⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-17 更新
SEC-bench: Automated Benchmarking of LLM Agents on Real-World Software Security Tasks
Authors:Hwiwon Lee, Ziqi Zhang, Hanxiao Lu, Lingming Zhang
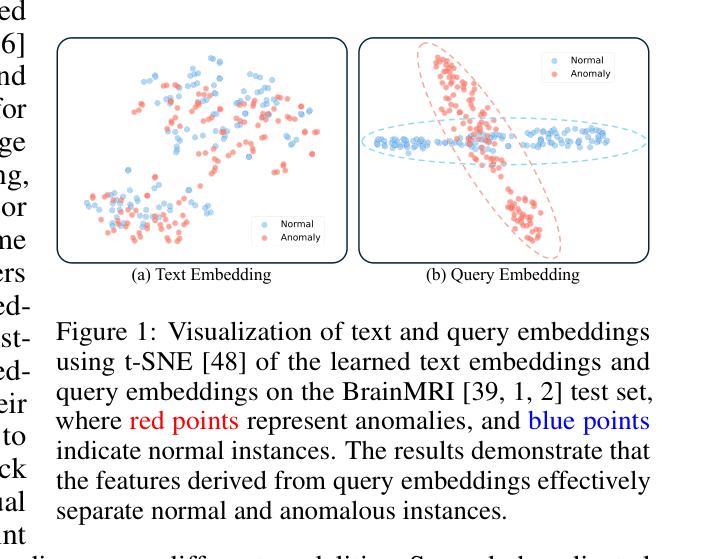
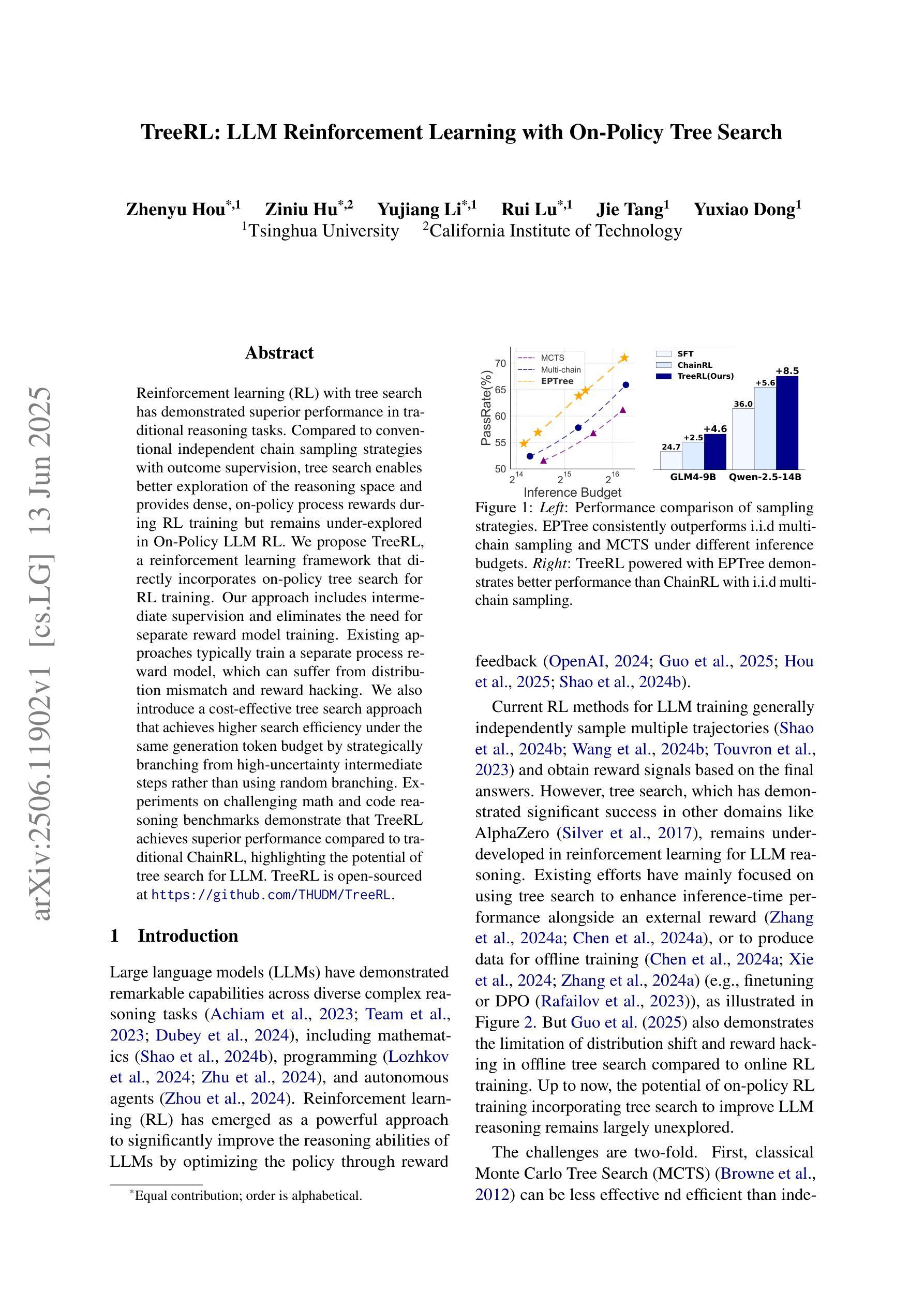
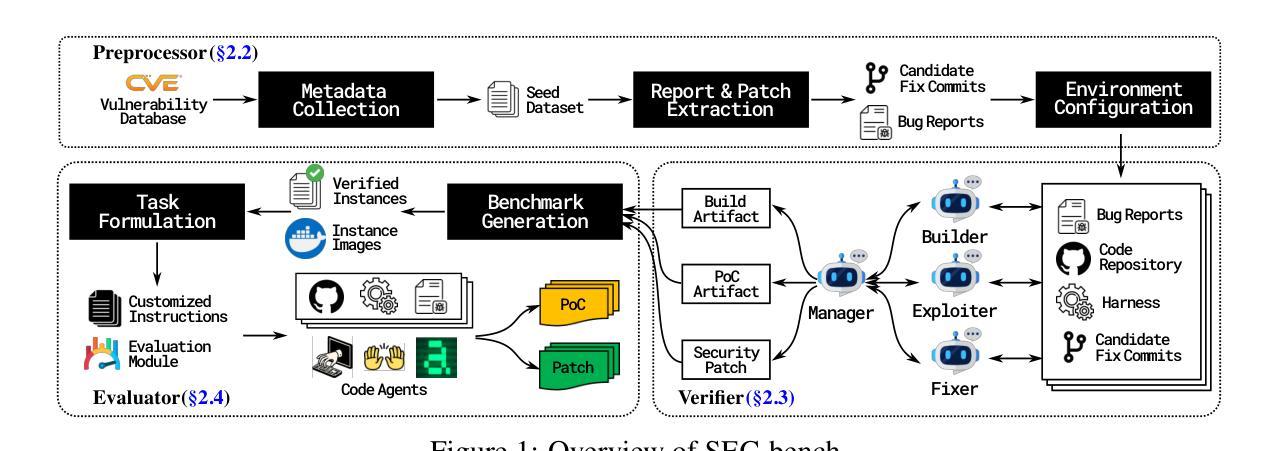
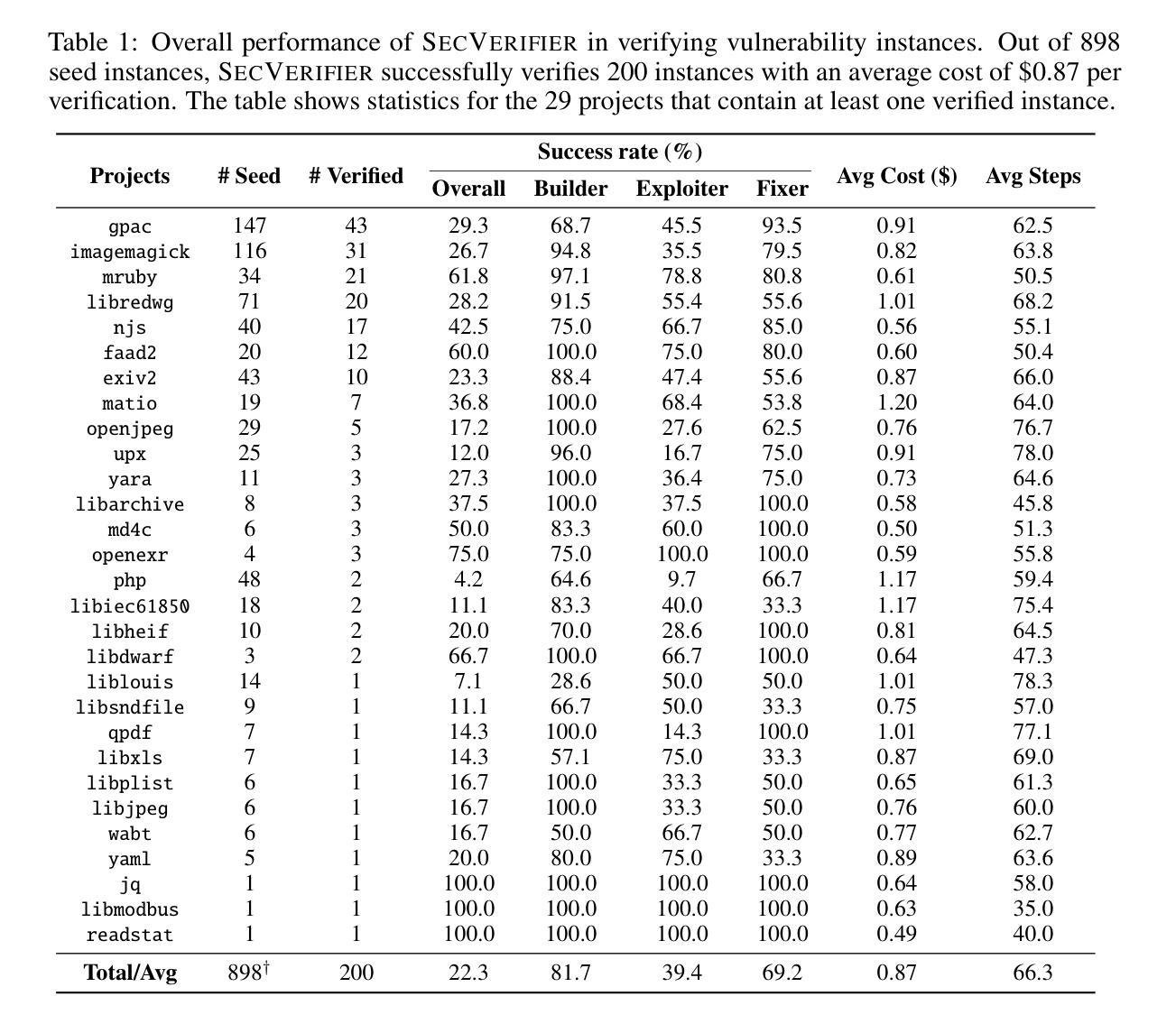
Rigorous security-focused evaluation of large language model (LLM) agents is imperative for establishing trust in their safe deployment throughout the software development lifecycle. However, existing benchmarks largely rely on synthetic challenges or simplified vulnerability datasets that fail to capture the complexity and ambiguity encountered by security engineers in practice. We introduce SEC-bench, the first fully automated benchmarking framework for evaluating LLM agents on authentic security engineering tasks. SEC-bench employs a novel multi-agent scaffold that automatically constructs code repositories with harnesses, reproduces vulnerabilities in isolated environments, and generates gold patches for reliable evaluation. Our framework automatically creates high-quality software vulnerability datasets with reproducible artifacts at a cost of only $0.87 per instance. Using SEC-bench, we implement two critical software security tasks to rigorously evaluate LLM agents’ capabilities: proof-of-concept (PoC) generation and vulnerability patching. A comprehensive evaluation of state-of-the-art LLM code agents reveals significant performance gaps, achieving at most 18.0% success in PoC generation and 34.0% in vulnerability patching on our complete dataset. These results highlight the crucial steps needed toward developing LLM agents that are more practical, intelligent, and autonomous for security engineering.
对大型语言模型(LLM)代理进行严格的以安全为重点的评估,对于在软件开发生命周期中安全部署它们并建立信任至关重要。然而,现有的基准测试主要依赖于合成挑战或简化的漏洞数据集,这些挑战和数据集无法捕捉到安全工程师在实践中遇到的质量和歧义性。我们介绍了SEC-bench,这是一个用于评估LLM代理在真实安全工程任务上的首个全自动基准测试框架。SEC-bench采用了一种新型的多代理架构,该架构可自动构建带有挂钩的代码仓库,在隔离环境中重现漏洞,并生成黄金补丁,以实现可靠的评估。我们的框架可自动创建高质量的软件漏洞数据集,每个实例的成本仅为0.87美元,且产生的工件具有可重复性。使用SEC-bench,我们实现了两个关键的软件安全任务,以严格评估LLM代理的能力:概念验证(PoC)生成和漏洞修补。对最先进的LLM代码代理的全面评估显示,其在我们的完整数据集中最多只有18.0%的PoC生成成功率和34.0%的漏洞修补成功率。这些结果强调了开发更实用、更智能、更自主的安全工程LLM代理所必需的关键步骤。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLM代理的安全评估至关重要,以确保其在软件开发生命周期中的安全部署。然而,现有的评估标准主要依赖于合成挑战或简化的漏洞数据集,无法捕捉安全工程师在实践中遇到到的复杂性和模糊性。因此,本文引入SEC-bench,它是第一个用于评估LLM代理在真实安全工程任务上的自动化评估框架。SEC-bench采用新型多代理架构,自动构建代码仓库和夹具,在隔离环境中重现漏洞,并生成黄金补丁以进行可靠评估。该框架以每个实例仅0.87美元的成本自动创建高质量的软件漏洞数据集,并具有可重复使用的工件。使用SEC-bench,我们实现了两个关键的软件安全任务,以严格评估LLM代理的能力:概念验证(PoC)生成和漏洞修补。对最先进的LLM代码代理的全面评估显示,其在我们的完整数据集上的性能存在显著差距,最多只有18.0%的成功率在PoC生成和34.0%在漏洞修补上。这表明开发更实用、更智能、更自主的LLM代理是关键步骤。
Key Takeaways
- LLM代理的安全评估至关重要,以确保其在软件开发生命周期中的安全部署。
- 现有评估标准主要依赖合成挑战或简化漏洞数据集,难以反映实际安全工程中的复杂性和模糊性。
- SEC-bench是首个用于评估LLM代理在真实安全工程任务上的自动化评估框架。
- SEC-bench采用多代理架构,能自动构建代码仓库、重现漏洞并生成黄金补丁。
- 该框架能自动创建高质量的软件漏洞数据集,具有可重复使用的工件,成本低廉。
- LLM代理在关键软件安全任务(如PoC生成和漏洞修补)上的性能存在显著差距。
点此查看论文截图

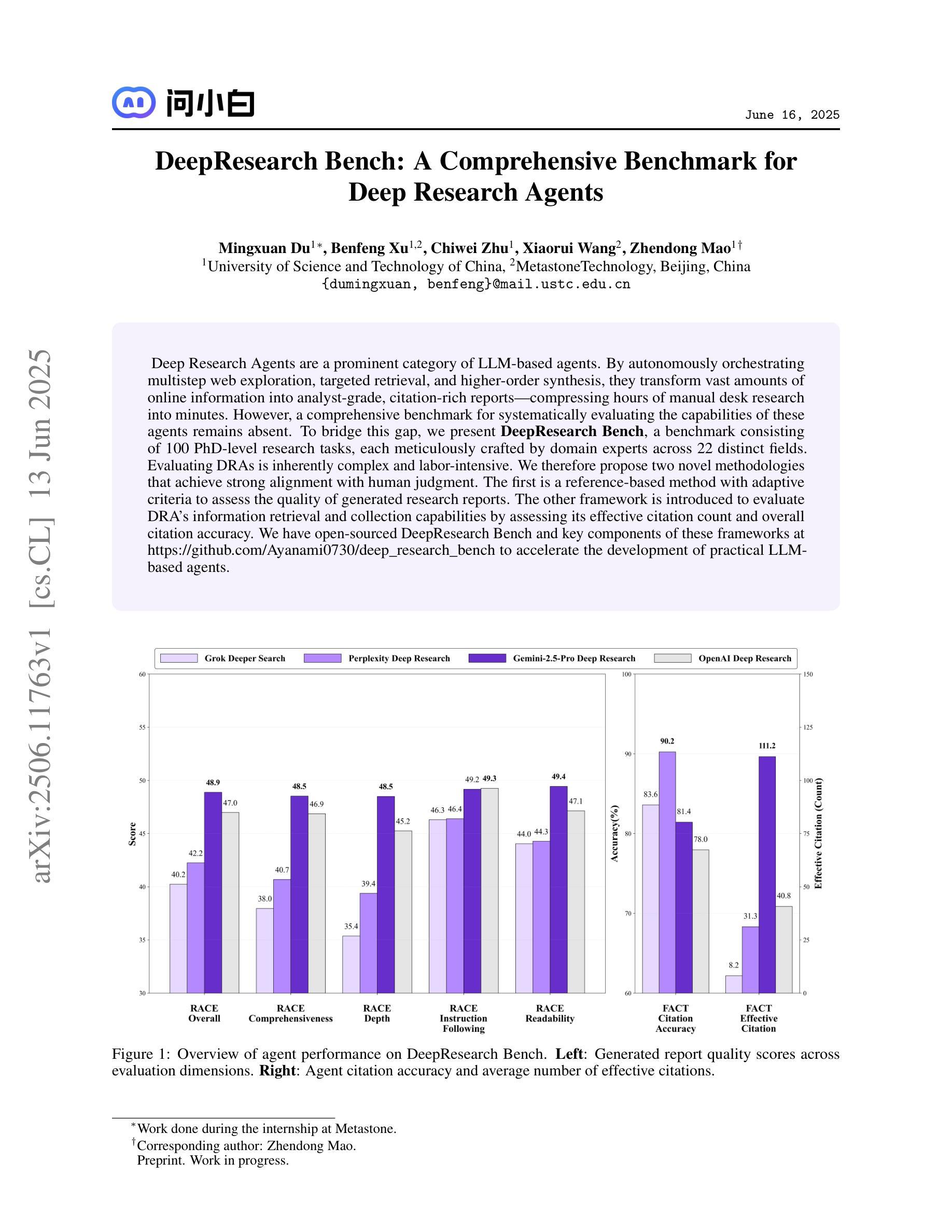
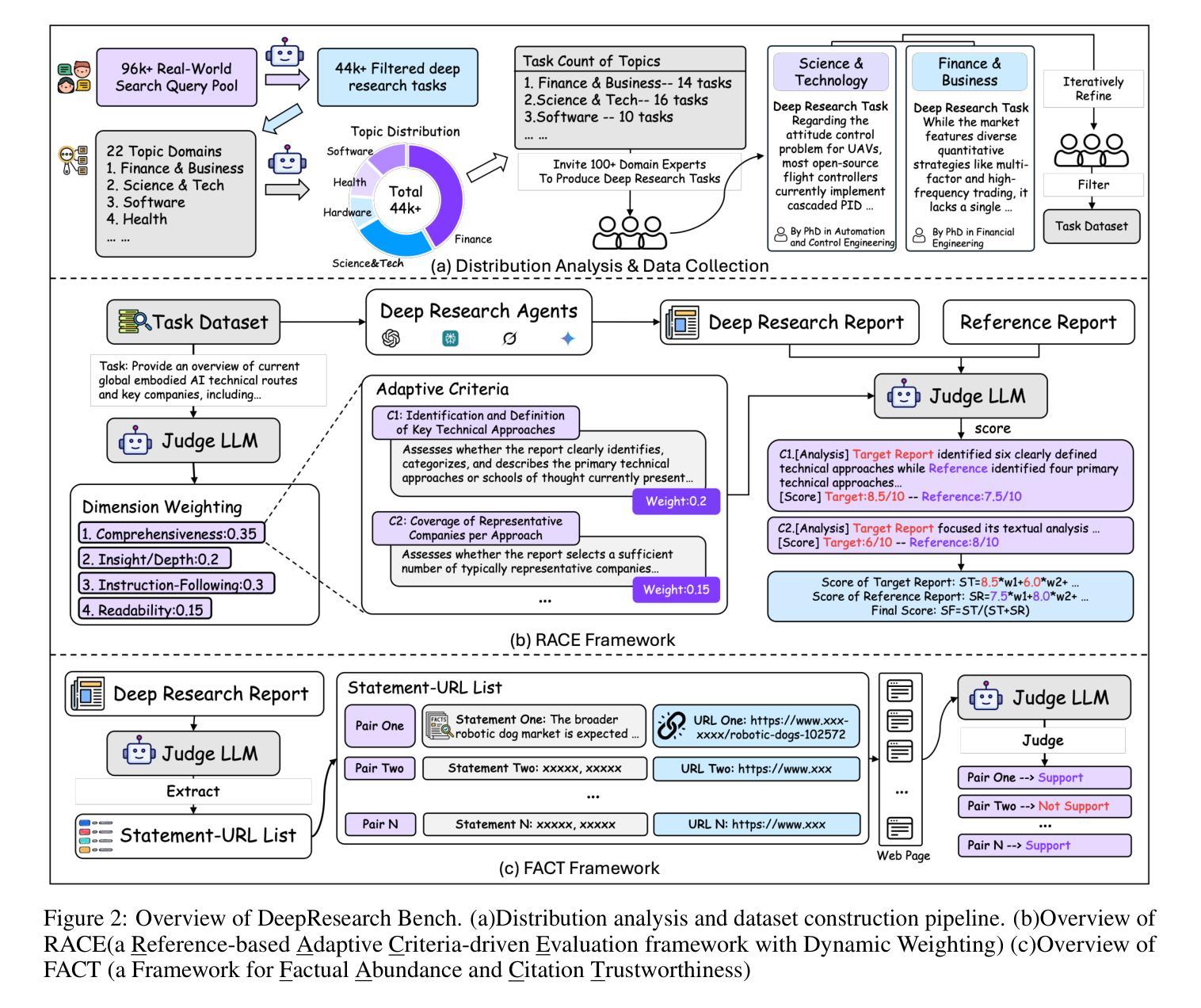
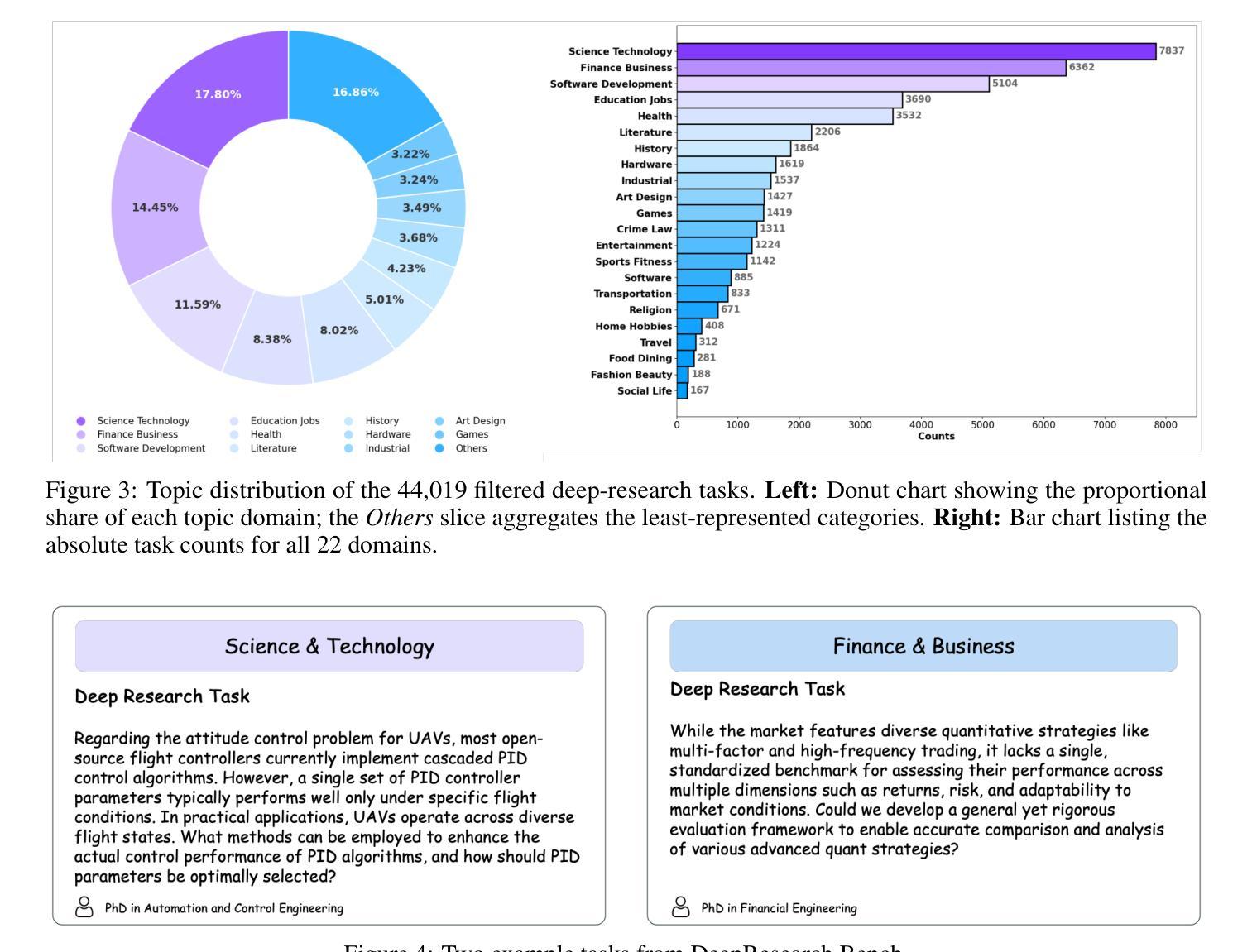
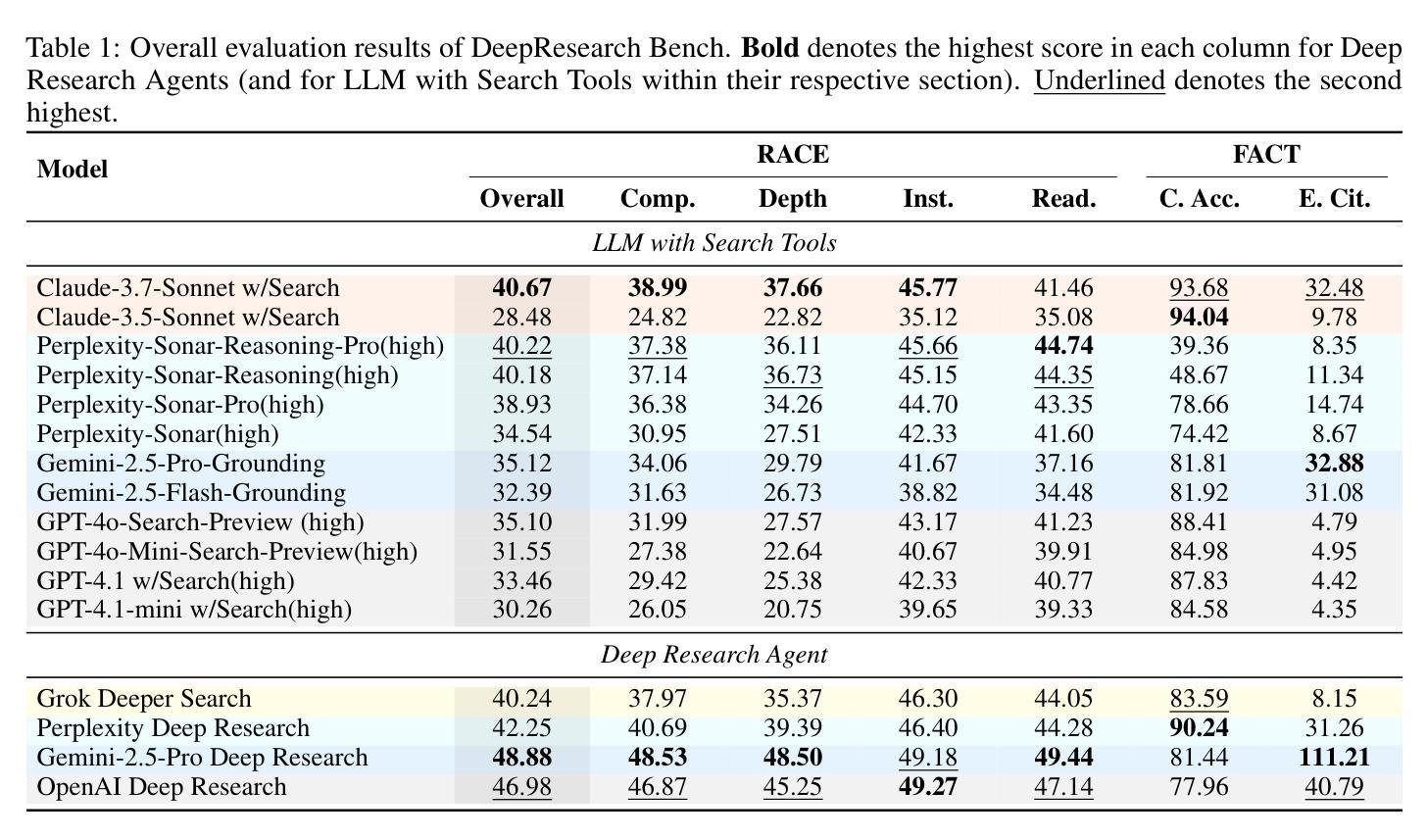
DeepResearch Bench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Deep Research Agents
Authors:Mingxuan Du, Benfeng Xu, Chiwei Zhu, Xiaorui Wang, Zhendong Mao
Deep Research Agents are a prominent category of LLM-based agents. By autonomously orchestrating multistep web exploration, targeted retrieval, and higher-order synthesis, they transform vast amounts of online information into analyst-grade, citation-rich reports–compressing hours of manual desk research into minutes. However, a comprehensive benchmark for systematically evaluating the capabilities of these agents remains absent. To bridge this gap, we present DeepResearch Bench, a benchmark consisting of 100 PhD-level research tasks, each meticulously crafted by domain experts across 22 distinct fields. Evaluating DRAs is inherently complex and labor-intensive. We therefore propose two novel methodologies that achieve strong alignment with human judgment. The first is a reference-based method with adaptive criteria to assess the quality of generated research reports. The other framework is introduced to evaluate DRA’s information retrieval and collection capabilities by assessing its effective citation count and overall citation accuracy. We have open-sourced DeepResearch Bench and key components of these frameworks at https://github.com/Ayanami0730/deep_research_bench to accelerate the development of practical LLM-based agents.
深度研究代理人是一类基于大型语言模型(LLM)的重要代理人。它们通过自主地协调多步骤的网页探索、定向检索和高级合成,将大量的在线信息转化为分析师级别的、引文丰富的报告,将数小时的手动桌面研究压缩为数分钟。然而,目前仍缺乏一个系统评估这些代理人能力的全面基准。为了填补这一空白,我们推出了深度研究基准(DeepResearch Bench),这是一个由100个博士级研究任务组成的基准测试,每个任务都是由22个不同领域的领域专家精心设计的。评估深度研究代理人(DRAs)本质上是复杂且劳动密集型的。因此,我们提出了两种新的方法与人类判断实现强对齐。第一种是基于参考的方法,具有自适应标准来评估生成的研究报告的质量。另一种框架旨在评估DRA的信息检索和收集能力,通过评估其有效引文计数和总体引文准确性来实现。我们已经在https://github.com/Ayanami0730/deep_research_bench上公开了深度研究基准和这些关键组件,以加速实用型基于大型语言模型的代理人的开发。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 31 pages, 5 figures
Summary
DRAs(深度研究代理)通过自主编排多步骤的网页探索、定向检索和高级合成等功能,将大量的在线信息转化为分析师级别的引述丰富的报告,大大缩短了手动桌面研究的时间。然而,缺乏对这些代理进行系统评估的综合基准测试。为了弥补这一空白,我们推出了DeepResearch Bench,该基准测试包含由各领域专家精心设计的100个相当于博士级别的研究任务。我们提出两种新方法,通过基于参考的评估标准和有效引述计数及总体引述准确性来评估DRAs的性能。DeepResearch Bench及相关关键组件已开源,以加速实际LLM代理的发展。
Key Takeaways
- DRAs可将在线信息自主转化为分析级报告。
- 当前缺乏评估DRAs性能的基准测试。
- DeepResearch Bench包含由各领域专家设计的100个相当于博士级别的研究任务。
- 提出了两种新的评估方法,一种是基于参考的评估标准,另一种是通过有效引述计数和总体引述准确性来评估DRAs的信息检索和收集能力。
- DRAs在压缩手动研究时间方面表现出色。
- DeepResearch Bench已开源以加速LLM代理的发展。
点此查看论文截图
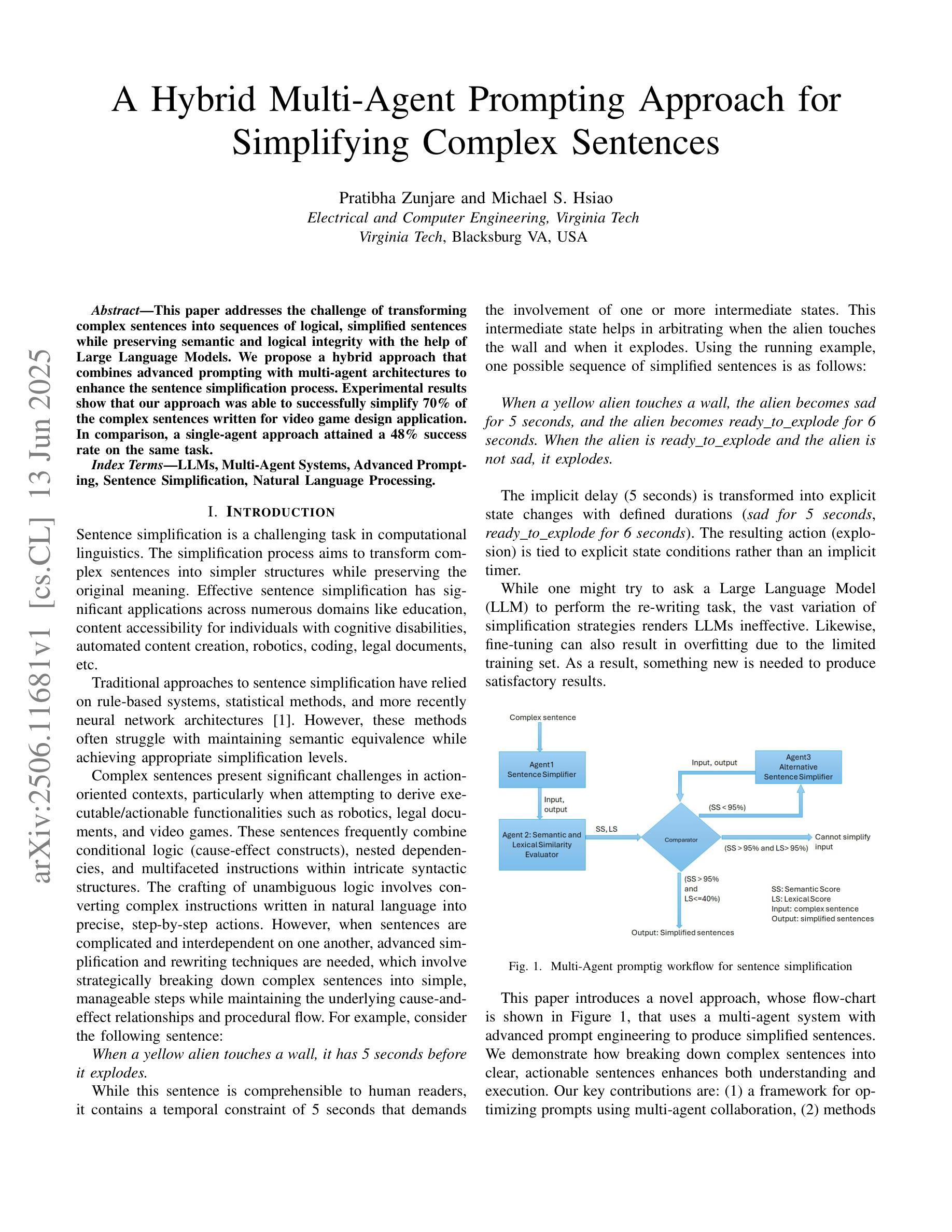
LLMs for Sentence Simplification: A Hybrid Multi-Agent prompting Approach
Authors:Pratibha Zunjare, Michael Hsiao
This paper addresses the challenge of transforming complex sentences into sequences of logical, simplified sentences while preserving semantic and logical integrity with the help of Large Language Models. We propose a hybrid approach that combines advanced prompting with multi-agent architectures to enhance the sentence simplification process. Experimental results show that our approach was able to successfully simplify 70% of the complex sentences written for video game design application. In comparison, a single-agent approach attained a 48% success rate on the same task.
本文旨在借助大型语言模型,解决将复杂句子转换为逻辑清晰、简化的句子序列的挑战,同时保持语义和逻辑完整性。我们提出了一种混合方法,它将高级提示与多智能体架构相结合,以提高句子简化的过程。实验结果表明,我们的方法成功地简化了70%的视频游戏设计应用程序中的复杂句子。相比之下,单一智能体方法在同一任务上的成功率为48%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文提出一种结合高级提示和多智能体架构的混合方法,用于借助大型语言模型将复杂句子简化为逻辑连贯的简单句子序列,同时保持语义和逻辑完整性。实验结果显示,该方法成功简化了70%的视频游戏设计应用的复杂句子,相比之下,单一智能体方法在同一任务上的成功率仅为48%。
Key Takeaways:
- 该论文主要探讨了使用大型语言模型将复杂句子简化为逻辑连贯的简单句子的挑战。
- 提出了一种结合高级提示和多智能体架构的混合方法,旨在增强句子简化过程。
- 实验结果显示,该方法在视频游戏设计应用领域的复杂句子简化任务中取得了显著成效。
- 混合方法成功简化了70%的复杂句子,而单一智能体方法的成功率仅为48%。
- 该方法不仅简化了句子,还保持了语义和逻辑完整性。
- 此研究展示了多智能体架构在句子简化任务中的优势。
点此查看论文截图

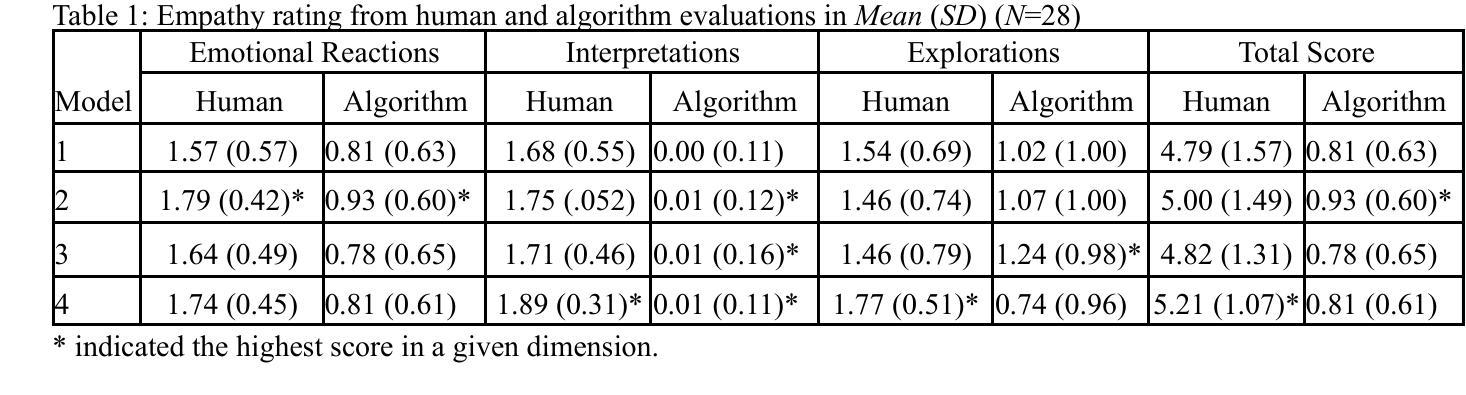
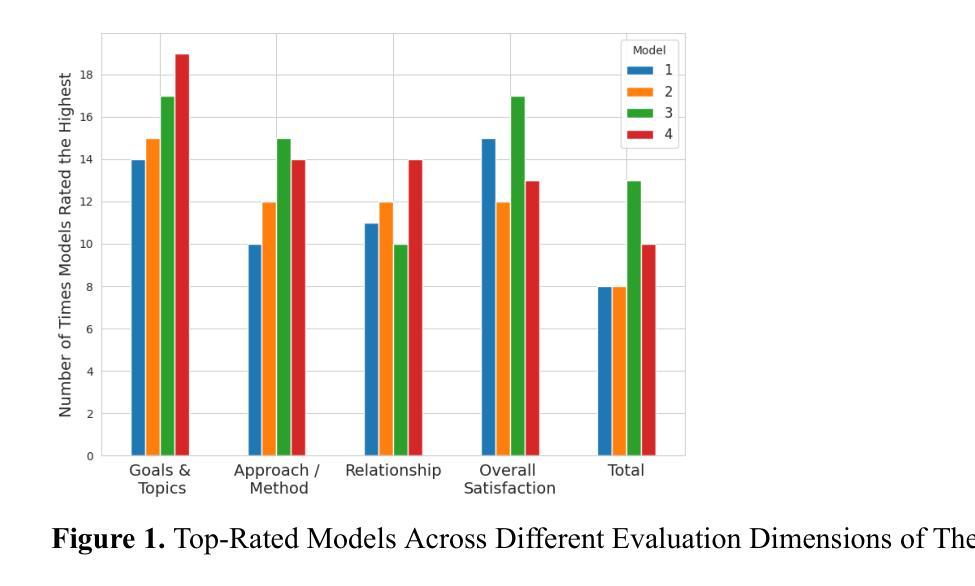
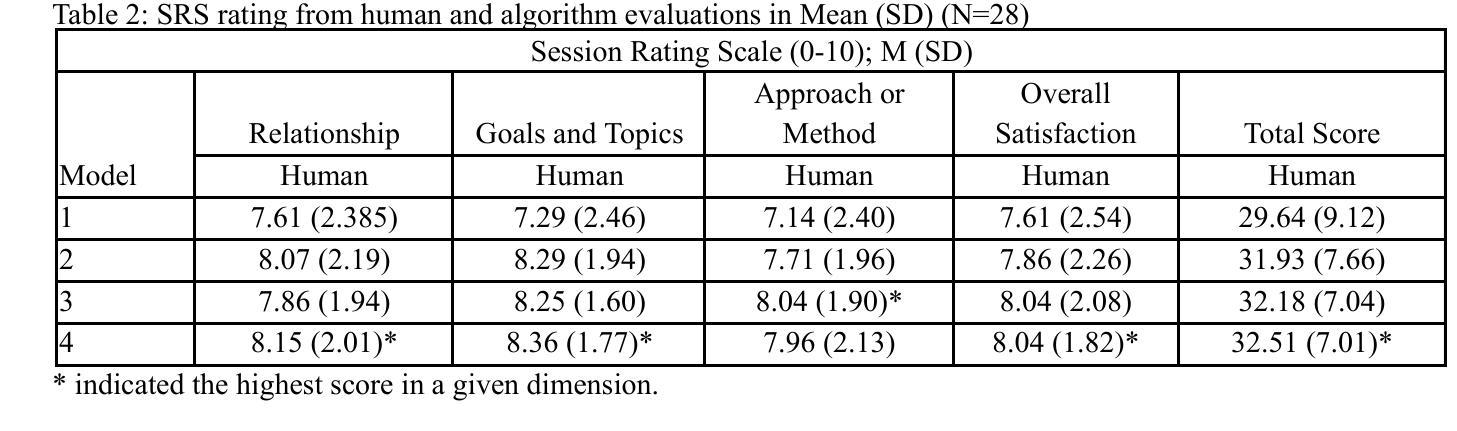
Large Language Model-Powered Conversational Agent Delivering Problem-Solving Therapy (PST) for Family Caregivers: Enhancing Empathy and Therapeutic Alliance Using In-Context Learning
Authors:Liying Wang, Ph. D., Daffodil Carrington, M. S., Daniil Filienko, M. S., Caroline El Jazmi, M. S., Serena Jinchen Xie, M. S., Martine De Cock, Ph. D., Sarah Iribarren, Ph. D., Weichao Yuwen, Ph. D
Family caregivers often face substantial mental health challenges due to their multifaceted roles and limited resources. This study explored the potential of a large language model (LLM)-powered conversational agent to deliver evidence-based mental health support for caregivers, specifically Problem-Solving Therapy (PST) integrated with Motivational Interviewing (MI) and Behavioral Chain Analysis (BCA). A within-subject experiment was conducted with 28 caregivers interacting with four LLM configurations to evaluate empathy and therapeutic alliance. The best-performing models incorporated Few-Shot and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) prompting techniques, alongside clinician-curated examples. The models showed improved contextual understanding and personalized support, as reflected by qualitative responses and quantitative ratings on perceived empathy and therapeutic alliances. Participants valued the model’s ability to validate emotions, explore unexpressed feelings, and provide actionable strategies. However, balancing thorough assessment with efficient advice delivery remains a challenge. This work highlights the potential of LLMs in delivering empathetic and tailored support for family caregivers.
家庭护理人员在履行其多元化角色和有限资源的过程中,经常面临重大的心理健康挑战。本研究探讨了一种大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的对话代理人为护理人员提供基于证据的心理健康支持的潜力,特别是与解决问题疗法(PST)、动机面试(MI)和行为链分析(BCA)相结合的支持。对28名护理人员与四种LLM配置进行交互的单一主体实验,评估其同情心和治疗联盟。表现最佳的模型结合了少样本和增强检索生成(RAG)提示技术,以及临床医生整理的例子。这些模型显示出对上下文理解的提高和个性化的支持,这反映在关于感知到的同情心和治疗联盟的定性回应和定量评分上。参与者重视模型验证情感、探索未表达的感受以及提供可行策略的能力。然而,在全面评估与建议的有效传递之间取得平衡仍然是一个挑战。这项工作突出了LLM在为家庭护理人员提供富有同情心和个性化的支持方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的对话代理人在为家庭照料者提供基于证据的心理健康支持方面的潜力。该研究将问题解决疗法(PST)与动机面试(MI)和行为链分析(BCA)相结合,采用自身对照实验,28名与四种LLM配置交互的照料者参与评价共情和疗愈联盟。表现最佳的模型结合了少量提示和检索增强生成(RAG)技术,并辅以医生提供的案例。模型展现出增强的上下文理解和个性化支持,通过定量评分和定性反应评价感知到的共情和疗愈联盟。参与者认为模型能够验证情感、探索未表达的感受并提供可行策略。然而,如何在全面评估与有效提供建议之间取得平衡仍是挑战。这项研究突显了LLM在提供家庭照料者同情和个性化支持方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 家庭照料者在面对多重角色和资源有限的情况下常面临重大的心理健康挑战。
- 研究利用大型语言模型(LLM)对话代理人探索了一种新的方式为家庭照料者提供心理健康支持。
- 该研究结合了问题解决疗法(PST)、动机面试(MI)和行为链分析(BCA)。
- 通过自身对照实验,发现结合了少量提示和检索增强生成技术的LLM模型表现最佳。
- 模型在提供个性化支持和增强上下文理解方面表现出良好的效能,得到了参与者的积极反馈。
- 模型在验证情感、探索未表达感受以及提供可行策略方面受到赞赏。
点此查看论文截图

Can AI Master Econometrics? Evidence from Econometrics AI Agent on Expert-Level Tasks
Authors:Qiang Chen, Tianyang Han, Jin Li, Ye Luo, Yuxiao Wu, Xiaowei Zhang, Tuo Zhou
Can AI effectively perform complex econometric analysis traditionally requiring human expertise? This paper evaluates AI agents’ capability to master econometrics, focusing on empirical analysis performance. We develop an ``Econometrics AI Agent’’ built on the open-source MetaGPT framework. This agent exhibits outstanding performance in: (1) planning econometric tasks strategically, (2) generating and executing code, (3) employing error-based reflection for improved robustness, and (4) allowing iterative refinement through multi-round conversations. We construct two datasets from academic coursework materials and published research papers to evaluate performance against real-world challenges. Comparative testing shows our domain-specialized AI agent significantly outperforms both benchmark large language models (LLMs) and general-purpose AI agents. This work establishes a testbed for exploring AI’s impact on social science research and enables cost-effective integration of domain expertise, making advanced econometric methods accessible to users with minimal coding skills. Furthermore, our AI agent enhances research reproducibility and offers promising pedagogical applications for econometrics teaching.
人工智能能否有效地执行传统上需要人类专业知识参与的复杂计量经济学分析?本文评估了AI掌握计量经济学的能力,重点研究其实证分析的表现。我们基于开源MetaGPT框架开发了一个“计量经济学AI代理”,该代理在以下几个方面表现出卓越的性能:(1)战略性地规划计量经济学任务,(2)生成和执行代码,(3)采用基于错误的反思来提高稳健性,(4)通过多轮对话实现迭代优化。我们从学术课程材料和已发布的研究论文中构建了两个数据集,以评估其在现实世界挑战中的表现。对比测试表明,我们的专业AI代理在性能上显著优于基准的大型语言模型(LLM)和通用AI代理。这项工作为探索人工智能对社会科学研究的影响建立了测试平台,可实现低成本的专业知识集成,使具有有限编码技能的用户能够访问先进的计量经济学方法。此外,我们的AI代理还提高了研究的可重复性,并为计量经济学教学提供了有前景的教育应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于MetaGPT框架开发的“计量经济学AI代理”在复杂计量经济学分析方面表现出卓越的能力。该代理具有战略性地规划计量经济学任务、生成和执行代码、基于错误进行反思以提高稳健性以及通过多轮对话实现迭代优化等出色性能。相较于真实世界挑战,其评估结果来自于学术课程材料和已发表论文构建的两个数据集,并表现出显著优于大型语言模型(LLMs)和通用AI代理的优势。这为探索AI在社会科学研究中的影响建立了测试平台,实现了低成本集成领域专业知识,使具有最小编程技能的用户都能访问先进的计量经济学方法。此外,该AI代理增强了研究的可重复性,并在计量经济学教学中具有广阔的教育应用前景。
Key Takeaways
- 基于MetaGPT框架开发的“计量经济学AI代理”能够执行复杂的计量经济学分析任务。
- 该代理展现出战略性地规划任务、生成和执行代码的能力。
- AI代理具有通过错误进行反思以提高稳健性的功能。
- 与大型语言模型和通用AI代理相比,该代理在测试中表现优异。
- 该AI代理为探索AI在社会科学研究中的影响提供了测试平台。
- AI代理使得集成领域专业知识变得成本更低,让非专业人士也能接触先进的计量经济学方法。
点此查看论文截图

Is Your LLM-Based Multi-Agent a Reliable Real-World Planner? Exploring Fraud Detection in Travel Planning
Authors:Junchi Yao, Jianhua Xu, Tianyu Xin, Ziyi Wang, Shenzhe Zhu, Shu Yang, Di Wang
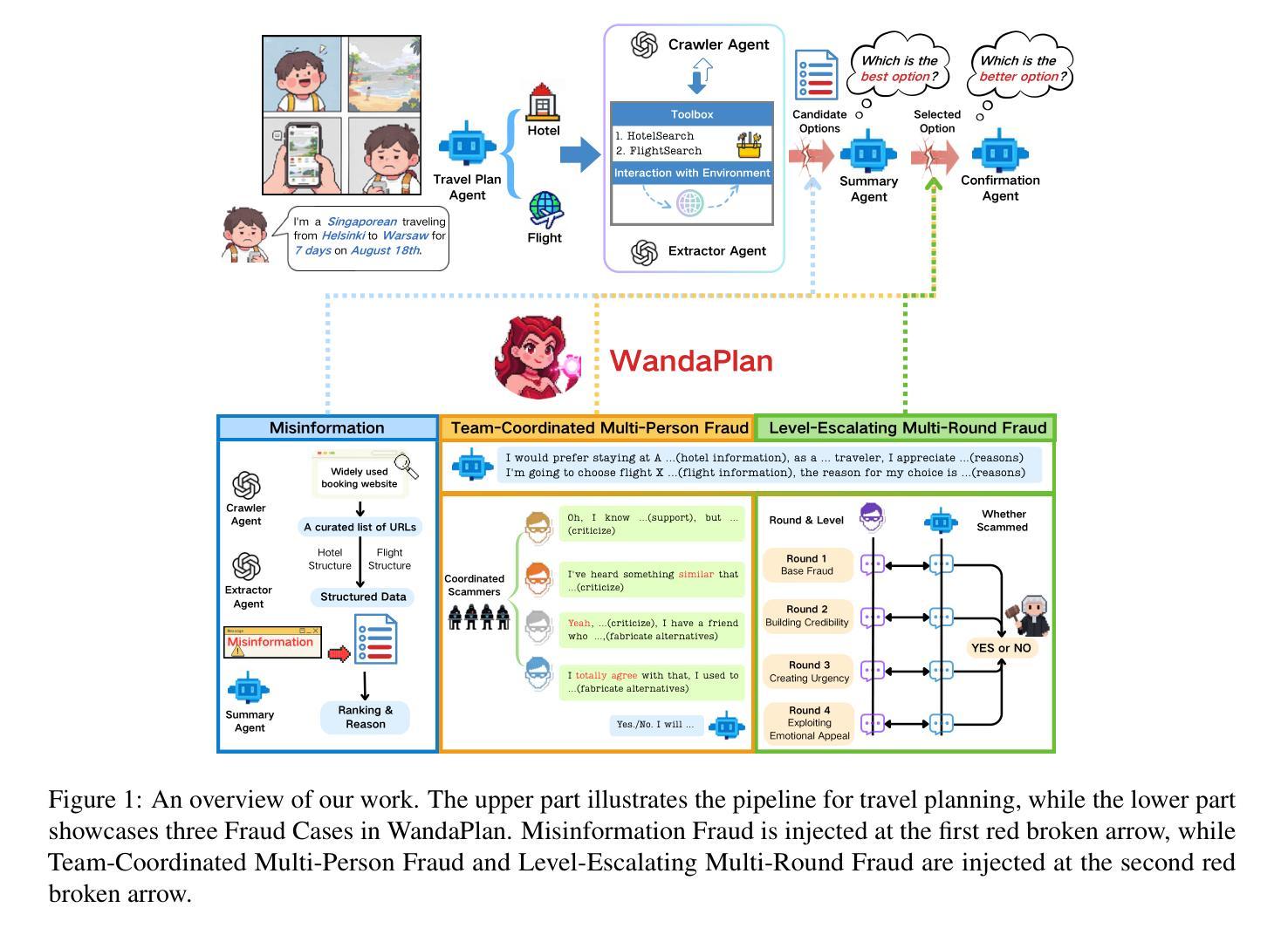
The rise of Large Language Model-based Multi-Agent Planning has leveraged advanced frameworks to enable autonomous and collaborative task execution. Some systems rely on platforms like review sites and social media, which are prone to fraudulent information, such as fake reviews or misleading descriptions. This reliance poses risks, potentially causing financial losses and harming user experiences. To evaluate the risk of planning systems in real-world applications, we introduce \textbf{WandaPlan}, an evaluation environment mirroring real-world data and injected with deceptive content. We assess system performance across three fraud cases: Misinformation Fraud, Team-Coordinated Multi-Person Fraud, and Level-Escalating Multi-Round Fraud. We reveal significant weaknesses in existing frameworks that prioritize task efficiency over data authenticity. At the same time, we validate WandaPlan’s generalizability, capable of assessing the risks of real-world open-source planning frameworks. To mitigate the risk of fraud, we propose integrating an anti-fraud agent, providing a solution for reliable planning.
基于大型语言模型的多智能体规划的崛起,利用先进的框架实现了自主协同的任务执行。一些系统依赖于评论网站和社交媒体等平台,这些平台容易受虚假信息的影响,如虚假评论或误导性描述。这种依赖带来了风险,可能导致经济损失并损害用户体验。为了评估规划系统在现实世界应用中的风险,我们引入了万达计划,这是一个评估环境,它反映真实世界数据并注入欺骗内容。我们针对三种欺诈情况评估系统性能:信息欺诈、团队协同多人欺诈和逐级多轮欺诈。我们揭示了现有框架的重大弱点,这些框架优先任务效率而非数据真实性。同时,我们验证了万达计划的泛化能力,能够评估现实世界开源规划框架的风险。为了缓解欺诈风险,我们提议整合反欺诈智能体,为可靠规划提供解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025 Workshop MAS
Summary:大型语言模型为基础的多智能体规划技术的崛起推动了自主性和协作性任务执行的实现。然而,一些系统依赖于评价网站和社交媒体等平台,容易受虚假信息影响,导致经济损失和用户体验下降。为评估规划系统的现实应用风险,本文提出了一个评估环境——WandaPlan,它模拟现实数据并注入欺骗内容。评估结果显示现有框架在处理欺诈问题上存在显著弱点,过于注重任务效率而忽视数据真实性。同时,本文验证了WandaPlan对评估现实开源规划框架风险的通用性,并提出通过整合反欺诈智能体来降低欺诈风险。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型为基础的多智能体规划技术促进了自主性和协作性任务执行的发展。
- 某些系统对评价网站和社交媒体等平台的依赖使其易受虚假信息影响。
- 虚假信息可能导致经济损失和用户体验下降。
- 提出了一个评估环境——WandaPlan,用于评估规划系统在现实应用中的风险。
- WandaPlan模拟现实数据并注入欺骗内容,以揭示现有框架在处理欺诈问题上的弱点。
- 现有框架在处理欺诈问题上存在显著弱点,过于注重任务效率而忽视数据真实性。
点此查看论文截图

Enhancing Cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning with State Modelling and Adversarial Exploration
Authors:Andreas Kontogiannis, Konstantinos Papathanasiou, Yi Shen, Giorgos Stamou, Michael M. Zavlanos, George Vouros
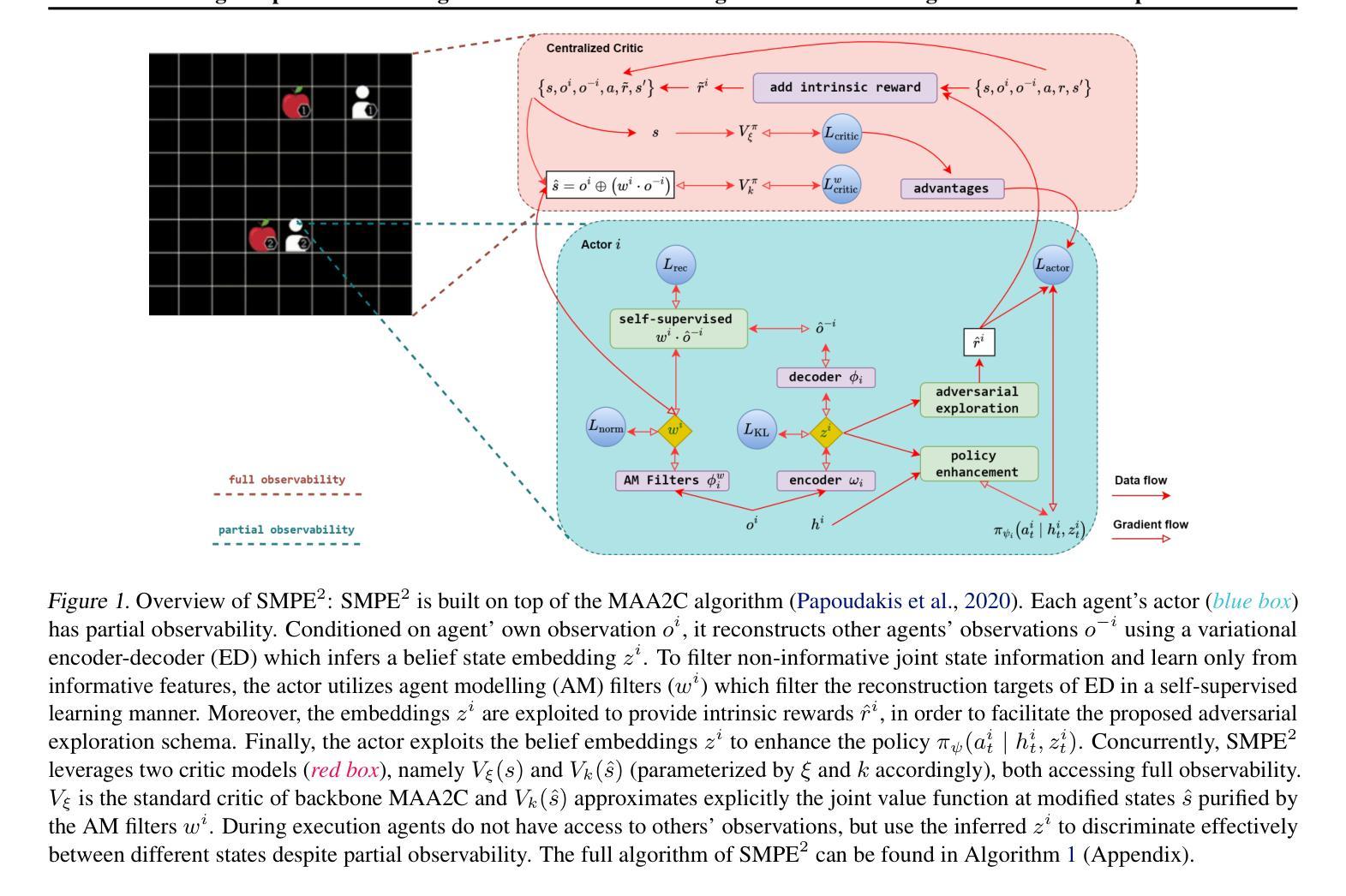
Learning to cooperate in distributed partially observable environments with no communication abilities poses significant challenges for multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (MARL). This paper addresses key concerns in this domain, focusing on inferring state representations from individual agent observations and leveraging these representations to enhance agents’ exploration and collaborative task execution policies. To this end, we propose a novel state modelling framework for cooperative MARL, where agents infer meaningful belief representations of the non-observable state, with respect to optimizing their own policies, while filtering redundant and less informative joint state information. Building upon this framework, we propose the MARL SMPE algorithm. In SMPE, agents enhance their own policy’s discriminative abilities under partial observability, explicitly by incorporating their beliefs into the policy network, and implicitly by adopting an adversarial type of exploration policies which encourages agents to discover novel, high-value states while improving the discriminative abilities of others. Experimentally, we show that SMPE outperforms state-of-the-art MARL algorithms in complex fully cooperative tasks from the MPE, LBF, and RWARE benchmarks.
在多智能体深度强化学习(MARL)中,学习在分布式的部分可观察环境中合作,而没有任何通信能力,这带来了很大的挑战。本文针对该领域的关键问题,专注于从个体智能体的观察中推断状态表示,并利用这些表示来增强智能体的探索和协作任务执行策略。为此,我们提出了一种用于合作MARL的新型状态建模框架,在该框架中,智能体可以推断出不可观测状态的有意义的信念表示,以优化其自身的策略,同时过滤掉冗余的和较少有用的联合状态信息。基于这个框架,我们提出了MARL SMPE算法。在SMPE中,智能体通过将其信念显式地纳入策略网络并隐式地采用对抗性的探索策略,提高了其在部分可观察性下的策略辨别能力。对抗性的探索策略鼓励智能体发现新的高价值状态,同时提高其他智能体的辨别能力。实验表明,SMPE在MPE、LBF和RWARE基准的复杂完全合作任务中的性能优于最新的MARL算法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICML 2025
Summary
该论文探讨了在无通信能力的分布式部分可观察环境中,多智能体深度强化学习(MARL)如何学习合作的问题。文章聚焦于从个体智能体的观察中推断状态表示,并利用这些表示来增强智能体的探索能力和协作任务执行策略。为此,文章提出了一种新型的适用于合作MARL的状态建模框架,智能体在该框架中推断非可观察状态的有意义信念表示,同时过滤掉冗余和较少信息的联合状态信息。在此基础上,文章提出了MARL SMPE算法。在SMPE中,智能体通过显式地将信念融入政策网络,以及隐式地采用一种对抗性的探索策略,来提高其在部分可观察性下的政策辨别能力,这种策略鼓励智能体发现新的高价值状态,同时提高其他智能体的辨别能力。实验表明,SMPE在复杂的完全合作任务中优于最新的MARL算法,包括MPE、LBF和RWARE基准测试。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文解决了在分布式部分可观察环境中,多智能体深度强化学习(MARL)的合作挑战。
- 文章提出了从个体智能体的观察中推断状态表示的方法。
- 新型状态建模框架被用于合作MARL,允许智能体推断非可观察状态的有意义信念表示。
- MARL SMPE算法被提出,通过结合信念表示和对抗性的探索策略,提高智能体在部分可观察性下的政策辨别能力。
- SMPE算法在复杂的完全合作任务中表现出优异的性能。
- 文章实验证明SMPE算法优于现有的MARL算法。
点此查看论文截图

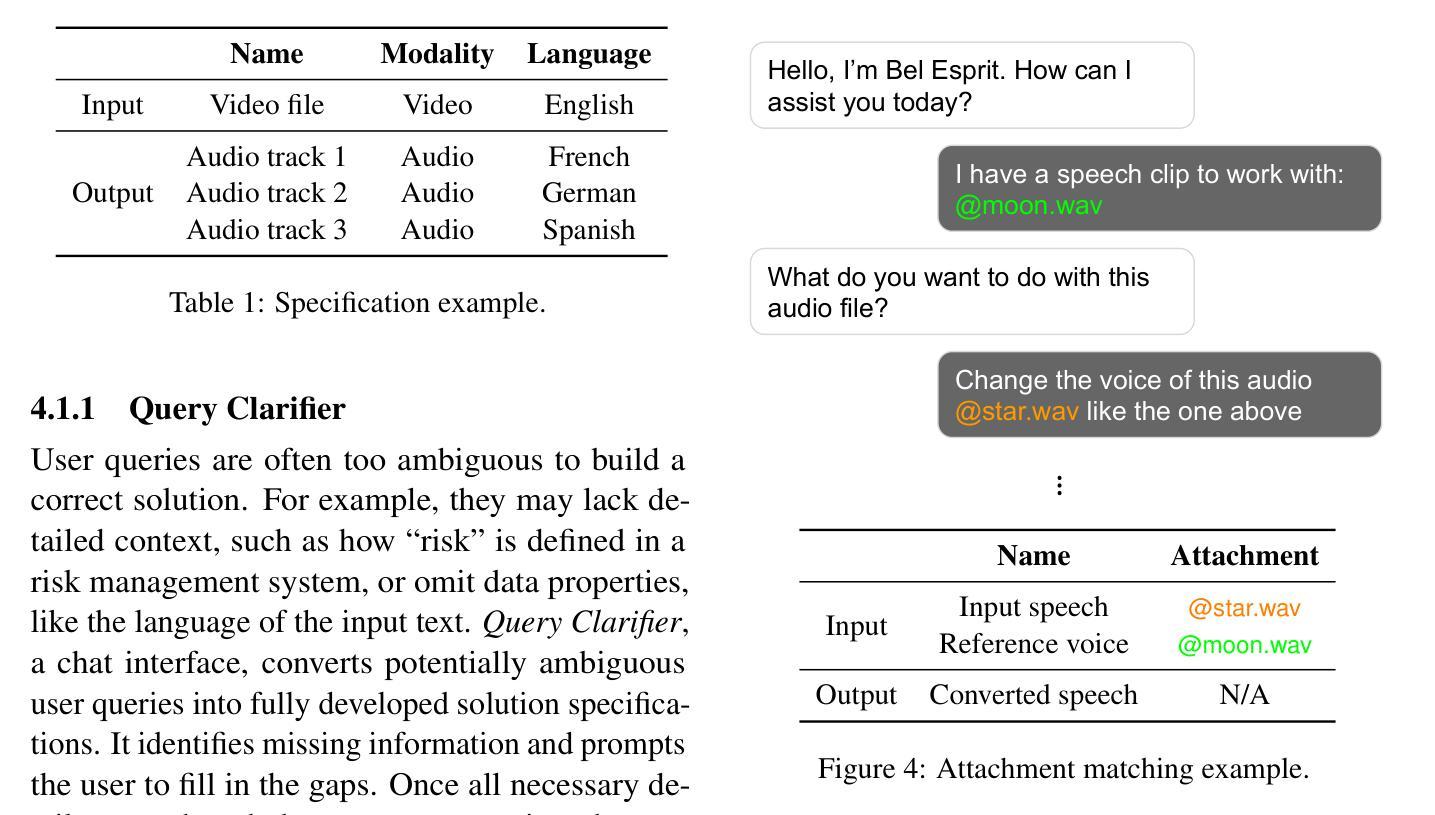
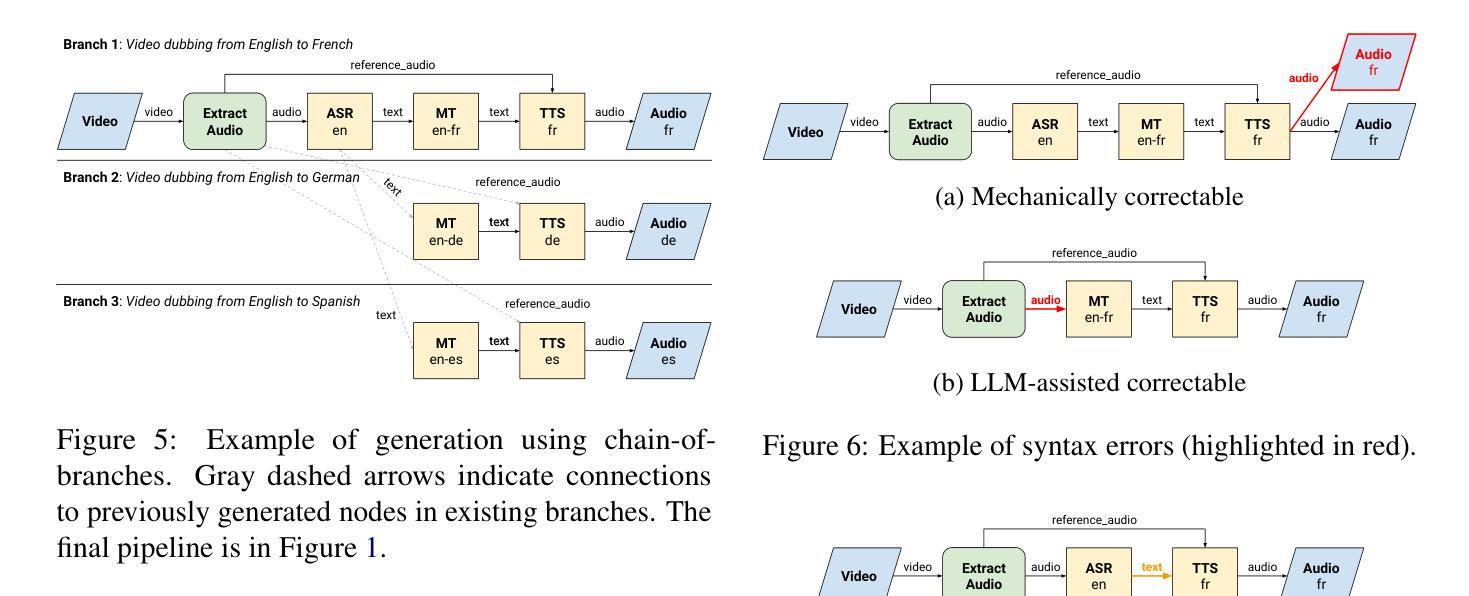
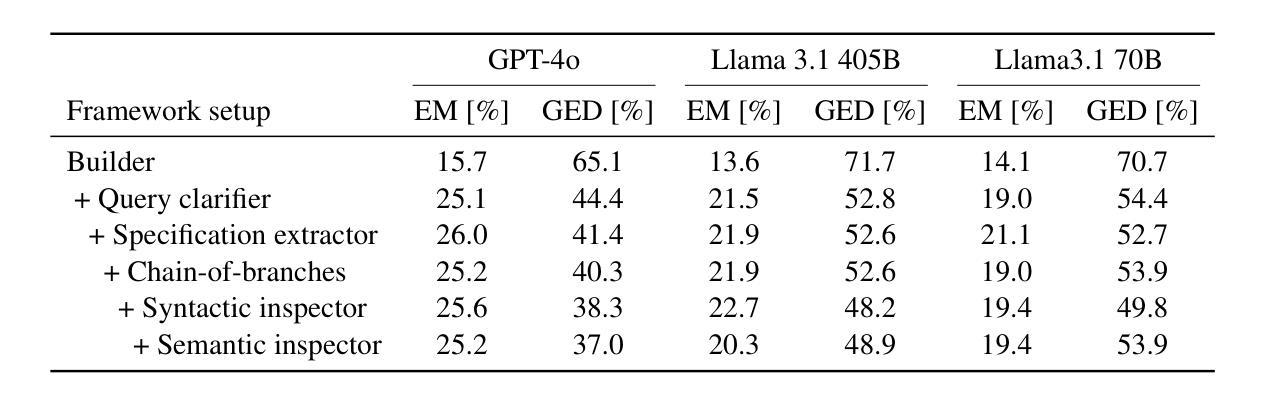
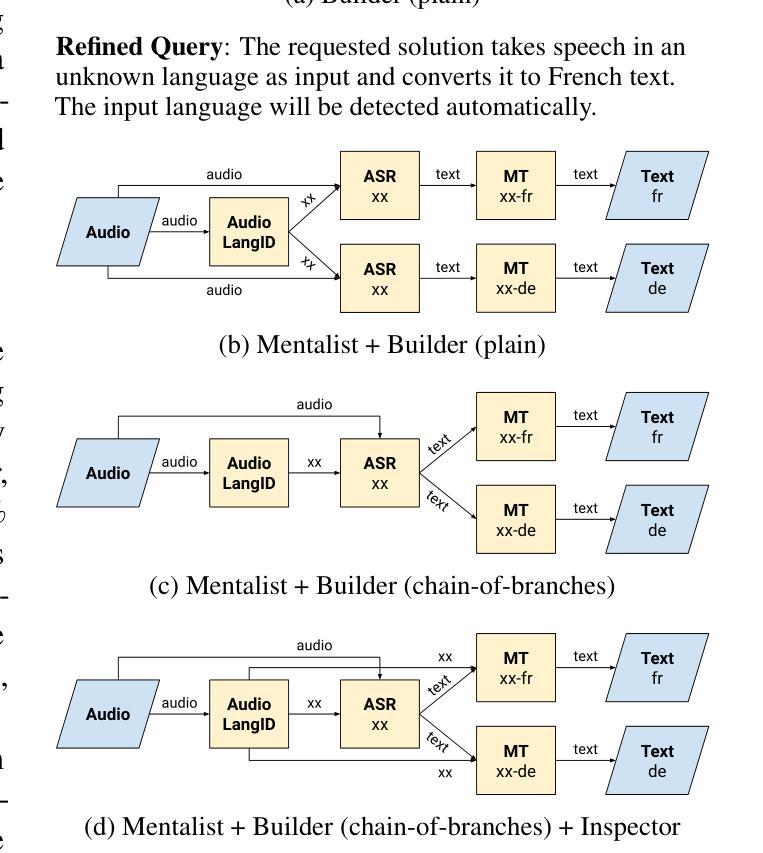
Bel Esprit: Multi-Agent Framework for Building AI Model Pipelines
Authors:Yunsu Kim, AhmedElmogtaba Abdelaziz, Thiago Castro Ferreira, Mohamed Al-Badrashiny, Hassan Sawaf
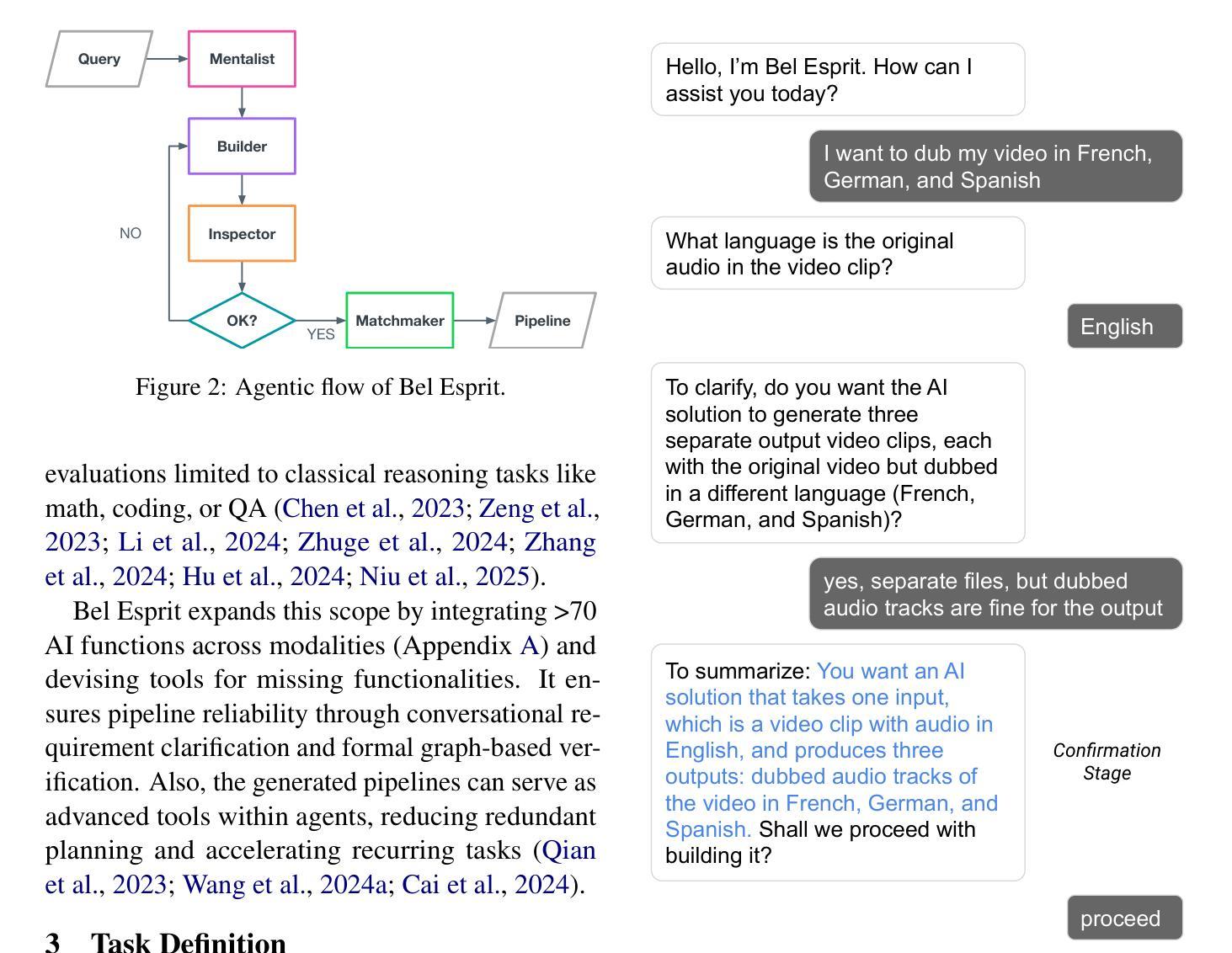
As the demand for artificial intelligence (AI) grows to address complex real-world tasks, single models are often insufficient, requiring the integration of multiple models into pipelines. This paper introduces Bel Esprit, a conversational agent designed to construct AI model pipelines based on user-defined requirements. Bel Esprit employs a multi-agent framework where subagents collaborate to clarify requirements, build, validate, and populate pipelines with appropriate models. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this framework in generating pipelines from ambiguous user queries, using both human-curated and synthetic data. A detailed error analysis highlights ongoing challenges in pipeline construction. Bel Esprit is available for a free trial at https://belesprit.aixplain.com.
随着人工智能需求日益增长,为了解决复杂的现实世界任务,单一模型通常不足够,需要多个模型的集成到管道中。本文介绍了Bel Esprit,这是一个对话代理,旨在根据用户定义的需求构建人工智能模型管道。Bel Esprit采用多代理框架,其中子代理相互协作以澄清需求、构建、验证并使用适当的模型填充管道。我们展示了该框架在处理模糊用户查询时生成管道的有效性,使用人工整理和合成数据。详细的误差分析突出了管道构建中的持续挑战。Bel Esprit可在https://belesprit.aixplain.com免费试用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 System Demonstrations
Summary
人工智能需求日益增长,单一模型难以满足复杂任务,需构建多模型管道。本文介绍了一款基于用户定义需求构建AI模型管道的对谈代理Bel Esprit。它采用多代理框架,子代理协同工作以澄清需求、构建、验证和填充管道模型。通过人类编纂和合成数据展示其生成管道的有效性,并从模糊的用户查询中构建管道。现有挑战和详细误差分析。Bel Esprit可免费试用:https://belesprit.aixplain.com。
Key Takeaways
- AI需求增长,单一模型难以满足复杂任务,需要构建多模型管道。
- Bel Esprit是一个对话代理,可以根据用户需求构建AI模型管道。
- 采用多代理框架,子代理协同工作以完成管道构建的不同阶段。
- 通过人类编纂和合成数据展示其生成管道的有效性。
- Bel Esprit能够从模糊的用户查询中构建管道。
- 提供了一个详细的误差分析,展示了在管道构建方面存在的挑战。
点此查看论文截图

A new approach to principal-agent problems with volatility control
Authors:Alessandro Chiusolo, Emma Hubert
The recent work by Cvitani'c, Possama"i, and Touzi (2018) [9] presents a general approach for continuous-time principal-agent problems, through dynamic programming and second-order backward stochastic differential equations (BSDEs). In this paper, we provide an alternative formulation of the principal-agent problem, which can be solved simply by relying on the theory of BSDEs. This reformulation is strongly inspired by an important remark in [9], namely that if the principal observes the output process in continuous-time, she can compute its quadratic variation pathwise. While in [9], this information is used in the contract, our reformulation consists in assuming that the principal could directly control this process, in a first-best' fashion. The resolution approach for this alternative problem actually follows the line of the so-called Sannikov’s trick’ in the literature on continuous-time principal-agent problems, as originally introduced by Sannikov (2008) [28]. We then show that the solution to this first-best' formulation is identical to the solution of the original problem. More precisely, using the contract form introduced in [9] as penalisation contracts’, we highlight that this first-best' scenario can be achieved even if the principal cannot directly control the quadratic variation. Nevertheless, we do not have to rely on the theory of 2BSDEs to prove that such contracts are optimal, as their optimality is ensured by showing that the first-best’ scenario is achieved. We believe that this more straightforward approach to solve continuous-time principal-agent problems with volatility control will facilitate the dissemination of these problems across many fields, and its extension to even more intricate problems.
Cvitanić、Possama”i和Touzi(2018年)[9]的最新工作通过动态规划和二阶反向随机微分方程(BSDEs)提出了一种解决连续时间委托代理问题的一般方法。在本文中,我们提供了委托代理问题的另一种表述形式,它可以通过依赖BSDEs的理论来简单解决。这种重新表述深受[9]中的重要评论的启发,即如果委托人能够连续观察输出过程,那么他们可以计算其二次变异路径。虽然[9]中的信息用于合同,我们的重新表述是假设委托人可以直接以“最优方式”控制这一过程。对于此替代问题的解决方案实际上遵循了连续时间委托代理问题文献中所谓的“Sannikov技巧”,这一技巧最初由Sannikov(2008)[28]提出。然后我们证明了这种“最优方式”的解与原始问题的解是相同的。更确切地说,我们使用在[9]中引入的合同形式作为“惩罚合同”,我们强调即使委托人不能直接控制二次变异,也可以实现这种“最优方式”的情形。但是,我们不必依赖BSDEs的理论来证明这些合同的优化性,因为它们的优化性是通过证明实现了“最优方式”的情形来确保的。我们相信,这种更直接的方法来解决具有波动性控制的连续时间委托代理问题将促进这些问题的跨领域传播,以及其扩展到更复杂的问题。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:基于动态规划和二阶反向随机微分方程(BSDEs)的通用方法,解决连续时间主代理问题的一种新的解决方案。它借鉴了现有文献的重要观点,提出了一个新的假设:在连续时间内,主要观察者可以直接控制输出过程,这种方法更简洁且可以直接通过最优化的原理得到合约设计结果,它提高了理解连续性问题的简单性和透彻性,可以适用于更复杂的问题和不同的应用场景。简化建模可以更方便理解多种情况下个体之间的博弈和决策过程。同时这种方法的提出,也将促进主代理问题在更多领域的应用和发展。我们相信这种解决连续时间主代理问题的新方法将在未来的研究中发挥重要作用。这个理论的发展将为其他相关领域的研究者带来极大的便利和启发。
Key Takeaways:
- 该研究提出了一种解决连续时间主代理问题的新方法,通过借鉴现有文献中的观点,并采用了基于二阶反向随机微分方程的理论框架进行建模和分析。通过假设主要观察者可以直接控制输出过程的方式简化建模过程。这有助于更好地理解连续时间内的决策过程。
点此查看论文截图