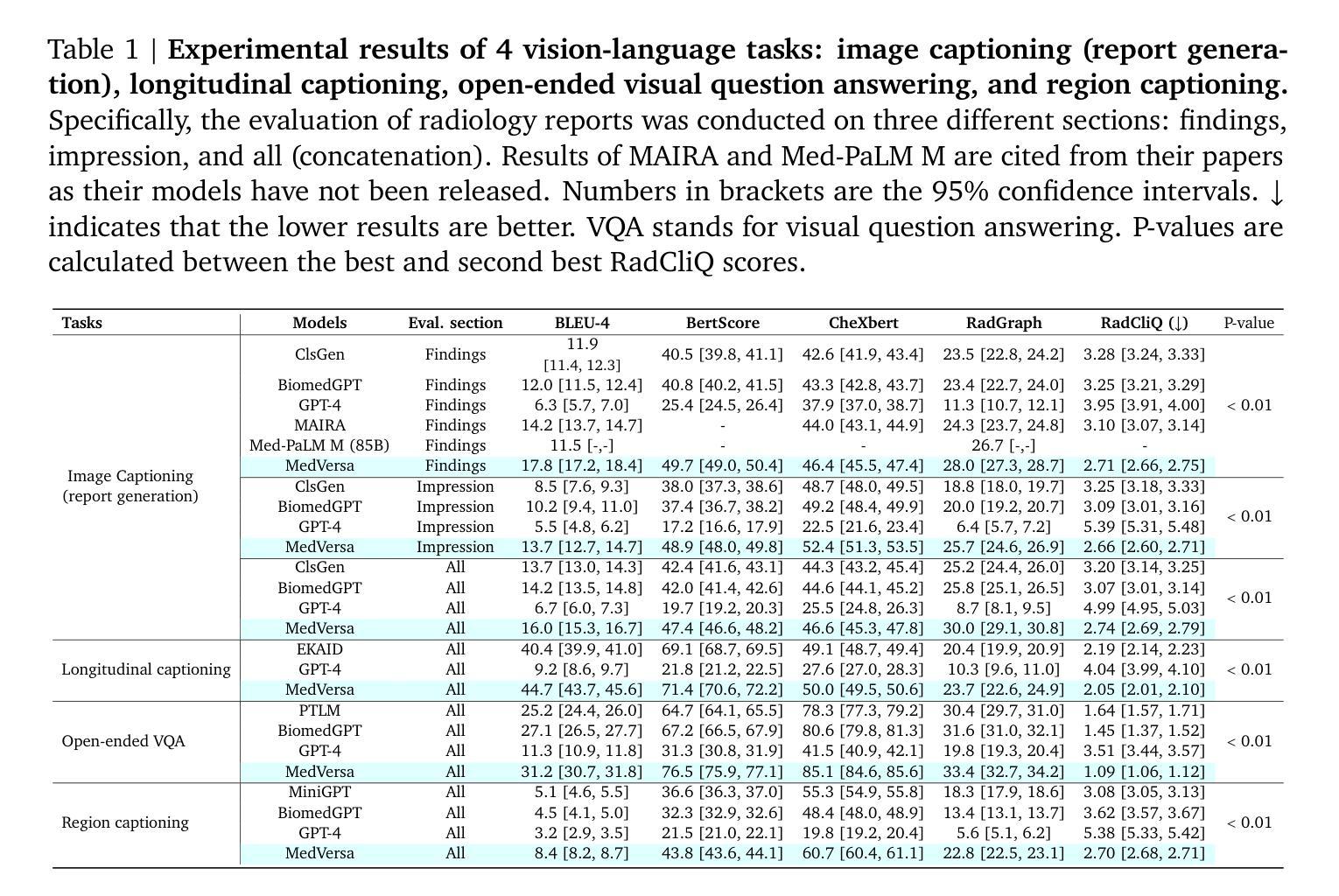
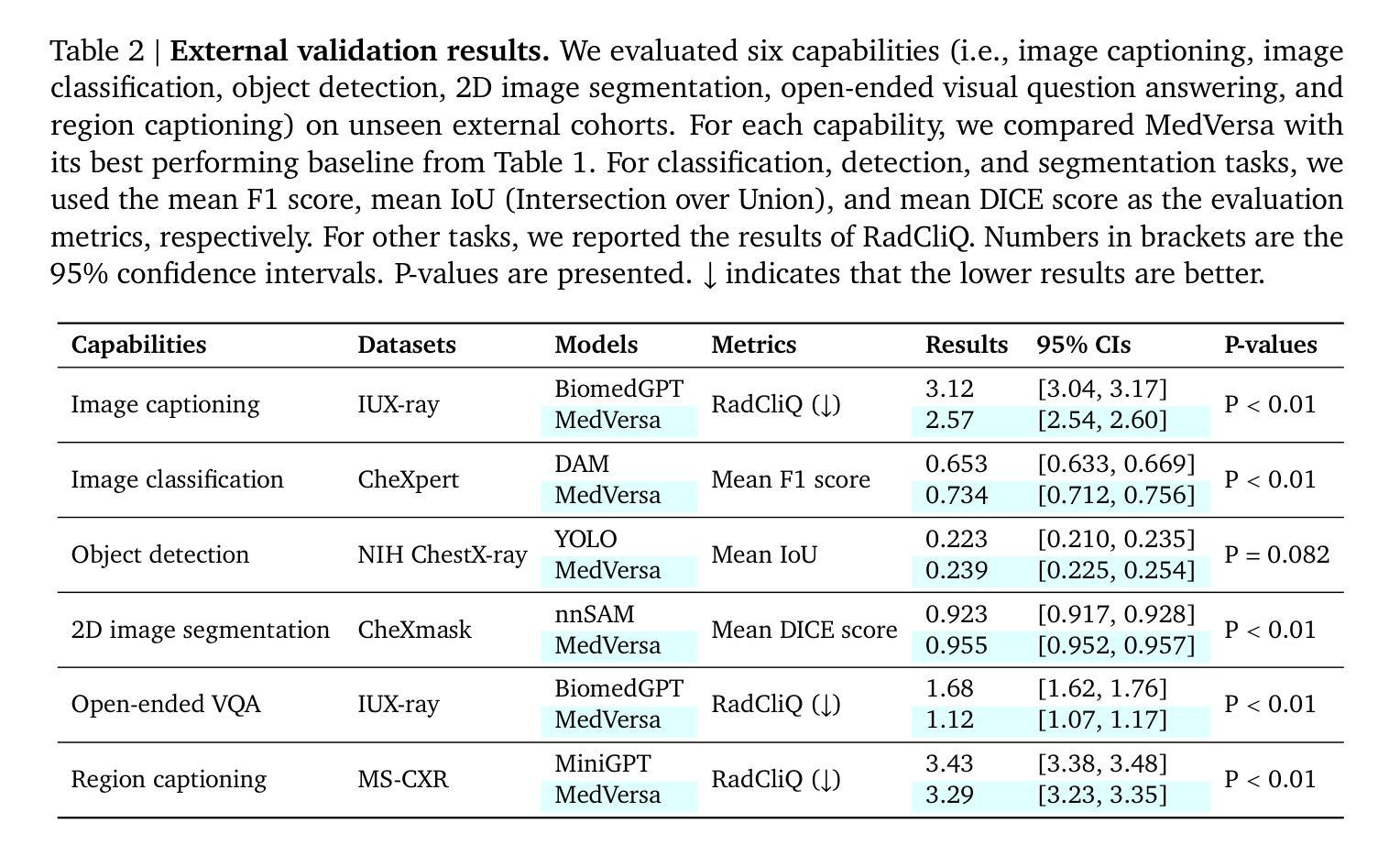
MedVersa: A Generalist Foundation Model for Medical Image Interpretation
Authors:Hong-Yu Zhou, Julián Nicolás Acosta, Subathra Adithan, Suvrankar Datta, Eric J. Topol, Pranav Rajpurkar
Current medical AI systems are often limited to narrow applications, hindering widespread adoption. We present MedVersa, a generalist foundation model trained on tens of millions of compiled medical instances. MedVersa unlocks generalist learning from multimodal inputs and outputs, representing the first example of a generalist model reaching competitive performance with leading specialized solutions across a variety of medical imaging scenarios. MedVersa achieves state-of-the-art performance in nine tasks, sometimes outperforming counterparts by over 10%. Radiologist evaluation shows MedVersa-generated reports get superior performance in 95% of normal studies, while matching or exceeding human reports in 71% of cases overall. User studies showed notable reductions in report writing time and discrepancies with the use of MedVersa. Our findings underscore the value of flexible, multimodal AI systems in advancing medical image interpretation and supporting clinical expertise.
当前医疗人工智能系统往往局限于特定应用,阻碍了其广泛应用。我们推出了MedVersa,这是一款在数百万医疗实例上训练的通用基础模型。MedVersa解锁了从多模式输入和输出中学习通用知识的能力,成为第一个在多种医学成像场景中达到领先专业解决方案竞争力的通用模型。MedVersa在九个任务中达到了最新技术水平,有时较同类产品的性能高出超过10%。放射科医生评价显示,MedVersa生成的报告在正常研究的95%中表现优越,并在总体情况下有71%与人类报告相匹配或超越人类报告。用户研究表明,使用MedVersa显著减少了报告编写时间和差异。我们的研究强调了灵活、多模式人工智能系统在推进医学图像解读和支持临床专业知识方面的价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical study
Summary
医学AI系统通常局限于特定应用,阻碍其广泛应用。我们推出MedVersa,这是一种经过数百万医疗实例训练的基础通用模型。MedVersa支持从多模式输入和输出中学习通用知识,成为首个在多种医学成像场景中与领先的专业解决方案相竞争的通用模型。在九项任务中,MedVersa取得了最先进的性能,有时较同类产品的性能高出超过10%。放射科医生评估显示,MedVersa生成的报告在正常研究的95%中表现优越,并在总体上以匹配或超过人类报告的速度在71%的案例中表现良好。用户研究表明,使用MedVersa显著减少了报告编写时间和差异。我们的研究强调了灵活的多模式AI系统在推进医学图像解读和支持临床专业知识方面的价值。
Key Takeaways
- 医学AI系统的局限性:当前医学AI系统通常仅限于特定应用,限制了其广泛应用。
- MedVersa的引入:提出了一种名为MedVersa的通用基础模型,该模型经过数百万医疗实例训练。
- 多模态学习与输出:MedVersa支持从多模式输入和输出中学习,这是一个创新特点。
- 竞争性能:MedVersa在多种医学成像场景中表现出与领先的专业解决方案相当的竞争力。
- 先进性能表现:在九项任务中,MedVersa达到最先进的性能水平,并在某些情况下显著优于其他系统。
- 放射科医生评估结果:在放射科医生评估中,MedVersa生成的报告在大部分情况下表现良好。
点此查看论文截图