⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-17 更新
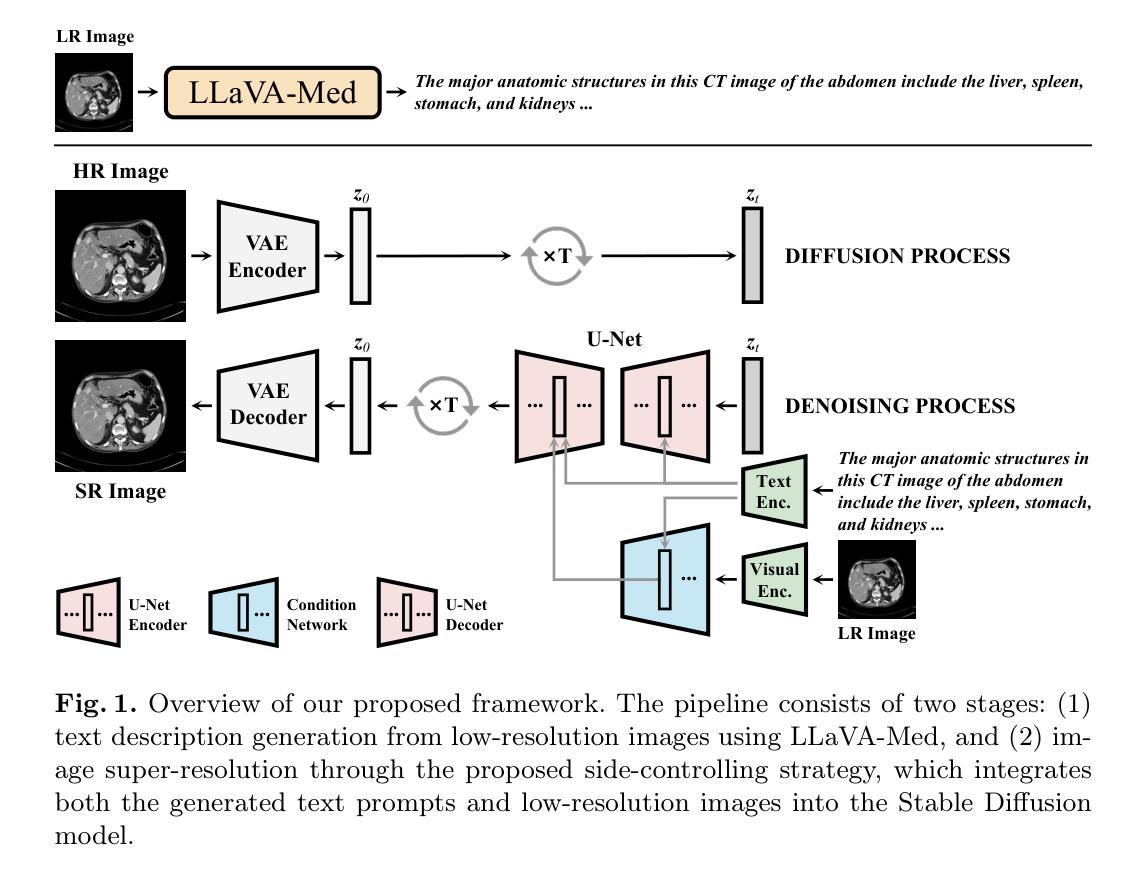
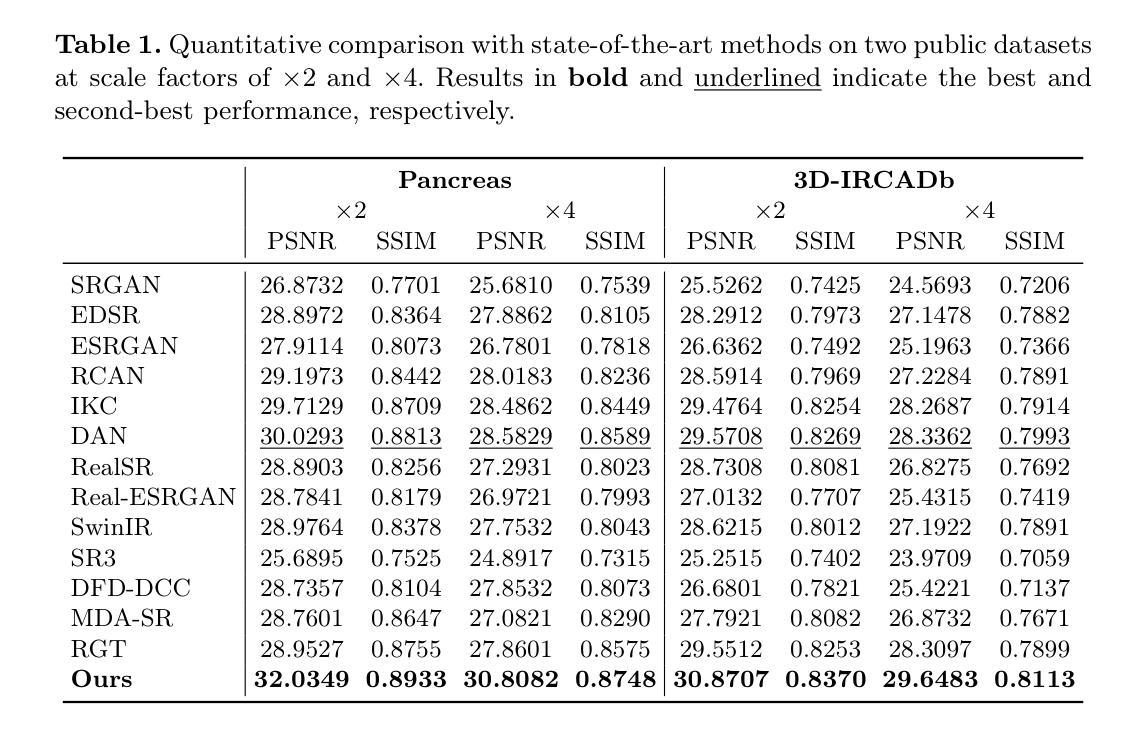
Taming Stable Diffusion for Computed Tomography Blind Super-Resolution
Authors:Chunlei Li, Yilei Shi, Haoxi Hu, Jingliang Hu, Xiao Xiang Zhu, Lichao Mou
High-resolution computed tomography (CT) imaging is essential for medical diagnosis but requires increased radiation exposure, creating a critical trade-off between image quality and patient safety. While deep learning methods have shown promise in CT super-resolution, they face challenges with complex degradations and limited medical training data. Meanwhile, large-scale pre-trained diffusion models, particularly Stable Diffusion, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in synthesizing fine details across various vision tasks. Motivated by this, we propose a novel framework that adapts Stable Diffusion for CT blind super-resolution. We employ a practical degradation model to synthesize realistic low-quality images and leverage a pre-trained vision-language model to generate corresponding descriptions. Subsequently, we perform super-resolution using Stable Diffusion with a specialized controlling strategy, conditioned on both low-resolution inputs and the generated text descriptions. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms existing approaches, demonstrating its potential for achieving high-quality CT imaging at reduced radiation doses. Our code will be made publicly available.
高分辨率计算机断层扫描(CT)成像对于医学诊断至关重要,但需要进行较高的辐射暴露,因此需要在图像质量和患者安全之间进行权衡。虽然深度学习方法在CT超分辨率方面显示出潜力,但它们面临着复杂的退化和有限的医学训练数据的挑战。与此同时,大规模预训练的扩散模型,特别是Stable Diffusion,在各种视觉任务中合成精细细节方面表现出了惊人的能力。受此启发,我们提出了一种新型框架,该框架将Stable Diffusion适应于CT盲超分辨率。我们采用实用的退化模型来合成逼真的低质量图像,并利用预训练的视觉语言模型生成相应的描述。随后,我们使用稳定扩散进行超分辨率处理,并采用特殊的控制策略,该策略基于低分辨率输入和生成的文本描述进行条件处理。大量实验表明,我们的方法优于现有方法,展现出在降低辐射剂量下实现高质量CT成像的潜力。我们的代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了在医学诊断中高分辨率计算机断层扫描(CT)成像的重要性与其对患者辐射暴露的增加之间的矛盾。深度学习虽然在CT超分辨率技术中展现出潜力,但在处理复杂退化和有限医疗训练数据时面临挑战。受大型预训练扩散模型,特别是Stable Diffusion在各项视觉任务中合成精细细节方面的出色表现的启发,本文提出了一种适应于CT盲超分辨率的新型框架。该框架采用实用退化模型合成逼真的低质量图像,并利用预训练的视觉语言模型生成相应描述。随后,使用Stable Diffusion进行超分辨率处理,采用专门的控制策略,以低分辨率输入和生成的文本描述为条件。实验表明,该方法优于现有技术,有望在降低辐射剂量的同时实现高质量的CT成像。
关键见解
- 高分辨率CT成像在医学诊断中至关重要,但会增加患者辐射暴露,需要在图像质量和患者安全之间取得平衡。
- 深度学习在CT超分辨率技术中的应用虽具潜力,但处理复杂退化和有限医疗训练数据时面临挑战。
- 大型预训练扩散模型,如Stable Diffusion,在合成精细视觉细节方面表现出色。
- 本文提出了一种新型框架,适应于CT盲超分辨率,结合实用退化模型、预训练视觉语言模型和Stable Diffusion。
- 该框架通过合成低质量图像和生成相应描述,利用Stable Diffusion进行超分辨率处理。
- 实验结果表明,该方法优于现有技术,有望提高CT成像质量并降低辐射剂量。
- 该研究的代码将公开发布。
点此查看论文截图

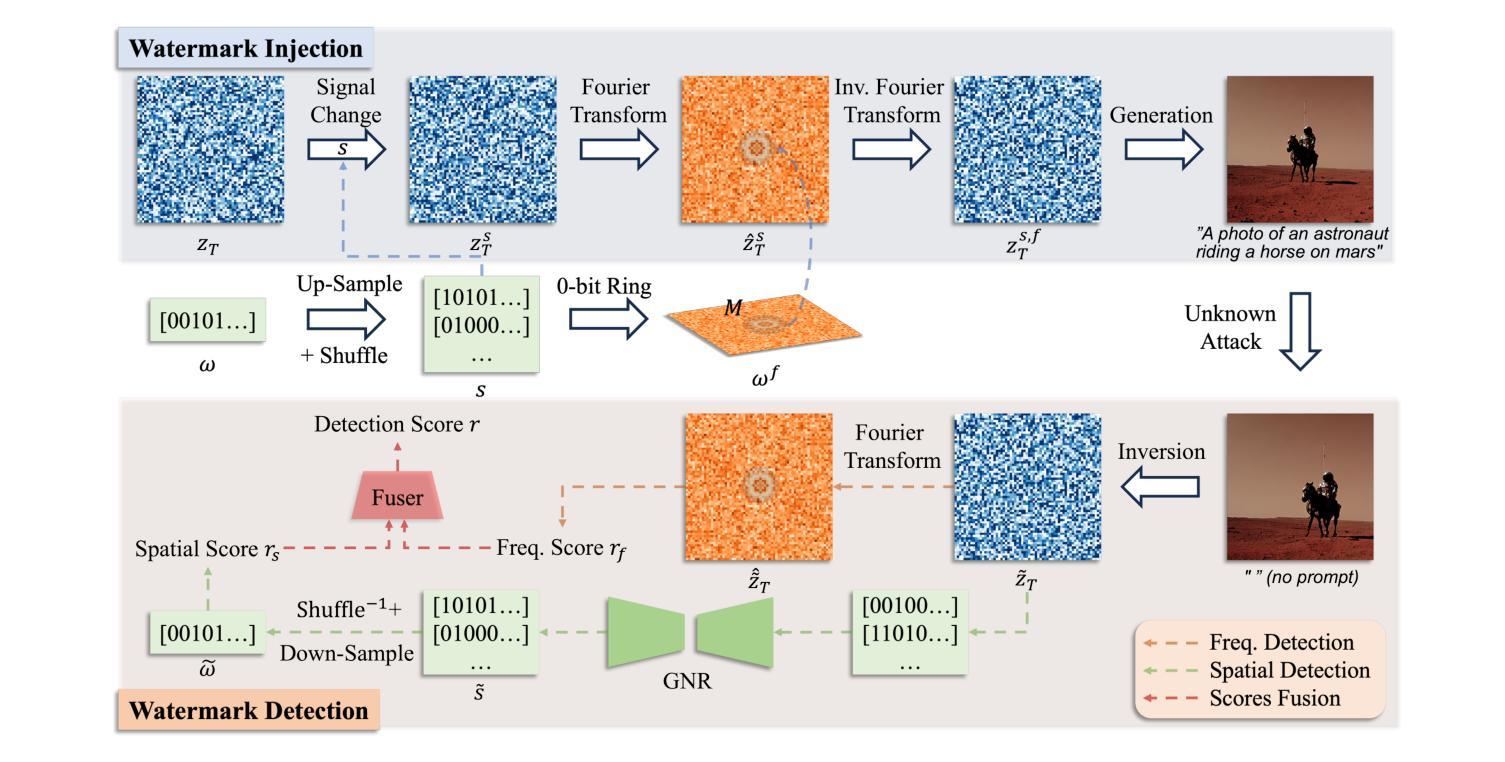
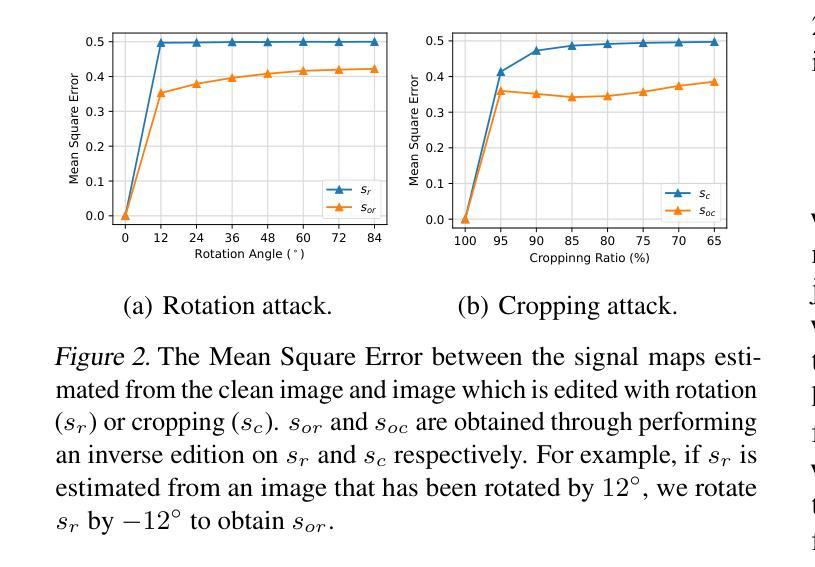
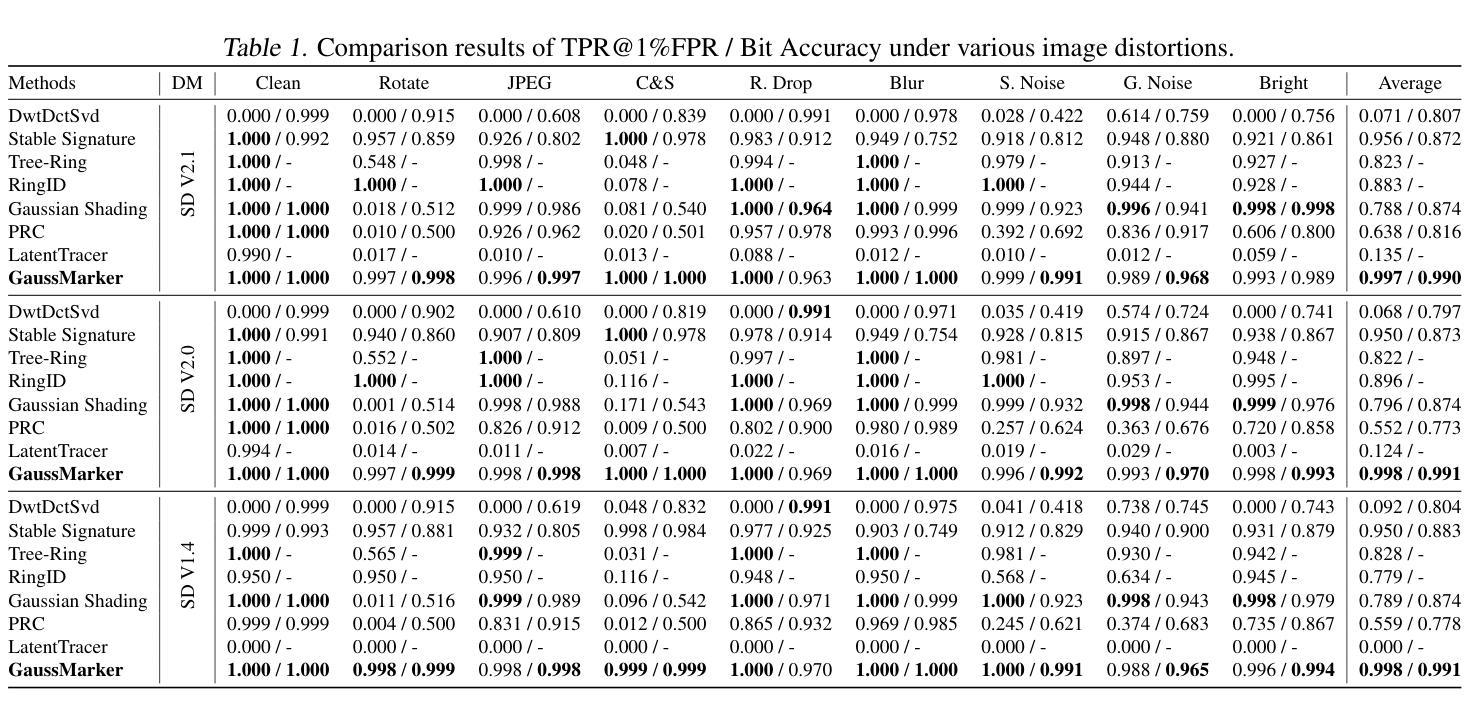
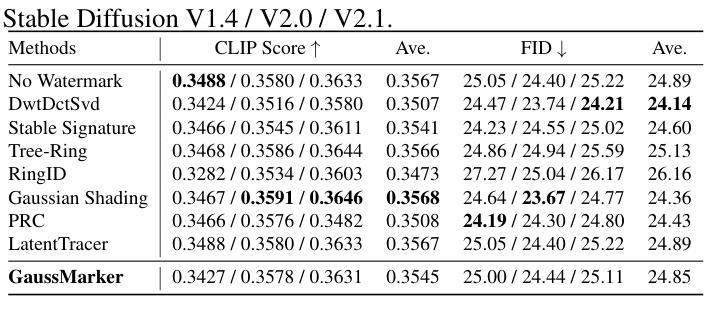
GaussMarker: Robust Dual-Domain Watermark for Diffusion Models
Authors:Kecen Li, Zhicong Huang, Xinwen Hou, Cheng Hong
As Diffusion Models (DM) generate increasingly realistic images, related issues such as copyright and misuse have become a growing concern. Watermarking is one of the promising solutions. Existing methods inject the watermark into the single-domain of initial Gaussian noise for generation, which suffers from unsatisfactory robustness. This paper presents the first dual-domain DM watermarking approach using a pipelined injector to consistently embed watermarks in both the spatial and frequency domains. To further boost robustness against certain image manipulations and advanced attacks, we introduce a model-independent learnable Gaussian Noise Restorer (GNR) to refine Gaussian noise extracted from manipulated images and enhance detection robustness by integrating the detection scores of both watermarks. GaussMarker efficiently achieves state-of-the-art performance under eight image distortions and four advanced attacks across three versions of Stable Diffusion with better recall and lower false positive rates, as preferred in real applications.
随着扩散模型(DM)生成的图像越来越真实,版权和误用等相关问题已成为越来越大的关注点。水印是一种有前途的解决方案。现有方法将水印注入初始高斯噪声的单一领域中进行生成,这导致鲁棒性不佳。本文提出了第一种双域DM水印方法,使用流水线注入器在空间和频率两个领域中持续嵌入水印。为了进一步增强对某些图像操作和高级攻击的鲁棒性,我们引入了一个模型独立的可学习高斯噪声修复器(GNR),以改进从操作过的图像中提取的高斯噪声,并通过整合两个水印的检测分数来提高检测稳健性。GaussMarker在三种版本的Stable Diffusion下,在八种图像失真和四种高级攻击中实现了卓越的性能,具有更好的召回率和更低的误报率,适合在真实应用中使用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICML 2025
Summary
扩散模型(DM)生成的图像越来越逼真,相关的版权和滥用问题逐渐成为关注的焦点。水印是一种有前景的解决方案。现有方法将水印注入初始高斯噪声的单域生成,其稳健性并不理想。本文首次提出双域DM水印方法,采用管道注入器在空间和频率域中持续嵌入水印。为提高对特定图像操作和高级攻击的稳健性,引入模型无关的可学习高斯噪声修复器(GNR),修复从操作图像中提取的高斯噪声,并通过整合两个水印的检测分数提高检测稳健性。GaussMarker在三种版本的Stable Diffusion下,面对八种图像失真和四种高级攻击,实现了高效性能,召回率更高,误报率更低,适用于实际应用。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DM)生成的图像日益逼真,引发版权和滥用问题的关注。
- 水印是解决这些问题的有前景的方案。
- 现有方法在水印嵌入单域的高斯噪声生成中存在稳健性问题。
- 本文首次提出双域DM水印方法,同时嵌入空间和频率域。
- 为提高稳健性,引入模型无关的可学习高斯噪声修复器(GNR)。
- GaussMarker在多种图像失真和高级攻击下表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

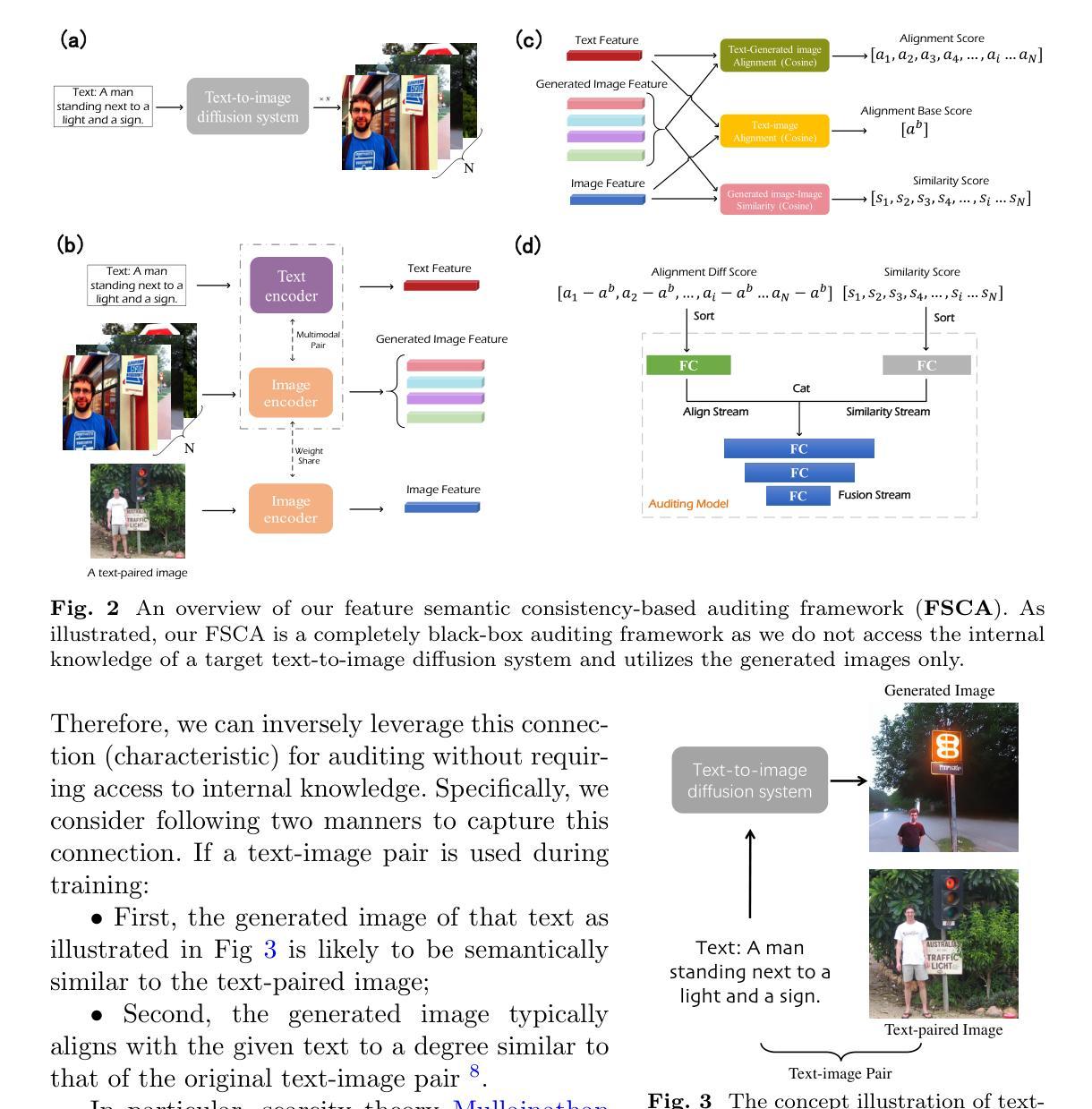
Auditing Data Provenance in Real-world Text-to-Image Diffusion Models for Privacy and Copyright Protection
Authors:Jie Zhu, Leye Wang
Text-to-image diffusion model since its propose has significantly influenced the content creation due to its impressive generation capability. However, this capability depends on large-scale text-image datasets gathered from web platforms like social media, posing substantial challenges in copyright compliance and personal privacy leakage. Though there are some efforts devoted to explore approaches for auditing data provenance in text-to-image diffusion models, existing work has unrealistic assumptions that can obtain model internal knowledge, e.g., intermediate results, or the evaluation is not reliable. To fill this gap, we propose a completely black-box auditing framework called Feature Semantic Consistency-based Auditing (FSCA). It utilizes two types of semantic connections within the text-to-image diffusion model for auditing, eliminating the need for access to internal knowledge. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our FSCA framework, we perform extensive experiments on LAION-mi dataset and COCO dataset, and compare with eight state-of-the-art baseline approaches. The results show that FSCA surpasses previous baseline approaches across various metrics and different data distributions, showcasing the superiority of our FSCA. Moreover, we introduce a recall balance strategy and a threshold adjustment strategy, which collectively allows FSCA to reach up a user-level accuracy of 90% in a real-world auditing scenario with only 10 samples/user, highlighting its strong auditing potential in real-world applications. Our code is made available at https://github.com/JiePKU/FSCA.
自从文本到图像的扩散模型提出以来,由于其令人印象深刻的生成能力,它显著影响了内容创作。然而,这种能力依赖于从社交平台如社交媒体等网络上收集的大规模文本图像数据集,这带来了版权合规和个人隐私泄露的实质挑战。尽管有了一些努力来探索审计文本到图像扩散模型中数据来源的方法,但现有工作在假设能够获得模型内部知识(如中间结果)方面并不现实,或者评估结果不可靠。为了填补这一空白,我们提出了一种名为基于特征语义一致性的审计(FSCA)的完全黑箱审计框架。它利用文本到图像扩散模型中的两种语义连接来进行审计,无需访问内部知识。为了证明我们的FSCA框架的有效性,我们在LAION-mi数据集和COCO数据集上进行了大量实验,并与八种最先进的基线方法进行了比较。结果表明,FSCA在各项指标和不同数据分布方面都超越了之前的基线方法,展示了我们的FSCA的优越性。此外,我们引入了一种召回平衡策略和阈值调整策略,共同使FSCA在只有10个样本/用户的情况下,真实世界的审计场景中达到了90%的用户级准确率,凸显了其在真实世界应用中的强大审计潜力。我们的代码可在https://github.com/JiePKU/FSCA上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review; A user-level accuracy of 90% in a real-world auditing scenario
Summary
文本转图像扩散模型的影响显著,但其生成能力依赖于从社交平台如社交媒体等搜集的大规模数据集,存在版权合规和个人隐私泄露的挑战。针对现有审计方法的不切实际假设和评估不可靠问题,我们提出了基于特征语义一致性的审计框架FSCA。它在无需访问模型内部知识的情况下,利用两种语义连接进行审计。实验证明,FSCA在多种指标和不同数据分布上超越了八种最新基线方法,并引入了召回平衡策略和阈值调整策略,在真实世界审计场景中实现了用户级90%的准确率,显示出其在真实世界应用中的强大审计潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 文本转图像扩散模型生成能力依赖于大规模数据集,引发版权和个人隐私泄露问题。
- 目前审计数据溯源的方法存在不现实的假设或评估不可靠的问题。
- 提出的FSCA框架无需访问模型内部知识,利用两种语义连接进行审计。
- 实验证明FSCA在各种指标和数据分布上优于其他方法。
- FSCA框架引入了召回平衡策略和阈值调整策略以提高审计准确性。
- 在真实世界审计场景中,FSCA达到了用户级90%的准确率。
点此查看论文截图

Score-based Generative Diffusion Models to Synthesize Full-dose FDG Brain PET from MRI in Epilepsy Patients
Authors:Jiaqi Wu, Jiahong Ouyang, Farshad Moradi, Mohammad Mehdi Khalighi, Greg Zaharchuk
Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET to evaluate patients with epilepsy is one of the most common applications for simultaneous PET/MRI, given the need to image both brain structure and metabolism, but is suboptimal due to the radiation dose in this young population. Little work has been done synthesizing diagnostic quality PET images from MRI data or MRI data with ultralow-dose PET using advanced generative AI methods, such as diffusion models, with attention to clinical evaluations tailored for the epilepsy population. Here we compared the performance of diffusion- and non-diffusion-based deep learning models for the MRI-to-PET image translation task for epilepsy imaging using simultaneous PET/MRI in 52 subjects (40 train/2 validate/10 hold-out test). We tested three different models: 2 score-based generative diffusion models (SGM-Karras Diffusion [SGM-KD] and SGM-variance preserving [SGM-VP]) and a Transformer-Unet. We report results on standard image processing metrics as well as clinically relevant metrics, including congruency measures (Congruence Index and Congruency Mean Absolute Error) that assess hemispheric metabolic asymmetry, which is a key part of the clinical analysis of these images. The SGM-KD produced the best qualitative and quantitative results when synthesizing PET purely from T1w and T2 FLAIR images with the least mean absolute error in whole-brain specific uptake value ratio (SUVR) and highest intraclass correlation coefficient. When 1% low-dose PET images are included in the inputs, all models improve significantly and are interchangeable for quantitative performance and visual quality. In summary, SGMs hold great potential for pure MRI-to-PET translation, while all 3 model types can synthesize full-dose FDG-PET accurately using MRI and ultralow-dose PET.
氟脱氧葡萄糖(FDG)PET在评估癫痫患者方面的应用是最常见的PET/MRI同步应用之一,由于需要同时成像脑结构和代谢。但是,由于年轻人群中的辐射剂量问题,其效果并不理想。目前鲜有研究利用先进的生成式人工智能方法(如扩散模型)合成诊断质量的PET图像或结合MRI数据和超低剂量PET数据的扩散模型,并针对癫痫人群进行临床评估。在这里,我们比较了基于扩散和非扩散的深度学习方法在MRI到PET图像转换任务中的表现,该任务使用同步PET/MRI对52名癫痫患者(训练集40人,验证集2人,保留测试集10人)进行成像。我们测试了三种不同的模型:两种基于分数的生成扩散模型(SGM-Karras扩散[SGM-KD]和SGM方差保持[SGM-VP])以及一个Transformer-Unet模型。我们报告了标准图像处理指标的结果,以及具有临床意义的指标,包括评估半球代谢不对称性的一致性度量(一致指数和一致性平均绝对误差),这是这些图像临床分析的关键部分。当仅使用T1w和T2 FLAIR图像合成PET时,SGM-KD产生了最佳的主观和客观结果,其在全脑特定摄取值比率(SUVR)中的平均绝对误差最小,并且同类相关系数最高。当包含1%的低剂量PET图像时,所有模型的定量性能和视觉质量均得到显著提高并可互换使用。总之,SGMs在纯MRI到PET转换方面显示出巨大潜力,而三种模型类型都可以利用MRI和超低剂量PET准确合成全剂量FDG-PET图像。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究使用深度学习模型,包括扩散模型和非扩散模型,对MRI-to-PET图像转换任务进行了对比研究。实验针对癫痫患者群体,使用了包含MRI数据和超低剂量PET数据的样本数据集。实验结果表明,基于SGM-KD模型的图像合成效果最佳,具有最小的平均绝对误差和最高的评分一致性。当包含超低剂量PET数据时,所有模型的定量性能和视觉质量均有显著提高。扩散模型在纯MRI到PET的转换方面展现出巨大潜力,能够合成高质量的PET图像。这对于减少癫痫患者的辐射剂量并改善诊断图像质量具有重要意义。
关键见解
- 扩散模型和非扩散模型在MRI到PET图像转换任务中进行了比较研究。
- 实验针对癫痫患者群体进行,涉及多种深度学习模型的性能评估。
- SGM-KD模型在合成PET图像方面表现出最佳性能,具有最小的平均绝对误差和最高的一致性评分。
- 当结合超低剂量PET数据时,所有模型的性能均显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

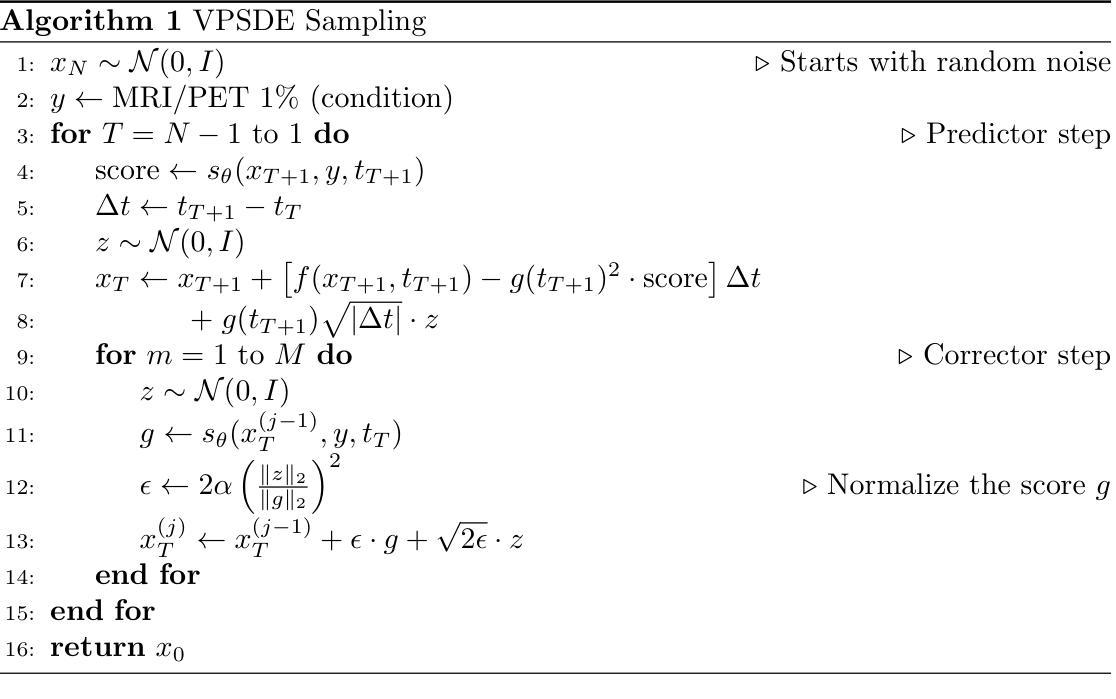
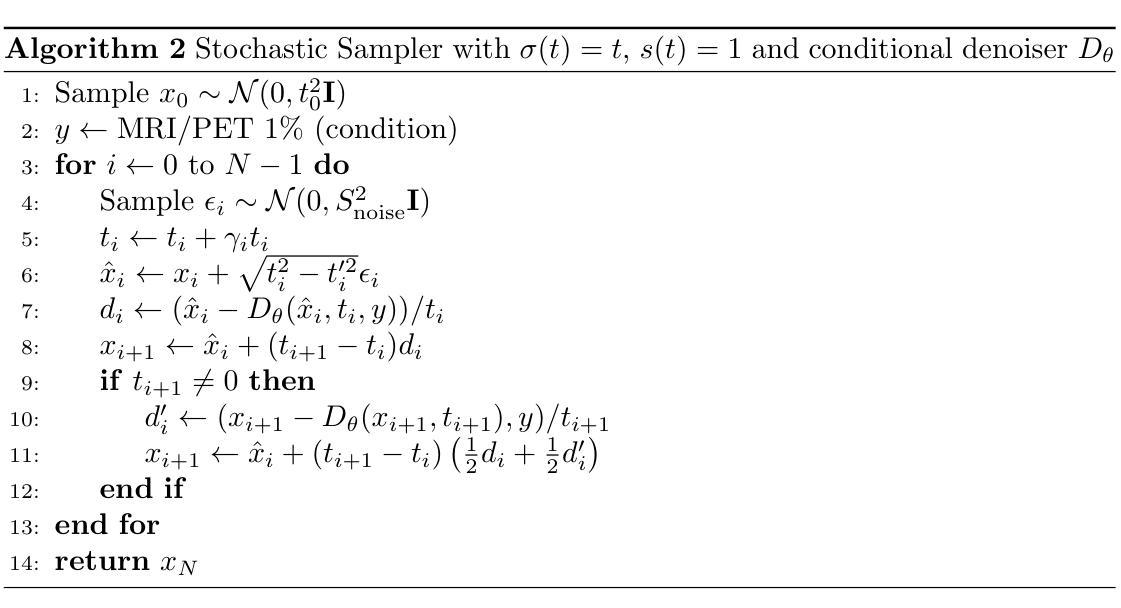
DiffPR: Diffusion-Based Phase Reconstruction via Frequency-Decoupled Learning
Authors:Yi Zhang
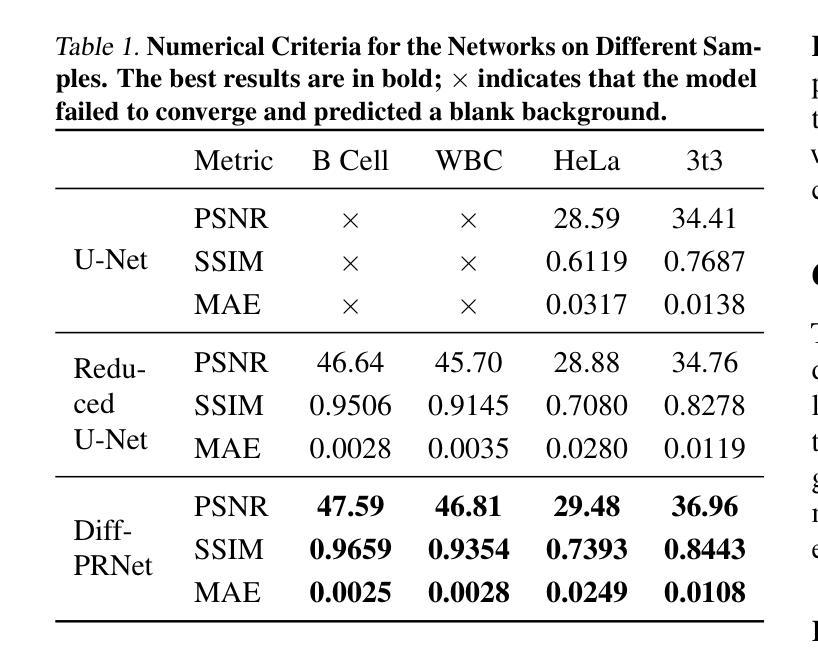
Oversmoothing remains a persistent problem when applying deep learning to off-axis quantitative phase imaging (QPI). End-to-end U-Nets favour low-frequency content and under-represent fine, diagnostic detail. We trace this issue to spectral bias and show that the bias is reinforced by high-level skip connections that feed high-frequency features directly into the decoder. Removing those deepest skips thus supervising the network only at a low resolution significantly improves generalisation and fidelity. Building on this insight, we introduce DiffPR, a two-stage frequency-decoupled framework. Stage 1: an asymmetric U-Net with cancelled high-frequency skips predicts a quarter-scale phase map from the interferogram, capturing reliable low-frequency structure while avoiding spectral bias. Stage 2: the upsampled prediction, lightly perturbed with Gaussian noise, is refined by an unconditional diffusion model that iteratively recovers the missing high-frequency residuals through reverse denoising. Experiments on four QPI datasets (B-Cell, WBC, HeLa, 3T3) show that DiffPR outperforms strong U-Net baselines, boosting PSNR by up to 1.1 dB and reducing MAE by 11 percent, while delivering markedly sharper membrane ridges and speckle patterns. The results demonstrate that cancelling high-level skips and delegating detail synthesis to a diffusion prior is an effective remedy for the spectral bias that limits conventional phase-retrieval networks.
在深光学偏轴定量相位成像(QPI)中应用深度学习时,过平滑仍然是一个持续存在的问题。端到端U-Net倾向于低频内容,并且未能充分表示精细的诊断细节。我们追查这个问题到光谱偏差,并表明这种偏差是由高级跳跃连接所加强的,这些连接直接将高频特征输入解码器。因此,移除最深的跳跃连接,只在低分辨率下监督网络,能显著改进通用性和保真度。基于这一见解,我们引入了DiffPR,这是一个两阶段的频率解耦框架。第一阶段:一个具有取消的高频跳跃的不对称U-Net从干涉图中预测四分之一规模的相位图,捕捉可靠的低频结构,同时避免光谱偏差。第二阶段:通过高斯噪声轻微扰动的上采样预测结果,由无条件扩散模型进行细化,该模型通过反向去噪迭代恢复丢失的高频残差。在四个QPI数据集(B细胞、WBC、HeLa、3T3)上的实验表明,DiffPR优于强大的U-Net基准测试,提高了峰值信噪比(PSNR)高达1.1分贝,降低了平均绝对误差(MAE)11%,同时显著提高了膜脊和斑点模式的清晰度。结果表明,取消高级跳跃并将细节合成委托给扩散先验,是克服限制传统相位检索网络的光谱偏差的有效方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对深度学习在轴外定量相位成像(QPI)中的应用,存在过平滑问题。我们追踪到频谱偏见,并发现高级跳跃连接会强化这一偏见。移除最深层次的跳跃连接,仅在低分辨率下对网络进行监督,能显著提高泛化能力和保真度。基于此,我们引入了DiffPR,一个两阶段的频率解耦框架。第一阶段:一个具有取消高频跳跃的不对称U-Net,从干涉图预测四分之一尺度的相位图,捕捉可靠的低频结构,避免频谱偏见。第二阶段:通过高斯噪声轻微扰动上采样预测值,由无条件扩散模型进行细化,通过反向去噪迭代恢复缺失的高频残差。在四个QPI数据集上的实验表明,DiffPR优于强大的U-Net基准测试,提高了峰值信噪比(PSNR)达1.1分贝,平均绝对误差(MAE)降低11%,同时呈现出更清晰的膜脊和斑点模式。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在轴外定量相位成像中面临过平滑问题。
- 问题根源在于频谱偏见,高级跳跃连接强化了这一偏见。
- 移除高级跳跃连接并只在低分辨率下对网络进行监督,能改善网络泛化能力和保真度。
- 引入了一个两阶段的频率解耦框架DiffPR来解决这一问题。
- 第一阶段预测低频率结构,避免频谱偏见。
- 第二阶段通过扩散模型细化预测结果,恢复高频细节。
点此查看论文截图


MMMG: A Massive, Multidisciplinary, Multi-Tier Generation Benchmark for Text-to-Image Reasoning
Authors:Yuxuan Luo, Yuhui Yuan, Junwen Chen, Haonan Cai, Ziyi Yue, Yuwei Yang, Fatima Zohra Daha, Ji Li, Zhouhui Lian
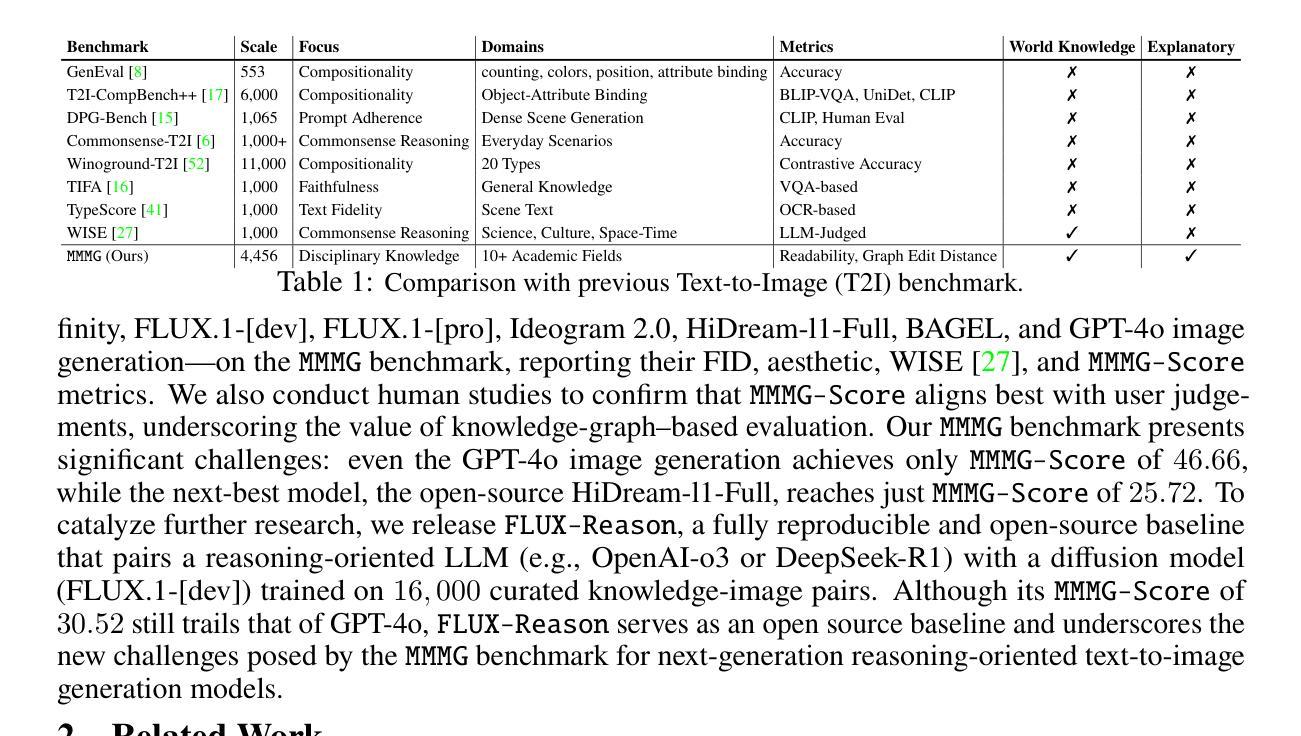
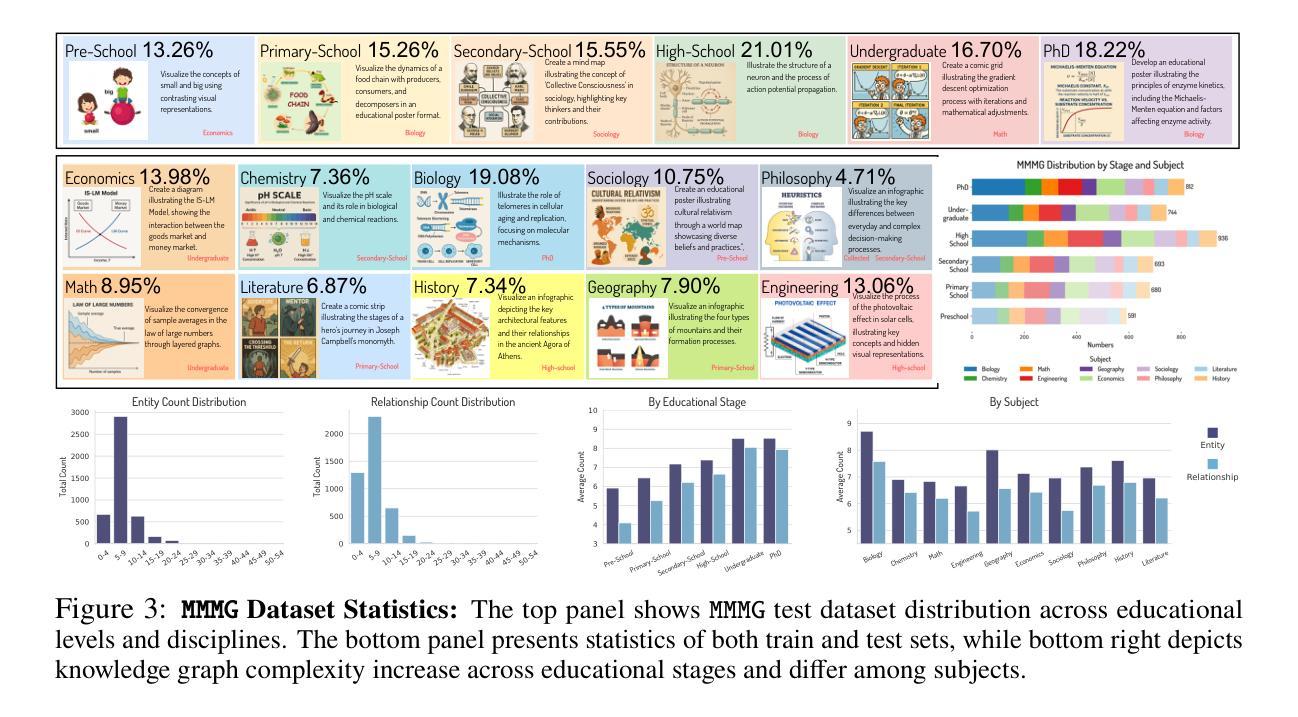
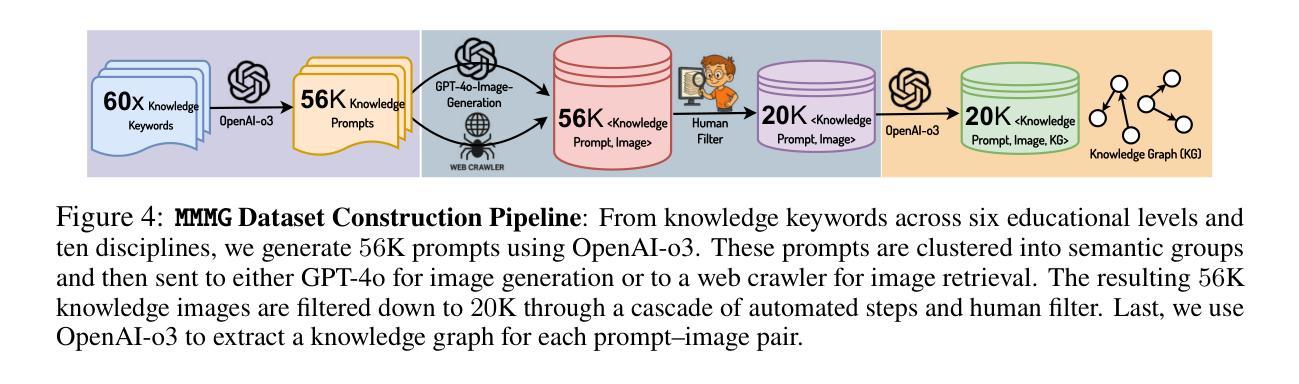
In this paper, we introduce knowledge image generation as a new task, alongside the Massive Multi-Discipline Multi-Tier Knowledge-Image Generation Benchmark (MMMG) to probe the reasoning capability of image generation models. Knowledge images have been central to human civilization and to the mechanisms of human learning – a fact underscored by dual-coding theory and the picture-superiority effect. Generating such images is challenging, demanding multimodal reasoning that fuses world knowledge with pixel-level grounding into clear explanatory visuals. To enable comprehensive evaluation, MMMG offers 4,456 expert-validated (knowledge) image-prompt pairs spanning 10 disciplines, 6 educational levels, and diverse knowledge formats such as charts, diagrams, and mind maps. To eliminate confounding complexity during evaluation, we adopt a unified Knowledge Graph (KG) representation. Each KG explicitly delineates a target image’s core entities and their dependencies. We further introduce MMMG-Score to evaluate generated knowledge images. This metric combines factual fidelity, measured by graph-edit distance between KGs, with visual clarity assessment. Comprehensive evaluations of 16 state-of-the-art text-to-image generation models expose serious reasoning deficits – low entity fidelity, weak relations, and clutter – with GPT-4o achieving an MMMG-Score of only 50.20, underscoring the benchmark’s difficulty. To spur further progress, we release FLUX-Reason (MMMG-Score of 34.45), an effective and open baseline that combines a reasoning LLM with diffusion models and is trained on 16,000 curated knowledge image-prompt pairs.
本文中,我们引入了一项新知识图像生成任务,并伴随推出了大规模多学科多层次知识图像生成基准测试(MMMG),以探测图像生成模型的推理能力。知识图像在人类文明和人类学习机制中占据核心地位,这一事实在双重编码理论和图像优势效应中得到了强调。生成这样的图像具有挑战性,它要求多模态推理,将世界知识与像素级地面融合成清晰的解释性视觉。为了进行全面的评估,MMMG提供了4456个专家验证过的(知识)图像提示对,涵盖10个学科,6个教育水平,以及多样化的知识形式,如图表、图解和思维导图。为了消除评估过程中的混淆复杂性,我们采用统一的知识图谱(KG)表示法。每个知识图谱都明确地勾勒出目标图像的核心实体及其依赖关系。我们还介绍了MMMG评分,以评估生成的知识图像。该指标结合了事实准确性(通过知识图谱之间的图编辑距离来衡量)和视觉清晰度评估。对16款最先进的文本到图像生成模型的全面评估揭示了严重的推理缺陷——实体保真度低、关系弱、杂乱无章——GPT-4o的MMMG评分仅为50.20,突显了基准测试的困难。为了促进进一步的进步,我们发布了FLUX-Reason(MMMG评分为34.45),这是一个有效的开放基线,它结合了推理LLM和扩散模型,并在16000个精选的知识图像提示对上进行了训练。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 85 pages, 70 figures, code: https://github.com/MMMGBench/MMMG, project page: https://mmmgbench.github.io/
Summary
本文引入知识图像生成任务,并推出大规模多学科多级知识图像生成基准测试(MMMG),以检测图像生成模型的推理能力。知识图像在人类文明和机制学习中占据核心地位,生成此类图像需要融合多学科知识,并进行像素级推理。MMMG提供包含十个学科、六个教育水平的专业验证知识图像提示对,并采用统一的知识图谱表示进行综合评估。同时引入MMMG评分来评估生成的知识图像质量,包括事实准确性和视觉清晰度。对现有文本到图像生成模型的全面评估显示存在推理缺陷,GPT-4o得分仅为50.20,凸显该基准的难度。为推进进步,推出有效且开放的基线FLUX-Reason,结合推理大型语言模型和扩散模型,在知识图像提示对上进行训练。
Key Takeaways
- 知识图像生成被引入作为新任务,伴随大规模多学科多级知识图像生成基准测试(MMMG),旨在评估图像生成模型的推理能力。
- 知识图像在人类学习和文明中占据核心地位,生成这类图像需要融合世界知识与像素级推理。
- MMMG提供涵盖10个学科、6个教育水平的专家验证知识图像提示对,并采用统一的知识图谱表示进行评价。
- MMMG评分结合了事实准确性与视觉清晰度的评估,来评价生成的知识图像质量。
- 对现有文本到图像生成模型的全面评估显示存在推理缺陷,强调该基准测试的难度。
- GPT-4o在MMMG评分中的表现不佳,得分为50.20。
点此查看论文截图

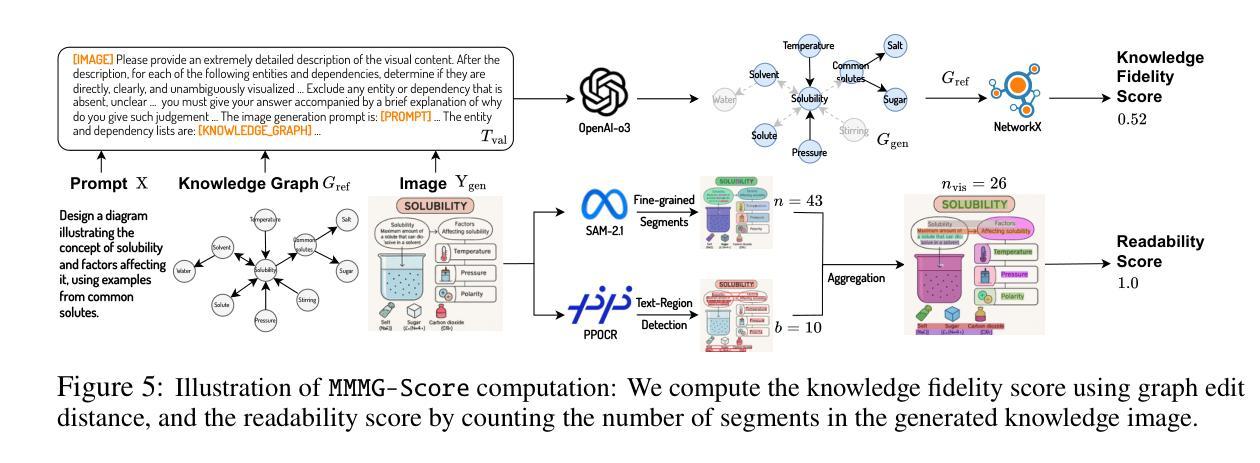
Diffuse Everything: Multimodal Diffusion Models on Arbitrary State Spaces
Authors:Kevin Rojas, Yuchen Zhu, Sichen Zhu, Felix X. -F. Ye, Molei Tao
Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable performance in generating unimodal data across various tasks, including image, video, and text generation. On the contrary, the joint generation of multimodal data through diffusion models is still in the early stages of exploration. Existing approaches heavily rely on external preprocessing protocols, such as tokenizers and variational autoencoders, to harmonize varied data representations into a unified, unimodal format. This process heavily demands the high accuracy of encoders and decoders, which can be problematic for applications with limited data. To lift this restriction, we propose a novel framework for building multimodal diffusion models on arbitrary state spaces, enabling native generation of coupled data across different modalities. By introducing an innovative decoupled noise schedule for each modality, we enable both unconditional and modality-conditioned generation within a single model simultaneously. We empirically validate our approach for text-image generation and mixed-type tabular data synthesis, demonstrating that it achieves competitive performance.
扩散模型在不同任务上生成单模态数据方面表现出了卓越的性能,包括图像、视频和文本生成。相反,通过扩散模型进行多模态数据的联合生成仍在早期探索阶段。现有方法严重依赖于外部预处理协议,如标记器和变分自动编码器,以将各种数据表示协调统一成一种单一的单模态格式。这一过程对编码器和解码器的高准确性提出了苛刻的要求,对于数据有限的应用可能会带来问题。为了消除这一限制,我们提出了一种在任意状态空间上构建多模态扩散模型的新型框架,能够实现不同模态的耦合数据本地生成。通过引入针对每个模态的创新性解耦噪声时间表,我们可以在单个模型中同时实现无条件和模态条件生成。我们通过文本图像生成和混合类型表格数据合成的实证研究验证了我们的方法,证明其性能具有竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICML 2025. Code available at https://github.com/KevinRojas1499/Diffuse-Everything
摘要
扩散模型在各种任务中表现出生成单模态数据的显著性能,包括图像、视频和文本生成。相反,通过扩散模型进行多模态数据的联合生成仍处于探索的早期阶段。现有方法严重依赖于外部预处理协议,如标记器和变分自动编码器,以将不同的数据表示协调成统一、单模态的格式。这一过程对编码器和解码器的高准确性提出了很高的要求,对于数据有限的应用来说可能是个问题。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种在任意状态空间上构建多模态扩散模型的新框架,能够在不同模态之间实现本地生成耦合数据。通过引入针对每种模态的创新解耦噪声调度,我们能够在单个模型中同时实现无条件生成和模态条件生成。我们对文本图像生成和混合类型表数据的合成进行了实证验证,证明了该方法具有竞争力。
关键见解
- 扩散模型在生成单模态数据方面表现出卓越性能,包括图像、视频和文本生成。
- 多模态数据的联合生成通过扩散模型仍处于早期探索阶段。
- 现有方法依赖外部预处理协议来协调不同数据表示,这可能对缺乏数据的应用造成问题。
- 提出了一种新的多模态扩散模型框架,适用于任意状态空间,能够在不同模态之间实现本地生成耦合数据。
- 通过引入针对每种模态的解耦噪声调度,实现了无条件生成和模态条件生成。
- 该方法在文本图像生成和混合类型表数据合成方面进行了实证验证。
- 该方法具有竞争力,能够应对各种生成任务。
点此查看论文截图



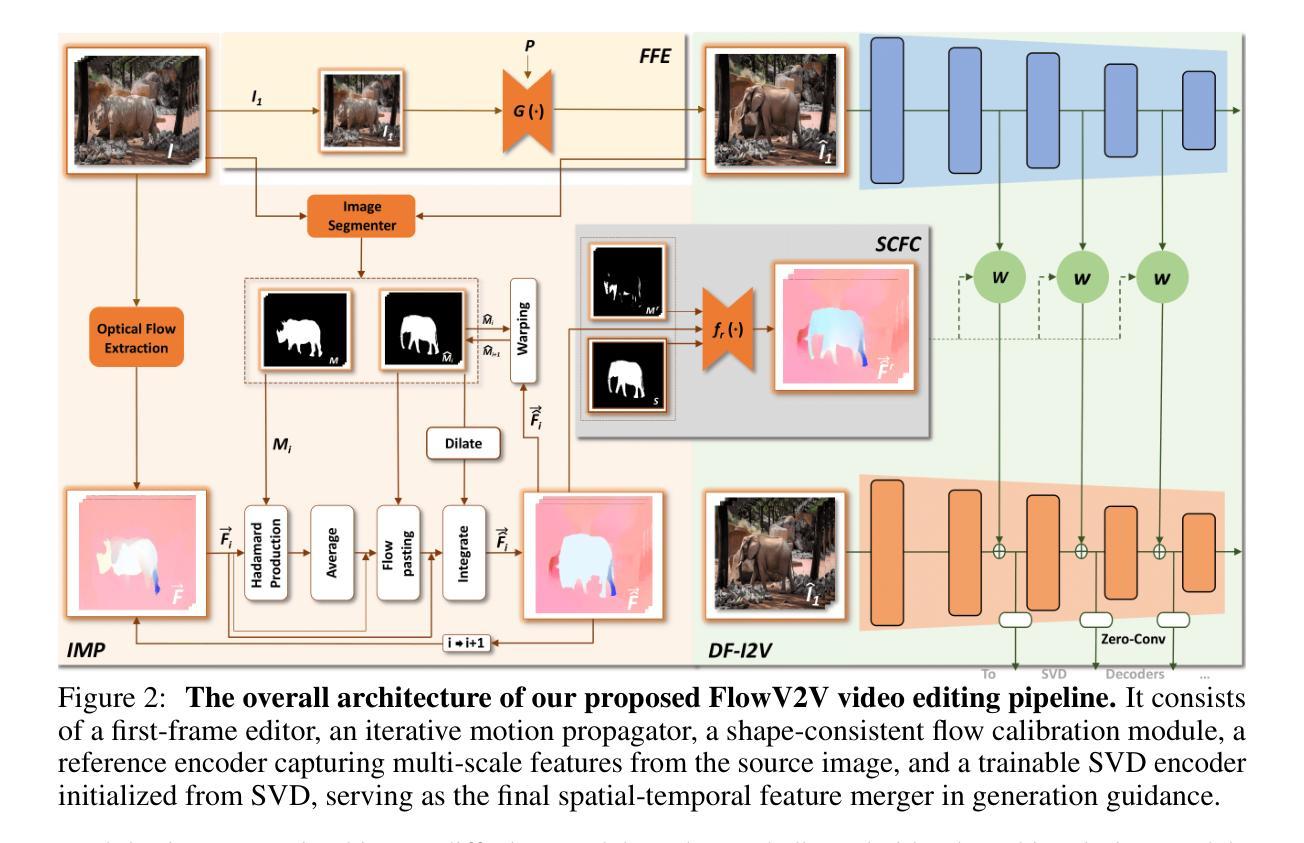
Consistent Video Editing as Flow-Driven Image-to-Video Generation
Authors:Ge Wang, Songlin Fan, Hangxu Liu, Quanjian Song, Hewei Wang, Jinfeng Xu
With the prosper of video diffusion models, down-stream applications like video editing have been significantly promoted without consuming much computational cost. One particular challenge in this task lies at the motion transfer process from the source video to the edited one, where it requires the consideration of the shape deformation in between, meanwhile maintaining the temporal consistency in the generated video sequence. However, existing methods fail to model complicated motion patterns for video editing, and are fundamentally limited to object replacement, where tasks with non-rigid object motions like multi-object and portrait editing are largely neglected. In this paper, we observe that optical flows offer a promising alternative in complex motion modeling, and present FlowV2V to re-investigate video editing as a task of flow-driven Image-to-Video (I2V) generation. Specifically, FlowV2V decomposes the entire pipeline into first-frame editing and conditional I2V generation, and simulates pseudo flow sequence that aligns with the deformed shape, thus ensuring the consistency during editing. Experimental results on DAVIS-EDIT with improvements of 13.67% and 50.66% on DOVER and warping error illustrate the superior temporal consistency and sample quality of FlowV2V compared to existing state-of-the-art ones. Furthermore, we conduct comprehensive ablation studies to analyze the internal functionalities of the first-frame paradigm and flow alignment in the proposed method.
随着视频扩散模型的繁荣,下游应用如视频编辑得到了极大的推动,而且不需要消耗大量的计算成本。在该任务中,一个特别的挑战在于从源视频到编辑视频的动态转移过程,这需要考虑两者之间的形状变形,同时保持生成视频序列的时间一致性。然而,现有方法无法对视频编辑中的复杂运动模式进行建模,并且基本上仅限于对象替换,对于非刚性对象运动的任务,如多对象和人像编辑,却被大大忽视了。在本文中,我们观察到光学流在复杂运动建模中提供了有前景的替代方案,并提出FlowV2V来重新研究视频编辑作为流驱动图像到视频(I2V)生成的任务。具体来说,FlowV2V将整个管道分解为第一帧编辑和条件I2V生成,并模拟与变形形状对齐的伪流序列,从而确保编辑过程中的一致性。在DAVIS-EDIT上的实验结果显示,与现有最先进的模型相比,FlowV2V在DOVER和warping error上分别提高了13.67%和50.66%,证明了其在时间一致性和样本质量方面的优越性。此外,我们还进行了全面的消融研究,分析了第一帧范式和流对齐在所提出的方法中的内部功能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 12 figures
Summary
视频扩散模型的发展极大地推动了视频编辑等下游应用的发展,降低了计算成本。该文针对现有方法在复杂运动模式建模方面的不足,提出了一种基于光学流的FlowV2V模型,用于处理形状变形和时序一致性等挑战。FlowV2V将视频编辑任务分解为帧编辑和条件I2V生成两个步骤,模拟与变形形状对齐的伪流序列。在DAVIS-EDIT上的实验结果表明,FlowV2V在时序一致性和样本质量方面优于现有方法。同时,文章还进行了全面的消融研究,分析了该方法的内部功能。
Key Takeaways
- 视频扩散模型促进了视频编辑领域的发展,降低了计算成本。
- 视频编辑任务面临从源视频到目标视频的复杂运动转移挑战。需要兼顾形状变形和时间序列一致性。
- 现有方法难以处理复杂运动模式建模,尤其针对非刚体对象运动的编辑任务受限。
- 光学流在复杂运动建模中展现出潜力,被用于FlowV2V模型。
- FlowV2V模型将视频编辑分解为帧编辑和条件I2V生成两个步骤。
- 通过模拟与变形形状对齐的伪流序列,FlowV2V确保编辑过程中的一致性。
- 在DAVIS-EDIT上的实验验证了FlowV2V模型的优势,在时序一致性和样本质量方面优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

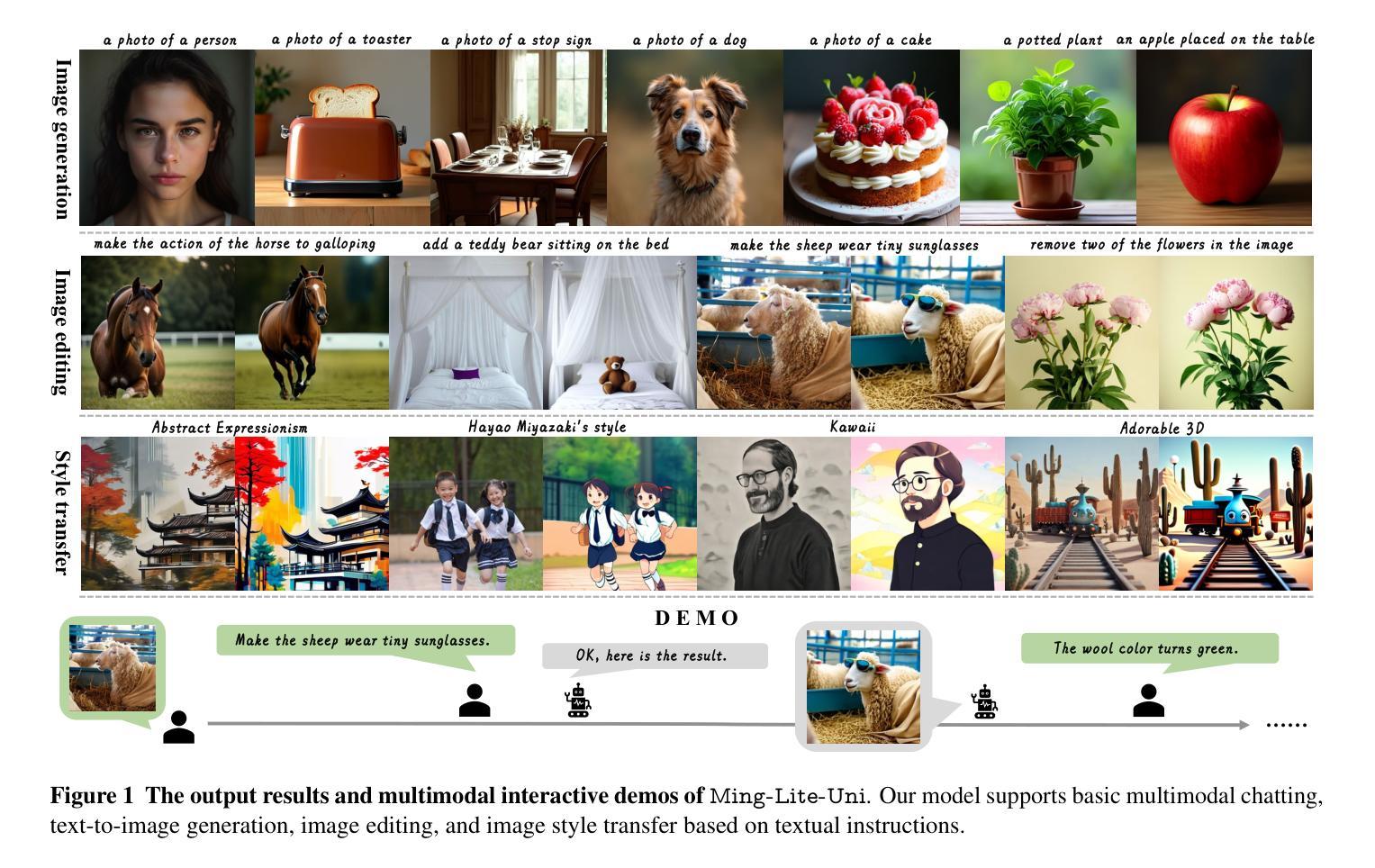
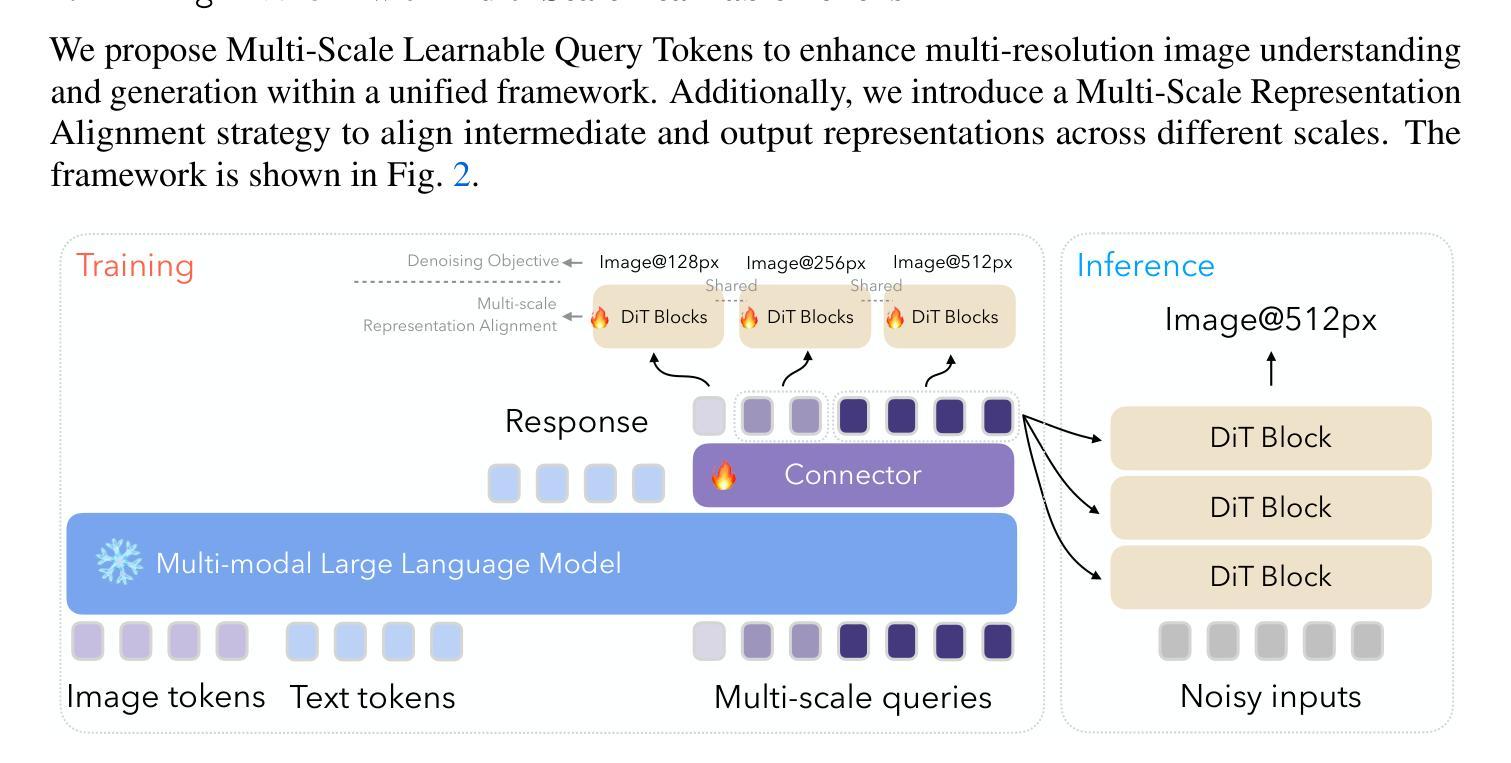
Ming-Lite-Uni: Advancements in Unified Architecture for Natural Multimodal Interaction
Authors:Inclusion AI, Biao Gong, Cheng Zou, Dandan Zheng, Hu Yu, Jingdong Chen, Jianxin Sun, Junbo Zhao, Jun Zhou, Kaixiang Ji, Lixiang Ru, Libin Wang, Qingpei Guo, Rui Liu, Weilong Chai, Xinyu Xiao, Ziyuan Huang
We introduce Ming-Lite-Uni, an open-source multimodal framework featuring a newly designed unified visual generator and a native multimodal autoregressive model tailored for unifying vision and language. Specifically, this project provides an open-source implementation of the integrated MetaQueries and M2-omni framework, while introducing the novel multi-scale learnable tokens and multi-scale representation alignment strategy. By leveraging a fixed MLLM and a learnable diffusion model, Ming-Lite-Uni enables native multimodal AR models to perform both text-to-image generation and instruction based image editing tasks, expanding their capabilities beyond pure visual understanding. Our experimental results demonstrate the strong performance of Ming-Lite-Uni and illustrate the impressive fluid nature of its interactive process. All code and model weights are open-sourced to foster further exploration within the community. Notably, this work aligns with concurrent multimodal AI milestones - such as ChatGPT-4o with native image generation updated in March 25, 2025 - underscoring the broader significance of unified models like Ming-Lite-Uni on the path toward AGI. Ming-Lite-Uni is in alpha stage and will soon be further refined.
我们介绍了Ming-Lite-Uni,这是一个开源的多模式框架,具有新设计的统一视觉生成器和针对视觉和语言的统一本地图层自适应模型。具体来说,此项目提供了集成MetaQueries和M2-omni框架的开源实现,同时引入了新型的多尺度可学习令牌和多尺度表示对齐策略。通过利用固定的MLLM和可学习的扩散模型,Ming-Lite-Uni使本地多模式AR模型能够执行文本到图像生成和基于指令的图像编辑任务,扩展了其超越纯视觉理解的能力。我们的实验结果证明了Ming-Lite-Uni的强大性能,并展示了其交互过程的流畅性。所有代码和模型权重均已开源,以促进社区内的进一步探索。值得注意的是,这项工作与当前的多媒体人工智能里程碑保持一致,如ChatGPT-4在2025年3月25日更新的本地图像生成功能,强调了像Ming-Lite-Uni这样的统一模型在通往人工智能通用化道路上的重要性。Ming-Lite-Uni目前处于Alpha阶段,未来将会进一步完善。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/inclusionAI/Ming/tree/Ming-Lite-Omni-Preview/Ming-unify
Summary
本文介绍了Ming-Lite-Uni这一开源多模态框架,其特点为全新设计的统一视觉生成器以及针对视觉和语言统一化的本地多模态自回归模型。该项目实现了集成MetaQueries和M2-omni框架的开源实现,并引入新型多尺度可学习令牌和多尺度表示对齐策略。Ming-Lite-Uni利用固定的MLLM和可学习的扩散模型,使本地多模态AR模型能够执行文本到图像生成和基于指令的图像编辑任务,超越了纯视觉理解的能力。实验结果证明了Ming-Lite-Uni的强大性能,其交互过程表现出令人印象深刻的流畅性。所有代码和模型权重均已开源,以促进社区内的进一步探索。
Key Takeaways
- Ming-Lite-Uni是一个开源多模态框架,集视觉和语言于一体。
- 框架包含新设计的统一视觉生成器和本地多模态自回归模型。
- 实现了MetaQueries和M2-omni框架的集成。
- 引入多尺度可学习令牌和多尺度表示对齐策略。
- 利用固定的MLLM和可学习的扩散模型,支持文本到图像生成和基于指令的图像编辑任务。
- 实验结果展示了Ming-Lite-Uni的强大性能,其交互过程流畅。
点此查看论文截图




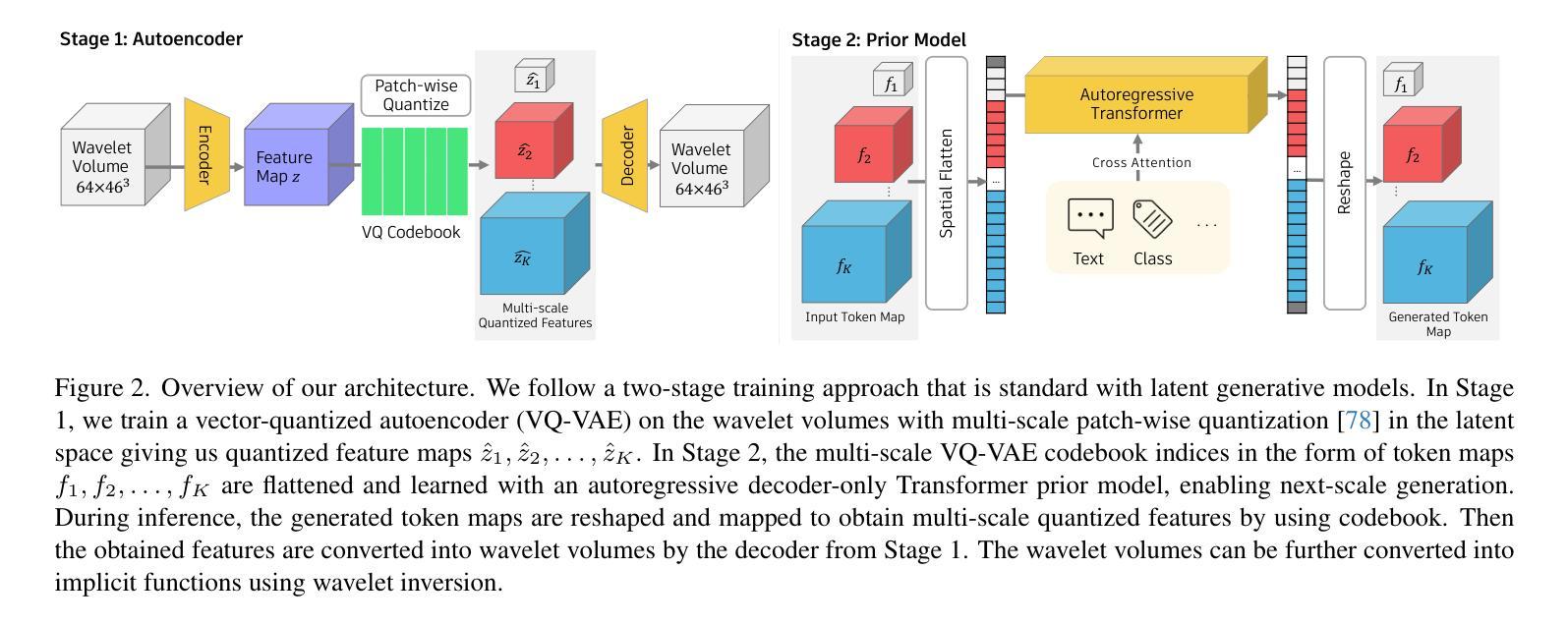
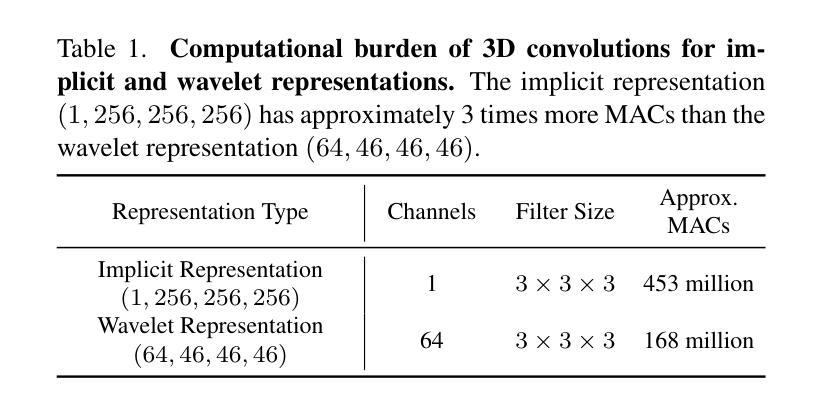
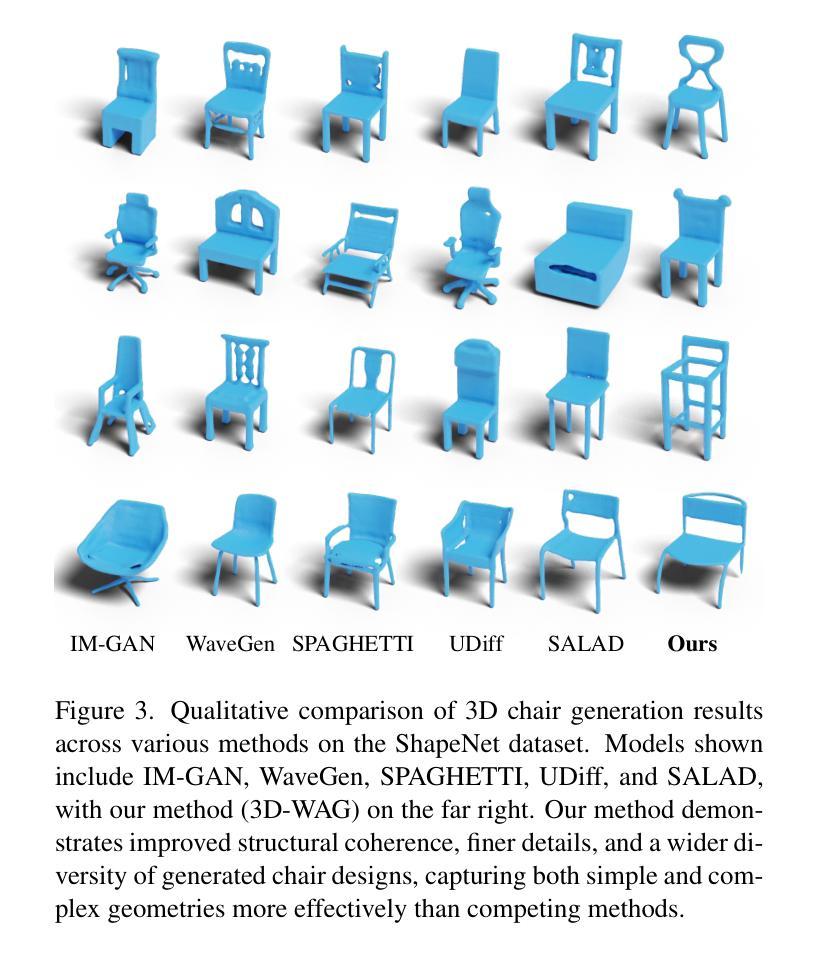
3D-WAG: Hierarchical Wavelet-Guided Autoregressive Generation for High-Fidelity 3D Shapes
Authors:Tejaswini Medi, Arianna Rampini, Pradyumna Reddy, Pradeep Kumar Jayaraman, Margret Keuper
Autoregressive (AR) models have achieved remarkable success in natural language and image generation, but their application to 3D shape modeling remains largely unexplored. Unlike diffusion models, AR models enable more efficient and controllable generation with faster inference times, making them especially suitable for data-intensive domains. Traditional 3D generative models using AR approaches often rely on next-token" predictions at the voxel or point level. While effective for certain applications, these methods can be restrictive and computationally expensive when dealing with large-scale 3D data. To tackle these challenges, we introduce 3D-WAG, an AR model for 3D implicit distance fields that can perform unconditional shape generation, class-conditioned and also text-conditioned shape generation. Our key idea is to encode shapes as multi-scale wavelet token maps and use a Transformer to predict the next higher-resolution token map” in an autoregressive manner. By redefining 3D AR generation task as next-scale" prediction, we reduce the computational cost of generation compared to traditional next-token” prediction models, while preserving essential geometric details of 3D shapes in a more structured and hierarchical manner. We evaluate 3D-WAG to showcase its benefit by quantitative and qualitative comparisons with state-of-the-art methods on widely used benchmarks. Our results show 3D-WAG achieves superior performance in key metrics like Coverage and MMD, generating high-fidelity 3D shapes that closely match the real data distribution.
自回归(AR)模型在自然语言和图像生成方面取得了显著的成就,但在3D形状建模方面的应用仍待探索。不同于扩散模型,AR模型能够实现更高效可控的生成,具有更快的推理时间,使其特别适合数据密集型领域。传统的采用AR方法的3D生成模型通常依赖于体素或点级的“下一个令牌”预测。虽然这在某些应用中很有效,但在处理大规模3D数据时,这些方法可能会受到限制并且计算成本高昂。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了3D-WAG,这是一个用于3D隐距离场的AR模型,可以执行无条件形状生成、类别条件形状生成和文本条件形状生成。我们的核心思想是将形状编码为多尺度小波令牌图,并使用Transformer以自回归的方式预测“下一个更高分辨率的令牌图”。通过重新将3DAR生成任务定义为“下一个尺度”预测,我们与传统的“下一个令牌”预测模型相比,降低了生成的计算成本,同时以更结构和分层的方式保留了3D形状的基本几何细节。我们通过定量和定性的方法评估了3D-WAG与最先进的方法在广泛使用基准测试上的比较,以展示其优势。结果表明,3D-WAG在覆盖率和MMD等关键指标上表现优越,生成的高保真3D形状与真实数据分布紧密匹配。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对三维隐距离场的自回归模型3D-WAG,该模型可进行无条件形状生成、类别条件形状生成和文本条件形状生成。通过编码形状为多级小波标记图,并利用Transformer以自回归方式预测“下一个更高分辨率的标记图”,该模型降低了生成的计算成本,同时保留了三维形状的几何细节。在广泛使用的基准测试中与最先进的方法进行了定量和定性的比较,结果表明,在关键指标如覆盖率和MMD上,3D-WAG实现了卓越的性能,生成的三维形状与真实数据分布高度匹配。
Key Takeaways
- AR模型在自然语言和图像生成方面取得了显著成功,但在3D形状建模方面的应用尚未得到充分探索。
- 传统的基于AR方法的3D生成模型通常依赖于“下一个标记”预测,在处理大规模数据时可能受到限制。
- 3D-WAG模型是一种针对三维隐距离场的自回归模型,通过编码形状为多级小波标记图进行预测,降低了计算成本。
- 3D-WAG模型可实现无条件、类别条件和文本条件的形状生成。
- 与现有方法相比,3D-WAG在覆盖率和MMD等关键指标上实现了卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图